Communication Systems, 5e
|
|
|
- Beatrix Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Communiation Systems, 5e Chapter 7: Analog Communiation Systems A. Brue Carlson Paul B. Crilly 010 The Mraw-Hill Companies
2 Chapter 7: Analog Communiation Systems Reeiver blok diagram design Image requeny bands that may ause spurious responses (more ilter requirements) Signal Multiplexing Frequeny division (FDM) and Time division (TDM) Phase-Lok Loops (PLL) 010 The Mraw-Hill Companies
3 Objetives Reeiver blok diagram design Image requeny bands that may ause spurious responses (more ilter requirements) Signal Multiplexing Frequeny division (FDM) and Time division (TDM) Phase-Lok Loops (PLL) 3
4 Tuned RF Reeiver (TRF) RF ampliier + demodulator All gain is aomplished with RF ampliier For the produt detetor TRF, seletivity and station seletion is aomplished via a tuned RF ampliier Crystal radio is lassi TRF Diret to digital implementation, otherwise not typial Antenna Put ADC here x () t Tunable BPF RF Amp Demod Amp x() t 010 The Mraw-Hill Companies
5 Superheterodyne Reeiver (Superhet) Copyright The Mraw-Hill Companies, In. Permission required or reprodution or display. Figure RF: Radio Frequeny : Intermediate Frequeny 5
6 Superheterodyne Input bandpass signal at heterodyned (or beat ) down to an intermediate requeny beore detetion. Tuning done via hanging the loal osillator Adjaent hannels are rejeted via a seletive BPF in the stage The stage additional stage o gain the RF ampliier is not required to supply all the gain better stability 010 The Mraw-Hill Companies
7 Superhet reeiver waveorms Copyright The Mraw-Hill Companies, In. Permission required or reprodution or display. Figure 7.1- Image RF Filter Pass entire tuning band Filter Deine signal bandwidth 7
8 Why the Superhetrodyne vs the Tuned RF Easier to design a seletive BPF with ixed requeny or adjaent hannel rejetion versus a tunable ilter Speial ilters or bandwidths! Examples: SAW, rystal ilters stages o gain versus 1 stage o gain inherently more stable (i.e. it is diiulty to design a high gain, stable RF amp) 010 The Mraw-Hill Companies
9 Superhet Reeiver Intermediate Frequeny Typially at a known ixed requeny, Usually where a bandpass ilter sets the predemodulation signal bandwidth Common requenies ( ) Television reeivers: 30 MHz to 900 MHz FM radio reeivers: 5.5 MHz, 10.7 MHz, 98 MHz. In double onversion superheterodyne reeivers, oten a irst intermediate requeny o 1.6 MHz is used ollowed by a seond intermediate requeny o 470 khz. AM radio reeivers: 455 khz, 460 khz, 465 khz, 470 khz, 475 khz, 480 khz Satellite uplink downlink equipment 70 MHz, Downink irst Terrestrial mirowave equipment 50 MHz, 70 MHz Radar 30 MHz RF Test Equipment MHz, 160 MHz, 1.4 MHz 9
10 High and Low Side s Low Side Loal Osillator ( < RF) image image image High Side Loal Osillator (>RF) image image image 10
11 Image Bands Mixed to The image bands will mix to the bands with one exeption, omplex mixing/proessing Image bands should be iltered out prior to mixing Bandpass iltering For a square wave mixing, multiple images bands exist and must be iltered t os t os3 t os t 11
12 AM and FM Radio Parameters AM FM Carrier Frequeny khz MHz Carrier Spaing 10 khz 00 khz Intermediate Frequeny 455 khz 10.7 MHz Bandwidth 6-10 khz khz Audio Bandwidth 3-5 khz 15 khz High Side khz MHz Tuning Ratio.06:1 1.0:1 Low Side khz MHz Tuning Ratio 13.47:1 1.6:1 C C RF tuning High Side C Low Side C Image Spetrum ' C ' C C ' C ' C C 1
13 Nonlinear Mixing Produts nd and 3 rd harmonis may be generated and appear in the or baseband strips o a reeiver The ollowing images may also our Harmoni Produts C11 C1 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C C1 C C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C
14 @ 500 khz F/RF Band: Low Side mixing Example 7.1-1a 4.0 to 4.5 MHz 3.5 to 4.0 MHz 3 rd harmoni present in (mixer more likely) (@ 10.5 to 1 MHz) Draw Piture! They help. 1 st Image Band: 3.0 to 3.5 MHz 3 rd Image Band Low: 10.0 to 11.5 MHz 3 rd Image Band High: 11 to 1.5 MHz 14
15 Example 500 khz F/RF Band: 4.0 to 4.5 MHz High Side Mixing 4.5 to 5.0 MHz 3 rd harmoni present in (mixer more likely) (13.5 to 15 MHz) Draw Piture! They help. 1 st Image Band: 3.5 to 4.0 MHz 3 rd Image Band Low: 13.0 to 14.5 MHz 3 rd Image Band High: 14 to 15.5 MHz 15
16 Diret onversion reeiver Copyright The Mraw-Hill Companies, In. Permission required or reprodution or display. Figure y x i t A os t A os i t A os t A os t os t y 1 A A 1 t os t os i os 1 t t os 1 t t y LPF A A i 1 t os t os t 16
17 Diret onversion reeiver with opposite sideband rejetion Copyright The Mraw-Hill Companies, In. Permission required or reprodution or display. Figure Canellation o lower sideband requenies! Equivalent to Complex Mixing and iltering 17
18 Image Rejetion Diret Conversion y y sin os x i t A os t A os i t A os 1t A os t sin t i t A t A os t os t y 1 y os 1 y t sin t sin t A A A A i sin LPF 1 A A i sin LPF 90 1 t os t os t i oslpf 1 t os t os t t y sum t A os t 1 y di i t A os t 18
