ITER Vacuum Vessel Supports
|
|
|
- Christian Watkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ITER Vacuum Vessel Supports Intermediate report Contract EFDA ENEA n 07/ Andrea Capriccioli FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 1 of 49
2 Outline Abstract pag.3 1. Forces evaluation pag.4 2. VV supports actual design pag.6 2.a) Forces evaluation; 2.b) Sizes and degrees of freedom; 2.c) Toroidal restraint system; 3. Vertical Supports alternative solutions pag.11 3.a) flexible plates; 3.b) pendulum W7-X style 3.c) connection rods Ignitor style 4. Toroidal Supports alternative solutions pag.25 4.a) pendulum W7-X style.; 4.b) central guide; 4.c) flexible plates. 5. Clamping sleeves Kostyrka pag Conclusions pag.34 References Appendix 1 (AGOM pot bearings) Appendix 2 (Alternative solution: connection rods and flexible plates) pag.35 pag.36 pag.47 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 2 of 49
3 Abstract In the ITER experimental Tokamak reactor, high currents flow in the Vacuum Vessel (VV) during Plasma disruptions. The interaction between these currents and the toroidal-poloidal magnetic field produces high local forces. The direction of the electromagnetic forces acting on the VV can be upward or downward, while horizontal net force arises from the plasma tilting: their combination with the VV dead weight gives resultants both in vertical (up or downward) and horizontal directions. The VV supports have to withstand all these forces, allowing only the slow radial displacements due to the thermal expansion. Other local forces appear around the ports (discontinuities in the VV shell) during the pulse: these last forces have null resultant but produce local moments and ports distortions. The present work includes the evaluation of the reference design (see also the presentation in the VV DR meeting in Cadarache on the 28 th June 2007). As a consequence of the previous activity, alternative proposals will be evaluated: the main differences consist in bidirectional vertical supports (working in up/down directions) and in metallic components (avoiding elastomers or in general organic materials). In this case there are no problems with radiations, temperature, vacuum conditions. In the present work a first identification and a preliminary analysis of the proposed alternative solutions have been performed. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 3 of 49
4 1. Forces evaluation The total downward force on the VV supports, due to the weight, results equal to 90 MN; The electromagnetic upward forces during VDE (III) result [1]: total VDE vertical force : 60 MN (by ampl. fact. 1.1; asymmetry peak = 2 MN) total VDE net horizontal force: 20 MN (by ampl. fact. 1.7; application point 11 m) The force on the VV vertical support n 3 closest to the peak of the vertical force results MN downward due to the vertical forces only. The total net horizontal force results 20 MN, Supp. n 1 20 MN Fz1 n 2 Fz m 12 m 40 n 3 Fz m 9.96 m 13 m Fz4 n 4 Fz5 n 5 90 rotated with respect to the max vertical peak (see the figure on the right side). In this case the max vertical (z) upward contribution, due to the net horizontal force, results: 2*Fz1*12 + 2*Fz2* *Fz3* *Fz4* Fz5*13 = 20*11*1.7 Fz1=0.92 * Fz5 Fz2=0.50 * Fz5 Fz3=0.17 * Fz5 Fz4=0.77 * Fz5 2*Fz1 + 2*Fz2 = 2*Fz3 + 2*Fz4 + Fz5 Fz5 = 6.5 MN Fz3 = 0.17*6.5 MN = 1.1 MN upward. Finally, for the upward disruptions: on each n 3 supports (3+symmetric) the total force results: = 0.3 MN downward and on the n 5 support the total force results : = 4.1 MN upward FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 4 of 49
5 For the downward disruptions we have to add the dead weight and the total vertical force of 72 MN downward [1]. If the same vertical amplification and the peak factors are applied, we obtain a vertical force equal to /9 * = 20.8 MN downward. In this case the application point of the net horizontal force (25 MN) is not clear and it isn t possible to calculate its contribution to the vertical compression. A reference value of 22 MN can be assumed as first approximation. Summarizing, the VV supports must bear vertical forces from 4.1 MN upward to 22 MN downward. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 5 of 49
6 2. VV supports actual design 2.a) Materials TEFLON Teflon is the DuPont trade name (PTFE: Poli Tetra Fluorine Ethylene ) and/or Fiberslip: are material typically used when the radiation dose results lower then rad (DOE Handbook Design Considerations April 1999). In ITER a peak dose to the pad of rad is estimated (to be carefully checked). If higher doses would occur additional shields could be necessary (Teflon/Fiberslip contains Fluorine and under radiation could produce sulphuric acid if Oxygen or Hydrogen are present). NEOPRENE Neoprene is the DuPont Performance Elastomers trade name for a family of synthetic rubbers based on polychloroprene. On the market several types of rubber insulators/ supports are available (see figures next page AGOM company only for example). These kind of bearings can carry very high loads (>50 MN) and are designed for combined vertical plus horizontal loads ( 15% of the max vertical load). Rotations ±0.01 radiant are also allowed. The average contact pressure should be less than 20 N/mm2 with max value 40 MPa. The ITER VV dead weight results about 10 MN per support and a diameter of 800 mm is enough to take only this load. If the VDE downward vertical forces are considered (VDE III Slow) the compression can reaches 22 MN (see Chapter 2. Forces evaluation). In this case the diameter should be 1.5 m. In Appendix 1 the AGOM pot bearing catalog and technical data sheet are reported. Both Teflon and Neoprene could need of an active temperature control. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 6 of 49
7 [1] Design Description Document -DDD15- Vacuum Vessel - September Pag.107 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 7 of 49
8 2.b) Sizes and degrees of freedom The limit seems to be the maximum pressure ( 40 MPa) on the Neoprene: this involves large dimensions of the pot bearings. The first solution could be to double the number of supports. In this last hypothesis, the diameter of each support results close to 1 m (1.5/ 2). About the degrees of freedom, in a cylindrical reference system, the slow radial VV thermal expansion must be guaranteed; all the other displacements (toroidal, axial and fast radial too) should be restrained. The elements in order to assure this task are the VV supports: they should have a bilateral behavior (up/down effect in vertical direction). To obtain a bilateral behavior of the actual vertical supports, groups of ropes without preload were used. But the preload is necessary because, when an upward disruption occurs (4.1 MN upward), a detachment with the consequent impact between VV feet and bearing pads will increase the local pressure on the Teflon and Neoprene pads. This behavior is generally avoided using preloaded systems. In this case it s possible to preload the ropes without influence on the bearing pads; the rough sketch shows an example of possible solutions [3]: INCONEL SA-637 Gr The point is that the ropes preloading is practically equivalent to rigid rods (easier and chipper). ASTM A453 Gr A more efficient system could be the use of dumpers, instead of ropes or rods. The only note regards the absence of a vertical displacement amplification. It should be necessary to verify the pressure transient on the bearing pads during the VDEs and increase the dampers efficiency, with the same system used for the radial restraints (vert.+hor.levers see the figure below). Preloading system: some examples (wedges; thread link) FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 8 of 49
9 Other point is the radial arm configuration: Bearing Radial arm Vertical ropes Horizontal lever Vertical link Vertical lever - the radial arm is subjected to bending (at least a spherical joint is necessary); - the radial arm cooperates with the toroidal restraints against rotations around a local vertical axis. To make free the radial arm from the vertical rotations also, it s necessary a design review linking the support with the horizontal lever through two spherical joints. Dampers The first intermediate conclusion of the previous evaluation is the adequacy of the sliding bearing pads and the neoprene use to the ITER compression loads. The limit seems to be the size necessary to place the bearing pads themselves and the systems to avoid VV vertical displacements during upward VDE. A minor change regards the introduction of two spherical joints in the radial arm connection between VV and horizontal lever. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 9 of 49
10 2.c) Toroidal restraint system In the actual design a couple of toroidal restraints are added under each lower port. This configuration, where the port is placed between two elements, seems to be particularly critical. The main reason is the possibility to reach the seizing in some conditions (port thermal expansion, vertical displacements, influence on the vertical reaction forces, port rotations, etc.). The seizing of only one port can lead the whole VV to lose its central position and to increase the bending stress on the perpendicular ports. Only large tolerances could avoid the seizing probability, leaving the VV free to move radially yet. The possibility to change with continuity the toroidal stiffness of the restraint system (in this case through the vertical displacement of the VV) is an element that can be preserved with other systems, without the disadvantages shown in actual solution. The toroidal restraint systems that seem to fit well with actual geometry are both the central rail and the pendulum solutions. With both the previous systems it s possible to change the stiffness with continuity and a brief explanation will be presented in the second part of the present document (see Chapter 4). FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 10 of 49
