GPS receivers built for various
|
|
|
- Nathaniel Lambert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GNSS Solutions: Measuring GNSS Signal Strength angelo joseph GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions to the columnist, Dr. Mark Petovello, Department of Geomatics Engineering, University of Calgary, who will find experts to answer them. His address can be found with his biography at the conclusion of the column. What is the difference between SNR and? GPS receivers built for various applications, such as handhelds, automobiles, mobile phones, and avionics, all have a method for indicating the signal strength of the different satellites they are tracking. Some receivers display the signal strength in the form of vertical bars, some in terms of normalized signal strength, and others in terms of carrier-to-noise density ( ) or signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The latter two terms are regularly used so interchangeably that their fundamental differences are often overlooked. A full understanding of the differences between SNR and is useful both for users of GPS receivers and for GPS receiver designers and testers. SNR and SNR is usually expressed in terms of decibels. It refers to the ratio of the signal power and noise power in a given bandwidth. SNR(dB) = S N (1) S is the signal power, usually the carrier power expressed in units of decibel/milliwatt (dbm) or decibel/ watts (dbw); N is the noise power in a given bandwidth in units of dbm or dbw., on the other hand, is usually expressed in decibel-hertz (db-hz) and refers to the ratio of the carrier power and the noise power per unit bandwidth. For the GPS L1 C/A signal, one can consider the received signal power as the power of the original unmodulated carrier power (at the point of reception in a receiver) that has been spread by the spreading (ranging) codes when transmitted from a satellite. We can express as follows: (db-hz) = C (N BW) = C = SNR + BW (2) C is the carrier power in dbm or dbw; N is the noise power in dbm or dbw; is the noise power density in dbm-hz or dbw-hz; BW is the bandwidth of observation, which is usually the noise equivalent bandwidth of the last filter stage in a receiver s RF front-end. Typical values in an L1 C/A code receiver are as follows: : ~ 37 to 45dB-Hz Receiver front-end bandwidth: ~ 4MHz => BW = 10*log (4,000,000) = 66dB SNR = BW => SNR ~ (37 66) to (45 66) => SNR ~ -29dB to -21dB In order to determine, then, one clearly needs to determine the carrier power and noise density at the input to the receiver. Noise and Signal Power The sources of white noise in a GNSS receiver are usually described by the antenna noise temperature and the receiver noise temperature. The antenna temperature models the noise entering the antenna from the sky as the receiver noise temperature models the thermal noise due to the motion of charges within a device such as the GPS receiver front-end. These noise sources specify the noise density, which may be described as follows: (dbw/hz) = 10*log (k*t), k is the Boltzmann s constant J/K; 20 InsideGNSS november / december
2 GNSS SOLUTIONS T is the noise temperature in degrees on the Kelvin scale. The noise density for a typical receiver noise temperature of 290K is -204dBW/Hz or -174dBm/Hz. We may express the received carrier power as P R = P T L + G R, P R is the received carrier power; P T is the transmitted carrier power; L is the signal power loss primarily due to path loss; G R is the gain of the receiver s antenna in the direction of the received satellite signal. The nominal carrier power received by the receiver is around dBW. Hence, for GPS L1 C/A, if one just considers thermal noise and the nominal signal power, the nominal is given as (-204) = 45.5dB-Hz. Signal and Noise Paths from Antenna to Receiver Figure 1 illustrates the stages of a typical GPS RF front-end. Depending on the particular receiver design, some of these components may be situated either inside or outside of the receiver itself. When considering signal and noise paths through the front-end, one needs to consider the noise figure of the various components in the front-end. The noise figure is given as NF = SNR in / SNR out and provides an estimate of the amount of noise added by an active component, such as a low-noise amplifier (LNA), or even a passive component, such as a filter or the cable. The noise figure is related to the noise temperature as NF = 10*log(1 + T / T o ), T is the noise temperature T o is the reference temperature usually 290K. The well-known Friis formulas can be used to determine the cascaded noise figure or cascaded noise temperature by measuring noise temperatures or noise figures of the individual components in the receiver front-end. For our discussion, we need only mention that the cascaded noise figure is primarily dependent on the noise figure and gain of the first LNA in the chain as well as any losses incurred prior to the LNA (e.g., caused by cables or filtering) because losses incurred after the LNA will be attenuated by the reciprocal of the LNA gain. Band-limiting and quantization schemes chosen within the receiver add additional losses to the. The received is now given as: = (nominal) NF RX - NF IMP NF RX is the cascaded noise figure of the receiver; 22 InsideGNSS november / december
3 NF IMP represents the losses due to band-limiting and quantization. For purposes of this discussion, if we assume a cascaded noise figure of two decibels, then the nominal is degraded by two decibels. We can assume an additional noise figure of one decibel due to band-limiting and quantization, which is typical for a two-bit quantized receiver front-end. For our example, the received nominal is given as: = = 42.5dB-Hz Taking into consideration the noise environment and the receiver front-end components, the of a particular tracked satellite will scale relative to the signal power. The signal power of the various satellites being tracked by the receiver will vary in relation to the satellite elevation angle due to differences in path loss and the satellite and receiver antennas gain patterns. So, for example, if the signal power varies ±4dB of the nominal signal power of dBW, the corresponding will vary from 38.5dB-Hz to 46.5dB-Hz. Interpretation and Significance of From our discussions thus far, the output by a receiver clearly provides an indication of the signal power of the tracked satellite and the noise density as seen by the receiver s front-end. Two different GPS receivers connected to the same antenna and tracking the same GPS satellite at the same time may output different values. If one assumes that the values are computed accurately by both the receivers, the differences in the values can be attributed to differences in the noise figure of the two front-ends and/or the receivers respective band-limiting and quantization schemes. The value provides an indication of the signal quality that is independent of the acquisition and tracking algorithms used by a receiver. In contrast to SNR, is also independent of the receiver s front-end bandwidth and can be readily used to indicate the quality of the received signal. (C/ is bandwidth-independent from the noise perspective but bandwidth-dependent if one considers the correlation losses associated with bandlimiting. However, the latter losses are usually within the error uncertainty of computation algorithm itself; so, for most practical purposes we can say that is bandwidth-independent.) For a given satellite signal and receiver front-end, the value may also vary due to set up and installation considerations. For example, the use of a long cable before the first LNA stage of the receiver will affect the noise figure and, consequently, the. However, the remains constant through the different signal processing stages of the receiver, such as pre-detection, acquisition, and tracking. Receiver Acquisition, Processing Blocks, and SNR The signal-to-noise ratio is most useful when considered november / december 2010 InsideGNSS 23
