Chapter 5 Amplitude Modulation
|
|
|
- Mervin Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chaper 5 pliude Modulaion 68
2 nalog Couniaion Syse Inoraion Soure Signal Modulaor Propagaion Channel Signal Deodulaor Inoraion Desinaion nalog signals ay be ransied direly via arrier odulaion over he propagaion hannel and o be arrier-deodulaed a he reeiver. ransier Modulaor Reeiver Deodulaor 69
3 Modulaion: he proess by whih soe haraerisis o a arrier signal (i.e. odulaed signal) is varied in aordane wih essage signal (i.e. odulaing signal) (): essage signal bandliied signal whose requeny onen is in he neighbourhood o =0 (DC) baseband signal (): he arrier signal, independen o () ()= os(π +Ө ) : Carrier apliude : Carrier requeny w =π (radian requeny) Ө : Carrier phase () odulaes () in eiher apliude, requeny or phase. In ee, odulaion onvers () o a bandpass or, in he neighborhood o he ener requeny. 70
4 Why is Modulaion Required? o ahieve easy radiaion: I he ouniaion hannel onsiss o ree spae, anennas are required o radiae and reeive he signal. Diension o he anennas is liied by he orresponding wavelengh. Exaple: Voie signal bandwidh =3kHz /4=5000!! 3 0 I we odulae a arrier = 00MHz wih he voie signal /4=
5 Why is Modulaion Required? (Con d) o aoodae or siulaneous ransission o several signals s C s C s 3 C3 Exaple: Radio/V broadasing 7
6 Why is Modulaion Required? (Con d) o expand he bandwidh o he ransied signal or beer ransission qualiy (o redue noise and inererene) C B log SNR Channel apaiy Bandwidh Signal-o-noise raio Channel apaiy: Maxiu ahievable inoraion rae ha an be ransied over he hannel SNR C B B he required SNR (or ixed noise level, orresponding signal power) dereases 73
7 pliude Modulaion (M) (Ch. 5 in exbook) Objeives: o sudy dieren apliude odulaion shee o sudy generaion and deeion o M signals o sudy appliaion o M We will sudy Double Sideband Large Carrier (DSB-LC) Modulaion: Coerial broadas saions use his ype and i is oonly known as jus apliude odulaion (M). Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier (DSB-SC) Modulaion Single Sideband (SSB) Modulaion Vesigial Sideband (VSB) Modulaion 74
8 Double Side Band Large Carrier (DSB-LC) (5. in exbook) F F F Modulaor os os os os 75 j j e e os F F F os os F j j j j e e e e F F F
9 () F()= F [()] F(0) baseband -B B () os F [() os ] F(0)/ passband - -B +B os π F [ os ] π - os + ()os envelope F [ os + ()os ] - 76
10 baseband F()= F [()] passband ()= F [ os + ()os ] -B F(0) B π F(0)/ Lower sideband π Upper sideband - -B +B Bandwidh=B [Hz] Bandwidh=B Observaions: Modulaion shis he onen o F() o he neighbourhood o. F() or [-B, 0] is shied o () or [ -B, ] and alled as lower sideband. F() or [0, B] is shied o () or [, +B] and alled as upper sideband. Le B denoe he highes requeny oponen o (). ssue >> B () is deined as a narrowband signal (i.e. is speral onen is loaed in he iediae viiniy o soe high ener requeny) 77
11 F()= F [()] ()= F [ os + ()os ] -B F(0) B π F(0)/ Lower π Upper sideband sideband - -B +B Bandwidh=B [Hz] Bandwidh=B Observaions (on d) he bandwidh o essage signal is B. he ransission bandwidh =B (i.e. DSB-LC is waseul o bandwidh) he arrier er does no arry any inoraion and hene he arrier power is wased. 78
12 Envelope has he sae shape o () Envelope disorion Observaions (on d) Zero rossings I +()>0 or all, he envelope o () o has essenially he sae shape as he (). I +()<0 or any, he arrier wave beoes over-odulaed, resuling in arrier phase reversal whenever +() rosses zero. () has envelope disorion 79
13 80
14 overodulaed envelope dis. Ees o varying odulaion indexes 8
15 Carrier and Sideband Power in DSB-LC os os os os os os os ssue and () varies slowly wih respe o os 0 8 os os d / / os li os d / / os li os li li / / / / d = 0
16 Carrier Power Sideband Power (arries inoraion) Modulaion (Power) Eiieny µ= useul power oal power 83
17 8 os os os os os Exaple (Con d) Upper sideband power Lower sideband power 84 8 os power oal useul power oal power µ= 4 4 For µ 33%. Under he bes ondiion, i.e. =, 67% o he oal power is used in he arrier and represens wased power.
18 Generaion o DSB-LC Signals Ciruiry aspes o his opi will no be in any exainaion, aheaial aspes ay be esed. Given (), how will be he odulaed signal () be generaed? Modulaor os os Chopper Modulaor os () D () V () V () Bandpass V 0 ()=() 85
19 D V V g V () V () V () Gain g () V () V os ssue D is an ideal diode, and () <, hen V V, i 0 0, i 0 i.e. he load volage V () varies periodially beween he values V () and 0 a a rae equal o he arrier requeny. When he diode is on, g () = is o, g () = 0 hopper odulaion 86
20 Expand g () using Fourier Series, we have os n n g n n g () /4 / - -/4 -/ he diode an be represened by a reangle pulse generaor. = / = / 87 os os n n V n n g V V ers oher 3 os 3 3 os os 3 os os os
Principles of Communications Lecture 3: Analog Modulation Techniques (1) Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 National Chiao Tung University
 Priniples of ouniaions Leure 3: nalog Modulaion Tehniques 1 hih-wei Liu 劉志尉 Naional hiao Tung Universiy wliu@wins.ee.nu.edu.w Oulines Linear Modulaion ngle Modulaion Inerferene Feedbak Deodulaors nalog
Priniples of ouniaions Leure 3: nalog Modulaion Tehniques 1 hih-wei Liu 劉志尉 Naional hiao Tung Universiy wliu@wins.ee.nu.edu.w Oulines Linear Modulaion ngle Modulaion Inerferene Feedbak Deodulaors nalog
Example Message bandwidth and the transmitted signal bandwidth
 4.6 Bandwidh-Eiien Modulaions 4.74. We are now going o deine a quaniy alled he bandwidh o a signal. Unorunaely, in praie, here isn jus one deiniion o bandwidh. Deiniion 4.75. The bandwidh (BW) o a signal
4.6 Bandwidh-Eiien Modulaions 4.74. We are now going o deine a quaniy alled he bandwidh o a signal. Unorunaely, in praie, here isn jus one deiniion o bandwidh. Deiniion 4.75. The bandwidh (BW) o a signal
Chapter 2 Amplitude Modulation
 Couniaion Syses (Theory) Chaper pliude Modulaion Objeive Upon opleion of his haper you will be able o: Undersand he proess of pliude Modulaion. Undersand differen ypes of pliude Modulaion. Design differen
Couniaion Syses (Theory) Chaper pliude Modulaion Objeive Upon opleion of his haper you will be able o: Undersand he proess of pliude Modulaion. Undersand differen ypes of pliude Modulaion. Design differen
Intermediate Frequency (IF)
 Inerediae Frequeny IF Iage frequeny p. II-33 Apliude Modulaion: SSB DSB odulaion: By ixing wih a inuoidal arrier a rad/e, half of hi peral deniy i ranlaed up in frequeny and enered abou and half i ranlaed
Inerediae Frequeny IF Iage frequeny p. II-33 Apliude Modulaion: SSB DSB odulaion: By ixing wih a inuoidal arrier a rad/e, half of hi peral deniy i ranlaed up in frequeny and enered abou and half i ranlaed
Modulation Technique:
 Modulation Tehnique: There are two basi failies of ontinuous-wave odulation tehniques: 1. Aplitude odulation, in whih the aplitude of a sinusoidal arrier is varied in aordane with an inoing essage signal.
