TMC Channel CAMAC Multi-Hit TDC. Module Manual
|
|
|
- Lilian Cobb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TMC Channel CAMAC Multi-Hit TDC Module Manual (Rev.1.0 Mar. 19, 1991) Rev.1.5 Aug. 3, 1993 Prepared by Y. Arai KEK, National Laboratory for High Energy Physics 1-1 Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan Tel : ex.6212 Fax : Internet : araiy@kekvax.kek.jp DECNET : KEKVAX::ARAIY
2 TMC Channel Multi- Hit TDC Module 32CH TMC RUN STRT STOP TRIG OUT I N channels in single-w idth module 1ns / bit least count, σ= 0.52 ns time resoluti on 1024 bits / channel (or 2kbit / 2 ch, or 4kbit/ 4ch) Common stop or Common start operation No clear/dizitization t ime needed Rising edge detection a nd 6 bit encoded data output for each 32 ns data, or raw data dump for full d ata Very stable for tempera ture, voltage variation Q stop block transfer r eadout for encoded data ECL differential input for signal NIM level start / stop signal input NIM level trigger outpu t for test purpose I N KEK
3 Specifications Signal Inputs : 32 Channel. ECL-differential. Input Impedance 100 Ω. Two 40-pin Flat Cable Connector. Input signal is stretched to about 32 ns internally if the width is less than 32 ns. START Input : STOP Input : TRIGGER Output : Least Time Count : Time Range : Double Hit Resolution : One, common to all channels, 50 Ω impedance; Lemo-type connector; NIM level. Used in common Start mode. One, common to all channels, 50 Ω impedance; Lemo-type connector; NIM level. Used in common Stop mode. Lemo-type connector; NIM level. Generate synchronous output pulse with internal clock when started. Used for test purpose. 1 ns/bit µs (4 ch), µs (2 ch) or µs (1 ch) 32 ns Timing Measurement Error : σ = 0.52 ns (including digitization error) Integral Linearity Error : < 1.5 bit Differential Linearity : < 0.2 ns Variation of Slope : < 0.1 % ( V) (time-to-digital conversion factor) < 0.1 % (15-55 C) < 0.1 % (chip to chip) Channel to Channel Discontinuity: < 0.5 bit Data Readout : Data : Fast readout is done through encoded data readout (6 bit/ch) by F(0). The row which is read out is pointed by the Read Pointer (CSR1). For debugging and other purpose which requires entire data, Serial I/O mode through CSR0 can be used. This mode read out entire data of the TMC chip, but takes much longer readout time. The proper CAMAC address and F(1) gates the 4 channel data of a TMC chip onto the R(1) to R(24). A(0) through A(7) are used for chip number. R24 R18 R12 R6 R1 Chip 0 : A(0) Ch 3 Ch 2 Ch 1 Ch 0 Chip 1 : A(1) Ch 7 Ch 6 Ch 5 Ch 4 : : : : Chip 7 : A(7) Ch 31 Ch 30 Ch 29 Ch 28 CAMAC Commands : Z or C : All registers are simultaneously cleared by the CAMAC "Clear" or "Initialize" command. Requires "S2". X : An X=1 (Command Accepted) response is generated when a valid F, N, and A command is generated.
4 CAMAC Function Code : F(0) : Read Data; requires N and A. A(0) through A(7) are used for chip address. F(1) : Read CSR0 register; requires N and A. A(0) through A(7) are used for chip address. F(4) : Read CSR1 (Read Pointer) register; requires N and A. A(0) through A(7) are used for chip address. F(6) : Read CSR2 (Write Pointer) register; requires N and A. A(0) through A(7) are used for chip address. F(9) : Reset. Reset all CSR registers and internal circuit. F(17) : Write CSR0 register; requires N and A. A(0) through A(7) are used for chip address. F(20) : Write CSR1 (Read Pointer) register; requires N and A. A(0) through A(7) are used for chip address. F(22) : Write CSR2 (Write Pointer) register; requires N and A. A(0) through A(7) are used for chip address. F(25) : Start signal recording. Used in common start mode. Functions as same as the START input, but F(25) starts signal recording with synchronous to the internal clock. Packaging : CAMAC 1 width module. Power Requirement : +6 V at 1.2 A, -6V at 0.5 A.
5 Settings There are several switches and jumpers in the module. User should set up these settings correctly. The meaning of each switches and jumpers are described below. SW1, SW2, and SW3 : Common Stop / Common Start selection switches. These switches select Common Stop or Common Start mode in accordance with measurement style. All these switches must be same position as indicated in PC board, otherwise the circuit does not work correctly. SW4 : Stop Counter value (default = 32). Used in common start mode; selectable between 0 to 255. In Common Start mode, input signal is written to TMC's after receiving "START" signal or F(25) command. The operation will stop after passing the period defined in this switch. The period is selected from a multiple of 32 ns. The bit where switch is off has value "1". If you set the period longer than the depth of the channel, first part of the data and the start mark will be lost naturally. Ex) If the position "1", "2", and "4" is off and others are on, the period will be 32 ns x 7 = 224 ns. CONF0, CONF1 : Configuration select pin (default = 0). Each chip has these jumper pins, so there are 8 sets of jumpers. They select depth of a channel in each chip. CONF CONF0 CONF1 Depth Channel/chip 0 close close 1 k bit 4 channels 1 open close 2 k bit 2 Channels. Ch0 and 1, Ch2 and 3 are connected together. Each channel needs same signal in inputs. 2 close open 4 k bit 1 Channels. Ch0, 1, 2 and 3are connected together. Each channel needs same signal in input. OVWRP : Always open.
6 Input Connector Pin Assignment Upper Connector Pin No. Assignment Pin No. Assignment 1 no connection 2 no connection 3 Ch Ch 0-5 Ch Ch 1-7 Ch Ch 2-9 Ch Ch 3-11 Ch Ch 4-13 Ch Ch 5-15 Ch Ch 6-17 Ch Ch 7-19 Ch Ch 8-21 Ch Ch 9-23 Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch no connection 36 no connection 37 no connection 38 no connection 39 no connection 40 no connection Lower Connector Pin No. Assignment Pin No. Assignment 1 no connection 2 no connection 3 Ch Ch 16-5 Ch Ch 17-7 Ch Ch 18-9 Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch Ch no connection 36 no connection 37 no connection 38 no connection 39 no connection 40 no connection
7 General Description The TMC 32-Ch CAMAC module was designed to evaluate the newly developed TMC1004 chip which is a low-power and high-resolution Multi-hit Time-to-Digital Converter chip. The TMC chip is developed for readout of a drift chamber in high-rate experiment such as the SSC. The chip has special kind of memories which record input pulses in 1 ns time resolution. TMC1004 chip has 4 channels of circuit and each channel has 1024 bits of memories. Thus each channel records signal of 1 µsec period. The chip also can be configured to 2 channels times 2 k bits or 1 channel times 4 k bits. The TMC 32-Ch CAMAC module consists of 8 TMC1004 chips, so it has 32 input channel. Although the TMC1004 is designed for deadtime-less readout, this CAMAC module can not operate as deadtime-less because the CAMAC cycle is very slow comparing with the input data bandwidth. The module runs in "Common Stop" or "Common Start" mode which is selectable by internal switches. Detailed explanation of the CAMAC circuit is also found in reference 1. CAMAC Module Circuit Description Figure 1 shows the block diagram of the TMC 32-channel CAMAC module. The module contains 8 TMC chips, thus the 4 channels are grouped and most of the operations are applied to one of eight chips. These eight chips are accesses by using subaddress A(0) through A(7). Four channel data are read out at once as the format shown in Fig. 1. Each chip has three CSR registers. The contents of the registers are shown in Table 1.
