Superheterodyne Receiver Tutorial
|
|
|
- Daniela Gray
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 of 6 Superheterodyne Receiver Tutorial J P Silver john@rfic.co.uk 1 ABSTRACT This paper discusses the basic design concepts of the Superheterodyne receiver in both single and double conversion forms, together with potential problems associated with each architecture. Mixer Bandpass DETECTOR 2 INTRODUCTION This tutorial will describe a simple receiver architecture based on the super-heterodyne method of translation. A simple receiver could consist of an amplifier, band-pass and some form of demodulator. There is however a problem with this scheme in that the bandpass needs to be (1) Very narrow) and (2) tuneable. We only want a single carrier and so the needs to be wide enough to allow the carrier (and it s associated modulation side-bands) to pass through the whilst rejecting everything else. Secondly the narrow has to be tuneable over the frequencies of interest. This is a very difficult requirement especially if the wanted signal is very high. A possible solution to this problem is to use the superheterodyne receiver. 3 SUPERHETERODYNE RECEIVER In a superheterodyne (superhet) receiver the is ed through a wideband bandpass to a mixer. Also feeding the mixer is a local oscillator that is tuneable and differs from the input signal by a fixed amount known as the Intermediate (). Therefore, to tune for a particular input signal the Local Oscillator () is tuned accordingly. As the output of the mixer will always be the fixed then highly selective fixed low- s can be used. bandpass Tuneable Figure 1 Basic single conversion superheterodyne receiver The signal is generated by mixing the (ω ) with a single (ω ) carrier as shown by the equation below: V = V cosϖ.t * V cosϖ.t This multiplication will produce two products the sum of the frequencies and the difference in frequencies ie the we want: V V =.V 2 Baseband ( cos[ ( ϖ -ϖ.) φ] + cos[ ( ϖ + ϖ.) + φ] ) The s will only select the wanted difference (=-) and reject the much higher sum (+). The diagram shown in Error! Reference source not found. shows graphically the frequencies produced as a result of the mixing process: The bock diagram of the superhet is shown in Figure 1.
2 2 of 6 -ω Negative ie -ω +ω +ω It is important to note that the band is reversed after mixing ie the highest signal becomes the lowest and the lowest signal becomes the highest. This translation is also shown in Error! Reference source not found., by the shaped passbands. The wanted will be the ϖ -ϖ passband as indicated, therefore a bandpass will be used to select this band and reject all other frequencies. -ω - ω Negative ie Negative ie -ω + ω +ω + ω +ω - ω Wanted 4 SUPERHET PROBLEMS Assuming there is no ing at the front end of the receiver then not only will the mix with the wanted to form an but also will mix with a 2 s above the wanted as shown in Error! Reference source not found. Figure 2 Frequencies produced in the superhet as a result of the mixing process. Image band -ω IM -ω +ω +ω IM -ω +ω Negative ie Wanted + Image -ω - ω IM -ω - ω -ω + ω +ω - ω +ω + ω +ω + ω IM Negative ie
3 3 of 6 Figure 3 Shows shows the translation of the image band onto the band. This will result in noise or other unwanted signals at the image being added to the and could increase the noise figure of the receiver by 3dB.
4 4 of 6 Figure 3 shows that not only the wanted is translated to but also the image that will be 2 * higher in than the wanted signal. Even without any signal at this image the channel noise will still be translated resulting in a 3dB increase in the noise figure of the receiver. Therefore, it is normal to include a band-pass at the front end of the receiver to out any unwanted signal or noise from the image band. It is always an advantage to make the as high as possible to simplify the design of the input band-pass. On the other hand it is more difficult to design a very narrow bandpass for the section if the centre is high. The can be above or below the wanted signal band. When the is higher than the this is known as high side rejection. There would appear to be a design conflict. This conflict however, can be solved by having more than one conversion typically two hence the dual conversion term. This receiver will use two frequencies but most importantly allows for a low final (for easier design) but also a large first two separate the wanted and Image bands to allow use of a simpler band pass at the front end. The simplified block diagram of the dual conversion superhet receiver is shown in Figure 4. 1 st Mixer First Bandpass Filter (wide) This has an advantage on the design of the, for example assume that we have a receiver with a 200MHz, a bandwidth is 1300MHz and the is set to 1500MHz. This would yield the required of 200MHz and the tuning bandwidth ratio of the would be (100/1500)*100% = 6%. bandpass/ lowpass Fixed 1 st High 1 st If we picked the to give low side rejection, then we would pick the to be 200MHz below the at 1100MHz. In this case although the is at at lower the percentage tuning bandwidth will increase to (100/1100) * 100% = 9%. 2 nd Mixer Second Bandpass DETECTOR Baseband As a general rule it much easier to design a high narrow tuning band oscillator than a lower wider tuning band one. Tuneable 2 nd Low 2nd A second advantage of high side rejection is that the image can be a low pass design which is easier to design than a high pass. 5 DUAL CONVERSION (DOUBLE SUPERHETERODYNE RECEIVER) The previous discussion argued that the receiver design of the is simplified if the center is low but this will reduce the difference between the wanted band and the Image band necessitating in the design of a narrow band which could be difficult. Figure 4 Basic dual conversion superheterodyne receiver. Note to further improve performance (by eliminating unwanted spurious signals from the mixers) s can be added between the s and their associated mixers. In some applications instead of the difference being used at the first the sum frequencies are used. This will make the a lot higher (and greatly increases the image separation making design of the second easier) and if a tunable 1 st is used it will have a lower percentage tuning bandwidth.