19 Double onversion reeiver Copyright The Mraw-Hill Companies, In. Permission required or reprodution or display. Figure Dual Conversion Superhet, typially using a high side s 19
20 RFID Reeiver Downonversion ISM Band Downonversion (90-98 MHz) Only mixing and ilters shown High-side Los Synthesizer provides enter requeny seletion ilter sets bandwidth LPF or ADC anti-aliasing Convert to s/4 or post- ADC omplex proessing Fs > 4 x max 0
21 Casaded ain Multiple the gain (loss) o eah stage together I gain in db, add the gains (in db) and subtrat the losses (in db) db db db db db db predemod RF 1stMixer 1 ndmixer I the mixers have loss instead o gain (passive mixers) db db L db db L db db predemod RF 1stMixer 1 ndmixer 1
22 Noise Figure The noise igure is a measure o the additional noise that is added by any iruit element. Eetive additional input noise xt y t F SNR SNR in out P Sin P Sin N N in in N amp F SNR SNR in in amp 1 out N N N in N N amp in
23 Casaded Noise Figure The noise igure is a measure o the additional noise that is added by any iruit element. Eetive additional input noise xt yt F SNR SNR in out 1 P Sin P Sin 1 N N in in N amp1 N amp SNR N in amp in in Namp N amp 1 F SNR out 1 N in N N N amp in N F 1 N N amp1 1 amp 1 F 1 1 F1 1 F 1 F1 in 1 Nin 1 1 N 3
24 Basi Reeiver x t Bandpass Filter Ampliier Bandpass Filter Lowpass Filter x PreD t Demod x M t Pr ed Tuning os 1 t RF Filter removes images Low Noise Ampliier Mixer to BPF sets the system BW Mixer to baseband Baseband LPF to remove mixing produts db db db db db db db RF BPF LNA 1stMixer BPF ndmixer os t LPF F Pr ed F RF BPF RF BPF F F RF BPF ndmixer Amp 1stMixer 1 1 1stMixer Amp BPF F 1stMixer RF BPF 1 RF BPF Amp Amp F RF BPF LPF 1 1stMixer F BPF Amp BPF 1 1stMixer ndmixer 4
25 Thermal Noise Power Modeled as additive white aussian noise (AWN) N T B Where N is the noise power κ is Boltzmann s onstant T is absolute temperature in degrees Kelvin B is the bandwidth in Hertz 8.6 dbw / K Hz T 0 90K IEEE re N 0 0 T 1.38e e 1 N 0 04 dbw / Hz 174 dbm / Hz 5
26 Reeiver Operating Charateristis Sensitivity minimum input value Dynami Range usable signal range Seletivity ilter out adjaent noise and intererene Adjaent Channel Intererene (ACI) Rejetion Building a perormane diagram or a sotware radio Antenna to the Input o the ADC 6
27 FM Radio Design Diagram FM reeiver 00 khz BW 1-bit ADC with 10-bit perormane Multiple signal environment SOI detetion threshold 7
28 Sanning spetrum analyzer Copyright The Mraw-Hill Companies, In. Permission required or reprodution or display. a) blok diagram (b) amplitude response Figure
29 Spetrum Analyzer Considerations Resolution Bandwidth The bandwidth o the signal power measurement Adjustable with orresponding noise power hange Filter setting Video Bandwidth The ilter prior to displaying the san Baseband ilter setting Sweep time must support the ilters! Move slow enough or the ilter time onstant Most automatially set the RB, VB and sweep time 9
30 Multiplexing Combining multiple signals into a wider bandwidth system or transmission Typially multiplex in time or requeny TDM time division multiplexing FDM requeny division multiplexing For time multiplexing, PAM sampling, bandwidth based on PAM pulse periods For requeny multiplexing, bandwidth is the sum o all the multiplexed elements plus their guard bands 30
31 Frequeny-Division Multiplexing (FDM) Stallings, Wireless Communiations & Networks, Seond Edition, 005 Pearson Eduation, In. ISBN:
32 Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) Stallings, Wireless Communiations & Networks, Seond Edition, 005 Pearson Eduation, In. ISBN:
33 FDM transmitter Copyright The Mraw-Hill Companies, In. Permission required or reprodution or display. Figure 7.-1 uard Bands: allow or ilter transition bands Transmitter Reeiver 33
34 FDM reeiver Copyright The Mraw-Hill Companies, In. Permission required or reprodution or display. uard Bands: allow or reeiver ilter transition bands Cross Talk: unwanted energy rom adjaent FDM hannels Figure 7.- Post-De-FDM Baseband Bandwidths: Signal Passband + both guard bands 34
35 FDMA satellite repeater system Copyright The Mraw-Hill Companies, In. Permission required or reprodution or display. Figure 7.-3 Nominally 36 MHz BW Links 336 to 900 Voie Channels or 4 groups 1.5 MHz/group 35
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Analog Signal Transmission and Reception. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communiations Theory and Systems: I Analog Signal Transmission and Reeption ELEC 350 Fall 2007 1 ELEC 350 Fall 2007 2 Analog Modulation A large number o signals are analog speeh musi video These
ELEC 350 Communiations Theory and Systems: I Analog Signal Transmission and Reeption ELEC 350 Fall 2007 1 ELEC 350 Fall 2007 2 Analog Modulation A large number o signals are analog speeh musi video These
Figure 4.11: Double conversion FM receiver
 74 4.8 FM Reeivers FM reeivers, like their AM ounterparts, are superheterodyne reeivers. Figure 4.11 shows a simplified blok diagram for a double onversion superheterodyne FM reeiver Figure 4.11: Double
