584 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 7, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008
|
|
|
- Warren Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 584 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL 7, NO 2, FEBRUARY 28 An Optiiztion Frework for Blncing Throughput nd Firness in Wireless Networks With QoS Support Ho Ting Cheng, Student Meber, IEEE, nd Weihu Zhung, Senior Meber, IEEE Abstrct Qulity-of-service (QoS) provisioning, high syste throughput, nd firness ssurnce re indispensble for heterogeneous trffic in future wireless brodbnd networks With liited rdio resources, incresing syste throughput nd intining firness re conflicting perfornce etrics, leding to nturl trdeoff between these two esures Blncing syste throughput nd firness is desired In this pper, we consider n interference-liited wireless network, nd derive generic optiiztion frework to obtin n optil reltionship of syste throughput nd firness with QoS support nd efficient resource utiliztion, by introducing the brgining floor Fro the reltionship curve, different degrees of perfornce trdeoff between throughput nd firness cn be obtined by choosing different brgining floors In ddition, our frework fcilittes cll dission control to effectively gurntee QoS of ultiedi trffic The solutions of resource lloction obtined fro the optiiztion frework chieve the Preto Optility, deonstrting efficient use of network resources Index Ters Firness, optiiztion, Preto optility, qulity-of-service (QoS), throughput I INTRODUCTION FUTURE wireless brodbnd networks re expected to support ubiquitous counictions nd obile coputing, the notion of which hs been ttrcting plethor of ttention fro cdei nd industry Ubiquitous wireless ccess cn be relized in vrious prcticl scenrios, nely hoe networking, office networking, nd city networking [1] Copred with the trditionl networking dependent on cbles, wireless network is fster in deployent with lower cost, fcilitted by voiding tie-consuing nd costly opertions such s lnd construction nd cble plceent The wireless networking prdig provides not only vible, but lso econoicl solution for both peer-to-peer pplictions nd Internet ccess In order to fully exploit proising wireless technologies, efficient nd effective rdio resource ngeent in wireless networks is crucil In wireless networks, syste throughput is usully coon perfornce etric [2] However, next-genertion wireless networks such s wireless esh networks re nticipted Mnuscript received July 25, 26; revised Deceber 5, 26, Februry 23, 27, nd My 1, 27; ccepted July 5, 27 The ssocite editor coordinting the review of this pper nd pproving it for publiction ws M Zorzi This work ws supported in prt by the Nturl Science nd Engineering Reserch Council (NSERC) of Cnd The uthors re with the Centre for Wireless Counictions, Deprtent of Electricl nd Coputer Engineering, University of Wterloo, 2 University Avenue West, Wterloo, Ontrio, Cnd N2L 3G1 (e-il: {htcheng,wzhung@bbcruwterlooc) Digitl Object Identifier 1119/TWC /8$25 c 28 IEEE to support ultiedi trffic (eg, voice, video, nd dt trffic) With heterogeneous trffic, qulity-of-service (QoS) provisioning nd firness support re lso iportnt With liited vilble rdio resources, incresing syste throughput nd intining firness re usully conflicting with ech other [3], leding to nturl trdeoff between these two perfornce esures In prticulr, blncing syste throughput nd firness with QoS support nd high resource efficiency is necessry, depending on different pplictionspecific scenrios [1] In literture, only liited work ddresses the optil reltionship of throughput nd firness [4] [13] To the best of our knowledge, there is no widely ccepted unified frework to effectively ttin different degrees of perfornce trdeoff between throughput nd firness with QoS support nd efficient resource utiliztion, which is the otivtion of this reserch With focus on interference-liited wireless networks, the key contribution of this pper is to derive unified optiiztion frework to obtin the optil reltionship (ie, trdeoff curve) of syste throughput nd firness with QoS support By introducing brgining floor, the reltionship curve is obtined by solving the optiiztion proble itertively Different degrees of perfornce trdeoff between throughput nd firness cn be chieved by siply choosing pproprite vlues of the brgining floor Given n ppliction of interest, the desired operting trdeoff cn be deterined Resource utiliztion is efficient, which is verified by ge theory, chieving Preto Optility [14] To effectively provision QoS of ultiedi trffic, cll dission control is vitl to gurntee the QoS requireents of ditted clls Whether new incoing cll should be ditted or rejected is contingent upon the wy how the resources re llocted to wireless links nd how uch resources re left in the network Contributing to the criterion of cll dission, our optiiztion frework plys n iportnt role in cll dission control so s to fcilitte the opertion of blncing throughput nd firness The rest of the pper is orgnized s follows Relted work is discussed in Section II The syste odel is given in Section III The optiiztion proble forultion is presented in Section IV Efficiency of the proposed resource lloction is ddressed in Section V Nuericl results re given in Section VI Prcticl ipleenttion issues re discussed in Section VII Finlly, conclusion is drwn in Section VIII
2 CHENG et l: AN OPTIMIZATION FRAMEWORK FOR BALANCING THROUGHPUT AND FAIRNESS IN WIRELESS NETWORKS WITH QOS SUPPORT 585 II RELATED WORK In the literture, utility optiiztion is tool to esure syste perfornce subject to certin constrints (eg, QoS requireents) [4] [7], where utility function is described s esure of user stisfction Proportionl firness cn be obtined by choosing suitble utility functions (eg, logrithic functions) [4] Other perfornce esure (such s throughput) cn lso be incorported into this optiiztion forultion [6] With different proble forultions (ie, utility functions), different optil solutions cn be obtined (eg, optil throughput) Pricing schees [4] cn be eployed to chieve trdeoff between throughput nd firness, to certin extent However, the utility functions used in these work y not hve ny physicl ening How to find eningful utility function with n pproprite pricing schee cn lso be probletic In ddition, ost of the current work ssues tht the utility functions cn be seprble in the dul proble [4] [7], which y not lwys be the cse, especilly for interference-liited systes such s code-division ultiple ccess (CDMA) nd ultr-widebnd (UWB) systes, ening tht pplying existing pproches (eg, [7]) generlly results in suboptil solutions In the interference-liited systes, optility should be obtined by considering ll (user) utility functions together Idel (weighted x-in) firness cn be obtined by generlized processor shring (GPS) [8], [9] or its vrints [1], where ll nodes in the network shre the totl resources With GPS, the resource llocted to ech node is dependent on its own weight, whereby ech node cn hve fir shre of resources However, the notion of weight is n bstrct concept nd the question of how to relte QoS requireents to the weight effectively reins unsolved In GPS, even though ll the weights or QoS requireents