MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) SUMMER 16 EXAMINATION
|
|
|
- Theresa Laura Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may vary but the examiner may try to assess the understanding level of the candidate. 3) The language errors such as grammatical, spelling errors should not be given more Importance (Not applicable for subject English and Communication Skills). 4) While assessing figures, examiner may give credit for principal components indicated in the figure. The figures drawn by candidate and model answer may vary. The examiner may give credit for any equivalent figure drawn. 5) Credits may be given step wise for numerical problems. In some cases, the assumed constant values may vary and there may be some difference in the candidate s answers and model answer. 6) In case of some questions credit may be given by judgement on part of examiner of relevant answer based on candidate s understanding. 7) For programming language papers, credit may be given to any other program based on equivalent concept. Q. NO. 1A ) i) ( 04 marks, one for each, any four ) Ideal characteristics of electrode materials used in EDM.: 1) It should be a good conductor of electricity 2) It should be a good conductor of heat 3) It should be easily machinable to any shape at economical cost 4) It should have efficient rate of material removal from the workpiece during machining 5) It should resist deformation during the machining by erosion process 6) It should have low or minimum wear rate 7) It should be available in variety of shape ii) ( 04 marks, one for each, any four ) Differences between subroutine and canned cycles : Canned cycles Canned cycle or fixed cycle may be defined as a set of instructions, inbuilt or stored in the system memory, to perform a fixed sequence of operations. Canned cycles are used for repetitive and commonly used machining operations. Subroutine programme Subroutines provide the capability of programming certain fixed sequence or frequently repeated patterns. Subroutine may be called any time or repeated any number of times. It consists of some very common moves of These are repeating some moves on a Page 1 of 23
2 different machines coded They don t allow optimization of program in their movements fixed for operation component for variable number of times They allow making their own cycles with different parametric dimensions at different locations. i.e. user defined canned cycles iii) (02 marks for explanation and 02 for sketch ) Down Milling: In this process milling cutter is rotated in the same direction in which the work piece travels.. The thickness of chip is maximum when the tooth begins its cut and it reaches to the minimum when the cut terminates. the cutter tooth starts removing metal immediately on reaching the work surface without sliding. The cutter force in this milling is variable throughout the cut. The chips are disposed off easily and do not interfere during cutting. It is not recommended on light or old machines but it is carried out on rigid machines provided with backlash eliminator. iv) ( 04 marks for explanation ) Down Milling Cutting process Grinding wheel dressing : Dressing is the operation of removal of the dull and workout grains, metal particles from the cutting surface of a grinding wheel to restore its cutting ability for grinding. The frequency of dressing will depends upon type of wheel, application, and material to be grounded. After use, the wheel becomes dull or glazed. Glazing of the wheel is a condition in which the face or cutting edge takes a glass like appearance. It indicates that the cutting points of the abrasives have become dull and worn down the bond. It decreases the cutting capacity. Wheel becomes smooth and it instead of cutting action provides a sort of rubbing action only. Dressing of grinding is done to improve the surface finish and accuracy of the work piece. It also increases the material removal rate. Single point and multipoint dressers are used for dressing of the grinding wheels. Q. NO. 1B ) i) (02 marks for principle, 02 for working and 02 for sketch ) Principle of Electro discharge machining: It works on the principle of metal removal by using combination of electrical and thermal energy. The energy is utilized to create electrical spark ;and heat is produced for erosion of metal. The principle of spark erosion is utilized in Electro discharge machining. Page 2 of 23
3 Working : The Figure shows the workpiece and the tool are electrically to DC electric power supply. The workpiece is connected to positive acts as an anode and electrode to negative as a cathode. Both tool electrode and workpiece are separated by a spark gap of about to 0.50 mm. Electrical input given will create a spark due to small gap producing a strong electrostatic field to emit electrons causing ionization gap. The electrical energy discharged in the gap and caused breakdown of dielectric within few microseconds. Shock waves in the dielectric are created and impact of electrons on the work material causes transient pressure of 1000 kg/cm 2. It creates a high temperature of work material and the metal melts instantaneously. Q. NO. 1B ) ( 02 marks each, any three ) ii) Process parameters of Laser Beam Machining :The performance of the LBM process can be studied with the help of controlling following parameters, a) Intensity of laser beam: By focusing a laser beam in a spot of 0.01 m 2, it can give power density of kW/ cm 2. The focused beam radius is directly proportional to the laser wavelength and the focal length. b) Pulse duration of laser beam: The pulse durations about 6 to 12 pulse/ min. It depends upon the application to be performed like welding, drilling, cutting etc. c) Focal length: It is the distance between laser beam and the workpiece. If the laser is very close to the workpiece the divergence of the beam occurs for small focal length in the metal cutting. : It is important in drilling operation. d) Mode of laser operation : It can operate in continuous mode and pulsed wave mode Page 3 of 23
4 Q. NO. 2 a) (02 marks for sketch and 02 for Advantages,Any four) Abrasive Jet Machining (AJM) : Applications of AJM: 1. Deburring, etching and cleaning of hard and brittle materials, alloys and non metals. 2. Machining brittle and heat sensitive materials like glass, quartz, and ceramics etc 3. It is used for drilling holes, cutting slots, cleaning hard surfaces polishing etc 4. Abrasive jet cutting is used for removal of metallic smears on ceramics, oxides on metals, resistive coating 5. Frosting and abrading of glass articles. 6. Trimming of resistors used in hybrid power amplifier circuit Q. NO. 2 b) ( 02m marks for advantages and 02 for disadvantages any four ) Advantages of Plasma arc machining : 1. High speed of cutting e.g. 6 mm mild steel plate can be cut at a speed of 3 m/min. 2. Equally effective on any metal regardless its hardness 3. Smooth cuts free from contaminants are obtained in the process. 4. There is no contact between tool and workpiece 5. It is three to eight times faster than oxy fuel cutting 6. Profile cutting of stainless steel can be very easily done by this process Page 4 of 23
5 Disadvantages : 1. Due to high heat, metallurgical change on the workpiece surface 2. Safety precautions are necessary for the operator and those in nearby working area 3. It increases cost of process 4. On the thicker material it will lead noise, fume and arc glare hence water cooling is needed. Q. NO. 2 c)( 01 mark for each shape any four ) Shapes that can be machined by broaching process are shown in the figure Q. NO. 2 d) ( 02m marks for advantages and 02 for disadvantages any four ) Advantages of CNC Machines : 1. Reduced lead time 2. Elimination of operator error 3. Lower labour cost 4. High accuracy 5. Elimination of jigs and fixture 6. Flexibility 7. Reduced inspection 8. Less scrap Page 5 of 23
6 Disadvantages : 1. Higher investment cost 2. Higher maintenance cost 3. Costlier CNC personnel 4. Planned support facility Q. NO. 2 e) (04 marks ) Classification of grinding machines : a) According to quality of surface finish i) Rough and non precision grinding machines 1) Floor stand and bench grinders 2) Portable and flexible shaft grinders 3) Swing frame grinders 4) Abrasive belt grinders ii) Precision grinding machines 1) External or internal cylindrical grinding 2) Surface grinders 3) Form grinders b) According to type of surface generated i) Cylindrical grinder 1) Center type plain 2) Centre type universal 3) Centre less ii) Centre less grinder 1) Through feed grinders 2) In feed grinders Page 6 of 23
7 3) End feed grinders iii) Internal grinders 1) Chucking grinder 2) Planetary grinder 3) Centreless grinder iv) Surface grinder 1) Horizontal grinders a. Reciprocating table b. Rotary tables 2) Vertical spindle a. Reciprocating table b. Rotary table c) According to specialized application i) Tool and cutter grinder ii) iii) iv) Form grinder Hand grinder Crankshaft grinder v) Thread grinder vi) Cam grinder Q.3. Answer any two of the following. ( 2*8=16) a) Write a part program to machine the part given in figure 1. On a CNC milling machine. Point X Y Ps -5-5 P Page 7 of 23
8 P P P P P P Cutter path Ps p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 p6 p7 p8 Co-ordinate as per G90 Part program :- P N10 G28 U00 V00 W00 EOB N20 G90 G21 G94 G40 EOB N30 M03 S900 M08 EOB N40 G00 Z5 EOB N50 G00 X5 Y-5 EOB Ps N60 G00 Z-3 F80 EOB N70 G00 X-5 Y45 EOB P1 N80 G01 X-5 Y65 EOB P2 N90 G01 X87.5 Y65 EOB------P3 N100 G01 X87.5 Y-5 EOB------P4 N110 G01 X62.5 Y-5 EOB-----P5 N120 G02 X62.5 Y30 R15 EOB ----P6 N130 G01 X47.5 Y45 EOB ---P7 N140 G01 X-5 Y45 EOB -----P8 N150 G00 X-5 Y-5 EOB N160 G00 Z5 M05 EOB N170 G28 U00 V00 W00 EOB N180 M09 EOB N190 M30 EOB. Q. 3 b) How are the axes identification in CNC machines? Justify your answer with neat sketches for VMC,HMC,and CNC lathes. (02 marks for explanation of axis identification and 02 each for axis explanation ) To obtain desired shape of the work piece it is necessary to move the spindle, slides in a different direction. In part programming the requirement is to determine co-ordinates for given product as per drawing and it is essential to identify the machine axes to determine the coordinate as per the standardized system. As per three dimensional Cartesian co-ordinate system the axis identification consist of--- 1) Linear Axis--- X,Y,Z axes ( Straight Movement) 2) Rotary Axis---- A,B,C axes ( Rotary Movement) Page 8 of 23