74 4.8 FM Reeivers FM reeivers, like their AM ounterparts, are superheterodyne reeivers. Figure 4.11 shows a simplified blok diagram for a double onversion superheterodyne FM reeiver Figure 4.11: Double
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
ENSC327 Communications Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation. School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required Bakground DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required Bakground DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Associate Professor Department of EEE, BUET
 EEE 309 Communiation Theory Semester: January 06 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Assoiate Proessor Department o EEE, BUET Email: marhadhossain@eee.buet.a.bd Oie: ECE 33, ECE Building Part 03-3 Single-sideband Suppressed
EEE 309 Communiation Theory Semester: January 06 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Assoiate Proessor Department o EEE, BUET Email: marhadhossain@eee.buet.a.bd Oie: ECE 33, ECE Building Part 03-3 Single-sideband Suppressed
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
ENSC327 Communications Systems 5: Frequency Translation (3.6) and Superhet Receiver (3.9)
 ENSC327 Communications Systems 5: Frequency Translation (3.6) and Superhet Receiver (3.9) Jie Liang School o Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Frequency translation (page 128) Superhet
ENSC327 Communications Systems 5: Frequency Translation (3.6) and Superhet Receiver (3.9) Jie Liang School o Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Frequency translation (page 128) Superhet
ENSC327 Communications Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation. Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Jie Liang Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Jie Liang Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
Introduction to Receivers
 Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
EE140 Introduction to Communication Systems Lecture 7
 3/4/08 EE40 Introdution to Communiation Systems Leture 7 Instrutor: Prof. Xiliang Luo ShanghaiTeh University, Spring 08 Arhiteture of a (Digital) Communiation System Transmitter Soure A/D onverter Soure
3/4/08 EE40 Introdution to Communiation Systems Leture 7 Instrutor: Prof. Xiliang Luo ShanghaiTeh University, Spring 08 Arhiteture of a (Digital) Communiation System Transmitter Soure A/D onverter Soure
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits. Module 7
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering. Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University
 ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
Module 8 Theory. dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain. Functional Blocks Parameters. IRTS Region 4
 Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B1 - Radio systems architecture» Basic radio systems» Image rejection» Digital and SW radio» Functional units 19/03/2012-1 ATLCE
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B1 - Radio systems architecture» Basic radio systems» Image rejection» Digital and SW radio» Functional units 19/03/2012-1 ATLCE
Receiver Design. Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21
 Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
AMPLITUDE MODULATION AND DEMODULATION
 Modulation is a tehnique to transit inforation via radio arrier wavefor. It is a non-linear proess that generates additional frequenies, as we will see. Aplitude Modulation (AM) works by varying the aplitude
Modulation is a tehnique to transit inforation via radio arrier wavefor. It is a non-linear proess that generates additional frequenies, as we will see. Aplitude Modulation (AM) works by varying the aplitude
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture
 RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
Receiver Architecture
 Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
ECEN 5014, Spring 2013 Special Topics: Active Microwave Circuits and MMICs Zoya Popovic, University of Colorado, Boulder
 ECEN 5014, Spring 2013 Special Topics: Active Microwave Circuits and MMICs Zoya Popovic, University o Colorado, Boulder LECTURE 13 PHASE NOISE L13.1. INTRODUCTION The requency stability o an oscillator
ECEN 5014, Spring 2013 Special Topics: Active Microwave Circuits and MMICs Zoya Popovic, University o Colorado, Boulder LECTURE 13 PHASE NOISE L13.1. INTRODUCTION The requency stability o an oscillator
Superheterodyne Receiver Tutorial
 1 of 6 Superheterodyne Receiver Tutorial J P Silver E-mail: john@rfic.co.uk 1 ABSTRACT This paper discusses the basic design concepts of the Superheterodyne receiver in both single and double conversion
1 of 6 Superheterodyne Receiver Tutorial J P Silver E-mail: john@rfic.co.uk 1 ABSTRACT This paper discusses the basic design concepts of the Superheterodyne receiver in both single and double conversion
TELE3013 Mid-session QUIZ 1
 TELE3013 Mid-session QUIZ 1 Week 7 10 th April, 2006 Name: Student No: Instrutions to Candidates (1) Time allowed: 90 minutes or so (2) Answer all questions. Total Marks = 90. (3) Marks are as indiated.
