signals Mo: signals 36+1
|
|
|
- Chad Dawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 signals Mo: signals 36+1
2 examples of signals length of column of mercury in a thermometer angles of hands on a clock or needle of automobile speedometer intensity and frequency of sound when a tool removes metal from stock turning in a lathe electrical signals: voltage ~ power collected by antenna, current ~ light intensity, etc digital signals: ADC + microprocessor convert electrical signal to message in some protocol mws@cmu.edu Mo: signals 36+2
3 and unwanted signals (== noise) light leaks thru a crack in your camera s body people talk at the table next to yours strong radio station near weak one you want observation-to-observation variation measurand fluctuates (slouch or stand straight) instrument fluctuates (meter stick trembles) fundamental natural sources of fluctuation: thermal motion ( Johnson or Nyquist noise) interval-to-interval statistical count variations (shot noise) chaos, uncertainty principle, etc (1/f noise) mws@cmu.edu Mo: signals 36+3
4 transduction Mo: signals 36+4
5 transduction (between modalities) conversion of an environmental parameter into a signal is what we call sensing temperature length of mercury column force resistance of (stretched) length of wire conversion of a signal into an environmental change is what we call actuation finger pushes lever moves toilet flushes signal power amplifier current through a resistor heating of the environment signal power amplifier robot arm motor motion the signal is almost always electrical in modern times; it wasn t always so! mws@cmu.edu Mo: signals 36+5
6 electrical signals before ~1960s almost all signals were effectively length measurements: temperature length of column of mercury voltage position of meter needle along arc and occasionally some digital counting e.g., geiger tube + electrical or electronic counter by the 1980s almost all signals were electrical quantities represented digitally: voltage light frequency (color) on sensor current light intensity (power) on sensor parameters: resistance = voltage / current mws@cmu.edu Mo: signals 36+6
7 review of elementary electricity & electronics Mo: signals 36+7
8 basic electrical concepts charge: number of electrons, protons, etc (each carrying a fundamental unit of charge) current: charge per unit time flowing through an imagined surface that cuts a wire, or flowing into or out of a device terminal voltage: potential energy per unit charge, pressure in response to which current flows general rule of transport: measure of x {energy} per unit y {charge} measure of y {charge} per unit time rate {power} = (x/y) {voltage} * (y/t) {current} mws@cmu.edu Mo: signals 36+8
9 basic electrical devices resistor R (or, generally, impedance): current I that flows thru it ~ voltage V applied across it capacitor C: time derivative of voltage applied across it ~ current that flows into or out of it inductor L: time integral of voltage applied across it ~ current that flows through it I = {V/R, C dv/dt, V dt/l} V = {R I, I dt/c, L di/dt} most usual form = {R dq/dt, Q/C, L d 2 Q/dt 2 } Q = { Vdt/R, CV, V dt dt /L} mws@cmu.edu Mo: signals 36+9
10 16722 Mo: signals 36+10
11 electrical & electronic sensors Mo: signals 36+11
12 basic electrical sensors many are sources of voltage, current, or charge CCD pixel voltage ~ integrated light intensity Ionscan signal current ~ explosive vapor concentration Geiger tube charge pulse ~ incident ionizing radiation particle energy many others are parametric strain gauge resistance ~ stretching of wire humidity sensor capacitance ~ relative humidity proximity sensor inductance ~ nearby metal mws@cmu.edu Mo: signals 36+12
13 that in series resistances, inductances, and reciprocal capacitances add, whereas in parallel reciprocal resistances, reciprocal inductances, and capacitances add (with the proviso, for inductors, that they are really independent, i.e., they do not share each others magnetic fields) Mo: signals 36+13
14 We will see later, when we discuss AC signals and their decomposition into Fourier frequency components, that dot or d/dt is usefully written j2πf and integral dt is usefully written 1/ j2πf Mo: signals 36+14
15 basic principle is often concealed! Mo: signals 36+15
Sensors. Chapter 3. Storey: Electrical & Electronic Systems Pearson Education Limited 2004 OHT 3.1
 Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
Electronic Systems - B1 23/04/ /04/ SisElnB DDC. Chapter 2
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS. Introduction. B1 - Sensors and actuators. Introduction
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
In the name of God, the most merciful Electromagnetic Radiation Measurement
 In the name of God, the most merciful Electromagnetic Radiation Measurement In these slides, many figures have been taken from the Internet during my search in Google. Due to the lack of space and diversity
In the name of God, the most merciful Electromagnetic Radiation Measurement In these slides, many figures have been taken from the Internet during my search in Google. Due to the lack of space and diversity
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements
 Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
Panca Mudji Rahardjo, ST.MT. Electrical Engineering - UB
 Panca Mudji Rahardjo, ST.MT. Electrical Engineering - UB A sensor is a device that converts a physical phenomenon into an electrical signal. As such, sensors represent part of the interface between the
Panca Mudji Rahardjo, ST.MT. Electrical Engineering - UB A sensor is a device that converts a physical phenomenon into an electrical signal. As such, sensors represent part of the interface between the
Inductance. Chapter 30. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman. Lectures by Wayne Anderson
 Chapter 30 Inductance PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 30 To learn how current in one coil
Chapter 30 Inductance PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 30 To learn how current in one coil
