DAT105: Computer Architecture
|
|
|
- Byron Charles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Department of Computer Science & Engineering Chalmers University of Techlogy DAT05: Computer Architecture Exercise 6 (Old exam questions) By Minh Quang Do
2 Question 4a [2006/2/22] () Loop: LD F0,0(R) SD F4, 0(R) SUBI R, R, #8 BNEZ R, Loop Unroll the loop once (branch-taken assumed) Loop: LD F0,0(R) SD F4, 0(R) SUBI R, R, #8 LD F0,0(R) SD F4, 0(R) SUBI R, R, #8 BNEZ R, Loop /8/2007 2
3 Question 4a [2006/2/22] (2) Loop: LD F0,0(R) SD F4, 0(R) SUBI R, R, #8 LD F0,0(R) SD F4, 0(R) SUBI R, R, #8 BNEZ R, Loop Loop: LD F0,0(R) LD F0,8(R) re-ordering (re-scheduling) SD F4, 0(R) SD F4, 8(R) SUBI R, R, #6 BNEZ R, Loop /8/2007 3
4 Question 4a [2006/2/22] (3) T9, T0, T, T2, ============= Loop: LD F0,0(R) LD F0,8(R) SD F4, 0(R) SD F4, 8(R) SUBI R, R, #6 BNEZ R, Loop Register renaming Loop: LD F0, 0(R) LD T9, 8(R) ADDD T0, T9, F2 SD F4, 0(R) SD T0, 8(R) SUBI R, R, #6 BNEZ R, Loop /8/2007 4
5 Question 4b [2006/2/22] Execution time (original): 8 cycles/loop Execution time (modified): 9/2 = 4.5 cycles/loop Speedup = 8 / 4.5 =.78 X /8/2007 5
6 Question 4c [2006/2/22] Given: VLIW-architecture with 2 memory ports (LD/ST), integer Functional Units, 2 Addition Functional Units How many cycles to execute the code?: 8 / 2 = 4 cycles/loop Integer Funct. U Add Funct. U Add Funct. U2 LD/ST LD/ST2 Branch 2 LD F0,0(R) LD T9,8(R) 3 4 ADDD T0, T9, F2 5 SD F4, 0(R) SD T0, 8(R) 6 SUBI R, R, #6 7 BNEZ R, Loop 8 /8/2007 6
7 Question 4c [2006/2/22] Extra Discussion () Given: Unroll loop in 4 times; The same VLIW-architecture How many cycles to execute the code? Loop: LD F0,0(R) T9, T0, T, T2, T3, T4, T5 LD T9,8(R) ========================== LD T,6(R) LD T3,24(R) Loop: LD F0,0(R) ADDD T0, T9, F2 ADDD T2, T, F2 ADDD T4, T3, F2 SD F4, 0(R) SD F4, 0(R) SD T0, 8(R) SUBI R, R, #8 SD T2, 6(R) BNEZ R, Loop SD T4, 24(R) SUBI R, R, #32 BNEZ R, Loop /8/2007 7
8 Question 4c [2006/2/22] Extra Discussion (2) Integer Funct. U Add Funct. U Add Funct. U2 LD/ST LD/ST2 Branch LD F0,0(R) LD T9,8(R) 2 LD T,6(R) LD T3,24(R) 3 ADDD T0, T9, F2 4 ADDD T2, T, F2 ADDD T4, T3, F2 SD F4, 0(R) SD T0, 8(R) 5 SD T2, 6(R) SD T4, 24(R) 6 SUBI R, R, #32 7 BNEZ R, Loop 8 How many cycles to execute the code?: 8 / 4 = 2 cycles/loop /8/2007 8
9 Question 2a [2005/2/2] Given: mix: condition branch (20%); Others (80%) Prediction accuracy: for Less than : 50% (penalty=0 cycles); for other branches: 00% (CPI = cycle) CPI for the integer applications? /8/2007 9
10 Question 2a [2005/2/2] Relative occurence of the less than branches among all instructions: 0.2 x 0.35 = 0.07 Relative occurence of the mispredicted less than branches among all instructions: 0.2 x 0.35 x 0.5 = CPI for integer applications: = x 0 + ( ) x =.35 cycles For checking: CPI = 0.2 x [(0.5 x x ) x x ] x =.35 cycles /8/2007 0
11 /8/2007
12 /8/2007 2
13 Question 3 [2006/2/22] A pipeline with Tomasulo s Algorithm SUB F0, F, F2 (8 cycles) DIV F3, F0, F4 (0 cycles) ADD F4, F5, F6 (6 cycles) /8/2007 3
14 Question 3a [2006/2/22] RAW WAR True data dependence SUB F0, F, F2 (8 cycles) DIV F3, F0, F4 (0 cycles) ADD F4, F5, F6 (6 cycles) Name dependence /8/2007 4
15 Question 3b [2006/2/22] (cycle ) From Iteration Issue Execute Write Result SUB F0, F, F2 DIV F3, F0, F4 ADD F4, F5, F6 Reservation Station Name Busy Op Vj Vk Qj Qk A Add SUB Regs[F] Regs[F2] ADD Regs[F5] Regs[F6] DIV Regs[F4] Add Register Field F0 F F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 Qi Add /8/2007 5
16 Question 3b [2006/2/22] (cycle 2) From Iteration Issue Execute Write Result SUB F0, F, F2 DIV F3, F0, F4 ADD F4, F5, F6 Reservation Station Name Busy Op Vj Vk Qj Qk A Add SUB Regs[F] Regs[F2] ADD Regs[F5] Regs[F6] DIV Regs[F4] Add Register Field F0 F F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 Qi Add /8/2007 6
17 Question 3b [2006/2/22] (cycles 3 6) From Iteration Issue Execute Write Result SUB F0, F, F2 DIV F3, F0, F4 ADD F4, F5, F6 Reservation Station Name Busy Op Vj Vk Qj Qk A Add SUB Regs[F] Regs[F2] ADD Regs[F5] Regs[F6] DIV Regs[F4] Add Register Field F0 F F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 Qi Add /8/2007 7
18 Question 3b [2006/2/22] (cycle 7) From Iteration Issue Execute Write Result SUB F0, F, F2 DIV F3, F0, F4 ADD F4, F5, F6 Reservation Station Name Busy Op Vj Vk Qj Qk A Add SUB Regs[F] Regs[F2] ADD Regs[F5] Regs[F6] DIV Regs[F4] Add Register Field F0 F F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 Qi Add /8/2007 8
19 Question 3b [2006/2/22] (cycle 8) From Iteration Issue Execute Write Result SUB F0, F, F2 DIV F3, F0, F4 ADD F4, F5, F6 Reservation Station Name Busy Op Vj Vk Qj Qk A Add SUB Regs[F] Regs[F2] ADD Regs[F5] Regs[F6] DIV Regs[F4] Add Register Field F0 F F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 Qi Add /8/2007 9
20 Question 3b [2006/2/22] (cycle 9) From Iteration Issue Execute Write Result SUB F0, F, F2 DIV F3, F0, F4 ADD F4, F5, F6 Reservation Station Name Busy Op Vj Vk Qj Qk A Add SUB Regs[F] Regs[F2] ADD Regs[F5] Regs[F6] DIV Regs[F4] Add Register Field F0 F F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 Qi Add /8/
21 Question 3b [2006/2/22] (cycles 0 8) From Iteration Issue Execute Write Result SUB F0, F, F2 DIV F3, F0, F4 ADD F4, F5, F6 Reservation Station Name Busy Op Vj Vk Qj Qk A Add SUB Regs[F] Regs[F2] ADD Regs[F5] Regs[F6] DIV Regs[F4] Add Register Field F0 F F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 Qi Add /8/2007 2
22 Question 3b [2006/2/22] (cycle 9) From Iteration Issue Execute Write Result SUB F0, F, F2 DIV F3, F0, F4 ADD F4, F5, F6 Reservation Station Name Busy Op Vj Vk Qj Qk A Add SUB Regs[F] Regs[F2] ADD Regs[F5] Regs[F6] DIV Regs[F4] Add Register Field F0 F F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 Qi Add /8/