4 GNSS SOLUTIONS LNA Antenna FIGURE 1 GPS receiver RF front-end = 40dB-Hz 4MHz Front-End SNR = 26dB SNR = 23dB FIGURE 2 GPS baseband processing stages Mixer within the baseband processing blocks of a GNSS receiver. In dealing with SNR, the bandwidth of interest needs to be specified. Typically the noise equivalent bandwidth is used, which is defined as the bandwidth of an ideal (i.e., brick-wall) filter whose bandwidth when multiplied by the white noise density of /2 will result in the total noise power at the output of the original filter. As an example, the transfer function of the integrate and dump filters that are used in GPS signal processing is given by: H(f) = sin(π*δf*t) / π*δf*t, δf is the frequency error in the acquisition or tracking block; T is the integration time. The total noise power passed through the filter H(f) is given by However, the noise power passed by an ideal filter is the product of /2 and Acquisition 1ms integration PLL 20ms Integration AGC RF BPF IF Filter ADC AMP LO Loop Filter PLL Synthesizer VGA SNR = 10dB SNR = 17dB TCXO/ OCXO Digital Samples BIT Synchronization 1ms integration FLL 5ms Integration SNR = 10dB bandwidth (i.e., BW in Equation 2). As such, the integral in the preceding equation is actually the noise equivalent bandwidth of the filter. For the integrate and dump filter the integral evaluates to 1/T. The noise equivalent bandwidth allows one to go back and forth between and SNR as per Equation 2. A typical GPS receiver implemented using either hardware correlators or a software-based approach needs to acquire and track the satellite signal before pseudoranges and carrier phase measurements can be made. Figure 2 presents the typical stages in the receiver s baseband processing. The integration times indicated in the different blocks of the figure refer to the integration or accumulation time of the integrate and dump filters. For illustrative purposes, we chose the following integration times: 1 millisecond for acquisition, 1 millisecond for synchronization with the navigation symbols, 5 milliseconds for completing the frequency lock loop (FLL), and 20 milliseconds for the phase lock loop (PLL). Actual receivers may use different schemes, like coherent and non-coherent integrations and longer integration times, which will change the effective SNR. A receiver s front-end bandwidth determines the SNR that is seen by the input side of the various baseband processing stages of the receiver. In Figure 2 the receiver s front-end bandwidth of four megahertz establishes the SNR of 26 decibels that enters the receiver s base band processing stages. In Figure 2 we can see that before integration the signal power is below the noise floor, but as the integration time is increased the SNR increases and the signal power rises above the noise power. The SNR gain in this case is also referred to as processing gain. The improvement in SNR as the result of a longer integration occurs because of the reduction in the noise equivalent bandwidth. Note that the performance of the PLL and FLL in the presence of thermal noise is further affected by the bandwidths of the respective loops themselves. The integration time in this case establishes the input SNR and the loop update time for the respective loops. Interpretation and Significance of SNR As we have seen, the SNR in a GPS receiver depends on the receiver s front-end bandwidth, acquisition, and tracking parameters. Referencing just the SNR value in a GPS receiver does not usually make sense unless one also specifies the bandwidth and processing stage within the receiver. The SNR is very useful when evaluating the performance of the acquisition and tracking stages in a receiver. For example, when performing Monte Carlo simulations, the SNR needs to be determined at the various stages of the signal processing chain to properly 24 InsideGNSS november / december
5 simulate the receiver. In simulations the required needs to be first converted to an SNR from which the appropriate noise variance can be readily determined. Furthermore, the SNR is an indication of the level of noise present in the measurement, as alone does not provide this information. In conclusion, we can see that both the and SNR are useful quantities that can be used when designing, evaluating or verifying the performance of a GPS receiver. However the use of one quantity over the other very much depends upon the context and the purpose for which the signal quality measurement is being made or is to be used for and this should be carefully considered when choosing between the two. Additional Resources For information on how is computed within a GNSS receiver, refer to the GNSS Solutions columns by B. Badke (Inside GNSS, September/October 2009) and E. Falletti et alia (January/February 2010). Angelo Joseph is currently a principal systems engineer with Rockwell Collins in Melbourne, Florida, he works on airborne GNSS receiver design and development. Previously, he was at Avidyne Corporation he developed Avidyne s first Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) Beta-3 GPS receiver. Angelo was also a senior GPS systems engineer with NovAtel Inc., Calgary, Alberta, Canada he played a primary role in designing the next-generation WAAS reference receiver. He has a masters in geomatics engineering from the University of Calgary and is currently completing a Ph.D. at the same institution. Mark Petovello is an associate professor in the Department of Geomatics Engineering at the University of Calgary. He has been actively involved in many aspects of positioning and navigation since 1997 including GNSS algorithm development, inertial navigation, sensor integration, and software development. <mark.petovello@ ucalgary.ca> november / december 2010 InsideGNSS 25
Vector tracking loops are a type
 GNSS Solutions: What are vector tracking loops, and what are their benefits and drawbacks? GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are
GNSS Solutions: What are vector tracking loops, and what are their benefits and drawbacks? GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are
Every GNSS receiver processes
 GNSS Solutions: Code Tracking & Pseudoranges GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions to the columnist,
GNSS Solutions: Code Tracking & Pseudoranges GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions to the columnist,
It is well known that GNSS signals
 GNSS Solutions: Multipath vs. NLOS signals GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions to the columnist,