Robot Sensors Introduction to Robotics Lecture Handout September 20, H. Harry Asada Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 Robot Sensors 2.12 Introduction to Robotics Lecture Handout September 20, 2004 H. Harry Asada Massachusetts Institute of Technology Touch Sensor CCD Camera Vision System Ultrasonic Sensor Photo removed
Robot Sensors 2.12 Introduction to Robotics Lecture Handout September 20, 2004 H. Harry Asada Massachusetts Institute of Technology Touch Sensor CCD Camera Vision System Ultrasonic Sensor Photo removed
Filters And Waveform Shaping
 Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
An Example of robots with their sensors
 ROBOTICA 03CFIOR DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 1 An Example of robots with their sensors 3 Another example Omnivision Camera (360 ) Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) camera
ROBOTICA 03CFIOR DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 1 An Example of robots with their sensors 3 Another example Omnivision Camera (360 ) Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) camera
Sensors (Transducer) Introduction By Sintayehu Challa
 Sensors (Transducer) Introduction What are Sensors? Basically the quantities to be measured are Non-Electrical quantities such as temperature, pressure,displacement,humidity, fluid flow, speed etc, but
Sensors (Transducer) Introduction What are Sensors? Basically the quantities to be measured are Non-Electrical quantities such as temperature, pressure,displacement,humidity, fluid flow, speed etc, but
Lecture 3: Sensors, signals, ADC and DAC
 Instrumentation and data acquisition Spring 2010 Lecture 3: Sensors, signals, ADC and DAC Zheng-Hua Tan Multimedia Information and Signal Processing Department of Electronic Systems Aalborg University,
Instrumentation and data acquisition Spring 2010 Lecture 3: Sensors, signals, ADC and DAC Zheng-Hua Tan Multimedia Information and Signal Processing Department of Electronic Systems Aalborg University,
Lecture 2: Sensors. Zheng-Hua Tan
 Instrumentation and data acquisition Spring 2010 Lecture 2: Sensors Zheng-Hua Tan Multimedia Information and Signal Processing Department of Electronic Systems Aalborg University, Denmark zt@es.aau.dk
Instrumentation and data acquisition Spring 2010 Lecture 2: Sensors Zheng-Hua Tan Multimedia Information and Signal Processing Department of Electronic Systems Aalborg University, Denmark zt@es.aau.dk
Introduction to Electronic Circuit for Instrumentation
 Introduction to Electronic Circuit for Instrumentation Fundamental quantities Length Mass Time Charge and electric current Heat and temperature Light and luminous intensity Matter (atom, ion and molecule)
Introduction to Electronic Circuit for Instrumentation Fundamental quantities Length Mass Time Charge and electric current Heat and temperature Light and luminous intensity Matter (atom, ion and molecule)
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCE. BEng (HONS)/MEng BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING. BEng (HONS) MEDICAL ENGINEERING
 LH29 SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCE BEng (HONS)/MEng BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING BEng (HONS) MEDICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 MODULE NO: BME4004 Date: Wednesday 18 May 2016 Time:
LH29 SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCE BEng (HONS)/MEng BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING BEng (HONS) MEDICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 MODULE NO: BME4004 Date: Wednesday 18 May 2016 Time:
Semiconductor Detector Systems
 Semiconductor Detector Systems Helmuth Spieler Physics Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS ix CONTENTS 1 Detector systems overview 1 1.1 Sensor 2 1.2 Preamplifier 3
Semiconductor Detector Systems Helmuth Spieler Physics Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS ix CONTENTS 1 Detector systems overview 1 1.1 Sensor 2 1.2 Preamplifier 3
MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers. Final Exam. December 11, 2006
 MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Exam December 11, 2006 o Closed Book and Notes o No Calculators 1. Fill in your name on side 2 of the scoring sheet (Last name first!) 2. Fill
MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Exam December 11, 2006 o Closed Book and Notes o No Calculators 1. Fill in your name on side 2 of the scoring sheet (Last name first!) 2. Fill
Introduction to Measurement Systems
 MFE 3004 Mechatronics I Measurement Systems Dr Conrad Pace Page 4.1 Introduction to Measurement Systems Role of Measurement Systems Detection receive an external stimulus (ex. Displacement) Selection measurement
MFE 3004 Mechatronics I Measurement Systems Dr Conrad Pace Page 4.1 Introduction to Measurement Systems Role of Measurement Systems Detection receive an external stimulus (ex. Displacement) Selection measurement
Deficiency (R - A) Sl. No. (A) (R) 7. Pspice / Matlab /other Equivalent software Package) with PC Single Phase Wattmeter
 (R 03) Semester II EE6 Electric Circuits Laboratory.. 3. 4. 5. 6. Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (0 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
(R 03) Semester II EE6 Electric Circuits Laboratory.. 3. 4. 5. 6. Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (0 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
An Example of robots with their sensors
 ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 1 An Example of robots with their sensors Basilio Bona ROBOTICS 01PEEQW 3 Another example Omnivision
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 1 An Example of robots with their sensors Basilio Bona ROBOTICS 01PEEQW 3 Another example Omnivision
Measurement Techniques
 Measurement Techniques Anders Sjöström Juan Negreira Montero Department of Construction Sciences. Division of Engineering Acoustics. Lund University Disposition Introduction Errors in Measurements Signals
