Generation of Quadrupole Magnetic Field for Trapping Atoms in Cs Fountain being Developed at NPL India
|
|
|
- Robyn Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MAPAN - Journal of Metrology Society of India, Vol. 26, No. 4, 2011; pp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Generation of Quadrupole Magnetic Field for Trapping Atoms in Cs Fountain being Developed at NPL India K. PANT*, P. ARORA, S. YADAV and A. SENGUPTA National Physical Laboratory India (NPLI) Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Dr. K.S. Krishnan Marg, New Delhi * pantk@mail.nplindia.ernet.in [Received: ; Revised: ; Accepted: ] Abstract We describe the development of a constant current source for magneto-optical trap (MOT) coils. The system is designed to supply maximum 5 A current in continuous or pulsed mode to the anti- Helmholtz (AH) coils which produce quadrupole magnetic field inside the chamber for trapping of Cs atoms. To obtain a stable field gradient the coils are operated at low current to minimize current fluctuations. With AH coils having 100 turns and 5 Ù resistances, we achieved rise and fall times of current as 5 ms and 7 ms, respectively. With a field gradient of 6 G/cm at the center of the MOT, 7 number of atoms trapped is about 10. To prevent burning of coils due to failure of current source, a thermal protection circuit has been incorporated. Measurements made for switching times of current profile in coils is also reported. 1. Introduction the laser (by the magnetic field the Zeeman effect), will absorb a photon, and the momentum received Cesium (Cs) fountain frequency standard is one from the photon will give the atom a kick towards of the highly accurate measurement devices the center of the trap [4]. currently available. Such atomic fountains are being developed at several laboratories around the world Figure 2 shows anti-helmholtz coil and the [1-3] and a few of them operate as primary frequency octagonal MOT chamber which is a part of the standards. In a Cs fountain, atoms are first cooled physics package of Cs fountain being developed at and trapped in a MOT. The MOT consists of two NPL India [3]. Generation of quadrupole magnetic coils with currents flowing in opposite directions field is crucial for trapping the atoms. Quadrupole that produce a quadrupole magnetic field as shown magnetic field means the magnetic field at the center in Fig. 1. There are three sets of counter-propagating, between the two coils is zero and there is a uniform circularly polarized laser beams that are at a field gradient as one moves away from the center. frequency slightly less than that of the atomic The axial gradient, B z, is twice as compared to the resonance (red-detuned). Atoms that drift towards radial gradient, B ñ, of the field as estimated with the one of the lasers will be brought into resonance with following equations: Metrology Society of India, All rights reserved
2 K. Pant, P. Arora, S. Yadav and A. Sengupta Fig. 1. Schematic of a MOT dr B NI3 z, B z 3 NI d r 0 5/2 dr d r 0 5/2. where is 0 the magnetic permeability, I is the current flowing through the coils, N is the number of turns in each coil, is any vector in the x-y plane, r is the radius of the coils and 2d is the distance between the centers of the two coils. All the electronic modules required for the development of Cs fountain-cs source temperature controller, acousto-optic modulator (AOM) driver, sequence control circuits; various current sources etc. are indigenously developed in our laboratory. In (1) this paper, we report the development of constant current source for generating quadrupole magnetic field for trapping atoms. It is designed to operate in pulsed current mode as well as in continuous current mode when power dissipation in power devices is very high. For this reason power devices are mounted on a large heat sink. Operation in continuous current mode is required during initial testing of MOT. The design details of current source are discussed in detail in the next section. 2. Constant Current Source - Design Details The current source is composed of seven circuit elements viz. anti-helmholtz (AH) coils, DC supply, power circuit for driving the coils, control circuit, optically isolated switching interface, current display circuit and thermal protection circuit. 286
3 Generation of Quadrupole Magnetic Field for Trapping Atoms in Cs Fountain being Developed at NPL India Fig. 2. One of the anti-helmholtz coils fixed on the top of octagonal chamber which is a part of physics package of Cs fountain The block diagram and schematic diagram of field gradient at the cost of higher switching times complete circuit are shown in Figs. 3 and 4, because lower currents and power are easier to respectively. handle [ 5]. 2.1 Anti-Helmholtz Coils (MOT Coils) 2.2 Power Supply These coils act as load for the current source. For There are three power supplies viz. 50 V/6 A magneto optical trapping of cold neutral atoms, two unregulated for supplying power to anti Helmholtz coils are arranged in anti-helmholtz configuration (AH) coils, ±12 V/1 A regulated for control and (current passing in opposite directions) and fixed on thermal protection circuits and +5 V/1 A for current the top and bottom of the octagonal cooling chamber display module (Fig. 3). These supplies are derived (Fig. 2) of the physics package of the Cs fountain. from the secondary windings of the same These coils are wound on a non magnetic aluminum transformer. Input to the primary winding is 230 frame of 150 mm diameter, have 100 turns each and V/50 Hz mains supply. We have chosen create a magnetic field gradient of 6 G/cm (for a unregulated supply to lower the weight of supply current of 3.5 A) at the centre of the MOT chamber. and moreover it does not impair the magnetic field DC resistance of both coils in series is 5. Instead of gradient inside the chamber. Bleeder resistors are operating the coils at higher currents with few turns connected after LC filter of unregulated supply to we have used many turns to operate the coils at low stabilize it to some level. At no load output voltage currents. This ensures a well stabilized magnetic of supply is about 50 V and is chosen to be the 287
4 K. Pant, P. Arora, S. Yadav and A. Sengupta DPM: Digital Panel Meter D : Schottky Diode (SB2060CT) AH Coils: Anti-Helmholtz Coils F Fig. 3. Block diagram of Constant Current Source for Anti-Helmholtz Coils minimum by selecting proper secondary winding of transformer for minimum power dissipation in the power devices. Table 1 Power dissipation in MOSFETs when operated in continuous current mode 2.3 Coil Driving Power Circuit S. No Vs IL VDS PD (Volts) (Amps) (Volts) (Watts) The circuit diagram is shown in Fig.4. For operating the circuit in continuous current mode a constant DC voltage proportional to the set-current (adjusted by potentiometer P) is applied from the control circuit to the junction A of gate resistances The MOSFETs (IRF-250) turn-on and a steady DC current flows in the AH coils to produce a magnetic field gradient for trapping the Cs atoms. VS Unregulated DC supply voltage I L Load current through anti Helmholtz coils During this mode the Schottky diodes (also VDS Voltage across MOSFETs called flyback or freewheeling diodes) connected PD Power dissipation in MOSFETs across the coils do not play any role and remain reverse biased for the entire period. Table 1 shows power dissipation in MOSFETs at different load currents. The maximum power dissipation is at 3 A. The current source is designed for maximum current rating of 5 A and a single MOSFET (I D=30 A 288
