Mixer Goal. Translate the carrier frequency of a RF signal. Conceptually this implies a multiplication: cos. V V t t t.
|
|
|
- Melissa Cummings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MICROWAVE MIXERS
2 Mixer Goal Translate the carrier frequency of a RF signal. Conceptually this implies a multiplication: cos ( ) V V cos t V V t t t RF M RF cos ( ) cos o V V V V t V t t t U RF M 0 RF V0 V M t RF t t V M t RF t t cos ( ) cos ( ) Filter RF RF RF +
3 Mixer in communication systems Frequency conversion receiver: Segnale Immagine Segnale RF im RF Mixer RF Filtro RF Filtro A Demodulatore Oscillatore Locale ( )
4 Practical implementation of a microwave mixer At microwave frequency is more easy to realize the frequency conversion exploiting port the non linear devices: V in =V RF +V Non linear V out F() non linear characteristic: port: 3 V out =F{V in } Vout av 1 in av in av 3 in... Substituting V RF and V and using the first non linear terms of the expansion: a Vout V0 VM a1v0cos0tvm cosrft a V t V t a V V t t 0 0 M RF 0 M 0 RF cos cos cos cos...
5 Classes of microwave mixers The most used non linear device is a Schotcky diode. There are two main classes of microwave mixers: Mixers with a single diode (single ended) Balanced Mixers (with o 4 diodes) Parameters of a microwave mixer: Conversion Loss(dB) (5 15 db) Linearity (referred to the translated RF signal) Noise Suppression of spurious products Input output match Isolation(RF, )
6 Analysis of single-ended mixers Equivalent circuit: Z RF Z LO Rd Z V RF V LO Pumped diode The diode (R d ) is represented by the exponential curve: VD VT ID IS e 1 It can be assumed memoryless (in a first as approximation)
7 Distortion in a mixer Effects of distortion: The spectrum of the frequency translated signal around the new carrier frequency is different from the original one New replicas of the original RF signal, LO and combination of them are generated at different carrier frequencies The local linearity is described by the same parameters used for amplifiers (P 1dB, IP); in the mixers case the input output frequencies are different. Moreover the mentioned parameters depend also on the power level of the local oscillator
8 Single-balanced mixers They allow an intrinsic suppression of some spurious products. An higher power from the LO is requested. A better linearity is obtained, together with higher losses (compared to single ended mixers)
9 VRF Vr cosrft V V cos t P P V1 VRF V V V V RF Balance mixer with a hybrid 3 ID av 1 D av D av 3 D I av 1 av av 3... I/V characteristic of diodes: Then: V RF V HYB 3 db I av av av The overall current is given by: Filtro r RF r P RF P RF P I a V V a V V a V V... av 4aV V a V 3 V V RF RF 3 RF RF av cos( t) a cos t cos t 3 a 3 Vr cos RFt3 r P cos Ptcos RFt... I 1 V 1 V I I I I I 1 Z
10 Characteristics of hybrid mixer All harmonics of LO are suppressed at Also the even harmonics of RF are suppressed AM Noise of LO is eliminated (NOT the phase noise) RF LO ports are intrinsically isolated V RF V + V HYB 3 db V V 1 d d V V V 1 V V V V d 1 d d d dv d RF V V, V dv1 dv dv dv 0 SRF 0
11 Double-balanced Mixer Z 0 RF HYB 3 db V RF V RF I 3 I 4 I 1 I V V HYB 3 db VA kia k I I k av a V av a V k a V V a V V k av 1 4aV VRF VB kib kii4kav 1 av av 1 4aV 4ka1V V4 av V4 k av 1 4aV VRF VA VB k V 8aV VRF I A I B Z V V I av av D 1 D D V V V V, V V V V V, V RF RF 1 RF RF 3 4
12 Characteristics of double-balanced mixers ALL harmonics of LO and RF are suppressed ALL even intermodulation products are suppressed Perfect isolation LO RF High LO power required Worsens conversion loss Linearity improvement
13 Image-suppression mixers Z 0 RF V RF HYB (3 db) A V R B VR Splitter V A V I B V I HYB (3 db) LSB USB This configuration separates the translated and image signals. The image filter is then no more necessary (or its requirements are strongly reduced)
14 RF V RF Z HYB 3 db A V R V B R Div. Per V V cos t, V V cos t V cos t 0 0 RF U 0 L 0 V A VU VL B VU VL VR sin 0 t sin 0 t, VR cos0 t cos0 t A U 0 L 0 VI k sin 0 tcos 0t k sin 0 tcos 0t U 0 L 0 k sin 0 tsin tk 4 sin 0 sin 4 t t B U 0 L 0 VI k cos 0 cos 0 cos 0 cos 0 t t k t t U 0 L 0 k cos0 t cost k cos0 t cost 4 4 A B I I L 0 VLSB j k cost A V I 9 B V I 9 B A V I VI U 0 L 0 VUSB j k sin 0 tsin tk sin 0 t V V HYB 3 db LSB USB
Receiver Architectures
 Receiver Architectures Direct Detection of radio signals 1 2.. n f C,i Antenna Amplifier RF Filter A Demodulation Base Band 1 f C,i Not convenient: - RF filter must be very selective and tunable - Amplifier
Receiver Architectures Direct Detection of radio signals 1 2.. n f C,i Antenna Amplifier RF Filter A Demodulation Base Band 1 f C,i Not convenient: - RF filter must be very selective and tunable - Amplifier
General configuration
 Transmitter General configuration In some cases the modulator operates directly at the transmission frequency (no up conversion required) In digital transmitters, the information is represented by the
Transmitter General configuration In some cases the modulator operates directly at the transmission frequency (no up conversion required) In digital transmitters, the information is represented by the
Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance
 Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance Mixer Terms Defined Statistical Processing Applied to Mixers Today's stringent demands for precise electronic systems place a heavy burden
Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance Mixer Terms Defined Statistical Processing Applied to Mixers Today's stringent demands for precise electronic systems place a heavy burden
Advanced RFIC Design ELEN359A, Lecture 3: Gilbert Cell Mixers. Instructor: Dr. Allen A Sweet
 Advanced RFIC Design ELEN359A, Lecture 3: Gilbert Cell Mixers Instructor: Dr. Allen A Sweet All of Design is the Art and Science of Navigating Tradeoffs Science gives us the tools to understand what nature,
Advanced RFIC Design ELEN359A, Lecture 3: Gilbert Cell Mixers Instructor: Dr. Allen A Sweet All of Design is the Art and Science of Navigating Tradeoffs Science gives us the tools to understand what nature,
