A High-Bandwidth Electrical-Waveform Generator Based on Aperture-Coupled Striplines for OMEGA Pulse-Shaping Applications
|
|
|
- Sylvia Henry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A High-Bandwidth Electrical-Waveform Generator Based on Aperture-Coupled Striplines for OMEGA Pulse-Shaping Applications Pulsed-laser systems emit optical pulses having a temporal pulse shape characteristic of the particular type of laser design. Advances in technology have produced laser-pulseshaping systems where the laser temporal profile can be specified in advance and controlled to a high degree of accuracy. 1 3 A pulse-shaping system has been in operation on OMEGA for several years. Temporally shaped optical pulses can be produced by applying shaped electrical waveforms to a dual-channel integrated-optics modulator. 1 3 These shaped electrical waveforms are sent to the optical modulator synchronized with the passage through the modulator of an optical pulse from a single-longitudinal-mode (SLM) laser. 4 The optical pulse exiting the modulator is then shaped in accordance with the voltage-dependent transfer function of the modulator. Hence, the electrical-waveform generator is an important component in any optical-pulse-shaping system incorporating optical modulators. This article discusses a greatly simplified pulse-shaping system based on an aperturecoupled-stripline (ACSL) electrical-waveform generator under development for OMEGA, and compares its many advantages over the existing OMEGA pulse-shaping system. The Present OMEGA Pulse-Shaping System The OMEGA pulse-shaping system uses an electricalwaveform generator based on an electrical reflection from a variable-impedance microstrip line (VIMSL). 3 Electricalwaveform generators based on stripline technology offer the highest temporal resolution over other systems due to their high-bandwidth capabilities, stripline-fabrication procedures, and achievable tolerances. The present OMEGA pulse-shaping system (outlined in Fig. 73.1) consists of many components. A cw mode-locked (CWML) laser is used to seed a regenerative amplifier (regen). The temporal width of the optical pulse injected into this regen is stretched in time with an intracavity etalon. 5 The output of the regenerative amplifier is amplified, and its leading edge is steepened with a stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) reflection from CCL 4. 6 This SBS pulse is amplified and sent to a fiber distribution system to illuminate photoconductive (PC) switches. Illumination of the PC switches activates the electrical-waveform generator, which produces the temporally shaped electrical waveforms that are sent to the optical modulator. 3,7 The subsequently shaped optical pulse from the modulator is sent to the OMEGA E8890 CWML laser and master timing reference SLM laser Regen Amplifier SBS mirror Electrical gate SBS-steepened pulse Fiber-coupled PC-switched electrical-waveform generator Optical modulator Shaped electrical waveform Shaped optical pulse VIMSL Figure 73.1 The OMEGA optical-pulse-shaping system. A cw mode-locked (CWML) laser seeds a regenerative amplifier (regen) whose output pulse is amplified and steepened by a stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) mirror. The SBS pulse activates a photoconductively (PC) switched electricalwaveform generator that drives the two channels of an optical modulator. The output from a singlelongitudinal-mode (SLM) laser is temporally shaped by the optical modulator and injected into the OMEGA laser. LLE Review, Volume 73 1
2 amplifiers with timing referenced with respect to the activation of the PC switches by the SBS pulse. The VIMSL in OMEGA s electrical-waveform generator is a two-port electrical device. 3,7 A square electrical pulse is sent into one port of the device and propagates to the second terminated port. A shaped electrical waveform, generated by reflections along the length of the VIMSL, exits from the VIMSL through the input port and is sent to the optical modulator. This electrical-waveform generator has some anomalies that must be mitigated to achieve a high contrast (i.e., the ratio of the maximum pulse amplitude to the prepulse noise). The square electrical waveform sent to the VIMSL has a voltage stair step that is attributable to the finite off impedance and nonzero on impedance of the PC switches. The effects of this dc step are substantially minimized by applying a temporal delay to the shaped electrical waveform. In addition, there is a capacitively coupled voltage spike on the voltage waveform applied to the modulator that is attributable to the capacitance of the PC switch in the off state. To eliminate this prepulse and improve the contrast of the shaped optical pulses, a square electrical gate pulse is applied to the second channel of the modulator. The ACSL Pulse-Shaping System A pulse-shaping system with an electrical-waveform generator based on an ACSL has been developed. A layout of this ACSL pulse-shaping system is shown in Fig A square electrical waveform from a commercially available pulse generator is sent to an ACSL. The ACSL generates a shaped electrical waveform that is sent directly to the optical modulator for pulse shaping. The design of the electrical-waveform generator is based on a four-layer, four-port ACSL and is modeled as a four-port electrical directional coupler. An exploded view of a practical device with four layers of material having dielectric constant is shown in Fig The important region of the ACSL for pulse shaping is the coupling region shown in cross section in Fig In operation, a square electrical waveform is launched into port 1 and propagates along electrode 1 to the terminated port 2 of the ACSL. As the square electrical waveform propagates along electrode 1 in the coupling region, the electrical signal is coupled through an aperture to electrode 2 in the backward direction and exits at port 4. By properly varying the width of the coupling aperture (s in Fig. 73.4) along the length of the ACSL, any desired temporally shaped electrical waveform can be generated at port 4 and sent to optical modulators for pulse shaping. The ACSL system is characterized by an input and output impedance. The characteristic impedance Z 0 of the system is chosen to be 50 Ω to match the input impedance of the modulator channels. Ports 2 and 3 of the ACSL are terminated with this characteristic impedance to prevent reflections at these ports. The transition section of the ACSL is designed to accommodate the electrical connectors (stripline end launchers) required to transmit electrical signals from the standard coaxial electrical cables used as input and output to the ACSL to the coupling region of the ACSL (illustrated by the crosssectional geometry in Fig 73.4). In the transition region (and in the coupling region when the aperture width is zero), the system can be thought of as two separate uncoupled and noninteracting ordinary striplines. To achieve a 50-Ω stripline in this section, the width of the electrode w is determined from well-known relations 8 involving the material parameters and the geometry of the ACSL. To design and produce shaped voltage waveforms at port 4 of an ACSL, the electrical coupling coefficient from electrode 1 to electrode 2 (i.e., the ratio of the output-pulse voltage at port 4 to the input-pulse voltage at port 1) as a function of Electrical squarepulse generator ACSL Electrical squarepulse generator Gate Shaped electrical waveform Figure 73.2 The aperture-coupled-stripline (ACSL) optical-pulse-shaping system. The output from an electrical square-pulse generator is temporally shaped by an ACSL and used to drive an optical modulator. A separate electrical square-pulse generator is used to gate the second channel of the modulator. E8891 SLM laser Optical modulator Shaped optical pulse 2 LLE Review, Volume 73