23 Question 3b [2006/2/22] (cycle 20) From Iteration Issue Execute Write Result SUB F0, F, F2 DIV F3, F0, F4 ADD F4, F5, F6 Reservation Station Name Busy Op Vj Vk Qj Qk A Add SUB Regs[F] Regs[F2] ADD Regs[F5] Regs[F6] DIV Regs[F4] Add Register Field F0 F F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 Qi Add /8/
24 Question 3c,d [2006/2/22] C). Assumed: in the instruction DIV F3, F0, F4 data stored in F4 are provided by other previous instructions that are also loaded in the reservation station Vk stores the result in an entry of reservation station so that DIV instruction would point to it It makes DIV and ADD independent instructions from each other, and eliminating the WAR hazard involving F4 D). Value of F0 is provided by the first entry (add) of the reservation station (See previous slides for more details) /8/
Tomasulo s Algorithm. Tomasulo s Algorithm
 Tomasulo s Algorithm Load and store buffers Contain data and addresses, act like reservation stations Branch Prediction Top-level design: 56 Tomasulo s Algorithm Three Steps: Issue Get next instruction
Tomasulo s Algorithm Load and store buffers Contain data and addresses, act like reservation stations Branch Prediction Top-level design: 56 Tomasulo s Algorithm Three Steps: Issue Get next instruction
Computer Science 246. Advanced Computer Architecture. Spring 2010 Harvard University. Instructor: Prof. David Brooks
 Advanced Computer Architecture Spring 2010 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture Outline Instruction-Level Parallelism Scoreboarding (A.8) Instruction Level Parallelism
Advanced Computer Architecture Spring 2010 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture Outline Instruction-Level Parallelism Scoreboarding (A.8) Instruction Level Parallelism
Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier
 Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science !!! Basic MIPS integer pipeline Branches with one
Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science !!! Basic MIPS integer pipeline Branches with one
Problem: hazards delay instruction completion & increase the CPI. Compiler scheduling (static scheduling) reduces impact of hazards
 Dynamic Scheduling Pipelining: Issue instructions in every cycle (CPI 1) Problem: hazards delay instruction completion & increase the CPI Compiler scheduling (static scheduling) reduces impact of hazards
Dynamic Scheduling Pipelining: Issue instructions in every cycle (CPI 1) Problem: hazards delay instruction completion & increase the CPI Compiler scheduling (static scheduling) reduces impact of hazards
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 22: Processor / ILP 3
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 22: Processor / ILP 3 Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 22: Processor / ILP 3 Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard
 Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Basic Assumptions We consider
Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Basic Assumptions We consider
CS521 CSE IITG 11/23/2012
 Parallel Decoding and issue Parallel execution Preserving the sequential consistency of execution and exception processing 1 slide 2 Decode/issue data Issue bound fetch Dispatch bound fetch RS RS RS RS
Parallel Decoding and issue Parallel execution Preserving the sequential consistency of execution and exception processing 1 slide 2 Decode/issue data Issue bound fetch Dispatch bound fetch RS RS RS RS
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture. Lecture 9 - Scoreboard
 CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 9 - Scoreboard Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture tes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 9 - Scoreboard Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture tes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer
COSC4201. Scoreboard
 COSC4201 Scoreboard Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) 1 Overcoming Data Hazards with Dynamic Scheduling In the pipeline, if there is
COSC4201 Scoreboard Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) 1 Overcoming Data Hazards with Dynamic Scheduling In the pipeline, if there is
CMP 301B Computer Architecture. Appendix C
 CMP 301B Computer Architecture Appendix C Dealing with Exceptions What should be done when an exception arises and many instructions are in the pipeline??!! Force a trap instruction in the next IF stage
CMP 301B Computer Architecture Appendix C Dealing with Exceptions What should be done when an exception arises and many instructions are in the pipeline??!! Force a trap instruction in the next IF stage
Instruction Level Parallelism. Data Dependence Static Scheduling
 Instruction Level Parallelism Data Dependence Static Scheduling Basic Block A straight line code sequence with no branches in except to the entry and no branches out except at the exit Loop: L.D ADD.D
Instruction Level Parallelism Data Dependence Static Scheduling Basic Block A straight line code sequence with no branches in except to the entry and no branches out except at the exit Loop: L.D ADD.D
Parallel architectures Electronic Computers LM
 Parallel architectures Electronic Computers LM 1 Architecture Architecture: functional behaviour of a computer. For instance a processor which executes DLX code Implementation: a logical network implementing
Parallel architectures Electronic Computers LM 1 Architecture Architecture: functional behaviour of a computer. For instance a processor which executes DLX code Implementation: a logical network implementing
EECS 470 Lecture 5. Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont
 Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides.
Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides.
Out-of-Order Execution. Register Renaming. Nima Honarmand
 Out-of-Order Execution & Register Renaming Nima Honarmand Out-of-Order (OOO) Execution (1) Essence of OOO execution is Dynamic Scheduling Dynamic scheduling: processor hardware determines instruction execution
Out-of-Order Execution & Register Renaming Nima Honarmand Out-of-Order (OOO) Execution (1) Essence of OOO execution is Dynamic Scheduling Dynamic scheduling: processor hardware determines instruction execution
U. Wisconsin CS/ECE 752 Advanced Computer Architecture I
 U. Wisconsin CS/ECE 752 Advanced Computer Architecture I Prof. Karu Sankaralingam Unit 5: Dynamic Scheduling I Slides developed by Amir Roth of University of Pennsylvania with sources that included University
U. Wisconsin CS/ECE 752 Advanced Computer Architecture I Prof. Karu Sankaralingam Unit 5: Dynamic Scheduling I Slides developed by Amir Roth of University of Pennsylvania with sources that included University
Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel
 Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel Overview Project guidelines Benchmarking Library OoO CPUs Project Guidelines Use optimizations from lectures as your arsenal If you decide to implement one, look at Whale
Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel Overview Project guidelines Benchmarking Library OoO CPUs Project Guidelines Use optimizations from lectures as your arsenal If you decide to implement one, look at Whale
Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling
 Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling Reading: Appendix A (A-67) H&P Chapter 2 Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling 1 his Unit: Dynamic Scheduling Application OS Compiler
Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling Reading: Appendix A (A-67) H&P Chapter 2 Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling 1 his Unit: Dynamic Scheduling Application OS Compiler
Dynamic Scheduling I
 basic pipeline started with single, in-order issue, single-cycle operations have extended this basic pipeline with multi-cycle operations multiple issue (superscalar) now: dynamic scheduling (out-of-order
basic pipeline started with single, in-order issue, single-cycle operations have extended this basic pipeline with multi-cycle operations multiple issue (superscalar) now: dynamic scheduling (out-of-order
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
Pipelined Processor Design
 Pipelined Processor Design COE 38 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Pipelining versus Serial
Pipelined Processor Design COE 38 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Pipelining versus Serial
Compiler Optimisation
 Compiler Optimisation 6 Instruction Scheduling Hugh Leather IF 1.18a hleather@inf.ed.ac.uk Institute for Computing Systems Architecture School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 2018 Introduction This
Compiler Optimisation 6 Instruction Scheduling Hugh Leather IF 1.18a hleather@inf.ed.ac.uk Institute for Computing Systems Architecture School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 2018 Introduction This
Tomasolu s s Algorithm
 omasolu s s Algorithm Fall 2007 Prof. homas Wenisch http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4 70 Floating Point Buffers (FLB) ag ag ag Storage Bus Floating Point 4 3 Buffers FLB 6 5 5 4 Control 2 1 1 Result
omasolu s s Algorithm Fall 2007 Prof. homas Wenisch http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4 70 Floating Point Buffers (FLB) ag ag ag Storage Bus Floating Point 4 3 Buffers FLB 6 5 5 4 Control 2 1 1 Result
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
Chapter 4. Pipelining Analogy. The Processor. Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution. Parallelism improves performance. Four loads: Non-stop:
 Chapter 4 The Processor Part II Pipelining Analogy Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution Parallelism improves performance Four loads: Speedup = 8/3.5 = 2.3 Non-stop: Speedup p = 2n/(0.5n + 1.5) 4 =
Chapter 4 The Processor Part II Pipelining Analogy Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution Parallelism improves performance Four loads: Speedup = 8/3.5 = 2.3 Non-stop: Speedup p = 2n/(0.5n + 1.5) 4 =
EECS 470. Lecture 9. MIPS R10000 Case Study. Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont
 MIPS R10000 Case Study Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Multiprocessor SGI Origin Using MIPS R10K Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for
MIPS R10000 Case Study Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Multiprocessor SGI Origin Using MIPS R10K Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for
EECS 470. Tomasulo s Algorithm. Lecture 4 Winter 2018
 omasulo s Algorithm Winter 2018 Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti, Martin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, yson, Vijaykumar, and Wenisch of Carnegie Mellon University,
omasulo s Algorithm Winter 2018 Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti, Martin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, yson, Vijaykumar, and Wenisch of Carnegie Mellon University,
IF ID EX MEM WB 400 ps 225 ps 350 ps 450 ps 300 ps
 CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2011 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 75 points Assigned: November 1, 2011 Due: November 8, 2011 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (15 points)
CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2011 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 75 points Assigned: November 1, 2011 Due: November 8, 2011 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (15 points)
7/11/2012. Single Cycle (Review) CSE 2021: Computer Organization. Multi-Cycle Implementation. Single Cycle with Jump. Pipelining Analogy
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10 CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-12-2012 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10 CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-12-2012 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation
OOO Execution & Precise State MIPS R10000 (R10K)
 OOO Execution & Precise State in MIPS R10000 (R10K) Nima Honarmand CDB. CDB.V Spring 2018 :: CSE 502 he Problem with P6 Map able + Regfile value R value Head Retire Dispatch op RS 1 2 V1 FU V2 ail Dispatch