11 3. Vertical Supports alternative solutions Three alternative solutions were analyzed, as first approximation (the radial restraint against fast horizontal forces remains necessary for all; only the introduction of two spherical joints between the radial arm and the horizontal lever is required). Flexible plates for vertical and toroidal supports The first alternative solution is the use of flexible plates both as vertical and toroidal restraint. A brief parametric analysis is shown in Tab.1 next page. The first results seem not to exclude the possibility of vertical plates with a total height lower than 1000 mm. Other structural analyses are necessary to take into account all the loads and/or displacements. The second alternative solution is the use of spherical joints both for vertical and toroidal restraint (type W7-X). Some analyses were performed, but other analyses are necessary to verify if 9 vertical supports are enough to support the vertical reference max load (22 MN downward). For the toroidal restraint with spherical joints no analyses were performed (no problems seem to be). Spherical joints for vertical and toroidal supports The third alternative is the use of Connection roads (type Ignitor) for the vertical supports and flexible plates (or central guide) for the toroidal restraint. Some analyses were performed and the results are shown in the following pages. Connection rods and flexible plates or central guides FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 11 of 49
12 3.a) flexible plates FPN FUSTEC Frascati, 10 August 2007 Tab.1 Plates thicknesses [mm] Net height (Total=Net+300 mm) N of plates / total width Max SEQV [MPa] * F=22 MN; rad displ=40 mm Radial Reaction Force [MN] full support (40 mm) 24/ / / 220 (tot: 345) / / / 269 (tot: 422) / / / 295 (tot: 454) / / / 304 (tot: 461) Common tangential length = 950 mm Gap between plates =10 mm NO VDE TANGENTIAL FORCES NO MOMENTS (around Vertical and Toroidal axes) NO Buckilng *UX >< 0 (if UX=0 stress picks are present at the 4 corners: for example ) Tick.2 Tick.1 Loaded elements FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 12 of 49 X Grounded or fixed elements
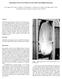
13 3.b) pendulum W7-X style The pendulum system in the W7-X reactor was possible because the vertical supports constrain only vertical displacements (downward). The W7-X Plasma Vessel is free to move on the horizontal plane, both with the previous plane sliding design and the actual spherical pendulum system. As result of this, an auto centering system (ACS) was possible as the easiest way to leave the PV free to expand, keeping its centre. It s to note that, with the selected vertical supports, a rotation of all the PV around the vertical axis, can be allowed. Another important point is the absence of electromagnetic forces on the PV: the dimensioning of the ACS was performed to balance the forces from the vertical supports friction coeff. and the elastic reaction of the connections (bellows) between PV and Cryostat. In case of not sliding vertical supports, the only free degree of freedom is the radial one (in a cylindrical ref. sys.). This means that a toroidal pendulum system (with the stiffness necessary to withstand the VDE forces) goes in contrast with the vertical ones. For this reason the toroidal pendulum system is compatible only with the spherical vertical supports (or, in general, with sliding supports). The analysis of this last type of supports is not part of the present document but a first dimensioning step is reported in the next pages. Only for example purpose, the figures below show the pendulum system (only for compression forces): Spherical joint: inner pendulum plus external shells (total height remains 780 mm) FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 13 of 49
14 Inner pendulum: the diameter of the two spherical joints is 400 mm and the height of the cylinder connecting the two half spheres, is 210mm. View of the inner spherical side of the lower pendulum support: In the following pages preliminary stress analysis results are reported. The aim of the analysis is only a first evaluation of the stresses level and the reaction friction forces. A further detailed analysis with the real maximum acceptable dimensions should be necessary. Basic point is the right definition of the friction coefficient between the two half parts of each spherical joint, to minimize the reaction friction forces: in this case the conservative value of 0.2 was set. As preliminary result, a double number of supports could be the first feasible solution. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 14 of 49
15 The max SEQV stress results of 738 MPa, with this dimensions: to decrease the maximum value it should be necessary to increase the diameter of the cylindrical connection and the total height of the joint. This last point it s also necessary to insert the other halves of spheres to give a bilateral behavior to the joint itself. The following figures show the system sliding (with a friction factor = 0.2) under the VV dead weight, as vertical load, and a radial displacements of 1 mm. The reaction force due to the friction between inner spheres and outer spherical housings results now about 3 MN (per each vertical support). In this case, the max SEQV results about 370 MPa in the cylindrical connection (see the two figures below). FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 15 of 49
16 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 16 of 49
17 3.c) connection rods Ignitor style A general support scheme, designed for Ignitor reactor, is shown in fig 1 and the cross (a) and longitudinal (b) sections are shown in fig.2: only one sector 174 mm width is visible in the section (b). The total number of sectors will be defined on the basis of the maximum vertical load and materials properties. The distance between the two rotation centres (400 mm) has been defined to have a maximum vertical displacement < 2mm during baking (40 mm max radial displacement [2]). (a) 380 mm 60 (b) 174 mm 60 fig mm φ140 mm mm 220 mm mm fig.2 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 17 of 49
18 The maximum height results of 780 mm that should be available between the pedestrian ring and the green zone of the lower port (see fig. below and the yellow rectangle that schematizes the connection rods vertical supports area). Vertical ropes Radial arm Horizontal lever Bearing Vertical link Vertical lever Dampers An ANSYS model of half sector was performed to evaluate the stresses in the components (forged external shell, connection rod, cylindrical insert). Fig. 3 next page, shows the model with the components and the main geometrical dimensions. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 18 of 49
19 fig The external forged shell is ASTM-A 453 Gr 660 while the connection rod and cylindrical inserts are in INCONEL 718. A total vertical force downward of 22 MN [2] was applied to the vertical support: this load requires 8 Nodes with applied Vertical Force modules (fig.2 shows only Symmetry plane half module). A preliminary structural analysis is shown in the following pages. Symmetry plane ANSYS FEM model: Grounded nodes FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 19 of 49
20 Material Prop.: ASTM-A 453 INCONEL 718 Sy 0.2 =589 MPa (RT) Su=893 MPa (RT) Sy 0.2 =1010 MPa (RT) Su=1246 MPa (RT) Sm = 295 MPa (RT) Sm = 451 MPa (77 K) Sm = 667 MPA (RT) Sm = 863 MPA (77 K) Vertical displacements UY (mm) in CSYS 0 Inserts displacements (x200) [mm] FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 20 of 49
21 von Mises stress (MPa) von Mises stress (MPa) FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 21 of 49
22 von Mises stress (MPa) The zone of max stress (377 MPa) is in the forged shell and (512 MPa) in the connection rod: the results seem to be acceptable compared with only (Pm+Pb) at RT <1.5 Sm = 442 MPa (ASTM-A) and 677 MPa (Inconel). The following figures show the system sliding (with a friction factor=0.2) under the VV dead weight, as vertical load, and a radial displacements of 1 mm. The reaction force due to the friction between connection rod and cylindrical inserts results about 0.84 MN (per each whole vertical support formed by 8 modules). In this case the max SEQV results of 287 MPa in the connection rod (see the two figures below). FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 22 of 49
23 Displacements USUM [mm] von Mises stress [MPa] FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 23 of 49
24 The figure on the right side shows two halves (87 mm width) and the next figure shows the single module 174 mm width. Clearly the division in modules is for calculation purpose only In the real manufacturing the forged shell (part A in fig.1) will be a single forging piece and all the parts (connection rods included) will be drilled together and at the same time n 8 units (1400 mm) FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 24 of 49
25 4. Toroidal Supports alternative solutions 4.a) pendulum W7-X style When the vertical supports allow toroidal displacements, as in actual bearing pads solution, the pendulum restraint system seems to be a really good choice. The figures below show the W7-X Auto Centering System [2]. In the W7-X reactor no electromagnetic forces act on the Vacuum Vessel and the pendulums stiffness is not a critical point. In the figure below it is possible to note the relative high L/D ratio M The system allows Vacuum Vessel vertical displacements and radial thermal expansion with small toroidal rotations of the whole VV itself. The pendulum solution for ITER reactor has to take into account several basic points: - the presence and the entity of the net horizontal force; - the presence of the radial restraint system; - during the disruption event, the opportunity to spread the reaction forces with different weights between radial and tangential ports (to minimize the stress level in the Ports-VV connection). FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 25 of 49