GNSS Solutions: Multipath vs. NLOS signals GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions to the columnist,
Satellite Navigation Principle and performance of GPS receivers
 Satellite Navigation Principle and performance of GPS receivers AE4E08 GPS Block IIF satellite Boeing North America Christian Tiberius Course 2010 2011, lecture 3 Today s topics Introduction basic idea
Satellite Navigation Principle and performance of GPS receivers AE4E08 GPS Block IIF satellite Boeing North America Christian Tiberius Course 2010 2011, lecture 3 Today s topics Introduction basic idea
HY448 Sample Problems
 HY448 Sample Problems 10 November 2014 These sample problems include the material in the lectures and the guided lab exercises. 1 Part 1 1.1 Combining logarithmic quantities A carrier signal with power
HY448 Sample Problems 10 November 2014 These sample problems include the material in the lectures and the guided lab exercises. 1 Part 1 1.1 Combining logarithmic quantities A carrier signal with power
The Galileo signal in space (SiS)
 GNSS Solutions: Galileo Open Service and weak signal acquisition GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions
GNSS Solutions: Galileo Open Service and weak signal acquisition GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 5
 Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
The Friis Transmission Formula
 The Friis Transmission Formula If we assume that the antennas are aligned for maximum transmission and reception, then in free space, P RX = G TXA e P TX 4πr 2 where A e is the receiving aperture of the
The Friis Transmission Formula If we assume that the antennas are aligned for maximum transmission and reception, then in free space, P RX = G TXA e P TX 4πr 2 where A e is the receiving aperture of the
Noise Temperature. Concept of a Black Body
 Noise emperature In the last lecture, we introduced the Link Equation, which allows us to determine the amount of received power in terms of the transmitted power, the gains of the transmitting and receiving
Noise emperature In the last lecture, we introduced the Link Equation, which allows us to determine the amount of received power in terms of the transmitted power, the gains of the transmitting and receiving
LOW POWER GLOBAL NAVIGATION SATELLITE SYSTEM (GNSS) SIGNAL DETECTION AND PROCESSING
 LOW POWER GLOBAL NAVIGATION SATELLITE SYSTEM (GNSS) SIGNAL DETECTION AND PROCESSING Dennis M. Akos, Per-Ludvig Normark, Jeong-Taek Lee, Konstantin G. Gromov Stanford University James B. Y. Tsui, John Schamus
LOW POWER GLOBAL NAVIGATION SATELLITE SYSTEM (GNSS) SIGNAL DETECTION AND PROCESSING Dennis M. Akos, Per-Ludvig Normark, Jeong-Taek Lee, Konstantin G. Gromov Stanford University James B. Y. Tsui, John Schamus
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
Case Study: and Test Wireless Receivers
 Case Study: Using New Technologies to Design and Test Wireless Receivers Agenda Architecture of a receiver Basic GPS Receiver Measurements Case Study 1: GPS Simulation How Testing Works Simulation vs.
Case Study: Using New Technologies to Design and Test Wireless Receivers Agenda Architecture of a receiver Basic GPS Receiver Measurements Case Study 1: GPS Simulation How Testing Works Simulation vs.
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 5
 Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
Introduction to Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Signal Structure
 Introduction to Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Signal Structure Dinesh Manandhar Center for Spatial Information Science The University of Tokyo Contact Information: dinesh@iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Introduction to Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Signal Structure Dinesh Manandhar Center for Spatial Information Science The University of Tokyo Contact Information: dinesh@iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation RX nonlinearities (parts of 2.2) System Nonlinearity Sensitivity
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation RX nonlinearities (parts of 2.2) System Nonlinearity Sensitivity
Noise and Interference Limited Systems
 Chapter 3 Noise and Interference Limited Systems 47 Basics of link budgets Link budgets show how different components and propagation processes influence the available SNR Link budgets can be used to compute
Chapter 3 Noise and Interference Limited Systems 47 Basics of link budgets Link budgets show how different components and propagation processes influence the available SNR Link budgets can be used to compute
Receiver Design for Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) Imaging
 Introduction Receiver Design for Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) Imaging Millimeter Wave Systems, LLC Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) sensors are used for remote sensing and security applications. They rely
Introduction Receiver Design for Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) Imaging Millimeter Wave Systems, LLC Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) sensors are used for remote sensing and security applications. They rely
Analysis on GNSS Receiver with the Principles of Signal and Information
 Analysis on GNSS Receiver with the Principles of Signal and Information Lishu Guo 1,2, Xuyou Li 1, Xiaoying Kong 2 1. College of Automation, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China 2. School of Computing
Analysis on GNSS Receiver with the Principles of Signal and Information Lishu Guo 1,2, Xuyou Li 1, Xiaoying Kong 2 1. College of Automation, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China 2. School of Computing
Reference Clock Distribution for a 325MHz IF Sampling System with over 30MHz Bandwidth, 64dB SNR and 80dB SFDR
 Reference Clock Distribution for a 325MHz IF Sampling System with over 30MHz Bandwidth, 64dB SNR and 80dB SFDR Michel Azarian Clock jitter introduced in an RF receiver through reference clock buffering
Reference Clock Distribution for a 325MHz IF Sampling System with over 30MHz Bandwidth, 64dB SNR and 80dB SFDR Michel Azarian Clock jitter introduced in an RF receiver through reference clock buffering
Spacecraft Communications
 Antennas Orbits Modulation Noise Link Budgets 1 2012 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu The Problem Pointing Loss Polarization Loss Atmospheric Loss, Rain Loss Space Loss
Antennas Orbits Modulation Noise Link Budgets 1 2012 David L. Akin - All rights reserved http://spacecraft.ssl.umd.edu The Problem Pointing Loss Polarization Loss Atmospheric Loss, Rain Loss Space Loss
Antennas and Propagation
 Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication
 6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute of Technology Copyright 2003 by Michael H. Perrott
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute of Technology Copyright 2003 by Michael H. Perrott
Antennas and Propagation
 Mobile Networks Module D-1 Antennas and Propagation 1. Introduction 2. Propagation modes 3. Line-of-sight transmission 4. Fading Slides adapted from Stallings, Wireless Communications & Networks, Second
Mobile Networks Module D-1 Antennas and Propagation 1. Introduction 2. Propagation modes 3. Line-of-sight transmission 4. Fading Slides adapted from Stallings, Wireless Communications & Networks, Second
Noise Figure: What is it and why does it matter?
