Analysis on IGBT Developments
|
|
|
- Julie Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Analysis on IGBT Developments Mahato G.C., Niranjan and Waquar Aarif Abu RVS College of Engineering and Technology, Jamshedpur India Abstract Silicon based high power devices continue to play an important role in modern high power systems, especially in the fields of traction, industry and grid applications. Today, approximately 30 years after its invention, a Bipolar-MOS BiMOS controlled switch referred to as the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor IGBT is the device of choice for the majority of power electronics converters with power ratings ranging from few kws to beyond the 1GW mark. Following a brief introduction into power devices and applications in general, this paper will provide an overview of the development history and recent advancements of the IGBT. More importantly the future technology trends purely from the device design viewpoint will be discussed, including the predicted performance impact such technology platforms will have at the system level especially in the high power range. Keywords Bipolar MOS Controlled, IGBT, gain, ON state resistance I. INTRODUCTION The Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) is a minority-carrier device with high input impedance and large bipolar current-carrying capability. Many designers view IGBT as a device with MOS input characteristics and bipolar output characteristic that is a voltage-controlled bipolar device. To make use of the advantages of both Power MOSFET and BJT, the IGBT has been introduced. It s a functional integration of Power MOSFET and BJT devices in monolithic form. It combines the best attributes of both to achieve optimal device characteristics [1] II. PERFORMANCE The Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor also called an IGBT for short, is something of a cross between a conventional Bipolar Junction Transistor and a Field Effect Transistor, making it ideal as a semiconductor switching device. The IGBT transistor takes the best parts of these two types of transistors, the high input impedance and high switching speeds of a MOSFET with a lower saturation voltage of a bipolar transistor, and combines them together to produce another type of transistor switching device that is capable of handling large collector-emitter currents with virtually zero gate current drive. IGBT uses the insulated gate (hence the first part of its name) technology of the MOSFET with the output performance characteristics of a conventional bipolar transistor. The result of this hybrid combination is that the IGBT Transistor has the output switching and conduction characteristics of a bipolar transistor but is voltage-controlled like a MOSFET. The advantage gained by the insulated gate bipolar transistor device over a BJT or MOSFET is that it offers greater power gain than the standard bipolar type transistor combined with the higher voltage operation and lower input losses of the MOSFET. In effect it is an FET integrated with a bipolar transistor in a form of Darlington type configuration as shown in Fig. 1. Fig.1. MOSFET Configuration. The IGBT has a much lower on-state resistance, R ON than an equivalent MOSFET. The forward blocking operation of the IGBT transistor is identical to a power MOSFET. When used as a static controlled switch, the insulated gate bipolar transistor has voltage and current ratings similar to that of the bipolar transistor. However, the presence of an isolated gate in an IGBT makes it a lot simpler to drive than the BJT as much less drive power is needed. It has the high voltage capability, low ON-resistance, ease of drive, relatively fast switching speeds and combined with zero gate drive current makes it a good choice for moderate speed, high voltage applications such as in pulse-width modulated (PWM) solar powered DC-AC inverter and frequency converter applications operating in the hundreds of Kilohertz range. Device Characteristic Table1: Comparison between different transistors Power BJT Power MOSFET IGBT Voltage Rating High <1kV High <1kV Very High >1kV Current Rating High <500A Low <200A High >500A Input Drive Current h FE Voltage V GS 3-10V Voltage V GE 4-8V Input Impedance Low High High Output Impedance Low Medium Low Switching Speed Slow (us) Fast (ns) Medium Cost Low Medium High
3 III. BASIC STRUCTURE The basic schematic of a typical N-channel IGBT based upon the DMOS process is shown in Fig. 2. This is one of several structures possible for this device. It is evident that the silicon cross-section of an IGBT is almost identical to that of a vertical Power MOSFET except for the P+ injecting layer. It shares similar MOS gate structure and P wells with N+ source regions. The N+ layer at the top is the source or emitter and the P+ layer at the bottom is the drain or collector. It is also feasible to make P-channel IGBTs and for which the doping profile in each layer will be reversed. IGBT has a parasitic thyristor comprising the four-layer NPNP structure. Turn-on of this thyristor is undesirable. Fig. 2. IGBT IGBT takes a parasitic thyristor includes the 4-layer NPN structures as shown in Fig. 2. The constituent p-n-p transistor, n-p-n transistor and the driver MOSFET are shown by dotted lines in this figure. There are some IGBs that are fabricated without the N+ buffer layer is called as NPT IGBTS non punch through), whereas some IGBTs are fabricated with the N+ buffer layer called as PT IGBTs (punch through). The performance of the device can considerably increase by exciting the buffer layer. The operation of an IGBT is faster to that of power BJT than a power MOSFET. Fig. 3 shows the exact equivalent circuit of the IGBT cell structure. The top p-n-p transistor is formed by the p+ injecting layer as the emitter, the n type drain layer as the base and the p type body layer as the collector. The lower n-p-n transistor has the n+ type source, the p type the base of the lower n-p-n transistor is shorted to the emitter by the emitter metallization. However, due to imperfect shorting, the exact equivalent circuit of the IGBT includes the body spreading resistance between the base and the emitter of the lower n-p-n transistor. If the output current is large enough, the voltage drop across this resistance may forward bias the lower n-p-n transistor and initiate the latch up process of the p-n-p-n thyristor structure. Body and the n type drain as the emitter, base and collector respectively [2] Fig. 3: Equivalent diagram of an IGBT IV. OPERATING PRINCIPLE OF IGBT 1. From the input side the IGBT behaves essentially as a MOSFET. 2. Therefore, when the gate emitter voltage is less than the threshold voltage no inversion layer is formed in the p type body region and the device is in the off state. 3. The forward voltage applied between the collector and the emitter drops almost entirely across the junction J2. 4. Very small leakage current flows through the device under this condition. 5. In terms of the equivalent current of Fig.3(c), when the gate emitter voltage is lower than the threshold voltage the driving MOSFET of the Darlington configuration remains off and hence the output p-n-p transistor also remains off. 6. When the gate emitter voltage exceeds the threshold, an inversion layer forms in the p type body region under the gate. 7. This inversion layer (channel) shorts the emitter and the drain drift layer and electron current flows from the emitter through this channel to the drain drift region. 8. This in turn causes substantial hole injection from the p+ type collector to the drain drift region. 9. A portion of these holes recombine with the electrons arriving at the drain drift region through the channel. The rest of the holes, cross the drift region to reach the p type body, where they are collected by the source. V. CHARACTERISTICS OF IGBT 1. The V-I characteristics of an n channel IGBT are shown in Fig They appear qualitatively similar to those of a logic level BJT except that the controlling parameter is not a base current but the gate-emitter voltage. 3. When the gate emitter voltage is below the threshold voltage only a very small leakage current flows though the device while the collector emitter voltage almost equals the supply voltage (point C in Fig. 4)
