Princeton University COS429 Computer Vision Problem Set 1: Building a Camera
|
|
|
- Jessica Johnson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Princeton University COS429 Computer Vision Problem Set 1: Building a Camera What to submit: You need to submit two files: one PDF file for the report that contains your name, Princeton NetID, all the pictures taken and text to answer the questions; one ZIP file (not RAR or any other format) that contains all source code for your system, and a main.m file that takes no parameter as input and run directly in Matlab to generate the results reported in your PDF file. Both the PDF and ZIP file should be named using your Princeton NetID underscore cos429ps1. As an example using my account, they should be named xj cos429ps1.pdf and xj cos429ps1.zip. To verify your result and detect plagiarism to make sure there is no cheating, we will use an automatic program to run your code and compare your code with other students (including both this year and all previous years) and public available implementations (e.g. from Google, Bing, Github). Therefore, please follow the file format to make our grading job easier. Failure to follow these rules will result in losing your grade. Awards: We will give some awards to people who build a special camera, such as biggest camera award, smallest camera award, craziest camera award, lightest camera award. Please write down what is special about your construction! Problem 1 Build the camera obscura You need to build your own camera obscura, or pinhole camera. A camera obscura is a dark chamber with a single hole in one extreme that lets light in. The light gets projected into the opposite wall forming an image. In order to capture the projected image we will use a digital camera. One of the problems with pinhole cameras is that the amount of light that enters the device is very small. Therefore, we will need to use long exposure time to capture images with enough contrast. Many digital cameras with a manual mode allow setting the exposure time. We used a Canon DSLR for the pictures in this problem set. Let s first start building the device (we followed the instructions in here 1 ): 1. Take a box (we used a card box with inches). 2. Make a hole in the center of one of the faces. The hole has to be small (a diameter of 5 milimeters). 3. Make a second hole so that you can fit the lens of the camera inside (if your box is big enough to contain your digital camera and you can set auto-capture or wirelessly control the camera, then you don t need a second hole). 4. Cover the inside walls with black paper to reduce inter-reflections
2 5. Cover the inside wall facing the pinhole with white paper. The white paper will be the screen on which the image will be projected. The digital camera will be used to take pictures of the image that gets projected onto the white paper. Using a paper of standard size (e.g. standard letter size), will assist you in calibrating the camera later on (Section ). Figure 1: Building the pinhole camera. Figure 1 shows some pictures of our construction. In this construction, the distance between the pinhole and the white wall is 11 inches. The big hole visible in the pictures is the hole we used to insert the digital camera. The pinhole is a very small hole in the center and it is hard to see in these pictures. It is important that the camera fits tightly so that no light enters via that aperture. Make sure that light enters only via the small hole in the center of the box. Once you have built your camera obscura, take some pictures of your construction to put on the report. Report the size, and we will give an award to the biggest camera obscura built in the class. Problem 2 Take some pictures with your camera For this you will need a digital camera for which you can set the exposure time. We used a Cannon G11 with exposure time of 15 seconds and set the ISO to maximum sensibility. Figure 2 shows a few images taken with our setup. If the images appear too blurry, you can increase the sharpness by reducing the size of the hole. But then you will need to increase the exposure time. 2
3 Figure 2: Upper left: this is a picture of a bright light source. This picture makes the white screen on the back of the wall appear clearly. Upper right: a picture on a cloudy day. Bottom row: a couple of images we have taken during a sunny day. You need to take pictures under bright light (sunny day outdoors). But you can play first by shining a light at the hole. If you see nothing, then there might be something wrong with the camera settings. Explain the geometry of the construction and write down why the pictures appear slightly deformed. Problem 3 Calibration and image correction The captured images contain distortion due to the angle between the digital camera and the principle axis of the pinhole camera. If the digital camera could be precisely calibrated (i.e. we knew the exact angle and its distance to the image plane, we could calculate an exact homography that transforms the image from the digital camera viewpoint to the viewpoint of the pinhole. Since we cannot measure this accurately in our setup, we will use a simplified calibration procedure. At each time you setup your camera, take one picture with a strong light source that will make the four corners of the white sheet apparent (Figure 2 top left; this can also be done by reducing the contrast of a capture image). Write a small program H = calibrate(im) in MATLAB that allows you to mark those four corners manually on the image, and computes the (homogeneous) transformation matrix H that rectifies the camera distortion. To figure 3
4 (a) Captured image (b) Image correction tool (c) Rectified image Figure 3: Correcting projective distortions. Rectified Image Original Image Homography Homography Homography Figure 4: More example of homography rectificiation. out the dimensions of the white sheet when viewed from the pinhole direction at a distance focal length away, take a picture of the white sheet with your digital camera at the same focal length and height as the pinhole (this need only be done once). This process will give you four point correspondences, from which you can compute an homography that transforms one set of points to the other, as discussed in class. Note that this mapping will need to be computed each time you move your digital camera. You d might also want to add to your transformation matrix reflection about the x-axis. This will rectify the image and flip it with a single warp. Figure 3 shows an example of the rectification process. Figure 4 shows more examples. Hints: you can use the MATLAB function ginput or impoly for entering the corner locations, and the functions interp2 or griddata to warp the image. If your images are noisy, you can further play with different filtering techniques such as medfilt2. Extra credit (optional) Anaglyph camera obscura 4
5 One interesting aspect of this device is that you can build different types of cameras by playing with the shape of the pinhole. So, let s make a new kind of camera obscura. In particular, we can build a camera that produces anaglyph images in a single shot by making two pinholes instead of just one. There are several ways of taking stereo pictures and viewing them. The most common mechanism is that two pictures are taken independently (with two cameras) and then they are combined to form anaglyph images, or viewed with special devices (e.g., LCD shutter glasses, polarized 3d glasses, stereoscopes,...) that show each image from the stereo pair to each of the two eyes. Anaglyph images are a particular method to produce 3D images. Anaglyph images are formed by superimposing a pair of stereo images into two different color channels. They provide a 3D effect when viewed with color glasses. We will transform the camera obscura into an anaglyph camera obscura by making two holes and placing different color filters on each hole. This will produce an image that will be the superposition of two images taken from slightly different viewpoints. Each image will have a different color. Then, to see the 3D image we can look at the picture by placing the same color filters in front of our eyes. In order to do this, we used color glasses with blue and red filters: We used one of the glasses to get the filters and placed them in front of the two holes. Figure 5 shows two