SUPERCONDUCTING GANTRY AND OTHER DEVELOPMENTS AT HIMAC
|
|
|
- Sophia Pope
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPERCONDUCTING GANTRY AND OTHER DEVELOPMENTS AT HIMAC Y. Iwata *, K. Noda, T. Shirai, T. Murakami, T. Fujita, T. Furukawa, K. Mizushima, Y. Hara, S. Suzuki, S. Sato, and K. Shouda, NIRS, Anagawa, Inage, Chiba , Japan T. Fujimoto, and H. Arai, AEC, Konakadai, Inage, Chiba , Japan T. Ogitsu, KEK, 1-1 Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan T. Obana, NIFS, Oroshi-cho, Toki-city , Japan N. Amemiya, Kyoto Univ., Kyoto-Daigaku-Katsura, Nishikyo, Kyoto , Japan T. Orikasa, S. Takayama, Y. Nagamoto, and T. Yazawa, Toshiba Corp., Shibaura, Minatoku, Tokyo , Japan Abstract New developments at HIMAC include a superconducting carbon gantry, a new therapy area with three new treatment rooms, and substantial enhancements to the synchrotron extraction system to enable energy-variation through multiple flattops within a synchrotron cycle to match characteristics of the gantry and three-dimensional raster scanning. The carbon gantry consists of ten combined-function superconducting magnets, allowing a very compact geometry the length and the radius of the gantry are approximately 13 and 5.5 m, respectively, comparable to the dimensions of existing proton gantries. Further, these superconducting magnets are designed for fast slewing of the magnetic field to follow the multiple flattop operation of the synchrotron. In this paper, the recent developments of HIMAC are presented. INTRODUCTION Heavy-ion cancer-therapy using the Heavy-Ion Medical Accelerator in Chiba (HIMAC) has been carried out since June The successful cancer treatments have led us to construct a new treatment facility [1]. The new treatment facility equips with three treatment rooms; two of them have both horizontal and vertical fixedirradiation-ports, and the other is a rotating gantry port as schematically shown in Fig. 1. For all the ports, the threedimensional raster-scanning irradiation method with pencil beam will be employed [2]. In raster-scanning irradiation, a target is directly irradiated with high-energy carbon-ions, after being accelerated by a synchrotron ring. Since the position of the focused beam on a target is controlled by the fast horizontal and vertical scanning-magnets, the lateral dose distribution is determined by these scanning magnets. On the other hand, the depth dose-distribution is determined by beam energy. To control the depth dose-distribution, it is preferable to change the beam energy directly by the accelerators, instead of using energy degraders, since energy degraders may broaden the spot size of the beam on a target, and concurrently produce secondary fragments, which could adversely affect the depth dosedistribution. To quickly change the energy of the beam, as provided *corresponding author. y_iwata@nirs.go.jp (Y. Iwata) by the synchrotron ring, we developed a multiple-energy operation with extended flattops [3]. The proposed operation enables us to provide carbon ions having various energies in a single synchrotron cycle; namely, the beam energy would be successively changed within a single synchrotron pulse. With this operation, the beam range could be controlled without using any energy degraders. To further obtain precise dose distributions, we developed an isocentric superconducting rotating-gantry for carbon therapy [4]. This rotating gantry is designed to transport carbon ions having 430 MeV/u to an isocenter with irradiation angles of over ±180 degrees, and is further capable of performing the fast raster-scanning irradiation. The combined-function superconducting magnets will be employed for the rotating gantry. Use of the superconducting magnets with optimized beam optics allow a compact gantry design with a large scan size at the isocenter; the length and the radius of the gantry will be approximately 13 and 5.5 m, respectively, which are comparable to those for the existing proton gantries. This rotating gantry is currently under construction, and will be installed in the room G of the new treatment facility. We report the recent developments of the multiple flattop operation as well as the superconducting rotatinggantry. Figure 1: Layout of the HIMAC complex. 1463
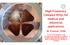
2 Proceedings of PAC2013, Pasadena, CA USA Figure 2: (a) Schematic drawing of synchrotron pattern for multiple-energy operation. (b) The same pattern as (a), but with the extended flattops. The beam is extracted from the synchrotron ring during these extended flattops Figure 3: A current pattern for the main-bending magnets in the ring as a function of time. The currents of the 11 flattops correspond to the beam energies of 430, 400, 380, 350, 320, 290, 260, 230, 200, 170, and 140 MeV/u. MULTIPLE FLATTOP OPERATION The multiple-energy operation employs operation patterns having a stepwise flattop, as schematically shown in Fig. 2(a). With these operation patterns, the carbon ions injected in the ring are initially accelerated to the maximum energy, and then successively decelerated to lower energies. Although the stepwise pattern only has short flattops, where the beam can be extracted from the ring, we can extend the flattop and extract the beam during the extended flattop. 90s 40ms 150ms ms BM current pattern Beam current in synchrotron RFKO Amp. Beam current of extracted beams 430MeV/n 380MeV/n 320MeV/n 260MeV/n 200MeV/n 140MeV/n 400MeV/n 350MeV/n 290MeV/n 230MeV/n 170MeV/n Figure 4: Current patterns for the main bending magnets, beam current in the synchrotron ring, RFKO amplitude, and the beam current of the extracted beam Figure 5: A current pattern for the main-bending magnets in the ring. This pattern has 201 flattops. Having consecutively extended the flattops, as illustrated in Fig. 2(b), the beams having various energies can be extracted from the ring within a single synchrotron cycle, and hence the total irradiation time can be considerably reduced. 11-flattop pattern To prove the principle of multiple-energy operation with extended flattops, we have performed beam acceleration and extraction tests using the stepwise operation pattern. In the tests, a current pattern for the main bending magnet having 11 short flattops, corresponding to 11 beam energies, was prepared as shown in Fig. 3. Further, similar patterns were prepared for other devices, such as the main quadrupole, sextupole magnets, the RF-acceleration cavity, and the beamextraction devices in the extraction channel. By using the prepared operation patterns, the beam will be initially accelerated to 430 MeV/u, and then consecutively decelerated down to 140 MeV/u at an energy step of 20 MeV/u or 30 MeV/u. Results of the beam test are shown in Fig. 4. As can be seen in the figure, beams having 11 different energies were successively extracted from the synchrotron ring. The multiple-energy operation using this pattern was successfully commissioned, and has been used for scanning treatments since FY Full energy-scan with 201-flattop pattern The final goal of this project is to control the depth dose-distribution by varying the beam energy from the accelerators, namely, full energy scanning. To accomplish DCCT output in the ring 200 Current pattern of synchrotron BM MeV/u 11 Figure 6: Current patterns for the main bending magnets, DCCT output in the synchrotron ring during beam acceleration tests using the 201-flattop pattern.
3 extended flattop. Hence, with this operation pattern having the 201 flattops - the universal pattern, the depth dose-distribution could be controlled without using any energy degrader. Figure 7: Three-dimensional image of the superconducting rotating gantry for carbon therapy. this, it is required to change, the beam energy successively by an energy step corresponding to the water range of 1 or 2 mm. Since the maximum and minimum energies, as used in the raster-scanning irradiation, are 430 and 56 MeV/u, respectively, the synchrotron patterns having the 201 flattops will be needed to cover the entire energy range. Fig. 5 shows a current pattern of the main bending magnets having the 201 flattops. Beam acceleration and extraction tests using the 201- flattop patterns were successfully made as shown in Fig. 6. In the test, we found that any of the 201 flattops can be extended, and that the beam can be extracted during the SUPERCONDUCTING ROTATING- GANTRY A three-dimensional image of the isocentric rotating gantry for the new treatment facility is presented in Fig. 7. This rotating gantry has a cylindrical structure with two large rings at both ends. The end rings support the total weight of the entire structure, and are placed on turning rollers so as to rotate the beam line on the rotating gantry along the central axis over ±180 degrees. Carbon beams, provided by the HIMAC, are transported with ten sectorbending magnets, mounted on the gantry structure through each of their supporting structures; they are directed on a target located at the isocenter. In the treatment room, a tumour in a patient is precisely positioned to the isocenter by using a robotic couch. Layout and beam optics A layout of the compact rotating-gantry is presented in Fig. 8. The rotating gantry has ten superconducting magnets (BM01-10), a pair of the scanning magnets (SCM-X and SCM-Y), and two pairs of beam profilemonitor and steering magnets (ST01-02 and PRN01-02). A total length and radius of the rotating gantry is 13 m and 5.45 m, respectively. All of these devices are installed and mounted on the cylindrical structure. Since beam focusing can be made only with the combined-function Figure 8: Layout of the superconducting rotating gantry. The gantry consists of ten combined-function superconducting magnets (BM01-10), a pair of the scanning magnets (SCM-X and SCM-Y), and two pairs of beam profile-monitor and steering magnets (ST01-02 and PRN01-02). Representative results of 3D magnetic field calculations for the five kinds of the superconducting magnets are also shown. 1465
4 Proceedings of PAC2013, Pasadena, CA USA Figure 9: Picture of the test bench during rotation tests of the model superconducting-magnet. superconducting magnets, no quadrupole magnets are needed to install in the rotating gantry, and thus we could design the compact rotating gantry. Details of the beam optics are provided in Ref. [4]. Field calculations Based on the design of the beam optics, specification of the superconducting magnets was determined. According to their apertures, the magnets are categorized into five kinds. All the magnets have the surface-winding coil structure, and were designed by using a 3D electromagnetic field-solver, the Opera-3d code [5]. In the code, the curved superconducting coils, having typically a few thousand turns per pole, as well as the cold yoke and vacuum chamber were precisely modelled, and a threedimensional magnetic field was calculated. Representative results of the calculations are shown in Fig. 8. Having optimized the conductor position, we obtained the required uniformity of the calculated field. Figure 10: Picture of BM10 and its superconducting coil Figure 11: Measured magnetic field, B, and magnetic field as divided by coil current, B/I, as functions of coil current, I, for BM10. For comparison, calculated magnetic field is shown by the filled and open dots. Rotation tests Since the superconducting magnets on the rotating gantry are to be rotated over ±180 degrees during treatments, an unexpected quench of the superconducting magnets, as caused by rotations, is a concern. To verify this, a model superconducting magnet was developed and tested by Toshiba Corporation. This model magnet has a similar magnet structure as that of BM01-06, although this model magnet only has a dipole coil. Fig. 9 shows a picture of a test bench during rotation tests. Prior to the tests, the coil of the model magnet was cooled down to below 4K by cryocoolers, installed on the magnet. While exciting the superconducting coil with the maximum current, the model magnet was rotated by ±180 degrees, and the coil temperatures in the magnets were monitored. As a result, no unexpected temperature increase, which may cause quench problems, was observed. Magnetic field measurements The five superconducting magnets of BM01-BM04 and BM10 (Fig. 10) were constructed, and the rest of the five will be constructed within a year. Firstly, we measured central magnetic field by using an NMR probe. The NMR probe was installed in the middle of the magnet, and current of between I= A was applied for the dipole Figure 12: Measured BL products as a function of X. Current for the dipole coil is I=231.2A. The solid curve show calculated result with the Opera-3d code.