re lredy stisfied, only (weighted x-in) firness is considered Further, the throughput perfornce of GPS needs further investigtion Although soe reserch is t the trdeoff between throughput nd firness in telecounictions networks, only heuristic schees re proposed without ny optility considertion [11] [13] Thus fr, only liited reltionship of syste throughput nd firness is ddressed Joint considertion of both perfornce etrics nd hence unified frework ttining different degrees of perfornce trdeoff between the with QoS support re desired Further, with scrce rdio resources, efficient resource utiliztion is vitl, which cn be verified by ge theory [14] All these spects re ddressed in this pper III SYSTEM MODEL We consider generic syste odel which is n interference-liited wireless network We ssue tht the chnnel gins re known in dvnce or cn be estited ccurtely vi pilot sybols Let R d denote the effective bndwidth of cll on the th link, which is the iniu rte required to stisfy the QoS requireents nd depends on source trffic chrcteristics [16], [17] Let R () denote the ctul trnsission rte of the th link where = ( 1, 2,,,, M ) nd is the power scling fctor of the th link s trnsitter, ie, [, 1], nd M the totl nuber of ctive links in the network For siplicity, the ctul trnsission rte of the th link is given by [18] R () =B log 2 (1 + γ ) (1) where B is the chnnel bndwidth nd γ is the signl-tointerference-plus-noise rtio of the th link In (1), γ = G P σ n G np n n + η where P is xiu trnsit power level of the th link s trnsitter, G n is the chnnel gin fro the n th link s trnsitter to the th link s receiver, σ is the cross-correltion fctor between ny two signls, ie, σ (, 1], nd η is the bckground noise power Notice tht (1) cn be esily extended to incorporte bit-error-rte (BER) requireents, coding nd odultion schees to copute the ttinble chnnel trnsission rte (or cpcity) [19] This ttinble chnnel trnsission rte is equl to the chievble throughput t the physicl lyer In prctice, the throughput (or goodput) obtined t the ediu ccess control lyer (nd higher lyers) is usully lower thn the chnnel trnsission rte due to the overhed of pcketiztion, ediu ccess control, etc Given ll the detils of syste preters, the ctul throughput cn be coputed fro the chnnel trnsission rte In order to effectively blnce syste throughput nd firness, cll dission control is indispensble, which cn be contingent on our optiiztion frework (to be discussed in Section IV) The cll dission routine 1 is invoked whenever new cll rrives For ech incoing new cll, it is ditted s long s there exists fesible solution of the optiiztion proble, ening tht the QoS requireents (ie, in ters of effective bndwidth) of this new cll nd ll other clls in service cn be stisfied If there is no fesible solution of the optiiztion proble, the new cll is rejected due to insufficient resources vilble to eet its QoS requireents In other words, the criterion of cll dission is tntount to the fesibility of the solution of our optiiztion frework With the cll dission control in plce, the QoS requireents of ll ditted clls cn be gurnteed nd the opertion of blncing throughput nd firness cn be crried out effectively Given tht the QoS requireents cn be et, the network perfornce cn be further iproved for incresing syste throughput nd/or intining (weighted x-in) firness, utilizing the resources efficiently In this reserch, the notion of weighted x-in firness is tken s the firness perfornce of interest, which corresponds to the idel firness chieved by the GPS A sury of iportnt sybols used in this pper is given in Tble I IV OPTIMIZATION PROBLEM FORMULATION In this section, we first consider two optiiztion proble forultions, nely syste throughput optiiztion nd 1 Notice tht routing is involved in the cll dission control Prticulrly, the tsks of QoS routing include 1) route discovery; 2) cll dission control over ech link; nd 3) route repir Therefore, which link cll is to trverse long cn be deterined [15] (2)
3 586 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL 7, NO 2, FEBRUARY 28 Sybol Definition TABLE I SUMMARY OF IMPORTANT SYMBOLS R d effective bndwidth of cll on the th link R () ctul trnsission rte of the th link Q () utility function (ie, extr throughput obtined) of the th link, ie, Q () =R () R d w weighting fctor of the th link, ie, w > P xiu trnsit power level of the th link s trnsitter G n chnnel gin fro the n th link s trnsitter to the th link s receiver power scling fctor of the th link s trnsitter, ie, [, 1] γ signl-to-interference-plus-noise rtio of the th link σ cross-correltion fctor between ny two signls, ie, σ (, 1] η bckground noise power M totl nuber of ctive links in the network B chnnel bndwidth J brgining floor, ie, J [,J ],wherej is the xiu vlue of J D devition of in {w Q () fro J, ie, D = J in {w Q () U esure of syste throughput, ie, U [, 1] V esure of firness, ie, V [, 1] W shped Jin s firness index, ie, W [, 1] weighted x-in firness optiiztion Next, the generic optiiztion proble forultion with syste throughput nd firness considertion is presented For the syste throughput optiiztion, the optiiztion proble is given by { M x R () (3) =1 subject to R () R, d 1, (4) where =( 1, 2,,,, M ) is the optiiztion vrible In fct, (3) cn be rewritten s { M ( x R () R d ) (5) =1 s the optility still intins for liner-shifted objective function [2] The syste throughput optiiztion proble (STOP) cn be rewritten s { M x Q () (6) =1 subject to Q (), 1, (7) where Q () = R () R d The physicl ening of Q () is the ount of extr resources llocted to (ie, excess throughput obtined by) the th link As coprison, Q () cn be viewed s the utility function of user in the conventionl utility xiiztion [4] [6], s Q () of user is: 1) incresing; 2) strictly concve; nd 3) twice differentible (ie, continuous) on Then, the interprettion of (6) is to chieve socil optility (ie, xiu of totl utility functions) However, in our cse, the utility functions re not seprble in the dul proble s Q () only increses with but not over Consider the following (prtil) dul proble [5]: in D(λ) (8) λ where λ = (λ 1,λ 2,, λ,, λ M ) is set of Lgrnge ultipliers nd { D(λ) = x Q ()+ λ Q () (9) Suppose tht the optility still intins when ech (user) utility function, Q (), is optiized seprtely Intuitively, ech user will siply choose the xiu power scling fctor, ie, = 1, In ost cses, due to the crossinterference (ie, σ ), the overll result will not contribute to the xiu vlue of (6), though Nsh Equilibriu is chieved [14] Optiizing individul user utility function seprtely y not lwys result in the xil solution of the STOP, s in generl fro (9), D(λ) = x = x { Q ()+ λ Q () { (1 + λ ) Q () (1) (11) x {(1 + λ ) Q () (12) Thus, the solution spce (ie, resource lloction) is not necessrily the se s those proposed in the literture (eg, [5]) Obtining the optil solution requires joint considertion of ll user utility functions, ening tht existing solutions cnnot be directly pplied For the weighted x-in firness optiiztion proble
