Projection. Announcements. Müller-Lyer Illusion. Image formation. Readings Nalwa 2.1
|
|
|
- Vincent Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Announcements Mailing list (you should have received messages) Project 1 additional test sequences online Projection Readings Nalwa 2.1 Müller-Lyer Illusion Image formation object film by Pravin Bhat Let s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object Do we get a reasonable image?
2 Pinhole camera Camera Obscura object barrier film Add a barrier to block off most of the rays This reduces blurring The opening known as the aperture How does this transform the image? The first camera Known to Aristotle How does the aperture size affect the image? Shrinking the aperture Shrinking the aperture Why not make the aperture as small as possible? Less light gets through Diffraction effects...
3 Adding a lens Lenses object lens film F circle of confusion optical center (Center Of Projection) focal point A lens focuses light onto the film There is a specific distance at which objects are in focus other points project to a circle of confusion in the image Changing the shape of the lens changes this distance A lens focuses parallel rays onto a single focal point focal point at a distance f beyond the plane of the lens f is a function of the shape and index of refraction of the lens Aperture of diameter D restricts the range of rays aperture may be on either side of the lens Lenses are typically spherical (easier to produce) Thin lenses Depth of field Thin lens equation: Any object point satisfying this equation is in focus What is the shape of the focus region? How can we change the focus region? Thin lens applet: (by Fu-Kwun Hwang ) Changing the aperture size affects depth of field A smaller aperture increases the range in which the object is approximately in focus
4 The eye Digital camera The human eye is a camera Iris - colored annulus with radial muscles Pupil - the hole (aperture) whose size is controlled by the iris What s the film? photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) in the retina A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons Two common types Charge Coupled Device (CCD) CMOS Digital camera issues Some things that affect digital cameras blooming color issues noise interlace scanning Blooming Theuseissen 1995
5 Handling Color: 3-chip cameras Mosaicing and Demosaicing Theuseissen 1995 Input Bilinear Cok Freeman LaRoche Noise Some factors affecting how noisy the image is CCD vs. CMOS size of sensor elements 5 to 10 µm; scientific up to 20 µm often hear 1/3, 1/2 inch chips (bigger is better) Fill factor (25% to 100%) What else? Interlace vs. progressive scan
6 Progressive scan Interlace Progressive scan vs. intelaced sensors Modeling projection Most camcorders are interlaced several exceptions (check the specs before you buy!) some can be switched between progressive and interlaced Used to be true also for video cameras (interlaced) But now it s becoming the opposite many/most digital video cameras are progressive scan The coordinate system We will use the pin-hole model as an approximation Put the optical center (Center Of Projection) at the origin Put the image plane (Projection Plane) in front of the COP Why? The camera looks down the negative z axis we need this if we want right-handed-coordinates
7 Modeling projection Homogeneous coordinates Is this a linear transformation? no division by z is nonlinear Trick: add one more coordinate: Projection equations Compute intersection with PP of ray from (x,y,z) to COP Derived using similar triangles (on board) homogeneous image coordinates Converting from homogeneous coordinates homogeneous scene coordinates We get the projection by throwing out the last coordinate: Perspective Projection Projection is a matrix multiply using homogeneous coordinates: Perspective Projection How does scaling the projection matrix change the transformation? divide by third coordinate This is known as perspective projection The matrix is the projection matrix Can also formulate as a 4x4 (today s reading does this) divide by fourth coordinate
8 Orthographic projection Special case of perspective projection Distance from the COP to the PP is infinite Other types of projection Scaled orthographic Also called weak perspective Image World Affine projection Also called paraperspective Also called parallel projection : (x, y, z) (x, y) What s the projection matrix? Camera parameters A camera is described by several parameters Translation T of the optical center from the origin of world coords Rotation R of the image plane focal length f, principle point (x c, y c ), pixel size (s x, s y ) blue parameters are called extrinsics, red are intrinsics Projection equation X sx * * * * x Y = sy = * * * * = ΠX Z s * * * * 1 The projection matrix models the cumulative effect of all parameters Useful to decompose into a series of operations identity matrix fsx 0 x' c = 0 ' x x1 Π R I T fs x x y y c 01x3 1 01x intrinsics projection rotation translation The definitions of these parameters are not completely standardized especially intrinsics varies from one book to another Distortion No distortion Pin cushion Barrel Radial distortion of the image Caused by imperfect lenses Deviations are most noticeable for rays that pass through the edge of the lens
9 Correcting radial distortion Distortion from Helmut Dersch Modeling distortion Project to normalized image coordinates Apply radial distortion Apply focal length translate image center To model lens distortion Use above projection operation instead of standard projection matrix multiplication
Projection. Projection. Image formation. Müller-Lyer Illusion. Readings. Readings. Let s design a camera. Szeliski 2.1. Szeliski 2.
