1. The Lathe. 1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Main parts of a lathe
|
|
|
- Eunice Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. The Lathe 1.1 Introduction Lathe is considered as one of the oldest machine tools and is widely used in industries. It is called as mother of machine tools. It is said that the first screw cutting lathe was developed by an Englishman named Henry Maudslay in the year Modern high speed, heavy duty lathes are developed based on this machine. The primary task of a lathe is to generate cylindrical workpieces. The process of machining a workpiece to the required shape and size by moving the cutting tool either parallel or perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the workpiece is known as turning. In this process, excess unwanted metal is removed. The machine tool useful in performing plain turning, taper turning, thread cutting, chamfering and knurling by adopting the above method is known as lathe. 1.2 Main parts of a lathe Every individual part performs an important task in a lathe. Some important parts of a lathe are listed below: Bed 1. Bed 2. Headstock 3. Spindle 4. Tailstock 5. Carriage a. Saddle b. Apron c. Cross-slide d. Compound rest e. Compound slide f. Tool post 6. Feed mechanism 7. Lead screw 8. Feed rod Bed is mounted on the legs of the lathe which are bolted to the floor. It forms the base of the machine. It is made of cast iron and its top surface is machined accurately and precisely. Headstock of the lathe is located at the extreme left of the bed and the tailstock at the right extreme. Carriage is positioned in between the headstock and tailstock and slides on the bed guide ways. Fig 1 : Lathe bed with V shaped guideway noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 1
2 The top of the bed has flat or V shaped guide ways. The tailstock and the carriage slides on these guide ways. Inverted V shaped guide ways are useful in better guide and accurate alignment of saddle and tailstock. The metal burrs resulting from turning operation automatically fall through. Flat bed guide ways can be found in older machine tools. It is useful in heavy machines handling large workpieces. But then the accuracy is not high Headstock Headstock is mounted permanently on the inner guide ways at the left hand side of the leg bed. The headstock houses a hollow spindle and the mechanism for driving the spindle at multiple speeds. The headstock will have any of the following arrangements for driving and altering the spindle speeds: (i) Stepped cone pulley drive (ii) Back gear drive (iii) All gear drive Fig 3: All gear drive Fig 2: Stepped cone pulley with back gear Spindle The spindle rotates on two large bearings housed on the headstock casting. A hole extends through the spindle so that a long bar stock may be passed through the hole. The front end of the spindle is threaded on which chucks, faceplate, driving plate and catch plate are screwed. The front end of the hole is tapered to receive live centre which supports the work. On the other side of the spindle, a gear known as a spindle gear is fitted. Through this gear, tumbler gears and a main gear train, the power is transmitted to the gear on the Fig 4: Head stock spindle leadscrew. noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 2
3 1.2.4 Tailstock Tailstock is located on the inner guide ways at the right side of the bed opposite to the headstock. The body of the tailstock is bored and houses the tailstock spindle. The spindle moves front and back inside the hole. The spindle has a taper hole to receive the dead centre or shanks of tools like drill or reamer. If the tailstock hand wheel is rotated in the clockwise direction, the spindle advances. The spindle will be withdrawn inside the hole, if the hand wheel is rotated in anticlockwise direction. The main uses of tailstock are: 1. It supports the other end of the long workpiece when it is machined between centres. 2. It is useful in holding tools like drills, reamers and taps when performing drilling, reaming and tapping Carriage Carriage is located between the headstock and tailstock on the lathe bed guide ways. It can be moved along the bed either towards or away from the headstock. It has several parts to support, move and control the cutting tool. The parts of the carriage are: a) saddle b) apron c) cross-slide d) compound rest e) compound slide f) tool post Saddle: It is an H shaped casting. It connects the pair of bed guide ways like a bridge. It fits over the bed and slides along the bed between headstock and tailstock. The saddle or the entire carriage can be moved by providing hand feed or automatic feed. Fig 5: Tail stock Fig 6: Carriage noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 3
4 Cross slide: Cross-slide is situated on the saddle and slides on the dovetail guide ways at right angles to the bed guide ways. It carries compound rest, compound slide and tool post. Cross slide hand wheel is rotated to move it at right angles to the lathe axis. It can also be power driven. The cross slide hand wheel is graduated on its rim to enable to give known amount of feed as accurate as 0.05mm. Compound rest: Compound rest is a part which connects cross slide and compound slide. It is mounted on the crossslide by tongue and groove joint. It has a circular base on which angular graduations are marked. The compound rest can be swivelled to the required angle while turning tapers. A top slide known as compound slide is attached to the compound rest by dove tail joint. The tool post is situated on the compound slide. Tool post: This is located on top of the compound slide. It is used to hold the tools rigidly. Tools are selected according to the type of operation and mounted on the tool post and adjusted to a convenient working position. There are different types of tool posts and they are: 1. Single way tool post 3. Four way tool post 4. Quick change tool post Single way tool post The tool is held by a screw in this tool post. It consists of a round bar with a slotted hole in the centre for fixing the tool by means of a setscrew. A concave ring and a convex rocker are used to set the height of the tool point at the right position. The tool fits on the flat top surface of the rocker. The tool post is not rigid enough for heavy works as only one clamping screw is used to clamp the tool. Four way tool post This type of tool post can accommodate four tools at a time on the four open sides of the post. The tools are held in position by separate screws and a locking bolt is located at the centre. The required tool may be set for machining by swivelling the tool post. Machining can be completed in a shorter time because the required tools are pre-set. Fig 6: Types of tool posts noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 4
5 1.2.6 Lead screw The leadscrew is a long threaded shaft used as master screw. It is brought into operation during thread cutting to move the carriage to a calculated distance. Mostly leadscrew are Acme threaded. The leadscrew is held by two bearings on the face of the bed. A gear is attached to the lead screw and it is called as gear on leadscrew. A half nut lever is provided in the apron to engage half nuts with the leadscrew Feed rod Feed rod is placed parallel to the leadscrew on the front side of the bed. It is a long shaft which has a keyway along its length. The power is transmitted from the spindle to the feed rod through tumbler gears and a gear train. It is useful in providing feed movement to the carriage except for thread cutting and to move cross-slide. A worm mounted on the feed rod enables the power feed movements. 1.3 Types of lathe Various designs and constructions of lathe have been developed to suit different machining conditions and usage. The following are the different types of lathe: 1. Speed lathe a. Woodworking lathe b. Centering lathe c. Polishing lathe d. Metal spinning lathe 2. Engine lathe a. Belt driven lathe b. Individual motor driven lathe c. Gear head lathe 3. Bench lathe 1.4 Size of a lathe (Specification of Lathe) 4. Tool room lathe 5. Semi automatic lathe a. Capstan lathe b. Turret lathe 6. Automatic lathe 7. Special purpose lathe a. Wheel lathe b. Gap bed lathe c. T lathe The size of a lathe is specified by the following points 1. The length of the bed 2. Maximum distance between live and dead centres. 3. The height of centres from the bed 4. The swing diameter: d. Duplicating lathe The swing diameter over bed - It refers to the largest diameter of the work that will be rotated without touching the bed The swing diameter over carriage - It is the largest diameter of the work that will revolve over the saddle. 5. The bore diameter of the spindle 6. The width of the bed 7. The type of the bed 8. Pitch value of the lead screw 9. Horse power of the motor 10. Number and range of spindle speeds 11. Number of feeds 12. Spindle nose diameter 13. Floor space required 14. The type of the machine noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 5
6 1.5 Work holding devices used in a lathe (accessories) The work holding devices are used to hold and rotate the workpieces along with the spindle. Different work holding devices are used according to the shape, length, diameter and weight of the workpiece and the location of turning on the work. They are: 1. Chucks 5. Carriers 2. Face plate 6. Mandrels 3. Driving plate 7. Centres 4. Catch plate 8. Rests Chucks Workpieces of short length, large diameter and irregular shapes, which can not be mounted between centres, are held quickly and rigidly in chuck. There are different types of chucks namely, Three jaw universal chuck, Four jaw independent chuck, Magnetic chuck, Collet chuck and Combination chuck. Three jaw self-centering chuck The three jaws fitted in the three slots may be made to slide at the same time by an equal amount by rotating any one of the three pinions by a chuck key. This type of chuck is suitable for holding and rotating regular shaped workpieces like round or hexagonal rods about the axis of the lathe. Workpieces of irregular shapes cannot be held by this chuck. The work is held quickly and easily as the three jaws move at the same time. Four jaw independent chuck There are four jaws in this chuck. Each jaw is moved independently by rotating a screw with the help of a chuck key. A particular jaw may be moved according to the shape of the work. Hence this type of chuck can hold woks of irregular shapes. But it requires more time to set the work aligned with the lathe axis. Experienced turners can set the work about the axis quickly. Concentric circles are inscribed on the face of the chuck to enable quick Centering of the workpiece. noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 6