Measurement Techniques Anders Sjöström Juan Negreira Montero Department of Construction Sciences. Division of Engineering Acoustics. Lund University Disposition Introduction Errors in Measurements Signals
Quantity available (A) Quantity required (R) Sl. No. Deficiency (R - A) Description of Equipment
 . 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (R 203) Semester II EE62 Electric Circuits Laboratory Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (20 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (R 203) Semester II EE62 Electric Circuits Laboratory Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (20 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
Course Introduction. Content 16 pages. Learning Time 30 minutes
 Course Introduction Purpose This course discusses techniques for analyzing and eliminating noise in microcontroller (MCU) and microprocessor (MPU) based embedded systems. Objectives Learn what EMI is and
Course Introduction Purpose This course discusses techniques for analyzing and eliminating noise in microcontroller (MCU) and microprocessor (MPU) based embedded systems. Objectives Learn what EMI is and
A Tutorial on Acoustical Transducers: Microphones and Loudspeakers
 A Tutorial on Acoustical Transducers: Microphones and Loudspeakers Robert C. Maher Montana State University EELE 217 Science of Sound Spring 2012 Test Sound Outline Introduction: What is sound? Microphones
A Tutorial on Acoustical Transducers: Microphones and Loudspeakers Robert C. Maher Montana State University EELE 217 Science of Sound Spring 2012 Test Sound Outline Introduction: What is sound? Microphones
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SYSTEMS LABORATORY
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SYSTEMS LABORATORY Group 02 Asst. Prof. Dr. E. İlhan KONUKSEVEN FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS IN MEASUREMENT AND EXPERIMENTATION HOW TO MEASURE? BY MEANS OF SENSING DEVICES OFTEN CALLED:
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SYSTEMS LABORATORY Group 02 Asst. Prof. Dr. E. İlhan KONUKSEVEN FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS IN MEASUREMENT AND EXPERIMENTATION HOW TO MEASURE? BY MEANS OF SENSING DEVICES OFTEN CALLED:
Measurement, Sensors, and Data Acquisition in the Two-Can System
 Measurement, Sensors, and Data Acquisition in the Two-Can System Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 2010 Goal of this week s lab Gain familiarity with using sensors Gain familiarity with using DAQ hardware
Measurement, Sensors, and Data Acquisition in the Two-Can System Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 2010 Goal of this week s lab Gain familiarity with using sensors Gain familiarity with using DAQ hardware
electronics for computer engineering (Sensor) by KrisMT Computer Engineering, ICT, University of Phayao
 305222 electronics for computer engineering (Sensor) by KrisMT Computer Engineering, ICT, University of Phayao ห วข อ Sensor =? Each type of sensor Technology Interpolation Sensor =? is a device that measures
305222 electronics for computer engineering (Sensor) by KrisMT Computer Engineering, ICT, University of Phayao ห วข อ Sensor =? Each type of sensor Technology Interpolation Sensor =? is a device that measures
5. Transducers Definition and General Concept of Transducer Classification of Transducers
 5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS
 M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS M.D. SINGH Formerly Principal Sagar Institute of Technology and Research Bhopal J.G. JOSHI Lecturer Department of Electronics and Telecommunication
M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS M.D. SINGH Formerly Principal Sagar Institute of Technology and Research Bhopal J.G. JOSHI Lecturer Department of Electronics and Telecommunication
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems INDUCTIVE SENSORS (Chapter 3.4, 7.3) 3 Inductive sensors 4 Inductive
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems INDUCTIVE SENSORS (Chapter 3.4, 7.3) 3 Inductive sensors 4 Inductive
Introduction. ELCT903, Sensor Technology Electronics and Electrical Engineering Department 1. Dr.-Eng. Hisham El-Sherif
 Introduction In automation industry every mechatronic system has some sensors to measure the status of the process variables. The analogy between the human controlled system and a computer controlled system
Introduction In automation industry every mechatronic system has some sensors to measure the status of the process variables. The analogy between the human controlled system and a computer controlled system
Energy Bank Capacitor Applications
 Energy Bank Capacitor Applications Table of Contents Introduction Electrical parameters Energy Peak current (discharge voltage) Voltage ripple Pulse Current Principle Pulse Forming Network AVX realizations
Energy Bank Capacitor Applications Table of Contents Introduction Electrical parameters Energy Peak current (discharge voltage) Voltage ripple Pulse Current Principle Pulse Forming Network AVX realizations
GSM BASED PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM
 GSM BASED PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM ABSTRACT This project deals with the monitoring of the patient parameters such as humidity, temperature and heartbeat. Here we have designed a microcontroller based
GSM BASED PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM ABSTRACT This project deals with the monitoring of the patient parameters such as humidity, temperature and heartbeat. Here we have designed a microcontroller based
Power Electronics. Exercise: Circuit Feedback
 Lehrstuhl für Elektrische Antriebssysteme und Leistungselektronik Technische Universität München Prof Dr-Ing Ralph Kennel Aricsstr 21 Email: eat@eitumde Tel: +49 (0)89 289-28358 D-80333 München Internet:
Lehrstuhl für Elektrische Antriebssysteme und Leistungselektronik Technische Universität München Prof Dr-Ing Ralph Kennel Aricsstr 21 Email: eat@eitumde Tel: +49 (0)89 289-28358 D-80333 München Internet:
Control of Noise and Background in Scientific CMOS Technology
 Control of Noise and Background in Scientific CMOS Technology Introduction Scientific CMOS (Complementary metal oxide semiconductor) camera technology has enabled advancement in many areas of microscopy
Control of Noise and Background in Scientific CMOS Technology Introduction Scientific CMOS (Complementary metal oxide semiconductor) camera technology has enabled advancement in many areas of microscopy
Analog to Digital Conversion
 Analog to Digital Conversion Why It s Needed Embedded systems often need to measure values of physical parameters These parameters are usually continuous (analog) and not in a digital form which computers
Analog to Digital Conversion Why It s Needed Embedded systems often need to measure values of physical parameters These parameters are usually continuous (analog) and not in a digital form which computers
Instrumentation (ch. 4 in Lecture notes)
 TMR7 Experimental methods in Marine Hydrodynamics week 35 Instrumentation (ch. 4 in Lecture notes) Measurement systems short introduction Measurement using strain gauges Calibration Data acquisition Different
TMR7 Experimental methods in Marine Hydrodynamics week 35 Instrumentation (ch. 4 in Lecture notes) Measurement systems short introduction Measurement using strain gauges Calibration Data acquisition Different
SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT EXPERIMENTS
 SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT EXPERIMENTS Page: 1 Contents 1. Capacitive sensors 2. Temperature measurements 3. Signal processing and data analysis using LabVIEW 4. Load measurements 5. Noise and noise reduction
SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT EXPERIMENTS Page: 1 Contents 1. Capacitive sensors 2. Temperature measurements 3. Signal processing and data analysis using LabVIEW 4. Load measurements 5. Noise and noise reduction
Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics Week 32 Transformers
 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics Week 32 Transformers Administration: o Prayer o Turn in quiz Electricity and Electronics, Section 12.1, Transformer Theory: o A transformer is a device that
Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics Week 32 Transformers Administration: o Prayer o Turn in quiz Electricity and Electronics, Section 12.1, Transformer Theory: o A transformer is a device that
SENSOR. Definition. Basics. There are a lot of different types of sensors. Sensors are used in everyday objects.
 SENSOR Definition A sensor is a device that measures a physical quantity and converts it into a signal which can be read by an observer or by an instrument. Basics A sensor is a device that measures a
SENSOR Definition A sensor is a device that measures a physical quantity and converts it into a signal which can be read by an observer or by an instrument. Basics A sensor is a device that measures a
CURRENT ELECTRICITY. 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour Ans: c
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour 2. Electric pressure is also called (a) resistance (b) power (c) voltage (d) energy 3. The substances which
CURRENT ELECTRICITY 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour 2. Electric pressure is also called (a) resistance (b) power (c) voltage (d) energy 3. The substances which
Course of Instrumentation. and Measurement. National School of Engineers of Tunis ENIT. Karim Bourouni. Dipl.Dr-Ing.
 1 Course of Instrumentation and Measurement Karim Bourouni National School of Engineers of Tunis ENIT Dipl.Dr-Ing. (R.U. Energetic of Buildings and Solar Systems) Industrial Engineering Department 2 Plan
1 Course of Instrumentation and Measurement Karim Bourouni National School of Engineers of Tunis ENIT Dipl.Dr-Ing. (R.U. Energetic of Buildings and Solar Systems) Industrial Engineering Department 2 Plan
Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation. 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance?
 UNIT -6 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance? Ans: Maxwell's bridge, shown in Fig. 1.1, measures an unknown inductance in of standard arm offers
UNIT -6 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance? Ans: Maxwell's bridge, shown in Fig. 1.1, measures an unknown inductance in of standard arm offers
Today s menu. Last lecture. Series mode interference. Noise and interferences R/2 V SM Z L. E Th R/2. Voltage transmission system
 Last lecture Introduction to statistics s? Random? Deterministic? Probability density functions and probabilities? Properties of random signals. Today s menu Effects of noise and interferences in measurement
Last lecture Introduction to statistics s? Random? Deterministic? Probability density functions and probabilities? Properties of random signals. Today s menu Effects of noise and interferences in measurement
4. Digital Measurement of Electrical Quantities
 4.1. Concept of Digital Systems Concept A digital system is a combination of devices designed for manipulating physical quantities or information represented in digital from, i.e. they can take only discrete
4.1. Concept of Digital Systems Concept A digital system is a combination of devices designed for manipulating physical quantities or information represented in digital from, i.e. they can take only discrete
Putting It All Together: Computer Architecture and the Digital Camera
 461 Putting It All Together: Computer Architecture and the Digital Camera This book covers many topics in circuit analysis and design, so it is only natural to wonder how they all fit together and how
461 Putting It All Together: Computer Architecture and the Digital Camera This book covers many topics in circuit analysis and design, so it is only natural to wonder how they all fit together and how
1. A transducer converts
 1. A transducer converts a. temperature to resistance b. force into current c. position into voltage d. one form of energy to another 2. Whose of the following transducers the output is a change in resistance?