 Noise Figure: What is it and why does it matter? White Paper Noise Figure: What is it and why does it matter? Introduction Noise figure is one of the key parameters for quantifying receiver performance,
Noise Figure: What is it and why does it matter? White Paper Noise Figure: What is it and why does it matter? Introduction Noise figure is one of the key parameters for quantifying receiver performance,
It comprises filters, amplifiers and a mixer. Each stage has a noise figure, gain and noise bandwidth: f. , and
 Disclaimer his paper is supplied only on the understanding that I do not accept any responsibility for the consequences of any errors, omissions or misunderstandings that it might contain. Chris Angove,
Disclaimer his paper is supplied only on the understanding that I do not accept any responsibility for the consequences of any errors, omissions or misunderstandings that it might contain. Chris Angove,
SX-NSR 2.0 A Multi-frequency and Multi-sensor Software Receiver with a Quad-band RF Front End
 SX-NSR 2.0 A Multi-frequency and Multi-sensor Software Receiver with a Quad-band RF Front End - with its use for Reflectometry - N. Falk, T. Hartmann, H. Kern, B. Riedl, T. Pany, R. Wolf, J.Winkel, IFEN
SX-NSR 2.0 A Multi-frequency and Multi-sensor Software Receiver with a Quad-band RF Front End - with its use for Reflectometry - N. Falk, T. Hartmann, H. Kern, B. Riedl, T. Pany, R. Wolf, J.Winkel, IFEN
THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN
 THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN Mark Hunter * Abstract This paper is intended to give an overview of the design of radio transceivers to the engineer new to the field. It is shown how the requirements
THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN Mark Hunter * Abstract This paper is intended to give an overview of the design of radio transceivers to the engineer new to the field. It is shown how the requirements
Antennas & Propagation. CSG 250 Fall 2007 Rajmohan Rajaraman
 Antennas & Propagation CSG 250 Fall 2007 Rajmohan Rajaraman Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors o Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space o Reception
Antennas & Propagation CSG 250 Fall 2007 Rajmohan Rajaraman Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors o Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space o Reception
How Effective Are Signal. Quality Monitoring Techniques
 How Effective Are Signal Quality Monitoring Techniques for GNSS Multipath Detection? istockphoto.com/ppampicture An analytical discussion on the sensitivity and effectiveness of signal quality monitoring
How Effective Are Signal Quality Monitoring Techniques for GNSS Multipath Detection? istockphoto.com/ppampicture An analytical discussion on the sensitivity and effectiveness of signal quality monitoring
Adapted from Dr. Joe Montana (George mason University) Dr. James
 ink Budget Adapted from Dr. Joe Montana (George mason University) Dr. James W. apean course notes Dr. Jeremy Allnutt course notes And some internet resources + Tim Pratt book 1 ink Power Budget Tx EIRP
ink Budget Adapted from Dr. Joe Montana (George mason University) Dr. James W. apean course notes Dr. Jeremy Allnutt course notes And some internet resources + Tim Pratt book 1 ink Power Budget Tx EIRP
It is well recognized that the spacequalified. GNSS Solutions: Atomic clocks on satellites and mitigating multipath
 GNSS Solutions: Atomic clocks on satellites and mitigating multipath GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their
GNSS Solutions: Atomic clocks on satellites and mitigating multipath GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their
Antennas and Propagation
 CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Lecture 3: Antennas and Propagation Antennas Propagation Modes Line of Sight Transmission Fading in the Mobile Environment Introduction An antenna is an electrical
CMPE 477 Wireless and Mobile Networks Lecture 3: Antennas and Propagation Antennas Propagation Modes Line of Sight Transmission Fading in the Mobile Environment Introduction An antenna is an electrical
HIGH GAIN ADVANCED GPS RECEIVER
 ABSTRACT HIGH GAIN ADVANCED GPS RECEIVER NAVSYS High Gain Advanced () uses a digital beam-steering antenna array to enable up to eight GPS satellites to be tracked, each with up to dbi of additional antenna
ABSTRACT HIGH GAIN ADVANCED GPS RECEIVER NAVSYS High Gain Advanced () uses a digital beam-steering antenna array to enable up to eight GPS satellites to be tracked, each with up to dbi of additional antenna
Technical Note. HVM Receiver Noise Figure Measurements
 Technical Note HVM Receiver Noise Figure Measurements Joe Kelly, Ph.D. Verigy 1/13 Abstract In the last few years, low-noise amplifiers (LNA) have become integrated into receiver devices that bring signals
Technical Note HVM Receiver Noise Figure Measurements Joe Kelly, Ph.D. Verigy 1/13 Abstract In the last few years, low-noise amplifiers (LNA) have become integrated into receiver devices that bring signals
Satellite System Parameters
 Satellite System Parameters Lecture 3 MUHAMAD ASVIAL Center for Information and Communication Engineering Research (CICER) Electrical Engineering Department, University of Indonesia Kampus UI Depok, 16424,
Satellite System Parameters Lecture 3 MUHAMAD ASVIAL Center for Information and Communication Engineering Research (CICER) Electrical Engineering Department, University of Indonesia Kampus UI Depok, 16424,
Chapter 1: Introduction. EET-223: RF Communication Circuits Walter Lara
 Chapter 1: Introduction EET-223: RF Communication Circuits Walter Lara Introduction Electronic communication involves transmission over medium from source to destination Information can contain voice,
Chapter 1: Introduction EET-223: RF Communication Circuits Walter Lara Introduction Electronic communication involves transmission over medium from source to destination Information can contain voice,
A DISCUSSION ON QAM SNARE SENSITIVITY
 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY A DISCUSSION ON QAM SNARE SENSITIVITY HOW PROCESSING GAIN DELIVERS BEST SENSITIVITY IN THE CATEGORY 185 AINSLEY DRIVE SYRACUSE, NY 13210 800.448.1655 / WWW.ARCOMDIGITAL.COM ADVANCED
ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY A DISCUSSION ON QAM SNARE SENSITIVITY HOW PROCESSING GAIN DELIVERS BEST SENSITIVITY IN THE CATEGORY 185 AINSLEY DRIVE SYRACUSE, NY 13210 800.448.1655 / WWW.ARCOMDIGITAL.COM ADVANCED
RF Receiver Hardware Design
 RF Receiver Hardware Design Bill Sward bsward@rtlogic.com February 18, 2011 Topics Customer Requirements Communication link environment Performance Parameters/Metrics Frequency Conversion Architectures
RF Receiver Hardware Design Bill Sward bsward@rtlogic.com February 18, 2011 Topics Customer Requirements Communication link environment Performance Parameters/Metrics Frequency Conversion Architectures
System Noise Power 1
 System Noise Power 1 System Noise Power 1 Performance of system is determined by C/N ratio. Most systems require C/N > 10 db. (Remember, in dbs: C N > 10 db) Hence usually: C > N + 10 db We need to know
System Noise Power 1 System Noise Power 1 Performance of system is determined by C/N ratio. Most systems require C/N > 10 db. (Remember, in dbs: C N > 10 db) Hence usually: C > N + 10 db We need to know
