Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Engineering Graphics
|
|
|
- Hubert Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Engineering Graphics Lecture 10 Isometric Projections-Part-II by Prof. Nihar Ranjan Patra Department of Civil engineering, IIT Kanpur Last class we have covered isometric projections. (Refer Slide Time: 00:18) Isometric views, so in isometric view the object is rotated by 45 about the vertical axis and 35, 15 minute, and 52 second about the profile axis. It results in why, why it has been rotated 45 about the vertical axis, then 35 approximately about the profile axis because it results in equal amount of foreshortening of the object along the isometric axes.
2 (Refer Slide Time: 00:52) Upto this, I have finished upto the last class.
3 (Refer Slide Time: 01:00) Go to this viewing direction is fixed just in terms of this is a cube and this direction is fixed and it has been rotated with your vertical axis by means of 45, it has been rotated 45, cube is rotated.
4 (Refer Slide Time: 01:17) Step 1, so step 1 all length will be let us say length, width and height will be one in 11 unit dimensions, then it has been rotated about the vertical axis by 45.
5 (Refer Slide Time: 01:34) Once it has been rotated by 45, this is the cube how it looks then you can see both the faces so it will be 1/ 2 and 1/ 2 at one side and other side will be 1, then further.
6 (Refer Slide Time: 01:54) It has been rotated at an angle of minute about the profile axis, about the profile axis. Now in step 3 the view comes out to be all around length, height, and depth, all will be foreshortened by means of 0.82 times, it will be shorten by means of 0.82 times that means equal shortened.
7 (Refer Slide Time: 02:22) So this is step 1, all the sides having unit dimension 111, then it has been rotated by 45 then it become 1 and here 1/ 2+1/ 2, then it has been rotated my in step 3 about the profile axis it has been rotated, so it will be 2/ 6 so all the sides now seems to be, all the sides has been reduced to 0.82 times.
8 (Refer Slide Time: 02:54) Axonometric views, isometric views lengths are foreshortened equally in the direction of the three principal axes, this please remember and dimetric views, lengths are foreshortened equally in direction of any two principal axes, difference between isometric and dimetric views in isometric views lengths has been foreshortened equally in the direction of three principal axes, and dimetric views lengths are foreshortened equally in the direction of any two principal axes, but not in the direction of third principal axis. Dimetric views lengths are foreshortened unequally, remember this lengths are foreshortened unequally in the direction of the three principal axes, the difference between isometric and dimetric views, isometric views lengths has been equally foreshortened in the three principal axes that means X, Y and Z, in dimetric views lengths are foreshortened unequally in X, Y and Z direction. In dimetric views lengths are foreshortened equally in the direction of any two principal axes, for example X and Y equally it will be foreshortened, however in the third axis it is not going to be foreshortened.
9 (Refer Slide Time: 04:23) Procedure for the isometric projection, axis, views and dimensions, look at here this is your horizontal plane, this is the case of third angle projections and this is your frontal plane, so this is your top view and this is your front view, this is your profile view and I have marked this points here, then this points has been marked and the axes, principal axes, isometric axes has been marked, it has to be 120 angle it will make 120 angle with each other, so you mark it X, Y and Z look at here. If I mark it here, this and this it is in the front view, then this and this, this is in the profile view and this and this, this is in the top view. Now in the top view it is your depth and width, in the front view generally height and width and this is the case, depth and width, look at here depth and width, this is your depth and width, then height and width, sorry in the front view it is height and width, in the top view it is the depth and width. So isometric width, isometric depth, isometric height, this is your front, this is your right side view, this is your top view. So this is your case of your 3D isometric view.
10 (Refer Slide Time: 06:00) Now how do you start it isometric projections, now prepare isometric box, one can draw isometric figure with the help of isometric box, this is your isometric box then these are all your isometric axes X, Y and Z direction, then isometric projections this is foreshortened by means of equally foreshortened 0.81 times. Isometric drawing no foreshortening, remember this is the difference if sometimes some questions it has been asked go for isometric drawing, in that case it has not been foreshortened, that means all lengths will be equal lengths or whatever in the view this will be equal lengths, that view will be projected as equal lengths.
11 (Refer Slide Time: 06:54) But isometric projections the length will be foreshortened by means of 0.81 times.
12 (Refer Slide Time: 07:00) All lines parallel to isometric axes called isometric lines. All isometric lines are foreshortened equally in terms of isometric projections, this is your 0.81 or 81/100. All non-isometric lines may or may not foreshortened and foreshortening ratio of such lines may vary disproportionately. Projections of parallel lines will be parallel in isometric views. All measurement can only be marked on isometric lines. All measurements while doing the dimensioning, all measurements can only be marked on isometric lines.
13 (Refer Slide Time: 07:48) Isometric projections versus drawing or views, look at here this is isomeric projections, this is your isometric drawing or isometric view. Isometric projections are foreshortened because the object is tipped with respect to the viewing plane. How you are viewing, in isometric projections how you are behaving depending upon that it has been foreshortened, so isometric sketches or drawings are usually not foreshortened because they will appear proportionate when showing the dimensions full size along isometric axis or lines. It is easier just to sketch the full dimensions.
14 (Refer Slide Time: 08:32) So A is your isometric projections or isometric projection of a cube, that means equally length width and height equally it has been foreshortened, but B is your isometric view not foreshortened, it is 100/100 what is the exact length it is there that length.
15 (Refer Slide Time: 08:57) Now to do this you have to prepare a isometric scale, for preparing this isometric scale in the drawing you cannot use the calculators for foreshortening the lengths, all lengths in three directions by 0.81 times you cannot do it by means of calculator, rather you have to do prepare by means of drawings.
16 (Refer Slide Time: 09:22) So prepare your isometric scale before going for isometric projections, so at 45 this is your normal scale you mark it with your scale, one centimeter you can mark it, one centimeter is equal to one meter length, this is one is to one scale you can plot it or one is to ten depending on that Then this is your regular scale, then go to isometric scale prepare it at an angle 30, then from there from the regular scale you project it back, project it back and this will be giving suppose you are giving you, your regular scale is one centimeter that means you mark it one centimeter. Then our this point has been projected back to this point, so if you take it 0 to 1 in your isometric scale here this is your regular scale, and this is your isometric scale automatically it has been reduced to 0.81 times. So for example means this isometric scale how you are going to prepare, suppose there is a cube, for example if it is not a cube it is any shape maybe in the depth directions, in the depth directions. Suppose this is your, this is your, you can say that this is your two centimeter, this is your two centimeter then this is your ten centimeter in the depth directions, so this ten centimeter, this is your largest dimensions in depth directions, that dimensions you have to take in the regular scale.