1. A transducer converts a. temperature to resistance b. force into current c. position into voltage d. one form of energy to another 2. Whose of the following transducers the output is a change in resistance?
Electromechanical Technology /Electromechanical Engineering Technology CIP Task Grid
 1 Secondary Task List 100 DEMONSTRATE KNOWLEDGE OF TECHNICAL REPORTS 101 Identify components of technical reports. 102 Demonstrate knowledge of the common components of technical documents. 103 Maintain
1 Secondary Task List 100 DEMONSTRATE KNOWLEDGE OF TECHNICAL REPORTS 101 Identify components of technical reports. 102 Demonstrate knowledge of the common components of technical documents. 103 Maintain
Physical electronics, various electronics devices, ICs form the core of Electronics and Telecommunication branch. This part includes
 Paper-1 Syllabus for Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering: This part is for both objective and conventional type papers: 1) Materials and Components Materials and Components are the vertebral column
Paper-1 Syllabus for Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering: This part is for both objective and conventional type papers: 1) Materials and Components Materials and Components are the vertebral column
Read pp Impossible to detect a signal when the S/N becomes less than about 2. mean Std. Deviation. X s S N 1 RSD
 Chapter 5 Signals and Noise Read pp. 110-123 Impossible to detect a signal when the S/N becomes less than about 2. S N = mean Std. Deviation = X s = 1 RSD Signal Transduction Internet: Wikipedia (Signals
Chapter 5 Signals and Noise Read pp. 110-123 Impossible to detect a signal when the S/N becomes less than about 2. S N = mean Std. Deviation = X s = 1 RSD Signal Transduction Internet: Wikipedia (Signals
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits 30-7 AC Circuits with AC Source Resistors, capacitors, and inductors have different phase relationships between current and voltage
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits 30-7 AC Circuits with AC Source Resistors, capacitors, and inductors have different phase relationships between current and voltage
Chapter 5 Electric Logic Sensors and Actuators
 Chapter 5: Electric logic sensors and actuators -IE337 Chapter 5 Electric Logic Sensors and Actuators 1 5.1 Introduction to Electric Logic Sensors and Actuators Electric sensors and actuators can be classified
Chapter 5: Electric logic sensors and actuators -IE337 Chapter 5 Electric Logic Sensors and Actuators 1 5.1 Introduction to Electric Logic Sensors and Actuators Electric sensors and actuators can be classified
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 527 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 527 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
Signal Conditioning Systems
 Note-13 1 Signal Conditioning Systems 2 Generalized Measurement System: The output signal from a sensor has generally to be processed or conditioned to make it suitable for the next stage Signal conditioning
Note-13 1 Signal Conditioning Systems 2 Generalized Measurement System: The output signal from a sensor has generally to be processed or conditioned to make it suitable for the next stage Signal conditioning
An Instrumentation System
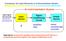 Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Sensors for Mechatronics
 Sensors for Mechatronics Paul P.L Regtien Hertgelo The Netherlands AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK' OXFORD ELSEVIER PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Contents Preface xi
Sensors for Mechatronics Paul P.L Regtien Hertgelo The Netherlands AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK' OXFORD ELSEVIER PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Contents Preface xi
Electronics Test and Development Centre, STQC Directorate, Agriculture College Campus, Shivajinagar, Pune, Maharashtra
 Last Amended on 23.02.2015 Page 1 of 8 SOURCE 1. DC VOLTAGE # 100 V to 1 mv 0.5 % to 0.06 % Using Multi-Function Calibrator 1 mv to 10 mv 0.06 % to 0.007 % by 10 mv to 100 mv 0.007 % to 0.0014 % 100 mv
Last Amended on 23.02.2015 Page 1 of 8 SOURCE 1. DC VOLTAGE # 100 V to 1 mv 0.5 % to 0.06 % Using Multi-Function Calibrator 1 mv to 10 mv 0.06 % to 0.007 % by 10 mv to 100 mv 0.007 % to 0.0014 % 100 mv
9/28/2010. Chapter , The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Readout Electronics. P. Fischer, Heidelberg University. Silicon Detectors - Readout Electronics P. Fischer, ziti, Uni Heidelberg, page 1
 Readout Electronics P. Fischer, Heidelberg University Silicon Detectors - Readout Electronics P. Fischer, ziti, Uni Heidelberg, page 1 We will treat the following questions: 1. How is the sensor modeled?
