Effect of Coolant on Carbide Tool Life
|
|
|
- Noah Warner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Effect of Coolant on Carbide Tool Life U. Dileep Kumar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sistam Engineering College, Srikakulam, A.P , India. ABSTRACT Any liquid or gas applied directly to machining operation to improve cutting performance two main problems addressed by cutting fluids: Heat generation at shear zone and friction zone, Friction at the tool chip and tool work interfaces. Other functions and benefits: Wash away chips (e.g., grinding and milling), Reduce temperature of work part for easier handling, Improve dimensional stability of work part. Cutting fluids are used in machining for a variety of reasons such as improving tool life, reducing work-piece thermal deformation, improving surface finish. Mota and Machado (1995) concluded that reducing cutting tool cost and increased production can be achieved through the use of appropriate cutting fluids. In this thesis soluble oil, water and palm kernel oil were used as coolants in machining operations. Tungsten carbide cutting tools are employed as cutter with different cutting speeds. The main aim of this thesis is to conduct test on milling machine by changing cooling system and finding grain structure changed inside the cutting tool in different cases. Transient thermal analysis is done on the parametric model to determine the effect of different cutting fluids on the cutters. Parametric Modeling is done in Pro/Engineer and analysis is done in Ansys. Key words: Friction, Tool cost, Cutting fluids 1. INTRODUCTION Milling is the process of cutting away material by feeding a work piece past a rotating multiple tooth cutter. The cutting action of the many teeth around the milling cutter provides a fast method of machining. G. Sireesh Kumar Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sistam Engineering College, Srikakulam, A.P , India. 1.1 TYPES OF MILLING MACHINES 1.2 KNEE-TYPE MILLING MACHINE Knee-type milling machines are characterized by a vertically adjustable worktable resting on a saddle which is supported by a knee. The knee is a massive casting that rides vertically on the milling machine column and can be clamped rigidly to the column in a position where the milling head and milling machine spindle are properly adjusted vertically for operation [1]. The plain vertical machines are characterized by a spindle located vertically, parallel to the column face, and mounted in a sliding head that can be fed up and down by hand or power. Modern vertical milling machines are designed so the entire head can also swivel to permit working on angular surfaces. The turret and swivel head assembly is designed for making precision cuts and can be swung 360 on its base. Angular cuts to the horizontal plane may be made with precision by setting the head at any required angle within a 180 arc. The plain horizontal milling machine s column contains the drive motor and gearing and a fixed position horizontal milling machine spindle. An adjustable overhead arm containing one or more arbor supports projects forward from the top of the column. The arm and arbor supports are used to stabilize long arbors. Supports can be moved along the overhead arm to support the arbor where support is desired depending on the position of the milling cutter or cutters [2]. Cite this article as: U. Dileep Kumar & G. Sireesh Kumar, "Effect of Coolant on Carbide Tool Life", International Journal & Magazine of Engineering, Technology, Management and Research, Volume 5 Issue 2, 2018, Page Page 95
2 The milling machine s knee rides up or down the column on a rigid track. A heavy, vertical positioning screw beneath past the milling cutter. The milling machine is excellent for forming flat surfaces, cutting dovetails and keyways, forming and fluting milling cutters and reamers, cutting gears, and so forth. Many special operations can be performed with the attachments available for milling machine use. The knee is used for raising and lowering. The saddle rests upon the knee and supports the worktable. The saddle moves in and out on a dovetail to control cross feed of the worktable. The worktable traverses to the right or left upon the saddle for feeding the work piece past the milling cutter. The table may be manually controlled or power fed. 1.3 UNIVERSAL HORIZONTAL MILLING MACHINE The basic difference between a universal horizontal milling machine and a plain horizontal milling machine is the addition of a table swivel housing between the table and the saddle of the universal machine. This permits the table to swing up to 45 in either direction for angular and helical milling operations. The universal machine can be fitted with various attachments such as the indexing fixture, rotary table, slotting and rack cutting attachments, and various special fixtures [3]. 1.4 RAM-TYPE MILLING MACHINE The ram-type milling machine is characterized by a spindle mounted to a movable housing on the column to permit positioning the milling cutter forward or rearward in ahorizontal plane. Two popular ram-type milling machines are the universal milling machine and the swivel cutter head ram-type milling machine. 1.5 UNIVERSAL RAM-TYPE MILLING MACHINE The universal ram-type milling machine is similar to the universal horizontal milling machine, the difference being, as its name implies, the spindle is mounted on a ram ormovable housing. Fig:1.2 Fig: 1.1 Fig:1.3 Page 96
3 1.6 SWIVEL CUTTER HEAD RAM-TYPE MILLING MACHINE The cutter head containing the milling machine spindle is attached to the ram. The cutter head can be swiveled from a vertical spindle position to a horizontal spindle position or can be fixed at any desired angular position between vertical and horizontal [4]. The saddle and knee are hand driven for vertical and cross feed adjustment while the worktable can be either hand or power driven at the operator s choice. 1.7 SAFETY RULES FOR MILLING MACHINES Milling machines require special safety precautions while being used. Do not make contact with the revolving cutter. Place a wooden pad or suitable cover over the table surface to protect it from possible damage. Use the buddy system when moving heavy attachments. Do not attempt to tighten arbor nuts using machine power. When installing or removing milling cutters, always hold them with a rag to prevent cutting your hands. While setting up work, install the cutter last to avoid being cut. Never adjust the work piece or work mounting devices when the machine is operating. Chips should be removed from the work piece with anappropriate rake and a brush. Shut the machine off before making any adjustments or measurements. When using cutting oil, prevent splashing by using appropriate splash guards. Cutting oil on the floor can cause a slippery condition that could result in operator Injury. 1.8 TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT MILLING CUTTERS 1.9 Classification of Milling Cutters Milling cutters are usually made of high-speed steel and are available in a great variety of shapes and sizes for various purposes. You should know the names of the most common classifications of cutters, their uses, and, in a general way, the sizes best suited to the work at hand [5] Milling Cutter Nomenclature Figure 8-3 shows two views of a common milling cutter with its parts and angles identified. These parts and angles in some form are common to all cutter types. The pitch refers to the angular distance between like or adjacent teeth. The pitch is determined by the number of teeth. The tooth face is the forwardforms the cutting edge. The cutting edge is the angle on each tooth that performs the cutting. The land is the narrow surface behind the cutting edge on each tooth. The rake angle is the angle formed between the face of the tooth and the centerline of the cutter. The rake angle defines the cutting edge and provides a path for chips that are cut from the work piece. The primary clearance angle is the angle of the land of each tooth measured from a line tangent to the centerline of the cutter at the cutting edge. This angle prevents each tooth from rubbing against the work piece after it makes its cut. This angle defines the land of each tooth and provides additional clearance for passage of cutting oil and chips.. Fig:1.4 Page 97