17 Then with the regular scale you convert it into isometric scale that means once you have taken the largest dimensions ten centimeter in the regular scale, it is obvious that two centimeter and two centimeter will come into in the regular scale. If you take two centimeter in the regular scale then latter part it will be very difficult to foreshorten your ten centimeter. So first you prepare isometric scale depending upon the dimensions, then from the isometric scale while doing the isometric projections you take the dimensions, suppose in isometric scale it is two centimeter that means in regular scale where is your two centimeter, this is my two centimeter. So this has been projected back, so this to this dimension is your isometric projection scale, it is reduced by 0.81 times. So prepare your isometric scale first starting your isometric projections, so it has been foreshortened by 81/100 or 0.81 times used in isometric projections only. (Refer Slide Time: 12:20) Isometric drawing, how you are going to start it by means of boxing method, object is enclosed in a regular box which is drawn around orthographic projections, by means of boxing method it has to be enclosed, that means object has to be enclosed in a regular rectangular box which is
18 drawn around orthographic projection. Then box is then drawn in isometric and object is located by its points of contact, we will explain. Offset method, in offset method when object is made up of planes at different angles locate the points on the base plane that means isometric plane passed, then vertical isometric lines are drawn from these points for given height dimensions. These are the two methods, one is your boxing method, other is your offset method to draw your isometric projections. (Refer Slide Time: 13:23)
19 (Refer Slide Time: 13:24) So next we will start it this is all about basics of isometric projections, next we will solve few examples by means of isometric scale, as well as by means of boxing or offset methods.
20 (Refer Slide Time: 13:41) So isometric views what I have covered till now, all lines parallel to isometric axis is called isometric lines. All isometric lines are foreshortened equally, remember this for isometric projections. All non-isometric lines may or may not foreshortened and foreshortening ratio of such lines may vary disproportionately. Then projections of parallel lines will be parallel in isometric view. All measurement can only be marked along isometric lines, for dimensioning all measurements can only be marked along isometric lines, while doing the dimensioning or dimensions can be marked along the isometric lines, this is your important points you keep it in your mind.
21 (Refer Slide Time: 14:37) Then you start with your procedure for isometric projections, choose the origin as the starting point, does not have to be the point on the object, remember if there is a object not necessarily any point in the object it can take as origin not necessarily, you choose the origin as the starting point.
22 (Refer Slide Time: 15:00) Draw the isometric axis from the origin at an angle of 120 X, Y and Z. Then draw an isometric box corresponding to the maximum object dimensions, as I said what is your maximum object dimensions, in X-direction in Y direction as well as in Z directions, then draw an isometric box corresponding to the maximum.
23 (Refer Slide Time: 15:30) Object dimensions. All object edges parallel to the three principal axis are also parallel to the corresponding isometric axis, these object edges are called isometric lines. All the object planes parallel to the three principal planes are called isometric planes. Draw the isometric edges planes first remember, draw the isometric edge and planes first, locate key points, locate key points in isometric drawing then draw non isometric object lines, planes using the key points. So hidden lines are generally not drawn, hidden lines as far as possible in case of isometric projections are not drawn.
24 (Refer Slide Time: 16:21) Let us start isometric drawing procedure, this is your views top, front, as well as side views, then take the grid lines, draw first, first principal is draw isometric box of overall dimensions, that means overall dimensions means these dimensions you measure, these dimensions you measure, then these dimensions you measure, start with this, see the dimension I have marked, then again bottom part it has been marked, choose your, choose your origin, the origin has been, it has been chosen then, this is what, width directions, this is your width directions. So in the top view this is your width, so choose it and you take it this is your width direction, draw it and take it what is your largest dimensions, in the width direction this is your largest dimension, you take it. Then height directions, height is your vertical here, you can take it this is your height and take your largest dimension here, draw it, then finish it width and height, then depth directions. Obviously this is your depth directions, you take the largest dimension then finish your cube, this is your isometric box, this is your isometric box, first what I have
25 (Refer Slide Time: 18:23) Done it generally you mark your top view, front view, and side view and measure your dimensions largest dimensions in depth, width and height directions and choose your origin any point draw the grid lines to the origin, from with respect to origin draw the three principal axis, isometric axes, this angle has to be prepared with your 120 or you can do it, you can take it here then you can prepare your 30, 30 or you can take it this directions you can prepare it then once choose your origin and draw the width directions, then depth directions, then height directions, complete your isometric box first. So isometric box has been completed, then draw isometric lines first, isometric lines first then we will go, in width directions, in width directions these dimensions you draw it. Similarly in height directions you take the dimension, then what happen, in again width direction these are all your called isometric lines, this is your width directions, this is your height directions, these are all your isometric lines, then this is called your isometric plane, then draw non isometric lines, what are your non isometric lines, if I take it from here to here in height directions. I will find it out this point, I cannot draw the non isometric lines rather I marked the points along the isometric lines. What are the points are there? From here to here in height direction in front
26 view this point has been located, from here to here in width directions at the top view this point has been located. So this point has been located and this to this line if I draw this is your non isometric lines. So locate the points then draw your non isometric lines, this is your non isometric lines, then similarly take other part, one by one you take other part and finish this box, mark the points first then do it, do it, finish it up by means of your SV pencils because this is your, this is your object line drawn, this is your particularly your construction lines, means object lines. So this is your construction lines, this is your object lines, it has to be marked by means of HB pencils, then this plane, this plane is called your non isometric plane. Then once you draw your object lines, then construction lines slowly, slowly raise it or you can put it with a lighter mark if this is your construction lines. If I take it out how it looks, this is my object, this is your isometric drawing. Now there are two difference, one is your isometric projection other is your isometric drawing or isometric view. If it is your isometric drawing or isometric view, first of all for both the cases forget about isometric drawing or isometric projections for both these cases this is your procedure you have to draw, draw the isometric box first to clear your overall dimensions, that means largest dimensions.
27 (Refer Slide Time: 22:26) In width, in height direction, as well as in depth direction finish your isometric box first, then draw your isometric lines, then draw non isometric lines by marking points along the isometric lines.
28 (Refer Slide Time: 22:44) Marking the points, then draw your non isometric line as well as non isometric plane. Then, then there are isometric view, then there are isometric projections. In case of isometric projections this length particularly width, height, and depth it will be foreshortened equally by means of 0.81 times. So then you have to draw your isometric scale, with respect to isometric scale suppose this is your two centimeter from there, from there this is your regular scale 45 then this is your 30 with this is your 30 then you draw this scale, suppose these to this is your two centimeter from there you project it back, this is your reduced scale of your two centimeter. So width with directions then you mark your two centimeter. Similarly height direction you mark because it has to be equally foreshortened, then this view will become a isometric projections. So isometric view there is no foreshortened, isometric projections there is a foreshortened of all along three axis, X, Y and Z directions. This is all about how to start isometric drawing the procedure.
29 (Refer Slide Time: 24:09) Measurements, linear measurements can be made on isometric lines, then lines which are not parallel to the isometric axis are called non isometric lines. Lines which are not parallel to the isometric axis are called non isometric lines.
30 (Refer Slide Time: 24:31) Here lines which are not parallel to your isometric lines these are a non isometric lines.
31 (Refer Slide Time: 24:37) Measurement cannot be made on non isometric lines, remember you cannot measure along your non isometric lines. Angles specified in degrees do not appear in their true size on isometric drawings. Angles must be laid off with coordinates which are parallel to isometric axes. This is all about your measurement, so measurement cannot be made on non isometric lines. So in summary measurements, isometric measurement can be made on isometric lines, remember measurements cannot be made on non isometric lines. So this is all about isometric how do you start it, so next class I will start by means of boxing method where origin is not an object, few examples we are going to solve it, and step-by-step boxing method as well as offset method will complete your isometric view as well as isometric projections. Thank you.