5 5 of 6 Example: A terrestrial TV tuning receiver is designed to cover the range of 45 to 860MHz, with channel spacings of 8MHz and an of 40MHz. (1) Downconverting at 1 st. Using high-sided rejection the required will be: 85MHz to 900MHz a tuning ratio of (~1:10) ie - 85MHz 45MHz = 40MHz + 640MHz + 860MHz = 1500MHz The resulting images frequencies are: IM MHz = 1500MHz IM- 2140MHz - 640MHz = 1500MHz Image Band 2140MHz 2955MHz - 900MHz 860MHz = 40MHz The resulting images frequencies are: Image- 125MHz - 85MHz = 40MHz Image- 940MHz - 900MHz = 40MHz To eliminate the image Band, a narrow band tuneable is required 45MHz 125MHz Wanted Band Image Band 860MHz 940MHz Figure 5 Wanted band and resulting image band of the downconverting receiver solution, showing how the image and bands overlap requiring the use of a tunable front-end. 45MHz Wanted Band 860MHz Figure 6 Wanted band and resulting image band of the upconverting receiver solution, showing how the image and bands are now well spaced from each other. The diagram of Figure 6 shows the position of the image and wanted bands Now we see that the wanted and image bands are very well separated and in this situation there is no need for an image reject. However without a at the input the front-end LNA (Low Noise Amplifier) will be subject to possibly large out of band signals that may degrade the front end or overload it. Therefore, the use of this scheme requires a high linearity front-end. The diagram of Figure 5 shows the position of the image and wanted bands. A substantial amount of the image pass-band will overlap the wanted band requiring a tunable narrow-band front-end. (2) Upconverting at 1 st Lets pick an of say 1.5GHz. then the required will be: 640MHz to 1455MHz a tuning ratio of (~1:2) MHz + 45MHz = 1500MHz
6 6 of 6 6 CONCLUSION This paper was written to give a brief overview of the superheterodyne receiver architecture in both the single and dual conversion variants. Discussion was given to the problem with image frequencies degrading the noise performance of the receiver and ways to improve the image performance, by the use of up-converting to higher intermediate frequencies. Further tutorials will discuss the Direct Conversion (DC) receiver so popular with systems on a chip design and better (but more complicated) ways of eliminating the image response problem associated with superhets.
Introduction to Receivers
 Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
ENSC327 Communications Systems 5: Frequency Translation (3.6) and Superhet Receiver (3.9)
 ENSC327 Communications Systems 5: Frequency Translation (3.6) and Superhet Receiver (3.9) Jie Liang School o Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Frequency translation (page 128) Superhet
ENSC327 Communications Systems 5: Frequency Translation (3.6) and Superhet Receiver (3.9) Jie Liang School o Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Frequency translation (page 128) Superhet
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis
 Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSCEIVER DESIGN ECE3103 ADVANCED TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 INTRODUCTION TO TRANSCEIVER DESIGN ECE3103 ADVANCED TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A TRANSMITTER The basic functions of a transmitter are: a) up-conversion: move signal to desired RF carrier frequency.
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSCEIVER DESIGN ECE3103 ADVANCED TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A TRANSMITTER The basic functions of a transmitter are: a) up-conversion: move signal to desired RF carrier frequency.