Readout Electronics P. Fischer, Heidelberg University Silicon Detectors - Readout Electronics P. Fischer, ziti, Uni Heidelberg, page 1 We will treat the following questions: 1. How is the sensor modeled?
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers
 Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
Lecture 2. Part 2 (Semiconductor detectors =sensors + electronics) Segmented detectors with pn-junction. Strip/pixel detectors
 Lecture 2 Part 1 (Electronics) Signal formation Readout electronics Noise Part 2 (Semiconductor detectors =sensors + electronics) Segmented detectors with pn-junction Strip/pixel detectors Drift detectors
Lecture 2 Part 1 (Electronics) Signal formation Readout electronics Noise Part 2 (Semiconductor detectors =sensors + electronics) Segmented detectors with pn-junction Strip/pixel detectors Drift detectors
Telecommunication Wiring Questions
 Telecommunication Wiring Questions 1. is the process of modifying a carrier frequency in rhythm to the audio frequency. A, Modulation B. Amplitude C. Change of phase D. Interference 2. is the property
Telecommunication Wiring Questions 1. is the process of modifying a carrier frequency in rhythm to the audio frequency. A, Modulation B. Amplitude C. Change of phase D. Interference 2. is the property
Hardware Platforms and Sensors
 Hardware Platforms and Sensors Tom Spink Including material adapted from Bjoern Franke and Michael O Boyle Hardware Platform A hardware platform describes the physical components that go to make up a particular
Hardware Platforms and Sensors Tom Spink Including material adapted from Bjoern Franke and Michael O Boyle Hardware Platform A hardware platform describes the physical components that go to make up a particular
Radiation Detection Instrumentation
 Radiation Detection Instrumentation Principles of Detection and Gas-filled Ionization Chambers Neutron Sensitive Ionization Chambers Detection of radiation is a consequence of radiation interaction with
Radiation Detection Instrumentation Principles of Detection and Gas-filled Ionization Chambers Neutron Sensitive Ionization Chambers Detection of radiation is a consequence of radiation interaction with
HARMONICS CAUSES AND EFFECTS
 HARMONICS CAUSES AND EFFECTS What is Harmonics? Harmonics is defined as the content of the signal whose frequency is an integral multiple of the system frequency of the fundamentals. Harmonics current
HARMONICS CAUSES AND EFFECTS What is Harmonics? Harmonics is defined as the content of the signal whose frequency is an integral multiple of the system frequency of the fundamentals. Harmonics current
Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months
 PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
IE1206 Embedded Electronics
 E06 Embedded Electronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex PC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors,, R, P, serial and parallel KC LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs laws ode analysis
E06 Embedded Electronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex PC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors,, R, P, serial and parallel KC LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs laws ode analysis
ECE 528 Understanding Power Quality
 ECE 528 Understanding Power Quality http://www.ece.uidaho.edu/ee/power/ece528/ Paul Ortmann portmann@uidaho.edu 208-733-7972 (voice) Lecture 15 1 Today Transient voltages Homework 3 discussion How transients
ECE 528 Understanding Power Quality http://www.ece.uidaho.edu/ee/power/ece528/ Paul Ortmann portmann@uidaho.edu 208-733-7972 (voice) Lecture 15 1 Today Transient voltages Homework 3 discussion How transients
Sensors & Actuators. Transduction principles Sensors & Actuators - H.Sarmento
 Sensors & Actuators Transduction principles 2014-2015 Sensors & Actuators - H.Sarmento Outline Resistive transduction. Photoconductive transduction (resistive). Capacitive transduction. Inductive transduction.
Sensors & Actuators Transduction principles 2014-2015 Sensors & Actuators - H.Sarmento Outline Resistive transduction. Photoconductive transduction (resistive). Capacitive transduction. Inductive transduction.
GRID CONTROLLED POWER SUPPLY IS A VERSATILE UNIT Uses Pair of RCA-2050 s for Wide Voltage Range
 10/30/07 11:55 PM Thyratrons GRID CONTROLLED POWER SUPPLY IS A VERSATILE UNIT Uses Pair of RCA-2050 s for Wide Voltage Range By J. H. OWENS, W2FTW and G. D. HANCHETT, W1AK/2 RCA Ham Tips Volume 6, Number
10/30/07 11:55 PM Thyratrons GRID CONTROLLED POWER SUPPLY IS A VERSATILE UNIT Uses Pair of RCA-2050 s for Wide Voltage Range By J. H. OWENS, W2FTW and G. D. HANCHETT, W1AK/2 RCA Ham Tips Volume 6, Number
Application Note # 5438
 Application Note # 5438 Electrical Noise in Motion Control Circuits 1. Origins of Electrical Noise Electrical noise appears in an electrical circuit through one of four routes: a. Impedance (Ground Loop)
Application Note # 5438 Electrical Noise in Motion Control Circuits 1. Origins of Electrical Noise Electrical noise appears in an electrical circuit through one of four routes: a. Impedance (Ground Loop)
Systems & Devices Part 1
 Systems & Devices Part 1 Alexander Nelson February 5th, 2018 University of Arkansas - Department of Computer Science and Computer Engineering What composes wearable, ubiquitous, or invisible systems? 0
Systems & Devices Part 1 Alexander Nelson February 5th, 2018 University of Arkansas - Department of Computer Science and Computer Engineering What composes wearable, ubiquitous, or invisible systems? 0
PHYS225 Lecture 10. Electronic Circuits
 PHYS225 Lecture 10 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Operational Amplifiers Many applications Use feedback for control Negative feedback Ideal case rules Output is whatever is needed to make inputs equal
PHYS225 Lecture 10 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Operational Amplifiers Many applications Use feedback for control Negative feedback Ideal case rules Output is whatever is needed to make inputs equal
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers. Final Examination.
 Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2003 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2003 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Frequency Multiplier (using PLL 565)
 Frequency Multiplier (using PLL 565) In electronics, a frequency multiplier is an electronic circuit that generates an output signal whose output frequency is a harmonic (multiple) of its input frequency.
Frequency Multiplier (using PLL 565) In electronics, a frequency multiplier is an electronic circuit that generates an output signal whose output frequency is a harmonic (multiple) of its input frequency.
Electronics II. Calibration and Curve Fitting
 Objective Find components on Digikey Electronics II Calibration and Curve Fitting Determine the parameters for a sensor from the data sheets Predict the voltage vs. temperature relationship for a thermistor
Objective Find components on Digikey Electronics II Calibration and Curve Fitting Determine the parameters for a sensor from the data sheets Predict the voltage vs. temperature relationship for a thermistor
Sensors. CS Embedded Systems p. 1/1
 CS 445 - Embedded Systems p. 1/1 Sensors A device that provides measurements of a physical process. Many sensors are transducers, devices that convert energy from one form to another. Examples: Pressure
CS 445 - Embedded Systems p. 1/1 Sensors A device that provides measurements of a physical process. Many sensors are transducers, devices that convert energy from one form to another. Examples: Pressure
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER
 VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
Workshop 1 Measurement techniques and sensors
 The University of British Columbia GEOG 309 / Andreas Christen January 31, 2008 Workshop 1 Measurement techniques and sensors Goals 1 Use components and a multi-meter to understand measurement principles
The University of British Columbia GEOG 309 / Andreas Christen January 31, 2008 Workshop 1 Measurement techniques and sensors Goals 1 Use components and a multi-meter to understand measurement principles
TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION. Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service
 Code No.207 TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Code No.207 TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL TUTORIAL 3 SIGNAL PROCESSORS AND RECEIVERS
 INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL TUTORIAL 3 SIGNAL PROCESSORS AND RECEIVERS This tutorial provides an overview of signal processing and conditioning for use in instrumentation and automatic control systems.
INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL TUTORIAL 3 SIGNAL PROCESSORS AND RECEIVERS This tutorial provides an overview of signal processing and conditioning for use in instrumentation and automatic control systems.
Resonance Tube. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory. 2.1 Air As A Spring. 2.2 Traveling Sound Waves in Air
 Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Measurement system applications. Measurement System
 Measurement system applications Measurement System The Figure above hows a functional block diagram of a simple temperature control system in which the temperature Ta of a room is maintained at a reference
Measurement system applications Measurement System The Figure above hows a functional block diagram of a simple temperature control system in which the temperature Ta of a room is maintained at a reference
WebSeminar: Signal Chain Overview
 WebSeminar: December, 2005 Hello, and welcome to the Microchip Technology Web Seminar overview of signal chains. My name is Kevin Tretter and I am a Product Marketing Engineer within Microchip Technology
WebSeminar: December, 2005 Hello, and welcome to the Microchip Technology Web Seminar overview of signal chains. My name is Kevin Tretter and I am a Product Marketing Engineer within Microchip Technology
Heat sink. Insulator. µp Package. Heatsink is shown with parasitic coupling.