4 CHENG et l: AN OPTIMIZATION FRAMEWORK FOR BALANCING THROUGHPUT AND FAIRNESS IN WIRELESS NETWORKS WITH QOS SUPPORT 587 (WMMFOP), the corresponding forultion is given by [21] { x in {w Q () (13) subject to Q (), 1, (14) where w is weighting fctor of the th link, ie, w >, which indictes the unwillingness of obtining extr llocted resources, ie, the sller the vlue of w, the ore eger is the th link to obtin ore extr resources The use of w is necessry for effective nd efficient resource lloction in wireless networks with heterogeneous trffic (eg, voice, video, nd dt trffic) For exple, for voice trffic, fter its effective bndwidth requireent is stisfied, llocting extr resources to it y be wsteful s the qulity of signl reception is lredy good, nd hence this trffic should be ssigned lrger weighting fctor On the other hnd, sller weighting fctor should be ssigned to dt trffic, s it dends ore throughput even though its effective bndwidth requireent is lredy et With different weighting fctors, different trffic clsses cn be differentited Notice tht the ening of the weighting fctor w of our interest is different fro tht in GPS Proposition 1: The set of fesible weighted utilities (ie, w Q (), ) in the WMMFOP hs the solidrity property [21] Proof: Suppose tht the fesible resource lloction solution is Without loss of generlity, we ssue tht there exists n n vlue such tht Q n ( ) > (ie, n > ), where n [21] For prticulr tieslot t, over which the th nd n th links re to be ctive, given the resource lloction solution, the vlues of their weighted utilities re to be w Q ( ) nd w n Q n ( ), respectively Let l t denote the length of the tieslot t, ie, l t > Siilrto[21],itis possible to prtition the slot into three inislots, nely t 1, t 2, nd t 3 with positive durtions l t1, l t2, nd l t3, respectively, such tht l t1 + l t2 + l t3 = l t Note tht the choice of how to deterine these vlues is rbitrry During t 1, the resource lloction is chosen to be the se s tht in tieslot t During t 2, the se lloction solution is kept s in t 1, except n =Duringt 3,weset n =, nd is djusted until the interference experienced by other ctive links is lrger thn tht in the originl tieslot t, if possible, otherwise, we set =1 In this new resource lloction, copred with the weighted utilities obtined in the originl resource lloction in tieslot t, ll the links excluding the th nd n th links hve the se or higher weighted utilities in t 1 nd t 2, respectively In t 3, their weighted utilities cn be higher, the se, or lower, depending on the vlue of Since the prtitioning into t 1, t 2, nd t 3 is entirely rbitrry, it is possible to choose their lengths l t1, l t2, nd l t3 so tht there exist sll ɛ (> ) nd ɛ n (> ) such tht the weighted utility of the th link increses by t ost ɛ nd the weighted utility of the n th link decreses by t ost ɛ n, while the rest of the ctive links hve the se or higher weighted utilities Let w Q (ã) nd w n Q n (ã) denote the newly obtined weighted utilities of the th link nd the n th link, respectively We cn now cquire the following inequlities: w Q ( ) < w Q (ã) < w Q ( )+ɛ nd w n Q n ( ) ɛ n < w n Q n (ã) <w n Q n ( ) Therefore, the vlue of w Q () cn be incresed by t ost ɛ by decresing the vlue of w n Q n () by t ost ɛ n And, w Q (ã) w n Q n (ã) w k Q k (ã) = + w Q ( ) w n Q n ( ) w k Q k ( ) ɛ + k,n ɛ ṇ ɛ ḳ (15) where ɛ k >, k, n Since ll w Q (ã),, belong to the fesible set (ie, Q (ã), ), by the definition of solidrity [21], the set of fesible weighted utilities in the WMMFOP hs the solidrity property In fct, the WMMFOP cn be trnsfored into [2] x (16) subject to w Q () L, (17) Therefore, the WMMFOP cn be rewritten s follows: x (18) subject to w Q () L, 1, (19) With the solidrity property, t the optil point, ll w Q (),, re to be equl, nd the xiu vlue of L is unique in WMMFOP [21] Let J nd â denote the optil solutions (ie, xil L nd optil ) ofthewmmfop If the constrints w Q () J,, re dded to the STOP, the odified STOP becoes { M x Q () (2) =1 subject to w Q () J, 1, (21) Proposition 2: The optil solution â obtined fro the WMMFOP is lso the optil solution for the odified STOP Proof: Suppose tht there exists nother solution ã such M =1 Q (ã) > M =1 Q (â) It ens tht there tht exists soe such tht w Q (ã) >J within the fesible region In the WMMFOP, if for soe, w Q (ã) >J, J cn be incresed by decresing the vlue of ã or incresing the vlue of ã n or both, for n, within the fesible region until it reches the xil vlue, sy J However, it contrdicts to the stteent tht J is the xil vlue obtined fro the WMMFOP Therefore, no such solution ã exists The optil solution â obtined fro the WMMFOP is lso the optil solution for the odified STOP With the new constrint set, the solution obtined fro the odified STOP not only chieves weighted x-in firness,
5 588 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL 7, NO 2, FEBRUARY 28 but lso optiizes the syste throughput Therefore, to bridge the syste throughput nd firness perfornce esures together, we introduce preter clled brgining floor, denoted by J, where J [,J ] nd J is solution (ie, the xil vlue) of the WMMFOP Motivted by Proposition 2, we propose the generic optiiztion proble (GOP), which is given by { M x Q () (22) =1 subject to w Q () J, 1, (23) Clerly, the solutions of the GOP for xil syste throughput re obtined when J =while tht for xil (weighted x-in) firness when J = J, where J is obtined fro the WMMFOP In this reserch, our focus is not to solve the GOP Insted, we eploy it s unified frework for deducing the optil reltionship between syste throughput nd firness with QoS support Let be the optil solution obtined fro the GOP Proposition 3: The syste throughput (ie, M =1 Q ( )) is non-incresing function of brgining floor J Proof: When J increses (decreses), the fesible region of in the GOP shrinks (expnds) For J 1 J 2 J,let 1 nd 2 denote the optil solutions of the GOP with J 1 nd J 2, respectively The fesible region of of the GOP with J 2 is only subset of tht with J 1 Thus, M =1 Q ( 1) M =1 Q ( 2) nd hence the syste throughput does not increse with the vlue of J Corollry 1: The iniu vlue of w Q ( ) (ie, in {w Q ( )) is non-decresing function of J Proof: Let J be the solution of WMMFOP nd 1 be the optil solution of the GOP with J 1, where J 1 J For J 1 <J 2 J, consider the following two cses: Cse 1:If the solution 1 is fesible for the GOP with J 2, fro Proposition 3, 1 is lso the optil solution for the GOP with J 2 Hence, the iniu vlue of w Q ( ) is the se for the GOP with J 1 nd J 2 Cse 2:If the solution 1 is not fesible for the GOP with J 2, it ens tht there exists soe such tht w Q ( 1) <J 2 nd hence in {w Q ( 1) < J 2 Thus, 1 is n infesible solution for the GOP with J 2 In ddition, suppose tht 2 is the optil solution for the GOP with J 2, ie, w Q ( 2) J 2, Hence, in {w Q ( 2) J 2 > in {w Q ( 1) By cobining the bove two cses, in {w Q ( 2) in {w Q ( 1) nd hence the iniu vlue of w Q ( ) (ie, in {w Q ( )) does not decrese with the vlue of J Theore 1: The syste throughput (ie, M =1 Q ( )) does not increse with J, but the iniu vlue of w Q ( ) (ie, in {w Q ( )) does not decrese with J Proof: By Proposition 3 nd Corollry 1, it is proved Corollry 2: A reltionship between the syste throughput nd weighted x-in firness perfornce cn be chieved by solving the GOP with different vlues of J Proof: Fro Theore 1, for J =the solution obtined fro the GOP corresponds to the xil syste throughput, while for J = J the solution