5 Generation of Quadrupole Magnetic Field for Trapping Atoms in Cs Fountain being Developed at NPL India Fig. 4. Schematic diagram of Constant Current Source for anti-helmholtz coils for IRF-250) is sufficient for carrying this current but the current and voltage waveforms across the AH to share the large power dissipation we have used 3 coils during this mode. MOSFETs in parallel which are mounted on a large heat sink.to ensure that power devices operate The fountain is in initial testing phase, hence the within their safe operating areas the current MOT current period is kept little more ( 500 ms) unbalance in the parallel devices should be than what is normally used in the working fountains minimised. Unbalance of current is generated due to in order to increase the number of trapped atoms mismatch of i) drain source resistance- R DS (on); ii) and hence improve the return signal and signal to gate threshold voltage V T ; iii) gate decoupling noise ratio. resistance- R G ; iv) gate drain and gate source capacitances-c GD, C GS. Except R DS (on), unbalance We are using unregulated supply for powering due to other factors is very small. Difference in R DS the coils. Therefore during turn-on initially the (on) causes current unbalance and extra conduction current in the coils reaches a peak value of 5.6 A in 5 losses but these are limited due to positive ms and falls smoothly to a 3.8 A in about 150 ms. This temperature coefficient of the MOSFETs [6]. We is shown in Figs. 6 and 7 respectively. measured current in each device and found improvement in current sharing by connecting When the MOSFETs are switched-off, the resistances r 1, r 2, r 3 (0.2 /2 w) in the source circuit. magnetic field energy stored in the inductance of the coils resists the sudden drop of current by reversing When the circuit is operated in pulsed current the voltage across its ends. At this instant the mode, a steady current flows in the coils for a very Schottky diode becomes forward biased, clamps small period (about a few milliseconds) during voltage across coils to about 1 V and conducts which the AH coils behave like a simple resistor and current until the energy stored in the inductor is get fully energized by the DC current. Fig. 5 shows dissipated in the resistance of the wire and diode. 289
6 K. Pant, P. Arora, S. Yadav and A. Sengupta Fig. 5. V A voltage across AH coils, I A current in AH coils Fig. 6. Rise time of current in AH coils. Due to unregulated supply voltage, current (I ) in coils rises to A 5.6 A in 5 ms and reaches a stable value after some time (shown in Fig. 7) 290
7 Generation of Quadrupole Magnetic Field for Trapping Atoms in Cs Fountain being Developed at NPL India Fig. 7. Current in AH coils takes 150 ms to reach the stable value of 3.8 A As shown in Fig. 8 the freewheeling diode DF reference formed by precision voltage reference ensures smooth fall of current in about 7 ms. LM431 (IC-3), 1 kù current setting potentiometer and associated resistances constitute the control When the devices are switched-off high dv/dt circuit [8]. Current in the MOT coils is sensed by R S and di/dt values in the drain source circuits inject and amplified by IC-1. The gain of this IC is adjusted currents into the gate circuit through reverse such that at maximum load current output voltage at transfer drain-gate capacitance and induce high pin-6 of IC1 is 2.5V which is the maximum reference frequency parasitic oscillations in the gate circuits. voltage that can be set by the potentiometer. When These undesirable oscillations cause over voltage some reference is given to non-inverting pin-3 of ICtransients on the gates which may lead to 2 its output goes high and turns-on the MOSFETs. destruction of one or more devices. We have used 56 The current is sensed by R S, amplified by IC-1 and (ferrite beads are also used) resistances connected fed back to the inverting input of IC-2. IC-2 adjusts to gates of each MOSFET for damping these its output voltage and hence the drain current (I D) undesirable oscillations. 15 V zeners across gate such that the voltage drop across R S is very close to source of each MOSFET reduce low frequency reference voltage after amplification by IC 1. This oscillations and protects gate source from high ensures a constant current in R S which is the current voltage transients when the devices are switched off in MOT coils. [7]. 2.5 Optically Isolated Switching Interface 2.4 Control Circuit As shown in Fig. 4, two operational amplifiers IC1 and IC2, current sensing resistor R S, current Switching cycle and on-off time of current source is decided by timing and sequence control circuit. Opto-coupler 4N35 (IC-4 in Fig. 4) isolates 291
8 K. Pant, P. Arora, S. Yadav and A. Sengupta Fig. 8. Fall time of current in AH coils is 7ms and interfaces these two circuits and a BNC The temperature is sensed by a thermistor (T h) mounted on the front panel is used for feeding the glued on the MOT coil fixed on the top of the input signal. The current source is operated in octagonal chamber (Fig. 3). Voltage reference point continuous mode by grounding the BNC input and P connected to threshold pin 6 of IC555 sets the cutin pulsed mode by giving signal to the BNC input. off temperature. One of the secondary windings of the high current transformer is directly connected to 2.6 Current Display Circuit the 25 A bridge and another winding is connected through a relay (RL). When switch SW1 is pressed The circuit is shown in Fig. 4. For displaying the and released, output of timer (IC 555) goes high and current in the MOT coils, voltage across current transistor T1 turns on. This energizes relay RL and sense resistor R S is filtered by a low pass R-C filter, the supply to current source is switched-on. With amplified and given to the digital panel meter rise in temperature resistance of thermistor (DPM) mounted on the front panel. decreases resulting in increase of Vref or the voltage at threshold pin of IC 555. When this voltage reaches 2.7 Thermal Protection Circuit rd 2/3 of supply voltage, output of this IC goes low, switching-off the supply to the current source. The circuit is shown in Fig. 9. It protects MOT coils from overheating when they are subjected to 3. Results maximum current (5 A) continuously for long duration or in the event of burning of the MOSFETs The magnetic field gradient inside the chamber which causes the current to exceed 5 A and only follows the current in the AH coils; hence limited by the DC resistance of the coil. observations were taken for rise and fall times of 292
9 Generation of Quadrupole Magnetic Field for Trapping Atoms in Cs Fountain being Developed at NPL India Fig. 9. Thermal Protection Circuit current in the coils. Voltage and current in the coils and period of the fountain cycle. Our fountain is in are measured with Tektronix TDS2012C the initial stage of testing.. Therefore to increase the oscilloscope as shown in Fig. 3. Voltage across 1 Ù/2 number of atoms in the return signal and improve W resistance gives directly current in amperes. the signal to noise ratio the loading time is kept little Summary of the results corresponding to Figs. 5 to 8 more about 500ms. As shown in figures 6 and 8 rise is given in Table 2. and fall of current in the coils is smooth and without any transients. Before starting the next sequence Table 2 after the mot current is switched-off a dead time of Summary of measurements taken for current about 20ms when all the lasers are off has been profile in anti-helmholtz coils corresponding to included to take care of 7ms fall time of the current. Figs. 5 to 8 4. Conclusion S. No. Parameter ms Fig. 1. Mot current duration T h e c u r r e n t s o u r c e w a s t e s t e d f o r 2. Current rise time 5 6 characterization of atomic cloud in the magneto- 3. Stabilisation time of current optical trap. The effect of changing the magnetic 4. Current fall time 7 8 field gradient was also investigated by changing current from 0 A to 5 A. The effect of changing the The relation of magnetic field gradient and current and hence the magnetic field gradient on number of trapped atoms is shown in Fig. 10. total number of trapped atoms is shown in Fig. 10. Duration of mot current and switching times of mot As the field gradient increases, the restoring force current pulse influence number of atoms trapped becomes stronger and helps in trapping more 293
10 K. Pant, P. Arora, S. Yadav and A. Sengupta Fig. 10. Number of trapped atoms as a function of magnetic field gradient produced by the anti-helmholtz coils number of atoms. This confirms that the current [3] A. Sen Gupta, A. Agarwal, P. Arora and K. source for the AH coils works as per the Pant, Development of Cesium Fountain requirement. The module has been working Frequency Standard at NPL, India, Current satisfactorily since last few months. Science, 100 (2011) [4] C.J. Foot, in Atomic Physics, Oxford Acknowledgement University Press, Oxford, (2005), The authors are highly thankful for the sustained support and encouragement to the NPLI fountain project by its present and previous Directors - Dr. R.C. Budhani, Dr. V. Kumar, Dr. K. Lal and Dr. A.K. Raychoudhury. Financial support from CSIR is gratefully acknowledged. [5] T.P. Meyrath, Electromagnetic Design Basics for Cold Atom Experiments, (2004) www. george.ph.utexas.edu/ meyrath/informal/ electromagnets.pdf. [6] J.B. Forsythe, Paralleling of Power MOSFETs For Higher Power Output. technical-info/ appnotes/para.pdf References [7] J.Dodge, Eliminating Parasitic Oscillation between Parallel MOSFETs, Application [1] D.M. Meekhof, S.R. Jefferts, M. Stepanovic Note-APT-0402, Rev. A, Advanced Power and T.E. Parker, Accuracy Evaluation of a Technology, (2004). Cesium Fountain Frequency Standard at [8] AN-968 Current Sources: Options and NIST, IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., 50 (2001) Circuits Application Note, /static/imported-files/application_notes/ [2] S. Weyers, U. Huebner, R. Schroeder, C. AN-968.pdf Tamm and A. Bauch, Uncertainty Evaluation of the Atomic Cesium Fountain of the PTB, Metrologia, 38 (2001)