26 At the moment no possibilities there are to perform a detailed design and analysis of a proper toroidal restraint style W7-X. Only a scheme of pendulum with variable axial stiffness is shown in fig 4: Fig.4 It will be possible to change with continuity the axial stiffness at constant pendulum length, if the screws pitches are identical. This could be fixed on one end to the lower port and on the other end to the pedestal ring. 4.b) Central guide A sketch of toroidal restraint with only one central guide (or rail) is shown in the figures: VV Pedestal ring In this case the possibility to reach the seizing is lower than the actual design, and the same toroidal stiffness variability (with VV vertical displacement) is maintained. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 26 of 49
27 4.c) Flexible plates The flexible plates could be used for toroidal restraint 272 mm only; the scheme of the cross section is shown in fig.5: the total number of plates will be defined on the basis of the maximum toroidal load and materials properties. 300 mm 100 mm 60 mm If we consider a net horizontal force of 20 MN (VDE III slow) [1] and the fault of all the radial restraints (worst fault condition), the max tangential force occurs in the two 300 mm toroidal supports closest to the plane perpendicular to the 8 mm axis of the horiz. force. 780 mm 10 mm 100 mm fig. 5 f f Ft3 Toroidal restraint Vacuum Vessel and Ports f Ft1 Ft2 20 MN f Ft4 40 f Ft5 x In the scheme left side, the max force occurs in the toroidal support n 3 (and symmetric). In this hypothetical worst condition the max force results of 7.6 MN and 10 is the total number of plates per each toroidal support. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 27 of 49
28 The figure below show the group of 10 plates 10 mm thick (without the heads in the yellow zones: grounded and loaded parts). The gap between each plate is 8 mm and the total radial width will be about 270 mm (if other 50mm as initial and final heads radial thickness can be assigned). Loaded region 10 mm thick (tangential forces) Lateral flexible regions 10 mm thick Central flexible region 8 mm thick Grounded region 10 mm thick The figure on the right shows the ANSYS FEM model of the single plate in INCONEL: In the figure next page the single plate and its global dimensions are reported. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 28 of 49
29 1400 mm 60 mm loaded 60 mm grounded All the degree of freedom are blocked in the lower part of the plate while the upper part can slides only along the tangential (Z) axis only. No moments around vertical axis have been applied. A preliminary structural analysis of the single plate is shown below: Displacements (x10) [mm] FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 29 of 49
30 SEQV stress middle section [MPa] SEQV stress top position [MPa] FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 30 of 49
31 The stress in the middle of the shell thickness results very low = 201 MPa with a Sm = 451 MPa, while in the shell top position (membrane+bending) there are local values of 852 MPa. In these 4 nodes the high level of stress is due to a stress concentration and a factor 3 can be applied in these points for peak values (moreover the previous results have been obtained for the worst fault conditions, at RT and without proper design rules). During baking, displacements of 40 mm radially and max 2 mm vertically are expected. In this situation each toroidal support (10 plates) reacts with a vertical force of 0.62 MN and a radial one of 0.34 MN. 40 mm 2 mm SEQV top [MPa] FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 31 of 49
32 SEQV mid [MPa] The stress of the plates results mainly from bending: 580 MPa (against 60 MPa in mid sec). This value results less than 1.5 Sm = 677 MPa (at RT). Clearly the initial position of the vertical supports can be set to obtain the connection rods in vertical position during operation (VV temperature =100 C): in this case both at RT and baking temperature (200 C) the max vertical displacement results of 1mm instead of 2. In this last configuration the vertical force decreases to one half and the max stress to 530 MPa. In this first solution the global restraint system consists of vertical supports (connection rods) and toroidal supports (flexible plates): both the systems cooperate to take the vertical force (up or downward) during VDE event. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 32 of 49
33 5. Clamping sleeves Kostyrka A possible alternative to the dumpers (hydraulic or mechanical) are the clamping sleeves. The figure below shows the very simple item with the central axis and the external sleeve. When the hydraulic chamber inside the sleeve is under pressure, the elastic membrane presses on the cylinder, blocking it. During the pulse the VV remains blocked and it can expand after, completely free. For a reference diameter of 100 mm per 200 mm length, each sleeve is able to support 0.3 MN. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 33 of 49
34 6. Conclusions 1. The bearing pad solution, as Vertical support system, results acceptable for the maximum load. The limit is the large size and to double the number of supports seems to be a feasible solution (see Appendix 1). 2. The replacement of the ropes with other system (rods or dampers) doesn t involve complex design review (nevertheless further analyses are necessary). 3. The actual Toroidal restraint system shows potential risks. The proposal of the pendulum system seems to be the right choice: a further detailed analysis is recommended. The other typology (central rail and flexible plates) are feasible if in accordance with the selected vertical support system. 4. The alternative solution for the Vertical supports with connection rods seems to be achievable but the space allocation in the toroidal direction has be verified (see Appendix 2 also). 5. The solution with spherical joints (W7-X type), as Vertical supports, could be analyzed too (high reaction forces by friction) but higher vertical space seems to be necessary. To double the number of vertical supports can be another possibility. 6. The Radial restraint system (with secondary implementations) remains basically unchangeable and common to all the actual and proposed systems. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 34 of 49
35 References [1] Design Description Document - DDD15 - Vacuum Vessel - September 2004 [2] A. Cardella ITER Vacuum Vessel Support System, ITER Vacuum Vessel Design Review Working Group Meeting, Cadarache 28 June 2007 [3] A. Capriccioli ITER VV Vertical Supports, presentation at the Working Group Meeting - Cadarache 28 June 2007 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 35 of 49
36 APPENDIX 1 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 36 of 49
37 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 37 of 49
38 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 38 of 49
39 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 39 of 49
40 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 40 of 49
41 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 41 of 49
42 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 42 of 49
43 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 43 of 49
44 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 44 of 49
45 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 45 of 49
46 FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 46 of 49
47 APPENDIX 2 Alternative solution with connection rods as vertical supports and flexible plates as toroidal restraint In this solution the global restraint system consists of vertical supports (connection rods) and toroidal supports (flexible plates): both the systems cooperate to take the vertical force (up or downward) during the vertical plasma disruption event. The radial support system (radial arm, horizontal and vertical levers, dumpers etc.) has to be translated upward (through the part ocgs) to intercept the radial forces coming from the ports. In the figure below, a rough scheme shows the global system: Radial arm with spherical connection Central rail Horizontal lever VV lower ports level ocgs Pedestal ring level To explain the meaning of the central rail, it s necessary to note that, when a net horizontal force pushes the VV in its same direction, the ports bend and rotations around local vertical axes occur. As a result of that, high stress will appear in the VV-Ports connection zone (see the reinforcement proposal; Cadarache 28/06/2007). FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 47 of 49
48 The following figure shows a rough scheme of the ports distortion: F Both the proposed supports show lability against these rotations (in the actual reference design the moment should be partially balanced by only one -of the two per ports- toroidal supports and by the connection radial arm / horizontal lever). In the present alternative design, the radial arm itself and the vertical translation support have been used to insert a central guide. This guide and the toroidal support help the Ports to take the VV, decreasing both the maximum stress level of the VV-Ports connection and the VV horizontal displacement (see the fig. on the right) and avoiding F the connection rods to support dangerous rotations around a vertical axis. In this case the stiffness ratio (~20% between the toroidal and radial supports stiffness) changes, because the stress passes from the VV-Ports connection to Ports-Supports system. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 48 of 49
49 Easier than the previous scheme and with similar characteristics is the following: the only difference consists in replacing the group of flexible plates with another central guide system (icgs inner central guide system). Clearly, as in the outer central guide system, proper vertical gap will be foreseen between the parts (a) and (b). b icgs a If the guides show evidence of problems with reference to the sliding assurance, two half groups of flexible plates can be used. In this case also, other analyses are necessary to evaluate the effects of horizontal displacements induced by the ports bending, during the VDE. FPN FUSTEC doc. FUSTEC-TVV-CKSUP-001 Rev.0 page 49 of 49
Load application in load cells - Tips for users
 Load application in load cells - Tips for users Correct load application on the load cells is a prerequisite for precise weighing results. Be it load direction, support structure or mounting aids load