 Projection Projection Readings Szeliski 2.1 Readings Szeliski 2.1 Müller-Lyer Illusion Image formation object film by Pravin Bhat http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/sze_muelue/index.html Let s design a camera
Projection Projection Readings Szeliski 2.1 Readings Szeliski 2.1 Müller-Lyer Illusion Image formation object film by Pravin Bhat http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/sze_muelue/index.html Let s design a camera
Projection. Readings. Szeliski 2.1. Wednesday, October 23, 13
 Projection Readings Szeliski 2.1 Projection Readings Szeliski 2.1 Müller-Lyer Illusion by Pravin Bhat Müller-Lyer Illusion by Pravin Bhat http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/sze_muelue/index.html Müller-Lyer
Projection Readings Szeliski 2.1 Projection Readings Szeliski 2.1 Müller-Lyer Illusion by Pravin Bhat Müller-Lyer Illusion by Pravin Bhat http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/sze_muelue/index.html Müller-Lyer
Cameras. CSE 455, Winter 2010 January 25, 2010
 Cameras CSE 455, Winter 2010 January 25, 2010 Announcements New Lecturer! Neel Joshi, Ph.D. Post-Doctoral Researcher Microsoft Research neel@cs Project 1b (seam carving) was due on Friday the 22 nd Project
Cameras CSE 455, Winter 2010 January 25, 2010 Announcements New Lecturer! Neel Joshi, Ph.D. Post-Doctoral Researcher Microsoft Research neel@cs Project 1b (seam carving) was due on Friday the 22 nd Project
Unit 1: Image Formation
 Unit 1: Image Formation 1. Geometry 2. Optics 3. Photometry 4. Sensor Readings Szeliski 2.1-2.3 & 6.3.5 1 Physical parameters of image formation Geometric Type of projection Camera pose Optical Sensor
Unit 1: Image Formation 1. Geometry 2. Optics 3. Photometry 4. Sensor Readings Szeliski 2.1-2.3 & 6.3.5 1 Physical parameters of image formation Geometric Type of projection Camera pose Optical Sensor
CS6670: Computer Vision
 CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 5: Cameras and Projection Szeliski 2.1.3-2.1.6 Reading Announcements Project 1 assigned, see projects page: http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs6670/2011sp/projects/projects.html
CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 5: Cameras and Projection Szeliski 2.1.3-2.1.6 Reading Announcements Project 1 assigned, see projects page: http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs6670/2011sp/projects/projects.html
The Camera : Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008
 The Camera 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 How do we see the world? object film Let s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object Do we get a reasonable
The Camera 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 How do we see the world? object film Let s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object Do we get a reasonable
Two strategies for realistic rendering capture real world data synthesize from bottom up
 Recap from Wednesday Two strategies for realistic rendering capture real world data synthesize from bottom up Both have existed for 500 years. Both are successful. Attempts to take the best of both world
Recap from Wednesday Two strategies for realistic rendering capture real world data synthesize from bottom up Both have existed for 500 years. Both are successful. Attempts to take the best of both world
LENSES. INEL 6088 Computer Vision
 LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
The Camera : Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005
 The Camera 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 How do we see the world? object film Let s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object Do we get a reasonable
The Camera 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 How do we see the world? object film Let s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object Do we get a reasonable
How do we see the world?
 The Camera 1 How do we see the world? Let s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object Do we get a reasonable image? Credit: Steve Seitz 2 Pinhole camera Idea 2: Add a barrier to
The Camera 1 How do we see the world? Let s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object Do we get a reasonable image? Credit: Steve Seitz 2 Pinhole camera Idea 2: Add a barrier to
CS6670: Computer Vision
 CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 4a: Cameras Source: S. Lazebnik Reading Szeliski chapter 2.2.3, 2.3 Image formation Let s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object
CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 4a: Cameras Source: S. Lazebnik Reading Szeliski chapter 2.2.3, 2.3 Image formation Let s design a camera Idea 1: put a piece of film in front of an object
Cameras. Outline. Pinhole camera. Camera trial #1. Pinhole camera Film camera Digital camera Video camera
 Outline Cameras Pinhole camera Film camera Digital camera Video camera Digital Visual Effects, Spring 2007 Yung-Yu Chuang 2007/3/6 with slides by Fredo Durand, Brian Curless, Steve Seitz and Alexei Efros
Outline Cameras Pinhole camera Film camera Digital camera Video camera Digital Visual Effects, Spring 2007 Yung-Yu Chuang 2007/3/6 with slides by Fredo Durand, Brian Curless, Steve Seitz and Alexei Efros
Building a Real Camera. Slides Credit: Svetlana Lazebnik
 Building a Real Camera Slides Credit: Svetlana Lazebnik Home-made pinhole camera Slide by A. Efros http://www.debevec.org/pinhole/ Shrinking the aperture Why not make the aperture as small as possible?
Building a Real Camera Slides Credit: Svetlana Lazebnik Home-made pinhole camera Slide by A. Efros http://www.debevec.org/pinhole/ Shrinking the aperture Why not make the aperture as small as possible?
Overview. Pinhole camera model Projective geometry Vanishing points and lines Projection matrix Cameras with Lenses Color Digital image
 Camera & Color Overview Pinhole camera model Projective geometry Vanishing points and lines Projection matrix Cameras with Lenses Color Digital image Book: Hartley 6.1, Szeliski 2.1.5, 2.2, 2.3 The trip
Camera & Color Overview Pinhole camera model Projective geometry Vanishing points and lines Projection matrix Cameras with Lenses Color Digital image Book: Hartley 6.1, Szeliski 2.1.5, 2.2, 2.3 The trip
Cameras. Digital Visual Effects, Spring 2008 Yung-Yu Chuang 2008/2/26. with slides by Fredo Durand, Brian Curless, Steve Seitz and Alexei Efros
 Cameras Digital Visual Effects, Spring 2008 Yung-Yu Chuang 2008/2/26 with slides by Fredo Durand, Brian Curless, Steve Seitz and Alexei Efros Camera trial #1 scene film Put a piece of film in front of
Cameras Digital Visual Effects, Spring 2008 Yung-Yu Chuang 2008/2/26 with slides by Fredo Durand, Brian Curless, Steve Seitz and Alexei Efros Camera trial #1 scene film Put a piece of film in front of
Building a Real Camera
 Building a Real Camera Home-made pinhole camera Slide by A. Efros http://www.debevec.org/pinhole/ Shrinking the aperture Why not make the aperture as small as possible? Less light gets through Diffraction
Building a Real Camera Home-made pinhole camera Slide by A. Efros http://www.debevec.org/pinhole/ Shrinking the aperture Why not make the aperture as small as possible? Less light gets through Diffraction
Cameras. Shrinking the aperture. Camera trial #1. Pinhole camera. Digital Visual Effects Yung-Yu Chuang. Put a piece of film in front of an object.