TELE3013 Mid-session QUIZ 1 Week 7 10 th April, 2006 Name: Student No: Instrutions to Candidates (1) Time allowed: 90 minutes or so (2) Answer all questions. Total Marks = 90. (3) Marks are as indiated.
Communication Systems Lecture 7. Dong In Kim School of Info/Comm Engineering Sungkyunkwan University
 Communiation Systems Leture 7 Dong In Kim Shool o Ino/Comm Engineering Sungkyunkwan University 1 Outline Expression o SSB signals Waveorm o SSB signals Modulators or SSB: Frequeny disrimination Phase disrimination
Communiation Systems Leture 7 Dong In Kim Shool o Ino/Comm Engineering Sungkyunkwan University 1 Outline Expression o SSB signals Waveorm o SSB signals Modulators or SSB: Frequeny disrimination Phase disrimination
ECE 4600 Communication Systems
 ECE 4600 Communication Systems Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Course Topics Course Introduction
ECE 4600 Communication Systems Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Course Topics Course Introduction
Introduction to Analog And Digital Communications
 Introdution to Analog And Digital Communiations Seond Edition Simon Haykin, Mihael Moher Chapter 9 Noise in Analog Communiations 9.1 Noise in Communiation Systems 9. Signal-to-Noise Ratios 9.3 Band-Pass
Introdution to Analog And Digital Communiations Seond Edition Simon Haykin, Mihael Moher Chapter 9 Noise in Analog Communiations 9.1 Noise in Communiation Systems 9. Signal-to-Noise Ratios 9.3 Band-Pass
High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 10 Mixers
 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture Mixers Michael H. Perrott March 5, 24 Copyright 24 by Michael H. Perrott All rights reserved. Mixer Design or Wireless Systems From Antenna and Bandpass
High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture Mixers Michael H. Perrott March 5, 24 Copyright 24 by Michael H. Perrott All rights reserved. Mixer Design or Wireless Systems From Antenna and Bandpass
HF Receivers, Part 2
 HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation. Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communiations Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introdution 3.2 Amplitude Modulation 3.3
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communiations Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introdution 3.2 Amplitude Modulation 3.3
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Lecture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa
 Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
6. Amplitude Modulation
 6. Amplitude Modulation Modulation is a proess by whih some parameter of a arrier signal is varied in aordane with a message signal. The message signal is alled a modulating signal. Definitions A bandpass
6. Amplitude Modulation Modulation is a proess by whih some parameter of a arrier signal is varied in aordane with a message signal. The message signal is alled a modulating signal. Definitions A bandpass
BPSK so that we have a discrete set of RF signals. t)cos(
 BPSK. BPSK Introdution Reall that the most general modulation has the form s( t) a( t)os[ t ( t)]. We remared earlier that phase modulation was not an effetive way to implement analog ommuniation, one
BPSK. BPSK Introdution Reall that the most general modulation has the form s( t) a( t)os[ t ( t)]. We remared earlier that phase modulation was not an effetive way to implement analog ommuniation, one
Coherent Detection Method with Compensation at Transmitter in Time Division Duplex System
 Coherent Detetion Method with Compensation at Transmitter in Time Division Duplex System Young An Kim 1, Choong Seon Hong 1 1 Department o Eletronis and Inormation, Kyung Hee University, 1 Seoheon, Giheung,
Coherent Detetion Method with Compensation at Transmitter in Time Division Duplex System Young An Kim 1, Choong Seon Hong 1 1 Department o Eletronis and Inormation, Kyung Hee University, 1 Seoheon, Giheung,
Accurate Phase Noise Measurements Made Cost Effective
 MTTS 2008 MicroApps Accurate Phase Noise Measurements Made Cost Effective author : Jason Breitbarth, PhD. Boulder, Colorado, USA Presentation Outline Phase Noise Intro Additive and Absolute Oscillator
MTTS 2008 MicroApps Accurate Phase Noise Measurements Made Cost Effective author : Jason Breitbarth, PhD. Boulder, Colorado, USA Presentation Outline Phase Noise Intro Additive and Absolute Oscillator
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation RX nonlinearities (parts of 2.2) System Nonlinearity Sensitivity
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation RX nonlinearities (parts of 2.2) System Nonlinearity Sensitivity
Lecture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa
 Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
Leture 4: Amplitude Modulation (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier, DSB-SC) Dr. Mohammed Hawa Eletrial Engineering Department University of Jordan EE421: Communiations I Notation 2 1 Three Modulation Types
THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN
 THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN Mark Hunter * Abstract This paper is intended to give an overview of the design of radio transceivers to the engineer new to the field. It is shown how the requirements
THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN Mark Hunter * Abstract This paper is intended to give an overview of the design of radio transceivers to the engineer new to the field. It is shown how the requirements
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
ANALOG COMMUNICATION (9)
 11/5/013 DEARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ANALOG COMMUNICATION (9) Fall 013 Original slides by Yrd. Doç. Dr. Burak Kellei Modified by Yrd. Doç. Dr. Didem Kivan Tureli OUTLINE Noise in Analog