32 Acknowledgement Ministry of Human Resource & Development Prof. Satyaki Roy Co-ordinator, NPTEL IIT Kanpur NPTEL Team Sanjay Pal Ashish Singh Badal Pradhan Tapobrata Das Ram Chandra Dilip Tripathi Manoj Shrivastava Padam Shukla Sanjay Mishra Shubham Rawat Shikha Gupta K. K. Mishra Aradhana Singh Sweta Ashutosh Gairola Dilip Katiyar Sharwan Hari Ram Bhadra Rao Puneet Kumar Bajpai Lalty Dutta Ajay Kanaujia Shivendra Kumar Tiwari an IIT Kanpur Production copyright reserved
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Engineering Graphics
 Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Engineering Graphics Lecture 18 Missing Lines & Missing Views by Prof. Nihar Ranjan Patra Department
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Engineering Graphics Lecture 18 Missing Lines & Missing Views by Prof. Nihar Ranjan Patra Department
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Engineering Graphics
 Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Engineering Graphics Lecture 15 Oblique Projections-Part-III by Prof. Nihar Ranjan Patre Department
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Engineering Graphics Lecture 15 Oblique Projections-Part-III by Prof. Nihar Ranjan Patre Department
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur. National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Manufacturing Process Technology-Part-2
 Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Manufacturing Process Technology-Part-2 Module 01 Introduction to Advanced Machining Processes
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Manufacturing Process Technology-Part-2 Module 01 Introduction to Advanced Machining Processes
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS 1E9
 Lecture 3 Monday, 15 December 2014 1 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS 1E9 Lecture 3: Isometric Projections Lecture 3 Monday, 15 December 2014 2 What is ISOMETRIC? It is a method of producing pictorial view of an object
Lecture 3 Monday, 15 December 2014 1 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS 1E9 Lecture 3: Isometric Projections Lecture 3 Monday, 15 December 2014 2 What is ISOMETRIC? It is a method of producing pictorial view of an object
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur. National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Enhancing Soft Skills And Personality
 Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Enhancing Soft Skills And Personality Lecture - 06 Managing Time-1: Importance of Time & Understanding
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Enhancing Soft Skills And Personality Lecture - 06 Managing Time-1: Importance of Time & Understanding
I B.TECH- I SEMESTER DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGINEERING DRAWING
 I B.TECH- I SEMESTER DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGINEERING DRAWING ENGINEERING DRAWING UNIT-V DEFINITIONS: Axonometric Trimetric Dimetric Isometric It is a parallel technique used to create
I B.TECH- I SEMESTER DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGINEERING DRAWING ENGINEERING DRAWING UNIT-V DEFINITIONS: Axonometric Trimetric Dimetric Isometric It is a parallel technique used to create
Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching
 Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching Contents Freehand sketching techniques Pictorial projections - Axonometric - Oblique Isometric projection vs isometric sketch Isometric sketch from an orthographic views Isometric
Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching Contents Freehand sketching techniques Pictorial projections - Axonometric - Oblique Isometric projection vs isometric sketch Isometric sketch from an orthographic views Isometric
Describing an Angle Bracket
 Basics of Drafting Describing an Angle Bracket Orthographic Projection Orthographic drawings represent three dimensional objects in three separate views arranged in a standard manner. Orthographic Views
Basics of Drafting Describing an Angle Bracket Orthographic Projection Orthographic drawings represent three dimensional objects in three separate views arranged in a standard manner. Orthographic Views
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur. National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Enhancing Soft Skills And Personality
 Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Enhancing Soft Skills And Personality Lecture - 07 Managing Time-2: Using Time Efficiently
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning (NPTEL) Course Title Enhancing Soft Skills And Personality Lecture - 07 Managing Time-2: Using Time Efficiently
ME1105 Engineering Drawing & Design
 City University London Term 1 Assessment 2008/2009 School of Engineering and Mathematical Sciences ME1105 Engineering Drawing & Design Student Name:.., Group: Examination duration: Reading time: This paper
City University London Term 1 Assessment 2008/2009 School of Engineering and Mathematical Sciences ME1105 Engineering Drawing & Design Student Name:.., Group: Examination duration: Reading time: This paper
Chapter 5 Pictorial Projection
 Chapter 5 Pictorial Projection Objectives After completing this chapter, the students will be able to Create freehand sketches using the correct sketching techniques. Explainthe difference between axonometric
Chapter 5 Pictorial Projection Objectives After completing this chapter, the students will be able to Create freehand sketches using the correct sketching techniques. Explainthe difference between axonometric
Beginning Engineering Graphics 3 rd Week Lecture Notes Instructor: Edward N. Locke Topic: The Coordinate System, Types of Drawings and Orthographic
 Beginning Engineering Graphics 3 rd Week Lecture Notes Instructor: Edward N. Locke Topic: The Coordinate System, Types of Drawings and Orthographic 1 st Subject: The Cartesian Coordinate System The Cartesian
Beginning Engineering Graphics 3 rd Week Lecture Notes Instructor: Edward N. Locke Topic: The Coordinate System, Types of Drawings and Orthographic 1 st Subject: The Cartesian Coordinate System The Cartesian
technical drawing
 technical drawing school of art, design and architecture nust spring 2011 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q6mk9hpxwvo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bnu2gb7w4qs Objective abstraction - axonometric view
technical drawing school of art, design and architecture nust spring 2011 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q6mk9hpxwvo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bnu2gb7w4qs Objective abstraction - axonometric view
11/12/2015 CHAPTER 7. Axonometric Drawings (cont.) Axonometric Drawings (cont.) Isometric Projections (cont.) 1) Axonometric Drawings
 CHAPTER 7 1) Axonometric Drawings 1) Introduction Isometric & Oblique Projection Axonometric projection is a parallel projection technique used to create a pictorial drawing of an object by rotating the
CHAPTER 7 1) Axonometric Drawings 1) Introduction Isometric & Oblique Projection Axonometric projection is a parallel projection technique used to create a pictorial drawing of an object by rotating the
Bridge Course On Engineering Drawing for Mechanical Engineers
 G. PULLAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY Accredited by NAAC with A Grade of UGC, Approved by AICTE, New Delhi Permanently Affiliated to JNTUA, Ananthapuramu (Recognized by UGC under 2(f) and 12(B)
G. PULLAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY Accredited by NAAC with A Grade of UGC, Approved by AICTE, New Delhi Permanently Affiliated to JNTUA, Ananthapuramu (Recognized by UGC under 2(f) and 12(B)
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan. Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1. Description: Unit C - Sketching - Test 2.
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1 Description: Unit C - Sketching - Test 2 Form: 501 1. The most often used combination of views includes the:
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1 Description: Unit C - Sketching - Test 2 Form: 501 1. The most often used combination of views includes the:
UNIT 5a STANDARD ORTHOGRAPHIC VIEW DRAWINGS
 UNIT 5a STANDARD ORTHOGRAPHIC VIEW DRAWINGS 5.1 Introduction Orthographic views are 2D images of a 3D object obtained by viewing it from different orthogonal directions. Six principal views are possible
UNIT 5a STANDARD ORTHOGRAPHIC VIEW DRAWINGS 5.1 Introduction Orthographic views are 2D images of a 3D object obtained by viewing it from different orthogonal directions. Six principal views are possible
Isometric Projection Drawing CHAPTER 6
 Isometric Projection Drawing CHAPTER 6 Content Overview Pictorial projection Parallel projection Axonometric projection Isometric projection Axes and selection Isometric lines and planes Isometric scale
Isometric Projection Drawing CHAPTER 6 Content Overview Pictorial projection Parallel projection Axonometric projection Isometric projection Axes and selection Isometric lines and planes Isometric scale
ENGR 1182 Exam 1 First Mid Term Exam Study Guide and Practice Problems
 Spring Semester 2016 ENGR 1182 Exam 1 First Mid Term Exam Study Guide and Practice Problems Disclaimer Problems in this study guide resemble problems relating mainly to the pertinent homework assignments.