pictures of the two holes (top left) and the filters positioned in front of each hole (top right). On the bottom of that figure is a resulting 3D image, with the two views superimposed. That image should give you a 3D percept when viewed with anaglyph glasses. Suggestions: For this to work you will have to experiment with the distance between the two holes. We tried two distances: 3 inches and 1.5 inches. We found it easier to see the 3D for the 1.5 inches images. Try to take good quality images. Once you would have placed the color filters on each hole, you will need longer exposure times in order to get the same image quality than before. If the images are too blurry, it will be hard to perceive 3D. Also, as you increase the distance between the pinholes, you will increase the range of distances that will provide 3D information. However, the images will be farther apart which makes the 3D perception harder. If the images are too far apart, the visual system will not be able to fuse them and you will not see a 3D image when looking with the color glasses. You can also try viewing the images by changing the image size. Extra credit (optional) Anaglyph camera obscura: A device to measure distances to objects We can all measure distances to an object by using a ruler. However, using a ruler is an intrusive procedure, as it requires physically placing one extreme of the ruler touching the 5
6 Figure 5: Anaglyph camera obscura. object. Some objects do not like to be constantly approached by rulers. Stereovision provides a way of measuring distances between the camera and other objects in the world remotely, without touching them. Figure 6 shows two example pictures of a light taken at two different distances. As you can see, a single light produces two spots in the picture. This is due to the fact that the light enters the camera obscura through two pinholes instead of one. Each spot has a different color because we placed two colored filters on each pinhole to form the anaglyph image. The interesting property is that the distance between the two spots, d, changes with respect to the distance, Z, between the camera and the light. Therefore, we could measure the distance Z to the light by just measuring d and if we had a perfect model of the geometry of the camera. We will do this in the next part. Extra credit (optional) Find the relation between the separation of the lights and distance Place the light at various known distances from the pinhole and take a set of pictures. You can decompose the anaglyph image into the images projected by each pinhole by visual- 6
7 Figure 6: Light at different distances as captured by the anaglyph camera izing the red and blue channels separately: img = imread ( yourfilename.jpg ); figure imshow([img(:,:,1); img(:,:,3)]) Plot the relationship between Z and d. You should think about the geometry of the camera in order to derive an analytical expression that relates the distance between the two spots in the picture with the distance of the light with respect to the camera and the parameters of the camera (distance to the back wall, separation between the two holes, etc.). Check that your predictions fit the experimental data. Extra credit (optional) A manual stereo algorithm In this part, the goal is to apply manually a stereo reconstruction algorithm. The goal is: given two images, to recover the full 3D structure of the image (we will only produce a coarse approximation to it). Automatic algorithms for measuring depths from stereo can be challenging. However, we will do it manually by following the next steps: 1. Take a picture with the anaglyph camera. Try to take a picture in which there are many clear elements that can be easily identified in the image. Also, select a scene with enough depth differences (with some elements very close to the camera and others far away). 2. Use MATLAB to select a number of matching points between the two color channels of the anaglyph image manually. 3. Use the function from the previous section that relates the horizontal distance between matching points to recover the distance between the camera and the selected points. 4. Now you will need to interpolate the distance in order to create a continuous image of depths. You can use the function griddata. Figure 7 (top) shows one example showing the red and blue channels of the stereo picture. We used the top image as the reference image, and then computed depth at a set of selected points on the top image. Once you have a depth map (the value of the distance at each pixel in the image), you can do different things like trying to rotate the image in 3D. Figure 7 shows two different viewpoints of the car. 7
8 Figure 7: Point correspondences (top) and viewpoint interpolation (bottom) of the car image. Acknowledgement: This assignment is designed based on a related assignment from MIT
MIT CSAIL Advances in Computer Vision Fall Problem Set 6: Anaglyph Camera Obscura
 MIT CSAIL 6.869 Advances in Computer Vision Fall 2013 Problem Set 6: Anaglyph Camera Obscura Posted: Tuesday, October 8, 2013 Due: Thursday, October 17, 2013 You should submit a hard copy of your work
MIT CSAIL 6.869 Advances in Computer Vision Fall 2013 Problem Set 6: Anaglyph Camera Obscura Posted: Tuesday, October 8, 2013 Due: Thursday, October 17, 2013 You should submit a hard copy of your work
6.869 Advances in Computer Vision Spring 2010, A. Torralba
 6.869 Advances in Computer Vision Spring 2010, A. Torralba Due date: Wednesday, Feb 17, 2010 Problem set 1 You need to submit a report with brief descriptions of what you did. The most important part is
6.869 Advances in Computer Vision Spring 2010, A. Torralba Due date: Wednesday, Feb 17, 2010 Problem set 1 You need to submit a report with brief descriptions of what you did. The most important part is
Photography Help Sheets
 Photography Help Sheets Phone: 01233 771915 Web: www.bigcatsanctuary.org Using your Digital SLR What is Exposure? Exposure is basically the process of recording light onto your digital sensor (or film).
Photography Help Sheets Phone: 01233 771915 Web: www.bigcatsanctuary.org Using your Digital SLR What is Exposure? Exposure is basically the process of recording light onto your digital sensor (or film).
Nova Full-Screen Calibration System
 Nova Full-Screen Calibration System Version: 5.0 1 Preparation Before the Calibration 1 Preparation Before the Calibration 1.1 Description of Operating Environments Full-screen calibration, which is used
Nova Full-Screen Calibration System Version: 5.0 1 Preparation Before the Calibration 1 Preparation Before the Calibration 1.1 Description of Operating Environments Full-screen calibration, which is used
Photographing Long Scenes with Multiviewpoint
 Photographing Long Scenes with Multiviewpoint Panoramas A. Agarwala, M. Agrawala, M. Cohen, D. Salesin, R. Szeliski Presenter: Stacy Hsueh Discussant: VasilyVolkov Motivation Want an image that shows an
Photographing Long Scenes with Multiviewpoint Panoramas A. Agarwala, M. Agrawala, M. Cohen, D. Salesin, R. Szeliski Presenter: Stacy Hsueh Discussant: VasilyVolkov Motivation Want an image that shows an
Home Lab 3 Pinhole Viewer Box Continued and Measuring the Diameter of the Sun
 1 Home Lab 3 Pinhole Viewer Box Continued and Measuring the Diameter of the Sun Activity 3-1: Effect of the distance between the viewing screen and the pinhole on the image size. Objective: To investigate
1 Home Lab 3 Pinhole Viewer Box Continued and Measuring the Diameter of the Sun Activity 3-1: Effect of the distance between the viewing screen and the pinhole on the image size. Objective: To investigate
DIGITAL PHOTOGRAPHY CAMERA MANUAL
 DIGITAL PHOTOGRAPHY CAMERA MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENTS KNOW YOUR CAMERA...1 SETTINGS SHUTTER SPEED...2 WHITE BALANCE...3 ISO SPEED...4 APERTURE...5 DEPTH OF FIELD...6 WORKING WITH LIGHT CAMERA SETUP...7 LIGHTING
DIGITAL PHOTOGRAPHY CAMERA MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENTS KNOW YOUR CAMERA...1 SETTINGS SHUTTER SPEED...2 WHITE BALANCE...3 ISO SPEED...4 APERTURE...5 DEPTH OF FIELD...6 WORKING WITH LIGHT CAMERA SETUP...7 LIGHTING
FOCUS, EXPOSURE (& METERING) BVCC May 2018
 FOCUS, EXPOSURE (& METERING) BVCC May 2018 SUMMARY Metering in digital cameras. Metering modes. Exposure, quick recap. Exposure settings and modes. Focus system(s) and camera controls. Challenges & Experiments.
