inverse collimator-based radiation imaging detector system
|
|
|
- Noah Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TECHNICAL NOTE Abstract A radiation imaging system has been developed using the concept of inverse collimation, where a narrow shielding pencil is used instead of a classical collimator. This imaging detector is smaller, lighter and less expensive than a traditionally collimated detector, and can produce a spherical raster image of radiation sources in its surroundings. A prototype was developed at Atomic Energy of Canada Limited Chalk River Laboratories, and the concept has been successfully proven in experiments using a point source as well as real sources in a high ambient field area. Such a radiation imaging system is effective in locating radiation sources in areas where accessibility is low and risk of radiological contamination is high, with applications in decontamination and decommissioning activities, nuclear material processing labs, etc. inverse collimator-based radiation imaging detector system A. Das*, B. Sur, S. Yue, G. Jonkmans Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River, Ontario, Canada, K0J 1J0 Article Info Article history: Received 29 May 2012, Accepted 20 June 2012, Available online 30 June *Corresponding Author: (613) ext.43468, DasA@aecl.ca 1. Introduction Imaging and visual representation of radiation sources and radiological contamination have applications in several fields: radiation protection, decommissioning and cleanup, waste management, to name a few. Improvements in techniques for imaging high radiation fields are making such imaging systems smaller, faster and more cost effective. Development of a radiation source imaging system at Chalk River Laboratories (CRL) was motivated in part by a need to image the sources of radiation inside a radioactive isotope processing hot-cell. Manual access inside the hot-cell is restricted for radiological safety reasons and equipment entering the cell has size and weight restrictions. In imaging of radiation sources using non-directional sensors, directionality is achieved through use of heavy shielding collimators. The use of collimators, including variations such as pinhole and parallel hole collimators, is a common technique in many prior applications [1, 2, 3, 4] for imaging radiation sources. However, the bulk and weight of this general collimator design often requires a robust assembly and relatively powerful actuators to manoeuvre the collimated detector, which is expensive in terms of the material and actuators. There exists a need in many applications for an inexpensive light-weight radiation imaging system. This paper describes a novel approach to the collimator design for a lighter and economical radiation detector system, developed at CRL. 2. Materials and Methods The sensor of choice for this application is a silicon PIN photodiode. Si diodes are simple, robust, low-cost, and have been widely used for measuring gamma dose rates. The total charge generated in a Si diode is well known to be proportional to the ionization energy deposited in the diode depletion region, and thus the radiation dose [5]. Consequently, the current in an unbiased Si diode is a measure of the radiation field or dose rate. In current generation mode, p-n junction diodes as well as PIN photodiodes have been successfully used as high radiation field detectors in many facilities at CRL [6, 7, 8]. The photodiode sensor used in this application is sensitive to gamma dose rates in the range of 10-3 Gy.h -1 to 10 3 Gy.h -1. A collimator enables a non-directional sensor to be used in a directional detector system, usually by surrounding the sensor with dense shielding material with a small aperture, such that radiation from all directions except the aperture is blocked. In a typical collimator, the detector response is high when the aperture faces the direction of a source and low elsewhere. An inverse collimator instead comprises a shielding pencil a thin rod or cone, of dense material that blocks radiation from a narrow solid angle. The detector response is relatively low when the shielding pencil is pointed towards a strong radiation source, and high otherwise. This concept is illustrated in Figure 1 for the case of a single point source. The concept of inverse collimation exists in literature [9], albeit purely for planar imaging of relatively low radiation sources as applicable to nuclear medicine imaging. AECL NUCLEAR REVIEW 61
2 Figure 1 Collimator vs. inverse collimator, and their ideal response functions To realize the inverse collimator concept in an imaging system, a thin rod of gamma blocking material needs to be assembled with the sensor and integrated with a mechanism that allows the detector and inverse collimator assembly to be pointed in all directions. A suitable pan-tilt solution was not found commercially; therefore, an inexpensive module to pan and tilt the detector and inverse collimator assembly was designed and built at CRL. The pan-tilt module employs two stepper motors; one at the base for rotation in the horizontal plane (pan functionality) and one higher up on the body for rotation in the vertical plane (tilt function). A thin lead (Pb) pencil serves as the inverse collimator material in this design; see Figure 2. The sensor and the inverse collimator pencil are mounted in a diametric spoke of the vertical gear wheel (175 mm in diameter), which is driven by the tilt motor through a driver gear. The gear wheel, driver gear and tilt motor are mounted on a wheel base, which is rotated on the horizontal plane by the pan motor [10]. A low-noise signal cable attaches to the sensor at its mounting location, with sufficient slack-length to prevent cable wind-up; a separate power connection is not required. The entire body of the pan-tilt device is constructed out of high-performance composite material using a 3D printer. This provided an inexpensive and radiologically unobtrusive body, especially for the tilt mechanism that houses the sensor. This complete imaging system has been patented by AECL. 3. Results and Discussion The imaging detector system was tested using a 37 GBq (10 Ci) 60 Co providing a conical gamma beam. The source was placed roughly 380 mm from the center of the imaging Figure 2 Light yield variation versus 2,5-diphenyloxazole (PPO) concentration in LAB. system. This test served as a proof-of-concept, and allowed measurement of the detector s response to a simple source configuration to analyse the accuracy and limitations of the system. The image generated from this test is presented in Figure 3, as a plot of the gamma field intensities versus directions, represented on a unit sphere. Note that the numbers on the scale bar are only to be used as a relative measure. The utility of such an image is to visually present the directions of all sources that contribute to the radiation field at the detector location, and to identify the source with the highest contribution. It must be noted that the raw data collected by the system represents the inverse (or photo-negative) of the desired image; thus a photo-negation algorithm is applied to obtain the image [10]. Figure 3 (a) shows the location of the source as represented on the sphere. The high signal area on the side away from the source [Figure 3 (b)], is a result of the sensor s directionality. The photodiode sensor is rectangular prism shaped; its sensitivity to gamma rays incident on the tips is roughly 60% that of the sensitivity along the sides of the sensor. The detector system is configured such that the sensor is longitudinally in line with the inverse collimator, with the tips facing towards and directly away from the inverse collimator. As a result, a false low measurement occurs when the 62