C. Mixers. frequencies? limit? specifications? Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device.
 9/13/2007 Mixers notes 1/1 C. Mixers Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device. HO: Mixers Q: How efficient is a typical mixer at creating signals
9/13/2007 Mixers notes 1/1 C. Mixers Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device. HO: Mixers Q: How efficient is a typical mixer at creating signals
IC design for wireless system
 IC design for wireless system Lecture 6 Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Ahmed.madian@guc.edu.eg 1 outlines Introduction to mixers Mixer metrics Mixer topologies Mixer performance analysis Mixer design issues Dr. Ahmed
IC design for wireless system Lecture 6 Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Ahmed.madian@guc.edu.eg 1 outlines Introduction to mixers Mixer metrics Mixer topologies Mixer performance analysis Mixer design issues Dr. Ahmed
1 MHz 6 GHz RF Mixer with built in PLL Synthesizer
 Windfreak Technologies Preliminary Data Sheet v0.1a MixNV Active Mixer v1.4a $499.00US 1 MHz 6 GHz RF Mixer with built in PLL Synthesizer Features Open source Labveiw GUI software control via USB Run hardware
Windfreak Technologies Preliminary Data Sheet v0.1a MixNV Active Mixer v1.4a $499.00US 1 MHz 6 GHz RF Mixer with built in PLL Synthesizer Features Open source Labveiw GUI software control via USB Run hardware
37-40GHz MMIC Sub-Harmonically Pumped Image Rejection Diode Mixer
 37-40GHz MMIC Sub-Harmonically Pumped Image Rejection Diode Mixer F. Rasà, F. Celestino, M. Remonti, B. Gabbrielli, P. Quentin ALCATEL ITALIA, TSD-HCMW R&D, Str. Provinciale per Monza, 33, 20049 Concorezzo
37-40GHz MMIC Sub-Harmonically Pumped Image Rejection Diode Mixer F. Rasà, F. Celestino, M. Remonti, B. Gabbrielli, P. Quentin ALCATEL ITALIA, TSD-HCMW R&D, Str. Provinciale per Monza, 33, 20049 Concorezzo
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY
 Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
The Schottky Diode Mixer. Application Note 995
 The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
RF, Microwave & Wireless. All rights reserved
 RF, Microwave & Wireless All rights reserved 1 Non-Linearity Phenomenon All rights reserved 2 Physical causes of nonlinearity Operation under finite power-supply voltages Essential non-linear characteristics
RF, Microwave & Wireless All rights reserved 1 Non-Linearity Phenomenon All rights reserved 2 Physical causes of nonlinearity Operation under finite power-supply voltages Essential non-linear characteristics
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based and Shooting Method Based RF Simulation
 SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based and Shooting Method Based RF Simulation Silvaco Overview SSRF Attributes Harmonic balance approach to solve system of equations in frequency domain Well suited for
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based and Shooting Method Based RF Simulation Silvaco Overview SSRF Attributes Harmonic balance approach to solve system of equations in frequency domain Well suited for
QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A 40MHZ TO 900MHZ DIRECT CONVERSION QUADRATURE DEMODULATOR
 DESCRIPTION QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A LT5517 Demonstration circuit 678A is a 40MHz to 900MHz Direct Conversion Quadrature Demodulator featuring the LT5517. The LT 5517 is a direct
DESCRIPTION QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A LT5517 Demonstration circuit 678A is a 40MHz to 900MHz Direct Conversion Quadrature Demodulator featuring the LT5517. The LT 5517 is a direct
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B5 - Multipliers/mixer circuits» Error taxonomy» Basic multiplier circuits» Gilbert cell» Bridge MOS and diode circuits» Balanced
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B5 - Multipliers/mixer circuits» Error taxonomy» Basic multiplier circuits» Gilbert cell» Bridge MOS and diode circuits» Balanced
Lecture 17 - Microwave Mixers
 Lecture 17 - Microwave Mixers Microwave Active Circuit Analysis and Design Clive Poole and Izzat Darwazeh Academic Press Inc. Poole-Darwazeh 2015 Lecture 17 - Microwave Mixers Slide1 of 42 Intended Learning
Lecture 17 - Microwave Mixers Microwave Active Circuit Analysis and Design Clive Poole and Izzat Darwazeh Academic Press Inc. Poole-Darwazeh 2015 Lecture 17 - Microwave Mixers Slide1 of 42 Intended Learning
Advance Information: AI1016. QFN Packaged 10-16GHz Direct Modulator. GaAs Monolithic Microwave IC GND QB Q VG I VD3 VD2 VD1
 VD1 VD2 VD3 QB Q VG I IB Advance Information: AI1016 QFN Packaged 10-16GHz Direct Modulator GaAs Monolithic Microwave IC 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 1 24 2 23 3 22 RF IN 4 21 5 20 6 19 LO IN 7 18 8 17 9 10