5 Figure 13: Results of the fast slewing tests for BM10. Average coil temperatures were converged below 4K. coil of BM10. The measured magnetic field, B, and magnetic field as divided by the coil current, B/I, are shown by the solid and dashed curves in Fig. 11, respectively. For comparison, calculated results of B and B/I using the Opera-3d code are also plotted by the filled and open dots in Fig. 11, respectively. We found that the measured and calculated magnetic field agreed with each other, although the measured B/I curve at the maximum current slightly differs with the calculated curve. This discrepancy might be attributed to a difference in estimation of a packing factor for the laminated cold yoke. Secondarily, measurements of magnetic field distributions along beam trajectories were performed. Measured-magnetic field distributions along the central beam trajectory were measured and integrated over the beam trajectories to determine a BL product and an effective length. The same analysis was made for the calculated distribution with the Opera-3d code. Fig. 12 shows the BL products of various beam trajectories, as shifted horizontally by X, for the dipole current of I=231.2A. Here, the values of the BL products are normalized, so as to have the same effective length of L==2.8m 22.5 for all the trajectories. Corresponding results, as calculated by the Opera-3d code, are also shown by the solid curves in the figures. The absolute values of the measured BL agreed with the calculated values within accuracy of a few times 10-3 ; however we clearly see the quadrupole component of approximately GL~ T for the measured field in Fig. 12. We presume that this unexpected quadrupole component might be attributed to an alignment error between the superconducting coil and cold yoke. However, since this magnet has the quadrupole coil, this quadrupole component can be corrected by adding or reducing current for the quadrupole coil by approximately I=5 A from the applied quadrupole current of I~200 A. Fast slewing tests To simulate the multiple flattop operation, fast slewing tests were made. In the tests, currents of both the dipole and quadrupole coils were maximized to initialize the magnet, and then were decreased by 201 steps. In each step, coil currents were kept for 0.3 s, where carbon beams would be extracted from accelerators and transported through a beam-transport line including the rotating-gantry during this constant-current region. Further, the coil temperatures were measured with resistance temperature sensors, installed in the inner, middle and outer sides of the coil. A representative result for BM10 is provided in Fig. 13. Although the coil temperature gradually increases, we found that the average coil temperatures were converged around 4 K, while the critical temperature is approximately 6.8 K. SUMMARY AND FUTURE PLAN Recent developments of the HIMAC accelerator complex are reported. To take advantage of the fast raster-scanning irradiation, the multiple energy operation was developed. This operation using 11-flattop pattern was successfully commissioned, and is presently used in scanning-treatment operations. Furthermore, we successfully made beam acceleration and extraction tests with 201-flattop pattern, which enables us to perform the full energy scanning; this operation will be used for treatment operation in near future. A compact superconducting rotating-gantry for carbon therapy is being developed. Having optimized the layout using the combined-function superconducting magnets, we could design the compact rotating-gantry. The design study as well as major tests of the superconducting magnets was completed, and the construction of the superconducting rotating-gantry is in progress. The rotating-gantry will be completed at the end of FY2014, and be commissioned in FY2015. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work is supported by Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan. REFERENCES [1] K. Noda, et al., Nucl. Instrum. and Meth. in Phys. Res. B 266 (2008) [2] T. Furukawa, et al., Med. Phys. 37 (2010) [3] Y. Iwata, et al., Nucl. Instrum. and Meth. in Phys. Res. A 624 (2010) 33. [4] Y. Iwata, et al., Phys, Rev. ST Accel. Beams 15 (2012) [5] Opera Version 16,
New Tracking Gantry-Synchrotron Idea. G H Rees, ASTeC, RAL, U.K,
 New Tracking Gantry-Synchrotron Idea G H Rees, ASTeC, RAL, U.K, Scheme makes use of the following: simple synchrotron and gantry magnet lattices series connection of magnets for 5 Hz tracking one main
New Tracking Gantry-Synchrotron Idea G H Rees, ASTeC, RAL, U.K, Scheme makes use of the following: simple synchrotron and gantry magnet lattices series connection of magnets for 5 Hz tracking one main
NIRS accelerator present and future activities
 NIRS accelerator present and future activities Koji Noda Research Center for Charged Particle Therapy National Institute of Radiological Sciences 2 nd Workshop on Hadron Therapy of Cancer, Erice, 23rd
NIRS accelerator present and future activities Koji Noda Research Center for Charged Particle Therapy National Institute of Radiological Sciences 2 nd Workshop on Hadron Therapy of Cancer, Erice, 23rd
HITACHI Proton Therapy System with Spot Scanning
 Workshop on Hadron Therapy of Cancer 27 th April, Erice, Sicily, Italy HITACHI Proton Therapy System with Spot Scanning Kazuo Hiramoto Energy & Environmental Systems Laboratory, Hitachi, Ltd. Contents
Workshop on Hadron Therapy of Cancer 27 th April, Erice, Sicily, Italy HITACHI Proton Therapy System with Spot Scanning Kazuo Hiramoto Energy & Environmental Systems Laboratory, Hitachi, Ltd. Contents
MULTIPACTING IN THE CRAB CAVITY
 MULTIPACTING IN TH CRAB CAVITY Y. Morita, K. Hara, K. Hosoyama, A. Kabe, Y. Kojima, H. Nakai, KK, 1-1, Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 3-81, JAPAN Md. M. Rahman, K. Nakanishi, Graduate University for Advanced Studies,
MULTIPACTING IN TH CRAB CAVITY Y. Morita, K. Hara, K. Hosoyama, A. Kabe, Y. Kojima, H. Nakai, KK, 1-1, Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 3-81, JAPAN Md. M. Rahman, K. Nakanishi, Graduate University for Advanced Studies,
The VARIAN 250 MeV Superconducting Compact Proton Cyclotron
 The VARIAN 250 MeV Superconducting Compact Proton Cyclotron VARIAN Medical Systems Particle Therapy GmbH Friedrich-Ebert-Str. 1 D-51429 BERGISCH GLADBACH GERMANY OUTLINE 1. Why having a Superconducting
The VARIAN 250 MeV Superconducting Compact Proton Cyclotron VARIAN Medical Systems Particle Therapy GmbH Friedrich-Ebert-Str. 1 D-51429 BERGISCH GLADBACH GERMANY OUTLINE 1. Why having a Superconducting
Title Coil Wound by Surface Winding Techn.