Load application in load cells - Tips for users Correct load application on the load cells is a prerequisite for precise weighing results. Be it load direction, support structure or mounting aids load
Finite Element Analysis per ASME B31.3
 Brief Discussion: Split-Body 12in Butterfly valve, Ph: 520-265-3657 Page 1 of 13 Finite Element Analysis per ASME B31.3 Prepared by: Michael Rodgers, P.Eng. Date: July 16, 2010 Page 2 of 13 Section Headings:
Brief Discussion: Split-Body 12in Butterfly valve, Ph: 520-265-3657 Page 1 of 13 Finite Element Analysis per ASME B31.3 Prepared by: Michael Rodgers, P.Eng. Date: July 16, 2010 Page 2 of 13 Section Headings:
Failure of Engineering Materials & Structures. Code 34. Bolted Joint s Relaxation Behavior: A FEA Study. Muhammad Abid and Saad Hussain
 Failure of Engineering Materials & Structures Code 3 UET TAXILA MECHNICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Bolted Joint s Relaxation Behavior: A FEA Study Muhammad Abid and Saad Hussain Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
Failure of Engineering Materials & Structures Code 3 UET TAXILA MECHNICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Bolted Joint s Relaxation Behavior: A FEA Study Muhammad Abid and Saad Hussain Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
1/2/2016. Lecture Slides. Screws, Fasteners, and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints. Reasons for Non-permanent Fasteners
 Lecture Slides Screws, Fasteners, and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints Reasons for Non-permanent Fasteners Field assembly Disassembly Maintenance Adjustment 1 Introduction There are two distinct uses
Lecture Slides Screws, Fasteners, and the Design of Nonpermanent Joints Reasons for Non-permanent Fasteners Field assembly Disassembly Maintenance Adjustment 1 Introduction There are two distinct uses
An Investigation of Optimal Pitch Selection to Reduce Self-Loosening of Threaded Fastener under Transverse Loading
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 3 Issue 01 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X An Investigation of Optimal Pitch Selection to Reduce Self-Loosening of Threaded Fastener
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 3 Issue 01 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X An Investigation of Optimal Pitch Selection to Reduce Self-Loosening of Threaded Fastener
3-D Finite Element Analysis of Bolted Joint Using Helical Thread Model
 3-D Finite Element Analysis of Bolted Joint Using Helical Thread Model Shaik Gousia Yasmin 1, P. Punna Rao 2, Kondaiah Bommisetty 3 1 M.Tech(CAD/CAM), Nimra College of Engineering & Technology, Vijayawada,
3-D Finite Element Analysis of Bolted Joint Using Helical Thread Model Shaik Gousia Yasmin 1, P. Punna Rao 2, Kondaiah Bommisetty 3 1 M.Tech(CAD/CAM), Nimra College of Engineering & Technology, Vijayawada,
Fastener Modeling for Joining Parts Modeled by Shell and Solid Elements
 2007-08 Fastener Modeling for Joining Parts Modeled by Shell and Solid Elements Aleander Rutman, Chris Boshers Spirit AeroSystems Larry Pearce, John Parady MSC.Software Corporation 2007 Americas Virtual
2007-08 Fastener Modeling for Joining Parts Modeled by Shell and Solid Elements Aleander Rutman, Chris Boshers Spirit AeroSystems Larry Pearce, John Parady MSC.Software Corporation 2007 Americas Virtual
0.20. Record Page 1 of 19
 Page 1 of 19 Page 2 of 19 Page 3 of 19 Page 4 of 19 Page 5 of 19 ASME BPVC.III.1.ND-2015 Page 6 of 19 ð15þ Figure ND-3325-1 Some Acceptable Types of Unstayed Flat Heads and Covers GENERAL NOTE: The illustrations
Page 1 of 19 Page 2 of 19 Page 3 of 19 Page 4 of 19 Page 5 of 19 ASME BPVC.III.1.ND-2015 Page 6 of 19 ð15þ Figure ND-3325-1 Some Acceptable Types of Unstayed Flat Heads and Covers GENERAL NOTE: The illustrations
CHAPTER 2 ELECTROMAGNETIC FORCE AND DEFORMATION
 18 CHAPTER 2 ELECTROMAGNETIC FORCE AND DEFORMATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION Transformers are subjected to a variety of electrical, mechanical and thermal stresses during normal life time and they fail when these
18 CHAPTER 2 ELECTROMAGNETIC FORCE AND DEFORMATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION Transformers are subjected to a variety of electrical, mechanical and thermal stresses during normal life time and they fail when these
RF, Disruption and Thermal Analyses of EAST Antennas*
 RF, Disruption and Thermal Analyses of EAST Antennas* L. Zhou, W.K. Beck, P. Koert, J. Doody, R.F. Vieira, S.J. Wukitch, R.S. Granetz, and J.H. Irby Plasma Science and Fusion Center (PSFC) Massachusetts
RF, Disruption and Thermal Analyses of EAST Antennas* L. Zhou, W.K. Beck, P. Koert, J. Doody, R.F. Vieira, S.J. Wukitch, R.S. Granetz, and J.H. Irby Plasma Science and Fusion Center (PSFC) Massachusetts
1. Enumerate the most commonly used engineering materials and state some important properties and their engineering applications.
 Code No: R05310305 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Production Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks:
Code No: R05310305 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Production Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks:
TEST SERIES TO EVALUATE THE STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF ISOBOARD OVER RAFTER SYSTEM
 TEST SERIES TO EVALUATE THE STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF ISOBOARD OVER RAFTER SYSTEM J A Wium Institute of Structural Engineering 19 November 2007 ISI2007-3 TEST SERIES TO EVALUATE THE STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR
TEST SERIES TO EVALUATE THE STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR OF ISOBOARD OVER RAFTER SYSTEM J A Wium Institute of Structural Engineering 19 November 2007 ISI2007-3 TEST SERIES TO EVALUATE THE STRUCTURAL BEHAVIOUR
IDEA Connections. User guide
 IDEA Connections user guide IDEA Connections User guide IDEA Connections user guide Content 1.1 Program requirements... 4 1.1 Installation guidelines... 4 2 User interface... 5 2.1 3D view in the main
IDEA Connections user guide IDEA Connections User guide IDEA Connections user guide Content 1.1 Program requirements... 4 1.1 Installation guidelines... 4 2 User interface... 5 2.1 3D view in the main
Technical Report Synopsis: Chapter 4: Mounting Individual Lenses Opto-Mechanical System Design Paul R. Yoder, Jr.
 Technical Report Synopsis: Chapter 4: Mounting Individual Lenses Opto-Mechanical System Design Paul R. Yoder, Jr. Introduction Chapter 4 of Opto-Mechanical Systems Design by Paul R. Yoder, Jr. is an introduction
Technical Report Synopsis: Chapter 4: Mounting Individual Lenses Opto-Mechanical System Design Paul R. Yoder, Jr. Introduction Chapter 4 of Opto-Mechanical Systems Design by Paul R. Yoder, Jr. is an introduction
TUTORIAL 4: Combined Axial and Bending Problem Sketch Path Sweep Initial Project Space Setup Static Structural ANSYS
 TUTORIAL 4: Combined Axial and Bending Problem In this tutorial you will learn how to draw a bar that has bends along its length and therefore will have both axial and bending stresses acting on cross-sections
TUTORIAL 4: Combined Axial and Bending Problem In this tutorial you will learn how to draw a bar that has bends along its length and therefore will have both axial and bending stresses acting on cross-sections
Module 4 General Purpose Machine Tools. Version 2 ME, IIT Kharagpur
 Module 4 General urpose Machine Tools Lesson 24 Forces developing and acting in machine tools Instructional objectives At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to; (i) Identify the sources
Module 4 General urpose Machine Tools Lesson 24 Forces developing and acting in machine tools Instructional objectives At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to; (i) Identify the sources
Answers to Questions and Problems
 Fundamentals of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Using Critical Thinking Skills 3 rd Edition By Alex Krulikowski Answers to Questions and Problems Second Printing Product #: 1103 Price: $25.00 Copyright
Fundamentals of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Using Critical Thinking Skills 3 rd Edition By Alex Krulikowski Answers to Questions and Problems Second Printing Product #: 1103 Price: $25.00 Copyright
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing
 Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (Known as GDT) What is GDT Helps ensure interchangeability of parts. Use is dictated by function and relationship of the part feature. It does not take the place
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (Known as GDT) What is GDT Helps ensure interchangeability of parts. Use is dictated by function and relationship of the part feature. It does not take the place
LS-DYNA USED TO ANALYZE THE MANUFACTURING OF THIN WALLED CANS AUTHOR: CORRESPONDENCE: ABSTRACT
 LS-DYNA USED TO ANALYZE THE MANUFACTURING OF THIN WALLED CANS AUTHOR: Joachim Danckert Department of Production Aalborg University CORRESPONDENCE: Joachim Danckert Department of Production Fibigerstraede
LS-DYNA USED TO ANALYZE THE MANUFACTURING OF THIN WALLED CANS AUTHOR: Joachim Danckert Department of Production Aalborg University CORRESPONDENCE: Joachim Danckert Department of Production Fibigerstraede
Modeling Multi-Bolted Systems
 Modeling Multi-Bolted Systems Jerome Montgomery Siemens Power Generation Abstract Modeling a single bolt in a finite element analysis raises questions of how much complexity to include. But, modeling a
Modeling Multi-Bolted Systems Jerome Montgomery Siemens Power Generation Abstract Modeling a single bolt in a finite element analysis raises questions of how much complexity to include. But, modeling a
Mechanical study of the «Saclay piezo tuner» PTS (Piezo Tuning System) P. Bosland, Bo Wu DAPNIA - CEA Saclay. Abstract
 SRF Mechanical study of the «Saclay piezo tuner» PTS (Piezo Tuning System) P. Bosland, Bo Wu DAPNIA - CEA Saclay Abstract This report presents the piezo tuner developed at Saclay in the framework of CARE/SRF.
SRF Mechanical study of the «Saclay piezo tuner» PTS (Piezo Tuning System) P. Bosland, Bo Wu DAPNIA - CEA Saclay Abstract This report presents the piezo tuner developed at Saclay in the framework of CARE/SRF.
Bhagwan mahavir college of Engineering & Technology, Surat.