 Camera trial #1 Cameras Digital Visual Effects Yung-Yu Chuang scene film with slides by Fredo Durand, Brian Curless, Steve Seitz and Alexei Efros Put a piece of film in front of an object. Pinhole camera
Camera trial #1 Cameras Digital Visual Effects Yung-Yu Chuang scene film with slides by Fredo Durand, Brian Curless, Steve Seitz and Alexei Efros Put a piece of film in front of an object. Pinhole camera
Computer Vision. The Pinhole Camera Model
 Computer Vision The Pinhole Camera Model Filippo Bergamasco (filippo.bergamasco@unive.it) http://www.dais.unive.it/~bergamasco DAIS, Ca Foscari University of Venice Academic year 2017/2018 Imaging device
Computer Vision The Pinhole Camera Model Filippo Bergamasco (filippo.bergamasco@unive.it) http://www.dais.unive.it/~bergamasco DAIS, Ca Foscari University of Venice Academic year 2017/2018 Imaging device
Announcement A total of 5 (five) late days are allowed for projects. Office hours
 Announcement A total of 5 (five) late days are allowed for projects. Office hours Me: 3:50-4:50pm Thursday (or by appointment) Jake: 12:30-1:30PM Monday and Wednesday Image Formation Digital Camera Film
Announcement A total of 5 (five) late days are allowed for projects. Office hours Me: 3:50-4:50pm Thursday (or by appointment) Jake: 12:30-1:30PM Monday and Wednesday Image Formation Digital Camera Film
CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP)
 CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP) Ifeoma Nwogu inwogu@buffalo.edu Lecture 4 Image formation(part I) Schedule Last class linear algebra overview Today Image formation and camera properties
CSE 473/573 Computer Vision and Image Processing (CVIP) Ifeoma Nwogu inwogu@buffalo.edu Lecture 4 Image formation(part I) Schedule Last class linear algebra overview Today Image formation and camera properties
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision
 CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 2 - Class 2: Vision, Physics, Cameras September 7th, 2017 Today Physics Human Vision Eye Brain Perspective Projection Camera Models Image Formation Digital
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 2 - Class 2: Vision, Physics, Cameras September 7th, 2017 Today Physics Human Vision Eye Brain Perspective Projection Camera Models Image Formation Digital
IMAGE FORMATION. Light source properties. Sensor characteristics Surface. Surface reflectance properties. Optics
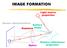 IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
Cameras. Outline. Pinhole camera. Camera trial #1. Pinhole camera Film camera Digital camera Video camera High dynamic range imaging
 Outline Cameras Pinhole camera Film camera Digital camera Video camera High dynamic range imaging Digital Visual Effects, Spring 2006 Yung-Yu Chuang 2006/3/1 with slides by Fedro Durand, Brian Curless,
Outline Cameras Pinhole camera Film camera Digital camera Video camera High dynamic range imaging Digital Visual Effects, Spring 2006 Yung-Yu Chuang 2006/3/1 with slides by Fedro Durand, Brian Curless,
Image formation - Cameras. Grading & Project. About the course. Tentative Schedule. Course Content. Students introduction
 About the course Instructors: Haibin Ling (hbling@temple, Wachman 35) Hours Lecture: Tuesda 5:3-8:pm, TTLMAN 43B Office hour: Tuesda 3: - 5:pm, or b appointment Textbook Computer Vision: Models, Learning,
About the course Instructors: Haibin Ling (hbling@temple, Wachman 35) Hours Lecture: Tuesda 5:3-8:pm, TTLMAN 43B Office hour: Tuesda 3: - 5:pm, or b appointment Textbook Computer Vision: Models, Learning,
Colorado School of Mines. Computer Vision. Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science.
 Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Sensors and Image Formation Imaging sensors and models of image formation Coordinate systems Digital
Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Sensors and Image Formation Imaging sensors and models of image formation Coordinate systems Digital
Acquisition. Some slides from: Yung-Yu Chuang (DigiVfx) Jan Neumann, Pat Hanrahan, Alexei Efros
 Acquisition Some slides from: Yung-Yu Chuang (DigiVfx) Jan Neumann, Pat Hanrahan, Alexei Efros Image Acquisition Digital Camera Film Outline Pinhole camera Lens Lens aberrations Exposure Sensors Noise
Acquisition Some slides from: Yung-Yu Chuang (DigiVfx) Jan Neumann, Pat Hanrahan, Alexei Efros Image Acquisition Digital Camera Film Outline Pinhole camera Lens Lens aberrations Exposure Sensors Noise
To Do. Advanced Computer Graphics. Outline. Computational Imaging. How do we see the world? Pinhole camera
 Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 163 [Spring 2017], Lecture 14 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir To Do Assignment 2 due May 19 Any last minute issues or questions? Next two lectures: Imaging,
Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 163 [Spring 2017], Lecture 14 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir To Do Assignment 2 due May 19 Any last minute issues or questions? Next two lectures: Imaging,
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 2: Image Formation in Eyes and Cameras Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: Image Formation in Eyes and Cameras Li Zhang Spring 2008 Today Eyes Cameras Light Why can we see? Visible Light and Beyond Infrared, e.g. radio wave longer wavelength
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: Image Formation in Eyes and Cameras Li Zhang Spring 2008 Today Eyes Cameras Light Why can we see? Visible Light and Beyond Infrared, e.g. radio wave longer wavelength
VC 16/17 TP2 Image Formation
 VC 16/17 TP2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Hélder Filipe Pinto de Oliveira Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual
VC 16/17 TP2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Hélder Filipe Pinto de Oliveira Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual
Image Formation and Capture. Acknowledgment: some figures by B. Curless, E. Hecht, W.J. Smith, B.K.P. Horn, and A. Theuwissen
 Image Formation and Capture Acknowledgment: some figures by B. Curless, E. Hecht, W.J. Smith, B.K.P. Horn, and A. Theuwissen Image Formation and Capture Real world Optics Sensor Devices Sources of Error
Image Formation and Capture Acknowledgment: some figures by B. Curless, E. Hecht, W.J. Smith, B.K.P. Horn, and A. Theuwissen Image Formation and Capture Real world Optics Sensor Devices Sources of Error
Image Formation: Camera Model
 Image Formation: Camera Model Ruigang Yang COMP 684 Fall 2005, CS684-IBMR Outline Camera Models Pinhole Perspective Projection Affine Projection Camera with Lenses Digital Image Formation The Human Eye
Image Formation: Camera Model Ruigang Yang COMP 684 Fall 2005, CS684-IBMR Outline Camera Models Pinhole Perspective Projection Affine Projection Camera with Lenses Digital Image Formation The Human Eye
Lecture 02 Image Formation 1
 Institute of Informatics Institute of Neuroinformatics Lecture 02 Image Formation 1 Davide Scaramuzza http://rpg.ifi.uzh.ch 1 Lab Exercise 1 - Today afternoon Room ETH HG E 1.1 from 13:15 to 15:00 Work
Institute of Informatics Institute of Neuroinformatics Lecture 02 Image Formation 1 Davide Scaramuzza http://rpg.ifi.uzh.ch 1 Lab Exercise 1 - Today afternoon Room ETH HG E 1.1 from 13:15 to 15:00 Work
Image Formation and Capture
 Figure credits: B. Curless, E. Hecht, W.J. Smith, B.K.P. Horn, A. Theuwissen, and J. Malik Image Formation and Capture COS 429: Computer Vision Image Formation and Capture Real world Optics Sensor Devices
Figure credits: B. Curless, E. Hecht, W.J. Smith, B.K.P. Horn, A. Theuwissen, and J. Malik Image Formation and Capture COS 429: Computer Vision Image Formation and Capture Real world Optics Sensor Devices
VC 14/15 TP2 Image Formation
 VC 14/15 TP2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
VC 14/15 TP2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
VC 11/12 T2 Image Formation
 VC 11/12 T2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
VC 11/12 T2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
Cameras, lenses and sensors
 Cameras, lenses and sensors Marc Pollefeys COMP 256 Cameras, lenses and sensors Camera Models Pinhole Perspective Projection Affine Projection Camera with Lenses Sensing The Human Eye Reading: Chapter.
Cameras, lenses and sensors Marc Pollefeys COMP 256 Cameras, lenses and sensors Camera Models Pinhole Perspective Projection Affine Projection Camera with Lenses Sensing The Human Eye Reading: Chapter.
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 2 Aug 24 th, 2017 Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, Rajesh Rao and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu 1 Instructor TA Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Pranav Mantini
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 2 Aug 24 th, 2017 Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, Rajesh Rao and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu 1 Instructor TA Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Pranav Mantini
Dr F. Cuzzolin 1. September 29, 2015
 P00407 Principles of Computer Vision 1 1 Department of Computing and Communication Technologies Oxford Brookes University, UK September 29, 2015 September 29, 2015 1 / 73 Outline of the Lecture 1 2 Basics
P00407 Principles of Computer Vision 1 1 Department of Computing and Communication Technologies Oxford Brookes University, UK September 29, 2015 September 29, 2015 1 / 73 Outline of the Lecture 1 2 Basics
Image Formation. Dr. Gerhard Roth. COMP 4102A Winter 2015 Version 3
 Image Formation Dr. Gerhard Roth COMP 4102A Winter 2015 Version 3 1 Image Formation Two type of images Intensity image encodes light intensities (passive sensor) Range (depth) image encodes shape and distance
