High-Yield Bang Time Detector for the OMEGA Laser
|
|
|
- Chrystal Snow
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 High-Yield Bang Time Detector for the OMEGA Laser Introduction The time interval from the beginning of the laser pulse to the peak of neutron emission (bang time) is an important parameter in inertial confinement fusion (ICF) 1 experiments. The neutron bang time is very sensitive to energy absorption and the subsequent hydrodynamic response of the target and can be directly compared with numerical simulation. Several detectors 2 4 that have been developed to measure the neutron bang time in ICF experiments include a fast (<25-ps) streakcamera based neutron temporal diagnostic (NTD). 5 An NTD is currently installed on the OMEGA laser 6 at LLE. The NTD streak camera, located at about 3 m from the target, is saturated by neutron yields above 3 # OMEGA has produced yields of 1 14 (Ref. 7), and fast-ignition experiments currently planned 8 at the OMEGA Laser Facility are expected to produce neutron yields above A new high-yield neutron bang time (HYNBT) detector has been developed at LLE to measure the bang time in these very high yield experiments. The HYNBT has also been developed as a prototype neutron bang time detector for high neutron yields at the National Ignition Facility (NIF). The present work is a continuation of the NIF prototype development published earlier. 9 HYNBT Design and Setup The HYNBT detector design, shown in Fig , consists of three chemical-vapor-deposition (CVD) diamond detectors of different sizes and sensitivities placed in a lead-shielded housing. The HYNBT uses commercially purchased 1 opticalquality polycrystalline DIAFILM CVD wafers. The HYNBT wafers are disks with the following dimensions: 1 mm diameter,.5 mm thick (Ch1); 5-mm diameter,.25 mm thick (Ch2); and 2-mm diameter,.5 mm thick (Ch3). On each side of the CVD wafer 1 nm of Cr and 5 nm of Au were deposited to provide electrical contact. Each CVD wafer was assembled in an individual aluminum housing with an SMA connector. Figure 17.2 shows the Ch3 housing before and after assembly. Each detector was pre-tested, and the three channels were assembled in a stainless steel cylinder. Figure shows the HYNBT before and after assembly. The thin-walled 36 mm 25 mm E14428JRC Lead 1 mm Lead 6 mm Ch 2 Ch 1 Ch 3 Figure Design of the HYNBT detector. Stainless steel 1.8 mm 254 mm 2-mm-diam,.5-mm-thick CVD wafer E14429JRC CVD wafer Figure 17.2 The HYNBT Ch3 housing before and after assembly. LLE Review, Volume
2 High-Yield Bang Time Detector for the OMEGA Laser train is recorded on the fourth channel, using a fast photodiode to provide a time reference to the laser. The fiducial analysis and fitting procedure are described in Ref. 4. HYNBT Performance The HYNBT was tested on OMEGA with both DT and D2 implosions. Figure shows typical oscilloscope traces of the three HYNBT channels for a shot yielding 4.4 # 112 DT neutrons. The measured signals were fit by a convolution of a Gaussian and an exponential decay, as described in Ref. 4. The parameter of the exponential decay represents the collection time of the carriers in the CVD diamond wafer. At a constant bias voltage, the decay parameter depends on the thickness and diameter of the CVD wafer. The optimum decay parameter for 1 Ch1 (a) E1443JRC (V) Figure The HYNBT before and after final assembly. 148 (V) Ch2 (b) 2 4 Decay.5 ns (V) stainless steel cylinder acts as a Faraday cage decreasing the electromagnetic pulse (EMP) noise. Lead shielding inside the steel cylinder protects the CVD diamond detectors from hard x rays. This shielding is not necessary for current experiments on OMEGA and was installed in anticipation of hard x rays produced by the interaction of the short laser pulse with the gold cone or shell in fast-ignition experiments.8 RG-142 coaxial cables are used because of their double-braid shielding design and low sensitivity to neutrons.11 The 3-m-long, RG-142 cables are connected to 22-m-long, LMR-4 cables. Inside the OMEGA Target Bay, the cables are routed radially with respect to the target chamber center to minimize the interaction of neutrons with the cables. The bandwidth of the LMR-4 cables is higher than that of the RG-142 cables, but they are much more sensitive to neutrons.11 This two-cable solution is a compromise between bandwidth and neutroninduced background signals. The HYNBT is deployed in the same re-entrant tube as LLE s NBT,4 5 cm from the target chamber center. All of the HYNBT channels were biased at 75 V using a bias-tee (Picosecond Pulse Labs, model 5531). The signals from the HYNBT CVD diamond detectors were recorded on three channels of a 3-GHz, 1-GS/s, Tektronix TDS-694 oscilloscope. The OMEGA optical fiducial pulse 4 2 Decay 1.25 ns Ch3 (c).5.1 Decay 1. ns.15.2 E14431JRC Figure The HYNBT signal for shot 4212 with a DT neutron yield of 4.4 # 112. LLE Review, Volume 17
3 each HYNBT channel was determined from the fit of a large number of the shots for each channel (low noise, not saturated) and was fixed for the timing analysis of all shots. The Gaussian fit parameters are free parameters for every shot to account for different yields, bang times, ion temperatures, and trigger shifts. The neutron pulse s arrival time is defined to be the center of the Gaussian portion of the fit. Figure shows the signal amplitude of three HYNBT channels as a function of DT neutron yield. The straight lines are linear fits to the data for each channel. The first HYNBT channel saturates above a 1-V signal, and the second channel saturates above 8 V. At a yield of 1 # 1 15, the third channel will have a signal of ~2 V and will not be saturated. The three HYNBT channels can measure the neutron bang time in DT implosions over the yield range from 1 # 1 1 to 1 # Ch1 Ch2 (ps) 1 (a) (b) HYNBT: Ch1 Ch2 rms = 13 ps Shot number The timing accuracy of the HYNBT was studied by measuring the time differences among channels. Figure 17.24(a) shows the time difference between two HYNBT channels recorded on multiple shots over two shot days in May 25. The DT yields varied from 8.4 # 1 12 to 3.5 # The rms of the time difference between these two channels is 13 ps. The HYNBT was tested five times during 25. Figure 17.24(b) shows the time difference between the HYNBT channels appropriate for the neutron yield range during the tests. In November 25, Ch2 of the HYNBT was used to test a gamma bang time (GBT) detector based on an optical light pipe concept; 12 the time difference between the HYNBT and the GBT had an rms of 15 ps. In all cases the internal time resolution of the HYNBT was better than 2 ps. rms (ps) E14432JRC 1 Ch1 Ch2 Ch1 Ch3 3 Ch2 Ch3 Ch2 GBT Month (25) Figure (a) Time difference between HYNBT Ch1 and Ch2 in May 25; (b) rms of time differences between the HYNBT channels in 25. amplitude (V) 1 E14434JRC HYNBT DT Figure amplitudes of the HYNBT channels. Ch1 Ch2 Ch Neutron yield The timing calibration of the HYNBT bang time relative to the OMEGA laser pulse was established by cross-calibration against the NTD. 5 Figure shows the cross-calibration of the HYNBT channels and the NTD performed in December 25, with DT yields varying from 3. # 1 12 to 1.4 # A good correlation between the NTD and the HYNBT is observed with an rms difference of 4 ps. This is larger than the 28-ps rms expected for the difference between two independent measurements, each with a time precision of 2 ps. The discrepancy is explained by direct neutron hits on the NTD, charged-coupled-device (CCD) camera that reduces its temporal resolution. Although the HYNBT was designed to measure DT neutron bang time, it can also measure bang time in high-yield D 2 shots on OMEGA. Since CVD diamond detectors are less sensitive to D 2 than to DT neutrons, only the first HYNBT channel LLE Review, Volume