PCB layout guidelines. From the IGBT team at IR September 2012
 PCB layout guidelines From the IGBT team at IR September 2012 1 PCB layout and parasitics Parasitics (unwanted L, R, C) have much influence on switching waveforms and losses. The IGBT itself has its own
PCB layout guidelines From the IGBT team at IR September 2012 1 PCB layout and parasitics Parasitics (unwanted L, R, C) have much influence on switching waveforms and losses. The IGBT itself has its own
Design and development of atomic flux controller for cesium Fountain clock at NPL, India
 Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 50, August 2012, pp. 593-599 Design and development of atomic flux controller for cesium Fountain clock at NPL, India *Kavindra Pant, Poonam Arora, Suchi Yadav
Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics Vol. 50, August 2012, pp. 593-599 Design and development of atomic flux controller for cesium Fountain clock at NPL, India *Kavindra Pant, Poonam Arora, Suchi Yadav
Status Report on Time and Frequency Activities at National Physical Laboratory India
 Status Report on Time and Frequency Activities at National Physical Laboratory India (TCTF 2015) Ashish Agarwal *, S. Panja. P. Arora, P. Thorat, S. De, S. Yadav, P. Kandpal, M. P. Olaniya, S S Rajput,
Status Report on Time and Frequency Activities at National Physical Laboratory India (TCTF 2015) Ashish Agarwal *, S. Panja. P. Arora, P. Thorat, S. De, S. Yadav, P. Kandpal, M. P. Olaniya, S S Rajput,
Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals
 1.1a. Semiconductors - Diodes. Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals Question Number. 1. What gives the colour of an LED?. Option A. The active element. Option B. The plastic it is encased in. Option
1.1a. Semiconductors - Diodes. Module 04.(B1) Electronic Fundamentals Question Number. 1. What gives the colour of an LED?. Option A. The active element. Option B. The plastic it is encased in. Option
SRM TM A Synchronous Rectifier Module. Figure 1 Figure 2
 SRM TM 00 The SRM TM 00 Module is a complete solution for implementing very high efficiency Synchronous Rectification and eliminates many of the problems with selfdriven approaches. The module connects
SRM TM 00 The SRM TM 00 Module is a complete solution for implementing very high efficiency Synchronous Rectification and eliminates many of the problems with selfdriven approaches. The module connects
Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter
 Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter 3.1 Introduction DC/DC Converter efficiently converts unregulated DC voltage to a regulated DC voltage with better efficiency and high power density.
Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter 3.1 Introduction DC/DC Converter efficiently converts unregulated DC voltage to a regulated DC voltage with better efficiency and high power density.
AN2170 APPLICATION NOTE MOSFET Device Effects on Phase Node Ringing in VRM Power Converters INTRODUCTION
 AN2170 APPLICATION NOTE MOSFET Device Effects on Phase Node Ringing in VRM Power Converters INTRODUCTION The growth in production volume of industrial equipment (e.g., power DC-DC converters devoted to
AN2170 APPLICATION NOTE MOSFET Device Effects on Phase Node Ringing in VRM Power Converters INTRODUCTION The growth in production volume of industrial equipment (e.g., power DC-DC converters devoted to
UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
 UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING POWER ELECTRONICS LAB HANDBOOK Dr P.R. Palmer Dr P.R. Palmer 1 2004 1 AIM The aim of the project is to design, construct
UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING POWER ELECTRONICS LAB HANDBOOK Dr P.R. Palmer Dr P.R. Palmer 1 2004 1 AIM The aim of the project is to design, construct
PAiA 4780 Twelve Stage Analog Sequencer Design Analysis Originally published 1974
 PAiA 4780 Twelve Stage Analog Sequencer Design Analysis Originally published 1974 DESIGN ANALYSIS: CLOCK As is shown in the block diagram of the sequencer (fig. 1) and the schematic (fig. 2), the clock
PAiA 4780 Twelve Stage Analog Sequencer Design Analysis Originally published 1974 DESIGN ANALYSIS: CLOCK As is shown in the block diagram of the sequencer (fig. 1) and the schematic (fig. 2), the clock
Fast IC Power Transistor with Thermal Protection
 Fast IC Power Transistor with Thermal Protection Introduction Overload protection is perhaps most necessary in power circuitry. This is shown by recent trends in power transistor technology. Safe-area,
Fast IC Power Transistor with Thermal Protection Introduction Overload protection is perhaps most necessary in power circuitry. This is shown by recent trends in power transistor technology. Safe-area,
Transporting Atoms Using a Magnetic Coil Transfer System
 Transporting Atoms Using a Magnetic Coil Transfer System Aaron Sharpe Advisor: Deborah Jin University of Colorado at Boulder Summer Physics REU 2012 August 10, 2012 Abstract Transporting atomic clouds
Transporting Atoms Using a Magnetic Coil Transfer System Aaron Sharpe Advisor: Deborah Jin University of Colorado at Boulder Summer Physics REU 2012 August 10, 2012 Abstract Transporting atomic clouds
Experiment (1) Principles of Switching
 Experiment (1) Principles of Switching Introduction When you use microcontrollers, sometimes you need to control devices that requires more electrical current than a microcontroller can supply; for this,
Experiment (1) Principles of Switching Introduction When you use microcontrollers, sometimes you need to control devices that requires more electrical current than a microcontroller can supply; for this,
Lecture 4 ECEN 4517/5517
 Lecture 4 ECEN 4517/5517 Experiment 3 weeks 2 and 3: interleaved flyback and feedback loop Battery 12 VDC HVDC: 120-200 VDC DC-DC converter Isolated flyback DC-AC inverter H-bridge v ac AC load 120 Vrms
Lecture 4 ECEN 4517/5517 Experiment 3 weeks 2 and 3: interleaved flyback and feedback loop Battery 12 VDC HVDC: 120-200 VDC DC-DC converter Isolated flyback DC-AC inverter H-bridge v ac AC load 120 Vrms
3 Circuit Theory. 3.2 Balanced Gain Stage (BGS) Input to the amplifier is balanced. The shield is isolated
 Rev. D CE Series Power Amplifier Service Manual 3 Circuit Theory 3.0 Overview This section of the manual explains the general operation of the CE power amplifier. Topics covered include Front End Operation,
Rev. D CE Series Power Amplifier Service Manual 3 Circuit Theory 3.0 Overview This section of the manual explains the general operation of the CE power amplifier. Topics covered include Front End Operation,
Flyback Converter for High Voltage Capacitor Charging
 Flyback Converter for High Voltage Capacitor Charging Tony Alfrey (tonyalfrey at earthlink dot net) A Flyback Converter is a type of switching power supply that may be used to generate an output voltage
Flyback Converter for High Voltage Capacitor Charging Tony Alfrey (tonyalfrey at earthlink dot net) A Flyback Converter is a type of switching power supply that may be used to generate an output voltage
State the application of negative feedback and positive feedback (one in each case)
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
MICROCONTROLLER BASED BOOST PID MUNAJAH BINTI MOHD RUBAEE
 MICROCONTROLLER BASED BOOST PID MUNAJAH BINTI MOHD RUBAEE This thesis is submitted as partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of Bachelor of Electrical Engineering (Power System) Faculty of
MICROCONTROLLER BASED BOOST PID MUNAJAH BINTI MOHD RUBAEE This thesis is submitted as partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of Bachelor of Electrical Engineering (Power System) Faculty of
In addition to the power circuit a commercial power supply will require:
 Power Supply Auxiliary Circuits In addition to the power circuit a commercial power supply will require: -Voltage feedback circuits to feed a signal back to the error amplifier which is proportional to
Power Supply Auxiliary Circuits In addition to the power circuit a commercial power supply will require: -Voltage feedback circuits to feed a signal back to the error amplifier which is proportional to
Zero Voltage Switching In Practical Active Clamp Forward Converter
 Zero Voltage Switching In Practical Active Clamp Forward Converter Laishram Ritu VTU; POWER ELECTRONICS; India ABSTRACT In this paper; zero voltage switching in active clamp forward converter is investigated.