3 Cu Output Port 4 Port 3 Electrode 2 z 0 Aperture Cu Input Port 1 Electrode 1 Port 2 z 0 E8416 Transition region Coupling region Figure 73.3 Exploded view of a practical four-layer, four-port ACSL. A square electrical waveform is launched into port 1 and propagates along electrode 1 to the terminated port 2. The electrical signal is coupled through an aperture to electrode 2 in the backward direction and a shaped electrical waveform exits at port 4. aperture width s must be known. It is difficult to calculate this explicitly; however, simple experiments have been performed to measure this dependence. The data from these measurements are used in our model for designing ACSL devices. Electrode 2 Electrode 1 E8892 w s Aperture Ground planes Figure 73.4 Cross-sectional view of an ACSL in the coupling region of Fig The electrode width w is chosen to provide a 50-Ω impedance structure. The amount of electrical coupling from electrode 1 to electrode 2 depends on the aperture width s. Several ACSL devices have been fabricated and tested to determine the dependence of the electrical coupling coefficient on the aperture width s. A typical structure consists of four layers of RT/duroid microwave laminate material ( = 2.2) sandwiched together as illustrated in Fig The two outer layers are in. thick with 1 oz/ft 2 of copper on their outer surfaces. The stripline electrode width (w in Fig. 73.4) on the opposite side of these layers is in. (experimentally verified to provide a 50-Ω impedance) and is machined with a precision programmable milling machine. (Note that electrode 2 in Fig is shown on an intermediate layer. This is for illustration purposes only. This electrode in our device is machined on the bottom of the layer above it, making the two outer layers completely identical.) The two center layers are in. thick. One center layer has no copper on either surface and is used as a dielectric spacer. The other center layer has 1 oz/ft 2 of copper on one side only, with copper removed to form the appropriate coupling aperture. The LLE Review, Volume 73 3
4 structure is easily disassembled to replace the aperture layer to produce different shaped electrical waveforms. Several other ACSL geometries with different layer thickness and electrode widths were tested, but as will be shown below, the above geometry produces a sufficiently high electrical coupling coefficient for our pulse-shaping application. Three apertures having a width s that varies along the length of the line with the functional form of a simple Gaussian are used in the above structure to determine the dependence of the electrical coupling coefficient on the aperture width s. The maximum aperture widths of the three Gaussians are 5, 10, and 20 mm. Voltage measurements are made with a high-bandwidth (20-GHz) 10 sampling oscilloscope equipped with an electrical square-pulse generator for time domain reflectometer (TDR) measurements. The pulse from the TDR channel is sent into port 1 of the ACSL, and the output from port 4 is measured with a separate, high-bandwidth (20-GHz) channel of the oscilloscope. The time axis of the measured voltage waveforms is mapped to position along the ACSL using the electrical propagation velocity in the RT/duroid material. From our measurements on the three Gaussian apertures, the electrical coupling coefficient versus aperture width is obtained and shown in Fig The data in Fig are used in our model to design ACSL devices that produce specific voltage waveforms for the optical-pulse-shaping system. Electrical coupling coefficient E Aperture width (mm) Figure 73.5 The electrical coupling coefficient, defined as the ratio of the output voltage at port 4 to the input voltage at port 1 in Fig. 73.3, plotted as a function of aperture width for an ACSL with the geometry discussed in the text. The output voltage measured at port 4 of an ACSL with 5-mm-Gaussian aperture is plotted with a solid line in Fig (normalized to the voltage of the input square pulse applied to port 1) along with the prediction of our model plotted with a dashed line. For high coupling coefficients, depletion of the input square-pulse voltage as it propagates along electrode 1 cannot be neglected and is included in our model. Normalized voltage E Measured Calculated Time (ns) Figure 73.6 The measured output voltage waveform (solid line) from an ACSL having a Gaussian aperture along the length of the coupling region with a 5-mm maximum aperture width. The calculated output voltage from this structure (dashed line) is also shown. Temporally shaped optical pulses have been produced using the pulse-shaping system shown in Fig with the ACSL geometry described above. A commercially available squarepulse generator 11 that provides a 35-V square pulse with 100-ps rise time is used as input to the ACSL. The half-wave voltage of the optical modulators used for pulse shaping is approximately 8 V. Hence, the coupling coefficients of 0.25 (shown in Fig. 73.5) obtainable with the ACSL structure described above are adequate for this application. To verify our ACSL model, the output voltage at port 4 of an ACSL designed to produce a specific optical pulse shape is sent to an optical modulator. The measured shaped optical pulse from the modulator is plotted with a solid line in Fig. 73.7; the optical pulse shape that is desired from this system is plotted with a dashed line. This figure illustrates the excellent performance and predictability of the ACSL pulse-shaping system. Pulse-Shaping-Systems Comparison By comparing the pulse-shaping systems shown in Figs and 73.2, it can be seen that the ACSL system eliminates the need for the CWML laser, the regen with SBS pulse steepener and amplifier, the fiber distribution system, and the PC switches. The key operational advantage of the ACSL pulse-shaping system that allows this simplification is 5 4 LLE Review, Volume 73
5 Normalized voltage E Measured Design Time (ns) Figure 73.7 The measured temporally shaped optical pulse from an ACSL pulse-shaping system (solid line). The desired optical pulse shape (dashed line) from this system is also shown. that the shaped electrical waveform from the ACSL exits from a different port than that used to input the square electrical pulse. Consequently, any suitable electrical square-pulse generator can be used to generate shaped electrical waveforms. In addition to this enormous simplification, there is no source of prepulse noise (capacitive voltage spike or dc offset voltage) since coupling cannot occur before application of the square electrical pulse to the ACSL. The system can also be accurately timed to the OMEGA master timing reference (38-MHz rf or 76-MHz CWML-laser optical pulses). The rms timing jitter between the 76-MHz CWML-laser optical pulses and the generation of the shaped electrical waveforms is measured to be less than 10 ps. Conclusions An optical-pulse-shaping system based on an ACSL has been designed and tested. This system produces temporally shaped optical pulses with high bandwidth suitable for OMEGA pulse-shaping applications. The design is a significant simplification over existing technology with improved performance capabilities. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Inertial Confinement Fusion under Cooperative Agreement No. DE-FC03-92SF19460, the University of Rochester, and the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority. The support of DOE does not constitute an endorsement by DOE of the views expressed in this article. REFERENCES 1. R. B. Wilcox, U.S. Patent No. 4,667,161 (19 May 1987). 2. R. B. Wilcox et al., in Laser Coherence Control: Technology and Applications, edited by H. T. Powell and T. J. Kessler (SPIE, Bellingham, WA, 1993), Vol. 1870, pp A. Okishev, M. D. Skeldon, S. A. Letzring, W. R. Donaldson, A. Babushkin, and W. Seka, in Superintense Laser Fields, edited by A. A. Andreev and V. M. Gordienko (SPIE, Bellingham, WA, 1996), Vol. 2770, pp A. V. Okishev and W. Seka, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 3, 59 (1997). 5. M. D. Skeldon and S. T. Bui, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 10, 677 (1993). 6. M. D. Skeldon, A. Okishev, A. Babushkin, and W. Seka, in First Annual International Conference on Solid State Lasers for Application to Inertial Confinement Fusion, edited by M. André and H. T. Powell (SPIE, Bellingham, WA, 1995), Vol. 2633, pp M. D. Skeldon, A. Okishev, S. A. Letzring, W. R. Donaldson, K. Green, W. Seka, and L. Fuller, in Optically Activated Switching IV, edited by W. R. Donaldson (SPIE, Bellingham, WA, 1994), Vol. 2343, pp B. C. Wadell, Transmission Line Design Handbook (Artech House, Boston, 1991). 9. RT/duroid, Rogers Corporation, Microwave Division, Chandler, AZ GHz sampling oscilloscope, Model No. HP54120B/54124A, Hewlett Packard, Santa Clara, CA Pulse generator, Model No. 4500E, Picosecond Pulse Labs, Boulder, CO LLE Review, Volume 73 5
High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses
 High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses Since its invention in the early 199s, 1 optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification
High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses Since its invention in the early 199s, 1 optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification
Design and experimental realization of the chirped microstrip line
 Chapter 4 Design and experimental realization of the chirped microstrip line 4.1. Introduction In chapter 2 it has been shown that by using a microstrip line, uniform insertion losses A 0 (ω) and linear