4 24.5 (a) HYNBT bang time (ps) E14541JRC 18 2 NTD bang time (ps) Ch1 Ch2 Ch (V) Shot 42956, Y n = (b) Shot 42932, Y n = Figure Timing cross-calibration between the HYNBT and the NTD for DT implosions. A line of equal bang times for both instruments is shown for comparison. is sufficiently sensitive for D 2 implosions on OMEGA. Figure shows oscilloscope traces of the first HYNBT channel for shots yielding 1.1 # 1 1 and 9.3 # 1 1. At a D 2 yield of 1 # 1 1 the signal amplitude is only 1 mv and is affected by EMP and digital noise since the minimum scale setting of the TDS-694 oscilloscope is 1 mv/div. Figure shows the first-channel signal amplitude as a function of D 2 yield, and Fig shows the cross-calibration against the NTD. To minimize the influence of noise on the cross-calibration timing, only shots with yields above 3 # 1 1 were included. With ~5-ps rms, the D 2 cross-calibration is not as accurate as the DT cross-calibration because most of the signal amplitudes in Fig were below 1 mv. (V) E148JRC Figure The oscilloscope traces of the first HYNBT channel for D 2 shots: (a) shot with a yield of 1.1 # 1 1 ; (b) shot with a yield of 9.3 # EMP mitigation techniques used with the HYNBT design reduced the EMP noise to a level about 1# smaller than that measured with LLE s NBT. 4 Figure shows the EMP noise levels in the least-sensitive Ch3 for different shot conditions. Figure 17.29(a) shows less-than-2-mv noise levels for the standard direct-drive shot. Figure 17.29(b) shows the EMP noise level for a direct-drive shot with backlighting. Backlighting produced additional EMP noise, and for these shot types, the noise level is below 4 mv. The indirect-drive shot with a scale-5/8 hohlraum is shown in Fig (c) with the EMP noise below 4 mv. For all shots on OMEGA the EMP noise level in the HYNBT is below 4 mv. amplitude (mv) E1481JRC HYNBT D 2 Linear fit Neutron yield Due to the lead shielding, the HYNBT is insensitive to hard-x-ray signals in direct-drive and most typical indirect- Figure The HYNBT first-channel signal amplitude as a function of D 2 yield. 15 LLE Review, Volume 17
5 HYNBT bang time (ps) E14435JRC rms = 47 ps NTD bang time (ps) Figure Timing cross-calibration between the HYNBT first channel and the NTD for D 2 implosions. A line of equal bang time for both instruments is shown for comparison. (mv) E1482JRC Indirect drive, scale-5/8 hohlraum Shot 4431, Ch1, x-ray signal Figure 17.3 X-ray signal from the scale-5/8-hohlraum, indirect-drive shot 4433 on the HYNBT first channel. drive shots. Only the most sensitive HYNBT channel was able to record a 3-mV x-ray signal from a scale-5/8 hohlraum, indirect-drive shot that produces ~1# more hard x rays than direct-drive shots (shown in Fig. 17.3). This relatively low signal is temporally separated from the neutron signal and will not compromise the HYNBT bang time. HYNBT on the NIF The HYNBT was also developed as a prototype neutron bang time detector for the NIF. This is a continuation of earlier work 9 on a NIF bang time prototype. Since publication of this earlier work, the design requirements have changed: Instead of a low-to-moderate-yield, general-purpose diagnostic, the NIF NBT detector is now required for moderate-to-high yields in the pre-ignition and early-ignition campaigns. At these yields, the original scintillator and photomultiplier channel described in Ref. 9 cannot be used. The NIF NBT is virtually identical to the OMEGA HYNBT with three or four CVD diamond channels. This design will make the NIF NBT more compact, simpler, and less expensive than an NBT employing a photomultiplier. It will be located about 4 to 6 cm from the target in a diagnostic insertion manipulator, together with other NIF diagnostics. In contrast to the OMEGA HYNBT, the shielding on the front of the NIF NBT (facing the target) will be remov- 2 (a) Standard direct-drive shot 42857, Ch3, EMP < 2 mv 4 (b) Direct-drive shot 42955, with backlighting Ch3, EMP < 4 mv 4 (c) Indirect-drive shot 4431, with scale-5/8 hohlraum Ch2, EMP < 4 mv (mv) E14436JRC Figure EMP noise in HYNBT Ch3 for different shots conditions: (a) standard direct-drive shot 42857; (b) direct-drive shot with backlighting; and (c) indirectdrive shot 4431 with a scale-5/8 hohlraum. LLE Review, Volume
6 able so that x rays can be used for temporal calibration. 9 The calibration will use x-ray emission from a gold target irradiated by a short laser pulse. The distance from the target, x-ray shielding, and cable length of the HYNBT on OMEGA are comparable to those required on the NIF. The sensitivity of the NIF NBT channels will be comparable to the corresponding HYNBT channels. The dynamic range of the NIF NBT can be increased by increasing the sensitivity of the first channel, decreasing the sensitivity of the third channel, and adding an even less sensitive fourth channel. The first-channel CVD wafer can be changed from a 1-mm-diam,.5-mm-thick CVD wafer to a 1-mm-diam, 1-mm-thick CVD wafer. This will increase the sensitivity by a factor of 2, which corresponds to yields of 2.5 # 1 1 in D 2 and 5 # 1 9 in DT implosions. If NIF NBT operation will be required at lower yields, the detector can be moved closer to the target. The fourth, least-sensitive channel can be made from a smaller and thinner CVD wafer, from a neutron-hardened CVD wafer, or from a CVD wafer with impurities. All of these factors decrease the sensitivity of the CVD diamonds and shorten the temporal response. The maximum operational yield of the NIF NBT will not be determined by CVD diamond saturation but by neutron-induced signals in the coaxial cables. 11 The study of neutron-induced signals in the coaxial cables will continue on OMEGA. With an optimal cable, the upper-yield range of the NIF NBT is expected to be about Summary A simple, low-cost, high-yield neutron bang time (HYNBT) detector has been developed and implemented on OMEGA. The HYNBT consists of three chemical-vapor-deposition (CVD) diamond detectors of different sizes and sensitivities placed in a lead-shielded housing. The HYNBT is located in a re-entrant tube 5 cm from the center of the target chamber. The HYNBT has been temporally cross-calibrated against the streak-camera based neutron temporal diagnostic (NTD) for both D 2 and DT implosions. The HYNBT has an internal time resolution better than 2 ps. The three HYNBT channels can measure the neutron bang time in DT implosions over a yield range of 1 # 1 1 to 1 # 1 15 and above 5 # 1 1 for D 2 implosions. The HYNBT can be implemented on the National Ignition Facility. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inertial Confinement Fusion under Cooperative Agreement No. DE-FC52-92SF1946, the University of Rochester, and the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority. The support of DOE does not constitute an endorsement by DOE of the views expressed in this article. REFERENCES 1. J. D. Lindl, Inertial Confinement Fusion: The Quest for Ignition and Energy Gain Using Indirect Drive (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1998). 2. R. A. Lerche et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 59, 1697 (1988). 3. N. Miyanaga et al., Rev. Sci. Instrum. 61, 3592 (199). 4. C. Stoeckl, V. Yu. Glebov, J. D. Zuegel, D. D. Meyerhofer, and R. A. Lerche, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 73, 3796 (22). 5. R. A. Lerche, D. W. Phillion, and G. L. Tietbohl, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 66, 933 (1995). 6. T. R. Boehly, D. L. Brown, R. S. Craxton, R. L. Keck, J. P. Knauer, J. H. Kelly, T. J. Kessler, S. A. Kumpan, S. J. Loucks, S. A. Letzring, F. J. Marshall, R. L. McCrory, S. F. B. Morse, W. Seka, J. M. Soures, and C. P. Verdon, Opt. Commun. 133, 495 (1997). 7. J. M. Soures, R. L. McCrory, C. P. Verdon, A. Babushkin, R. E. Bahr, T. R. Boehly, R. Boni, D. K. Bradley, D. L. Brown, R. S. Craxton, J. A. Delettrez, W. R. Donaldson, R. Epstein, P. A. Jaanimagi, S. D. Jacobs, K. Kearney, R. L. Keck, J. H. Kelly, T. J. Kessler, R. L. Kremens, J. P. Knauer, S. A. Kumpan, S. A. Letzring, D. J. Lonobile, S. J. Loucks, L. D. Lund, F. J. Marshall, P. W. McKenty, D. D. Meyerhofer, S. F. B. Morse, A. Okishev, S. Papernov, G. Pien, W. Seka, R. Short, M. J. Shoup III, M. Skeldon, S. Skupsky, A. W. Schmid, D. J. Smith, S. Swales, M. Wittman, and B. Yaakobi, Phys. Plasmas 3, 218 (1996). 8. C. Stoeckl, J. A. Delettrez, J. H. Kelly, T. J. Kessler, B. E. Kruschwitz, S. J. Loucks, R. L. McCrory, D. D. Meyerhofer, D. N. Maywar, S. F. B. Morse, J. Myatt, A. L. Rigatti, L. J. Waxer, J. D. Zuegel, and R. B. Stephens, Fusion Sci. Technol. 49, 367 (26). 9. V. Yu. Glebov, C. Stoeckl, T. C. Sangster, S. Roberts, R. A. Lerche, and G. J. Schmid, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 33, 7 (25). 1. Harris International, New York, NY V. Yu. Glebov, R. A. Lerche, C. Stoeckl, G. J. Schmid, T. C. Sangster, J. A. Koch, T. W. Phillips, C. Mileham, and S. Roberts, presented at ICOPS 25, International Conference on Plasma Sciences, Monterey, CA, 2 23 June 25 (Paper 1281). 12. M. Moran, G. Mant, V. Glebov, C. Sangster, and J. Mack, presented at the 16th Annual Conference on High-Temperature Plasma Diagnostics, Williamsburg, VA, 7 11 May 26 (Paper TP22). 152 LLE Review, Volume 17
NIF Neutron Bang Time Detector Development on OMEGA
 NIF Neutron Bang Time Detector Development on OMEGA 2400 2200 NBT2 scintillator bang time (ps) 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 rms = 54 ps 1000 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 2400 V. Yu. Glebov University
NIF Neutron Bang Time Detector Development on OMEGA 2400 2200 NBT2 scintillator bang time (ps) 2000 1800 1600 1400 1200 rms = 54 ps 1000 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 2400 V. Yu. Glebov University