11/5/013 DEARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL &ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ANALOG COMMUNICATION (9) Fall 013 Original slides by Yrd. Doç. Dr. Burak Kellei Modified by Yrd. Doç. Dr. Didem Kivan Tureli OUTLINE Noise in Analog
Analog Transmission of Digital Data: ASK, FSK, PSK, QAM
 Analog Transmission of Digital Data: ASK, FSK, PSK, QAM Required reading: Forouzan 5. Garia 3.7 CSE 33, Fall 6 Instrutor: N. Vlaji Why Do We Need Digital-to-Analog Conversion?! ) The transmission medium
Analog Transmission of Digital Data: ASK, FSK, PSK, QAM Required reading: Forouzan 5. Garia 3.7 CSE 33, Fall 6 Instrutor: N. Vlaji Why Do We Need Digital-to-Analog Conversion?! ) The transmission medium
Analog Communications
 1 Analog Communiations Amplitude Modulation (AM) Frequeny Modulation (FM) 2 Radio broadasting 30-300M Hz SOURCE Soure Transmitter Transmitted signal Channel Reeived signal Reeiver User Analog baseband
1 Analog Communiations Amplitude Modulation (AM) Frequeny Modulation (FM) 2 Radio broadasting 30-300M Hz SOURCE Soure Transmitter Transmitted signal Channel Reeived signal Reeiver User Analog baseband
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 16 Noise in Integer-N Frequency Synthesizers
 6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 16 in Integer-N Frequency Synthesizers Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute o Technology Copyright 23 by Michael H. Perrott Frequency Synthesizer
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 16 in Integer-N Frequency Synthesizers Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute o Technology Copyright 23 by Michael H. Perrott Frequency Synthesizer
INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA
 COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/9/2017 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/9/2017 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
Page 1. Telecommunication Electronics TLCE - A1 03/05/ DDC 1. Politecnico di Torino ICT School. Lesson A1
 Politecnico di Torino ICT School Lesson A1 A1 Telecommunication Electronics Radio systems architecture» Basic radio systems» Image rejection» Digital and SW radio» Functional units Basic radio systems
Politecnico di Torino ICT School Lesson A1 A1 Telecommunication Electronics Radio systems architecture» Basic radio systems» Image rejection» Digital and SW radio» Functional units Basic radio systems
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Lecture 14: FDM, AM Radio, and the Superheterodyne Receiver. Dr. Mohammed Hawa. Electrical Engineering Department, University of Jordan
 Lecture 14: FDM, AM Radio, and the Superheterodyne Receiver Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University o Jordan EE421: Communications I: Lecture 14. For more inormation read Chapter
Lecture 14: FDM, AM Radio, and the Superheterodyne Receiver Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University o Jordan EE421: Communications I: Lecture 14. For more inormation read Chapter
Second Edition Simon Haykin, Michael Moher
 Introdution to Analog And Digital Communiations Seond Edition Simon Haykin, Mihael Moher Chapter 6 Baseband Delta Transmission 6. Baseband Transmission o Digital Data 6.2 The Intersymbol Intererene Problem
Introdution to Analog And Digital Communiations Seond Edition Simon Haykin, Mihael Moher Chapter 6 Baseband Delta Transmission 6. Baseband Transmission o Digital Data 6.2 The Intersymbol Intererene Problem
Chapter 7. Multiple Division Techniques
 Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
Analog Communication (10EC53) Unit 3 Quadrature Carrier Multiplexing
 Analog Couniation (0EC53) Unit 3 Quadrature Carrier Multiplexing A Quadrature Carrier Multiplexing (QCM) or Quadrature Aplitude Modulation (QAM) ethod enables two DSBSC odulated waves, resulting ro two
Analog Couniation (0EC53) Unit 3 Quadrature Carrier Multiplexing A Quadrature Carrier Multiplexing (QCM) or Quadrature Aplitude Modulation (QAM) ethod enables two DSBSC odulated waves, resulting ro two
Introduction & Amplitude Modulation
 Departent of Eletronis and Couniation Engineering, KUET Introdution & Aplitude Modulation Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET Departent of Eletronis and Couniation Engineering, KUET Introdution (1/) Long distane
Departent of Eletronis and Couniation Engineering, KUET Introdution & Aplitude Modulation Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET Departent of Eletronis and Couniation Engineering, KUET Introdution (1/) Long distane
ADI 2006 RF Seminar. Chapter VI A Detailed Look at Wireless Signal Chain Architectures
 DI 2006 R Seminar Chapter VI Detailed Look at Wireless Chain rchitectures 1 Receiver rchitectures Receivers are designed to detect and demodulate the desired signal and remove unwanted blockers Receiver
DI 2006 R Seminar Chapter VI Detailed Look at Wireless Chain rchitectures 1 Receiver rchitectures Receivers are designed to detect and demodulate the desired signal and remove unwanted blockers Receiver
McGill University. Department. of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Communications systems A
 McGill University Department. o Electrical and Computer Engineering Communications systems 304-411A 1 The Super-heterodyne Receiver 1.1 Principle and motivation or the use o the super-heterodyne receiver
McGill University Department. o Electrical and Computer Engineering Communications systems 304-411A 1 The Super-heterodyne Receiver 1.1 Principle and motivation or the use o the super-heterodyne receiver
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
EKT358 Communication Systems