Modulation Tehnique: There are two basi failies of ontinuous-wave odulation tehniques: 1. Aplitude odulation, in whih the aplitude of a sinusoidal arrier is varied in aordane with an inoing essage signal.
Double Side Band Suppressed Carrier
 Leure 4 Double Side Band Suppressed Carrier Dr. Ahed El-Mahdy Double Side Band (DSB) Copare beween his equaion and he equaion o onvenional AM Dr. Ahed El-Mahdy SDSB() () S() 0 CARRIER SIGNAL 0-0 0 0.05
Leure 4 Double Side Band Suppressed Carrier Dr. Ahed El-Mahdy Double Side Band (DSB) Copare beween his equaion and he equaion o onvenional AM Dr. Ahed El-Mahdy SDSB() () S() 0 CARRIER SIGNAL 0-0 0 0.05
Lecture 12: Modulation Techniques for Mobile Radio. Amplitude Modulation (Full AM or Double Sideband with Carrier)
 EE 499: Wireless & Mobile Communiaions (08) Leure : Modulaion Tehniques or Mobile Radio Dr. Wajih. bu-l-saud mpliude Modulaion Tehniques mpliude Modulaion (Full M or Double Sideband wih Carrier) The general
EE 499: Wireless & Mobile Communiaions (08) Leure : Modulaion Tehniques or Mobile Radio Dr. Wajih. bu-l-saud mpliude Modulaion Tehniques mpliude Modulaion (Full M or Double Sideband wih Carrier) The general
Analog Modulation. Amplitude modulation F. Dellsperger
 Analog Modulaion Apliude odulaion AM -8 F. Dellsperger Conen. Analog odulaion ehniques... 36. Apliude odulaion... 36.. Conenional apliude odulaion... 36.. Double Sideband Modulaion DSB and Single Sideband
Analog Modulaion Apliude odulaion AM -8 F. Dellsperger Conen. Analog odulaion ehniques... 36. Apliude odulaion... 36.. Conenional apliude odulaion... 36.. Double Sideband Modulaion DSB and Single Sideband
COMM702: Modulation II
 COMM70: Modulaion II Leure 4 - Coheren and non-oheren inary pass-and daa ransmission Binary Digial Modulaion Sinusoidal Carrier Digial Message ASK FSK PSK Parameers o Digial Pass-and ransmission Proailiy
COMM70: Modulaion II Leure 4 - Coheren and non-oheren inary pass-and daa ransmission Binary Digial Modulaion Sinusoidal Carrier Digial Message ASK FSK PSK Parameers o Digial Pass-and ransmission Proailiy
dm t t A cos 2 10 t 10
 T.C. OKAN ÜNİVERSİTESİ Fauly o Engineering and Arhieure Elerial and Eleroni Engineering Program EEE 3 Analog Communiaions Fall 23 In Class Work Par 4 Soluions:. Skeh he FM and PM modulaed waveorms or he
T.C. OKAN ÜNİVERSİTESİ Fauly o Engineering and Arhieure Elerial and Eleroni Engineering Program EEE 3 Analog Communiaions Fall 23 In Class Work Par 4 Soluions:. Skeh he FM and PM modulaed waveorms or he
EE (082) Chapter IV: Angle Modulation Lecture 19 Dr. Wajih Abu-Al-Saud
 EE 370-3 (082) Chaer IV: Angle Modulaion Lecure 19 Dr. Wajih Abu-Al-Saud Wideband and PM For he signal shown below, he value o k ay no saisy he condiion k 1, and hereore he aroxiaion used in narrowband
EE 370-3 (082) Chaer IV: Angle Modulaion Lecure 19 Dr. Wajih Abu-Al-Saud Wideband and PM For he signal shown below, he value o k ay no saisy he condiion k 1, and hereore he aroxiaion used in narrowband
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Analog Signal Transmission and Reception. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communiations Theory and Systems: I Analog Signal Transmission and Reeption ELEC 350 Fall 2007 1 ELEC 350 Fall 2007 2 Analog Modulation A large number o signals are analog speeh musi video These
ELEC 350 Communiations Theory and Systems: I Analog Signal Transmission and Reeption ELEC 350 Fall 2007 1 ELEC 350 Fall 2007 2 Analog Modulation A large number o signals are analog speeh musi video These
6. Amplitude Modulation
 6. Amplitude Modulation Modulation is a proess by whih some parameter of a arrier signal is varied in aordane with a message signal. The message signal is alled a modulating signal. Definitions A bandpass
6. Amplitude Modulation Modulation is a proess by whih some parameter of a arrier signal is varied in aordane with a message signal. The message signal is alled a modulating signal. Definitions A bandpass
ECE ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS - INVESTIGATION 7 INTRODUCTION TO AMPLITUDE MODULATION - PART II
 ECE 405 - ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS - INVESTIGATION 7 INTRODUCTION TO AMPLITUDE MODULATION - PART II FALL 2005 A.P. FELZER To do "well" on his invesigaion you mus no only ge he righ answers bu mus also do
ECE 405 - ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS - INVESTIGATION 7 INTRODUCTION TO AMPLITUDE MODULATION - PART II FALL 2005 A.P. FELZER To do "well" on his invesigaion you mus no only ge he righ answers bu mus also do
Analog Communications
 1 Analog Communiations Amplitude Modulation (AM) Frequeny Modulation (FM) 2 Radio broadasting 30-300M Hz SOURCE Soure Transmitter Transmitted signal Channel Reeived signal Reeiver User Analog baseband
1 Analog Communiations Amplitude Modulation (AM) Frequeny Modulation (FM) 2 Radio broadasting 30-300M Hz SOURCE Soure Transmitter Transmitted signal Channel Reeived signal Reeiver User Analog baseband
Lecture 13: Capacity of Cellular Systems
 Leure : apaiy of ellular Sysems Afer ha we onsidered he apaiy of a ommuniaion hannel in he erms of raffi load of daa in bis per seond and speral effiieny in erms of bi per seond per herz, le us now disuss