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits. Module 7
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
Session 3. CMOS RF IC Design Principles
 Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
Wideband Receiver for Communications Receiver or Spectrum Analysis Usage: A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion
 A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion Tony Manicone, Vanteon Corporation There are many different system architectures which can be used in the design of High Frequency wideband
A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion Tony Manicone, Vanteon Corporation There are many different system architectures which can be used in the design of High Frequency wideband
McGill University. Department. of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Communications systems A
 McGill University Department. o Electrical and Computer Engineering Communications systems 304-411A 1 The Super-heterodyne Receiver 1.1 Principle and motivation or the use o the super-heterodyne receiver
McGill University Department. o Electrical and Computer Engineering Communications systems 304-411A 1 The Super-heterodyne Receiver 1.1 Principle and motivation or the use o the super-heterodyne receiver
Receiver Design. Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21
 Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
HF Receivers, Part 2
 HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
Receiver Architecture
 Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Dual-Frequency GNSS Front-End ASIC Design
 Dual-Frequency GNSS Front-End ASIC Design Ed. 01 15/06/11 In the last years Acorde has been involved in the design of ASIC prototypes for several EU-funded projects in the fields of FM-UWB communications
Dual-Frequency GNSS Front-End ASIC Design Ed. 01 15/06/11 In the last years Acorde has been involved in the design of ASIC prototypes for several EU-funded projects in the fields of FM-UWB communications
Recap of Last 2 Classes
 Recap of Last 2 Classes Transmission Media Analog versus Digital Signals Bandwidth Considerations Attentuation, Delay Distortion and Noise Nyquist and Shannon Analog Modulation Digital Modulation What
Recap of Last 2 Classes Transmission Media Analog versus Digital Signals Bandwidth Considerations Attentuation, Delay Distortion and Noise Nyquist and Shannon Analog Modulation Digital Modulation What
Receiver Architectures
 Receiver Architectures Modules: VCO (2), Quadrature Utilities (2), Utilities, Adder, Multiplier, Phase Shifter (2), Tuneable LPF (2), 100-kHz Channel Filters, Audio Oscillator, Noise Generator, Speech,
Receiver Architectures Modules: VCO (2), Quadrature Utilities (2), Utilities, Adder, Multiplier, Phase Shifter (2), Tuneable LPF (2), 100-kHz Channel Filters, Audio Oscillator, Noise Generator, Speech,
THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN
 THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN Mark Hunter * Abstract This paper is intended to give an overview of the design of radio transceivers to the engineer new to the field. It is shown how the requirements
THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN Mark Hunter * Abstract This paper is intended to give an overview of the design of radio transceivers to the engineer new to the field. It is shown how the requirements
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
ADI 2006 RF Seminar. Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers
 ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
Module 8 Theory. dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain. Functional Blocks Parameters. IRTS Region 4
 Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
Chapter 3. Question Mar No
 Chapter 3 Sr Question Mar No k. 1 Write any two drawbacks of TRF radio receiver 1. Instability due to oscillatory nature of RF amplifier.. Variation in bandwidth over tuning range. 3. Insufficient selectivity
Chapter 3 Sr Question Mar No k. 1 Write any two drawbacks of TRF radio receiver 1. Instability due to oscillatory nature of RF amplifier.. Variation in bandwidth over tuning range. 3. Insufficient selectivity
Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers
 EECS 142 Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
EECS 142 Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
Low Cost Mixer for the 10.7 to 12.8 GHz Direct Broadcast Satellite Market
 Low Cost Mixer for the.7 to 12.8 GHz Direct Broadcast Satellite Market Application Note 1136 Introduction The wide bandwidth requirement in DBS satellite applications places a big performance demand on
Low Cost Mixer for the.7 to 12.8 GHz Direct Broadcast Satellite Market Application Note 1136 Introduction The wide bandwidth requirement in DBS satellite applications places a big performance demand on
4- Single Side Band (SSB)
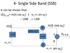 4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