OOO Execution & Precise State in MIPS R10000 (R10K) Nima Honarmand CDB. CDB.V Spring 2018 :: CSE 502 he Problem with P6 Map able + Regfile value R value Head Retire Dispatch op RS 1 2 V1 FU V2 ail Dispatch
Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors
 Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 16 - Superscalar Processors 1 / 78 Table of Contents I 1 Overview
Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 16 - Superscalar Processors 1 / 78 Table of Contents I 1 Overview
IF ID EX MEM WB 400 ps 225 ps 350 ps 450 ps 300 ps
 CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2010 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 85 points Assigned: November 2, 2010 Due: November 9, 2010 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (25 points)
CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2010 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 85 points Assigned: November 2, 2010 Due: November 9, 2010 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (25 points)
6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors
 6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors Options for dealing with data and control hazards: stall, bypass, speculate 6.S084 Worksheet - 1 of 10 - L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined
6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors Options for dealing with data and control hazards: stall, bypass, speculate 6.S084 Worksheet - 1 of 10 - L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined
ECE 4750 Computer Architecture, Fall 2016 T09 Advanced Processors: Superscalar Execution
 ECE 4750 Computer Architecture, Fall 2016 T09 Advanced Processors: Superscalar Execution School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2016-11-28-17-33 1 In-Order Dual-Issue
ECE 4750 Computer Architecture, Fall 2016 T09 Advanced Processors: Superscalar Execution School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2016-11-28-17-33 1 In-Order Dual-Issue
Lecture 8-1 Vector Processors 2 A. Sohn
 Lecture 8-1 Vector Processors Vector Processors How many iterations does the following loop go through? For i=1 to n do A[i] = B[i] + C[i] Sequential Processor: n times. Vector processor: 1 instruction!
Lecture 8-1 Vector Processors Vector Processors How many iterations does the following loop go through? For i=1 to n do A[i] = B[i] + C[i] Sequential Processor: n times. Vector processor: 1 instruction!
Dynamic Scheduling II
 so far: dynamic scheduling (out-of-order execution) Scoreboard omasulo s algorithm register renaming: removing artificial dependences (WAR/WAW) now: out-of-order execution + precise state advanced topic:
so far: dynamic scheduling (out-of-order execution) Scoreboard omasulo s algorithm register renaming: removing artificial dependences (WAR/WAW) now: out-of-order execution + precise state advanced topic:
Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining
 Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Schedulers Data-Capture Scheduler Dispatch: read available operands from ARF/ROB, store in scheduler Commit: Missing operands filled in from bypass Issue: When
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Schedulers Data-Capture Scheduler Dispatch: read available operands from ARF/ROB, store in scheduler Commit: Missing operands filled in from bypass Issue: When
7/19/2012. IF for Load (Review) CSE 2021: Computer Organization. EX for Load (Review) ID for Load (Review) WB for Load (Review) MEM for Load (Review)
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization IF for Load (Review) Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-19-2012 2 ID for Load (Review) EX for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-19-2012
CSE 2021: Computer Organization IF for Load (Review) Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-19-2012 2 ID for Load (Review) EX for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-19-2012
Precise State Recovery. Out-of-Order Pipelines
 Precise State Recovery in Out-of-Order Pipelines Nima Honarmand Recall Our Generic OOO Pipeline Instruction flow (pipeline front-end) is in-order Register and memory execution are OOO And, we need a final
Precise State Recovery in Out-of-Order Pipelines Nima Honarmand Recall Our Generic OOO Pipeline Instruction flow (pipeline front-end) is in-order Register and memory execution are OOO And, we need a final
CSE 2021: Computer Organization
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan IF for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 2 ID for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 3 EX for Load
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan IF for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 2 ID for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 3 EX for Load
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Speculation and raps in Out-of-Order Cores What is wrong with omasulo s? Branch instructions Need branch prediction to guess what to fetch next Need speculative execution
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Speculation and raps in Out-of-Order Cores What is wrong with omasulo s? Branch instructions Need branch prediction to guess what to fetch next Need speculative execution
SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation
 SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation Mark Wolff Linda Wills School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology {wolff,linda.wills}@ece.gatech.edu
SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation Mark Wolff Linda Wills School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology {wolff,linda.wills}@ece.gatech.edu
EECS 470 Lecture 4. Pipelining & Hazards II. Winter Prof. Ronald Dreslinski h8p://
 Wenisch 26 -- Portions ustin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, ipasti, artin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, Tyson, Vijaykumar EECS 4 ecture 4 Pipelining & Hazards II Winter 29 GS STTION Prof. Ronald Dreslinski h8p://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4
Wenisch 26 -- Portions ustin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, ipasti, artin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, Tyson, Vijaykumar EECS 4 ecture 4 Pipelining & Hazards II Winter 29 GS STTION Prof. Ronald Dreslinski h8p://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4
Suggested Readings! Lecture 12" Introduction to Pipelining! Example: We have to build x cars...! ...Each car takes 6 steps to build...! ! Readings!