Measuring 8- to 250-ps Short Pulses Using a High-Speed Streak Camera on Kilojule, Petawatt-Class Laser Systems
 Measuring 8- to 25-ps Short Pulses Using a High-Speed Streak Camera on Kilojule, Petawatt-Class Laser Systems Measuring 8- to 25-ps Short Pulses Using a High-Speed Streak Camera on Kilojoule, Petawatt-Class
Measuring 8- to 25-ps Short Pulses Using a High-Speed Streak Camera on Kilojule, Petawatt-Class Laser Systems Measuring 8- to 25-ps Short Pulses Using a High-Speed Streak Camera on Kilojoule, Petawatt-Class
A stable mid-ir, GaSb-based diode laser source for the cryogenic target layering at the Omega Laser Facility
 A stable mid-ir, GaSb-based diode laser source for the cryogenic target layering at the Omega Laser Facility A. V. Okishev 1*, D. Westerfeld 2, L. Shterengas 3, and G. Belenky 3 1 Laboratory for Laser
A stable mid-ir, GaSb-based diode laser source for the cryogenic target layering at the Omega Laser Facility A. V. Okishev 1*, D. Westerfeld 2, L. Shterengas 3, and G. Belenky 3 1 Laboratory for Laser
Investigating the Causes of and Possible Remedies for Sensor Damage in Digital Cameras Used on the OMEGA Laser Systems.
 Investigating the Causes of and Possible Remedies for Sensor Damage in Digital Cameras Used on the OMEGA Laser Systems Krysta Boccuzzi Our Lady of Mercy High School Rochester, NY Advisor: Eugene Kowaluk
Investigating the Causes of and Possible Remedies for Sensor Damage in Digital Cameras Used on the OMEGA Laser Systems Krysta Boccuzzi Our Lady of Mercy High School Rochester, NY Advisor: Eugene Kowaluk
Publications and Conference Presentations
 Publications and Conference Presentations ---------- Publications ---------- R. Betti, Y. N. Goncharov, R. L. McCrory, P. Sorotokin, and C. P. Verdon, "Self-Consistent Stability Analysis of Ablation Fronts
Publications and Conference Presentations ---------- Publications ---------- R. Betti, Y. N. Goncharov, R. L. McCrory, P. Sorotokin, and C. P. Verdon, "Self-Consistent Stability Analysis of Ablation Fronts
PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS
 PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS Publications S. Augst, D. D. Meyerhofer, J. Peatross, and C. I. Moore, "Spatial Distribution of High-Order Harmonics Generated in the Tunneling Regime," in the
PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS Publications S. Augst, D. D. Meyerhofer, J. Peatross, and C. I. Moore, "Spatial Distribution of High-Order Harmonics Generated in the Tunneling Regime," in the
Determination and Correction of Optical Distortion in Cryogenic Target Characterization
 Determination and Correction of Optical Distortion in Cryogenic Target Characterization Francis White McQuaid Jesuit High School Rochester, NY Advisors: Dana Edgell, Mark Wittman Laboratory for Laser Energetics
Determination and Correction of Optical Distortion in Cryogenic Target Characterization Francis White McQuaid Jesuit High School Rochester, NY Advisors: Dana Edgell, Mark Wittman Laboratory for Laser Energetics
Direct-Drive Implosions Using Cryogenic D2 Fuel
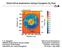 Direct-Drive Implosions Using Cryogenic D2 Fuel Distance (μm) 200 View from H11 +zω 0.0 2.6 0.5 400 600 1.0 800 1.5 1000 1200 2.4 2.2 Time (ms) 0 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.0 Y-TED 0.8 2.0 0.6 200 400 600 800
Direct-Drive Implosions Using Cryogenic D2 Fuel Distance (μm) 200 View from H11 +zω 0.0 2.6 0.5 400 600 1.0 800 1.5 1000 1200 2.4 2.2 Time (ms) 0 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.0 Y-TED 0.8 2.0 0.6 200 400 600 800
A High-Bandwidth Electrical-Waveform Generator Based on Aperture-Coupled Striplines for OMEGA Pulse-Shaping Applications
 A High-Bandwidth Electrical-Waveform Generator Based on Aperture-Coupled Striplines for OMEGA Pulse-Shaping Applications Pulsed-laser systems emit optical pulses having a temporal pulse shape characteristic
A High-Bandwidth Electrical-Waveform Generator Based on Aperture-Coupled Striplines for OMEGA Pulse-Shaping Applications Pulsed-laser systems emit optical pulses having a temporal pulse shape characteristic
PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS
 PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS Publicat ions G. F. Albrecht, "Temporal Shape Analysis of Nd:YLiF Active Mode- LockedlQ-Switched Oscillator," Opt. Commun. 41, 287-291 (1982). D. Glockerand R.
PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS Publicat ions G. F. Albrecht, "Temporal Shape Analysis of Nd:YLiF Active Mode- LockedlQ-Switched Oscillator," Opt. Commun. 41, 287-291 (1982). D. Glockerand R.
PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS
 PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS Publications S. Alexandrou, R. Sobolewski, and T. Y. Hsiang, "Bend-Induced Even and Odd Modes in Picosecond Electrical Transients Propagated ona Coplanar Waveguide,"
PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS Publications S. Alexandrou, R. Sobolewski, and T. Y. Hsiang, "Bend-Induced Even and Odd Modes in Picosecond Electrical Transients Propagated ona Coplanar Waveguide,"
Recent Developments in Ultra-High Speed and Large Area Photomultiplier Tubes
 Recent Developments in Ultra-High Speed and Large Area Photomultiplier Tubes 1, Tom Conneely and Jon Howorth Photek Ltd 26 Castleham Road, St Leonards-on-Sea, East Sussex, TN38 0NR UK E-mail: james.milnes@photek.co.uk
Recent Developments in Ultra-High Speed and Large Area Photomultiplier Tubes 1, Tom Conneely and Jon Howorth Photek Ltd 26 Castleham Road, St Leonards-on-Sea, East Sussex, TN38 0NR UK E-mail: james.milnes@photek.co.uk
A Framed Monochromatic X-Ray Microscope for ICF
 A Framed Monochromatic X-Ray Microscope for ICF The Laser Fusion Experiments Groups from the Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) and the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) have jointly developed an
A Framed Monochromatic X-Ray Microscope for ICF The Laser Fusion Experiments Groups from the Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) and the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) have jointly developed an
Spectral and Temporal Properties of Optical Signals with Multiple Sinusoidal Phase Modulations
 Spectral and Temporal Properties of Optical Signals with Multiple Sinusoidal Phase Modulations Introduction High-energy laser systems have been developed for exploring regimes of high-intensity interaction
Spectral and Temporal Properties of Optical Signals with Multiple Sinusoidal Phase Modulations Introduction High-energy laser systems have been developed for exploring regimes of high-intensity interaction
A High-Resolution X-Ray Microscope for Laser-Driven Planar-Foil Experiments
 A High-Resolution X-Ray Microscope for Laser-Driven Planar-Foil Experiments A soft x-ray microscope (E 3 kev) with high spatial resolution (~3 µm) has been characterized at LLE and used for initial experiments
A High-Resolution X-Ray Microscope for Laser-Driven Planar-Foil Experiments A soft x-ray microscope (E 3 kev) with high spatial resolution (~3 µm) has been characterized at LLE and used for initial experiments
Initial Results from the National Ignition Campaign on NIF
 Initial Results from the National Ignition Campaign on NIF Presentation to 23 rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference October 10-16, 2010 Daejeon, Republic of Korea John Lindl for the National Ignition Campaign
Initial Results from the National Ignition Campaign on NIF Presentation to 23 rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference October 10-16, 2010 Daejeon, Republic of Korea John Lindl for the National Ignition Campaign
X-Ray Radiographic System Used to Measure the Evolution of Broadband Imprint in Laser-Driven Planar Targets
 X-Ray Radiographic System Used to Measure the Evolution of Broadband Imprint in Laser-Driven Planar Targets In an inertial confinement fusion (ICF) implosion, the target is hydrodynamically unstable, and,
X-Ray Radiographic System Used to Measure the Evolution of Broadband Imprint in Laser-Driven Planar Targets In an inertial confinement fusion (ICF) implosion, the target is hydrodynamically unstable, and,
Proton core imaging of the nuclear burn in inertial confinement fusion implosions
 REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 77, 043503 2006 Proton core imaging of the nuclear burn in inertial confinement fusion implosions J. L. DeCiantis, F. H. Séguin, a J. A. Frenje, V. Berube, M. J. Canavan,
REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 77, 043503 2006 Proton core imaging of the nuclear burn in inertial confinement fusion implosions J. L. DeCiantis, F. H. Séguin, a J. A. Frenje, V. Berube, M. J. Canavan,
Evaluation of Confocal Microscopy. for Measurement of the Roughness of Deuterium Ice. Ryan Menezes. Webster Schroeder High School.
