Suppression of FM-to-AM conversion in third-harmonic. generation at the retracing point of a crystal
|
|
|
- Whitney Shields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Suppression of FM-to-AM conversion in third-harmonic generation at the retracing point of a crystal Yisheng Yang, 1,,* Bin Feng, Wei Han, Wanguo Zheng, Fuquan Li, and Jichun Tan 1 1 College of Science, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha , China Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 61900, China * Corresponding author: ysyang@nudt.edu.cn FM-to-AM conversion can cause many negative effects (e.g., reducing of margin against damage to the optics, and etc.) on performances of third-harmonic conversion system. In this letter, the FM-to-AM conversion effect in third-harmonic generation is investigated both at and away from the retracing point of type-ii KDP crystal. Obtained results indicate that the FM-to-AM conversion can be suppressed effectively when the crystal works at the retracing point. OCIS codes: , , In broadband third-harmonic generation (THG), phase modulation (i.e., frequency modulation, FM) of input field can be converted to intensity modulation (i.e., amplitude modulation, AM) of output harmonic field, which is called as the FM-to-AM conversion [1]. Generally, this conversion adversely affects the laser performance, and needs to be prevented. The resulting AM can cause damage to optical elements slightly outside the near-field (e.g., image relay optics), or may lead to some higher-order nonlinear effects due to instantaneous ultra-high intensity in process [, 3]. 1
2 With the purpose of weakening or averaging the resulting AM, some specific approaches were proposed. For example, plane gratings (NIF configuration) or focusing gratings (LMJ configuration) are introduced in the SSD (smoothing by spectral dispersion) systems, and have been demonstrated to be able to reduce the AM strongly [4, 5]. As well, adding a second mixer to the baseline configuration (i.e., one doubler followed by one mixer) can lower the resulting AM to some certain extent [6]. In this letter, the issue of FM-to-AM conversion in the THG process is investigated from the viewpoint of retracing properties of nonlinear crystal, and a criterion to suppress the FM-to-AM conversion purposely is also presented. Retracing point refers to the point or wavelength of a phase-matching curve (phase-matching angle θ PM versus wavelength λ) at which slope vanishes, as the point R shown in Fig. 1. It has the characteristic of zero group-velocity-mismatch (i.e., the first-order wavelength-sensitivity of phase-mismatch ( K ) Δ λ equals to zero at the retracing point.) [7]. According to Ref. [8], the THG retracing point corresponds to a special group-velocity-matching (GVM) relationship of 3 = 1 +, where υ 1, υ, and υ 3 υ3 υ1 υ are the group-velocities of 1ω, ω, and 3ω pulses propagating in crystal, respectively, as presented in Fig. 1. For third-harmonic generation of sinusoidally phase-modulated Gaussian pulses, the input amplitude profile E () t can be written in the following form: t E() t = E0 exp exp i sin σ ( πω t) T, (1) 0 where E 0 is original amplitude which is equal to I0 ncε 0, and T 0, σ, and Ω are the pulse duration (i.e., half-width at 1/e intensity), modulation amplitude, and modulation frequency, respectively. Optical spectrum of the sinusoidal phase modulation exp iσsin ( π t) Ω can be
3 given by a sum over Bessel functions (i.e., J ( σδ ) ( f nω) n= n ), which has a frequency bandwidth (FWHM) of about σω [9]. Based on the split-step Fourier transform and the fourth-order Runge-Kutta algorithm, the THG process in type-ii KDP crystal is numerically investigated in two cases: at the retracing point and away from the retracing point (i.e., group-velocity matched and group-velocity mismatched cases). In accordance with Fig. 1, we refer to the above two cases as line n and line m, respectively. For better comparison of conversion performances in above two cases, both input 1ω wavelengths in simulation are set to be μm. For the line m case, group-velocities of three waves can be easily obtained through the Sellmeier equations of KDP crystal (i.e., m/s, υ = m/s, and υ = m/s) [10]. υ 1 = While for the other case, just substitute the value of υ by m/s to satisfy the special 3 GVM relationship 3 = 1 + υ υ υ. Values of other basic parameters of the input 1ω and ω 3 1 pulses in simulation are given in Table 1. Figs. and 3 compare the intensity temporal profiles of the three output harmonics in above two cases. We find that, the intensity profiles in Fig. are severely modulated while curves of Fig. 3 appear to be much smoother, which implies that the FM-to-AM conversion in the THG process can be suppressed effectively provided the nonlinear crystal works at its THG retracing point. Such suppression of the FM-to-AM conversion can be interpreted via f in out in the spectrum contrast defined by I ( f ) I ( ), where I ( f ) and I ( f ) are the spectrum intensity of input and output fields, respectively. Fig. 4 gives the spectrum contrast of 1ω pulses in the two cases. It can be seen that, working at the retracing point, the shape of spectrum contrast is symmetrically distributed and centralized while it is asymmetric and dispersed in the case of working away from the retracing point. According to the definition in ( ) ( ) I f I f, value of the spectrum contrast is inversely proportional to the output (i.e., out out 3
4 residual for 1ω pulse) spectrum intensity, and thereby is proportional to the conversion efficiency. Compared with the chaotic spectrum contrast in the line m case, the regular one in the case of line n reflects that the optical spectrum of pulse are almost not filtered when the crystal operates at its THG retracing point [4]. To quantitatively compare the FM-to-AM conversion in above two cases, an index α is introduced to evaluate the distortion of resulting AM, which is defined by the following expression [5]: α = max min I I I max + I min. () where I and I are the maximum and minimum value of pulse intensity at the time max min scale of [-T 0 /100, T 0 /100], respectively. α ranges from 0 to, and is ideally equal to 0 (namely, no intensity modulation). Fig. 5 shows the dependence of α on the bandwidth of 1ω pulse in the cases of line m and line n. Numerical result reveals that the distortion of the resulting AM increases much slower (See the curve marked red star) when the crystal works at the retracing point. In addition, for a given distortion index α, the acceptable fundamental bandwidth can be dramatically extended while working at the retracing point. In conclusion, the FM-to-AM conversion in the process of THG can be suppressed successfully through adopting crystals with appropriate THG retracing point (or in other words, by satisfying the special group-velocity-matching relationship 3 = 1 + υ υ υ [8]), 3 1 which gives theoretical guidance for the suppression of AM in practical applications. This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China ( ), Science and Technology Foundation of Chinese State Key Laboratory of High Temperature and Density Plasma Physics (9140C ), and Development Foundation of China Academy of Engineering Physics (008B ). References 4