8 CH0 CH1 TMC A(0) Data 24 TMC A(1) C A M A C C R AT CAMAC I/F E CH32 TMC A(7) Control Com. Start Com. Stop Start/Stop Control [Data Format] CH3 data CH2 data CH1 data CH0 data F( 0) A(0-7) : Read Data F( 1) A(0-7) : Read CSR0 F( 4) A(0-7) : Read CSR1 F( 6) A(0-7) : Read CSR2 F(17) A(0-7) : Write CSR0 F(20) A(0-7) : Write CSR1 F(22) A(0-7) : Write CSR2 F( 9) : Reset F(25) : Start Fig.1 Block Diagram of the TMC 32-Channel CAMAC module
9 Table 1 CSR Registers bit CSR0 - MOD1 MOD0 SIO3 SIO2 SIO1 SIO0 CSR1 Read Pointer Value [RP] CSR2 Write Pointer Value [WP] * CSR0 ( = 0 after reset [read/write]) SIO3 ~ 0 : Serial I/O bits. These bits are valid only in the serial i/o mode. One bit data for each channel is read/written through these bits from/to the address pointed by the read counter(row position) and the write counter(column position). MOD0,1 : MODE = [MOD1,MOD0]. * MODE = 0 (Stand alone Mode) : Usually this mode is used. Data are read out from the row pointed by the Read Pointer. (Caution: If the data recording is in progress, the Read Pointer will also be counted up with the Write Pointer.) * MODE = 1 (Slave Mode) : Not use. * MODE = 2 (Serial I/O Mode) : This mode is used mainly for testing each bit in the memory. Data are read/write from/to the address pointed by the CSR1(row address) and CSR2(column address) through bit 0 ~ 3 in the CSR0. Bit 0 corresponds to the data in the CH0 and bit 1 corresponds to CH1 and so on. * CSR1 ( = 2 after reset [read/write]) RP : Read Pointer Value. The contents of the read counter are set through this register. The value read back indicates present value of the read counter. The counter is incremented by the system clock (31.25 MHz) during data recording. This register also works as a row address register in the Serial I/O mode. * CSR2 ( = 0 after reset [read/write]) WP : Write Pointer Value. The contents of the write counter are set through this register. Present value of the write counter is read back. The counter is incremented by the system clock (31.25 MHz) during data recording. This register also works as a column address register in the Serial I/O mode.
10 Data Format and Conversion Since the TMC1004 chip is designed for high-rate application, the time recording is continuous and does not have any timing reference point inherently. However, for usual application, we need a start time or a stop time information. In this CAMAC module, these timing are recorded in TMC in addition to the input signal timing. Start or Stop timing is recorded in the first or the last 2 columns as shown in Table 2. In common start mode, input multiplexer will change inputs from start signal to input signal at third row (N+2). In common stop mode, input multiplexer will change inputs from input signal to stop signal when reciving stop pulse (M-3), and record the stop pulse which is delayed internally in row M-2 and M-1. Start/Stop pulse has about 12 ns width, and can be discriminated from input signal which has more than 32 ns pulse width. Table 2. Raw data map of the TMC chip for Common Start/Stop mode [Common Start Mode] Start pulse recording area Row N Start pulse recording area Row N+1... Input signal recording area Row N+2 Input signal recording area Row N+3 : : Input signal recording area Row N+31 ( N = Initial Value of the Write Pointer.) [Common Stop Mode] Input signal recording area Row M-32 Input signal recording area Row M-31 : : Input signal recording area... Row M-3 Stop pulse recording area Row M-2 Stop pulse recording area Row M-1 ( M = Final Value of the Write Pointer.) Fig. 2 Timing for (a) common start,, and (b) common stop mode. (a) Common START Mode CLK START* WSTART CP 32ns ROW N-1 Counter N 0 A COM SEL (P=Q)*
11 (b) Common STOP Mode CLK 32ns STOP* WSTART ROW M-4 M-3 M-2 M-1 M A COM SEL (P=Q)* Each Row data (32 bits) is encoded to 6 bit as shown in Table 3. The most significant bit shows the value of the first bit of a row, and the remaining 5 bits show the position of the "0" to first "1" transition. Table 3 Data Encoding Schme Bit Pattern of inside TMC Encoded Data < Time * x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x : : : : (not appear) x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x 1 0 x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x 1 0 x x : : : : 1 0 x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x (*) Bit 5 of the encoded data is used for distinguish the transition between row. An example of data taking and conversion flow is shown below. The common stop mode and CONF=0 are assumed in the example.
12 TMC Chip Circuit Description The idea of Time Memory Cell (TMC) was proposed by us and tested by making a TEG chip 2. The cell utilizes low-power and high-density characteristics of a CMOS memory cell and gate delay time. Figure 2 shows the basic operation of the TMC. As the write signal (WL) timing in each TMC cell is delayed by 1 ns, timing information of the input lines (TIN and TIN*) is recorded to memory cells sequentially. To keep the delay time constant, the delay time of the delay element is controlled through the Vg line by a feedback circuit which refers to an external system clock period. TIN* TIN TMC Cell Vg WL WL TIN 1 ns Time Fig.2 Input signal write operation in the TMC cells. The TMC1004 has been developed using an 0.8 µm CMOS process. It contains 4 channels and each channel has 1024 TMC cells (32 rows and 32 columns). The chip achieves more than 10 times the density of a 1 GHz GaAs shift register while dissipating less than 1/100 of the power. The schematic of the TMC cell is shown in Fig. 3. Each cell has one timing-information write port (TIN and TIN*) and one data-read/write port (BL and BL*). Two PMOS transistors (M1 and M2) are added to the previous design 1 to ease write operation by cutting the F/F paths in the cell. Transistor parameters of the delay element were selected to obtain a gate delay time close to 1 ns/bit. To get high precision and consistency between rows a feedback circuit adjust the total delay of the 32 cells in a row to be 32 ± 0.5 ns.
13 BL WORD Dual Port Cell BL* M1 M2 TIN* TIN Vg WL Delay Element Fig.3. TMC cell circuit. Figure 4 shows the schematic of the feedback circuit. When an external clock (φ1) sets two flipflops (F1 and F2) at the falling edge, capacitors C1 and C2 begin to charge. The charging of C1 is stopped by the falling edge of the pulse at the end of the delay line. The charging of C2 stops at the next falling edge of the clock pulse (φ2). Hence, the voltage difference between C1 and C2 is proportional to the time difference between the delay line and clock period. If the delay time is less than the clock period, C3 charges during a store period increasing the delay of the delay line. If the delay time is longer than the one clock period, C3 discharges reducing the delay.
14 Φ 1 1 ns x 32 Vg Reference Cell F1 32 ns Start R S Q + C1 - C3 Φ 2 Reference Time F2 R Q S Vg Reset Fig.4. Feedback circuit. C2 Store The Block diagram of the TMC1004 is shown in Fig. 5. The chip has four TMC arrays, each with 32 rows by 32 columns of TMC cells. For accessing the four arrays, there are two pointers (Write and Read) each of which consists of 7 bit counter and decoder. The write pointer is incremented in each clock (CLK) cycle which initiates a pulse in the delay line of the designated row. The read pointer selects a row for readout and is incremented by the same clock (CLK). This scheme with two pointers and dual port cells enables read and write operations to proceed simultaneously. The four TMC arrays can be configured as 1, 2, or 4 channels by setting external pins. The 1, 2, and 4 channel modes utilize respectively the lower 5, 6 or 7 bits of the counters.
15 DOUT0 DOUT1 DOUT2 DOUT3 CIO CS* Encoder Encoder Encoder Encoder COLUMN I/O COLUMN I/O COLUMN I/O COLUMN I/O CSR W R P I O T I E N T E R CH 0 32 X 32 TMC CH 1 32 X 32 TMC CH 2 32 X 32 TMC CH 3 32 X 32 TMC Feedback Feedback Feedback Feedback R E P A O D I N T E R CLK CLK DS* TIN0 TIN1 TIN2 TIN3 Fig. 5. Block diagram of the TMC1004. The 32 bit row data is encoded to 6 bits. The most significant bit shows the value of the first bit of a row, and the remaining 5 bits show the position of the "0" to first "1" transition. Since the transition times will be spaced by at least 32 ns, the encoding reduces the output pin requirement and the amount of data without sacrificing information. The readout cycle is pipelined to 2 stage and the cycle continues while the trigger signal DS* is asserted. The data are read out through the DOUT lines. There are 3 CSR registers which set/show the operating mode and the settings of the pointers. All TMC cells can also be read and written through the CSR register. This access path is used for testing each TMC cell. The CSR register is accessed through the CS* and the CIO lines. Fig.6. Photograph of the TMC1004 chip. References [1]Y. Arai, T. Matsumura and K. Endo, IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits. Vol. 27, No. 3, 359(1992).
16 [2] Y. Arai and T. Baba, 1988 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Tokyo, Aug.1988, IEEE CAT. No. 88 TH Page 121.