7 Magnetic chuck The holding power of this chuck is obtained by the magnetic flux radiating from the electromagnet placed inside the chuck. Magnets are adjusted inside the chuck to hold or release the work. Workpieces made of magnetic material only are held in this chuck. Very small, thin and light works which can not be held in an ordinary chuck are held in this chuck. Collet chuck Collet chuck has a cylindrical bushing known as collet. It is made of spring steel and has slots cut lengthwise on its circumference. So, it holds the work with more grips. Collet chucks are used in capstan lathes and automatic lathes for holding bar stock in production work Face plate Faceplate is used to hold large, heavy and irregular shaped workpieces which can not be conveniently held between centres. It is a circular disc bored out and threaded to fit to the nose of the lathe spindle. It is provided with radial plain and T slots for holding the work by bolts and clamps. noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 7
8 1.5.3 Driving plate The driving plate is used to drive a workpiece when it is held between centres. It is a circular disc screwed to the nose of the lathe spindle. It is provided with small bolts or pins on its face. Workpieces fitted inside straight tail carriers are held and rotated by driving plates. Fig: Face plate Fig: Driving plate Catch plate When a workpiece is held between centres, the catch plate is used to drive it. It is a circular disc bored and threaded at the centre. Catch plates are designed with U slots or elliptical slots to receive the bent tail of the carrier. Positive drive between the lathe spindle and the workpiece is affected when the workpiece fitted with the carrier fits into the slot of the catch plate Carrier When a workpiece is held and machined between centres, carriers are useful in transmitting the driving force of the spindle to the work by means of driving plates and catch plates. The work is held inside the eye of the carrier and tightened by a screw. Carriers are of two types and they are: 1. Straight tail carrier 2. Bent tail carrier Straight tail carrier is used to drive the work by means of the pin provided in the driving plate. The tail of the bent tail carrier fits into the slot of the catch plate to drive the work. Carrier Catch plate noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 8
9 1.5.6 Mandrel A previously drilled or bored workpiece is held on a mandrel to be driven in a lathe and machined. There are centre holes provided on both faces of the mandrel. The live centre and the dead centre fit into the centre holes. A carrier is attached at the left side of the mandrel. The mandrel gets the drive either through a catch plate or a driving plate. The workpiece rotates along with the mandrel. There are several types of mandrels and they are: 1. Plain mandrel 5. Collar mandrel 2. Step mandrel 6. Cone mandrel 3. Gang mandrel 7. Expansion mandrel Plain mandrel The body of the plain mandrel is slightly tapered to provide proper gripping of the workpiece. The taper will be around 1 to 2mm for a length of 100mm. It is also known as solid mandrel. It is the type mostly commonly used and has wide application. Gang mandrel It has a fixed collar at one end and a movable collar at the threaded end. This mandrel is used to hold a set of hollow workpieces between the two collars by tightening the nut. Screwed mandrel It is threaded at one end and a collar is attached to it. Workpieces having internal threads are screwed on to it against the collar for machining. noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 9
10 Cone mandrel It consists of a solid cone attached to one end of the body and a sliding cone, which can be adjusted by turning a nut at the threaded end. This type is suitable for driving workpieces having different hole diameters Centres Centres are useful in holding the work in a lathe between centres. The shank of a centre has Morse taper on it and the face is conical in shape. There are two types of centres namely (i) Live centre (ii) Dead centre The live centre is fitted on the headstock spindle and rotates with the work. The centre fitted on the tailstock spindle is called dead centre. It is useful in supporting the other end of the work. Centres are made of high carbon steel and hardened and then tempered. So the tip of the centres are wear resistant. Different types of centres are available according to the shape of the work and the operation to be performed. They are: 1. Ordinary centre 2. Ball centre 3. Half centre 4. Tipped centre 5. Pipe centre 6. Revolving centre 7. Inserted type centre Fig : Ordinary centre noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 10
11 Fig: Types of centres Rests A rest is a mechanical device to support a long slender workpiece when it is turned between centres or by a chuck. It is placed at some intermediate point to prevent the workpiece from bending due to its own weight and vibrations setup due to the cutting force. There are two different types of rests 1. Steady rest 2. Follower rest Steady rest Steady rest is made of cast iron. It may be made to slide on the lathe bed ways and clamped at any desired position where the workpiece needs support. It has three jaws. These jaws can be adjusted according to the diameter of the work. Machining is done upon the distance starting from the headstock to the point of support of the rest. One or more steady rests may be used to support the free end of a long work. Follower rest It consists of a C like casting having two adjustable jaws to support the workpiece. The rest is bolted to the back end of the carriage. During machining, it supports the work and moves with the carriage. So, it follows the tool to give continuous support to the work to be able to machine along the entire length of the work. In order to reduce friction between the work and the jaws, proper lubricant should be used. noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 11
12 1.6 Operations performed in a lathe Various operations are performed in a lathe other than plain turning. They are: 1. Facing 7. Undercutting 2. Turning 8. Eccentric turning a. Straight turning 9. Taper turning b. Step turning 10. Thread cutting 3. Chamfering 11. Drilling 4. Grooving 12. Reaming 5. Forming 13. Boring 6. Knurling 14. Tapping Facing Facing is the operation of machining the ends of a piece of work to produce flat surface which is square with the axis. The operation involves feeding the tool perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the work Turning Turning in a lathe is to remove excess material from the workpiece to produce a cylindrical surface of required shape and size. Straight turning The work is turned straight when it is made to rotate about the lathe axis and the tool is fed parallel to the lathe axis. The straight turning produces a cylindrical surface by removing excess metal from the workpieces. Step turning Step turning is the process of turning different surfaces having different diameters. The work is held between centres and the tool is moved parallel to the axis of the lathe. It is also called shoulder turning. noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 12
13 1.6.3 Chamfering Chamfering is the operation of bevelling the extreme end of the workpiece. The form tool used for taper turning may be used for this purpose. Chamfering is an essential operation after thread cutting so that the nut may pass freely on the threaded workpiece Grooving Grooving is the process of cutting a narrow groove on the cylindrical surface of the workpiece. It is often done at end of a thread or adjacent to a shoulder to leave a small margin. The groove may be square, radial or bevelled in shape Forming Forming is a process of turning a convex, concave or any irregular shape. For turning a small length formed surface, a forming tool having cutting edges conforming to the shape required is fed straight into the work Knurling Knurling is the process of embossing a diamond shaped pattern on the surface of the workpiece. The knurling tool holder has one or two hardened steel rollers with edges of required pattern. The tool holder is pressed against the rotating work. The rollers emboss the required pattern. The tool holder is fed automatically to the required length. Knurls are available in coarse, medium and fine pitches. The patterns may be straight, inclined or diamond shaped. The purpose of knurling is 1. To provide an effective gripping surface 2. To provide better appearance to the work 3. To slightly increase the diameter of the work noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 13
14 1.6.7 Undercutting Undercutting is done (i) at the end of a hole (ii) near the shoulder of stepped cylindrical surfaces (iii) at the end of the threaded portion in bolts. It is a process of enlarging the diameter if done internally and reducing the diameter if done externally over a short length. It is useful mainly to make fits perfect. Boring tools and parting tools are used for this operation Taper turning Taper A taper may be defined as a uniform increase or decrease in diameter of a piece of work measured along its length. Taper turning methods 1. Form tool method 2. Compound rest method 3. Tailstock set over method 4. Taper turning attachment method 5. Combined feed method (i) Form tool method A broad nose tool is ground to the required length and angle. It is set on the work by providing feed to the cross-slide. When the tool is fed into the work at right angles to the lathe axis, a tapered surface is generated. This method is limited to turn short lengths of taper only. The length of the taper is shorter than the length of the cutting edge. Less feed is given as the entire cutting edge will be in contact with the work. noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 14
15 (ii) Compound rest method The compound rest of the lathe is attached to a circular base graduated in degrees, which may be swivelled and clamped at any desired angle. The angle of taper is calculated using the formula: where D = Larger diameter d = Smaller diameter l = Length of the taper Ɵ = Half taper angle The compound rest is swivelled to the angle calculated as above and clamped. Feed is given to the compound slide to generate the required taper. (iii) Tailstock set over method Turning taper by the set over method is done by shifting the axis of rotation of the workpiece at an angle to the lathe axis and feeding the tool parallel to the lathe axis. The construction of tailstock is designed to have two parts namely the base and the body. The base is fitted on the bed guide ways and the body having the dead centre can be moved at cross to shift the lathe axis. The amount of set over (s) can be calculated as follows: The dead centre is suitably shifted from its original position to the calculated distance. The work is held between centres and longitudinal feed is given by the carriage to generate the taper. The advantage of this method is that the taper can be turned to the entire length of the work. Taper threads can also be cut by this method. The amount of set over being limited, this method is suitable for turning small tapers (approx. upto 8 ). Internal tapers cannot be done by this method. noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 15