Chapter 4 Design and experimental realization of the chirped microstrip line 4.1. Introduction In chapter 2 it has been shown that by using a microstrip line, uniform insertion losses A 0 (ω) and linear
Time-Multiplexed Pulse Shaping
 Time-Multiplexed Pulse Shaping Introduction Optical pulses are used to transmit information, perform remote sensing and metrology, and study physical processes in matter. These optics and photonics applications
Time-Multiplexed Pulse Shaping Introduction Optical pulses are used to transmit information, perform remote sensing and metrology, and study physical processes in matter. These optics and photonics applications
Comparison of IC Conducted Emission Measurement Methods
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 52, NO. 3, JUNE 2003 839 Comparison of IC Conducted Emission Measurement Methods Franco Fiori, Member, IEEE, and Francesco Musolino, Member, IEEE
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INSTRUMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT, VOL. 52, NO. 3, JUNE 2003 839 Comparison of IC Conducted Emission Measurement Methods Franco Fiori, Member, IEEE, and Francesco Musolino, Member, IEEE
Measuring PCB, Cable and Interconnect Impedance, Dielectric Constants, Velocity Factor, and Lengths
 Measuring PCB, Cable and Interconnect Impedance, Dielectric Constants, Velocity Factor, and Lengths Controlled impedance printed circuit boards (PCBs) often include a measurement coupon, which typically
Measuring PCB, Cable and Interconnect Impedance, Dielectric Constants, Velocity Factor, and Lengths Controlled impedance printed circuit boards (PCBs) often include a measurement coupon, which typically
Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH. Competence Area: Fiber Devices
 Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH Competence Area: Fiber Devices Topics in this Area Fiber lasers, including exotic types Fiber amplifiers, including telecom-type devices and high power
Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH Competence Area: Fiber Devices Topics in this Area Fiber lasers, including exotic types Fiber amplifiers, including telecom-type devices and high power
ModBox Pulse Shaper Arbitrary Optical Waveform Generator
 Delivering Modulation Solutions ModBox The Photline Modbox-Pulse-Shaper is an Optical Modulation Unit to generate short shaped pulses with high extinction ratio at 1030 nm, 1053 nm or 1064 nm. It allows
Delivering Modulation Solutions ModBox The Photline Modbox-Pulse-Shaper is an Optical Modulation Unit to generate short shaped pulses with high extinction ratio at 1030 nm, 1053 nm or 1064 nm. It allows
Rectangular Patch Antenna to Operate in Flame Retardant 4 Using Coaxial Feeding Technique
 International Journal of Electronics Engineering Research. ISSN 0975-6450 Volume 9, Number 3 (2017) pp. 399-407 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Rectangular Patch Antenna to Operate
International Journal of Electronics Engineering Research. ISSN 0975-6450 Volume 9, Number 3 (2017) pp. 399-407 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Rectangular Patch Antenna to Operate
ECE 4265/6265 Laboratory Project 7 Network Analyzer Calibration
 ECE 4265/6265 Laboratory Project 7 Network Analyzer Calibration Objectives The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concepts of calibration and error correction for microwave s-parameter measurements.
ECE 4265/6265 Laboratory Project 7 Network Analyzer Calibration Objectives The purpose of this lab is to introduce the concepts of calibration and error correction for microwave s-parameter measurements.
Improving TDR/TDT Measurements Using Normalization Application Note
 Improving TDR/TDT Measurements Using Normalization Application Note 1304-5 2 TDR/TDT and Normalization Normalization, an error-correction process, helps ensure that time domain reflectometer (TDR) and
Improving TDR/TDT Measurements Using Normalization Application Note 1304-5 2 TDR/TDT and Normalization Normalization, an error-correction process, helps ensure that time domain reflectometer (TDR) and
Experiment No. 6 Pre-Lab Transmission Lines and Time Domain Reflectometry
 Experiment No. 6 Pre-Lab Transmission Lines and Time Domain Reflectometry The Pre-Labs are informational and although they follow the procedures in the experiment, they are to be completed outside of the
Experiment No. 6 Pre-Lab Transmission Lines and Time Domain Reflectometry The Pre-Labs are informational and although they follow the procedures in the experiment, they are to be completed outside of the
High Rep-Rate KrF Laser Development and Intense Pulse Interaction Experiments for IFE*
 High Rep-Rate KrF Laser Development and Intense Pulse Interaction Experiments for IFE* Y. Owadano, E. Takahashi, I. Okuda, I. Matsushima, Y. Matsumoto, S. Kato, E. Miura and H.Yashiro 1), K. Kuwahara 2)
High Rep-Rate KrF Laser Development and Intense Pulse Interaction Experiments for IFE* Y. Owadano, E. Takahashi, I. Okuda, I. Matsushima, Y. Matsumoto, S. Kato, E. Miura and H.Yashiro 1), K. Kuwahara 2)
Testing with Femtosecond Pulses
 Testing with Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.3 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
Testing with Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.3 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
Electronic Package Failure Analysis Using TDR
 Application Note Electronic Package Failure Analysis Using TDR Introduction Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) measurement methodology is increasing in importance as a nondestructive method for fault location
Application Note Electronic Package Failure Analysis Using TDR Introduction Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) measurement methodology is increasing in importance as a nondestructive method for fault location
Design and Performance of a Selectable-Rate Streak-Camera Deflection Ramp Generator
 Design and Performance of a Selectable-Rate Streak-Camera Deflection Ramp Generator Introduction Electro-optic streak cameras have been used at LLE for many years to resolve high-bandwidth, low-repetition-rate,
Design and Performance of a Selectable-Rate Streak-Camera Deflection Ramp Generator Introduction Electro-optic streak cameras have been used at LLE for many years to resolve high-bandwidth, low-repetition-rate,
3.6 An Ultra-Stable Nd:YAG-Based Laser Source. 8. Jayatna Venkataraman (private communication). ACKNOWLEDGMENT
 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was supported by the following sponsors of the Laser Fusion Feasibil~ty Project at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics-Empire State Electric Energy
ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was supported by the following sponsors of the Laser Fusion Feasibil~ty Project at the Laboratory for Laser Energetics-Empire State Electric Energy
ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating
 ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating Spectral density (db) 0 10 20 30 40 Mirror VBG 1053.0 1053.3 1053.6 Wavelength (nm) Frontiers in Optics 2007/Laser
ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating Spectral density (db) 0 10 20 30 40 Mirror VBG 1053.0 1053.3 1053.6 Wavelength (nm) Frontiers in Optics 2007/Laser
ModBox-FE-125ps-10mJ. Performance Highlights FEATURES APPLICATIONS. Electrical & Optical Pulse Diagrams
 The System-FE-1064nm is set to generate short shaped pulses with high extinction ratio at 1064.1 nm. It allows dynamic extinction ratio up to 55 db with user adjustable pulse duration, repetition rate
The System-FE-1064nm is set to generate short shaped pulses with high extinction ratio at 1064.1 nm. It allows dynamic extinction ratio up to 55 db with user adjustable pulse duration, repetition rate
ModBox - Spectral Broadening Unit
 ModBox - Spectral Broadening Unit The ModBox Family The ModBox systems are a family of turnkey optical transmitters and external modulation benchtop units for digital and analog transmission, pulsed and
ModBox - Spectral Broadening Unit The ModBox Family The ModBox systems are a family of turnkey optical transmitters and external modulation benchtop units for digital and analog transmission, pulsed and
A Pin-Loaded Microstrip Patch Antenna with the Ability to Suppress Surface Wave Excitation
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 62, 131 137, 2016 A Pin-Loaded Microstrip Patch Antenna with the Ability to Suppress Surface Wave Excitation Ayed R. AlAjmi and Mohammad A. Saed * Abstract
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 62, 131 137, 2016 A Pin-Loaded Microstrip Patch Antenna with the Ability to Suppress Surface Wave Excitation Ayed R. AlAjmi and Mohammad A. Saed * Abstract
DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M.
 DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M. Published in: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium of the IEEE Photonics
DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M. Published in: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium of the IEEE Photonics
Keysight Technologies Signal Integrity Tips and Techniques Using TDR, VNA and Modeling
 Keysight Technologies Signal Integrity Tips and Techniques Using, VNA and Modeling Article Reprint This article first appeared in the March 216 edition of Microwave Journal. Reprinted with kind permission
Keysight Technologies Signal Integrity Tips and Techniques Using, VNA and Modeling Article Reprint This article first appeared in the March 216 edition of Microwave Journal. Reprinted with kind permission
High-Yield Bang Time Detector for the OMEGA Laser
 High-Yield Bang Time Detector for the OMEGA Laser Introduction The time interval from the beginning of the laser pulse to the peak of neutron emission (bang time) is an important parameter in inertial
High-Yield Bang Time Detector for the OMEGA Laser Introduction The time interval from the beginning of the laser pulse to the peak of neutron emission (bang time) is an important parameter in inertial
Microwave Characterization and Modeling of Multilayered Cofired Ceramic Waveguides
 Microwave Characterization and Modeling of Multilayered Cofired Ceramic Waveguides Microwave Characterization and Modeling of Multilayered Cofired Ceramic Waveguides Daniel Stevens and John Gipprich Northrop
Microwave Characterization and Modeling of Multilayered Cofired Ceramic Waveguides Microwave Characterization and Modeling of Multilayered Cofired Ceramic Waveguides Daniel Stevens and John Gipprich Northrop
Using Pcb-Techniques And Dielectric Design Band Pass Filter Resonators For Ku - Band Applications
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 2, ISSUE 5 149 Using Pcb-Techniques And Dielectric Design Band Pass Filter Resonators For Ku - Band Applications
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 2, ISSUE 5 149 Using Pcb-Techniques And Dielectric Design Band Pass Filter Resonators For Ku - Band Applications
Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification
 Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification Input pulse (single frequency) AWG RF amp Output pulse (chirped) Phase modulator Normalized spectral intensity (db) 64 65 66 67 68 69 1052.4
Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification Input pulse (single frequency) AWG RF amp Output pulse (chirped) Phase modulator Normalized spectral intensity (db) 64 65 66 67 68 69 1052.4
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers
 Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
Module 16 : Integrated Optics I
 Module 16 : Integrated Optics I Lecture : Integrated Optics I Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Electro-Optic Effect Optical Phase Modulator Optical Amplitude Modulator
Module 16 : Integrated Optics I Lecture : Integrated Optics I Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Introduction Electro-Optic Effect Optical Phase Modulator Optical Amplitude Modulator
High Speed Digital Systems Require Advanced Probing Techniques for Logic Analyzer Debug
 JEDEX 2003 Memory Futures (Track 2) High Speed Digital Systems Require Advanced Probing Techniques for Logic Analyzer Debug Brock J. LaMeres Agilent Technologies Abstract Digital systems are turning out
JEDEX 2003 Memory Futures (Track 2) High Speed Digital Systems Require Advanced Probing Techniques for Logic Analyzer Debug Brock J. LaMeres Agilent Technologies Abstract Digital systems are turning out
THE PROPAGATION OF PARTIAL DISCHARGE PULSES IN A HIGH VOLTAGE CABLE
 THE PROPAGATION OF PARTIAL DISCHARGE PULSES IN A HIGH VOLTAGE CABLE Z.Liu, B.T.Phung, T.R.Blackburn and R.E.James School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommuniications University of New South Wales
THE PROPAGATION OF PARTIAL DISCHARGE PULSES IN A HIGH VOLTAGE CABLE Z.Liu, B.T.Phung, T.R.Blackburn and R.E.James School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommuniications University of New South Wales
ModBox-FE-NIR Near-Infra Red Front-End Laser Source
 FEATURES Optical waveform flexibility Low jitter Low rise & fall times Very high extinction ratio and stability Proven solution APPLICATIONS Inertial confinement fusion Interaction of intense light with
FEATURES Optical waveform flexibility Low jitter Low rise & fall times Very high extinction ratio and stability Proven solution APPLICATIONS Inertial confinement fusion Interaction of intense light with
There is a twenty db improvement in the reflection measurements when the port match errors are removed.
 ABSTRACT Many improvements have occurred in microwave error correction techniques the past few years. The various error sources which degrade calibration accuracy is better understood. Standards have been
ABSTRACT Many improvements have occurred in microwave error correction techniques the past few years. The various error sources which degrade calibration accuracy is better understood. Standards have been
Design Guide for High-Speed Controlled Impedance Circuit Boards
 IPC-2141A ASSOCIATION CONNECTING ELECTRONICS INDUSTRIES Design Guide for High-Speed Controlled Impedance Circuit Boards Developed by the IPC Controlled Impedance Task Group (D-21c) of the High Speed/High
IPC-2141A ASSOCIATION CONNECTING ELECTRONICS INDUSTRIES Design Guide for High-Speed Controlled Impedance Circuit Boards Developed by the IPC Controlled Impedance Task Group (D-21c) of the High Speed/High
The data rates of today s highspeed
 HIGH PERFORMANCE Measure specific parameters of an IEEE 1394 interface with Time Domain Reflectometry. Michael J. Resso, Hewlett-Packard and Michael Lee, Zayante Evaluating Signal Integrity of IEEE 1394
HIGH PERFORMANCE Measure specific parameters of an IEEE 1394 interface with Time Domain Reflectometry. Michael J. Resso, Hewlett-Packard and Michael Lee, Zayante Evaluating Signal Integrity of IEEE 1394
PoS(PhotoDet 2012)051
 Optical to electrical detection delay in avalanche photodiode based detector and its interpretation Josef Blažej 1 E-mail: blazej@fjfi.cvut.cz Ivan Procházka Jan Kodet Technical University in Munich FSG,
Optical to electrical detection delay in avalanche photodiode based detector and its interpretation Josef Blažej 1 E-mail: blazej@fjfi.cvut.cz Ivan Procházka Jan Kodet Technical University in Munich FSG,
Design and Characterization of a Micro-Strip RF Anode for Large- Area based Photodetectors Orsay- Friday, June Hervé Grabas UChicago / CEA
 Design and Characterization of a Micro-Strip RF Anode for Large- Area based Photodetectors Orsay- Friday, June 15. 2012 Hervé Grabas UChicago / CEA Saclay Irfu. Outline Introduction Precise timing in physics
Design and Characterization of a Micro-Strip RF Anode for Large- Area based Photodetectors Orsay- Friday, June 15. 2012 Hervé Grabas UChicago / CEA Saclay Irfu. Outline Introduction Precise timing in physics
Measuring 8- to 250-ps Short Pulses Using a High-Speed Streak Camera on Kilojule, Petawatt-Class Laser Systems
 Measuring 8- to 25-ps Short Pulses Using a High-Speed Streak Camera on Kilojule, Petawatt-Class Laser Systems Measuring 8- to 25-ps Short Pulses Using a High-Speed Streak Camera on Kilojoule, Petawatt-Class
Measuring 8- to 25-ps Short Pulses Using a High-Speed Streak Camera on Kilojule, Petawatt-Class Laser Systems Measuring 8- to 25-ps Short Pulses Using a High-Speed Streak Camera on Kilojoule, Petawatt-Class
2.C A Substrate-Independent Noncontact Electro-Optic Probe Using Total Internal Reflection. 5. LLE Review 27, (1986).