 Bhagwan mahavir college of Engineering & Technology, Surat. Department of automobile Engineering Assignment Subject: Machine Design & Industrial Drafting B.E. Second year Instructions: 1. This set of tutorial
Bhagwan mahavir college of Engineering & Technology, Surat. Department of automobile Engineering Assignment Subject: Machine Design & Industrial Drafting B.E. Second year Instructions: 1. This set of tutorial
2.3 PF System. WU Weiyue PF5 PF PF1
 2.3 PF System WU Weiyue 2.3.1 Introduction The poloidal field (PF) system consists of fourteen superconducting coils, including 6 pieces of central selenoid coils, 4 pieces of divertor coils and 4 pieces
2.3 PF System WU Weiyue 2.3.1 Introduction The poloidal field (PF) system consists of fourteen superconducting coils, including 6 pieces of central selenoid coils, 4 pieces of divertor coils and 4 pieces
Essex County College - West Essex Campus Addition And Renovations dlb # / SECTION EXPANSION FITTINGS AND LOOPS FOR HVAC PIPING
 SECTION 230516 - EXPANSION FITTINGS AND LOOPS FOR HVAC PIPING PART I - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and
SECTION 230516 - EXPANSION FITTINGS AND LOOPS FOR HVAC PIPING PART I - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET
 LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
Load-carrying capacity of timber frame diaphragms with unidirectional support
 Load-carrying capacity of timber frame diaphragms with unidirectional support Jørgen Munch-Andersen, Danish Timber Information, 2012-06-26 Introduction The rules for determining the load-carrying capacity
Load-carrying capacity of timber frame diaphragms with unidirectional support Jørgen Munch-Andersen, Danish Timber Information, 2012-06-26 Introduction The rules for determining the load-carrying capacity
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 05, 2016 ISSN (online):
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 05, 2016 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Static Analysis of VMC Spindle for Maximum Cutting Force Mahesh M. Ghadage 1 Prof. Anurag
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 05, 2016 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Static Analysis of VMC Spindle for Maximum Cutting Force Mahesh M. Ghadage 1 Prof. Anurag
In-plane capacitance probe holding mechanism Shorya Awtar Alexander Slocum Mechanical Engineering, MIT
 In-plane capacitance probe holding mechanism Shorya Awtar Alexander Slocum Mechanical Engineering, MIT In precision metrology it is frequently required to hold capacitance probes such that they are properly
In-plane capacitance probe holding mechanism Shorya Awtar Alexander Slocum Mechanical Engineering, MIT In precision metrology it is frequently required to hold capacitance probes such that they are properly
Formulae for calculations A) Nomenclature
 Formulae for calculations A) Nomenclature do= Nominal diameter {Outside diameter of screw} dc= Core diameter of screw d= Mean Diameter of the screw p= Pitch of the screw. ) Thread angle ( α) α = tan 1
Formulae for calculations A) Nomenclature do= Nominal diameter {Outside diameter of screw} dc= Core diameter of screw d= Mean Diameter of the screw p= Pitch of the screw. ) Thread angle ( α) α = tan 1
Design study for JT-60SA ECRF system and the latest results of JT-60U ECRF system
 Japan-Korea : Workshop on Physics of Wave Heating and Current Drive, NFRI, Daejon, Korea, Jan. 14-15, 2008 R F &LHRF& ECRF ICRF JT - 60 JT-60 RF group Japan Atomic Energy Agency Design study for JT-60SA
Japan-Korea : Workshop on Physics of Wave Heating and Current Drive, NFRI, Daejon, Korea, Jan. 14-15, 2008 R F &LHRF& ECRF ICRF JT - 60 JT-60 RF group Japan Atomic Energy Agency Design study for JT-60SA
AutoCAD Inventor - Solid Modeling, Stress and Dynamic Analysis
 PDHonline Course G280 (15 PDH) AutoCAD Inventor - Solid Modeling, Stress and Dynamic Analysis Instructor: John R. Andrew, P.E. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658
PDHonline Course G280 (15 PDH) AutoCAD Inventor - Solid Modeling, Stress and Dynamic Analysis Instructor: John R. Andrew, P.E. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658
DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-I
 Code No: R31035 R10 Set No: 1 JNT University Kakinada III B.Tech. I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2014/Jan -2015 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours
Code No: R31035 R10 Set No: 1 JNT University Kakinada III B.Tech. I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2014/Jan -2015 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-I (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours
MFG 316 Chapter 4 //Workholding Principles
 Workholding Principles All devices that grip, hold, chuck, or retain a workpiece in order to perform a manufacturing operation. Force=hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, mechanical Force multiplication by
Workholding Principles All devices that grip, hold, chuck, or retain a workpiece in order to perform a manufacturing operation. Force=hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, mechanical Force multiplication by
Experimental Evaluation of Metal Composite Multi Bolt Radial Joint on Laminate Level, under uni Axial Tensile Loading
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Evaluation of Metal Composite Multi Bolt Radial Joint on Laminate Level, under uni Axial Tensile Loading C Sharada Prabhakar *, P Rameshbabu** *Scientist, Advanced
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Experimental Evaluation of Metal Composite Multi Bolt Radial Joint on Laminate Level, under uni Axial Tensile Loading C Sharada Prabhakar *, P Rameshbabu** *Scientist, Advanced
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17610 15116 4 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
17610 15116 4 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (4)
CH # 8. Two rectangular metal pieces, the aim is to join them
 CH # 8 Screws, Fasteners, and the Design of Non-permanent Joints Department of Mechanical Engineering King Saud University Two rectangular metal pieces, the aim is to join them How this can be done? Function
CH # 8 Screws, Fasteners, and the Design of Non-permanent Joints Department of Mechanical Engineering King Saud University Two rectangular metal pieces, the aim is to join them How this can be done? Function
COMMON SYMBOLS/ ISO SYMBOL ASME Y14.5M ISO FEATURE CONTROL FRAME DIAMETER/ SPHERICAL DIAMETER/ AT MAXIMUM MATERIAL CONDITION
 1 82 COMMON SYMBOLS/ Shown below are the most common symbols that are used with geometric tolerancing and other related dimensional requirements on engineering drawings. Note the comparison with the ISO
1 82 COMMON SYMBOLS/ Shown below are the most common symbols that are used with geometric tolerancing and other related dimensional requirements on engineering drawings. Note the comparison with the ISO
Chapter VI Vessel Supports
 Chapter VI Vessel Supports 1 2 Vessel Supports Vessel support is to a. Support the weight of the container b. Fix the container position c. Keep the container in operation. Classified by the type of vessels:
Chapter VI Vessel Supports 1 2 Vessel Supports Vessel support is to a. Support the weight of the container b. Fix the container position c. Keep the container in operation. Classified by the type of vessels:
Development of a New-Generation Dowel and Screw Combination 2014 International Crosstie and Fastening System Symposium Urbana, IL, USA 3 June 2014
 Development of a New-Generation Dowel and Screw Combination 2014 International Crosstie and Fastening System Symposium Urbana, IL, USA Brandon Van Dyk, Christopher Kenyon, Artur Wroblewski, Dr. Michael
Development of a New-Generation Dowel and Screw Combination 2014 International Crosstie and Fastening System Symposium Urbana, IL, USA Brandon Van Dyk, Christopher Kenyon, Artur Wroblewski, Dr. Michael
Structural Analysis of High-field-Side RF antennas during a disruption on the Advanced Divertor experiment (ADX)
 Structural Analysis of High-field-Side RF antennas during a disruption on the Advanced Divertor experiment (ADX) J. Doody, B. LaBombard, R. Leccacorvi, S. Shiraiwa, R. Vieira, G.M. Wallace, S.J. Wukitch,
Structural Analysis of High-field-Side RF antennas during a disruption on the Advanced Divertor experiment (ADX) J. Doody, B. LaBombard, R. Leccacorvi, S. Shiraiwa, R. Vieira, G.M. Wallace, S.J. Wukitch,
SECTION EXPANSION FITTINGS AND LOOPS FOR HVAC PIPING
 SECTION 230516 - EXPANSION FITTINGS AND LOOPS FOR HVAC PIPING PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and
SECTION 230516 - EXPANSION FITTINGS AND LOOPS FOR HVAC PIPING PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 RELATED DOCUMENTS A. Drawings and general provisions of the Contract, including General and Supplementary Conditions and
Module 2 WAVE PROPAGATION (Lectures 7 to 9)
 Module 2 WAVE PROPAGATION (Lectures 7 to 9) Lecture 9 Topics 2.4 WAVES IN A LAYERED BODY 2.4.1 One-dimensional case: material boundary in an infinite rod 2.4.2 Three dimensional case: inclined waves 2.5
Module 2 WAVE PROPAGATION (Lectures 7 to 9) Lecture 9 Topics 2.4 WAVES IN A LAYERED BODY 2.4.1 One-dimensional case: material boundary in an infinite rod 2.4.2 Three dimensional case: inclined waves 2.5
ABSTRACT II. OBJECTIVE I. INTRODUCTION III. METHODOLOGY
 2017 IJSRSET Volume 3 Issue 3 Print ISSN: 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology Analysis of Cylinder Head Bolt Cross Pattern Tightening and Its Effect on Gasket Sealing
2017 IJSRSET Volume 3 Issue 3 Print ISSN: 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology Analysis of Cylinder Head Bolt Cross Pattern Tightening and Its Effect on Gasket Sealing
Moment Resisting Connections for Load Bearing Walls
 PRECAST: MOMENT RESISTING CONNECTIONS Moment Resisting Connections for Load Bearing Walls Manish Khandelwal Sr. Structural Engineer, Building Structures, Sweco India Private Limited Design philosophy for
PRECAST: MOMENT RESISTING CONNECTIONS Moment Resisting Connections for Load Bearing Walls Manish Khandelwal Sr. Structural Engineer, Building Structures, Sweco India Private Limited Design philosophy for
IDEA Connection 8. User guide. IDEA Connection user guide
 IDEA Connection user guide IDEA Connection 8 User guide IDEA Connection user guide Content 1.1 Program requirements... 5 1.2 Installation guidelines... 5 2 User interface... 6 2.1 3D view in the main window...