 Evaluation of Confocal Microscopy for Measurement of the Roughness of Deuterium Ice Webster Schroeder High School Webster, NY Advisor: Dr. David Harding Senior Scientist Laboratory for Laser Energetics
Evaluation of Confocal Microscopy for Measurement of the Roughness of Deuterium Ice Webster Schroeder High School Webster, NY Advisor: Dr. David Harding Senior Scientist Laboratory for Laser Energetics
OMEGA EP: High-Energy Petawatt Capability for the OMEGA Laser Facility
 OMEGA EP: High-Energy Petawatt Capability for the OMEGA Laser Facility Complete in 2007 J. Kelly, et al. University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Inertial Fusion Sciences and Applications
OMEGA EP: High-Energy Petawatt Capability for the OMEGA Laser Facility Complete in 2007 J. Kelly, et al. University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics Inertial Fusion Sciences and Applications
A Focal-Spot Diagnostic for On-Shot Characterization of High-Energy Petawatt Lasers
 A Focal-Spot Diagnostic for On-Shot Characterization of High-Energy Petawatt Lasers Introduction Knowledge of the laser focus is an essential part of accurately controlling and interpreting target experiments
A Focal-Spot Diagnostic for On-Shot Characterization of High-Energy Petawatt Lasers Introduction Knowledge of the laser focus is an essential part of accurately controlling and interpreting target experiments
Neutron Detection With Bubble Chambers
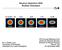 Neutron Detection With Bubble Chambers H (mrad) = (0) (0.4) (0.8) (1.6) (2.36) 50 nm 50 nm 50 nm 50 nm 50 nm M. C. Ghilea, et al. University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 47th Annual Meeting
Neutron Detection With Bubble Chambers H (mrad) = (0) (0.4) (0.8) (1.6) (2.36) 50 nm 50 nm 50 nm 50 nm 50 nm M. C. Ghilea, et al. University of Rochester Laboratory for Laser Energetics 47th Annual Meeting
Measuring Kinetics of Luminescence with TDS 744 oscilloscope
 Measuring Kinetics of Luminescence with TDS 744 oscilloscope Eex Nex Luminescence Photon E 0 Disclaimer Safety the first!!! This presentation is not manual. It is just brief set of rule to remind procedure
Measuring Kinetics of Luminescence with TDS 744 oscilloscope Eex Nex Luminescence Photon E 0 Disclaimer Safety the first!!! This presentation is not manual. It is just brief set of rule to remind procedure
High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses
 High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses Since its invention in the early 199s, 1 optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification
High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses Since its invention in the early 199s, 1 optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification
ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating
 ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating Spectral density (db) 0 10 20 30 40 Mirror VBG 1053.0 1053.3 1053.6 Wavelength (nm) Frontiers in Optics 2007/Laser
ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating Spectral density (db) 0 10 20 30 40 Mirror VBG 1053.0 1053.3 1053.6 Wavelength (nm) Frontiers in Optics 2007/Laser
Time-Multiplexed Pulse Shaping
 Time-Multiplexed Pulse Shaping Introduction Optical pulses are used to transmit information, perform remote sensing and metrology, and study physical processes in matter. These optics and photonics applications
Time-Multiplexed Pulse Shaping Introduction Optical pulses are used to transmit information, perform remote sensing and metrology, and study physical processes in matter. These optics and photonics applications
Relative Quantum Efficiency Measurements of the ROSS Streak Camera Photocathode. Alex Grammar
 Relative Quantum Efficiency Measurements of the ROSS Streak Camera Photocathode Alex Grammar Relative Quantum Efficiency Measurements of the ROSS Streak Camera Photocathode Alex Grammar Advised by Dr.
Relative Quantum Efficiency Measurements of the ROSS Streak Camera Photocathode Alex Grammar Relative Quantum Efficiency Measurements of the ROSS Streak Camera Photocathode Alex Grammar Advised by Dr.
A High-Resolution Optical Transition Radiation Diagnostic for Fast-Electron Transport Studies
 A High-Resolution Optical Transition Radiation Diagnostic for Fast-Electron Transport Studies Introduction High-current relativistic electron beams are generated by highintensity laser interactions with
A High-Resolution Optical Transition Radiation Diagnostic for Fast-Electron Transport Studies Introduction High-current relativistic electron beams are generated by highintensity laser interactions with
PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
 Becker & Hickl GmbH Kolonnenstr. 29 10829 Berlin Tel. 030 / 787 56 32 Fax. 030 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de PCSAPP.DOC PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
Becker & Hickl GmbH Kolonnenstr. 29 10829 Berlin Tel. 030 / 787 56 32 Fax. 030 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de PCSAPP.DOC PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
Development of a GaAs Photoconductive Switch for the Magneto-Inertial Fusion Electrical Discharge System. Joshua Bell
 Development of a GaAs Photoconductive Switch for the Magneto-Inertial Fusion Electrical Discharge System Joshua Bell Development of a GaAs Photoconductive Switch for the Magneto-Inertial Fusion Electrical
Development of a GaAs Photoconductive Switch for the Magneto-Inertial Fusion Electrical Discharge System Joshua Bell Development of a GaAs Photoconductive Switch for the Magneto-Inertial Fusion Electrical
Far field intensity distributions of an OMEGA laser beam were measured with
 Experimental Investigation of the Far Field on OMEGA with an Annular Apertured Near Field Uyen Tran Advisor: Sean P. Regan Laboratory for Laser Energetics Summer High School Research Program 200 1 Abstract
Experimental Investigation of the Far Field on OMEGA with an Annular Apertured Near Field Uyen Tran Advisor: Sean P. Regan Laboratory for Laser Energetics Summer High School Research Program 200 1 Abstract
Design and Performance of a Selectable-Rate Streak-Camera Deflection Ramp Generator
 Design and Performance of a Selectable-Rate Streak-Camera Deflection Ramp Generator Introduction Electro-optic streak cameras have been used at LLE for many years to resolve high-bandwidth, low-repetition-rate,
Design and Performance of a Selectable-Rate Streak-Camera Deflection Ramp Generator Introduction Electro-optic streak cameras have been used at LLE for many years to resolve high-bandwidth, low-repetition-rate,
Commissioning of Thomson Scattering on the Pegasus Toroidal Experiment
 Commissioning of Thomson Scattering on the Pegasus Toroidal Experiment D.J. Schlossberg, R.J. Fonck, L.M. Peguero, G.R. Winz University of Wisconsin-Madison 55 th Annual Meeting of the APS Division of
Commissioning of Thomson Scattering on the Pegasus Toroidal Experiment D.J. Schlossberg, R.J. Fonck, L.M. Peguero, G.R. Winz University of Wisconsin-Madison 55 th Annual Meeting of the APS Division of
PoS(PhotoDet 2012)051
 Optical to electrical detection delay in avalanche photodiode based detector and its interpretation Josef Blažej 1 E-mail: blazej@fjfi.cvut.cz Ivan Procházka Jan Kodet Technical University in Munich FSG,
Optical to electrical detection delay in avalanche photodiode based detector and its interpretation Josef Blažej 1 E-mail: blazej@fjfi.cvut.cz Ivan Procházka Jan Kodet Technical University in Munich FSG,
Silicon Photomultiplier Evaluation Kit. Quick Start Guide. Eval Kit SiPM. KETEK GmbH. Hofer Str Munich Germany.