Leure : apaiy of ellular Sysems Afer ha we onsidered he apaiy of a ommuniaion hannel in he erms of raffi load of daa in bis per seond and speral effiieny in erms of bi per seond per herz, le us now disuss
Chapter 2 Summary: Continuous-Wave Modulation. Belkacem Derras
 ECEN 44 Communicaion Theory Chaper Summary: Coninuous-Wave Modulaion.1 Modulaion Modulaion is a process in which a parameer of a carrier waveform is varied in accordance wih a given message (baseband)
ECEN 44 Communicaion Theory Chaper Summary: Coninuous-Wave Modulaion.1 Modulaion Modulaion is a process in which a parameer of a carrier waveform is varied in accordance wih a given message (baseband)
Modulation exercises. Chapter 3
 Chaper 3 Modulaion exercises Each problem is annoaed wih he leer E, T, C which sands for exercise, requires some hough, requires some concepualizaion. Problems labeled E are usually mechanical, hose labeled
Chaper 3 Modulaion exercises Each problem is annoaed wih he leer E, T, C which sands for exercise, requires some hough, requires some concepualizaion. Problems labeled E are usually mechanical, hose labeled
x(at) 1 x(t) h(t) H( jω )X( jω ) x(t)p(t) 1 X( jω ) P( jω) x(t t d ) e jωt d x(t)e jω 0t X( j(ω ω 0 )) LECTURE OBJECTIVES Signal Processing First
 Signal Proessing Firs Leure 4 Ampliude Modulaion AM LECURE OBJECIVES Review of F properies Convoluion mulipliaion Frequen shifing Sinewave Ampliude Modulaion AM radio Frequen-division mulipleing FDM
Signal Proessing Firs Leure 4 Ampliude Modulaion AM LECURE OBJECIVES Review of F properies Convoluion mulipliaion Frequen shifing Sinewave Ampliude Modulaion AM radio Frequen-division mulipleing FDM
Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Associate Professor Department of EEE, BUET
 EEE 309 Communiation Theory Semester: January 06 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Assoiate Proessor Department o EEE, BUET Email: marhadhossain@eee.buet.a.bd Oie: ECE 33, ECE Building Part 03-3 Single-sideband Suppressed
EEE 309 Communiation Theory Semester: January 06 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Assoiate Proessor Department o EEE, BUET Email: marhadhossain@eee.buet.a.bd Oie: ECE 33, ECE Building Part 03-3 Single-sideband Suppressed
ENSC327 Communications Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation. Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Jie Liang Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Jie Liang Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
ENSC327 Communications Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation. School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required Bakground DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required Bakground DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
TELE3013 Mid-session QUIZ 1
 TELE3013 Mid-session QUIZ 1 Week 7 10 th April, 2006 Name: Student No: Instrutions to Candidates (1) Time allowed: 90 minutes or so (2) Answer all questions. Total Marks = 90. (3) Marks are as indiated.
TELE3013 Mid-session QUIZ 1 Week 7 10 th April, 2006 Name: Student No: Instrutions to Candidates (1) Time allowed: 90 minutes or so (2) Answer all questions. Total Marks = 90. (3) Marks are as indiated.
Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless Transmission
 Frequenies or ommuniaion wised pair oa able opial ransmission Mobile Communiaions Chaper : Wireless Transmission Frequenies Signals Anenna Signal propagaion Mulipleing Spread sperum Modulaion Cellular
Frequenies or ommuniaion wised pair oa able opial ransmission Mobile Communiaions Chaper : Wireless Transmission Frequenies Signals Anenna Signal propagaion Mulipleing Spread sperum Modulaion Cellular
Chapter 2 Continuous-Wave Modulation. 2.1 Introduction
 Chaper Coninuous-Wave Modulaion.1 Inroduion 1 . mpliude Modulaion os : arrier ampliude : arrier requeny 1+k a m S X.1 os The oupu o he modulaor s 1 kam os. Where m is he baseband signal, k a is he ampliude
Chaper Coninuous-Wave Modulaion.1 Inroduion 1 . mpliude Modulaion os : arrier ampliude : arrier requeny 1+k a m S X.1 os The oupu o he modulaor s 1 kam os. Where m is he baseband signal, k a is he ampliude
Wireless Transmission Basics
 Areas o researh in mobile ommuniaion Wireless Transmission Basis Frequenies Signals Anenna Signal propagaion Mulipleing Spread sperum Modulaion Cellular sysems Wireless Communiaion ransmission qualiy (bandwidh,
Areas o researh in mobile ommuniaion Wireless Transmission Basis Frequenies Signals Anenna Signal propagaion Mulipleing Spread sperum Modulaion Cellular sysems Wireless Communiaion ransmission qualiy (bandwidh,
Page 1. Spreading and frequency selective fading. #4: Spread Spectrum Technology. How do we overcome limitations imposed by the radio channel?
 EEC173B/ECS15C, Spring 009 How do we overome limiaions imposed by he radio hannel? Fundamenals o Wireless Communiaions #4: Spread Sperum #5: Muliplexing #6: Frequeny euse (Cellular Conep) Case Sudy: Wireless
EEC173B/ECS15C, Spring 009 How do we overome limiaions imposed by he radio hannel? Fundamenals o Wireless Communiaions #4: Spread Sperum #5: Muliplexing #6: Frequeny euse (Cellular Conep) Case Sudy: Wireless
f t 2cos 2 Modulator Figure 21: DSB-SC modulation.