FOCUS, EXPOSURE (& METERING) BVCC May 2018 SUMMARY Metering in digital cameras. Metering modes. Exposure, quick recap. Exposure settings and modes. Focus system(s) and camera controls. Challenges & Experiments.
Unit 5.B Geometric Optics
 Unit 5.B Geometric Optics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.B Hwk. Pts.: / 18 Unit 5.B Lab Pts.: / 25 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N Essential Fundamentals of Geometric Optics 1. Convex surfaces
Unit 5.B Geometric Optics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.B Hwk. Pts.: / 18 Unit 5.B Lab Pts.: / 25 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N Essential Fundamentals of Geometric Optics 1. Convex surfaces
How to Take a Great Booth Picture by Larry Berman
 1 How to Take a Great Booth Picture by Larry Berman The importance of a good booth picture How important is the booth photo? Besides the artwork images, the booth image can easily make or break an artist's
1 How to Take a Great Booth Picture by Larry Berman The importance of a good booth picture How important is the booth photo? Besides the artwork images, the booth image can easily make or break an artist's
Creating Stitched Panoramas
 Creating Stitched Panoramas Here are the topics that we ll cover 1. What is a stitched panorama? 2. What equipment will I need? 3. What settings & techniques do I use? 4. How do I stitch my images together
Creating Stitched Panoramas Here are the topics that we ll cover 1. What is a stitched panorama? 2. What equipment will I need? 3. What settings & techniques do I use? 4. How do I stitch my images together
Midterm Examination CS 534: Computational Photography
 Midterm Examination CS 534: Computational Photography November 3, 2015 NAME: SOLUTIONS Problem Score Max Score 1 8 2 8 3 9 4 4 5 3 6 4 7 6 8 13 9 7 10 4 11 7 12 10 13 9 14 8 Total 100 1 1. [8] What are
Midterm Examination CS 534: Computational Photography November 3, 2015 NAME: SOLUTIONS Problem Score Max Score 1 8 2 8 3 9 4 4 5 3 6 4 7 6 8 13 9 7 10 4 11 7 12 10 13 9 14 8 Total 100 1 1. [8] What are
Computer Vision Slides curtesy of Professor Gregory Dudek
 Computer Vision Slides curtesy of Professor Gregory Dudek Ioannis Rekleitis Why vision? Passive (emits nothing). Discreet. Energy efficient. Intuitive. Powerful (works well for us, right?) Long and short
Computer Vision Slides curtesy of Professor Gregory Dudek Ioannis Rekleitis Why vision? Passive (emits nothing). Discreet. Energy efficient. Intuitive. Powerful (works well for us, right?) Long and short
Basic Camera Craft. Roy Killen, GMAPS, EFIAP, MPSA. (c) 2016 Roy Killen Basic Camera Craft, Page 1
 Basic Camera Craft Roy Killen, GMAPS, EFIAP, MPSA (c) 2016 Roy Killen Basic Camera Craft, Page 1 Basic Camera Craft Whether you use a camera that cost $100 or one that cost $10,000, you need to be able
Basic Camera Craft Roy Killen, GMAPS, EFIAP, MPSA (c) 2016 Roy Killen Basic Camera Craft, Page 1 Basic Camera Craft Whether you use a camera that cost $100 or one that cost $10,000, you need to be able
IMAGE FORMATION. Light source properties. Sensor characteristics Surface. Surface reflectance properties. Optics
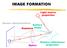 IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
CPSC 425: Computer Vision
 1 / 55 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Fred Tung ftung@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2015/2016 Term 2 2 / 55 Menu January 7, 2016 Topics: Image
1 / 55 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Fred Tung ftung@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2015/2016 Term 2 2 / 55 Menu January 7, 2016 Topics: Image
Basic principles of photography. David Capel 346B IST
 Basic principles of photography David Capel 346B IST Latin Camera Obscura = Dark Room Light passing through a small hole produces an inverted image on the opposite wall Safely observing the solar eclipse
Basic principles of photography David Capel 346B IST Latin Camera Obscura = Dark Room Light passing through a small hole produces an inverted image on the opposite wall Safely observing the solar eclipse
CAMERA BASICS. Stops of light
 CAMERA BASICS Stops of light A stop of light isn t a quantifiable measurement it s a relative measurement. A stop of light is defined as a doubling or halving of any quantity of light. The word stop is
CAMERA BASICS Stops of light A stop of light isn t a quantifiable measurement it s a relative measurement. A stop of light is defined as a doubling or halving of any quantity of light. The word stop is
CIS581: Computer Vision and Computational Photography Homework: Cameras and Convolution Due: Sept. 14, 2017 at 3:00 pm
 CIS58: Computer Vision and Computational Photography Homework: Cameras and Convolution Due: Sept. 4, 207 at 3:00 pm Instructions This is an individual assignment. Individual means each student must hand
CIS58: Computer Vision and Computational Photography Homework: Cameras and Convolution Due: Sept. 4, 207 at 3:00 pm Instructions This is an individual assignment. Individual means each student must hand
Chapter 6-Existing Light Photography
 Chapter 6-Existing Light Photography All of these images were taken with available light. Painting with light-using available light Photography that includes artificial light which naturally exists in
Chapter 6-Existing Light Photography All of these images were taken with available light. Painting with light-using available light Photography that includes artificial light which naturally exists in
Get the Shot! Photography + Instagram Workshop September 21, 2013 BlogPodium. Saturday, 21 September, 13
 Get the Shot! Photography + Instagram Workshop September 21, 2013 BlogPodium Part One: Taking your camera off manual Technical details Common problems and how to fix them Practice Ways to make your photos
Get the Shot! Photography + Instagram Workshop September 21, 2013 BlogPodium Part One: Taking your camera off manual Technical details Common problems and how to fix them Practice Ways to make your photos
LENSES. INEL 6088 Computer Vision
 LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
Which equipment is necessary? How is the panorama created?
 Congratulations! By purchasing your Panorama-VR-System you have acquired a tool, which enables you - together with a digital or analog camera, a tripod and a personal computer - to generate high quality
Congratulations! By purchasing your Panorama-VR-System you have acquired a tool, which enables you - together with a digital or analog camera, a tripod and a personal computer - to generate high quality
To start there are three key properties that you need to understand: ISO (sensitivity)
 Some Photo Fundamentals Photography is at once relatively simple and technically confusing at the same time. The camera is basically a black box with a hole in its side camera comes from camera obscura,
Some Photo Fundamentals Photography is at once relatively simple and technically confusing at the same time. The camera is basically a black box with a hole in its side camera comes from camera obscura,
Comparison of the diameter of different f/stops.