 KETEK GmbH Hofer Str. 3 81737 Munich Germany www.ketek.net info@ketek.net phone +49 89 673 467 70 fax +49 89 673 467 77 Silicon Photomultiplier Evaluation Kit Quick Start Guide Eval Kit Table of Contents
KETEK GmbH Hofer Str. 3 81737 Munich Germany www.ketek.net info@ketek.net phone +49 89 673 467 70 fax +49 89 673 467 77 Silicon Photomultiplier Evaluation Kit Quick Start Guide Eval Kit Table of Contents
On the initiation of lightning in thunderclouds (Instrumentation, Supplementary information)
 On the initiation of lightning in thunderclouds (Instrumentation, Supplementary information) Ashot Chilingarian 1,2, Suren Chilingaryan 1, Tigran Karapetyan 1, Lev Kozliner 1, Yeghia Khanikyants 1, Gagik
On the initiation of lightning in thunderclouds (Instrumentation, Supplementary information) Ashot Chilingarian 1,2, Suren Chilingaryan 1, Tigran Karapetyan 1, Lev Kozliner 1, Yeghia Khanikyants 1, Gagik
Measure the roll-off frequency of an acousto-optic modulator
 Slide 1 Goals of the Lab: Get to know some of the properties of pin photodiodes Measure the roll-off frequency of an acousto-optic modulator Measure the cut-off frequency of a pin photodiode as a function
Slide 1 Goals of the Lab: Get to know some of the properties of pin photodiodes Measure the roll-off frequency of an acousto-optic modulator Measure the cut-off frequency of a pin photodiode as a function
Measurements of MeV Photon Flashes in Petawatt Laser Experiments
 UCRL-JC-131359 PREPRINT Measurements of MeV Photon Flashes in Petawatt Laser Experiments M. J. Moran, C. G. Brown, T. Cowan, S. Hatchett, A. Hunt, M. Key, D.M. Pennington, M. D. Perry, T. Phillips, C.
UCRL-JC-131359 PREPRINT Measurements of MeV Photon Flashes in Petawatt Laser Experiments M. J. Moran, C. G. Brown, T. Cowan, S. Hatchett, A. Hunt, M. Key, D.M. Pennington, M. D. Perry, T. Phillips, C.
Data Compression and Analysis Methods for High- Throughput Radiation Detector Systems
 1 Data Compression and Analysis Methods for High- Throughput Radiation Detector Systems John Mattingly Associate Professor, Nuclear Engineering North Carolina State University 2 Introduction The capabilities
1 Data Compression and Analysis Methods for High- Throughput Radiation Detector Systems John Mattingly Associate Professor, Nuclear Engineering North Carolina State University 2 Introduction The capabilities
GFT1504 4/8/10 channel Delay Generator
 Features 4 independent Delay Channels (10 in option) 100 ps resolution (1ps in option) 25 ps RMS jitter (channel to channel) 10 second range Channel Output pulse 6 V/50 Ω, 3 ns rise time Independent control
Features 4 independent Delay Channels (10 in option) 100 ps resolution (1ps in option) 25 ps RMS jitter (channel to channel) 10 second range Channel Output pulse 6 V/50 Ω, 3 ns rise time Independent control
Diagnosing Cross-Beam Energy Transfer Using Beamlets of Unabsorbed Light from Direct-Drive Implosions
 Diagnosing Cross-Beam Energy Transfer Using Beamlets of Unabsorbed Light from Direct-Drive Implosions Image of 351-nm light from OMEGA implosions Gated Camera D. H. Edgell University of Rochester Laboratory
Diagnosing Cross-Beam Energy Transfer Using Beamlets of Unabsorbed Light from Direct-Drive Implosions Image of 351-nm light from OMEGA implosions Gated Camera D. H. Edgell University of Rochester Laboratory
Report on BLP Spectroscopy Experiments Conducted on October 6, 2017: M. Nansteel
 Report on BLP Spectroscopy Experiments Conducted on October 6, 2017: M. Nansteel Summary Several spectroscopic measurements were conducted on October 6, 2017 at BLP to characterize the radiant power of
Report on BLP Spectroscopy Experiments Conducted on October 6, 2017: M. Nansteel Summary Several spectroscopic measurements were conducted on October 6, 2017 at BLP to characterize the radiant power of
ModBox Pulse Shaper Arbitrary Optical Waveform Generator
 Delivering Modulation Solutions ModBox The Photline Modbox-Pulse-Shaper is an Optical Modulation Unit to generate short shaped pulses with high extinction ratio at 1030 nm, 1053 nm or 1064 nm. It allows
Delivering Modulation Solutions ModBox The Photline Modbox-Pulse-Shaper is an Optical Modulation Unit to generate short shaped pulses with high extinction ratio at 1030 nm, 1053 nm or 1064 nm. It allows
Optimal Pinhole Loading via Beam Apodization. Ted Lambropoulos
 Optimal Pinhole Loading via Beam Apodization Ted Lambropoulos Optimal Pinhole Loading Via Beam Apodization Ted Lambropoulos Pittsford-Mendon High School Pittsford, NY 14534 Advisor: Dr. John Marozas Laboratory
Optimal Pinhole Loading via Beam Apodization Ted Lambropoulos Optimal Pinhole Loading Via Beam Apodization Ted Lambropoulos Pittsford-Mendon High School Pittsford, NY 14534 Advisor: Dr. John Marozas Laboratory
Performance of Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) with Frequency Conversion on the Beamlet Laser for the National Ignition Facility
 UCRL-JC-128870 PREPRINT Performance of Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) with Frequency Conversion on the Beamlet Laser for the National Ignition Facility J. E. Rothenberg, B. Moran, P. Wegner, T.
UCRL-JC-128870 PREPRINT Performance of Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) with Frequency Conversion on the Beamlet Laser for the National Ignition Facility J. E. Rothenberg, B. Moran, P. Wegner, T.