4 VI. OPERATING MODES Fig. 4. V-I Characteristics of IGBT The device, under this condition is said to be operating in the cut off region. 1. The maximum forward voltage the device can withstand in this mode (marked V CES in Fig.5) is determined by the avalanche break down voltage of the body drain p-n junction. 2. Unlike a BJT, however, this break down voltage is independent of the collector current as shown in Fig IGBTs of Non-punch through design can block a maximum reverse voltage (V RM) equal to V CES in the cut off mode. 4. However, for Punch through IGBTs V RM is negligible (only a few tens of volts) due the presence of the heavily doped n+ drain buffer layer. 5. As the gate emitter voltage increases beyond the threshold voltage the IGBT enters into the active region of operation. 6. In this mode, the collector current i c is determined by the transfer characteristics of the device as shown in Fig. 4.b. 7. As the gate emitter voltage is increased further i c also increases and for a given load resistance (R L) v CE decreases. 8. At one point V CE becomes less than V GE V GE(th). Under this condition the driving MOSFET part of the IGBT (Fig. 4.a) enters into the ohmic region and drives the output p-n-p transistor to saturation. 9. Under this condition the device is said to be in the saturation mode. 10. In the saturation mode the voltage drop across the IGBT remains almost constant reducing only slightly with increasing V GE. 11. If a short circuit fault occurs in the load resistance R L (shown in the inset of Fig. 4.b). The fault load line is given by CF. Fig. 5. Operating modes of an IGBT A. Forward Conduction Mode: An IGBT in the forward-blocking state can be transferred to the forward conducting state by removing the gate-emitter shorting and applying a positive voltage of sufficient level to invert the Si below gate in the P base region. This forms a conducting channel which connects the N+ emitter to the N- drift region. Through this channel, electrons are transported from the N+ emitter to the N- drift Result: conductivity modulation. B. Reverse blocking mode: When a negative voltage is applied across the collector-toemitter terminal, the junction J1 becomes reverse-biased and its depletion layer extends into the N- drift region. The break down voltage during the reverse-blocking is determined by an open-base BJT formed by the P+ collector/ N- drift/p base regions. The device is prone to punch-through if the N-drift region is very lightly-doped. The desired reverse voltage capability can be obtained by optimizing the resistivity and thickness of the N- drift region. Reverse blocking IGBT is rare and in most applications, an anti - parallel diode (FRED) is used. C. Reverse-Blocking IGBT: The reverse-blocking IGBT is a new device with reverse withstands voltage performance that is not possible with conventional IGBTs. Fig. 6 shows a bidirectional switch with a conventional IGBT and a bidirectional switch with a reverse-blocking IGBT. When the reverse blocking IGBT is used in direct linked type converter such as matrix converters, the diodes required for obtaining reverse withstand voltage in conventional switch are no longer necessary. Elimination of the diodes should lead to the following benefits: 1. Lower cost and smaller packages because there are fewer chips.
5 2. Lower on-state voltage: About 4 V in conventional IGBTs + diodes, but about 2 V in reverse-blocking IGBT only. Described next is the reverse withstand voltage structure of a reverse-blocking IGBT. In the final stage of the chip manufacturing process, chips are cut out from the wafer (dicing process), leaving the side surfaces of the chips with crystal deformations and high density crystal defects. In a conventional IGBT, if a reverse bias is applied, the depletion layer extending from the p-n junction at the back surface - that is, a high electric field region - also appears on the dicing surface. Because carriers generated continuously from the crystal defects are transported by the electric field, resulting in a large leakage current, we could not obtain any reverse withstand voltage. In a mesa-type reverse-blocking IGBT, the chip periphery is etched through the n-layer to isolate the active area and dicing surface electrically. Because there is no electric field on the dicing surface, there is no leakage current. When a reverse bias is applied, the depletion layer extends from the p-n junction that appears on the etching groove surface. Because no silicon crystal deformation exists in this area, the leakage current is small. In addition, because the p-n junction has a positive bevel structure, the electric field is relaxed, preventing local enhancement of the electric field. In an isolation type reverse-blocking IGBT, a very deep isolation region (p+) is formed from the wafer surface in advance so that an isolation region appears at the back surface after back lap of the wafer, and the dicing surface is completely covered with the isolation region. Next, formation of the p+ collector layer on the back surface extends the depletion layer along the adjacent collector layer at the back surface and the isolation region. Because it does not reach the dicing surface, generation of the leakage current can be prevented. RB IGBT is a new device with reverse withstand voltage performance that is not possible with conventional IGBT: 1. Conventional IGBT - Uni -directional - Leakage current - Non -Punch Through or Field Stop structure Biasing of IGBT RB IGBT structure prevents leakage current generation: 1. Conventional IGBT - NPT structure - Mech Diced Side Wall - Leakage Current 2. RB IGBT - Special Structure - Isolation Region - Well Designed - Reliable for +/- Bias - Mech Diced Side Wall 2. True RB-IGBT - Reverse Blocking capability - NPT structure - Isolation region - Bi-directional switch (2x RB)
6 and effect of these stresses are dependent on the trigger point and the electrical behavior of the switching scheme. But they are also influenced by the carrier densities inside the IGBT at the start of the commutation process. A further improvement of switching performance may be achieved by optimizing trigger points and substituting the supplementary diode in different NPT-IGBT applications. There is an immense risk in these schemes to expose the non-protected IGBT to a high reverse stress caused by changing driving and load conditions. Fig. 6.-RB-IGBT main structure with RB capability VIII. CLASSIFICATION OF REVERSE STATES The reverse states can be distinguished by different parameters of the switching configuration. First of all the switching state allows to qualify the carrier density inside the IGBT at current zero crossing. The state is predicted by the drive only. Secondly the commutation is characterized by the derivatives of current and voltage at the device with respect to the time. The commutation rates determine the behavior of the circuit. A third parameter is based on the energy impressed into the IGBT [6]. A parameter summarizing the properties of the IGBT is the energy E REV, which the inverter impresses into the IGBT during the reverse state: E REV = i * rev v rev t i REV and v REV the current through the collector and the voltage from collector to emitter during the whole time of reverse stress t REV. A parameter characterizing the IGBT is the energy E REV (Q) which can be stored by displacement of charge until reverse breakdown at Vbr rev: rev E Q i v Q, REV REV vrev Fig. 7. IGBT isolation region without RB capability. VII. REVERSE STATES OF THE IGBT The use of the IGBT in inverter circuits does not come without its problems. During the switching cycle the signs of current and voltage applied to the switching device change temporarily caused by the inversion of the flux of energy between supply and load. The IGBT has no provision for carrying negative voltages; therefore it must be terminated with an anti-parallel or a series diode. However, it is not possible to completely suppress transient reverse states of the IGBT, which are caused by the transient behavior of the diode (which shows forward and reverse recovery) and are also due to parasitic inductance within the Circuit. Character Q REV is the charge displaced by the reverse stress until reverse breakdown. The ratio of the energies E REV/E REV (Q) can be taken as an extension of the reverse stress of the IGBT. Whereas E REV can be obtained recording v rev, and i rev the calculation for E REV (Q) is more difficult. In the steady off-state only Q REV reduces to the value of the fixed charges in the depleted region and is a function of v rev alone. In the on-state Q REV depends on the forward current and is expected to follow a square root law. The influence of the reverse bias appears more complicated. But mostly the commutation rates do not affect QREV due to the order of minority lifetime in common IGBTs. IX. CONCLUSIONS In an ever increasing power electronics applications market, the fundamental contribution power semiconductor devices have on the system level performance will ensure the continuous drive for improving both the device functionality and operational parameters. The paper presented a review of the recent advancements achieved in the field of Bipolar MOS controlled silicon devices with the main component under the spotlight being the IGBT. Conduction losses of an IGBT play an important role in the designing, development of
7 the family. The new L5 IGBT [7] is a fresh example of this. The L5 in combination with the TO pin package provides the lowest possible switching and conduction losses. Future developments will maintain similar past trends for the growing system demands in terms of increased power levels, improved efficiency, greater control and reliability. REFERENCES [1] Abdus Sattar, IXYS Corporation, PDF [2] Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) Basics Abdus Sattar, IXYS Corporation 1 IXAN0063. [3] ( ) [4] APPLICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF REVERSE BIASED IGBT by Monabu Takei, Akihiro Odaka and Hisashi Fujimoto, Fuji Electric. [5] [ Massimo Caprioli Fuji Electric Europe Semiconductors Italy Power Road Show 2013 Padova, 11 Aprile Torino, 16 Aprile Milano, 29 Maggio ] [6] Reverse behaviour_npt_igbt Siemens [7] Infinion Technologies [8] [9] future trends in high power MOS controlled power semiconductors: MUNAF RAHIMO, ABB Switzerland ltd;semiconductors,fabrikstrasse 3,CH-5600 Lenz burg, Switzerland. [10] [11] Indo german winter academy 2010: tutor- prof heiner ryssel, university of Erlangen, Nuremberg, Germany.