17 [Appendix A : Sample Program] C...A part of Sample Readout Program for the TMC CAMAC module C... Common Start mode. C C...Start : C...Stop : C...Read out Final Row Position from CSR2 (Write Pointer) IADD=0 CALL CAM16(CHAN,CRATE,ISLOT,IADD, 6,MM,ERRSTAT) MM = MM - 32 IF (MM.lt.0) MM=MM + 32! MM points first Row of data recording C...Find Start Time STIME=0 C...Set Start Row to CSR1 (Read Pointer) DO RR=MM,MM+1 CALL CAM16(CHAN,CRATE,ISLOT,IADD,20,RR,ERRSTAT) C...Read out strt time CALL CAM24(CHAN,CRATE,ISLOT,IADD,0,IDATA_4,ERRSTAT) DD=IAND(IDATA_4,'3F'x) ZQ=IAND(DD,'20'x) TT=IAND(DD,'1F'x) IF(ZQ.EQ.0) GO TO 556 STIME=RR*32 GO TO CONTINUE IF(TT.EQ.0) GO TO 71 STIME=RR*32+TT GO TO CONTINUE ENDDO TYPE *,'Error! No Start Time Data' C CONTINUE C...Find Stop Time DO 70 IADD = 0,7 DO RR=MM+2,MM+31 C...Write Start Row to CSR1 CALL CAM16(CHAN,CRATE,ISLOT,IADD,20,RR,ERRSTAT) C...Read out one chip data CALL CAM24(CHAN,CRATE,ISLOT,IADD,0,IDATA_4,ERRSTAT) IDATA_S(RR)=IDATA_4 ENDDO C...Extract one channel data DO 70 JL=0,3 ICHAN=4*IADD+JL+1 IT1=6*JL ZZ = 0 DO 70 RR=MM+2,MM+31 IDATA_4=IDATA_S(RR) DD=ISHFT(IDATA_4,-IT1) DD=IAND(DD,'77'O) TT=0 IF(ZZ.NE.0) GO TO 511 ZQ=IAND(DD,'40'O) IF(ZQ.NE.0) GO TO CONTINUE TT=IAND(DD,'37'O)
18 IF(TT.EQ.0) GO TO CONTINUE M(1,ICNT) = ICHAN M(2,ICNT) = RR*32 + TT - STIME ICNT = ICNT + 1 ZZ=1 GO TO CONTINUE ZQ=IAND(DD,'40'O) IF(ZQ.NE.0) GO TO 70 ZZ=0 GO TO CONTINUE! Channel No. of ICNT data! Timing data of ICNT data
TABLE OF CONTENTS LIST OF FIGURES LIST OF TABLES
 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...i LIST OF FIGURES...i LIST OF TABLES...i 1. DESCRIPTION...1 1.1. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION...1 2. SPECIFICATIONS...3 2.1. EXTERNAL COMPONENTS...3 2.2. INTERNAL COMPONENTS...4
TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...i LIST OF FIGURES...i LIST OF TABLES...i 1. DESCRIPTION...1 1.1. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION...1 2. SPECIFICATIONS...3 2.1. EXTERNAL COMPONENTS...3 2.2. INTERNAL COMPONENTS...4
Requirements and Specifications of the TDC for the ATLAS Precision Muon Tracker
 ATLAS Internal Note MUON-NO-179 14 May 1997 Requirements and Specifications of the TDC for the ATLAS Precision Muon Tracker Yasuo Arai KEK, National High Energy Accelerator Research Organization Institute
ATLAS Internal Note MUON-NO-179 14 May 1997 Requirements and Specifications of the TDC for the ATLAS Precision Muon Tracker Yasuo Arai KEK, National High Energy Accelerator Research Organization Institute
DESIGN & IMPLEMENTATION OF SELF TIME DUMMY REPLICA TECHNIQUE IN 128X128 LOW VOLTAGE SRAM
 DESIGN & IMPLEMENTATION OF SELF TIME DUMMY REPLICA TECHNIQUE IN 128X128 LOW VOLTAGE SRAM 1 Mitali Agarwal, 2 Taru Tevatia 1 Research Scholar, 2 Associate Professor 1 Department of Electronics & Communication
DESIGN & IMPLEMENTATION OF SELF TIME DUMMY REPLICA TECHNIQUE IN 128X128 LOW VOLTAGE SRAM 1 Mitali Agarwal, 2 Taru Tevatia 1 Research Scholar, 2 Associate Professor 1 Department of Electronics & Communication
Electronic Circuits EE359A
 Electronic Circuits EE359A Bruce McNair B206 bmcnair@stevens.edu 201-216-5549 1 Memory and Advanced Digital Circuits - 2 Chapter 11 2 Figure 11.1 (a) Basic latch. (b) The latch with the feedback loop opened.
Electronic Circuits EE359A Bruce McNair B206 bmcnair@stevens.edu 201-216-5549 1 Memory and Advanced Digital Circuits - 2 Chapter 11 2 Figure 11.1 (a) Basic latch. (b) The latch with the feedback loop opened.
The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip
 The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip D.C. Christian, dcc@fnal.gov Fermilab, POBox 500 Batavia, IL 60510, USA 1 Introduction The most striking feature of BTeV, a dedicated b physics experiment
The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip D.C. Christian, dcc@fnal.gov Fermilab, POBox 500 Batavia, IL 60510, USA 1 Introduction The most striking feature of BTeV, a dedicated b physics experiment
電子電路. Memory and Advanced Digital Circuits
 電子電路 Memory and Advanced Digital Circuits Hsun-Hsiang Chen ( 陳勛祥 ) Department of Electronic Engineering National Changhua University of Education Email: chenhh@cc.ncue.edu.tw Spring 2010 2 Reference Microelectronic
電子電路 Memory and Advanced Digital Circuits Hsun-Hsiang Chen ( 陳勛祥 ) Department of Electronic Engineering National Changhua University of Education Email: chenhh@cc.ncue.edu.tw Spring 2010 2 Reference Microelectronic
Technical Information Manual
 Technical Information Manual Revision n. 0 21 April 1999 MOD. N 145 QUAD SCALER AND PRESET COUNTER/TIMER User's Manual (MUT) Mod. N145 Quad Scaler and Preset Counter/Timer Quad Scaler 20/04/1999 0 and
Technical Information Manual Revision n. 0 21 April 1999 MOD. N 145 QUAD SCALER AND PRESET COUNTER/TIMER User's Manual (MUT) Mod. N145 Quad Scaler and Preset Counter/Timer Quad Scaler 20/04/1999 0 and
Module -18 Flip flops
 1 Module -18 Flip flops 1. Introduction 2. Comparison of latches and flip flops. 3. Clock the trigger signal 4. Flip flops 4.1. Level triggered flip flops SR, D and JK flip flops 4.2. Edge triggered flip
1 Module -18 Flip flops 1. Introduction 2. Comparison of latches and flip flops. 3. Clock the trigger signal 4. Flip flops 4.1. Level triggered flip flops SR, D and JK flip flops 4.2. Edge triggered flip
Clock and control fast signal specification M.Postranecky, M.Warren and D.Wilson 02.Mar.2010
 Clock and control fast signal specification M.Postranecky, M.Warren and D.Wilson 02.Mar.2010 1 Introduction...1 2 Fast signal connectors and cables...1 3 Timing interfaces...2 XFEL Timing Interfaces...2
Clock and control fast signal specification M.Postranecky, M.Warren and D.Wilson 02.Mar.2010 1 Introduction...1 2 Fast signal connectors and cables...1 3 Timing interfaces...2 XFEL Timing Interfaces...2
Dual 500ns ADC User Manual
 7072 Dual 500ns ADC User Manual copyright FAST ComTec GmbH Grünwalder Weg 28a, D-82041 Oberhaching Germany Version 2.3, May 11, 2009 Copyright Information Copyright Information Copyright 2001-2009 FAST
7072 Dual 500ns ADC User Manual copyright FAST ComTec GmbH Grünwalder Weg 28a, D-82041 Oberhaching Germany Version 2.3, May 11, 2009 Copyright Information Copyright Information Copyright 2001-2009 FAST
HD44102D. (Dot Matrix Liquid Crystal Graphic Display Column Driver) Features. Description. Ordering Information
 HD442 (Dot Matrix Liquid Crystal Graphic Display Column Driver) Description The HD442 is a column (segment) driver for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display systems, storing the display data transferred
HD442 (Dot Matrix Liquid Crystal Graphic Display Column Driver) Description The HD442 is a column (segment) driver for dot matrix liquid crystal graphic display systems, storing the display data transferred
PC-OSCILLOSCOPE PCS500. Analog and digital circuit sections. Description of the operation
 PC-OSCILLOSCOPE PCS500 Analog and digital circuit sections Description of the operation Operation of the analog section This description concerns only channel 1 (CH1) input stages. The operation of CH2
PC-OSCILLOSCOPE PCS500 Analog and digital circuit sections Description of the operation Operation of the analog section This description concerns only channel 1 (CH1) input stages. The operation of CH2
Electronic Readout System for Belle II Imaging Time of Propagation Detector
 Electronic Readout System for Belle II Imaging Time of Propagation Detector Dmitri Kotchetkov University of Hawaii at Manoa for Belle II itop Detector Group March 3, 2017 Barrel Particle Identification
Electronic Readout System for Belle II Imaging Time of Propagation Detector Dmitri Kotchetkov University of Hawaii at Manoa for Belle II itop Detector Group March 3, 2017 Barrel Particle Identification
All-digital ramp waveform generator for two-step single-slope ADC
 All-digital ramp waveform generator for two-step single-slope ADC Tetsuya Iizuka a) and Kunihiro Asada VLSI Design and Education Center (VDEC), University of Tokyo 2-11-16 Yayoi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0032,
All-digital ramp waveform generator for two-step single-slope ADC Tetsuya Iizuka a) and Kunihiro Asada VLSI Design and Education Center (VDEC), University of Tokyo 2-11-16 Yayoi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0032,
Analog CMOS Interface Circuits for UMSI Chip of Environmental Monitoring Microsystem
 Analog CMOS Interface Circuits for UMSI Chip of Environmental Monitoring Microsystem A report Submitted to Canopus Systems Inc. Zuhail Sainudeen and Navid Yazdi Arizona State University July 2001 1. Overview
Analog CMOS Interface Circuits for UMSI Chip of Environmental Monitoring Microsystem A report Submitted to Canopus Systems Inc. Zuhail Sainudeen and Navid Yazdi Arizona State University July 2001 1. Overview
Fan in: The number of inputs of a logic gate can handle.
 Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Dedan Kimathi University of technology. Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering. EEE2406: Instrumentation. Lab 2
 Dedan Kimathi University of technology Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering EEE2406: Instrumentation Lab 2 Title: Analogue to Digital Conversion October 2, 2015 1 Analogue to Digital Conversion
Dedan Kimathi University of technology Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering EEE2406: Instrumentation Lab 2 Title: Analogue to Digital Conversion October 2, 2015 1 Analogue to Digital Conversion
CAMAC products. CAEN Short Form Catalog Function Model Description Page
 products Function Model Description Page Controller C111C Ethernet Crate Controller 44 Discriminator C808 16 Channel Constant Fraction Discriminator 44 Discriminator C894 16 Channel Leading Edge Discriminator
products Function Model Description Page Controller C111C Ethernet Crate Controller 44 Discriminator C808 16 Channel Constant Fraction Discriminator 44 Discriminator C894 16 Channel Leading Edge Discriminator
The domino sampling chip: a 1.2 GHz waveform sampling CMOS chip
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 420 (1999) 264 269 The domino sampling chip: a 1.2 GHz waveform sampling CMOS chip Christian Brönnimann *, Roland Horisberger, Roger Schnyder Swiss
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 420 (1999) 264 269 The domino sampling chip: a 1.2 GHz waveform sampling CMOS chip Christian Brönnimann *, Roland Horisberger, Roger Schnyder Swiss
Analog-to-Digital-Converter User Manual
 7070 Analog-to-Digital-Converter User Manual copyright FAST ComTec GmbH Grünwalder Weg 28a, D-82041 Oberhaching Germany Version 2.0, July 7, 2005 Software Warranty FAST ComTec warrants proper operation
7070 Analog-to-Digital-Converter User Manual copyright FAST ComTec GmbH Grünwalder Weg 28a, D-82041 Oberhaching Germany Version 2.0, July 7, 2005 Software Warranty FAST ComTec warrants proper operation
4413 UPDATING PROGRAMMABLE DISCRIMINATOR 4415A NON-UPDATING PROGRAMMABLE DISCRIMINATOR
 TECHNICAL DATA 4413 UPDATING PROGRAMMABLE DISCRIMINATOR 4415A NON-UPDATING PROGRAMMABLE DISCRIMINATOR CAMAC Packaging 16 Inputs Per Module ECLine Compatible Adjustable Output Widths Remote or Local Threshold
TECHNICAL DATA 4413 UPDATING PROGRAMMABLE DISCRIMINATOR 4415A NON-UPDATING PROGRAMMABLE DISCRIMINATOR CAMAC Packaging 16 Inputs Per Module ECLine Compatible Adjustable Output Widths Remote or Local Threshold
Analogue to Digital Conversion
 Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Static Random Access Memory - SRAM Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage:
 ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Static Random Access Memory - SRAM Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Email:
ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MICROELECTRONIC ENGINEERING Static Random Access Memory - SRAM Dr. Lynn Fuller Webpage: http://people.rit.edu/lffeee 82 Lomb Memorial Drive Rochester, NY 14623-5604 Email:
LM12L Bit + Sign Data Acquisition System with Self-Calibration
 LM12L458 12-Bit + Sign Data Acquisition System with Self-Calibration General Description The LM12L458 is a highly integrated 3.3V Data Acquisition System. It combines a fully-differential self-calibrating
LM12L458 12-Bit + Sign Data Acquisition System with Self-Calibration General Description The LM12L458 is a highly integrated 3.3V Data Acquisition System. It combines a fully-differential self-calibrating
MSCF-16-LN (Data sheet V5.0_01)
 (Data sheet V5.0_01) 16 fold Spectroscopy Amplifier with active BLR, CFDs, and Multiplicity Trigger mesytec MSCF-16-LN is an ultra low noise spectroscopy amplifier with active baseline restorer. It provides
(Data sheet V5.0_01) 16 fold Spectroscopy Amplifier with active BLR, CFDs, and Multiplicity Trigger mesytec MSCF-16-LN is an ultra low noise spectroscopy amplifier with active baseline restorer. It provides
Memory Basics. historically defined as memory array with individual bit access refers to memory with both Read and Write capabilities
 Memory Basics RAM: Random Access Memory historically defined as memory array with individual bit access refers to memory with both Read and Write capabilities ROM: Read Only Memory no capabilities for
Memory Basics RAM: Random Access Memory historically defined as memory array with individual bit access refers to memory with both Read and Write capabilities ROM: Read Only Memory no capabilities for
Data Sheet HSDL IR 3/16 Encode/Decode IC. Description. Features. Applications Interfaces with SIR infrared transceivers to perform: Pin Out
 HSDL-7000 IR 3/16 Encode/Decode IC Data Sheet Description The HSDL-7000 performs the modulation/ demodulation function used to both encode and decode the electrical pulses from the IR transceiver. These
HSDL-7000 IR 3/16 Encode/Decode IC Data Sheet Description The HSDL-7000 performs the modulation/ demodulation function used to both encode and decode the electrical pulses from the IR transceiver. These
MT8980D Digital Switch
 ISO-CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT0D Digital Switch Features February 00 Zarlink ST-BUS compatible Ordering Information -line x -channel inputs MT0DE 0 Pin PDIP Tubes MT0DP Pin PLCC Tubes -line x -channel outputs
ISO-CMOS ST-BUS TM Family MT0D Digital Switch Features February 00 Zarlink ST-BUS compatible Ordering Information -line x -channel inputs MT0DE 0 Pin PDIP Tubes MT0DP Pin PLCC Tubes -line x -channel outputs
SH X Grayscale Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Driver with Controller. Features. General Description 1 V2.2
 256 X 64 16 Grayscale Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Driver with Controller Features Support maximum 256 X 64 dot matrix panel with 16 grayscale Embedded 256 X 64 X 4bits SRAM Operating voltage: - I/O voltage supply:
256 X 64 16 Grayscale Dot Matrix OLED/PLED Driver with Controller Features Support maximum 256 X 64 dot matrix panel with 16 grayscale Embedded 256 X 64 X 4bits SRAM Operating voltage: - I/O voltage supply:
Auto refresh and self refresh refresh cycles / 64ms. Programmable CAS Latency ; 2, 3 Clocks
 4 Banks x 1M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The Hynix HY57V641620HG is a 67,108,864-bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density and
4 Banks x 1M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The Hynix HY57V641620HG is a 67,108,864-bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density and
Analog Peak Detector and Derandomizer
 Analog Peak Detector and Derandomizer G. De Geronimo, A. Kandasamy, P. O Connor Brookhaven National Laboratory IEEE Nuclear Sciences Symposium, San Diego November 7, 2001 Multichannel Readout Alternatives
Analog Peak Detector and Derandomizer G. De Geronimo, A. Kandasamy, P. O Connor Brookhaven National Laboratory IEEE Nuclear Sciences Symposium, San Diego November 7, 2001 Multichannel Readout Alternatives
GFT1012 2/4 Channel Precise Slave Generator
 Features Two Independent Delay Channels (Four channels available as an option) 1 ps Time Resolution < 5 ps RMS Jitter (Slave-to-Slave) < 6 ps / C Drift (Slave-to-slave) 1 Second Range Output Pulse Up to
Features Two Independent Delay Channels (Four channels available as an option) 1 ps Time Resolution < 5 ps RMS Jitter (Slave-to-Slave) < 6 ps / C Drift (Slave-to-slave) 1 Second Range Output Pulse Up to
HY57V281620HC(L/S)T-S
 4 Banks x 2M x 16bits Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The Hynix HY57V281620HC(L/S)T is a 134,217,728bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density
4 Banks x 2M x 16bits Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The Hynix HY57V281620HC(L/S)T is a 134,217,728bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density
An ASIC dedicated to the RPCs front-end. of the dimuon arm trigger in the ALICE experiment.