5 1. J. E. Rothenberg, D. F. Browning, and R. B. Wilcox, Issue of FM to AM conversion on the national ignition facility, Proc. SPIE 349, (1999).. J. A. Marozas, Self- and cross-phase modulation of high-intensity laser beams emerging from a diamond-turned KDP wedge, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 19, 75-8 (00). 3. S. Skupsky, R. W. Short, T. Kessler, R. S. Craxton, S. Letzring, and J. M. Soures, Improved laser-beam uniformity using the angular dispersion of frequency-modulated light, J. Appl. Phys. 66, (1989). 4. J. D. Eimerl, J. M. Auerbach, C. E. Barker, D. Milam, and P. W. Milonni, Multicrystal designs for efficient third-harmonic generation, Opt. Lett., (1997). 5. S. Hocquet, D. Penninckx, E. bordenave, C. Gouedard, and Y. Jaouen, FM-to-AM conversion in high-power lasers, Appl. Opt. 47, (008). 6. S. Hocquet, G. Lacroix, and D. Penninckx, Compensation of frequency modulation to amplitude modulation conversion in frequency conversion systems, Appl. Opt. 48, (009). 7. M. S. Webb, D. Eimerl, and S. P. Velsko, Wavelength insensitive phase-matched second-harmonic generation in partially deuterated KDP, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 9, (199). 8. Y. Yang, W. Zheng, W. Han, Y. Che, J. Tan, Y. Xiang, and H. Jia, Group-velocity-matching relationship in the mixing process of broadband third-harmonic generation, Acta Physica Sinica 56, (007). 9. R. Boyd, Nonlinear Optics, nd ed. (Academic, 00). 10. K. W. Kirby and L. G. DeShazer, Refractive indices of 14 nonlinear crystals isomorphic KH PO 4, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 4, (1987). 5
6 Figures and Figure Captions Fig. 1. Phase-matching curve (blue) and group-velocity curves (red) of type-ii KDP mixer. The retracing point R just corresponds with the crossing point O of group-velocity curves at λ 1ω = 1.577μm. Phase-Matching Angle θ PM ( deg) m 3/υ 3 λ=1.053μm O R n /υ +1/υ Reciprocal of Group-Velocity (10-8 s/m) Fundamental Wavelength λ 1ω (mm) Fig.. Temporal profiles of output harmonic pulses in line m case. Propagation length in KDP crystal is 6 mm. Intensity Profile (W/m ) 1.x ω ω 1.0x ω 8.0x x x x Time (ns) 6
7 Fig. 3. Temporal profiles of output harmonic pulses in line n case. Propagation length in KDP crystal is 16 mm. Intensity profile (W/cm ) 1.6x ω ω 3ω 1.x x x Time (ns) Fig. 4. Spectrum contrast of 1ω pulse in the cases of line m and line n (a) "line m" case Spectrum contrast of 1ω wavelength λ (μm) 4.5x x10 4 (b) "line n" case Spectrum contrast of 1ω 3.5x x10 4.5x10 4.0x x x x wavelength λ (μm) 7
8 Fig. 5. Dependence of distortion index α on the phase-modulated bandwidth of 1ω pulse in the cases of line m and line n line m line n Distortion Index α frequency bandwidth of 1ω σω (GHz) Tables Table 1. Values of basic parameters of input 1ω and ω pulses Peak Intensity Pulse Duration Modulation Amplitude Modulation Frequency Frequency Bandwidth I 0 (GW/cm ) T 0 (ns) σ Ω (GHz) σω (GHz) 1ω/1.053 μm ω/0.57 μm
Performance of Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) with Frequency Conversion on the Beamlet Laser for the National Ignition Facility
 UCRL-JC-128870 PREPRINT Performance of Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) with Frequency Conversion on the Beamlet Laser for the National Ignition Facility J. E. Rothenberg, B. Moran, P. Wegner, T.
UCRL-JC-128870 PREPRINT Performance of Smoothing by Spectral Dispersion (SSD) with Frequency Conversion on the Beamlet Laser for the National Ignition Facility J. E. Rothenberg, B. Moran, P. Wegner, T.
Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse
 Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse Nan Yang 1, Hai-Wei Du * 1 Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry of Education) and Department of Physics, Shanghai Jiaotong
Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse Nan Yang 1, Hai-Wei Du * 1 Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry of Education) and Department of Physics, Shanghai Jiaotong
Frequency-doubling broadband light in multiple crystals
 Alford and Smith Vol. 18, No. 4/April 2001/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 515 Frequency-doubling broadband light in multiple crystals William J. Alford and Arlee V. Smith Department 1118, Lasers, Optics and Remote
Alford and Smith Vol. 18, No. 4/April 2001/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 515 Frequency-doubling broadband light in multiple crystals William J. Alford and Arlee V. Smith Department 1118, Lasers, Optics and Remote
A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier
 Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2004 Vol.47 No.6 767 772 767 A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier ZHU Heyuan, XU Guang, WANG Tao, QIAN Liejia & FAN Dianyuan State
Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2004 Vol.47 No.6 767 772 767 A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier ZHU Heyuan, XU Guang, WANG Tao, QIAN Liejia & FAN Dianyuan State
Modeling Characterization of the National Ignition Facility Focal Spot
 UCRL-JC-12797 PREPRINT Modeling Characterization of the National Ignition Facility Focal Spot W. H. Williams J. M. Auerbach M. A. Henesian J. K. Lawson J. T. Hunt R. A. Sacks C. C. Widmayer This paper
UCRL-JC-12797 PREPRINT Modeling Characterization of the National Ignition Facility Focal Spot W. H. Williams J. M. Auerbach M. A. Henesian J. K. Lawson J. T. Hunt R. A. Sacks C. C. Widmayer This paper
High Average Power Frequency Conversion on the Mercury Laser
 UCRL-POST-213237 High Average Power Frequency Conversion on the Laser Zhi M. Liao, Christopher Ebbers, Andy Bayramian, Mike Benapfl, Barry Freitas, Bob Kent, Dave van Lue, Kathleen Schaffers, Steve Telford,
UCRL-POST-213237 High Average Power Frequency Conversion on the Laser Zhi M. Liao, Christopher Ebbers, Andy Bayramian, Mike Benapfl, Barry Freitas, Bob Kent, Dave van Lue, Kathleen Schaffers, Steve Telford,
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Comprehensive Numerical Modelling of a Low-Gain Optical Parametric Amplifier as a Front-End Contrast Enhancement Unit
 Comprehensive Numerical Modelling of a Low-Gain Optical Parametric Amplifier as a Front-End Contrast Enhancement Unit arxiv:161.5558v1 [physics.optics] 21 Jan 216 A. B. Sharba, G. Nersisyan, M. Zepf, M.