Today s subject MOSFET and IGBT
 Today s subject MOSFET and IGBT 2018-05-22 MOSFET metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor Drain Gate n-channel Source p-channel The MOSFET - Source Gate G D n + p p n + S body body n - drift
Today s subject MOSFET and IGBT 2018-05-22 MOSFET metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor Drain Gate n-channel Source p-channel The MOSFET - Source Gate G D n + p p n + S body body n - drift
Power Semiconductor Devices
 TRADEMARK OF INNOVATION Power Semiconductor Devices Introduction This technical article is dedicated to the review of the following power electronics devices which act as solid-state switches in the circuits.
TRADEMARK OF INNOVATION Power Semiconductor Devices Introduction This technical article is dedicated to the review of the following power electronics devices which act as solid-state switches in the circuits.
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION High performance semiconductor devices with better voltage and current handling capability are required in different fields like power electronics, computer and automation. Since
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION High performance semiconductor devices with better voltage and current handling capability are required in different fields like power electronics, computer and automation. Since
Power Electronics Power semiconductor devices. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Power Electronics Power semiconductor devices Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Introduction 2 Classifications of Power Switches 3 Power Diodes 4 Thyristors (SCRs) 5 The Triac 6 The Gate Turn-Off
Power Electronics Power semiconductor devices Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Introduction 2 Classifications of Power Switches 3 Power Diodes 4 Thyristors (SCRs) 5 The Triac 6 The Gate Turn-Off
Fundamentals of Power Semiconductor Devices
 В. Jayant Baliga Fundamentals of Power Semiconductor Devices 4y Spri ringer Contents Preface vii Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Ideal and Typical Power Switching Waveforms 3 1.2 Ideal and Typical Power Device
В. Jayant Baliga Fundamentals of Power Semiconductor Devices 4y Spri ringer Contents Preface vii Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Ideal and Typical Power Switching Waveforms 3 1.2 Ideal and Typical Power Device
Power semiconductors. José M. Cámara V 1.0
 Power semiconductors José M. Cámara V 1.0 Introduction Here we are going to study semiconductor devices used in power electronics. They work under medium and high currents and voltages. Some of them only
Power semiconductors José M. Cámara V 1.0 Introduction Here we are going to study semiconductor devices used in power electronics. They work under medium and high currents and voltages. Some of them only
3. Draw the two transistor model of a SCR and mention its applications. (MAY 2016)
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6503 POWER ELECTRONICS UNIT I- POWER SEMI-CONDUCTOR DEVICES PART - A 1. What is a SCR? A silicon-controlled rectifier
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EE6503 POWER ELECTRONICS UNIT I- POWER SEMI-CONDUCTOR DEVICES PART - A 1. What is a SCR? A silicon-controlled rectifier
Power Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
 ECE442 Power Semiconductor Devices and Integrated Circuits Power Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) Power Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Background The
ECE442 Power Semiconductor Devices and Integrated Circuits Power Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) Power Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Background The
Switching and Semiconductor Switches
 1 Switching and Semiconductor Switches 1.1 POWER FLOW CONTROL BY SWITCHES The flow of electrical energy between a fixed voltage supply and a load is often controlled by interposing a controller, as shown
1 Switching and Semiconductor Switches 1.1 POWER FLOW CONTROL BY SWITCHES The flow of electrical energy between a fixed voltage supply and a load is often controlled by interposing a controller, as shown
Solid State Devices- Part- II. Module- IV
 Solid State Devices- Part- II Module- IV MOS Capacitor Two terminal MOS device MOS = Metal- Oxide- Semiconductor MOS capacitor - the heart of the MOSFET The MOS capacitor is used to induce charge at the
Solid State Devices- Part- II Module- IV MOS Capacitor Two terminal MOS device MOS = Metal- Oxide- Semiconductor MOS capacitor - the heart of the MOSFET The MOS capacitor is used to induce charge at the
DOWNLOAD PDF POWER ELECTRONICS DEVICES DRIVERS AND APPLICATIONS
 Chapter 1 : Power Electronics Devices, Drivers, Applications, and Passive theinnatdunvilla.com - Google D Download Power Electronics: Devices, Drivers and Applications By B.W. Williams - Provides a wide
Chapter 1 : Power Electronics Devices, Drivers, Applications, and Passive theinnatdunvilla.com - Google D Download Power Electronics: Devices, Drivers and Applications By B.W. Williams - Provides a wide
Lecture 3: Transistors
 Lecture 3: Transistors Now that we know about diodes, let s put two of them together, as follows: collector base emitter n p n moderately doped lightly doped, and very thin heavily doped At first glance,
Lecture 3: Transistors Now that we know about diodes, let s put two of them together, as follows: collector base emitter n p n moderately doped lightly doped, and very thin heavily doped At first glance,
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics F2 Active power devices»mos»bjt» IGBT, TRIAC» Safe Operating Area» Thermal analysis 30/05/2012-1 ATLCE - F2-2011 DDC Lesson F2:
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics F2 Active power devices»mos»bjt» IGBT, TRIAC» Safe Operating Area» Thermal analysis 30/05/2012-1 ATLCE - F2-2011 DDC Lesson F2:
CONTENTS. 2.2 Schrodinger's Wave Equation 31. PART I Semiconductor Material Properties. 2.3 Applications of Schrodinger's Wave Equation 34
 CONTENTS Preface x Prologue Semiconductors and the Integrated Circuit xvii PART I Semiconductor Material Properties CHAPTER 1 The Crystal Structure of Solids 1 1.0 Preview 1 1.1 Semiconductor Materials
CONTENTS Preface x Prologue Semiconductors and the Integrated Circuit xvii PART I Semiconductor Material Properties CHAPTER 1 The Crystal Structure of Solids 1 1.0 Preview 1 1.1 Semiconductor Materials
Semiconductor Devices
 Semiconductor Devices Modelling and Technology Source Electrons Gate Holes Drain Insulator Nandita DasGupta Amitava DasGupta SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES Modelling and Technology NANDITA DASGUPTA Professor Department
Semiconductor Devices Modelling and Technology Source Electrons Gate Holes Drain Insulator Nandita DasGupta Amitava DasGupta SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES Modelling and Technology NANDITA DASGUPTA Professor Department
Cosmic Ray Withstand Capability of RB-IGBT Utilizing different gate conditions
 Cosmic Ray Withstand Capability of RB-IGBT Utilizing different gate conditions Daniel Hofmann ISPS 2016, August 31 st September 2 nd Topics - Overview 1. Motivation 2. IGBT Device: NPT vs. RB-IGBT 3. Effect
Cosmic Ray Withstand Capability of RB-IGBT Utilizing different gate conditions Daniel Hofmann ISPS 2016, August 31 st September 2 nd Topics - Overview 1. Motivation 2. IGBT Device: NPT vs. RB-IGBT 3. Effect