3 Figure 3 Gamma radiation source distribution image of a point source (a) side facing source (b) side away from source. tip of the sensor is facing the source, which translates to a peak upon image inversion. Thus, for each strong source, there will be a secondary area of high signal directly opposite to the direction of the source. This effect proves to be useful in distinguishing erroneous signals and verifying true source locations. A practical and more realistic test was performed in order to test the ability of the system to image two highly radioactive items in the presence of a high background field. A section of pressure tube removed from a CANDU reactor, and an irradiated CANDU fuel pin were placed in a radioactive materials handling hot-cell, operated by the Materials and Mechanics branch at CRL. A Si diode gamma detector calibrated in a Co-60 gamma cell [7] was used to measure the near contact gamma radiation fields for these objects; they were found to be roughly 1.3 Gy.h -1 for the pressure tube section and 33 Gy.h -1 for the fuel pin. The roughly 5 m wide by 3 m deep hot-cell also contained miscellaneous pieces of equipment and tools that contributed to the ambient gamma field. The detector system was placed to one side of the cell and the two items used for this study were placed around it, as depicted in Figure 4. The fuel pin was laid flat on the floor, roughly 0.3 m from the base of the detector, and the pressure tube section was placed vertically around 1 m from the detector. Figure 4 Multi-source image generation study setup inside hot-cell the direction expected for the fuel pin. The secondary high signal area due to the fuel pin can be observed in Figure 5 (b), directly opposite to the fuel pin location. As expected, the radiation fields observed from the fuel pin were much higher than the fields from the piece of pressure tube. The radiation exposure at the detector due to the pressure tube piece was too small to be resolved in the presence of the much higher radiation field of the fuel pin. 4. Conclusion The image obtained of this setup is shown in Figure 5, with the outlines of the sources projected onto the surface of the sphere. The high signal area observed in Figure 5 (a) is in Imaging of radiological environments can be performed using a directional sensor, where directionality is usually achieved through heavy collimation. The concept of using AECL NUCLEAR REVIEW 63
4 Figure 5 Radiation image generated in the hot-cell with the outline of the two sources overlaid as projections onto the sphere. (a) Bright spot corresponding to the fuel pin, along with superimposed outlines of pressure tube and fuel pin (b) Secondary bright spot associated with fuel pin, along with pressure tube outline an inverse collimator, consisting of shielding material in a narrow solid angle where a typical collimator would have an aperture, has been proven at CRL. An inverse collimator is lighter and less expensive, both in terms of material cost and cost of actuators. A radiation imaging detector system was designed and built in-house at CRL, using a silicon photodiode as the gamma sensor and a lead (Pb) pencil as the shielding material, assembled in a 3D printed composite body. The image is generated by rotating the sensor assembly, performing exposure rate measurements across the 4π solid angle around the sensor, and assembling the data as a spherical raster image. The raw image is then inverted to correct the photonegative effect due to the inverse collimator. This system was demonstrated successfully in a controlled environment using a 60 Co point source. A test was conducted to determine the ability of the detector system to image two highly radioactive materials in the presence of high radiation background. The near contact gamma fields for the two items differed by a factor of 25, and the less radioactive item was placed farther from the detector. The system was able to detect and image the more radioactive item, but not the less radioactive item. It is concluded that changes in radiation exposure at the detector as the inverse collimator was swept through the direction of the weaker source were too small to be resolved in the presence of the much higher radiation field due to the stronger source. The test showed a limitation of inverse collimator systems in detecting radiation sources in the presence of much stronger sources. Further work is required to better define and improve the detection thresholds of the system so that weaker sources may be successfully imaged. 5. Acknowledgements The authors wish to thank Elzbieta Rochon, Heather Chaput, Joseph Bida and Kevin McCarthy from AECL CRL, for providing use of their facilities and their assistance in sensor study and testing of the imaging system. The authors would also like to acknowledge the contributions of Alexandar Mechev and Hinkel Yeung, undergraduate students from the University of Waterloo, in post-processing for image reconstruction and mechanical design of the hardware, respectively. 64
5 References [1] R. Redus, et. al., October 1995 An Imaging Nuclear Survey System, Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference Record, IEEE, 1, pp [2] W. Lee, G. Cho, 2002, Pinhole Collimator Design for Nuclear Survey System. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 29(17), pp [3] A.N. Sudarkin, O.P. Ivanov, V.E. Stepanov, A.G. Volkovich, A.S. Turin, A.S. Danilovich, D.D. Rybakov, L.I.N. Urutskoev, 1996, High-energy Radiation Visualizer (HERV): a New System for Imaging in X-ray and Ramma-ray Emission Regions. Recom Ltd., Kurchatov (I.V.) Inst. of Atomic Energy, Moscow, IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 43(4), part 2, pp [4] M. Woodring, D. Souza, S. Tipnis, P. Waer, M. Squillante, G. Entine, K.P. Ziock, 1999, Advanced Radiation Imaging of Low-intensity Gamma-ray Sources. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, 422(1-3), pp [5] Knoll, G.F., 1989, Radiation Detection and Measurement, 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons [6] B. Sur, S. Yue, and A. Thekkevarriam, June 2007, Radiation Exposure Rate and Liquid Level Measurement Inside a High Level Liquid Waste (HLLW) Storage Tank, Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference of the Canadian Nuclear Society, Saint John, New Brunswick, Canada [7] B. Sur, S. Yue, G. Jonkmans, A Detector System for Measuring High Radiation Fields, April 2009, 6th American Nuclear Society International Topical Meeting On Nuclear Plant Instrumentation, Control, And Human-Machine Interface Technologies (NPIC & HMIT), Knoxville, Tennessee, USA [8] A. Das, S. Yue, B. Sur, et al., May 2010 Gamma Radiation Scanning of Nuclear Waste Storage Tile Holes, Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference of the Canadian Nuclear Society, Montréal, Québec, Canada. [9] D. J. Wagenaar et. al., July 2007 Inverse Collimation for Nuclear Medicine Imaging, US Patent [10] A. Das, B. Sur, S. Yue, G. Jonkmans, Detector System for Radiation Imaging Using Inverse Collimation, June 2011, Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Conference of the Canadian Nuclear Society, Niagara Falls, Ontario, Canada
VERIFYING NUCLEAR WASTE TILE-HOLES USING GAMMA RADIATION SCANNING
 FULL ARTICLE Nuclear waste management facilities at Chalk River Laboratories (CRL) use below-ground tile-holes to store solid waste from various activities such as medical isotope production. After long