VD1 VD2 VD3 QB Q VG I IB Advance Information: AI1016 QFN Packaged 10-16GHz Direct Modulator GaAs Monolithic Microwave IC 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 1 24 2 23 3 22 RF IN 4 21 5 20 6 19 LO IN 7 18 8 17 9 10
RFIC DESIGN ELEN 351 Lecture 7: Mixer Design
 RFIC DESIGN ELEN 351 Lecture 7: Mixer Design Dr. Allen Sweet Copy Right 2003 ELEN 351 1 Mixer Specifications Conversion Gain / Loss (Gain defined as the ratio of power at the I freq to the power at the
RFIC DESIGN ELEN 351 Lecture 7: Mixer Design Dr. Allen Sweet Copy Right 2003 ELEN 351 1 Mixer Specifications Conversion Gain / Loss (Gain defined as the ratio of power at the I freq to the power at the
A n I/Q modulator is frequently used in
 A Simplified Subharmonic I/Q Modulator This passive vector modulator uses opposite polarity diode pairs for frequency doubling to extend the range of operation By Ian Doyle M/A-COM Eurotec Operations A
A Simplified Subharmonic I/Q Modulator This passive vector modulator uses opposite polarity diode pairs for frequency doubling to extend the range of operation By Ian Doyle M/A-COM Eurotec Operations A
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
PROJECT ON MIXED SIGNAL VLSI
 PROJECT ON MXED SGNAL VLS Submitted by Vipul Patel TOPC: A GLBERT CELL MXER N CMOS AND BJT TECHNOLOGY 1 A Gilbert Cell Mixer in CMOS and BJT technology Vipul Patel Abstract This paper describes a doubly
PROJECT ON MXED SGNAL VLS Submitted by Vipul Patel TOPC: A GLBERT CELL MXER N CMOS AND BJT TECHNOLOGY 1 A Gilbert Cell Mixer in CMOS and BJT technology Vipul Patel Abstract This paper describes a doubly
The Digital Linear Amplifier
 The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
HF Receivers, Part 2
 HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis
 Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED
 Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK 17 Product Application Notes Introduction
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK 17 Product Application Notes Introduction
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED
 Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK v01.05.00 HMC141/142 MIXER OPERATION
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK v01.05.00 HMC141/142 MIXER OPERATION
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator. Advanced RF Circuit Simulation
 SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator Advanced RF Circuit Simulation SmartSpice RF Overview Uses harmonic balance approach to solve system equations in frequency domain Well suited for RF and
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator Advanced RF Circuit Simulation SmartSpice RF Overview Uses harmonic balance approach to solve system equations in frequency domain Well suited for RF and
ATLCE - B5 07/03/2016. Analog and Telecommunication Electronics 2016 DDC 1. Politecnico di Torino - ICT School. Lesson B5: multipliers and mixers
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Lesson B5: multipliers and mixers Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B5 - Multipliers/mixer circuits» Error taxonomy» Basic multiplier circuits» Gilbert cell» Bridge
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Lesson B5: multipliers and mixers Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B5 - Multipliers/mixer circuits» Error taxonomy» Basic multiplier circuits» Gilbert cell» Bridge
IQ Demodulator David C. Nelson 14 December 2009
 IQ Demodulator David C. Nelson 14 December 2009 ABSTRACT The IQ Demodulator is an RF down-converter that converts an RF input into two IF outputs with a 90 degree phase difference. The demodulator has
IQ Demodulator David C. Nelson 14 December 2009 ABSTRACT The IQ Demodulator is an RF down-converter that converts an RF input into two IF outputs with a 90 degree phase difference. The demodulator has
OBJECTIVES EQUIPMENT LIST
 1 Reception of Amplitude Modulated Signals AM Demodulation OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to show how the amplitude-modulated signals are demodulated to obtain the original signal. Also,
1 Reception of Amplitude Modulated Signals AM Demodulation OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to show how the amplitude-modulated signals are demodulated to obtain the original signal. Also,
BROADBAND DISTRIBUTED AMPLIFIER
 ADM1-26PA The ADM1-26PA is a complete LO driver solution for use with all Marki mixers up to 26. GHz. This single-stage packaged GaAs MMIC distributed amplifier integrates all required biasing circuitry.
ADM1-26PA The ADM1-26PA is a complete LO driver solution for use with all Marki mixers up to 26. GHz. This single-stage packaged GaAs MMIC distributed amplifier integrates all required biasing circuitry.