 EKT358 Communiation Systems Chapter 2 Amplitude Modulation Topis Covered in Chapter 2 2-1: AM Conepts 2-2: Modulation Index and Perentage of Modulation 2-3: Sidebands and the Frequeny Domain 2-4: Single-Sideband
EKT358 Communiation Systems Chapter 2 Amplitude Modulation Topis Covered in Chapter 2 2-1: AM Conepts 2-2: Modulation Index and Perentage of Modulation 2-3: Sidebands and the Frequeny Domain 2-4: Single-Sideband
Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING. Radar Signal Processing Dr. Aamer Iqbal Bhatti. Dr. Aamer Iqbal Bhatti
 Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING Signal Reception Receiver Bandwidth Pulse Shape Power Relation Beam Width Pulse Repetition Frequency Antenna Gain Radar Cross Section of Target. Signal-to-noise ratio Receiver
Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING Signal Reception Receiver Bandwidth Pulse Shape Power Relation Beam Width Pulse Repetition Frequency Antenna Gain Radar Cross Section of Target. Signal-to-noise ratio Receiver
Chapter 3 Digital Transmission Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Digital Transmission Fundamentals Modems and Digital Modulation CSE 33, Winter Instrutor: Foroohar Foroozan Modulation of Digital Data Modulation of Digital Data Modulation proess of onverting
Chapter 3 Digital Transmission Fundamentals Modems and Digital Modulation CSE 33, Winter Instrutor: Foroohar Foroozan Modulation of Digital Data Modulation of Digital Data Modulation proess of onverting
The New England Radio Discussion Society electronics course (Phase 4, cont d) Introduction to receivers
 The New England Radio Discussion Society electronics course (Phase 4, cont d) Introduction to receivers AI2Q April 2017 REVIEW: a VFO, phase-locked loop (PLL), or direct digital synthesizer (DDS), can
The New England Radio Discussion Society electronics course (Phase 4, cont d) Introduction to receivers AI2Q April 2017 REVIEW: a VFO, phase-locked loop (PLL), or direct digital synthesizer (DDS), can
Radio Frequency Design to Support Software Transceiver for Wireless Communications
 Radio Frequency Design to Support Software Transceiver for Wireless Communications Author: Cazzie Williams Western Michigan University Whirlpool Corporation Advisor/Sponsor: Dr. Frank Severance and Dr.
Radio Frequency Design to Support Software Transceiver for Wireless Communications Author: Cazzie Williams Western Michigan University Whirlpool Corporation Advisor/Sponsor: Dr. Frank Severance and Dr.
ELG3175 Introduction to Communication Systems. Conventional AM
 ELG317 Introdution to Communiation Systems Conventional AM Disadvantages o DSB-SC The reeiver must generate a replia o the arrier in order to demodulate a DSB-SC signal. Any phase and/or requeny error
ELG317 Introdution to Communiation Systems Conventional AM Disadvantages o DSB-SC The reeiver must generate a replia o the arrier in order to demodulate a DSB-SC signal. Any phase and/or requeny error
Reconfigurable Low-Power Continuous-Time Sigma-Delta Converter for Multi- Standard Applications
 ECEN-60: Mixed-Signal Interfaces Instructor: Sebastian Hoyos ASSIGNMENT 6 Reconfigurable Low-Power Continuous-Time Sigma-Delta Converter for Multi- Standard Applications ) Please use SIMULINK to design
ECEN-60: Mixed-Signal Interfaces Instructor: Sebastian Hoyos ASSIGNMENT 6 Reconfigurable Low-Power Continuous-Time Sigma-Delta Converter for Multi- Standard Applications ) Please use SIMULINK to design
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Recap of Last 2 Classes
 Recap of Last 2 Classes Transmission Media Analog versus Digital Signals Bandwidth Considerations Attentuation, Delay Distortion and Noise Nyquist and Shannon Analog Modulation Digital Modulation What
Recap of Last 2 Classes Transmission Media Analog versus Digital Signals Bandwidth Considerations Attentuation, Delay Distortion and Noise Nyquist and Shannon Analog Modulation Digital Modulation What
ELT Receiver Architectures and Signal Processing Exam Requirements and Model Questions 2018
 TUT/ICE 1 ELT-44006 Receiver Architectures and Signal Processing Exam Requirements and Model Questions 2018 General idea of these Model Questions is to highlight the central knowledge expected to be known
TUT/ICE 1 ELT-44006 Receiver Architectures and Signal Processing Exam Requirements and Model Questions 2018 General idea of these Model Questions is to highlight the central knowledge expected to be known
Analog Communication.
 Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
4- Single Side Band (SSB)
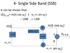 4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
OBJECTIVES EQUIPMENT LIST
 1 Reception of Amplitude Modulated Signals AM Demodulation OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to show how the amplitude-modulated signals are demodulated to obtain the original signal. Also,
1 Reception of Amplitude Modulated Signals AM Demodulation OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to show how the amplitude-modulated signals are demodulated to obtain the original signal. Also,
Instantaneous frequency Up to now, we have defined the frequency as the speed of rotation of a phasor (constant frequency phasor) φ( t) = A exp
 Exponential modulation Instantaneous requency Up to now, we have deined the requency as the speed o rotation o a phasor (constant requency phasor) φ( t) = A exp j( ω t + θ ). We are going to generalize
Exponential modulation Instantaneous requency Up to now, we have deined the requency as the speed o rotation o a phasor (constant requency phasor) φ( t) = A exp j( ω t + θ ). We are going to generalize
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM)
 Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
SC5407A/SC5408A 100 khz to 6 GHz RF Upconverter. Datasheet. Rev SignalCore, Inc.