 LESSON 2 HANDOUT INTRODUCTION TO PHOTOGRAPHY Summer Session 2009 SHUTTER SPEED, ISO, APERTURE What is exposure? Exposure is a combination of 3 factors which determine the amount of light which enters your
LESSON 2 HANDOUT INTRODUCTION TO PHOTOGRAPHY Summer Session 2009 SHUTTER SPEED, ISO, APERTURE What is exposure? Exposure is a combination of 3 factors which determine the amount of light which enters your
Image Formation. Dr. Gerhard Roth. COMP 4102A Winter 2015 Version 3
 Image Formation Dr. Gerhard Roth COMP 4102A Winter 2015 Version 3 1 Image Formation Two type of images Intensity image encodes light intensities (passive sensor) Range (depth) image encodes shape and distance
Image Formation Dr. Gerhard Roth COMP 4102A Winter 2015 Version 3 1 Image Formation Two type of images Intensity image encodes light intensities (passive sensor) Range (depth) image encodes shape and distance
Instructions for the Experiment
 Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
Basics of Photogrammetry Note#6
 Basics of Photogrammetry Note#6 Photogrammetry Art and science of making accurate measurements by means of aerial photography Analog: visual and manual analysis of aerial photographs in hard-copy format
Basics of Photogrammetry Note#6 Photogrammetry Art and science of making accurate measurements by means of aerial photography Analog: visual and manual analysis of aerial photographs in hard-copy format
Chapter 11-Shooting Action
 Chapter 11-Shooting Action Interpreting Action There are three basic ways of interpreting action in a still photograph: Stopping action (42) Blurring movement Combining both in the same image Any
Chapter 11-Shooting Action Interpreting Action There are three basic ways of interpreting action in a still photograph: Stopping action (42) Blurring movement Combining both in the same image Any
Reikan FoCal Aperture Sharpness Test Report
 Focus Calibration and Analysis Software Test run on: 26/01/2016 17:02:00 with FoCal 2.0.6.2416W Report created on: 26/01/2016 17:03:39 with FoCal 2.0.6W Overview Test Information Property Description Data
Focus Calibration and Analysis Software Test run on: 26/01/2016 17:02:00 with FoCal 2.0.6.2416W Report created on: 26/01/2016 17:03:39 with FoCal 2.0.6W Overview Test Information Property Description Data
Computer Vision. The Pinhole Camera Model
 Computer Vision The Pinhole Camera Model Filippo Bergamasco (filippo.bergamasco@unive.it) http://www.dais.unive.it/~bergamasco DAIS, Ca Foscari University of Venice Academic year 2017/2018 Imaging device
Computer Vision The Pinhole Camera Model Filippo Bergamasco (filippo.bergamasco@unive.it) http://www.dais.unive.it/~bergamasco DAIS, Ca Foscari University of Venice Academic year 2017/2018 Imaging device
AgilEye Manual Version 2.0 February 28, 2007
 AgilEye Manual Version 2.0 February 28, 2007 1717 Louisiana NE Suite 202 Albuquerque, NM 87110 (505) 268-4742 support@agiloptics.com 2 (505) 268-4742 v. 2.0 February 07, 2007 3 Introduction AgilEye Wavefront
AgilEye Manual Version 2.0 February 28, 2007 1717 Louisiana NE Suite 202 Albuquerque, NM 87110 (505) 268-4742 support@agiloptics.com 2 (505) 268-4742 v. 2.0 February 07, 2007 3 Introduction AgilEye Wavefront
CSC Stereography Course I. What is Stereoscopic Photography?... 3 A. Binocular Vision Depth perception due to stereopsis
 CSC Stereography Course 101... 3 I. What is Stereoscopic Photography?... 3 A. Binocular Vision... 3 1. Depth perception due to stereopsis... 3 2. Concept was understood hundreds of years ago... 3 3. Stereo
CSC Stereography Course 101... 3 I. What is Stereoscopic Photography?... 3 A. Binocular Vision... 3 1. Depth perception due to stereopsis... 3 2. Concept was understood hundreds of years ago... 3 3. Stereo
This talk is oriented toward artists.
 Hello, My name is Sébastien Lagarde, I am a graphics programmer at Unity and with my two artist co-workers Sébastien Lachambre and Cyril Jover, we have tried to setup an easy method to capture accurate
Hello, My name is Sébastien Lagarde, I am a graphics programmer at Unity and with my two artist co-workers Sébastien Lachambre and Cyril Jover, we have tried to setup an easy method to capture accurate
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision
 CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 2 - Class 2: Vision, Physics, Cameras September 7th, 2017 Today Physics Human Vision Eye Brain Perspective Projection Camera Models Image Formation Digital
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 2 - Class 2: Vision, Physics, Cameras September 7th, 2017 Today Physics Human Vision Eye Brain Perspective Projection Camera Models Image Formation Digital
Funded from the Scottish Hydro Gordonbush Community Fund. Metering exposure
 Funded from the Scottish Hydro Gordonbush Community Fund Metering exposure We have looked at the three components of exposure: Shutter speed time light allowed in. Aperture size of hole through which light
Funded from the Scottish Hydro Gordonbush Community Fund Metering exposure We have looked at the three components of exposure: Shutter speed time light allowed in. Aperture size of hole through which light
ECEN. Spectroscopy. Lab 8. copy. constituents HOMEWORK PR. Figure. 1. Layout of. of the
 ECEN 4606 Lab 8 Spectroscopy SUMMARY: ROBLEM 1: Pedrotti 3 12-10. In this lab, you will design, build and test an optical spectrum analyzer and use it for both absorption and emission spectroscopy. The
ECEN 4606 Lab 8 Spectroscopy SUMMARY: ROBLEM 1: Pedrotti 3 12-10. In this lab, you will design, build and test an optical spectrum analyzer and use it for both absorption and emission spectroscopy. The
Reikan FoCal Aperture Sharpness Test Report
 Focus Calibration and Analysis Software Reikan FoCal Sharpness Test Report Test run on: 26/01/2016 17:14:35 with FoCal 2.0.6.2416W Report created on: 26/01/2016 17:16:16 with FoCal 2.0.6W Overview Test
Focus Calibration and Analysis Software Reikan FoCal Sharpness Test Report Test run on: 26/01/2016 17:14:35 with FoCal 2.0.6.2416W Report created on: 26/01/2016 17:16:16 with FoCal 2.0.6W Overview Test
Standard Operating Procedure for Flat Port Camera Calibration
 Standard Operating Procedure for Flat Port Camera Calibration Kevin Köser and Anne Jordt Revision 0.1 - Draft February 27, 2015 1 Goal This document specifies the practical procedure to obtain good images
Standard Operating Procedure for Flat Port Camera Calibration Kevin Köser and Anne Jordt Revision 0.1 - Draft February 27, 2015 1 Goal This document specifies the practical procedure to obtain good images
Quintic Hardware Tutorial Camera Set-Up
 Quintic Hardware Tutorial Camera Set-Up 1 All Quintic Live High-Speed cameras are specifically designed to meet a wide range of needs including coaching, performance analysis and research. Quintic LIVE
Quintic Hardware Tutorial Camera Set-Up 1 All Quintic Live High-Speed cameras are specifically designed to meet a wide range of needs including coaching, performance analysis and research. Quintic LIVE
Great (Focal) Lengths Assignment #2. Due 5:30PM on Monday, October 19, 2009.