9 i) VMC Z axis---1) Main spindle axis. 2) In VMC Z(+ve) means cutter movement upward. 3) In VMC Z(-ve) means cutter movement downward. X axis---1) Horizontal work holding device. 2) X (+ve) means as being to the right when looking from the spindle towards column. 3) X (-ve) means as being to the left when looking from the spindle towards column. Y axis It is perpendicular to X and Z axes. It indicates cross travel of the work table ii) HMC Page 9 of 23
10 CNC lathe Z axis---1) spindle axis. 2) In HMC Z(+ve) increases distance between work piece and tool. 3) In HMC Z(-ve) used to specify depth of cutting. X axis---1) Always Horizontal and parallel work holding device. Indicates longitudinal movement of worktable. 2) X (+ve) means motion is to the right when looking from the spindle towards the work piece. Y axis It is perpendicular to X and Z axes. Y (+ve) with (+ve ) X and (+ve) Z. In lathe only two axes are--- Z axis--- The axis of rotation of the workpiece is spevified by Z axis X axis--- The radiac location of the cutting tool is represented by X axis (if the figure of right hand rule to indentify the axes of CNC Machine is drawn then also full marks to be given.) Q 3) C) (04 marks one for each differentiation any four) a) Differentiate between EDM and LBM processes. Sr No. Point EDM LBM Page 10 of 23
11 1 Principle It works on the principle of spark erosion by interrupted electric sparks between tool and work piece. 2 Setup Tool, electrolyte. w/p and electrical power supply. 3 Tool electrode It required in physical from made of graphite, copper. 4 Material removal It is high about 5000 rate 5 Accuracy / surface finish mm3/min. Less accuracy and surface finish. It works on the principle of heat energy produced by laser beam for metal removal. Ruby rod, lash. Cooling unit, w/p. lens, electrical power supply. No need of electrode, laser beam is a cutting source. It is very low about 5mm3/min More accuracy and better surface finish. Q 3 c) b) Classification of non-traditional process on the basis of type of energy used- (04 marks one for each classification ) Sr No. Types of Energy Mechanism of metal removal Transfer media 1 Mechanical Erosion, shear Physical contact, high velocity particles. 2 Chemical Chemical dissolution, etching 3 Electrochemical 4 Thermal / Electrothrmal Ion displacement. Fusion, vaporisation Reactive environment. Energy source for metal removal Hydraulic/ pneumatic Corrosive agent Process. AJM,USM, WJM CHM, Electrolyte. High current. ECM Hot gases, electrons, radiation. High voltage, high amplification, ionized material. EDM, LBM,PAM,EBM, IBM. Q4 A) i) Differentiate between pull broach and push broach any 4 points,01 mark each Pull Broach Push Broach 1. Pulled through work piece Pushed through work piece 2. Subjected to tensile load Subjected to compressive load 3. Long in length Short in length Page 11 of 23
12 4. More stock can be removed Less stock is removed 5. More no. of teeth s Less no. of teeth s Q 4 A )ii) Explain salient features of capstan and turret lathe any 4 points,01 mark each 1. Suitable for batch or mass production 2. More productive for quick engagement and over lapped functioning of the tools 3. feeding of the job and rapid speed change 4. Enable repetitive production of same job requiring less involvement, effort and attention of worker 5. An axially movable indexable turret in place of tail stock 6. Series of operations can be performed 7. Manufacturing of large identical pieces in a minimum time Q 4 A iii) Sketch a planer and explain its working Sketch 02 marks, Working 02 marks Planing is a machining process in which metal is removed by the relative linear movement of the tool over the surface of the work. The planning machine consists of a reciprocating table on work is held. A single point cutting tool is held in a tool post carried on a vertical slide, the saddle of which can be traversed on a cross rail. The cutting takes place during forward stroke of the table and the tool is lifted by a mechanism to avoid rubbing during the return stroke. The tool slide and saddle on the cross slide provide feed in vertical and horizontal directions respectively. To machine angular surfaces, the tool slide can be swiveled to the desired angle. (Block diagram should be given full marks.) Page 12 of 23
13 Q 4 A iv) List gear finishing methods and explain any one of them in detail list 1M, explanation 3M Gear finishing methods are; 1. Gear shaving 2. Gear grinding 3. Gear lapping 4. Gear honing 5. Gear burnishing Gear shaving: It is a corrective process. It will not make a bad gear good, but will make good gear better. This method is widely adopted for finishing spur and helical gears, before hardening. The metal is removed from the teeth with a cutter resembling a gear or a rack. Each tooth of the cutting tool is serrated to provide a series of cutting edges. Gear grinding: It is a finishing process to remove considerable amount of the metal after heat treatment to obtain predetermined quality gear. There are three general methods of gear grinding 1. Form wheel grinding 2. Generation grinding 3.Threaded wheel grinding Gear lapping: It is the process of refining the gear element after the heat treatment. The process is done by rotating the gear and the lap tool as inter meshing gears, with abrasive compound forced between the teeth. Gear honing: The process is carried out on high speed machines. The work is meshed with the honing tool in a cross axes relationship. The honing tool drives the work gear while it traverses back and forth in a parallel path to the work gear axis. The gear is run in both the directions during the process. Gear burnishing: The operation consists essentially of rolling the work gear with one or several burnishing gears whose teeth are very hard, smooth and accurate. The latter gears are driven by a motor. Q 4 B) i) What is boring operation? Give specifications of vertical boring machine (Boring 2M, Specifications 4M) Boring is a machining process in which internal surfaces of revolution are generated with single point tool. It is enlarging of drilled, cored holes. Boring machine are specified on following parameters; 1.Boring capacity 2. Max boring depth 3. Max spindle travel 4. Table surface 5. Table traverse 6. Spindle rotation 7. Spindle feed 8. Spindle motor (values of above parameter of machine may change according to manufacturer) Q 4 B ii) Name the methods by which gears are produced by machining. Explain any one method (List of methods1m, explanition5m) Page 13 of 23
14 Gear production by machining the various methods are; 1. Gear milling 2. Gear Hobbing 3. Gear shaping 4. Shear cutting of gears 5. Gear broaching 6. Bevel gear cutting Gear milling; Here a formed cutter is passed through the gear blank to effect tooth gap. Spur, helical, worm wheels and bevel gears can be manufactured by milling. Gear milling is less costlier and less accurate process. As the tooth depends upon the module, pressure angle and number of teeth, a series of cutters are selected for gear cutting. Each cutter cuts only limited range Gear hobbing: Gear hobbing is a continuous generating process in which the tooth flanks of constantly moving work piece are formed by equally spaced cutting edges of the hob. Every hob tooth, which contacts the gear along the line of action, produces one enveloping cut. Thus all enveloping cuts form a polygon of tangents to the involutes which on its corners forms a crest and deviates from the involutes curve. The direction of feed of the hob can be achevied in three ways Page 14 of 23
15 Gear shaping: In gear shaping the pinion type cutter is gear with cutting edges and means are provided to rotate the cutter in mesh with the gear to be produced. ( Block diagram or line diagram should also be given full marks.) Q5 i) Draw and state use of any two standard milling cutters ( sketch 01 mark; use 01 mark of each any of the above types. Students might have drawn sub types of cutters then also weight age to be given, any 02) Type of cutter Sketch Use Plain Milling Cutter Production of flat surfaces parallel to the axis of rotation of spindle Page 15 of 23
16 Side milling cutter Intended to removing metals from side of the work Metal slitting saw Parting off or slotting operations Angle milling cutter These cutters are used for machine angles End mill End mills are used for light milling operations T slot milling cutters Special form of end mills for producing T slots Woodruff key slot milling cutters Production of Woodruff key slot Page 16 of 23
17 Fly cutters Used in experimental shops or tool rooms Formed cutters Used to generate irregular outline of work Tap and reamer cutters Intended for producing grooves or flutes in taps or reamers Q 5 ii) What is dividing head in gear cutting process? With neat sketch explain the construction of any one dividing head (Definition of dividing head 01 mark, Sketch 02 marks, construction 01 mark, any 01) Indexing is the operation of dividing the periphery of a piece of work into any number of equal parts. In cutting spur gear, equal spacing of teeth on the gear blank is performed by indexing. Indexing is accomplished by using a special attachment known as dividing head or index head. Dividing heads are of three types; 1. Plain or Simple dividing head It comprises of a cylindrical spindle housed in a frame and a base bolted to machine table. The index crank is connected to tail of the spindle directly, crank & spindle rotate as one unit. Work is mounted at nose end of the spindle by chuck. Tail stock is separately bolted to the machine table. Page 17 of 23
18 2. Universal dividing head As the name implies, this type dividing head can be used to execute all forms of indexing. The important parts are worm and worm gear, index plate, sector arm, change gear & spindle. The worm gear has 40 teeth s & worm is single threaded, thus 40 turn of the crank will rotate the spindle through one complete revolution 3. Optical dividing head It is used for precise angular indexing during machining. The mechanism comprises a worm gear which is keyed to the spindle and may be rotated by a worm. A circular glass scale graduated in 1 0 division is rigidly mounted on the worm wheel. Any movement of the spindle effected by rotating the worm is read off by means of a microscope fitted on the dividing head body, the eye piece has a scale having 60 divisions & each division is equivalent to 1 movement of circular scale Q 5 iii) Give the cutting parameters of milling operation (01 mark for each parameter ) Page 18 of 23