 1! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 4.5-4.7!! (Over the next 3-4 lectures)! Lecture 12"
1! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 4.5-4.7!! (Over the next 3-4 lectures)! Lecture 12"
CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining
 CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on
CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on
Pipelined Beta. Handouts: Lecture Slides. Where are the registers? Spring /10/01. L16 Pipelined Beta 1
 Pipelined Beta Where are the registers? Handouts: Lecture Slides L16 Pipelined Beta 1 Increasing CPU Performance MIPS = Freq CPI MIPS = Millions of Instructions/Second Freq = Clock Frequency, MHz CPI =
Pipelined Beta Where are the registers? Handouts: Lecture Slides L16 Pipelined Beta 1 Increasing CPU Performance MIPS = Freq CPI MIPS = Millions of Instructions/Second Freq = Clock Frequency, MHz CPI =
Reading Material + Announcements
 Reading Material + Announcements Reminder HW 1» Before asking questions: 1) Read all threads on piazza, 2) Think a bit Ÿ Then, post question Ÿ talk to Animesh if you are stuck Today s class» Wrap up Control
Reading Material + Announcements Reminder HW 1» Before asking questions: 1) Read all threads on piazza, 2) Think a bit Ÿ Then, post question Ÿ talk to Animesh if you are stuck Today s class» Wrap up Control
A B C D. Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold. Time
 Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry A B C D Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry A B C D Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
Pipelining A B C D. Readings: Example: Doing the laundry. Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave. each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold
 Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave A B C D each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave A B C D each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
EECS 470 Lecture 8. P6 µarchitecture. Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont Core 2 Microarchitecture
 P6 µarchitecture Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Core 2 Microarchitecture Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides. Portions
P6 µarchitecture Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Core 2 Microarchitecture Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides. Portions
CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture
 CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture Pipelining Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science
CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture Pipelining Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science
Embedded Systems. 9. Power and Energy. Lothar Thiele. Computer Engineering and Networks Laboratory
 Embedded Systems 9. Power and Energy Lothar Thiele Computer Engineering and Networks Laboratory General Remarks 9 2 Power and Energy Consumption Statements that are true since a decade or longer: Power
Embedded Systems 9. Power and Energy Lothar Thiele Computer Engineering and Networks Laboratory General Remarks 9 2 Power and Energy Consumption Statements that are true since a decade or longer: Power
RISC Central Processing Unit
 RISC Central Processing Unit Lan-Da Van ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Spring, 2014 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/
RISC Central Processing Unit Lan-Da Van ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Spring, 2014 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/
Computer Architecture ( L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS
 Computer Architecture (263-2210-00L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS Instructor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Mohammad Sadr, Lois Orosa, Juan Gomez Luna Assigned:
Computer Architecture (263-2210-00L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS Instructor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Mohammad Sadr, Lois Orosa, Juan Gomez Luna Assigned:
Games in Extensive Form
 Games in Extensive Form the extensive form of a game is a tree diagram except that my trees grow sideways any game can be represented either using the extensive form or the strategic form but the extensive
Games in Extensive Form the extensive form of a game is a tree diagram except that my trees grow sideways any game can be represented either using the extensive form or the strategic form but the extensive
Electrical Circuits Question Paper 6
 Electrical Circuits Question Paper 6 Level IGCSE Subject Physics Exam Board CIE Topic Electricity and Magnetism Sub-Topic Electrical Circuits Paper Type lternative to Practical Booklet Question Paper 6
Electrical Circuits Question Paper 6 Level IGCSE Subject Physics Exam Board CIE Topic Electricity and Magnetism Sub-Topic Electrical Circuits Paper Type lternative to Practical Booklet Question Paper 6
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: November 8, 2017 at 09:27 CS429 Slideset 14: 1 Overview What s wrong
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: November 8, 2017 at 09:27 CS429 Slideset 14: 1 Overview What s wrong
Chapter 12. Cross-Layer Optimization for Multi- Hop Cognitive Radio Networks
 Chapter 12 Cross-Layer Optimization for Multi- Hop Cognitive Radio Networks 1 Outline CR network (CRN) properties Mathematical models at multiple layers Case study 2 Traditional Radio vs CR Traditional
Chapter 12 Cross-Layer Optimization for Multi- Hop Cognitive Radio Networks 1 Outline CR network (CRN) properties Mathematical models at multiple layers Case study 2 Traditional Radio vs CR Traditional
Asanovic/Devadas Spring Pipeline Hazards. Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T.
 Pipeline Hazards Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. Pipelined DLX Datapath without interlocks and jumps 31 0x4 RegDst RegWrite inst Inst rs1 rs2 rd1 ws wd rd2 GPRs Imm Ext A B OpSel
Pipeline Hazards Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. Pipelined DLX Datapath without interlocks and jumps 31 0x4 RegDst RegWrite inst Inst rs1 rs2 rd1 ws wd rd2 GPRs Imm Ext A B OpSel
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach Fourth Edition John L. Hennessy Stanford University David A. Patterson University of California at Berkeley With Contributions by Andrea C. Arpaci-Dusseau
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach Fourth Edition John L. Hennessy Stanford University David A. Patterson University of California at Berkeley With Contributions by Andrea C. Arpaci-Dusseau
COMP 4550 Servo Motors
 COMP 4550 Servo Motors Autonomous Agents Lab, University of Manitoba jacky@cs.umanitoba.ca http://www.cs.umanitoba.ca/~jacky http://aalab.cs.umanitoba.ca Servo Motors A servo motor consists of three components
COMP 4550 Servo Motors Autonomous Agents Lab, University of Manitoba jacky@cs.umanitoba.ca http://www.cs.umanitoba.ca/~jacky http://aalab.cs.umanitoba.ca Servo Motors A servo motor consists of three components
EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on
 EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on Mohammad M. Mansour Dept. of Electrical and Compute Engineering American University of Beirut Lecture 21: Pipelining Processor Pipelining Same principles can be applied to
EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on Mohammad M. Mansour Dept. of Electrical and Compute Engineering American University of Beirut Lecture 21: Pipelining Processor Pipelining Same principles can be applied to
CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture
 CMSC 611: Advanced Compute Achitectue Pipelining Some mateial adapted fom Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Sp 2003 couse slides Some mateial adapted fom Hennessy & Patteson / 2003 Elsevie Science Pipeline
CMSC 611: Advanced Compute Achitectue Pipelining Some mateial adapted fom Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Sp 2003 couse slides Some mateial adapted fom Hennessy & Patteson / 2003 Elsevie Science Pipeline
Computer Elements and Datapath. Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA
 6.823, L5--1 Computer Elements and atapath Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 status lines Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA ler control points 6.823, L5--2
6.823, L5--1 Computer Elements and atapath Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 status lines Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA ler control points 6.823, L5--2
Cyclops User s Manual
 Cyclops User s Manual Revision 5.x.x March 14, 2017 Contents Background... 1 Interface... 1 Normal Operation... 1 Controller Input Type... 1 Communication... 2 Sensitivity... 3 Operating Modes... 3 Normal...