4.1 REPRESENTATION OF FM AND PM SIGNALS An angle-modulated signal generally can be written as
 1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering. Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University
 ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters
 High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
Piezoelectric Discriminators
 Introduction Piezoelectric Discriminators Ceramic discriminators are designed to be used in quadrature detection circuits to remove a FM carrier wave. These circuits receive a FM signal, like in a FM radio,
Introduction Piezoelectric Discriminators Ceramic discriminators are designed to be used in quadrature detection circuits to remove a FM carrier wave. These circuits receive a FM signal, like in a FM radio,
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY
 Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
ADI 2006 RF Seminar. Chapter VI A Detailed Look at Wireless Signal Chain Architectures
 DI 2006 R Seminar Chapter VI Detailed Look at Wireless Chain rchitectures 1 Receiver rchitectures Receivers are designed to detect and demodulate the desired signal and remove unwanted blockers Receiver
DI 2006 R Seminar Chapter VI Detailed Look at Wireless Chain rchitectures 1 Receiver rchitectures Receivers are designed to detect and demodulate the desired signal and remove unwanted blockers Receiver
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED
 Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK v01.05.00 HMC141/142 MIXER OPERATION
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK v01.05.00 HMC141/142 MIXER OPERATION
8.5 Modulation of Signals
 8.5 Modulation of Signals basic idea and goals measuring atomic absorption without modulation measuring atomic absorption with modulation the tuned amplifier, diode rectifier and low pass the lock-in amplifier
8.5 Modulation of Signals basic idea and goals measuring atomic absorption without modulation measuring atomic absorption with modulation the tuned amplifier, diode rectifier and low pass the lock-in amplifier
Instrumentation Receiver: Analog Signal Processing for a DSP World. Rick Campbell Portland State University
 Instrumentation Receiver: Analog Signal Processing for a DSP World Rick Campbell Portland State University Tonight s Talk discusses 3 questions: What is an Instrumentation Receiver? How does Rick design
Instrumentation Receiver: Analog Signal Processing for a DSP World Rick Campbell Portland State University Tonight s Talk discusses 3 questions: What is an Instrumentation Receiver? How does Rick design
Lecture 14: FDM, AM Radio, and the Superheterodyne Receiver. Dr. Mohammed Hawa. Electrical Engineering Department, University of Jordan
 Lecture 14: FDM, AM Radio, and the Superheterodyne Receiver Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University o Jordan EE421: Communications I: Lecture 14. For more inormation read Chapter
Lecture 14: FDM, AM Radio, and the Superheterodyne Receiver Dr. Mohammed Hawa Electrical Engineering Department University o Jordan EE421: Communications I: Lecture 14. For more inormation read Chapter
Chapter 5 AM Receivers
 Chapter 5 AM Receivers Prepared by Prof.V.K.Jain 1 Lecture outcome After studying this lecture, you should be able to: Describe the basic superheterodyne system Choose suitable intermediate frequencies
Chapter 5 AM Receivers Prepared by Prof.V.K.Jain 1 Lecture outcome After studying this lecture, you should be able to: Describe the basic superheterodyne system Choose suitable intermediate frequencies
What s inside. Highlights. Welcome. Mixer test third in a series. New time-domain technique for measuring mixer group delay
 What s inside 2 New time-domain technique for measuring mixer group delay 3 Uncertainty in mixer group-delay measurements 5 Isolation a problem? Here s how to measure mixer group delay 6 Low-power mixer
What s inside 2 New time-domain technique for measuring mixer group delay 3 Uncertainty in mixer group-delay measurements 5 Isolation a problem? Here s how to measure mixer group delay 6 Low-power mixer
FM Superheterodyne Receiver
 EE321 Final Project Chun-Hao Lo XiaoKai Sun Background: FM Superheterodyne Receiver Superheterodyne Receiver is the receiver that convert a received signal from the transmitter to an intermediate frequency.
EE321 Final Project Chun-Hao Lo XiaoKai Sun Background: FM Superheterodyne Receiver Superheterodyne Receiver is the receiver that convert a received signal from the transmitter to an intermediate frequency.
Software Defined Radio in Ham Radio Dennis Silage K3DS TS EPA Section ARRL
 Software Defined Radio in Ham Radio Dennis Silage K3DS silage@arrl.net TS EPA Section ARRL TUARC K3TU SDR in HR The crystal radio was once a simple introduction to radio electronics and Amateur Radio.
Software Defined Radio in Ham Radio Dennis Silage K3DS silage@arrl.net TS EPA Section ARRL TUARC K3TU SDR in HR The crystal radio was once a simple introduction to radio electronics and Amateur Radio.