 An ASIC dedicated to the RPCs front-end of the dimuon arm trigger in the ALICE experiment. L. Royer, G. Bohner, J. Lecoq for the ALICE collaboration Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire de Clermont-Ferrand
An ASIC dedicated to the RPCs front-end of the dimuon arm trigger in the ALICE experiment. L. Royer, G. Bohner, J. Lecoq for the ALICE collaboration Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire de Clermont-Ferrand
EE584 Introduction to VLSI Design Final Project Document Group 9 Ring Oscillator with Frequency selector
 EE584 Introduction to VLSI Design Final Project Document Group 9 Ring Oscillator with Frequency selector Group Members Uttam Kumar Boda Rajesh Tenukuntla Mohammad M Iftakhar Srikanth Yanamanagandla 1 Table
EE584 Introduction to VLSI Design Final Project Document Group 9 Ring Oscillator with Frequency selector Group Members Uttam Kumar Boda Rajesh Tenukuntla Mohammad M Iftakhar Srikanth Yanamanagandla 1 Table
Revision No. History Draft Date Remark. 0.1 Initial Draft Jul Preliminary. 1.0 Release Aug. 2009
 128Mb Synchronous DRAM based on 2M x 4Bank x16 I/O Document Title 4Bank x 2M x 16bits Synchronous DRAM Revision History Revision No. History Draft Date Remark 0.1 Initial Draft Jul. 2009 Preliminary 1.0
128Mb Synchronous DRAM based on 2M x 4Bank x16 I/O Document Title 4Bank x 2M x 16bits Synchronous DRAM Revision History Revision No. History Draft Date Remark 0.1 Initial Draft Jul. 2009 Preliminary 1.0
Quad 12-Bit Digital-to-Analog Converter (Serial Interface)
 Quad 1-Bit Digital-to-Analog Converter (Serial Interface) FEATURES COMPLETE QUAD DAC INCLUDES INTERNAL REFERENCES AND OUTPUT AMPLIFIERS GUARANTEED SPECIFICATIONS OVER TEMPERATURE GUARANTEED MONOTONIC OVER
Quad 1-Bit Digital-to-Analog Converter (Serial Interface) FEATURES COMPLETE QUAD DAC INCLUDES INTERNAL REFERENCES AND OUTPUT AMPLIFIERS GUARANTEED SPECIFICATIONS OVER TEMPERATURE GUARANTEED MONOTONIC OVER
WaveStation Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generators
 WaveStation Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generators Key Features High performance with 14-bit, 125 MS/s and 16 kpts 2 channels on all models Large 3.5 color display for easy waveform preview Over 40 built-in
WaveStation Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generators Key Features High performance with 14-bit, 125 MS/s and 16 kpts 2 channels on all models Large 3.5 color display for easy waveform preview Over 40 built-in
A10-Gb/slow-power adaptive continuous-time linear equalizer using asynchronous under-sampling histogram
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.10, No.4, 1 8 A10-Gb/slow-power adaptive continuous-time linear equalizer using asynchronous under-sampling histogram Wang-Soo Kim and Woo-Young Choi a) Department
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.10, No.4, 1 8 A10-Gb/slow-power adaptive continuous-time linear equalizer using asynchronous under-sampling histogram Wang-Soo Kim and Woo-Young Choi a) Department
OPERATOR'S MANUAL MODEL 3341 CAMAC 8-INPUT CHARGE ADC
 OPERATOR'S MANUAL MODEL 3341 CAMAC 8-INPUT CHARGE ADC 1 Innovators in Instrumentation Corporate Headquarters 700 Chestnut Ridge Road Chestnut Ridge, NY 10977-6499 Tel: (914) 578-6013 Fax: (914) 578-5984
OPERATOR'S MANUAL MODEL 3341 CAMAC 8-INPUT CHARGE ADC 1 Innovators in Instrumentation Corporate Headquarters 700 Chestnut Ridge Road Chestnut Ridge, NY 10977-6499 Tel: (914) 578-6013 Fax: (914) 578-5984
SKY2000. Data Sheet DUAL-TRACK MAGNETIC STRIPE F2F DECODER IC. For More Information. Solution Way Co., Ltd
 SKY2000 Data Sheet MAGNETIC STRIPE F2F DECODER IC For More Information www.solutionway.com ydlee@solutionway.com Tel:+82-31-605-3800 Fax:+82-31-605-3801 1 Introduction 1. Description..3 2. Features...3
SKY2000 Data Sheet MAGNETIC STRIPE F2F DECODER IC For More Information www.solutionway.com ydlee@solutionway.com Tel:+82-31-605-3800 Fax:+82-31-605-3801 1 Introduction 1. Description..3 2. Features...3
Digital Fundamentals 8/25/2016. Summary. Summary. Floyd. Chapter 1. Analog Quantities
 8/25/206 Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd Chapter Analog Quantities Most natural quantities that we see are analog and vary continuously. Analog systems can generally handle higher power than digital
8/25/206 Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd Chapter Analog Quantities Most natural quantities that we see are analog and vary continuously. Analog systems can generally handle higher power than digital
I hope you have completed Part 2 of the Experiment and is ready for Part 3.