 4.5 Ampliude modulaion: AM 4.55. DSB-SC ampliude modulaion (which is summarized in Figure 21) is easy o undersand and analyze in boh ime and frequency domains. However, analyical simpliciy is no always
4.5 Ampliude modulaion: AM 4.55. DSB-SC ampliude modulaion (which is summarized in Figure 21) is easy o undersand and analyze in boh ime and frequency domains. However, analyical simpliciy is no always
Introduction to Analog And Digital Communications
 Introdution to Analog And Digital Communiations Seond Edition Simon Haykin, Mihael Moher Chapter 9 Noise in Analog Communiations 9.1 Noise in Communiation Systems 9. Signal-to-Noise Ratios 9.3 Band-Pass
Introdution to Analog And Digital Communiations Seond Edition Simon Haykin, Mihael Moher Chapter 9 Noise in Analog Communiations 9.1 Noise in Communiation Systems 9. Signal-to-Noise Ratios 9.3 Band-Pass
UNIT-5 ANGLE MODULATION (FM) I
 UNIT-5 ANGLE MODULATION (FM) I Topis: Basi deinitions, FM, narrow band FM, wide band FM, transission bandwidth o FM waves, and generation o FM waves: indiret FM and diret FM. Angle odulation is a ethod
UNIT-5 ANGLE MODULATION (FM) I Topis: Basi deinitions, FM, narrow band FM, wide band FM, transission bandwidth o FM waves, and generation o FM waves: indiret FM and diret FM. Angle odulation is a ethod
Communications II Lecture 5: Effects of Noise on FM. Professor Kin K. Leung EEE and Computing Departments Imperial College London Copyright reserved
 Communicaions II Lecure 5: Eecs o Noise on FM Proessor Kin K. Leung EEE and Compuing Deparmens Imperial College London Copyrigh reserved Ouline Recap o FM FM sysem model in noise Derivaion o oupu SNR Pre/de-emphasis
Communicaions II Lecure 5: Eecs o Noise on FM Proessor Kin K. Leung EEE and Compuing Deparmens Imperial College London Copyrigh reserved Ouline Recap o FM FM sysem model in noise Derivaion o oupu SNR Pre/de-emphasis
Analog Communication (10EC53) Unit 3 Quadrature Carrier Multiplexing
 Analog Couniation (0EC53) Unit 3 Quadrature Carrier Multiplexing A Quadrature Carrier Multiplexing (QCM) or Quadrature Aplitude Modulation (QAM) ethod enables two DSBSC odulated waves, resulting ro two
Analog Couniation (0EC53) Unit 3 Quadrature Carrier Multiplexing A Quadrature Carrier Multiplexing (QCM) or Quadrature Aplitude Modulation (QAM) ethod enables two DSBSC odulated waves, resulting ro two
END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Friday, 19 November 2004, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time.
 END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS 2004 Uni: Day and Time: Time Allowed: ELEC32 Communiaion Sysems (D2) Friday, 9 November 2004, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 0 minues reading ime. Toal Number of Quesions: SIX (6)
END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS 2004 Uni: Day and Time: Time Allowed: ELEC32 Communiaion Sysems (D2) Friday, 9 November 2004, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 0 minues reading ime. Toal Number of Quesions: SIX (6)
Test 1 Review. Test 1 Review. Communication Systems: Foundational Theories. Communication System. Reference: Sections and
 Tes 1 Review Tes 1 Review Proessor Deepa Kundur Universiy o Torono Reerence: Secions 2.2-2.7 and 3.1-3.6 o S. Haykin and M. Moher, Inroducion o Analog & Digial Communicaions, 2nd ed., John iley & Sons,
Tes 1 Review Tes 1 Review Proessor Deepa Kundur Universiy o Torono Reerence: Secions 2.2-2.7 and 3.1-3.6 o S. Haykin and M. Moher, Inroducion o Analog & Digial Communicaions, 2nd ed., John iley & Sons,
UNIT-6 ANGLE MODULATION (FM) II
 UNI-6 ANGLE MODULAION FM II opis: Demodulaion o FM waes, Phase Loed Loop, Non-linear Model o he phase loed loop, Linear model o he phase loed loop, FM sereo muliplexing, Nonlinear ees in FM sysems, and
UNI-6 ANGLE MODULAION FM II opis: Demodulaion o FM waes, Phase Loed Loop, Non-linear Model o he phase loed loop, Linear model o he phase loed loop, FM sereo muliplexing, Nonlinear ees in FM sysems, and
Solution of ECE 342 Test 2 S12
 Soluion of ECE 342 Tes 2 S2. All quesions regarding superheerodyne receivers refer o his diagram. x c () Anenna B T < B RF < 2 f B = B T Oher Signals f c Mixer f Baseband x RFi RF () x RFo () () () x i
Soluion of ECE 342 Tes 2 S2. All quesions regarding superheerodyne receivers refer o his diagram. x c () Anenna B T < B RF < 2 f B = B T Oher Signals f c Mixer f Baseband x RFi RF () x RFo () () () x i
Laboratory #2. Spectral Analysis of Digital Baseband Signals. SYSC 4600 Digital Communications
 Laboraory #2 Speral Analysis of Digial Baseband Signals SYSC 4600 Digial Communiaions Deparmen of Sysems and Compuer Engineering Fauly of Engineering Carleon Universiy Oober 206 Deparmen of Sysems & Compuer
Laboraory #2 Speral Analysis of Digial Baseband Signals SYSC 4600 Digial Communiaions Deparmen of Sysems and Compuer Engineering Fauly of Engineering Carleon Universiy Oober 206 Deparmen of Sysems & Compuer
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation. Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communiations Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introdution 3.2 Amplitude Modulation 3.3
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communiations Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introdution 3.2 Amplitude Modulation 3.3
EE140 Introduction to Communication Systems Lecture 7
 3/4/08 EE40 Introdution to Communiation Systems Leture 7 Instrutor: Prof. Xiliang Luo ShanghaiTeh University, Spring 08 Arhiteture of a (Digital) Communiation System Transmitter Soure A/D onverter Soure