Spring Semester 2016 ENGR 1182 Exam 1 First Mid Term Exam Study Guide and Practice Problems Disclaimer Problems in this study guide resemble problems relating mainly to the pertinent homework assignments.
3D Viewing I. Acknowledgement: Some slides are from the Dr. Andries van Dam lecture. CMSC 435/634 August D Viewing I # /27
 3D Viewing I Acknowledgement: Some slides are from the Dr. Andries van Dam lecture. From 3D to 2D: Orthographic and Perspective Projection Part 1 Geometrical Constructions Types of Projection Projection
3D Viewing I Acknowledgement: Some slides are from the Dr. Andries van Dam lecture. From 3D to 2D: Orthographic and Perspective Projection Part 1 Geometrical Constructions Types of Projection Projection
ISOMETRIC PROJECTION. Contents. Isometric Scale. Construction of Isometric Scale. Methods to draw isometric projections/isometric views
 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION Contents Introduction Principle of Isometric Projection Isometric Scale Construction of Isometric Scale Isometric View (Isometric Drawings) Methods to draw isometric projections/isometric
ISOMETRIC PROJECTION Contents Introduction Principle of Isometric Projection Isometric Scale Construction of Isometric Scale Isometric View (Isometric Drawings) Methods to draw isometric projections/isometric
(Ans:d) a. A0 b. A1 c. A2 d. A3. (Ans:b) (Ans:a) (Ans:d) (Ans:d)
 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) on Engineering Drawing (Instruments) The mini drafter serves the purpose of everything except a. Scales b. Set square c. Protractor d. Compass (Ans:d) During operation,
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) on Engineering Drawing (Instruments) The mini drafter serves the purpose of everything except a. Scales b. Set square c. Protractor d. Compass (Ans:d) During operation,
ENGINEERING DRAWING. 1. Set squares are used to draw different angles. What is the angel a formed by the 45⁰ set square? Give a brief answer.
 ENGINEERING DRAWING 1. Set squares are used to draw different angles. What is the angel a formed by the 45⁰ set square? Give a brief answer. 2. Which is the correct method of hatching a plane surface?
ENGINEERING DRAWING 1. Set squares are used to draw different angles. What is the angel a formed by the 45⁰ set square? Give a brief answer. 2. Which is the correct method of hatching a plane surface?
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 6
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 6 1. The selection of the front view in executing a multiview drawing of an object is dependent upon the following factors: a. size and shape of the object and their
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS - CHAPTER 6 1. The selection of the front view in executing a multiview drawing of an object is dependent upon the following factors: a. size and shape of the object and their
3D COMPUTER GRAPHICS
 3D COMPUTER GRAPHICS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_graphics/3d_computer_graphics.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com In the 2D system, we use only two coordinates X and Y but in 3D, an extra coordinate
3D COMPUTER GRAPHICS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/computer_graphics/3d_computer_graphics.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com In the 2D system, we use only two coordinates X and Y but in 3D, an extra coordinate
Isometric Drawing (Architectural Board drafting)
 Design and Drafting Description Isometric drawings use perspective to communicate a large amount of information in a single drawing. Isometric drawings show three sides of an object, making it easier to
Design and Drafting Description Isometric drawings use perspective to communicate a large amount of information in a single drawing. Isometric drawings show three sides of an object, making it easier to
Graphical Communication for Engineering ENSC 204 Final Exam
 Name: Student #: Graphical Communication for Engineering ENSC 204 Final Exam December 16, 2015 Time: 3 hours CLOSED BOOK EXAM Read all the instructions below. Do NOT start the exam until you are told to.
Name: Student #: Graphical Communication for Engineering ENSC 204 Final Exam December 16, 2015 Time: 3 hours CLOSED BOOK EXAM Read all the instructions below. Do NOT start the exam until you are told to.
ENGINEERING DRAWING SKKK 1021 ISOMETRIC DRAWING. Agus Arsad, Azizul Azri Bin Mustaffa 10/2/2012 1
 ENGINEERING DRAWING SKKK 1021 ISOMETRIC DRAWING Agus Arsad, Azizul Azri Bin Mustaffa 10/2/2012 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES ISOMETRIC DRAWING It is expected that students will be able to: Understand the significance
ENGINEERING DRAWING SKKK 1021 ISOMETRIC DRAWING Agus Arsad, Azizul Azri Bin Mustaffa 10/2/2012 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES ISOMETRIC DRAWING It is expected that students will be able to: Understand the significance
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION
 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION C H A P T E R S I X OBJECTIVES 1. Recognize and the symbol for third-angle projection. 2. List the six principal views of projection. 3. Understand which views show depth in a drawing
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION C H A P T E R S I X OBJECTIVES 1. Recognize and the symbol for third-angle projection. 2. List the six principal views of projection. 3. Understand which views show depth in a drawing
JUNIOR CERTIFICATE 2009 MARKING SCHEME TECHNICAL GRAPHICS HIGHER LEVEL
 . JUNIOR CERTIFICATE 2009 MARKING SCHEME TECHNICAL GRAPHICS HIGHER LEVEL Sections A and B Section A any ten questions from this section Q1 12 Four diagrams, 3 marks for each correct label. Q2 12 2 marks
. JUNIOR CERTIFICATE 2009 MARKING SCHEME TECHNICAL GRAPHICS HIGHER LEVEL Sections A and B Section A any ten questions from this section Q1 12 Four diagrams, 3 marks for each correct label. Q2 12 2 marks
ME 111: Engineering Drawing
 ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 5 12-08-2011 Orthographic projection and Projection of Points Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 1 Orthographic Projection A parallel projection
ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 5 12-08-2011 Orthographic projection and Projection of Points Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 1 Orthographic Projection A parallel projection
ENGR 1182 Midterm Exam 1: Study Guide and Practice Problems
 ENGR 1182 Midterm Exam 1: Study Guide and Practice Problems Disclaimer Problems seen in this study guide may resemble problems relating mainly to the pertinent homework assignments. Reading this study
ENGR 1182 Midterm Exam 1: Study Guide and Practice Problems Disclaimer Problems seen in this study guide may resemble problems relating mainly to the pertinent homework assignments. Reading this study
Peter Clements Art Studios
 Peter Clements Art Studios How to Erase Pencil Axonometric Projection or drawing is referred to as a projection as they do not have vanishing points as the conventional perspective drawing. Consequently,
Peter Clements Art Studios How to Erase Pencil Axonometric Projection or drawing is referred to as a projection as they do not have vanishing points as the conventional perspective drawing. Consequently,
1. When sketching long, narrow objects in OBLIQUE, distortion can be lessened by placing the long dimension along:
 Draft Student Name: Teacher: District: Date: Wake County Test: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 2 Description: 3.03 Apply 3D sketching Form: 501 1. When sketching long, narrow objects in OBLIQUE, distortion
Draft Student Name: Teacher: District: Date: Wake County Test: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 2 Description: 3.03 Apply 3D sketching Form: 501 1. When sketching long, narrow objects in OBLIQUE, distortion
Extension material for Level 2 Design and Visual Communication Study Guide
 3-D formal drawing Extension material for Level 2 Design and Visual Communication Study Guide ISBN 978-1-927194-15-7 For individual student use only. No other use permitted. ESA Publications (NZ) Ltd,
3-D formal drawing Extension material for Level 2 Design and Visual Communication Study Guide ISBN 978-1-927194-15-7 For individual student use only. No other use permitted. ESA Publications (NZ) Ltd,
Copyrighted Material. Copyrighted Material. Copyrighted. Copyrighted. Material
 Engineering Graphics ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION People who work with drawings develop the ability to look at lines on paper or on a computer screen and "see" the shapes of the objects the lines represent.