ModBox-FE-125ps-10mJ. Performance Highlights FEATURES APPLICATIONS. Electrical & Optical Pulse Diagrams
 The System-FE-1064nm is set to generate short shaped pulses with high extinction ratio at 1064.1 nm. It allows dynamic extinction ratio up to 55 db with user adjustable pulse duration, repetition rate
The System-FE-1064nm is set to generate short shaped pulses with high extinction ratio at 1064.1 nm. It allows dynamic extinction ratio up to 55 db with user adjustable pulse duration, repetition rate
Penumbral imaging with multi-penumbral-apertures and its heuristic reconstruction for nuclear reaction region diagnostics
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Penumbral imaging with multi-penumbral-apertures and its heuristic reconstruction for nuclear reaction region diagnostics To cite this article: Tatsuki Ueda et al
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Penumbral imaging with multi-penumbral-apertures and its heuristic reconstruction for nuclear reaction region diagnostics To cite this article: Tatsuki Ueda et al
Ultrashort Pulse Measurement Using High Sensitivity Two Photon Absorption Waveguide Semiconductor
 Ultrashort Pulse Measurement Using High Sensitivity Two Photon Absorption Wguide Semiconductor MOHAMMAD MEHDI KARKHANEHCHI Department of Electronics, Faculty of Engineering Razi University Taghbostan,
Ultrashort Pulse Measurement Using High Sensitivity Two Photon Absorption Wguide Semiconductor MOHAMMAD MEHDI KARKHANEHCHI Department of Electronics, Faculty of Engineering Razi University Taghbostan,
Development of dual MCP x-ray imager for 40 ~ 200 kev region
 Development of dual MCP x-ray imager for 40 ~ 200 kev region National ICF Diagnostics Working Group Meeting - October 6-8, 2015 N. Izumi, G. N. Hall, A. C. Carpenter, F. V. Allen, J. G. Cruz, B. Felker,
Development of dual MCP x-ray imager for 40 ~ 200 kev region National ICF Diagnostics Working Group Meeting - October 6-8, 2015 N. Izumi, G. N. Hall, A. C. Carpenter, F. V. Allen, J. G. Cruz, B. Felker,
Investigation Into the Electromagnetic Impulses From Long- Pulse Laser Illuminating Solid Targets Inside a Laser Facility
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 3, 16: 9 55 Investigation Into the Electromagnetic Impulses From Long- Pulse Laser Illuminating Solid s Inside a Laser Facility Tao YI 1, Jinwen YANG 1,, Ming YANG, Chuanke
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 3, 16: 9 55 Investigation Into the Electromagnetic Impulses From Long- Pulse Laser Illuminating Solid s Inside a Laser Facility Tao YI 1, Jinwen YANG 1,, Ming YANG, Chuanke
Publications and Conference Presentations
 Publications and Conference Presentations Publications S.-W. Bahk, C. Dorrer, R. G. Roides, and J. Bromage, Chromatic-Aberration Diagnostic Based on a Spectrally Resolved Lateral-Shearing Interferometer,
Publications and Conference Presentations Publications S.-W. Bahk, C. Dorrer, R. G. Roides, and J. Bromage, Chromatic-Aberration Diagnostic Based on a Spectrally Resolved Lateral-Shearing Interferometer,
HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE
 HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your High Speed Fiber Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe use and optimal
HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your High Speed Fiber Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe use and optimal
Advances in x-ray framing cameras at NIF to improve quantitative precision in x-ray imaging
 Advances in x-ray framing cameras at NIF to improve quantitative precision in x-ray imaging L. R. Benedetti, 1 J. P. Holder, 1 M. Perkins, 1,2 C. G. Brown, 1 C. S. Anderson, 1 F. V. Allen, 1 R. B. Petre,
Advances in x-ray framing cameras at NIF to improve quantitative precision in x-ray imaging L. R. Benedetti, 1 J. P. Holder, 1 M. Perkins, 1,2 C. G. Brown, 1 C. S. Anderson, 1 F. V. Allen, 1 R. B. Petre,
Radiographic sensitivity improved by optimized high resolution X -ray detector design.
 DIR 2007 - International Symposium on Digital industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography, June 25-27, 2007, Lyon, France Radiographic sensitivity improved by optimized high resolution X -ray detector
DIR 2007 - International Symposium on Digital industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography, June 25-27, 2007, Lyon, France Radiographic sensitivity improved by optimized high resolution X -ray detector
A high energy gamma camera using a multiple hole collimator
 ELSEVIER Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 353 (1994) 328-333 A high energy gamma camera using a multiple hole collimator and PSPMT SV Guru *, Z He, JC Ferreria, DK Wehe, G F Knoll
ELSEVIER Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 353 (1994) 328-333 A high energy gamma camera using a multiple hole collimator and PSPMT SV Guru *, Z He, JC Ferreria, DK Wehe, G F Knoll
3.6 An Ultra-Stable Nd:YAG-Based Laser Source. 8. Jayatna Venkataraman (private communication). ACKNOWLEDGMENT
 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was supported by the following sponsors of the Laser Fusion Feasibil~ty Project at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics-Empire State Electric Energy
ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was supported by the following sponsors of the Laser Fusion Feasibil~ty Project at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics-Empire State Electric Energy
Spot-shadowing optimization to mitigate damage growth in a high-energy-laser amplifier chain
 Spot-shadowing optimization to mitigate damage growth in a high-energy-laser amplifier chain Seung-Whan Bahk, 1, * Jonathan D. Zuegel, 1 James R. Fienup, 2 C. Clay Widmayer, 3 and John Heebner 3 1 Laboratory
Spot-shadowing optimization to mitigate damage growth in a high-energy-laser amplifier chain Seung-Whan Bahk, 1, * Jonathan D. Zuegel, 1 James R. Fienup, 2 C. Clay Widmayer, 3 and John Heebner 3 1 Laboratory
A simple and compact high-voltage switch mode power supply for streak cameras
 Meas. Sci. Technol. 7 (1996) 1668 1672. Printed in the UK DESIGN NOTE A simple and compact high-voltage switch mode power supply for streak cameras M Shukla, V N Rai and H C Pant Laser Plasma Group, Center
Meas. Sci. Technol. 7 (1996) 1668 1672. Printed in the UK DESIGN NOTE A simple and compact high-voltage switch mode power supply for streak cameras M Shukla, V N Rai and H C Pant Laser Plasma Group, Center
Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Laser
 Chapter 4 Optical-pumped Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Laser The booming laser techniques named VECSEL combine the flexibility of semiconductor band structure and advantages of solid-state
Chapter 4 Optical-pumped Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Laser The booming laser techniques named VECSEL combine the flexibility of semiconductor band structure and advantages of solid-state
Scintillation Counters
 PHY311/312 Detectors for Nuclear and Particle Physics Dr. C.N. Booth Scintillation Counters Unlike many other particle detectors, which exploit the ionisation produced by the passage of a charged particle,
PHY311/312 Detectors for Nuclear and Particle Physics Dr. C.N. Booth Scintillation Counters Unlike many other particle detectors, which exploit the ionisation produced by the passage of a charged particle,
NON-AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE
 NON-AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Non-amplified High Speed Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe
NON-AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Non-amplified High Speed Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe
A NEW MULTI-POINT, MULTI-PULSE THOMSON SCATTERING SYSTEM FOR THE MST RFP
 A NEW MULTI-POINT, MULTI-PULSE THOMSON SCATTERING SYSTEM FOR THE MST RFP D. J. HOLLY, P. ANDREW, and D. J. DEN HARTOG Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Madison, 1150 University Avenue, Madison,
A NEW MULTI-POINT, MULTI-PULSE THOMSON SCATTERING SYSTEM FOR THE MST RFP D. J. HOLLY, P. ANDREW, and D. J. DEN HARTOG Department of Physics, University of Wisconsin Madison, 1150 University Avenue, Madison,
Quantum-Well Semiconductor Saturable Absorber Mirror
 Chapter 3 Quantum-Well Semiconductor Saturable Absorber Mirror The shallow modulation depth of quantum-dot saturable absorber is unfavorable to increasing pulse energy and peak power of Q-switched laser.
Chapter 3 Quantum-Well Semiconductor Saturable Absorber Mirror The shallow modulation depth of quantum-dot saturable absorber is unfavorable to increasing pulse energy and peak power of Q-switched laser.
SPM Series Quick Start Experiment Guide Rev.1.0, May 2011
 Experiment Guide Rev.1.0, May 2011 This document will assist a new user of SPM detectors to make observations and measurements that will verify that the detector is set-up and functioning correctly. The
Experiment Guide Rev.1.0, May 2011 This document will assist a new user of SPM detectors to make observations and measurements that will verify that the detector is set-up and functioning correctly. The
The KrF alternative for fast ignition inertial fusion
 The KrF alternative for fast ignition inertial fusion IstvánB Földes 1, Sándor Szatmári 2 Students: A. Barna, R. Dajka, B. Gilicze, Zs. Kovács 1 Wigner Research Centre of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences,
The KrF alternative for fast ignition inertial fusion IstvánB Földes 1, Sándor Szatmári 2 Students: A. Barna, R. Dajka, B. Gilicze, Zs. Kovács 1 Wigner Research Centre of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences,
PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS
 PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS Publications S. Alexandrou, C.-C. Wang, T. Y. Hsiang, M. Y. Liu. and S. Y. Chou, "A 75-GHz Silicon Metal-Sen~iconductor-Metal Schottky Photodiode," Appl. Phys.
PUBLICATIONS AND CONFERENCE PRESENTATIONS Publications S. Alexandrou, C.-C. Wang, T. Y. Hsiang, M. Y. Liu. and S. Y. Chou, "A 75-GHz Silicon Metal-Sen~iconductor-Metal Schottky Photodiode," Appl. Phys.