 LLE REVIEW, Volume 32 transmission lines and the DUT may be fabricated on a common substrate, eliminating the need for wirebond connections. 3. Photoconductive switching and electro-optic sampling allow
LLE REVIEW, Volume 32 transmission lines and the DUT may be fabricated on a common substrate, eliminating the need for wirebond connections. 3. Photoconductive switching and electro-optic sampling allow
Line Impedance Analyzer TDR 3000
 Line Impedance Analyzer TDR 3000 Line Impedance Analyzer TDR 3000 Key Features ˆ Compact Instrument for TDR Measurement ˆ Simple Measurement of Line Impedances and Reections even on Internal Layers of
Line Impedance Analyzer TDR 3000 Line Impedance Analyzer TDR 3000 Key Features ˆ Compact Instrument for TDR Measurement ˆ Simple Measurement of Line Impedances and Reections even on Internal Layers of
Estimation of the Loss in the ECH Transmission Lines for ITER
 Estimation of the Loss in the ECH Transmission Lines for ITER S. T. Han, M. A. Shapiro, J. R. Sirigiri, D. Tax, R. J. Temkin and P. P. Woskov MIT Plasma Science and Fusion Center, MIT Building NW16-186,
Estimation of the Loss in the ECH Transmission Lines for ITER S. T. Han, M. A. Shapiro, J. R. Sirigiri, D. Tax, R. J. Temkin and P. P. Woskov MIT Plasma Science and Fusion Center, MIT Building NW16-186,
Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) and Time Domain Transmission (TDT) Measurement Fundamentals
 Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) and Time Domain Transmission (TDT) Measurement Fundamentals James R. Andrews, Ph.D., IEEE Fellow PSPL Founder & former President (retired) INTRODUCTION Many different kinds
Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) and Time Domain Transmission (TDT) Measurement Fundamentals James R. Andrews, Ph.D., IEEE Fellow PSPL Founder & former President (retired) INTRODUCTION Many different kinds
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: /NPHOTON
 Supplementary Methods and Data 1. Apparatus Design The time-of-flight measurement apparatus built in this study is shown in Supplementary Figure 1. An erbium-doped femtosecond fibre oscillator (C-Fiber,
Supplementary Methods and Data 1. Apparatus Design The time-of-flight measurement apparatus built in this study is shown in Supplementary Figure 1. An erbium-doped femtosecond fibre oscillator (C-Fiber,
Status on Pulsed Timing Distribution Systems and Implementations at DESY, FERMI and XFEL
 FLS Meeting March 7, 2012 Status on Pulsed Timing Distribution Systems and Implementations at DESY, FERMI and XFEL Franz X. Kärtner Center for Free-Electron Laser Science, DESY and Department of Physics,
FLS Meeting March 7, 2012 Status on Pulsed Timing Distribution Systems and Implementations at DESY, FERMI and XFEL Franz X. Kärtner Center for Free-Electron Laser Science, DESY and Department of Physics,
Microstrip Filter Design
 Practical Aspects of Microwave Filter Design and Realization IMS 5 Workshop-WMB Microstrip Filter Design Jia-Sheng Hong Heriot-Watt University Edinburgh, UK Outline Introduction Design considerations Design
Practical Aspects of Microwave Filter Design and Realization IMS 5 Workshop-WMB Microstrip Filter Design Jia-Sheng Hong Heriot-Watt University Edinburgh, UK Outline Introduction Design considerations Design
Investigate the characteristics of PIN Photodiodes and understand the usage of the Lightwave Analyzer component.
 PIN Photodiode 1 OBJECTIVE Investigate the characteristics of PIN Photodiodes and understand the usage of the Lightwave Analyzer component. 2 PRE-LAB In a similar way photons can be generated in a semiconductor,
PIN Photodiode 1 OBJECTIVE Investigate the characteristics of PIN Photodiodes and understand the usage of the Lightwave Analyzer component. 2 PRE-LAB In a similar way photons can be generated in a semiconductor,
Detection of Lower Hybrid Waves on Alcator C-Mod with Phase Contrast Imaging Using Electro-Optic Modulators
 Detection of Lower Hybrid Waves on Alcator C-Mod with Phase Contrast Imaging Using Electro-Optic Modulators K. Arai, M. Porkolab, N. Tsujii, P. Koert, R. Parker, P. Woskov, S. Wukitch MIT Plasma Science
Detection of Lower Hybrid Waves on Alcator C-Mod with Phase Contrast Imaging Using Electro-Optic Modulators K. Arai, M. Porkolab, N. Tsujii, P. Koert, R. Parker, P. Woskov, S. Wukitch MIT Plasma Science
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017
 R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
Switch-less Dual-frequency Reconfigurable CMOS Oscillator using One Single Piezoelectric AlN MEMS Resonator with Co-existing S0 and S1 Lamb-wave Modes
 From the SelectedWorks of Chengjie Zuo January, 11 Switch-less Dual-frequency Reconfigurable CMOS Oscillator using One Single Piezoelectric AlN MEMS Resonator with Co-existing S and S1 Lamb-wave Modes
From the SelectedWorks of Chengjie Zuo January, 11 Switch-less Dual-frequency Reconfigurable CMOS Oscillator using One Single Piezoelectric AlN MEMS Resonator with Co-existing S and S1 Lamb-wave Modes
Application Note 5525
 Using the Wafer Scale Packaged Detector in 2 to 6 GHz Applications Application Note 5525 Introduction The is a broadband directional coupler with integrated temperature compensated detector designed for
Using the Wafer Scale Packaged Detector in 2 to 6 GHz Applications Application Note 5525 Introduction The is a broadband directional coupler with integrated temperature compensated detector designed for
Experiment 9: Microwave Directional Couplers and Hybrids
 Experiment 9: Microwave Directional Couplers and Hybrids 1. Directional Couplers and Hybrids Directional couplers and hybrids are used in a variety of important applications at microwave frequencies. The
Experiment 9: Microwave Directional Couplers and Hybrids 1. Directional Couplers and Hybrids Directional couplers and hybrids are used in a variety of important applications at microwave frequencies. The
Radio over Fiber technology for 5G Cloud Radio Access Network Fronthaul
 Radio over Fiber technology for 5G Cloud Radio Access Network Fronthaul Using a highly linear fiber optic transceiver with IIP3 > 35 dbm, operating at noise level of -160dB/Hz, we demonstrate 71 km RF
Radio over Fiber technology for 5G Cloud Radio Access Network Fronthaul Using a highly linear fiber optic transceiver with IIP3 > 35 dbm, operating at noise level of -160dB/Hz, we demonstrate 71 km RF
GHZ STRIPLINE TRANSVERSAL FILTER FOR SUB-PICOSECOND BUNCH TIMING MEASUREMENTS*
 Proceedings of BIW1, Santa Fe, New Mexico, US TUPSM8 11.424 GHZ STRIPLINE TRANSVERSAL FILTER FOR SUB-PICOSECOND BUNCH TIMING MEASUREMENTS* D. Van Winkle, A. Young, J. D. Fox SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory,
Proceedings of BIW1, Santa Fe, New Mexico, US TUPSM8 11.424 GHZ STRIPLINE TRANSVERSAL FILTER FOR SUB-PICOSECOND BUNCH TIMING MEASUREMENTS* D. Van Winkle, A. Young, J. D. Fox SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory,
Laboratory investigation of an intensiometric dual FBG-based hybrid voltage sensor
 Fusiek, Grzegorz and Niewczas, Pawel (215) Laboratory investigation of an intensiometric dual FBG-based hybrid voltage sensor. In: Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering.