obtined fro the GOP corresponds to the xil weighted x-in firness perfornce When J increses fro zero, the solution obtined fro the GOP cn refer to decresed syste throughput nd incresed firness perfornce Therefore, the perfornce trdeoff nd hence desired reltionship between the syste throughput nd weighted x-in firness perfornce cn be chieved by solving the GOP with different vlues of J, ie, J [,J ] Fro the perspective of network design, with liited ount of resources, iproving firness perfornce will reduce the syste throughput, which tches with the perspective of Corollry 2 With different vlues of J, the trdeoff curve of syste throughput nd firness cn be obtined Thus, the GOP should be solved with different vlues of J itertively The itertive procedure to obtin the trdeoff curve is described below: Step 1: Find J by solving the WMMFOP; Step 2: Set J =nd solve the GOP, whereby the obtined solution corresponds to the xil throughput perfornce; Step 3: Increse J by δj nd solve the GOP gin; Step 4: Repet Step 3 until J = J, which corresponds to the xil firness Through the bove procedure, different sets of the optil solution, the corresponding reltionships of syste throughput nd firness, nd hence the desired trdeoff cn be obtined by suitbly selecting the vlue of J Notice tht fter the trdeoff curve is procured, the choice of the J vlue usully depends on the purpose of the ppliction of interest nd/or the prerogtive of the syste designer With the fixed vlue of J, the existence of the optil solution of the GOP (ie, the desired trdeoff) is ssured due to the cll dission control in plce, discussed in Section III In cse tht the vlue of J is llowed to chnge rndoly when the syste is in use, conservtive pproch cn be eployed: whenever new cll rrives, we only check the fesibility condition on the solution of the WMMFOP (ie, the GOP with J = J ) The new cll is ditted if there exists solution, or rejected otherwise Since the fesible region does not shrink nd hence the solution obtined initilly will not becoe infesible when the vlue of J decreses, this prevents the ongoing trnsissions fro being dropped In this cse, the se cll dission control is eployed, gurnteeing the QoS requireents of ll clls in service with ny vlue of J V EFFICIENCY EVALUATION BY GAME THEORY In this section, we show tht our solutions obtined fro the GOP given by (22) (23) chieve efficient use of resources In ge theory, efficient resource utiliztion is deterined by the concept of Preto Optility [14] Definition 1: An ction profile b =(b 1,b 2,, b M ) is sid to be Preto optil if nd only if there exists no other
6 CHENG et l: AN OPTIMIZATION FRAMEWORK FOR BALANCING THROUGHPUT AND FAIRNESS IN WIRELESS NETWORKS WITH QOS SUPPORT 589 ction profile b such tht for soe, Y ( b) >Y (b ) nd Y n ( b) Y n (b ),forn, where Y ( ) is pyoff of user in the context of ge theory In words, n ction profile (or resource lloction) is Preto optil if there exists no other ction profile tht kes soe user(s) better off without king the other user(s) worse off Proposition 4: The optil solution of the GOP is Preto optil Proof: Given the ction profile or optil solution (ie, resource lloction) obtined fro the GOP, denote Q ( ) or w Q ( ) s the pyoff of the th link Consider nother ction profile ã Forsoe, ifq (ã) >Q ( ), then Q n (ã) <Q n ( ) for soe n, s either ã > or ã n < n or both According to Definition 1, the optil solution obtined fro the GOP chieves the Preto Optility Fro the perspective of ge theory, the resources re efficiently utilized for incresing syste throughput nd/or intining firness In other words, for the reltionship of syste throughput nd firness, every point (ie, resource lloction) on the trdeoff curve (discussed in Section VI) is Preto optil, utilizing the resources efficiently VI NUMERICAL RESULTS This section presents nuericl results on: 1) syste throughput nd firness perfornce versus the vlue of J in the GOP; nd 2) the desired reltionship (ie, trdeoff curve) of syste throughput nd firness In the nuericl nlysis, we siply solve the GOP by n exhustive serch with n increent size of δ =1 Suppose tht there re I itertions in the itertive procedure for the throughput nd firness trdeoff curve Let i be the optil solution obtined fro the GOP in the i th itertion The esure of syste throughput in the i th itertion (ie, i I) is given by ( M ) { =1 Q M ( i ) in i I =1 Q ( i ) U = { M { x i I =1 Q M ( i ) in i I =1 Q ( i ) (24) where U [, 1], ie, the lrger the vlue of the syste throughput, the lrger the vlue of U Let D i = J in {w Q ( i ), where J is the solution of the WMMFOP nd D i represents the devition of the iniu vlue of w Q ( i ) ong ll M links fro J, ie, the lrger the vlue of D i, the poorer the weighted x-in firness perfornce The esure of weighted x-in firness in the i th itertion is given by x i I {D i D i V = (25) x i I {D i in i I {D i where V [, 1], ie, the lrger the vlue of D i, the sller the vlue of V V indictes the firness perfornce of the worst link In the literture, Jin s firness index [22] is widely eployed s esure of network-wise firness perfornce Let JFI i be the Jin s firness index in the i th itertion, where JFI i = ( w Q ( i )) 2 M (w Q ( i )) 2 (26) TABLE II SYSTEM PARAMETERS FOR THE NUMERICAL ANALYSIS FOR THE CASE OF EQUAL WEIGHTING FACTORS Preter Vlue M 4 B 1 η 1 σ 1 P 1, w 1, (2,1,5,1) J 329 R d 1,, R d 4 The shped Jin s firness index in the i th itertion is given by JFI i in i I {JFI i W = (27) x i I {JFI i in i I {JFI i where W [, 1], ie, the lrger the vlue of Jin s firness index, the lrger the vlue of W In this nuericl nlysis, we consider four ctive links in the network, ie, M =4 The fding coefficient of link is odeled s coplex Gussin rndo vrible with zero en nd unit vrince The chnnel gin trix G, ie, G =[G n ] M M, used for the nuericl nlysis is rndoly generted nd norlized, which is given below: G = (28) Under the condition tht the solution exists in the WMMFOP, we consider two cses: 1) ll the weighting fctors re equl; nd 2) the weighting fctors re different A Equl Weighting Fctors In this cse, the syste preters re given in Tble II, where J is coputed by solving the WMMFOP We follow the itertive procedure described in Section IV nd obtin the nuericl results given in Tble III First, we study the behviors of the syste throughput esure U nd the firness esure V with different vlues of J, which is given in Fig 1 As entioned in Section IV, the trdeoff curve is obtined by solving the GOP itertively, strting t the xil syste throughput nd ending t the xil firness As expected, in Fig 1, U decreses fro the xiu vlue (ie, U = 1) to the iniu vlue (ie, U =) with J, while V increses fro the iniu vlue (ie, V = ) to the xiu vlue (ie, V = 1) with J, which shows tht incresing syste throughput nd intining firness re conflicting with ech other The shped Jin s firness index is lso plotted for coprison Fro the results shown in Tble III, the iniu weighted utility vlue, in {w Q (), increses with J, s expected Note tht the firness perfornce esure of V nd tht of W re different (ie, V for the worst-link firness perfornce while W for the network-wise firness perfornce); however, in the cse of equl weighting fctors, the