Engineering Graphics ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION People who work with drawings develop the ability to look at lines on paper or on a computer screen and "see" the shapes of the objects the lines represent.
Exploring 3D in Flash
 1 Exploring 3D in Flash We live in a three-dimensional world. Objects and spaces have width, height, and depth. Various specialized immersive technologies such as special helmets, gloves, and 3D monitors
1 Exploring 3D in Flash We live in a three-dimensional world. Objects and spaces have width, height, and depth. Various specialized immersive technologies such as special helmets, gloves, and 3D monitors
 6.1 INTRODUCTION Chapter 6 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS OF SIMPLE MACHINE BLOCKS We have already made you aware of many simple geometrical shapes (laminae), projected on such planes (vertical plane, horizontal
6.1 INTRODUCTION Chapter 6 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS OF SIMPLE MACHINE BLOCKS We have already made you aware of many simple geometrical shapes (laminae), projected on such planes (vertical plane, horizontal
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS. Ms. Sicola
 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS Ms. Sicola Objectives List the six principal views of projection Sketch the top, front and right-side views of an object with normal, inclined, and oblique surfaces Objectives
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS Ms. Sicola Objectives List the six principal views of projection Sketch the top, front and right-side views of an object with normal, inclined, and oblique surfaces Objectives
Engineering Drawing Lecture 5 PROJECTION THEORY
 University of Palestine College of Engineering & Urban Planning First Level Engineering Drawing Lecture 5 PROJECTION THEORY Lecturer: Eng. Eman Al.Swaity Eng.Heba hamad PART 1 PROJECTION METHOD TOPICS
University of Palestine College of Engineering & Urban Planning First Level Engineering Drawing Lecture 5 PROJECTION THEORY Lecturer: Eng. Eman Al.Swaity Eng.Heba hamad PART 1 PROJECTION METHOD TOPICS
AUXILIARY VIEWS C H A P T E R N I N E
 AUXILIARY VIEWS C H A P T E R N I N E Giesecke, Hill, Spencer, Dygdon, Novak, Lockhart, Goodman 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Create an auxiliary view from orthographic views. 2. Draw folding lines or reference-plane
AUXILIARY VIEWS C H A P T E R N I N E Giesecke, Hill, Spencer, Dygdon, Novak, Lockhart, Goodman 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Create an auxiliary view from orthographic views. 2. Draw folding lines or reference-plane
60 Most Important Engineering Drawing Questions
 1. If a client of yours is having difficulty visualizing a design, what type of drawing would be the easiest to understand? A. axonometric B. three-view orthographic C. one-view orthographic D. bimetric
1. If a client of yours is having difficulty visualizing a design, what type of drawing would be the easiest to understand? A. axonometric B. three-view orthographic C. one-view orthographic D. bimetric
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
 Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Activity: TEKS: Treasure Hunting (5.8) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student models transformations. The student is expected to: (A) sketch the results of translations,
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Activity: TEKS: Treasure Hunting (5.8) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student models transformations. The student is expected to: (A) sketch the results of translations,
Perspective in 2D Games
 Lecture 16 in 2D Games Drawing Images Graphics Lectures SpriteBatch interface Coordinates and Transforms bare minimum to draw graphics Drawing Camera Projections side-scroller vs. top down Drawing Primitives
Lecture 16 in 2D Games Drawing Images Graphics Lectures SpriteBatch interface Coordinates and Transforms bare minimum to draw graphics Drawing Camera Projections side-scroller vs. top down Drawing Primitives
Transform 3D objects on to a 2D plane using projections
 PROJECTIONS 1 Transform 3D objects on to a 2D plane using projections 2 types of projections Perspective Parallel In parallel projection, coordinate positions are transformed to the view plane along parallel
PROJECTIONS 1 Transform 3D objects on to a 2D plane using projections 2 types of projections Perspective Parallel In parallel projection, coordinate positions are transformed to the view plane along parallel
EDUCATIONAL REND LAKE COLLEGE CAD INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER-AIDED DRAFTING ISOMETRIC DRAWING REVISED: FALL 2010 INSTRUCTOR: THOMAS ARPASI
 INSTRUCTOR: THOMAS ARPASI REND LAKE COLLEGE CAD 1201-51 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER-AIDED DRAFTING ISOMETRIC DRAWING 1 Pictoral Drawing Pictoral drawing have evolved from cave paintings to photorealistic
INSTRUCTOR: THOMAS ARPASI REND LAKE COLLEGE CAD 1201-51 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER-AIDED DRAFTING ISOMETRIC DRAWING 1 Pictoral Drawing Pictoral drawing have evolved from cave paintings to photorealistic
Isometric Drawing Chapter 26
 Isometric Drawing Chapter 26 Sacramento City College EDT 310 EDT 310 - Chapter 26 - Isometric Drawing 1 Drawing Types Pictorial Drawing types: Perspective Orthographic Isometric Oblique Pictorial - like
Isometric Drawing Chapter 26 Sacramento City College EDT 310 EDT 310 - Chapter 26 - Isometric Drawing 1 Drawing Types Pictorial Drawing types: Perspective Orthographic Isometric Oblique Pictorial - like
Pull Down Menu View Toolbar Design Toolbar
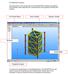 Pro/DESKTOP Interface The instructions in this tutorial refer to the Pro/DESKTOP interface and toolbars. The illustration below describes the main elements of the graphical interface and toolbars. Pull
Pro/DESKTOP Interface The instructions in this tutorial refer to the Pro/DESKTOP interface and toolbars. The illustration below describes the main elements of the graphical interface and toolbars. Pull
Classical Viewing. Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico
 Classical Viewing Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Introduce the classical views Compare and contrast image
Classical Viewing Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Introduce the classical views Compare and contrast image
Perspective in 2D Games
 Lecture 16 in 2D Games Take Away for Today What is game camera? How does it relate to screen space? Object space? How does camera work in a 2D game? 3D? How do we give 2D games depth? Advantages, disadvantages
Lecture 16 in 2D Games Take Away for Today What is game camera? How does it relate to screen space? Object space? How does camera work in a 2D game? 3D? How do we give 2D games depth? Advantages, disadvantages
At the conclusion of this unit you should be able to accomplish the following with a 70% accuracy
 7 Multiview Drawing OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this unit you should be able to accomplish the following with a 70% accuracy 1. explain the importance of mulitview drawing as a communication tool far
7 Multiview Drawing OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this unit you should be able to accomplish the following with a 70% accuracy 1. explain the importance of mulitview drawing as a communication tool far
CLASS views from detail on a grid paper. (use appropriate line types to show features) - Optional views. Turn in for grading on class 6 (06/04)
 CLASS 4 Review: - Projections - Orthographic projections Lab: - 3 views from detail on a grid paper. (use appropriate line types to show features) - Optional views. Turn in for grading on class 6 (06/04)
