RIGHTSTART MATHEMATICS
|
|
|
- Dylan Carr
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Activities for Learning, Inc. RIGHTSTART MATHEMATICS by Joan A Cotter Ph D A HANDS-ON GEOMETRIC APPROACH LESSONS
2 Copyright 2009 by Joan A. Cotter All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without written permission of Activities for Learning. Three-D images are made with Pedagoguery Software, Inc s Poly ( Printed in the United States of America For questions or for more information: info@rightstartmath.com To place an order or for additional supplies: order@rightstartmath.com Activities for Learning, Inc. PO Box 68; 321 Hill Street Hazelton ND or fax ISBN December 201
3 Table of Contents Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson Lesson 5 Lesson 6 Lesson 7 Lesson 8 Lesson 9 Lesson 10 Lesson 11 Lesson 12 Lesson 13 Lesson 1 Lesson 15 Lesson 16 Lesson 17 Lesson 18 Lesson 19 Lesson 20 Lesson 21 Lesson 22 Lesson 23 Lesson 2 Lesson 25 Lesson 26 Lesson 27 Lesson 28 Lesson 29 Lesson 30 Lesson 31 Lesson 32 Lesson 33 Lesson 3 Lesson 35 Lesson 36 Lesson 37 Lesson 38 Lesson 39 Lesson 0 Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson Lesson 5 Lesson 6 Lesson 7 Getting Started Drawing Diagonals Drawing Stars Equilateral Triangles into Halves Equilateral Triangles into Sixths & Thirds Equilateral Triangles into Fourths & Eighths Equilateral Triangles into Ninths Hexagrams and Solomon's Seal Equilateral Triangles into Twelfths and More Measuring Perimeter in Centimeters Drawing Parallelograms in Centimeters Measuring Perimeter in Inches Drawing Parallelograms in Inches Drawing Rectangles Drawing Rhombuses Drawing Squares Classifying Quadrilaterals The Fraction Chart Patterns in Fractions Measuring With Sixteenths A Fraction of Geometry Figures Making the Whole Ratios and Nested Squares Square Centimeters Square Inches Area of a Rectangle Comparing Areas of Rectangles Product of a Number and Two More Area of Consecutive Squares Perimeter Formula for Rectangles Area of a Parallelogram Comparing Calculated Areas of Parallelograms Area of a Triangle Comparing Calculated Areas of Triangles Converting Inches to Centimeters Name that Figure Finding the Areas of More Triangles Area of Trapezoids Area of Hexagons Area of Octagons Ratios of Areas Measuring Angles Supplementary and Vertical Angles Measure of the Angles in a Polygon Classifying Triangles by Sides and Angles (First Quarter test) External Angles of a Triangle Angles Formed With Parallel Lines
4 Table of Contents Lesson 8 Lesson 9 Lesson 50 Lesson 51 Lesson 52 Lesson 53 Lesson 5 Lesson 55 Lesson 56 Lesson 57 Lesson 58 Lesson 59 Lesson 60 Lesson 61 Lesson 62 Lesson 63 Lesson 6 Lesson 65 Lesson 66 Lesson 67 Lesson 68 Lesson 69 Lesson 70 Lesson 71 Lesson 72 Lesson 73 Lesson 7 Lesson 75 Lesson 76 Lesson 77 Lesson 78 Lesson 79 Lesson 80 Lesson 81 Lesson 82 Lesson 83 Lesson 8 Lesson 85 Lesson 86 Lesson 87 Lesson 88 Lesson 89 Lesson 90 Lesson 91 Lesson 92 Lesson 93 Lesson 9 Triangles With Congruent Sides (SSS) Other Congruent Triangles (SAS, ASA) Side and Angle Relationships in Triangles Medians in Triangles More About Medians in Triangles Midpoints in a Triangle Rectangles Inscribed in a Triangle Connecting Midpoints in a Quadrilateral Introducing the Pythagorean Theorem Squares on Right Triangles Proofs of the Pythagorean Theorem Finding Square Roots More Right Angle Problems The Square Root Spiral Circle Basics Ratio of Circumference to Diameter Inscribed Polygons Tangents to Circles Circumscribed Polygons Pi, a Special Number Circle Designs Rounding Edges With Tangents Tangent Circles Bisecting Angles Perpendicular Bisectors The Amazing Nine-Point Circle Drawing Arcs Angles 'n Arcs Arc Length Area of a Circle Finding the Area of a Circle Finding More Area Pizza Problems Revisiting Tangrams Aligning Objects Reflecting Rotating Making Wheel Designs Identifying Reflections & Rotations Translations Transformations Double Reflections Finding the Line of Reflection (Second Quarter test) Finding the Center of Rotation More Double Reflections Angles of Incidence and Reflection Lines of Symmetry
5 Table of Contents Lesson 95 Lesson 96 Lesson 97 Lesson 98 Lesson 99 Lesson 100 Lesson 101 Lesson 102 Lesson 103 Lesson 10 Lesson 105 Lesson 106 Lesson 107 Lesson 108 Lesson 109 Lesson 110 Lesson 111 Lesson 112 Lesson 113 Lesson 11 Lesson 115 Lesson 116 Lesson 117 Lesson 118 Lesson 119 Lesson 120 Lesson 121 Lesson 122 Lesson 123 Lesson 12 Lesson 125 Lesson 126 Lesson 127 Lesson 128 Lesson 129 Lesson 130 Lesson 131 Lesson 132 Lesson 133 Lesson 13 Lesson 135 Lesson 136 Lesson 137 Lesson 138 Lesson 139 Lesson 10 Lesson 11 Rotation Symmetry Symmetry Connections Frieze Patterns Introduction to Tessellations Two Pentagon Tessellations Regular Tessellations Semiregular Tessellations Demiregular Tessellations Pattern Units Dual Tessellations Tartan Plaids Tessellating Triangles Tessellating Quadrilaterals Escher Tessellations Tessellation Summary & Mondrian Art Box Fractal Sierpinski Triangle Koch Snowflake Cotter Tens Fractal Similar Triangles Fractions on the Multiplication Table Cross Multiplying on the Multiplication Table Measuring Heights Golden Ratio More Golden Goodies Fibonacci Sequence Fibonacci Numbers and Phi Golden Ratios and Other Ratios Around Us Napoleon s Theorem Pick s Theorem Pick s Theorem With the Stomachion Pick s Theorem and Pythagorean Theorem Estimating Area With Pick s Theorem Distance Formula Euler Paths Using Ratios to Find Sides of Triangles Basic Trigonometry Solving Trig Problems Comparing Calculators Solving Problems With a Scientific Calculator Angle of Elevation More Angle Problems Introduction to Sine Waves Solids and Polyhedrons Nets of Cubes Volume of Cubes Volume of Boxes
6 Table of Contents Lesson 12 Lesson 13 Lesson 1 Lesson 15 Lesson 16 Lesson 17 Lesson 18 Lesson 19 Lesson 150 Lesson 151 Lesson 152 Lesson 153 Lesson 15 Lesson 155 Lesson 156 Lesson 157 Lesson 158 Lesson 159 Lesson 160 Lesson 161 Lesson 162 Lesson 163 Lesson 16 Lesson 165 Volume of Prisms Diagonals in a Rectangular Prism Cylinders Cones Pyramids Polygons n Polyhedrons Tetrahedron in a Cube Platonic Solids Views of the Platonic Solids Duals of the Platonic Solids Surface Area and Volume of Spheres Plane Symmetry in Polyhedra Rotating Symmetry in Polyhedra Circumscribed Platonic Solids Cubes in a Dodecahedron Stella Octangula Truncated Tetrahedra Truncated Octahedron Truncated Isocahedron Cuboctahedron Rhombicuboctahedron Icosidodecahedron Snub Polyhedra Archimedean Solids (Final test)
7 RightStart Mathematics: A Hands-On Geometric Approach RightStart Mathematics: A Hands-On Geometric Approach is an innovative approach for teaching many middle school mathematics topics, including perimeter, area, volume, metric system, decimals, rounding numbers, ratio, and proportion. The student is also introduced to traditional geometric concepts: parallel lines, angles, midpoints, triangle congruence, Pythagorean theorem, as well as some modern topics: golden ratio, Fibonacci numbers, tessellations, Pick s theorem, and fractals. In this program the student does not write out proofs, although an organized and logical approach is expected. Understanding mathematics is of prime importance. Since the vast majority of middle school students are visual learners, approaching mathematics through geometry gives the student an excellent way to understand and remember concepts. The hands-on activities often create deeper learning. For example, to find the area of a triangle, the student must first construct the altitude and then measure it. If possible, students work with a partner and discuss their observations and results. Much of the work is done with a drawing board, T-square, triangle, 5 triangle, a template for circles, and goniometer (device for measuring angles). Constructions with these tools are simpler than the standard Euclid constructions. It is interesting to note that CAD (computer aided design) software is based on the drawing board and tools. This program incorporates other branches of mathematics, including arithmetic, algebra, and trigonometry. Some lessons have an art flavor, for example, constructing Gothic arches. Other lessons have a scientific background, sine waves, and angles of incidence and reflection; or a technological background, creating a design for car wheels. Still other lessons are purely mathematical, Napoleon s theorem and Archimedes stomachion. The history of mathematics is woven throughout the lessons. Several recent discoveries are discussed to give the student the perspective that mathematics is a growing discipline. Good study habits are encouraged through asking the student to read the lesson before, during, and following the worksheets. Learning to read a math textbook is a necessary skill for success in advanced math classes. Learning to follow directions is a necessary skill for studying and everyday life. Occasionally, an activity or lesson refers to previous work making it necessary for the student to keep all work organized. The student is asked to maintain a list of new terms. This text was written with several goals for the student: a) to use mathematics previously learned, b) to learn to read math texts, c) to lay a good foundation for more advanced mathematics, d) to discover mathematics everywhere, and e) to enjoy mathematics. About the author Joan A. Cotter, Ph.D., author of RightStart Mathematics: A Hands-On Geometric Approach and RightStart Mathematics elementary program has a degree in electrical engineering, a Montessori diploma, a masters degree in curriculum and instruction, and a doctorate in mathematics education. She taught preschool, children with special needs, and mathematics to grades 6-8. by Joan Cotter 2005 info@rightstartmath.com