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
Chapter 5 AM Receivers
 Chapter 5 AM Receivers Prepared by Prof.V.K.Jain 1 Lecture outcome After studying this lecture, you should be able to: Describe the basic superheterodyne system Choose suitable intermediate frequencies
Chapter 5 AM Receivers Prepared by Prof.V.K.Jain 1 Lecture outcome After studying this lecture, you should be able to: Describe the basic superheterodyne system Choose suitable intermediate frequencies
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters
 High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
Design of High Gain and Low Noise CMOS Gilbert Cell Mixer for Receiver Front End Design
 2016 International Conference on Information Technology Design of High Gain and Low Noise CMOS Gilbert Cell Mixer for Receiver Front End Design Shasanka Sekhar Rout Department of Electronics & Telecommunication
2016 International Conference on Information Technology Design of High Gain and Low Noise CMOS Gilbert Cell Mixer for Receiver Front End Design Shasanka Sekhar Rout Department of Electronics & Telecommunication
Microwave Right/Left-Handed Transmission Line and its Applications
 Microwave Right/Left-Handed Transmission Line and its Applications 2008.3.12 1 Outlines Introduction of composite right/left-handed handed (CRLH) transmission line (TL) Microwave passive components using
Microwave Right/Left-Handed Transmission Line and its Applications 2008.3.12 1 Outlines Introduction of composite right/left-handed handed (CRLH) transmission line (TL) Microwave passive components using
A 3rd- and 5th-order intermodulation products generator for predistortion of base-station HPAs
 Title A 3rd- and 5th-order intermodulation products generator for predistortion of base-station HPAs Author(s) Sun, XL; Cheung, SW; Yuk, TI Citation The 200 International Conference on Advanced Technologies
Title A 3rd- and 5th-order intermodulation products generator for predistortion of base-station HPAs Author(s) Sun, XL; Cheung, SW; Yuk, TI Citation The 200 International Conference on Advanced Technologies
Millimeter Wave Spectrum Analyzer with Built-in >100 GHz Preselector
 Millimeter Wave Spectrum Analyzer with Built-in >1 GHz Preselector Yukiyasu Kimura, Masaaki Fuse, Akihito Otani [Summary] Fifth-generation (5G) mobile communications technologies are being actively developed
Millimeter Wave Spectrum Analyzer with Built-in >1 GHz Preselector Yukiyasu Kimura, Masaaki Fuse, Akihito Otani [Summary] Fifth-generation (5G) mobile communications technologies are being actively developed
TLCE - A3 08/09/ /09/ TLCE - A DDC. IF channel Zc. - Low noise, wide dynamic Ie Vo 08/09/ TLCE - A DDC
 Politecnico di Torino ICT School Telecommunication Electronics A3 Amplifiers nonlinearity» Reference circuit» Nonlinear models» Effects of nonlinearity» Applications of nonlinearity Large signal amplifiers
Politecnico di Torino ICT School Telecommunication Electronics A3 Amplifiers nonlinearity» Reference circuit» Nonlinear models» Effects of nonlinearity» Applications of nonlinearity Large signal amplifiers
Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS. EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez. April 15, 2004
 Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez April 15, 2004 The University of Texas at El Paso Dr Tim S. Yao ABSTRACT Two circuits satisfying the
Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez April 15, 2004 The University of Texas at El Paso Dr Tim S. Yao ABSTRACT Two circuits satisfying the
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent
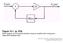 Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Experiment No. 2 Pre-Lab Signal Mixing and Amplitude Modulation
 Experiment No. 2 Pre-Lab Signal Mixing and Amplitude Modulation Read the information presented in this pre-lab and answer the questions given. Submit the answers to your lab instructor before the experimental
Experiment No. 2 Pre-Lab Signal Mixing and Amplitude Modulation Read the information presented in this pre-lab and answer the questions given. Submit the answers to your lab instructor before the experimental
KWM-2/2A Transceiver THE COLLINS KWM-2/2A TRANSCEIVER
 KWM-2/2A Transceiver Click the photo to see a larger photo Click "Back" button on browser to return Courtesy of Norm - WA3KEY THE COLLINS KWM-2/2A TRANSCEIVER Unmatched for versatility, dependability and
KWM-2/2A Transceiver Click the photo to see a larger photo Click "Back" button on browser to return Courtesy of Norm - WA3KEY THE COLLINS KWM-2/2A TRANSCEIVER Unmatched for versatility, dependability and
DOUBLE-SIDEBAND MIXER CIRCUITS
 DOUBLE-SIDEBAND MIXER CIRCUITS SBW SERIES Waveguide, SMA / SBB SERIES DC Biasable, Low Power DB, DM SERIES General Purpose SBE SERIES Even Harmonic (1/2 ) TB, TBR SERIES Best Spurs, Overlap / W Y W Y Z
DOUBLE-SIDEBAND MIXER CIRCUITS SBW SERIES Waveguide, SMA / SBB SERIES DC Biasable, Low Power DB, DM SERIES General Purpose SBE SERIES Even Harmonic (1/2 ) TB, TBR SERIES Best Spurs, Overlap / W Y W Y Z
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation RX nonlinearities (parts of 2.2) System Nonlinearity Sensitivity
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation RX nonlinearities (parts of 2.2) System Nonlinearity Sensitivity
10 V (Vpp) into 50 Ω load < 115 dbc (1 Hz) (typ.) 70 dbc (f < 1 MHz) AM, FM, pulse, PWM, 70 dbc + (f = 1 GHz)
 /designation Frequency range Max. output power/voltage SSB phase noise Nonharmonics Modulation HMF arbitrary function generator 10 μhz to 25 MHz/50 MHz 10 V (Vpp) into 50 Ω load < 115 dbc (1 Hz) (typ.)
/designation Frequency range Max. output power/voltage SSB phase noise Nonharmonics Modulation HMF arbitrary function generator 10 μhz to 25 MHz/50 MHz 10 V (Vpp) into 50 Ω load < 115 dbc (1 Hz) (typ.)
Measurements 2: Network Analysis
 Measurements 2: Network Analysis Fritz Caspers CAS, Aarhus, June 2010 Contents Scalar network analysis Vector network analysis Early concepts Modern instrumentation Calibration methods Time domain (synthetic
Measurements 2: Network Analysis Fritz Caspers CAS, Aarhus, June 2010 Contents Scalar network analysis Vector network analysis Early concepts Modern instrumentation Calibration methods Time domain (synthetic
1. Device Overview. 1.2 Electrical Summary. 1.3 Applications. 1.4 Functional Block Diagram. 1.5 Part Ordering Options 1 QFN
 Passive GaAs MMIC IQ Mixer MMIQ-0520HSM 1. Device Overview General Description MMIQ-0520HSM is a high linearity, passive GaAs MMIC IQ mixer. This is an ultra-broadband mixer spanning 5 to 20GHz on the
Passive GaAs MMIC IQ Mixer MMIQ-0520HSM 1. Device Overview General Description MMIQ-0520HSM is a high linearity, passive GaAs MMIC IQ mixer. This is an ultra-broadband mixer spanning 5 to 20GHz on the
Description Package Green Status. Refer to our website for a list of definitions for terminology presented in this table.