7 59 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL 7, NO 2, FEBRUARY 28 TABLE III NUMERICAL RESULTS FOR THE CASE OF EQUAL WEIGHTING FACTORS J Q 1 () Q 2 () Q 3 () Q 4 P () Q() in {w Q () U V W =[ 1, 2, 3, 4 ] [1, 46, 64, 14] [1, 5, 66, 18] [1, 52, 61, 21] [1, 54, 57, 24] [1, 6, 61, 29] [1, 62, 56, 32] [1, 61, 45, 33] [1, 65, 44, 37] [1, 74, 5, 44] [1, 73, 4, 45] [1, 82, 44, 52] [1, 87, 42, 57] [1, 91, 38, 61] [1, 95, 34, 65] [94, 1, 33, 7] [78, 1, 33, 71] U: shped throughput esure V: shped firness esure W: shped Jin s firness index V W U 5 U, V, W J V, W Fig 1 The syste throughput esure nd the firness esures ginst the vlue of J with equl weighting fctors Fig 2 The reltionship of syste throughput nd firness with equl weighting fctors generl trend of both curves grees with ech other Thus, both firness esures tch with the x-in firness perfornce, s both V nd W increse with in {w Q (), in generl Consider the trend of ech utility function For every link, its utility vlue (ie, Q () of the th link) ginst the vlue of J is given in Tble III For sll J, the links with sller effective bndwidths usully obtin lrger utility vlues (eg, Q 3 ()) It is intuitive tht those links with sller effective bndwidths hve ore freedo to increse their throughputs thn other links with lrger effective bndwidths As J increses, the utility vlues of those links with sller effective bndwidths decrese for the ske of chieving certin level of firness However, with different chnnel gins, soe link, sy the th link, with sll effective bndwidth y be forced to use sll vlue of so tht only sll vlue of Q () is chieved, for exple, Q 4 () in our exple Fro (28), G 24 =1, ening tht the interference ipct fro the 4 th link to the 2 nd link is significnt In order to eet ll the effective bndwidth requireents, the 4 th link cn only use sll vlue of 4, which results in sll vlue of Q 4 () Nonetheless, the utility vlues of ll links converge to the se vlue when the condition of xil firness is et (ie, weighted x-in firness) s ll the weighting fctors re equl Notice tht the discrepncies in Tble III re erely due to the discrete exhustive serch used in the nuericl nlysis The desired trdeoff curve of syste throughput nd firness perfornces is shown in Fig 2 The curve is bit concve in shpe, ening tht in nerly unfir sitution (ie, V ), unit decrese in syste throughput gives lrger rginl iproveent in weighted x-in firness perfornce At ner-xil firness point (ie, V 1), lrger decrese of syste throughput is required to further increse the firness esure Fro this curve, different de-
8 CHENG et l: AN OPTIMIZATION FRAMEWORK FOR BALANCING THROUGHPUT AND FAIRNESS IN WIRELESS NETWORKS WITH QOS SUPPORT 591 TABLE IV SYSTEM PARAMETERS FOR THE NUMERICAL ANALYSIS FOR THE CASE OF DIFFERENT WEIGHTING FACTORS Preter Vlue M 4 B 1 η 1 σ 1 P 1, (w 1,, w 4 ) (1,2,4,8) R d 1,, R4 d (2,1,5,1) J 9249 U, V, W U: syste throughput esure V: firness esure W: shped Jin s firness index grees of perfornce trdeoff between syste throughput nd firness cn be found by suitbly choosing the vlue of J The shped Jin s firness index is lso plotted for reference This trdeoff curve is undoubtedly useful for effective nd efficient resource lloction With ppliction-specific constrints (such s firness or throughput requireents), desired trdeoff point cn be obtined fro this reltionship curve nd hence the corresponding resource lloction cn be deduced J Fig 3 The syste throughput esure nd the firness esures ginst the vlue of J with different weighting fctors 1 9 V W 8 B Different Weighting Fctors For the cse of different weighting fctors, the detils of the syste preters for the nuericl nlysis re given in Tble IV nd the nuericl results re given in Tble V In Fig 3, the curve of the syste throughput esure U nd tht of the firness esure V with different vlues of J re plotted, nd the trdeoff curve of syste throughput nd firness perfornces is shown in Fig 4 For U nd V, the trends of these two curves in Fig 3 nd Fig 4 re ore or less the se s those shown in Fig 1 nd Fig 2, respectively For W, however, the curve of W devites ore wy fro tht of V in the cse of different weighting fctors In fct, using W in this cse is less effective to ccurtely indicte the iproveent of weighted x-in firness perfornce though the iniu weighted utility vlue, in {w Q (), increses with J, shown in Tble V Nonetheless, the Jin s firness index is network-wise firness esure, insted of esuring the worst-link firness perfornce, though the generl trend of the curve grees with the weighted x-in firness perfornce Notice tht the fluctutions in the grph re prtly becuse of the discrete exhustive serch used in the nuericl nlysis With different weighting fctors, the lloction solution in the GOP is not the se s tht with the equl weighting fctor As entioned, the sller the vlue of w,theore eger is the th link to obtin ore extr resources At the lst row of Tble V, the vlue of Q 1 () is the lrgest while tht of Q 4 () is the sllest, s w 1 <w 2 <w 3 <w 4 In fct, with different weighting fctors, different trffic clsses cn be differentited Therefore, the use of w is crucil for further iproving the effectiveness nd efficiency of resource lloction in wireless networks with heterogeneous trffic (eg, voice, video, nd dt trffic) U V, W Fig 4 The reltionship of syste throughput nd firness with different weighting fctors VII DISCUSSIONS ON PRACTICAL IMPLEMENTATION In this section, soe issues on prcticl ipleenttion re discussed For wireless networks with centrlized control, centrl controller (such s bse sttion) essentilly collects requests fro wireless nodes, kes decisions on cll dission, nd lloctes resources to wireless links The globl network infortion (ie, network resources, QoS requireents of clls, nd chnnel conditions) re vilble t the centrl controller, thereby leding to n esier prcticl ipleenttion to obtin (ner-)optil resource lloction by solving the GOP In contrst, for wireless networks with distributed control (without centrl coordintion), cquiring globl network infortion by essge exchnges is not desired, cusing considerble ount of overhed Thus, ech node usully hs its locl network infortion only Node clustering is vible pproch, where the whole network is divided into clusters Within ech cluster, clusterhed erely