8 Hints on Tutoring RightStart Mathematics: A Hands-On Geometric Approach Before starting a lesson, the student should look over the Materials list and gather all the supplies, including a mechanical pencil or a sharp #2 pencil and a good eraser. Then the student reads over the goals, keeping in mind that italicized words will be explained in the lesson. (These new words are to be recorded in the student s math dictionary.) Next the student begins reading the Activities, carefully studying any accompanying figures. It is a good habit to summarize the activity after reading it. If a paragraph is unclear, the student should reread the paragraph, keeping in mind that sometimes more is explained in the following paragraph. No one learns mathematics by reading the text only once. Each activity needs to be understood before going to the next activity. Make sure the student understands the importance of completing the problems on the worksheet when called for in the lesson. Sometimes it will be necessary to refer to the lesson while completing the worksheet. All work needs to be kept neatly in a three-ring binder for future reference. Be careful how you react to the I don t get it plea. Tell the student you need a question to answer. You do not want to get in the habit of reading the text for your student and then regurgitating to her like a mother robin feeding her young. The text is written for students to read for themselves. Learning how to ask questions is an important skill to acquire toward becoming an independent learner. If questions remain after diligent study, the student can contact the author at JoanCotter@RightStartMath.com. If a child has a serious reading problem, read the text aloud while he follows along and then ask him to read it aloud. Be sure each word is understood. For less severe reading problems, you might model aloud the process of reading an activity, commenting on the figure, and summarizing the paragraph. Some of the time, students need encouragement to overcome frustration, which is inherent in the learning process. Occasionally, a student may have a knowledge gap needed for a particular lesson, requiring other resources to resolve. Incidentally, research shows one of the major causes of difficulties in learning new concepts for this age group is insufficient sleep. After the student has completed the worksheet, ask her to compare her work with the solution. If the student has a partner, they can compare and discuss their work before referring to the solutions. Ask her to explain what she learned and any discrepancies. Keep in mind that some activities have more than one solution. You might also ask her to grade her work on some agreed upon scale. It also is a good idea for the student to reread the goals of the lesson to see if they have been met. Encourage discussion on practical applications of the topic. by Joan Cotter 2005 info@rightstartmath.com 8/06
9 Vocabulary First Introduced Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson Lesson 5 Lesson 6 Lesson 10 Lesson 13 Lesson 1 Lesson 15 Lesson 16 Lesson 17 Lesson 18 Lesson 19 Lesson 21 Lesson 23 Lesson 2 Lesson 25 Lesson 26 Lesson 28 Lesson 30 Lesson 32 Lesson 3 Lesson 36 Lesson 38 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 5 Lesson 6 Lesson 7 Lesson 8 Lesson 9 Lesson 50 Lesson 51 Lesson 52 Lesson 5 Lesson 55 Lesson 56 Lesson 57 Lesson 58 Lesson 59 Lesson 60 Lesson 62 Lesson 6 Lesson 65 Lesson 66 Lesson 67 line segments, parallel lines, intersection horizontal, vertical, diagonal, hexagon polygon, vertex, vertexes, vertices quadrilateral, equilateral triangle congruent bisect, tick mark, tetrahedron perimeter parallelogram rectangle, right angle, perpendicular rhombus 90 degrees, square trapezoid, Venn diagram fraction numerator, denominator crosshatch ratio area, square centimeter area, square inch formula exponent factor millimeter, square millimeter little square, altitude isosceles distributive property, straightedge goniometer supplementary, vertical, complementary acute, obtuse, scalene external, internal, adjacent angle corresponding, alternate, interior, exterior angles SSS similar, SAS, ASA vertex angle, base angles, base median of a triangle centroid inscribed convex, concave hypotenuse, leg oblique Pythagorean theorem square root, integer, perfect square Pythagorean triple point, line, and plane, circumference, diameter, radius, arc, sector inscribed polygon, regular polygon tangent, tangent segment circumscribed polygon pi, π
10 Vocabulary First Introduced Lesson 68 Lesson 69 Lesson 70 Lesson 71 Lesson 72 Lesson 73 Lesson 7 Lesson 75 Lesson 76 Lesson 80 Lesson 81 Lesson 83 Lesson 86 Lesson 87 Lesson 88 Lesson 93 Lesson 9 Lesson 95 Lesson 97 Lesson 98 Lesson 99 Lesson 100 Lesson 101 Lesson 102 Lesson 103 Lesson 105 Lesson 108 Lesson 109 Lesson 110 Lesson 111 Lesson 112 Lesson 11 Lesson 115 Lesson 116 Lesson 118 Lesson 119 Lesson 120 Lesson 121 Lesson 123 Lesson 129 Lesson 131 Lesson 133 Lesson 135 Lesson 136 Lesson 137 clockwise, counterclockwise concentric, semicircle internally tangent circles, externally tangent circles, trefoil, quatrefoil angle bisector, incenter chord, circumcenter* foot, feet central angle inscribed angle, intercepted arc kilometer per, unit cost tangram reflection, image, line of reflection, flip horizontal, flip vertical transformation translation, image, absolute, relative transformation angle of incidence, angle of reflection line of symmetry, maximum, minimum, order of rotation symmetry, point symmetry frieze, cell, tile tessellation pure tessellation nonagon, decagon, dodecagon semiregular tessellation demiregular tessellation, semi-pure tessellation unit, pattern tartan, plaid, warp, weft, woof Escher Mondrian fractals and the terms iteration and self-similar, exponent Sierpinski Triangle Koch Snowflake similar, similar triangles proportion cross-multiplying golden rectangle, golden ratio, phi, φ golden spiral, golden triangle sequence, Fibonacci sequence Fibonacci spiral generalize Euler path trigonometry, opposite, adjacent, sine, cosine, tangent scientific calculator angle of elevation, stride, clinometer angle of depression sine wave
11 Vocabulary First Introduced Lesson 138 Lesson 10 Lesson 11 Lesson 12 Lesson 13 Lesson 1 Lesson 15 Lesson 16 Lesson 19 Lesson 151 Lesson 152 Lesson 153 Lesson 15 Lesson 155 Lesson 157 Lesson 158 Lesson 159 Lesson 160 Lesson 161 Lesson 162 Lesson 163 Lesson 16 Lesson 165 solid, polyhedron, polyhedra, face, edge, vertex, net, dimension volume, cubic centimeter, surface area decimeter, dm prism short diagonal, long diagonal cylinder cone apex, regular pyramid, right pyramid Platonic solids dual polyhedra sphere, great circle, small circle planes of symmetry axes of symmetry reciprocal stella octangula, concave polyhedron truncate, semiregular polyhedra, Archimedean solids quasiregular polyhedron
12 Lesson 2 A sharp pencil, an eraser, and tape are essentials. They will not be listed in future lessons. GOALS MATERIALS ACTIVITIES Drawing Diagonals 1. To review the terms horizontal and vertical 2. To learn the mathematical meaning of diagonal 3. To review the term hexagon. To find the correct edge of the triangle to draw diagonals Worksheet 2, Math Dictionary Drawing board, T-square, triangle Horizontal and vertical. Horizontal refers to the horizon, the intersection between the earth and sky. You can see it if there aren t too many buildings and trees in the way. Vertical refers to straight up and down, like a flagpole. A horizontal line on paper is a line drawn straight across the paper. It usually is parallel to the top and bottom of the paper. A vertical line on paper goes from top to bottom, parallel to the sides of the paper. Diagonals. In common everyday English, the word diagonal usually means at a slant. It often means a road that runs neither north and south nor east and west. In mathematics, a diagonal is a line connecting points in a closed figure. For example, the line segments AC and DB drawn in the square below on the left are diagonals. If we turn the square, as in the next figure, the lines segments are still diagonals. Now diagonal DB is horizontal and diagonal AC is vertical. A A B diagonal diagonals D diagonal B Diagonal lines on a building. D C C In the word diagonal, dia means across and gon means angle. So, a diagonal is a line across angles, that is, a line connecting two vertices. Worksheet. The worksheet asks you to draw two hexagons and all their diagonals. A hexagon is a closed six-sided figure. One way to remember the word is that hexagon and six both have x s. Draw the sides of the hexagon and the diagonals using your tools. The horizontal and vertical lines need only a T-square. The left figure below is a hexagon; the right figure shows the diagonals.