19 Cutting speed in m/min or rpm Feed per tooth Feed per cutter revolution in mm/rev Depth of cut in mm Number of cutter teeth Q 5 iv) Give the advantages and disadvantages of gear hobbing process (Any two advantages 01 mark each & Any two disadvantages 01 mark each) Advantages; 1. Versatility,covers variety of gear types. 2. Indexing is continuous hence no error 3. High rate of production. Disadvantages; 1. Not adopted to generate internal gears. 2. Restricted adjacent shoulders larger than root diameter of the gear. 3. Splines and serrations are not suitable for hobbing. Q 5 v) Sketch surface grinding machine and explain its working (Sketch 02 marks, Working 02 marks) Surface grinding machines are employed to finish plane or flat surfaces. They are are also capable of grinding irregular, curved, convex and concave surfaces. Conventional surface grinders are divided into two classes reciprocating table and rotary table. Also vertical or horizontal grinding wheel spindles. Grinding is normally done on the periphery of the wheel. The area of contact is small and the speed is uniform over the grinding surface while in vertical grinders area of contact is large and more material is removed. Q 5 vi) What are the advantages and disadvantages of honing process. each & Any two disadvantages 01 mark each) (Any two advantages 01 mark Advantages Page 19 of 23
20 1. High geometrical and dimensional accuracies are obtained 2. High surface finish is achieved. 3. Suitable for through as well as blind holes Disadvantages 1. Construction of honing tool is complicated. 2. Relationship between different honing conditions. 3. Determination of honing pressure. Q6) Answer any four of the following. (4*4 =16) (02 marks for explanation and 02 for advantages ) Q 6 i) Buffing:- Buffing is a final operation to improve the poish of a metal and to bring out maximum luster. It is a operation prior to plating. Buffing does not mountain flatness or roundness, it is used only to obtain very smooth reflective surfaces. It removes negligible amounts of metal. The size of the work is changed very little sometimes to mm In buffing the rubbing action is more gentle than aggressive cutting action used in polishing. Principle of operation.--- Buffing may be done by holding the workpiece in hand and bringing it into contact with a revolving buffing wheel. The operator presses the part against the charged buffing wheel at considerable pressure. Advantages:- 1) No surface preparation is required. 2) Suitable for ferrous/ non ferrous alloys. Q. 6 ii) Machine lapping:- Page 20 of 23
21 (02 marks for sketch and 02 for explanation ) It is preferred for finishing work in larger quantities and it is applicable for both flat and cylindrical lapping. Cylindrical work may be lapped by ratating the work in lathe or drill press and reciprocating the lap over the work in an everchaning path. Matched flat surfaces may be lapped by holding the work against the rotating disc, or work max be moved by hand in an irregular path over a stationary face plate lap. Types of lapping machines. 1) vertical axis lapping m/c 2) centre less lapping m/c 3) abrasive belt lapping. Advantages 1) No burrs are created. 2) Any material hard or soft can be lapped. 3) There is no warping of the lapped components. Applications 1) Precision lpug gauges, slip gauges. 2) Cylindrical valves and roller bearings. 3) crankshaft, small engine pistons, small valve piston. 4) piston rings,inner and outer bearing races etc. Q. 6 iii) Types of maintenance:----(02 marks for list and 02 for explanation any one ) Basically two types of maintenances---- 1) Unplanned maintenance-----i) Breakdown maintenance ii) Corrective maintenance iii) Opportunistic maintenance 2) Planned maintenance-----i) Preventive maintenance ii) Predictive maintenance iii) Corrective maintenance iv) Routine maintenance v) Design out maintenance vi) Total productive maintenance. Breakdown Maintenance--- It is the conventional type of maintenance in which the breakdown of machine tool will occur and then maintenance is carried out to remove the faults. Page 21 of 23
22 The basic concept of this maintenance is not to do anything until and unless the machine stops its function. It receives attention only after breakdown of machine tool for ex- belt is broken. Failure of Gears, couplings, springs, shafts. It is risky and provides no guarantee of reliable, smooth running of machine tools. It is good for small scale units where 1) No maintenance expert is available. 2) sudden breakdown will not cause major loss. 3) number of machine tools are few. 4) no effect on production line directly due to small quantity production. Q 6 iv) Maintenance practice of couplings and machine belts---- (04 marks ) 1) coupling-- They are used to connect the shaft ends together for transmitting torque or rotary motion directly from one shaft to the other. The bearings are classified 1) Rigid coupling. 2) Flexible coupling. e.g.flanged coupling, muff coupling, bushed-pin coupling, and Oldham coupling. Maintenance procedure of coupling--- Due to misalignment, loose bolts etc abnormal noise comes out. Observe the vibrations due to run out. Visual inspection for misalignment, wear out parts. Checking the lubrication regularly and change oil after certain interval. Prepare maintenance report for showing history of maintenance of each coupling. 2)V-belt maintenance 1. Entry of any metal particles, sawdust etc should be avoided otherwise it may cause abrasion of belt. Protection covers maybe provided at the top and side for this purpose. 2. Excess loading causes excessive stretching of belts. It should be avoided to reduce stretching of V belts. 3. V belts should be preserved free from conditions like heat, acids Which may cause damage to the rubber components. 4. Periodically check for slippage is to be carried out to ensure transmission of rated load. Q 6 V) Repair complexity : ( 02 marks for explanation and 02 for utility ) It is important for maintenance planning to consider complexity of repair of machine tool. In a simple manner. If machine tool has more number of mechanisms and devices then it is called as complex one and its maintenance is also complicated. The complexity of the machine tool play a very important role In the maintenance and it decides the nature of small / major repair and repair cycle, maintenance staff, spares requirement, repair cost is also dependent on the complexity of the machine tool. An index is generally used to designate a coparatively complexity of different machines. This index has been finalized taking into account the power transmission devices, hydraulic units guides surfaces, intricate mechanisms, etc Types of machine / Repair complexity number equipment Boiler 12 Air compressor 8 Turbine 14 Rolling mill 15 Centre lathe 5 Page 22 of 23
23 Higher the repair complexity index, high number of activities i.e. longer repair cycle for the machine. Uses of Repair Complexity :- 1. To calculate maintenance staff size. 2. To design the inventory required for spares. 3. To forecast the maintenance cost. 4. To design repair cycle of the machine tool. 5. Number of critical maintenance points can be find out. Q 6 vi) Maintenance Manual : (02 marks for explanation and 02 for contents ) When purchase anew vehicle then maintenance booklet or service booklet is provided by manufacturer, called as maintenance manual. This booklet in printed format given the user of the equipment about the preventive maintenance to be done with respect to time scale of that machine tool. It is prepared on the vast experience of manufacturer and feedback collected from the customers who had used that type of machine tool already. It is a systematically maintenance of m/c tool in a right manner. Standardized maintenance procedure are adopted. Contents of maintenance manuals Maintenance manuals contents following things ) safety precautions. 2) service center details. 3) procedure for maintenance of different parts one by one. 4) maintenance schedule for different parts. 5) instructions for safe handling. 6) important terms and abbreviations. (if formats of the manuals given with explanation should be given full marks.) Page 23 of 23
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT-I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? (BT1) 2. Explain how chip
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT-I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? (BT1) 2. Explain how chip
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? 2. How chip formation occurs in metal cutting? 3. What is
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? 2. How chip formation occurs in metal cutting? 3. What is
ABRASIVE PROCESSES AND BROACHING
 UNIT 4 www.studentsfocus.com ABRASIVE PROCESSES AND BROACHING 1. What are the types of surfaces that could de produced using plain cylindrical grinders? Plain cylindrical parts, cylindrical parts, cylinders,
UNIT 4 www.studentsfocus.com ABRASIVE PROCESSES AND BROACHING 1. What are the types of surfaces that could de produced using plain cylindrical grinders? Plain cylindrical parts, cylindrical parts, cylinders,
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology (AUST) Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering
 Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology (AUST) Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering LABORATORY MANUAL For the students of Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering 1 st
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology (AUST) Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering LABORATORY MANUAL For the students of Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering 1 st
Module 1. Classification of Metal Removal Processes and Machine tools. Version 2 ME IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Classification of Metal Removal Processes and Machine tools Lesson 2 Basic working principle, configuration, specification and classification of machine tools Instructional Objectives At the end
Module 1 Classification of Metal Removal Processes and Machine tools Lesson 2 Basic working principle, configuration, specification and classification of machine tools Instructional Objectives At the end
Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes.
 Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes. 24.1 Introduction In addition to parts with various external or internal round profiles, machining operations can produce many other parts
Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes. 24.1 Introduction In addition to parts with various external or internal round profiles, machining operations can produce many other parts
Typical Parts Made with These Processes
 Turning Typical Parts Made with These Processes Machine Components Engine Blocks and Heads Parts with Complex Shapes Parts with Close Tolerances Externally and Internally Threaded Parts Products and Parts
Turning Typical Parts Made with These Processes Machine Components Engine Blocks and Heads Parts with Complex Shapes Parts with Close Tolerances Externally and Internally Threaded Parts Products and Parts
PLANING MACHINE. Crossrail. Tool head. Table. Table. reciprocating movement Roller. Bed. Open Side Planer Sketch S-8.1-A. Feed screws.
 8 PLANING MACHINE A8.1 : Planing Machine Tool head Table reciprocating movement Roller Table Cross-rail Bed Column Open Side Planer Sketch S-8.1-A Introduction This is also a reciprocating type of machine
8 PLANING MACHINE A8.1 : Planing Machine Tool head Table reciprocating movement Roller Table Cross-rail Bed Column Open Side Planer Sketch S-8.1-A Introduction This is also a reciprocating type of machine
Turning and Lathe Basics
 Training Objectives After watching the video and reviewing this printed material, the viewer will gain knowledge and understanding of lathe principles and be able to identify the basic tools and techniques
Training Objectives After watching the video and reviewing this printed material, the viewer will gain knowledge and understanding of lathe principles and be able to identify the basic tools and techniques
Materials Removal Processes (Machining)
 Chapter Six Materials Removal Processes (Machining) 6.1 Theory of Material Removal Processes 6.1.1 Machining Definition Machining is a manufacturing process in which a cutting tool is used to remove excess
Chapter Six Materials Removal Processes (Machining) 6.1 Theory of Material Removal Processes 6.1.1 Machining Definition Machining is a manufacturing process in which a cutting tool is used to remove excess
Lecture 18. Chapter 24 Milling, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing (cont.) Planing
 Lecture 18 Chapter 24 Milling, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing (cont.) Planing For production of: Flat surfaces Grooves Notches Performed on long (on average 10 m) workpieces Workpiece moves / Tool
Lecture 18 Chapter 24 Milling, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing (cont.) Planing For production of: Flat surfaces Grooves Notches Performed on long (on average 10 m) workpieces Workpiece moves / Tool
Module 4 General Purpose Machine Tools. Version 2 ME, IIT Kharagpur
 Module 4 General Purpose Machine Tools Lesson 22 Use of various Attachments in Machine Tools. Instructional objectives At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to; (i) Comprehend and state
Module 4 General Purpose Machine Tools Lesson 22 Use of various Attachments in Machine Tools. Instructional objectives At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to; (i) Comprehend and state
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLAGE Manufacturing Technology - II SUBCODE: MEB520 UNIT- I PART-A
 PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLAGE Manufacturing Technology - II 1. List out the cutting tool materials. 2. Define rake angle. 3. Define clearance angle. 4. What is meant by drilling? 5. What is the
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLAGE Manufacturing Technology - II 1. List out the cutting tool materials. 2. Define rake angle. 3. Define clearance angle. 4. What is meant by drilling? 5. What is the
NON-TRADITIONAL MACHINING PROCESSES ULTRASONIC, ELECTRO-DISCHARGE MACHINING (EDM), ELECTRO-CHEMICAL MACHINING (ECM)
 NON-TRADITIONAL MACHINING PROCESSES ULTRASONIC, ELECTRO-DISCHARGE MACHINING (EDM), ELECTRO-CHEMICAL MACHINING (ECM) A machining process is called non-traditional if its material removal mechanism is basically
NON-TRADITIONAL MACHINING PROCESSES ULTRASONIC, ELECTRO-DISCHARGE MACHINING (EDM), ELECTRO-CHEMICAL MACHINING (ECM) A machining process is called non-traditional if its material removal mechanism is basically
Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making
 Manufacturing Engineering Technology in SI Units, 6 th Edition Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making Chapter Outline 1. Introduction 2. The Turning Process 3. Lathes and Lathe Operations
Manufacturing Engineering Technology in SI Units, 6 th Edition Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Turning and Hole Making Chapter Outline 1. Introduction 2. The Turning Process 3. Lathes and Lathe Operations
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY
 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT V Machine Tools Milling cutters Classification of milling cutters according to their design HSS cutters: Many cutters like end mills, slitting cutters, slab cutters, angular
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT V Machine Tools Milling cutters Classification of milling cutters according to their design HSS cutters: Many cutters like end mills, slitting cutters, slab cutters, angular
Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS
 Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS Turning and Related Operations Drilling and Related Operations Milling Machining Centers and Turning Centers Other Machining Operations High Speed Machining
Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS Turning and Related Operations Drilling and Related Operations Milling Machining Centers and Turning Centers Other Machining Operations High Speed Machining
MACHINE TOOLS GRINDING MACHINE TOOLS
 MACHINE TOOLS GRINDING MACHINE TOOLS GRINDING MACHINE TOOLS Grinding in generally considered a finishing operation. It removes metal comparatively in smaller volume. The material is removed in the form
MACHINE TOOLS GRINDING MACHINE TOOLS GRINDING MACHINE TOOLS Grinding in generally considered a finishing operation. It removes metal comparatively in smaller volume. The material is removed in the form
SHAPER, MILLING AND GEAR CUTTING MACHINES
 UNIT 3 SHAPER, MILLING AND GEAR CUTTING MACHINES 1. Compare hydraulic shaper with mechanical shaper? SL.NO Hydrulic shaper Mechanical shaper 1. smooth cutting operation Rough and noisy cutting operation
UNIT 3 SHAPER, MILLING AND GEAR CUTTING MACHINES 1. Compare hydraulic shaper with mechanical shaper? SL.NO Hydrulic shaper Mechanical shaper 1. smooth cutting operation Rough and noisy cutting operation
SURFACE FINISHING GRINDING MACHINES
 SURFACE FINISHING GRINDING MACHINES Introduction :- Grinding is a metal cutting operation which is performed by means of a rotating abrasive wheel acts as a cutting tool. Material removal is in the form
SURFACE FINISHING GRINDING MACHINES Introduction :- Grinding is a metal cutting operation which is performed by means of a rotating abrasive wheel acts as a cutting tool. Material removal is in the form
UNIT 5: Indexing: Simple, compound, differential and angular indexing calculations. Simple problems on simple and compound indexing.