Comprehensive Numerical Modelling of a Low-Gain Optical Parametric Amplifier as a Front-End Contrast Enhancement Unit arxiv:161.5558v1 [physics.optics] 21 Jan 216 A. B. Sharba, G. Nersisyan, M. Zepf, M.
Incident IR Bandwidth Effects on Efficiency and Shaping for Third Harmonic Generation of Quasi-Rectangular UV Longitudinal Profiles *
 LCLS-TN-05-29 Incident IR Bandwidth Effects on Efficiency and Shaping for Third Harmonic Generation of Quasi-Rectangular UV Longitudinal Profiles * I. Introduction Paul R. Bolton and Cecile Limborg-Deprey,
LCLS-TN-05-29 Incident IR Bandwidth Effects on Efficiency and Shaping for Third Harmonic Generation of Quasi-Rectangular UV Longitudinal Profiles * I. Introduction Paul R. Bolton and Cecile Limborg-Deprey,
The Effect of Radiation Coupling in Higher Order Fiber Bragg Gratings
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 3, NO. 4, 27 462 The Effect of Radiation Coupling in Higher Order Fiber Bragg Gratings Li Yang 1, Wei-Ping Huang 2, and Xi-Jia Gu 3 1 Department EEIS, University of Science and Technology
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 3, NO. 4, 27 462 The Effect of Radiation Coupling in Higher Order Fiber Bragg Gratings Li Yang 1, Wei-Ping Huang 2, and Xi-Jia Gu 3 1 Department EEIS, University of Science and Technology
A STUDY OF AM AND FM SIGNAL RECEPTION OF TIME MODULATED LINEAR ANTENNA ARRAYS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 171 181, 2009 A STUDY OF AM AND FM SIGNAL RECEPTION OF TIME MODULATED LINEAR ANTENNA ARRAYS G.Li,S.Yang,Z.Zhao,andZ.Nie Department of Microwave Engineering
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 171 181, 2009 A STUDY OF AM AND FM SIGNAL RECEPTION OF TIME MODULATED LINEAR ANTENNA ARRAYS G.Li,S.Yang,Z.Zhao,andZ.Nie Department of Microwave Engineering
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
Fundamental Optics ULTRAFAST THEORY ( ) = ( ) ( q) FUNDAMENTAL OPTICS. q q = ( A150 Ultrafast Theory
 ULTRAFAST THEORY The distinguishing aspect of femtosecond laser optics design is the need to control the phase characteristic of the optical system over the requisite wide pulse bandwidth. CVI Laser Optics
ULTRAFAST THEORY The distinguishing aspect of femtosecond laser optics design is the need to control the phase characteristic of the optical system over the requisite wide pulse bandwidth. CVI Laser Optics
Lecture 10. Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers
 Lecture 10 Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide Dispersions Step-Index Fiber, Multimode and Single Mode Fibers Numerical Aperture, Coupling
Lecture 10 Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide Dispersions Step-Index Fiber, Multimode and Single Mode Fibers Numerical Aperture, Coupling
STUDIES OF INTERACTION OF PARTIALLY COHERENT LASER RADIATION WITH PLASMA
 STUDIES OF INTERACTION OF PARTIALLY COHERENT LASER RADIATION WITH PLASMA Alexander N. Starodub Deputy Director N.G.Basov Institute of Quantum Radiophysics of P.N.Lebedev Physical Institute of the RAS Leninsky
STUDIES OF INTERACTION OF PARTIALLY COHERENT LASER RADIATION WITH PLASMA Alexander N. Starodub Deputy Director N.G.Basov Institute of Quantum Radiophysics of P.N.Lebedev Physical Institute of the RAS Leninsky
Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses
 Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses Table of Contents 1. Theory 2. Pulse propagation through various materials o Calculating the index of refraction Glass materials Air Index of
Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses Table of Contents 1. Theory 2. Pulse propagation through various materials o Calculating the index of refraction Glass materials Air Index of
Narrow- and wideband channels
 RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15 Lecture no: 3 Narrow- and wideband channels Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2012-03-19 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Contents Short review
RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15 Lecture no: 3 Narrow- and wideband channels Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2012-03-19 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Contents Short review
Diffractive Axicon application note
 Diffractive Axicon application note. Introduction 2. General definition 3. General specifications of Diffractive Axicons 4. Typical applications 5. Advantages of the Diffractive Axicon 6. Principle of
Diffractive Axicon application note. Introduction 2. General definition 3. General specifications of Diffractive Axicons 4. Typical applications 5. Advantages of the Diffractive Axicon 6. Principle of
Chad A. Husko 1,, Sylvain Combrié 2, Pierre Colman 2, Jiangjun Zheng 1, Alfredo De Rossi 2, Chee Wei Wong 1,
 SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
GRENOUILLE.
 GRENOUILLE Measuring ultrashort laser pulses the shortest events ever created has always been a challenge. For many years, it was possible to create ultrashort pulses, but not to measure them. Techniques
GRENOUILLE Measuring ultrashort laser pulses the shortest events ever created has always been a challenge. For many years, it was possible to create ultrashort pulses, but not to measure them. Techniques
Dispersion properties of mid infrared optical materials
 Dispersion properties of mid infrared optical materials Andrei Tokmakoff December 16 Contents 1) Dispersion calculations for ultrafast mid IR pulses ) Index of refraction of optical materials in the mid
Dispersion properties of mid infrared optical materials Andrei Tokmakoff December 16 Contents 1) Dispersion calculations for ultrafast mid IR pulses ) Index of refraction of optical materials in the mid
Channel. Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Campus, Pakistan. Multi-Path Fading. Dr. Noor M Khan EE, MAJU
 Instructor: Prof. Dr. Noor M. Khan Department of Electronic Engineering, Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Campus, Islamabad, PAKISTAN Ph: +9 (51) 111-878787, Ext. 19 (Office), 186 (Lab) Fax: +9
Instructor: Prof. Dr. Noor M. Khan Department of Electronic Engineering, Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Campus, Islamabad, PAKISTAN Ph: +9 (51) 111-878787, Ext. 19 (Office), 186 (Lab) Fax: +9
Figure1. To construct a light pulse, the electric component of the plane wave should be multiplied with a bell shaped function.