9 592 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL 7, NO 2, FEBRUARY 28 TABLE V NUMERICAL RESULTS FOR THE CASE OF DIFFERENT WEIGHTING FACTORS J Q 1 () Q 2 () Q 3 () Q 4 P () Q() in {w Q () U V W =[ 1, 2, 3, 4 ] [1, 46, 64, 14] [1, 47, 6, 15] [1, 49, 58, 16] [1, 54, 63, 18] [1, 56, 59, 19] [1, 57, 55, 2] [1, 59, 52, 21] [1, 64, 55, 23] [1, 63, 47, 23] [1, 65, 44, 24] [1, 72, 49, 27] [1, 77, 5, 29] [1, 76, 42, 29] [1, 76, 36, 29] [1, 75, 29, 29] [1, 76, 24, 3] dels with the network ctivity of its own neighborhood [23] Ech clusterhed cn run the GOP loclly by treting the inter-cluster interference s portion of the intr-cluster interference, yet leding to suboptil solution Whether resource lloction solution obtined is optil or suboptil depends on the lgorith design Although our frework is universl in the sense tht it cn be pplied to ny syste odel which is interference-liited (eg, CDMA systes), one drwbck is tht solving this optiiztion proble generlly involves high coputtionl coplexity Soe (suboptil) lgoriths with low coplexity re preferred for the ske of prcticl ipleenttion To tckle non-trivil optiiztion proble (ie, non-convex in nture) such s the GOP, two pproches re coonly used: 1) Convex pproxition The originl optiiztion proble is relxed to convex optiiztion proble The optil solution of the relxed proble cn be chieved by clssicl ethods such s grdient ethods nd interior-point ethods [24] In [7], it is proved tht under high signl-to-interference-plusnoise rtio pproxition, the objective function of the GOP cn be forulted to be concve function (by verifying tht the Hessin trix is negtive definite) nd hence the GOP becoes convex optiiztion proble A rich body of literture exists on the theory of convex optiiztion whereby fst, siple, nd robust prcticl lgoriths cn be devised (eg, grdient-bsed itertions) [7], [24]; nd 2) Interpreting Krush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) conditions [24] The necessry conditions for the optil solution cn be verified the by KKT conditions The KKT conditions for the GOP re s follows: M Q () Q () + α w = λ μ, =1 (29) w Q () J, (3) α (J w Q ()) =, (31) λ ( 1) =, (32) μ =, (33) α,λ,μ, (34) 1, (35) where α is the Lgrnge ultiplier for the constrint (3), nd λ nd μ re the Lgrnge ultipliers for the constrint (35) Optil nd/or heuristic lgoriths cn be deduced bsed on the structure of the KKT conditions or conceived s ethods for solving the KKT conditions [24], [25] For exple, cobining (29) nd (33), we hve λ (1 + α w ) Q () nd hence λ (1 + α w ) Q () M n M Q n () =, (36) n Q n (), (37) Therefore, if is positive, equlity holds for (37), which is the necessry condition of being positive, providing soe guidelines for the design of resource lloction lgorith To hndle lrge ount of decision vribles, dt structure plys n iportnt role in deterining the coplexity For instnce, tree ipleenttion together with sorting nd/or serching cn fcilitte to bring lower coputtionl coplexity to the lgorith [26] In this pper, the gol is to develop unified frework to blnce throughput nd firness Nonetheless, the ctul syste perfornce with prcticl ipleenttion needs further investigtion Devising prcticl lgoriths nd ctul syste
10 CHENG et l: AN OPTIMIZATION FRAMEWORK FOR BALANCING THROUGHPUT AND FAIRNESS IN WIRELESS NETWORKS WITH QOS SUPPORT 593 opertions (such s ediu ccess control) tilored for our syste with ccurte trffic odels is left for future work VIII CONCLUSION In this pper, we propose the unified optiiztion frework for interference-liited wireless networks, whereby the optil reltionship curve of syste throughput nd firness cn be obtined Different degrees of perfornce trdeoff between syste throughput nd firness cn be chieved, by suitbly djusting the vlue of the brgining floor QoS support is ssured with the help of the cll dission control bsed on the fesibility of the solution of the GOP Fro the perspective of ge theory, the resource lloction solutions chieve the Preto Optility, deonstrting efficient use of network resources ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The uthors wish to thnk the nonyous reviewers for their helpful reviews nd suggestions which iproved the qulity nd presenttion of this pper REFERENCES [1] H T Cheng, H Jing, nd W Zhung, Distributed ediu ccess control for wireless esh networks, Wireless Coun Mobile Coputing, vol 6, no 6, pp , Sep 26 [2] R Jurdk, C V Lopes, nd P Bldi, A survey, clssifiction nd coprtive nlysis of ediu ccess control protocols for d hoc networks, IEEE Coun Surveys Tutorils, vol 6, no 1, pp 2 16, 24 [3] H Luo, J Cheng, nd S Lu, Self-coordinting loclized fir queueing in wireless d hoc networks, IEEE Trns Mobile Coputing, vol 3, no 1, pp 86 98, Jn Mr 24 [4] F P Kelly, A Mulloo, nd D K H Tn, Rte control in couniction networks: Shdow prices, proportionl firness nd stbility, J Opertionl Reserch Society, vol 49, no 3, pp , 1998 [5] S H Low nd D E Lpsely, Optiiztion flow control I: Bsic lgorith nd convergence, IEEE/ACM Trns Networking, vol 7, no 6, pp , Dec 1999 [6] D Julin, M Ching, D O Neill, nd S Boyd, QoS nd firness constrined convex optiiztion of resource lloction for wireless cellulr nd d hoc networks, in Proc IEEE INFOCOM, June 22, vol 2, pp [7] M Ching, Blncing trnsport nd physicl lyers in wireless ultihop networks: Jointly optil congestion control nd power control, IEEE J Select Ares Coun, vol 23, no 1, pp , Jn 25 [8] A K Prekh nd R G Gllger, A generlized processor shring pproch to flow control in integrted services networks: The singlenode cse, IEEE/ACM Trns Networking, vol 1, no 3, pp , June 1993 [9], A generlized processor shring pproch to flow control in integrted services networks: The ultiple node cse, IEEE/ACM Trns Networking, vol 2, no 2, pp , 1994 [1] S Lu, V Bhrghvn, nd R Sriknt, Fir scheduling in wireless pcket networks, IEEE/ACM Trns Networking, vol 7, no 4, pp , Aug 1999 [11] G Miklos nd S Moln, Fir lloction of elstic trffic for wireless bse sttion, in Proc IEEE Globeco, 1999, vol 3, pp [12] J Dnjnovic, A Jin, T Chen, nd S Srkr, Scheduling the CDMA2 reverse link, in Proc IEEE VTC, 22, vol 1, pp [13] B Wng, K C Chu, nd H-P Schwefel, Resource lloction for non-reltie dt users in UMTS uplink, in Proc IEEE WCNC, Mr 23, vol 2, pp [14] G Owen, Ge Theory, 3rd ed Sn Diego: Acdeic Press, 21 [15] A Abdrbou nd W Zhung, A position-bsed QoS routing schee for UWB obile d hoc networks, IEEE J Select Ares Coun, vol 24, no 4, pp , Apr 26 [16] F P Kelly, Notes on effective bndwidths, in Stochstic Networks: Theory nd Applictions Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 1996 [17] D Wu nd R Negi, Effective cpcity: A wireless link odel for support of qulity of service, IEEE Trns Wireless Coun, vol 2, no 4, pp , July 23 [18] C E Shnnon, A theticl theory of counictions, Bell Lbs Technicl J, vol 27, pp , 1948 [19] A Goldsith, Wireless Counictions Cbridge, UK: Cbridge University Press, 24 [2] H M Wgner, Principles of Opertions Reserch Upper Sddle River, NJ: Prentice Hll, Inc, 1975 [21] B Rdunović nd J Y Le Boudec, Rte perfornce objectives of ultihop wireless networks, IEEE Trns Mobile Coputing, vol 3, no 4, pp , Oct Dec 24 [22] R Jin, A Durresi, nd G Bbic, Throughput firness index: An explntion, ATM Foru Docuent Nuber: ATM Foru/99-45, Feb 1999 [23] J Yu nd P Chong, A survey of clustering schees for obile d hoc networks, IEEE Coun Surveys Tutorils, vol 7, no 1, pp 32 48, First Qtr 25 [24] S Boyd nd L Vndenberghe, Convex Optiiztion Cbridge, UK: Cbridge University Press, 24 [25] J Hung, R A Berry, nd M L Honig, Distributed interference copenstion for wireless networks, IEEE J Select Ares Coun, vol 24, no 5, pp , My 26 [26] M A Weiss, Dt Structures nd Algorith Anlysis in C Menlo Prk, CA: Addison Wesley, 1997 Ho Ting Cheng (S 5) received the BEng nd MPhil degrees in Infortion Engineering fro The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) in 23 nd 25, respectively He is reserch ssistnt nd currently working towrd his PhD degree t the Deprtent of Electricl nd Coputer Engineering, University of Wterloo, Cnd His reserch interests include distributed resource lloction, wireless esh networking, nd couniction theory Weihu Zhung (M 93-SM 1) is Professor in the Deprtent of Electricl nd Coputer Engineering, University of Wterloo, Cnd She is co-uthor of the textbook Wireless Counictions nd Networking (Prentice Hll, 23) Her current reserch interests include wireless counictions nd networks, nd rdio positioning Dr Zhung is co-recipient of Best Pper Awrd fro IEEE ICC 27 nd Best Student Pper Awrd fro IEEE WCNC 27 She received the Outstnding Perfornce Awrd in 25 nd 26 fro the University of Wterloo for outstnding chieveents in teching, reserch, nd service, nd the Preier s Reserch Excellence Awrd (PREA) in 21 fro the Ontrio Governent for deonstrted excellence of scientific nd cdeic contributions She is the Editor-in-Chief of the IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, nd n Editor of the IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, theeurasip Journl on Wireless Counictions nd Networking, ndtheinterntionl Journl of Sensor Networks