Fusiek, Grzegorz and Niewczas, Pawel (215) Laboratory investigation of an intensiometric dual FBG-based hybrid voltage sensor. In: Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering.
P a g e 1 ST985. TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual. Analog Arts Inc.
 P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
ANALYSIS OF DISPERSION COMPENSATION IN A SINGLE MODE OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
 ANAYSIS OF DISPERSION COMPENSATION IN A SINGE MODE OPTICA FIBER COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Sani Abdullahi Mohammed 1, Engr. Yahya Adamu and Engr. Matthew Kwatri uka 3 1,,3 Department of Electrical and Electronics
ANAYSIS OF DISPERSION COMPENSATION IN A SINGE MODE OPTICA FIBER COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Sani Abdullahi Mohammed 1, Engr. Yahya Adamu and Engr. Matthew Kwatri uka 3 1,,3 Department of Electrical and Electronics
High Speed Competitive Comparison Report. Samtec MMCX-J-P-H-ST-TH1 Mated With MMCX-P-P-H-ST-TH1 Competitor A (Mated Set) Competitor B (Mated Set)
 High Speed Competitive Comparison Report Samtec MMCX-J-P-H-ST-TH1 Mated With MMCX-P-P-H-ST-TH1 Competitor A (Mated Set) Competitor B (Mated Set) REVISION DATE: January 6, 2005 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...
High Speed Competitive Comparison Report Samtec MMCX-J-P-H-ST-TH1 Mated With MMCX-P-P-H-ST-TH1 Competitor A (Mated Set) Competitor B (Mated Set) REVISION DATE: January 6, 2005 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...
High-frequency transmission line transitions
 High-frequency transmission line transitions Leonard T. Hall a,b,hedleyj.hansen a,b,c, and Derek Abbott a,b a Centre for Biomedical Engineering, The University of Adelaide, SA 55 Australia b Department
High-frequency transmission line transitions Leonard T. Hall a,b,hedleyj.hansen a,b,c, and Derek Abbott a,b a Centre for Biomedical Engineering, The University of Adelaide, SA 55 Australia b Department
FAST KICKERS LNF-INFN
 ILC Damping Rings R&D Workshop - ILCDR06 September 26-28, 2006 at Cornell University FAST KICKERS R&D @ LNF-INFN Fabio Marcellini for the LNF fast kickers study group* * D. Alesini, F. Marcellini P. Raimondi,
ILC Damping Rings R&D Workshop - ILCDR06 September 26-28, 2006 at Cornell University FAST KICKERS R&D @ LNF-INFN Fabio Marcellini for the LNF fast kickers study group* * D. Alesini, F. Marcellini P. Raimondi,
What s inside. Highlights. Welcome. Mixer test third in a series. New time-domain technique for measuring mixer group delay
 What s inside 2 New time-domain technique for measuring mixer group delay 3 Uncertainty in mixer group-delay measurements 5 Isolation a problem? Here s how to measure mixer group delay 6 Low-power mixer
What s inside 2 New time-domain technique for measuring mixer group delay 3 Uncertainty in mixer group-delay measurements 5 Isolation a problem? Here s how to measure mixer group delay 6 Low-power mixer
Investigations on the performance of lidar measurements with different pulse shapes using a multi-channel Doppler lidar system
 Th12 Albert Töws Investigations on the performance of lidar measurements with different pulse shapes using a multi-channel Doppler lidar system Albert Töws and Alfred Kurtz Cologne University of Applied
Th12 Albert Töws Investigations on the performance of lidar measurements with different pulse shapes using a multi-channel Doppler lidar system Albert Töws and Alfred Kurtz Cologne University of Applied
Agilent Time Domain Analysis Using a Network Analyzer
 Agilent Time Domain Analysis Using a Network Analyzer Application Note 1287-12 0.0 0.045 0.6 0.035 Cable S(1,1) 0.4 0.2 Cable S(1,1) 0.025 0.015 0.005 0.0 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 Frequency (GHz) 0.005
Agilent Time Domain Analysis Using a Network Analyzer Application Note 1287-12 0.0 0.045 0.6 0.035 Cable S(1,1) 0.4 0.2 Cable S(1,1) 0.025 0.015 0.005 0.0 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 Frequency (GHz) 0.005
THROUGHOUT the last several years, many contributions
 244 IEEE ANTENNAS AND WIRELESS PROPAGATION LETTERS, VOL. 6, 2007 Design and Analysis of Microstrip Bi-Yagi and Quad-Yagi Antenna Arrays for WLAN Applications Gerald R. DeJean, Member, IEEE, Trang T. Thai,
244 IEEE ANTENNAS AND WIRELESS PROPAGATION LETTERS, VOL. 6, 2007 Design and Analysis of Microstrip Bi-Yagi and Quad-Yagi Antenna Arrays for WLAN Applications Gerald R. DeJean, Member, IEEE, Trang T. Thai,
Challenges and Solutions for Removing Fixture Effects in Multi-port Measurements
 DesignCon 2008 Challenges and Solutions for Removing Fixture Effects in Multi-port Measurements Robert Schaefer, Agilent Technologies schaefer-public@agilent.com Abstract As data rates continue to rise
DesignCon 2008 Challenges and Solutions for Removing Fixture Effects in Multi-port Measurements Robert Schaefer, Agilent Technologies schaefer-public@agilent.com Abstract As data rates continue to rise
Measurement and Analysis for Switchmode Power Design
 Measurement and Analysis for Switchmode Power Design Switched Mode Power Supply Measurements AC Input Power measurements Safe operating area Harmonics and compliance Efficiency Switching Transistor Losses
Measurement and Analysis for Switchmode Power Design Switched Mode Power Supply Measurements AC Input Power measurements Safe operating area Harmonics and compliance Efficiency Switching Transistor Losses
Analysis of Microstrip Circuits Using a Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method
 Analysis of Microstrip Circuits Using a Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method M.G. BANCIU and R. RAMER School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications University of New South Wales Sydney 5 NSW
Analysis of Microstrip Circuits Using a Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method M.G. BANCIU and R. RAMER School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunications University of New South Wales Sydney 5 NSW
Characterization of Silicon-based Ultrasonic Nozzles
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 7, No. 2, pp. 123 127 (24) 123 Characterization of licon-based Ultrasonic Nozzles Y. L. Song 1,2 *, S. C. Tsai 1,3, Y. F. Chou 4, W. J. Chen 1, T. K. Tseng
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 7, No. 2, pp. 123 127 (24) 123 Characterization of licon-based Ultrasonic Nozzles Y. L. Song 1,2 *, S. C. Tsai 1,3, Y. F. Chou 4, W. J. Chen 1, T. K. Tseng
Politecnico di Torino. Porto Institutional Repository
 Politecnico di Torino Porto Institutional Repository [Proceeding] Integrated miniaturized antennas for automotive applications Original Citation: Vietti G., Dassano G., Orefice M. (2010). Integrated miniaturized
Politecnico di Torino Porto Institutional Repository [Proceeding] Integrated miniaturized antennas for automotive applications Original Citation: Vietti G., Dassano G., Orefice M. (2010). Integrated miniaturized
Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications by Stuart M. Wentworth Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
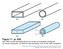 Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
UNIT Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion?