 SC5407A/SC5408A 100 khz to 6 GHz RF Upconverter Datasheet Rev 1.2 2017 SignalCore, Inc. support@signalcore.com P R O D U C T S P E C I F I C A T I O N S Definition of Terms The following terms are used
SC5407A/SC5408A 100 khz to 6 GHz RF Upconverter Datasheet Rev 1.2 2017 SignalCore, Inc. support@signalcore.com P R O D U C T S P E C I F I C A T I O N S Definition of Terms The following terms are used
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B1 - Radio systems architecture» Basic radio systems» Image rejection» Digital and SW radio» Functional units AY 2015-16 05/03/2016-1
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B1 - Radio systems architecture» Basic radio systems» Image rejection» Digital and SW radio» Functional units AY 2015-16 05/03/2016-1
Principles of Communications
 Priniples of Communiations Meixia Tao Dept. of Eletroni Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 3: Analog Modulation Seleted from Ch 3, Ch 4.-4.4, Ch 6.-6. of of Fundamentals of Communiations
Priniples of Communiations Meixia Tao Dept. of Eletroni Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University Chapter 3: Analog Modulation Seleted from Ch 3, Ch 4.-4.4, Ch 6.-6. of of Fundamentals of Communiations
S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC211 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem
S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC211 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem
Objectives. Presentation Outline. Digital Modulation Lecture 04
 Digital Modulation Leture 04 Filters Digital Modulation Tehniques Rihard Harris Objetives To be able to disuss the purpose of filtering and determine the properties of well known filters. You will be able
Digital Modulation Leture 04 Filters Digital Modulation Tehniques Rihard Harris Objetives To be able to disuss the purpose of filtering and determine the properties of well known filters. You will be able
ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS IV Sem. Prepared by Mr. T. Nagarjuna ECE Department
 ANALOG COMMUNICAIONS IV Sem Prepared by Mr.. Nagaruna ECE Department UNI I SIGNAL ANALYSIS AND LI SYSEMS Classifiation of Signals Deterministi & Non Deterministi Signals Periodi & A periodi Signals Even
ANALOG COMMUNICAIONS IV Sem Prepared by Mr.. Nagaruna ECE Department UNI I SIGNAL ANALYSIS AND LI SYSEMS Classifiation of Signals Deterministi & Non Deterministi Signals Periodi & A periodi Signals Even
GPS receivers built for various
 GNSS Solutions: Measuring GNSS Signal Strength angelo joseph GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions
GNSS Solutions: Measuring GNSS Signal Strength angelo joseph GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions
S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC314 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem : III Year, 6th Sem (EEE)
S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC314 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem : III Year, 6th Sem (EEE)
Real and Complex Modulation
 Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Wideband Receiver for Communications Receiver or Spectrum Analysis Usage: A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion
 A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion Tony Manicone, Vanteon Corporation There are many different system architectures which can be used in the design of High Frequency wideband
A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion Tony Manicone, Vanteon Corporation There are many different system architectures which can be used in the design of High Frequency wideband
ADI 2006 RF Seminar. Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers
 ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
Digitally Demodulating Binary Phase Shift Keyed Data Signals
 Digitally Demodulating Binary Phase Shift Keyed Signals Cornelis J. Kikkert, Craig Blakburn Eletrial and Computer Engineering James Cook University Townsville, Qld, Australia, 4811. E-mail: Keith.Kikkert@ju.edu.au,
Digitally Demodulating Binary Phase Shift Keyed Signals Cornelis J. Kikkert, Craig Blakburn Eletrial and Computer Engineering James Cook University Townsville, Qld, Australia, 4811. E-mail: Keith.Kikkert@ju.edu.au,
LNS ultra low phase noise Synthesizer 8 MHz to 18 GHz
 LNS ultra low phase noise Synthesizer 8 MHz to 18 GHz Datasheet The LNS is an easy to use 18 GHz synthesizer that exhibits outstanding phase noise and jitter performance in a 3U rack mountable chassis.
LNS ultra low phase noise Synthesizer 8 MHz to 18 GHz Datasheet The LNS is an easy to use 18 GHz synthesizer that exhibits outstanding phase noise and jitter performance in a 3U rack mountable chassis.