 Great (Focal) Lengths Assignment #2. Due 5:30PM on Monday, October 19, 2009. Part I. Pick Your Brain! (50 points) Type your answers for the following questions in a word processor; we will accept Word
Great (Focal) Lengths Assignment #2. Due 5:30PM on Monday, October 19, 2009. Part I. Pick Your Brain! (50 points) Type your answers for the following questions in a word processor; we will accept Word
Sharpness, Resolution and Interpolation
 Sharpness, Resolution and Interpolation Introduction There are a lot of misconceptions about resolution, camera pixel count, interpolation and their effect on astronomical images. Some of the confusion
Sharpness, Resolution and Interpolation Introduction There are a lot of misconceptions about resolution, camera pixel count, interpolation and their effect on astronomical images. Some of the confusion
MEM: Intro to Robotics. Assignment 3I. Due: Wednesday 10/15 11:59 EST
 MEM: Intro to Robotics Assignment 3I Due: Wednesday 10/15 11:59 EST 1. Basic Optics You are shopping for a new lens for your Canon D30 digital camera and there are lots of lens options at the store. Your
MEM: Intro to Robotics Assignment 3I Due: Wednesday 10/15 11:59 EST 1. Basic Optics You are shopping for a new lens for your Canon D30 digital camera and there are lots of lens options at the store. Your
Focus Stacking Tutorial (Rev. 1.)
 Focus Stacking Tutorial (Rev. 1.) Written by Gerry Gerling Focus stacking is a method used to dramatically increase the depth of field (DOF) by incrementally changing the focus distance while taking multiple
Focus Stacking Tutorial (Rev. 1.) Written by Gerry Gerling Focus stacking is a method used to dramatically increase the depth of field (DOF) by incrementally changing the focus distance while taking multiple
Overview. Pinhole camera model Projective geometry Vanishing points and lines Projection matrix Cameras with Lenses Color Digital image
 Camera & Color Overview Pinhole camera model Projective geometry Vanishing points and lines Projection matrix Cameras with Lenses Color Digital image Book: Hartley 6.1, Szeliski 2.1.5, 2.2, 2.3 The trip
Camera & Color Overview Pinhole camera model Projective geometry Vanishing points and lines Projection matrix Cameras with Lenses Color Digital image Book: Hartley 6.1, Szeliski 2.1.5, 2.2, 2.3 The trip
How do we see the world?
 The Camera 1 How do we see the world? Let s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object Do we get a reasonable image? Credit: Steve Seitz 2 Pinhole camera Idea 2: Add a barrier to
The Camera 1 How do we see the world? Let s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object Do we get a reasonable image? Credit: Steve Seitz 2 Pinhole camera Idea 2: Add a barrier to
Home Lab 2 Pinhole Viewer Box
 1 Home Lab 2 Pinhole Viewer Box Overview A pinhole camera, also known as camera obscura, or "dark chamber", is a simple optical imaging device in the shape of a closed box or chamber. In one of its sides
1 Home Lab 2 Pinhole Viewer Box Overview A pinhole camera, also known as camera obscura, or "dark chamber", is a simple optical imaging device in the shape of a closed box or chamber. In one of its sides
Reikan FoCal Aperture Sharpness Test Report
 Focus Calibration and Analysis Software Reikan FoCal Sharpness Test Report Test run on: 10/02/2016 19:57:05 with FoCal 2.0.6.2416W Report created on: 10/02/2016 19:59:09 with FoCal 2.0.6W Overview Test
Focus Calibration and Analysis Software Reikan FoCal Sharpness Test Report Test run on: 10/02/2016 19:57:05 with FoCal 2.0.6.2416W Report created on: 10/02/2016 19:59:09 with FoCal 2.0.6W Overview Test
Capturing Realistic HDR Images. Dave Curtin Nassau County Camera Club February 24 th, 2016
 Capturing Realistic HDR Images Dave Curtin Nassau County Camera Club February 24 th, 2016 Capturing Realistic HDR Images Topics: What is HDR? In Camera. Post-Processing. Sample Workflow. Q & A. Capturing
Capturing Realistic HDR Images Dave Curtin Nassau County Camera Club February 24 th, 2016 Capturing Realistic HDR Images Topics: What is HDR? In Camera. Post-Processing. Sample Workflow. Q & A. Capturing
Using PhotoModeler for 2D Template Digitizing Eos Systems Inc.
 Using PhotoModeler for 2D Template Digitizing 2017 Eos Systems Inc. Table of Contents The Problem... 3 Why use a photogrammetry package?... 3 Caveats and License to Use... 3 The Basic Premise... 3 The
Using PhotoModeler for 2D Template Digitizing 2017 Eos Systems Inc. Table of Contents The Problem... 3 Why use a photogrammetry package?... 3 Caveats and License to Use... 3 The Basic Premise... 3 The
Working with your Camera
 Topic 5 Introduction to Shutter, Aperture and ISO Learning Outcomes In this topic, you will learn about the three main functions on a DSLR: Shutter, Aperture and ISO. We must also consider white balance
Topic 5 Introduction to Shutter, Aperture and ISO Learning Outcomes In this topic, you will learn about the three main functions on a DSLR: Shutter, Aperture and ISO. We must also consider white balance
Reikan FoCal Aperture Sharpness Test Report
 Focus Calibration and Analysis Software Reikan FoCal Sharpness Test Report Test run on: 27/01/2016 00:35:25 with FoCal 2.0.6.2416W Report created on: 27/01/2016 00:41:43 with FoCal 2.0.6W Overview Test
Focus Calibration and Analysis Software Reikan FoCal Sharpness Test Report Test run on: 27/01/2016 00:35:25 with FoCal 2.0.6.2416W Report created on: 27/01/2016 00:41:43 with FoCal 2.0.6W Overview Test
High Dynamic Range Photography
 JUNE 13, 2018 ADVANCED High Dynamic Range Photography Featuring TONY SWEET Tony Sweet D3, AF-S NIKKOR 14-24mm f/2.8g ED. f/22, ISO 200, aperture priority, Matrix metering. Basically there are two reasons
JUNE 13, 2018 ADVANCED High Dynamic Range Photography Featuring TONY SWEET Tony Sweet D3, AF-S NIKKOR 14-24mm f/2.8g ED. f/22, ISO 200, aperture priority, Matrix metering. Basically there are two reasons
TAKING GREAT PICTURES. A Modest Introduction
 TAKING GREAT PICTURES A Modest Introduction HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT CAMERA EQUIPMENT WE ARE NOW LIVING THROUGH THE GOLDEN AGE OF PHOTOGRAPHY Rapid innovation gives us much better cameras and photo software...