Cyclops User s Manual Revision 5.x.x March 14, 2017 Contents Background... 1 Interface... 1 Normal Operation... 1 Controller Input Type... 1 Communication... 2 Sensitivity... 3 Operating Modes... 3 Normal...
LECTURE 8. Pipelining: Datapath and Control
 LECTURE 8 Pipelining: Datapath and Control PIPELINED DATAPATH As with the single-cycle and multi-cycle implementations, we will start by looking at the datapath for pipelining. We already know that pipelining
LECTURE 8 Pipelining: Datapath and Control PIPELINED DATAPATH As with the single-cycle and multi-cycle implementations, we will start by looking at the datapath for pipelining. We already know that pipelining
On the Rules of Low-Power Design
 On the Rules of Low-Power Design (and Why You Should Break Them) Prof. Todd Austin University of Michigan austin@umich.edu A long time ago, in a not so far away place The Rules of Low-Power Design P =
On the Rules of Low-Power Design (and Why You Should Break Them) Prof. Todd Austin University of Michigan austin@umich.edu A long time ago, in a not so far away place The Rules of Low-Power Design P =
COMMUNICATION LABORATORY
 LAB 6: (PAM) PULSE AMPLITUDE MODULATION/DEMODULAT ION ON MATLAB/SIMULINK STUDENT NAME: STUDENT ID: SUBMISSION DATE : 15.04.2013 1/8 1. TECHNICAL BACKGROUND In pulse amplitude modulation, the amplitude
LAB 6: (PAM) PULSE AMPLITUDE MODULATION/DEMODULAT ION ON MATLAB/SIMULINK STUDENT NAME: STUDENT ID: SUBMISSION DATE : 15.04.2013 1/8 1. TECHNICAL BACKGROUND In pulse amplitude modulation, the amplitude
CS Computer Architecture Spring Lecture 04: Understanding Performance
 CS 35101 Computer Architecture Spring 2008 Lecture 04: Understanding Performance Taken from Mary Jane Irwin (www.cse.psu.edu/~mji) and Kevin Schaffer [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson
CS 35101 Computer Architecture Spring 2008 Lecture 04: Understanding Performance Taken from Mary Jane Irwin (www.cse.psu.edu/~mji) and Kevin Schaffer [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson
SAMPLE EXAM PROBLEM PROTECTION (6 OF 80 PROBLEMS)
 SAMPLE EXAM PROBLEM PROTECTION (6 OF 80 PROBLEMS) SLIDE In this video, we will cover a sample exam problem for the Power PE Exam. This exam problem falls under the topic of Protection, which accounts for
SAMPLE EXAM PROBLEM PROTECTION (6 OF 80 PROBLEMS) SLIDE In this video, we will cover a sample exam problem for the Power PE Exam. This exam problem falls under the topic of Protection, which accounts for
Final Report: DBmbench
 18-741 Final Report: DBmbench Yan Ke (yke@cs.cmu.edu) Justin Weisz (jweisz@cs.cmu.edu) Dec. 8, 2006 1 Introduction Conventional database benchmarks, such as the TPC-C and TPC-H, are extremely computationally
18-741 Final Report: DBmbench Yan Ke (yke@cs.cmu.edu) Justin Weisz (jweisz@cs.cmu.edu) Dec. 8, 2006 1 Introduction Conventional database benchmarks, such as the TPC-C and TPC-H, are extremely computationally
Trace Based Switching For A Tightly Coupled Heterogeneous Core
 Trace Based Switching For A Tightly Coupled Heterogeneous Core Shru% Padmanabha, Andrew Lukefahr, Reetuparna Das, Sco@ Mahlke Micro- 46 December 2013 University of Michigan Electrical Engineering and Computer
Trace Based Switching For A Tightly Coupled Heterogeneous Core Shru% Padmanabha, Andrew Lukefahr, Reetuparna Das, Sco@ Mahlke Micro- 46 December 2013 University of Michigan Electrical Engineering and Computer
Midterm Examination. CSCI 561: Artificial Intelligence
 Midterm Examination CSCI 561: Artificial Intelligence October 10, 2002 Instructions: 1. Date: 10/10/2002 from 11:00am 12:20 pm 2. Maximum credits/points for this midterm: 100 points (corresponding to 35%
Midterm Examination CSCI 561: Artificial Intelligence October 10, 2002 Instructions: 1. Date: 10/10/2002 from 11:00am 12:20 pm 2. Maximum credits/points for this midterm: 100 points (corresponding to 35%
Using Variable-MHz Microprocessors to Efficiently Handle Uncertainty in Real-Time Systems
 Using Variable-MHz Microprocessors to Efficiently Handle Uncertainty in Real-Time Systems Eric Rotenberg Center for Embedded Systems Research (CESR) Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering North
Using Variable-MHz Microprocessors to Efficiently Handle Uncertainty in Real-Time Systems Eric Rotenberg Center for Embedded Systems Research (CESR) Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering North
Computer Architecture Lab Session
 Computer Architecture Lab Session The 4 th week / Sep 24 th, 2015 Su-Jin Oh sujinohkor@gmail.com 1 Index Review Little Bit Different Kinds of Instructions Shift Instructions Some Ways for Console I/O Task
Computer Architecture Lab Session The 4 th week / Sep 24 th, 2015 Su-Jin Oh sujinohkor@gmail.com 1 Index Review Little Bit Different Kinds of Instructions Shift Instructions Some Ways for Console I/O Task
Issue. Execute. Finish
 Specula1on & Precise Interrupts Fall 2017 Prof. Ron Dreslinski h6p://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 In Order Out of Order In Order Issue Execute Finish Fetch Decode Dispatch Complete Retire Instruction/Decode
Specula1on & Precise Interrupts Fall 2017 Prof. Ron Dreslinski h6p://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 In Order Out of Order In Order Issue Execute Finish Fetch Decode Dispatch Complete Retire Instruction/Decode