13 Name 1. Use your T-square to draw horizontal lines in the octagon below. Be sure your T-square is snug against the edge of the drawing board. Date 2. Use your T-square and triangle to draw vertical lines in the hexagon. Be sure that your triangle is snug against the T-square. 3. Draw lines parallel to the sides of this equilateral triangle. Use your T-square and triangle to draw the lines. Hold your pencil about 2.5 cm from the tip ( ).. In which figure(s) have you drawn parallel octagon hexagon lines? 5. In which figure(s) have you drawn intersecting triangle lines? Worksheet 1, Getting Started Joan A. Cotter 2009 Name 1. First, trace the dotted lines forming the two hexagons. Use your T-square for drawing all lines. Use your triangle for all lines except horizontal lines. 2. Next, draw all the diagonals in the hexagons, using your drawing tools. There are 3 diagonals at each vertex. Date Include both hexagons: 3. How many diagonals are horizontal? 3 3. How many diagonals are vertical? How many diagonals at each vertex are either horizontal or vertical? 6. How many diagonals at each vertex are not horizontal or vertical? Worksheet 2, Drawing Diagonals Joan A. Cotter 2009
14 12 Lesson 9 Equilateral Triangle into Twelfths and More GOALS 1. To discover how to divide an equilateral triangle into congruent pieces greater than 9 2. To divide an equilateral triangle into twelfths 3. To divide an equilateral triangle into a number greater than 12 MATERIALS Worksheets 9-1, 9-2 Drawing board, T-square, triangle Colored pencil, optional ACTIVITIES Dividing a triangle into twelfths. How would you divide an equilateral triangle into twelfths into twelve congruent parts? Think about it for a while before reading further. Would it work to divide the triangle into thirds and divide each third into fourths? One student even suggested dividing the triangle into tenths and then dividing each tenth in half. Let s hope he was joking! If you have thought about it, you probably realize you first divide the triangle into fourths and then each fourth into thirds. Dividing a triangle by higher numbers. How would you divide the triangle into sixteenths? What other numbers could you divide it into? Two kindergarten girls divided the equilateral triangle into 256 equal parts. After hearing about the girls, a teacher learning drawing board geometry divided his triangle into 32 equal parts. Some divisions are shown below. Sixteenths Eighteenths Eighteenths Triangle into 32nds by Joseph Hermodson-Olsen, 1. How could he have done it? The answer is at the bottom of the page. Twenty-fourths Twenty-sevenths Twenty-sevenths Worksheet 9-1. For this worksheet, you will divide the equilateral triangle into twelfths. Work carefully. For Problem 2, figure out how you would divide equilateral triangles into various congruent pieces. Worksheet 9-2. After drawing the equilateral triangle, divide it into congruent triangles. Either copy one of the designs above, or better yet, design your own. You might like to color your design. [Answer: ninths, fourths, fourths, and thirds.] Thirty-seconds
15 1. Draw an equilateral triangle. Divide it into fourths. Then divide each fourth into thirds, as shown. Name Date 2. Fill in the chart. Number of Pieces First Division Second Division [or 6] 3 9 Third Division 2 3 Worksheet 9-1, Equilateral Triangle into Twelfths and More Joan A. Cotter 2009 Name 3. Draw an equilateral triangle. Divide it into more than 12 equal parts. Date. Describe how you did it. [RESULTS WILL VARY.] Worksheet 9-2, Equilateral Triangle into Twelfths and More Joan A. Cotter 2009
16 32 Lesson 27 Comparing Areas of Rectangles GOALS 1. To calculate more areas of rectangles 2. To compare areas of rectangles with constant perimeter MATERIALS Worksheets 27-1, 27-2 Drawing board, T-square, triangle -in-1 ruler ACTIVITIES Frame problem. Consider the following problem. You have 12 cm of gold edging to place around a rectangular frame. You want the maximum amount of space inside the frame. First think about the possible dimensions of the rectangles, so the perimeters will be 12 cm. Then study the figures below. 3 cm cm 5 cm 2 cm 1 cm 2 cm 3 cm cm 5 cm 1 cm This type of problem is easily solved with a branch of mathematics called calculus. The areas, which you can do in your head using A = wh, are from left to right, 5 cm 2, 8 cm 2, 9 cm 2, 8 cm 2, and 5 cm 2. Graphing the frame problem. It is interesting to graph the results as shown below. Why is the area equal to 0 when the width is equal to 0 or 6? cm 2 The area in Rectangle Areas with Perimeter = 12 cm The width of the rectangle in cm The shape of this graph is called a parabola. You can see the greatest area occurs when the width of the rectangle is to 3. What is the height when the width is 3? The answer is at the bottom of the page. Worksheets. There is a similar problem on Worksheets 27-1 and Draw the rectangles by measuring with your ruler like you did on Worksheet 11. [Answer: 3]
17 Name 1. Find the areas of the small groups of squares. Write the answer in the lower right square. Also write it in corresponding space in the large square. Then fill in the remaining spaces in the large square Date 2. What do you call the large square in Problem 1? Multiplication table 3. If a rectangle is 8 cm wide by 9 cm high, how many square centimeters do you need to cover it? 72 cm 2. If a rectangle is w cm wide and h cm high, how many square centimeters do you need to cover it? w h cm 2 Read Lesson 26 before answering the next question. 5. What is the area of the figure below? cm cm cm or or 16 cm 6 cm A = lg rect sm rect A = A = 1 cm 2 A = A = 1 cm 2 A = A = 1 cm 2 Worksheet 26, Area of a Rectangle Joan A. Cotter 2009 Name Date If you had 20 cm of expensive trim to decorate the edge of a rectangular bulletin board, what should the dimensions of the rectangle be to give you the most area for photos and notes? Follow the steps below for the solution. 1. On each of the five lines below, draw a rectangle with a perimeter of 20 cm. Write the dimensions. 9cm 1cm A = wh A = 1 9 A = 9cm 2 8cm 2 2. Below each rectangle, calculate its area in cm. Which rectangle gives the most area? 5 cm by 5 cm 2 cm A = wh A = 2 8 7cm A = 16 cm 2 3cm A = wh A = 3 7 A = 21 cm 2 6cm cm A = wh A = 6 A = 2 cm 2 5cm 5cm A = wh A = 5 5 A = 25 cm 2 Worksheet 27-1, Comparing Areas of Rectangles Joan A. Cotter 2009
18 Name Date. On the graph below, place a point showing the area for each rectangle from the previous page. Also find the areas for the remaining rectangle widths: 0, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10. Plot those areas on the graph. Then connect the points in a smooth curve; do this freehand (without any drawing tools). 2 Areas in cm Area of Rectangles with a Perimeter of 20 cm The base of the rectangle in cm parabola 5. What is the name of the shape of the curve? 6. According to the graph, what is the maximum area? 25 cm2 The square has the greatest area. 7. How does the graph compare with the example in the lesson? Worksheet 27-2, Comparing Areas of Rectangles Joan A. Cotter 2011 Name 1. For problems, A-C, crosshatch the top row of squares. Place the crosshatched squares on the right of the new figure. Complete the square with dashed lines. The steps are shown below. Date n n B. C. A. 2. Complete the table. A. B. C. n (n 1) (n + 1) Squares in the Original Fig. 2 = = 15 6 = = 7 9 = 10 8 = 11 9 = n 1 Squares in the New Fig = = = = = = = Write the results (or rule) you found in your own words. When multiplying two numbers that are two numbers apart, square the number between them and subtract one. Apply this result to find the following: = = = = = = 299 = n (n 1) (n + 1) Worksheet 28, Product of a Number and Two More Joan A. Cotter 2009