FULL ARTICLE Nuclear waste management facilities at Chalk River Laboratories (CRL) use below-ground tile-holes to store solid waste from various activities such as medical isotope production. After long
Cartogam Real-Time Portable Gamma-Ray Imaging System
 Features Complete tool for in situ cartography, saving time, cost and dose Real-time acquisition and immediate display Two dimensional gamma mapping and dose range Dose rate estimation of hot spots Excellent
Features Complete tool for in situ cartography, saving time, cost and dose Real-time acquisition and immediate display Two dimensional gamma mapping and dose range Dose rate estimation of hot spots Excellent
Pinhole collimator design for nuclear survey system
 Annals of Nuclear Energy 29 (2002) 2029 2040 www.elsevier.com/locate/anucene Pinhole collimator design for nuclear survey system Wanno Lee*, Gyuseong Cho Department of Nuclear Engineering, Korea Advanced
Annals of Nuclear Energy 29 (2002) 2029 2040 www.elsevier.com/locate/anucene Pinhole collimator design for nuclear survey system Wanno Lee*, Gyuseong Cho Department of Nuclear Engineering, Korea Advanced
WM2016 Conference, March 6 10, 2016, Phoenix, Arizona, USA. GrayQb Single-Faced Version 2 Open Environment Test 16344
 GrayQb Single-Faced Version 2 Open Environment Test 16344 Jean Plummer *, David Immel *, John Bobbitt *, Mike Negron ** * Savannah River National Laboratory ** Savannah River Nuclear Solutions ABSTRACT
GrayQb Single-Faced Version 2 Open Environment Test 16344 Jean Plummer *, David Immel *, John Bobbitt *, Mike Negron ** * Savannah River National Laboratory ** Savannah River Nuclear Solutions ABSTRACT
ipix Gamma Imager Product Introduction Steve Laskos Product Management Director
 ipix Gamma Imager Product Introduction Steve Laskos Product Management Director ipix: The Next Generation Gamma Imaging System ipix the new generation of gamma camera Simple, easy to use for experts and
ipix Gamma Imager Product Introduction Steve Laskos Product Management Director ipix: The Next Generation Gamma Imaging System ipix the new generation of gamma camera Simple, easy to use for experts and
Application of Remote Gamma Imaging Surveys at the Turkey Point PWR Reactor Facility
 Application of Remote Gamma Imaging Surveys at the Turkey Point PWR Reactor Facility James T. Santo, Mike Maul, Randy Lucero, Martin Clapham, Becky Battle BIL Solutions Inc. 4001 Office Court Drive #800
Application of Remote Gamma Imaging Surveys at the Turkey Point PWR Reactor Facility James T. Santo, Mike Maul, Randy Lucero, Martin Clapham, Becky Battle BIL Solutions Inc. 4001 Office Court Drive #800
HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE
 HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE Takeyuki Hashimoto 1), Morio Onoe 2), Hiroshi Nakamura 3), Tamon Inouye 4), Hiromichi Jumonji 5), Iwao Takahashi 6); 1)Yokohama Soei
HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE Takeyuki Hashimoto 1), Morio Onoe 2), Hiroshi Nakamura 3), Tamon Inouye 4), Hiromichi Jumonji 5), Iwao Takahashi 6); 1)Yokohama Soei
Advanced Digital Radiography for Field NDT
 International Symposium on Digital Industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography - We.2.3 Advanced Digital Radiography for Field NDT Ron PINCU, Ofra KLEINBERGER-RIEDRICH Vidisco Ltd. 32 Haharoshet Street,
International Symposium on Digital Industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography - We.2.3 Advanced Digital Radiography for Field NDT Ron PINCU, Ofra KLEINBERGER-RIEDRICH Vidisco Ltd. 32 Haharoshet Street,
Experimental Analysis of Luminescence in Printed Materials
 Experimental Analysis of Luminescence in Printed Materials A. D. McGrath, S. M. Vaezi-Nejad Abstract - This paper is based on a printing industry research project nearing completion [1]. While luminescent
Experimental Analysis of Luminescence in Printed Materials A. D. McGrath, S. M. Vaezi-Nejad Abstract - This paper is based on a printing industry research project nearing completion [1]. While luminescent
EDDY CURRENT MEASUREMENT OF REMOTE TUBE POSITIONS IN CANDU REACTORS S.T. Craig, T.W. Krause, B.V. Luloff and J.J. Schankula Atomic Energy of Canada
 EDDY CURRENT MEASUREMENT OF REMOTE TUBE POSITIONS IN CANDU REACTORS S.T. Craig, T.W. Krause, B.V. Luloff and J.J. Schankula Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River, Ontario, Canada Abstract: Regular
EDDY CURRENT MEASUREMENT OF REMOTE TUBE POSITIONS IN CANDU REACTORS S.T. Craig, T.W. Krause, B.V. Luloff and J.J. Schankula Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River, Ontario, Canada Abstract: Regular
Spectroscopy Lab 2. Reading Your text books. Look under spectra, spectrometer, diffraction.
 1 Spectroscopy Lab 2 Reading Your text books. Look under spectra, spectrometer, diffraction. Consult Sargent Welch Spectrum Charts on wall of lab. Note that only the most prominent wavelengths are displayed
1 Spectroscopy Lab 2 Reading Your text books. Look under spectra, spectrometer, diffraction. Consult Sargent Welch Spectrum Charts on wall of lab. Note that only the most prominent wavelengths are displayed
Final Project: FEDX X-ray Radiation Detector
 Final Project: FEDX X-ray Radiation Detector Keita Todoroki Keita Fukushima December 12, 2011 Introduction The application of radiation detectors has played an important role in physical science, especially
Final Project: FEDX X-ray Radiation Detector Keita Todoroki Keita Fukushima December 12, 2011 Introduction The application of radiation detectors has played an important role in physical science, especially
Real Time Linear Array Imaging. Brian Caccamise
 Real Time Linear Array Imaging Brian Caccamise 1 Real Time Linear Array Imaging What is Real Time Linear Array Imaging? Or Real Time Radiography (RTR)? 2 Real Time Linear Array Imaging It s Not This! Shoe
Real Time Linear Array Imaging Brian Caccamise 1 Real Time Linear Array Imaging What is Real Time Linear Array Imaging? Or Real Time Radiography (RTR)? 2 Real Time Linear Array Imaging It s Not This! Shoe
Development of Personal Dosimeter Using Electronic Dose Conversion Method
 Proceedings of the Korean Nuclear Spring Meeting Gyeong ju, Korea, May 2003 Development of Personal Dosimeter Using Electronic Dose Conversion Method Wanno Lee, Bong Jae Lee, and Chang Woo Lee Korea Atomic
Proceedings of the Korean Nuclear Spring Meeting Gyeong ju, Korea, May 2003 Development of Personal Dosimeter Using Electronic Dose Conversion Method Wanno Lee, Bong Jae Lee, and Chang Woo Lee Korea Atomic
Introduction. Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology. Primary radiological image. Primary radiological image
 Introduction Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther In diagnostic radiology
Introduction Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther In diagnostic radiology
A high energy gamma camera using a multiple hole collimator
 ELSEVIER Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 353 (1994) 328-333 A high energy gamma camera using a multiple hole collimator and PSPMT SV Guru *, Z He, JC Ferreria, DK Wehe, G F Knoll
ELSEVIER Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 353 (1994) 328-333 A high energy gamma camera using a multiple hole collimator and PSPMT SV Guru *, Z He, JC Ferreria, DK Wehe, G F Knoll
Measurement of SQUID noise levels for SuperCDMS SNOLAB detectors
 Measurement of SQUID noise levels for SuperCDMS SNOLAB detectors Maxwell Lee SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, CA, 94025, MS29 SLAC-TN-15-051 Abstract SuperCDMS SNOLAB is a second generation