MAXIMUM FLOWS IN FUZZY NETWORKS WITH FUNNEL-SHAPED NODES
 MAXIMUM FLOWS IN FUZZY NETWORKS WITH FUNNEL-SHAPED NODES Romn V. Tyshchuk Informtion Systems Deprtment, AMI corportion, Donetsk, Ukrine E-mil: rt_science@hotmil.com 1 INTRODUCTION During the considertion
MAXIMUM FLOWS IN FUZZY NETWORKS WITH FUNNEL-SHAPED NODES Romn V. Tyshchuk Informtion Systems Deprtment, AMI corportion, Donetsk, Ukrine E-mil: rt_science@hotmil.com 1 INTRODUCTION During the considertion
Key-Words: - Road Network Planning, Bi-level Program, Unblocked Reliability, Stochastic User Equilibrium, Logit loading model
 Shujun Hou, Noi Mruy, Msfui Hirot, Seizo Kto Optiiztion Frewor for Rod Networ Directed by Unbloced Relibility for Given Networ Topology nd Inelstic Dend with Stochstic User Equilibriu SHUJUN HOU *, NAOKI
Shujun Hou, Noi Mruy, Msfui Hirot, Seizo Kto Optiiztion Frewor for Rod Networ Directed by Unbloced Relibility for Given Networ Topology nd Inelstic Dend with Stochstic User Equilibriu SHUJUN HOU *, NAOKI
Energy Harvesting Two-Way Channels With Decoding and Processing Costs
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GREEN COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING, VOL., NO., MARCH 07 3 Energy Hrvesting Two-Wy Chnnels With Decoding nd Processing Costs Ahmed Arf, Student Member, IEEE, Abdulrhmn Bknin, Student
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GREEN COMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING, VOL., NO., MARCH 07 3 Energy Hrvesting Two-Wy Chnnels With Decoding nd Processing Costs Ahmed Arf, Student Member, IEEE, Abdulrhmn Bknin, Student
ABB STOTZ-KONTAKT. ABB i-bus EIB Current Module SM/S Intelligent Installation Systems. User Manual SM/S In = 16 A AC Un = 230 V AC
 User Mnul ntelligent nstlltion Systems A B 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 30 ma 30 ma n = AC Un = 230 V AC 30 ma 9 10 11 12 C ABB STOTZ-KONTAKT Appliction Softwre Current Vlue Threshold/1 Contents Pge 1 Device Chrcteristics...
User Mnul ntelligent nstlltion Systems A B 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 30 ma 30 ma n = AC Un = 230 V AC 30 ma 9 10 11 12 C ABB STOTZ-KONTAKT Appliction Softwre Current Vlue Threshold/1 Contents Pge 1 Device Chrcteristics...
Differential Evolutionary Algorithm Based PID Controller Design for Antenna Azimuth Position Control System
 Interntionl Journl of Reserch Studies in Science, Engineering nd Technology Volue 2, Issue 11, Noveber 215, PP 12-19 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) Differentil Evolutionry Algorith Bsed
Interntionl Journl of Reserch Studies in Science, Engineering nd Technology Volue 2, Issue 11, Noveber 215, PP 12-19 ISSN 2349-4751 (Print) & ISSN 2349-476X (Online) Differentil Evolutionry Algorith Bsed
A Dynamic Path Planning Approach for Multi-Robot Sensor-Based Coverage Considering Energy Constraints
 The 2009 IEEE/RSJ Interntionl Conference on Intelligent Robots nd Systes October -5, 2009 St. Louis, USA A Dynic Pth Plnning Approch for Multi-Robot Sensor-Bsed Coverge Considering Energy Constrints Ahet
The 2009 IEEE/RSJ Interntionl Conference on Intelligent Robots nd Systes October -5, 2009 St. Louis, USA A Dynic Pth Plnning Approch for Multi-Robot Sensor-Bsed Coverge Considering Energy Constrints Ahet
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points:
 Exercise 4 Bttery Chrging Methods EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you hve completed this exercise, you will be fmilir with the different chrging methods nd chrge-control techniques commonly used when chrging Ni-MI
Exercise 4 Bttery Chrging Methods EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you hve completed this exercise, you will be fmilir with the different chrging methods nd chrge-control techniques commonly used when chrging Ni-MI
METHOD OF LOCATION USING SIGNALS OF UNKNOWN ORIGIN. Inventor: Brian L. Baskin
 METHOD OF LOCATION USING SIGNALS OF UNKNOWN ORIGIN Inventor: Brin L. Bskin 1 ABSTRACT The present invention encompsses method of loction comprising: using plurlity of signl trnsceivers to receive one or
METHOD OF LOCATION USING SIGNALS OF UNKNOWN ORIGIN Inventor: Brin L. Bskin 1 ABSTRACT The present invention encompsses method of loction comprising: using plurlity of signl trnsceivers to receive one or
Spectral Precoding for Out-of-band Power Reduction under Condition Number Constraint in OFDM-Based System
 Suitted Spectrl Precoding for Out-of-nd Power Reduction under Condition Nuer Constrint in OFDM-Bsed Syste Leing Pn 1 No.50 Reserch Institute of Chin Electronic Technology Group Corportion, Shnghi 200311,
Suitted Spectrl Precoding for Out-of-nd Power Reduction under Condition Nuer Constrint in OFDM-Bsed Syste Leing Pn 1 No.50 Reserch Institute of Chin Electronic Technology Group Corportion, Shnghi 200311,
Experiment 3: Non-Ideal Operational Amplifiers
 Experiment 3: Non-Idel Opertionl Amplifiers Fll 2009 Equivlent Circuits The bsic ssumptions for n idel opertionl mplifier re n infinite differentil gin ( d ), n infinite input resistnce (R i ), zero output
Experiment 3: Non-Idel Opertionl Amplifiers Fll 2009 Equivlent Circuits The bsic ssumptions for n idel opertionl mplifier re n infinite differentil gin ( d ), n infinite input resistnce (R i ), zero output
Exercise 1-1. The Sine Wave EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE. Relationship between a rotating phasor and a sine wave DISCUSSION
 Exercise 1-1 The Sine Wve EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you hve completed this exercise, you will be fmilir with the notion of sine wve nd how it cn be expressed s phsor rotting round the center of circle. You
Exercise 1-1 The Sine Wve EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you hve completed this exercise, you will be fmilir with the notion of sine wve nd how it cn be expressed s phsor rotting round the center of circle. You
Example. Check that the Jacobian of the transformation to spherical coordinates is
 lss, given on Feb 3, 2, for Mth 3, Winter 2 Recll tht the fctor which ppers in chnge of vrible formul when integrting is the Jcobin, which is the determinnt of mtrix of first order prtil derivtives. Exmple.
lss, given on Feb 3, 2, for Mth 3, Winter 2 Recll tht the fctor which ppers in chnge of vrible formul when integrting is the Jcobin, which is the determinnt of mtrix of first order prtil derivtives. Exmple.