 UNIT 5: Milling machines: Classification, constructional features, milling cutters nomenclature, milling operations, up milling and down milling concepts. Indexing: Simple, compound, differential and angular
UNIT 5: Milling machines: Classification, constructional features, milling cutters nomenclature, milling operations, up milling and down milling concepts. Indexing: Simple, compound, differential and angular
061 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CRAFT PRACTICE
 061 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CRAFT PRACTICE EXAMINATION STRUCTURE The examination for this syllabus wills cover the underlisted two major areas of groupings and 193 Building/Engineering Drawing as the related
061 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CRAFT PRACTICE EXAMINATION STRUCTURE The examination for this syllabus wills cover the underlisted two major areas of groupings and 193 Building/Engineering Drawing as the related
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN
 LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE: DRILLING. COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGR. ALIYU, S.J Course code: MCE
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE: DRILLING. COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGR. ALIYU, S.J Course code: MCE
Scheme - G. Sample Test Paper-I
 Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks. 4. Assume suitable
Sample Test Paper-I Marks : 25 Time:1 hour 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. 3. Figures to the right indicate full marks. 4. Assume suitable
TURNING BORING TURNING:
 TURNING BORING TURNING: FACING: Machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. Work spins and the single cutting tool does the cutting. Done in Lathe. Single point tool, longitudinal feed. Single
TURNING BORING TURNING: FACING: Machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. Work spins and the single cutting tool does the cutting. Done in Lathe. Single point tool, longitudinal feed. Single
UNIT 4: (iii) Illustrate the general kinematic system of drilling machine and explain its working principle
 UNIT 4: Drilling machines: Classification, constructional features, drilling & related operations, types of drill & drill bit nomenclature, drill materials. Instructional Objectives At the end of this
UNIT 4: Drilling machines: Classification, constructional features, drilling & related operations, types of drill & drill bit nomenclature, drill materials. Instructional Objectives At the end of this
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) WINTER 15 EXAMINATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY
 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT IV SURFACE FINISHING PROCESS Grinding Grinding is the most common form of abrasive machining. It is a material cutting process which engages an abrasive tool whose cutting
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT IV SURFACE FINISHING PROCESS Grinding Grinding is the most common form of abrasive machining. It is a material cutting process which engages an abrasive tool whose cutting
MILLING and GRINDING MACHINES Machine Tools
 ELEMENTS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PART B UNIT VI MILLING and GRINDING MACHINES Machine Tools 1 Objectives: 1.1 To understand the Principle of working of Milling, Horizontal & Vertical Milling. 1.2 Classification/Types
ELEMENTS OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PART B UNIT VI MILLING and GRINDING MACHINES Machine Tools 1 Objectives: 1.1 To understand the Principle of working of Milling, Horizontal & Vertical Milling. 1.2 Classification/Types
Machinist NOA (1998) Subtask to Unit Comparison
 Machinist NOA (1998) Subtask to Unit Comparison NOA Subtask Task 1 Demonstrates safe working practices. 1.01 Recognizes potential health and safety hazards. A1 Safety in the Machine Shop 1.02 Recognizes
Machinist NOA (1998) Subtask to Unit Comparison NOA Subtask Task 1 Demonstrates safe working practices. 1.01 Recognizes potential health and safety hazards. A1 Safety in the Machine Shop 1.02 Recognizes
Roll No. :.. Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (ME)/SEM-5/ME-504/ TECHNOLOGY OF MACHINING. Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70
 Name : Roll No. :.. Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (ME)/SEM-5/ME-504/2009-10 2009 TECHNOLOGY OF MACHINING Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates
Name : Roll No. :.. Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.Tech (ME)/SEM-5/ME-504/2009-10 2009 TECHNOLOGY OF MACHINING Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates
A H M 531 The Civil Engineering Center
 Title Page Introduction 2 Objectives 2 Theory 2 Fitting 3 Turning 5 Shaping and Grinding 7 Milling 8 Conclusion 11 Reference 11 1 Introduction Machining Machining is a manufacturing process in which a
Title Page Introduction 2 Objectives 2 Theory 2 Fitting 3 Turning 5 Shaping and Grinding 7 Milling 8 Conclusion 11 Reference 11 1 Introduction Machining Machining is a manufacturing process in which a
CHAPTER 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes Kalpakjian Schmid Manufacturing Engineering and Technology 2001 Prentice-Hall Page 23-1
 CHAPTER 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes Manufacturing Engineering and Technology 2001 Prentice-Hall Page 23-1 Examples of Parts Produced Using the Machining Processes in the Chapter
CHAPTER 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes Manufacturing Engineering and Technology 2001 Prentice-Hall Page 23-1 Examples of Parts Produced Using the Machining Processes in the Chapter
U.S. Census Bureau Metalworking Machinery MQ333W(08)-5 Issued August 2009
 U.S. Census Bureau Metalworking Machinery - 2008 MQ333W(08)-5 Issued August 2009 Address inquiries concerning these data to Investment Goods Industries Branch, U.S. Department of Commerce, Census Bureau,
U.S. Census Bureau Metalworking Machinery - 2008 MQ333W(08)-5 Issued August 2009 Address inquiries concerning these data to Investment Goods Industries Branch, U.S. Department of Commerce, Census Bureau,
INTRODUCTION TO GRINDING PROCESS
 GRINDING PART 2 Grinding Grinding is a material removal process accomplished by abrasive particles that are contained in a bonded grinding wheel rotating at very high surface speeds. The rotating grinding
GRINDING PART 2 Grinding Grinding is a material removal process accomplished by abrasive particles that are contained in a bonded grinding wheel rotating at very high surface speeds. The rotating grinding
Introduction to Manufacturing Processes
 Introduction to Manufacturing Processes Products and Manufacturing Product Creation Cycle Design Material Selection Process Selection Manufacture Inspection Feedback Typical product cost breakdown Manufacturing
Introduction to Manufacturing Processes Products and Manufacturing Product Creation Cycle Design Material Selection Process Selection Manufacture Inspection Feedback Typical product cost breakdown Manufacturing
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTRAMPALLI DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY MANUAL ME6411-MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LAB- II
 BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTRAMPALLI 635 854 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY MANUAL ME6411-MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LAB- II YEAR / SEMESTER : II / IV DEPARTMENT : Mechanical REGULATION
BHARATHIDASAN ENGINEERING COLLEGE NATTRAMPALLI 635 854 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY MANUAL ME6411-MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LAB- II YEAR / SEMESTER : II / IV DEPARTMENT : Mechanical REGULATION
GEARS MACHINING. GEAR TYPES Cylindrical gears: - spur - helical Bevel gears: - straight - curved (spiral) Worm wheels and worms
 GEARS MACHINING GEAR TYPES Cylindrical gears: - spur - helical Bevel gears: - straight - curved (spiral) Worm wheels and worms 1 Involute tooth profile 2 Spur and helical gears cutting METHODS: form milling
GEARS MACHINING GEAR TYPES Cylindrical gears: - spur - helical Bevel gears: - straight - curved (spiral) Worm wheels and worms 1 Involute tooth profile 2 Spur and helical gears cutting METHODS: form milling
Lathes. CADD SPHERE Place for innovation Introduction
 Lathes Introduction Lathe is one of the most versatile and widely used machine tools all over the world. It is commonly known as the mother of all other machine tool. The main function of a lathe is to
Lathes Introduction Lathe is one of the most versatile and widely used machine tools all over the world. It is commonly known as the mother of all other machine tool. The main function of a lathe is to
TOP WORK ISO 9001.CE UNIVERSAL CUTTER & TOOL GRINDER
 TOP WORK ISO 9001.CE UNIVERSAL CUTTER Precise ball groove of conformation Inclination of Wheelhead The wheelhead can easily tilt up to ±15 degrees, with a 360-degrees swivel on the horizontal plane. The
TOP WORK ISO 9001.CE UNIVERSAL CUTTER Precise ball groove of conformation Inclination of Wheelhead The wheelhead can easily tilt up to ±15 degrees, with a 360-degrees swivel on the horizontal plane. The
CNC Cooltool - Milling Machine
 CNC Cooltool - Milling Machine Module 1: Introduction to CNC Machining 1 Prepared By: Tareq Al Sawafta Module Objectives: 1. Define machining. 2. Know the milling machine parts 3. Understand safety rules
CNC Cooltool - Milling Machine Module 1: Introduction to CNC Machining 1 Prepared By: Tareq Al Sawafta Module Objectives: 1. Define machining. 2. Know the milling machine parts 3. Understand safety rules
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 SCSVMV UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SUBJECT NAME : SUBJECT CODE : MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-II EBM4DT055 QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 1. What is Grinding? 2. Briefly classify the Grinding Process.
SCSVMV UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING SUBJECT NAME : SUBJECT CODE : MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-II EBM4DT055 QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 1. What is Grinding? 2. Briefly classify the Grinding Process.