4 The hole diameter determines the size of the arbor necessary to mount the milling cutter. Plain milling cutters that are more than 3/4 inch in width are usually made with spiral or helical teeth. A plain spiral-tooth milling cutter produces a better and smoother finish and requires less power to operate. A plain helical tooth milling cutter is especially desirable when milling an uneven surface or one with holes in it. Fig:1.6 Fig:1.5 Types of Teeth The teeth of milling cutters may be made for right-hand or left-hand rotation, and with either right-hand or lefthand helix. Determine the hand of the cutter by looking at the face of the cutter when mounted on the spindle. A right-hand cutter must rotate counterclockwise; a lefthand cutter must rotate clockwise. The right-hand helix is shown by the flutes leading to the right; a left-hand helix is shown by the flutes leading to the left. The direction of the helix does not affect the cutting ability of the cutter, but take care to see that the direction of rotation is correct for the hand of the cutter 1.11Helical Milling Cutters The helical milling cutter is similar, to the plain milling cutter, but the teeth have a helix angle of 45 to 60. The steep helix produces a shearing action that results in smooth, vibration-free cuts. They are available for arbor mounting, or with an integral shank with or without a pilot. This type of helical cutter is particularly useful for milling elongated slots and for light cuts on soft metal. See Figure Metal Slitting Saw Milling Cutter The metal slitting saw milling cutter is essentially a very thin plain milling cutter. It is ground slightly thinner toward the center to provide side clearance. These cutters are used for cutoff operations and for milling deep, narrow slots, and are made in widths from 1/32 to 3/16 inch. Saw teeth similar to those shown in Figure 8-3 are either straight or helical in the smaller sizes of plain milling cutters, metal slitting saw milling cutters, and end milling cutters. The cutting edge is usually given about 5 degrees primary clearance [6]. Sometimes the teeth are provided with off-set nicks which break up chips and make coarser feeds possible. Fig:1.7 Page 98
5 1.13 Side Milling Cutters Side milling cutters are essentially plain milling cutters with the addition of teeth on one or both sides. A plain side milling cutter has teeth on both sides and on the periphery [7]. When teeth are added to one side only, the cutter is called a half-side milling cutter and is identified as being either a right-hand or left-hand cutter. Side milling cutters are generally used for slotting and straddle milling. Interlocking tooth side milling cutters and staggered tooth side milling cutters are used for cutting relatively wide slots with accuracy (Figure 8-6). Interlocking tooth side milling cutters can be repeatedly sharpened without changing the width of the slot they will machine [8]. After sharpening, a washer is placed between the two cutters to compensate for the ground off metal. The staggered tooth cutter is the most washer is placed between the two cutters to compensate for efficient type for milling slots where the depth exceeds the width End Milling Cutters The end milling cutter, also called an end mill, has teeth on the end as well as the periphery. The smaller end milling cutters have shanks for chuck mounting or direct spindle mounting. End milling cutters may have straight or spiral flutes. Spiral flute end milling cutters are classified as left hand or right-hand cutters depending on the direction of rotation of the flutes. If they are small cutters, they may have either a straight or tapered shank. Fig:1.8 The most common end milling cutter is the spiral flute cutter containing four flutes. Two-flute end milling cutters, sometimes referred to as two-lip end mill cutters, are used for milling slots and keyways where no drilled hole is providedfor starting the cut. These cutters drill their own starting holes.straight flute end milling cutters are generally used for milling both soft or tough materials, while spiral flute cutters are used mostly for cutting steel. Large end milling cutters (normally over 2 inches in diameter) (Figure 8-10) are called shell end mills and are recessed on the face to receive a screw or nut for mounting on a separate shank or mounting on an arbor, like plain milling cutters. The teeth are usually helical and the cutter is used particularly for face milling operations requiring the facing of two surfaces at right angles to each other. 4. INTRODUCTION TO PRO/ENGINEER Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire is the standard in 3D product design, featuring industry-leading productivity tools that promote best practices in design while ensuring compliance with your industry and company standards. Integrated Pro/ENGINEER CAD/CAM/CAE solutions allow you to design faster than ever, while maximizing innovation and quality to ultimately create exceptional products [9]. Customer requirements may change and time pressures may continue to mount, but your product design needs remain the same - regardless of your project's scope, you need the powerful, easy-to-use, affordable solution that Pro/ENGINEER provides. LITERATURE SURVEY PAPER 1 - Optimization of Machining Parameters of Titanium Alloy for Tool Life by Dinesh Kumar Chauhan, Kapil Kumar Chauhan High speed machining of highly reactive material like titanium and its alloys is still far away uncertain. For this reason, it is wiser to study the optimization of Machining parameters under transient cutting speed before Page 99
6 advancing to high speed machining.this paper presents the influence of machining parameters like coolant flow rate, cutting speed on Tool life of Titanium alloy during machining. Machining process is carried out in dry or nearly dry condition using Physical Vapor Disposition (PVD) coated cemented carbide tools. For near dry machining, two levels of coolant flow rate of 50 and 100 ml/h were investigated.a plan of experiments based on Taguchi technique has been used to acquire the data. An Orthogonal array and signal to noise (S/N) ratio are employed to investigate the machining characteristics of titanium alloy & optimize the machining parameters. In optimization technique, Taguchi method is used for optimization for Variable parameters coolant flow rate (0, 50& 100mL/Hr), cutting speed (120, 135 & 150m/min), feed rate (0.1, 0.125, 0.25mm/tooth) and depth of cut (2, 2.25 & 2.5 mm). Finally Minitab 15, a comprehensive DOE tool is used for multilevel factorial screening designs to help you find the critical factors that lead to breakthrough improvements PAPER 2 - Surface Roughness and Tool Wear Study on Milling of AISI 304 Stainless SteelUsing Different Cooling Conditions by P. Chockalingam, Lee Hong Wee This research deals with the effect of different coolant conditions on milling of AISI 304 stainless steel. Cooling methods used in this investigation were flooding of synthetic oil, water-based emulsion, and compressed cold air. Cutting forces and the surface roughness were studied and tool flank wears observed. In this study, the comparison between different coolants effect to the milling of AISI 304 stainless steel is done and the results from the study can provide very useful information in manufacturing field. The experiment results showed that water-based emulsion gave better surface finish and lower cutting force followed by synthetic oil and compressed cold air. Different cooling condition required different parameters in order to obtain lower surface roughness and cutting force. Chipping was the initial wear mode in the milling of AISI 304 stainless steel. 4.1 Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire Benefits: Unsurpassed geometry creation capabilities allow superior product differentiation and manufacturability Fully integrated applications allow you to develop everything from concept to manufacturing within one application Automatic propagation of design changes to all downstream deliverables allows you to design with confidence Complete virtual simulation capabilities enable you to improve product performance and exceed product quality goals Automated generation of associative tooling design, assembly instructions, and machine code allow for maximum production efficiency Pro ENGINEER can be packaged in different versions to suit your needs, from Pro/ENGINEER Foundation XE, to Advanced XE Package and Enterprise XE Package, Pro/ENGINEER Foundation XE Package brings together a broad base of functionality. From robust part modelling to advanced surfacing, powerful assembly modelling and simulation, your needs will be met with this scaleable solution. Flex3C and Flex Advantage Build on this base offering extended functionality of ourchoosing. 4.2 DIFFERENT MODULES IN PRO/ENGINEER PART DESIGN ASSEMBLY DRAWING SHEETMETAL MANUFACTURING MODEL OF CUTTER Fig:4.1 Designed model of milling cutter Page 100