 Title Measurements of Magnetic Field Harm Coil Wound by Surface Winding Techn Amemiya, Naoyuki; Mizuta, Shingo; N Author(s) Ogitsu, Toru; Orikasa, Tomofumi; Ku Tetsuhiro; Noda, Koji Citation IEEE Transactions
Title Measurements of Magnetic Field Harm Coil Wound by Surface Winding Techn Amemiya, Naoyuki; Mizuta, Shingo; N Author(s) Ogitsu, Toru; Orikasa, Tomofumi; Ku Tetsuhiro; Noda, Koji Citation IEEE Transactions
DEVELOPMENT OF CAPACITIVE LINEAR-CUT BEAM POSITION MONITOR FOR HEAVY-ION SYNCHROTRON OF KHIMA PROJECT
 DEVELOPMENT OF CAPACITIVE LINEAR-CUT BEAM POSITION MONITOR FOR HEAVY-ION SYNCHROTRON OF KHIMA PROJECT Ji-Gwang Hwang, Tae-Keun Yang, Seon Yeong Noh Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences,
DEVELOPMENT OF CAPACITIVE LINEAR-CUT BEAM POSITION MONITOR FOR HEAVY-ION SYNCHROTRON OF KHIMA PROJECT Ji-Gwang Hwang, Tae-Keun Yang, Seon Yeong Noh Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences,
LINAC EXPERIENCE IN THE FIRST TWO YEARS OF CNAO (CENTRO NAZIONALE ADROTERAPIA ONCOLOGICA)
 LINAC EXPERIENCE IN THE FIRST TWO YEARS OF OPERATION @ CNAO (CENTRO NAZIONALE ADROTERAPIA ONCOLOGICA) S. Vitulli, E. Vacchieri, CNAO Foundation, Pavia, Italy A. Reiter, B. Schlitt, GSI, Darmstadt, Germany
LINAC EXPERIENCE IN THE FIRST TWO YEARS OF OPERATION @ CNAO (CENTRO NAZIONALE ADROTERAPIA ONCOLOGICA) S. Vitulli, E. Vacchieri, CNAO Foundation, Pavia, Italy A. Reiter, B. Schlitt, GSI, Darmstadt, Germany
HIGH MAGNETIC FIELD SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNETS FABRICATED IN BUDKER INP FOR SR GENERATION
 HIGH MAGNETIC FIELD SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNETS FABRICATED IN BUDKER INP FOR SR GENERATION K.V. Zolotarev *, A.M. Batrakov, S.V. Khruschev, G.N. Kulipanov, V.H. Lev, N.A. Mezentsev, E.G. Miginsky, V.A. Shkaruba,
HIGH MAGNETIC FIELD SUPERCONDUCTING MAGNETS FABRICATED IN BUDKER INP FOR SR GENERATION K.V. Zolotarev *, A.M. Batrakov, S.V. Khruschev, G.N. Kulipanov, V.H. Lev, N.A. Mezentsev, E.G. Miginsky, V.A. Shkaruba,
Circumference 187 m (bending radius = 8.66 m)
 4. Specifications of the Accelerators Table 1. General parameters of the PF storage ring. Energy 2.5 GeV (max 3.0 GeV) Initial stored current multi-bunch 450 ma (max 500 ma at 2.5GeV) single bunch 70 ma
4. Specifications of the Accelerators Table 1. General parameters of the PF storage ring. Energy 2.5 GeV (max 3.0 GeV) Initial stored current multi-bunch 450 ma (max 500 ma at 2.5GeV) single bunch 70 ma
Chapter 9. Magnet System. 9.1 Magnets in the Arc and Straight Sections
 Chapter 9 Magnet System This chapter discusses the parameters and the design of the magnets to use at KEKB. Plans on the magnet power supply systems, magnet installation procedure and alignment strategies
Chapter 9 Magnet System This chapter discusses the parameters and the design of the magnets to use at KEKB. Plans on the magnet power supply systems, magnet installation procedure and alignment strategies
Experience with Insertion Device Photon Beam Position Monitors at the APS
 Experience with Insertion Device Photon Beam Position Monitors at the APS 27.6 meters (The APS has forty sectors - 1104 meters total circumference) Beam Position Monitors and Magnets in One Sector 18m
Experience with Insertion Device Photon Beam Position Monitors at the APS 27.6 meters (The APS has forty sectors - 1104 meters total circumference) Beam Position Monitors and Magnets in One Sector 18m
CAVITY DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM FOR THE VERTICAL TEST OF THE BASELINE SC CAVITY IN KEK-STF
 CAVITY DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM FOR THE VERTICAL TEST OF THE BASELINE SC CAVITY IN KEK-STF Y. Yamamoto #, H. Hayano, E. Kako, S. Noguchi, T. Shishido, K. Umemori, K. Watanabe, KEK, Tsukuba, 305-0801, Japan, H.
CAVITY DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM FOR THE VERTICAL TEST OF THE BASELINE SC CAVITY IN KEK-STF Y. Yamamoto #, H. Hayano, E. Kako, S. Noguchi, T. Shishido, K. Umemori, K. Watanabe, KEK, Tsukuba, 305-0801, Japan, H.
KEK ERL CRYOMODULE DEVELOPMENT
 KEK ERL CRYOMODULE DEVELOPMENT H. Sakai*, T. Furuya, E. Kako, S. Noguchi, M. Sato, S. Sakanaka, T. Shishido, T. Takahashi, K. Umemori, K. Watanabe and Y. Yamamoto KEK, 1-1, Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-0801,
KEK ERL CRYOMODULE DEVELOPMENT H. Sakai*, T. Furuya, E. Kako, S. Noguchi, M. Sato, S. Sakanaka, T. Shishido, T. Takahashi, K. Umemori, K. Watanabe and Y. Yamamoto KEK, 1-1, Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-0801,
Beam Extraction Control for Fast 3D Scanning Irradiation in Medical Synchrotron
 Beam Extraction Control for Fast 3D Scanning Irradiation in Medical Synchrotron January 1 Kota Mizushima Graduate School of Science CHIBA UNIVERSITY ( 千葉大学学位申請論文 ) Beam Extraction Control for Fast 3D Scanning
Beam Extraction Control for Fast 3D Scanning Irradiation in Medical Synchrotron January 1 Kota Mizushima Graduate School of Science CHIBA UNIVERSITY ( 千葉大学学位申請論文 ) Beam Extraction Control for Fast 3D Scanning
The design of a radio frequency quadrupole LINAC for the RIB project at VECC Kolkata
 PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 59, No. 6 journal of December 2002 physics pp. 957 962 The design of a radio frequency quadrupole LINAC for the RIB project at VECC Kolkata V BANERJEE 1;Λ, ALOK
PRAMANA cfl Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 59, No. 6 journal of December 2002 physics pp. 957 962 The design of a radio frequency quadrupole LINAC for the RIB project at VECC Kolkata V BANERJEE 1;Λ, ALOK
Recent Developments of Variably Polarizing Undulators at the APS. By Mark Jaski
 Recent Developments of Variably Polarizing Undulators at the APS By Mark Jaski Outline What is an Undulator IEX device Analysis Prototypes Final device EMVPU Device Analysis Prototypes Final device 2 What
Recent Developments of Variably Polarizing Undulators at the APS By Mark Jaski Outline What is an Undulator IEX device Analysis Prototypes Final device EMVPU Device Analysis Prototypes Final device 2 What
Development of a Vibration Measurement Method for Cryocoolers
 REVTEX 3.1 Released September 2 Development of a Vibration Measurement Method for Cryocoolers Takayuki Tomaru, Toshikazu Suzuki, Tomiyoshi Haruyama, Takakazu Shintomi, Akira Yamamoto High Energy Accelerator
REVTEX 3.1 Released September 2 Development of a Vibration Measurement Method for Cryocoolers Takayuki Tomaru, Toshikazu Suzuki, Tomiyoshi Haruyama, Takakazu Shintomi, Akira Yamamoto High Energy Accelerator
Experiences of the QSBPM System on MAX II
 Experiences of the QSBPM System on MAX II Peter Röjsel MAX-lab, Lund University, Lund, Sweden Abstract. The MAX II is a third-generation synchrotron radiation source. The first beamline is in operation
Experiences of the QSBPM System on MAX II Peter Röjsel MAX-lab, Lund University, Lund, Sweden Abstract. The MAX II is a third-generation synchrotron radiation source. The first beamline is in operation
Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou , China. 2
 Successful High Power Acceleration of the HSC Type Injector for Cancer Therapy in IMP LU Liang 1, HATTORI Toshiyuki 2, ZHAO Huan-yu 1, KAWASAKI Katsunori 3, SUN Liepeng 1, JIN Qianyu 1, ZHANG Jun-jie 1,
Successful High Power Acceleration of the HSC Type Injector for Cancer Therapy in IMP LU Liang 1, HATTORI Toshiyuki 2, ZHAO Huan-yu 1, KAWASAKI Katsunori 3, SUN Liepeng 1, JIN Qianyu 1, ZHANG Jun-jie 1,
Herwig Schopper CERN 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland. Introduction
 THE LEP PROJECT - STATUS REPORT Herwig Schopper CERN 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Introduction LEP is an e + e - collider ring designed and optimized for 2 100 GeV. In an initial phase an energy of 2 55