 UNIT 3 1. Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion? Ans: The dispersion of the transmitted optical signal causes distortion for both digital and analog transmission along optical fibers.
UNIT 3 1. Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion? Ans: The dispersion of the transmitted optical signal causes distortion for both digital and analog transmission along optical fibers.
DC to 3.5-GHz Amplified Photoreceivers Models 1591 & 1592
 USER S GUIDE DC to 3.5-GHz Amplified Photoreceivers Models 1591 & 1592 These photoreceivers are sensitive to electrostatic discharges and could be permanently damaged if subjected even to small discharges.
USER S GUIDE DC to 3.5-GHz Amplified Photoreceivers Models 1591 & 1592 These photoreceivers are sensitive to electrostatic discharges and could be permanently damaged if subjected even to small discharges.
Signal Integrity Testing with a Vector Network Analyzer. Neil Jarvis Applications Engineer
 Signal Integrity Testing with a Vector Network Analyzer Neil Jarvis Applications Engineer 1 Agenda RF Connectors A significant factor in repeatability and accuracy Selecting the best of several types for
Signal Integrity Testing with a Vector Network Analyzer Neil Jarvis Applications Engineer 1 Agenda RF Connectors A significant factor in repeatability and accuracy Selecting the best of several types for
Measurements 2: Network Analysis
 Measurements 2: Network Analysis Fritz Caspers CAS, Aarhus, June 2010 Contents Scalar network analysis Vector network analysis Early concepts Modern instrumentation Calibration methods Time domain (synthetic
Measurements 2: Network Analysis Fritz Caspers CAS, Aarhus, June 2010 Contents Scalar network analysis Vector network analysis Early concepts Modern instrumentation Calibration methods Time domain (synthetic
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE319
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE39 Laboratory Experiment Parasitic Capacitance and Oscilloscope Loading This lab is designed to familiarize you with some
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE39 Laboratory Experiment Parasitic Capacitance and Oscilloscope Loading This lab is designed to familiarize you with some
Measurement of Laddering Wave in Lossy Serpentine Delay Line
 International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2006.4, 3: 291-295 Measurement of Laddering Wave in Lossy Serpentine Delay Line Fang-Lin Chao * Department of industrial Design, Chaoyang University
International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2006.4, 3: 291-295 Measurement of Laddering Wave in Lossy Serpentine Delay Line Fang-Lin Chao * Department of industrial Design, Chaoyang University
High Speed Characterization Report
 QTH-030-01-L-D-A Mates with QSH-030-01-L-D-A Description: High Speed Ground Plane Header Board-to-Board, 0.5mm (.0197 ) Pitch, 5mm (.1969 ) Stack Height Samtec, Inc. 2005 All Rights Reserved Table of Contents
QTH-030-01-L-D-A Mates with QSH-030-01-L-D-A Description: High Speed Ground Plane Header Board-to-Board, 0.5mm (.0197 ) Pitch, 5mm (.1969 ) Stack Height Samtec, Inc. 2005 All Rights Reserved Table of Contents
All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating
 All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating Pavel Honzatko a, a Institute of Photonics and Electronics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, v.v.i.,
All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating Pavel Honzatko a, a Institute of Photonics and Electronics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, v.v.i.,
SAMPULSE50GHz and SAMPULSE70GHzANT PULSER/SAMPLER DEMO BOARD
 SAMPULSE50GHz and SAMPULSE70GHzANT PULSER/SAMPLER DEMO BOARD REV B. PRELIMINARY USER MANUAL 2/25/15 Figure 1. Connections to SAMPULSE50GHz (left) or SAMPULSE70GHzANT (right). INTRODUCTION: The SAMPULSE50GHz
SAMPULSE50GHz and SAMPULSE70GHzANT PULSER/SAMPLER DEMO BOARD REV B. PRELIMINARY USER MANUAL 2/25/15 Figure 1. Connections to SAMPULSE50GHz (left) or SAMPULSE70GHzANT (right). INTRODUCTION: The SAMPULSE50GHz
Broadband Rectangular Waveguide to GCPW Transition
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 46, 107 112, 2014 Broadband Rectangular Waveguide to GCPW Transition Jun Dong 1, *, Tao Yang 1, Yu Liu 1, Ziqiang Yang 1, and Yihong Zhou 2 Abstract
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 46, 107 112, 2014 Broadband Rectangular Waveguide to GCPW Transition Jun Dong 1, *, Tao Yang 1, Yu Liu 1, Ziqiang Yang 1, and Yihong Zhou 2 Abstract
Suppression of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering
 Suppression of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering 42 2 5 W i de l y T u n a b l e L a s e r T ra n s m i t te r www.lumentum.com Technical Note Introduction This technical note discusses the phenomenon and
Suppression of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering 42 2 5 W i de l y T u n a b l e L a s e r T ra n s m i t te r www.lumentum.com Technical Note Introduction This technical note discusses the phenomenon and
Model 305 Synchronous Countdown System
 Model 305 Synchronous Countdown System Introduction: The Model 305 pre-settable countdown electronics is a high-speed synchronous divider that generates an electronic trigger pulse, locked in time with
Model 305 Synchronous Countdown System Introduction: The Model 305 pre-settable countdown electronics is a high-speed synchronous divider that generates an electronic trigger pulse, locked in time with
Agilent 83440B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters
 Agilent 8344B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters DC-6/2/3 GHz, to 6 nm Technical Specifications Fast optical detector for characterizing lightwave signals Fast 5, 22, or 73 ps full-width half-max (FWHM)
Agilent 8344B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters DC-6/2/3 GHz, to 6 nm Technical Specifications Fast optical detector for characterizing lightwave signals Fast 5, 22, or 73 ps full-width half-max (FWHM)
Microwave Wireless Power Transmission System
 1 Microwave Wireless Power Transmission System Omar Alsaleh, Yousef Alkharraz, Khaled Aldousari, Talal Mustafawi, and Abdullah Aljadi Prof. Bradley Jackson California State University, Northridge November
1 Microwave Wireless Power Transmission System Omar Alsaleh, Yousef Alkharraz, Khaled Aldousari, Talal Mustafawi, and Abdullah Aljadi Prof. Bradley Jackson California State University, Northridge November
Application Note. Signal Integrity Modeling. SCSI Connector and Cable Modeling from TDR Measurements
 Application Note SCSI Connector and Cable Modeling from TDR Measurements Signal Integrity Modeling SCSI Connector and Cable Modeling from TDR Measurements Dima Smolyansky TDA Systems, Inc. http://www.tdasystems.com
Application Note SCSI Connector and Cable Modeling from TDR Measurements Signal Integrity Modeling SCSI Connector and Cable Modeling from TDR Measurements Dima Smolyansky TDA Systems, Inc. http://www.tdasystems.com
High Frequency Single & Multi-chip Modules based on LCP Substrates
 High Frequency Single & Multi-chip Modules based on Substrates Overview Labtech Microwave has produced modules for MMIC s (microwave monolithic integrated circuits) based on (liquid crystal polymer) substrates