16 (iv) Taper turning by an attachment The taper attachment consists of a bracket which is attached to the rear end of the lathe bed. It supports a guide bar pivoted at the centre. The bar having graduation in degrees may be swivelled on either side of the zero graduation and set at the desired angle to the lathe axis. A guide block is mounted on the guide bar and slides on it. The cross slide is made free from its screw by removing the binder screw. The rear end of the cross slide is tightened with the guide block by means of a bolt. When the longitudinal feed is engaged, the tool mounted on the cross slide will follow the angular path as the guide block will slide on the guide bar set at an angle of the lathe axis. The depth of cut is provided by the compound slide which is set parallel to the cross-slide. The advantage of this method is that long tapers can be machined. As power feed can be employed, the work is completed at a shorter time. The disadvantage of this method is that internal tapers cannot be machined Thread cutting Thread cutting is one of the most important operations performed in a lathe. The process of thread cutting is to produce a helical groove on a cylindrical surface by feeding the tool longitudinally. The job is revolved between centres or by a chuck. The longitudinal feed should be equal to the pitch of the thread to be cut per revolution of the work piece. noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 16
17 1.7 Tools used in a lathe Tools used in a lathe are classified as follows A. According to the construction, the lathe tools are classified into three types 1. Solid tool 2. Brazed tipped tool 3. Tool bit and tool holders B.According to the operation to be performed, the cutting tools are classified as 1. Turning tool 2. Thread cutting tool 3. Facing tool 4. Forming tool 5. Parting tool 6. Grooving tool 7. Boring tool 8. Internal thread cutting tool 9. Knurling tool C. According to the direction of feed movement, the following tools are used 1. Right hand tool 2. Left hand tool 3. Round nose tool Fig : Types of tools noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 17
18 1.8 Cutting Tool Nomenclature It means the systematic naming of the various parts and angles of a cutting tool. 1.9 Cutting tool signature The signature is a sequence of numbers listing the various angles in degrees and the size of the nose radius in mm. This is a standardised numerical method of identification of a tool. The seven elements that comprise signature of a single point cutting tool are always stated in the order as follows: 1. Back rake angle (in degrees) 2. Side rake angle 3. End relief angle 4. Side relief angle 5. End cutting edge angle 6. Side cutting edge angle 7. Nose radius (in mm) noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 18
19 1.10 Cutting speed & Feed Speed can be defined as the distance an object moves in a particular time. The cutting speed of a tool is the speed at which the metal is removed by the tool from the workpiece. In a lathe, the cutting speed is the peripheral speed of the work past the cutting tool expressed in meters per minute. Where d - is the diameter of the work in mm. n - is the r.p.m. of the work. Feed of a cutting tool in a lathe work is the distance that the tool advances for each revolution of the work. It is expressed in mm/revolution Reference: 1. P.Kannaiah and K.L.Narayana Workshop Manual. Scitech Publications, D. Venugopal Basic Engineering Workshops: Pheory and Practice. Arathy Publications, Hajra Choudhary Workshop technology Vol. II 4. G.Sukumaran Basic Engineering Workshops. Link Books, 2003 noushadar76@gmail.com Study of Lathe & Accessories Page 19
Lathes. CADD SPHERE Place for innovation Introduction
 Lathes Introduction Lathe is one of the most versatile and widely used machine tools all over the world. It is commonly known as the mother of all other machine tool. The main function of a lathe is to
Lathes Introduction Lathe is one of the most versatile and widely used machine tools all over the world. It is commonly known as the mother of all other machine tool. The main function of a lathe is to
GENERAL MACHINIST THEORY
 GENERAL MACHINIST THEORY VOCATIONAL EDUCATION HIGHER SECONDARY - SECOND YEAR A Publication under Government of Tamilnadu Distribution of Free Textbook Programme ( NOT FOR SALE ) Untouchability is a sin
GENERAL MACHINIST THEORY VOCATIONAL EDUCATION HIGHER SECONDARY - SECOND YEAR A Publication under Government of Tamilnadu Distribution of Free Textbook Programme ( NOT FOR SALE ) Untouchability is a sin
Lathe is a machine, which removes the metal from a piece of work to the required shape & size HENRY MAUDSLAY
 TURNING MACHINES LATHE Introduction Lathe is a machine, which removes the metal from a piece of work to the required shape & size HENRY MAUDSLAY - 1797 Types of Lathe Engine Lathe The most common form
TURNING MACHINES LATHE Introduction Lathe is a machine, which removes the metal from a piece of work to the required shape & size HENRY MAUDSLAY - 1797 Types of Lathe Engine Lathe The most common form
Turning and Lathe Basics
 Training Objectives After watching the video and reviewing this printed material, the viewer will gain knowledge and understanding of lathe principles and be able to identify the basic tools and techniques
Training Objectives After watching the video and reviewing this printed material, the viewer will gain knowledge and understanding of lathe principles and be able to identify the basic tools and techniques
TURNING BORING TURNING:
 TURNING BORING TURNING: FACING: Machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. Work spins and the single cutting tool does the cutting. Done in Lathe. Single point tool, longitudinal feed. Single
TURNING BORING TURNING: FACING: Machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. Work spins and the single cutting tool does the cutting. Done in Lathe. Single point tool, longitudinal feed. Single
ME MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LABORATORY-I VARUVAN VADIVELAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DHARMAPURI LAB MANUAL
 VARUVAN VADIVELAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DHARMAPURI 636 703 ME 6311 - MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LABORATORY-I REGULATION 2013 LAB MANUAL BRANCH YEAR / SEM MECHANICAL ENGINEERING II YEAR & III SEMESTER D
VARUVAN VADIVELAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DHARMAPURI 636 703 ME 6311 - MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LABORATORY-I REGULATION 2013 LAB MANUAL BRANCH YEAR / SEM MECHANICAL ENGINEERING II YEAR & III SEMESTER D
Trade of Toolmaking Module 2: Turning Unit 1: Machine Controls and Operations Phase 2
 Trade of Toolmaking Module 2: Turning Unit 1: Machine Controls and Operations Phase 2 Published by SOLAS 2014 Unit 1 1 Table of Contents Document Release History... 3 Unit Objective... 4 Introduction...
Trade of Toolmaking Module 2: Turning Unit 1: Machine Controls and Operations Phase 2 Published by SOLAS 2014 Unit 1 1 Table of Contents Document Release History... 3 Unit Objective... 4 Introduction...
ROOP LAL Unit-6 Lathe (Turning) Mechanical Engineering Department
 Notes: Lathe (Turning) Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B) 1 Introduction: In previous Lecture 2, we have seen that with the help of forging and casting processes, we can manufacture machine parts of
Notes: Lathe (Turning) Basic Mechanical Engineering (Part B) 1 Introduction: In previous Lecture 2, we have seen that with the help of forging and casting processes, we can manufacture machine parts of
Lathe Accessories. Work-holding, -supporting, and driving devices
 46-1 Lathe Accessories Divided into two categories Work-holding, -supporting, and driving devices Lathe centers, chucks, faceplates Mandrels, steady and follower rests Lathe dogs, drive plates Cutting-tool-holding
46-1 Lathe Accessories Divided into two categories Work-holding, -supporting, and driving devices Lathe centers, chucks, faceplates Mandrels, steady and follower rests Lathe dogs, drive plates Cutting-tool-holding
Introduction to Machining: Lathe Operation
 Introduction to Machining: Lathe Operation Lathe Operation Lathe The purpose of a lathe is to rotate a part against a tool whose position it controls. It is useful for fabricating parts and/or features
Introduction to Machining: Lathe Operation Lathe Operation Lathe The purpose of a lathe is to rotate a part against a tool whose position it controls. It is useful for fabricating parts and/or features
Typical Parts Made with These Processes
 Turning Typical Parts Made with These Processes Machine Components Engine Blocks and Heads Parts with Complex Shapes Parts with Close Tolerances Externally and Internally Threaded Parts Products and Parts
Turning Typical Parts Made with These Processes Machine Components Engine Blocks and Heads Parts with Complex Shapes Parts with Close Tolerances Externally and Internally Threaded Parts Products and Parts
Lathe. A Lathe. Photo by Curt Newton
 Lathe Photo by Curt Newton A Lathe Labeled Photograph Description Choosing a Cutting Tool Installing a Cutting Tool Positioning the Tool Feed, Speed, and Depth of Cut Turning Facing Parting Drilling Boring
Lathe Photo by Curt Newton A Lathe Labeled Photograph Description Choosing a Cutting Tool Installing a Cutting Tool Positioning the Tool Feed, Speed, and Depth of Cut Turning Facing Parting Drilling Boring
TYPES OF LATHE. Bench lathe It is mounted on bench, and has the same features like engine lathe
 TYPES OF LATHE 1. Speed Lathe a) Wood working b) Centering c) Polishing d) Spinning 2. Engine lathe a) Belt drive b) Individual motor drive c) Gear head lathe 3. Bench lathe 4. Tool room lathe 5. Capstan
TYPES OF LATHE 1. Speed Lathe a) Wood working b) Centering c) Polishing d) Spinning 2. Engine lathe a) Belt drive b) Individual motor drive c) Gear head lathe 3. Bench lathe 4. Tool room lathe 5. Capstan
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology (AUST) Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering
 Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology (AUST) Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering LABORATORY MANUAL For the students of Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering 1 st
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology (AUST) Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering LABORATORY MANUAL For the students of Department of Mechanical and Production Engineering 1 st
Machining. Module 6: Lathe Setup and Operations. (Part 2) Curriculum Development Unit PREPARED BY. August 2013
 Machining Module 6: Lathe Setup and Operations (Part 2) PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 6: Lathe Setup and Operations (Part 2) Module Objectives
Machining Module 6: Lathe Setup and Operations (Part 2) PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 6: Lathe Setup and Operations (Part 2) Module Objectives
Precision made in Germany. As per DIN The heart of a system, versatile and expandable.