 X2Y Heatsink EMI Reduction Solution Summary Many OEM s have EMI problems caused by fast switching gates of IC devices. For end products sold to consumers, products must meet FCC Class B regulations for
X2Y Heatsink EMI Reduction Solution Summary Many OEM s have EMI problems caused by fast switching gates of IC devices. For end products sold to consumers, products must meet FCC Class B regulations for
Microcomputer Systems 1. Introduction to DSP S
 Microcomputer Systems 1 Introduction to DSP S Introduction to DSP s Definition: DSP Digital Signal Processing/Processor It refers to: Theoretical signal processing by digital means (subject of ECE3222,
Microcomputer Systems 1 Introduction to DSP S Introduction to DSP s Definition: DSP Digital Signal Processing/Processor It refers to: Theoretical signal processing by digital means (subject of ECE3222,
Micro-sensors - what happens when you make "classical" devices "small": MEMS devices and integrated bolometric IR detectors
 Micro-sensors - what happens when you make "classical" devices "small": MEMS devices and integrated bolometric IR detectors Dean P. Neikirk 1 MURI bio-ir sensors kick-off 6/16/98 Where are the targets
Micro-sensors - what happens when you make "classical" devices "small": MEMS devices and integrated bolometric IR detectors Dean P. Neikirk 1 MURI bio-ir sensors kick-off 6/16/98 Where are the targets
Basic Analog Circuits
 Basic Analog Circuits Overview This tutorial is part of the National Instruments Measurement Fundamentals series. Each tutorial in this series, will teach you a specific topic of common measurement applications,
Basic Analog Circuits Overview This tutorial is part of the National Instruments Measurement Fundamentals series. Each tutorial in this series, will teach you a specific topic of common measurement applications,
Wireless Communication
 Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Part 10: Transducers
 Part 10: Transducers 10.1: Classification of Transducers An instrument may be defined as a device or a system which is designed to maintain a functional relationship between prescribed properties of physical
Part 10: Transducers 10.1: Classification of Transducers An instrument may be defined as a device or a system which is designed to maintain a functional relationship between prescribed properties of physical
1.5 kw Automatic Remote Controlled Antenna Tuner for Verticals and other Unbalanced Antennas
 1.5 kw Automatic Remote Controlled Antenna Tuner for Verticals and other Unbalanced Antennas Mod. AT- 615U Short Form Manual 10/2010 Dipl.Ing. Klaus Bemmerer RF Communication Electronics Niendorf-Middeldor
1.5 kw Automatic Remote Controlled Antenna Tuner for Verticals and other Unbalanced Antennas Mod. AT- 615U Short Form Manual 10/2010 Dipl.Ing. Klaus Bemmerer RF Communication Electronics Niendorf-Middeldor
IT.MLD900 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER. Signal Conditioning
 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
SIGNAL RECOVERY: Sensors, Signals, Noise and Information Recovery
 SIGNAL RECOVERY: Sensors, Signals, Noise and Information Recovery http://home.deib.polimi.it/cova/ 1 Signal Recovery COURSE OUTLINE Scenery preview: typical examples and problems of Sensors and Signal
SIGNAL RECOVERY: Sensors, Signals, Noise and Information Recovery http://home.deib.polimi.it/cova/ 1 Signal Recovery COURSE OUTLINE Scenery preview: typical examples and problems of Sensors and Signal
AERO2705 Space Engineering 1 Week 7 The University of Sydney
 AERO2705 Space Engineering 1 Week 7 The University of Sydney Presenter Mr. Warwick Holmes Executive Director Space Engineering School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering The University
AERO2705 Space Engineering 1 Week 7 The University of Sydney Presenter Mr. Warwick Holmes Executive Director Space Engineering School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering The University
Lecture 10. Thermal Sensors
 Lecture 10 Thermal Sensors DS1620 Digital thermometer Provides 9-bit temperature readings Temperature range from -55 o C to 125 o C Acts as a thermostat Detail Description DS1620 with BS2 Programming for
Lecture 10 Thermal Sensors DS1620 Digital thermometer Provides 9-bit temperature readings Temperature range from -55 o C to 125 o C Acts as a thermostat Detail Description DS1620 with BS2 Programming for
Sonic Distance Sensors
 Sonic Distance Sensors Introduction - Sound is transmitted through the propagation of pressure in the air. - The speed of sound in the air is normally 331m/sec at 0 o C. - Two of the important characteristics
Sonic Distance Sensors Introduction - Sound is transmitted through the propagation of pressure in the air. - The speed of sound in the air is normally 331m/sec at 0 o C. - Two of the important characteristics
Analog-Digital Interface
 Analog-Digital Interface Tuesday 24 November 15 Summary Previous Class Dependability Today: Redundancy Error Correcting Codes Analog-Digital Interface Converters, Sensors / Actuators Sampling DSP Frequency
Analog-Digital Interface Tuesday 24 November 15 Summary Previous Class Dependability Today: Redundancy Error Correcting Codes Analog-Digital Interface Converters, Sensors / Actuators Sampling DSP Frequency
Sensing. Autonomous systems. Properties. Classification. Key requirement of autonomous systems. An AS should be connected to the outside world.
 Sensing Key requirement of autonomous systems. An AS should be connected to the outside world. Autonomous systems Convert a physical value to an electrical value. From temperature, humidity, light, to
Sensing Key requirement of autonomous systems. An AS should be connected to the outside world. Autonomous systems Convert a physical value to an electrical value. From temperature, humidity, light, to
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK PRESSURE Hydraulic Pressure (Gauge) Hewett Road Gapton Hall Industrial Estate Great Yarmouth Norfolk NR31 0NN Contact: Mr J Gunn Tel: +44
2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK PRESSURE Hydraulic Pressure (Gauge) Hewett Road Gapton Hall Industrial Estate Great Yarmouth Norfolk NR31 0NN Contact: Mr J Gunn Tel: +44
Pressure Transducer Handbook
 123 Pressure Transducer Handbook Date: February 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 - Introduction 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Product Overview SECTION 2 - Kulite Sensing Technology 2.1 Pressure Transducers 2.2
123 Pressure Transducer Handbook Date: February 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 - Introduction 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Product Overview SECTION 2 - Kulite Sensing Technology 2.1 Pressure Transducers 2.2