Image Formation Dr. Gerhard Roth COMP 4102A Winter 2015 Version 3 1 Image Formation Two type of images Intensity image encodes light intensities (passive sensor) Range (depth) image encodes shape and distance
Lecture 2 Camera Models
 Lecture 2 Camera Models Professor Silvio Savarese Computational Vision and Geometr Lab Silvio Savarese Lecture 2-4-Jan-4 Announcements Prerequisites: an questions? This course requires knowledge of linear
Lecture 2 Camera Models Professor Silvio Savarese Computational Vision and Geometr Lab Silvio Savarese Lecture 2-4-Jan-4 Announcements Prerequisites: an questions? This course requires knowledge of linear
Lecture 7: Camera Models
 Lecture 7: Camera Models Professor Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn toda? Pinhole cameras Cameras & lenses The geometr of pinhole cameras Reading: [FP]Chapters 1 3 [HZ] Chapter 6 2 What we will
Lecture 7: Camera Models Professor Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn toda? Pinhole cameras Cameras & lenses The geometr of pinhole cameras Reading: [FP]Chapters 1 3 [HZ] Chapter 6 2 What we will
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 2 Aug 23 rd, 2018 Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, Rajesh Rao and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu 1 Instructor Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Pranav Mantini
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 2 Aug 23 rd, 2018 Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, Rajesh Rao and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu 1 Instructor Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Pranav Mantini
Single-view Metrology and Cameras
 Single-view Metrology and Cameras 10/10/17 Computational Photography Derek Hoiem, University of Illinois Project 2 Results Incomplete list of great project pages Haohang Huang: Best presented project;
Single-view Metrology and Cameras 10/10/17 Computational Photography Derek Hoiem, University of Illinois Project 2 Results Incomplete list of great project pages Haohang Huang: Best presented project;
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
Capturing Light in man and machine 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2008 Image Formation Digital Camera Film The Eye Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments
 Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 25 Cameras, Film, and Digital The Human Eye; Corrective Lenses Magnifying Glass Telescopes Compound Microscope Aberrations of Lenses and Mirrors Limits of
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 25 Cameras, Film, and Digital The Human Eye; Corrective Lenses Magnifying Glass Telescopes Compound Microscope Aberrations of Lenses and Mirrors Limits of
Lenses. Overview. Terminology. The pinhole camera. Pinhole camera Lenses Principles of operation Limitations
 Overview Pinhole camera Principles of operation Limitations 1 Terminology The pinhole camera The first camera - camera obscura - known to Aristotle. In 3D, we can visualize the blur induced by the pinhole
Overview Pinhole camera Principles of operation Limitations 1 Terminology The pinhole camera The first camera - camera obscura - known to Aristotle. In 3D, we can visualize the blur induced by the pinhole
The eye & corrective lenses
 Phys 102 Lecture 20 The eye & corrective lenses 1 Today we will... Apply concepts from ray optics & lenses Simple optical instruments the camera & the eye Learn about the human eye Accommodation Myopia,
Phys 102 Lecture 20 The eye & corrective lenses 1 Today we will... Apply concepts from ray optics & lenses Simple optical instruments the camera & the eye Learn about the human eye Accommodation Myopia,
Lecture 2 Camera Models
 Lecture 2 Camera Models Professor Silvio Savarese Computational Vision and Geometr Lab Silvio Savarese Lecture 2 - -Jan-8 Lecture 2 Camera Models Pinhole cameras Cameras lenses The geometr of pinhole cameras
Lecture 2 Camera Models Professor Silvio Savarese Computational Vision and Geometr Lab Silvio Savarese Lecture 2 - -Jan-8 Lecture 2 Camera Models Pinhole cameras Cameras lenses The geometr of pinhole cameras
Image Formation. Dr. Gerhard Roth. COMP 4102A Winter 2014 Version 1
 Image Formation Dr. Gerhard Roth COMP 4102A Winter 2014 Version 1 Image Formation Two type of images Intensity image encodes light intensities (passive sensor) Range (depth) image encodes shape and distance
Image Formation Dr. Gerhard Roth COMP 4102A Winter 2014 Version 1 Image Formation Two type of images Intensity image encodes light intensities (passive sensor) Range (depth) image encodes shape and distance
Lecture 8 Camera Models
 Lecture 8 Caera Models Professor Silvio Savarese Coputational Vision and Geoetr Lab Silvio Savarese Lecture 8-5-Oct-4 Lecture 8 Caera Models Pinhole caeras Caeras & lenses The geoetr of pinhole caeras
Lecture 8 Caera Models Professor Silvio Savarese Coputational Vision and Geoetr Lab Silvio Savarese Lecture 8-5-Oct-4 Lecture 8 Caera Models Pinhole caeras Caeras & lenses The geoetr of pinhole caeras
Image Formation. World Optics Sensor Signal. Computer Vision. Introduction to. Light (Energy) Source. Surface Imaging Plane. Pinhole Lens.
 Image Formation Light (Energy) Source Surface Imaging Plane Pinhole Lens World Optics Sensor Signal B&W Film Color Film TV Camera Silver Density Silver density in three color layers Electrical Today Optics:
Image Formation Light (Energy) Source Surface Imaging Plane Pinhole Lens World Optics Sensor Signal B&W Film Color Film TV Camera Silver Density Silver density in three color layers Electrical Today Optics:
Lecture 7: homogeneous coordinates
 Lecture 7: homogeneous Dr. Richard E. Turner (ret26@cam.ac.uk) October 31, 2013 House keeping webpage: http://cbl.eng.cam.ac.uk/public/turner/teaching Recap of last lecture: Pin hole camera image plane
Lecture 7: homogeneous Dr. Richard E. Turner (ret26@cam.ac.uk) October 31, 2013 House keeping webpage: http://cbl.eng.cam.ac.uk/public/turner/teaching Recap of last lecture: Pin hole camera image plane
Capturing Light in man and machine. Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al.