Zero Voltage Switching In Practical Active Clamp Forward Converter Laishram Ritu VTU; POWER ELECTRONICS; India ABSTRACT In this paper; zero voltage switching in active clamp forward converter is investigated.
Controlling Power Up and Power Down of the Synchronous MOSFETs in a Half-Bridge Converter
 This paper was originally presented at the Power Electronics Technology Exhibition & Conference, part of PowerSystems World 2005, held October 25-27, 2005, in Baltimore, MD. To inquire about PowerSystems
This paper was originally presented at the Power Electronics Technology Exhibition & Conference, part of PowerSystems World 2005, held October 25-27, 2005, in Baltimore, MD. To inquire about PowerSystems
DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER
 DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a switch-mode (chopper), constant-current driver with two channels: one for each winding of a two-phase stepper motor. is equipped with a Disable input
DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a switch-mode (chopper), constant-current driver with two channels: one for each winding of a two-phase stepper motor. is equipped with a Disable input
Application Note 0009
 Recommended External Circuitry for Transphorm GaN FETs Application Note 9 Table of Contents Part I: Introduction... 2 Part II: Solutions to Suppress Oscillation... 2 Part III: The di/dt Limits of GaN Switching
Recommended External Circuitry for Transphorm GaN FETs Application Note 9 Table of Contents Part I: Introduction... 2 Part II: Solutions to Suppress Oscillation... 2 Part III: The di/dt Limits of GaN Switching
LM78S40 Switching Voltage Regulator Applications
 LM78S40 Switching Voltage Regulator Applications Contents Introduction Principle of Operation Architecture Analysis Design Inductor Design Transistor and Diode Selection Capacitor Selection EMI Design
LM78S40 Switching Voltage Regulator Applications Contents Introduction Principle of Operation Architecture Analysis Design Inductor Design Transistor and Diode Selection Capacitor Selection EMI Design
Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP Task Grid
 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Describe OSHA safety regulations. 102 Identify, select, and demonstrate proper hand tool use for electronics work. 103 Recognize the types and usages of fire extinguishers.
Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Describe OSHA safety regulations. 102 Identify, select, and demonstrate proper hand tool use for electronics work. 103 Recognize the types and usages of fire extinguishers.
Application Note MHz, Class D Push-Pull, 1.7KW RF Generator with Microsemi DRF1300 Power MOSFET Hybrid
 13.56 MHz, Class D Push-Pull, 1.7KW RF Generator with Microsemi DRF1300 Power MOSFET Hybrid June 26, 2008 By Gui Choi Sr. RF Application Engineer The DRF1300/CLASS-D Reference design is available to expedite
13.56 MHz, Class D Push-Pull, 1.7KW RF Generator with Microsemi DRF1300 Power MOSFET Hybrid June 26, 2008 By Gui Choi Sr. RF Application Engineer The DRF1300/CLASS-D Reference design is available to expedite
MOSFET as a Switch. MOSFET Characteristics Curves
 MOSFET as a Switch MOSFET s make very good electronic switches for controlling loads and in CMOS digital circuits as they operate between their cut-off and saturation regions. We saw previously, that the
MOSFET as a Switch MOSFET s make very good electronic switches for controlling loads and in CMOS digital circuits as they operate between their cut-off and saturation regions. We saw previously, that the
An Improvement in the Virtually Isolated Transformerless Off - Line Power Supply
 An Improvement in the Virtually Isolated Transformerless Off - Line Power Supply Spiros Cofinas Department of Electrotechnics and Computer Science Hellenic Naval Academy Terma Hatzikyriakou, Piraeus GREECE
An Improvement in the Virtually Isolated Transformerless Off - Line Power Supply Spiros Cofinas Department of Electrotechnics and Computer Science Hellenic Naval Academy Terma Hatzikyriakou, Piraeus GREECE
Scheme Q.1 Attempt any SIX of following: 12-Total Marks a) Draw symbol NPN and PNP transistor. 2 M Ans: Symbol Of NPN and PNP BJT (1M each)
 Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17319) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17319) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
SINGLE-STAGE HIGH-POWER-FACTOR SELF-OSCILLATING ELECTRONIC BALLAST FOR FLUORESCENT LAMPS WITH SOFT START
 SINGLE-STAGE HIGH-POWER-FACTOR SELF-OSCILLATING ELECTRONIC BALLAST FOR FLUORESCENT S WITH SOFT START Abstract: In this paper a new solution to implement and control a single-stage electronic ballast based
SINGLE-STAGE HIGH-POWER-FACTOR SELF-OSCILLATING ELECTRONIC BALLAST FOR FLUORESCENT S WITH SOFT START Abstract: In this paper a new solution to implement and control a single-stage electronic ballast based
V DSS R DS(on) max I D. 20V GS = 10V 8.9A. 71 P A = 25 C Power Dissipation 2.0 P A = 70 C Power Dissipation Linear Derating Factor
 Applications Dual SO-8 MOSFET for POL converters in desktop, servers, graphics cards, game consoles and set-top box PD - 95858A IRF895 HEXFET Power MOSFET V DSS R DS(on) max I D 20V 8.3m:@V GS = V 8.9A
Applications Dual SO-8 MOSFET for POL converters in desktop, servers, graphics cards, game consoles and set-top box PD - 95858A IRF895 HEXFET Power MOSFET V DSS R DS(on) max I D 20V 8.3m:@V GS = V 8.9A
APPLICATION NOTE AN-009. GaN Essentials. AN-009: Bias Sequencing and Temperature Compensation for GaN HEMTs
 GaN Essentials AN-009: Bias Sequencing and Temperature Compensation for GaN HEMTs NITRONEX CORPORATION 1 OCTOBER 2008 GaN Essentials: Bias Sequencing and Temperature Compensation of GaN HEMTs 1. Table
GaN Essentials AN-009: Bias Sequencing and Temperature Compensation for GaN HEMTs NITRONEX CORPORATION 1 OCTOBER 2008 GaN Essentials: Bias Sequencing and Temperature Compensation of GaN HEMTs 1. Table
Long Loopstick Antenna
 Long Loopstick Antenna Wound on a 3 foot length of PVC pipe, the long loopstick antenna was an experiment to try to improve AM radio reception without using a long wire or ground. It works fairly well
Long Loopstick Antenna Wound on a 3 foot length of PVC pipe, the long loopstick antenna was an experiment to try to improve AM radio reception without using a long wire or ground. It works fairly well
Conventional Single-Switch Forward Converter Design
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Amplifier and Comparator Circuits > APP 3983 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Power-Supply Circuits
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Amplifier and Comparator Circuits > APP 3983 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Power-Supply Circuits
4/30/2012. General Class Element 3 Course Presentation. Circuit CoCircuit Componentsmponents. Subelement G6. 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups
 General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G6 Circuit Components 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3
General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G6 Circuit Components 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3
AE103 ELECTRONIC DEVICES & CIRCUITS DEC 2014
 Q.2 a. State and explain the Reciprocity Theorem and Thevenins Theorem. a. Reciprocity Theorem: If we consider two loops A and B of network N and if an ideal voltage source E in loop A produces current
Q.2 a. State and explain the Reciprocity Theorem and Thevenins Theorem. a. Reciprocity Theorem: If we consider two loops A and B of network N and if an ideal voltage source E in loop A produces current