Measurement of SQUID noise levels for SuperCDMS SNOLAB detectors Maxwell Lee SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, CA, 94025, MS29 SLAC-TN-15-051 Abstract SuperCDMS SNOLAB is a second generation
Gamma-ray spectral imaging using a single-shutter radiation camera
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A299 (1990) 495-500 North-Holland 495 Gamma-ray spectral imaging using a single-shutter radiation camera T.A. DeVol, D.K. Wehe and G.F. Knoll The University
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A299 (1990) 495-500 North-Holland 495 Gamma-ray spectral imaging using a single-shutter radiation camera T.A. DeVol, D.K. Wehe and G.F. Knoll The University
Energy Measurements with a Si Surface Barrier Detector and a 5.5-MeV 241 Am α Source
 Energy Measurements with a Si Surface Barrier Detector and a 5.5-MeV 241 Am α Source October 18, 2017 The goals of this experiment are to become familiar with semiconductor detectors, which are widely
Energy Measurements with a Si Surface Barrier Detector and a 5.5-MeV 241 Am α Source October 18, 2017 The goals of this experiment are to become familiar with semiconductor detectors, which are widely
Observational Astronomy
 Observational Astronomy Instruments The telescope- instruments combination forms a tightly coupled system: Telescope = collecting photons and forming an image Instruments = registering and analyzing the
Observational Astronomy Instruments The telescope- instruments combination forms a tightly coupled system: Telescope = collecting photons and forming an image Instruments = registering and analyzing the
DESIGN AND OPERATION OF A WIDE RANGE SEGMENTED GAMMA RAY SCANNING ASSAY INSTRUMENT FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF BOTH LOW AND INTERMEDIATE LEVEL WASTE
 11-A-424-INMM DESIGN AND OPERATION OF A WIDE RANGE SEGMENTED GAMMA RAY SCANNING ASSAY INSTRUMENT FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF BOTH LOW AND INTERMEDIATE LEVEL WASTE John A. Mason, Marc R. Looman, Robert A. Price
11-A-424-INMM DESIGN AND OPERATION OF A WIDE RANGE SEGMENTED GAMMA RAY SCANNING ASSAY INSTRUMENT FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF BOTH LOW AND INTERMEDIATE LEVEL WASTE John A. Mason, Marc R. Looman, Robert A. Price
Application Note. ipix A Gamma imager to support various applications. Introduction. An easy to carry and deploy instrument
 Application Note ipix A Gamma imager to support various applications Introduction ipix is a unique gamma imager that quickly locates low level radioactive sources from a distance and estimates the dose
Application Note ipix A Gamma imager to support various applications Introduction ipix is a unique gamma imager that quickly locates low level radioactive sources from a distance and estimates the dose
Recent Advances in Low-Level Nuclear Measurements at the CEA 9212
 Recent Advances in Low-Level Nuclear Measurements at the CEA 9212 C. Mahé, F. Lamadie, C. Le Goaller Commissariat à l Énergie Atomique CEA, DEN, SDTC, 30207 Bagnols-sur-Cèze, France. ABSTRACT For several
Recent Advances in Low-Level Nuclear Measurements at the CEA 9212 C. Mahé, F. Lamadie, C. Le Goaller Commissariat à l Énergie Atomique CEA, DEN, SDTC, 30207 Bagnols-sur-Cèze, France. ABSTRACT For several
A Novel Multipass Optical System Oleg Matveev University of Florida, Department of Chemistry, Gainesville, Fl
 A Novel Multipass Optical System Oleg Matveev University of Florida, Department of Chemistry, Gainesville, Fl BACKGROUND Multipass optical systems (MOS) are broadly used in absorption, Raman, fluorescence,
A Novel Multipass Optical System Oleg Matveev University of Florida, Department of Chemistry, Gainesville, Fl BACKGROUND Multipass optical systems (MOS) are broadly used in absorption, Raman, fluorescence,
Decommissioning in Canada
 Decommissioning in Canada IAEA Work Shop INT9175 9001 A.E Aikens 2012 September 27 UNRESTRICTED / ILLIMITÉ Decommissioning in Canada Overview of work in Canada Port Hope Area Initiative Low Level Radioactive
Decommissioning in Canada IAEA Work Shop INT9175 9001 A.E Aikens 2012 September 27 UNRESTRICTED / ILLIMITÉ Decommissioning in Canada Overview of work in Canada Port Hope Area Initiative Low Level Radioactive
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY 1
 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY 1 Why CT? Conventional X ray picture of a chest 2 Introduction Why CT? In a normal X-ray picture, most soft tissue doesn't show up clearly. To focus in on organs, or to examine the
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY 1 Why CT? Conventional X ray picture of a chest 2 Introduction Why CT? In a normal X-ray picture, most soft tissue doesn't show up clearly. To focus in on organs, or to examine the
LINEARPYROMETER LP4. Technical Documentation KE November TN
 1 LINEARPYROMETER LP4 Technical Documentation KE 256-6.2007 November 2010 5-TN-1622-100 2 1. General Description With the Linearpyrometer Type LP4 a measuring instrument has been made available for pyrometric
1 LINEARPYROMETER LP4 Technical Documentation KE 256-6.2007 November 2010 5-TN-1622-100 2 1. General Description With the Linearpyrometer Type LP4 a measuring instrument has been made available for pyrometric
ISO-CART-85. Mobile Low-Level Waste Assay System
 Mobile Low-Level Waste Assay System Complete In-Situ NDA Gamma-Ray Analysis Solutions for a Wide Variety of Samples, including Free-Release Decommissioning Waste. ISO-CART -85 : A Complete Turnkey Solution
Mobile Low-Level Waste Assay System Complete In-Situ NDA Gamma-Ray Analysis Solutions for a Wide Variety of Samples, including Free-Release Decommissioning Waste. ISO-CART -85 : A Complete Turnkey Solution
IMAGE FORMATION. Light source properties. Sensor characteristics Surface. Surface reflectance properties. Optics
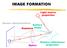 IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017
 R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Semiconductor Lasers (2 weeks) Semiconductor (diode) lasers are by far the most widely used lasers today. Their small size and properties of the light output
R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Semiconductor Lasers (2 weeks) Semiconductor (diode) lasers are by far the most widely used lasers today. Their small size and properties of the light output
Development of the Pixelated Photon Detector. Using Silicon on Insulator Technology. for TOF-PET
 July 24, 2015 Development of the Pixelated Photon Detector Using Silicon on Insulator Technology for TOF-PET A.Koyama 1, K.Shimazoe 1, H.Takahashi 1, T. Orita 2, Y.Arai 3, I.Kurachi 3, T.Miyoshi 3, D.Nio
July 24, 2015 Development of the Pixelated Photon Detector Using Silicon on Insulator Technology for TOF-PET A.Koyama 1, K.Shimazoe 1, H.Takahashi 1, T. Orita 2, Y.Arai 3, I.Kurachi 3, T.Miyoshi 3, D.Nio
ANALYTICAL MICRO X-RAY FLUORESCENCE SPECTROMETER
 Copyright(c)JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data 2001,Advances in X-ray Analysis,Vol.44 325 ANALYTICAL MICRO X-RAY FLUORESCENCE SPECTROMETER ABSTRACT William Chang, Jonathan Kerner, and Edward
Copyright(c)JCPDS-International Centre for Diffraction Data 2001,Advances in X-ray Analysis,Vol.44 325 ANALYTICAL MICRO X-RAY FLUORESCENCE SPECTROMETER ABSTRACT William Chang, Jonathan Kerner, and Edward
YOUNGS MODULUS BY UNIFORM & NON UNIFORM BENDING OF A BEAM
 YOUNGS MODULUS BY UNIFORM & NON UNIFORM BENDING OF A BEAM RECTANGULAR BEAM PLACED OVER TWO KNIFE EDGES & DISTANCE BETWEEN KNIFE EDGES IS KEPT CONSTANT AS l= 50cm UNIFORM WEIGHT HANGERS ARE SUSPENDED WITH