3/4/08 EE40 Introdution to Communiation Systems Leture 7 Instrutor: Prof. Xiliang Luo ShanghaiTeh University, Spring 08 Arhiteture of a (Digital) Communiation System Transmitter Soure A/D onverter Soure
ECS455: Chapter 4 Multiple Access
 Spread specrum (SS) ECS455: Chaper 4 Muliple Access Dr.Prapun Suksompong prapun.com/ecs455 4.3 DS/SS Oice Hours: BKD, 6h loor o Sirindhralai building Tuesday 4:20-5:20 Wednesday 4:20-5:20 Friday 9:5-0:5
Spread specrum (SS) ECS455: Chaper 4 Muliple Access Dr.Prapun Suksompong prapun.com/ecs455 4.3 DS/SS Oice Hours: BKD, 6h loor o Sirindhralai building Tuesday 4:20-5:20 Wednesday 4:20-5:20 Friday 9:5-0:5
Angle Modulation (Phase & Frequency Modulation) EE442 Lecture 8. Spring 2017
 Angle Modulaion (Phase & Frequency Modulaion) EE442 Lecure 8 Spring 2017 1 Ampliude, Frequency and Phase Modulaion Wih ew excepions, Phase Modulaion (PM) is used primarily in digial communicaion 2 Why
Angle Modulaion (Phase & Frequency Modulaion) EE442 Lecure 8 Spring 2017 1 Ampliude, Frequency and Phase Modulaion Wih ew excepions, Phase Modulaion (PM) is used primarily in digial communicaion 2 Why
Properties of Leakage Current on 20 kv Ceramic Insulators and Computer Simulation Based on Electrical Equivalent Circuit
 Proceedings of he World Congress on Engineering 2 Vol II WCE 2, June 3 - July 2, 2, London, U.K. Properies of Leakage Curren on 2 kv Ceraic Insulaors and Copuer Siulaion Based on Elecrical Equivalen Circui
Proceedings of he World Congress on Engineering 2 Vol II WCE 2, June 3 - July 2, 2, London, U.K. Properies of Leakage Curren on 2 kv Ceraic Insulaors and Copuer Siulaion Based on Elecrical Equivalen Circui
Chapter 2 PHYSICAL AND LINK LAYER
 Overview Chaper 2 PHYSICAL AND LINK LAYER Mobile Compuing Summer 2004 Disribued Compuing Group Frequenies Signals Anenna Modulaion Signal propagaion Mulipleing Spread sperum CDMA Disribued Compuing Group
Overview Chaper 2 PHYSICAL AND LINK LAYER Mobile Compuing Summer 2004 Disribued Compuing Group Frequenies Signals Anenna Modulaion Signal propagaion Mulipleing Spread sperum CDMA Disribued Compuing Group
Passband Data Transmission II References Frequency-shift keying Chapter 6.5, S. Haykin, Communication Systems, Wiley. H.1
 Passand Daa ransmission II Reerences Frequency-shi keying Chaper 6.5, S. Haykin, Communicaion Sysems, Wiley. H. Inroducion Inroducion PSK and QAM are linear modulaion FSK is a nonlinear modulaion Similar
Passand Daa ransmission II Reerences Frequency-shi keying Chaper 6.5, S. Haykin, Communicaion Sysems, Wiley. H. Inroducion Inroducion PSK and QAM are linear modulaion FSK is a nonlinear modulaion Similar
COURSE OUTLINE. Introduction Signals and Noise Filtering: Band-Pass Filters 1 - BPF1 Sensors and associated electronics. Sensors, Signals and Noise 1
 ensors, ignals and Noise 1 COURE OUTLINE Inroducion ignals and Noise Filering: and-pass Filers 1 - PF1 ensors and associaed elecronics ignal Recovery, 017/018 PF 1 and-pass Filers 1 Narrow-and ignals Recovering
ensors, ignals and Noise 1 COURE OUTLINE Inroducion ignals and Noise Filering: and-pass Filers 1 - PF1 ensors and associaed elecronics ignal Recovery, 017/018 PF 1 and-pass Filers 1 Narrow-and ignals Recovering
Chapter 2: Fourier Representation of Signals and Systems
 Tes 1 Review Tes 1 Review Proessor Deepa Kundur Universiy o Torono Reerence: Secions: 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6 o S. Haykin and M. Moher, Inroducion o Analog & Digial
Tes 1 Review Tes 1 Review Proessor Deepa Kundur Universiy o Torono Reerence: Secions: 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5, 3.6 o S. Haykin and M. Moher, Inroducion o Analog & Digial
2. Continuous-wave modulation
 . Continuous-wave odulation 1. Appliation goal We study representations in tie and frequeny doain for two types of ontinuous wave odulation: aplitude odulation (AM) and frequeny odulation (FM).. Continuous-wave
. Continuous-wave odulation 1. Appliation goal We study representations in tie and frequeny doain for two types of ontinuous wave odulation: aplitude odulation (AM) and frequeny odulation (FM).. Continuous-wave
Power losses in pulsed voltage source inverters/rectifiers with sinusoidal currents
 ree-wheeling diode Turn-off power dissipaion: off/d = f s * E off/d (v d, i LL, T j/d ) orward power dissipaion: fw/t = 1 T T 1 v () i () d Neglecing he load curren ripple will resul in: fw/d = i Lavg
ree-wheeling diode Turn-off power dissipaion: off/d = f s * E off/d (v d, i LL, T j/d ) orward power dissipaion: fw/t = 1 T T 1 v () i () d Neglecing he load curren ripple will resul in: fw/d = i Lavg
Communication Systems Lecture 7. Dong In Kim School of Info/Comm Engineering Sungkyunkwan University
 Communiation Systems Leture 7 Dong In Kim Shool o Ino/Comm Engineering Sungkyunkwan University 1 Outline Expression o SSB signals Waveorm o SSB signals Modulators or SSB: Frequeny disrimination Phase disrimination
Communiation Systems Leture 7 Dong In Kim Shool o Ino/Comm Engineering Sungkyunkwan University 1 Outline Expression o SSB signals Waveorm o SSB signals Modulators or SSB: Frequeny disrimination Phase disrimination
EKT358 Communication Systems
 EKT358 Communiation Systems Chapter 2 Amplitude Modulation Topis Covered in Chapter 2 2-1: AM Conepts 2-2: Modulation Index and Perentage of Modulation 2-3: Sidebands and the Frequeny Domain 2-4: Single-Sideband
EKT358 Communiation Systems Chapter 2 Amplitude Modulation Topis Covered in Chapter 2 2-1: AM Conepts 2-2: Modulation Index and Perentage of Modulation 2-3: Sidebands and the Frequeny Domain 2-4: Single-Sideband
AM Demodulation (peak detect.)