4.5V to 32V Input High Current LED Driver IC For Buck or Buck-Boost Topology CN5816. Features: SHDN COMP OVP CSP CSN
 4.5V to 32V Input High Current LED Driver IC For Buck or Buck-Boost Topology CN5816 General Description: The CN5816 is a current mode fixed-frequency PWM controller for high current LED applications. The
4.5V to 32V Input High Current LED Driver IC For Buck or Buck-Boost Topology CN5816 General Description: The CN5816 is a current mode fixed-frequency PWM controller for high current LED applications. The
ML4818 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller
 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
PIEZOELECTRIC TRANSFORMER FOR INTEGRATED MOSFET AND IGBT GATE DRIVER
 1 PIEZOELECTRIC TRANSFORMER FOR INTEGRATED MOSFET AND IGBT GATE DRIVER Prasanna kumar N. & Dileep sagar N. prasukumar@gmail.com & dileepsagar.n@gmail.com RGMCET, NANDYAL CONTENTS I. ABSTRACT -03- II. INTRODUCTION
1 PIEZOELECTRIC TRANSFORMER FOR INTEGRATED MOSFET AND IGBT GATE DRIVER Prasanna kumar N. & Dileep sagar N. prasukumar@gmail.com & dileepsagar.n@gmail.com RGMCET, NANDYAL CONTENTS I. ABSTRACT -03- II. INTRODUCTION
Page 1 of 10. Introduction. Inductive Loads and Diode Protection
 Keywords: Digital output, high side switch, fast demag, fast demagnetization, safe demagnetization, free wheel diode, inductive load APPLICATION NOTE 6307 SWITCHING INDUCTIVE LOADS WITH SAFE DEMAGNETIZATION
Keywords: Digital output, high side switch, fast demag, fast demagnetization, safe demagnetization, free wheel diode, inductive load APPLICATION NOTE 6307 SWITCHING INDUCTIVE LOADS WITH SAFE DEMAGNETIZATION
IRF7821PbF. HEXFET Power MOSFET
 Applications l High Frequency Point-of-Load Synchronous Buck Converter for Applications in Networking & Computing Systems. l Lead-Free Benefits l Very Low R DS(on) at 4.5V V GS l Low Gate Charge l Fully
Applications l High Frequency Point-of-Load Synchronous Buck Converter for Applications in Networking & Computing Systems. l Lead-Free Benefits l Very Low R DS(on) at 4.5V V GS l Low Gate Charge l Fully
Chapter 3 HARD SWITCHED PUSH-PULL TOPOLOGY
 35 Chapter 3 HARD SWITCHED PUSH-PULL TOPOLOGY S.No. Name of the Sub-Title Page No. 3.1 Introduction 36 3.2 Single Output Push Pull Converter 36 3.3 Multi-Output Push-Pull Converter 37 3.4 Closed Loop Simulation
35 Chapter 3 HARD SWITCHED PUSH-PULL TOPOLOGY S.No. Name of the Sub-Title Page No. 3.1 Introduction 36 3.2 Single Output Push Pull Converter 36 3.3 Multi-Output Push-Pull Converter 37 3.4 Closed Loop Simulation
8 S1, D2. Storage Temperature Range Soldering Temperature, for 10 seconds 300 (1.6mm from case )
 Co-Pack Dual N-channel HEXFET Power MOSFET and Schottky Diode Ideal for Synchronous Buck DC-DC Converters Up to A Peak Output Low Conduction Losses Low Switching Losses Low Vf Schottky Rectifier D D 2
Co-Pack Dual N-channel HEXFET Power MOSFET and Schottky Diode Ideal for Synchronous Buck DC-DC Converters Up to A Peak Output Low Conduction Losses Low Switching Losses Low Vf Schottky Rectifier D D 2
3. PARALLELING TECHNIQUES. Chapter Three. high-power applications to achieve the desired output power with smaller size power
 3. PARALLELING TECHNIQUES Chapter Three PARALLELING TECHNIQUES Paralleling of converter power modules is a well-known technique that is often used in high-power applications to achieve the desired output
3. PARALLELING TECHNIQUES Chapter Three PARALLELING TECHNIQUES Paralleling of converter power modules is a well-known technique that is often used in high-power applications to achieve the desired output
Positive to Negative Buck-Boost Converter Using LM267X SIMPLE SWITCHER Regulators
 Positive to Negative Buck-Boost Converter Using LM267X SIMPLE SWITCHER Regulators Abstract The 3rd generation Simple Switcher LM267X series of regulators are monolithic integrated circuits with an internal
Positive to Negative Buck-Boost Converter Using LM267X SIMPLE SWITCHER Regulators Abstract The 3rd generation Simple Switcher LM267X series of regulators are monolithic integrated circuits with an internal
A simple and compact high-voltage switch mode power supply for streak cameras
 Meas. Sci. Technol. 7 (1996) 1668 1672. Printed in the UK DESIGN NOTE A simple and compact high-voltage switch mode power supply for streak cameras M Shukla, V N Rai and H C Pant Laser Plasma Group, Center
Meas. Sci. Technol. 7 (1996) 1668 1672. Printed in the UK DESIGN NOTE A simple and compact high-voltage switch mode power supply for streak cameras M Shukla, V N Rai and H C Pant Laser Plasma Group, Center
Keywords: No-opto flyback, synchronous flyback converter, peak current mode controller
 Keywords: No-opto flyback, synchronous flyback converter, peak current mode controller APPLICATION NOTE 6394 HOW TO DESIGN A NO-OPTO FLYBACK CONVERTER WITH SECONDARY-SIDE SYNCHRONOUS RECTIFICATION By:
Keywords: No-opto flyback, synchronous flyback converter, peak current mode controller APPLICATION NOTE 6394 HOW TO DESIGN A NO-OPTO FLYBACK CONVERTER WITH SECONDARY-SIDE SYNCHRONOUS RECTIFICATION By:
MICROCONTROLLER BASED THREE PHASE INVERTER Project index: PRJ 012
 MICROCONTROLLER BASED THREE PHASE INVERTER Project index: PRJ 012 By SANG GIDEON KIPCHIRCHIR F17/2161/2004 Supervisor: Dr.-Ing. W. Mwema Examiner: Mr. Ogaba OBJECTIVE INTRODUCTION This project presents
MICROCONTROLLER BASED THREE PHASE INVERTER Project index: PRJ 012 By SANG GIDEON KIPCHIRCHIR F17/2161/2004 Supervisor: Dr.-Ing. W. Mwema Examiner: Mr. Ogaba OBJECTIVE INTRODUCTION This project presents
5.0V 5.0V. 20µs PULSE WIDTH Tj = 25 C. Tj = 150 C. V DS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V) T J = 150 C 1.5. V GS, Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
 9MT050XF "FULL-BRIDGE" FREDFET MTP HEXFET Power MOSFET Features Low On-Resistance High Performance Optimised Built-in Fast Recovery Diodes Fully Characterized Capacitance and Avalanche Voltage and Current
9MT050XF "FULL-BRIDGE" FREDFET MTP HEXFET Power MOSFET Features Low On-Resistance High Performance Optimised Built-in Fast Recovery Diodes Fully Characterized Capacitance and Avalanche Voltage and Current
Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: / N
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Gate drive card converts logic level turn on/off commands. Gate Drive Card for High Power Three Phase PWM Converters. Engineer R&D
 Gate Drive Card for High Power Three Phase PWM Converters 1 Anil Kumar Adapa Engineer R&D Medha Servo Drive Pvt. Ltd., India Email: anilkumaradapa@gmail.com Vinod John Department of Electrical Engineering
Gate Drive Card for High Power Three Phase PWM Converters 1 Anil Kumar Adapa Engineer R&D Medha Servo Drive Pvt. Ltd., India Email: anilkumaradapa@gmail.com Vinod John Department of Electrical Engineering
Features. +12V to +36V MIC nf. High-Side Driver with Overcurrent Trip and Retry
 MIC0 MIC0 High-Speed High-Side MOSFET Driver General Description The MIC0 high-side MOSFET driver is designed to operate at frequencies up to 00kHz (khz PWM for % to 00% duty cycle) and is an ideal choice
MIC0 MIC0 High-Speed High-Side MOSFET Driver General Description The MIC0 high-side MOSFET driver is designed to operate at frequencies up to 00kHz (khz PWM for % to 00% duty cycle) and is an ideal choice
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Power Semiconductor Devices
 TRADEMARK OF INNOVATION Power Semiconductor Devices Introduction This technical article is dedicated to the review of the following power electronics devices which act as solid-state switches in the circuits.