 Passive GaAs MMIC IQ Mixer MMIQ-0416HSM 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description MMIQ-0416HSM is a high linearity, passive GaAs MMIC IQ mixer. This is an ultra-broadband mixer spanning 4 to 16 GHz on
Passive GaAs MMIC IQ Mixer MMIQ-0416HSM 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description MMIQ-0416HSM is a high linearity, passive GaAs MMIC IQ mixer. This is an ultra-broadband mixer spanning 4 to 16 GHz on
TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers
 TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Overview 2 Razavi: Chapter 6.1-6.3, pp. 343-398. Lee: Chapter 13. 6.1 Mixers general
TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Overview 2 Razavi: Chapter 6.1-6.3, pp. 343-398. Lee: Chapter 13. 6.1 Mixers general
Measuring Non-linear Amplifiers
 Measuring Non-linear Amplifiers Transceiver Components & Measuring Techniques MM3 Jan Hvolgaard Mikkelsen Radio Frequency Integrated Systems and Circuits Division Aalborg University 27 Agenda Non-linear
Measuring Non-linear Amplifiers Transceiver Components & Measuring Techniques MM3 Jan Hvolgaard Mikkelsen Radio Frequency Integrated Systems and Circuits Division Aalborg University 27 Agenda Non-linear
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
Effects of Mismatch on CMOS Monolithic Mixers Image Rejection
 Effects of Mismatch on CMOS Monolithic Mixers Image Rejection Fernando Azevedo, M. João Rosário, J. Costa Freire Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, Instituto Superior Técnico,,3 Instituto de Telecomunicações,
Effects of Mismatch on CMOS Monolithic Mixers Image Rejection Fernando Azevedo, M. João Rosário, J. Costa Freire Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, Instituto Superior Técnico,,3 Instituto de Telecomunicações,
PRACTICAL RF SYSTEM DESIGN
 PRACTICAL RF SYSTEM DESIGN WILLIAM F. EGAN, Ph.D. Lecturer in Electrical Engineering Santa Clara University The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc., New York A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC.,
PRACTICAL RF SYSTEM DESIGN WILLIAM F. EGAN, Ph.D. Lecturer in Electrical Engineering Santa Clara University The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc., New York A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC.,
Technical Article A DIRECT QUADRATURE MODULATOR IC FOR 0.9 TO 2.5 GHZ WIRELESS SYSTEMS
 Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
Session 3. CMOS RF IC Design Principles
 Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 3: Superheterodyne TRX design
 TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 3: Superheterodyne TRX design Ted Johansson, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se 2 Outline of lecture 3 Introduction RF TRX architectures (3) Superheterodyne architecture
TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 3: Superheterodyne TRX design Ted Johansson, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se 2 Outline of lecture 3 Introduction RF TRX architectures (3) Superheterodyne architecture
Demo board DC365A Quick Start Guide.
 August 02, 2001. Demo board DC365A Quick Start Guide. I. Introduction The DC365A demo board is intended to demonstrate the capabilities of the LT5503 RF transmitter IC. This IC incorporates a 1.2 GHz to
August 02, 2001. Demo board DC365A Quick Start Guide. I. Introduction The DC365A demo board is intended to demonstrate the capabilities of the LT5503 RF transmitter IC. This IC incorporates a 1.2 GHz to
Introduction. In the frequency domain, complex signals are separated into their frequency components, and the level at each frequency is displayed
 SPECTRUM ANALYZER Introduction A spectrum analyzer measures the amplitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument The spectrum analyzer is to the frequency
SPECTRUM ANALYZER Introduction A spectrum analyzer measures the amplitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument The spectrum analyzer is to the frequency
Mixer. General Considerations V RF VLO. Noise. nonlinear, R ON
 007/Nov/7 Mixer General Considerations LO S M F F LO L Noise ( a) nonlinearity (b) Figure 6.5 (a) Simple switch used as mixer (b) implementation of switch with an NMOS device. espect to espect to It is
007/Nov/7 Mixer General Considerations LO S M F F LO L Noise ( a) nonlinearity (b) Figure 6.5 (a) Simple switch used as mixer (b) implementation of switch with an NMOS device. espect to espect to It is
Features OBSOLETE. = +25 C, IF= 1 GHz, USB, LO = +15 dbm [1]
![Features OBSOLETE. = +25 C, IF= 1 GHz, USB, LO = +15 dbm [1] Features OBSOLETE. = +25 C, IF= 1 GHz, USB, LO = +15 dbm [1]](/thumbs/82/84974573.jpg) v1.414 HMC141LC4 Typical Applications The HMC141LC4 is Ideal for: Point-to-Point Radio Point-to-Multi-Point Radio Test Equipment & Sensors Military End Use Functional Diagram Features Wide IF Bandwidth:
v1.414 HMC141LC4 Typical Applications The HMC141LC4 is Ideal for: Point-to-Point Radio Point-to-Multi-Point Radio Test Equipment & Sensors Military End Use Functional Diagram Features Wide IF Bandwidth:
Low LO Drive Surface Mount MMIC IQ Mixer. Refer to our website for a list of definitions for terminology presented in this table.