THE LEP PROJECT - STATUS REPORT Herwig Schopper CERN 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Introduction LEP is an e + e - collider ring designed and optimized for 2 100 GeV. In an initial phase an energy of 2 55
Lattice Design for PRISM-FFAG. A. Sato Osaka University for the PRISM working group
 Lattice Design for PRISM-FFAG A. Sato Osaka University for the PRISM working group contents PRISM overview PRISM-FFAG dynamics study & its method PRISM Phase Rotated Intense Slow Muon source Anticipated
Lattice Design for PRISM-FFAG A. Sato Osaka University for the PRISM working group contents PRISM overview PRISM-FFAG dynamics study & its method PRISM Phase Rotated Intense Slow Muon source Anticipated
The Current Cyclotron Development Activities at CIAE. Current acyclotron
 Current Cyclotron Development Activities Shizhong An, Tianjue Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy (CIAE) Beijing 2010-11.22 Greatful acknowledged is very fruitful and long lasting collaboration with
Current Cyclotron Development Activities Shizhong An, Tianjue Zhang China Institute of Atomic Energy (CIAE) Beijing 2010-11.22 Greatful acknowledged is very fruitful and long lasting collaboration with
Design of a new 18 GHz ECRIS for RIKEN RIBF
 Design of a new 18 GHz ECRIS for RIKEN RIBF Kazutaka Ozeki Yoshihide Higurashi Takahide Nakagawa Jun-ichi Ohnishi RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science Contents RIKEN RIBF, RILAC RIKEN 18
Design of a new 18 GHz ECRIS for RIKEN RIBF Kazutaka Ozeki Yoshihide Higurashi Takahide Nakagawa Jun-ichi Ohnishi RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science Contents RIKEN RIBF, RILAC RIKEN 18
Superconducting Medical Accelerators at IBA
 Superconducting Medical Accelerators at IBA Wiel Kleeven and Eric Forton on behalf of IBA 1), AIMA 2) JINR 3) ASG 4) Sigmaphi 5) 1) Ion Beam Applications, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium 2) AIMA, Developpement,
Superconducting Medical Accelerators at IBA Wiel Kleeven and Eric Forton on behalf of IBA 1), AIMA 2) JINR 3) ASG 4) Sigmaphi 5) 1) Ion Beam Applications, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium 2) AIMA, Developpement,
Electromagnetic Field Simulation for ICRF Antenna and Comparison with Experimental Results in LHD
 Electromagnetic Field Simulation for ICRF Antenna and Comparison with Experimental Results in LHD Takashi MUTOH, Hiroshi KASAHARA, Tetsuo SEKI, Kenji SAITO, Ryuhei KUMAZAWA, Fujio SHIMPO and Goro NOMURA
Electromagnetic Field Simulation for ICRF Antenna and Comparison with Experimental Results in LHD Takashi MUTOH, Hiroshi KASAHARA, Tetsuo SEKI, Kenji SAITO, Ryuhei KUMAZAWA, Fujio SHIMPO and Goro NOMURA
A Study of undulator magnets characterization using the Vibrating Wire technique
 A Study of undulator magnets characterization using the Vibrating Wire technique Alexander. Temnykh a, Yurii Levashov b and Zachary Wolf b a Cornell University, Laboratory for Elem-Particle Physics, Ithaca,
A Study of undulator magnets characterization using the Vibrating Wire technique Alexander. Temnykh a, Yurii Levashov b and Zachary Wolf b a Cornell University, Laboratory for Elem-Particle Physics, Ithaca,
Gantry design and experience at PSI
 Gantry design and experience at PSI Eros Pedroni for the R&D Technology Team Center for Proton Therapy Paul Scherrer Institute Villigen-PSI SWITZERLAND Workshop on Hadron Beam Therapy of Cancer Erice April
Gantry design and experience at PSI Eros Pedroni for the R&D Technology Team Center for Proton Therapy Paul Scherrer Institute Villigen-PSI SWITZERLAND Workshop on Hadron Beam Therapy of Cancer Erice April
Brett Parker, representing the
 Compact Superconducting Magnet Solution for the 20 mr Crossing Angle Final Focus Brett Parker, representing the Brookhaven Superconducting Magnet Division Message: Progress continues on the compact superconducting
Compact Superconducting Magnet Solution for the 20 mr Crossing Angle Final Focus Brett Parker, representing the Brookhaven Superconducting Magnet Division Message: Progress continues on the compact superconducting
Rotating Coil Measurement Errors*
 Rotating Coil Measurement Errors* Animesh Jain Superconducting Magnet Division Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973, USA 2 nd Workshop on Beam Dynamics Meets Magnets (BeMa2014) December 1-4,
Rotating Coil Measurement Errors* Animesh Jain Superconducting Magnet Division Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973, USA 2 nd Workshop on Beam Dynamics Meets Magnets (BeMa2014) December 1-4,
COMMISSIONING OF A COMPACT SYNCHROTRON RADIATION SOURCE AT HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY
 COMMISSIONING OF A COMPACT SYNCHROTRON RADIATION SOURCE AT HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY K. Yoshida, M. Andreyashkin, K. Goto, E. Hashimoto, G. Kutluk, K. Matsui, K. Mimura,H. Namatame, N. Ojima, K. Shimada, M.
COMMISSIONING OF A COMPACT SYNCHROTRON RADIATION SOURCE AT HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY K. Yoshida, M. Andreyashkin, K. Goto, E. Hashimoto, G. Kutluk, K. Matsui, K. Mimura,H. Namatame, N. Ojima, K. Shimada, M.
CONICAL HALF-WAVE RESONATOR INVESTIGATIONS
 CONICAL HALF-WAVE RESONATOR INVESTIGATIONS E. Zaplatin, Forschungszentrum Juelich, Germany Abstract In the low energy part of accelerators the magnets usually alternate accelerating cavities. For these
CONICAL HALF-WAVE RESONATOR INVESTIGATIONS E. Zaplatin, Forschungszentrum Juelich, Germany Abstract In the low energy part of accelerators the magnets usually alternate accelerating cavities. For these
200 MHz 350 MHz 750 MHz Linac2 RFQ2 202 MHz 0.5 MeV /m Weight : 1000 kg/m Ext. diameter : 45 cm
 M. Vretenar, CERN for the HF-RFQ Working Group (V.A. Dimov, M. Garlasché, A. Grudiev, B. Koubek, A.M. Lombardi, S. Mathot, D. Mazur, E. Montesinos, M. Timmins, M. Vretenar) 1 1988-92 Linac2 RFQ2 202 MHz
M. Vretenar, CERN for the HF-RFQ Working Group (V.A. Dimov, M. Garlasché, A. Grudiev, B. Koubek, A.M. Lombardi, S. Mathot, D. Mazur, E. Montesinos, M. Timmins, M. Vretenar) 1 1988-92 Linac2 RFQ2 202 MHz
version 7.6 RF separator
 version 7.6 RF separator www.nscl.msu.edu/lise dnr080.jinr.ru/lise East Lansing August-2006 Contents: 1. RF SEPARATOR...3 1.1. RF SEPARATION SYSTEM (RFSS) PROPOSAL AT NSCL... 3 1.2. CONSTRUCTION OF THE
version 7.6 RF separator www.nscl.msu.edu/lise dnr080.jinr.ru/lise East Lansing August-2006 Contents: 1. RF SEPARATOR...3 1.1. RF SEPARATION SYSTEM (RFSS) PROPOSAL AT NSCL... 3 1.2. CONSTRUCTION OF THE
Monte Carlo study on a new concept of a scanning photon beam system for IMRT
 NUKLEONIKA 2011;56(4):291 297 ORIGINAL PAPER Monte Carlo study on a new concept of a scanning photon beam system for IMRT Anna M. Wysocka-Rabin, Günter H. Hartmann Abstract. Intensity-modulated radiation
NUKLEONIKA 2011;56(4):291 297 ORIGINAL PAPER Monte Carlo study on a new concept of a scanning photon beam system for IMRT Anna M. Wysocka-Rabin, Günter H. Hartmann Abstract. Intensity-modulated radiation
Insertion Devices Lecture 4 Undulator Magnet Designs. Jim Clarke ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory
 Insertion Devices Lecture 4 Undulator Magnet Designs Jim Clarke ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory Hybrid Insertion Devices Inclusion of Iron Simple hybrid example Top Array e - Bottom Array 2 Lines of Magnetic
Insertion Devices Lecture 4 Undulator Magnet Designs Jim Clarke ASTeC Daresbury Laboratory Hybrid Insertion Devices Inclusion of Iron Simple hybrid example Top Array e - Bottom Array 2 Lines of Magnetic
Development of toroidal bending magnets for Hadron Beam Therapy. L. Bromberg, P. Michael, J.V. Minervini MIT E. Pearson, E.