19 96 Lesson 8 Rotating GOALS 1. To learn the mathematical meaning of rotation 2. To construct rotations at various angles MATERIALS Worksheet 8 Goniometer A set of tangrams Drawing board, T-square, 5 triangle ACTIVITIES Rotating. A clock is a good example of rotation. Both the hour and minute hands rotate about the center of the clock. The hands move in a clockwise direction. However, when we discuss rotations mathematically, we start with a horizontal ray extending right and measure the amount of rotation counterclockwise. So, for a clock to behave mathematically, the hand would start at the 3 o clock position and travel backward. Rotating the ship. Build the ship shown below in the left figure with four tangram triangles and tape them together Then tape the ship to the upper arm of the goniometer. Hold the lower arm of the goniometer still with your right hand. Use your left hand to rotate and upper arm of the goniometer with the attached ship. See the middle figure above. Keep rotating to 90 as shown in the right figure above. (The seas are getting very rough.) Continue rotating to 180. (Disaster.) See the left figure below Star design on the floor. Construct every line accurately. Don t guess. To set your ship aright, un-tape it, turn your goniometer upside down, re-tape it, and continue rotating as in the right figure above. Worksheet. The first half of the worksheet asks you to construct the ship at various angles with your tools. You may find it helpful to set the ship model at the desired angle. Start your construction at the and draw the first line at the correct angle. Measure only the line for the ship s bottom (3 cm); construct the other lines. For the second half, build and rotate the model to the various angles before attempting the constructions. Measure only the 2.5 cm line.
20 Worksheet 8, Rotating Construct the figures at the angles given with your geometry tools. Use your ruler only to measure the line representing the bottom of the ship and the side of the arrow. Name Date The shows you where to start. Name Date cm Worksheet 83-2, Reflecting For each figure, flip horizontal and flip vertical about the center lines Joan A. Cotter cm 9. What angle of rotation is the same turning something 180 upside down? 10. Is a rotation of 180 the same as reflecting about a no horizontal line? Joan A. Cotter 2010
AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School
 AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved AGS Math Algebra 2 Grade
AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved AGS Math Algebra 2 Grade
Geometry Mrs. Crocker Spring 2014 Final Exam Review
 Name: Mod: Geometry Mrs. Crocker Spring 2014 Final Exam Review Use this exam review to complete your flip book and to study for your upcoming exam. You must bring with you to the exam: 1. Pencil, eraser,
Name: Mod: Geometry Mrs. Crocker Spring 2014 Final Exam Review Use this exam review to complete your flip book and to study for your upcoming exam. You must bring with you to the exam: 1. Pencil, eraser,
16. DOK 1, I will succeed." In this conditional statement, the underlined portion is
 Geometry Semester 1 REVIEW 1. DOK 1 The point that divides a line segment into two congruent segments. 2. DOK 1 lines have the same slope. 3. DOK 1 If you have two parallel lines and a transversal, then
Geometry Semester 1 REVIEW 1. DOK 1 The point that divides a line segment into two congruent segments. 2. DOK 1 lines have the same slope. 3. DOK 1 If you have two parallel lines and a transversal, then
Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook
 Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook Almost everything you need to know for 7 th grade math Plus a little about 6 th grade math And a little about 8 th grade math 1 Table of Contents by Outcome Outcome Topic Page
Mrs. Ambre s Math Notebook Almost everything you need to know for 7 th grade math Plus a little about 6 th grade math And a little about 8 th grade math 1 Table of Contents by Outcome Outcome Topic Page
1 st Subject: 2D Geometric Shape Construction and Division
 Joint Beginning and Intermediate Engineering Graphics 2 nd Week 1st Meeting Lecture Notes Instructor: Edward N. Locke Topic: Geometric Construction 1 st Subject: 2D Geometric Shape Construction and Division
Joint Beginning and Intermediate Engineering Graphics 2 nd Week 1st Meeting Lecture Notes Instructor: Edward N. Locke Topic: Geometric Construction 1 st Subject: 2D Geometric Shape Construction and Division
Geometry 2001 part 1
 Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
S1/2 Checklist S1/2 Checklist. Whole Numbers. No. Skill Done CfE Code(s) 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting
 Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
Geometry by Jurgensen, Brown and Jurgensen Postulates and Theorems from Chapter 1
 Postulates and Theorems from Chapter 1 Postulate 1: The Ruler Postulate 1. The points on a line can be paired with the real numbers in such a way that any two points can have coordinates 0 and 1. 2. Once
Postulates and Theorems from Chapter 1 Postulate 1: The Ruler Postulate 1. The points on a line can be paired with the real numbers in such a way that any two points can have coordinates 0 and 1. 2. Once
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry
 Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Course: Math Grade: 7. Unit Plan: Geometry. Length of Unit:
 Course: Math Grade: 7 Unit Plan: Geometry Length of Unit: Enduring Understanding(s): Geometry is found in the visual world in two and three dimension. We use geometry daily in problem solving. Essential
Course: Math Grade: 7 Unit Plan: Geometry Length of Unit: Enduring Understanding(s): Geometry is found in the visual world in two and three dimension. We use geometry daily in problem solving. Essential
Refer to Blackboard for Activities and/or Resources
 Lafayette Parish School System Curriculum Map Mathematics: Grade 5 Unit 4: Properties in Geometry (LCC Unit 5) Time frame: 16 Instructional Days Assess2know Testing Date: March 23, 2012 Refer to Blackboard
Lafayette Parish School System Curriculum Map Mathematics: Grade 5 Unit 4: Properties in Geometry (LCC Unit 5) Time frame: 16 Instructional Days Assess2know Testing Date: March 23, 2012 Refer to Blackboard
DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET
 DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET This booklet is an optional revision aid for the Summer Exam Name: Maths Teacher: Revision List for Summer Exam Topic Junior Maths Bk 3 Place Value Chapter
DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET This booklet is an optional revision aid for the Summer Exam Name: Maths Teacher: Revision List for Summer Exam Topic Junior Maths Bk 3 Place Value Chapter
RightStart Mathematics
 Most recent update: Decdember 28, 2017 RightStart Mathematics Corrections and Updates for Level E/Grade 4 Lessons and Worksheets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET Lesson 38 Classroom version only CHANGE
Most recent update: Decdember 28, 2017 RightStart Mathematics Corrections and Updates for Level E/Grade 4 Lessons and Worksheets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET Lesson 38 Classroom version only CHANGE
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII. Mathematics Laboratory
 LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan. Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1. Form: 501
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1 Description: Test 4 A (Diagrams) Form: 501 Please use the following figure for this question. 1. In the GEOMETRIC
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1 Description: Test 4 A (Diagrams) Form: 501 Please use the following figure for this question. 1. In the GEOMETRIC
3. Given the similarity transformation shown below; identify the composition:
 Midterm Multiple Choice Practice 1. Based on the construction below, which statement must be true? 1 1) m ABD m CBD 2 2) m ABD m CBD 3) m ABD m ABC 1 4) m CBD m ABD 2 2. Line segment AB is shown in the
Midterm Multiple Choice Practice 1. Based on the construction below, which statement must be true? 1 1) m ABD m CBD 2 2) m ABD m CBD 3) m ABD m ABC 1 4) m CBD m ABD 2 2. Line segment AB is shown in the
RightStart Mathematics
 Most recent update: April 18, 2018 RightStart Mathematics Corrections and Updates for Level E/Grade 4 Lessons and Worksheets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET CHANGE DATE Lesson 8 04/18/2018 Lesson 36
Most recent update: April 18, 2018 RightStart Mathematics Corrections and Updates for Level E/Grade 4 Lessons and Worksheets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET CHANGE DATE Lesson 8 04/18/2018 Lesson 36
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets
 Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Introduction. It gives you some handy activities that you can do with your child to consolidate key ideas.