TAKING GREAT PICTURES A Modest Introduction HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT CAMERA EQUIPMENT WE ARE NOW LIVING THROUGH THE GOLDEN AGE OF PHOTOGRAPHY Rapid innovation gives us much better cameras and photo software...
Reikan FoCal Aperture Sharpness Test Report
 Focus Calibration and Analysis Software Test run on: 26/01/2016 17:56:23 with FoCal 2.0.6.2416W Report created on: 26/01/2016 17:59:12 with FoCal 2.0.6W Overview Test Information Property Description Data
Focus Calibration and Analysis Software Test run on: 26/01/2016 17:56:23 with FoCal 2.0.6.2416W Report created on: 26/01/2016 17:59:12 with FoCal 2.0.6W Overview Test Information Property Description Data
Lens Aperture. South Pasadena High School Final Exam Study Guide- 1 st Semester Photo ½. Study Guide Topics that will be on the Final Exam
 South Pasadena High School Final Exam Study Guide- 1 st Semester Photo ½ Study Guide Topics that will be on the Final Exam The Rule of Thirds Depth of Field Lens and its properties Aperture and F-Stop
South Pasadena High School Final Exam Study Guide- 1 st Semester Photo ½ Study Guide Topics that will be on the Final Exam The Rule of Thirds Depth of Field Lens and its properties Aperture and F-Stop
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION
 FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
As can be seen in the example pictures below showing over exposure (too much light) to under exposure (too little light):
 Hopefully after we are done with this you will resist any temptations you may have to use the automatic settings provided by your camera. Once you understand exposure, especially f-stops and shutter speeds,
Hopefully after we are done with this you will resist any temptations you may have to use the automatic settings provided by your camera. Once you understand exposure, especially f-stops and shutter speeds,
P202/219 Laboratory IUPUI Physics Department THIN LENSES
 THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
Lenses, exposure, and (de)focus
 Lenses, exposure, and (de)focus http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 15 Course announcements Homework 4 is out. - Due October 26
Lenses, exposure, and (de)focus http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 15 Course announcements Homework 4 is out. - Due October 26
Projection. Announcements. Müller-Lyer Illusion. Image formation. Readings Nalwa 2.1
 Announcements Mailing list (you should have received messages) Project 1 additional test sequences online Projection Readings Nalwa 2.1 Müller-Lyer Illusion Image formation object film by Pravin Bhat http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/sze_muelue/index.html
Announcements Mailing list (you should have received messages) Project 1 additional test sequences online Projection Readings Nalwa 2.1 Müller-Lyer Illusion Image formation object film by Pravin Bhat http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/sze_muelue/index.html
Camera Exposure Modes
 What is Exposure? Exposure refers to how bright or dark your photo is. This is affected by the amount of light that is recorded by your camera s sensor. A properly exposed photo should typically resemble
What is Exposure? Exposure refers to how bright or dark your photo is. This is affected by the amount of light that is recorded by your camera s sensor. A properly exposed photo should typically resemble
Modeling and Synthesis of Aperture Effects in Cameras
 Modeling and Synthesis of Aperture Effects in Cameras Douglas Lanman, Ramesh Raskar, and Gabriel Taubin Computational Aesthetics 2008 20 June, 2008 1 Outline Introduction and Related Work Modeling Vignetting
Modeling and Synthesis of Aperture Effects in Cameras Douglas Lanman, Ramesh Raskar, and Gabriel Taubin Computational Aesthetics 2008 20 June, 2008 1 Outline Introduction and Related Work Modeling Vignetting
Aperture Explained. helping you to better understand your digital SLR camera SLR PHOTOGRAPHY GUIDE
 Aperture Explained helping you to better understand your digital SLR camera SLR PHOTOGRAPHY GUIDE WELCOME 1 helping you to better understand your digital SLR camera. This 4 part series will cover Aperture,
Aperture Explained helping you to better understand your digital SLR camera SLR PHOTOGRAPHY GUIDE WELCOME 1 helping you to better understand your digital SLR camera. This 4 part series will cover Aperture,
Term 1 Study Guide for Digital Photography
 Name: Period Term 1 Study Guide for Digital Photography History: 1. The first type of camera was a camera obscura. 2. took the world s first permanent camera image. 3. invented film and the prototype of
Name: Period Term 1 Study Guide for Digital Photography History: 1. The first type of camera was a camera obscura. 2. took the world s first permanent camera image. 3. invented film and the prototype of
Name: Date: Math in Special Effects: Try Other Challenges. Student Handout
 Name: Date: Math in Special Effects: Try Other Challenges When filming special effects, a high-speed photographer needs to control the duration and impact of light by adjusting a number of settings, including
Name: Date: Math in Special Effects: Try Other Challenges When filming special effects, a high-speed photographer needs to control the duration and impact of light by adjusting a number of settings, including
6.098 Digital and Computational Photography Advanced Computational Photography. Bill Freeman Frédo Durand MIT - EECS
 6.098 Digital and Computational Photography 6.882 Advanced Computational Photography Bill Freeman Frédo Durand MIT - EECS Administrivia PSet 1 is out Due Thursday February 23 Digital SLR initiation? During
6.098 Digital and Computational Photography 6.882 Advanced Computational Photography Bill Freeman Frédo Durand MIT - EECS Administrivia PSet 1 is out Due Thursday February 23 Digital SLR initiation? During
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB
 ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
Forest Inventory System. User manual v.1.2
 Forest Inventory System User manual v.1.2 Table of contents 1. How TRESTIMA works... 3 1.2 How TRESTIMA calculates basal area... 3 2. Usage in the forest... 5 2.1. Measuring basal area by shooting pictures...
Forest Inventory System User manual v.1.2 Table of contents 1. How TRESTIMA works... 3 1.2 How TRESTIMA calculates basal area... 3 2. Usage in the forest... 5 2.1. Measuring basal area by shooting pictures...