 AM Deodulaion (peak deec.) Deodulaion is abou recovering he original signal--crysal Radio Exaple Anenna = Long Wire FM AM Tuning Circui A siple Diode! Deodulaion Circui (envelop of AM Signal) Filer (Mechanical)
AM Deodulaion (peak deec.) Deodulaion is abou recovering he original signal--crysal Radio Exaple Anenna = Long Wire FM AM Tuning Circui A siple Diode! Deodulaion Circui (envelop of AM Signal) Filer (Mechanical)
Communication involves the transfer of information from one point to another. Three basic elements
 Wha s Communiaions? Communiaion involves he ransfer of informaion from one poin o anoher. Three basi elemens Transmier: onvers message ino a form suiable for ransmission Channel: he physial medium, inrodues
Wha s Communiaions? Communiaion involves he ransfer of informaion from one poin o anoher. Three basi elemens Transmier: onvers message ino a form suiable for ransmission Channel: he physial medium, inrodues
Mobile Communications Chapter 2: Wireless Transmission
 This book ocuses on higher layer aspecs o mobile communicaions, he compuer science elemens raher han on he radio and ransmission aspecs, he elecrical engineering par. This chaper inroduces only hose undamenal
This book ocuses on higher layer aspecs o mobile communicaions, he compuer science elemens raher han on he radio and ransmission aspecs, he elecrical engineering par. This chaper inroduces only hose undamenal
Lecture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa
 Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
ELG3175 Introduction to Communication Systems. Conventional AM
 ELG317 Introdution to Communiation Systems Conventional AM Disadvantages o DSB-SC The reeiver must generate a replia o the arrier in order to demodulate a DSB-SC signal. Any phase and/or requeny error
ELG317 Introdution to Communiation Systems Conventional AM Disadvantages o DSB-SC The reeiver must generate a replia o the arrier in order to demodulate a DSB-SC signal. Any phase and/or requeny error
Principles of Communications
 Sae Key Lab. on ISN, Xidian Universiy Principles of Communicaions Chaper VI: Elemenary Digial Modulaion Sysem Email: ychwang@mail.xidian.edu.cn Xidian Universiy Sae Key Lab. on ISN December 13, 2013 Sae
Sae Key Lab. on ISN, Xidian Universiy Principles of Communicaions Chaper VI: Elemenary Digial Modulaion Sysem Email: ychwang@mail.xidian.edu.cn Xidian Universiy Sae Key Lab. on ISN December 13, 2013 Sae
Hata's Path Loss Model Calibration for Prediction DTTV Propagation in Urban Area of Southern Thailand
 IOP Conferene Series: Maerials Siene and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Haa's Pah Loss Model Calibraion for Prediion DTTV Propagaion in Urban Area of Souhern Thailand To ie his arile: P Keawbunsong e al
IOP Conferene Series: Maerials Siene and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Haa's Pah Loss Model Calibraion for Prediion DTTV Propagaion in Urban Area of Souhern Thailand To ie his arile: P Keawbunsong e al
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Communications. AM, DSBSC, VSB, SSB, FM, PM, Narrow band FM, PLL Demodulators, and FLL Loops Sampling Systems
 Couniations Contents Introdution to Couniation Systes Analogue Modulation AM, DSBSC, SB, SSB, FM, PM, Narrow band FM, PLL Deodulators, and FLL Loops Sapling Systes Tie and Frequeny Division ultiplexing
Couniations Contents Introdution to Couniation Systes Analogue Modulation AM, DSBSC, SB, SSB, FM, PM, Narrow band FM, PLL Deodulators, and FLL Loops Sapling Systes Tie and Frequeny Division ultiplexing
AMPLITUDE MODULATION AND DEMODULATION
 Modulation is a tehnique to transit inforation via radio arrier wavefor. It is a non-linear proess that generates additional frequenies, as we will see. Aplitude Modulation (AM) works by varying the aplitude
Modulation is a tehnique to transit inforation via radio arrier wavefor. It is a non-linear proess that generates additional frequenies, as we will see. Aplitude Modulation (AM) works by varying the aplitude
Lecture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa
 Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
Angle Modulation Frequency Modulation
 Angle Modulation Frequeny Modulation Consider again the general arrier v t =V osω t + φ ωt + φ represents the angle o the arrier. There are two ways o varying the angle o the arrier. a) By varying the
Angle Modulation Frequeny Modulation Consider again the general arrier v t =V osω t + φ ωt + φ represents the angle o the arrier. There are two ways o varying the angle o the arrier. a) By varying the
Chapter 2. Signal Processing and Modulation
 Chaper 2. Signal Proessing and Modulaion 2.1. The Naure of Eleroni Signals 2.1.1. Sai and Quasi-Sai Signals Sai signals are by definiion unhanging over a long period of ime. Suh signals are essenially
Chaper 2. Signal Proessing and Modulaion 2.1. The Naure of Eleroni Signals 2.1.1. Sai and Quasi-Sai Signals Sai signals are by definiion unhanging over a long period of ime. Suh signals are essenially
pair 1 Mm 300 Hz ! VLF = Very Low Frequency UHF = Ultra High Frequency ! LF = Low Frequency SHF = Super High Frequency
 nroduion o Wireless Neworks: proools and perormane analsis Luiano Bononi bononi@s.unibo.i Tesi onsigliai: William Sallings, Wireless Communiaions & Neworks, Prenie Hall,, SBN 348646 Johen H. Shiller, Mobile
nroduion o Wireless Neworks: proools and perormane analsis Luiano Bononi bononi@s.unibo.i Tesi onsigliai: William Sallings, Wireless Communiaions & Neworks, Prenie Hall,, SBN 348646 Johen H. Shiller, Mobile
Receiver Architectures
 27/Dec/26 1 Receiver Archiecures Image-Rejec Receivers Shif-by-9 o For narrowband signal: sin cos +j /2 +j (a) T / 4 X = j j /2 G( ) = j sgn( ) 1/2 (b) Figure 5.23 Shif by 9 o in (a) ime and (b) frequency
27/Dec/26 1 Receiver Archiecures Image-Rejec Receivers Shif-by-9 o For narrowband signal: sin cos +j /2 +j (a) T / 4 X = j j /2 G( ) = j sgn( ) 1/2 (b) Figure 5.23 Shif by 9 o in (a) ime and (b) frequency
Second Edition Simon Haykin, Michael Moher
 Introdution to Analog And Digital Communiations Seond Edition Simon Haykin, Mihael Moher Chapter 6 Baseband Delta Transmission 6. Baseband Transmission o Digital Data 6.2 The Intersymbol Intererene Problem
Introdution to Analog And Digital Communiations Seond Edition Simon Haykin, Mihael Moher Chapter 6 Baseband Delta Transmission 6. Baseband Transmission o Digital Data 6.2 The Intersymbol Intererene Problem
EE201 Circuit Theory I Fall
 EE1 Circui Theory I 17 Fall 1. Basic Conceps Chaper 1 of Nilsson - 3 Hrs. Inroducion, Curren and Volage, Power and Energy. Basic Laws Chaper &3 of Nilsson - 6 Hrs. Volage and Curren Sources, Ohm s Law,