 Development of toroidal bending magnets for Hadron Beam Therapy L. Bromberg, P. Michael, J.V. Minervini MIT E. Pearson, E. Forton IBA IntroducEon Toroidal magnets Array of idenecal coils, revolved around
Development of toroidal bending magnets for Hadron Beam Therapy L. Bromberg, P. Michael, J.V. Minervini MIT E. Pearson, E. Forton IBA IntroducEon Toroidal magnets Array of idenecal coils, revolved around
Cavity BPMs for the NLC
 SLAC-PUB-9211 May 2002 Cavity BPMs for the NLC Ronald Johnson, Zenghai Li, Takashi Naito, Jeffrey Rifkin, Stephen Smith, and Vernon Smith Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, 2575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo
SLAC-PUB-9211 May 2002 Cavity BPMs for the NLC Ronald Johnson, Zenghai Li, Takashi Naito, Jeffrey Rifkin, Stephen Smith, and Vernon Smith Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, 2575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo
Commissioning of a respiratory gating system involving a pressure sensor in carbon ion scanning radiotherapy
 Received: 14 March 2018 Revised: 29 August 2018 Accepted: 31 August 2018 DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12463 RADIATION ONCOLOGY PHYSICS Commissioning of a respiratory gating system involving a pressure sensor in carbon
Received: 14 March 2018 Revised: 29 August 2018 Accepted: 31 August 2018 DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12463 RADIATION ONCOLOGY PHYSICS Commissioning of a respiratory gating system involving a pressure sensor in carbon
RF CAVITY SIMULATIONS FOR SUPERCONDUCTING CYCLOTRON C400 Y. Jongen, M. Abs, W. Kleeven, S. Zaremba IBA, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium
 Ó³ Ÿ. 2011.. 8, º 4(167).. 647Ä654 ˆ ˆŠ ˆ ˆŠ Š ˆ RF CAVITY SIMULATIONS FOR SUPERCONDUCTING CYCLOTRON C400 Y. Jongen, M. Abs, W. Kleeven, S. Zaremba IBA, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium A. A. Glazov, S. V. Gurskiy,
Ó³ Ÿ. 2011.. 8, º 4(167).. 647Ä654 ˆ ˆŠ ˆ ˆŠ Š ˆ RF CAVITY SIMULATIONS FOR SUPERCONDUCTING CYCLOTRON C400 Y. Jongen, M. Abs, W. Kleeven, S. Zaremba IBA, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium A. A. Glazov, S. V. Gurskiy,
Design study for JT-60SA ECRF system and the latest results of JT-60U ECRF system
 Japan-Korea : Workshop on Physics of Wave Heating and Current Drive, NFRI, Daejon, Korea, Jan. 14-15, 2008 R F &LHRF& ECRF ICRF JT - 60 JT-60 RF group Japan Atomic Energy Agency Design study for JT-60SA
Japan-Korea : Workshop on Physics of Wave Heating and Current Drive, NFRI, Daejon, Korea, Jan. 14-15, 2008 R F &LHRF& ECRF ICRF JT - 60 JT-60 RF group Japan Atomic Energy Agency Design study for JT-60SA
Mapping of the New IBA Superconducting Synchrocyclotron (S2C2) for Proton Therapy
 Mapping of the New IBA Superconducting Synchrocyclotron (S2C2) for Proton Therapy J. Van de Walle, W. Kleeven, C. L'Abbate, Y. Paradis, V. Nuttens - IBA M. Conjat, J. Mandrillon, P. Mandrillon - AIMA Developpement
Mapping of the New IBA Superconducting Synchrocyclotron (S2C2) for Proton Therapy J. Van de Walle, W. Kleeven, C. L'Abbate, Y. Paradis, V. Nuttens - IBA M. Conjat, J. Mandrillon, P. Mandrillon - AIMA Developpement
Design of the magnets for the MAX IV project. Martin Johansson, Beam Dynamics meets Magnets-II workshop, Bad Zurzach, Dec.
 Design of the magnets for the MAX IV project Martin Johansson, Beam Dynamics meets Magnets-II workshop, Bad Zurzach, 01-04 Dec. 2014 MAX IV 3 GeV ring magnets key aspects: Relatively small magnet aperture
Design of the magnets for the MAX IV project Martin Johansson, Beam Dynamics meets Magnets-II workshop, Bad Zurzach, 01-04 Dec. 2014 MAX IV 3 GeV ring magnets key aspects: Relatively small magnet aperture
ALIGNMENT METHODS APPLIED TO THE LEP MAGNET MEASUREMENTS. J. Billan, G. Brun, K. N. Henrichsen, P. Legrand, 0. Pagano, P. Rohmig and L. Walckiers.
 295 ALIGNMENT METHODS APPLIED TO THE LEP MAGNET MEASUREMENTS J. Billan, G. Brun, K. N. Henrichsen, P. Legrand, 0. Pagano, P. Rohmig and L. Walckiers. CERN, CH-1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Introduction Electromagnets
295 ALIGNMENT METHODS APPLIED TO THE LEP MAGNET MEASUREMENTS J. Billan, G. Brun, K. N. Henrichsen, P. Legrand, 0. Pagano, P. Rohmig and L. Walckiers. CERN, CH-1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Introduction Electromagnets
Vibration measurement in the cryogenic interferometric gravitational wave detector (CLIO interferometer)
 Vibration measurement in the cryogenic interferometric gravitational wave detector (CLIO interferometer) ICRR Univ. of Tokyo, Dept. of geophysics Kyoto University A, KEK B, Dept. of advanced materials
Vibration measurement in the cryogenic interferometric gravitational wave detector (CLIO interferometer) ICRR Univ. of Tokyo, Dept. of geophysics Kyoto University A, KEK B, Dept. of advanced materials
PArticles in an accelerator generally oscillate in directions
 1 Real-Time Betatron Tune Correction with the Precise Measurement of Magnet Current Yoshinori Kurimoto, Tetsushi Shimogawa and Daichi Naito arxiv:1806.04022v1 [physics.acc-ph] 11 Jun 2018 Abstract The
1 Real-Time Betatron Tune Correction with the Precise Measurement of Magnet Current Yoshinori Kurimoto, Tetsushi Shimogawa and Daichi Naito arxiv:1806.04022v1 [physics.acc-ph] 11 Jun 2018 Abstract The
Test results on hybrid photodiodes
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 421 (1999) 512 521 Test results on hybrid photodiodes N. Kanaya*, Y. Fujii, K. Hara, T. Ishizaki, F. Kajino, K. Kawagoe, A. Nakagawa, M. Nozaki, T.Ota,
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 421 (1999) 512 521 Test results on hybrid photodiodes N. Kanaya*, Y. Fujii, K. Hara, T. Ishizaki, F. Kajino, K. Kawagoe, A. Nakagawa, M. Nozaki, T.Ota,
JEDI. Status of the commissioning of the waveguide RF Wien Filter
 COSY Beam Time Request For Lab. use Exp. No.: Session No. E 005.4 7 Collaboration: JEDI Status of the commissioning of the waveguide RF Wien Filter Spokespersons for the beam time: Ralf Gebel (Jülich)
COSY Beam Time Request For Lab. use Exp. No.: Session No. E 005.4 7 Collaboration: JEDI Status of the commissioning of the waveguide RF Wien Filter Spokespersons for the beam time: Ralf Gebel (Jülich)
Coaxial-type water load for measuring high voltage, high current and short pulse of a compact Marx system for a high power microwave source
 PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS 12, 113501 (2009) Coaxial-type water load for measuring high voltage, high current and short pulse of a compact Marx system for a high power microwave
PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS 12, 113501 (2009) Coaxial-type water load for measuring high voltage, high current and short pulse of a compact Marx system for a high power microwave
Physical Design of Superconducting Magnet for ADS Injection I
 Submitted to Chinese Physics C' Physical Design of Superconducting Magnet for ADS Injection I PENG Quan-ling( 彭全岭 ), WANG Bing( 王冰 ), CHEN Yuan( 陈沅 ) YANG Xiang-chen( 杨向臣 ) Institute of High Energy Physics,
Submitted to Chinese Physics C' Physical Design of Superconducting Magnet for ADS Injection I PENG Quan-ling( 彭全岭 ), WANG Bing( 王冰 ), CHEN Yuan( 陈沅 ) YANG Xiang-chen( 杨向臣 ) Institute of High Energy Physics,
CRYOGENIC CURRENT COMPARATOR FOR STORAGE RINGS AND ACCELERATORS
 CRYOGENIC CURRENT COMPARATOR FOR STORAGE RINGS AND ACCELERATORS R. Geithner #, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Germany & Helmholtz-Institut Jena, Germany T. Stöhlker, Helmholtz-Institut Jena, Germany
CRYOGENIC CURRENT COMPARATOR FOR STORAGE RINGS AND ACCELERATORS R. Geithner #, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Germany & Helmholtz-Institut Jena, Germany T. Stöhlker, Helmholtz-Institut Jena, Germany
Residual Resistivity Ratio (RRR) Measurements of LHC Superconducting NbTi Cable Strands
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH European Laboratory for Particle Physics Large Hadron Collider Project LHC Project Report 896 Residual Resistivity Ratio (RRR) Measurements of LHC Superconducting
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH European Laboratory for Particle Physics Large Hadron Collider Project LHC Project Report 896 Residual Resistivity Ratio (RRR) Measurements of LHC Superconducting
DEVELOPMENT OF OFFNER RELAY OPTICAL SYSTEM FOR OTR MONITOR AT 3-50 BEAM TRANSPORT LINE OF J-PARC
 Proceedings of IBIC01, Tsukuba, Japan DEVELOPMENT OF OFFNER RELAY OPTICAL SYSTEM FOR OTR MONITOR AT 3-50 BEAM TRANSPORT LINE OF J-PARC M. Tejima #, Y. Hashimoto, T. Toyama, KEK/J-PARC, Tokai, Ibaraki,
Proceedings of IBIC01, Tsukuba, Japan DEVELOPMENT OF OFFNER RELAY OPTICAL SYSTEM FOR OTR MONITOR AT 3-50 BEAM TRANSPORT LINE OF J-PARC M. Tejima #, Y. Hashimoto, T. Toyama, KEK/J-PARC, Tokai, Ibaraki,
A Penning Trap for Precision Spectroscopy of Highly Charged Ions at HITRAP. Jörg Krämer University of Mainz
 A Penning Trap for Precision Spectroscopy of Highly Charged Ions at HITRAP University of Mainz Experimental Goal Precise measurement of the hyperfine splitting in highly charged ions (HCI) as a test of
A Penning Trap for Precision Spectroscopy of Highly Charged Ions at HITRAP University of Mainz Experimental Goal Precise measurement of the hyperfine splitting in highly charged ions (HCI) as a test of