IDEA Connection user guide IDEA Connection 8 User guide IDEA Connection user guide Content 1.1 Program requirements... 5 1.2 Installation guidelines... 5 2 User interface... 6 2.1 3D view in the main window...
bolts: G Cr-1/5Mo (A193 B7) 16 x M20 (EN ISO 4014) MPR GASKET 'SP' PETRO 4,0mm 363 x 323 x 4,5 mm (2 pieces)
 test condition: 20 C 44 bar load condition 1: 206 C 18 bar load condition 2: 210 C 26 bar bolts: G41400 1Cr-1/5Mo (A193 B7) 16 x M20 (EN ISO 4014) gasket: MPR GASKET 'SP' PETRO 4,0mm 363 x 323 x 4,5 mm
test condition: 20 C 44 bar load condition 1: 206 C 18 bar load condition 2: 210 C 26 bar bolts: G41400 1Cr-1/5Mo (A193 B7) 16 x M20 (EN ISO 4014) gasket: MPR GASKET 'SP' PETRO 4,0mm 363 x 323 x 4,5 mm
Finite Element Modeling of Early Stage Self-loosening of Bolted Joints Haoliang Xu 1, a, Lihua Yang 1, b,, Lie Yu 1,2, c
 International Conference on Information Sciences, Machinery, Materials and Energy (ICISMME 2015) Finite Element Modeling of Early Stage Self-loosening of Bolted Joints Haoliang Xu 1, a, Lihua Yang 1, b,,
International Conference on Information Sciences, Machinery, Materials and Energy (ICISMME 2015) Finite Element Modeling of Early Stage Self-loosening of Bolted Joints Haoliang Xu 1, a, Lihua Yang 1, b,,
Vertex Detector Mechanics
 Vertex Detector Mechanics Bill Cooper Fermilab (Layer 5) (Layer 1) VXD Introduction The overall approach to mechanical support and cooling has been developed in conjunction with SiD. The support structures
Vertex Detector Mechanics Bill Cooper Fermilab (Layer 5) (Layer 1) VXD Introduction The overall approach to mechanical support and cooling has been developed in conjunction with SiD. The support structures
Dörries CONTUMAT VCE, VC, VC-V Vertical turning lathes Vertical turning centres
 Engineering precisely what you value Dörries Dörries CONTUMAT VCE, VC, VC-V Vertical turning lathes Vertical turning centres 02 All of a piece From a modular design concept Dörries CONTUMAT vertical turning
Engineering precisely what you value Dörries Dörries CONTUMAT VCE, VC, VC-V Vertical turning lathes Vertical turning centres 02 All of a piece From a modular design concept Dörries CONTUMAT vertical turning
Seal Mechanism of Tip Seal in Scroll Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 214 Seal Mechanism of Tip Seal in Scroll Compressor Mitsuhiro Fukuta Shizuoka University,
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 214 Seal Mechanism of Tip Seal in Scroll Compressor Mitsuhiro Fukuta Shizuoka University,
PRO LIGNO Vol. 11 N pp
 FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION OF NAILED GLULAM TIMBER JOINTS Mats EKEVAD Luleå University of Technology Division of Wood Science and Engineering SE-931 87 Skellefteå, Sweden Tel: +46 910 585377; E-mail: mats.ekevad@ltu.se
FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION OF NAILED GLULAM TIMBER JOINTS Mats EKEVAD Luleå University of Technology Division of Wood Science and Engineering SE-931 87 Skellefteå, Sweden Tel: +46 910 585377; E-mail: mats.ekevad@ltu.se
MIL-STD-1580B REQUIREMENT 11 DETAILED REQUIREMENTS FOR CONNECTORS
 DETAILED REQUIREMENTS FOR CONNECTORS 11. General. This section describes detailed requirements for a DPA of commonly used connectors. These requirements supplement the general requirements in section 4.
DETAILED REQUIREMENTS FOR CONNECTORS 11. General. This section describes detailed requirements for a DPA of commonly used connectors. These requirements supplement the general requirements in section 4.
Creo Parametric 2.0: Introduction to Solid Modeling. Creo Parametric 2.0: Introduction to Solid Modeling
 Creo Parametric 2.0: Introduction to Solid Modeling 1 2 Part 1 Class Files... xiii Chapter 1 Introduction to Creo Parametric... 1-1 1.1 Solid Modeling... 1-4 1.2 Creo Parametric Fundamentals... 1-6 Feature-Based...
Creo Parametric 2.0: Introduction to Solid Modeling 1 2 Part 1 Class Files... xiii Chapter 1 Introduction to Creo Parametric... 1-1 1.1 Solid Modeling... 1-4 1.2 Creo Parametric Fundamentals... 1-6 Feature-Based...
Research on Casting Edge Grinding Machine of Tracking Type Chang-Chun LI a,*, Nai-Jian CHEN b, Chang-Zhong WU c
 2016 International Conference on Mechanics Design, Manufacturing and Automation (MDM 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-354-0 Research on Casting Edge Grinding Machine of Tracking Type Chang-Chun LI a,*, Nai-Jian
2016 International Conference on Mechanics Design, Manufacturing and Automation (MDM 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-354-0 Research on Casting Edge Grinding Machine of Tracking Type Chang-Chun LI a,*, Nai-Jian
AN INNOVATIVE FEA METHODOLOGY FOR MODELING FASTENERS
 AN INNOVATIVE FEA METHODOLOGY FOR MODELING FASTENERS MacArthur L. Stewart 1 1 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering Technology Department, Eastern Michigan University, MI, USA Abstract Abstract Researchers
AN INNOVATIVE FEA METHODOLOGY FOR MODELING FASTENERS MacArthur L. Stewart 1 1 Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering Technology Department, Eastern Michigan University, MI, USA Abstract Abstract Researchers
FEKO-Based Method for Electromagnetic Simulation of Carcass Wires Embedded in Vehicle Tires
 ACES JOURNAL, VOL. 26, NO. 3, MARCH 2011 217 FEKO-Based Method for Electromagnetic Simulation of Carcass Wires Embedded in Vehicle Tires Nguyen Quoc Dinh 1, Takashi Teranishi 1, Naobumi Michishita 1, Yoshihide
ACES JOURNAL, VOL. 26, NO. 3, MARCH 2011 217 FEKO-Based Method for Electromagnetic Simulation of Carcass Wires Embedded in Vehicle Tires Nguyen Quoc Dinh 1, Takashi Teranishi 1, Naobumi Michishita 1, Yoshihide
Plasma Confinement by Pressure of Rotating Magnetic Field in Toroidal Device
 1 ICC/P5-41 Plasma Confinement by Pressure of Rotating Magnetic Field in Toroidal Device V. Svidzinski 1 1 FAR-TECH, Inc., San Diego, USA Corresponding Author: svidzinski@far-tech.com Abstract: Plasma
1 ICC/P5-41 Plasma Confinement by Pressure of Rotating Magnetic Field in Toroidal Device V. Svidzinski 1 1 FAR-TECH, Inc., San Diego, USA Corresponding Author: svidzinski@far-tech.com Abstract: Plasma
INFLUENCE OF PILES ON LOAD- SETTLEMENT BEHAVIOUR OF RAFT FOUNDATION
 INFLUENCE OF PILES ON LOAD- SETTLEMENT BEHAVIOUR OF RAFT FOUNDATION BALESHWAR SINGH Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 78139, India NINGOMBAM THOIBA SINGH
INFLUENCE OF PILES ON LOAD- SETTLEMENT BEHAVIOUR OF RAFT FOUNDATION BALESHWAR SINGH Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 78139, India NINGOMBAM THOIBA SINGH
Prying of a Large Span Base Plate Undergoing a Moment Load Applied by a Round Pier
 Prying of a Large Span Base Plate Undergoing a Moment Load Applied by a Round Pier by Anastasia Wickeler A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Masters of Applied Science
Prying of a Large Span Base Plate Undergoing a Moment Load Applied by a Round Pier by Anastasia Wickeler A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Masters of Applied Science
CLAMPING TECHNOLOGY Individual special clamping tools
 CLAMPING TECHNOLOGY Individual special clamping tools 1 QUALITY SINCE 1958 Know-how, the highest quality and first class engineering. We see ourselves as a system supplier and offer our customers a full
CLAMPING TECHNOLOGY Individual special clamping tools 1 QUALITY SINCE 1958 Know-how, the highest quality and first class engineering. We see ourselves as a system supplier and offer our customers a full
Power Threads. Shigley s Mechanical Engineering Design
 Power Threads Power screw Mechanics of Power Screws Used to change angular motion into linear motion Usually transmits power Examples include vises, presses, jacks, lead screw on lathe Fig. 8 4 Square
Power Threads Power screw Mechanics of Power Screws Used to change angular motion into linear motion Usually transmits power Examples include vises, presses, jacks, lead screw on lathe Fig. 8 4 Square
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS
 3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS Equipment Set for Wave Optics with Laser U17303 Instruction sheet 10/08 Alf 1. Safety instructions The laser emits visible radiation at a wavelength of 635 nm with a maximum power
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS Equipment Set for Wave Optics with Laser U17303 Instruction sheet 10/08 Alf 1. Safety instructions The laser emits visible radiation at a wavelength of 635 nm with a maximum power
Design and Analysis of Self Centering Steady Rest for Supercut-6 CNC Turning Machine Using CAD & FEA
 Design and Analysis of Self Centering Steady Rest for Supercut-6 CNC Turning Machine Using CAD & FEA 1 Satish G. Bahaley, 2 Rajendra L. Bharambe Prof. Ram Meghe Institute of Technology & Research, Badnera,
Design and Analysis of Self Centering Steady Rest for Supercut-6 CNC Turning Machine Using CAD & FEA 1 Satish G. Bahaley, 2 Rajendra L. Bharambe Prof. Ram Meghe Institute of Technology & Research, Badnera,
Product Catalogue O-Rings & Back Up Rings O-Ring C