Speed your Radio Frequency (RF) Development with a Building-Block Approach
 Speed your Radio Frequency (RF) Development with a Building-Block Approach Whitepaper - May 2018 Nigel Wilson, CTO, CML Microcircuits. 2018 CML Microcircuits Page 1 of 13 May 2018 Executive Summary and
Speed your Radio Frequency (RF) Development with a Building-Block Approach Whitepaper - May 2018 Nigel Wilson, CTO, CML Microcircuits. 2018 CML Microcircuits Page 1 of 13 May 2018 Executive Summary and
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture
 RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
GHz Radiometer. Technical Description and User Manual
 46 Robezu str. LV-1004 Riga Latvia Fax : +371-7-065102 Mm-wave Division in St. Petersburg, Russia Fax: +7-812-326-10-60 Tel: +7-812-326-59-24 E-mail: korneev@exch.nnz.spb.su 113-153 GHz Radiometer Technical
46 Robezu str. LV-1004 Riga Latvia Fax : +371-7-065102 Mm-wave Division in St. Petersburg, Russia Fax: +7-812-326-10-60 Tel: +7-812-326-59-24 E-mail: korneev@exch.nnz.spb.su 113-153 GHz Radiometer Technical
A Low Noise Amplifier with HF Selectivity
 A Low Noise Amplifier with HF Selectivity Johan Karlsson Mikael Grudd Radio project 2008 Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Abstract This report
A Low Noise Amplifier with HF Selectivity Johan Karlsson Mikael Grudd Radio project 2008 Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund University Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Abstract This report
DISCRETE-TIME CHANNELIZERS FOR AERONAUTICAL TELEMETRY: PART II VARIABLE BANDWIDTH
 DISCRETE-TIME CHANNELIZERS FOR AERONAUTICAL TELEMETRY: PART II VARIABLE BANDWIDTH Brian Swenson, Michael Rice Brigham Young University Provo, Utah, USA ABSTRACT A discrete-time channelizer capable of variable
DISCRETE-TIME CHANNELIZERS FOR AERONAUTICAL TELEMETRY: PART II VARIABLE BANDWIDTH Brian Swenson, Michael Rice Brigham Young University Provo, Utah, USA ABSTRACT A discrete-time channelizer capable of variable
An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer. An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer
 1 An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer 2 Chapter 1. Introduction As a result of rapidly advancement in communication technology, all the mobile technology of applications has significantly and profoundly
1 An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer 2 Chapter 1. Introduction As a result of rapidly advancement in communication technology, all the mobile technology of applications has significantly and profoundly
Receiver Architectures
 83080RA/1 Receiver Architectures Markku Renfors Tampere University of Technology Digital Media Institute/Telecommunications 83080RA/2 Topics 1. Main analog components for receivers - amplifiers - filters
83080RA/1 Receiver Architectures Markku Renfors Tampere University of Technology Digital Media Institute/Telecommunications 83080RA/2 Topics 1. Main analog components for receivers - amplifiers - filters
Today s communication
 From October 2009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2009 Summit Technical Media, LLC Selecting High-Linearity Mixers for Wireless Base Stations By Stephanie Overhoff Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
From October 2009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2009 Summit Technical Media, LLC Selecting High-Linearity Mixers for Wireless Base Stations By Stephanie Overhoff Maxim Integrated Products, Inc.
Topic Advanced Radio Receivers. Explain that an RF amplifier can be used to improve sensitivity;
 Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; Explain that an RF amplifier can be used to improve sensitivity; Explain that a superheterodyne receiver offers improved selectivity and
Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; Explain that an RF amplifier can be used to improve sensitivity; Explain that a superheterodyne receiver offers improved selectivity and
Receiver Losses when using Quadrature Bandpass Sampling
 International Global Navigation Satellite Systems Associatio IGNSS Conference 2016 Colombo Theatres, Kensington Campus, UNSW Australia 6 8 December 2016 Receiver Losses when using Quadrature Bandpass Sampling
International Global Navigation Satellite Systems Associatio IGNSS Conference 2016 Colombo Theatres, Kensington Campus, UNSW Australia 6 8 December 2016 Receiver Losses when using Quadrature Bandpass Sampling
Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper
 Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
Wideband Receiver Design
 Wideband Receiver Design Challenges and Trade-offs of a Wideband Tuning Range in Wireless Microphone Receivers in the UHF Television Band About this White Paper Professional wireless microphone systems
Wideband Receiver Design Challenges and Trade-offs of a Wideband Tuning Range in Wireless Microphone Receivers in the UHF Television Band About this White Paper Professional wireless microphone systems
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Description of the AM Superheterodyne Radio Receiver
 Superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver Since the inception of the AM radio, it spread widely due to its ease of use and more importantly, it low cost. The low cost of most AM radios sold in the market is due
Superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver Since the inception of the AM radio, it spread widely due to its ease of use and more importantly, it low cost. The low cost of most AM radios sold in the market is due
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
Radio Receivers Al Penney VO1NO Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is
UNIT-3. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
APPLICATION NOTE 3942 Optimize the Buffer Amplifier/ADC Connection
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Communications Circuits > APP 3942 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > High-Speed Interconnect > APP 3942