 1 Precision made in Germany. As per DIN 8606. The heart of a system, versatile and expandable. Main switch with auto-start protection and emergency off. Precision lathe chuck as per DIN 6386 (Ø 100mm).
1 Precision made in Germany. As per DIN 8606. The heart of a system, versatile and expandable. Main switch with auto-start protection and emergency off. Precision lathe chuck as per DIN 6386 (Ø 100mm).
Chapter 22: Turning and Boring Processes. DeGarmo s Materials and Processes in Manufacturing
 Chapter 22: Turning and Boring Processes DeGarmo s Materials and Processes in Manufacturing 22.1 Introduction Turning is the process of machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. Boring is a
Chapter 22: Turning and Boring Processes DeGarmo s Materials and Processes in Manufacturing 22.1 Introduction Turning is the process of machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. Boring is a
Turning and Related Operations
 Turning and Related Operations Turning is widely used for machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. The workpiece rotates and a longitudinally fed single point cutting tool does the cutting.
Turning and Related Operations Turning is widely used for machining external cylindrical and conical surfaces. The workpiece rotates and a longitudinally fed single point cutting tool does the cutting.
Turning Operations. L a t h e
 Turning Operations L a t h e Turning Operations Machine Tool LATHE Job (workpiece) rotary motion Tool linear motions Mother of Machine Tools Cylindrical and flat surfaces Some Typical Lathe Jobs Turning/Drilling/Grooving/
Turning Operations L a t h e Turning Operations Machine Tool LATHE Job (workpiece) rotary motion Tool linear motions Mother of Machine Tools Cylindrical and flat surfaces Some Typical Lathe Jobs Turning/Drilling/Grooving/
PREVIEW COPY. Table of Contents. Lathes and Attachments...3. Basic Lathe Operations Lesson Five Threads and Threading...73
 Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Lesson Four Lathes and Attachments...3 Basic Lathe Operations...21 Drilling and Boring...39 Reaming...57 Lesson Five Threads and Threading...73 Copyright
Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Lesson Four Lathes and Attachments...3 Basic Lathe Operations...21 Drilling and Boring...39 Reaming...57 Lesson Five Threads and Threading...73 Copyright
The new generation with system accessories. Made in Europe!
 1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Europe! Of cast iron, wide-legged prismatic guide. For vibration-free work even at high loads. Rear flange for mounting the mill/drill head PF 230.
1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Europe! Of cast iron, wide-legged prismatic guide. For vibration-free work even at high loads. Rear flange for mounting the mill/drill head PF 230.
The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany!
 1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany! For face, longitudinal and taper turning, thread-cutting. For machining steel, brass, aluminium and plastic. Mounting flange for fastening
1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany! For face, longitudinal and taper turning, thread-cutting. For machining steel, brass, aluminium and plastic. Mounting flange for fastening
Smt. S. R. PATEL ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dabhi, unjha pin
 EXPERIMENTS IN MANUFACTURING PROCESSES-I Smt. S. R. PATEL ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dabhi, unjha pin- 384 170 Department of MECHANICAL engineering Subject : MANUFACTURING PROCESSES-I Subject code: 131903 Experiments
EXPERIMENTS IN MANUFACTURING PROCESSES-I Smt. S. R. PATEL ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dabhi, unjha pin- 384 170 Department of MECHANICAL engineering Subject : MANUFACTURING PROCESSES-I Subject code: 131903 Experiments
The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany!
 1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany! For face, longitudinal and taper turning, thread-cutting. For machining steel, brass, aluminium and plastic. Mounting flange for fastening
1 The new generation with system accessories. Made in Germany! For face, longitudinal and taper turning, thread-cutting. For machining steel, brass, aluminium and plastic. Mounting flange for fastening
Module 1. Classification of Metal Removal Processes and Machine tools. Version 2 ME IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Classification of Metal Removal Processes and Machine tools Lesson 2 Basic working principle, configuration, specification and classification of machine tools Instructional Objectives At the end
Module 1 Classification of Metal Removal Processes and Machine tools Lesson 2 Basic working principle, configuration, specification and classification of machine tools Instructional Objectives At the end
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN
 LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE: DRILLING. COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGR. ALIYU, S.J Course code: MCE
LANDMARK UNIVERSITY, OMU-ARAN LECTURE NOTE: DRILLING. COLLEGE: COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGR. ALIYU, S.J Course code: MCE
MACHINE TOOLS LAB MANUAL. B. Tech III Year - I Semester DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Aurora s Technological And Research Institute
 MACHINE TOOLS LAB MANUAL B. Tech III Year - I Semester NAME : ROLL NO : BRANCH : DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Aurora s Technological And Research Institute Parvathapur, Uppal, Hyderabad-98. 1 MACHINE
MACHINE TOOLS LAB MANUAL B. Tech III Year - I Semester NAME : ROLL NO : BRANCH : DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Aurora s Technological And Research Institute Parvathapur, Uppal, Hyderabad-98. 1 MACHINE
Various other types of drilling machines are available for specialized jobs. These may be portable, bench type, multiple spindle, gang, multiple
 Drilling The process of making holes is known as drilling and generally drilling machines are used to produce the holes. Drilling is an extensively used process by which blind or though holes are originated
Drilling The process of making holes is known as drilling and generally drilling machines are used to produce the holes. Drilling is an extensively used process by which blind or though holes are originated
MACHINE TOOLS LAB LABORATORY MANUAL
 Vanjari Seethaiah Memorial Engineering College Patancheru, Medak MACHINE TOOLS LAB LABORATORY MANUAL Department of Mechanical Engineering PREFACE Industrial Revolution has given man a lot many luxuries,
Vanjari Seethaiah Memorial Engineering College Patancheru, Medak MACHINE TOOLS LAB LABORATORY MANUAL Department of Mechanical Engineering PREFACE Industrial Revolution has given man a lot many luxuries,
MACHINING PROCESSES: TURNING AND HOLE MAKING. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba 1
 MACHINING PROCESSES: TURNING AND HOLE MAKING Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba 1 HoweWork Assignment Due Wensday 7/7/2010 1. Estimate the machining time required to rough cut a 0.5 m long annealed copper alloy round
MACHINING PROCESSES: TURNING AND HOLE MAKING Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba 1 HoweWork Assignment Due Wensday 7/7/2010 1. Estimate the machining time required to rough cut a 0.5 m long annealed copper alloy round
PREVIEW COPY. Table of Contents. Lesson One Machining Cylindrical Shapes...3. Lesson Two Drilling, Reaming, and Honing...21
 Table of Contents Lesson One Machining Cylindrical Shapes...3 Lesson Two Drilling, Reaming, and Honing...21 Lesson Three Lesson Four Machining Flat Surfaces...37 Determining Tolerances and Finishes...53
Table of Contents Lesson One Machining Cylindrical Shapes...3 Lesson Two Drilling, Reaming, and Honing...21 Lesson Three Lesson Four Machining Flat Surfaces...37 Determining Tolerances and Finishes...53
TU-3008G-16M - Opti-Turn Lathe & Mill Drill Combination Package Deal 300 x 700mm Included BF-16AV Mill Head