CEBAF Overview June 4, 2010
 CEBAF Overview June 4, 2010 Yan Wang Deputy Group Leader of the Operations Group Outline CEBAF Timeline Machine Overview Injector Linear Accelerators Recirculation Arcs Extraction Systems Beam Specifications
CEBAF Overview June 4, 2010 Yan Wang Deputy Group Leader of the Operations Group Outline CEBAF Timeline Machine Overview Injector Linear Accelerators Recirculation Arcs Extraction Systems Beam Specifications
LOW BETA CAVITY DEVELOPMENT FOR AN ATLAS INTENSITY UPGRADE
 LOW BETA CAVITY DEVELOPMENT FOR AN ATLAS INTENSITY UPGRADE M. P. Kelly, Z. A. Conway, S. M. Gerbick, M. Kedzie, T. C. Reid, R. C. Murphy, B. Mustapha, S.H. Kim, P. N. Ostroumov, Argonne National Laboratory,
LOW BETA CAVITY DEVELOPMENT FOR AN ATLAS INTENSITY UPGRADE M. P. Kelly, Z. A. Conway, S. M. Gerbick, M. Kedzie, T. C. Reid, R. C. Murphy, B. Mustapha, S.H. Kim, P. N. Ostroumov, Argonne National Laboratory,
two pairs of dipole steering windings that t inside the quadrupole yoke an RF beam position monitor (BPM) consisting of a pill box RF cavity,
 Chapter 6 Quadrupole Package The quadrupole package is shown in Fig. 6.1. It consists of a superferric quadrupole doublet powered in series enclosed in a stainless steel vessel and cooled by 4 K LHe; two
Chapter 6 Quadrupole Package The quadrupole package is shown in Fig. 6.1. It consists of a superferric quadrupole doublet powered in series enclosed in a stainless steel vessel and cooled by 4 K LHe; two
The Primary Design of the Ridgetron
 The Primary Design of the Ridgetron Li Jinhai #, Li Chunguang China Institute of Atomic Energy Abstract: The ridgetron is used to accelerate the intense beam for the electron irradiation. According to
The Primary Design of the Ridgetron Li Jinhai #, Li Chunguang China Institute of Atomic Energy Abstract: The ridgetron is used to accelerate the intense beam for the electron irradiation. According to
QUARTER WAVE COAXIAL LINE CAVITY FOR NEW DELHI LINAC BOOSTER*
 QUARTER WAVE COAXIAL LINE CAVITY FOR NEW DELHI LINAC BOOSTER* P.N. Prakash and A.Roy Nuclear Science Centre, P.O.Box 10502, New Delhi 110 067, INDIA and K.W.Shepard Physics Division, Argonne National Laboratory,
QUARTER WAVE COAXIAL LINE CAVITY FOR NEW DELHI LINAC BOOSTER* P.N. Prakash and A.Roy Nuclear Science Centre, P.O.Box 10502, New Delhi 110 067, INDIA and K.W.Shepard Physics Division, Argonne National Laboratory,
3 General layout of the XFEL Facility
 3 General layout of the XFEL Facility 3.1 Introduction The present chapter provides an overview of the whole European X-Ray Free-Electron Laser (XFEL) Facility layout, enumerating its main components and
3 General layout of the XFEL Facility 3.1 Introduction The present chapter provides an overview of the whole European X-Ray Free-Electron Laser (XFEL) Facility layout, enumerating its main components and
Impact of energy variation on Cone Ratio, PDD10, TMR20 10 and IMRT doses for flattening filter free (FFF) beam of TomoTherapy Hi-Art TM machines
 JBUON 2014; 19(4): 1105-1110 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of energy variation on Cone Ratio, PDD10, TMR20 10 and IMRT
JBUON 2014; 19(4): 1105-1110 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of energy variation on Cone Ratio, PDD10, TMR20 10 and IMRT
Study of the HD target spin rotations during G14
 Study of the HD target spin rotations during G14 A. Deur, deurpam@jlab.org April 18, 2013 1 Introduction During the G14 run, the target spin was reversed using either magnetic field rotations or RF spin
Study of the HD target spin rotations during G14 A. Deur, deurpam@jlab.org April 18, 2013 1 Introduction During the G14 run, the target spin was reversed using either magnetic field rotations or RF spin
Proton beam for UCN. UCN TAC-Meeting, May 12-13, 2005 Urs Rohrer, beam line physicist
 Proton beam for UCN UCN TAC-Meeting, May 12-13, 2005 Urs Rohrer, beam line physicist PSI Accelerator Division Department of Large Research Facilities Introduction Important parameters of the PSI proton
Proton beam for UCN UCN TAC-Meeting, May 12-13, 2005 Urs Rohrer, beam line physicist PSI Accelerator Division Department of Large Research Facilities Introduction Important parameters of the PSI proton
Construction of Phase-I Insertion Devices at TPS
 FACILITY STATUS 071 Construction of Phase-I Insertion Devices at TPS Taiwan Photon Source (TPS), a third-generation light source based on a 3-GeV storage ring, is featured with high brilliant insertion
FACILITY STATUS 071 Construction of Phase-I Insertion Devices at TPS Taiwan Photon Source (TPS), a third-generation light source based on a 3-GeV storage ring, is featured with high brilliant insertion
HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE
 HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE Takeyuki Hashimoto 1), Morio Onoe 2), Hiroshi Nakamura 3), Tamon Inouye 4), Hiromichi Jumonji 5), Iwao Takahashi 6); 1)Yokohama Soei
HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE Takeyuki Hashimoto 1), Morio Onoe 2), Hiroshi Nakamura 3), Tamon Inouye 4), Hiromichi Jumonji 5), Iwao Takahashi 6); 1)Yokohama Soei
Magnetic measurement system for superconducting final focus quadrupoles for SuperKEKB
 Magnetic measurement system for superconducting final focus quadrupoles for SuperKEKB Y. Arimoto (KEK) IMMW 20 @ Diamond Light Source 2017/Jun/8 SuperKEKB Final focus magnet system Magnetic field measurement
Magnetic measurement system for superconducting final focus quadrupoles for SuperKEKB Y. Arimoto (KEK) IMMW 20 @ Diamond Light Source 2017/Jun/8 SuperKEKB Final focus magnet system Magnetic field measurement
Mode Error Analysis of Impedance Measurement using Twin Wires *
 Mode Error Analysis of Impedance Measurement using Twin Wires * Huang Liang-Sheng( 黄良生 ) a,b), Yoshiro Irie( 入江吉郎 ) a,c), Liu Yu-Dong( 刘瑜冬 ) a,b), a,b, #) Wang Sheng( 王生 ) a China Spallation Neutron Source
Mode Error Analysis of Impedance Measurement using Twin Wires * Huang Liang-Sheng( 黄良生 ) a,b), Yoshiro Irie( 入江吉郎 ) a,c), Liu Yu-Dong( 刘瑜冬 ) a,b), a,b, #) Wang Sheng( 王生 ) a China Spallation Neutron Source
Design of ESS-Bilbao RFQ Linear Accelerator
 Design of ESS-Bilbao RFQ Linear Accelerator J.L. Muñoz 1*, D. de Cos 1, I. Madariaga 1 and I. Bustinduy 1 1 ESS-Bilbao *Corresponding author: Ugaldeguren III, Polígono A - 7 B, 48170 Zamudio SPAIN, jlmunoz@essbilbao.org
Design of ESS-Bilbao RFQ Linear Accelerator J.L. Muñoz 1*, D. de Cos 1, I. Madariaga 1 and I. Bustinduy 1 1 ESS-Bilbao *Corresponding author: Ugaldeguren III, Polígono A - 7 B, 48170 Zamudio SPAIN, jlmunoz@essbilbao.org
Production Measurements of Magnets for the NSLS-II Storage Ring*
 Production Measurements of Magnets for the NSLS-II Storage Ring* Animesh Jain Superconducting Magnet Division Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973 17 th International Magnetic Measurement Workshop
Production Measurements of Magnets for the NSLS-II Storage Ring* Animesh Jain Superconducting Magnet Division Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973 17 th International Magnetic Measurement Workshop
X-ray generation by femtosecond laser pulses and its application to soft X-ray imaging microscope
 X-ray generation by femtosecond laser pulses and its application to soft X-ray imaging microscope Kenichi Ikeda 1, Hideyuki Kotaki 1 ' 2 and Kazuhisa Nakajima 1 ' 2 ' 3 1 Graduate University for Advanced
X-ray generation by femtosecond laser pulses and its application to soft X-ray imaging microscope Kenichi Ikeda 1, Hideyuki Kotaki 1 ' 2 and Kazuhisa Nakajima 1 ' 2 ' 3 1 Graduate University for Advanced
Conceptual Design of a Table-top Terahertz Free-electron Laser
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 59, No. 5, November 2011, pp. 3251 3255 Conceptual Design of a Table-top Terahertz Free-electron Laser Y. U. Jeong, S. H. Park, K. Lee, J. Mun, K. H. Jang,
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 59, No. 5, November 2011, pp. 3251 3255 Conceptual Design of a Table-top Terahertz Free-electron Laser Y. U. Jeong, S. H. Park, K. Lee, J. Mun, K. H. Jang,
Examination of Microphonic Effects in SRF Cavities
 Examination of Microphonic Effects in SRF Cavities Christina Leidel Department of Physics, Ohio Northern University, Ada, OH, 45810 (Dated: August 13, 2004) Superconducting RF cavities in Cornell s proposed
Examination of Microphonic Effects in SRF Cavities Christina Leidel Department of Physics, Ohio Northern University, Ada, OH, 45810 (Dated: August 13, 2004) Superconducting RF cavities in Cornell s proposed
4. Superconducting sector magnets for the SRC 4.1 Introduction
 4. Superconducting sector magnets for the SRC 4.1 Introduction The key components for the realization for the SRC are: the superconducting sector magnet and the superconducting bending magnet (SBM) for
4. Superconducting sector magnets for the SRC 4.1 Introduction The key components for the realization for the SRC are: the superconducting sector magnet and the superconducting bending magnet (SBM) for
COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT MAGNETIC MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES.
 COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT MAGNETIC MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES. Isaac Vasserman, Shigemi Sasaki Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL 60439, USA Abstract The magnetic measurement system at APS was upgraded.
COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT MAGNETIC MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES. Isaac Vasserman, Shigemi Sasaki Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL 60439, USA Abstract The magnetic measurement system at APS was upgraded.
DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION PROGRESS OF CYCIAE-100, A 100 MEV H- CYCLOTRON AT CIAE *
 DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION PROGRESS OF CYCIAE-100, A 100 MEV H- CYCLOTRON AT CIAE * CYCIAE-100 Project Team, Written by Tianjue Zhang #, Zhenguo Li and Chengjie Chu China Institute of Atomic Energy, P.O.Box
DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION PROGRESS OF CYCIAE-100, A 100 MEV H- CYCLOTRON AT CIAE * CYCIAE-100 Project Team, Written by Tianjue Zhang #, Zhenguo Li and Chengjie Chu China Institute of Atomic Energy, P.O.Box
Hall C Polarimetry at 12 GeV Dave Gaskell Hall C Users Meeting January 14, 2012
 Hall C Polarimetry at 12 GeV Dave Gaskell Hall C Users Meeting January 14, 2012 1. Møller Polarimeter 2. Compton Polarimeter Hall C 12 GeV Polarimetry Møller Polarimeter 6 GeV operation: uses 2 quads to
Hall C Polarimetry at 12 GeV Dave Gaskell Hall C Users Meeting January 14, 2012 1. Møller Polarimeter 2. Compton Polarimeter Hall C 12 GeV Polarimetry Møller Polarimeter 6 GeV operation: uses 2 quads to
DEVELOPMENT OF A BETA 0.12, 88 MHZ, QUARTER WAVE RESONATOR AND ITS CRYOMODULE FOR THE SPIRAL2 PROJECT
 DEVELOPMENT OF A BETA 0.12, 88 MHZ, QUARTER WAVE RESONATOR AND ITS CRYOMODULE FOR THE SPIRAL2 PROJECT G. Olry, J-L. Biarrotte, S. Blivet, S. Bousson, C. Commeaux, C. Joly, T. Junquera, J. Lesrel, E. Roy,
DEVELOPMENT OF A BETA 0.12, 88 MHZ, QUARTER WAVE RESONATOR AND ITS CRYOMODULE FOR THE SPIRAL2 PROJECT G. Olry, J-L. Biarrotte, S. Blivet, S. Bousson, C. Commeaux, C. Joly, T. Junquera, J. Lesrel, E. Roy,
Status of Proton Beam Commissioning at MedAustron Ion Beam Therapy Center
 Status of Proton Beam Commissioning at MedAustron Ion Beam Therapy Center A. Garonna, A. Wastl, C. Kurfuerst, T. Kulenkampff, C. Schmitzer, L. Penescu, M. Pivi, M. Kronberger, F. Osmic, P. Urschuetz On
Status of Proton Beam Commissioning at MedAustron Ion Beam Therapy Center A. Garonna, A. Wastl, C. Kurfuerst, T. Kulenkampff, C. Schmitzer, L. Penescu, M. Pivi, M. Kronberger, F. Osmic, P. Urschuetz On
Review of the magnetic measurement technique (experience of the SLC, LEP, CEBAF)
 Review of the magnetic measurement technique (experience of the SLC, LEP, CEBAF) N.A.Morozov Workshop on the TESLA spectrometer, Dubna, 13-14 October 2003 1..Stanford Linear Collider (SLC) To implement
Review of the magnetic measurement technique (experience of the SLC, LEP, CEBAF) N.A.Morozov Workshop on the TESLA spectrometer, Dubna, 13-14 October 2003 1..Stanford Linear Collider (SLC) To implement
RESULTS ON FIELD MEASUREMENTS IN A FLAT POLE MAGNET WITH THE CURRENT CARING SHEETS
 CBN 14-01 March 10, 2014 RESULTS ON FIELD MEASUREMENTS IN A FLAT POLE MAGNET WITH THE CURRENT CARING SHEETS Alexander Mikhailichenko Abstract. The results of measurements with a gradient magnet, arranged
CBN 14-01 March 10, 2014 RESULTS ON FIELD MEASUREMENTS IN A FLAT POLE MAGNET WITH THE CURRENT CARING SHEETS Alexander Mikhailichenko Abstract. The results of measurements with a gradient magnet, arranged
PINGER MAGNET SYSTEM FOR THE ALBA SYNCHROTRON LIGHT SOURCE
 ACDIV-2015-03 May, 2015 PINGER MAGNET SYSTEM FOR THE ALBA SYNCHROTRON LIGHT SOURCE M.Pont, N.Ayala, G.Benedetti, M.Carla, Z.Marti, R.Nuñez ALBA Synchrotron, Barcelona, Spain Abstract A pinger magnet system
ACDIV-2015-03 May, 2015 PINGER MAGNET SYSTEM FOR THE ALBA SYNCHROTRON LIGHT SOURCE M.Pont, N.Ayala, G.Benedetti, M.Carla, Z.Marti, R.Nuñez ALBA Synchrotron, Barcelona, Spain Abstract A pinger magnet system
MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One
 MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One 1 MAIN COMPONENTS Magnet Gradient Coils RF Coils Host Computer / Electronic Support System Operator Console and Display Systems 2 3 4 5 Magnet Components 6 The magnet The
MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One 1 MAIN COMPONENTS Magnet Gradient Coils RF Coils Host Computer / Electronic Support System Operator Console and Display Systems 2 3 4 5 Magnet Components 6 The magnet The
HIGH POWER INPUT COUPLERS FOR THE STF BASELINE CAVITY SYSTEM AT KEK
 HIGH POWER INPUT COUPLERS FOR THE STF BASELINE CAVITY SYSTEM AT KEK E. Kako #, H. Hayano, S. Noguchi, T. Shishido, K. Watanabe and Y. Yamamoto KEK, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-0801, Japan Abstract An input coupler,
HIGH POWER INPUT COUPLERS FOR THE STF BASELINE CAVITY SYSTEM AT KEK E. Kako #, H. Hayano, S. Noguchi, T. Shishido, K. Watanabe and Y. Yamamoto KEK, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-0801, Japan Abstract An input coupler,
Physics Requirements Document Document Title: SCRF 1.3 GHz Cryomodule Document Number: LCLSII-4.1-PR-0146-R0 Page 1 of 7
 Document Number: LCLSII-4.1-PR-0146-R0 Page 1 of 7 Document Approval: Originator: Tor Raubenheimer, Physics Support Lead Date Approved Approver: Marc Ross, Cryogenic System Manager Approver: Jose Chan,
Document Number: LCLSII-4.1-PR-0146-R0 Page 1 of 7 Document Approval: Originator: Tor Raubenheimer, Physics Support Lead Date Approved Approver: Marc Ross, Cryogenic System Manager Approver: Jose Chan,
Development of the accelerometer for cryogenic experiments II
 Development of the accelerometer for cryogenic experiments II ICRR Univ. of Tokyo, KEK A, Dept. of advanced materials science Univ. of Tokyo B K. Yamamoto, H. Hayakawa, T. Uchiyama, S. Miyoki, H. Ishitsuka,
Development of the accelerometer for cryogenic experiments II ICRR Univ. of Tokyo, KEK A, Dept. of advanced materials science Univ. of Tokyo B K. Yamamoto, H. Hayakawa, T. Uchiyama, S. Miyoki, H. Ishitsuka,
K1200 Stripper Foil Mechanism RF Shielding
 R.F. Note #121 Sept. 21, 2000 John Vincent Shelly Alfredson John Bonofiglio John Brandon Dan Pedtke Guenter Stork K1200 Stripper Foil Mechanism RF Shielding INTRODUCTION... 2 MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES AND
R.F. Note #121 Sept. 21, 2000 John Vincent Shelly Alfredson John Bonofiglio John Brandon Dan Pedtke Guenter Stork K1200 Stripper Foil Mechanism RF Shielding INTRODUCTION... 2 MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES AND
ELECTRON CLOUD MITIGATION INVESTIGATIONS AT CESR-TA