TRADEMARK OF INNOVATION Power Semiconductor Devices Introduction This technical article is dedicated to the review of the following power electronics devices which act as solid-state switches in the circuits.
Current-mode PWM controller
 DESCRIPTION The is available in an 8-Pin mini-dip the necessary features to implement off-line, fixed-frequency current-mode control schemes with a minimal external parts count. This technique results
DESCRIPTION The is available in an 8-Pin mini-dip the necessary features to implement off-line, fixed-frequency current-mode control schemes with a minimal external parts count. This technique results
LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator
 LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator INTRODUCTION The LM125 is a precision, dual, tracking, monolithic voltage regulator. It provides separate positive and negative regulated outputs, thus simplifying
LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator INTRODUCTION The LM125 is a precision, dual, tracking, monolithic voltage regulator. It provides separate positive and negative regulated outputs, thus simplifying
Type Ordering Code Package TDA Q67000-A5066 P-DIP-8-1
 Control IC for Switched-Mode Power Supplies using MOS-Transistor TDA 4605-3 Bipolar IC Features Fold-back characteristics provides overload protection for external components Burst operation under secondary
Control IC for Switched-Mode Power Supplies using MOS-Transistor TDA 4605-3 Bipolar IC Features Fold-back characteristics provides overload protection for external components Burst operation under secondary
Dr.Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth Class. Commutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-I
 Commutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-I ١ This lesson provides the reader the following: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Requirements to be satisfied for the successful turn-off of a SCR The turn-off groups
Commutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-I ١ This lesson provides the reader the following: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Requirements to be satisfied for the successful turn-off of a SCR The turn-off groups
V DSS R DS(on) max Qg (typ.) 60V GS = 10V 24nC
 Applications l Synchronous Rectifier MOSFET for Isolated DC-DC Converters l Low Power Motor Drive Systems PD - 97436 IRF735PbF HEXFET Power MOSFET V DSS R DS(on) max Qg (typ.) 60V 7.8mΩ@V GS = 0V 24nC
Applications l Synchronous Rectifier MOSFET for Isolated DC-DC Converters l Low Power Motor Drive Systems PD - 97436 IRF735PbF HEXFET Power MOSFET V DSS R DS(on) max Qg (typ.) 60V 7.8mΩ@V GS = 0V 24nC
Ordering Information Base part number Package Type Standard Pack Complete Part Form Quantity Number IRFB7437PbF TO-220 Tube 50 IRFB7437PbF
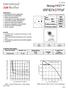 R DS (on), Drain-to -Source On Resistance (m ) I D, Drain Current (A) Applications l Brushed Motor drive applications l BLDC Motor drive applications l Battery powered circuits l Half-bridge and full-bridge
R DS (on), Drain-to -Source On Resistance (m ) I D, Drain Current (A) Applications l Brushed Motor drive applications l BLDC Motor drive applications l Battery powered circuits l Half-bridge and full-bridge
Testing and Stabilizing Feedback Loops in Today s Power Supplies
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, open loop transfer function, voltage loop gain, error amplifier,
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, open loop transfer function, voltage loop gain, error amplifier,
AUTOMOTIVE MOSFET. I D = 140A Fast Switching
 IRF3808 AUTOMOTIVE MOSFET Typical Applications HEXFET Power MOSFET Integrated Starter Alternator D 42 Volts Automotive Electrical Systems V DSS = 75V Benefits Advanced Process Technology R DS(on) = 0.007Ω
IRF3808 AUTOMOTIVE MOSFET Typical Applications HEXFET Power MOSFET Integrated Starter Alternator D 42 Volts Automotive Electrical Systems V DSS = 75V Benefits Advanced Process Technology R DS(on) = 0.007Ω
Experiment DC-DC converter
 POWER ELECTRONIC LAB Experiment-7-8-9 DC-DC converter Power Electronics Lab Ali Shafique, Ijhar Khan, Dr. Syed Abdul Rahman Kashif 10/11/2015 This manual needs to be completed before the mid-term examination.
POWER ELECTRONIC LAB Experiment-7-8-9 DC-DC converter Power Electronics Lab Ali Shafique, Ijhar Khan, Dr. Syed Abdul Rahman Kashif 10/11/2015 This manual needs to be completed before the mid-term examination.
Revised April Unit/Standard Number. Proficiency Level Achieved: (X) Indicates Competency Achieved to Industry Proficiency Level
 Unit/Standard Number Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of state,
Unit/Standard Number Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of state,
Vishay Siliconix AN724 Designing A High-Frequency, Self-Resonant Reset Forward DC/DC For Telecom Using Si9118/9 PWM/PSM Controller.