TEST RESULTS OF A HIGH GAIN ADVANCED GPS RECEIVER
 TEST RESULTS OF A HIGH GAIN ADVANCED GPS RECEIVER ABSTRACT Dr. Alison Brown, Randy Silva, Gengsheng Zhang,; NAVSYS Corporation. NAVSYS High Gain Advanced GPS Receiver () uses a digital beam-steering antenna
TEST RESULTS OF A HIGH GAIN ADVANCED GPS RECEIVER ABSTRACT Dr. Alison Brown, Randy Silva, Gengsheng Zhang,; NAVSYS Corporation. NAVSYS High Gain Advanced GPS Receiver () uses a digital beam-steering antenna
Impact of ATC transponder transmission to onboard GPS-L5 signal environment
 SCRSP-WG IP-A10 18 May 2006 SURVEILLANCE AND CONFLICT RESOLUTION SYSTEMS PANEL (SCRSP) TENTH MEETING WG-A Montreal, May, 2006 WG-A Agenda Item 9 Any Other Bussiness Impact of ATC transponder transmission
SCRSP-WG IP-A10 18 May 2006 SURVEILLANCE AND CONFLICT RESOLUTION SYSTEMS PANEL (SCRSP) TENTH MEETING WG-A Montreal, May, 2006 WG-A Agenda Item 9 Any Other Bussiness Impact of ATC transponder transmission
Antennas Orbits Modulation Noise Link Budgets U N I V E R S I T Y O F. Spacecraft Communications MARYLAND. Principles of Space Systems Design
 Antennas Orbits Modulation Noise Link Budgets The Problem Pointing Loss Polarization Loss Atmospheric Loss, Rain Loss Space Loss Pointing Loss Transmitter Antenna SPACE CHANNEL Receiver Power Amplifier
Antennas Orbits Modulation Noise Link Budgets The Problem Pointing Loss Polarization Loss Atmospheric Loss, Rain Loss Space Loss Pointing Loss Transmitter Antenna SPACE CHANNEL Receiver Power Amplifier
Solution: NF=6 db, B=2.1 GHz, SNR min =7dB T=290 k, P in,1db = 10.5 dbm
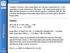 Consider a receiver with a noise figure of 6 db and a bandwidth of 2.1 GHz operating at room temperature. The input 1-dB compression point is 10.5 dbm and the detector at receiver output requires a minimum
Consider a receiver with a noise figure of 6 db and a bandwidth of 2.1 GHz operating at room temperature. The input 1-dB compression point is 10.5 dbm and the detector at receiver output requires a minimum
Over the past decade an
 GNSS SOLUTIONS Are there low-cost and low-weight options for GNSS IF storage? GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to
GNSS SOLUTIONS Are there low-cost and low-weight options for GNSS IF storage? GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to
Understanding Noise Figure
 Understanding Noise Figure Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul One of the most frequently discussed forms of noise is known as Thermal Noise. Thermal noise is a random fluctuation in
Understanding Noise Figure Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul One of the most frequently discussed forms of noise is known as Thermal Noise. Thermal noise is a random fluctuation in
HF Receivers, Part 3
 HF Receivers, Part 3 Introduction to frequency synthesis; ancillary receiver functions Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers Another link to receiver principles NSARC HF Operators HF
HF Receivers, Part 3 Introduction to frequency synthesis; ancillary receiver functions Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers Another link to receiver principles NSARC HF Operators HF
GNSS Solutions: Do GNSS augmentation systems certified for aviation use,
 GNSS Solutions: WAAS Functions and Differential Biases GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions to
GNSS Solutions: WAAS Functions and Differential Biases GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions to
Module 8 Theory. dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain. Functional Blocks Parameters. IRTS Region 4
 Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
RECEIVER SENSITIVITY / NOISE
 RECEIVER SENSITIVITY / NOISE RECEIVER SENSITIVITY Sensitivity in a receiver is normally taken as the imum input signal (S ) required to produce a specified output signal having a specified signal-to-noise
RECEIVER SENSITIVITY / NOISE RECEIVER SENSITIVITY Sensitivity in a receiver is normally taken as the imum input signal (S ) required to produce a specified output signal having a specified signal-to-noise
Keywords: GPS, receiver, GPS receiver, MAX2769, 2769, 1575MHz, Integrated GPS Receiver, Global Positioning System
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > User Guides > APP 3910 Keywords: GPS, receiver, GPS receiver, MAX2769, 2769, 1575MHz, Integrated GPS Receiver, Global Positioning System USER GUIDE 3910 User's
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > User Guides > APP 3910 Keywords: GPS, receiver, GPS receiver, MAX2769, 2769, 1575MHz, Integrated GPS Receiver, Global Positioning System USER GUIDE 3910 User's
MICROWAVE RADIO SYSTEMS GAIN. PENTel.Com Engr. Josephine Bagay, Ece faculty
 MICROWAVE RADIO SYSTEMS GAIN PENTel.Com Engr. Josephine Bagay, Ece faculty SYSTEM GAIN G s is the difference between the nominal output power of a transmitter (P t ) and the minimum input power to a receiver
MICROWAVE RADIO SYSTEMS GAIN PENTel.Com Engr. Josephine Bagay, Ece faculty SYSTEM GAIN G s is the difference between the nominal output power of a transmitter (P t ) and the minimum input power to a receiver
GNSS jammers are an ongoing
 GNSS SOLUTIONS Is it possible to build a low-cost system to detect and locate a single GNSS jammer in near-real time? GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical
GNSS SOLUTIONS Is it possible to build a low-cost system to detect and locate a single GNSS jammer in near-real time? GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SA Protection criteria for deep-space research
 Rec. ITU-R SA.1157-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SA.1157-1 Protection criteria for deep-space research (1995-2006) Scope This Recommendation specifies the protection criteria needed to success fully control,
Rec. ITU-R SA.1157-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SA.1157-1 Protection criteria for deep-space research (1995-2006) Scope This Recommendation specifies the protection criteria needed to success fully control,
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 6: Propagation and Noise. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 6: Propagation and Noise Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Propagation and Noise - Channel and antenna: not in the Razavi book - Noise: 2.3 The wireless channel The antenna Signal
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 6: Propagation and Noise Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Propagation and Noise - Channel and antenna: not in the Razavi book - Noise: 2.3 The wireless channel The antenna Signal
Antenna Measurements using Modulated Signals
 Antenna Measurements using Modulated Signals Roger Dygert MI Technologies, 1125 Satellite Boulevard, Suite 100 Suwanee, GA 30024-4629 Abstract Antenna test engineers are faced with testing increasingly
Antenna Measurements using Modulated Signals Roger Dygert MI Technologies, 1125 Satellite Boulevard, Suite 100 Suwanee, GA 30024-4629 Abstract Antenna test engineers are faced with testing increasingly
R&D White Paper WHP 066. Specifying UHF active antennas and calculating system performance. Research & Development BRITISH BROADCASTING CORPORATION
 R&D White Paper WHP 066 July 2003 Specifying UHF active antennas and calculating system performance J. Salter Research & Development BRITISH BROADCASTING CORPORATION BBC Research & Development White Paper