 Proceedings of ECLOUD1, Ithaca, New York, USA MIT1 ELECTRON CLOUD MITIGATION INVESTIGATIONS AT CESR-TA J.R. Calvey, J. Makita, M.A. Palmer, R.M. Schwartz, C.R. Strohman, CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca,
Proceedings of ECLOUD1, Ithaca, New York, USA MIT1 ELECTRON CLOUD MITIGATION INVESTIGATIONS AT CESR-TA J.R. Calvey, J. Makita, M.A. Palmer, R.M. Schwartz, C.R. Strohman, CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca,
ADVANCES IN CW ION LINACS*
 Abstract Substantial research and development related to continuous wave (CW) proton and ion accelerators is being performed at ANL. A 4-meter long 60.625-MHz normal conducting (NC) CW radio frequency
Abstract Substantial research and development related to continuous wave (CW) proton and ion accelerators is being performed at ANL. A 4-meter long 60.625-MHz normal conducting (NC) CW radio frequency
A Superconducting Helical Undulator-Based FEL Prototype Cryomodule
 A Superconducting Helical Undulator-Based FEL Prototype Cryomodule E. Gluskin PI, APS/ANL P. Emma Co-PI, SLAC, Y. Ivanyushenkov Co-PI, APS/ANL Sep. 19, 2016 1. Introduction and Motivation Undulators serve
A Superconducting Helical Undulator-Based FEL Prototype Cryomodule E. Gluskin PI, APS/ANL P. Emma Co-PI, SLAC, Y. Ivanyushenkov Co-PI, APS/ANL Sep. 19, 2016 1. Introduction and Motivation Undulators serve
SUPPRESSING ELECTRON MULTIPACTING IN TTF III COLD WINDOW BY DC BIAS
 SUPPRESSING ELECTRON MULTIPACTING IN TTF III COLD WINDOW BY DC BIAS PASI YLÄ-OIJALA and MARKO UKKOLA Rolf Nevanlinna Institute, University of Helsinki, PO Box 4, (Yliopistonkatu 5) FIN 4 Helsinki, Finland
SUPPRESSING ELECTRON MULTIPACTING IN TTF III COLD WINDOW BY DC BIAS PASI YLÄ-OIJALA and MARKO UKKOLA Rolf Nevanlinna Institute, University of Helsinki, PO Box 4, (Yliopistonkatu 5) FIN 4 Helsinki, Finland
LINEAR INDUCTION ACCELERATOR WITH MAGNETIC STEERING FOR INERTIAL FUSION TARGET INJECTION
 LINEAR INDUCTION ACCELERATOR WITH MAGNETIC STEERING FOR INERTIAL FUSION TARGET INJECTION Ronald Petzoldt,* Neil Alexander, Lane Carlson, Eric Cotner, Dan Goodin and Robert Kratz General Atomics, 3550 General
LINEAR INDUCTION ACCELERATOR WITH MAGNETIC STEERING FOR INERTIAL FUSION TARGET INJECTION Ronald Petzoldt,* Neil Alexander, Lane Carlson, Eric Cotner, Dan Goodin and Robert Kratz General Atomics, 3550 General
Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Cyclotrons and their Applications, Berlin, Germany
 HISTRAP PROTOTYPE HARDWARE STUDIES* D. K. Olsen, W. H. Atkins, D. T. Dowling, J. W. Johnson, R. S. Lord,** J. W. McConnell, W. T. Milner, S. W. Mosko, and B. A. Tatum Oak Ridge National Laboratory Post
HISTRAP PROTOTYPE HARDWARE STUDIES* D. K. Olsen, W. H. Atkins, D. T. Dowling, J. W. Johnson, R. S. Lord,** J. W. McConnell, W. T. Milner, S. W. Mosko, and B. A. Tatum Oak Ridge National Laboratory Post
Pedroni Eros Paul Scherrer Institute - Villigen PSI, Switzerland
 Pedroni Eros Paul Scherrer Institute - Villigen PSI, Switzerland Center for proton therapy - PSI GANTRY DESIGN AND RECENT EXPERIENCE AT PSI 2nd Workshop on Hadron Beam Therapy of Cancer ERICE May 23 th,
Pedroni Eros Paul Scherrer Institute - Villigen PSI, Switzerland Center for proton therapy - PSI GANTRY DESIGN AND RECENT EXPERIENCE AT PSI 2nd Workshop on Hadron Beam Therapy of Cancer ERICE May 23 th,
HIGHER ORDER MODES FOR BEAM DIAGNOSTICS IN THIRD HARMONIC 3.9 GHZ ACCELERATING MODULES *
 HIGHER ORDER MODES FOR BEAM DIAGNOSTICS IN THIRD HARMONIC 3.9 GHZ ACCELERATING MODULES * N. Baboi #, N. Eddy, T. Flisgen, H.-W. Glock, R. M. Jones, I. R. R. Shinton, and P. Zhang # # Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron
HIGHER ORDER MODES FOR BEAM DIAGNOSTICS IN THIRD HARMONIC 3.9 GHZ ACCELERATING MODULES * N. Baboi #, N. Eddy, T. Flisgen, H.-W. Glock, R. M. Jones, I. R. R. Shinton, and P. Zhang # # Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron
Attosecond Diagnostics of Muti GeV Electron Beams Using W Band Deflectors
 Attosecond Diagnostics of Muti GeV Electron Beams Using W Band Deflectors V.A. Dolgashev, P. Emma, M. Dal Forno, A. Novokhatski, S. Weathersby SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory FEIS 2: Femtosecond Electron
Attosecond Diagnostics of Muti GeV Electron Beams Using W Band Deflectors V.A. Dolgashev, P. Emma, M. Dal Forno, A. Novokhatski, S. Weathersby SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory FEIS 2: Femtosecond Electron
SIGNAL TRANSMISSION CHARACTERISTICS IN STRIPLINE-TYPE BEAM POSITION MONITOR
 Proceedings of IBIC01, Tsukuba, Japan SIGNAL TRANSISSION CHARACTERISTICS IN STRIPLINE-TYPE BEA POSITION ONITOR T. Suwada, KEK, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0801, Japan Abstract A new stripline-type beam position
Proceedings of IBIC01, Tsukuba, Japan SIGNAL TRANSISSION CHARACTERISTICS IN STRIPLINE-TYPE BEA POSITION ONITOR T. Suwada, KEK, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0801, Japan Abstract A new stripline-type beam position
Precision RF Beam Position Monitors for Measuring Beam Position and Tilt Progress Report
 Precision RF Beam Position Monitors for Measuring Beam Position and Tilt Progress Report UC Berkeley Senior Personnel Yury G. Kolomensky Collaborating Institutions Stanford Linear Accelerator Center: Marc
Precision RF Beam Position Monitors for Measuring Beam Position and Tilt Progress Report UC Berkeley Senior Personnel Yury G. Kolomensky Collaborating Institutions Stanford Linear Accelerator Center: Marc
KEK Digital Accelerator and Its Beam Commissioning
 KEK Digital Accelerator and Its Beam Commissioning Ken Takayama High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) Tokyo Institute of Technology on behalf of KEK Digital Accelerator Project Team September
KEK Digital Accelerator and Its Beam Commissioning Ken Takayama High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK) Tokyo Institute of Technology on behalf of KEK Digital Accelerator Project Team September
Far field intensity distributions of an OMEGA laser beam were measured with
 Experimental Investigation of the Far Field on OMEGA with an Annular Apertured Near Field Uyen Tran Advisor: Sean P. Regan Laboratory for Laser Energetics Summer High School Research Program 200 1 Abstract
Experimental Investigation of the Far Field on OMEGA with an Annular Apertured Near Field Uyen Tran Advisor: Sean P. Regan Laboratory for Laser Energetics Summer High School Research Program 200 1 Abstract
Pulsed 5 MeV standing wave electron linac for radiation processing
 PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS, VOLUME 7, 030101 (2004) Pulsed 5 MeV standing wave electron linac for radiation processing L. Auditore, R. C. Barnà, D. De Pasquale, A. Italiano,
PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS, VOLUME 7, 030101 (2004) Pulsed 5 MeV standing wave electron linac for radiation processing L. Auditore, R. C. Barnà, D. De Pasquale, A. Italiano,