T-series and U-series IGBT Modules (600 V)
 T-series and U-series IGBT Modules (6 V) Seiji Momota Syuuji Miyashita Hiroki Wakimoto 1. Introduction The IGBT (insulated gate bipolar transistor) module is the most popular power device in power electronics
T-series and U-series IGBT Modules (6 V) Seiji Momota Syuuji Miyashita Hiroki Wakimoto 1. Introduction The IGBT (insulated gate bipolar transistor) module is the most popular power device in power electronics
Lecture - 18 Transistors
 Electronic Materials, Devices and Fabrication Dr. S. Prarasuraman Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 18 Transistors Last couple of classes
Electronic Materials, Devices and Fabrication Dr. S. Prarasuraman Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 18 Transistors Last couple of classes
PARAMETRIC STUDY OF AN IGBT COLD PLATE AND AFFECT OF DEVICE LEVEL MODELLING ON SYSTEM LEVEL THERMAL PREDICTIONS ABHISHEK RAJ URS KADABA NAGARAJA URS
 PARAMETRIC STUDY OF AN IGBT COLD PLATE AND AFFECT OF DEVICE LEVEL MODELLING ON SYSTEM LEVEL THERMAL PREDICTIONS by ABHISHEK RAJ URS KADABA NAGARAJA URS Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of
PARAMETRIC STUDY OF AN IGBT COLD PLATE AND AFFECT OF DEVICE LEVEL MODELLING ON SYSTEM LEVEL THERMAL PREDICTIONS by ABHISHEK RAJ URS KADABA NAGARAJA URS Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of
Learning Material Ver 1.1
 Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) ST2701 Learning Material Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) ST2701 Learning Material Ver 1.1 An ISO 9001:2008 company Scientech Technologies Pvt. Ltd. 94, Electronic Complex, Pardesipura, Indore - 452 010 India, + 91-731
SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY)
 SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY) QUESTION BANK I YEAR B.Tech (II Semester) ELECTRONIC DEVICES (COMMON FOR EC102, EE104, IC108, BM106) UNIT-I PART-A 1. What are intrinsic and
SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY) QUESTION BANK I YEAR B.Tech (II Semester) ELECTRONIC DEVICES (COMMON FOR EC102, EE104, IC108, BM106) UNIT-I PART-A 1. What are intrinsic and
Unit III FET and its Applications. 2 Marks Questions and Answers
 Unit III FET and its Applications 2 Marks Questions and Answers 1. Why do you call FET as field effect transistor? The name field effect is derived from the fact that the current is controlled by an electric
Unit III FET and its Applications 2 Marks Questions and Answers 1. Why do you call FET as field effect transistor? The name field effect is derived from the fact that the current is controlled by an electric
Power MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017,
 ECE442 Power Semiconductor Devices and Integrated Circuits Power MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) Evolution of low-voltage (
ECE442 Power Semiconductor Devices and Integrated Circuits Power MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) Evolution of low-voltage (
IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor)
 IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) Description This document describes the basic structures, ratings, and electrical characteristics of IGBTs. It also provides usage considerations for IGBTs. 1
IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) Description This document describes the basic structures, ratings, and electrical characteristics of IGBTs. It also provides usage considerations for IGBTs. 1
2 Marks - Question Bank. Unit 1- INTRODUCTION
 Two marks 1. What is power electronics? EE6503 POWER ELECTRONICS 2 Marks - Question Bank Unit 1- INTRODUCTION Power electronics is a subject that concerns the applications electronics principles into situations
Two marks 1. What is power electronics? EE6503 POWER ELECTRONICS 2 Marks - Question Bank Unit 1- INTRODUCTION Power electronics is a subject that concerns the applications electronics principles into situations
INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY 1. The MOS transistor The most basic element in the design of a large scale integrated circuit is the transistor. For the processes we will discuss, the type of transistor
INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY 1. The MOS transistor The most basic element in the design of a large scale integrated circuit is the transistor. For the processes we will discuss, the type of transistor
1. Introduction Device structure and operation Structure Operation...
 Application Note 96 February, 2 IGBT Basics by K.S. Oh CONTENTS. Introduction... 2. Device structure and operation... 2-. Structure... 2-2. Operation... 3. Basic Characteristics... 3-. Advantages, Disadvantages
Application Note 96 February, 2 IGBT Basics by K.S. Oh CONTENTS. Introduction... 2. Device structure and operation... 2-. Structure... 2-2. Operation... 3. Basic Characteristics... 3-. Advantages, Disadvantages
BJT. Bipolar Junction Transistor BJT BJT 11/6/2018. Dr. Satish Chandra, Assistant Professor, P P N College, Kanpur 1
 BJT Bipolar Junction Transistor Satish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics P P N College, Kanpur www.satish0402.weebly.com The Bipolar Junction Transistor is a semiconductor device which
BJT Bipolar Junction Transistor Satish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics P P N College, Kanpur www.satish0402.weebly.com The Bipolar Junction Transistor is a semiconductor device which
COLLECTOR DRAIN BASE GATE EMITTER. Applying a voltage to the Gate connection allows current to flow between the Drain and Source connections.
 MOSFETS Although the base current in a transistor is usually small (< 0.1 ma), some input devices (e.g. a crystal microphone) may be limited in their output. In order to overcome this, a Field Effect Transistor
MOSFETS Although the base current in a transistor is usually small (< 0.1 ma), some input devices (e.g. a crystal microphone) may be limited in their output. In order to overcome this, a Field Effect Transistor
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
 nsulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (GBT) Comparison between BJT and MOS power devices: BJT MOS pros cons pros cons low V O thermal instability thermal stability high R O at V MAX > 400 V high C current complex
nsulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (GBT) Comparison between BJT and MOS power devices: BJT MOS pros cons pros cons low V O thermal instability thermal stability high R O at V MAX > 400 V high C current complex
Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Second Semester
 WK 5 Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 27184 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Time : Three hours Second Semester Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 6201 ELECTRONIC DEVICES
WK 5 Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 27184 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Time : Three hours Second Semester Electronics and Communication Engineering EC 6201 ELECTRONIC DEVICES
Switching-Self-Clamping-Mode SSCM, a breakthrough in SOA performance for high voltage IGBTs and Diodes
 Switching-Self-Clamping-Mode, a breakthrough in SOA performance for high voltage IGBTs and M. Rahimo, A. Kopta, S. Eicher, U. Schlapbach, S. Linder ISPSD, May 24, Kitakyushu, Japan Copyright [24] IEEE.