CLASS 4 Review: - Projections - Orthographic projections Lab: - 3 views from detail on a grid paper. (use appropriate line types to show features) - Optional views. Turn in for grading on class 6 (06/04)
Introduction to Computer Graphics (CS602) Lecture 19 Projections
 Introduction to Computer Graphics (CS602) Lecture 19 Projections For centuries, artists, engineers, designers, drafters, and architects have been facing difficulties and constraints imposed by the problem
Introduction to Computer Graphics (CS602) Lecture 19 Projections For centuries, artists, engineers, designers, drafters, and architects have been facing difficulties and constraints imposed by the problem
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS UNIT V ISOMETRIC PROJECTION PERSPECTIVE PROJECTION
 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS UNIT V ISOMETRIC PROJECTION PERSPECTIVE PROJECTION 1.PICTORIAL PROJECTIONS To visualize the shape of the whole object in its 3- D form, all the two or three orthographic views of the
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS UNIT V ISOMETRIC PROJECTION PERSPECTIVE PROJECTION 1.PICTORIAL PROJECTIONS To visualize the shape of the whole object in its 3- D form, all the two or three orthographic views of the
Unit-5 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION
 Unit-5 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION Importance Points in Isometric: 1. For drawing the isometric, the object must be viewed such that either the front -right or the left edges becomes nearest. 2. All vertical
Unit-5 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION Importance Points in Isometric: 1. For drawing the isometric, the object must be viewed such that either the front -right or the left edges becomes nearest. 2. All vertical
Auxiliary view KCEC1101
 Auxiliary view KCEC1101 Introduction There are times when one of the six principal views will not completely describe an object. This is especially true when there are inclined or oblique planes or features
Auxiliary view KCEC1101 Introduction There are times when one of the six principal views will not completely describe an object. This is especially true when there are inclined or oblique planes or features
Lecture 6 ( ): Theory of Multi-view Orthographic Projections
 Lecture 6 (06.08.12): Theory of Multi-view Orthographic Projections Dr. Sharad Gokhale Civil Engineering Department, IIT Guwahati 208, M-Block, Academic Complex Email: sharadbg@iitg.ernet.in Telephone
Lecture 6 (06.08.12): Theory of Multi-view Orthographic Projections Dr. Sharad Gokhale Civil Engineering Department, IIT Guwahati 208, M-Block, Academic Complex Email: sharadbg@iitg.ernet.in Telephone
Chapter 1 Overview of an Engineering Drawing
 Chapter 1 Overview of an Engineering Drawing TOPICS Graphics language Engineering drawing Projection methods Orthographic projection Drawing standards TOPICS Traditional Drawing Tools Lettering Freehand
Chapter 1 Overview of an Engineering Drawing TOPICS Graphics language Engineering drawing Projection methods Orthographic projection Drawing standards TOPICS Traditional Drawing Tools Lettering Freehand
Civil Engineering Drawing
 Civil Engineering Drawing Third Angle Projection In third angle projection, front view is always drawn at the bottom, top view just above the front view, and end view, is drawn on that side of the front
Civil Engineering Drawing Third Angle Projection In third angle projection, front view is always drawn at the bottom, top view just above the front view, and end view, is drawn on that side of the front
DELHI TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING GRAPHICS LAB MANUAL
 DELHI TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING GRAPHICS LAB MANUAL NAME: - ROLL NO: - GROUP: - BRANCH: - GROUP TEACHER: Page 1 www.rooplalrana.com 1 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGG. GRAPHICS LAB 1) Students
DELHI TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING GRAPHICS LAB MANUAL NAME: - ROLL NO: - GROUP: - BRANCH: - GROUP TEACHER: Page 1 www.rooplalrana.com 1 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR ENGG. GRAPHICS LAB 1) Students
Engineering Graphics- Basics.
 Engineering Graphics- Basics DRAWINGS: ( A Graphical Representation) The Fact about: If compared with Verbal or Written Description, Drawings offer far better idea about the Shape, Size & Appearance of
Engineering Graphics- Basics DRAWINGS: ( A Graphical Representation) The Fact about: If compared with Verbal or Written Description, Drawings offer far better idea about the Shape, Size & Appearance of
2. Line composed of closely and evenly spaced short dashes in a drawing represents
 1. Hidden lines are drawn as (a) dashed narrow lines (b) dashed wide lines (c) long-dashed dotted wide line (d) long-dashed double dotted wide line Ans: (a) 2. Line composed of closely and evenly spaced
1. Hidden lines are drawn as (a) dashed narrow lines (b) dashed wide lines (c) long-dashed dotted wide line (d) long-dashed double dotted wide line Ans: (a) 2. Line composed of closely and evenly spaced
Multiview Drawing. Definition: Graphical representation of a 3- dimensional object on one plane (sheet of paper) using two or more views.
 Multiview Drawing Definition: Graphical representation of a 3- dimensional object on one plane (sheet of paper) using two or more views. Multiview Drawing Another name for multiview drawing is orthographic
Multiview Drawing Definition: Graphical representation of a 3- dimensional object on one plane (sheet of paper) using two or more views. Multiview Drawing Another name for multiview drawing is orthographic
Hello, welcome to the video lecture series on Digital image processing. (Refer Slide Time: 00:30)
 Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module 11 Lecture Number 52 Conversion of one Color
Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module 11 Lecture Number 52 Conversion of one Color
Horizon - The horizontal line that contains the vanishing point(s) in a perspective drawing.
 Representing Solids Perspective Drawing A drawing where non-vertical parallel lines appear to meet at a point called a vanishing point. Example: If you look straight down a highway, it appears that the
Representing Solids Perspective Drawing A drawing where non-vertical parallel lines appear to meet at a point called a vanishing point. Example: If you look straight down a highway, it appears that the
Tile based games. Piotr Fulma«ski. 8 pa¹dziernika Wydziaª Matematyki i Informatyki, Uniwersytet Šódzki, Polska
 Tile based games Piotr Fulma«ski Wydziaª Matematyki i Informatyki, Uniwersytet Šódzki, Polska 8 pa¹dziernika 2015 Table of contents Aim of this lecture In this lecture we discusse how axonometric projections
Tile based games Piotr Fulma«ski Wydziaª Matematyki i Informatyki, Uniwersytet Šódzki, Polska 8 pa¹dziernika 2015 Table of contents Aim of this lecture In this lecture we discusse how axonometric projections
Reading. Angel. Chapter 5. Optional
 Projections Reading Angel. Chapter 5 Optional David F. Rogers and J. Alan Adams, Mathematical Elements for Computer Graphics, Second edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1990, Chapter 3. The 3D synthetic camera
Projections Reading Angel. Chapter 5 Optional David F. Rogers and J. Alan Adams, Mathematical Elements for Computer Graphics, Second edition, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1990, Chapter 3. The 3D synthetic camera
Drawing: technical drawing TECHNOLOGY
 Drawing: technical drawing Introduction Humans have always used images to communicate. Cave paintings, some of which are over 40,000 years old, are the earliest example of this artistic form of communication.