 Low LO Drive Surface Mount MMIC IQ Mixer MMIQ-0520LSM 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description The MMIQ-0520LSM is a low LO drive, passive GaAs MMIC IQ mixer that operates down to an unrivaled +3 dbm
Low LO Drive Surface Mount MMIC IQ Mixer MMIQ-0520LSM 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description The MMIQ-0520LSM is a low LO drive, passive GaAs MMIC IQ mixer that operates down to an unrivaled +3 dbm
5.8 GHz Single-Balanced Hybrid Mixer
 Single-Balanced Hybrid Mixer James McKnight MMIC Design EE 525.787 JHU Fall 200 Professor John Penn Abstract This report details the design of a C-Band monolithic microwave integrated circuit (MMIC) single-balanced
Single-Balanced Hybrid Mixer James McKnight MMIC Design EE 525.787 JHU Fall 200 Professor John Penn Abstract This report details the design of a C-Band monolithic microwave integrated circuit (MMIC) single-balanced
Self-Mixing Amplifier for CW Sensors
 Self-Mixing Amplifier for CW Sensors Master thesis presentation Congying Chen Supervisor: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus Solbach Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology Microwave and RF Technology
Self-Mixing Amplifier for CW Sensors Master thesis presentation Congying Chen Supervisor: Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus Solbach Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology Microwave and RF Technology
ET Envelope Path from digits to PA
 pushing the envelope of PA efficiency ET Envelope Path from digits to PA Gerard Wimpenny Nujira Ltd ARMMS Conference 19 th /2 th November 212 Agenda Envelope Processing ET PA Characterisation Isogain shaping
pushing the envelope of PA efficiency ET Envelope Path from digits to PA Gerard Wimpenny Nujira Ltd ARMMS Conference 19 th /2 th November 212 Agenda Envelope Processing ET PA Characterisation Isogain shaping
Preface Introduction p. 1 History and Fundamentals p. 1 Devices for Mixers p. 6 Balanced and Single-Device Mixers p. 7 Mixer Design p.
 Preface Introduction p. 1 History and Fundamentals p. 1 Devices for Mixers p. 6 Balanced and Single-Device Mixers p. 7 Mixer Design p. 9 Monolithic Circuits p. 10 Schottky-Barrier Diodes p. 11 Schottky-Diode
Preface Introduction p. 1 History and Fundamentals p. 1 Devices for Mixers p. 6 Balanced and Single-Device Mixers p. 7 Mixer Design p. 9 Monolithic Circuits p. 10 Schottky-Barrier Diodes p. 11 Schottky-Diode
GaAs MMIC Double Balanced Mixer. Description Package Green Status
 GaAs MMIC Double Balanced Mixer MM1-0212SSM 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description The MM1-0212SSM is a highly linear GaAs MMIC double balanced mixer. MM1-0212SSM is a low frequency, high linearity
GaAs MMIC Double Balanced Mixer MM1-0212SSM 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description The MM1-0212SSM is a highly linear GaAs MMIC double balanced mixer. MM1-0212SSM is a low frequency, high linearity
Receiver Design. Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21
 Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
Analysis of diode. 2-Analysis of diode on paper- We can study behaviour of diode on paper in two ways.
 Analysis of diode Analysis of diode means study of response of diode for different applied voltages. We can analyse diode in three ways. 1) Analysis of diode in laboratory 2) Analysis of diode on paper
Analysis of diode Analysis of diode means study of response of diode for different applied voltages. We can analyse diode in three ways. 1) Analysis of diode in laboratory 2) Analysis of diode on paper
RF Integrated Circuits
 Introduction and Motivation RF Integrated Circuits The recent explosion in the radio frequency (RF) and wireless market has caught the semiconductor industry by surprise. The increasing demand for affordable
Introduction and Motivation RF Integrated Circuits The recent explosion in the radio frequency (RF) and wireless market has caught the semiconductor industry by surprise. The increasing demand for affordable
Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers
 EECS 142 Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
EECS 142 Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
Linear networks analysis
 Linear networks analysis For microwave linear networks analysis is performed in frequency domain. The analysis is based on the evaluation of the scattering matrix of the n port network From S matrix all
Linear networks analysis For microwave linear networks analysis is performed in frequency domain. The analysis is based on the evaluation of the scattering matrix of the n port network From S matrix all
Using Harmonic External Mixers To Extend the Frequency Range Application Note
 Using Harmonic External Mixers To Extend the Frequency Range Application Note Products: R&S FSV R&S FSVR R&S FSQ R&S FSU R&S FSP R&S FSE This application note gives a short summary on how to use harmonic
Using Harmonic External Mixers To Extend the Frequency Range Application Note Products: R&S FSV R&S FSVR R&S FSQ R&S FSU R&S FSP R&S FSE This application note gives a short summary on how to use harmonic
Microwave Metrology -ECE 684 Spring Lab Exercise I&Q.v3: I&Q Time and Frequency Domain Measurements
 Lab Exercise I&Q.v3: I&Q Time and Frequency Domain Measurements In this lab exercise you will perform measurements both in time and in frequency to establish the relationship between these two dimension