7 4.3 2-D DRAWING Fig:4.2 Wire frame model of milling cutter D DRAWING THERMAL ANALYSIS OF MILLING CUTTER - TUNGSTEN CARBIDE COOLANT - WATER Element Type: Solid 20 node 90 Material Properties: Thermal Conductivity 70w/mk Specific Heat 320 j/kg k Density kg/mm 3 Apply Loads Loads Define Loads Apply Thermal Temperature Temperature 393k Loads define Loads Apply Thermal Heat flow On nodes Heat flow 2kj/sec Loads define Loads Apply Thermal Convection on areas Bulk Temperature 313k Film coefficient of water = 0.005W/mm 2 K Solution Solution Solve Current LS ok Post Processor Nodal Solution DOF Solution Nodal Temperature Vector sum Imported model Fig:4.3 Imported model of cutter Meshed model Fig::4.5 Stress variations Nodal Solution Thermal Gradient Vector sum Fig:4.4 Meshed model of cutter Fig:4.6 Stress induced Page 101
8 Nodal Solution Thermal flux vector sum Fig:4.7 Principal stress distributed COOLANT - SOLUBLE OIL Film coefficient of soluble oil = W/mm 2 K Nodal Solution DOF Solution Nodal Temperature Vector sum Fig:4.9 Strain diagrams Nodal Solution Thermal flux vector sum Fig:4.10 Normal temperature variation Fig:4.8 Coolant applied Nodal Solution Thermal Gradient Vector sum PALM KERNEL OIL Film coefficient of palm kernel oil =0.007 W/mm 2 K Nodal Solution DOF Solution Nodal Temperature Vector sum Page 102
9 RESULTS TABLE Fig:4.11 At 0.007W/mm Nodal Solution Thermal Gradient Vector sum Fig:4.12 Nodal Solution Thermal flux vector sum Fig: TOOL LIFE CALCULATIONS ROUGHING OPERATION The Taylor's Equation for Tool Life Expectancy provides a good approximation. where =Cutting Speed = 2500rpm = m/min T=tool life n and C are constants found by experimentation or published data; they are properties of tool material, workpiece and feed rate. For Tool Material of Carbide and Machining of Steel, n = 0.25 C = 500m/min Carbide Cutter 50R6 V c T n = C T 0.25 = 500 T 0.25 = T = /0.25 T = min = 13.2hrs FINISHING OPERATION Carbide Cutter 50R0.8 Cutting Speed = 3500rpm = 44m/min V c T n = C 44 T 0.25 = 500 T 0.25 = T = /0.25 T = min = hrs four tips this type of cutter is having four corner radius for each insert. For each corner= 277/4= 69 hours Page 103
10 6 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION A machining process is performed using carbide cutter with cutting parameters of spindle speed 2300rpm, feed rate 1000mm/min and depth of cut 0.3mm. The machining process is done for 6 hrs for roughing [10]. The cutter used is Solid carbide end mill This type of end mill cutters is used for roughing and sharp corner finishing. Cutter material is solid carbide. 6.1 TYPES OF MILLING CUTTERS 1.METRIC SLOT DRILLS Flute center cutting type This cutter is used to drill blind and through holes. Its material is HSS. Fig:6.2 Milling Cutter MCROSTRUCTURAL ANALYSIS BEFORE MACHINING Fig:6.1 Cutter Fig 6.3 Failed milling cutter Fig:6.15 Micro structure Page 104
11 COOLANT WATER COOLANT PALM KERNAL OIL Fig:6.16 Water as Coolant COOLANT SOLUABLE OIL Fig:6.18 PALM KERNAL OIL 6.3 HARDNESS TEST Fig:6.17 COOLANT SOLUABLE OIL CONCLUSION In this thesis soluble oil, water and palm kernel oil were used as coolants in machining operations. Tungsten carbide cutting tool is employed as cutter for a machining process is performed using carbide cutter with cutting parameters of spindle speed 2300rpm, feed rate 1000mm/min and depth of cut 0.3mm. The machining process is done for 6 hrs for roughing. Page 105
12 Microstructure test and hardness test are performed on the cutter before machining and after machining. By observing the microstructure test, there is not much difference in the microstructure before machining and after machining. By observing the hardness test, the hardness is increasing after machining and it is more for soluble oil. So when soluble oil is used the cutter fails fast than by using water and palm kernel oil. Thermal analysis is done on the cutter to determine the heat transfer rate when the coolants are used. By observing the analysis results, the heat transfer rate is more for palm kernel oil since thermal flux is more. Water is also good coolant which is easily available. REFERENCES [1]. Optimization of Machining Parameters of Titanium Alloy for Tool Life by Dinesh Kumar Chauhan, Kapil Kumar Chauhan Manufacturing Science and Engineering, (2): p [8]. Li, K.-M. and S.Y. Liang, Modeling of cutting forces in near dry machining under tool wear effect. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, (7-8): p [9]. Su, Y., et al., Refrigerated cooling air cutting of difficult-to-cut materials. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, (6): p [10]. Hong, S.Y., I. Markus, and W. Jeong, New cooling approach and tool life improvement in cryogenic machining of titaniumalloy Ti-6Al-4V. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, (15): p [2]. Surface Roughness and Tool Wear Study on Milling of AISI 304 Stainless Steel Using Different Cooling Conditions by P. Chockalingam, Lee Hong Wee [3]. The Effects of a High-Pressure Coolant Jet on Machining by A R Machado, J Wallbank [4]. Effect of high pressure coolant on surface finish in turning operation by Mr. R. A. Patil, Prof. V. D. Shinde, Prof. H. V. Shete, Prof. S. P. Nevagi [5]. Effects of Cryogenic Cooling on the Surface Quality and Tool Wearin End-Milling 6061-T6 Aluminium [6]. López de Lacalle, L.N., et al., Experimental and numerical investigation of the effect of spray cutting fluids in high speed milling. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, (1): p [7]. Li, K.-M. and S.Y. Liang, Modeling of Cutting Temperature in Near Dry Machining. Journal of Page 106
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY
 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT V Machine Tools Milling cutters Classification of milling cutters according to their design HSS cutters: Many cutters like end mills, slitting cutters, slab cutters, angular
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT V Machine Tools Milling cutters Classification of milling cutters according to their design HSS cutters: Many cutters like end mills, slitting cutters, slab cutters, angular
Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes.
 Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes. 24.1 Introduction In addition to parts with various external or internal round profiles, machining operations can produce many other parts
Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes. 24.1 Introduction In addition to parts with various external or internal round profiles, machining operations can produce many other parts
Metal Cutting - 5. Content. Milling Characteristics. Parts made by milling Example of Part Produced on a CNC Milling Machine 7.
 Content Metal Cutting - 5 Assoc Prof Zainal Abidin Ahmad Dept. of Manufacturing & Industrial Engineering Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 7. MILLING Introduction Horizontal
Content Metal Cutting - 5 Assoc Prof Zainal Abidin Ahmad Dept. of Manufacturing & Industrial Engineering Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 7. MILLING Introduction Horizontal
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN
 LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE: DRILLING. COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGR. ALIYU, S.J Course code: MCE
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE: DRILLING. COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGR. ALIYU, S.J Course code: MCE
Lecture 18. Chapter 24 Milling, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing (cont.) Planing
 Lecture 18 Chapter 24 Milling, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing (cont.) Planing For production of: Flat surfaces Grooves Notches Performed on long (on average 10 m) workpieces Workpiece moves / Tool
Lecture 18 Chapter 24 Milling, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing (cont.) Planing For production of: Flat surfaces Grooves Notches Performed on long (on average 10 m) workpieces Workpiece moves / Tool
Milling Machine Operations
 03/05/2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson 1 Objectives......3 Vertical Mill 4 Milling Machine Accessories......23 Common Milling Cutters......24 Metal Saws 24 End Mills 25 T-Slot Cutter 25 Dovetail Cutter......25
03/05/2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson 1 Objectives......3 Vertical Mill 4 Milling Machine Accessories......23 Common Milling Cutters......24 Metal Saws 24 End Mills 25 T-Slot Cutter 25 Dovetail Cutter......25
HOW TO USE MILLING MACHINE?