YOUNGS MODULUS BY UNIFORM & NON UNIFORM BENDING OF A BEAM RECTANGULAR BEAM PLACED OVER TWO KNIFE EDGES & DISTANCE BETWEEN KNIFE EDGES IS KEPT CONSTANT AS l= 50cm UNIFORM WEIGHT HANGERS ARE SUSPENDED WITH
CATHENA Void Fraction Accuracy and Uncertainty Using RD-14M LOCA Tests
 CATHENA Void Fraction Accuracy and Uncertainty Using RD-14M LOCA Tests Geoff Waddington, Songyu Liu AECL Nuclear Laboratories Chalk River, Ontario, Canada 2012 May 3 UNRESTRICTED / ILLIMITÉ Outline Introduction
CATHENA Void Fraction Accuracy and Uncertainty Using RD-14M LOCA Tests Geoff Waddington, Songyu Liu AECL Nuclear Laboratories Chalk River, Ontario, Canada 2012 May 3 UNRESTRICTED / ILLIMITÉ Outline Introduction
LENSES. INEL 6088 Computer Vision
 LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
Functions of the SEM subsystems
 Functions of the SEM subsystems Electronic column It consists of an electron gun and two or more electron lenses, which influence the path of electrons traveling down an evacuated tube. The base of the
Functions of the SEM subsystems Electronic column It consists of an electron gun and two or more electron lenses, which influence the path of electrons traveling down an evacuated tube. The base of the
Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH1498MW Dual Precision Op Amp for Linear Technology
 Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH1498MW Dual Precision Op Amp for Linear Technology Customer: Linear Technology (PO# 54873L) RAD Job Number: 09-579 Part Type Tested:
Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH1498MW Dual Precision Op Amp for Linear Technology Customer: Linear Technology (PO# 54873L) RAD Job Number: 09-579 Part Type Tested:
GAMMA-IMAGING SYSTEMS FOR ECOLOGICAL AND NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT MEASUREMENTS
 GAMMA-IMAGING SYSTEMS FOR ECOLOGICAL AND NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT MEASUREMENTS Oleg P. Ivanov, Vyacheslav E. Stepanov, Alexey S. Danilovich - RRC Kurchatov Institute, Boris V. Artemiev JSC RII MSIA «Spectrum»,
GAMMA-IMAGING SYSTEMS FOR ECOLOGICAL AND NUCLEAR ENVIRONMENT MEASUREMENTS Oleg P. Ivanov, Vyacheslav E. Stepanov, Alexey S. Danilovich - RRC Kurchatov Institute, Boris V. Artemiev JSC RII MSIA «Spectrum»,
Atomic and nuclear physics
 Atomic and nuclear physics X-ray physics Physics of the atomic shell LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Investigating the energy spectrum of an x-ray tube as a function of the high voltage and the emission current
Atomic and nuclear physics X-ray physics Physics of the atomic shell LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Investigating the energy spectrum of an x-ray tube as a function of the high voltage and the emission current
ECEN. Spectroscopy. Lab 8. copy. constituents HOMEWORK PR. Figure. 1. Layout of. of the
 ECEN 4606 Lab 8 Spectroscopy SUMMARY: ROBLEM 1: Pedrotti 3 12-10. In this lab, you will design, build and test an optical spectrum analyzer and use it for both absorption and emission spectroscopy. The
ECEN 4606 Lab 8 Spectroscopy SUMMARY: ROBLEM 1: Pedrotti 3 12-10. In this lab, you will design, build and test an optical spectrum analyzer and use it for both absorption and emission spectroscopy. The
HISTORY. CT Physics with an Emphasis on Application in Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging SUNDAY. Shawn D. Teague, MD
 CT Physics with an Emphasis on Application in Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging Shawn D. Teague, MD DISCLOSURES 3DR- advisory committee CT PHYSICS WITH AN EMPHASIS ON APPLICATION IN THORACIC AND CARDIAC IMAGING
CT Physics with an Emphasis on Application in Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging Shawn D. Teague, MD DISCLOSURES 3DR- advisory committee CT PHYSICS WITH AN EMPHASIS ON APPLICATION IN THORACIC AND CARDIAC IMAGING
Radionuclide Imaging MII 3073 RADIONUCLIDE IMAGING SYSTEM
 Radionuclide Imaging MII 3073 RADIONUCLIDE IMAGING SYSTEM Preamplifiers and amplifiers The current from PMT must be further amplified before it can be processed and counted (the number of electrons yielded
Radionuclide Imaging MII 3073 RADIONUCLIDE IMAGING SYSTEM Preamplifiers and amplifiers The current from PMT must be further amplified before it can be processed and counted (the number of electrons yielded
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION
 FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
High-resolution Penumbral Imaging on the NIF
 High-resolution Penumbral Imaging on the NIF October 6, 21 Benjamin Bachmann T. Hilsabeck (GA), J. Field, A. MacPhee, N. Masters, C. Reed (GA), T. Pardini, B. Spears, L. BenedeB, S. Nagel, N. Izumi, V.
High-resolution Penumbral Imaging on the NIF October 6, 21 Benjamin Bachmann T. Hilsabeck (GA), J. Field, A. MacPhee, N. Masters, C. Reed (GA), T. Pardini, B. Spears, L. BenedeB, S. Nagel, N. Izumi, V.
Single Slit Diffraction
 PC1142 Physics II Single Slit Diffraction 1 Objectives Investigate the single-slit diffraction pattern produced by monochromatic laser light. Determine the wavelength of the laser light from measurements
PC1142 Physics II Single Slit Diffraction 1 Objectives Investigate the single-slit diffraction pattern produced by monochromatic laser light. Determine the wavelength of the laser light from measurements
Performance Comparison of Spectrometers Featuring On-Axis and Off-Axis Grating Rotation
 Performance Comparison of Spectrometers Featuring On-Axis and Off-Axis Rotation By: Michael Case and Roy Grayzel, Acton Research Corporation Introduction The majority of modern spectrographs and scanning
Performance Comparison of Spectrometers Featuring On-Axis and Off-Axis Rotation By: Michael Case and Roy Grayzel, Acton Research Corporation Introduction The majority of modern spectrographs and scanning
Positron Emission Tomography
 Positron Emission Tomography UBC Physics & Astronomy / PHYS 409 1 Introduction Positron emission tomography (PET) is a non-invasive way to produce the functional 1 image of a patient. It works by injecting
Positron Emission Tomography UBC Physics & Astronomy / PHYS 409 1 Introduction Positron emission tomography (PET) is a non-invasive way to produce the functional 1 image of a patient. It works by injecting
Cameras. CSE 455, Winter 2010 January 25, 2010
 Cameras CSE 455, Winter 2010 January 25, 2010 Announcements New Lecturer! Neel Joshi, Ph.D. Post-Doctoral Researcher Microsoft Research neel@cs Project 1b (seam carving) was due on Friday the 22 nd Project
Cameras CSE 455, Winter 2010 January 25, 2010 Announcements New Lecturer! Neel Joshi, Ph.D. Post-Doctoral Researcher Microsoft Research neel@cs Project 1b (seam carving) was due on Friday the 22 nd Project
Physics Laboratory Scattering of Photons from Electrons: Compton Scattering
 RR Oct 2001 SS Dec 2001 MJ Oct 2009 Physics 34000 Laboratory Scattering of Photons from Electrons: Compton Scattering Objective: To measure the energy of high energy photons scattered from electrons in
RR Oct 2001 SS Dec 2001 MJ Oct 2009 Physics 34000 Laboratory Scattering of Photons from Electrons: Compton Scattering Objective: To measure the energy of high energy photons scattered from electrons in
Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH1814MW Quad Op Amp for Linear Technology
 Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH1814MW Quad Op Amp for Linear Technology Customer: Linear Technology (PO 57472L) RAD Job Number: 10-417 Part Type Tested: Linear Technology
Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH1814MW Quad Op Amp for Linear Technology Customer: Linear Technology (PO 57472L) RAD Job Number: 10-417 Part Type Tested: Linear Technology
Title: A COMPARISON OF Cs-137 AND X-RAY SOURCES AS CALIBRATION REFERENCES FOR THERMOLUMINESCENT DOSIMETER CHIPS
 Title: A COMPARISON OF Cs-137 AND X-RAY SOURCES AS CALIBRATION REFERENCES FOR THERMOLUMINESCENT DOSIMETER CHIPS By Aravind Ravichandran arr192@mail.usask.ca University of Saskatchewan Address: 2424 Cumberland
Title: A COMPARISON OF Cs-137 AND X-RAY SOURCES AS CALIBRATION REFERENCES FOR THERMOLUMINESCENT DOSIMETER CHIPS By Aravind Ravichandran arr192@mail.usask.ca University of Saskatchewan Address: 2424 Cumberland
Strip Detectors. Principal: Silicon strip detector. Ingrid--MariaGregor,SemiconductorsasParticleDetectors. metallization (Al) p +--strips
 Strip Detectors First detector devices using the lithographic capabilities of microelectronics First Silicon detectors -- > strip detectors Can be found in all high energy physics experiments of the last
Strip Detectors First detector devices using the lithographic capabilities of microelectronics First Silicon detectors -- > strip detectors Can be found in all high energy physics experiments of the last
Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH118W Op-Amp for Linear Technology
 Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH118W Op-Amp for Linear Technology Customer: Linear Technology, PO# 60225L RAD Job Number: 11-351 Part Type Tested: RH118W Op-Amp, RH118
Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH118W Op-Amp for Linear Technology Customer: Linear Technology, PO# 60225L RAD Job Number: 11-351 Part Type Tested: RH118W Op-Amp, RH118
Recent Technological Developments on LGAD and ilgad Detectors for Tracking and Timing Applications
 Recent Technological Developments on LGAD and ilgad Detectors for Tracking and Timing Applications G. Pellegrini 1, M. Baselga 1, M. Carulla 1, V. Fadeyev 2, P. Fernández-Martínez 1, M. Fernández García
Recent Technological Developments on LGAD and ilgad Detectors for Tracking and Timing Applications G. Pellegrini 1, M. Baselga 1, M. Carulla 1, V. Fadeyev 2, P. Fernández-Martínez 1, M. Fernández García
Laboratory experiment aberrations
 Laboratory experiment aberrations Obligatory laboratory experiment on course in Optical design, SK2330/SK3330, KTH. Date Name Pass Objective This laboratory experiment is intended to demonstrate the most
Laboratory experiment aberrations Obligatory laboratory experiment on course in Optical design, SK2330/SK3330, KTH. Date Name Pass Objective This laboratory experiment is intended to demonstrate the most
MC SIMULATION OF SCATTER INTENSITIES IN A CONE-BEAM CT SYSTEM EMPLOYING A 450 kv X-RAY TUBE
 MC SIMULATION OF SCATTER INTENSITIES IN A CONE-BEAM CT SYSTEM EMPLOYING A 450 kv X-RAY TUBE A. Miceli ab, R. Thierry a, A. Flisch a, U. Sennhauser a, F. Casali b a Empa - Swiss Federal Laboratories for
MC SIMULATION OF SCATTER INTENSITIES IN A CONE-BEAM CT SYSTEM EMPLOYING A 450 kv X-RAY TUBE A. Miceli ab, R. Thierry a, A. Flisch a, U. Sennhauser a, F. Casali b a Empa - Swiss Federal Laboratories for
DISPLAY metrology measurement
 Curved Displays Challenge Display Metrology Non-planar displays require a close look at the components involved in taking their measurements. by Michael E. Becker, Jürgen Neumeier, and Martin Wolf DISPLAY
Curved Displays Challenge Display Metrology Non-planar displays require a close look at the components involved in taking their measurements. by Michael E. Becker, Jürgen Neumeier, and Martin Wolf DISPLAY
CHAPTER 9 POSITION SENSITIVE PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES
 CHAPTER 9 POSITION SENSITIVE PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES The current multiplication mechanism offered by dynodes makes photomultiplier tubes ideal for low-light-level measurement. As explained earlier, there
CHAPTER 9 POSITION SENSITIVE PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES The current multiplication mechanism offered by dynodes makes photomultiplier tubes ideal for low-light-level measurement. As explained earlier, there
Chromatic X-Ray imaging with a fine pitch CdTe sensor coupled to a large area photon counting pixel ASIC
 Chromatic X-Ray imaging with a fine pitch CdTe sensor coupled to a large area photon counting pixel ASIC R. Bellazzini a,b, G. Spandre a*, A. Brez a, M. Minuti a, M. Pinchera a and P. Mozzo b a INFN Pisa
Chromatic X-Ray imaging with a fine pitch CdTe sensor coupled to a large area photon counting pixel ASIC R. Bellazzini a,b, G. Spandre a*, A. Brez a, M. Minuti a, M. Pinchera a and P. Mozzo b a INFN Pisa
SPECIFICATION. Kilovoltage X-ray calibration system for protection and diagnostic level dosimetry. Prepared by
 SPECIFICATION Kilovoltage X-ray Prepared by Igor Gomola, Technical Officer, Project ECU6023, Date 2015-Oct-06 Revision Date Status Comments 0.1 2015-Oct-06 Draft Igor Gomola Page 1 of 12 1. Scope This
SPECIFICATION Kilovoltage X-ray Prepared by Igor Gomola, Technical Officer, Project ECU6023, Date 2015-Oct-06 Revision Date Status Comments 0.1 2015-Oct-06 Draft Igor Gomola Page 1 of 12 1. Scope This
Instructions for the Experiment
 Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
AgilEye Manual Version 2.0 February 28, 2007
 AgilEye Manual Version 2.0 February 28, 2007 1717 Louisiana NE Suite 202 Albuquerque, NM 87110 (505) 268-4742 support@agiloptics.com 2 (505) 268-4742 v. 2.0 February 07, 2007 3 Introduction AgilEye Wavefront
AgilEye Manual Version 2.0 February 28, 2007 1717 Louisiana NE Suite 202 Albuquerque, NM 87110 (505) 268-4742 support@agiloptics.com 2 (505) 268-4742 v. 2.0 February 07, 2007 3 Introduction AgilEye Wavefront
Improved Radiometry for LED Arrays
 RadTech Europe 2017 Prague, Czech Republic Oct. 18, 2017 Improved Radiometry for LED Arrays Dr. Robin E. Wright 3M Corporate Research Process Laboratory, retired 3M 2017 All Rights Reserved. 1 Personal
RadTech Europe 2017 Prague, Czech Republic Oct. 18, 2017 Improved Radiometry for LED Arrays Dr. Robin E. Wright 3M Corporate Research Process Laboratory, retired 3M 2017 All Rights Reserved. 1 Personal
National 4. Waves and Radiation. Summary Notes. Name:
 National 4 Waves and Radiation Summary Notes Name: Mr Downie 2014 1 Sound Waves To produce a sound the particles in an object must vibrate. This means that sound can travel through solids, liquids and
National 4 Waves and Radiation Summary Notes Name: Mr Downie 2014 1 Sound Waves To produce a sound the particles in an object must vibrate. This means that sound can travel through solids, liquids and
FAST NEUTRON AND GAMMA-RAY INTERROGATION OF AIR CARGO CONTAINERS
 Third Research Coordination Meeting: IAEA CRP on Neutron Based Techniques for the Detection of Illicit Materials and Explosives, Johannesburg, 16-20 November 2009 FAST NEUTRON AND GAMMA-RAY INTERROGATION
Third Research Coordination Meeting: IAEA CRP on Neutron Based Techniques for the Detection of Illicit Materials and Explosives, Johannesburg, 16-20 November 2009 FAST NEUTRON AND GAMMA-RAY INTERROGATION
An Activity in Computed Tomography
 Pre-lab Discussion An Activity in Computed Tomography X-rays X-rays are high energy electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths smaller than those in the visible spectrum (0.01-10nm and 4000-800nm respectively).
Pre-lab Discussion An Activity in Computed Tomography X-rays X-rays are high energy electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths smaller than those in the visible spectrum (0.01-10nm and 4000-800nm respectively).