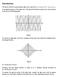 Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin
 Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
200-GHz 8-µs LFM Optical Waveform Generation for High- Resolution Coherent Imaging
 Th7 Holman, K.W. 200-GHz 8-µs LFM Optical Waveform Generation for High- Resolution Coherent Imaging Kevin W. Holman MIT Lincoln Laboratory 244 Wood Street, Lexington, MA 02420 USA kholman@ll.mit.edu Abstract:
Th7 Holman, K.W. 200-GHz 8-µs LFM Optical Waveform Generation for High- Resolution Coherent Imaging Kevin W. Holman MIT Lincoln Laboratory 244 Wood Street, Lexington, MA 02420 USA kholman@ll.mit.edu Abstract:
Investigation of the tapered waveguide structures for terahertz quantum cascade lasers
 Invited Paper Investigation of the tapered waveguide structures for terahertz quantum cascade lasers T. H. Xu, and J. C. Cao * Key Laboratory of Terahertz Solid-State Technology, Shanghai Institute of
Invited Paper Investigation of the tapered waveguide structures for terahertz quantum cascade lasers T. H. Xu, and J. C. Cao * Key Laboratory of Terahertz Solid-State Technology, Shanghai Institute of
Lithium Triborate (LiB 3 O 5, LBO)
 NLO Cr ys tals Introduction Lithium Triborate (LiB 3 O 5, LBO) Lithium Triborate (LiB 3 O 5 or LBO) is an excellent nonlinear optical crystal discovered and developed by FIRSM, CAS (Fujian Institute of
NLO Cr ys tals Introduction Lithium Triborate (LiB 3 O 5, LBO) Lithium Triborate (LiB 3 O 5 or LBO) is an excellent nonlinear optical crystal discovered and developed by FIRSM, CAS (Fujian Institute of
Far field intensity distributions of an OMEGA laser beam were measured with
 Experimental Investigation of the Far Field on OMEGA with an Annular Apertured Near Field Uyen Tran Advisor: Sean P. Regan Laboratory for Laser Energetics Summer High School Research Program 200 1 Abstract
Experimental Investigation of the Far Field on OMEGA with an Annular Apertured Near Field Uyen Tran Advisor: Sean P. Regan Laboratory for Laser Energetics Summer High School Research Program 200 1 Abstract
Beam Shaping in High-Power Laser Systems with Using Refractive Beam Shapers
 - 1 - Beam Shaping in High-Power Laser Systems with Using Refractive Beam Shapers Alexander Laskin, Vadim Laskin AdlOptica GmbH, Rudower Chaussee 29, 12489 Berlin, Germany ABSTRACT Beam Shaping of the
- 1 - Beam Shaping in High-Power Laser Systems with Using Refractive Beam Shapers Alexander Laskin, Vadim Laskin AdlOptica GmbH, Rudower Chaussee 29, 12489 Berlin, Germany ABSTRACT Beam Shaping of the
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression
 Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
101 W of average green beam from diode-side-pumped Nd:YAG/LBO-based system in a relay imaged cavity
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 75, No. 5 journal of November 2010 physics pp. 935 940 101 W of average green beam from diode-side-pumped Nd:YAG/LBO-based system in a relay imaged cavity S K
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 75, No. 5 journal of November 2010 physics pp. 935 940 101 W of average green beam from diode-side-pumped Nd:YAG/LBO-based system in a relay imaged cavity S K
ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating
 ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating Spectral density (db) 0 10 20 30 40 Mirror VBG 1053.0 1053.3 1053.6 Wavelength (nm) Frontiers in Optics 2007/Laser
ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating Spectral density (db) 0 10 20 30 40 Mirror VBG 1053.0 1053.3 1053.6 Wavelength (nm) Frontiers in Optics 2007/Laser
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017
 R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
Measurement of phase velocity dispersion curves and group velocities in a plate using leaky Lamb waves
 Measurement of phase velocity dispersion curves and group velocities in a plate using leaky Lamb waves NDE2002 predict. assure. improve. National Seminar of ISNT Chennai, 5. 7. 12. 2002 www.nde2002.org
Measurement of phase velocity dispersion curves and group velocities in a plate using leaky Lamb waves NDE2002 predict. assure. improve. National Seminar of ISNT Chennai, 5. 7. 12. 2002 www.nde2002.org
The KrF alternative for fast ignition inertial fusion
 The KrF alternative for fast ignition inertial fusion IstvánB Földes 1, Sándor Szatmári 2 Students: A. Barna, R. Dajka, B. Gilicze, Zs. Kovács 1 Wigner Research Centre of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences,
The KrF alternative for fast ignition inertial fusion IstvánB Földes 1, Sándor Szatmári 2 Students: A. Barna, R. Dajka, B. Gilicze, Zs. Kovács 1 Wigner Research Centre of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences,
High-Speed Optical Modulators and Photonic Sideband Management
 114 High-Speed Optical Modulators and Photonic Sideband Management Tetsuya Kawanishi National Institute of Information and Communications Technology 4-2-1 Nukui-Kita, Koganei, Tokyo, Japan Tel: 81-42-327-7490;
114 High-Speed Optical Modulators and Photonic Sideband Management Tetsuya Kawanishi National Institute of Information and Communications Technology 4-2-1 Nukui-Kita, Koganei, Tokyo, Japan Tel: 81-42-327-7490;
Spectral and Temporal Properties of Optical Signals with Multiple Sinusoidal Phase Modulations
 Spectral and Temporal Properties of Optical Signals with Multiple Sinusoidal Phase Modulations Introduction High-energy laser systems have been developed for exploring regimes of high-intensity interaction
Spectral and Temporal Properties of Optical Signals with Multiple Sinusoidal Phase Modulations Introduction High-energy laser systems have been developed for exploring regimes of high-intensity interaction
Experimental Physics. Experiment C & D: Pulsed Laser & Dye Laser. Course: FY12. Project: The Pulsed Laser. Done by: Wael Al-Assadi & Irvin Mangwiza
 Experiment C & D: Course: FY1 The Pulsed Laser Done by: Wael Al-Assadi Mangwiza 8/1/ Wael Al Assadi Mangwiza Experiment C & D : Introduction: Course: FY1 Rev. 35. Page: of 16 1// In this experiment we