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Advanced Topics in Computer Science Grades 9-12
 West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Advanced Topics in Computer Science Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Recursion Content Area: Technology Course & Grade Level: Advanced Topics in Computer Science, 9
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Advanced Topics in Computer Science Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Recursion Content Area: Technology Course & Grade Level: Advanced Topics in Computer Science, 9
Design of FIR Filter Using Modified Montgomery Multiplier with Pipelining Technique
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 3 (March 2014), PP.55-63 Design of FIR Filter Using Modified Montgomery
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 3 (March 2014), PP.55-63 Design of FIR Filter Using Modified Montgomery
DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall Class # 07. October 16, 2008
 DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall 2008 Class # 07 October 16, 2008 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Course Admin Lab #3 next week Exam in two weeks 10/30/08 Detailed Technical Discussions Digital
DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall 2008 Class # 07 October 16, 2008 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Course Admin Lab #3 next week Exam in two weeks 10/30/08 Detailed Technical Discussions Digital
Digital Integrated CircuitDesign
 Digital Integrated CircuitDesign Lecture 13 Building Blocks (Multipliers) Register Adder Shift Register Adib Abrishamifar EE Department IUST Acknowledgement This lecture note has been summarized and categorized
Digital Integrated CircuitDesign Lecture 13 Building Blocks (Multipliers) Register Adder Shift Register Adib Abrishamifar EE Department IUST Acknowledgement This lecture note has been summarized and categorized
Throttling: Infrastructure, Dead Time, Monitoring. Beat Jost Cern EP
 Throttling: Infrastructure, Dead Time, Monitoring Beat Jost Cern EP TFC Architecture TTCmi L0 Local trig. L-0 L0 L-1 L0 Local trig. Readout Supervisor Readout Supervisor Readout Supervisor gl0 g gl0 g
Throttling: Infrastructure, Dead Time, Monitoring Beat Jost Cern EP TFC Architecture TTCmi L0 Local trig. L-0 L0 L-1 L0 Local trig. Readout Supervisor Readout Supervisor Readout Supervisor gl0 g gl0 g
FCam: An architecture for computational cameras
 FCam: An architecture for computational cameras Dr. Kari Pulli, Research Fellow Palo Alto What is computational photography? All cameras have optics + sensors But the images have limitations they cannot
FCam: An architecture for computational cameras Dr. Kari Pulli, Research Fellow Palo Alto What is computational photography? All cameras have optics + sensors But the images have limitations they cannot
ECE 3410 Homework 4 (C) (B) (A) (F) (E) (D) (H) (I) Solution. Utah State University 1 D1 D2. D1 v OUT. v IN D1 D2 D1 (G)
 ECE 341 Homework 4 Problem 1. In each of the ideal-diode circuits shown below, is a 1 khz sinusoid with zero-to-peak amplitude 1 V. For each circuit, sketch the output waveform and state the values of
ECE 341 Homework 4 Problem 1. In each of the ideal-diode circuits shown below, is a 1 khz sinusoid with zero-to-peak amplitude 1 V. For each circuit, sketch the output waveform and state the values of
Software Pipelining Creates Parallelization Opportunities
 Software Pipelining Creates Parallelization Opportunities Jialu Huang, Arun Raman, Thomas B Jablin, Yun Zhang, Tzu-Han Hung David I August Liberty Research Group Princeton University 1 DSWP+ DOALL DSWP
Software Pipelining Creates Parallelization Opportunities Jialu Huang, Arun Raman, Thomas B Jablin, Yun Zhang, Tzu-Han Hung David I August Liberty Research Group Princeton University 1 DSWP+ DOALL DSWP
ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Pipeline: Introduction
 Computer Architecture and Organization Pipeline: Introduction Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 11.1 The Laundry Analogy Student A,
Computer Architecture and Organization Pipeline: Introduction Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 11.1 The Laundry Analogy Student A,
EECS 583 Class 7 Classic Code Optimization cont d
 EECS 583 Class 7 Classic Code Optimization cont d University of Michigan October 2, 2016 Global Constant Propagation Consider 2 ops, X and Y in different BBs» 1. X is a move» 2. src1(x) is a literal» 3.
EECS 583 Class 7 Classic Code Optimization cont d University of Michigan October 2, 2016 Global Constant Propagation Consider 2 ops, X and Y in different BBs» 1. X is a move» 2. src1(x) is a literal» 3.
SCHEDULING Giovanni De Micheli Stanford University
 SCHEDULING Giovanni De Micheli Stanford University Outline The scheduling problem. Scheduling without constraints. Scheduling under timing constraints. Relative scheduling. Scheduling under resource constraints.
SCHEDULING Giovanni De Micheli Stanford University Outline The scheduling problem. Scheduling without constraints. Scheduling under timing constraints. Relative scheduling. Scheduling under resource constraints.