Switching-Self-Clamping-Mode, a breakthrough in SOA performance for high voltage IGBTs and M. Rahimo, A. Kopta, S. Eicher, U. Schlapbach, S. Linder ISPSD, May 24, Kitakyushu, Japan Copyright [24] IEEE.
AN4503. An Introduction To IGBT Operation Application Note Replaces September 2000 version, AN AN July AN4503 Application Note
 AN4503 An Introduction To IBT Operation Application Note Replaces September 2000 version, AN45034.0 AN45034.1 July 2002 The power semiconductor devices available on the market can be categorised into three
AN4503 An Introduction To IBT Operation Application Note Replaces September 2000 version, AN45034.0 AN45034.1 July 2002 The power semiconductor devices available on the market can be categorised into three
UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
Lecture 23 Review of Emerging and Traditional Solid State Switches
 Lecture 23 Review of Emerging and Traditional Solid State Switches 1 A. Solid State Switches 1. Circuit conditions and circuit controlled switches A. Silicon Diode B. Silicon Carbide Diodes 2. Control
Lecture 23 Review of Emerging and Traditional Solid State Switches 1 A. Solid State Switches 1. Circuit conditions and circuit controlled switches A. Silicon Diode B. Silicon Carbide Diodes 2. Control
How to Design an R g Resistor for a Vishay Trench PT IGBT
 VISHAY SEMICONDUCTORS www.vishay.com Rectifiers By Carmelo Sanfilippo and Filippo Crudelini INTRODUCTION In low-switching-frequency applications like DC/AC stages for TIG welding equipment, the slow leg
VISHAY SEMICONDUCTORS www.vishay.com Rectifiers By Carmelo Sanfilippo and Filippo Crudelini INTRODUCTION In low-switching-frequency applications like DC/AC stages for TIG welding equipment, the slow leg
I E I C since I B is very small
 Figure 2: Symbols and nomenclature of a (a) npn and (b) pnp transistor. The BJT consists of three regions, emitter, base, and collector. The emitter and collector are usually of one type of doping, while
Figure 2: Symbols and nomenclature of a (a) npn and (b) pnp transistor. The BJT consists of three regions, emitter, base, and collector. The emitter and collector are usually of one type of doping, while
1200 V SiC Super Junction Transistors operating at 250 C with extremely low energy losses for power conversion applications
 1200 V SiC Super Junction Transistors operating at 250 C with extremely low energy losses for power conversion applications Ranbir Singh, Siddarth Sundaresan, Eric Lieser and Michael Digangi GeneSiC Semiconductor,
1200 V SiC Super Junction Transistors operating at 250 C with extremely low energy losses for power conversion applications Ranbir Singh, Siddarth Sundaresan, Eric Lieser and Michael Digangi GeneSiC Semiconductor,
The two-in-one chip. The bimode insulated-gate transistor (BIGT)
 The two-in-one chip The bimode insulated-gate transistor (BIGT) Munaf Rahimo, Liutauras Storasta, Chiara Corvasce, Arnost Kopta Power semiconductor devices employed in voltage source converter (VSC) applications
The two-in-one chip The bimode insulated-gate transistor (BIGT) Munaf Rahimo, Liutauras Storasta, Chiara Corvasce, Arnost Kopta Power semiconductor devices employed in voltage source converter (VSC) applications
Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination
 Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination Current Transport: Diffusion, Thermionic Emission & Tunneling For Diffusion current, the depletion layer is
Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination Current Transport: Diffusion, Thermionic Emission & Tunneling For Diffusion current, the depletion layer is
PHYS 3050 Electronics I
 PHYS 3050 Electronics I Chapter 4. Semiconductor Diodes and Transistors Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Dr. Jinjun Shan, Associate Professor of Space Engineering Department of Earth and Space Science and
PHYS 3050 Electronics I Chapter 4. Semiconductor Diodes and Transistors Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Dr. Jinjun Shan, Associate Professor of Space Engineering Department of Earth and Space Science and
A STUDY INTO THE APPLICABILITY OF P + N + (UNIVERSAL CONTACT) TO POWER SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES AND TRANSISTORS FOR FASTER REVERSE RECOVERY
 Thesis Title: Name: A STUDY INTO THE APPLICABILITY OF P + N + (UNIVERSAL CONTACT) TO POWER SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES AND TRANSISTORS FOR FASTER REVERSE RECOVERY RAGHUBIR SINGH ANAND Roll Number: 9410474 Thesis
Thesis Title: Name: A STUDY INTO THE APPLICABILITY OF P + N + (UNIVERSAL CONTACT) TO POWER SEMICONDUCTOR DIODES AND TRANSISTORS FOR FASTER REVERSE RECOVERY RAGHUBIR SINGH ANAND Roll Number: 9410474 Thesis
Power Electronics. P. T. Krein
 Power Electronics Day 10 Power Semiconductor Devices P. T. Krein Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 2011 Philip T. Krein. All rights reserved.
Power Electronics Day 10 Power Semiconductor Devices P. T. Krein Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 2011 Philip T. Krein. All rights reserved.
value of W max for the device. The at band voltage is -0.9 V. Problem 5: An Al-gate n-channel MOS capacitor has a doping of N a = cm ;3. The oxi
 Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 2001 EECS 320 Homework 10 This homework is due on December 6 Problem 1: An n-type In 0:53 Ga 0:47 As epitaxial layer doped at 10 16 cm ;3 is to be used as a channel in a FET. A
Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 2001 EECS 320 Homework 10 This homework is due on December 6 Problem 1: An n-type In 0:53 Ga 0:47 As epitaxial layer doped at 10 16 cm ;3 is to be used as a channel in a FET. A
UNIT 3 Transistors JFET
 UNIT 3 Transistors JFET Mosfet Definition of BJT A bipolar junction transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device consisting of two p-n junctions which is able to amplify or magnify a signal. It
UNIT 3 Transistors JFET Mosfet Definition of BJT A bipolar junction transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device consisting of two p-n junctions which is able to amplify or magnify a signal. It
Lecture 19 Real Semiconductor Switches and the Evolution of Power MOSFETS A.. Real Switches: I(D) through the switch and V(D) across the switch
 Lecture 19 Real Semiconductor Switches and the Evolution of Power MOSFETS 1 A.. Real Switches: I(D) through the switch and V(D) across the switch 1. Two quadrant switch implementation and device choice
Lecture 19 Real Semiconductor Switches and the Evolution of Power MOSFETS 1 A.. Real Switches: I(D) through the switch and V(D) across the switch 1. Two quadrant switch implementation and device choice
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras
 Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs
 Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs Single junction devices, such as p-n and Schottkty diodes can be used to obtain rectifying I-V characteristics, and to form electronic switching circuits
Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs Single junction devices, such as p-n and Schottkty diodes can be used to obtain rectifying I-V characteristics, and to form electronic switching circuits
Power Devices and ICs Chapter 15
 Power Devices and ICs Chapter 15 Syed Asad Alam DA, ISY 4/28/2015 1 Overview 4/28/2015 2 Overview Types of Power Devices PNPN Thyristor TRIAC (Triode Alternating Current) GTO (Gate Turn-Off Thyristor)
Power Devices and ICs Chapter 15 Syed Asad Alam DA, ISY 4/28/2015 1 Overview 4/28/2015 2 Overview Types of Power Devices PNPN Thyristor TRIAC (Triode Alternating Current) GTO (Gate Turn-Off Thyristor)
0 Operation principle of power semiconductors
 0 Operation principle of power semiconductors 0 Operation principle of power semiconductors 0.1 Basic switching processes Apart from a few special applications, power semiconductors are mainly used in
0 Operation principle of power semiconductors 0 Operation principle of power semiconductors 0.1 Basic switching processes Apart from a few special applications, power semiconductors are mainly used in
Chapter 8. Field Effect Transistor
 Chapter 8. Field Effect Transistor Field Effect Transistor: The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There
Chapter 8. Field Effect Transistor Field Effect Transistor: The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There
Questions on JFET: 1) Which of the following component is a unipolar device?