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication
 6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute of Technology Copyright 2003 by Michael H. Perrott
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute of Technology Copyright 2003 by Michael H. Perrott
RF Integrated Circuits
 Introduction and Motivation RF Integrated Circuits The recent explosion in the radio frequency (RF) and wireless market has caught the semiconductor industry by surprise. The increasing demand for affordable
Introduction and Motivation RF Integrated Circuits The recent explosion in the radio frequency (RF) and wireless market has caught the semiconductor industry by surprise. The increasing demand for affordable
PN9000 PULSED CARRIER MEASUREMENTS
 The specialist of Phase noise Measurements PN9000 PULSED CARRIER MEASUREMENTS Carrier frequency: 2.7 GHz - PRF: 5 khz Duty cycle: 1% Page 1 / 12 Introduction When measuring a pulse modulated signal the
The specialist of Phase noise Measurements PN9000 PULSED CARRIER MEASUREMENTS Carrier frequency: 2.7 GHz - PRF: 5 khz Duty cycle: 1% Page 1 / 12 Introduction When measuring a pulse modulated signal the
DT Filters 2/19. Atousa Hajshirmohammadi, SFU
 1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
FM Superheterodyne Receiver
 EE321 Final Project Chun-Hao Lo XiaoKai Sun Background: FM Superheterodyne Receiver Superheterodyne Receiver is the receiver that convert a received signal from the transmitter to an intermediate frequency.
EE321 Final Project Chun-Hao Lo XiaoKai Sun Background: FM Superheterodyne Receiver Superheterodyne Receiver is the receiver that convert a received signal from the transmitter to an intermediate frequency.
Keywords: GPS, receiver, GPS receiver, MAX2769, 2769, 1575MHz, Integrated GPS Receiver, Global Positioning System
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > User Guides > APP 3910 Keywords: GPS, receiver, GPS receiver, MAX2769, 2769, 1575MHz, Integrated GPS Receiver, Global Positioning System USER GUIDE 3910 User's
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > User Guides > APP 3910 Keywords: GPS, receiver, GPS receiver, MAX2769, 2769, 1575MHz, Integrated GPS Receiver, Global Positioning System USER GUIDE 3910 User's
A 24 GHz Band FM-CW Radar System for Detecting Closed Multiple Targets with Small Displacement
 A 24 GHz Band FM-CW Radar System for Deteting Closed Multiple Targets with Small Displaement Kazuhiro Yamaguhi, Mitsumasa Saito, Takuya Akiyama, Tomohiro Kobayashi and Hideaki Matsue Tokyo University of
A 24 GHz Band FM-CW Radar System for Deteting Closed Multiple Targets with Small Displaement Kazuhiro Yamaguhi, Mitsumasa Saito, Takuya Akiyama, Tomohiro Kobayashi and Hideaki Matsue Tokyo University of
AIRWAVE TECHNOLOGIES INC.
 Available from www.dpcav.com Part Number AWM682RX-OEM Doc No : AWM682RX 5.8GHz Wideband FM Receiver Module Page 1 of 9 Rev 0 AWM682 RX 5.8 GHz Wideband FM Receiver Copyright 2008 by Airwave Technologies
Available from www.dpcav.com Part Number AWM682RX-OEM Doc No : AWM682RX 5.8GHz Wideband FM Receiver Module Page 1 of 9 Rev 0 AWM682 RX 5.8 GHz Wideband FM Receiver Copyright 2008 by Airwave Technologies
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
Software Defined Radio in Ham Radio Dennis Silage K3DS TS EPA Section ARRL
 Software Defined Radio in Ham Radio Dennis Silage K3DS silage@arrl.net TS EPA Section ARRL TUARC K3TU SDR in HR The crystal radio was once a simple introduction to radio electronics and Amateur Radio.
Software Defined Radio in Ham Radio Dennis Silage K3DS silage@arrl.net TS EPA Section ARRL TUARC K3TU SDR in HR The crystal radio was once a simple introduction to radio electronics and Amateur Radio.
Research and Development Activities in RF and Analog IC Design. RFIC Building Blocks. Single-Chip Transceiver Systems (I) Howard Luong
 Research and Development Activities in RF and Analog IC Design Howard Luong Analog Research Laboratory Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
Research and Development Activities in RF and Analog IC Design Howard Luong Analog Research Laboratory Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
Interference Analysis and Spectrum Monitor Seminar
 Interference Analysis and Spectrum Monitor Seminar Handheld RF & Microwave Instruments Andrew Benn Business Development Manager Agilent Technologies Wednesday 12 th October 2011 1 Agilent Technologies,
Interference Analysis and Spectrum Monitor Seminar Handheld RF & Microwave Instruments Andrew Benn Business Development Manager Agilent Technologies Wednesday 12 th October 2011 1 Agilent Technologies,
VHF/UHF Wideband ViXIceptor WJ-8621
 Developmental Specification WATKINS-JOHNSON May 1997 VHF/UHF Wideband ViXIceptor WJ-8621 The WJ-8621 is a general-purpose VHF/UHF receiver covering a 20 to 2700 MHz frequency range. WJ packages the unit
Developmental Specification WATKINS-JOHNSON May 1997 VHF/UHF Wideband ViXIceptor WJ-8621 The WJ-8621 is a general-purpose VHF/UHF receiver covering a 20 to 2700 MHz frequency range. WJ packages the unit
Announcements : Wireless Networks Lecture 3: Physical Layer. Bird s Eye View. Outline. Page 1
 Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 3: Physical Layer Please start to form project teams» Updated project handout is available on the web site Also start to form teams for surveys» Send mail
Announcements 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 3: Physical Layer Please start to form project teams» Updated project handout is available on the web site Also start to form teams for surveys» Send mail
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System
 UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