ME MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LABORATORY-I VARUVAN VADIVELAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DHARMAPURI LAB MANUAL
 VARUVAN VADIVELAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DHARMAPURI 636 703 ME 6311 - MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LABORATORY-I REGULATION 2013 LAB MANUAL BRANCH YEAR / SEM MECHANICAL ENGINEERING II YEAR & III SEMESTER D
VARUVAN VADIVELAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DHARMAPURI 636 703 ME 6311 - MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LABORATORY-I REGULATION 2013 LAB MANUAL BRANCH YEAR / SEM MECHANICAL ENGINEERING II YEAR & III SEMESTER D
Design for machining
 Multiple choice questions Design for machining 1) Which one of the following process is not a machining process? A) Planing B) Boring C) Turning D) Forging 2) The angle made between the rake face of a
Multiple choice questions Design for machining 1) Which one of the following process is not a machining process? A) Planing B) Boring C) Turning D) Forging 2) The angle made between the rake face of a
Lecture 15. Chapter 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Round Shapes. Turning
 Lecture 15 Chapter 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Round Shapes Turning Turning part is rotating while it is being machined Typically performed on a lathe Turning produces straight, conical, curved,
Lecture 15 Chapter 23 Machining Processes Used to Produce Round Shapes Turning Turning part is rotating while it is being machined Typically performed on a lathe Turning produces straight, conical, curved,
K E E P I N G T H E W O R L D I N M O T I O N TM P 90 G. Grinding and Hobbing Machine
 K E E P I N G T H E W O R L D I N M O T I O N TM P 90 G Grinding and Hobbing Machine machine concept P 90 G three grinding methods + hobbing combined in one machine. The P 90 G is a new development based
K E E P I N G T H E W O R L D I N M O T I O N TM P 90 G Grinding and Hobbing Machine machine concept P 90 G three grinding methods + hobbing combined in one machine. The P 90 G is a new development based
Technology II. Manufacturing methods
 Technology II Manufacturing methods Gears Machining GEAR TYPES Cylindrical gears: - spur - helical Bevel gears: - straight - curved (spiral) Worm wheels and worms 2 Involute tooth profile 3 Spur and helical
Technology II Manufacturing methods Gears Machining GEAR TYPES Cylindrical gears: - spur - helical Bevel gears: - straight - curved (spiral) Worm wheels and worms 2 Involute tooth profile 3 Spur and helical
1. The Lathe. 1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Main parts of a lathe
 1. The Lathe 1.1 Introduction Lathe is considered as one of the oldest machine tools and is widely used in industries. It is called as mother of machine tools. It is said that the first screw cutting lathe
1. The Lathe 1.1 Introduction Lathe is considered as one of the oldest machine tools and is widely used in industries. It is called as mother of machine tools. It is said that the first screw cutting lathe
TIMTOS 2017 EXHIBITS PROFILE
 TIMTOS 2017 EXHIBITS PROFILE Product Code Product Name METAL CUTTING MACHINE TOOL Lathes and Turning Machines 160101 Lathes, Swiss Type 160502 Bench Lathes 160503 High Speed Lathes 160504 Automatic Lathes
TIMTOS 2017 EXHIBITS PROFILE Product Code Product Name METAL CUTTING MACHINE TOOL Lathes and Turning Machines 160101 Lathes, Swiss Type 160502 Bench Lathes 160503 High Speed Lathes 160504 Automatic Lathes
Turning and Related Operations
 Turning and Related Operations Turning is widely used for machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. The workpiece rotates and a longitudinally fed single point cutting tool does the cutting.
Turning and Related Operations Turning is widely used for machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. The workpiece rotates and a longitudinally fed single point cutting tool does the cutting.
The Analysis and Research of Gear Surface Machining Rong Zhang
 International Conference on Automation, Mechanical Control and Computational Engineering (AMCCE 2015) The Analysis and Research of Gear Surface Machining Rong Zhang Dalian Vocational Technical College,
International Conference on Automation, Mechanical Control and Computational Engineering (AMCCE 2015) The Analysis and Research of Gear Surface Machining Rong Zhang Dalian Vocational Technical College,
Chapter 24. Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling, Broaching, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing
 Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling, Broaching, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing Parts Made with Machining Processes of Chapter 24 Figure 24.1 Typical parts and
Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling, Broaching, Sawing, and Filing; Gear Manufacturing Parts Made with Machining Processes of Chapter 24 Figure 24.1 Typical parts and
Sheet Metal Tools. by:prem Mahendranathan
 Sheet Metal Tools by: SHEET METAL TOOL KIT SHEET METAL TOOLS Rivet Gun 3/32, 1/8, 5/32, 3/16",Cupped Set Mini Bucking Bar Footed Heel-Toe Bucking Bar Air Tool Oil Mechanics Tool Bag High-Speed Air Drill
Sheet Metal Tools by: SHEET METAL TOOL KIT SHEET METAL TOOLS Rivet Gun 3/32, 1/8, 5/32, 3/16",Cupped Set Mini Bucking Bar Footed Heel-Toe Bucking Bar Air Tool Oil Mechanics Tool Bag High-Speed Air Drill
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MACHINE SHOP FACILITIES AND PRACTICES Prepared by Mike Allen July 31, 2003 Edited by Scott Morton February 18, 2004
 1 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MACHINE SHOP FACILITIES AND PRACTICES Prepared by Mike Allen July 31, 2003 Edited by Scott Morton February 18, 2004 I. OBJECTIVE To provide an overview and basic knowledge of the
1 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MACHINE SHOP FACILITIES AND PRACTICES Prepared by Mike Allen July 31, 2003 Edited by Scott Morton February 18, 2004 I. OBJECTIVE To provide an overview and basic knowledge of the
Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba
 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes 1 Homework Assignment Due Wensday 28/4/2010 1. Show that the distance lc in slab milling is approximately equal to for situations where D>>d. (see Figure
Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes 1 Homework Assignment Due Wensday 28/4/2010 1. Show that the distance lc in slab milling is approximately equal to for situations where D>>d. (see Figure
Lathe is a machine, which removes the metal from a piece of work to the required shape & size HENRY MAUDSLAY
 TURNING MACHINES LATHE Introduction Lathe is a machine, which removes the metal from a piece of work to the required shape & size HENRY MAUDSLAY - 1797 Types of Lathe Engine Lathe The most common form
TURNING MACHINES LATHE Introduction Lathe is a machine, which removes the metal from a piece of work to the required shape & size HENRY MAUDSLAY - 1797 Types of Lathe Engine Lathe The most common form
INDEX. S.No. Name of the Experiment Page No.
 MACHINE TOOLS LAB INDEX S.No. Name of the Experiment Page No. 1 Step Turning and Taper Turning on Lathe 2 Thread Cutting and Knurling on Lathe 3 Machining Flat Surface using Shaper Machine 4 Manufacturing
MACHINE TOOLS LAB INDEX S.No. Name of the Experiment Page No. 1 Step Turning and Taper Turning on Lathe 2 Thread Cutting and Knurling on Lathe 3 Machining Flat Surface using Shaper Machine 4 Manufacturing
: ADVANCED PRODUCTION PROCESSSES COURSE CODE : 6021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5
 COURSE TITLE : ADVANCED PRODUCTION PROCESSSES COURSE CODE : 6021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Turret and Capstan lathes,
COURSE TITLE : ADVANCED PRODUCTION PROCESSSES COURSE CODE : 6021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Turret and Capstan lathes,
Hornsby Woodworking Men s Shed. Guide to the Shed s Woodworking Machines
 Guide to the Shed s Woodworking Machines SP00 Purpose The primary purpose of this document is to assist the induction of new members of the Hornsby Woodworking Men s Shed in the identification and understanding
Guide to the Shed s Woodworking Machines SP00 Purpose The primary purpose of this document is to assist the induction of new members of the Hornsby Woodworking Men s Shed in the identification and understanding
DM&E CORPORATION EQUIPMENT AND FACILITIES LISTING
 DM&E CORPORATION EQUIPMENT AND FACILITIES LISTING DM&E Corporation PO Box 580 Shelby, NC 28151-0580 (704) 482-8876 Fax: (704) 484-8326 Email: sales@dmecutter.com Website: www.dmecutter.com Updated January
DM&E CORPORATION EQUIPMENT AND FACILITIES LISTING DM&E Corporation PO Box 580 Shelby, NC 28151-0580 (704) 482-8876 Fax: (704) 484-8326 Email: sales@dmecutter.com Website: www.dmecutter.com Updated January
MLR Institute of Technology
 MLR Institute of Technology Dundigal, Quthbullapur (M), Hyderabad 500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MACHINE TOOLS OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS UNIT - I 1. A built up-edge is formed while machining [ B ] (Sep-2011,
MLR Institute of Technology Dundigal, Quthbullapur (M), Hyderabad 500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MACHINE TOOLS OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS UNIT - I 1. A built up-edge is formed while machining [ B ] (Sep-2011,
Specifications for Lathe L- 45/5000(for items from Sr. No.01 to Sr. No.22 in Indent)
 Specifications for Lathe L- 45/5000(for items from Sr. 01 to Sr. 22 in Indent) Annexure-1 Sr. Specification of Parameter Parameter Value 1.0 Capacity 1.1 Height of centers (nominal) (mm) 450 1.2 Type of