 TU-3008G-16M - Opti-Turn Lathe & Mill Drill Combination Package Deal 300 x 700mm Included BF-16AV Mill Head Package Deal Ex GST Inc GST $3,980.00 $4,577.00 Package Contents - SAVE $402.50 (Inc) 1 x L691
TU-3008G-16M - Opti-Turn Lathe & Mill Drill Combination Package Deal 300 x 700mm Included BF-16AV Mill Head Package Deal Ex GST Inc GST $3,980.00 $4,577.00 Package Contents - SAVE $402.50 (Inc) 1 x L691
TU-3008G-20M - Opti-Turn Lathe & Mill Drill Combination Package Deal 300 x 700mm Included BF-20AV Mill Head
 TU-3008G-20M - Opti-Turn Lathe & Mill Drill Combination Package Deal 300 x 700mm Included BF-20AV Mill Head Package Deal Ex GST Inc GST $3,850.00 $4,235.00 Package Contents - SAVE $209.00 (Inc) 1 x L691
TU-3008G-20M - Opti-Turn Lathe & Mill Drill Combination Package Deal 300 x 700mm Included BF-20AV Mill Head Package Deal Ex GST Inc GST $3,850.00 $4,235.00 Package Contents - SAVE $209.00 (Inc) 1 x L691
Motor Power (kw / hp): Voltage / Amperage (V / amp): Shipping Dimensions (L x W x H) (cm): Nett Weight (kg): Features
 AL-356V - Centre Lathe 356 x 1000mm Turning Capacity - 51mm Spindle Bore Includes Digital Readout, Quick Change Toolpost & Electronic Variable Speed With Digital Readout Ex GST Inc GST $7,150.00 $7,865.00
AL-356V - Centre Lathe 356 x 1000mm Turning Capacity - 51mm Spindle Bore Includes Digital Readout, Quick Change Toolpost & Electronic Variable Speed With Digital Readout Ex GST Inc GST $7,150.00 $7,865.00
Build a Drill Press Vise
 Youth Explore Trades Skills Introduction This activity plan will develop the student s machining and metalworking skills as they fabricate a multi-piece steel vise. The project will encompass basic lathe
Youth Explore Trades Skills Introduction This activity plan will develop the student s machining and metalworking skills as they fabricate a multi-piece steel vise. The project will encompass basic lathe
Product Brochure For L682D. Description. Features. Auckland: (09)
 AL-336D DELUXE - Centre Lathe 300 x 900mm Turning Capacity Includes Digital Readout, Quick Change Toolpost, Leadscrew Covers, Foot Brake & Cabinet Stand Ex GST Inc GST $5,200.00 $5,980.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL:
AL-336D DELUXE - Centre Lathe 300 x 900mm Turning Capacity Includes Digital Readout, Quick Change Toolpost, Leadscrew Covers, Foot Brake & Cabinet Stand Ex GST Inc GST $5,200.00 $5,980.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL:
AL-320G - Bench Lathe, Stand & Tooling Package Deal 320 x 600mm Turning Capacity
 AL-320G - Bench Lathe, Stand & Tooling Package Deal 320 x 600mm Turning Capacity Ex GST Inc GST $3,200.00 $3,680.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres (mm): Spindle Bore (mm):
AL-320G - Bench Lathe, Stand & Tooling Package Deal 320 x 600mm Turning Capacity Ex GST Inc GST $3,200.00 $3,680.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres (mm): Spindle Bore (mm):
Summer Junior Fellowship Experience at LUMS. Maliha Manzoor 13 June 15 July, 2011 LUMS Summer Internship
 Summer Junior Fellowship Experience at LUMS Maliha Manzoor 13 June 15 July, 2011 LUMS Summer Internship Internship Schedule June 13-17: 2D and 3D drawings in AutoCAD June 20-24: 2D and 3D drawings in AutoCAD
Summer Junior Fellowship Experience at LUMS Maliha Manzoor 13 June 15 July, 2011 LUMS Summer Internship Internship Schedule June 13-17: 2D and 3D drawings in AutoCAD June 20-24: 2D and 3D drawings in AutoCAD
STEEL RULE. Stock TRY SQUARE
 FITTING INTRODUCTION Fitting consists of a handwork involved in fitting together components usually performed at a bench equipped with a vice and hand tools. The matting components have a close relation
FITTING INTRODUCTION Fitting consists of a handwork involved in fitting together components usually performed at a bench equipped with a vice and hand tools. The matting components have a close relation
TM-1960G - Centre Lathe 480 x 1500mm Turning Capacity - 80mm Spindle Bore Includes Digital Readout
 TM-1960G - Centre Lathe 480 x 1500mm Turning Capacity - 80mm Spindle Bore Includes Digital Readout Ex GST Inc GST $23,900.00 $27,485.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres
TM-1960G - Centre Lathe 480 x 1500mm Turning Capacity - 80mm Spindle Bore Includes Digital Readout Ex GST Inc GST $23,900.00 $27,485.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres
AL Centre Lathe 300 x 900mm Turning Capacity Includes Cabinet Stand
 AL-336 - Centre Lathe 300 x 900mm Turning Capacity Includes Cabinet Stand Ex GST Inc GST $4,150.00 $4,565.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: L682 AL-336 Swing Over Bed (mm): 300 Distance Between Centres (mm): 900 Spindle
AL-336 - Centre Lathe 300 x 900mm Turning Capacity Includes Cabinet Stand Ex GST Inc GST $4,150.00 $4,565.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: L682 AL-336 Swing Over Bed (mm): 300 Distance Between Centres (mm): 900 Spindle
TU-3008G - Opti-Turn Bench Lathe 300 x 700mm Turning Capacity Geared Head-Stock & Enclosed Gearbox
 TU-3008G - Opti-Turn Bench Lathe 300 x 700mm Turning Capacity Geared Head-Stock & Enclosed Gearbox Ex GST Inc GST $3,460.00 $3,979.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres (mm):
TU-3008G - Opti-Turn Bench Lathe 300 x 700mm Turning Capacity Geared Head-Stock & Enclosed Gearbox Ex GST Inc GST $3,460.00 $3,979.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres (mm):
SECTION 10: PARTS. Headstock
 33 32 31 30 7 SECTION 10: PARTS 34 23 36 22 15 14 12 35 37 48 39 41 42 50 40 25 38 38 26 39 42 44 41 25 26 40 51 43 52 10 5 53 9 4 1 27 2 21 19 20 Headstock 8 16 11 17 18 14 13 7 6 45 47 46 3 1 P0768001
33 32 31 30 7 SECTION 10: PARTS 34 23 36 22 15 14 12 35 37 48 39 41 42 50 40 25 38 38 26 39 42 44 41 25 26 40 51 43 52 10 5 53 9 4 1 27 2 21 19 20 Headstock 8 16 11 17 18 14 13 7 6 45 47 46 3 1 P0768001
Precision & Heavy Duty Machining
 High Speed Precision Lathes Large capacity, Powerful, Universal & Precision ATRUMP 18, 21 and 25" Series Lathes have just the right amount of engineering to afford simplicity of operation, coupled with
High Speed Precision Lathes Large capacity, Powerful, Universal & Precision ATRUMP 18, 21 and 25" Series Lathes have just the right amount of engineering to afford simplicity of operation, coupled with
UNIT 4: (iii) Illustrate the general kinematic system of drilling machine and explain its working principle
 UNIT 4: Drilling machines: Classification, constructional features, drilling & related operations, types of drill & drill bit nomenclature, drill materials. Instructional Objectives At the end of this
UNIT 4: Drilling machines: Classification, constructional features, drilling & related operations, types of drill & drill bit nomenclature, drill materials. Instructional Objectives At the end of this
Review on Design of Jig and Fixture for Turning on Lathe
 Review on Design of Jig and Fixture for Turning on Lathe Gulam Shaikh 1, Siddiki Arshadali 2, Shaikh Masood 3, Thakur Aditya 4, Juberbhai Mansuri 5 1 Theem College of engineering, shaikhgulam45@gmail.com
Review on Design of Jig and Fixture for Turning on Lathe Gulam Shaikh 1, Siddiki Arshadali 2, Shaikh Masood 3, Thakur Aditya 4, Juberbhai Mansuri 5 1 Theem College of engineering, shaikhgulam45@gmail.com
MACHINE TOOL ACCESSORIES
 VERTICAL 5-C COLLET VISE SERIES 344: VERTICAL 3-C COLLET VISE SERIES 344: : 2-1/2 x 7-3/4 Height: 4 Small movement of lever opens or closes collet. 2030000 CAM OPERATED 5-C HORIZONTAL/VERTICAL COLLET FIXTURE
VERTICAL 5-C COLLET VISE SERIES 344: VERTICAL 3-C COLLET VISE SERIES 344: : 2-1/2 x 7-3/4 Height: 4 Small movement of lever opens or closes collet. 2030000 CAM OPERATED 5-C HORIZONTAL/VERTICAL COLLET FIXTURE
AL-960B - Centre Lathe 305 x 925mm Turning Capacity Includes Cabinet Stand
 AL-960B - Centre Lathe 305 x 925mm Turning Capacity Includes Cabinet Stand Ex GST Inc GST $4,690.00 $5,159.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres (mm): Spindle Bore (mm): Swing