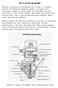 HOW TO USE MILLING MACHINE? Milling is the process of machining flat, curved, or irregular surfaces by feeding the workpiece against a rotating cutter containing a number of cutting edges. The usual Mill
HOW TO USE MILLING MACHINE? Milling is the process of machining flat, curved, or irregular surfaces by feeding the workpiece against a rotating cutter containing a number of cutting edges. The usual Mill
CHAPTER 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes Kalpakjian Schmid Manufacturing Engineering and Technology 2001 Prentice-Hall Page 23-1
 CHAPTER 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes Manufacturing Engineering and Technology 2001 Prentice-Hall Page 23-1 Examples of Parts Produced Using the Machining Processes in the Chapter
CHAPTER 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes Manufacturing Engineering and Technology 2001 Prentice-Hall Page 23-1 Examples of Parts Produced Using the Machining Processes in the Chapter
Chapter 23 Drilling and Hole Making Processes. Materials Processing. Hole Making Processes. MET Manufacturing Processes
 MET 33800 Manufacturing Processes Chapter 23 Drilling and Hole Making Processes Before you begin: Turn on the sound on your computer. There is audio to accompany this presentation. Materials Processing
MET 33800 Manufacturing Processes Chapter 23 Drilling and Hole Making Processes Before you begin: Turn on the sound on your computer. There is audio to accompany this presentation. Materials Processing
Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba
 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes 1 Homework Assignment Due Wensday 28/4/2010 1. Show that the distance lc in slab milling is approximately equal to for situations where D>>d. (see Figure
Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes 1 Homework Assignment Due Wensday 28/4/2010 1. Show that the distance lc in slab milling is approximately equal to for situations where D>>d. (see Figure
Typical Parts Made with These Processes
 Turning Typical Parts Made with These Processes Machine Components Engine Blocks and Heads Parts with Complex Shapes Parts with Close Tolerances Externally and Internally Threaded Parts Products and Parts
Turning Typical Parts Made with These Processes Machine Components Engine Blocks and Heads Parts with Complex Shapes Parts with Close Tolerances Externally and Internally Threaded Parts Products and Parts
ROOP LAL Unit-6 (Milling) Mechanical Engineering Department
 Notes: Milling Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B, Unit - I) 1 Introduction: Milling is a machining process which is performed with a rotary cutter with several cutting edges arranged on the periphery
Notes: Milling Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B, Unit - I) 1 Introduction: Milling is a machining process which is performed with a rotary cutter with several cutting edges arranged on the periphery
TOP WORK ISO 9001.CE UNIVERSAL CUTTER & TOOL GRINDER
 TOP WORK ISO 9001.CE UNIVERSAL CUTTER Precise ball groove of conformation Inclination of Wheelhead The wheelhead can easily tilt up to ±15 degrees, with a 360-degrees swivel on the horizontal plane. The
TOP WORK ISO 9001.CE UNIVERSAL CUTTER Precise ball groove of conformation Inclination of Wheelhead The wheelhead can easily tilt up to ±15 degrees, with a 360-degrees swivel on the horizontal plane. The
Materials Removal Processes (Machining)
 Chapter Six Materials Removal Processes (Machining) 6.1 Theory of Material Removal Processes 6.1.1 Machining Definition Machining is a manufacturing process in which a cutting tool is used to remove excess
Chapter Six Materials Removal Processes (Machining) 6.1 Theory of Material Removal Processes 6.1.1 Machining Definition Machining is a manufacturing process in which a cutting tool is used to remove excess
Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS
 Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS Turning and Related Operations Drilling and Related Operations Milling Machining Centers and Turning Centers Other Machining Operations High Speed Machining
Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS Turning and Related Operations Drilling and Related Operations Milling Machining Centers and Turning Centers Other Machining Operations High Speed Machining
PREVIEW COPY. Table of Contents. Using the Horizontal Milling Machine...3. Lesson Two Slab Milling Procedures...19
 Table of Contents Lesson One Using the Horizontal Milling Machine...3 Lesson Two Slab Milling Procedures...19 Lesson Three Milling Slots and Angles...35 Lesson Four Straddle, Side, and Face Milling...51
Table of Contents Lesson One Using the Horizontal Milling Machine...3 Lesson Two Slab Milling Procedures...19 Lesson Three Milling Slots and Angles...35 Lesson Four Straddle, Side, and Face Milling...51
Milling operations TA 102 Workshop Practice. By Prof.A.chANDRASHEKHAR
 Milling operations TA 102 Workshop Practice By Prof.A.chANDRASHEKHAR Introduction Milling machines are used to produce parts having flat as well as curved shapes. Milling machines are capable of performing
Milling operations TA 102 Workshop Practice By Prof.A.chANDRASHEKHAR Introduction Milling machines are used to produce parts having flat as well as curved shapes. Milling machines are capable of performing
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT-I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? (BT1) 2. Explain how chip
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT-I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? (BT1) 2. Explain how chip
UNIT 4: (iii) Illustrate the general kinematic system of drilling machine and explain its working principle
 UNIT 4: Drilling machines: Classification, constructional features, drilling & related operations, types of drill & drill bit nomenclature, drill materials. Instructional Objectives At the end of this
UNIT 4: Drilling machines: Classification, constructional features, drilling & related operations, types of drill & drill bit nomenclature, drill materials. Instructional Objectives At the end of this
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
 STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE MECH 121 - MANUFACTURING PROCESSES I Prepared By: Daniel Miller Updated By: Daniel Miller (April 2015) CANINO SCHOOL OF
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE MECH 121 - MANUFACTURING PROCESSES I Prepared By: Daniel Miller Updated By: Daniel Miller (April 2015) CANINO SCHOOL OF
Think efficiency, Think HSS MILLING
 Think efficiency, Think HSS MILLING SUMMARY MILLING TOOLS 2 Zoom on a milling cutter 3 Which HSS for maximum efficiency? 4 Coatings for the best performance 5 Vocabulary 6 Choose the right design 7 Select
Think efficiency, Think HSS MILLING SUMMARY MILLING TOOLS 2 Zoom on a milling cutter 3 Which HSS for maximum efficiency? 4 Coatings for the best performance 5 Vocabulary 6 Choose the right design 7 Select
Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making
 Manufacturing Engineering Technology in SI Units, 6 th Edition Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making Chapter Outline 1. Introduction 2. The Turning Process 3. Lathes and Lathe Operations
Manufacturing Engineering Technology in SI Units, 6 th Edition Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making Chapter Outline 1. Introduction 2. The Turning Process 3. Lathes and Lathe Operations
Milling. Chapter 24. Veljko Samardzic. ME-215 Engineering Materials and Processes
 Milling Chapter 24 24.1 Introduction Milling is the basic process of progressive chip removal to produce a surface. Mill cutters have single or multiple teeth that rotate about an axis, removing material.
Milling Chapter 24 24.1 Introduction Milling is the basic process of progressive chip removal to produce a surface. Mill cutters have single or multiple teeth that rotate about an axis, removing material.
Various other types of drilling machines are available for specialized jobs. These may be portable, bench type, multiple spindle, gang, multiple
 Drilling The process of making holes is known as drilling and generally drilling machines are used to produce the holes. Drilling is an extensively used process by which blind or though holes are originated
Drilling The process of making holes is known as drilling and generally drilling machines are used to produce the holes. Drilling is an extensively used process by which blind or though holes are originated
Machine Tools MILLING PROCESS. BY LAKSHMIPATHI YERRA Asst.professor Dept.of Mechanical Engg.
 Machine Tools MILLING PROCESS BY LAKSHMIPATHI YERRA Asst.professor Dept.of Mechanical Engg. FIG. 1 Typical parts and shapes produced by various cutting processes Fig. 2 Schematic illustration of milling