 Product Catalogue O-Rings & Back Up Rings O-Ring.98115 - C The information contained in this catalogue is based on many years of experience in the fluid power industry, specifically in the manufacturing
Product Catalogue O-Rings & Back Up Rings O-Ring.98115 - C The information contained in this catalogue is based on many years of experience in the fluid power industry, specifically in the manufacturing
GEM-P Progress Report Mechanics (July 2006)
 GEM-P Progress Report Mechanics (July 2006) 1. Pedestal The GEM-P scanning strategy relies on a stable antenna rotation. The original Vertex pedestal was unable to make a complete turn. This limitation
GEM-P Progress Report Mechanics (July 2006) 1. Pedestal The GEM-P scanning strategy relies on a stable antenna rotation. The original Vertex pedestal was unable to make a complete turn. This limitation
Acceptance test for the linear motion actuator for the scanning slit of the HIE ISOLDE short diagnostic boxes
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN ACC NOTE 2014 0099 HIE ISOLDE PROJECT Note 0036 Acceptance test for the linear motion actuator for the scanning slit of the HIE ISOLDE short diagnostic boxes
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN ACC NOTE 2014 0099 HIE ISOLDE PROJECT Note 0036 Acceptance test for the linear motion actuator for the scanning slit of the HIE ISOLDE short diagnostic boxes
Unit-25 Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM)
 Unit-5 Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) Objective: Imaging formation of scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is due to tunneling effect of quantum physics, which is in nano scale. This experiment shows
Unit-5 Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) Objective: Imaging formation of scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is due to tunneling effect of quantum physics, which is in nano scale. This experiment shows
The jigs and fixtures are the economical ways to produce a component in mass production system. These are special work holding and tool guiding device
 The jigs and fixtures are the economical ways to produce a component in mass production system. These are special work holding and tool guiding device Quality of the performance of a process largely influenced
The jigs and fixtures are the economical ways to produce a component in mass production system. These are special work holding and tool guiding device Quality of the performance of a process largely influenced
Shear force transmission in expansion joints
 for better solutions Shear dowel Shear force transmission in expansion joints Reliable expansion joint dowelling in concrete structural elements General Single shear dowel HED Expansion joint dowelling
for better solutions Shear dowel Shear force transmission in expansion joints Reliable expansion joint dowelling in concrete structural elements General Single shear dowel HED Expansion joint dowelling
Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes
 Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes H. M. Martin, R. G. Allen, J. H. Burge, L. R. Dettmann, D. A. Ketelsen, W. C. Kittrell, S. M. Miller and S. C. West Steward Observatory,
Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes H. M. Martin, R. G. Allen, J. H. Burge, L. R. Dettmann, D. A. Ketelsen, W. C. Kittrell, S. M. Miller and S. C. West Steward Observatory,
STUDY AND ANALYSIS OF ANGULAR TORQUING OF ENGINE CYLINDER-HEAD BOLTS USING TORQUE-TO-YIELD BOLTS: A CASE STUDY
 International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD) ISSN 2249-6890 Vol. 3, Issue 4, Oct 2013, 1-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. STUDY AND ANALYSIS OF ANGULAR TORQUING OF
International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD) ISSN 2249-6890 Vol. 3, Issue 4, Oct 2013, 1-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. STUDY AND ANALYSIS OF ANGULAR TORQUING OF
TECHNICAL MANUAL. TERADOWEL and ULTRADOWEL. Reliable Dowel System for Floor Joints
 TECHNICAL MANUAL TERADOWEL and ULTRADOWEL Reliable Dowel System for Floor Joints Version: PEIKKO GROUP 11/2018 TERADOWEL and ULTRADOWEL Reliable Dowel System for Floor Joints Dowels manufactured from high
TECHNICAL MANUAL TERADOWEL and ULTRADOWEL Reliable Dowel System for Floor Joints Version: PEIKKO GROUP 11/2018 TERADOWEL and ULTRADOWEL Reliable Dowel System for Floor Joints Dowels manufactured from high
Engineering Policy & Procedure
 FPD > Engineering > Global Standards Engineering Policy & Procedure Revision History Number: G2-4 Section: G Subject: Radiographic Examination Procedure 1.0 SCOPE This procedure specifies the requirements
FPD > Engineering > Global Standards Engineering Policy & Procedure Revision History Number: G2-4 Section: G Subject: Radiographic Examination Procedure 1.0 SCOPE This procedure specifies the requirements
001-Component-build. Build the following Contraptor components before assembly:
 001-Component-build Build the following Contraptor components before assembly: http://www.contraptor.org/make-linear-rail-v2#assembly http://www.contraptor.org/make-linear-bearings-v2#assembly http://www.contraptor.org/make-sliding-elements#assembly
001-Component-build Build the following Contraptor components before assembly: http://www.contraptor.org/make-linear-rail-v2#assembly http://www.contraptor.org/make-linear-bearings-v2#assembly http://www.contraptor.org/make-sliding-elements#assembly
400 (±2,5 V/ V/ ,3% V4A
 LVDT Inductive Position Transducer - Hydraulic Series Series Hydraulic position measurement in hydraulic cylinders of machine controls ranges 10...300 mm temperature -40...+150 C (sensors) 0...+60 C (external
LVDT Inductive Position Transducer - Hydraulic Series Series Hydraulic position measurement in hydraulic cylinders of machine controls ranges 10...300 mm temperature -40...+150 C (sensors) 0...+60 C (external
HILMA Quick Tool Change for Forging Applications
 HILMA Quick Tool Change for Forging Applications Upper tool is seated in pocket of the master die set clamped with Hilma Wedge Clamps Lower tool is clamped with vertical clamping bars locked in place with
HILMA Quick Tool Change for Forging Applications Upper tool is seated in pocket of the master die set clamped with Hilma Wedge Clamps Lower tool is clamped with vertical clamping bars locked in place with
Objectives. Inventor Part Modeling MA 23-1 Presented by Tom Short, P.E. Munro & Associates, Inc
 Objectives Inventor Part Modeling MA 23-1 Presented by Tom Short, P.E. Munro & Associates, Inc To demonstrate most of the sketch tools and part features in : Inventor Release 6 And, to show logical techniques
Objectives Inventor Part Modeling MA 23-1 Presented by Tom Short, P.E. Munro & Associates, Inc To demonstrate most of the sketch tools and part features in : Inventor Release 6 And, to show logical techniques
Friction Grip in Wellheads: An Innovative Approach to Load Support & Sealing
 Friction Grip in Wellheads: An Innovative Approach to Load Support & Sealing Brent Harrald Principal Engineer Plexus Ocean Systems Ltd. December 2009 Page 1 Table of Contents Introduction Plexus Ocean
Friction Grip in Wellheads: An Innovative Approach to Load Support & Sealing Brent Harrald Principal Engineer Plexus Ocean Systems Ltd. December 2009 Page 1 Table of Contents Introduction Plexus Ocean
DP-8 H. H. MØRCH. Instructions. Contents of the packing. Spatial requirements. Mounting the bush
 DP-8 Instructions H. H. MØRCH Contents of the packing In the packing of the tonearm you will find the arm base in which the bearings are encapsulated in a heavy body. This is the link between the moveable
DP-8 Instructions H. H. MØRCH Contents of the packing In the packing of the tonearm you will find the arm base in which the bearings are encapsulated in a heavy body. This is the link between the moveable
Pow-R-Feed Systems Service Manual
 Pow-R-Feed Systems Service Manual Important Safety Instructions Please read this manual carefully and follow its instructions. Improper use or failure to follow these instructions could result in serious
Pow-R-Feed Systems Service Manual Important Safety Instructions Please read this manual carefully and follow its instructions. Improper use or failure to follow these instructions could result in serious
SKF TOROIDAL ROLLER BEARING CARB PRODUCTIVITY IMPROVEMENT AND MAINTENANCE COST REDUCTION THROUGH RELIABILITY AND SUSTAINABILITY
 SKF TOROIDAL ROLLER BEARING CARB PRODUCTIVITY IMPROVEMENT AND MAINTENANCE COST REDUCTION THROUGH RELIABILITY AND SUSTAINABILITY Dr.eng. Tiberiu LAURIAN, Polytechnic University Bucharest, tlaurian@omtr.pub.ro
SKF TOROIDAL ROLLER BEARING CARB PRODUCTIVITY IMPROVEMENT AND MAINTENANCE COST REDUCTION THROUGH RELIABILITY AND SUSTAINABILITY Dr.eng. Tiberiu LAURIAN, Polytechnic University Bucharest, tlaurian@omtr.pub.ro
1825. Structure stability evaluation of offshore heave compensator using multi-body dynamics analysis method
 1825. Structure stability evaluation of offshore heave compensator using multi-body dynamics analysis method Gwi-Nam Kim 1, Sun-Chul Huh 2, Sung-Gu Hwang 3, Yong-Gil Jung 4, Jang-Hwan Hyun 5, Hee-Sung