R&D White Paper WHP 066 July 2003 Specifying UHF active antennas and calculating system performance J. Salter Research & Development BRITISH BROADCASTING CORPORATION BBC Research & Development White Paper
RNSS Wide band and narrow band performance against Interference from DME/TACAN in the band MHz (Over Europe)
 Liaison Statement to GNSS-P (copy to CEPT/CPG/PT3) RNSS Wide band and narrow band performance against Interference from DME/TACAN in the band 1151-1215 MHz (Over Europe) 1 Introduction : During the last
Liaison Statement to GNSS-P (copy to CEPT/CPG/PT3) RNSS Wide band and narrow band performance against Interference from DME/TACAN in the band 1151-1215 MHz (Over Europe) 1 Introduction : During the last
Session2 Antennas and Propagation
 Wireless Communication Presented by Dr. Mahmoud Daneshvar Session2 Antennas and Propagation 1. Introduction Types of Anttenas Free space Propagation 2. Propagation modes 3. Transmission Problems 4. Fading
Wireless Communication Presented by Dr. Mahmoud Daneshvar Session2 Antennas and Propagation 1. Introduction Types of Anttenas Free space Propagation 2. Propagation modes 3. Transmission Problems 4. Fading
Potential interference from spaceborne active sensors into radionavigation-satellite service receivers in the MHz band
 Rec. ITU-R RS.1347 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R RS.1347* Rec. ITU-R RS.1347 FEASIBILITY OF SHARING BETWEEN RADIONAVIGATION-SATELLITE SERVICE RECEIVERS AND THE EARTH EXPLORATION-SATELLITE (ACTIVE) AND SPACE RESEARCH
Rec. ITU-R RS.1347 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R RS.1347* Rec. ITU-R RS.1347 FEASIBILITY OF SHARING BETWEEN RADIONAVIGATION-SATELLITE SERVICE RECEIVERS AND THE EARTH EXPLORATION-SATELLITE (ACTIVE) AND SPACE RESEARCH
Evaluation of C/N 0 estimators performance for GNSS receivers
 International Conference and Exhibition The 14th IAIN Congress 2012 Seamless Navigation (Challenges & Opportunities) 01-03 October, 2012 - Cairo, Egypt Concorde EL Salam Hotel Evaluation of C/N 0 estimators
International Conference and Exhibition The 14th IAIN Congress 2012 Seamless Navigation (Challenges & Opportunities) 01-03 October, 2012 - Cairo, Egypt Concorde EL Salam Hotel Evaluation of C/N 0 estimators
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering. Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University
 ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
Utilizing Batch Processing for GNSS Signal Tracking
 Utilizing Batch Processing for GNSS Signal Tracking Andrey Soloviev Avionics Engineering Center, Ohio University Presented to: ION Alberta Section, Calgary, Canada February 27, 2007 Motivation: Outline
Utilizing Batch Processing for GNSS Signal Tracking Andrey Soloviev Avionics Engineering Center, Ohio University Presented to: ION Alberta Section, Calgary, Canada February 27, 2007 Motivation: Outline
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
Satellite Signals and Communications Principles. Dr. Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer (P.hD)
 Satellite Signals and Communications Principles Dr. Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) Principle of Satellite Signals In essence, satellite signals are electromagnetic waves that travel from the satellite
Satellite Signals and Communications Principles Dr. Ugur GUVEN Aerospace Engineer (P.hD) Principle of Satellite Signals In essence, satellite signals are electromagnetic waves that travel from the satellite
Maximizing MIMO Effectiveness by Multiplying WLAN Radios x3
 ATHEROS COMMUNICATIONS, INC. Maximizing MIMO Effectiveness by Multiplying WLAN Radios x3 By Winston Sun, Ph.D. Member of Technical Staff May 2006 Introduction The recent approval of the draft 802.11n specification
ATHEROS COMMUNICATIONS, INC. Maximizing MIMO Effectiveness by Multiplying WLAN Radios x3 By Winston Sun, Ph.D. Member of Technical Staff May 2006 Introduction The recent approval of the draft 802.11n specification
EEG 816: Radiowave Propagation 2009
 Student Matriculation No: Name: EEG 816: Radiowave Propagation 2009 Dr A Ogunsola This exam consists of 5 problems. The total number of pages is 5, including the cover page. You have 2.5 hours to solve
Student Matriculation No: Name: EEG 816: Radiowave Propagation 2009 Dr A Ogunsola This exam consists of 5 problems. The total number of pages is 5, including the cover page. You have 2.5 hours to solve
Data Communications and Networks
 Data Communications and Networks Abdul-Rahman Mahmood http://alphapeeler.sourceforge.net http://pk.linkedin.com/in/armahmood abdulmahmood-sss twitter.com/alphapeeler alphapeeler.sourceforge.net/pubkeys/pkey.htm
Data Communications and Networks Abdul-Rahman Mahmood http://alphapeeler.sourceforge.net http://pk.linkedin.com/in/armahmood abdulmahmood-sss twitter.com/alphapeeler alphapeeler.sourceforge.net/pubkeys/pkey.htm
SATELLITE LINK DESIGN
 1 SATELLITE LINK DESIGN Networks and Communication Department Dr. Marwah Ahmed Outlines 2 Introduction Basic Transmission Theory System Noise Temperature and G/T Ratio Design of Downlinks Satellite Communication
1 SATELLITE LINK DESIGN Networks and Communication Department Dr. Marwah Ahmed Outlines 2 Introduction Basic Transmission Theory System Noise Temperature and G/T Ratio Design of Downlinks Satellite Communication
RF Over Fiber Design Guide Overview. Provided by OPTICAL ZONU CORPORATION
 RF Over Fiber Design Guide Overview Provided by OPTICAL ZONU CORPORATION Why use fiber? Transmission of RF and Microwave Signals via waveguides or coaxial cable suffers high insertion loss and susceptibility
RF Over Fiber Design Guide Overview Provided by OPTICAL ZONU CORPORATION Why use fiber? Transmission of RF and Microwave Signals via waveguides or coaxial cable suffers high insertion loss and susceptibility
RF Fundamental Concepts and Performance Parameters
 RF Fundamental Concepts and erformance arameters CCE 50 RF and Microwave System Design Dr. Owen Casha B. Eng. (Hons.) h.d. 09/0/0 Overview Introduction Nonlinearity and Time Variance System Noise Thermal
RF Fundamental Concepts and erformance arameters CCE 50 RF and Microwave System Design Dr. Owen Casha B. Eng. (Hons.) h.d. 09/0/0 Overview Introduction Nonlinearity and Time Variance System Noise Thermal
RF System Aspects for SDR. A Tutorial. Dr. Ruediger Leschhorn, Rohde & Schwarz 29. November 2011
 RF System Aspects for SDR A Tutorial Dr. Ruediger Leschhorn, Rohde & Schwarz 29. November 2011 Content Radio System Some Basics Link Budget Cosite Examples Desensitization Blocking, Transmitter Noise,
RF System Aspects for SDR A Tutorial Dr. Ruediger Leschhorn, Rohde & Schwarz 29. November 2011 Content Radio System Some Basics Link Budget Cosite Examples Desensitization Blocking, Transmitter Noise,
Correlators for L2C. Some Considerations
 Correlators for L2C Some Considerations Andrew dempster Lockheed Martin With the launch of the first modernized GPS Block IIR satellite in September 2006, GNSS product designers have an additional, fully
Correlators for L2C Some Considerations Andrew dempster Lockheed Martin With the launch of the first modernized GPS Block IIR satellite in September 2006, GNSS product designers have an additional, fully
Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper
 Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