Lab Exercise I&Q.v3: I&Q Time and Frequency Domain Measurements In this lab exercise you will perform measurements both in time and in frequency to establish the relationship between these two dimension
6 GHz to 26 GHz, GaAs MMIC Fundamental Mixer HMC773ALC3B
 FEATURES Conversion loss: 9 db typical Local oscillator (LO) to radio frequency (RF) isolation: 37 db typical LO to intermediate frequency (IF) isolation: 37 db typical RF to IF isolation: db typical Input
FEATURES Conversion loss: 9 db typical Local oscillator (LO) to radio frequency (RF) isolation: 37 db typical LO to intermediate frequency (IF) isolation: 37 db typical RF to IF isolation: db typical Input
Residual Phase Noise Measurement Extracts DUT Noise from External Noise Sources By David Brandon and John Cavey
 Residual Phase Noise easurement xtracts DUT Noise from xternal Noise Sources By David Brandon [david.brandon@analog.com and John Cavey [john.cavey@analog.com Residual phase noise measurement cancels the
Residual Phase Noise easurement xtracts DUT Noise from xternal Noise Sources By David Brandon [david.brandon@analog.com and John Cavey [john.cavey@analog.com Residual phase noise measurement cancels the
6.002 Circuits and Electronics Final Exam Practice Set 1
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE 6.002 Circuits and Electronics Set 1 Problem 1 Figure 1 shows a simplified small-signal model of a certain
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE 6.002 Circuits and Electronics Set 1 Problem 1 Figure 1 shows a simplified small-signal model of a certain
Silicon Beam Lead Schottky Barrier Mixer Diodes
 ilicon chottky Barrier Mixer Diodes Features Ideal for MIC Low 1/f Noise Low Intermodulation Distortion Low Turn On Hermetically ealed Packages PC Controlled Wafer Fabrication Description Alpha beam lead
ilicon chottky Barrier Mixer Diodes Features Ideal for MIC Low 1/f Noise Low Intermodulation Distortion Low Turn On Hermetically ealed Packages PC Controlled Wafer Fabrication Description Alpha beam lead
PARAMETER CONDITIONS TYPICAL PERFORMANCE Operating Supply Voltage 3.1V to 3.5V Supply Current V CC = 3.3V, LO applied 152mA
 DESCRIPTION LT5578 Demonstration circuit 1545A-x is a high linearity upconverting mixer featuring the LT5578. The LT 5578 is a high performance upconverting mixer IC optimized for output frequencies in
DESCRIPTION LT5578 Demonstration circuit 1545A-x is a high linearity upconverting mixer featuring the LT5578. The LT 5578 is a high performance upconverting mixer IC optimized for output frequencies in
Introduction to Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Devices
 May 31, 2018 Introduction to Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Devices Part 7: Basics of RF Circuits Ken-ya Hashimoto Chiba University k.hashimoto@ieee.org http://www.te.chiba-u.jp/~ken Contents Noise Figure
May 31, 2018 Introduction to Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Devices Part 7: Basics of RF Circuits Ken-ya Hashimoto Chiba University k.hashimoto@ieee.org http://www.te.chiba-u.jp/~ken Contents Noise Figure
Hybrid Frequency Synthesizer Combines Octave Tuning Range and Millihertz Steps
 Hybrid Frequency Synthesizer Combines Octave Tuning Range and Millihertz Steps DDS and PLL techniques are combined in this high-resolution synthesizer By Benjamin Sam Analog Devices Northwest Laboratories
Hybrid Frequency Synthesizer Combines Octave Tuning Range and Millihertz Steps DDS and PLL techniques are combined in this high-resolution synthesizer By Benjamin Sam Analog Devices Northwest Laboratories
Selecting the Right Mixer for Your Application Using Yoni -the Advanced Search Engine (AN )
 Selecting the Right Mixer for Your Application Using Yoni -the Advanced Search Engine (AN-00-014) In spite of advances in digital processing components enabling direct digital conversion at higher frequencies,
Selecting the Right Mixer for Your Application Using Yoni -the Advanced Search Engine (AN-00-014) In spite of advances in digital processing components enabling direct digital conversion at higher frequencies,
3.1 Introduction to Modulation
 Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
A Comparative Analysis between Homodyne and Heterodyne Receiver Architecture Md Sarwar Hossain * & Muhammad Sajjad Hussain **
 A Comparative Analysis between Homodyne and Heterodyne Receiver Architecture Manarat International University Studies, 2 (1): 152-157, December 2011 ISSN 1815-6754 @ Manarat International University, 2011
A Comparative Analysis between Homodyne and Heterodyne Receiver Architecture Manarat International University Studies, 2 (1): 152-157, December 2011 ISSN 1815-6754 @ Manarat International University, 2011
Windfreak Technologies SynthHD v1.4 Preliminary Data Sheet v0.2b
 Windfreak Technologies SynthHD v1.4 Preliminary Data Sheet v0.2b $1299.00US 54 MHz 13.6 GHz Dual Channel RF Signal Generator Features Open source Labveiw GUI software control via USB Run hardware functions
Windfreak Technologies SynthHD v1.4 Preliminary Data Sheet v0.2b $1299.00US 54 MHz 13.6 GHz Dual Channel RF Signal Generator Features Open source Labveiw GUI software control via USB Run hardware functions
Contents H F T. fur Ingenieurwissenschaften Abteilung Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik. Fachgebiet Hochfrequenztechnik Prof. Dr. Ing. K.