GE420 Laboratory Assignment 8 Positioning Control of a Motor Using PD, PID, and Hybrid Control
 GE420 Laboratory Assignment 8 Positioning Control of a Motor Using PD, PID, and Hybrid Control Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Design a PD discrete control algorithm to allow the closed-loop combination
GE420 Laboratory Assignment 8 Positioning Control of a Motor Using PD, PID, and Hybrid Control Goals for this Lab Assignment: 1. Design a PD discrete control algorithm to allow the closed-loop combination
Algorithms and Data Structures: Network Flows. 24th & 28th Oct, 2014
 Algorithms and Data Structures: Network Flows 24th & 28th Oct, 2014 ADS: lects & 11 slide 1 24th & 28th Oct, 2014 Definition 1 A flow network consists of A directed graph G = (V, E). Flow Networks A capacity
Algorithms and Data Structures: Network Flows 24th & 28th Oct, 2014 ADS: lects & 11 slide 1 24th & 28th Oct, 2014 Definition 1 A flow network consists of A directed graph G = (V, E). Flow Networks A capacity
Instruction Selection via Tree-Pattern Matching Comp 412
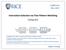 COMP FALL 017 Instruction Selection via TreePattern Matching Comp source code IR Front End Optimizer Back End IR target code Copyright 017, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. Students
COMP FALL 017 Instruction Selection via TreePattern Matching Comp source code IR Front End Optimizer Back End IR target code Copyright 017, Keith D. Cooper & Linda Torczon, all rights reserved. Students
Data Conversion and Lab (17.368) Fall Lecture Outline
 Data Conversion and Lab (17.368) Fall 2013 Lecture Outline Class # 07 October 17, 2013 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Administrative Detailed Technical Discussions Digital to Analog Conversion Lab
Data Conversion and Lab (17.368) Fall 2013 Lecture Outline Class # 07 October 17, 2013 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Administrative Detailed Technical Discussions Digital to Analog Conversion Lab
SCALCORE: DESIGNING A CORE
 SCALCORE: DESIGNING A CORE FOR VOLTAGE SCALABILITY Bhargava Gopireddy, Choungki Song, Josep Torrellas, Nam Sung Kim, Aditya Agrawal, Asit Mishra University of Illinois, University of Wisconsin, Nvidia,
SCALCORE: DESIGNING A CORE FOR VOLTAGE SCALABILITY Bhargava Gopireddy, Choungki Song, Josep Torrellas, Nam Sung Kim, Aditya Agrawal, Asit Mishra University of Illinois, University of Wisconsin, Nvidia,
Computer Arithmetic (2)
 Computer Arithmetic () Arithmetic Units How do we carry out,,, in FPGA? How do we perform sin, cos, e, etc? ELEC816/ELEC61 Spring 1 Hayden Kwok-Hay So H. So, Sp1 Lecture 7 - ELEC816/61 Addition Two ve
Computer Arithmetic () Arithmetic Units How do we carry out,,, in FPGA? How do we perform sin, cos, e, etc? ELEC816/ELEC61 Spring 1 Hayden Kwok-Hay So H. So, Sp1 Lecture 7 - ELEC816/61 Addition Two ve
Efficiently Exploiting Memory Level Parallelism on Asymmetric Coupled Cores in the Dark Silicon Era
 28 Efficiently Exploiting Memory Level Parallelism on Asymmetric Coupled Cores in the Dark Silicon Era GEORGE PATSILARAS, NIKET K. CHOUDHARY, and JAMES TUCK, North Carolina State University Extracting
28 Efficiently Exploiting Memory Level Parallelism on Asymmetric Coupled Cores in the Dark Silicon Era GEORGE PATSILARAS, NIKET K. CHOUDHARY, and JAMES TUCK, North Carolina State University Extracting
CUDA Threads. Terminology. How it works. Terminology. Streaming Multiprocessor (SM) A SM processes block of threads
 Terminology CUDA Threads Bedrich Benes, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Streaming Multiprocessor (SM) A SM processes block of threads Streaming Processors (SP) also called CUDA
Terminology CUDA Threads Bedrich Benes, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Streaming Multiprocessor (SM) A SM processes block of threads Streaming Processors (SP) also called CUDA
Multiple Predictors: BTB + Branch Direction Predictors
 Constructive Computer Architecture: Branch Prediction: Direction Predictors Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology October 28, 2015 http://csg.csail.mit.edu/6.175
Constructive Computer Architecture: Branch Prediction: Direction Predictors Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology October 28, 2015 http://csg.csail.mit.edu/6.175
A LOW POWER DESIGN FOR ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC UNIT
 A LOW POWER DESIGN FOR ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC UNIT NG KAR SIN (B.Tech. (Hons.), NUS) A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING NATIONAL
A LOW POWER DESIGN FOR ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC UNIT NG KAR SIN (B.Tech. (Hons.), NUS) A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING NATIONAL
SOFTWARE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE
 SOFTWARE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE IEEE 802.11A/P PHYSICAL LAYER SDR`12 WInnComm Europe 27 29 June, 2012 Brussels, Belgium T. Cupaiuolo, D. Lo Iacono, M. Siti and M. Odoni Advanced System Technologies STMicroelectronics,
SOFTWARE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE IEEE 802.11A/P PHYSICAL LAYER SDR`12 WInnComm Europe 27 29 June, 2012 Brussels, Belgium T. Cupaiuolo, D. Lo Iacono, M. Siti and M. Odoni Advanced System Technologies STMicroelectronics,
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis
![UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis](/thumbs/87/96626175.jpg) UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 3 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 3 Notes Goal for today: CL Section 3 Subsets,
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 3 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 3 Notes Goal for today: CL Section 3 Subsets,
Search Depth. 8. Search Depth. Investing. Investing in Search. Jonathan Schaeffer
 Search Depth 8. Search Depth Jonathan Schaeffer jonathan@cs.ualberta.ca www.cs.ualberta.ca/~jonathan So far, we have always assumed that all searches are to a fixed depth Nice properties in that the search
Search Depth 8. Search Depth Jonathan Schaeffer jonathan@cs.ualberta.ca www.cs.ualberta.ca/~jonathan So far, we have always assumed that all searches are to a fixed depth Nice properties in that the search