 AN724 Designing A High-Frequency, Self-Resonant Reset Forward DC/DC For Telecom Using Si9118/9 PWM/PSM Controller by Thong Huynh FEATURES Fixed Telecom Input Voltage Range: 30 V to 80 V 5-V Output Voltage,
AN724 Designing A High-Frequency, Self-Resonant Reset Forward DC/DC For Telecom Using Si9118/9 PWM/PSM Controller by Thong Huynh FEATURES Fixed Telecom Input Voltage Range: 30 V to 80 V 5-V Output Voltage,
Status Report on Time and Frequency Activities at CSIR-NPL India
 Status Report on Time and Frequency Activities at CSIR-NPL India (APMP -TCTF 2016) S. Panja, A. Agarwal, D. Chadha, P. Arora, P. Thorat, S. De, S. Yadav, P. Kandpal, M. P. Olaniya and V. N. Ojha (Da Nang,
Status Report on Time and Frequency Activities at CSIR-NPL India (APMP -TCTF 2016) S. Panja, A. Agarwal, D. Chadha, P. Arora, P. Thorat, S. De, S. Yadav, P. Kandpal, M. P. Olaniya and V. N. Ojha (Da Nang,
FSFR-XS Series Fairchild Power Switch (FPS ) for Half-Bridge Resonant Converters
 February 203 FSFR-XS Series Fairchild Power Switch (FPS ) for Half-Bridge Resonant Converters Features Variable Frequency Control with 50% Duty Cycle for Half-Bridge Resonant Converter Topology High Efficiency
February 203 FSFR-XS Series Fairchild Power Switch (FPS ) for Half-Bridge Resonant Converters Features Variable Frequency Control with 50% Duty Cycle for Half-Bridge Resonant Converter Topology High Efficiency
CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION
 168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
Designers Series XII. Switching Power Magazine. Copyright 2005
 Designers Series XII n this issue, and previous issues of SPM, we cover the latest technologies in exotic high-density power. Most power supplies in the commercial world, however, are built with the bread-and-butter
Designers Series XII n this issue, and previous issues of SPM, we cover the latest technologies in exotic high-density power. Most power supplies in the commercial world, however, are built with the bread-and-butter
NJM3777 DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER NJM3777E3(SOP24)
 DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The NJM3777 is a switch-mode (chopper), constant-current driver with two channels: one for each winding of a two-phase stepper motor. The NJM3777 is equipped
DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The NJM3777 is a switch-mode (chopper), constant-current driver with two channels: one for each winding of a two-phase stepper motor. The NJM3777 is equipped
High Current Amplifier
 High Current Amplifier - Introduction High Current Amplifier High current amplifier is often a very useful piece of instrument to have in the lab. It is very handy for increasing the current driving capability
High Current Amplifier - Introduction High Current Amplifier High current amplifier is often a very useful piece of instrument to have in the lab. It is very handy for increasing the current driving capability
Presentation Content Review of Active Clamp and Reset Technique in Single-Ended Forward Converters Design Material/Tools Design procedure and concern
 Active Clamp Forward Converters Design Using UCC2897 Hong Huang August 2007 1 Presentation Content Review of Active Clamp and Reset Technique in Single-Ended Forward Converters Design Material/Tools Design
Active Clamp Forward Converters Design Using UCC2897 Hong Huang August 2007 1 Presentation Content Review of Active Clamp and Reset Technique in Single-Ended Forward Converters Design Material/Tools Design
HIGH POWER DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 MILPRF8 CERTIFIED M.S.KENNEDY CORP. HIGH POWER DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER 707 Dey Road Liverpool, N.Y. 088 () 7067 FEATURES: Space Efficient Dual Power Amplifier Low Cost High oltage Operation: 0 Low Quiescent
MILPRF8 CERTIFIED M.S.KENNEDY CORP. HIGH POWER DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER 707 Dey Road Liverpool, N.Y. 088 () 7067 FEATURES: Space Efficient Dual Power Amplifier Low Cost High oltage Operation: 0 Low Quiescent
CPC1590 Application Technical Information
 Application Note: AN- CPC59 Application Technical Information AN--R www.ixysic.com AN- Using the CPC59 Isolated Gate Driver IC The CPC59 is an excellent choice for remote switching of DC and low frequency
Application Note: AN- CPC59 Application Technical Information AN--R www.ixysic.com AN- Using the CPC59 Isolated Gate Driver IC The CPC59 is an excellent choice for remote switching of DC and low frequency
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A
 Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
DC-DC Resonant converters with APWM control
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) ISSN: 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 5 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 43-49 DC-DC Resonant converters with APWM control Preeta John 1 Electronics Department,
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) ISSN: 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 5 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 43-49 DC-DC Resonant converters with APWM control Preeta John 1 Electronics Department,
UNDERSTANDING HORIZONTAL OUTPUT STAGES OF COMPUTER MONITORS
 UNDERSTANDING HORIZONTAL OUTPUT STAGES OF COMPUTER MONITORS Today's computer, medical, security, design and industrial video display monitors operate at a host of different horizontal resolutions or scanning
UNDERSTANDING HORIZONTAL OUTPUT STAGES OF COMPUTER MONITORS Today's computer, medical, security, design and industrial video display monitors operate at a host of different horizontal resolutions or scanning
NPLI Report. for. Technical workshop and inter-laboratory comparison exercise for GPS time-transfer and calibration techniques under MEDEA
 NPLI Report for Technical workshop and inter-laboratory comparison exercise for GPS time-transfer and calibration techniques under MEDEA Dr. V. N. Ojha, Dr. A. Agarwal, Mrs. D. Chaddha, Dr. S. Panja, Dr.
NPLI Report for Technical workshop and inter-laboratory comparison exercise for GPS time-transfer and calibration techniques under MEDEA Dr. V. N. Ojha, Dr. A. Agarwal, Mrs. D. Chaddha, Dr. S. Panja, Dr.
EXP 9 ESR (Electron Spin Resonance)
 EXP 9 ESR (Electron Spin Resonance) Introduction ESR in Theory The basic setup for electron spin resonance is shown in Fig 1. A test sample is placed in a uniform magnetic field. The sample is also wrapped
EXP 9 ESR (Electron Spin Resonance) Introduction ESR in Theory The basic setup for electron spin resonance is shown in Fig 1. A test sample is placed in a uniform magnetic field. The sample is also wrapped
SMPS MOSFET. V DSS Rds(on) max I D
 Applications Switch Mode Power Supply ( SMPS ) Uninterruptable Power Supply High speed power switching Lead-Free Benefits Low Gate Charge Qg results in Simple Drive Requirement Improved Gate, Avalanche
Applications Switch Mode Power Supply ( SMPS ) Uninterruptable Power Supply High speed power switching Lead-Free Benefits Low Gate Charge Qg results in Simple Drive Requirement Improved Gate, Avalanche
LD7889A 3/29/ Channel LED Backlight Driver. General Description. Features. Applications. Typical Application REV: 00
 3/29/2012 4-Channel LED Backlight Driver REV: 00 General Description The LD7889A is a 4-channel linear current controller which combines with a boost switching controller. It s an ideal solution for driving
3/29/2012 4-Channel LED Backlight Driver REV: 00 General Description The LD7889A is a 4-channel linear current controller which combines with a boost switching controller. It s an ideal solution for driving
Ametek, Inc. Rotron Technical Products Division. 100 East Erie St., Suite 200 Kent, Ohio User's Guide. Number Revision F
 Ametek, Inc. Rotron Technical Products Division 100 East Erie St., Suite 200 Kent, Ohio 44240 User's 120 Volt, 800 Watt and 240 Volt, 1200 Watt Brushless Motor Drive Electronics 5.7" (145 mm) and 7.2"
Ametek, Inc. Rotron Technical Products Division 100 East Erie St., Suite 200 Kent, Ohio 44240 User's 120 Volt, 800 Watt and 240 Volt, 1200 Watt Brushless Motor Drive Electronics 5.7" (145 mm) and 7.2"
Revised April Unit/Standard Number. High School Graduation Years 2016, 2017 and 2018
 Unit/Standard Number High School Graduation Years 2016, 2017 and 2018 Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100