 H F T Fachgebiet Hochfrequenztechnik Prof. Dr. Ing. K. Solbach Fakultat Universitat...... fur Ingenieurwissenschaften Duisburg Essen Abteilung Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik Komponenten für die
H F T Fachgebiet Hochfrequenztechnik Prof. Dr. Ing. K. Solbach Fakultat Universitat...... fur Ingenieurwissenschaften Duisburg Essen Abteilung Elektrotechnik und Informationstechnik Komponenten für die
Measuring 3rd order Intercept Point (IP3 / TOI) of an amplifier
 Measuring 3rd order Intercept Point (IP3 / TOI) of an amplifier Why measuring IP3 / TOI? IP3 is an important parameter for nonlinear systems like mixers or amplifiers which helps to verify the quality
Measuring 3rd order Intercept Point (IP3 / TOI) of an amplifier Why measuring IP3 / TOI? IP3 is an important parameter for nonlinear systems like mixers or amplifiers which helps to verify the quality
COMPACT BRANCH-LINE COUPLER FOR HARMONIC SUPPRESSION
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 16, 233 239, 2010 COMPACT BRANCH-LINE COUPLER FOR HARMONIC SUPPRESSION J. S. Kim Department of Information and Communications Engineering Kyungsung University
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 16, 233 239, 2010 COMPACT BRANCH-LINE COUPLER FOR HARMONIC SUPPRESSION J. S. Kim Department of Information and Communications Engineering Kyungsung University
Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: Part 1
 From May 009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 009 Summit Technical Media, LLC Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: art 1 By Andrei Grebennikov Bell Labs Ireland In modern telecommunication
From May 009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 009 Summit Technical Media, LLC Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: art 1 By Andrei Grebennikov Bell Labs Ireland In modern telecommunication
An electronic unit that behaves like a voltagecontrolled
 1 An electronic unit that behaves like a voltagecontrolled voltage source. An active circuit element that amplifies, sums, subtracts, multiply, divide, differentiate or integrates a signal 2 A typical
1 An electronic unit that behaves like a voltagecontrolled voltage source. An active circuit element that amplifies, sums, subtracts, multiply, divide, differentiate or integrates a signal 2 A typical
Receiver Architecture
 Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
244 Facta Universitatis ser.: Elec. & Energ. vol. 14, No. 2, August Introduction In telecommunications systems, the intermodulation (IM) espec
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NI»S) Series: Electronics and Energetics vol. 14, No. 2, August 2001, 243-252 A MULTICARRIER AMPLIFIER DESIGN LINEARIZED TROUGH SECOND HARMONICS AND SECOND-ORDER IM FEEDBACK This paper
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS (NI»S) Series: Electronics and Energetics vol. 14, No. 2, August 2001, 243-252 A MULTICARRIER AMPLIFIER DESIGN LINEARIZED TROUGH SECOND HARMONICS AND SECOND-ORDER IM FEEDBACK This paper
Understanding RF and Microwave Analysis Basics
 Understanding RF and Microwave Analysis Basics Kimberly Cassacia Product Line Brand Manager Keysight Technologies Agenda µw Analysis Basics Page 2 RF Signal Analyzer Overview & Basic Settings Overview
Understanding RF and Microwave Analysis Basics Kimberly Cassacia Product Line Brand Manager Keysight Technologies Agenda µw Analysis Basics Page 2 RF Signal Analyzer Overview & Basic Settings Overview
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units
 v4.112 Typical Applications The is ideal for: Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multi-Point Radio Military Radar, EW & ELINT Satellite Communications Functional Diagram Features General Description The is a
v4.112 Typical Applications The is ideal for: Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multi-Point Radio Military Radar, EW & ELINT Satellite Communications Functional Diagram Features General Description The is a
Module 1B RF Test & Measurement
 1 EECE 411 Antennas and Propagation Module 1B RF Test & Measurement Introduction to Spectrum Analyzers 2 Why Measure the Spectrum of a Signal? to characterize noise and interference to measure distortion
1 EECE 411 Antennas and Propagation Module 1B RF Test & Measurement Introduction to Spectrum Analyzers 2 Why Measure the Spectrum of a Signal? to characterize noise and interference to measure distortion
NOTTCE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 k t Serial Number 827 r 518 Filing Date 28 March 1997 Inventor Keith Y. Williams NOTTCE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed
k t Serial Number 827 r 518 Filing Date 28 March 1997 Inventor Keith Y. Williams NOTTCE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed
The best radio for worst events. Over HF links. Hana Rafi - CEO Eder Yehuda - VP R&D
 MOBAT MICOM The best radio for worst events Increasing Data Throughput Over HF links Hana Rafi - CEO Eder Yehuda - VP R&D 1 Traditional HF Radio -Analog voice & 50,75 bps New Trends on HF - Digital voice,
MOBAT MICOM The best radio for worst events Increasing Data Throughput Over HF links Hana Rafi - CEO Eder Yehuda - VP R&D 1 Traditional HF Radio -Analog voice & 50,75 bps New Trends on HF - Digital voice,
GaAs, MMIC Fundamental Mixer, 2.5 GHz to 7.0 GHz HMC557A
 FEATURES Conversion loss: db LO to RF isolation: db LO to IF isolation: 3 db Input third-order intercept (IP3): 1 dbm Input second-order intercept (IP2): dbm LO port return loss: dbm RF port return loss:
FEATURES Conversion loss: db LO to RF isolation: db LO to IF isolation: 3 db Input third-order intercept (IP3): 1 dbm Input second-order intercept (IP2): dbm LO port return loss: dbm RF port return loss:
AMPLIFIER/DOUBLER/AMPLIFIER
 AMPLIFIER/DOUBLER/AMPLIFIER ADA-2052 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description The ADA-2052 can be used as a frequency extender to enhance the frequency range of a
AMPLIFIER/DOUBLER/AMPLIFIER ADA-2052 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description The ADA-2052 can be used as a frequency extender to enhance the frequency range of a
8.5 GHz to 13.5 GHz, GaAs, MMIC, I/Q Mixer HMC521ALC4
 11 7 8 9 FEATURES Downconverter, 8. GHz to 13. GHz Conversion loss: 9 db typical Image rejection: 27. dbc typical LO to RF isolation: 39 db typical Input IP3: 16 dbm typical Wide IF bandwidth: dc to 3.
11 7 8 9 FEATURES Downconverter, 8. GHz to 13. GHz Conversion loss: 9 db typical Image rejection: 27. dbc typical LO to RF isolation: 39 db typical Input IP3: 16 dbm typical Wide IF bandwidth: dc to 3.