Specifications for Lathe L- 45/5000(for items from Sr. 01 to Sr. 22 in Indent) Annexure-1 Sr. Specification of Parameter Parameter Value 1.0 Capacity 1.1 Height of centers (nominal) (mm) 450 1.2 Type of
Roughing vs. finishing
 Finishing methods Roughing vs. finishing Roughing removing material as fast as possible, without special demands on surface and low demand on precision high Q, high IT, high Ra Finishing making final surface
Finishing methods Roughing vs. finishing Roughing removing material as fast as possible, without special demands on surface and low demand on precision high Q, high IT, high Ra Finishing making final surface
STEEL RULE. Stock TRY SQUARE
 FITTING INTRODUCTION Fitting consists of a handwork involved in fitting together components usually performed at a bench equipped with a vice and hand tools. The matting components have a close relation
FITTING INTRODUCTION Fitting consists of a handwork involved in fitting together components usually performed at a bench equipped with a vice and hand tools. The matting components have a close relation
APPENDIX A TOOLMAKER D.O.T. CODE O*NET CODE As Revised for MACNY, The Manufacturers Association
 STATE OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF LABOR APPENDIX A TOOLMAKER D.O.T. CODE 601.280-042 O*NET CODE 51-4111.00 As Revised for MACNY, The Manufacturers Association This training outline is a minimum standard
STATE OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF LABOR APPENDIX A TOOLMAKER D.O.T. CODE 601.280-042 O*NET CODE 51-4111.00 As Revised for MACNY, The Manufacturers Association This training outline is a minimum standard
Manufacturing Processes (continued)
 Manufacturing (continued) Machining Some other processes Material compatibilities Process (shape) capabilities Manufacturing costs Correct pg 142, question 34i should read Fig 6.18 question 34j should
Manufacturing (continued) Machining Some other processes Material compatibilities Process (shape) capabilities Manufacturing costs Correct pg 142, question 34i should read Fig 6.18 question 34j should
Agricultural Mechanics and Technology Power Tool Safety Rules
 Agricultural Mechanics and Technology Power Tool Safety Rules Name: BAND SAW Use: Cutting curves, circles and irregular shapes. 1. Use clean SHARP blades. 2. The teeth should always point DOWN. 3. Adjust
Agricultural Mechanics and Technology Power Tool Safety Rules Name: BAND SAW Use: Cutting curves, circles and irregular shapes. 1. Use clean SHARP blades. 2. The teeth should always point DOWN. 3. Adjust
THREAD CUTTING & FORMING
 THREAD CUTTING & FORMING Threading, Thread Cutting and Thread Rolling: Machining Threads on External Diameters (shafts) Tapping: Machining Threads on Internal Diameters (holes) Size: Watch to 10 shafts
THREAD CUTTING & FORMING Threading, Thread Cutting and Thread Rolling: Machining Threads on External Diameters (shafts) Tapping: Machining Threads on Internal Diameters (holes) Size: Watch to 10 shafts
MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
 XXXX B23 MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR XXXX PLANING; SLOTTING; SHEARING; BROACHING; SAWING; FILING; SCRAPING; LIKE OPERATIONS FOR WORKING METAL BY REMOVING MATERIAL, NOT OTHERWISE
XXXX B23 MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR XXXX PLANING; SLOTTING; SHEARING; BROACHING; SAWING; FILING; SCRAPING; LIKE OPERATIONS FOR WORKING METAL BY REMOVING MATERIAL, NOT OTHERWISE
Chapter 24. Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling
 Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling Parts Made with Machining Processes of Chapter 24 Figure 24.1 Typical parts and shapes that can be produced with the machining processes
Chapter 24 Machining Processes Used to Produce Various Shapes: Milling Parts Made with Machining Processes of Chapter 24 Figure 24.1 Typical parts and shapes that can be produced with the machining processes
Computer Numeric Control
 Computer Numeric Control TA202A 2017-18(2 nd ) Semester Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kanpur Computer Numeric Control A system in which actions are controlled by the direct
Computer Numeric Control TA202A 2017-18(2 nd ) Semester Prof. J. Ramkumar Department of Mechanical Engineering IIT Kanpur Computer Numeric Control A system in which actions are controlled by the direct
HOW TO USE MILLING MACHINE?
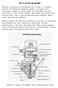 HOW TO USE MILLING MACHINE? Milling is the process of machining flat, curved, or irregular surfaces by feeding the workpiece against a rotating cutter containing a number of cutting edges. The usual Mill
HOW TO USE MILLING MACHINE? Milling is the process of machining flat, curved, or irregular surfaces by feeding the workpiece against a rotating cutter containing a number of cutting edges. The usual Mill
ROOP LAL Unit-6 Lathe (Turning) Mechanical Engineering Department
 Notes: Lathe (Turning) Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B) 1 Introduction: In previous Lecture 2, we have seen that with the help of forging and casting processes, we can manufacture machine parts of
Notes: Lathe (Turning) Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B) 1 Introduction: In previous Lecture 2, we have seen that with the help of forging and casting processes, we can manufacture machine parts of
ROOP LAL Unit-6 (Milling) Mechanical Engineering Department
 Notes: Milling Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B, Unit - I) 1 Introduction: Milling is a machining process which is performed with a rotary cutter with several cutting edges arranged on the periphery
Notes: Milling Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B, Unit - I) 1 Introduction: Milling is a machining process which is performed with a rotary cutter with several cutting edges arranged on the periphery
Metal Cutting - 5. Content. Milling Characteristics. Parts made by milling Example of Part Produced on a CNC Milling Machine 7.
 Content Metal Cutting - 5 Assoc Prof Zainal Abidin Ahmad Dept. of Manufacturing & Industrial Engineering Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 7. MILLING Introduction Horizontal
Content Metal Cutting - 5 Assoc Prof Zainal Abidin Ahmad Dept. of Manufacturing & Industrial Engineering Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 7. MILLING Introduction Horizontal
bcprecision Devices, Inc. HYDRAULIC ARBORS AND CHUCKS
 UNEQUALED WORK HOLDING ACCURACY for: grinding; balancing; inspection; boring; facing; reaming; drilling; turning; shaving; hobbing and honing b SQUARENESS r CONCENTRICITY f PARALLELISM e ROUNDNESS v ALIGNMENT
UNEQUALED WORK HOLDING ACCURACY for: grinding; balancing; inspection; boring; facing; reaming; drilling; turning; shaving; hobbing and honing b SQUARENESS r CONCENTRICITY f PARALLELISM e ROUNDNESS v ALIGNMENT
The jigs and fixtures are the economical ways to produce a component in mass production system. These are special work holding and tool guiding device
 The jigs and fixtures are the economical ways to produce a component in mass production system. These are special work holding and tool guiding device Quality of the performance of a process largely influenced
The jigs and fixtures are the economical ways to produce a component in mass production system. These are special work holding and tool guiding device Quality of the performance of a process largely influenced
CHAPTER 1- INTRODUCTION TO MACHINING
 CHAPTER 1- INTRODUCTION TO MACHINING LEARNING OBJECTIVES Introduction to Manufacturing, Manufacturing processes Broad classification of Manufacturing processes Kinematics elements involved in metal cutting
CHAPTER 1- INTRODUCTION TO MACHINING LEARNING OBJECTIVES Introduction to Manufacturing, Manufacturing processes Broad classification of Manufacturing processes Kinematics elements involved in metal cutting
MACHINE TOOLS LAB MANUAL. B. Tech III Year - I Semester DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Aurora s Technological And Research Institute
 MACHINE TOOLS LAB MANUAL B. Tech III Year - I Semester NAME : ROLL NO : BRANCH : DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Aurora s Technological And Research Institute Parvathapur, Uppal, Hyderabad-98. 1 MACHINE
MACHINE TOOLS LAB MANUAL B. Tech III Year - I Semester NAME : ROLL NO : BRANCH : DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Aurora s Technological And Research Institute Parvathapur, Uppal, Hyderabad-98. 1 MACHINE
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS SECONDARY EDUCATION CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY. Paper 02 - Technical Proficiency.
 FORM TP 2011094 CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS SECONDARY EDUCATION CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION TEST CODE 01335020 COUNCIL MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Paper 02 - Technical Proficiency 2'h hours MAY/JUNE 2011
FORM TP 2011094 CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS SECONDARY EDUCATION CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION TEST CODE 01335020 COUNCIL MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Paper 02 - Technical Proficiency 2'h hours MAY/JUNE 2011
International Journal of Science and Engineering Research (IJ0SER), Vol 3 Issue 3 March , (P) X
 Design And Optimization Techniques Using In Turning Fixture M Rajmohan 1, K S Sakthivel 1, S Sanjay 1, A Santhosh 1, P Satheesh 2 1 ( UG Student ) 2 (Assistant professor)mechanical Department, Jay Shriram
Design And Optimization Techniques Using In Turning Fixture M Rajmohan 1, K S Sakthivel 1, S Sanjay 1, A Santhosh 1, P Satheesh 2 1 ( UG Student ) 2 (Assistant professor)mechanical Department, Jay Shriram
Drilling. Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL.