 I hope you have completed Part 2 of the Experiment and is ready for Part 3. In part 3, you are going to use the FPGA to interface with the external world through a DAC and a ADC on the add-on card. You
I hope you have completed Part 2 of the Experiment and is ready for Part 3. In part 3, you are going to use the FPGA to interface with the external world through a DAC and a ADC on the add-on card. You
Part No. Clock Frequency Power Organization Interface Package. Normal. Low power
 4 Banks x 2M x 8Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The Hynix HY57V64820HG is a 67,108,864-bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density and
4 Banks x 2M x 8Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The Hynix HY57V64820HG is a 67,108,864-bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density and
IR 3/16 Encode/Decode IC. Technical Data. HSDL pc, tape and reel HSDL-7001# pc, 50/tube
 IR 3/16 Encode/Decode IC Technical Data HSDL-7001-2500 pc, tape and reel HSDL-7001#100-100pc, 50/tube Features Compliant with IrDA 1.0 Physical Layer Specs Interfaces with IrDA 1.0 Compliant IR Transceivers
IR 3/16 Encode/Decode IC Technical Data HSDL-7001-2500 pc, tape and reel HSDL-7001#100-100pc, 50/tube Features Compliant with IrDA 1.0 Physical Layer Specs Interfaces with IrDA 1.0 Compliant IR Transceivers
Technical Information Manual
 Technical Information Manual Revision n. 5 25 November 2002 MOD. N840-N841 8-16 CHANNEL LEADING EDGE DISCRIMINATOR NPO: 00103/00:840-1.MUTx/05 CAEN will repair or replace any product within the guarantee
Technical Information Manual Revision n. 5 25 November 2002 MOD. N840-N841 8-16 CHANNEL LEADING EDGE DISCRIMINATOR NPO: 00103/00:840-1.MUTx/05 CAEN will repair or replace any product within the guarantee
Computer Architecture (TT 2012)
 Computer Architecture (TT 212) Laws of Attraction aniel Kroening Oxford University, Computer Science epartment Version 1., 212 . Kroening: Computer Architecture (TT 212) 2 . Kroening: Computer Architecture
Computer Architecture (TT 212) Laws of Attraction aniel Kroening Oxford University, Computer Science epartment Version 1., 212 . Kroening: Computer Architecture (TT 212) 2 . Kroening: Computer Architecture
Part No. Clock Frequency Power Organization Interface Package. Normal. Low power
 4 Banks x 4M x 4Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The Hynix HY57V654020B is a 67,108,864-bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density and
4 Banks x 4M x 4Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The Hynix HY57V654020B is a 67,108,864-bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density and
Technical Information Manual
 Technical Information Manual Revision n. 27 August 2004 NPO: 008/0:V977X.MUTX/0 MOD. V977 6 CHANNEL I/O Register (Status A) MANUAL REV. CAEN will repair or replace any product within the guarantee period
Technical Information Manual Revision n. 27 August 2004 NPO: 008/0:V977X.MUTX/0 MOD. V977 6 CHANNEL I/O Register (Status A) MANUAL REV. CAEN will repair or replace any product within the guarantee period
MSCF-16 F (Data sheet V51_02)
 (Data sheet V51_02) 16 fold Spectroscopy Amplifier with CFDs and Multiplicity Trigger mesytec is a shaping / timing filter amplifier with constant fraction discriminator and multiplicity trigger and provides
(Data sheet V51_02) 16 fold Spectroscopy Amplifier with CFDs and Multiplicity Trigger mesytec is a shaping / timing filter amplifier with constant fraction discriminator and multiplicity trigger and provides
WaveStation Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generators
 Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generators Key Features High performance with 14-bit waveform generation, up to 500 MS/s sample rate and up to 512 kpts memory 2 channels on all models Large color display for
Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generators Key Features High performance with 14-bit waveform generation, up to 500 MS/s sample rate and up to 512 kpts memory 2 channels on all models Large color display for
TENTATIVE TOSHIBA MOS DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON GATE CMOS
 TENTATIVE TOSHIBA MOS DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON GATE CMOS 512-MBIT (64M 8 BITS) CMOS NAND E 2 PROM (64M BYTE SmartMedia TM ) DESCRIPTION TH58NS512DC The TH58NS512 is a single 3.3-V 512-Mbit (553,648,128)
TENTATIVE TOSHIBA MOS DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON GATE CMOS 512-MBIT (64M 8 BITS) CMOS NAND E 2 PROM (64M BYTE SmartMedia TM ) DESCRIPTION TH58NS512DC The TH58NS512 is a single 3.3-V 512-Mbit (553,648,128)
Revision No. History Draft Date Remark. 0.1 Initial Draft Jan Preliminary. 1.0 Final Version Apr. 2007
 64Mb Synchronous DRAM based on 1M x 4Bank x16 I/O Document Title 4Bank x 1M x 16bits Synchronous DRAM Revision History Revision No. History Draft Date Remark 0.1 Initial Draft Jan. 2007 Preliminary 1.0
64Mb Synchronous DRAM based on 1M x 4Bank x16 I/O Document Title 4Bank x 1M x 16bits Synchronous DRAM Revision History Revision No. History Draft Date Remark 0.1 Initial Draft Jan. 2007 Preliminary 1.0
Figure 1: Functional Block Diagram
 MagAlpha MA750 Key features 8 bit digital and 12 bit PWM output 500 khz refresh rate 7.5 ma supply current Serial interface for data readout and settings QFN16 3x3mm Package General Description The MagAlpha
MagAlpha MA750 Key features 8 bit digital and 12 bit PWM output 500 khz refresh rate 7.5 ma supply current Serial interface for data readout and settings QFN16 3x3mm Package General Description The MagAlpha
Auto refresh and self refresh refresh cycles / 64ms. Part No. Clock Frequency Power Organization Interface Package. Normal. 4Banks x 1Mbits x16
 4 Banks x 1M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The Hynix HY57V641620HG is a 67,108,864-bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density and
4 Banks x 1M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The Hynix HY57V641620HG is a 67,108,864-bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density and
DESIGN OF HIGH FREQUENCY CMOS FRACTIONAL-N FREQUENCY DIVIDER
 12 JAVA Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2003 DESIGN OF HIGH FREQUENCY CMOS FRACTIONAL-N FREQUENCY DIVIDER Totok Mujiono Dept. of Electrical Engineering, FTI ITS
12 JAVA Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, April 2003 DESIGN OF HIGH FREQUENCY CMOS FRACTIONAL-N FREQUENCY DIVIDER Totok Mujiono Dept. of Electrical Engineering, FTI ITS
HY57V561620C(L)T(P)-S
 4 Banks x 4M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The HY57V561620C(L)T(P) Series is a 268,435,456bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density
4 Banks x 4M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The HY57V561620C(L)T(P) Series is a 268,435,456bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density
Analogue to Digital Conversion
 Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Revision No. History Draft Date Remark. 1.0 First Version Release Dec Corrected PIN ASSIGNMENT A12 to NC Jan. 2005
 128Mb Synchronous DRAM based on 2M x 4Bank x16 I/O Document Title 4Bank x 2M x 16bits Synchronous DRAM Revision History Revision No. History Draft Date Remark 1.0 First Version Release Dec. 2004 1.1 1.
128Mb Synchronous DRAM based on 2M x 4Bank x16 I/O Document Title 4Bank x 2M x 16bits Synchronous DRAM Revision History Revision No. History Draft Date Remark 1.0 First Version Release Dec. 2004 1.1 1.
ECEN 720 High-Speed Links: Circuits and Systems. Lab3 Transmitter Circuits. Objective. Introduction. Transmitter Automatic Termination Adjustment
 1 ECEN 720 High-Speed Links: Circuits and Systems Lab3 Transmitter Circuits Objective To learn fundamentals of transmitter and receiver circuits. Introduction Transmitters are used to pass data stream
1 ECEN 720 High-Speed Links: Circuits and Systems Lab3 Transmitter Circuits Objective To learn fundamentals of transmitter and receiver circuits. Introduction Transmitters are used to pass data stream
QUARTZ-MM PC/104 Counter/Timer & Digital I/O Module
 QUARTZ-MM PC/104 Counter/Timer & Digital I/O Module User Manual V1.5 Copyright 2001 Diamond Systems Corporation 8430-D Central Ave. Newark, CA 94560 Tel (510) 456-7800 Fax (510) 45-7878 techinfo@diamondsystems.com
QUARTZ-MM PC/104 Counter/Timer & Digital I/O Module User Manual V1.5 Copyright 2001 Diamond Systems Corporation 8430-D Central Ave. Newark, CA 94560 Tel (510) 456-7800 Fax (510) 45-7878 techinfo@diamondsystems.com
MM58174A Microprocessor-Compatible Real-Time Clock
 MM58174A Microprocessor-Compatible Real-Time Clock General Description The MM58174A is a low-threshold metal-gate CMOS circuit that functions as a real-time clock and calendar in bus-oriented microprocessor
MM58174A Microprocessor-Compatible Real-Time Clock General Description The MM58174A is a low-threshold metal-gate CMOS circuit that functions as a real-time clock and calendar in bus-oriented microprocessor