EXPOSURE TIPS. Camera shake causing blurry pictures
 EXPOSURE TIPS Camera shake causing blurry pictures Hold your camera steady Digital cameras are usually held away from the body to view the LCD screen to compose the picture. This is less steady than the
EXPOSURE TIPS Camera shake causing blurry pictures Hold your camera steady Digital cameras are usually held away from the body to view the LCD screen to compose the picture. This is less steady than the
Name Digital Imaging I Chapters 9 12 Review Material
 Name Digital Imaging I Chapters 9 12 Review Material Chapter 9 Filters A filter is a glass or plastic lens attachment that you put on the front of your lens to protect the lens or alter the image as you
Name Digital Imaging I Chapters 9 12 Review Material Chapter 9 Filters A filter is a glass or plastic lens attachment that you put on the front of your lens to protect the lens or alter the image as you
Cameras. CSE 455, Winter 2010 January 25, 2010
 Cameras CSE 455, Winter 2010 January 25, 2010 Announcements New Lecturer! Neel Joshi, Ph.D. Post-Doctoral Researcher Microsoft Research neel@cs Project 1b (seam carving) was due on Friday the 22 nd Project
Cameras CSE 455, Winter 2010 January 25, 2010 Announcements New Lecturer! Neel Joshi, Ph.D. Post-Doctoral Researcher Microsoft Research neel@cs Project 1b (seam carving) was due on Friday the 22 nd Project
English PRO-642. Advanced Features: On-Screen Display
 English PRO-642 Advanced Features: On-Screen Display 1 Adjusting the Camera Settings The joystick has a middle button that you click to open the OSD menu. This button is also used to select an option that
English PRO-642 Advanced Features: On-Screen Display 1 Adjusting the Camera Settings The joystick has a middle button that you click to open the OSD menu. This button is also used to select an option that
Intro to Digital SLR and ILC Photography Week 1 The Camera Body
 Intro to Digital SLR and ILC Photography Week 1 The Camera Body Instructor: Roger Buchanan Class notes are available at www.thenerdworks.com Course Outline: Week 1 Camera Body; Week 2 Lenses; Week 3 Accessories,
Intro to Digital SLR and ILC Photography Week 1 The Camera Body Instructor: Roger Buchanan Class notes are available at www.thenerdworks.com Course Outline: Week 1 Camera Body; Week 2 Lenses; Week 3 Accessories,
OUTDOOR PORTRAITURE WORKSHOP
 OUTDOOR PORTRAITURE WORKSHOP SECOND EDITION Copyright Bryan A. Thompson, 2012 bryan@rollaphoto.com Goals The goals of this workshop are to present various techniques for creating portraits in an outdoor
OUTDOOR PORTRAITURE WORKSHOP SECOND EDITION Copyright Bryan A. Thompson, 2012 bryan@rollaphoto.com Goals The goals of this workshop are to present various techniques for creating portraits in an outdoor
Photography Basics. Exposure
 Photography Basics Exposure Impact Voice Transformation Creativity Narrative Composition Use of colour / tonality Depth of Field Use of Light Basics Focus Technical Exposure Courtesy of Bob Ryan Depth
Photography Basics Exposure Impact Voice Transformation Creativity Narrative Composition Use of colour / tonality Depth of Field Use of Light Basics Focus Technical Exposure Courtesy of Bob Ryan Depth
Understanding and Using Dynamic Range. Eagle River Camera Club October 2, 2014
 Understanding and Using Dynamic Range Eagle River Camera Club October 2, 2014 Dynamic Range Simplified Definition The number of exposure stops between the lightest usable white and the darkest useable
Understanding and Using Dynamic Range Eagle River Camera Club October 2, 2014 Dynamic Range Simplified Definition The number of exposure stops between the lightest usable white and the darkest useable
1 / 9
 WWW.RICHIEHUG.COM 1 / 9 A Beginner's Guide to Digital Photography Version 1.2 By Richie Hug November 24, 2016. Most people owning a digital camera have never used other settings than just the AUTO mode.
WWW.RICHIEHUG.COM 1 / 9 A Beginner's Guide to Digital Photography Version 1.2 By Richie Hug November 24, 2016. Most people owning a digital camera have never used other settings than just the AUTO mode.
HDR videos acquisition
 HDR videos acquisition dr. Francesco Banterle francesco.banterle@isti.cnr.it How to capture? Videos are challenging: We need to capture multiple frames at different exposure times and everything moves
HDR videos acquisition dr. Francesco Banterle francesco.banterle@isti.cnr.it How to capture? Videos are challenging: We need to capture multiple frames at different exposure times and everything moves
Sensors and Sensing Cameras and Camera Calibration
 Sensors and Sensing Cameras and Camera Calibration Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 20.11.2014
Sensors and Sensing Cameras and Camera Calibration Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 20.11.2014
Exposure settings & Lens choices
 Exposure settings & Lens choices Graham Relf Tynemouth Photographic Society September 2018 www.tynemouthps.org We will look at the 3 variables available for manual control of digital photos: Exposure time/duration,
Exposure settings & Lens choices Graham Relf Tynemouth Photographic Society September 2018 www.tynemouthps.org We will look at the 3 variables available for manual control of digital photos: Exposure time/duration,
Aperture & ƒ/stop Worksheet
 Tools and Program Needed: Digital C. Computer USB Drive Bridge PhotoShop Name: Manipulating Depth-of-Field Aperture & stop Worksheet The aperture setting (AV on the dial) is a setting to control the amount
Tools and Program Needed: Digital C. Computer USB Drive Bridge PhotoShop Name: Manipulating Depth-of-Field Aperture & stop Worksheet The aperture setting (AV on the dial) is a setting to control the amount
Introduction to Digital Photography
 Introduction to Digital Photography with Nick Davison Photography is The mastering of the technical aspects of the camera combined with, The artistic vision and creative know how to produce an interesting
Introduction to Digital Photography with Nick Davison Photography is The mastering of the technical aspects of the camera combined with, The artistic vision and creative know how to produce an interesting
One Week to Better Photography
 One Week to Better Photography Glossary Adobe Bridge Useful application packaged with Adobe Photoshop that previews, organizes and renames digital image files and creates digital contact sheets Adobe Photoshop
One Week to Better Photography Glossary Adobe Bridge Useful application packaged with Adobe Photoshop that previews, organizes and renames digital image files and creates digital contact sheets Adobe Photoshop
The Bellows Extension Exposure Factor: Including Useful Reference Charts for use in the Field
 The Bellows Extension Exposure Factor: Including Useful Reference Charts for use in the Field Robert B. Hallock hallock@physics.umass.edu revised May 23, 2005 Abstract: The need for a bellows correction
The Bellows Extension Exposure Factor: Including Useful Reference Charts for use in the Field Robert B. Hallock hallock@physics.umass.edu revised May 23, 2005 Abstract: The need for a bellows correction