 Capturing Light in man and machine Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al. 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Image Formation Digital
Capturing Light in man and machine Some figures from Steve Seitz, Steve Palmer, Paul Debevec, and Gonzalez et al. 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Image Formation Digital
INTRODUCTION THIN LENSES. Introduction. given by the paraxial refraction equation derived last lecture: Thin lenses (19.1) = 1. Double-lens systems
 Chapter 9 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Introduction Thin lenses Double-lens systems Aberrations Camera Human eye Compound microscope Summary INTRODUCTION Knowledge of geometrical optics, diffraction and interference,
Chapter 9 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Introduction Thin lenses Double-lens systems Aberrations Camera Human eye Compound microscope Summary INTRODUCTION Knowledge of geometrical optics, diffraction and interference,
ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008
 ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008 July 2003+ Chuck DiMarzio, Northeastern University 11270-04-1
ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008 July 2003+ Chuck DiMarzio, Northeastern University 11270-04-1
TSBB09 Image Sensors 2018-HT2. Image Formation Part 1
 TSBB09 Image Sensors 2018-HT2 Image Formation Part 1 Basic physics Electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves With energy That propagate through space The waves consist of transversal
TSBB09 Image Sensors 2018-HT2 Image Formation Part 1 Basic physics Electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves With energy That propagate through space The waves consist of transversal
Virtual and Digital Cameras
 CS148: Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging Virtual and Digital Cameras Ansel Adams Topics Effect Cause Field of view Film size, focal length Perspective Lens, focal length Focus Dist. of lens
CS148: Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging Virtual and Digital Cameras Ansel Adams Topics Effect Cause Field of view Film size, focal length Perspective Lens, focal length Focus Dist. of lens
CS 443: Imaging and Multimedia Cameras and Lenses
 CS 443: Imaging and Multimedia Cameras and Lenses Spring 2008 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines Cameras and lenses! 1 They are formed by the projection of 3D objects.
CS 443: Imaging and Multimedia Cameras and Lenses Spring 2008 Ahmed Elgammal Dept of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines Cameras and lenses! 1 They are formed by the projection of 3D objects.
Image Formation III Chapter 1 (Forsyth&Ponce) Cameras Lenses & Sensors
 Image Formation III Chapter 1 (Forsyth&Ponce) Cameras Lenses & Sensors Guido Gerig CS-GY 6643, Spring 2017 (slides modified from Marc Pollefeys, UNC Chapel Hill/ ETH Zurich, With content from Prof. Trevor
Image Formation III Chapter 1 (Forsyth&Ponce) Cameras Lenses & Sensors Guido Gerig CS-GY 6643, Spring 2017 (slides modified from Marc Pollefeys, UNC Chapel Hill/ ETH Zurich, With content from Prof. Trevor
Lenses, exposure, and (de)focus
 Lenses, exposure, and (de)focus http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 15 Course announcements Homework 4 is out. - Due October 26
Lenses, exposure, and (de)focus http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 15 Course announcements Homework 4 is out. - Due October 26
Capturing light and color
 Capturing light and color Friday, 10/02/2017 Antonis Argyros e-mail: argyros@csd.uoc.gr Szeliski 2.2, 2.3, 3.1 1 Recap from last lecture Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Focal length and depth/field
Capturing light and color Friday, 10/02/2017 Antonis Argyros e-mail: argyros@csd.uoc.gr Szeliski 2.2, 2.3, 3.1 1 Recap from last lecture Pinhole camera model Perspective projection Focal length and depth/field
Basic principles of photography. David Capel 346B IST
 Basic principles of photography David Capel 346B IST Latin Camera Obscura = Dark Room Light passing through a small hole produces an inverted image on the opposite wall Safely observing the solar eclipse
Basic principles of photography David Capel 346B IST Latin Camera Obscura = Dark Room Light passing through a small hole produces an inverted image on the opposite wall Safely observing the solar eclipse
Announcements. Image Formation: Outline. The course. How Cameras Produce Images. Earliest Surviving Photograph. Image Formation and Cameras
 Announcements Image ormation and Cameras CSE 252A Lecture 3 Assignment 0: Getting Started with Matlab is posted to web page, due Tuesday, ctober 4. Reading: Szeliski, Chapter 2 ptional Chapters 1 & 2 of
Announcements Image ormation and Cameras CSE 252A Lecture 3 Assignment 0: Getting Started with Matlab is posted to web page, due Tuesday, ctober 4. Reading: Szeliski, Chapter 2 ptional Chapters 1 & 2 of
The Human Visual System. Lecture 1. The Human Visual System. The Human Eye. The Human Retina. cones. rods. horizontal. bipolar. amacrine.
 Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
CPSC 425: Computer Vision
 1 / 55 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Fred Tung ftung@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2015/2016 Term 2 2 / 55 Menu January 7, 2016 Topics: Image
1 / 55 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Fred Tung ftung@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2015/2016 Term 2 2 / 55 Menu January 7, 2016 Topics: Image
Light. Path of Light. Looking at things. Depth and Distance. Getting light to imager. CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes
 CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes These are course notes (not used as slides) Written by Mike Gleicher, Sept. 2005 Adjusted after class stuff we didn t get to removed / mistakes fixed Light Electromagnetic
CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes These are course notes (not used as slides) Written by Mike Gleicher, Sept. 2005 Adjusted after class stuff we didn t get to removed / mistakes fixed Light Electromagnetic
Sensors and Sensing Cameras and Camera Calibration
 Sensors and Sensing Cameras and Camera Calibration Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 20.11.2014
Sensors and Sensing Cameras and Camera Calibration Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 20.11.2014
Overview. Image formation - 1
 Overview perspective imaging Image formation Refraction of light Thin-lens equation Optical power and accommodation Image irradiance and scene radiance Digital images Introduction to MATLAB Image formation
Overview perspective imaging Image formation Refraction of light Thin-lens equation Optical power and accommodation Image irradiance and scene radiance Digital images Introduction to MATLAB Image formation
Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Rays. Wavefronts. Aberrations. Outline
 Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2 Outline 1 Optical Systems 2 Images and Pupils 3 Rays 4 Wavefronts 5 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 4: Geometrical
Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2 Outline 1 Optical Systems 2 Images and Pupils 3 Rays 4 Wavefronts 5 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 4: Geometrical
Image Formation. Light from distant things. Geometrical optics. Pinhole camera. Chapter 36
 Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
Astronomical Cameras
 Astronomical Cameras I. The Pinhole Camera Pinhole Camera (or Camera Obscura) Whenever light passes through a small hole or aperture it creates an image opposite the hole This is an effect wherever apertures
Astronomical Cameras I. The Pinhole Camera Pinhole Camera (or Camera Obscura) Whenever light passes through a small hole or aperture it creates an image opposite the hole This is an effect wherever apertures
Applied Optics. , Physics Department (Room #36-401) , ,
 Applied Optics Professor, Physics Department (Room #36-401) 2290-0923, 019-539-0923, shsong@hanyang.ac.kr Office Hours Mondays 15:00-16:30, Wednesdays 15:00-16:30 TA (Ph.D. student, Room #36-415) 2290-0921,
Applied Optics Professor, Physics Department (Room #36-401) 2290-0923, 019-539-0923, shsong@hanyang.ac.kr Office Hours Mondays 15:00-16:30, Wednesdays 15:00-16:30 TA (Ph.D. student, Room #36-415) 2290-0921,
Intorduction to light sources, pinhole cameras, and lenses
 Intorduction to light sources, pinhole cameras, and lenses Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 October 26, 2011 Abstract 1 1 Analyzing
Intorduction to light sources, pinhole cameras, and lenses Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 October 26, 2011 Abstract 1 1 Analyzing
Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II. + 1 s i. = 1 f
 Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II Last time, developed idea of ray optics approximation to wave theory Introduced paraxial approximation: rays with θ 1 Will continue to use Started disussing
Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II Last time, developed idea of ray optics approximation to wave theory Introduced paraxial approximation: rays with θ 1 Will continue to use Started disussing
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB
 ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
Image Processing & Projective geometry
 Image Processing & Projective geometry Arunkumar Byravan Partial slides borrowed from Jianbo Shi & Steve Seitz Color spaces RGB Red, Green, Blue HSV Hue, Saturation, Value Why HSV? HSV separates luma,
Image Processing & Projective geometry Arunkumar Byravan Partial slides borrowed from Jianbo Shi & Steve Seitz Color spaces RGB Red, Green, Blue HSV Hue, Saturation, Value Why HSV? HSV separates luma,
Physics 1230: Light and Color. Guest Lecture, Jack again. Lecture 23: More about cameras
 Physics 1230: Light and Color Chuck Rogers, Charles.Rogers@colorado.edu Ryan Henley, Valyria McFarland, Peter Siegfried physicscourses.colorado.edu/phys1230 Guest Lecture, Jack again Lecture 23: More about
Physics 1230: Light and Color Chuck Rogers, Charles.Rogers@colorado.edu Ryan Henley, Valyria McFarland, Peter Siegfried physicscourses.colorado.edu/phys1230 Guest Lecture, Jack again Lecture 23: More about
Visual Perception. Readings and References. Forming an image. Pinhole camera. Readings. Other References. CSE 457, Autumn 2004 Computer Graphics
 Readings and References Visual Perception CSE 457, Autumn Computer Graphics Readings Sections 1.4-1.5, Interactive Computer Graphics, Angel Other References Foundations of Vision, Brian Wandell, pp. 45-50
Readings and References Visual Perception CSE 457, Autumn Computer Graphics Readings Sections 1.4-1.5, Interactive Computer Graphics, Angel Other References Foundations of Vision, Brian Wandell, pp. 45-50
Lenses. A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved.
 PHYSICS NOTES ON A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of There are two types of basic lenses. (1.)
PHYSICS NOTES ON A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of There are two types of basic lenses. (1.)
6.098 Digital and Computational Photography Advanced Computational Photography. Bill Freeman Frédo Durand MIT - EECS
 6.098 Digital and Computational Photography 6.882 Advanced Computational Photography Bill Freeman Frédo Durand MIT - EECS Administrivia PSet 1 is out Due Thursday February 23 Digital SLR initiation? During
6.098 Digital and Computational Photography 6.882 Advanced Computational Photography Bill Freeman Frédo Durand MIT - EECS Administrivia PSet 1 is out Due Thursday February 23 Digital SLR initiation? During
Cameras and Sensors. Today. Today. It receives light from all directions. BIL721: Computational Photography! Spring 2015, Lecture 2!