 Questions on JFET: 1) Which of the following component is a unipolar device? a) BJT b) FET c) DJT d) EFT 2) Current Conduction in FET takes place due e) Majority charge carriers only f) Minority charge
Questions on JFET: 1) Which of the following component is a unipolar device? a) BJT b) FET c) DJT d) EFT 2) Current Conduction in FET takes place due e) Majority charge carriers only f) Minority charge
Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004
 Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004 Lecture outline Historical introduction Semiconductor devices overview Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Field
Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004 Lecture outline Historical introduction Semiconductor devices overview Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Field
UNIT-VI FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR. 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s.
 UNIT-I FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s. The Field Effect Transistor, or simply FET however, uses the voltage that is applied to their
UNIT-I FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s. The Field Effect Transistor, or simply FET however, uses the voltage that is applied to their
SCR- SILICON CONTROLLED RECTIFIER
 SCR- SILICON CONTROLLED RECTIFIER Definition: When a pn junction is added to a junction transistor, the resulting three pn junction device is called a silicon controlled rectifier. SCR can change alternating
SCR- SILICON CONTROLLED RECTIFIER Definition: When a pn junction is added to a junction transistor, the resulting three pn junction device is called a silicon controlled rectifier. SCR can change alternating
6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 13 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Final Eam Closed Book: Formula sheet provided;
Page 1 of 13 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Final Eam Closed Book: Formula sheet provided;
Talk1: Overview of Power Devices and Technology Trends. Talk 2: Devices and Technologies for HVIC
 Talk1: Overview of Power Devices and Technology Trends Talk 2: Devices and Technologies for HVIC Prof. Florin Udrea Cambridge University Taiwan, January 2010 1 Outline Talk 1: Overview of Power Devices
Talk1: Overview of Power Devices and Technology Trends Talk 2: Devices and Technologies for HVIC Prof. Florin Udrea Cambridge University Taiwan, January 2010 1 Outline Talk 1: Overview of Power Devices
Comparison of Different Cell Concepts for 1200V- NPT-IGBT's
 Comparison of Different Cell Concepts for 12V- NPT-IGBT's R.Siemieniec, M.Netzel, R. Herzer, D.Schipanski Abstract - IGBT's are relatively new power devices combining bipolar and unipolar properties. In
Comparison of Different Cell Concepts for 12V- NPT-IGBT's R.Siemieniec, M.Netzel, R. Herzer, D.Schipanski Abstract - IGBT's are relatively new power devices combining bipolar and unipolar properties. In
Application Note. 3-Level Modules with Authentic RB-IGBT. Version 1.3
 Application Note 3-Level Modules with Authentic RB-IGBT Version 1.3 1 Content 1. Introduction... 2 2. Basics of T-type IGBT modules... 3 3. Characteristics of authentic RB-IGBT... 5 4. Leakage current
Application Note 3-Level Modules with Authentic RB-IGBT Version 1.3 1 Content 1. Introduction... 2 2. Basics of T-type IGBT modules... 3 3. Characteristics of authentic RB-IGBT... 5 4. Leakage current
FET(Field Effect Transistor)
 Field Effect Transistor: Construction and Characteristic of JFETs. Transfer Characteristic. CS,CD,CG amplifier and analysis of CS amplifier MOSFET (Depletion and Enhancement) Type, Transfer Characteristic,
Field Effect Transistor: Construction and Characteristic of JFETs. Transfer Characteristic. CS,CD,CG amplifier and analysis of CS amplifier MOSFET (Depletion and Enhancement) Type, Transfer Characteristic,
An introduction to Depletion-mode MOSFETs By Linden Harrison
 An introduction to Depletion-mode MOSFETs By Linden Harrison Since the mid-nineteen seventies the enhancement-mode MOSFET has been the subject of almost continuous global research, development, and refinement
An introduction to Depletion-mode MOSFETs By Linden Harrison Since the mid-nineteen seventies the enhancement-mode MOSFET has been the subject of almost continuous global research, development, and refinement
Field Effect Transistors (npn)
 Field Effect Transistors (npn) gate drain source FET 3 terminal device channel e - current from source to drain controlled by the electric field generated by the gate base collector emitter BJT 3 terminal
Field Effect Transistors (npn) gate drain source FET 3 terminal device channel e - current from source to drain controlled by the electric field generated by the gate base collector emitter BJT 3 terminal
IGBT Press-packs for the industrial market
 IGBT Press-packs for the industrial market Franc Dugal, Evgeny Tsyplakov, Andreas Baschnagel, Liutauras Storasta, Thomas Clausen ABB Switzerland Ltd, Semiconductors, Fabrikstrasse 3, CH-56 Lenzburg, Switzerland
IGBT Press-packs for the industrial market Franc Dugal, Evgeny Tsyplakov, Andreas Baschnagel, Liutauras Storasta, Thomas Clausen ABB Switzerland Ltd, Semiconductors, Fabrikstrasse 3, CH-56 Lenzburg, Switzerland