GPS Time and Frequency Reference Receiver
 $ GPS Time and Frequency Reference Receiver Symmetricom s 58540A GPS time and frequency reference receiver features: Eight-channel, parallel tracking GPS engine C/A Code, L1 Carrier GPS T-RAIM satellite
$ GPS Time and Frequency Reference Receiver Symmetricom s 58540A GPS time and frequency reference receiver features: Eight-channel, parallel tracking GPS engine C/A Code, L1 Carrier GPS T-RAIM satellite
TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 6: Receiver Synthesis (I)
 TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 6: Receiver Synthesis (I) Ted Johansson, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Systematic Receiver Synthesis (1) 4.1 Introduction 4. Sensitivity, Noise Figure Receiver
TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 6: Receiver Synthesis (I) Ted Johansson, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Systematic Receiver Synthesis (1) 4.1 Introduction 4. Sensitivity, Noise Figure Receiver
GPS Receiver Autonomous Interference Detection
 GPS Receiver Autonomous Interference Detection Awele Ndili, Stanford University Dr. Per Enge, Stanford University Presented at the 998 IEEE Position, Location and Navigation Symposium - PLANS 98 Palm Springs,
GPS Receiver Autonomous Interference Detection Awele Ndili, Stanford University Dr. Per Enge, Stanford University Presented at the 998 IEEE Position, Location and Navigation Symposium - PLANS 98 Palm Springs,
A Method for Gain over Temperature Measurements Using Two Hot Noise Sources
 A Method for Gain over Temperature Measurements Using Two Hot Noise Sources Vince Rodriguez and Charles Osborne MI Technologies: Suwanee, 30024 GA, USA vrodriguez@mitechnologies.com Abstract P Gain over
A Method for Gain over Temperature Measurements Using Two Hot Noise Sources Vince Rodriguez and Charles Osborne MI Technologies: Suwanee, 30024 GA, USA vrodriguez@mitechnologies.com Abstract P Gain over
Monitoring Station for GNSS and SBAS
 Monitoring Station for GNSS and SBAS Pavel Kovář, Czech Technical University in Prague Josef Špaček, Czech Technical University in Prague Libor Seidl, Czech Technical University in Prague Pavel Puričer,
Monitoring Station for GNSS and SBAS Pavel Kovář, Czech Technical University in Prague Josef Špaček, Czech Technical University in Prague Libor Seidl, Czech Technical University in Prague Pavel Puričer,
(2) Assume the measurements are at 245 MHz, which corresponds to a wavelength of
 To Preamplify or Not Whitham D. Reeve and Christian Monstein 1. Introduction A question frequently arises concerning the application of a low noise preamplifier to the Callisto instrument used in the e-callisto
To Preamplify or Not Whitham D. Reeve and Christian Monstein 1. Introduction A question frequently arises concerning the application of a low noise preamplifier to the Callisto instrument used in the e-callisto
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering. Lecture 4 October 11, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University
 ELEN 7 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 4 October, 26 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 5 Receiver System Analysis and Design, Part II Key Parameters Intermodulation Characteristics
ELEN 7 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 4 October, 26 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 5 Receiver System Analysis and Design, Part II Key Parameters Intermodulation Characteristics
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 6: Propagation and Noise. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 6: Propagation and Noise Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Propagation and Noise - Channel and antenna: not in the Razavi book - Noise: 2.3 The wireless channel The antenna Signal
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 6: Propagation and Noise Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Propagation and Noise - Channel and antenna: not in the Razavi book - Noise: 2.3 The wireless channel The antenna Signal
NOISE INTERNAL NOISE. Thermal Noise
 NOISE INTERNAL NOISE......1 Thermal Noise......1 Shot Noise......2 Frequency dependent noise......3 THERMAL NOISE......3 Resistors in series......3 Resistors in parallel......4 Power Spectral Density......4
NOISE INTERNAL NOISE......1 Thermal Noise......1 Shot Noise......2 Frequency dependent noise......3 THERMAL NOISE......3 Resistors in series......3 Resistors in parallel......4 Power Spectral Density......4
ADI 2006 RF Seminar. Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers
 ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
Copyright Teletronics International, Inc. Patent Pending
 Copyright 2003 By Teletronics International, Inc. Patent Pending FCC NOTICES Electronic Emission Notice: This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
Copyright 2003 By Teletronics International, Inc. Patent Pending FCC NOTICES Electronic Emission Notice: This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 7: Receiver Synthesis (II)
 TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 7: Receiver Synthesis (II) Ted Johansson, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Systematic Receiver Synthesis (II) 4.3 Intermodulation characteristics Phase noise
TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 7: Receiver Synthesis (II) Ted Johansson, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Systematic Receiver Synthesis (II) 4.3 Intermodulation characteristics Phase noise
Common Types of Noise
 Common Types of Noise Name Example Description Impulse Ignition, TVI Not Random, Cure by Shielding, Quantizing, Decoding, etc. BER Digital Systems, DAC's & ADC's. Often Bit Resolution and/or Bit Fidelity
Common Types of Noise Name Example Description Impulse Ignition, TVI Not Random, Cure by Shielding, Quantizing, Decoding, etc. BER Digital Systems, DAC's & ADC's. Often Bit Resolution and/or Bit Fidelity
System-Level Time-Domain Behavioral Modeling for A Mobile WiMax Transceiver
 System-Level Time-Domain Behavioral Modeling for A Mobile WiMax Transceiver Jie He, Jun Seo Yang, Yongsup Kim, and Austin S. Kim HIDS Lab, Telecommunication R&D Center, Samsung Electronics jie.he@samung.com,
System-Level Time-Domain Behavioral Modeling for A Mobile WiMax Transceiver Jie He, Jun Seo Yang, Yongsup Kim, and Austin S. Kim HIDS Lab, Telecommunication R&D Center, Samsung Electronics jie.he@samung.com,
Protection of fixed monitoring stations against interference from nearby or strong transmitters
 Recommendation ITU-R SM.575-2 (10/2013) Protection of fixed monitoring stations against interference from nearby or strong transmitters SM Series Spectrum management ii Rec. ITU-R SM.575-2 Foreword The
Recommendation ITU-R SM.575-2 (10/2013) Protection of fixed monitoring stations against interference from nearby or strong transmitters SM Series Spectrum management ii Rec. ITU-R SM.575-2 Foreword The
Session 3. CMOS RF IC Design Principles
 Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
Radio Frequency Design to Support Software Transceiver for Wireless Communications
 Radio Frequency Design to Support Software Transceiver for Wireless Communications Author: Cazzie Williams Western Michigan University Whirlpool Corporation Advisor/Sponsor: Dr. Frank Severance and Dr.