AL-960B - Centre Lathe 305 x 925mm Turning Capacity Includes Cabinet Stand Ex GST Inc GST $4,690.00 $5,159.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres (mm): Spindle Bore (mm): Swing
Machining. Module 5: Lathe Setup and Operations. (Part 1) Curriculum Development Unit PREPARED BY. August 2013
 Machining Module 5: Lathe Setup and Operations (Part 1) PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 5: Lathe Setup and Operations (Part 1) Module Objectives
Machining Module 5: Lathe Setup and Operations (Part 1) PREPARED BY Curriculum Development Unit August 2013 Applied Technology High Schools, 2013 Module 5: Lathe Setup and Operations (Part 1) Module Objectives
Other Lathe Operations
 Chapter 15 Other Lathe Operations LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, students will be able to: Safely set up and operate a lathe using various work-holding devices. Properly set up steady
Chapter 15 Other Lathe Operations LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, students will be able to: Safely set up and operate a lathe using various work-holding devices. Properly set up steady
AL-960B - Centre Lathe 305 x 925mm Turning Capacity Includes Digital Readout & Cabinet Stand
 AL-960B - Centre Lathe 305 x 925mm Turning Capacity Includes Digital Readout & Cabinet Stand Ex GST Inc GST $5,690.00 $6,259.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres (mm): Spindle
AL-960B - Centre Lathe 305 x 925mm Turning Capacity Includes Digital Readout & Cabinet Stand Ex GST Inc GST $5,690.00 $6,259.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres (mm): Spindle
SECTION 10: PARTS. Headstock
 33 32 31 30 7 SECTION 10: PARTS 34 23 36 22 15 14 12 35 37 48 39 41 42 50 40 25 38 38 26 39 42 44 41 25 26 40 51 43 52 10 5 53 9 4 1 27 2 21 19 20 Headstock 8 16 11 17 18 14 13 7 6 45 47 46 3 1 P0768001
33 32 31 30 7 SECTION 10: PARTS 34 23 36 22 15 14 12 35 37 48 39 41 42 50 40 25 38 38 26 39 42 44 41 25 26 40 51 43 52 10 5 53 9 4 1 27 2 21 19 20 Headstock 8 16 11 17 18 14 13 7 6 45 47 46 3 1 P0768001
PREVIEW COPY. Table of Contents. Lathe Setup and Workpiece Preparation...3. Lesson Two Rough Turning and Finish Turning...19
 Table of Contents Lesson One Lathe Setup and Workpiece Preparation...3 Lesson Two Rough Turning and Finish Turning...19 Lesson Three Lesson Four Boring and Counterboring...35 Cutting Internal Threads and
Table of Contents Lesson One Lathe Setup and Workpiece Preparation...3 Lesson Two Rough Turning and Finish Turning...19 Lesson Three Lesson Four Boring and Counterboring...35 Cutting Internal Threads and
Screws. Introduction. 1. Nuts, bolts and screws used to clamp things together. Screws are used for two purposes:
 Screws Introduction Screws are used for two purposes: 1. To clamp things together. 2. To control motion. 1. Nuts, bolts and screws used to clamp things together. Nuts, bolts and screws that are used for
Screws Introduction Screws are used for two purposes: 1. To clamp things together. 2. To control motion. 1. Nuts, bolts and screws used to clamp things together. Nuts, bolts and screws that are used for
Special reamers. Figure N 1 Reamer with descending cutting edges in carbide (Cerin)
 Special reamers There is a wide category of special reamers, ie non-standard, that are suitable to address particular problems encountered in the finishing holes, both for maintenance of individual pieces
Special reamers There is a wide category of special reamers, ie non-standard, that are suitable to address particular problems encountered in the finishing holes, both for maintenance of individual pieces
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY
 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT V Machine Tools Milling cutters Classification of milling cutters according to their design HSS cutters: Many cutters like end mills, slitting cutters, slab cutters, angular
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT V Machine Tools Milling cutters Classification of milling cutters according to their design HSS cutters: Many cutters like end mills, slitting cutters, slab cutters, angular
Cross Peen Hammer. Introduction. Lesson Objectives. Assumptions
 Introduction In this activity plan students will develop various machining and metalworking skills by building a two-piece steel hammer. This project will introduce basic operations for initial familiarization
Introduction In this activity plan students will develop various machining and metalworking skills by building a two-piece steel hammer. This project will introduce basic operations for initial familiarization
THREAD CUTTING & FORMING
 THREAD CUTTING & FORMING Threading, Thread Cutting and Thread Rolling: Machining Threads on External Diameters (shafts) Tapping: Machining Threads on Internal Diameters (holes) Size: Watch to 10 shafts
THREAD CUTTING & FORMING Threading, Thread Cutting and Thread Rolling: Machining Threads on External Diameters (shafts) Tapping: Machining Threads on Internal Diameters (holes) Size: Watch to 10 shafts
HAFCO METALMASTER AL-335. Centre Lathe. 300 x 910mm Turning Capacity. Product Brochure
 Product Brochure L183 HAFCO METALMASTER AL-335 Centre Lathe 300 x 910mm Turning Capacity Page 1 of 5 Specifications & Prices are subject to change without notification - 2018-10-08 L183.pdf Headstock Speed
Product Brochure L183 HAFCO METALMASTER AL-335 Centre Lathe 300 x 910mm Turning Capacity Page 1 of 5 Specifications & Prices are subject to change without notification - 2018-10-08 L183.pdf Headstock Speed
Chapter 23 Drilling and Hole Making Processes. Materials Processing. Hole Making Processes. MET Manufacturing Processes
 MET 33800 Manufacturing Processes Chapter 23 Drilling and Hole Making Processes Before you begin: Turn on the sound on your computer. There is audio to accompany this presentation. Materials Processing
MET 33800 Manufacturing Processes Chapter 23 Drilling and Hole Making Processes Before you begin: Turn on the sound on your computer. There is audio to accompany this presentation. Materials Processing
TOP WORK ISO 9001.CE UNIVERSAL CUTTER & TOOL GRINDER
 TOP WORK ISO 9001.CE UNIVERSAL CUTTER Precise ball groove of conformation Inclination of Wheelhead The wheelhead can easily tilt up to ±15 degrees, with a 360-degrees swivel on the horizontal plane. The
TOP WORK ISO 9001.CE UNIVERSAL CUTTER Precise ball groove of conformation Inclination of Wheelhead The wheelhead can easily tilt up to ±15 degrees, with a 360-degrees swivel on the horizontal plane. The
CL-38A - Centre Lathe 410 x 1000mm Turning Capacity - 52mm Spindle Bore Includes Digital Readout & Quick Change Toolpost
 CL-38A - Centre Lathe 410 x 1000mm Turning Capacity - 52mm Spindle Bore Includes Digital Readout & Quick Change Toolpost Ex GST Inc GST $9,490.00 $10,439.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance
CL-38A - Centre Lathe 410 x 1000mm Turning Capacity - 52mm Spindle Bore Includes Digital Readout & Quick Change Toolpost Ex GST Inc GST $9,490.00 $10,439.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance
IS THIS HAPPENING IN YOUR TOOL ROOM?
 FIFTY YEARS EXPERIENCE IN MANUFACTURING ACCURATE HIGH SPEED TOOL ROOM LATHES IS EMBODIED IN THIS MODERN MACHINE C IS THIS HAPPENING IN YOUR TOOL ROOM? LOSE observation in a tool room will reveal the use
FIFTY YEARS EXPERIENCE IN MANUFACTURING ACCURATE HIGH SPEED TOOL ROOM LATHES IS EMBODIED IN THIS MODERN MACHINE C IS THIS HAPPENING IN YOUR TOOL ROOM? LOSE observation in a tool room will reveal the use
OPTIMUM TU-3008G. Opti-Turn Bench Lathe. 300 x 700mm Turning Capacity. Product Brochure
 Product Brochure L691 OPTIMUM TU-3008G Opti-Turn Bench Lathe 300 x 700mm Turning Capacity Page 1 of 5 Specifications & Prices are subject to change without notification - 2018-10-30 L691.pdf Right Front
Product Brochure L691 OPTIMUM TU-3008G Opti-Turn Bench Lathe 300 x 700mm Turning Capacity Page 1 of 5 Specifications & Prices are subject to change without notification - 2018-10-30 L691.pdf Right Front
Drilling. Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL.