 (Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
(Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY HONORS. OPTIONS FOR NEXT COURSE Algebra II, Algebra II/Trigonometry, or Algebra, Functions, and Data Analysis
 Parent / Student Course Information MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY HONORS Counselors are available to assist parents and students with course selections and career planning. Parents may arrange to meet with the
Parent / Student Course Information MATHEMATICS GEOMETRY HONORS Counselors are available to assist parents and students with course selections and career planning. Parents may arrange to meet with the
FSA Geometry EOC Getting ready for. Circles, Geometric Measurement, and Geometric Properties with Equations.
 Getting ready for. FSA Geometry EOC Circles, Geometric Measurement, and Geometric Properties with Equations 2014-2015 Teacher Packet Shared by Miami-Dade Schools Shared by Miami-Dade Schools MAFS.912.G-C.1.1
Getting ready for. FSA Geometry EOC Circles, Geometric Measurement, and Geometric Properties with Equations 2014-2015 Teacher Packet Shared by Miami-Dade Schools Shared by Miami-Dade Schools MAFS.912.G-C.1.1
13. a) 4 planes of symmetry b) One, line through the apex and the center of the square in the base. c) Four rotational symmetries.
 1. b) 9 c) 9 d) 16 2. b)12 c) 8 d) 18 3. a) The base of the pyramid is a dodecagon. b) 24 c) 13 4. a) The base of the prism is a heptagon b) 14 c) 9 5. Drawing 6. Drawing 7. a) 46 faces b) No. If that
1. b) 9 c) 9 d) 16 2. b)12 c) 8 d) 18 3. a) The base of the pyramid is a dodecagon. b) 24 c) 13 4. a) The base of the prism is a heptagon b) 14 c) 9 5. Drawing 6. Drawing 7. a) 46 faces b) No. If that
Connected Mathematics 2, 6th Grade Units (c) 2006 Correlated to: Utah Core Curriculum for Math (Grade 6)
 Core Standards of the Course Standard I Students will acquire number sense and perform operations with rational numbers. Objective 1 Represent whole numbers and decimals in a variety of ways. A. Change
Core Standards of the Course Standard I Students will acquire number sense and perform operations with rational numbers. Objective 1 Represent whole numbers and decimals in a variety of ways. A. Change
Geometry For Technical Drawing Chapter 4
 Geometry For Technical Drawing Chapter 4 Sacramento City College EDT 300/ENGR 306 EDT 300/ENGR 306 1 Objectives Identify and describe geometric shapes and constructions used by drafters. Construct various
Geometry For Technical Drawing Chapter 4 Sacramento City College EDT 300/ENGR 306 EDT 300/ENGR 306 1 Objectives Identify and describe geometric shapes and constructions used by drafters. Construct various
Grade 6. Prentice Hall. Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units Alaska Standards and Grade Level Expectations. Grade 6
 Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units 2004 Grade 6 C O R R E L A T E D T O Expectations Grade 6 Content Standard A: Mathematical facts, concepts, principles, and theories Numeration: Understand
Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units 2004 Grade 6 C O R R E L A T E D T O Expectations Grade 6 Content Standard A: Mathematical facts, concepts, principles, and theories Numeration: Understand
Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards
 Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards WALCH EDUCATION Table of Contents Standards Correlations...................................................... v Introduction..............................................................vii
Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards WALCH EDUCATION Table of Contents Standards Correlations...................................................... v Introduction..............................................................vii
Developing geometric thinking. A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9
 Developing geometric thinking A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9 Developing geometric thinking ii Contents Van Hiele: Developing Geometric Thinking... 1 Sorting objects using Geostacks...
Developing geometric thinking A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9 Developing geometric thinking ii Contents Van Hiele: Developing Geometric Thinking... 1 Sorting objects using Geostacks...
Big Ideas Math: A Common Core Curriculum Geometry 2015 Correlated to Common Core State Standards for High School Geometry
 Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 MATH 121 SPRING 2017 - PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Given that point P is the midpoint of both and, it follows that. 2. If, then. 3. In a circle (or congruent
MATH 121 SPRING 2017 - PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Given that point P is the midpoint of both and, it follows that. 2. If, then. 3. In a circle (or congruent
June 2016 Regents GEOMETRY COMMON CORE
 1 A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation? 4) 2
1 A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation? 4) 2
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Table of Contents. Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x
 Table of Contents Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x...1...1 Set 2: Classifying Triangles and Angle Theorems... 13 Set 3: Corresponding Parts, Transformations, and Proof...
Table of Contents Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x...1...1 Set 2: Classifying Triangles and Angle Theorems... 13 Set 3: Corresponding Parts, Transformations, and Proof...
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Geometry 1 FINAL REVIEW 2011
 Geometry 1 FINL RVIW 2011 1) lways, Sometimes, or Never. If you answer sometimes, give an eample for when it is true and an eample for when it is not true. a) rhombus is a square. b) square is a parallelogram.
Geometry 1 FINL RVIW 2011 1) lways, Sometimes, or Never. If you answer sometimes, give an eample for when it is true and an eample for when it is not true. a) rhombus is a square. b) square is a parallelogram.
INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT
 INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT TABLE OF CONTENTS Format & Background Information...3-6 Learning Experience 1- Getting Started...6-7 Learning Experience 2 - Cube and Rectangular Prisms...8 Learning Experience
INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT TABLE OF CONTENTS Format & Background Information...3-6 Learning Experience 1- Getting Started...6-7 Learning Experience 2 - Cube and Rectangular Prisms...8 Learning Experience
Grade 6 Middle School Mathematics Contest A parking lot holds 64 cars. The parking lot is 7/8 filled. How many spaces remain in the lot?