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Communications Circuits > APP 3942 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > High-Speed Interconnect > APP 3942
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
Optimizing the Performance of Very Wideband Direct Conversion Receivers
 Optimizing the Performance of Very Wideband Direct Conversion Receivers Design Note 1027 John Myers, Michiel Kouwenhoven, James Wong, Vladimir Dvorkin Introduction Zero-IF receivers are not new; they have
Optimizing the Performance of Very Wideband Direct Conversion Receivers Design Note 1027 John Myers, Michiel Kouwenhoven, James Wong, Vladimir Dvorkin Introduction Zero-IF receivers are not new; they have
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
EMC / Field strength Signal generation and analysis
 EMC / Field strength Signal generation and analysis 48 Uncovers every disturbance Standard-compliant EMI test receivers must meet very high requirements with respect to their RF characteristics. Not only
EMC / Field strength Signal generation and analysis 48 Uncovers every disturbance Standard-compliant EMI test receivers must meet very high requirements with respect to their RF characteristics. Not only
Single Conversion LF Upconverter Andy Talbot G4JNT Jan 2009
 Single Conversion LF Upconverter Andy Talbot G4JNT Jan 2009 Mark 2 Version Oct 2010, see Appendix, Page 8 This upconverter is designed to directly translate the output from a soundcard from a PC running
Single Conversion LF Upconverter Andy Talbot G4JNT Jan 2009 Mark 2 Version Oct 2010, see Appendix, Page 8 This upconverter is designed to directly translate the output from a soundcard from a PC running
TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers
 TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Overview 2 Razavi: Chapter 6.1-6.3, pp. 343-398. Lee: Chapter 13. 6.1 Mixers general
TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Overview 2 Razavi: Chapter 6.1-6.3, pp. 343-398. Lee: Chapter 13. 6.1 Mixers general
for use Supervisor: on chip
 Local Oscillator for use in FM Broadcast Radio Receiver ETI 041: Radio Project Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Student: Yelin Wang and Hao Cai Master Program: System on chip Lund University Abstract Oscillator
Local Oscillator for use in FM Broadcast Radio Receiver ETI 041: Radio Project Supervisor: Göran Jönsson Student: Yelin Wang and Hao Cai Master Program: System on chip Lund University Abstract Oscillator
Lab course Analog Part of a State-of-the-Art Mobile Radio Receiver
 Communication Technology Laboratory Wireless Communications Group Prof. Dr. A. Wittneben ETH Zurich, ETF, Sternwartstrasse 7, 8092 Zurich Tel 41 44 632 36 11 Fax 41 44 632 12 09 Lab course Analog Part
Communication Technology Laboratory Wireless Communications Group Prof. Dr. A. Wittneben ETH Zurich, ETF, Sternwartstrasse 7, 8092 Zurich Tel 41 44 632 36 11 Fax 41 44 632 12 09 Lab course Analog Part
Radio Receivers. Al Penney VO1NO
 Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
Radio Receivers Role of the Receiver The Antenna must capture the radio wave. The desired frequency must be selected from all the EM waves captured by the antenna. The selected signal is usually very weak
Solution of ECE 342 Test 3 S12
 Solution of ECE 34 Test 3 S1 1 A random power signal has a mean of three and a standard deviation of five Find its numerical total average signal power Signal Power P = 3 + 5 = 34 A random energy signal
Solution of ECE 34 Test 3 S1 1 A random power signal has a mean of three and a standard deviation of five Find its numerical total average signal power Signal Power P = 3 + 5 = 34 A random energy signal
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
Selecting the Right Mixer for Your Application Using Yoni -the Advanced Search Engine (AN )
 Selecting the Right Mixer for Your Application Using Yoni -the Advanced Search Engine (AN-00-014) In spite of advances in digital processing components enabling direct digital conversion at higher frequencies,
Selecting the Right Mixer for Your Application Using Yoni -the Advanced Search Engine (AN-00-014) In spite of advances in digital processing components enabling direct digital conversion at higher frequencies,
High Speed & High Frequency based Digital Up/Down Converter for WCDMA System
 High Speed & High Frequency based Digital Up/Down Converter for WCDMA System Arun Raj S.R Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering University B.D.T College of Engineering Davangere-Karnataka,
High Speed & High Frequency based Digital Up/Down Converter for WCDMA System Arun Raj S.R Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering University B.D.T College of Engineering Davangere-Karnataka,
2 Gain Variation from the Receiver Output through the IF Path
 EVLA Memo #185 Bandwidth- and Frequency-Dependent Effects in the T34 Total Power Detector Keith Morris September 17, 214 1 Introduction The EVLA Intermediate Frequency (IF) system employs a system of power
EVLA Memo #185 Bandwidth- and Frequency-Dependent Effects in the T34 Total Power Detector Keith Morris September 17, 214 1 Introduction The EVLA Intermediate Frequency (IF) system employs a system of power
Fast Tuning Synthesizer
 Project Member: Nathan Roth Project Advisors: Dr. Brian Huggins Dr. Prasad Shastry Mr. James Jensen Date: November 18, 2003 Fast Tuning Synthesizer System Level Block Diagram Overview A frequency synthesizer
Project Member: Nathan Roth Project Advisors: Dr. Brian Huggins Dr. Prasad Shastry Mr. James Jensen Date: November 18, 2003 Fast Tuning Synthesizer System Level Block Diagram Overview A frequency synthesizer
Technical Article A DIRECT QUADRATURE MODULATOR IC FOR 0.9 TO 2.5 GHZ WIRELESS SYSTEMS
 Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
This place covers: Demodulation or transference of signals modulated on a sinusoidal carrier or on electromagnetic waves.