High Frequency Single & Multi-chip Modules based on Substrates Overview Labtech Microwave has produced modules for MMIC s (microwave monolithic integrated circuits) based on (liquid crystal polymer) substrates
Coherent power combination of two Masteroscillator-power-amplifier. semiconductor lasers using optical phase lock loops
 Coherent power combination of two Masteroscillator-power-amplifier (MOPA) semiconductor lasers using optical phase lock loops Wei Liang, Naresh Satyan and Amnon Yariv Department of Applied Physics, MS
Coherent power combination of two Masteroscillator-power-amplifier (MOPA) semiconductor lasers using optical phase lock loops Wei Liang, Naresh Satyan and Amnon Yariv Department of Applied Physics, MS
DC to 12-GHz Amplified Photoreceivers Models 1544-B, 1554-B, & 1580-B
 USER S GUIDE DC to 12-GHz Amplified Photoreceivers Models 1544-B, 1554-B, & 1580-B Including multimode -50 option These photoreceivers are sensitive to electrostatic discharges and could be permanently
USER S GUIDE DC to 12-GHz Amplified Photoreceivers Models 1544-B, 1554-B, & 1580-B Including multimode -50 option These photoreceivers are sensitive to electrostatic discharges and could be permanently
Extraction of Frequency Dependent Transmission Line Parameters Using TDIUTDT Measurements
 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Budapest, Hungary, May 21-23,2001. Extraction of Frequency Dependent Transmission Line Parameters Using TDIUTDT Measurements Madhavan Swaminathan',
IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Budapest, Hungary, May 21-23,2001. Extraction of Frequency Dependent Transmission Line Parameters Using TDIUTDT Measurements Madhavan Swaminathan',
ModBox Pulse C-Band 30 ps
 ModBox The Photline Modbox-Pulse-CBand-30ps is a high extinction ratio optical Pulse Generator operating in the C-Band. It allows dynamic extinction ratio of 40dB@1550nm with high stability over time,
ModBox The Photline Modbox-Pulse-CBand-30ps is a high extinction ratio optical Pulse Generator operating in the C-Band. It allows dynamic extinction ratio of 40dB@1550nm with high stability over time,
MICROWAVE SCATTERING FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF A DISC-SHAPE VOID IN DIELECTRIC MATERIALS AND COMPOSITES
 MICROWAVE SCATTERING FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF A DISC-SHAPE VOID IN DIELECTRIC MATERIALS AND COMPOSITES John M. Liu Code 684 Naval Surface Warfare Center Carderock Div. West Bethesda, Md. 20817-5700
MICROWAVE SCATTERING FOR THE CHARACTERIZATION OF A DISC-SHAPE VOID IN DIELECTRIC MATERIALS AND COMPOSITES John M. Liu Code 684 Naval Surface Warfare Center Carderock Div. West Bethesda, Md. 20817-5700
ModBox-PG-795nm-30ps 795 nm 30 ps Optical Pulse Generator
 The Modbox-PG-795nm-30ps is a very high extinction ratio optical Pulse Generator operating in the 800nm-Band and firstly optimized at 795 nm. The -PG-795nm allows very high dynamic extinction ratio from
The Modbox-PG-795nm-30ps is a very high extinction ratio optical Pulse Generator operating in the 800nm-Band and firstly optimized at 795 nm. The -PG-795nm allows very high dynamic extinction ratio from
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Custom MMIC Packaging Solutions for High Frequency Thermally Efficient Surface Mount Applications.
 Custom MMIC Packaging Solutions for High Frequency Thermally Efficient Surface Mount Applications. Steve Melvin Principal Engineer Teledyne-Labtech 8 Vincent Avenue, Crownhill, Milton Keynes, MK8 AB Tel
Custom MMIC Packaging Solutions for High Frequency Thermally Efficient Surface Mount Applications. Steve Melvin Principal Engineer Teledyne-Labtech 8 Vincent Avenue, Crownhill, Milton Keynes, MK8 AB Tel
1550 nm Programmable Picosecond Laser, PM
 1550 nm Programmable Picosecond Laser, PM The Optilab is a programmable laser that produces picosecond pulses with electrical input pulses. It functions as a seed pulse generator for Master Oscillator
1550 nm Programmable Picosecond Laser, PM The Optilab is a programmable laser that produces picosecond pulses with electrical input pulses. It functions as a seed pulse generator for Master Oscillator
ModBox-SB-NIR Near Infra Red Spectral Broadening Unit
 The Spectral Broadening ModBox achieves the broadening of an optical signal by modulating its phase via the mean of a very efficient LiNb0 3 phase modulator. A number of side bands are created over a spectral
The Spectral Broadening ModBox achieves the broadening of an optical signal by modulating its phase via the mean of a very efficient LiNb0 3 phase modulator. A number of side bands are created over a spectral
Validation & Analysis of Complex Serial Bus Link Models
 Validation & Analysis of Complex Serial Bus Link Models Version 1.0 John Pickerd, Tektronix, Inc John.J.Pickerd@Tek.com 503-627-5122 Kan Tan, Tektronix, Inc Kan.Tan@Tektronix.com 503-627-2049 Abstract
Validation & Analysis of Complex Serial Bus Link Models Version 1.0 John Pickerd, Tektronix, Inc John.J.Pickerd@Tek.com 503-627-5122 Kan Tan, Tektronix, Inc Kan.Tan@Tektronix.com 503-627-2049 Abstract
Measurement Notes. Note 61. November Windscreen Shield Monitoring Using a Spiral Transmission Line
 Measurement Notes Note 61 November 28 Windscreen Shield Monitoring Using a Spiral Transmission Line Everett G. Farr. W. Scott Bigelow, and Leland H. Bowen Farr Research, Inc. Carl E Baum University of
Measurement Notes Note 61 November 28 Windscreen Shield Monitoring Using a Spiral Transmission Line Everett G. Farr. W. Scott Bigelow, and Leland H. Bowen Farr Research, Inc. Carl E Baum University of
-- - #331 FIVE ~ New: SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS & TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO FIBER OPTICS COMM.
 / #331 SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS & TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE Course Tit.le: FIBER OPTICS COMM. Code No.: ELN 318-3 Program: Semester: ELECTRONIC FIVE TECHNOLOGY Da t e : JUNE,
/ #331 SAULT COLLEGE OF APPLIED ARTS & TECHNOLOGY SAULT STE. MARIE, ONTARIO COURSE OUTLINE Course Tit.le: FIBER OPTICS COMM. Code No.: ELN 318-3 Program: Semester: ELECTRONIC FIVE TECHNOLOGY Da t e : JUNE,
H. Arab 1, C. Akyel 2
 angle VIRTUAL TRANSMISSION LINE OF CONICAL TYPE COAXIALOPEN-ENDED PROBE FOR DIELECTRIC MEASUREMENT H. Arab 1, C. Akyel 2 ABSTRACT 1,2 Ecole Polytechnique of Montreal, Canada An improved virtually conical
angle VIRTUAL TRANSMISSION LINE OF CONICAL TYPE COAXIALOPEN-ENDED PROBE FOR DIELECTRIC MEASUREMENT H. Arab 1, C. Akyel 2 ABSTRACT 1,2 Ecole Polytechnique of Montreal, Canada An improved virtually conical
A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method.
 PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
A Comparative Study of Resonator Based Method To Estimate Permittivity
 A Comparative Study of Resonator Based Method To Estimate Permittivity Chanchal Yadav Department of Physics & Electronics Rajdhani College, University of Delhi Delhi, India Abstract In resonator based
A Comparative Study of Resonator Based Method To Estimate Permittivity Chanchal Yadav Department of Physics & Electronics Rajdhani College, University of Delhi Delhi, India Abstract In resonator based