 Grade 6 Middle School Mathematics Contest 2004 1 1. A parking lot holds 64 cars. The parking lot is 7/8 filled. How many spaces remain in the lot? a. 6 b. 8 c. 16 d. 48 e. 56 2. How many different prime
Grade 6 Middle School Mathematics Contest 2004 1 1. A parking lot holds 64 cars. The parking lot is 7/8 filled. How many spaces remain in the lot? a. 6 b. 8 c. 16 d. 48 e. 56 2. How many different prime
FINAL REVIEW. 1) Always, Sometimes, or Never. If you answer sometimes, give an example for when it is true and an example for when it is not true.
 FINL RVIW 1) lways, Sometimes, or Never. If you answer sometimes, give an eample for when it is true and an eample for when it is not true. a) rhombus is a square. b) square is a parallelogram. c) oth
FINL RVIW 1) lways, Sometimes, or Never. If you answer sometimes, give an eample for when it is true and an eample for when it is not true. a) rhombus is a square. b) square is a parallelogram. c) oth
GRADE VOCABULARY GUIDE
 Y across add add on after afternoon alike amount backwards balance before between big bottom boundary calendar cents clock coins corners count cover cross curve deep difference different distance down
Y across add add on after afternoon alike amount backwards balance before between big bottom boundary calendar cents clock coins corners count cover cross curve deep difference different distance down
Shelf, Treasure Chest, Tub. Math and Quiet!! Center, A. Quiet Dice for Make. (Talk! = Walk!) A. Warm Up or Lesson, CONTINUE ON!! B.
 Sandra White - snannyw@aol.com - CAMT 2012 No Wasted Time 9 12 1 12 1 11 10 11 2 10 11 2 3 9 3 8 4 8 4 7 6 5 7 6 5 from Beginningto End Procedures Traveling / Waiting Unexpected Visitors Finishing Early
Sandra White - snannyw@aol.com - CAMT 2012 No Wasted Time 9 12 1 12 1 11 10 11 2 10 11 2 3 9 3 8 4 8 4 7 6 5 7 6 5 from Beginningto End Procedures Traveling / Waiting Unexpected Visitors Finishing Early
WITH MATH INTERMEDIATE/MIDDLE (IM) GRADE 6
 May 06 VIRGINIA MATHEMATICS STANDARDS OF LEARNING CORRELATED TO MOVING WITH MATH INTERMEDIATE/MIDDLE (IM) GRADE 6 NUMBER AND NUMBER SENSE 6.1 The student will identify representations of a given percent
May 06 VIRGINIA MATHEMATICS STANDARDS OF LEARNING CORRELATED TO MOVING WITH MATH INTERMEDIATE/MIDDLE (IM) GRADE 6 NUMBER AND NUMBER SENSE 6.1 The student will identify representations of a given percent
Summer Solutions Problem Solving Level 4. Level 4. Problem Solving. Help Pages
 Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
is formed where the diameters intersect? Label the center.
 E 26 Get Into Shape Hints or notes: A circle will be folded into a variety of geometric shapes. This activity provides the opportunity to assess the concepts, vocabulary and knowledge of relationships
E 26 Get Into Shape Hints or notes: A circle will be folded into a variety of geometric shapes. This activity provides the opportunity to assess the concepts, vocabulary and knowledge of relationships
3 Kevin s work for deriving the equation of a circle is shown below.
 June 2016 1. A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation?
June 2016 1. A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation?
Math + 4 (Red) SEMESTER 1. { Pg. 1 } Unit 1: Whole Number Sense. Unit 2: Whole Number Operations. Unit 3: Applications of Operations
 Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions. For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8
 Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8 Table of Contents Change Log... 2 Introduction to TestNav TM 8: MC/TEI Document... 3 Guided
Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8 Table of Contents Change Log... 2 Introduction to TestNav TM 8: MC/TEI Document... 3 Guided
2011 Summer Math Packet Students entering Fifth Grade Math
 Name 0 Summer Math Packet Students entering Fifth Grade Math Rachel Carson Elementary PACKET MUST INCLUDE COVER SHEET WITH THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION CLEARLY PRINTED Students Name (first & last) 0-0 Homeroom
Name 0 Summer Math Packet Students entering Fifth Grade Math Rachel Carson Elementary PACKET MUST INCLUDE COVER SHEET WITH THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION CLEARLY PRINTED Students Name (first & last) 0-0 Homeroom
The Grade 6 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that students should
 The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
The focus for students in geometry at this level is reasoning about area, surface area, and volume. Students also learn to work with visual tools for representing shapes, such as graphs in the coordinate
University of Houston High School Mathematics Contest Geometry Exam Spring 2016
 University of Houston High School Mathematics ontest Geometry Exam Spring 016 nswer the following. Note that diagrams may not be drawn to scale. 1. In the figure below, E, =, = 4 and E = 0. Find the length
University of Houston High School Mathematics ontest Geometry Exam Spring 016 nswer the following. Note that diagrams may not be drawn to scale. 1. In the figure below, E, =, = 4 and E = 0. Find the length
Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers
 LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm.
 1 In the diagram below, ABC XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements identify
1 In the diagram below, ABC XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements identify
MATH MEASUREMENT AND GEOMETRY
 Students: 1. Students choose appropriate units of measure and use ratios to convert within and between measurement systems to solve problems. 1. Compare weights, capacities, geometric measures, time, and
Students: 1. Students choose appropriate units of measure and use ratios to convert within and between measurement systems to solve problems. 1. Compare weights, capacities, geometric measures, time, and
Euclid s Muse MATERIALS VOCABULARY. area perimeter triangle quadrilateral rectangle line point plane. TIME: 40 minutes
 Euclid s Muse In this activity, participants match geometry terms to definitions and definitions to words. MATERIALS Transparency: Euclid s Muse Directions Transparency/Page: Euclid s Muse Transparency/Page:
Euclid s Muse In this activity, participants match geometry terms to definitions and definitions to words. MATERIALS Transparency: Euclid s Muse Directions Transparency/Page: Euclid s Muse Transparency/Page:
Key Stage 3 Mathematics. Common entrance revision
 Key Stage 3 Mathematics Key Facts Common entrance revision Number and Algebra Solve the equation x³ + x = 20 Using trial and improvement and give your answer to the nearest tenth Guess Check Too Big/Too
Key Stage 3 Mathematics Key Facts Common entrance revision Number and Algebra Solve the equation x³ + x = 20 Using trial and improvement and give your answer to the nearest tenth Guess Check Too Big/Too
E G 2 3. MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland
 MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland Point A point is a location in space. It has no length or width. A point is represented by a dot and is named by writing a capital letter next to the dot.
MATH 1012 Section 8.1 Basic Geometric Terms Bland Point A point is a location in space. It has no length or width. A point is represented by a dot and is named by writing a capital letter next to the dot.
h r c On the ACT, remember that diagrams are usually drawn to scale, so you can always eyeball to determine measurements if you get stuck.
 ACT Plane Geometry Review Let s first take a look at the common formulas you need for the ACT. Then we ll review the rules for the tested shapes. There are also some practice problems at the end of this
ACT Plane Geometry Review Let s first take a look at the common formulas you need for the ACT. Then we ll review the rules for the tested shapes. There are also some practice problems at the end of this
Print n Play Collection. Of the 12 Geometrical Puzzles
 Print n Play Collection Of the 12 Geometrical Puzzles Puzzles Hexagon-Circle-Hexagon by Charles W. Trigg Regular hexagons are inscribed in and circumscribed outside a circle - as shown in the illustration.
Print n Play Collection Of the 12 Geometrical Puzzles Puzzles Hexagon-Circle-Hexagon by Charles W. Trigg Regular hexagons are inscribed in and circumscribed outside a circle - as shown in the illustration.
BREATHITT COUNTY SCHOOLS 3 rd Grade Math Curriculum Map Week Standard Key Vocabulary Learning Target Resources Assessment
 Number Operations/Fractions/Algebraic Expressions Week 1 Week 2 3.NBT.1: Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. 3.NBT.2: Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using
Number Operations/Fractions/Algebraic Expressions Week 1 Week 2 3.NBT.1: Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. 3.NBT.2: Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using
Session 1 What Is Geometry?