Plasma Sheath Velocity and Pinch Phenomenal Measurements in TPF-II Plasma Focus Device
 Plasma Sheath Velocity and Pinch Phenomenal Measurements in TPF-II Plasma Focus Device Arlee Tamman PE wave : Center of Excellence in Plasma Science and Electromagnetic Wave Walailak University, THAILAND
Plasma Sheath Velocity and Pinch Phenomenal Measurements in TPF-II Plasma Focus Device Arlee Tamman PE wave : Center of Excellence in Plasma Science and Electromagnetic Wave Walailak University, THAILAND
THE NATIONAL IGNITION FACILITY: STATUS AND PLANS FOR LASER FUSION AND HIGH-ENERGY-DENSITY EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES
 TUAI001 THE NATIONAL IGNITION FACILITY: STATUS AND PLANS FOR LASER FUSION AND HIGH-ENERGY-DENSITY EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES E.I. Moses LLNL, Livermore, CA 94550, USA Abstract The National Ignition Facility
TUAI001 THE NATIONAL IGNITION FACILITY: STATUS AND PLANS FOR LASER FUSION AND HIGH-ENERGY-DENSITY EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES E.I. Moses LLNL, Livermore, CA 94550, USA Abstract The National Ignition Facility
1.0-MJ CH-Foam Ignition Targets on the NIF Using 1-D MultiFM SSD with 0.5 THz of Bandwidth
 -MJ CH-Foam Ignition Targets on the NIF Using 1-D MultiFM SSD with.5 THz of Bandwidth -MJ CH-foam target; end of acceleration 4 1-D SSD, 1.8 Å 1-D MultiFM, 6 Å (1/2 THz) 2-D SSD, 11 Å Density (g/cm 3 )
-MJ CH-Foam Ignition Targets on the NIF Using 1-D MultiFM SSD with.5 THz of Bandwidth -MJ CH-foam target; end of acceleration 4 1-D SSD, 1.8 Å 1-D MultiFM, 6 Å (1/2 THz) 2-D SSD, 11 Å Density (g/cm 3 )
1.1 The Muon Veto Detector (MUV)
 1.1 The Muon Veto Detector (MUV) 1.1 The Muon Veto Detector (MUV) 1.1.1 Introduction 1.1.1.1 Physics Requirements and General Layout In addition to the straw chambers and the RICH detector, further muon
1.1 The Muon Veto Detector (MUV) 1.1 The Muon Veto Detector (MUV) 1.1.1 Introduction 1.1.1.1 Physics Requirements and General Layout In addition to the straw chambers and the RICH detector, further muon
TRINAT Amplifier-Shaper for Silicon Detector (TASS)
 Sept. 8, 20 L. Kurchaninov TRINAT Amplifier-Shaper for Silicon Detector (TASS). General description Preamplifier-shaper for TRINAT Si detector (Micron model BB) is charge-sensitive amplifier followed by
Sept. 8, 20 L. Kurchaninov TRINAT Amplifier-Shaper for Silicon Detector (TASS). General description Preamplifier-shaper for TRINAT Si detector (Micron model BB) is charge-sensitive amplifier followed by
The Argonne 6cm MCP-PMT System. Bob Wagner for Argonne LAPPD Collaboration ANNIE Collaboration Meeting Monday 27 Oct 2014
 The Argonne 6cm MCP-PMT System Bob Wagner for Argonne LAPPD Collaboration ANNIE Collaboration Meeting Monday 27 Oct 2014 Thanks to Argonne Postdocs Junqi Xie (photocathode) & Jingbo Wang (analysis) for
The Argonne 6cm MCP-PMT System Bob Wagner for Argonne LAPPD Collaboration ANNIE Collaboration Meeting Monday 27 Oct 2014 Thanks to Argonne Postdocs Junqi Xie (photocathode) & Jingbo Wang (analysis) for
Scintillators as an external trigger for cathode strip chambers
 Scintillators as an external trigger for cathode strip chambers J. A. Muñoz Department of Physics, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 An external trigger was set up to test cathode strip chambers
Scintillators as an external trigger for cathode strip chambers J. A. Muñoz Department of Physics, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 An external trigger was set up to test cathode strip chambers
High Energy Density Physics in the NNSA
 NATIONAL NUCLEAR SECURITY ADMINISTRATION OFFICE OF DEFENSE PROGRAMS High Energy Density Physics in the NNSA Presented to: National Academy of Sciences Board on Physics and Astronomy Spring Meeting Washington,
NATIONAL NUCLEAR SECURITY ADMINISTRATION OFFICE OF DEFENSE PROGRAMS High Energy Density Physics in the NNSA Presented to: National Academy of Sciences Board on Physics and Astronomy Spring Meeting Washington,
Laser Science and Technology at LLE
 Laser Science and Technology at LLE Nd:glass High energy Electrical Yb:YAG High peak power Mechanical OPCPA High average power Eye injuries OPO Exotic wavelengths Fire J. Bromage Group Leader, Sr. Scientist
Laser Science and Technology at LLE Nd:glass High energy Electrical Yb:YAG High peak power Mechanical OPCPA High average power Eye injuries OPO Exotic wavelengths Fire J. Bromage Group Leader, Sr. Scientist
A high-performance, low-cost, leading edge discriminator
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 2 journal of August 2005 physics pp. 273 283 A high-performance, low-cost, leading edge discriminator S K GUPTA a, Y HAYASHI b, A JAIN a, S KARTHIKEYAN
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 2 journal of August 2005 physics pp. 273 283 A high-performance, low-cost, leading edge discriminator S K GUPTA a, Y HAYASHI b, A JAIN a, S KARTHIKEYAN
NLUF. National Laser Users Facility. Users Guide
 NLUF National Laser Users Facility Users Guide Telephone Directory Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) Robert L. McCrory (Laboratory Director, LLE)...(585) 275-4973 David D. Meyerhofer (Director, Experimental
NLUF National Laser Users Facility Users Guide Telephone Directory Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) Robert L. McCrory (Laboratory Director, LLE)...(585) 275-4973 David D. Meyerhofer (Director, Experimental
Improvement in High-Frequency Properties of Beam Halo Monitor using Diamond Detectors for SPring-8 XFEL
 32 nd International Free Electron Laser Conference FEL 2010 Improvement in High-Frequency Properties of Beam Halo Monitor using Diamond Detectors for SPring-8 XFEL August 26, 2010 Thursday, THOC4 1 Hideki
32 nd International Free Electron Laser Conference FEL 2010 Improvement in High-Frequency Properties of Beam Halo Monitor using Diamond Detectors for SPring-8 XFEL August 26, 2010 Thursday, THOC4 1 Hideki
Time-of-flight PET with SiPM sensors on monolithic scintillation crystals Vinke, Ruud
 University of Groningen Time-of-flight PET with SiPM sensors on monolithic scintillation crystals Vinke, Ruud IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
University of Groningen Time-of-flight PET with SiPM sensors on monolithic scintillation crystals Vinke, Ruud IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you
A novel High Average Power High Brightness Soft X-ray Source using a Thin Disk Laser System for optimized Laser Produced Plasma Generation
 A novel High Average Power High Brightness Soft X-ray Source using a Thin Disk Laser System for optimized Laser Produced Plasma Generation I. Mantouvalou, K. Witte, R. Jung, J. Tümmler, G. Blobel, H. Legall,
A novel High Average Power High Brightness Soft X-ray Source using a Thin Disk Laser System for optimized Laser Produced Plasma Generation I. Mantouvalou, K. Witte, R. Jung, J. Tümmler, G. Blobel, H. Legall,
Diagnostic development to measure parallel wavenumber of lower hybrid waves on Alcator C-Mod
 Diagnostic development to measure parallel wavenumber of lower hybrid waves on Alcator C-Mod S. G. Baek, T. Shinya*, G. M. Wallace, S. Shiraiwa, R. R. Parker, Y. Takase*, D. Brunner MIT Plasma Science
Diagnostic development to measure parallel wavenumber of lower hybrid waves on Alcator C-Mod S. G. Baek, T. Shinya*, G. M. Wallace, S. Shiraiwa, R. R. Parker, Y. Takase*, D. Brunner MIT Plasma Science
Progress in the science and technology of direct drive laser fusion with the KrF laser
 Progress in the science and technology of direct drive laser fusion with the KrF laser Fusion Power Associates Meeting 1 December 2010 Presented by: Steve Obenschain Plasma Physics Division U.S. Naval
Progress in the science and technology of direct drive laser fusion with the KrF laser Fusion Power Associates Meeting 1 December 2010 Presented by: Steve Obenschain Plasma Physics Division U.S. Naval
Suppression of FM-to-AM conversion in third-harmonic. generation at the retracing point of a crystal
 Suppression of FM-to-AM conversion in third-harmonic generation at the retracing point of a crystal Yisheng Yang, 1,,* Bin Feng, Wei Han, Wanguo Zheng, Fuquan Li, and Jichun Tan 1 1 College of Science,
Suppression of FM-to-AM conversion in third-harmonic generation at the retracing point of a crystal Yisheng Yang, 1,,* Bin Feng, Wei Han, Wanguo Zheng, Fuquan Li, and Jichun Tan 1 1 College of Science,
GFT1012 2/4 Channel Precise Slave Generator
 Features Two Independent Delay Channels (Four channels available as an option) 1 ps Time Resolution < 5 ps RMS Jitter (Slave-to-Slave) < 6 ps / C Drift (Slave-to-slave) 1 Second Range Output Pulse Up to
Features Two Independent Delay Channels (Four channels available as an option) 1 ps Time Resolution < 5 ps RMS Jitter (Slave-to-Slave) < 6 ps / C Drift (Slave-to-slave) 1 Second Range Output Pulse Up to
NIF Target Diagnostic Automated Analysis: Operations & Calibrations
 NIF Target Diagnostic Automated Analysis: Operations & Calibrations Presentation to 14 th International Conference on Accelerator & Large Experimental Physics Control Systems (ICALEPCS) October 6-11, 2013
NIF Target Diagnostic Automated Analysis: Operations & Calibrations Presentation to 14 th International Conference on Accelerator & Large Experimental Physics Control Systems (ICALEPCS) October 6-11, 2013
High Data Rate Characterization Report
 High Data Rate Characterization Report ERDP-013-39.37-TTR-STL-1-D Mated with: ERF8-013-05.0-S-DV-DL-L and ERM8-013-05.0-S-DV-DS-L Description: Edge Rate Twin-Ax Cable Assembly, 0.8mm Pitch Samtec, Inc.