EE1 Circui Theory I 17 Fall 1. Basic Conceps Chaper 1 of Nilsson - 3 Hrs. Inroducion, Curren and Volage, Power and Energy. Basic Laws Chaper &3 of Nilsson - 6 Hrs. Volage and Curren Sources, Ohm s Law,
Introduction & Amplitude Modulation
 Departent of Eletronis and Couniation Engineering, KUET Introdution & Aplitude Modulation Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET Departent of Eletronis and Couniation Engineering, KUET Introdution (1/) Long distane
Departent of Eletronis and Couniation Engineering, KUET Introdution & Aplitude Modulation Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET Departent of Eletronis and Couniation Engineering, KUET Introdution (1/) Long distane
ANALOG COMMUNICATION (9)
 11/5/013 DEARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ANALOG COMMUNICATION (9) Fall 013 Original slides by Yrd. Doç. Dr. Burak Kellei Modified by Yrd. Doç. Dr. Didem Kivan Tureli OUTLINE Noise in Analog
11/5/013 DEARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ANALOG COMMUNICATION (9) Fall 013 Original slides by Yrd. Doç. Dr. Burak Kellei Modified by Yrd. Doç. Dr. Didem Kivan Tureli OUTLINE Noise in Analog
Chapter 4: Angle Modulation
 Tes 2 Review Tes 2 Review Professor Deepa Kundur Universiy of Torono Reference: Secions: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.6, 4.7, 4.8 of 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6 S. Haykin and M. Moher,
Tes 2 Review Tes 2 Review Professor Deepa Kundur Universiy of Torono Reference: Secions: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.6, 4.7, 4.8 of 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6 S. Haykin and M. Moher,
EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER
 EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER INTRODUCTION: Being able o ransmi a radio frequency carrier across space is of no use unless we can place informaion or inelligence upon i. This las ransmier
EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER INTRODUCTION: Being able o ransmi a radio frequency carrier across space is of no use unless we can place informaion or inelligence upon i. This las ransmier
Chapter 4: Angle Modulation
 Tes 2 Review Tes 2 Review Professor Deepa Kundur Universiy of Torono Reference: Secions: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.6, 4.7, 4.8 of 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6 S. Haykin and M. Moher,
Tes 2 Review Tes 2 Review Professor Deepa Kundur Universiy of Torono Reference: Secions: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.6, 4.7, 4.8 of 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6 S. Haykin and M. Moher,
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
ELG3175 Introduction to Communication Systems. VSB and Introduction to Angle Modulation
 ELG3175 Inoduion o Communiaion Sysems and Inoduion o ngle odulaion oivaion Fo wideband inomaion signals, SSB is diiul o implemen. Fo equeny disiminaion, he ile mus have a shap uo nea he equeny so as o
ELG3175 Inoduion o Communiaion Sysems and Inoduion o ngle odulaion oivaion Fo wideband inomaion signals, SSB is diiul o implemen. Fo equeny disiminaion, he ile mus have a shap uo nea he equeny so as o
(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]
![(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3] (b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]](/thumbs/85/91561193.jpg) Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Feedback interferometry with frequency modulation
 Feedbak inerferomery wih frequeny modulaion ior. obolev, Galina A. Kashheeva Insiue of Auomaion and Eleromery (IAE) iberian Branh of he Russian Aademy of ienes (B RA) 1, Kopuga prospe, Novosibirsk, 639,
Feedbak inerferomery wih frequeny modulaion ior. obolev, Galina A. Kashheeva Insiue of Auomaion and Eleromery (IAE) iberian Branh of he Russian Aademy of ienes (B RA) 1, Kopuga prospe, Novosibirsk, 639,
DS-CDMA with Frequency-domain Equalization for High Speed Downlink Packet Access
 wih Frequeny-domain Equalizaion for High Speed Downlink Pake Aess Deepshikha Garg and Fumiyuki Adahi Dep. of Elerial and Communiaions Engineering Tohoku Universiy, Sendai, Japan deep@mobile.eei.ohoku.a.jp
wih Frequeny-domain Equalizaion for High Speed Downlink Pake Aess Deepshikha Garg and Fumiyuki Adahi Dep. of Elerial and Communiaions Engineering Tohoku Universiy, Sendai, Japan deep@mobile.eei.ohoku.a.jp
Coherent Detection Method with Compensation at Transmitter in Time Division Duplex System
 Coherent Detetion Method with Compensation at Transmitter in Time Division Duplex System Young An Kim 1, Choong Seon Hong 1 1 Department o Eletronis and Inormation, Kyung Hee University, 1 Seoheon, Giheung,
Coherent Detetion Method with Compensation at Transmitter in Time Division Duplex System Young An Kim 1, Choong Seon Hong 1 1 Department o Eletronis and Inormation, Kyung Hee University, 1 Seoheon, Giheung,
Amplitude Modulation, II
 Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Module 5 Carrier Modulation. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 5 Carrier Modulation Version ECE II, Kharagpur Lesson 5 Quaternary Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) Modulation Version ECE II, Kharagpur After reading this lesson, you will learn about Quaternary Phase
Module 5 Carrier Modulation Version ECE II, Kharagpur Lesson 5 Quaternary Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) Modulation Version ECE II, Kharagpur After reading this lesson, you will learn about Quaternary Phase
Wrap Up. Fourier Transform Sampling, Modulation, Filtering Noise and the Digital Abstraction Binary signaling model and Shannon Capacity
 Wrap Up Fourier ransorm Sampling, Modulaion, Filering Noise and he Digial Absracion Binary signaling model and Shannon Capaciy Copyrigh 27 by M.H. Perro All righs reserved. M.H. Perro 27 Wrap Up, Slide
Wrap Up Fourier ransorm Sampling, Modulaion, Filering Noise and he Digial Absracion Binary signaling model and Shannon Capaciy Copyrigh 27 by M.H. Perro All righs reserved. M.H. Perro 27 Wrap Up, Slide
Optical Short Pulse Generation and Measurement Based on Fiber Polarization Effects
 Opical Shor Pulse Generaion and Measuremen Based on Fiber Polarizaion Effecs Changyuan Yu Deparmen of Elecrical & Compuer Engineering, Naional Universiy of Singapore, Singapore, 117576 A*STAR Insiue for
Opical Shor Pulse Generaion and Measuremen Based on Fiber Polarizaion Effecs Changyuan Yu Deparmen of Elecrical & Compuer Engineering, Naional Universiy of Singapore, Singapore, 117576 A*STAR Insiue for
Amplitude Modulation Chapter 2. Modulation process
 Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Communication Systems, 5e
 Communiation Systems, 5e Chapter 7: Analog Communiation Systems A. Brue Carlson Paul B. Crilly 010 The Mraw-Hill Companies Chapter 7: Analog Communiation Systems Reeiver blok diagram design Image requeny
Communiation Systems, 5e Chapter 7: Analog Communiation Systems A. Brue Carlson Paul B. Crilly 010 The Mraw-Hill Companies Chapter 7: Analog Communiation Systems Reeiver blok diagram design Image requeny
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Negative frequency communication
 Negaive frequency communicaion Fanping DU Email: dufanping@homail.com Qing Huo Liu arxiv:2.43v5 [cs.it] 26 Sep 2 Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Duke Universiy Email: Qing.Liu@duke.edu Absrac
Negaive frequency communicaion Fanping DU Email: dufanping@homail.com Qing Huo Liu arxiv:2.43v5 [cs.it] 26 Sep 2 Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Duke Universiy Email: Qing.Liu@duke.edu Absrac
7.1 Amplitude Modulation
 7. Ampliud Modulaion Samn or Q.-. An AM signal is rprsnd by v( ( 0 sin 000os( 0 6 V. Th modulaion indx is (A 0 (B (C 0. (D.5. Th oal signal powr is (A 08 (B 6 (C 00 (D. Th oal sid band powr is (A 8 (B
7. Ampliud Modulaion Samn or Q.-. An AM signal is rprsnd by v( ( 0 sin 000os( 0 6 V. Th modulaion indx is (A 0 (B (C 0. (D.5. Th oal signal powr is (A 08 (B 6 (C 00 (D. Th oal sid band powr is (A 8 (B
Signal Propagation. Jie Gao 01/27/2010
 Signal Propagaion Jie Gao /7/ Signal Signal are generae as physial represenaions o aa A signal is a union o ime an loaion ieal igial signal a speial ype o signal, sine waves, also alle harmonis: s() =
Signal Propagaion Jie Gao /7/ Signal Signal are generae as physial represenaions o aa A signal is a union o ime an loaion ieal igial signal a speial ype o signal, sine waves, also alle harmonis: s() =
Lecture 19: Lowpass, bandpass and highpass filters
 Leure 9: Lowpass, bandpass and higass filers UHTXHQF\6HOHFLYH LOHUV Ideal frequeny-seleive filers are filers ha le frequeny omponens over a given frequeny band (he passband pass hrough undisored, while
Leure 9: Lowpass, bandpass and higass filers UHTXHQF\6HOHFLYH LOHUV Ideal frequeny-seleive filers are filers ha le frequeny omponens over a given frequeny band (he passband pass hrough undisored, while
Examination Mobile & Wireless Networking ( ) April 12,
 Page 1 of 5 Examinaion Mobile & Wireless Neworking (192620010) April 12, 2017 13.45 16.45 Noes: Only he overhead shees used in he course, 2 double-sided shees of noes (any fon size/densiy!), and a dicionary
Page 1 of 5 Examinaion Mobile & Wireless Neworking (192620010) April 12, 2017 13.45 16.45 Noes: Only he overhead shees used in he course, 2 double-sided shees of noes (any fon size/densiy!), and a dicionary
Introduction: Analog Communication: Goal: Transmit a message from one location to another.
 ECE-5 Phil Schnier January 6, 8 Inroducion: Goal: Transmi a rom one locaion o anoher When is coninuous waveorm analog comm (eg, FM radio), sequence o numbers digial comm (eg, mp ile), hough he sequence
ECE-5 Phil Schnier January 6, 8 Inroducion: Goal: Transmi a rom one locaion o anoher When is coninuous waveorm analog comm (eg, FM radio), sequence o numbers digial comm (eg, mp ile), hough he sequence
Single Sideband (SSB) AM
 Single Sideband (SSB) AM Leture 7 Why SSB-AM? Spetral eiieny is o great importane. Conventional & DSB-SC oupy twie the message bandwidth. All the inormation is ontained in either hal the other is redundant.
Single Sideband (SSB) AM Leture 7 Why SSB-AM? Spetral eiieny is o great importane. Conventional & DSB-SC oupy twie the message bandwidth. All the inormation is ontained in either hal the other is redundant.
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR DCT-BASED CODED IMAGE COMMUNICATION IN WIRELESS MULTIMEDIA SENSOR NETWORKS
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL ON SMART SENSING AN INTELLIGENT SYSTEMS VOL. 6, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 013 ERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR CT-BASE COE IMAGE COMMUNICATION IN WIRELESS MULTIMEIA SENSOR NETWORKS Xiong Zheyuan 1,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL ON SMART SENSING AN INTELLIGENT SYSTEMS VOL. 6, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 013 ERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR CT-BASE COE IMAGE COMMUNICATION IN WIRELESS MULTIMEIA SENSOR NETWORKS Xiong Zheyuan 1,
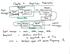 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
UNIT IV DIGITAL MODULATION SCHEME
 UNI IV DIGIAL MODULAION SCHEME Geomeric Represenaion of Signals Ojecive: o represen any se of M energy signals {s i (} as linear cominaions of N orhogonal asis funcions, where N M Real value energy signals
UNI IV DIGIAL MODULAION SCHEME Geomeric Represenaion of Signals Ojecive: o represen any se of M energy signals {s i (} as linear cominaions of N orhogonal asis funcions, where N M Real value energy signals
TELE4652 Mobile and Satellite Communications
 TELE465 Mobile and Saellie Communicaions Assignmen (Due: 4pm, Monday 7 h Ocober) To be submied o he lecurer before he beginning of he final lecure o be held a his ime.. This quesion considers Minimum Shif
TELE465 Mobile and Saellie Communicaions Assignmen (Due: 4pm, Monday 7 h Ocober) To be submied o he lecurer before he beginning of he final lecure o be held a his ime.. This quesion considers Minimum Shif
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Review. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS IV Sem. Prepared by Mr. T. Nagarjuna ECE Department
 ANALOG COMMUNICAIONS IV Sem Prepared by Mr.. Nagaruna ECE Department UNI I SIGNAL ANALYSIS AND LI SYSEMS Classifiation of Signals Deterministi & Non Deterministi Signals Periodi & A periodi Signals Even
ANALOG COMMUNICAIONS IV Sem Prepared by Mr.. Nagaruna ECE Department UNI I SIGNAL ANALYSIS AND LI SYSEMS Classifiation of Signals Deterministi & Non Deterministi Signals Periodi & A periodi Signals Even
Principles of Communications Lecture 4: Analog Modulation Techniques (2) Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 National Chiao Tung University
 Principles o Communicaions Lecure 4: Analog Modulaion Techniques Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 Naional Chiao Tung Universiy cwliu@wins.ee.ncu.edu.w Oulines Linear Modulaion Angle Modulaion Inererence Feedback Demodulaors
Principles o Communicaions Lecure 4: Analog Modulaion Techniques Chih-Wei Liu 劉志尉 Naional Chiao Tung Universiy cwliu@wins.ee.ncu.edu.w Oulines Linear Modulaion Angle Modulaion Inererence Feedback Demodulaors