IES Digital Mock Test
 . The circuit given below work as IES Digital Mock Test - 4 Logic A B C x y z (a) Binary to Gray code converter (c) Binary to ECESS- converter (b) Gray code to Binary converter (d) ECESS- To Gray code
. The circuit given below work as IES Digital Mock Test - 4 Logic A B C x y z (a) Binary to Gray code converter (c) Binary to ECESS- converter (b) Gray code to Binary converter (d) ECESS- To Gray code
A LOW POWER SINGLE PHASE CLOCK DISTRIBUTION USING 4/5 PRESCALER TECHNIQUE
 A LOW POWER SINGLE PHASE CLOCK DISTRIBUTION USING 4/5 PRESCALER TECHNIQUE MS. V.NIVEDITHA 1,D.MARUTHI KUMAR 2 1 PG Scholar in M.Tech, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of E.C.E,Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute
A LOW POWER SINGLE PHASE CLOCK DISTRIBUTION USING 4/5 PRESCALER TECHNIQUE MS. V.NIVEDITHA 1,D.MARUTHI KUMAR 2 1 PG Scholar in M.Tech, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of E.C.E,Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute
TIMING, TRIGGER AND CONTROL INTERFACE MODULE FOR ATLAS SCT READ OUT ELECTRONICS
 TIMING, TRIGGER AND CONTROL INTERFACE MODULE FOR ATLAS SCT READ OUT ELECTRONICS Jonathan Butterworth ( email : jmb@hep.ucl.ac.uk ) Dominic Hayes ( email : dah@hep.ucl.ac.uk ) John Lane ( email : jbl@hep.ucl.ac.uk
TIMING, TRIGGER AND CONTROL INTERFACE MODULE FOR ATLAS SCT READ OUT ELECTRONICS Jonathan Butterworth ( email : jmb@hep.ucl.ac.uk ) Dominic Hayes ( email : dah@hep.ucl.ac.uk ) John Lane ( email : jbl@hep.ucl.ac.uk
a8259 Features General Description Programmable Interrupt Controller
 a8259 Programmable Interrupt Controller July 1997, ver. 1 Data Sheet Features Optimized for FLEX and MAX architectures Offers eight levels of individually maskable interrupts Expandable to 64 interrupts
a8259 Programmable Interrupt Controller July 1997, ver. 1 Data Sheet Features Optimized for FLEX and MAX architectures Offers eight levels of individually maskable interrupts Expandable to 64 interrupts
10-Bit, Low-Power, Rail-to-Rail Voltage-Output Serial DAC in SOT23
 19-195; Rev 1; 1/4 1-Bit, Low-Power, Rail-to-Rail General Description The is a small footprint, low-power, 1-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) that operates from a single +.7V to +5.5V supply. The
19-195; Rev 1; 1/4 1-Bit, Low-Power, Rail-to-Rail General Description The is a small footprint, low-power, 1-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) that operates from a single +.7V to +5.5V supply. The
DFT for Testing High-Performance Pipelined Circuits with Slow-Speed Testers
 DFT for Testing High-Performance Pipelined Circuits with Slow-Speed Testers Muhammad Nummer and Manoj Sachdev University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada mnummer@vlsi.uwaterloo.ca, msachdev@ece.uwaterloo.ca
DFT for Testing High-Performance Pipelined Circuits with Slow-Speed Testers Muhammad Nummer and Manoj Sachdev University of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada mnummer@vlsi.uwaterloo.ca, msachdev@ece.uwaterloo.ca
Part No. Clock Frequency Power Organization Interface Package. Normal. Low power
 4 Banks x 4M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The HY57V561620C is a 268,435,456bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density and high
4 Banks x 4M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The HY57V561620C is a 268,435,456bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require large memory density and high
Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques
 Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques The electronics signals that we ve looked at so far have been analog that means the information is continuous. A voltage of 5.3V represents different information that
Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques The electronics signals that we ve looked at so far have been analog that means the information is continuous. A voltage of 5.3V represents different information that
Development of Front-end Electronics and TDC LSI. for the ATLAS MDT
 Development of Front-end Electronics and TDC LSI for the ATLAS MDT Y. Arai KEK, National High Energy Accelerator Research Organization Institute of Particle and Nuclear Studies, 1-1 Oho, Tsukuba, JAPAN
Development of Front-end Electronics and TDC LSI for the ATLAS MDT Y. Arai KEK, National High Energy Accelerator Research Organization Institute of Particle and Nuclear Studies, 1-1 Oho, Tsukuba, JAPAN
ZL Features. Description
 Features February 27 Zarlink ST-BUS compatible 8-line x 32-channel inputs 8-line x 32-channel outputs 256 ports non-blocking switch Single power supply (+5 V) Low power consumption: 3 mw Typ. Microprocessor-control
Features February 27 Zarlink ST-BUS compatible 8-line x 32-channel inputs 8-line x 32-channel outputs 256 ports non-blocking switch Single power supply (+5 V) Low power consumption: 3 mw Typ. Microprocessor-control
CS/EE Homework 9 Solutions
 S/EE 260 - Homework 9 Solutions ue 4/6/2000 1. onsider the synchronous ripple carry counter on page 5-8 of the notes. Assume that the flip flops have a setup time requirement of 2 ns and that the gates
S/EE 260 - Homework 9 Solutions ue 4/6/2000 1. onsider the synchronous ripple carry counter on page 5-8 of the notes. Assume that the flip flops have a setup time requirement of 2 ns and that the gates
SKY3000. Data Sheet TRIPLE-TRACK MAGNETIC STRIPE F2F DECODER IC. For More Information. Solution Way Co., Ltd
 SKY3000 Data Sheet MAGNETIC STRIPE F2F DECODER IC For More Information www.solutionway.com ydlee@solutionway.com Tel:+82-31-605-3800 Fax:+82-31-605-3801 1 Introduction 1. Description..3 2. Features...3
SKY3000 Data Sheet MAGNETIC STRIPE F2F DECODER IC For More Information www.solutionway.com ydlee@solutionway.com Tel:+82-31-605-3800 Fax:+82-31-605-3801 1 Introduction 1. Description..3 2. Features...3
HY57V561620B(L/S)T 4 Banks x 4M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM
 4 Banks x 4M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM Doucment Title 4 Bank x 4M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM Revision History Revision No. History Draft Date Remark 1.4 143MHz Speed Added July 14. 2003 This document is a
4 Banks x 4M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM Doucment Title 4 Bank x 4M x 16Bit Synchronous DRAM Revision History Revision No. History Draft Date Remark 1.4 143MHz Speed Added July 14. 2003 This document is a
WaveStation Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generators
 WaveStation Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generators Key Features High performance with 14-bit, 125 MS/s and 16 kpts 2 channels on all models Large 3.5 color display for easy waveform preview Over 40 built-in
WaveStation Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generators Key Features High performance with 14-bit, 125 MS/s and 16 kpts 2 channels on all models Large 3.5 color display for easy waveform preview Over 40 built-in
Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project
 Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 012-2009 (Draft) Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project H. P. Lima Jr, A. F. Barbosa, R. G. Gama Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas - CBPF L. F. G. Gonzalez
Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 012-2009 (Draft) Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project H. P. Lima Jr, A. F. Barbosa, R. G. Gama Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas - CBPF L. F. G. Gonzalez
512 x 8 Registered PROM
 512 x 8 Registered PROM Features CMOS for optimum speed/power High speed 25 ns address set-up 12 ns clock to output Low power 495 mw (Commercial) 660 mw (Military) Synchronous and asynchronous output enables
512 x 8 Registered PROM Features CMOS for optimum speed/power High speed 25 ns address set-up 12 ns clock to output Low power 495 mw (Commercial) 660 mw (Military) Synchronous and asynchronous output enables
INF3430 Clock and Synchronization
 INF3430 Clock and Synchronization P.P.Chu Using VHDL Chapter 16.1-6 INF 3430 - H12 : Chapter 16.1-6 1 Outline 1. Why synchronous? 2. Clock distribution network and skew 3. Multiple-clock system 4. Meta-stability
INF3430 Clock and Synchronization P.P.Chu Using VHDL Chapter 16.1-6 INF 3430 - H12 : Chapter 16.1-6 1 Outline 1. Why synchronous? 2. Clock distribution network and skew 3. Multiple-clock system 4. Meta-stability
Technical Information Manual
 echnical Information Manual Revision n. 3 19 March 29 MOD. V95 series NPO: 11/9:V95x.MUx/3 16 CHANNEL LEADING EDGE DISCRIMINAORS CAEN will repair or replace any product within the guarantee period if the
echnical Information Manual Revision n. 3 19 March 29 MOD. V95 series NPO: 11/9:V95x.MUx/3 16 CHANNEL LEADING EDGE DISCRIMINAORS CAEN will repair or replace any product within the guarantee period if the