Machine Tools MILLING PROCESS BY LAKSHMIPATHI YERRA Asst.professor Dept.of Mechanical Engg. FIG. 1 Typical parts and shapes produced by various cutting processes Fig. 2 Schematic illustration of milling
Metal Cutting Processes 1 - Turning
 You are here: Home > Handout > Metal Cutting Processes 1 - Turning Metal Cutting Processes 1 - Turning Contents 1. Introduction 2. Center Lathe 3. Cutting Tools 4. Basic Matel Cutting Theory 5. Tool Angles
You are here: Home > Handout > Metal Cutting Processes 1 - Turning Metal Cutting Processes 1 - Turning Contents 1. Introduction 2. Center Lathe 3. Cutting Tools 4. Basic Matel Cutting Theory 5. Tool Angles
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology (AUST) Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering
 Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology (AUST) Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering LABORATORY MANUAL For the students of Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering 1 st
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology (AUST) Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering LABORATORY MANUAL For the students of Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering 1 st
TRAINING MANUAL. Part INTRODUCTION TO TWIST DRILLS
 PRESTO INTERNATIONAL UK LTD TRAINING MANUAL Part 2 INTRODUCTION TO TWIST DRILLS - 1 - DEFINITION:- A rotary end cutting tool having two or more cutting lips, and having two or more spiral (helical) or
PRESTO INTERNATIONAL UK LTD TRAINING MANUAL Part 2 INTRODUCTION TO TWIST DRILLS - 1 - DEFINITION:- A rotary end cutting tool having two or more cutting lips, and having two or more spiral (helical) or
OD1644 MILLING MACHINE OPERATIONS
 SUBCOURSE OD1644 MILLING MACHINE OPERATIONS EDITION 8 US ARMY WARRANT OFFICER ADVANCED COURSE MOS/SKILL LEVEL: 441A MILLING MACHINE OPERATIONS SUBCOURSE NO. OD1644 EDITION 8 US Army Correspondence Course
SUBCOURSE OD1644 MILLING MACHINE OPERATIONS EDITION 8 US ARMY WARRANT OFFICER ADVANCED COURSE MOS/SKILL LEVEL: 441A MILLING MACHINE OPERATIONS SUBCOURSE NO. OD1644 EDITION 8 US Army Correspondence Course
Product Information Report Maximizing Drill Bit Performance
 Overview Drills perform three functions when making a hole: Forming the chip The drill point digs into the material and pushes up a piece of it. Cutting the chip The cutting lips take the formed chip away
Overview Drills perform three functions when making a hole: Forming the chip The drill point digs into the material and pushes up a piece of it. Cutting the chip The cutting lips take the formed chip away
Metal Cutting (Machining)
 Metal Cutting (Machining) Metal cutting, commonly called machining, is the removal of unwanted portions from a block of material in the form of chips so as to obtain a finished product of desired size,
Metal Cutting (Machining) Metal cutting, commonly called machining, is the removal of unwanted portions from a block of material in the form of chips so as to obtain a finished product of desired size,
SHAPER, MILLING AND GEAR CUTTING MACHINES
 UNIT 3 SHAPER, MILLING AND GEAR CUTTING MACHINES 1. Compare hydraulic shaper with mechanical shaper? SL.NO Hydrulic shaper Mechanical shaper 1. smooth cutting operation Rough and noisy cutting operation
UNIT 3 SHAPER, MILLING AND GEAR CUTTING MACHINES 1. Compare hydraulic shaper with mechanical shaper? SL.NO Hydrulic shaper Mechanical shaper 1. smooth cutting operation Rough and noisy cutting operation
SHAPING AND PLANING Shaping and planing
 SHAPING AND PLANING Shaping and planing the simplest of all machine operations Straight line cutting motion with single-point cutting tool creates smooth flat surfaces. Mainly plain surfaces are machined
SHAPING AND PLANING Shaping and planing the simplest of all machine operations Straight line cutting motion with single-point cutting tool creates smooth flat surfaces. Mainly plain surfaces are machined
March weeks. surcharge for
 March weeks valid until 31.03.2012 all quoted prices are incl. 19% VAT for deliveries in the EU countries to customers with a valid VAT-no. and for deliveries in not EU member countries the VAT is not
March weeks valid until 31.03.2012 all quoted prices are incl. 19% VAT for deliveries in the EU countries to customers with a valid VAT-no. and for deliveries in not EU member countries the VAT is not
GENERAL MACHINING PRACTICE FOR CMI ELECTROMAGNETIC IRON
 GENERAL MACHINING PRACTICE FOR CMI ELECTROMAGNETIC IRON Electromagnetic Iron can be readily machined when proper tool angles are used. Tools should be ground to more acute cutting edge angles than are
GENERAL MACHINING PRACTICE FOR CMI ELECTROMAGNETIC IRON Electromagnetic Iron can be readily machined when proper tool angles are used. Tools should be ground to more acute cutting edge angles than are
UNIT 5: Indexing: Simple, compound, differential and angular indexing calculations. Simple problems on simple and compound indexing.
 UNIT 5: Milling machines: Classification, constructional features, milling cutters nomenclature, milling operations, up milling and down milling concepts. Indexing: Simple, compound, differential and angular
UNIT 5: Milling machines: Classification, constructional features, milling cutters nomenclature, milling operations, up milling and down milling concepts. Indexing: Simple, compound, differential and angular
Chapter 25. Other Machining Processes. Materials Processing. MET Manufacturing Processes. Shaping Planing Broaching Sawing Filing
 MET 33800 Manufacturing Processes Chapter 25 Other Machining Processes Before you begin: Turn on the sound on your computer. There is audio to accompany this presentation. Other Machining Processes Shaping
MET 33800 Manufacturing Processes Chapter 25 Other Machining Processes Before you begin: Turn on the sound on your computer. There is audio to accompany this presentation. Other Machining Processes Shaping
Lathe. A Lathe. Photo by Curt Newton
 Lathe Photo by Curt Newton A Lathe Labeled Photograph Description Choosing a Cutting Tool Installing a Cutting Tool Positioning the Tool Feed, Speed, and Depth of Cut Turning Facing Parting Drilling Boring
Lathe Photo by Curt Newton A Lathe Labeled Photograph Description Choosing a Cutting Tool Installing a Cutting Tool Positioning the Tool Feed, Speed, and Depth of Cut Turning Facing Parting Drilling Boring
Thermal Analysis of Cutting Tools by Using Different Cutting Fluids
 Thermal Analysis of Cutting Tools by Using Different Cutting Fluids Murusu Dhanunjaya Post Graduate Student Department of Mechanical Engineering Global College of Engineering & Technology, Kadapa, YSR
Thermal Analysis of Cutting Tools by Using Different Cutting Fluids Murusu Dhanunjaya Post Graduate Student Department of Mechanical Engineering Global College of Engineering & Technology, Kadapa, YSR
Lecture 15. Chapter 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Round Shapes. Turning
 Lecture 15 Chapter 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Round Shapes Turning Turning part is rotating while it is being machined Typically performed on a lathe Turning produces straight, conical, curved,
Lecture 15 Chapter 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Round Shapes Turning Turning part is rotating while it is being machined Typically performed on a lathe Turning produces straight, conical, curved,
INDEX. S.No. Name of the Experiment Page No.
 MACHINE TOOLS LAB INDEX S.No. Name of the Experiment Page No. 1 Step Turning and Taper Turning on Lathe 2 Thread Cutting and Knurling on Lathe 3 Machining Flat Surface using Shaper Machine 4 Manufacturing
MACHINE TOOLS LAB INDEX S.No. Name of the Experiment Page No. 1 Step Turning and Taper Turning on Lathe 2 Thread Cutting and Knurling on Lathe 3 Machining Flat Surface using Shaper Machine 4 Manufacturing
PREVIEW COPY. Table of Contents. Lesson Two Shaping and Planing Lesson Three Grinding Operations Lesson Four Gear Cutting...
 Table of Contents Lesson One Milling Operations...3 Lesson Two Shaping and Planing...19 Lesson Three Grinding Operations...37 Lesson Four Gear Cutting...55 Lesson Five Power Sawing...73 Copyright 1975,
Table of Contents Lesson One Milling Operations...3 Lesson Two Shaping and Planing...19 Lesson Three Grinding Operations...37 Lesson Four Gear Cutting...55 Lesson Five Power Sawing...73 Copyright 1975,
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? 2. How chip formation occurs in metal cutting? 3. What is
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? 2. How chip formation occurs in metal cutting? 3. What is
11/15/2009. There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate
 s Geometry & Milling Processes There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate All three of these will be discussed in later lessons What is a cutting
s Geometry & Milling Processes There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate All three of these will be discussed in later lessons What is a cutting