1 Basics V GG. V GS(th) V GE(th) , i C. i D I L. v DS. , v CE V DD V CC. V DS(on) VCE(sat) (IGBT) I t MOSFET MOSFET.
 Reverse operation During reverse operation (Figure 1.10, III rd quadrant) the IGBT collector pn-junction is poled in reverse direction and there is no inverse conductivity, other than with MOSFETs. Although,
Reverse operation During reverse operation (Figure 1.10, III rd quadrant) the IGBT collector pn-junction is poled in reverse direction and there is no inverse conductivity, other than with MOSFETs. Although,
(anode) (also: I D, I F, I T )
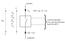 (anode) V R - V A or V D or VF or V T IA (also: I D, I F, I T ) control terminals (e.g. gate for thyrisr; basis for BJT) - (IR =-I A ) (cathode) I A I F conducting range A p n K (a) V A (V F ) - A anode
(anode) V R - V A or V D or VF or V T IA (also: I D, I F, I T ) control terminals (e.g. gate for thyrisr; basis for BJT) - (IR =-I A ) (cathode) I A I F conducting range A p n K (a) V A (V F ) - A anode
Chapter 1 Power Electronic Devices
 Chapter 1 Power Electronic Devices Outline 1.1 An introductory overview of power electronic devices 1.2 Uncontrolled device power diode 1.3 Half- controlled device thyristor 1.4 Typical fully- controlled
Chapter 1 Power Electronic Devices Outline 1.1 An introductory overview of power electronic devices 1.2 Uncontrolled device power diode 1.3 Half- controlled device thyristor 1.4 Typical fully- controlled
U-series IGBT Modules (1,700 V)
 U-series IGBT Modules (1,7 ) Yasuyuki Hoshi Yasushi Miyasaka Kentarou Muramatsu 1. Introduction In recent years, requirements have increased for high power semiconductor devices used in high power converters
U-series IGBT Modules (1,7 ) Yasuyuki Hoshi Yasushi Miyasaka Kentarou Muramatsu 1. Introduction In recent years, requirements have increased for high power semiconductor devices used in high power converters
Lecture 24: Bipolar Junction Transistors (1) Bipolar Junction Structure, Operating Regions, Biasing
 Lecture 24: Bipolar Junction Transistors (1) Bipolar Junction Structure, Operating Regions, Biasing BJT Structure the BJT is formed by doping three semiconductor regions (emitter, base, and collector)
Lecture 24: Bipolar Junction Transistors (1) Bipolar Junction Structure, Operating Regions, Biasing BJT Structure the BJT is formed by doping three semiconductor regions (emitter, base, and collector)
Experiment (1) Principles of Switching
 Experiment (1) Principles of Switching Introduction When you use microcontrollers, sometimes you need to control devices that requires more electrical current than a microcontroller can supply; for this,
Experiment (1) Principles of Switching Introduction When you use microcontrollers, sometimes you need to control devices that requires more electrical current than a microcontroller can supply; for this,
EDC UNIT IV- Transistor and FET Characteristics EDC Lesson 9- ", Raj Kamal, 1
 EDC UNIT IV- Transistor and FET Characteristics Lesson-9: JFET and Construction of JFET 2008 EDC Lesson 9- ", Raj Kamal, 1 1. Transistor 2008 EDC Lesson 9- ", Raj Kamal, 2 Transistor Definition The transferred-resistance
EDC UNIT IV- Transistor and FET Characteristics Lesson-9: JFET and Construction of JFET 2008 EDC Lesson 9- ", Raj Kamal, 1 1. Transistor 2008 EDC Lesson 9- ", Raj Kamal, 2 Transistor Definition The transferred-resistance
AN1491 APPLICATION NOTE
 AN1491 APPLICATION NOTE IGBT BASICS M. Aleo (mario.aleo@st.com) 1. INTRODUCTION. IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) combine the simplicity of drive and the excellent fast switching capability of
AN1491 APPLICATION NOTE IGBT BASICS M. Aleo (mario.aleo@st.com) 1. INTRODUCTION. IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) combine the simplicity of drive and the excellent fast switching capability of
In this lecture we will begin a new topic namely the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor.
 Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 MOS Field Effect Transistor In this lecture we will begin
Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 MOS Field Effect Transistor In this lecture we will begin
Lecture 4 -- Tuesday, Sept. 19: Non-uniform injection and/or doping. Diffusion. Continuity/conservation. The five basic equations.
 6.012 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Schedule -- Fall 1995 (8/31/95 version) Recitation 1 -- Wednesday, Sept. 6: Review of 6.002 models for BJT. Discussion of models and modeling; motivate need to go
6.012 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Schedule -- Fall 1995 (8/31/95 version) Recitation 1 -- Wednesday, Sept. 6: Review of 6.002 models for BJT. Discussion of models and modeling; motivate need to go
Some Key Researches on SiC Device Technologies and their Predicted Advantages
 18 POWER SEMICONDUCTORS www.mitsubishichips.com Some Key Researches on SiC Device Technologies and their Predicted Advantages SiC has proven to be a good candidate as a material for next generation power
18 POWER SEMICONDUCTORS www.mitsubishichips.com Some Key Researches on SiC Device Technologies and their Predicted Advantages SiC has proven to be a good candidate as a material for next generation power
Other Electronic Devices
 Other Electronic Devices 1 Contents Field-Effect Transistors(FETs) - JFETs - MOSFETs Insulate Gate Bipolar Transistors(IGBTs) H-bridge driver and PWM Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers(SCRs) TRIACs Device Selection
Other Electronic Devices 1 Contents Field-Effect Transistors(FETs) - JFETs - MOSFETs Insulate Gate Bipolar Transistors(IGBTs) H-bridge driver and PWM Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers(SCRs) TRIACs Device Selection
QUESTION BANK EC6201 ELECTRONIC DEVICES UNIT I SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE PART A. It has two types. 1. Intrinsic semiconductor 2. Extrinsic semiconductor.
 FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai - 625 020. [An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution] QUESTION BANK EC6201 ELECTRONIC DEVICES SEMESTER:
FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai - 625 020. [An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution] QUESTION BANK EC6201 ELECTRONIC DEVICES SEMESTER:
ECE 440 Lecture 29 : Introduction to the BJT-I Class Outline:
 ECE 440 Lecture 29 : Introduction to the BJT-I Class Outline: Narrow-Base Diode BJT Fundamentals BJT Amplification Things you should know when you leave Key Questions How does the narrow-base diode multiply
ECE 440 Lecture 29 : Introduction to the BJT-I Class Outline: Narrow-Base Diode BJT Fundamentals BJT Amplification Things you should know when you leave Key Questions How does the narrow-base diode multiply
Power Devices Prof. Dr. Ing. Hans Georg Herzog Prof. Dr. Ing. Ralph Kennel
 Power Devices Prof. Dr. Ing. Hans Georg Herzog (hg.herzog@tum.de) Prof. Dr. Ing. Ralph Kennel (ralph.kennel@tum.de) Technische Universität München Arcisstraße 21 80333 München Germany 1 Power Devices in
Power Devices Prof. Dr. Ing. Hans Georg Herzog (hg.herzog@tum.de) Prof. Dr. Ing. Ralph Kennel (ralph.kennel@tum.de) Technische Universität München Arcisstraße 21 80333 München Germany 1 Power Devices in
EEL 5245 POWER ELECTRONICS I Lecture #4: Chapter 2 Switching Concepts and Semiconductor Overview
 EEL 5245 POWER ELECTRONICS I Lecture #4: Chapter 2 Switching Concepts and Semiconductor Overview Objectives of Lecture Switch realizations Objective is to focus on terminal characteristics Blocking capability
EEL 5245 POWER ELECTRONICS I Lecture #4: Chapter 2 Switching Concepts and Semiconductor Overview Objectives of Lecture Switch realizations Objective is to focus on terminal characteristics Blocking capability
MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials. Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory. Reading: Kasap
 MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials 1 Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory Reading: Kasap 6.6-6.8 Vacuum tube diodes 2 Thermionic emission from cathode Electrons collected
MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials 1 Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory Reading: Kasap 6.6-6.8 Vacuum tube diodes 2 Thermionic emission from cathode Electrons collected
Grade of climate describes the permissible ambient test conditions (climate) according to DIN IEC 68-1
 Total power dissipation P tot Maximum power dissipation per transistor/ diode or within the whole power module P tot = (T jmax -T case )/R thjc, Parameter: case temperature T case = 25 C Operating temperature
Total power dissipation P tot Maximum power dissipation per transistor/ diode or within the whole power module P tot = (T jmax -T case )/R thjc, Parameter: case temperature T case = 25 C Operating temperature
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02
 EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
High Efficiency Power Conversion Using a Matrix Converter
 High Efficiency Power Conversion Using a Converter Jun-ichi Itoh Akihiro Odaka Ikuya Sato 1. Introduction As demands for energy savings have increased in recent years, inverters are being used in a wider
High Efficiency Power Conversion Using a Converter Jun-ichi Itoh Akihiro Odaka Ikuya Sato 1. Introduction As demands for energy savings have increased in recent years, inverters are being used in a wider
Chapter 3 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)
 Chapter 3 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) Transistors In analog circuits, transistors are used in amplifiers and linear regulated power supplies. In digital circuits they function as electrical switches,
Chapter 3 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) Transistors In analog circuits, transistors are used in amplifiers and linear regulated power supplies. In digital circuits they function as electrical switches,
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits
 EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture XI James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Review Review Introduced the idea of a dynamic resistance
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture XI James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Review Review Introduced the idea of a dynamic resistance
High Voltage SPT + HiPak Modules Rated at 4500V
 High Voltage SPT + HiPak Modules Rated at 45V High Voltage SPT + HiPak Modules Rated at 45V A. Kopta, M. Rahimo, U. Schlapbach, R. Schnell, D. Schneider ABB Switzerland Ltd, Semiconductors, Fabrikstrasse
High Voltage SPT + HiPak Modules Rated at 45V High Voltage SPT + HiPak Modules Rated at 45V A. Kopta, M. Rahimo, U. Schlapbach, R. Schnell, D. Schneider ABB Switzerland Ltd, Semiconductors, Fabrikstrasse
IGBT Module Chip Improvements for Industrial Motor Drives
 IGBT Module Chip Improvements for Industrial Motor Drives John F. Donlon Powerex, Inc. 173 Pavilion Lane Youngwood, PA USA Katsumi Satoh Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Power Semiconductor Device Works
IGBT Module Chip Improvements for Industrial Motor Drives John F. Donlon Powerex, Inc. 173 Pavilion Lane Youngwood, PA USA Katsumi Satoh Mitsubishi Electric Corporation Power Semiconductor Device Works
Abstract: Following fast on the successful market introduction of the 1200V Soft-Punch-Through. 1. Introduction
 Novel Soft-Punch-Through (SPT) 1700V IGBT Sets Benchmark on Technology Curve M. Rahimo, W. Lukasch *, C. von Arx, A. Kopta, R. Schnell, S. Dewar, S. Linder ABB Semiconductors AG, Lenzburg, Switzerland
Novel Soft-Punch-Through (SPT) 1700V IGBT Sets Benchmark on Technology Curve M. Rahimo, W. Lukasch *, C. von Arx, A. Kopta, R. Schnell, S. Dewar, S. Linder ABB Semiconductors AG, Lenzburg, Switzerland
UNIT I POWER SEMI-CONDUCTOR DEVICES
 UNIT I POWER SEMI-CONDUCTOR DEVICES SUBJECT CODE SUBJECT NAME STAFF NAME : EE6503 : Power Electronics : Ms.M.Uma Maheswari 1 SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES POWER DIODE POWER TRANSISTORS POWER BJT POWER MOSFET IGBT
UNIT I POWER SEMI-CONDUCTOR DEVICES SUBJECT CODE SUBJECT NAME STAFF NAME : EE6503 : Power Electronics : Ms.M.Uma Maheswari 1 SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES POWER DIODE POWER TRANSISTORS POWER BJT POWER MOSFET IGBT
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) Overview
 1 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) Asst. Prof. MONTREE SIRIPRUCHYANUN, D. Eng. Dept. of Teacher Training in Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Technical Education King Mongkut s Institute of Technology
1 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) Asst. Prof. MONTREE SIRIPRUCHYANUN, D. Eng. Dept. of Teacher Training in Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Technical Education King Mongkut s Institute of Technology
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
 PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES by J. P. Colinge Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis C. A. Colinge Department of Electrical
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES by J. P. Colinge Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis C. A. Colinge Department of Electrical
Sven Matthias, Arnost Kopta, Munaf Rahimo, Lydia Feller, Silvan Geissmann, Raffael Schnell, Sven Klaka
 33V HiPak modules for high-temperature applications Sven Matthias, Arnost Kopta, Munaf Rahimo, Lydia Feller, Silvan Geissmann, Raffael Schnell, Sven Klaka ABB Switzerland Ltd, Semiconductors, Fabrikstrasse
33V HiPak modules for high-temperature applications Sven Matthias, Arnost Kopta, Munaf Rahimo, Lydia Feller, Silvan Geissmann, Raffael Schnell, Sven Klaka ABB Switzerland Ltd, Semiconductors, Fabrikstrasse
Three Terminal Devices
 Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
POWER ELECTRONICS. Alpha. Science International Ltd. S.C. Tripathy. Oxford, U.K.
 POWER ELECTRONICS S.C. Tripathy Alpha Science International Ltd. Oxford, U.K. Contents Preface vii 1. SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE THEORY 1.1 1.1 Introduction 1.1 1.2 Charge Densities in a Doped Semiconductor 1.1
POWER ELECTRONICS S.C. Tripathy Alpha Science International Ltd. Oxford, U.K. Contents Preface vii 1. SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE THEORY 1.1 1.1 Introduction 1.1 1.2 Charge Densities in a Doped Semiconductor 1.1
UNIT I PN JUNCTION DEVICES
 UNIT I PN JUNCTION DEVICES 1. Define Semiconductor. 2. Classify Semiconductors. 3. Define Hole Current. 4. Define Knee voltage of a Diode. 5. What is Peak Inverse Voltage? 6. Define Depletion Region in
UNIT I PN JUNCTION DEVICES 1. Define Semiconductor. 2. Classify Semiconductors. 3. Define Hole Current. 4. Define Knee voltage of a Diode. 5. What is Peak Inverse Voltage? 6. Define Depletion Region in
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. At room temperature the current in an intrinsic semiconductor is due to A. holes B. electrons C. ions D. holes and electrons 2. Work function is the maximum energy required
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. At room temperature the current in an intrinsic semiconductor is due to A. holes B. electrons C. ions D. holes and electrons 2. Work function is the maximum energy required
Module 1. Power Semiconductor Devices. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 1 Power Semiconductor evices Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 6 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Constructional Features, operating principle
Module 1 Power Semiconductor evices Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 6 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Constructional Features, operating principle
UNIT IX ELECTRONIC DEVICES
 UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
Lecture 18: Photodetectors
 Lecture 18: Photodetectors Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Photodetector principle 2 3 Photoconductor 4 4 Photodiodes 6 4.1 Heterojunction photodiode.................... 8 4.2 Metal-semiconductor photodiode................
Lecture 18: Photodetectors Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Photodetector principle 2 3 Photoconductor 4 4 Photodiodes 6 4.1 Heterojunction photodiode.................... 8 4.2 Metal-semiconductor photodiode................