Circuit Design for a 2.2 GByte/s Memory Interface
 Circuit Design for a 2.2 GByte/s Memory Interface Stefanos Sidiropoulos Work done at Rambus Inc with A. Abhyankar, C. Chen, K. Chang, TJ Chin, N. Hays, J. Kim, Y. Li, G. Tsang, A. Wong, D. Stark Increasing
Circuit Design for a 2.2 GByte/s Memory Interface Stefanos Sidiropoulos Work done at Rambus Inc with A. Abhyankar, C. Chen, K. Chang, TJ Chin, N. Hays, J. Kim, Y. Li, G. Tsang, A. Wong, D. Stark Increasing
ICS PLL BUILDING BLOCK
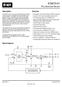 Description The ICS673-01 is a low cost, high performance Phase Locked Loop (PLL) designed for clock synthesis and synchronization. Included on the chip are the phase detector, charge pump, Voltage Controlled
Description The ICS673-01 is a low cost, high performance Phase Locked Loop (PLL) designed for clock synthesis and synchronization. Included on the chip are the phase detector, charge pump, Voltage Controlled
16 Meg FPM DRAM AS4LC4M4. 4M x 4 CMOS DRAM WITH FAST PAGE MODE, 3.3V PIN ASSIGNMENT ACTIVE POWER DISSIPATION PERFORMANCE RANGE
 4M x 4 CMOS DRAM WITH FAST PAGE MODE, 3.3V PIN ASSIGNMENT (Top View) AVAILABLE AS MILITARY SPECIFICATIONS MIL-STD-883 FEATURES Fast Page Mode Operation CAS\-before-RAS\ Refresh Capability RAS\-only and
4M x 4 CMOS DRAM WITH FAST PAGE MODE, 3.3V PIN ASSIGNMENT (Top View) AVAILABLE AS MILITARY SPECIFICATIONS MIL-STD-883 FEATURES Fast Page Mode Operation CAS\-before-RAS\ Refresh Capability RAS\-only and
64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs
 241/42 fax id: 549 CY7C4421/421/4211/4221 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs Features High-speed, low-power, first-in, first-out (FIFO) memories 64 x 9 (CY7C4421) 256 x 9 (CY7C421) 512 x 9 (CY7C4211)
241/42 fax id: 549 CY7C4421/421/4211/4221 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs Features High-speed, low-power, first-in, first-out (FIFO) memories 64 x 9 (CY7C4421) 256 x 9 (CY7C421) 512 x 9 (CY7C4211)
HY57V28420A. Revision History. Revision 1.1 (Dec. 2000)
 Revision History Revision 1.1 (Dec. 2000) Eleminated -10 Bining product. Changed DC Characteristics-ll. - tck to 15ns from min in Test condition - -K IDD1 to 120mA from 110mA - -K IDD4 CL2 to 120mA from
Revision History Revision 1.1 (Dec. 2000) Eleminated -10 Bining product. Changed DC Characteristics-ll. - tck to 15ns from min in Test condition - -K IDD1 to 120mA from 110mA - -K IDD4 CL2 to 120mA from
 Switch/ Jumper Table 1-1: Factory Settings Factory Settings (Jumpers Installed) Function Controlled Activates pull-up/ pull-down resistors on Port 0 digital P7 I/O lines Activates pull-up/ pull-down resistors
Switch/ Jumper Table 1-1: Factory Settings Factory Settings (Jumpers Installed) Function Controlled Activates pull-up/ pull-down resistors on Port 0 digital P7 I/O lines Activates pull-up/ pull-down resistors
Power And Area Optimization of Pulse Latch Shift Register
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 12, Issue 6 (June 2016), PP.41-45 Power And Area Optimization of Pulse Latch Shift
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 12, Issue 6 (June 2016), PP.41-45 Power And Area Optimization of Pulse Latch Shift
Design for Testability & Design for Debug
 EE-382M VLSI II Design for Testability & Design for Debug Bob Molyneaux Mark McDermott Anil Sabbavarapu EE 382M Class Notes Foil # 1 The University of Texas at Austin Agenda Why test? Scan: What is it?
EE-382M VLSI II Design for Testability & Design for Debug Bob Molyneaux Mark McDermott Anil Sabbavarapu EE 382M Class Notes Foil # 1 The University of Texas at Austin Agenda Why test? Scan: What is it?
GFT Channel Digital Delay Generator
 Features 20 independent delay Channels 100 ps resolution 25 ps rms jitter 10 second range Output pulse up to 6 V/50 Ω Independent trigger for every channel Four triggers Three are repetitive from three
Features 20 independent delay Channels 100 ps resolution 25 ps rms jitter 10 second range Output pulse up to 6 V/50 Ω Independent trigger for every channel Four triggers Three are repetitive from three
Quad Analog-to-Digital Converter Technical Documentation
 7074 Quad AnalogtoDigital Converter Technical Documentation copyright FAST ComTec GmbH Grünwalder Weg 28a, D82041 Oberhaching Germany Version 2.2, February 25, 2005 Table of Contents Table of Contents
7074 Quad AnalogtoDigital Converter Technical Documentation copyright FAST ComTec GmbH Grünwalder Weg 28a, D82041 Oberhaching Germany Version 2.2, February 25, 2005 Table of Contents Table of Contents
Microprocessor & Interfacing Lecture Programmable Interval Timer
 Microprocessor & Interfacing Lecture 30 8254 Programmable Interval Timer P A R U L B A N S A L A S S T P R O F E S S O R E C S D E P A R T M E N T D R O N A C H A R Y A C O L L E G E O F E N G I N E E
Microprocessor & Interfacing Lecture 30 8254 Programmable Interval Timer P A R U L B A N S A L A S S T P R O F E S S O R E C S D E P A R T M E N T D R O N A C H A R Y A C O L L E G E O F E N G I N E E
Winter 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer P a g e 1/28
 Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer P a g e 1/28 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer P a g e 1/28 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring Lecture 24: Peripheral Memory Circuits
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 24: Peripheral Memory Circuits [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 24: Peripheral Memory Circuits [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11
Development of a 20 GS/s Sampling Chip in 130nm CMOS Technology
 Development of a 20 GS/s Sampling Chip in 130nm CMOS Technology 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Orlando, Florida, October 28 th 2009 Jean-Francois Genat On behalf of Mircea Bogdan 1, Henry J. Frisch
Development of a 20 GS/s Sampling Chip in 130nm CMOS Technology 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Orlando, Florida, October 28 th 2009 Jean-Francois Genat On behalf of Mircea Bogdan 1, Henry J. Frisch
Digital Design and System Implementation. Overview of Physical Implementations
 Digital Design and System Implementation Overview of Physical Implementations CMOS devices CMOS transistor circuit functional behavior Basic logic gates Transmission gates Tri-state buffers Flip-flops
Digital Design and System Implementation Overview of Physical Implementations CMOS devices CMOS transistor circuit functional behavior Basic logic gates Transmission gates Tri-state buffers Flip-flops
A Fast Locking Digital Phase-Locked Loop using Frequency Difference Stage
 International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:14 No:04 75 A Fast Locking Digital Phase-Locked Loop using Frequency Difference Stage Mohamed A. Ahmed, Heba A. Shawkey, Hamed A. Elsemary,
International Journal of Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS Vol:14 No:04 75 A Fast Locking Digital Phase-Locked Loop using Frequency Difference Stage Mohamed A. Ahmed, Heba A. Shawkey, Hamed A. Elsemary,
TC55VBM316AFTN/ASTN40,55
 TENTATIVE TOSHIBA MOS DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON GATE CMOS 524,288-WORD BY 16-BIT/1,048,576-WORD BY 8-BIT FULL CMOS STATIC RAM DESCRIPTION The TC55VBM316AFTN/ASTN is a 8,388,608-bit static random
TENTATIVE TOSHIBA MOS DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON GATE CMOS 524,288-WORD BY 16-BIT/1,048,576-WORD BY 8-BIT FULL CMOS STATIC RAM DESCRIPTION The TC55VBM316AFTN/ASTN is a 8,388,608-bit static random
TAPR TICC Timestamping Counter Operation Manual. Introduction
 TAPR TICC Timestamping Counter Operation Manual Revised: 23 November 2016 2016 Tucson Amateur Packet Radio Corporation Introduction The TAPR TICC is a two-channel timestamping counter ("TSC") implemented
TAPR TICC Timestamping Counter Operation Manual Revised: 23 November 2016 2016 Tucson Amateur Packet Radio Corporation Introduction The TAPR TICC is a two-channel timestamping counter ("TSC") implemented
GFT1504 4/8/10 channel Delay Generator
 Features 4 independent Delay Channels (10 in option) 100 ps resolution (1ps in option) 25 ps RMS jitter (channel to channel) 10 second range Channel Output pulse 6 V/50 Ω, 3 ns rise time Independent control
Features 4 independent Delay Channels (10 in option) 100 ps resolution (1ps in option) 25 ps RMS jitter (channel to channel) 10 second range Channel Output pulse 6 V/50 Ω, 3 ns rise time Independent control
Datasheet C400. Four Channel Pulse Counting Detector Controller
 Four Channel Pulse Counting Detector Controller Features Four independent channels with fast discriminators, scalers, preamp power and high voltage. Able to control photomultipliers and APDs. 10 nsec pulse
Four Channel Pulse Counting Detector Controller Features Four independent channels with fast discriminators, scalers, preamp power and high voltage. Able to control photomultipliers and APDs. 10 nsec pulse