HM-50 - Turret Milling Machine (X) 600mm (Y) 200mm (Z) 340mm Includes Digital Readout, Vice & Collet Chuck System
 HM-50 - Turret Milling Machine (X) 600mm (Y) 200mm (Z) 340mm Includes Digital Readout, Vice & Collet Chuck System Ex GST Inc GST $5,500.00 $6,325.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Digital Readout: Type: Table Size
HM-50 - Turret Milling Machine (X) 600mm (Y) 200mm (Z) 340mm Includes Digital Readout, Vice & Collet Chuck System Ex GST Inc GST $5,500.00 $6,325.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Digital Readout: Type: Table Size
no mm no Dividers with scriber 150 mm NEW Square wedge-shaped knife edges on the length side
 Summer Promotion valid until 30.06.2013 all quoted prices are incl. VAT for deliveries to EU countries to customers with valid VAT-no. and for deliveries in non EU member countries the VAT is not applicable
Summer Promotion valid until 30.06.2013 all quoted prices are incl. VAT for deliveries to EU countries to customers with valid VAT-no. and for deliveries in non EU member countries the VAT is not applicable
Introduction to Machining: Lathe Operation
 Introduction to Machining: Lathe Operation Lathe Operation Lathe The purpose of a lathe is to rotate a part against a tool whose position it controls. It is useful for fabricating parts and/or features
Introduction to Machining: Lathe Operation Lathe Operation Lathe The purpose of a lathe is to rotate a part against a tool whose position it controls. It is useful for fabricating parts and/or features
THEORY OF METAL CUTTING
 THEORY OF METAL CUTTING INTRODUCTION Overview of Machining Technology Mechanism of chip formation Orthogonal and Oblique cutting Single Point and Multipoint Cutting Tools Machining forces - Merchant s
THEORY OF METAL CUTTING INTRODUCTION Overview of Machining Technology Mechanism of chip formation Orthogonal and Oblique cutting Single Point and Multipoint Cutting Tools Machining forces - Merchant s
Summer Junior Fellowship Experience at LUMS. Maliha Manzoor 13 June 15 July, 2011 LUMS Summer Internship
 Summer Junior Fellowship Experience at LUMS Maliha Manzoor 13 June 15 July, 2011 LUMS Summer Internship Internship Schedule June 13-17: 2D and 3D drawings in AutoCAD June 20-24: 2D and 3D drawings in AutoCAD
Summer Junior Fellowship Experience at LUMS Maliha Manzoor 13 June 15 July, 2011 LUMS Summer Internship Internship Schedule June 13-17: 2D and 3D drawings in AutoCAD June 20-24: 2D and 3D drawings in AutoCAD
Thread Mills. Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters
 Thread Mills Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than indexable
Thread Mills Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than indexable
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MACHINE SHOP FACILITIES AND PRACTICES Prepared by Mike Allen July 31, 2003 Edited by Scott Morton February 18, 2004
 1 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MACHINE SHOP FACILITIES AND PRACTICES Prepared by Mike Allen July 31, 2003 Edited by Scott Morton February 18, 2004 I. OBJECTIVE To provide an overview and basic knowledge of the
1 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MACHINE SHOP FACILITIES AND PRACTICES Prepared by Mike Allen July 31, 2003 Edited by Scott Morton February 18, 2004 I. OBJECTIVE To provide an overview and basic knowledge of the
HM-50 - Turret Milling Machine Package with Digital Readout & Tooling Accessories (X) 600mm (Y) 220mm (Z) 340mm
 HM-50 - Turret Milling Machine Package with Digital Readout & Tooling Accessories (X) 600mm (Y) 220mm (Z) 340mm ORDER CODE: MODEL: Digital Readout: Type: Table Size (mm): Column Type: Spindle Taper - Vertical:
HM-50 - Turret Milling Machine Package with Digital Readout & Tooling Accessories (X) 600mm (Y) 220mm (Z) 340mm ORDER CODE: MODEL: Digital Readout: Type: Table Size (mm): Column Type: Spindle Taper - Vertical:
A H M 531 The Civil Engineering Center
 Title Page Introduction 2 Objectives 2 Theory 2 Fitting 3 Turning 5 Shaping and Grinding 7 Milling 8 Conclusion 11 Reference 11 1 Introduction Machining Machining is a manufacturing process in which a
Title Page Introduction 2 Objectives 2 Theory 2 Fitting 3 Turning 5 Shaping and Grinding 7 Milling 8 Conclusion 11 Reference 11 1 Introduction Machining Machining is a manufacturing process in which a
Chapter 24. Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling
 Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling Parts Made with Machining Processes of Chapter 24 Figure 24.1 Typical parts and shapes that can be produced with the machining processes
Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling Parts Made with Machining Processes of Chapter 24 Figure 24.1 Typical parts and shapes that can be produced with the machining processes
LEADING SOLUTIONS IN THREAD MILLING TECHNOLOGY
 LEADING SOLUTIONS IN THREAD MILLING TECHNOLOGY Thread with Maximum Confidence, Depth, Versatility and Economy. Emuge Shur-Thread TM, Threads-All TM, Vario-Z and NPT Solid Carbide Thread Mills; and Gigant-ic
LEADING SOLUTIONS IN THREAD MILLING TECHNOLOGY Thread with Maximum Confidence, Depth, Versatility and Economy. Emuge Shur-Thread TM, Threads-All TM, Vario-Z and NPT Solid Carbide Thread Mills; and Gigant-ic
Reamer Basics. Fixed Reamers The reamer size is fixed and any size reduction due to wear or sharpening cannot be reclaimed
 1 Reamer Basics Reamers are available in a variety of types, materials, flute styles and sizes The typical reamer is a rotary cutting tools designed to machine a previously formed hole to an exact diameter
1 Reamer Basics Reamers are available in a variety of types, materials, flute styles and sizes The typical reamer is a rotary cutting tools designed to machine a previously formed hole to an exact diameter
HM-46 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head (X) 475mm (Y) 195mm (Z) 450mm Dovetail Column
 HM-46 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head (X) 475mm (Y) 195mm (Z) 450mm Dovetail Column Ex GST Inc GST $2,470.00 $2,840.50 ORDER CODE: M123 MODEL: HM-46 Digital Readout: Optional Type: Vertical Table
HM-46 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head (X) 475mm (Y) 195mm (Z) 450mm Dovetail Column Ex GST Inc GST $2,470.00 $2,840.50 ORDER CODE: M123 MODEL: HM-46 Digital Readout: Optional Type: Vertical Table
Optimized flute design Better chip evacuation. Carbide substrate Higher heat resistance, higher speed.
 Thread Mills Available for the first time, our solid thread mills are designed to be the highest quality thread milling solution. WIDIA-GTD Cut up to 63 HRC. Improved overall thread quality. Optimized
Thread Mills Available for the first time, our solid thread mills are designed to be the highest quality thread milling solution. WIDIA-GTD Cut up to 63 HRC. Improved overall thread quality. Optimized
Trade of Toolmaking. Module 3: Milling Unit 9: Precision Vee Block Assembly Phase 2. Published by. Trade of Toolmaking Phase 2 Module 3 Unit 9
 Trade of Toolmaking Module 3: Milling Unit 9: Precision Vee Block Assembly Phase 2 Published by SOLAS 2014 Unit 9 1 Table of Contents Document Release History... 3 Unit Objective... 4 Introduction... 4
Trade of Toolmaking Module 3: Milling Unit 9: Precision Vee Block Assembly Phase 2 Published by SOLAS 2014 Unit 9 1 Table of Contents Document Release History... 3 Unit Objective... 4 Introduction... 4
Machining Strenx and Hardox. Drilling, countersinking, tapping, turning and milling
 Machining and Drilling, countersinking, tapping, turning and milling and are registered trademarks. These steel grades are manufactured only by SSAB. high strength steel and wear plate are steel grades
Machining and Drilling, countersinking, tapping, turning and milling and are registered trademarks. These steel grades are manufactured only by SSAB. high strength steel and wear plate are steel grades
HM-46 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head (X) 475mm (Y) 195mm (Z) 450mm Dovetail Column
 HM-46 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head (X) 475mm (Y) 195mm (Z) 450mm Dovetail Column Ex GST Inc GST $2,600.00 $2,860.00 ORDER CODE: M124 MODEL: HM-46 Digital Readout: Optional Type: Vertical Table
HM-46 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head (X) 475mm (Y) 195mm (Z) 450mm Dovetail Column Ex GST Inc GST $2,600.00 $2,860.00 ORDER CODE: M124 MODEL: HM-46 Digital Readout: Optional Type: Vertical Table
HEAVY DUTY BENCH GRINDERS
 HEAVY DUTY BENCH GRINDERS BGC-6 (240153) / BGC-8 (240154) Heavy duty construction for maximum service life CSA electrics for safety and reliability All ball bearing construction Steel wheel covers with
HEAVY DUTY BENCH GRINDERS BGC-6 (240153) / BGC-8 (240154) Heavy duty construction for maximum service life CSA electrics for safety and reliability All ball bearing construction Steel wheel covers with
The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany!