 Drilling Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL. The machine used for drilling is called drilling machine. The drilling operation
Drilling Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL. The machine used for drilling is called drilling machine. The drilling operation
NEAT CUTTING & GRINDING OILS
 METALWORKING NEAT CUTTING & GRINDING OILS YOUR ADVANTAGE IN AN INDUSTRIAL WORLD A CHOICE TO SUIT YOUR NEEDS Castrol has a high performance and versatile range of neat oils designed to meet your metalworking
METALWORKING NEAT CUTTING & GRINDING OILS YOUR ADVANTAGE IN AN INDUSTRIAL WORLD A CHOICE TO SUIT YOUR NEEDS Castrol has a high performance and versatile range of neat oils designed to meet your metalworking
Ch. 1 Theory of Metal Cutting
 Ch. 1 Theory of Metal Cutting May 1 Nov - 1 1. Explain types of chips that occur in metal cutting. Why a built up edge on a tool is undesirable and also explain reason behind various chip formation. 4
Ch. 1 Theory of Metal Cutting May 1 Nov - 1 1. Explain types of chips that occur in metal cutting. Why a built up edge on a tool is undesirable and also explain reason behind various chip formation. 4
DIRECTORATE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION DIPLOMA IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. M SCHEME onwards II YEAR IV SEMESTER CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT CENTRE
 DIRECTORATE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION DIPLOMA IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING M SCHEME 2015-2016 onwards II YEAR IV SEMESTER 32042 SPECIAL MACHINES CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT CENTRE Curriculum Development Centre, DOTE.
DIRECTORATE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION DIPLOMA IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING M SCHEME 2015-2016 onwards II YEAR IV SEMESTER 32042 SPECIAL MACHINES CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT CENTRE Curriculum Development Centre, DOTE.
Updated January 2019 METAL CUTTING EQUIPMENT BORING & DRILLING MACHINES GRINDING MACHINES HORIZONTAL LATHES. Page 1 of 7 MACHINE DESCRIPTION 3541.
 METAL CUTTING EQUIPMENT BORING & DRILLING MACHINES JIG BORING 3541.205 BORING, HBM QUILL FEED SPINDLES CNC OR MANUAL 3541.207 DRILLING, NON-NC 3541.215 SENSITIVE VERTICAL DRILLING MACHINES, MANUAL 3541.216
METAL CUTTING EQUIPMENT BORING & DRILLING MACHINES JIG BORING 3541.205 BORING, HBM QUILL FEED SPINDLES CNC OR MANUAL 3541.207 DRILLING, NON-NC 3541.215 SENSITIVE VERTICAL DRILLING MACHINES, MANUAL 3541.216
Researches regarding the superfinishing on flat and cylindrical surfaces of gear pump pinions
 Researches regarding the superfinishing on flat and cylindrical surfaces of gear pump pinions BADEA LEPADATESCU ANISOR NEDELCU Department of Engineering Manufacturing Transilvania University of Brasov,
Researches regarding the superfinishing on flat and cylindrical surfaces of gear pump pinions BADEA LEPADATESCU ANISOR NEDELCU Department of Engineering Manufacturing Transilvania University of Brasov,
DESIGN FOR POLISHING AND PLATING
 DESIGN FOR POLISHING AND PLATING Polishing and plating are generally considered to be a part of finishing process. Polishing processes Conventional polishing In conventional polishing, surface irregularities
DESIGN FOR POLISHING AND PLATING Polishing and plating are generally considered to be a part of finishing process. Polishing processes Conventional polishing In conventional polishing, surface irregularities
College of Forestry 610: Power Tools
 College of Forestry 610: Power Tools Safety Policy & Procedure Manual Section 600: Workshops and Shop Tools Effective: 01 January 2007 Revised: August 2014 PURPOSE The purpose of this section is to provide
College of Forestry 610: Power Tools Safety Policy & Procedure Manual Section 600: Workshops and Shop Tools Effective: 01 January 2007 Revised: August 2014 PURPOSE The purpose of this section is to provide
Milling operations TA 102 Workshop Practice. By Prof.A.chANDRASHEKHAR
 Milling operations TA 102 Workshop Practice By Prof.A.chANDRASHEKHAR Introduction Milling machines are used to produce parts having flat as well as curved shapes. Milling machines are capable of performing
Milling operations TA 102 Workshop Practice By Prof.A.chANDRASHEKHAR Introduction Milling machines are used to produce parts having flat as well as curved shapes. Milling machines are capable of performing
PRODUCTION ENGINEERING LAB II
 Department of Mechanical Engineering LAB MANUAL FOR PRODUCTION ENGINEERING LAB II DEPT. OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 1. SHAPER 1.1 INTRODUCTION The shaper is a reciprocating type of machine tool intended
Department of Mechanical Engineering LAB MANUAL FOR PRODUCTION ENGINEERING LAB II DEPT. OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 1. SHAPER 1.1 INTRODUCTION The shaper is a reciprocating type of machine tool intended
SprutCAM. CAM Software Solution for Your Manufacturing Needs
 SprutCAM SprutCAM is is a CAM system for for NC NC program program generation for machining using; multi-axis milling, milling, turning, turn/mill, turn/mill, Wire Wire EDM numerically EDM numerically
SprutCAM SprutCAM is is a CAM system for for NC NC program program generation for machining using; multi-axis milling, milling, turning, turn/mill, turn/mill, Wire Wire EDM numerically EDM numerically
ELECTRIC DISCHARGE MACHINE
 INTRODUCTION HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT CLASSIFICATION OF MODERN MACHINING PROCESS PROCESS ELECTRICAL DISCHARGE MACHINE (EDM) CONSTRUCTION TYPES OF EDM SINKER EDM WIRE EDM ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT CLASSIFICATION OF MODERN MACHINING PROCESS PROCESS ELECTRICAL DISCHARGE MACHINE (EDM) CONSTRUCTION TYPES OF EDM SINKER EDM WIRE EDM ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES INTRODUCTION
Machining Processes IME 240
 Machining Processes IME 240 Material Removal Processes Machining is the broad term used to describe removal of material from a workpiece Includes Cutting, Abrasive Processes (grinding), Advanced Machining
Machining Processes IME 240 Material Removal Processes Machining is the broad term used to describe removal of material from a workpiece Includes Cutting, Abrasive Processes (grinding), Advanced Machining
SHAPING AND PLANING Shaping and planing
 SHAPING AND PLANING Shaping and planing the simplest of all machine operations Straight line cutting motion with single-point cutting tool creates smooth flat surfaces. Mainly plain surfaces are machined
SHAPING AND PLANING Shaping and planing the simplest of all machine operations Straight line cutting motion with single-point cutting tool creates smooth flat surfaces. Mainly plain surfaces are machined
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6411 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LAB-II (IV SEMESTER MECHANICAL) Regulation 2013 LAB MANUAL 2015-16 OBSERVATION NOTE BOOK ME6411 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LABORATORY
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6411 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LAB-II (IV SEMESTER MECHANICAL) Regulation 2013 LAB MANUAL 2015-16 OBSERVATION NOTE BOOK ME6411 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LABORATORY
Cross Peen Hammer. Introduction. Lesson Objectives. Assumptions
 Introduction In this activity plan students will develop various machining and metalworking skills by building a two-piece steel hammer. This project will introduce basic operations for initial familiarization
Introduction In this activity plan students will develop various machining and metalworking skills by building a two-piece steel hammer. This project will introduce basic operations for initial familiarization
Copyright 2002 Society of Manufacturing Engineers. FUNDAMENTAL MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Gears & Gear Manufacturing NARRATION (VO):
 FUNDAMENTAL MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Gears & Gear Manufacturing SCENE 1. CG: Gear Finishing Processes white text centered on black SCENE 2. tape 783, 01:12:24-01:17:06 peter carey narration tape 769, 05:14:02-05:14:30
FUNDAMENTAL MANUFACTURING PROCESSES Gears & Gear Manufacturing SCENE 1. CG: Gear Finishing Processes white text centered on black SCENE 2. tape 783, 01:12:24-01:17:06 peter carey narration tape 769, 05:14:02-05:14:30
11/15/2009. There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate
 s Geometry & Milling Processes There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate All three of these will be discussed in later lessons What is a cutting
s Geometry & Milling Processes There are three factors that make up the cutting conditions: cutting speed depth of cut feed rate All three of these will be discussed in later lessons What is a cutting
Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Hole Making Part A (Lathe Operations, Boring, Reaming, Tapping)
 1 Manufacturing Processes (2), IE-352 Ahmed M El-Sherbeeny, PhD Spring 2017 Manufacturing Engineering Technology in SI Units, 6 th Edition Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Hole Making Part A (Lathe Operations,
1 Manufacturing Processes (2), IE-352 Ahmed M El-Sherbeeny, PhD Spring 2017 Manufacturing Engineering Technology in SI Units, 6 th Edition Chapter 23: Machining Processes: Hole Making Part A (Lathe Operations,