 !! Cameras and Sensors Today Pinhole camera! Lenses! Exposure! Sensors! photo by Abelardo Morell BIL721: Computational Photography! Spring 2015, Lecture 2! Aykut Erdem! Hacettepe University! Computer Vision
!! Cameras and Sensors Today Pinhole camera! Lenses! Exposure! Sensors! photo by Abelardo Morell BIL721: Computational Photography! Spring 2015, Lecture 2! Aykut Erdem! Hacettepe University! Computer Vision
Lenses. Images. Difference between Real and Virtual Images
 Linear Magnification (m) This is the factor by which the size of the object has been magnified by the lens in a direction which is perpendicular to the axis of the lens. Linear magnification can be calculated
Linear Magnification (m) This is the factor by which the size of the object has been magnified by the lens in a direction which is perpendicular to the axis of the lens. Linear magnification can be calculated
Getting light to imager. Capturing Images. Depth and Distance. Ideal Imaging. CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes
 CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes Last time: what is an image idea of image-based (raster representation) Today: image capture/acquisition, focus cameras and eyes displays and intensities Corrected
CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes Last time: what is an image idea of image-based (raster representation) Today: image capture/acquisition, focus cameras and eyes displays and intensities Corrected
R 1 R 2 R 3. t 1 t 2. n 1 n 2
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 2.71/2.710 Optics Spring 14 Problem Set #2 Posted Feb. 19, 2014 Due Wed Feb. 26, 2014 1. (modified from Pedrotti 18-9) A positive thin lens of focal length 10cm is
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 2.71/2.710 Optics Spring 14 Problem Set #2 Posted Feb. 19, 2014 Due Wed Feb. 26, 2014 1. (modified from Pedrotti 18-9) A positive thin lens of focal length 10cm is
Chapters 1 & 2. Definitions and applications Conceptual basis of photogrammetric processing
 Chapters 1 & 2 Chapter 1: Photogrammetry Definitions and applications Conceptual basis of photogrammetric processing Transition from two-dimensional imagery to three-dimensional information Automation
Chapters 1 & 2 Chapter 1: Photogrammetry Definitions and applications Conceptual basis of photogrammetric processing Transition from two-dimensional imagery to three-dimensional information Automation
Image Acquisition Hardware. Image Acquisition and Representation. CCD Camera. Camera. how digital images are produced
 Image Acquisition Hardware Image Acquisition and Representation how digital images are produced how digital images are represented photometric models-basic radiometry image noises and noise suppression
Image Acquisition Hardware Image Acquisition and Representation how digital images are produced how digital images are represented photometric models-basic radiometry image noises and noise suppression
Image Acquisition and Representation. Camera. CCD Camera. Image Acquisition Hardware
 Image Acquisition and Representation Camera Slide 1 how digital images are produced how digital images are represented Slide 3 First photograph was due to Niepce of France in 1827. Basic abstraction is
Image Acquisition and Representation Camera Slide 1 how digital images are produced how digital images are represented Slide 3 First photograph was due to Niepce of France in 1827. Basic abstraction is
Image Acquisition and Representation
 Image Acquisition and Representation how digital images are produced how digital images are represented photometric models-basic radiometry image noises and noise suppression methods 1 Image Acquisition
Image Acquisition and Representation how digital images are produced how digital images are represented photometric models-basic radiometry image noises and noise suppression methods 1 Image Acquisition
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision. Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic
 Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
Laboratory experiment aberrations
 Laboratory experiment aberrations Obligatory laboratory experiment on course in Optical design, SK2330/SK3330, KTH. Date Name Pass Objective This laboratory experiment is intended to demonstrate the most
Laboratory experiment aberrations Obligatory laboratory experiment on course in Optical design, SK2330/SK3330, KTH. Date Name Pass Objective This laboratory experiment is intended to demonstrate the most
Lecture PowerPoint. Chapter 25 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoint Chapter 25 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture PowerPoint Chapter 25 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the
Lecture 7: Camera Models
 Lecture 7: Camera Models Professor Fei- Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab Lecture 7 -! 1 What we will learn toda? Pinhole cameras Cameras & lenses The geometr of pinhole cameras Reading: [FP] Chapters 1 3 [HZ]
Lecture 7: Camera Models Professor Fei- Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab Lecture 7 -! 1 What we will learn toda? Pinhole cameras Cameras & lenses The geometr of pinhole cameras Reading: [FP] Chapters 1 3 [HZ]
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital Image Processing. Human Visual System. Contents. Structure Of The Human Eye (cont.) Structure Of The Human Eye
 Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall,
Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: R. Gonzalez and R. Woods. Digital Image Processing, Prentice Hall,
Digital Image Fundamentals. Digital Image Processing. Human Visual System. Contents. Structure Of The Human Eye (cont.) Structure Of The Human Eye
 Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Those who wish to succeed must ask the right preliminary questions Aristotle Images
Digital Image Processing 2 Digital Image Fundamentals Digital Imaging Fundamentals Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Those who wish to succeed must ask the right preliminary questions Aristotle Images
IMAGE SENSOR SOLUTIONS. KAC-96-1/5" Lens Kit. KODAK KAC-96-1/5" Lens Kit. for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors. November 2004 Revision 2
 KODAK for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors November 2004 Revision 2 1.1 Introduction Choosing the right lens is a critical aspect of designing an imaging system. Typically the trade off between image
KODAK for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors November 2004 Revision 2 1.1 Introduction Choosing the right lens is a critical aspect of designing an imaging system. Typically the trade off between image
Point Spread Function. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Confocal Aperture. Optical aberrations. Alternative Scanning Microscopy
 Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Lecture 9. Lecture 9. t (min)
 Sensitivity of the Eye Lecture 9 The eye is capable of dark adaptation. This comes about by opening of the iris, as well as a change in rod cell photochemistry fovea only least perceptible brightness 10
Sensitivity of the Eye Lecture 9 The eye is capable of dark adaptation. This comes about by opening of the iris, as well as a change in rod cell photochemistry fovea only least perceptible brightness 10
Camera Simulation. References. Photography, B. London and J. Upton Optics in Photography, R. Kingslake The Camera, The Negative, The Print, A.
 Camera Simulation Effect Cause Field of view Film size, focal length Depth of field Aperture, focal length Exposure Film speed, aperture, shutter Motion blur Shutter References Photography, B. London and
Camera Simulation Effect Cause Field of view Film size, focal length Depth of field Aperture, focal length Exposure Film speed, aperture, shutter Motion blur Shutter References Photography, B. London and
MEM: Intro to Robotics. Assignment 3I. Due: Wednesday 10/15 11:59 EST
 MEM: Intro to Robotics Assignment 3I Due: Wednesday 10/15 11:59 EST 1. Basic Optics You are shopping for a new lens for your Canon D30 digital camera and there are lots of lens options at the store. Your
MEM: Intro to Robotics Assignment 3I Due: Wednesday 10/15 11:59 EST 1. Basic Optics You are shopping for a new lens for your Canon D30 digital camera and there are lots of lens options at the store. Your