 Drilling Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL. The machine used for drilling is called drilling machine. The drilling operation
Drilling Drilling is the operation of producing circular hole in the work-piece by using a rotating cutter called DRILL. The machine used for drilling is called drilling machine. The drilling operation
OD1644 MILLING MACHINE OPERATIONS
 SUBCOURSE OD1644 MILLING MACHINE OPERATIONS EDITION 8 US ARMY WARRANT OFFICER ADVANCED COURSE MOS/SKILL LEVEL: 441A MILLING MACHINE OPERATIONS SUBCOURSE NO. OD1644 EDITION 8 US Army Correspondence Course
SUBCOURSE OD1644 MILLING MACHINE OPERATIONS EDITION 8 US ARMY WARRANT OFFICER ADVANCED COURSE MOS/SKILL LEVEL: 441A MILLING MACHINE OPERATIONS SUBCOURSE NO. OD1644 EDITION 8 US Army Correspondence Course
HAFCO METALMASTER AL-336. Centre Lathe. 300 x 900mm Turning Capacity. Product Brochure
 Product Brochure L682 HAFCO METALMASTER AL-336 Centre Lathe 300 x 900mm Turning Capacity Page 1 of 5 Specifications & Prices are subject to change without notification - 2018-10-08 L682.pdf Headstock Metric
Product Brochure L682 HAFCO METALMASTER AL-336 Centre Lathe 300 x 900mm Turning Capacity Page 1 of 5 Specifications & Prices are subject to change without notification - 2018-10-08 L682.pdf Headstock Metric
 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? 2. How chip formation occurs in metal cutting? 3. What is
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? 2. How chip formation occurs in metal cutting? 3. What is
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MACHINE SHOP FACILITIES AND PRACTICES Prepared by Mike Allen July 31, 2003 Edited by Scott Morton February 18, 2004
 1 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MACHINE SHOP FACILITIES AND PRACTICES Prepared by Mike Allen July 31, 2003 Edited by Scott Morton February 18, 2004 I. OBJECTIVE To provide an overview and basic knowledge of the
1 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING MACHINE SHOP FACILITIES AND PRACTICES Prepared by Mike Allen July 31, 2003 Edited by Scott Morton February 18, 2004 I. OBJECTIVE To provide an overview and basic knowledge of the
March weeks. surcharge for
 March weeks valid until 31.03.2012 all quoted prices are incl. 19% VAT for deliveries in the EU countries to customers with a valid VAT-no. and for deliveries in not EU member countries the VAT is not
March weeks valid until 31.03.2012 all quoted prices are incl. 19% VAT for deliveries in the EU countries to customers with a valid VAT-no. and for deliveries in not EU member countries the VAT is not
BUILD YOUR OWN MACHINE TOOLS CASTINGS
 BUILD YOUR OWN MACHINE TOOLS CASTINGS We Supply The LATHES - SHAPERS - MILLING MACHINES No. 2 Bench Milling Machine with Overarm Constructed From One of Our Castings Sets. Not Counting Labor This Milling
BUILD YOUR OWN MACHINE TOOLS CASTINGS We Supply The LATHES - SHAPERS - MILLING MACHINES No. 2 Bench Milling Machine with Overarm Constructed From One of Our Castings Sets. Not Counting Labor This Milling
TU-2004V - Opti-Turn Bench Lathe 200 x 300mm Turning Capacity Electronic Variable Speeds
 TU-2004V - Opti-Turn Bench Lathe 200 x 300mm Turning Capacity Electronic Variable Speeds Ex GST Inc GST $1,150.00 $1,265.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres (mm): Spindle
TU-2004V - Opti-Turn Bench Lathe 200 x 300mm Turning Capacity Electronic Variable Speeds Ex GST Inc GST $1,150.00 $1,265.00 ORDER CODE: MODEL: Swing Over Bed (mm): Distance Between Centres (mm): Spindle
FLAT BED CNC LATHE. The Most Economical, User Friendly, Yet Highly Capable CNC Lathe Available!
 FLAT BED CNC LATHE The Most Economical, User Friendly, Yet Highly Capable CNC Lathe Available! Safe, Easy Operation And High Performance Are The Result Of Ingenuity And Quality Workmanship The extended
FLAT BED CNC LATHE The Most Economical, User Friendly, Yet Highly Capable CNC Lathe Available! Safe, Easy Operation And High Performance Are The Result Of Ingenuity And Quality Workmanship The extended
SECTION 9: PARTS. Headstock A 126A 127A-1 REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
 SECTION 9: PARTS Headstock 120 121 113 115 112 111 110 109 108 105 106 107 135 101 119A 121 120 118 114 115 107 106 104 123 122 118 114 126A 105 126 103 102 126B 127A-1 131 127A 124 133 134 126C 129 130
SECTION 9: PARTS Headstock 120 121 113 115 112 111 110 109 108 105 106 107 135 101 119A 121 120 118 114 115 107 106 104 123 122 118 114 126A 105 126 103 102 126B 127A-1 131 127A 124 133 134 126C 129 130
no mm no Dividers with scriber 150 mm NEW Square wedge-shaped knife edges on the length side
 Summer Promotion valid until 30.06.2013 all quoted prices are incl. VAT for deliveries to EU countries to customers with valid VAT-no. and for deliveries in non EU member countries the VAT is not applicable
Summer Promotion valid until 30.06.2013 all quoted prices are incl. VAT for deliveries to EU countries to customers with valid VAT-no. and for deliveries in non EU member countries the VAT is not applicable
TU-1503V - Opti-Turn Bench Lathe - Mini 150 x 300mm Turning Capacity Electronic Variable Speeds Ex GST Inc GST $ $908.50
 TU-1503V - Opti-Turn Bench Lathe - Mini 150 x 300mm Turning Capacity Electronic Variable Speeds Ex GST Inc GST $790.00 $908.50 ORDER CODE: L685 MODEL: TU-1503V Swing Over Bed (mm): 150 Distance Between
TU-1503V - Opti-Turn Bench Lathe - Mini 150 x 300mm Turning Capacity Electronic Variable Speeds Ex GST Inc GST $790.00 $908.50 ORDER CODE: L685 MODEL: TU-1503V Swing Over Bed (mm): 150 Distance Between
ACCESSORIES.
 Rotary, Dividing, & Cross Tables 166 Indexes 167 Dividing Heads 168 Screw Jack Sets 168 Angle Plates & V-Blocks 169 Quick Change Tool Posts & 170-171 CNC Tool Holder Bushings 171 Lathe Chucks 172-177 www.sowatool.com
Rotary, Dividing, & Cross Tables 166 Indexes 167 Dividing Heads 168 Screw Jack Sets 168 Angle Plates & V-Blocks 169 Quick Change Tool Posts & 170-171 CNC Tool Holder Bushings 171 Lathe Chucks 172-177 www.sowatool.com
An Adjustable Threading Feed Attachment for a Lathe Without Metric Threading Capability, by Ted Clarke
 An Adjustable Threading Feed Attachment for a Lathe Without Metric Threading Capability by Ted Clarke Metric pitch threads, with the exception of the Royal Microscopical Society (RMS) 36 threads per inch
An Adjustable Threading Feed Attachment for a Lathe Without Metric Threading Capability by Ted Clarke Metric pitch threads, with the exception of the Royal Microscopical Society (RMS) 36 threads per inch
QLD Schools / TAFE - AL-356 Centre Lathe with Digital Readout - Includes Tooling Package 356 x 1000mm
 QLD Schools / TAFE - AL-356 Centre Lathe with Digital Readout - Includes Tooling Package 356 x 1000mm Please Call ORDER CODE: K8710D NSW Contract No.: ~ QLD Contract No.: MODEL: Digital Readout: ~ Schools/TAFE
QLD Schools / TAFE - AL-356 Centre Lathe with Digital Readout - Includes Tooling Package 356 x 1000mm Please Call ORDER CODE: K8710D NSW Contract No.: ~ QLD Contract No.: MODEL: Digital Readout: ~ Schools/TAFE
Opti-Turn Lathe & Mill Drill Combination Package Deal
 Product Brochure K146 OPTIMUM TU-2506V-16M Opti-Turn Lathe & Mill Drill Combination Package Deal 250 x 550mm Page 1 of 7 Front View Lathe Toolpost Removed For Milling Application Left View Without Toolpost
Product Brochure K146 OPTIMUM TU-2506V-16M Opti-Turn Lathe & Mill Drill Combination Package Deal 250 x 550mm Page 1 of 7 Front View Lathe Toolpost Removed For Milling Application Left View Without Toolpost
SHARP STA, STB, STC, STF SERIES CNC big bore flat bed lathe
 SHARP STA, STB, STC, STF SERIES PRECISION MACHINE TOOLS Sharp Industries, Inc. 3501 Challenger Street Torrance, CA 90503 Tel 310-370-5990 Fax 310-542-6162 Email: info@sharp-industries.com Parts: parts@sharp-industries.com
SHARP STA, STB, STC, STF SERIES PRECISION MACHINE TOOLS Sharp Industries, Inc. 3501 Challenger Street Torrance, CA 90503 Tel 310-370-5990 Fax 310-542-6162 Email: info@sharp-industries.com Parts: parts@sharp-industries.com
16" X 60" EVS TOOLROOM LATHES
 16" X 60" EVS TOOLROOM LATHES MODEL SB1014-220V MODEL SB1015-440V SPECIFICATIONS Hundreds of Thousands of Lathes Sold With a Tradition of Quality Since 1906! March, 2010 by South Bend Lathe Co. For Machines
16" X 60" EVS TOOLROOM LATHES MODEL SB1014-220V MODEL SB1015-440V SPECIFICATIONS Hundreds of Thousands of Lathes Sold With a Tradition of Quality Since 1906! March, 2010 by South Bend Lathe Co. For Machines
Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS
 Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS Turning and Related Operations Drilling and Related Operations Milling Machining Centers and Turning Centers Other Machining Operations High Speed Machining