 1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany! For face, longitudinal and taper turning, thread-cutting. For machining steel, brass, aluminium and plastic. Mounting flange for fastening
1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany! For face, longitudinal and taper turning, thread-cutting. For machining steel, brass, aluminium and plastic. Mounting flange for fastening
HM-32 - Mill Drill - Belt Drive (X) 540mm (Y) 190mm (Z) 410mm
 HM-32 - Mill Drill - Belt Drive (X) 540mm (Y) 190mm (Z) 410mm On Sale Ex GST Inc GST $1,850.00 $1,690.00 $2,035.00 $1,859.00 ORDER CODE: M121 MODEL: Digital Readout: HM-32 Optional Type: Vertical Table
HM-32 - Mill Drill - Belt Drive (X) 540mm (Y) 190mm (Z) 410mm On Sale Ex GST Inc GST $1,850.00 $1,690.00 $2,035.00 $1,859.00 ORDER CODE: M121 MODEL: Digital Readout: HM-32 Optional Type: Vertical Table
HM-47 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head with DRO (X) 540mm (Y) 185mm (Z) 410mm Includes Digital Readout, Dovetail Column & Stand
 HM-47 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head with DRO (X) 540mm (Y) 185mm (Z) 410mm Includes Digital Readout, Dovetail Column & Stand Ex GST Inc GST $3,790.00 $3,280.00 $4,358.50 $3,772.00 Special Ends 30/06/2018
HM-47 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head with DRO (X) 540mm (Y) 185mm (Z) 410mm Includes Digital Readout, Dovetail Column & Stand Ex GST Inc GST $3,790.00 $3,280.00 $4,358.50 $3,772.00 Special Ends 30/06/2018
THREAD CUTTING & FORMING
 THREAD CUTTING & FORMING Threading, Thread Cutting and Thread Rolling: Machining Threads on External Diameters (shafts) Tapping: Machining Threads on Internal Diameters (holes) Size: Watch to 10 shafts
THREAD CUTTING & FORMING Threading, Thread Cutting and Thread Rolling: Machining Threads on External Diameters (shafts) Tapping: Machining Threads on Internal Diameters (holes) Size: Watch to 10 shafts
HM-48 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head with DRO (X) 540mm (Y) 185mm (Z) 410mm Includes Digital Readout, Dovetail Column, Power Feed & Stand
 HM-48 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head with DRO (X) 540mm (Y) 185mm (Z) 410mm Includes Digital Readout, Dovetail Column, Power Feed & Stand Ex GST Inc GST $4,350.00 $3,990.00 $4,785.00 $4,389.00 Special
HM-48 - Mill Drill - Geared & Tilting Head with DRO (X) 540mm (Y) 185mm (Z) 410mm Includes Digital Readout, Dovetail Column, Power Feed & Stand Ex GST Inc GST $4,350.00 $3,990.00 $4,785.00 $4,389.00 Special
Lathe is a machine, which removes the metal from a piece of work to the required shape & size HENRY MAUDSLAY
 TURNING MACHINES LATHE Introduction Lathe is a machine, which removes the metal from a piece of work to the required shape & size HENRY MAUDSLAY - 1797 Types of Lathe Engine Lathe The most common form
TURNING MACHINES LATHE Introduction Lathe is a machine, which removes the metal from a piece of work to the required shape & size HENRY MAUDSLAY - 1797 Types of Lathe Engine Lathe The most common form
MACHINING PROCESSES: TURNING AND HOLE MAKING. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba 1
 MACHINING PROCESSES: TURNING AND HOLE MAKING Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba 1 HoweWork Assignment Due Wensday 7/7/2010 1. Estimate the machining time required to rough cut a 0.5 m long annealed copper alloy round
MACHINING PROCESSES: TURNING AND HOLE MAKING Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba 1 HoweWork Assignment Due Wensday 7/7/2010 1. Estimate the machining time required to rough cut a 0.5 m long annealed copper alloy round
Special reamers. Figure N 1 Reamer with descending cutting edges in carbide (Cerin)
 Special reamers There is a wide category of special reamers, ie non-standard, that are suitable to address particular problems encountered in the finishing holes, both for maintenance of individual pieces
Special reamers There is a wide category of special reamers, ie non-standard, that are suitable to address particular problems encountered in the finishing holes, both for maintenance of individual pieces
Cutting with broach. You can find here some notices about broaching operation. Fig.N 1
 Cutting with broach You can find here some notices about broaching operation. Fig.N 1 Amount of cut per tooth This parameter depends on many characteristic of broaching operation like: Material of the
Cutting with broach You can find here some notices about broaching operation. Fig.N 1 Amount of cut per tooth This parameter depends on many characteristic of broaching operation like: Material of the
HM-54GV - Turret Milling Machine Inverter Variable Speed, Geared Head Horizontal & Vertical
 HM-54GV - Turret Milling Machine Inverter Variable Speed, Geared Head Horizontal & Vertical Ex GST Inc GST (X) 600mm (Y) 200mm (Z) 340mm Includes Digital Readout, Vice & Collet Chuck System $7,250.00 ORDER
HM-54GV - Turret Milling Machine Inverter Variable Speed, Geared Head Horizontal & Vertical Ex GST Inc GST (X) 600mm (Y) 200mm (Z) 340mm Includes Digital Readout, Vice & Collet Chuck System $7,250.00 ORDER
Turning and Lathe Basics
 Training Objectives After watching the video and reviewing this printed material, the viewer will gain knowledge and understanding of lathe principles and be able to identify the basic tools and techniques
Training Objectives After watching the video and reviewing this printed material, the viewer will gain knowledge and understanding of lathe principles and be able to identify the basic tools and techniques
New Item & New Concept Tools Aqua EX Flat Drill
 New Item & New Concept Tools Aqua EX Flat Drill Completely Flat Point Angle! (Point Angle 180 ) Multi-Function Drill Covering Wide Application Range Aqua EX Flat Drill Sharpness & Rigidity at the Same
New Item & New Concept Tools Aqua EX Flat Drill Completely Flat Point Angle! (Point Angle 180 ) Multi-Function Drill Covering Wide Application Range Aqua EX Flat Drill Sharpness & Rigidity at the Same
Unit-I: Theory of Metal Cutting
 Unit-I: Theory of Metal Cutting Type-I (Cutting Forces Analysis) 1. In orthogonal cutting of a 60mm diameter MS bar on lathe, the following data was obtained, Rake angle = 15 0, Cutting Speed = 100 m/min,
Unit-I: Theory of Metal Cutting Type-I (Cutting Forces Analysis) 1. In orthogonal cutting of a 60mm diameter MS bar on lathe, the following data was obtained, Rake angle = 15 0, Cutting Speed = 100 m/min,
Module 1. Classification of Metal Removal Processes and Machine tools. Version 2 ME IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Classification of Metal Removal Processes and Machine tools Lesson 2 Basic working principle, configuration, specification and classification of machine tools Instructional Objectives At the end
Module 1 Classification of Metal Removal Processes and Machine tools Lesson 2 Basic working principle, configuration, specification and classification of machine tools Instructional Objectives At the end
CNC Cooltool - Milling Machine
 CNC Cooltool - Milling Machine Module 1: Introduction to CNC Machining 1 Prepared By: Tareq Al Sawafta Module Objectives: 1. Define machining. 2. Know the milling machine parts 3. Understand safety rules
CNC Cooltool - Milling Machine Module 1: Introduction to CNC Machining 1 Prepared By: Tareq Al Sawafta Module Objectives: 1. Define machining. 2. Know the milling machine parts 3. Understand safety rules
Precision made in Germany. As per DIN The heart of a system, versatile and expandable.
 1 Precision made in Germany. As per DIN 8606. The heart of a system, versatile and expandable. Main switch with auto-start protection and emergency off. Precision lathe chuck as per DIN 6386 (Ø 100mm).
1 Precision made in Germany. As per DIN 8606. The heart of a system, versatile and expandable. Main switch with auto-start protection and emergency off. Precision lathe chuck as per DIN 6386 (Ø 100mm).