 Key Terms for This Session Session 1 What Is Geometry? New in This Session altitude angle bisector concurrent line line segment median midline perpendicular bisector plane point ray Introduction In this
Key Terms for This Session Session 1 What Is Geometry? New in This Session altitude angle bisector concurrent line line segment median midline perpendicular bisector plane point ray Introduction In this
Sample Questions from Ga. Department of Education
 Strand: Measurements & Geometry Sample Questions from Ga. Department of Education Name: Concept 1 (M18 M21): Measurements (including metric) Estimates measures in both customary and metric systems. 1.
Strand: Measurements & Geometry Sample Questions from Ga. Department of Education Name: Concept 1 (M18 M21): Measurements (including metric) Estimates measures in both customary and metric systems. 1.
KCATM Geometry
 Name School KCATM Geometry 9 10 2013 1) Find the minimum perimeter of a rectangle whose area is 169 square meters. a) 42 meters b) 13 meters c) 26 meters d) 52 meters 2) Find the coordinates of the midpoint
Name School KCATM Geometry 9 10 2013 1) Find the minimum perimeter of a rectangle whose area is 169 square meters. a) 42 meters b) 13 meters c) 26 meters d) 52 meters 2) Find the coordinates of the midpoint
Copying a Line Segment
 Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY. Thursday, August 17, :30 to 3:30 p.m.
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, August 17, 2017 12:30 to 3:30 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: The possession or use of any communications
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, August 17, 2017 12:30 to 3:30 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: The possession or use of any communications
RightStart Mathematics
 Most recent update: January, 019 RightStart Mathematics Corrections and Updates for Level C/Grade Lessons and Worksheets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET CHANGE DATE CORRECTION OR UPDATE Lesson /01/01
Most recent update: January, 019 RightStart Mathematics Corrections and Updates for Level C/Grade Lessons and Worksheets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET CHANGE DATE CORRECTION OR UPDATE Lesson /01/01
Math Review Questions
 Math Review Questions Working with Feet and Inches A foot is broken up into twelve equal parts called inches. On a tape measure, each inch is divided into sixteenths. To add or subtract, arrange the feet
Math Review Questions Working with Feet and Inches A foot is broken up into twelve equal parts called inches. On a tape measure, each inch is divided into sixteenths. To add or subtract, arrange the feet
6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT. Name Period Date
 6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT Name Period Date Perimeter and Area of Triangles and Rectangles The perimeter is the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT Name Period Date Perimeter and Area of Triangles and Rectangles The perimeter is the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
Class : VI - Mathematics
 O. P. JINDAL SCHOOL, RAIGARH (CG) 496 001 Phone : 07762-227042, 227293, (Extn. 227001-49801, 02, 04, 06); Fax : 07762-262613; e-mail: opjsraigarh@jspl.com; website : www.opjsrgh.in Class : VI - Mathematics
O. P. JINDAL SCHOOL, RAIGARH (CG) 496 001 Phone : 07762-227042, 227293, (Extn. 227001-49801, 02, 04, 06); Fax : 07762-262613; e-mail: opjsraigarh@jspl.com; website : www.opjsrgh.in Class : VI - Mathematics
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary. Correlations
 Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
UNIT PLAN. Grade Level: Unit #: 7 Unit Name: Circles
 UNIT PLAN Subject: Geometry Grade Level: 10-12 Unit #: 7 Unit Name: Circles Big Idea/Theme: The understanding of properties of circles, the lines that intersect them, and the use of their special segments
UNIT PLAN Subject: Geometry Grade Level: 10-12 Unit #: 7 Unit Name: Circles Big Idea/Theme: The understanding of properties of circles, the lines that intersect them, and the use of their special segments
VOCABULARY GUIDE Foundation-Year 7
 Y oundation-year 7 Y across backwards calendar deep group half add balance cents eight fast guess halves add on before difference eighteen few heavier after between clock different eleven fewer heaviest
Y oundation-year 7 Y across backwards calendar deep group half add balance cents eight fast guess halves add on before difference eighteen few heavier after between clock different eleven fewer heaviest
CCE Calendar for Session Delhi Region (Split-up Syllabus) Class VI- Mathematics TERM I
 CCE Calendar for Session 2016-2017 Delhi Region (Split-up Syllabus) Class VI- Mathematics TERM I MONTHS CHAPTER/TOPIC SUB TOPICS TO BE COVERED NUMB ER OF PERIO DS SUGGESTED ACTIVITIES CH 1. Knowing Our
CCE Calendar for Session 2016-2017 Delhi Region (Split-up Syllabus) Class VI- Mathematics TERM I MONTHS CHAPTER/TOPIC SUB TOPICS TO BE COVERED NUMB ER OF PERIO DS SUGGESTED ACTIVITIES CH 1. Knowing Our
Overview of Structure and Content
 Introduction The Math Test Specifications provide an overview of the structure and content of Ohio s State Test. This overview includes a description of the test design as well as information on the types
Introduction The Math Test Specifications provide an overview of the structure and content of Ohio s State Test. This overview includes a description of the test design as well as information on the types
Geometry. Teacher s Guide
 Geometry Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher.......................................................... vi Classroom Management..................................................
Geometry Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher.......................................................... vi Classroom Management..................................................
Analytic Geometry EOC Study Booklet Geometry Domain Units 1-3 & 6
 DOE Assessment Guide Questions (2015) Analytic Geometry EOC Study Booklet Geometry Domain Units 1-3 & 6 Question Example Item #1 Which transformation of ΔMNO results in a congruent triangle? Answer Example
DOE Assessment Guide Questions (2015) Analytic Geometry EOC Study Booklet Geometry Domain Units 1-3 & 6 Question Example Item #1 Which transformation of ΔMNO results in a congruent triangle? Answer Example
The Magic Circle Basic Lesson. Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation
 The Magic Circle Basic Lesson Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation The Tools Needed Compass Straightedge Pencil Paper (not graph paper, 8.5 x 11 is fine) Your Brain (the most important tool!)
The Magic Circle Basic Lesson Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation The Tools Needed Compass Straightedge Pencil Paper (not graph paper, 8.5 x 11 is fine) Your Brain (the most important tool!)
Problem of the Month What s Your Angle?
 Problem of the Month What s Your Angle? Overview: In the Problem of the Month What s Your Angle?, students use geometric reasoning to solve problems involving two dimensional objects and angle measurements.
Problem of the Month What s Your Angle? Overview: In the Problem of the Month What s Your Angle?, students use geometric reasoning to solve problems involving two dimensional objects and angle measurements.