 CPC - H03D - 2017.08 H03D DEMODULATION OR TRANSFERENCE OF MODULATION FROM ONE CARRIER TO ANOTHER (masers, lasers H01S; circuits capable of acting both as modulator and demodulator H03C; details applicable
CPC - H03D - 2017.08 H03D DEMODULATION OR TRANSFERENCE OF MODULATION FROM ONE CARRIER TO ANOTHER (masers, lasers H01S; circuits capable of acting both as modulator and demodulator H03C; details applicable
Communication Systems, 5e
 Communiation Systems, 5e Chapter 7: Analog Communiation Systems A. Brue Carlson Paul B. Crilly 010 The Mraw-Hill Companies Chapter 7: Analog Communiation Systems Reeiver blok diagram design Image requeny
Communiation Systems, 5e Chapter 7: Analog Communiation Systems A. Brue Carlson Paul B. Crilly 010 The Mraw-Hill Companies Chapter 7: Analog Communiation Systems Reeiver blok diagram design Image requeny
PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS
 PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS INTRODUCTION...98 frequency translation...98 the process...98 interpretation...99 the demodulator...100 synchronous operation: ω 0 = ω 1...100 carrier
PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS INTRODUCTION...98 frequency translation...98 the process...98 interpretation...99 the demodulator...100 synchronous operation: ω 0 = ω 1...100 carrier
AN X-BAND FREQUENCY AGILE SOURCE WITH EXTREMELY LOW PHASE NOISE FOR DOPPLER RADAR
 AN X-BAND FREQUENCY AGILE SOURCE WITH EXTREMELY LOW PHASE NOISE FOR DOPPLER RADAR H. McPherson Presented at IEE Conference Radar 92, Brighton, Spectral Line Systems Ltd England, UK., October 1992. Pages
AN X-BAND FREQUENCY AGILE SOURCE WITH EXTREMELY LOW PHASE NOISE FOR DOPPLER RADAR H. McPherson Presented at IEE Conference Radar 92, Brighton, Spectral Line Systems Ltd England, UK., October 1992. Pages
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
3.1 Introduction to Modulation
 Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
The Schottky Diode Mixer. Application Note 995
 The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B1 - Radio systems architecture» Basic radio systems» Image rejection» Digital and SW radio» Functional units 19/03/2012-1 ATLCE
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B1 - Radio systems architecture» Basic radio systems» Image rejection» Digital and SW radio» Functional units 19/03/2012-1 ATLCE
HOW TO UNDERSTAND THE WORKINGS OF RADIO CONTROL
 HOW TO UNDERSTAND THE WORKINGS OF RADIO CONTROL By: Roger Carignan This article resulted from a workshop hosted by a member of our R/C model club, the 495 th R/C Squadron. I was asked to make a presentation
HOW TO UNDERSTAND THE WORKINGS OF RADIO CONTROL By: Roger Carignan This article resulted from a workshop hosted by a member of our R/C model club, the 495 th R/C Squadron. I was asked to make a presentation
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Receiver Architectures
 Receiver Architectures Direct Detection of radio signals 1 2.. n f C,i Antenna Amplifier RF Filter A Demodulation Base Band 1 f C,i Not convenient: - RF filter must be very selective and tunable - Amplifier
Receiver Architectures Direct Detection of radio signals 1 2.. n f C,i Antenna Amplifier RF Filter A Demodulation Base Band 1 f C,i Not convenient: - RF filter must be very selective and tunable - Amplifier
PHYS225 Lecture 15. Electronic Circuits
 PHYS225 Lecture 15 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Difference amplifier Differential input; single output Good CMRR, accurate gain, moderate input impedance Instrumentation amplifier Differential input;
PHYS225 Lecture 15 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Difference amplifier Differential input; single output Good CMRR, accurate gain, moderate input impedance Instrumentation amplifier Differential input;
Third-Method Narrowband Direct Upconverter for the LF / MF Bands
 Third-Method Narrowband Direct Upconverter for the LF / MF Bands Introduction Andy Talbot G4JNT February 2016 Previous designs for upconverters from audio generated from a soundcard to RF have been published
Third-Method Narrowband Direct Upconverter for the LF / MF Bands Introduction Andy Talbot G4JNT February 2016 Previous designs for upconverters from audio generated from a soundcard to RF have been published
L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS
 L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Wurth, Timothy J.; Rodzinak, Jason Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering
L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Wurth, Timothy J.; Rodzinak, Jason Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks)
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
BANDPASS delta sigma ( ) modulators are used to digitize
 680 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 52, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2005 A Time-Delay Jitter-Insensitive Continuous-Time Bandpass 16 Modulator Architecture Anurag Pulincherry, Michael
680 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 52, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2005 A Time-Delay Jitter-Insensitive Continuous-Time Bandpass 16 Modulator Architecture Anurag Pulincherry, Michael