Chapter 22 MACHINING OPERATIONS AND MACHINE TOOLS Turning and Related Operations Drilling and Related Operations Milling Machining Centers and Turning Centers Other Machining Operations High Speed Machining
.com More than a machine. Power your life. Precise Centre Metal Lathes. Advanced Technology, Complete
 Precise Centre Metal Lathes. Advanced Technology, Complete Equipment, Easy-to-Operate. This kind of MM-D420X1000 universal metal lathe machine is a fantastic model for small to medium-size turning works
Precise Centre Metal Lathes. Advanced Technology, Complete Equipment, Easy-to-Operate. This kind of MM-D420X1000 universal metal lathe machine is a fantastic model for small to medium-size turning works
TCF 160 / TCF 200 / TCF 224 / TCF 250 TCF 275 / TCF 300 HEAVY CENTRE LATHES
 TCF 160 / TCF 200 / TCF 224 / TCF 250 TCF 275 / TCF 300 HEAVY CENTRE LATHES BASIC PARAMETERS 3-guideways bed Max. torque on spindle Nm Max. weight of workpiece between centre 30 tonnes Turning length 3,000
TCF 160 / TCF 200 / TCF 224 / TCF 250 TCF 275 / TCF 300 HEAVY CENTRE LATHES BASIC PARAMETERS 3-guideways bed Max. torque on spindle Nm Max. weight of workpiece between centre 30 tonnes Turning length 3,000
Module 4 General Purpose Machine Tools. Version 2 ME, IIT Kharagpur
 Module 4 General Purpose Machine Tools Lesson 22 Use of various Attachments in Machine Tools. Instructional objectives At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to; (i) Comprehend and state
Module 4 General Purpose Machine Tools Lesson 22 Use of various Attachments in Machine Tools. Instructional objectives At the end of this lesson, the students will be able to; (i) Comprehend and state
HAFCO METALMASTER AL-335F. Centre Lathe. 300 x 910mm Turning Capacity. Product Brochure
 Product Brochure L681 HAFCO METALMASTER AL-335F Centre Lathe 300 x 910mm Turning Capacity Page 1 of 6 Front View Left View Headstock Spindle Speed Levers Control Panel Switches Feed and Thread Gearbox
Product Brochure L681 HAFCO METALMASTER AL-335F Centre Lathe 300 x 910mm Turning Capacity Page 1 of 6 Front View Left View Headstock Spindle Speed Levers Control Panel Switches Feed and Thread Gearbox
PLANING MACHINE. Crossrail. Tool head. Table. Table. reciprocating movement Roller. Bed. Open Side Planer Sketch S-8.1-A. Feed screws.
 8 PLANING MACHINE A8.1 : Planing Machine Tool head Table reciprocating movement Roller Table Cross-rail Bed Column Open Side Planer Sketch S-8.1-A Introduction This is also a reciprocating type of machine
8 PLANING MACHINE A8.1 : Planing Machine Tool head Table reciprocating movement Roller Table Cross-rail Bed Column Open Side Planer Sketch S-8.1-A Introduction This is also a reciprocating type of machine
HAFCO METALMASTER AL-960B. Centre Lathe. 305 x 925mm Turning Capacity. Product Brochure
 Product Brochure L237 HAFCO METALMASTER AL-960B Centre Lathe 305 x 925mm Turning Capacity Page 1 of 5 Specifications & Prices are subject to change without notification - 2018-09-19 L237.pdf Head Stock
Product Brochure L237 HAFCO METALMASTER AL-960B Centre Lathe 305 x 925mm Turning Capacity Page 1 of 5 Specifications & Prices are subject to change without notification - 2018-09-19 L237.pdf Head Stock
UNIT 5: Indexing: Simple, compound, differential and angular indexing calculations. Simple problems on simple and compound indexing.
 UNIT 5: Milling machines: Classification, constructional features, milling cutters nomenclature, milling operations, up milling and down milling concepts. Indexing: Simple, compound, differential and angular
UNIT 5: Milling machines: Classification, constructional features, milling cutters nomenclature, milling operations, up milling and down milling concepts. Indexing: Simple, compound, differential and angular
.com More than a machine. Power your life. Precise Centre Metal Lathes. Advanced Technology, Complete
 Precise Centre Metal Lathes. Advanced Technology, Complete Equipment, Easy-to-Operate. This kind of MM-D420X1500 universal metal lathe machine is a fantastic model for small to medium-size turning works
Precise Centre Metal Lathes. Advanced Technology, Complete Equipment, Easy-to-Operate. This kind of MM-D420X1500 universal metal lathe machine is a fantastic model for small to medium-size turning works
SAMPLE. MEM07005C Perform general machining. Learner guide. MEM05 Metal and Engineering Training Package. Version 1.1
 MEM05 Metal and Engineering Training Package MEM07005C Perform general machining Learner guide Version 1.1 Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit Meadowbank Product code: 5790 Acknowledgments
MEM05 Metal and Engineering Training Package MEM07005C Perform general machining Learner guide Version 1.1 Training and Education Support Industry Skills Unit Meadowbank Product code: 5790 Acknowledgments
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT-I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? (BT1) 2. Explain how chip
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK ME6402 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY II UNIT-I PART A 1. List the various metal removal processes? (BT1) 2. Explain how chip
Page 1 Parts List for AL-51G (L160) 07/08/201. Headstock Assembly
 Page 1 Parts List for AL-51G (L160) 07/08/201 Headstock Assembly 1--------1002-------------------Headstock Casting 13-------1012------------------------------Nut M28 2--------1006---------------------------Flange
Page 1 Parts List for AL-51G (L160) 07/08/201 Headstock Assembly 1--------1002-------------------Headstock Casting 13-------1012------------------------------Nut M28 2--------1006---------------------------Flange
The premier source of parts and accessories for mini lathes and mini mills. Mini Lathe User s Guide. from LittleMachineShop.com
 The premier source of parts and accessories for mini lathes and mini mills. Mini Lathe User s Guide from LittleMachineShop.com Copyright 2002, LittleMachineShop.com All rights reserved. Some photos Copyright
The premier source of parts and accessories for mini lathes and mini mills. Mini Lathe User s Guide from LittleMachineShop.com Copyright 2002, LittleMachineShop.com All rights reserved. Some photos Copyright
Cutting Tools and Cutting materials
 Cutting Tools and Cutting materials Cutting Tools One of most important components in machining process Performance will determine efficiency of operation Two basic types (excluding abrasives) Single point
Cutting Tools and Cutting materials Cutting Tools One of most important components in machining process Performance will determine efficiency of operation Two basic types (excluding abrasives) Single point
By C.W. Woodson From the pages of Model Craftsman magazine June, 1937
 By C.W. Woodson From the pages of Model Craftsman magazine June, 1937 As shown in Fig. 1, the tool post grinder for which plans are given here can be used to finish up delicate work to more accurate dimensions
By C.W. Woodson From the pages of Model Craftsman magazine June, 1937 As shown in Fig. 1, the tool post grinder for which plans are given here can be used to finish up delicate work to more accurate dimensions
HOW TO USE MILLING MACHINE?
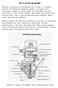 HOW TO USE MILLING MACHINE? Milling is the process of machining flat, curved, or irregular surfaces by feeding the workpiece against a rotating cutter containing a number of cutting edges. The usual Mill
HOW TO USE MILLING MACHINE? Milling is the process of machining flat, curved, or irregular surfaces by feeding the workpiece against a rotating cutter containing a number of cutting edges. The usual Mill
LocoGear. Technical Bulletin - 02 January 11, by LocoGear LIVE STEAM CASTINGS. Tech Bulletin - 02
 LIVE STEAM CASTINGS Tech Bulletin - 02 LocoGear Technical Bulletin - 02 January 11, 2003 2003 by LocoGear John D.L. Johnson 3879 Woods Walk Blvd. Lake Worth, FL 33467-2359 jjohnson@locogear.com www.locogear.com
LIVE STEAM CASTINGS Tech Bulletin - 02 LocoGear Technical Bulletin - 02 January 11, 2003 2003 by LocoGear John D.L. Johnson 3879 Woods Walk Blvd. Lake Worth, FL 33467-2359 jjohnson@locogear.com www.locogear.com
Universal Machining Chucks. 4-Jaw Vertical
 Universal Machining Chucks 4-Jaw Vertical Parts are gripped firmly by the formed jaws, ensuring high precision (deviation within 0.03mm) Large workpieces can be held tight with the low profile vise body
Universal Machining Chucks 4-Jaw Vertical Parts are gripped firmly by the formed jaws, ensuring high precision (deviation within 0.03mm) Large workpieces can be held tight with the low profile vise body