1 Version 2.0. Related Below-Grade and Above-Grade Standards for Purposes of Planning for Vertical Scaling:
 Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Geometry Target E [a]: Draw, construct,
Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Geometry Target E [a]: Draw, construct,
Date: Period: Quadrilateral Word Problems: Review Sheet
 Name: Quadrilateral Word Problems: Review Sheet Date: Period: Geometry Honors Directions: Please answer the following on a separate sheet of paper. Completing this review sheet will help you to do well
Name: Quadrilateral Word Problems: Review Sheet Date: Period: Geometry Honors Directions: Please answer the following on a separate sheet of paper. Completing this review sheet will help you to do well
Design Your Own Dream Home! Michael Daniels Olive Grove Charter School Grade Levels: 9-12 Subject: Mathematics
 Design Your Own Dream Home! Michael Daniels Olive Grove Charter School Grade Levels: 9-12 Subject: Mathematics Project Summary: Using Free CAD, a computer aided drafting software program, students design
Design Your Own Dream Home! Michael Daniels Olive Grove Charter School Grade Levels: 9-12 Subject: Mathematics Project Summary: Using Free CAD, a computer aided drafting software program, students design
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD. We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential
 Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Downloaded from
 Understanding Elementary Shapes 1 1.In the given figure, lines l and m are.. to each other. (A) perpendicular (B) parallel (C) intersect (D) None of them. 2.a) If a clock hand starts from 12 and stops
Understanding Elementary Shapes 1 1.In the given figure, lines l and m are.. to each other. (A) perpendicular (B) parallel (C) intersect (D) None of them. 2.a) If a clock hand starts from 12 and stops
Maths Makes Sense. 3 Medium-term plan
 Maths Makes Sense 3 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 3 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Respond to I will act the Real Story, you write the Maths Story (including the answer), for addition
Maths Makes Sense 3 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 3 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Respond to I will act the Real Story, you write the Maths Story (including the answer), for addition
Meet #5 March Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts
 Meet #5 March 2008 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #5 March 2008 Category 1 Mystery 1. In the diagram to the right, each nonoverlapping section of the large rectangle is
Meet #5 March 2008 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #5 March 2008 Category 1 Mystery 1. In the diagram to the right, each nonoverlapping section of the large rectangle is
Standard 4.G.1 4.G.2 5.G.3 5.G.4 4.MD.5
 Draw and identify lines and angles, as well as classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles (Standards 4.G.1 3). Standard 4.G.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute,
Draw and identify lines and angles, as well as classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles (Standards 4.G.1 3). Standard 4.G.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute,
Statue of Liberty Eiffel Tower Gothic Cathedral (p1) Gothic Cathedral (p2) Gothic Cathedral (p3) Medieval Manor (p1)
 ARCHITECTURE Statue of Liberty Eiffel Tower Gothic Cathedral (p1) Gothic Cathedral (p2) Gothic Cathedral (p3) Medieval Manor (p1) Medieval Manor (p1) Toltec sculpture Aqueduct Great Pyramid of Khufu (p1)
ARCHITECTURE Statue of Liberty Eiffel Tower Gothic Cathedral (p1) Gothic Cathedral (p2) Gothic Cathedral (p3) Medieval Manor (p1) Medieval Manor (p1) Toltec sculpture Aqueduct Great Pyramid of Khufu (p1)
Intermediate A. Help Pages & Who Knows
 & Who Knows 83 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication problem.
& Who Knows 83 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication problem.
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2011 KCATM Contest
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2011 KCATM Contest GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 4 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 15 minutes You may use calculators
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2011 KCATM Contest GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 4 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 15 minutes You may use calculators
2. Here are some triangles. (a) Write down the letter of the triangle that is. right-angled, ... (ii) isosceles. ... (2)
 Topic 8 Shapes 2. Here are some triangles. A B C D F E G (a) Write down the letter of the triangle that is (i) right-angled,... (ii) isosceles.... (2) Two of the triangles are congruent. (b) Write down
Topic 8 Shapes 2. Here are some triangles. A B C D F E G (a) Write down the letter of the triangle that is (i) right-angled,... (ii) isosceles.... (2) Two of the triangles are congruent. (b) Write down
Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles. Angle Bisector. Perpendicular Bisector
 Lessons and Activities GEOMETRY Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles Angle Bisector Perpendicular Bisector 1 Lessons and Activities POLYGONS are PLANE SHAPES (figures) with at least 3 STRAIGHT sides and
Lessons and Activities GEOMETRY Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles Angle Bisector Perpendicular Bisector 1 Lessons and Activities POLYGONS are PLANE SHAPES (figures) with at least 3 STRAIGHT sides and
Unit 1 Foundations of Geometry: Vocabulary, Reasoning and Tools
 Number of Days: 34 9/5/17-10/20/17 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Using building blocks from Algebra 1, students will use a variety of tools and techniques to construct, understand, and prove geometric
Number of Days: 34 9/5/17-10/20/17 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Using building blocks from Algebra 1, students will use a variety of tools and techniques to construct, understand, and prove geometric
0810ge. Geometry Regents Exam y # (x $ 3) 2 % 4 y # 2x $ 5 1) (0,%4) 2) (%4,0) 3) (%4,%3) and (0,5) 4) (%3,%4) and (5,0)
 0810ge 1 In the diagram below, ABC! XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements
0810ge 1 In the diagram below, ABC! XYZ. 3 In the diagram below, the vertices of DEF are the midpoints of the sides of equilateral triangle ABC, and the perimeter of ABC is 36 cm. Which two statements
Estimating Tolerance Accuracy (Rounding, including sig. fig.) Scientific notation
 S3 Pathways for learning in Maths Pathway 1 (Lower) Pathway 2 (Middle) Pathway 3 (Upper) Targets Complete coverage of level 3 experiences and outcomes in Mathematics Cover level 4 experiences and outcomes
S3 Pathways for learning in Maths Pathway 1 (Lower) Pathway 2 (Middle) Pathway 3 (Upper) Targets Complete coverage of level 3 experiences and outcomes in Mathematics Cover level 4 experiences and outcomes
4 What are and 31,100-19,876? (Two-part answer)
 1 What is 14+22? 2 What is 68-37? 3 What is 14+27+62+108? 4 What are 911-289 and 31,100-19,876? (Two-part answer) 5 What are 4 6, 7 8, and 12 5? (Three-part answer) 6 How many inches are in 4 feet? 7 How
1 What is 14+22? 2 What is 68-37? 3 What is 14+27+62+108? 4 What are 911-289 and 31,100-19,876? (Two-part answer) 5 What are 4 6, 7 8, and 12 5? (Three-part answer) 6 How many inches are in 4 feet? 7 How
Geometry. Practice Pack
 Geometry Practice Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents Unit 1: Lines and Angles Practice 1.1 What Is Geometry?........................ 1 Practice 1.2 What Is Geometry?........................ 2 Practice
Geometry Practice Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents Unit 1: Lines and Angles Practice 1.1 What Is Geometry?........................ 1 Practice 1.2 What Is Geometry?........................ 2 Practice
Magical Math G ROOVY G EOMETRY. Games and Activities That Make Math Easy and Fun. Lynette Long. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Magical Math G ROOVY G EOMETRY Games and Activities That Make Math Easy and Fun Lynette Long John Wiley & Sons, Inc. G ROOVY G EOMETRY Also in the Magical Math series Dazzling Division Delightful Decimals
Magical Math G ROOVY G EOMETRY Games and Activities That Make Math Easy and Fun Lynette Long John Wiley & Sons, Inc. G ROOVY G EOMETRY Also in the Magical Math series Dazzling Division Delightful Decimals
Whirlygigs for Sale! Rotating Two-Dimensional Figures through Space. LESSON 4.1 Skills Practice. Vocabulary. Problem Set
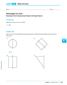 LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date Whirlygigs for Sale! Rotating Two-Dimensional Figures through Space Vocabulary Describe the term in your own words. 1. disc Problem Set Write the name of the solid figure
LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date Whirlygigs for Sale! Rotating Two-Dimensional Figures through Space Vocabulary Describe the term in your own words. 1. disc Problem Set Write the name of the solid figure
Directorate of Education
 Directorate of Education Govt. of NCT of Delhi Worksheets for the Session 2012-2013 Subject : Mathematics Class : VI Under the guidance of : Dr. Sunita S. Kaushik Addl. DE (School / Exam) Coordination
Directorate of Education Govt. of NCT of Delhi Worksheets for the Session 2012-2013 Subject : Mathematics Class : VI Under the guidance of : Dr. Sunita S. Kaushik Addl. DE (School / Exam) Coordination
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy
 The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
Grade 7 Mathematics Item Specifications Florida Standards Assessments
 Assessment Limit MAFS7.G.1 Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including
Assessment Limit MAFS7.G.1 Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including
Step 2: Extend the compass from the chosen endpoint so that the width of the compass is more than half the distance between the two points.
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 1 Description: GEO Topic 1 Test: Tools of Geometry Form: 201 1. A student followed the given
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 1 Description: GEO Topic 1 Test: Tools of Geometry Form: 201 1. A student followed the given
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures. Grade 9 Mathematics
 Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