Experiment C & D: Course: FY1 The Pulsed Laser Done by: Wael Al-Assadi Mangwiza 8/1/ Wael Al Assadi Mangwiza Experiment C & D : Introduction: Course: FY1 Rev. 35. Page: of 16 1// In this experiment we
Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II
 Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II Generating negative groupdelay dispersion angular dispersion Pulse compression Prisms Gratings Chirped mirrors Chirped vs. transform-limited A transform-limited pulse:
Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II Generating negative groupdelay dispersion angular dispersion Pulse compression Prisms Gratings Chirped mirrors Chirped vs. transform-limited A transform-limited pulse:
A Passive Suppressing Jamming Method for FMCW SAR Based on Micromotion Modulation
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 48, 37 44, 216 A Passive Suppressing Jamming Method for FMCW SAR Based on Micromotion Modulation Jia-Bing Yan *, Ying Liang, Yong-An Chen, Qun Zhang, and Li
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 48, 37 44, 216 A Passive Suppressing Jamming Method for FMCW SAR Based on Micromotion Modulation Jia-Bing Yan *, Ying Liang, Yong-An Chen, Qun Zhang, and Li
J-KAREN-P Session 1, 10:00 10:
 J-KAREN-P 2018 Session 1, 10:00 10:25 2018 5 8 Outline Introduction Capabilities of J-KAREN-P facility Optical architecture Status and implementation of J-KAREN-P facility Amplification performance Recompression
J-KAREN-P 2018 Session 1, 10:00 10:25 2018 5 8 Outline Introduction Capabilities of J-KAREN-P facility Optical architecture Status and implementation of J-KAREN-P facility Amplification performance Recompression
1 Abstract. 2 Introduction
 Analysis of Auto- and Cross-correlator Lee Teng Internship Paper D. Gutierrez Coronel Department of Physics, Illinois Institute of Technology August 11, 2017 Mentors: J. C. Dooling and Y. Sun Accelerator
Analysis of Auto- and Cross-correlator Lee Teng Internship Paper D. Gutierrez Coronel Department of Physics, Illinois Institute of Technology August 11, 2017 Mentors: J. C. Dooling and Y. Sun Accelerator
All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration
 1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
Narrowing spectral width of green LED by GMR structure to expand color mixing field
 Narrowing spectral width of green LED by GMR structure to expand color mixing field S. H. Tu 1, Y. C. Lee 2, C. L. Hsu 1, W. P. Lin 1, M. L. Wu 1, T. S. Yang 1, J. Y. Chang 1 1. Department of Optical and
Narrowing spectral width of green LED by GMR structure to expand color mixing field S. H. Tu 1, Y. C. Lee 2, C. L. Hsu 1, W. P. Lin 1, M. L. Wu 1, T. S. Yang 1, J. Y. Chang 1 1. Department of Optical and
Infrared broadband 50%-50% beam splitters for s- polarized light
 University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 7-1-2006 Infrared broadband 50%-50% beam splitters for s- polarized light R.
University of New Orleans ScholarWorks@UNO Electrical Engineering Faculty Publications Department of Electrical Engineering 7-1-2006 Infrared broadband 50%-50% beam splitters for s- polarized light R.
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 35. Self-Phase-Modulation
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion
 36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Princeton University Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University ABSTRACT
 Phase and Amplitude Control Ability using Spatial Light Modulators and Zero Path Length Difference Michelson Interferometer Michael G. Littman, Michael Carr, Jim Leighton, Ezekiel Burke, David Spergel
Phase and Amplitude Control Ability using Spatial Light Modulators and Zero Path Length Difference Michelson Interferometer Michael G. Littman, Michael Carr, Jim Leighton, Ezekiel Burke, David Spergel
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide
 Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
τ mod = T modal = longest ray path shortest ray path n 1 L 1 = L n 2 1
 S. Blair February 15, 2012 23 2.2. Pulse dispersion Pulse dispersion is the spreading of a pulse as it propagates down an optical fiber. Pulse spreading is an obvious detrimental effect that limits the
S. Blair February 15, 2012 23 2.2. Pulse dispersion Pulse dispersion is the spreading of a pulse as it propagates down an optical fiber. Pulse spreading is an obvious detrimental effect that limits the
G. Norris* & G. McConnell
 Relaxed damage threshold intensity conditions and nonlinear increase in the conversion efficiency of an optical parametric oscillator using a bi-directional pump geometry G. Norris* & G. McConnell Centre
Relaxed damage threshold intensity conditions and nonlinear increase in the conversion efficiency of an optical parametric oscillator using a bi-directional pump geometry G. Norris* & G. McConnell Centre
Linewidth control by overexposure in laser lithography
 Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXVIII, No. 2, 2008 Linewidth control by overexposure in laser lithography LIANG YIYONG*, YANG GUOGUANG State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instruments, Zhejiang University,
Optica Applicata, Vol. XXXVIII, No. 2, 2008 Linewidth control by overexposure in laser lithography LIANG YIYONG*, YANG GUOGUANG State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instruments, Zhejiang University,
Multi-Path Fading Channel
 Instructor: Prof. Dr. Noor M. Khan Department of Electronic Engineering, Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Campus, Islamabad, PAKISTAN Ph: +9 (51) 111-878787, Ext. 19 (Office), 186 (Lab) Fax: +9
Instructor: Prof. Dr. Noor M. Khan Department of Electronic Engineering, Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Campus, Islamabad, PAKISTAN Ph: +9 (51) 111-878787, Ext. 19 (Office), 186 (Lab) Fax: +9
Paul R. Bolton and Cecile Limborg-Deprey, Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, MS-18, 2575 Sandhill Road, Menlo Park, California