Drawing: technical drawing Introduction Humans have always used images to communicate. Cave paintings, some of which are over 40,000 years old, are the earliest example of this artistic form of communication.
Chapter 8. Technical Drawings
 Chapter 8 Technical Drawing Technical Drawings Multiview drawings Also called three-view drawings Simple objects take three views Front, top, one side Title block Identifies who did the design Gives date,
Chapter 8 Technical Drawing Technical Drawings Multiview drawings Also called three-view drawings Simple objects take three views Front, top, one side Title block Identifies who did the design Gives date,
3D Viewing I. From 3D to 2D: Orthographic and Perspective Projection Part 1
 From 3D to 2D: Orthographic and Perspective Projection Part 1 3D Viewing I By Andries van Dam Geometrical Constructions Types of Projection Projection in Computer Graphics Jian Chen January 15, 2010 3D
From 3D to 2D: Orthographic and Perspective Projection Part 1 3D Viewing I By Andries van Dam Geometrical Constructions Types of Projection Projection in Computer Graphics Jian Chen January 15, 2010 3D
Introduction to Projection The art of representing a three-dimensional object or scene in a 2D space is called projection.
 Introduction to Projection The art of representing a three-dimensional object or scene in a 2D space is called projection. Projection is carried out by passing projectors through each vertex and intersecting
Introduction to Projection The art of representing a three-dimensional object or scene in a 2D space is called projection. Projection is carried out by passing projectors through each vertex and intersecting
Interactive Computer Graphics A TOP-DOWN APPROACH WITH SHADER-BASED OPENGL
 International Edition Interactive Computer Graphics A TOP-DOWN APPROACH WITH SHADER-BASED OPENGL Sixth Edition Edward Angel Dave Shreiner 228 Chapter 4 Viewing Front elevation Elevation oblique Plan oblique
International Edition Interactive Computer Graphics A TOP-DOWN APPROACH WITH SHADER-BASED OPENGL Sixth Edition Edward Angel Dave Shreiner 228 Chapter 4 Viewing Front elevation Elevation oblique Plan oblique
Technological Design Mr. Wadowski. Orthographic & Isometric Drawing Lesson
 Technological Design Mr. Wadowski Orthographic & Isometric Drawing Lesson TOPICS Working Drawings, Isometric Drawings & Orthographic Drawings Glass box concept Multiview projection Orthographic projection
Technological Design Mr. Wadowski Orthographic & Isometric Drawing Lesson TOPICS Working Drawings, Isometric Drawings & Orthographic Drawings Glass box concept Multiview projection Orthographic projection
Pictorial Drawings. DFTG-1305 Technical Drafting Prepared by Francis Ha, Instructor
 DFTG-1305 Technical Drafting Prepared by Francis Ha, Instructor Pictorial Drawings Geisecke s textbook for reference: 14 th Ed. Ch. 15: p. 601 Ch. 16: p. 620 15 th Ed. Ch. 14: p. 518 Ch. 15: p. 552 Update:
DFTG-1305 Technical Drafting Prepared by Francis Ha, Instructor Pictorial Drawings Geisecke s textbook for reference: 14 th Ed. Ch. 15: p. 601 Ch. 16: p. 620 15 th Ed. Ch. 14: p. 518 Ch. 15: p. 552 Update:
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER III ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER III ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70 Note: (i) Attempt all the questions. (ii) Use both sides of the drawing sheet, if necessary. (iii) All dimensions
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER III ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70 Note: (i) Attempt all the questions. (ii) Use both sides of the drawing sheet, if necessary. (iii) All dimensions
4. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the part P of the cylinder whose front view is shown in figure 4. All dimensions are in cm.
 Code No: Z0122 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Bio-Medical Engineering, Mechatronics,
Code No: Z0122 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Bio-Medical Engineering, Mechatronics,
PROJECTIONS PARALLEL CONICAL PROJECTIONS PROJECTIONS OBLIQUE ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS PROJECTIONS
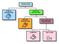 PROJECTIONS CONICAL PROJECTIONS PARALLEL PROJECTIONS OBLIQUE PROJECTIONS ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS ISOMETRIC MULTI-VIEW an object; The Description of Forms Behind every drawing of an object is space relationship
PROJECTIONS CONICAL PROJECTIONS PARALLEL PROJECTIONS OBLIQUE PROJECTIONS ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS ISOMETRIC MULTI-VIEW an object; The Description of Forms Behind every drawing of an object is space relationship
Lecture #4 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION RES 112E COMPUTER AIDED TECHNICAL DRAWING ITU
 Lecture #4 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION This week You will learn multi-view projection. The steps to follow are: Projections (ISO-E & ISO-A) Multi-view drawings Views (Basic,Auxiliary, Detailed etc.) Sketching
Lecture #4 MULTIVIEW PROJECTION This week You will learn multi-view projection. The steps to follow are: Projections (ISO-E & ISO-A) Multi-view drawings Views (Basic,Auxiliary, Detailed etc.) Sketching
Graphical Communication
 Chapter 9 Graphical Communication mmm Becoming a fully competent engineer is a long yet rewarding process that requires the acquisition of many diverse skills and a wide body of knowledge. Learning most
Chapter 9 Graphical Communication mmm Becoming a fully competent engineer is a long yet rewarding process that requires the acquisition of many diverse skills and a wide body of knowledge. Learning most
Multiviews and Auxiliary Views
 Multiviews and Auxiliary Views Multiviews and Auxiliary Views Objectives Explain orthographic and multiview projection. Identifying the six principal views. Apply standard line practices to multiviews
Multiviews and Auxiliary Views Multiviews and Auxiliary Views Objectives Explain orthographic and multiview projection. Identifying the six principal views. Apply standard line practices to multiviews
CS354 Computer Graphics Viewing and Projections
 Slide Credit: Donald S. Fussell CS354 Computer Graphics Viewing and Projections Qixing Huang February 19th 2018 Eye Coordinates (not NDC) Planar Geometric Projections Standard projections project onto
Slide Credit: Donald S. Fussell CS354 Computer Graphics Viewing and Projections Qixing Huang February 19th 2018 Eye Coordinates (not NDC) Planar Geometric Projections Standard projections project onto
DMT113 Engineering Drawing. Chapter 3 Stretch System
 DMT113 Engineering Drawing Chapter 3 Stretch System Contents Theory & Multiview Planes 6 Principle Views Multiview Sketching Technique & Perspective First & Third Angle Multiview Representations Theory
DMT113 Engineering Drawing Chapter 3 Stretch System Contents Theory & Multiview Planes 6 Principle Views Multiview Sketching Technique & Perspective First & Third Angle Multiview Representations Theory
Math Labs. Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates. Procedure
 Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Introduction to Engineering Design
 Introduction to Engineering Design Final Examination Parts A, B & C ANSWER KEY Spring 2008 For Teacher Use ONLY Part A Scoring Conversion Chart Raw Score Conversion Raw Score Conversion Raw Score Conversion
Introduction to Engineering Design Final Examination Parts A, B & C ANSWER KEY Spring 2008 For Teacher Use ONLY Part A Scoring Conversion Chart Raw Score Conversion Raw Score Conversion Raw Score Conversion
Perspective in 2D Games
 Lecture 15 in 2D Games Drawing Images Graphics Lectures SpriteBatch interface Coordinates and Transforms bare minimum to draw graphics Drawing Camera Projections side-scroller vs. top down Drawing Primitives
Lecture 15 in 2D Games Drawing Images Graphics Lectures SpriteBatch interface Coordinates and Transforms bare minimum to draw graphics Drawing Camera Projections side-scroller vs. top down Drawing Primitives
Chapter 2. Isometric Projection and Multi View Drawings. Below are the desired outcomes and usage competencies based on the completion of Chapter 2.