C. Mixers. frequencies? limit? specifications? Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device.
 9/13/2007 Mixers notes 1/1 C. Mixers Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device. HO: Mixers Q: How efficient is a typical mixer at creating signals
9/13/2007 Mixers notes 1/1 C. Mixers Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device. HO: Mixers Q: How efficient is a typical mixer at creating signals
R&S FPC-Z10 Teaching Kit Getting Started
 R&S FPC-Z10 Teaching Kit Getting Started 1178843602 Getting Started Version 04 This manual describes the following products: R&S FPC-Z10 Teaching Kit (1328.7338.02) 2018 Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co. KG Mühldorfstr.
R&S FPC-Z10 Teaching Kit Getting Started 1178843602 Getting Started Version 04 This manual describes the following products: R&S FPC-Z10 Teaching Kit (1328.7338.02) 2018 Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co. KG Mühldorfstr.
Signal Detection with EM1 Receivers
 Signal Detection with EM1 Receivers Werner Schaefer Hewlett-Packard Company Santa Rosa Systems Division 1400 Fountaingrove Parkway Santa Rosa, CA 95403-1799, USA Abstract - Certain EM1 receiver settings,
Signal Detection with EM1 Receivers Werner Schaefer Hewlett-Packard Company Santa Rosa Systems Division 1400 Fountaingrove Parkway Santa Rosa, CA 95403-1799, USA Abstract - Certain EM1 receiver settings,
Agilent Spectrum Analysis Basics. Application Note 150
 Agilent Spectrum Analysis Basics Application Note 150 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction.......................................................4 Frequency domain versus time domain.......................................4
Agilent Spectrum Analysis Basics Application Note 150 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction.......................................................4 Frequency domain versus time domain.......................................4
Radio-Frequency Conversion and Synthesis (for a 115mW GPS Receiver)
 Radio-Frequency Conversion and Synthesis (for a 115mW GPS Receiver) Arvin Shahani Stanford University Overview GPS Overview Frequency Conversion Frequency Synthesis Conclusion GPS Overview: Signal Structure
Radio-Frequency Conversion and Synthesis (for a 115mW GPS Receiver) Arvin Shahani Stanford University Overview GPS Overview Frequency Conversion Frequency Synthesis Conclusion GPS Overview: Signal Structure
A 3 TO 30 MHZ HIGH-RESOLUTION SYNTHESIZER CONSISTING OF A DDS, DIVIDE-AND-MIX MODULES, AND A M/N SYNTHESIZER. Richard K. Karlquist
 A 3 TO 30 MHZ HIGH-RESOLUTION SYNTHESIZER CONSISTING OF A DDS, -AND-MIX MODULES, AND A M/N SYNTHESIZER Richard K. Karlquist Hewlett-Packard Laboratories 3500 Deer Creek Rd., MS 26M-3 Palo Alto, CA 94303-1392
A 3 TO 30 MHZ HIGH-RESOLUTION SYNTHESIZER CONSISTING OF A DDS, -AND-MIX MODULES, AND A M/N SYNTHESIZER Richard K. Karlquist Hewlett-Packard Laboratories 3500 Deer Creek Rd., MS 26M-3 Palo Alto, CA 94303-1392
How It Works The PPM Radio Control System: Part 1
 Technical M.E.C. Technical Note Note How It Works The PPM Radio Control System: Part 1 Foreword This Technical Note is divided into 3 parts to reduce the file size when downloading each section from the
Technical M.E.C. Technical Note Note How It Works The PPM Radio Control System: Part 1 Foreword This Technical Note is divided into 3 parts to reduce the file size when downloading each section from the
A Simulation of Wideband CDMA System on Digital Up/Down Converters
 Scientific Journal Impact Factor (SJIF): 1.711 e-issn: 2349-9745 p-issn: 2393-8161 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com A Simulation of Wideband CDMA System
Scientific Journal Impact Factor (SJIF): 1.711 e-issn: 2349-9745 p-issn: 2393-8161 International Journal of Modern Trends in Engineering and Research www.ijmter.com A Simulation of Wideband CDMA System
A Wideband Precision Quadrature Phase Shifter
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2011-06-28 A Wideband Precision Quadrature Phase Shifter Steve T. Noall Brigham Young University - Provo Follow this and additional
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2011-06-28 A Wideband Precision Quadrature Phase Shifter Steve T. Noall Brigham Young University - Provo Follow this and additional