Application of Safeguards Procedures
 Application of Safeguards Procedures The earliest applications of safeguards procedures took place in a political and technical climate far different from that of today. In the early 1960's there was a
Application of Safeguards Procedures The earliest applications of safeguards procedures took place in a political and technical climate far different from that of today. In the early 1960's there was a
Application of CMOS sensors in radiation detection
 Application of CMOS sensors in radiation detection S. Ashrafi Physics Faculty University of Tabriz 1 CMOS is a technology for making low power integrated circuits. CMOS Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
Application of CMOS sensors in radiation detection S. Ashrafi Physics Faculty University of Tabriz 1 CMOS is a technology for making low power integrated circuits. CMOS Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
SPECIFICATIONS FOR GAMMA IMAGING SYSTEM
 SPECIFICATIONS FOR GAMMA 1. Scope This Statement of Work (SOW) describes the requirements for a System or subsystems pertaining to gamma imaging. The IAEA is considering acquiring gamma imaging systems
SPECIFICATIONS FOR GAMMA 1. Scope This Statement of Work (SOW) describes the requirements for a System or subsystems pertaining to gamma imaging. The IAEA is considering acquiring gamma imaging systems
LAB 1 AN EXAMPLE MECHATRONIC SYSTEM: THE FURBY
 LAB 1 AN EXAMPLE MECHATRONIC SYSTEM: THE FURBY Objectives Preparation Tools To see the inner workings of a commercial mechatronic system and to construct a simple manual motor speed controller and current
LAB 1 AN EXAMPLE MECHATRONIC SYSTEM: THE FURBY Objectives Preparation Tools To see the inner workings of a commercial mechatronic system and to construct a simple manual motor speed controller and current
Intorduction to light sources, pinhole cameras, and lenses
 Intorduction to light sources, pinhole cameras, and lenses Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 October 26, 2011 Abstract 1 1 Analyzing
Intorduction to light sources, pinhole cameras, and lenses Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 October 26, 2011 Abstract 1 1 Analyzing
Solid-state physics. Bragg reflection: determining the lattice constants of monocrystals. LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets P
 Solid-state physics Properties of crystals X-ray structural analysis LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Bragg reflection: determining the lattice constants of monocrystals P7.1.2.1 Objects of the experiment Investigating
Solid-state physics Properties of crystals X-ray structural analysis LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Bragg reflection: determining the lattice constants of monocrystals P7.1.2.1 Objects of the experiment Investigating
14.2 Photodiodes 411
 14.2 Photodiodes 411 Maximum reverse voltage is specified for Ge and Si photodiodes and photoconductive cells. Exceeding this voltage can cause the breakdown and severe deterioration of the sensor s performance.
14.2 Photodiodes 411 Maximum reverse voltage is specified for Ge and Si photodiodes and photoconductive cells. Exceeding this voltage can cause the breakdown and severe deterioration of the sensor s performance.
Effects of Incident Optical Power on the Effective Reverse Bias Voltage of Photodiodes This Lab Fact demonstrates how the effective reverse bias
 Effects of Incident Optical Power on the Effective Reverse Bias Voltage of Photodiodes This Lab Fact demonstrates how the effective reverse bias voltage on a photodiode can vary as a function of the incident
Effects of Incident Optical Power on the Effective Reverse Bias Voltage of Photodiodes This Lab Fact demonstrates how the effective reverse bias voltage on a photodiode can vary as a function of the incident
(Refer Slide Time: 00:10)
 Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 03 Unit-6 Instrumental details
Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 03 Unit-6 Instrumental details
Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH117H-Positive Adjustable Regulator for Linear Technology
 Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH117H-Positive Adjustable Regulator for Linear Technology Customer: Linear Technology (PO# 55339L) RAD Job Number: 10-121 Part Type
Enhanced Low Dose Rate Sensitivity (ELDRS) Radiation Testing of the RH117H-Positive Adjustable Regulator for Linear Technology Customer: Linear Technology (PO# 55339L) RAD Job Number: 10-121 Part Type
Introduction to the operating principles of the HyperFine spectrometer
 Introduction to the operating principles of the HyperFine spectrometer LightMachinery Inc., 80 Colonnade Road North, Ottawa ON Canada A spectrometer is an optical instrument designed to split light into
Introduction to the operating principles of the HyperFine spectrometer LightMachinery Inc., 80 Colonnade Road North, Ottawa ON Canada A spectrometer is an optical instrument designed to split light into
EXPERIENCE WITH FIXED IN-CORE DETECTORS AT SEABROOK STATION
 EXPERIENCE WITH FIXED IN-CORE DETECTORS AT SEABROOK STATION Joseph P. Gorski and Richard J. Cacciapouti Yankee Atomic Electric Co. 580 Main Street Bolton, MA 01740 Abstract A uniform set of analyses were
EXPERIENCE WITH FIXED IN-CORE DETECTORS AT SEABROOK STATION Joseph P. Gorski and Richard J. Cacciapouti Yankee Atomic Electric Co. 580 Main Street Bolton, MA 01740 Abstract A uniform set of analyses were
RD1000 Ground Probing Radar
 RD1000 Ground Probing Radar CONTENTS Product Introduction Product Features Competitor Analysis Customers Models, Pricing & Availability Promotional Material Practical Demonstration What to do now Summary
RD1000 Ground Probing Radar CONTENTS Product Introduction Product Features Competitor Analysis Customers Models, Pricing & Availability Promotional Material Practical Demonstration What to do now Summary
Laser Telemetric System (Metrology)
 Laser Telemetric System (Metrology) Laser telemetric system is a non-contact gauge that measures with a collimated laser beam (Refer Fig. 10.26). It measure at the rate of 150 scans per second. It basically
Laser Telemetric System (Metrology) Laser telemetric system is a non-contact gauge that measures with a collimated laser beam (Refer Fig. 10.26). It measure at the rate of 150 scans per second. It basically
An Activity in Computed Tomography
 Pre-lab Discussion An Activity in Computed Tomography X-rays X-rays are high energy electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths smaller than those in the visible spectrum (0.01-10nm and 4000-800nm respectively).
Pre-lab Discussion An Activity in Computed Tomography X-rays X-rays are high energy electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths smaller than those in the visible spectrum (0.01-10nm and 4000-800nm respectively).