Radio Frequency Design to Support Software Transceiver for Wireless Communications Author: Cazzie Williams Western Michigan University Whirlpool Corporation Advisor/Sponsor: Dr. Frank Severance and Dr.
The Case for Recording IF Data for GNSS Signal Forensic Analysis Using a SDR
 The Case for Recording IF Data for GNSS Signal Forensic Analysis Using a SDR Professor Gérard Lachapelle & Dr. Ali Broumandan PLAN Group, University of Calgary PLAN.geomatics.ucalgary.ca IGAW 2016-GNSS
The Case for Recording IF Data for GNSS Signal Forensic Analysis Using a SDR Professor Gérard Lachapelle & Dr. Ali Broumandan PLAN Group, University of Calgary PLAN.geomatics.ucalgary.ca IGAW 2016-GNSS
APPENDIX A TEST PLOTS. (Model: 15Z970)
 APPENDIX A APPENDIX A TEST PLOTS (Model: 15Z970) APPENDIX A-Page 1 of 36 TABLE OF CONTENTS A.1 6dB BANDWIDTH MEASUREMENT... 2 A.1.1 6dB Bandwidth Result... 2 A.1.2 Measurement Plots... 3 A.2 MAXIMUM PEAK
APPENDIX A APPENDIX A TEST PLOTS (Model: 15Z970) APPENDIX A-Page 1 of 36 TABLE OF CONTENTS A.1 6dB BANDWIDTH MEASUREMENT... 2 A.1.1 6dB Bandwidth Result... 2 A.1.2 Measurement Plots... 3 A.2 MAXIMUM PEAK
High-Linearity CMOS. RF Front-End Circuits
 High-Linearity CMOS RF Front-End Circuits Yongwang Ding Ramesh Harjani iigh-linearity CMOS tf Front-End Circuits - Springer Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data A C.I.P. Catalogue record
High-Linearity CMOS RF Front-End Circuits Yongwang Ding Ramesh Harjani iigh-linearity CMOS tf Front-End Circuits - Springer Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data A C.I.P. Catalogue record
Radio Frequency Interference Validation Testing for LAAS using the Stanford Integrity Monitor Testbed
 Radio Frequency Interference Validation Testing for LAAS using the Stanford Integrity Monitor Testbed Ming Luo, Gang Xie, Dennis Akos, Sam Pullen, Per Enge Stanford University ABSTRACT Since GPS signals
Radio Frequency Interference Validation Testing for LAAS using the Stanford Integrity Monitor Testbed Ming Luo, Gang Xie, Dennis Akos, Sam Pullen, Per Enge Stanford University ABSTRACT Since GPS signals
Receiver Architecture
 Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Advanced Self-Interference Cancellation and Multiantenna Techniques for Full-Duplex Radios
 Advanced Self-Interference Cancellation and Multiantenna Techniques for Full-Duplex Radios Dani Korpi 1, Sathya Venkatasubramanian 2, Taneli Riihonen 2, Lauri Anttila 1, Sergei Tretyakov 2, Mikko Valkama
Advanced Self-Interference Cancellation and Multiantenna Techniques for Full-Duplex Radios Dani Korpi 1, Sathya Venkatasubramanian 2, Taneli Riihonen 2, Lauri Anttila 1, Sergei Tretyakov 2, Mikko Valkama
Frequency Modulation
 Frequency Modulation transferred to the microwave carrier by means of FM. Instead of being done in one step, this modulation usually takes place at an intermediate frequency. signal is then frequency multiplied
Frequency Modulation transferred to the microwave carrier by means of FM. Instead of being done in one step, this modulation usually takes place at an intermediate frequency. signal is then frequency multiplied
Evaluation of L2C Observations and Limitations
 Evaluation of L2C Observations and Limitations O. al-fanek, S. Skone, G.Lachapelle Department of Geomatics Engineering, Schulich School of Engineering, University of Calgary, Canada; P. Fenton NovAtel
Evaluation of L2C Observations and Limitations O. al-fanek, S. Skone, G.Lachapelle Department of Geomatics Engineering, Schulich School of Engineering, University of Calgary, Canada; P. Fenton NovAtel
UHF Phased Array Ground Stations for Cubesat Applications
 UHF Phased Array Ground Stations for Cubesat Applications Colin Sheldon, Justin Bradfield, Erika Sanchez, Jeffrey Boye, David Copeland and Norman Adams 10 August 2016 Colin Sheldon, PhD 240-228-8519 Colin.Sheldon@jhuapl.edu
UHF Phased Array Ground Stations for Cubesat Applications Colin Sheldon, Justin Bradfield, Erika Sanchez, Jeffrey Boye, David Copeland and Norman Adams 10 August 2016 Colin Sheldon, PhD 240-228-8519 Colin.Sheldon@jhuapl.edu