Exercise questions for Machine vision
 Exercise questions for Machine vision This is a collection of exercise questions. These questions are all examination alike which means that similar questions may appear at the written exam. I ve divided
Exercise questions for Machine vision This is a collection of exercise questions. These questions are all examination alike which means that similar questions may appear at the written exam. I ve divided
Volume 1 - Module 6 Geometry of Aerial Photography. I. Classification of Photographs. Vertical
 RSCC Volume 1 Introduction to Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry Table of Contents Module 1 Module 2 Module 3.1 Module 3.2 Module 4 Module 5 Module 6 Module 7 Module 8 Labs Volume 1 - Module 6 Geometry
RSCC Volume 1 Introduction to Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry Table of Contents Module 1 Module 2 Module 3.1 Module 3.2 Module 4 Module 5 Module 6 Module 7 Module 8 Labs Volume 1 - Module 6 Geometry
3D Capture. Using Fujifilm 3D Camera. Copyright Apis Footwear
 3D Capture Using Fujifilm 3D Camera Copyright 201 4 Apis Footwear Camera Settings Before shooting 3D images, please make sure the camera is set as follows: a. Rotate the upper dial to position the red
3D Capture Using Fujifilm 3D Camera Copyright 201 4 Apis Footwear Camera Settings Before shooting 3D images, please make sure the camera is set as follows: a. Rotate the upper dial to position the red
3D Capture. Using Fujifilm 3D Camera. Copyright Apis Footwear
 3D Capture Using Fujifilm 3D Camera Copyright 201 3 Apis Footwear Assembly and Settings 1. Assembly If your camera came without the projector attached, then you need to do it yourself. First remove the
3D Capture Using Fujifilm 3D Camera Copyright 201 3 Apis Footwear Assembly and Settings 1. Assembly If your camera came without the projector attached, then you need to do it yourself. First remove the
Optics. Experiment #4
 Optics Experiment #4 NOTE: For submitting the report on this laboratory session you will need a report booklet of the type that can be purchased at the McGill Bookstore. The material of the course that
Optics Experiment #4 NOTE: For submitting the report on this laboratory session you will need a report booklet of the type that can be purchased at the McGill Bookstore. The material of the course that
Laboratory experiment aberrations
 Laboratory experiment aberrations Obligatory laboratory experiment on course in Optical design, SK2330/SK3330, KTH. Date Name Pass Objective This laboratory experiment is intended to demonstrate the most
Laboratory experiment aberrations Obligatory laboratory experiment on course in Optical design, SK2330/SK3330, KTH. Date Name Pass Objective This laboratory experiment is intended to demonstrate the most
IMAGE SENSOR SOLUTIONS. KAC-96-1/5" Lens Kit. KODAK KAC-96-1/5" Lens Kit. for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors. November 2004 Revision 2
 KODAK for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors November 2004 Revision 2 1.1 Introduction Choosing the right lens is a critical aspect of designing an imaging system. Typically the trade off between image
KODAK for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors November 2004 Revision 2 1.1 Introduction Choosing the right lens is a critical aspect of designing an imaging system. Typically the trade off between image
3D Flaming Liquid Group Gamma Project 3
 3D Flaming Liquid Group Gamma Project 3 Lucy Dean, Joseph Duggan, Melissa Lucht, Tim Jarrell Flow Visualization MCEN 4228 April 29 th, 2009 Intoduction The intent of this submission was to take the photographs
3D Flaming Liquid Group Gamma Project 3 Lucy Dean, Joseph Duggan, Melissa Lucht, Tim Jarrell Flow Visualization MCEN 4228 April 29 th, 2009 Intoduction The intent of this submission was to take the photographs
3DUNDERWORLD-SLS v.3.0
 3DUNDERWORLD-SLS v.3.0 Rapid Scanning and Automatic 3D Reconstruction of Underwater Sites FP7-PEOPLE-2010-RG - 268256 3DUNDERWORLD Software Developer(s): Kyriakos Herakleous Researcher(s): Kyriakos Herakleous,
3DUNDERWORLD-SLS v.3.0 Rapid Scanning and Automatic 3D Reconstruction of Underwater Sites FP7-PEOPLE-2010-RG - 268256 3DUNDERWORLD Software Developer(s): Kyriakos Herakleous Researcher(s): Kyriakos Herakleous,
PTC School of Photography. Beginning Course Class 2 - Exposure
 PTC School of Photography Beginning Course Class 2 - Exposure Today s Topics: What is Exposure Shutter Speed for Exposure Shutter Speed for Motion Aperture for Exposure Aperture for Depth of Field Exposure
PTC School of Photography Beginning Course Class 2 - Exposure Today s Topics: What is Exposure Shutter Speed for Exposure Shutter Speed for Motion Aperture for Exposure Aperture for Depth of Field Exposure
Problem Set 3. Assigned: March 9, 2006 Due: March 23, (Optional) Multiple-Exposure HDR Images
 6.098/6.882 Computational Photography 1 Problem Set 3 Assigned: March 9, 2006 Due: March 23, 2006 Problem 1 (Optional) Multiple-Exposure HDR Images Even though this problem is optional, we recommend you
6.098/6.882 Computational Photography 1 Problem Set 3 Assigned: March 9, 2006 Due: March 23, 2006 Problem 1 (Optional) Multiple-Exposure HDR Images Even though this problem is optional, we recommend you
Team Second Peter Brunsgaard. Flow Visualization. Professor Jean Hertzberg. 1 P a g e
 Team Second 2016 Peter Brunsgaard Flow Visualization Professor Jean Hertzberg 2016 1 P a g e Introduction The purpose of this assignment was to explore a fluid flow from an artistic perspective. The project
Team Second 2016 Peter Brunsgaard Flow Visualization Professor Jean Hertzberg 2016 1 P a g e Introduction The purpose of this assignment was to explore a fluid flow from an artistic perspective. The project
Introduction to 2-D Copy Work
 Introduction to 2-D Copy Work What is the purpose of creating digital copies of your analogue work? To use for digital editing To submit work electronically to professors or clients To share your work
Introduction to 2-D Copy Work What is the purpose of creating digital copies of your analogue work? To use for digital editing To submit work electronically to professors or clients To share your work
Multi Viewpoint Panoramas
 27. November 2007 1 Motivation 2 Methods Slit-Scan "The System" 3 "The System" Approach Preprocessing Surface Selection Panorama Creation Interactive Renement 4 Sources Motivation image showing long continous
27. November 2007 1 Motivation 2 Methods Slit-Scan "The System" 3 "The System" Approach Preprocessing Surface Selection Panorama Creation Interactive Renement 4 Sources Motivation image showing long continous
Photography. Taking better photos
 Photography Taking better photos Composition Composition is the arrangement of the visual elements of the photograph, such as Geometric elements, such as lines, shapes, and curves Contrasts of tone, color,
Photography Taking better photos Composition Composition is the arrangement of the visual elements of the photograph, such as Geometric elements, such as lines, shapes, and curves Contrasts of tone, color,