IMAGING TECHNIQUES FOR MEASURING PARTICLE SIZE SSA AND GSV
 IMAGING TECHNIQUES FOR MEASURING PARTICLE SIZE SSA AND GSV APPLICATION NOTE SSA-001 (A4) Particle Sizing through Imaging TSI provides several optical techniques for measuring particle size. Two of the
IMAGING TECHNIQUES FOR MEASURING PARTICLE SIZE SSA AND GSV APPLICATION NOTE SSA-001 (A4) Particle Sizing through Imaging TSI provides several optical techniques for measuring particle size. Two of the
Photomultiplier Tube
 Nuclear Medicine Uses a device known as a Gamma Camera. Also known as a Scintillation or Anger Camera. Detects the release of gamma rays from Radionuclide. The radionuclide can be injected, inhaled or
Nuclear Medicine Uses a device known as a Gamma Camera. Also known as a Scintillation or Anger Camera. Detects the release of gamma rays from Radionuclide. The radionuclide can be injected, inhaled or
Vertical Tests of ILC Cavities and Detection of X-Rays from Field Emission
 Vertical Tests of ILC Cavities and Detection of X-Rays from Field Emission Pardis Niknejadi California State Polytechnic University, Pomona, CA 91768 Elizabeth Olhsson University of Oregon, Eugene, OR
Vertical Tests of ILC Cavities and Detection of X-Rays from Field Emission Pardis Niknejadi California State Polytechnic University, Pomona, CA 91768 Elizabeth Olhsson University of Oregon, Eugene, OR
Nano Beam Position Monitor
 Introduction Transparent X-ray beam monitoring and imaging is a new enabling technology that will become the gold standard tool for beam characterisation at synchrotron radiation facilities. It allows
Introduction Transparent X-ray beam monitoring and imaging is a new enabling technology that will become the gold standard tool for beam characterisation at synchrotron radiation facilities. It allows
Test procedures Page: 1 of 5
 Test procedures Page: 1 of 5 1 Scope This part of document establishes uniform requirements for measuring the numerical aperture of optical fibre, thereby assisting in the inspection of fibres and cables
Test procedures Page: 1 of 5 1 Scope This part of document establishes uniform requirements for measuring the numerical aperture of optical fibre, thereby assisting in the inspection of fibres and cables
PERFORMANCE CHARACTERIZATION OF AMORPHOUS SILICON DIGITAL DETECTOR ARRAYS FOR GAMMA RADIOGRAPHY
 12 th A-PCNDT 2006 Asia-Pacific Conference on NDT, 5 th 10 th Nov 2006, Auckland, New Zealand PERFORMANCE CHARACTERIZATION OF AMORPHOUS SILICON DIGITAL DETECTOR ARRAYS FOR GAMMA RADIOGRAPHY Rajashekar
12 th A-PCNDT 2006 Asia-Pacific Conference on NDT, 5 th 10 th Nov 2006, Auckland, New Zealand PERFORMANCE CHARACTERIZATION OF AMORPHOUS SILICON DIGITAL DETECTOR ARRAYS FOR GAMMA RADIOGRAPHY Rajashekar
Chapter 8. The Telescope. 8.1 Purpose. 8.2 Introduction A Brief History of the Early Telescope
 Chapter 8 The Telescope 8.1 Purpose In this lab, you will measure the focal lengths of two lenses and use them to construct a simple telescope which inverts the image like the one developed by Johannes
Chapter 8 The Telescope 8.1 Purpose In this lab, you will measure the focal lengths of two lenses and use them to construct a simple telescope which inverts the image like the one developed by Johannes
Digital Photographic Imaging Using MOEMS
 Digital Photographic Imaging Using MOEMS Vasileios T. Nasis a, R. Andrew Hicks b and Timothy P. Kurzweg a a Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Drexel University, Philadelphia, USA b Department
Digital Photographic Imaging Using MOEMS Vasileios T. Nasis a, R. Andrew Hicks b and Timothy P. Kurzweg a a Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Drexel University, Philadelphia, USA b Department
Hardware for High Energy Applications 30 October 2009
 Paper No. 003 09 Hardware for High Energy Applications 30 October 2009 This document was created by the Federal Working Group on Industrial Digital Radiography. Reproduction is authorized. Federal Working
Paper No. 003 09 Hardware for High Energy Applications 30 October 2009 This document was created by the Federal Working Group on Industrial Digital Radiography. Reproduction is authorized. Federal Working
A GTEM BEST PRACTICE GUIDE APPLYING IEC TO THE USE OF GTEM CELLS
 - 27-39 H1 A BEST PRACTICE GUIDE APPLYING IEC 61-4-2 TO THE USE OF CELLS A. Nothofer, M.J. Alexander, National Physical Laboratory, Teddington, UK, D. Bozec, D. Welsh, L. Dawson, L. McCormack, A.C. Marvin,
- 27-39 H1 A BEST PRACTICE GUIDE APPLYING IEC 61-4-2 TO THE USE OF CELLS A. Nothofer, M.J. Alexander, National Physical Laboratory, Teddington, UK, D. Bozec, D. Welsh, L. Dawson, L. McCormack, A.C. Marvin,
Minnesota Rules, Chapter 4732 X-ray Revision
 Minnesota Rules, Chapter 4732 X-ray Revision DRAFT INDUSTRIAL X-RAY SYSTEMS DEFINTIONS, 1.0 4732.####. INDUSTRIAL X-RAY SYSTEMS DEFINITIONS. Subpart 1. Scope. For purposes of industrial x-ray systems under
Minnesota Rules, Chapter 4732 X-ray Revision DRAFT INDUSTRIAL X-RAY SYSTEMS DEFINTIONS, 1.0 4732.####. INDUSTRIAL X-RAY SYSTEMS DEFINITIONS. Subpart 1. Scope. For purposes of industrial x-ray systems under
Refraction of Light. Refraction of Light
 1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
Introduction To NDT. BY: Omid HEIDARY
 Introduction To NDT BY: Omid HEIDARY NDT Methods Penetrant Testing Magnetic Particle Testing Eddy Current Testing Ultrasonic Testing Radiographic Testing Acoustic Emission Infrared Testing Visual Testing
Introduction To NDT BY: Omid HEIDARY NDT Methods Penetrant Testing Magnetic Particle Testing Eddy Current Testing Ultrasonic Testing Radiographic Testing Acoustic Emission Infrared Testing Visual Testing
Armlication For United States Patent For HOT CELL SHIELD PLUG EXTRACTION APPARATUS. Philip A. Knapp Moore, ID. and. Larry K. Manhart Pingree, ID
 d d 0 co 0 co co I rl d u 4 I W n Armlication For United States Patent For HOT CELL SHIELD PLUG EXTRACTION APPARATUS Philip A. Knapp Moore, ID and Larry K. Manhart Pingree, ID Portions of this document
d d 0 co 0 co co I rl d u 4 I W n Armlication For United States Patent For HOT CELL SHIELD PLUG EXTRACTION APPARATUS Philip A. Knapp Moore, ID and Larry K. Manhart Pingree, ID Portions of this document
Initial Results from a Cryogenic Proton Irradiation of a p-channel CCD
 Centre for Electronic Imaging Initial Results from a Cryogenic Proton Irradiation of a p-channel CCD Jason Gow Daniel Wood, David Hall, Ben Dryer, Simeon Barber, Andrew Holland and Neil Murray Jason P.
Centre for Electronic Imaging Initial Results from a Cryogenic Proton Irradiation of a p-channel CCD Jason Gow Daniel Wood, David Hall, Ben Dryer, Simeon Barber, Andrew Holland and Neil Murray Jason P.
1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter
 8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
EXPERIENCE WITH AND STUDIES OF THE SNS* TARGET IMAGING SYSTEM
 EXPERIENCE WITH AND STUDIES OF THE SNS* TARGET IMAGING SYSTEM W. Blokland, ORNL, Oak Ridge, TN 37831, USA Abstract The Target Imaging System (TIS) shows the size and position of the proton beam by using
EXPERIENCE WITH AND STUDIES OF THE SNS* TARGET IMAGING SYSTEM W. Blokland, ORNL, Oak Ridge, TN 37831, USA Abstract The Target Imaging System (TIS) shows the size and position of the proton beam by using
TESTING OF BURIED PIPES BY SLOFEC TECHNIQUE IN COMBINATION WITH A MOTOR-DRIVEN CRAWLER SYSTEM. W. Kelb, KontrollTechnik, Germany
 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=18480 Introduction TESTING OF BURIED PIPES BY SLOFEC TECHNIQUE IN COMBINATION WITH A MOTOR-DRIVEN CRAWLER SYSTEM W. Kelb, KontrollTechnik, Germany In 2001
More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=18480 Introduction TESTING OF BURIED PIPES BY SLOFEC TECHNIQUE IN COMBINATION WITH A MOTOR-DRIVEN CRAWLER SYSTEM W. Kelb, KontrollTechnik, Germany In 2001