High Data Rate Characterization Report ERDP-013-39.37-TTR-STL-1-D Mated with: ERF8-013-05.0-S-DV-DL-L and ERM8-013-05.0-S-DV-DS-L Description: Edge Rate Twin-Ax Cable Assembly, 0.8mm Pitch Samtec, Inc.
Dark current Monitor for the European XFEL D. Lipka, W. Kleen, J. Lund-Nielsen, D. Nölle, S. Vilcins, V. Vogel; DESY Hamburg
 Dark current Monitor for the European XFEL D. Lipka, W. Kleen, J. Lund-Nielsen, D. Nölle, S. Vilcins, V. Vogel; DESY Hamburg Content 2 Dark current Principle of detecting weakly charged bunches with resonator
Dark current Monitor for the European XFEL D. Lipka, W. Kleen, J. Lund-Nielsen, D. Nölle, S. Vilcins, V. Vogel; DESY Hamburg Content 2 Dark current Principle of detecting weakly charged bunches with resonator
Fast first practical help -- detailed instructions will follow- preliminary Experiment F80
 Fast first practical help -- detailed instructions will follow- preliminary Experiment F80 Measurement Methods of Nuclear and Particle Physics Introduction: This experiment is going to introduce you to
Fast first practical help -- detailed instructions will follow- preliminary Experiment F80 Measurement Methods of Nuclear and Particle Physics Introduction: This experiment is going to introduce you to
Resonance and damping characteristics of cryogenic fusion targets
 Resonance and damping characteristics of cryogenic fusion targets Harvest Zhang Brighton High School Rochester, NY Advisor: Mr. L. D. Lund Laboratory for Laser Energetics University of Rochester Rochester,
Resonance and damping characteristics of cryogenic fusion targets Harvest Zhang Brighton High School Rochester, NY Advisor: Mr. L. D. Lund Laboratory for Laser Energetics University of Rochester Rochester,
Performance of Microchannel Plates Fabricated Using Atomic Layer Deposition
 Performance of Microchannel Plates Fabricated Using Atomic Layer Deposition Andrey Elagin on behalf of the LAPPD collaboration Introduction Performance (timing) Conclusions Large Area Picosecond Photo
Performance of Microchannel Plates Fabricated Using Atomic Layer Deposition Andrey Elagin on behalf of the LAPPD collaboration Introduction Performance (timing) Conclusions Large Area Picosecond Photo
This is an author-deposited version published in: Eprints ID: 7969
 Open Archive Toulouse Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and makes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Open Archive Toulouse Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and makes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Study of Silicon Photomultipliers for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Application
 Study of Silicon Photomultipliers for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Application Eric Oberla 5 June 29 Abstract A relatively new photodetector, the silicon photomultiplier (SiPM), is well suited for
Study of Silicon Photomultipliers for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Application Eric Oberla 5 June 29 Abstract A relatively new photodetector, the silicon photomultiplier (SiPM), is well suited for
Characterization of a prototype matrix of Silicon PhotoMultipliers (SiPM s)
 Characterization of a prototype matrix of Silicon PhotoMultipliers (SiPM s) N. Dinu, P. Barrillon, C. Bazin, S. Bondil-Blin, V. Chaumat, C. de La Taille, V. Puill, JF. Vagnucci Laboratory of Linear Accelerator
Characterization of a prototype matrix of Silicon PhotoMultipliers (SiPM s) N. Dinu, P. Barrillon, C. Bazin, S. Bondil-Blin, V. Chaumat, C. de La Taille, V. Puill, JF. Vagnucci Laboratory of Linear Accelerator
Appendix A: Specifications
 All specifications apply to the TDS 200-Series Digital Oscilloscopes and a P2100 probe with the Attenuation switch set to 10X unless noted otherwise. To meet specifications, two conditions must first be
All specifications apply to the TDS 200-Series Digital Oscilloscopes and a P2100 probe with the Attenuation switch set to 10X unless noted otherwise. To meet specifications, two conditions must first be
GFT Channel Digital Delay Generator
 Features 20 independent delay Channels 100 ps resolution 25 ps rms jitter 10 second range Output pulse up to 6 V/50 Ω Independent trigger for every channel Four triggers Three are repetitive from three
Features 20 independent delay Channels 100 ps resolution 25 ps rms jitter 10 second range Output pulse up to 6 V/50 Ω Independent trigger for every channel Four triggers Three are repetitive from three
Optoelectronic integrated circuits incorporating negative differential resistance devices
 Optoelectronic integrated circuits incorporating negative differential resistance devices José Figueiredo Centro de Electrónica, Optoelectrónica e Telecomunicações Departamento de Física da Faculdade de
Optoelectronic integrated circuits incorporating negative differential resistance devices José Figueiredo Centro de Electrónica, Optoelectrónica e Telecomunicações Departamento de Física da Faculdade de
Radiation Detection Instrumentation
 Radiation Detection Instrumentation Principles of Detection and Gas-filled Ionization Chambers Neutron Sensitive Ionization Chambers Detection of radiation is a consequence of radiation interaction with
Radiation Detection Instrumentation Principles of Detection and Gas-filled Ionization Chambers Neutron Sensitive Ionization Chambers Detection of radiation is a consequence of radiation interaction with
Specification. CTR 2 ESD calibration target
 Specification CTR 2 ESD calibration target IEC 61000-4-2 IEC 61000-4-2 77B/378/CDV ISO CD 10605 N1347 The CTR 2 is a coaxial current target to monitor Electro Static Discharges as required in the draft
Specification CTR 2 ESD calibration target IEC 61000-4-2 IEC 61000-4-2 77B/378/CDV ISO CD 10605 N1347 The CTR 2 is a coaxial current target to monitor Electro Static Discharges as required in the draft
Application Note AN-10 Copyright December, 2000
 Eye Diagrams of PSPL Coaxial Components James R. Andrews, Ph.D., IEEE Fellow & PSPL Founder PSPL has been designing and selling extremely broadband coaxial components since our founding in 1980. These
Eye Diagrams of PSPL Coaxial Components James R. Andrews, Ph.D., IEEE Fellow & PSPL Founder PSPL has been designing and selling extremely broadband coaxial components since our founding in 1980. These
ModBox-PG-795nm-30ps 795 nm 30 ps Optical Pulse Generator
 The Modbox-PG-795nm-30ps is a very high extinction ratio optical Pulse Generator operating in the 800nm-Band and firstly optimized at 795 nm. The -PG-795nm allows very high dynamic extinction ratio from
The Modbox-PG-795nm-30ps is a very high extinction ratio optical Pulse Generator operating in the 800nm-Band and firstly optimized at 795 nm. The -PG-795nm allows very high dynamic extinction ratio from