MACHINE TOOLS GRINDING MACHINE TOOLS
 MACHINE TOOLS GRINDING MACHINE TOOLS GRINDING MACHINE TOOLS Grinding in generally considered a finishing operation. It removes metal comparatively in smaller volume. The material is removed in the form
MACHINE TOOLS GRINDING MACHINE TOOLS GRINDING MACHINE TOOLS Grinding in generally considered a finishing operation. It removes metal comparatively in smaller volume. The material is removed in the form
Chapter 24. Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling, Broaching, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing
 Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling, Broaching, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing Parts Made with Machining Processes of Chapter 24 Figure 24.1 Typical parts and
Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling, Broaching, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing Parts Made with Machining Processes of Chapter 24 Figure 24.1 Typical parts and
A Review on Optimization of Process Parameters for Material Removal Rate and Surface Roughness for SS 202 Material During Face Milling Operation
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 A Review on Optimization of Process Parameters for Material Removal Rate
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 11 April 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 A Review on Optimization of Process Parameters for Material Removal Rate
Rotary Engraving Fact Sheet
 Rotary Engraving Fact Sheet Description Rotary engraving is the term used to describe engraving done with a rotating cutting tool in a motorized spindle. The tool, or cutter, cuts into the surface of the
Rotary Engraving Fact Sheet Description Rotary engraving is the term used to describe engraving done with a rotating cutting tool in a motorized spindle. The tool, or cutter, cuts into the surface of the
KTM-16/20 TECHNICAL DATA
 TECHNICAL DATA Table Diameter : 1,600mm Max. Turning Diameter : 2,000mm Max. Turning Height : 1,750mm Table Indexing Degree : 0.001mm CNC Controller : FANUC 18i-TB ** Bed The bed has symmetrical structure
TECHNICAL DATA Table Diameter : 1,600mm Max. Turning Diameter : 2,000mm Max. Turning Height : 1,750mm Table Indexing Degree : 0.001mm CNC Controller : FANUC 18i-TB ** Bed The bed has symmetrical structure
Workshop Practice TA 102 Lec 6 & 7 :Theory of Metal Cutting. By Prof.A.Chandrashekhar
 Workshop Practice TA 102 Lec 6 & 7 :Theory of Metal Cutting By Prof.A.Chandrashekhar Theory of Metal cutting INTRODUCTION: The process of manufacturing a component by removing the unwanted material using
Workshop Practice TA 102 Lec 6 & 7 :Theory of Metal Cutting By Prof.A.Chandrashekhar Theory of Metal cutting INTRODUCTION: The process of manufacturing a component by removing the unwanted material using
Machining Processes IME 240
 Machining Processes IME 240 Material Removal Processes Machining is the broad term used to describe removal of material from a workpiece Includes Cutting, Abrasive Processes (grinding), Advanced Machining
Machining Processes IME 240 Material Removal Processes Machining is the broad term used to describe removal of material from a workpiece Includes Cutting, Abrasive Processes (grinding), Advanced Machining
TURNING BORING TURNING:
 TURNING BORING TURNING: FACING: Machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. Work spins and the single cutting tool does the cutting. Done in Lathe. Single point tool, longitudinal feed. Single
TURNING BORING TURNING: FACING: Machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. Work spins and the single cutting tool does the cutting. Done in Lathe. Single point tool, longitudinal feed. Single
Band Machining. Chapter 20
 Chapter 20 Band Machining LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, students will be able to: Describe how a band machine operates. Explain the advantages of band machining. Select the proper blade
Chapter 20 Band Machining LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, students will be able to: Describe how a band machine operates. Explain the advantages of band machining. Select the proper blade
Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters
 Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Second Edition Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than
Solid Carbide Thread Milling Cutters Second Edition Thread milling cutters by Features and Benefits: Sub-micro grain carbide substrate Longer tool life with tighter tolerances More cost-effective than
The new generation with system accessories. Made in Europe!
 1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Europe! Of cast iron, wide-legged prismatic guide. For vibration-free work even at high loads. Rear flange for mounting the mill/drill head PF 230.
1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Europe! Of cast iron, wide-legged prismatic guide. For vibration-free work even at high loads. Rear flange for mounting the mill/drill head PF 230.
Metal Drilling.
 101 ENGINEERED FOR CONTROLLED PRECISION AND SPEED The IRWIN line of metal drill bits offers of solution for every professional application. Each metal drill bit is made of high speed steel with high precision-cut
101 ENGINEERED FOR CONTROLLED PRECISION AND SPEED The IRWIN line of metal drill bits offers of solution for every professional application. Each metal drill bit is made of high speed steel with high precision-cut
Drilling. Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL.
 Drilling Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL. The machine used for drilling is called drilling machine. The drilling operation
Drilling Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL. The machine used for drilling is called drilling machine. The drilling operation
Manufacturing Science-II (EME-503)
 Time: 1 Hour B.Tech. [SEM V (ME-5 All Groups)] QUIZ TEST-1 Manufacturing Science-II ` Max. Marks: 30 Note: Attempt all the questions Q1) How metal is removed in metal cutting? Explain by giving any simple
Time: 1 Hour B.Tech. [SEM V (ME-5 All Groups)] QUIZ TEST-1 Manufacturing Science-II ` Max. Marks: 30 Note: Attempt all the questions Q1) How metal is removed in metal cutting? Explain by giving any simple
FUNDAMENTAL MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Plastics Machining & Assembly NARRATION (VO): NARRATION (VO): NARRATION (VO): INCLUDING: METALS,
 Copyright 2002 Society of Manufacturing Engineers --- 1 --- FUNDAMENTAL MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Plastics Machining & Assembly SCENE 1. CG: Plastics Machining white text centered on black SCENE 2. tape
Copyright 2002 Society of Manufacturing Engineers --- 1 --- FUNDAMENTAL MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Plastics Machining & Assembly SCENE 1. CG: Plastics Machining white text centered on black SCENE 2. tape
Lathe Accessories. Work-holding, -supporting, and driving devices
 46-1 Lathe Accessories Divided into two categories Work-holding, -supporting, and driving devices Lathe centers, chucks, faceplates Mandrels, steady and follower rests Lathe dogs, drive plates Cutting-tool-holding
46-1 Lathe Accessories Divided into two categories Work-holding, -supporting, and driving devices Lathe centers, chucks, faceplates Mandrels, steady and follower rests Lathe dogs, drive plates Cutting-tool-holding
MLR Institute of Technology
 MLR Institute of Technology Dundigal, Quthbullapur (M), Hyderabad 500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MACHINE TOOLS OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS UNIT - I 1. A built up-edge is formed while machining [ B ] (Sep-2011,
MLR Institute of Technology Dundigal, Quthbullapur (M), Hyderabad 500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MACHINE TOOLS OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS UNIT - I 1. A built up-edge is formed while machining [ B ] (Sep-2011,
BASIC TECHNICAL INFORMATION FOR REAMERS FLUTE STYLES
 BASIC TECHNICAL INFORMATION FOR HANNIBAL CARBIDE would like to inform you of some basic technical knowledge regarding reamers. Following these guidelines will reduce overall set-up time, while increasing
BASIC TECHNICAL INFORMATION FOR HANNIBAL CARBIDE would like to inform you of some basic technical knowledge regarding reamers. Following these guidelines will reduce overall set-up time, while increasing
QUALITy. Implant machining. Guhring Precision tools for the machining of stainless steel and titanium-alloy implants
 QUALITy that goes under the skin Implant machining Precision tools for the machining of stainless steel and titanium-alloy implants 2012 2 Implant machining ingeniously close to ature Stainless steel and
QUALITy that goes under the skin Implant machining Precision tools for the machining of stainless steel and titanium-alloy implants 2012 2 Implant machining ingeniously close to ature Stainless steel and
The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany!
 1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany! For face, longitudinal and taper turning, thread-cutting. For machining steel, brass, aluminium and plastic. Mounting flange for fastening
1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany! For face, longitudinal and taper turning, thread-cutting. For machining steel, brass, aluminium and plastic. Mounting flange for fastening
Machining. Drilling Countersinking Tapping Turning Milling
 Machining Drilling Countersinking Tapping Turning Milling hardox and weldox are registered trademarks.these steel grades are manufactured only by SSAB Oxelösund AB. hardox wear plate and weldox extra-high
Machining Drilling Countersinking Tapping Turning Milling hardox and weldox are registered trademarks.these steel grades are manufactured only by SSAB Oxelösund AB. hardox wear plate and weldox extra-high
MACHINE TOOLS LAB MANUAL. B. Tech III Year - I Semester DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Aurora s Technological And Research Institute
 MACHINE TOOLS LAB MANUAL B. Tech III Year - I Semester NAME : ROLL NO : BRANCH : DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Aurora s Technological And Research Institute Parvathapur, Uppal, Hyderabad-98. 1 MACHINE
MACHINE TOOLS LAB MANUAL B. Tech III Year - I Semester NAME : ROLL NO : BRANCH : DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Aurora s Technological And Research Institute Parvathapur, Uppal, Hyderabad-98. 1 MACHINE