Unit/Standard Number High School Graduation Years 2016, 2017 and 2018 Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP 15.0303 Task Grid Secondary Competency Task List 100
Study of the Long Term Performance on the Calibration Data of the Coaxial Thermistor Mounts up to 18 GHz
 Study MAPAN of the - Journal Long Term of Metrology Performance Society on of the India, Calibration Vol. 3, Data No., of 008; the Coaxial pp. 71-78 Thermistor Mounts up to 18 GHz Study of the Long Term
Study MAPAN of the - Journal Long Term of Metrology Performance Society on of the India, Calibration Vol. 3, Data No., of 008; the Coaxial pp. 71-78 Thermistor Mounts up to 18 GHz Study of the Long Term
C Soldering Temperature, for 10 seconds 300 (1.6mm from case ) Mounting Torque, 6-32 or M3 screw 1.1 (10) N m (lbf in)
 Typical Applications l Industrial Motor Drive Features l Advanced Process Technology l Ultra Low On-Resistance l 175 C Operating Temperature l Fast Switching l Repetitive Avalanche Allowed up to Tjmax
Typical Applications l Industrial Motor Drive Features l Advanced Process Technology l Ultra Low On-Resistance l 175 C Operating Temperature l Fast Switching l Repetitive Avalanche Allowed up to Tjmax
IRF3808S IRF3808L HEXFET Power MOSFET
 Typical Applications Integrated Starter Alternator 42 Volts Automotive Electrical Systems Benefits Advanced Process Technology Ultra Low On-Resistance Dynamic dv/dt Rating G 175 C Operating Temperature
Typical Applications Integrated Starter Alternator 42 Volts Automotive Electrical Systems Benefits Advanced Process Technology Ultra Low On-Resistance Dynamic dv/dt Rating G 175 C Operating Temperature
LD /01/2013. Boost Controller for LED Backlight. General Description. Features. Applications. Typical Application REV: 00
 04/01/2013 Boost Controller for LED Backlight REV: 00 General Description The LD5861 is a wide-input asynchronous current mode boost controller, capable to operate in the range between 9V and 28V and to
04/01/2013 Boost Controller for LED Backlight REV: 00 General Description The LD5861 is a wide-input asynchronous current mode boost controller, capable to operate in the range between 9V and 28V and to
A New Class of Resonant Discharge Drive Topology for Switched Reluctance Motor
 A New Class of Resonant Discharge Drive Topology for Switched Reluctance Motor M. Asgar* and E. Afjei** Downloaded from ijeee.iust.ac.ir at : IRDT on Tuesday May 8th 18 Abstract: Switched reluctance motor
A New Class of Resonant Discharge Drive Topology for Switched Reluctance Motor M. Asgar* and E. Afjei** Downloaded from ijeee.iust.ac.ir at : IRDT on Tuesday May 8th 18 Abstract: Switched reluctance motor
IRF6646 DirectFET Power MOSFET
 Typical R DS(on) (Ω) V GS, Gate-to-Source Voltage (V) l RoHS compliant containing no lead or bromide l Low Profile (
Typical R DS(on) (Ω) V GS, Gate-to-Source Voltage (V) l RoHS compliant containing no lead or bromide l Low Profile (
High Performance ZVS Buck Regulator Removes Barriers To Increased Power Throughput In Wide Input Range Point-Of-Load Applications
 WHITE PAPER High Performance ZVS Buck Regulator Removes Barriers To Increased Power Throughput In Wide Input Range Point-Of-Load Applications Written by: C. R. Swartz Principal Engineer, Picor Semiconductor
WHITE PAPER High Performance ZVS Buck Regulator Removes Barriers To Increased Power Throughput In Wide Input Range Point-Of-Load Applications Written by: C. R. Swartz Principal Engineer, Picor Semiconductor
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics
 B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
Many applications. Mismatched Load Characterization for High-Power RF Amplifiers PA CHARACTERIZATION. This article discusses the
 From April 2004 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2004 Summit Technical Media, LLC Mismatched Load Characterization for High-Power RF Amplifiers By Richard W. Brounley, P.E. Brounley Engineering Many
From April 2004 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2004 Summit Technical Media, LLC Mismatched Load Characterization for High-Power RF Amplifiers By Richard W. Brounley, P.E. Brounley Engineering Many
High Current MOSFET Toggle Switch with Debounced Push Button
 Set/Reset Flip Flop This is an example of a set/reset flip flop using discrete components. When power is applied, only one of the transistors will conduct causing the other to remain off. The conducting
Set/Reset Flip Flop This is an example of a set/reset flip flop using discrete components. When power is applied, only one of the transistors will conduct causing the other to remain off. The conducting
Learn about the use, operation and limitations of thyristors, particularly triacs, in power control
 Exotic Triacs: The Gate to Power Control Learn about the use, operation and limitations of thyristors, particularly triacs, in power control D. Mohan Kumar Modern power control systems use electronic devices
Exotic Triacs: The Gate to Power Control Learn about the use, operation and limitations of thyristors, particularly triacs, in power control D. Mohan Kumar Modern power control systems use electronic devices
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. Subject Code: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 Subject Code: 17215 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Subject Code: 17215 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
High Voltage Pulser Circuits By Ching Chu, Sr. Applications Engineer
 High Voltage Circuits By Ching Chu, Sr. Applications Engineer AN-H53 Application Note Introduction The high voltage pulser circuit shown in Figure 1 utilizes s complementary P- and N-channel transistors
High Voltage Circuits By Ching Chu, Sr. Applications Engineer AN-H53 Application Note Introduction The high voltage pulser circuit shown in Figure 1 utilizes s complementary P- and N-channel transistors
Operation and Maintenance Manual
 WeiKedz 0-30V 2mA-3A Adjustable DC Regulated Power Supply DIY Kit Operation and Maintenance Manual The WeiKedz Adjustable DC Regulated Power Supply provides continuously variable output voltage between
WeiKedz 0-30V 2mA-3A Adjustable DC Regulated Power Supply DIY Kit Operation and Maintenance Manual The WeiKedz Adjustable DC Regulated Power Supply provides continuously variable output voltage between
Features. RAMP Feed Forward Ramp/ Volt Sec Clamp Reference & Isolation. Voltage-Mode Half-Bridge Converter CIrcuit
 MIC3838/3839 Flexible Push-Pull PWM Controller General Description The MIC3838 and MIC3839 are a family of complementary output push-pull PWM control ICs that feature high speed and low power consumption.
MIC3838/3839 Flexible Push-Pull PWM Controller General Description The MIC3838 and MIC3839 are a family of complementary output push-pull PWM control ICs that feature high speed and low power consumption.
Power MOSFET FEATURES. IRF510PbF SiHF510-E3 IRF510 SiHF510. PARAMETER SYMBOL LIMIT UNIT Drain-Source Voltage V DS 100 V Gate-Source Voltage V GS ± 20
 Power MOSFET PRODUCT SUMMARY V DS (V) 100 R DS(on) (Ω) = 10 V 0.54 Q g (Max.) (nc) 8.3 Q gs (nc) 2.3 Q gd (nc) 3.8 Configuration Single FEATURES Dynamic dv/dt Rating Repetitive Avalanche Rated 175 C Operating
Power MOSFET PRODUCT SUMMARY V DS (V) 100 R DS(on) (Ω) = 10 V 0.54 Q g (Max.) (nc) 8.3 Q gs (nc) 2.3 Q gd (nc) 3.8 Configuration Single FEATURES Dynamic dv/dt Rating Repetitive Avalanche Rated 175 C Operating
CHAPTER 4 MODIFIED H- BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER USING MPD-SPWM TECHNIQUE
 58 CHAPTER 4 MODIFIED H- BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER USING MPD-SPWM TECHNIQUE 4.1 INTRODUCTION Conventional voltage source inverter requires high switching frequency PWM technique to obtain a quality output
58 CHAPTER 4 MODIFIED H- BRIDGE MULTILEVEL INVERTER USING MPD-SPWM TECHNIQUE 4.1 INTRODUCTION Conventional voltage source inverter requires high switching frequency PWM technique to obtain a quality output
StrongIRFET IRFB7546PbF
 I D, Drain Current (A) StrongIRFET Application Brushed Motor drive applications BLDC Motor drive applications Battery powered circuits Half-bridge and full-bridge topologies Synchronous rectifier applications
I D, Drain Current (A) StrongIRFET Application Brushed Motor drive applications BLDC Motor drive applications Battery powered circuits Half-bridge and full-bridge topologies Synchronous rectifier applications