 Chapter 2 Below are the desired outcomes and usage competencies based on the completion of Chapter 2. Desired Outcomes: Understand Isometric Projection and 2D sketching. Knowledge of additional Projection
Chapter 2 Below are the desired outcomes and usage competencies based on the completion of Chapter 2. Desired Outcomes: Understand Isometric Projection and 2D sketching. Knowledge of additional Projection
CE 100 Civil Engineering Drawing Sessional (Lab Manual)
 CE 100 Civil Engineering Drawing Sessional (Lab Manual) Department of Civil Engineering Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology November, 2017 1 Preface This course is designed to provide civil
CE 100 Civil Engineering Drawing Sessional (Lab Manual) Department of Civil Engineering Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology November, 2017 1 Preface This course is designed to provide civil
NPTEL NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE. Course On Spur and Helical gear Cutting
 NPTEL NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE Course On Spur and Helical gear Cutting By Prof. Asimava Roy Choudhury Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kharagpur Lecture 04: Helical Gear Problems Welcome
NPTEL NPTEL ONLINE CERTIFICATION COURSE Course On Spur and Helical gear Cutting By Prof. Asimava Roy Choudhury Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kharagpur Lecture 04: Helical Gear Problems Welcome
Plane and Parallel Projections. Mies Van Der Rohe, Plan for a Brick Country House (1924)
 Plane and Parallel Projections Mies Van Der Rohe, Plan for a Brick Country House (1924) Plane projections in architecture include plans, sections, and elevations. Each of these drawings are constructed
Plane and Parallel Projections Mies Van Der Rohe, Plan for a Brick Country House (1924) Plane projections in architecture include plans, sections, and elevations. Each of these drawings are constructed
3D Viewing. Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller / Manfred Klaffenböck. Machiraju/Zhang/Möller
 3D Viewing Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller / Manfred Klaffenböck Machiraju/Zhang/Möller Reading Chapter 5 of Angel Chapter 13 of Hughes, van Dam, Chapter 7 of Shirley+Marschner Machiraju/Zhang/Möller
3D Viewing Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller / Manfred Klaffenböck Machiraju/Zhang/Möller Reading Chapter 5 of Angel Chapter 13 of Hughes, van Dam, Chapter 7 of Shirley+Marschner Machiraju/Zhang/Möller
Engineering Graphics with SolidWorks 2012
 INSIDE: Video Instruction DVD An audio/visual presentation of the tutorial projects Engineering Graphics with SolidWorks 2012 and Video Instruction DVD A Step-by-Step Project Based Approach Introductory
INSIDE: Video Instruction DVD An audio/visual presentation of the tutorial projects Engineering Graphics with SolidWorks 2012 and Video Instruction DVD A Step-by-Step Project Based Approach Introductory
1 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION SECTION I: INTRODUCTION TO ISOMETRIC PROJECTION
 1 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION SECTION I: INTRODUCTION TO ISOMETRIC PROJECTION Orthographic projection shows drawings of an object in a two-dimensional format, with views given in plan, elevation and end elevation
1 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION SECTION I: INTRODUCTION TO ISOMETRIC PROJECTION Orthographic projection shows drawings of an object in a two-dimensional format, with views given in plan, elevation and end elevation
CS475/CS675 Computer Graphics
 CS475/CS675 Computer Graphics Viewing Perspective Projection Projectors Centre of Projection Object Image Plane or Projection Plane 2 Parallel Projection Projectors Centre of Projection? Object Image Plane
CS475/CS675 Computer Graphics Viewing Perspective Projection Projectors Centre of Projection Object Image Plane or Projection Plane 2 Parallel Projection Projectors Centre of Projection? Object Image Plane
Engineering Graphics, Class 13 Descriptive Geometry. Mohammad I. Kilani. Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan
 Engineering Graphics, Class 13 Descriptive Geometry Mohammad I. Kilani Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan Projecting a line into other views Given the front and right side projections
Engineering Graphics, Class 13 Descriptive Geometry Mohammad I. Kilani Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan Projecting a line into other views Given the front and right side projections
Drawing sheet: - The various size of the drawing sheet used for engineering drawing as per IS Are listed in the table
 Dronacharya Group of Institutions, Greater Noida Computer Aided Engineering Graphics (CAEG) (NCE 151/251) List of Drawing Sheets: 1. Letter writing & Dimensioning. 2. Projection of Points & Lines. 3. Projection
Dronacharya Group of Institutions, Greater Noida Computer Aided Engineering Graphics (CAEG) (NCE 151/251) List of Drawing Sheets: 1. Letter writing & Dimensioning. 2. Projection of Points & Lines. 3. Projection
Introduction to sketching. Wooden Box. Set. Name. Madras College, St Andrews
 Introduction to sketching Wooden Box Name Set Madras College, St Andrews 16 1 This drawing unit aims to teach you the skills you need to make a range of sketches of craft models like the small wooden box
Introduction to sketching Wooden Box Name Set Madras College, St Andrews 16 1 This drawing unit aims to teach you the skills you need to make a range of sketches of craft models like the small wooden box
The Revolve Feature and Assembly Modeling
 The Revolve Feature and Assembly Modeling PTC Clock Page 52 PTC Contents Introduction... 54 The Revolve Feature... 55 Creating a revolved feature...57 Creating face details... 58 Using Text... 61 Assembling
The Revolve Feature and Assembly Modeling PTC Clock Page 52 PTC Contents Introduction... 54 The Revolve Feature... 55 Creating a revolved feature...57 Creating face details... 58 Using Text... 61 Assembling
Year 11 Graphing Notes
 Year 11 Graphing Notes Terminology It is very important that students understand, and always use, the correct terms. Indeed, not understanding or using the correct terms is one of the main reasons students
Year 11 Graphing Notes Terminology It is very important that students understand, and always use, the correct terms. Indeed, not understanding or using the correct terms is one of the main reasons students
Chapter 4 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION
 Chapter 4 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION 4.1 INTRODUCTION We, the human beings are gifted with power to think. The thoughts are to be shared. You will appreciate that different ways and means are available to
Chapter 4 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION 4.1 INTRODUCTION We, the human beings are gifted with power to think. The thoughts are to be shared. You will appreciate that different ways and means are available to
VIEWING 1. CLASSICAL AND COMPUTER VIEWING. Computer Graphics
 VIEWING We now investigate the multitude of ways in which we can describe our virtual camera. Along the way, we examine related topics, such as the relationship between classical viewing techniques and
VIEWING We now investigate the multitude of ways in which we can describe our virtual camera. Along the way, we examine related topics, such as the relationship between classical viewing techniques and