1825. Structure stability evaluation of offshore heave compensator using multi-body dynamics analysis method Gwi-Nam Kim 1, Sun-Chul Huh 2, Sung-Gu Hwang 3, Yong-Gil Jung 4, Jang-Hwan Hyun 5, Hee-Sung
Technical Data. 17. Technical data Deep groove ball bearing radial internal clearances and axial internal clearances A
 7. Technical data 7. Deep groove ball bearing radial internal clearances and axial internal clearances........8 68 68 68 68 68 68....8 6 6 6 6 6 6.6.......6...... Fig. 7.. Series 68 radial internal/axial
7. Technical data 7. Deep groove ball bearing radial internal clearances and axial internal clearances........8 68 68 68 68 68 68....8 6 6 6 6 6 6.6.......6...... Fig. 7.. Series 68 radial internal/axial
Locating Principles & Devices
 Locating Principles & Devices 1 LOCATING PRINCIPLES To position the work piece w.r.t. to tool, to ensure precision in machining Locating: dimensional and positional relationship b/w work piece and tool
Locating Principles & Devices 1 LOCATING PRINCIPLES To position the work piece w.r.t. to tool, to ensure precision in machining Locating: dimensional and positional relationship b/w work piece and tool
CAD-CAM-CAE Examples
 CAD-CAM-CAE Examples example title: example number: example level: CAx system: Related material part with TÁMOP Job Description: Shaft type component (CAD) ÓE-A06a basic - medium - advanced CATIA v5 CAD
CAD-CAM-CAE Examples example title: example number: example level: CAx system: Related material part with TÁMOP Job Description: Shaft type component (CAD) ÓE-A06a basic - medium - advanced CATIA v5 CAD
COIL WINDING ISSUES P. Fabbricatore INFN Genova LCD - Magnet 13Oct09. Coil winding issues
 Coil winding issues Based on experience acquired with CMS coil construction, some preliminary considerations about the envisaged winding (and in general manufacturing) issues of a large superconducting
Coil winding issues Based on experience acquired with CMS coil construction, some preliminary considerations about the envisaged winding (and in general manufacturing) issues of a large superconducting
HIGH PRECISION LINEAR ACTUATOR DEVELOPMENT
 HIGH PRECISION LINEAR ACTUATOR DEVELOPMENT I. Santos (1), G. Migliorero (2 (1) SENER-Structures & Mechanisms Section, Av. Zugazarte 56, 48930 Las Arenas (Vizcaya) Spain, Email: ignacio.santos@sener.es
HIGH PRECISION LINEAR ACTUATOR DEVELOPMENT I. Santos (1), G. Migliorero (2 (1) SENER-Structures & Mechanisms Section, Av. Zugazarte 56, 48930 Las Arenas (Vizcaya) Spain, Email: ignacio.santos@sener.es
Metrology Prof.Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere
 Metrology Prof.Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 33 Electrical and Electronic Comparators, Optical comparators (Refer Slide Time: 00:17) I welcome
Metrology Prof.Dr Kanakuppi Sadashivappa Bapuji Institute of Engineering and Technology Davangere Lecture 33 Electrical and Electronic Comparators, Optical comparators (Refer Slide Time: 00:17) I welcome
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS
 3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS Equipment Set for Wave Optics with Laser 1003053 Instruction sheet 06/18 Alf 1. Safety instructions The laser emits visible radiation at a wavelength of 635 nm with a maximum power
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS Equipment Set for Wave Optics with Laser 1003053 Instruction sheet 06/18 Alf 1. Safety instructions The laser emits visible radiation at a wavelength of 635 nm with a maximum power
Assembly instructions
 Assembly instructions Important notes on VOSS assembly instructions In order to ensure maximum performance and functional reliability of VOSS products, the respective assembly instructions, operating conditions
Assembly instructions Important notes on VOSS assembly instructions In order to ensure maximum performance and functional reliability of VOSS products, the respective assembly instructions, operating conditions
POWER PEAK TM ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS. step-by-step assembly and installation. Version 1, Rev D P/N
 POWER PEAK TM ASSEMBLY ISTRUCTIOS step-by-step assembly and installation Version 1, Rev D P/ 5803028 The Power Peak TM A few words about this product The Power Peak is designed to mount on standard I-Beams
POWER PEAK TM ASSEMBLY ISTRUCTIOS step-by-step assembly and installation Version 1, Rev D P/ 5803028 The Power Peak TM A few words about this product The Power Peak is designed to mount on standard I-Beams
SPIETH Locknuts. Series MSW. Works Standard SN 04.03
 SPIETH Locknuts Series MSW Works Standard SN 0.03 SPIETH Locknuts Series MSW SPIETH locknuts offer a range of technical benefits, qualified by their special system and production. Under high levels of
SPIETH Locknuts Series MSW Works Standard SN 0.03 SPIETH Locknuts Series MSW SPIETH locknuts offer a range of technical benefits, qualified by their special system and production. Under high levels of
Development of a Numerical Technique for the Static Analysis of Bolted Joints by the FEM
 , July 3-5, 2013, London, U.K. Development of a Numerical Technique for the Static Analysis of Bolted Joints by the FEM D. Valladares, M. Carrera, L. Castejon, C. Martin Abstract The use of numerical simulation
, July 3-5, 2013, London, U.K. Development of a Numerical Technique for the Static Analysis of Bolted Joints by the FEM D. Valladares, M. Carrera, L. Castejon, C. Martin Abstract The use of numerical simulation
JULY 2014 SECTION TITLE PAGE. 1 Description of Connectors and Intended Applications 2. 2 Marking of Connector and/or Package 2.
 M80 & M83 SERIES RECTANGULAR CONNECTORS JULY 204 SECTION TITLE PAGE Description of Connectors and Intended Applications 2 2 Marking of Connector and/or Package 2 3 Ratings 3 Appendix Contact Orientations
M80 & M83 SERIES RECTANGULAR CONNECTORS JULY 204 SECTION TITLE PAGE Description of Connectors and Intended Applications 2 2 Marking of Connector and/or Package 2 3 Ratings 3 Appendix Contact Orientations
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER III ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER III ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70 Note: (i) Attempt all the questions. (ii) Use both sides of the drawing sheet, if necessary. (iii) All dimensions
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER III ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70 Note: (i) Attempt all the questions. (ii) Use both sides of the drawing sheet, if necessary. (iii) All dimensions
n Measurable displacements between n Linearity: max. ± 0.05 % n Housing diameter 12.9 mm n Service life: 10 8 movements
 Potentiometric Displacement Sensor Miniature design Model 8709 Code: Delivery: Warranty: 8709 EN ex stock 24 months Application Potentiometric displacement sensors are used for direct, precise measurement
Potentiometric Displacement Sensor Miniature design Model 8709 Code: Delivery: Warranty: 8709 EN ex stock 24 months Application Potentiometric displacement sensors are used for direct, precise measurement
Application of Guided Wave Technology to Tube Inspection
 ECNDT 2006 - Th.3.1.5 Application of Guided Wave Technology to Tube Inspection T. VOGT, D. ALLEYNE, B. PAVLAKOVIC, Guided Ultrasonics Limited, Nottingham, United Kingdom 1. Introduction Abstract. The inspection
ECNDT 2006 - Th.3.1.5 Application of Guided Wave Technology to Tube Inspection T. VOGT, D. ALLEYNE, B. PAVLAKOVIC, Guided Ultrasonics Limited, Nottingham, United Kingdom 1. Introduction Abstract. The inspection
Skewed connections result when members frame to each
 Design of Skewed Connections LARRY KLOIBER and WILLIAM THORNTON ABSTRACT Skewed connections result when members frame to each other at an angle other than 90º. This paper provides some guidance in the
Design of Skewed Connections LARRY KLOIBER and WILLIAM THORNTON ABSTRACT Skewed connections result when members frame to each other at an angle other than 90º. This paper provides some guidance in the
Design and Manufacturing of Single sided expanding collet for Rotary VMC Fixture
 Proceedings of RK University s First International Conference on Research & Entrepreneurship (Jan. 5 th & Jan. 6 th, 2016) ISBN: 978-93-5254-061-7 (Proceedings available for download at rku.ac.in/icre)
Proceedings of RK University s First International Conference on Research & Entrepreneurship (Jan. 5 th & Jan. 6 th, 2016) ISBN: 978-93-5254-061-7 (Proceedings available for download at rku.ac.in/icre)
An Alternative Formulation for Determining Stiffness of Members with Bolted Connections
 An Alternative Formulation for Determining Stiffness of Members with Bolted Connections Mr. B. Routh Post Graduate Student Department of Civil Engineering National Institute of Technology Agartala Agartala,
An Alternative Formulation for Determining Stiffness of Members with Bolted Connections Mr. B. Routh Post Graduate Student Department of Civil Engineering National Institute of Technology Agartala Agartala,