 LCLS-TN-07-4 June 0, 2007 IR Bandwidth and Crystal Thickness Effects on THG Efficiency and Temporal Shaping of Quasi-rectangular UV pulses: Part II Incident IR Intensity Ripple * I. Introduction: Paul
LCLS-TN-07-4 June 0, 2007 IR Bandwidth and Crystal Thickness Effects on THG Efficiency and Temporal Shaping of Quasi-rectangular UV pulses: Part II Incident IR Intensity Ripple * I. Introduction: Paul
Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors
 846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
TIME-PRESERVING MONOCHROMATORS FOR ULTRASHORT EXTREME-ULTRAVIOLET PULSES
 TIME-PRESERVING MONOCHROMATORS FOR ULTRASHORT EXTREME-ULTRAVIOLET PULSES Luca Poletto CNR - Institute of Photonics and Nanotechnologies Laboratory for UV and X-Ray Optical Research Padova, Italy e-mail:
TIME-PRESERVING MONOCHROMATORS FOR ULTRASHORT EXTREME-ULTRAVIOLET PULSES Luca Poletto CNR - Institute of Photonics and Nanotechnologies Laboratory for UV and X-Ray Optical Research Padova, Italy e-mail:
2. Pulsed Acoustic Microscopy and Picosecond Ultrasonics
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Picosecond Ultrasonic Microscopy of Semiconductor Nanostructures Thomas J GRIMSLEY
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Picosecond Ultrasonic Microscopy of Semiconductor Nanostructures Thomas J GRIMSLEY
Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film
 Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film Hisashi Akiyama 1, Osami Sasaki 2, and Takamasa Suzuki
Sinusoidal wavelength-scanning interferometer using an acousto-optic tunable filter for measurement of thickness and surface profile of a thin film Hisashi Akiyama 1, Osami Sasaki 2, and Takamasa Suzuki
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P The prediction of the time and the spatial profile for broadband land mobile services using UHF and SHF bands
 Rec. ITU-R P.1816 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P.1816 The prediction of the time and the spatial profile for broadband land mobile services using UHF and SHF bands (Question ITU-R 211/3) (2007) Scope The purpose
Rec. ITU-R P.1816 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P.1816 The prediction of the time and the spatial profile for broadband land mobile services using UHF and SHF bands (Question ITU-R 211/3) (2007) Scope The purpose
Modified Spectrum Auto-Interferometric Correlation. (MOSAIC) for Single Shot Pulse Characterization
 To appear in OPTICS LETTERS, October 1, 2007 / Vol. 32, No. 19 Modified Spectrum Auto-Interferometric Correlation (MOSAIC) for Single Shot Pulse Characterization Daniel A. Bender* and Mansoor Sheik-Bahae
To appear in OPTICS LETTERS, October 1, 2007 / Vol. 32, No. 19 Modified Spectrum Auto-Interferometric Correlation (MOSAIC) for Single Shot Pulse Characterization Daniel A. Bender* and Mansoor Sheik-Bahae
Optical Fiber Technology. Photonic Network By Dr. M H Zaidi
 Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
Fiber Lasers for EUV Lithography
 Fiber Lasers for EUV Lithography A. Galvanauskas, Kai Chung Hou*, Cheng Zhu CUOS, EECS Department, University of Michigan P. Amaya Arbor Photonics, Inc. * Currently with Cymer, Inc 2009 International Workshop
Fiber Lasers for EUV Lithography A. Galvanauskas, Kai Chung Hou*, Cheng Zhu CUOS, EECS Department, University of Michigan P. Amaya Arbor Photonics, Inc. * Currently with Cymer, Inc 2009 International Workshop
Faraday Rotators and Isolators
 Faraday Rotators and I. Introduction The negative effects of optical feedback on laser oscillators and laser diodes have long been known. Problems include frequency instability, relaxation oscillations,
Faraday Rotators and I. Introduction The negative effects of optical feedback on laser oscillators and laser diodes have long been known. Problems include frequency instability, relaxation oscillations,
ME scope Application Note 01 The FFT, Leakage, and Windowing
 INTRODUCTION ME scope Application Note 01 The FFT, Leakage, and Windowing NOTE: The steps in this Application Note can be duplicated using any Package that includes the VES-3600 Advanced Signal Processing
INTRODUCTION ME scope Application Note 01 The FFT, Leakage, and Windowing NOTE: The steps in this Application Note can be duplicated using any Package that includes the VES-3600 Advanced Signal Processing
Lithium Triborate (LiB 3 O 5, LBO) Introductions
 s Laser s NLO s Birefringent s AO and EO s Lithium Triborate (LiB 3 O 5, ) Introductions Banner Union provide the high quality Broad transparency range from 160nm to 2600nm; High optical homogeneity (δn
s Laser s NLO s Birefringent s AO and EO s Lithium Triborate (LiB 3 O 5, ) Introductions Banner Union provide the high quality Broad transparency range from 160nm to 2600nm; High optical homogeneity (δn
Evaluation of RF power degradation in microwave photonic systems employing uniform period fibre Bragg gratings
 Evaluation of RF power degradation in microwave photonic systems employing uniform period fibre Bragg gratings G. Yu, W. Zhang and J. A. R. Williams Photonics Research Group, Department of EECS, Aston
Evaluation of RF power degradation in microwave photonic systems employing uniform period fibre Bragg gratings G. Yu, W. Zhang and J. A. R. Williams Photonics Research Group, Department of EECS, Aston
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT
 ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (E-O) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (E-O) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
Spectral Phase Modulation and chirped pulse amplification in High Gain Harmonic Generation
 Spectral Phase Modulation and chirped pulse amplification in High Gain Harmonic Generation Z. Wu, H. Loos, Y. Shen, B. Sheehy, E. D. Johnson, S. Krinsky, J. B. Murphy, T. Shaftan,, X.-J. Wang, L. H. Yu,
Spectral Phase Modulation and chirped pulse amplification in High Gain Harmonic Generation Z. Wu, H. Loos, Y. Shen, B. Sheehy, E. D. Johnson, S. Krinsky, J. B. Murphy, T. Shaftan,, X.-J. Wang, L. H. Yu,
Pulse Compression. Since each part of the pulse has unique frequency, the returns can be completely separated.
 Pulse Compression Pulse compression is a generic term that is used to describe a waveshaping process that is produced as a propagating waveform is modified by the electrical network properties of the transmission
Pulse Compression Pulse compression is a generic term that is used to describe a waveshaping process that is produced as a propagating waveform is modified by the electrical network properties of the transmission
Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Fading and Multi-path
 Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Fading and Multi-path 1 EE/TE 4365, UT Dallas 2 Small-scale Fading Small-scale fading, or simply fading describes the rapid fluctuation of the amplitude of a radio
Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Fading and Multi-path 1 EE/TE 4365, UT Dallas 2 Small-scale Fading Small-scale fading, or simply fading describes the rapid fluctuation of the amplitude of a radio
Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Campus, Pakistan. Fading Channel. Base Station
 Fading Lecturer: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Noor M Khan Department of Electronic Engineering, Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Campus, Islamabad, PAKISTAN Ph: +9 (51) 111-878787, Ext. 19 (Office), 186 (ARWiC
Fading Lecturer: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Noor M Khan Department of Electronic Engineering, Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad Campus, Islamabad, PAKISTAN Ph: +9 (51) 111-878787, Ext. 19 (Office), 186 (ARWiC
EENG473 Mobile Communications Module 3 : Week # (12) Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Path Loss
 EENG473 Mobile Communications Module 3 : Week # (12) Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Path Loss Introduction Small-scale fading is used to describe the rapid fluctuation of the amplitude of a radio
EENG473 Mobile Communications Module 3 : Week # (12) Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Path Loss Introduction Small-scale fading is used to describe the rapid fluctuation of the amplitude of a radio
Dynamic Phase-Shifting Electronic Speckle Pattern Interferometer
 Dynamic Phase-Shifting Electronic Speckle Pattern Interferometer Michael North Morris, James Millerd, Neal Brock, John Hayes and *Babak Saif 4D Technology Corporation, 3280 E. Hemisphere Loop Suite 146,
Dynamic Phase-Shifting Electronic Speckle Pattern Interferometer Michael North Morris, James Millerd, Neal Brock, John Hayes and *Babak Saif 4D Technology Corporation, 3280 E. Hemisphere Loop Suite 146,
Multiple wavelength resonant grating filters at oblique incidence with broad angular acceptance
 Multiple wavelength resonant grating filters at oblique incidence with broad angular acceptance Andrew B. Greenwell, Sakoolkan Boonruang, M.G. Moharam College of Optics and Photonics - CREOL, University
Multiple wavelength resonant grating filters at oblique incidence with broad angular acceptance Andrew B. Greenwell, Sakoolkan Boonruang, M.G. Moharam College of Optics and Photonics - CREOL, University
Photonic time-stretching of 102 GHz millimeter waves using 1.55 µm nonlinear optic polymer EO modulators
 Photonic time-stretching of 10 GHz millimeter waves using 1.55 µm nonlinear optic polymer EO modulators H. Erlig Pacific Wave Industries H. R. Fetterman and D. Chang University of California Los Angeles
Photonic time-stretching of 10 GHz millimeter waves using 1.55 µm nonlinear optic polymer EO modulators H. Erlig Pacific Wave Industries H. R. Fetterman and D. Chang University of California Los Angeles
Bragg and fiber gratings. Mikko Saarinen
 Bragg and fiber gratings Mikko Saarinen 27.10.2009 Bragg grating - Bragg gratings are periodic perturbations in the propagating medium, usually periodic variation of the refractive index - like diffraction
Bragg and fiber gratings Mikko Saarinen 27.10.2009 Bragg grating - Bragg gratings are periodic perturbations in the propagating medium, usually periodic variation of the refractive index - like diffraction
Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized Optical Signals in WDM System
 The Quarterly Journal of Optoelectronical Nanostructures Islamic Azad University Spring 2016 / Vol. 1, No.1 Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized
The Quarterly Journal of Optoelectronical Nanostructures Islamic Azad University Spring 2016 / Vol. 1, No.1 Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized
Performance Analysis on Beam-steering Algorithm for Parametric Array Loudspeaker Application
 (283 -- 917) Proceedings of the 3rd (211) CUTSE International Conference Miri, Sarawak, Malaysia, 8-9 Nov, 211 Performance Analysis on Beam-steering Algorithm for Parametric Array Loudspeaker Application
(283 -- 917) Proceedings of the 3rd (211) CUTSE International Conference Miri, Sarawak, Malaysia, 8-9 Nov, 211 Performance Analysis on Beam-steering Algorithm for Parametric Array Loudspeaker Application
dnx/dt = -9.3x10-6 / C dny/dt = -13.6x10-6 / C dnz/dt = ( λ)x10-6 / C
 Lithium Triborate Crystal LBO Lithium triborate (LiB3O5 or LBO) is an excellent nonlinear optical crystal for many applications. It is grown by an improved flux method. AOTK s LBO is Featured by High damage
Lithium Triborate Crystal LBO Lithium triborate (LiB3O5 or LBO) is an excellent nonlinear optical crystal for many applications. It is grown by an improved flux method. AOTK s LBO is Featured by High damage
High-Power, Passively Q-switched Microlaser - Power Amplifier System
 High-Power, Passively Q-switched Microlaser - Power Amplifier System Yelena Isyanova Q-Peak, Inc.,135 South Road, Bedford, MA 01730 isyanova@qpeak.com Jeff G. Manni JGM Associates, 6 New England Executive
High-Power, Passively Q-switched Microlaser - Power Amplifier System Yelena Isyanova Q-Peak, Inc.,135 South Road, Bedford, MA 01730 isyanova@qpeak.com Jeff G. Manni JGM Associates, 6 New England Executive
Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter
 Research Online ECU Publications 29 Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter Feng Xiao Mingya Shen Budi Juswardy Kamal Alameh This article was originally published as: Xiao, F., Shen, M., Juswardy,
Research Online ECU Publications 29 Opto-VLSI-based reconfigurable photonic RF filter Feng Xiao Mingya Shen Budi Juswardy Kamal Alameh This article was originally published as: Xiao, F., Shen, M., Juswardy,
Diffractive optical elements for high gain lasers with arbitrary output beam profiles
 Diffractive optical elements for high gain lasers with arbitrary output beam profiles Adam J. Caley, Martin J. Thomson 2, Jinsong Liu, Andrew J. Waddie and Mohammad R. Taghizadeh. Heriot-Watt University,
Diffractive optical elements for high gain lasers with arbitrary output beam profiles Adam J. Caley, Martin J. Thomson 2, Jinsong Liu, Andrew J. Waddie and Mohammad R. Taghizadeh. Heriot-Watt University,
High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses
 High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses Since its invention in the early 199s, 1 optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification
High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses Since its invention in the early 199s, 1 optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification
White-light interferometry, Hilbert transform, and noise
 White-light interferometry, Hilbert transform, and noise Pavel Pavlíček *a, Václav Michálek a a Institute of Physics of Academy of Science of the Czech Republic, Joint Laboratory of Optics, 17. listopadu
White-light interferometry, Hilbert transform, and noise Pavel Pavlíček *a, Václav Michálek a a Institute of Physics of Academy of Science of the Czech Republic, Joint Laboratory of Optics, 17. listopadu
Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings
 Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu Optical Engineering 52(9), 091708 (September 2013) Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu
Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu Optical Engineering 52(9), 091708 (September 2013) Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 20 at the start of class
 PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
Optical Isolator Tutorial (Page 1 of 2) νlh, where ν, L, and H are as defined below. ν: the Verdet Constant, a property of the
 Aspheric Optical Isolator Tutorial (Page 1 of 2) Function An optical isolator is a passive magneto-optic device that only allows light to travel in one direction. Isolators are used to protect a source
Aspheric Optical Isolator Tutorial (Page 1 of 2) Function An optical isolator is a passive magneto-optic device that only allows light to travel in one direction. Isolators are used to protect a source
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers
 Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG)
 Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides
 Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides Yaming Li, Chong Li, Chuanbo Li, Buwen Cheng, * and Chunlai Xue State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics,
Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides Yaming Li, Chong Li, Chuanbo Li, Buwen Cheng, * and Chunlai Xue State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics,
Shaping light in microscopy:
 Shaping light in microscopy: Adaptive optical methods and nonconventional beam shapes for enhanced imaging Martí Duocastella planet detector detector sample sample Aberrated wavefront Beamsplitter Adaptive
Shaping light in microscopy: Adaptive optical methods and nonconventional beam shapes for enhanced imaging Martí Duocastella planet detector detector sample sample Aberrated wavefront Beamsplitter Adaptive
Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser
 28 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/Vol. 17, No. 1/January 2000 Man et al. Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser W. S. Man, H. Y. Tam, and
28 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/Vol. 17, No. 1/January 2000 Man et al. Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser W. S. Man, H. Y. Tam, and
Extremely simple device for measuring 1.5-µm ultrashort laser pulses
 Extremely simple device for measuring 1.5-µm ultrashort laser pulses Selcuk Akturk, Mark Kimmel, and Rick Trebino School of Physics, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0430, USA akturk@socrates.physics.gatech.edu
Extremely simple device for measuring 1.5-µm ultrashort laser pulses Selcuk Akturk, Mark Kimmel, and Rick Trebino School of Physics, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 30332-0430, USA akturk@socrates.physics.gatech.edu
Far infrared generation by CO 2 lasers frequencies subtraction in a ZnGeP 2 crystal.
 Far infrared generation by CO 2 lasers frequencies subtraction in a ZnGeP 2 crystal. Yu.A.Shakir V.V.Apollonov A.M.Prokhorov A.G.Suzdal tsev General Physics Institute of RAS, 38 Vavilov st., Moscow 117333,
Far infrared generation by CO 2 lasers frequencies subtraction in a ZnGeP 2 crystal. Yu.A.Shakir V.V.Apollonov A.M.Prokhorov A.G.Suzdal tsev General Physics Institute of RAS, 38 Vavilov st., Moscow 117333,
Increased-bandwidth in ultrashort-pulse measurement using an angle-dithered nonlinear-optical crystal
 Increased-bandwidth in ultrashort-pulse measurement using an angle-dithered nonlinear-optical crystal PatrickO Shea,MarkKimmel,XunGu,andRickTrebino Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Physics, Atlanta,
Increased-bandwidth in ultrashort-pulse measurement using an angle-dithered nonlinear-optical crystal PatrickO Shea,MarkKimmel,XunGu,andRickTrebino Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Physics, Atlanta,
The electric field for the wave sketched in Fig. 3-1 can be written as
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Light consists of an electric field and a magnetic field that oscillate at very high rates, of the order of 10 14 Hz. These fields travel in wavelike fashion at very high speeds.
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Light consists of an electric field and a magnetic field that oscillate at very high rates, of the order of 10 14 Hz. These fields travel in wavelike fashion at very high speeds.
FWM Suppression in WDM Systems Using Advanced Modulation Formats
 FWM Suppression in WDM Systems Using Advanced Modulation Formats M.M. Ibrahim (eng.mohamed.ibrahim@gmail.com) and Moustafa H. Aly (drmosaly@gmail.com) OSA Member Arab Academy for Science, Technology and
FWM Suppression in WDM Systems Using Advanced Modulation Formats M.M. Ibrahim (eng.mohamed.ibrahim@gmail.com) and Moustafa H. Aly (drmosaly@gmail.com) OSA Member Arab Academy for Science, Technology and
Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm
 15 February 2000 Ž. Optics Communications 175 2000 209 213 www.elsevier.comrlocateroptcom Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm F. Koch ), S.V. Chernikov,
15 February 2000 Ž. Optics Communications 175 2000 209 213 www.elsevier.comrlocateroptcom Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm F. Koch ), S.V. Chernikov,
Broadband Optical Phased-Array Beam Steering
 Kent State University Digital Commons @ Kent State University Libraries Chemical Physics Publications Department of Chemical Physics 12-2005 Broadband Optical Phased-Array Beam Steering Paul F. McManamon
Kent State University Digital Commons @ Kent State University Libraries Chemical Physics Publications Department of Chemical Physics 12-2005 Broadband Optical Phased-Array Beam Steering Paul F. McManamon
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:0.038/nature727 Table of Contents S. Power and Phase Management in the Nanophotonic Phased Array 3 S.2 Nanoantenna Design 6 S.3 Synthesis of Large-Scale Nanophotonic Phased
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:0.038/nature727 Table of Contents S. Power and Phase Management in the Nanophotonic Phased Array 3 S.2 Nanoantenna Design 6 S.3 Synthesis of Large-Scale Nanophotonic Phased