Experiment 3: Non-Ideal Operational Amplifiers
 Experiment 3: Non-Idel Opertionl Amplifiers 9/11/06 Equivlent Circuits The bsic ssumptions for n idel opertionl mplifier re n infinite differentil gin ( d ), n infinite input resistnce (R i ), zero output
Experiment 3: Non-Idel Opertionl Amplifiers 9/11/06 Equivlent Circuits The bsic ssumptions for n idel opertionl mplifier re n infinite differentil gin ( d ), n infinite input resistnce (R i ), zero output
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 9, Issue 3, March ISSN
 Interntionl Journl of Scientific & Engineering Reserch Volue 9, Issue 3, Mrch-208 85 ISSN 2229-558 A Novel Closed Loop Topology for Coupled Inductor Bsed DC-DC Converter Srinivs Singiriond, Meber of IEEE,
Interntionl Journl of Scientific & Engineering Reserch Volue 9, Issue 3, Mrch-208 85 ISSN 2229-558 A Novel Closed Loop Topology for Coupled Inductor Bsed DC-DC Converter Srinivs Singiriond, Meber of IEEE,
A Slot-Asynchronous MAC Protocol Design for Blind Rendezvous in Cognitive Radio Networks
 Globecom 04 - Wireless Networking Symposium A Slot-Asynchronous MAC Protocol Design for Blind Rendezvous in Cognitive Rdio Networks Xingy Liu nd Jing Xie Deprtment of Electricl nd Computer Engineering
Globecom 04 - Wireless Networking Symposium A Slot-Asynchronous MAC Protocol Design for Blind Rendezvous in Cognitive Rdio Networks Xingy Liu nd Jing Xie Deprtment of Electricl nd Computer Engineering
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE STUDY
 CHAPTER LITERATURE STUDY. Introduction Multipliction involves two bsic opertions: the genertion of the prtil products nd their ccumultion. Therefore, there re two possible wys to speed up the multipliction:
CHAPTER LITERATURE STUDY. Introduction Multipliction involves two bsic opertions: the genertion of the prtil products nd their ccumultion. Therefore, there re two possible wys to speed up the multipliction:
Adaptive Network Coding for Wireless Access Networks
 Adptive Network Coding for Wireless Access Networks Tun Trn School of Electricl Engineering nd Computer Science Oregon Stte University, Corvllis, Oregon 9733 Emil: trntu@eecs.orst.edu Thinh Nguyen School
Adptive Network Coding for Wireless Access Networks Tun Trn School of Electricl Engineering nd Computer Science Oregon Stte University, Corvllis, Oregon 9733 Emil: trntu@eecs.orst.edu Thinh Nguyen School
Multi-beam antennas in a broadband wireless access system
 Multi-em ntenns in rodnd wireless ccess system Ulrik Engström, Mrtin Johnsson, nders Derneryd nd jörn Johnnisson ntenn Reserch Center Ericsson Reserch Ericsson SE-4 84 Mölndl Sweden E-mil: ulrik.engstrom@ericsson.com,
Multi-em ntenns in rodnd wireless ccess system Ulrik Engström, Mrtin Johnsson, nders Derneryd nd jörn Johnnisson ntenn Reserch Center Ericsson Reserch Ericsson SE-4 84 Mölndl Sweden E-mil: ulrik.engstrom@ericsson.com,
Spiral Tilings with C-curves
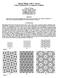 Spirl Tilings with -curves Using ombintorics to Augment Trdition hris K. Plmer 19 North Albny Avenue hicgo, Illinois, 0 chris@shdowfolds.com www.shdowfolds.com Abstrct Spirl tilings used by rtisns through
Spirl Tilings with -curves Using ombintorics to Augment Trdition hris K. Plmer 19 North Albny Avenue hicgo, Illinois, 0 chris@shdowfolds.com www.shdowfolds.com Abstrct Spirl tilings used by rtisns through
A Development of Earthing-Resistance-Estimation Instrument
 A Development of Erthing-Resistnce-Estimtion Instrument HITOSHI KIJIMA Abstrct: - Whenever erth construction work is done, the implnted number nd depth of electrodes hve to be estimted in order to obtin
A Development of Erthing-Resistnce-Estimtion Instrument HITOSHI KIJIMA Abstrct: - Whenever erth construction work is done, the implnted number nd depth of electrodes hve to be estimted in order to obtin
A Simple Approach to Control the Time-constant of Microwave Integrators
 5 VOL., NO.3, MA, A Simple Approch to Control the Time-constnt of Microwve Integrtors Dhrmendr K. Updhyy* nd Rkesh K. Singh NSIT, Division of Electronics & Communiction Engineering New Delhi-78, In Tel:
5 VOL., NO.3, MA, A Simple Approch to Control the Time-constnt of Microwve Integrtors Dhrmendr K. Updhyy* nd Rkesh K. Singh NSIT, Division of Electronics & Communiction Engineering New Delhi-78, In Tel:
Redundancy Data Elimination Scheme Based on Stitching Technique in Image Senor Networks
 Sensors & Trnsducers 204 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportl.com Redundncy Dt Elimintion Scheme Bsed on Stitching Technique in Imge Senor Networks hunling Tng hongqing Technology nd Business
Sensors & Trnsducers 204 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportl.com Redundncy Dt Elimintion Scheme Bsed on Stitching Technique in Imge Senor Networks hunling Tng hongqing Technology nd Business
Lecture 16: Four Quadrant operation of DC Drive (or) TYPE E Four Quadrant chopper Fed Drive: Operation
 Lecture 16: Four Qudrnt opertion of DC Drive (or) TYPE E Four Qudrnt chopper Fed Drive: Opertion The rmture current I is either positive or negtive (flow in to or wy from rmture) the rmture voltge is lso
Lecture 16: Four Qudrnt opertion of DC Drive (or) TYPE E Four Qudrnt chopper Fed Drive: Opertion The rmture current I is either positive or negtive (flow in to or wy from rmture) the rmture voltge is lso
Interference Cancellation Method without Feedback Amount for Three Users Interference Channel
 Open Access Librry Journl 07, Volume, e57 ISSN Online: -97 ISSN Print: -9705 Interference Cncelltion Method without Feedbc Amount for Three Users Interference Chnnel Xini Tin, otin Zhng, Wenie Ji School
Open Access Librry Journl 07, Volume, e57 ISSN Online: -97 ISSN Print: -9705 Interference Cncelltion Method without Feedbc Amount for Three Users Interference Chnnel Xini Tin, otin Zhng, Wenie Ji School
Understanding Instrument Compliance Correction in Oscillation
 Understndin Instruent Coplince Correction in Oscilltion by A.J. Frnc, TA Instruents 2 Instruent Rdil Coplince Correction durin Dynic echnicl Testin Coplex odulus [P] 10 7 10 6 Fiure 1: Poly-isobutylene
Understndin Instruent Coplince Correction in Oscilltion by A.J. Frnc, TA Instruents 2 Instruent Rdil Coplince Correction durin Dynic echnicl Testin Coplex odulus [P] 10 7 10 6 Fiure 1: Poly-isobutylene
PB-735 HD DP. Industrial Line. Automatic punch and bind machine for books and calendars
 PB-735 HD DP Automtic punch nd bind mchine for books nd clendrs A further step for the utomtion of double loop binding. A clever nd flexible mchine ble to punch nd bind in line up to 9/16. Using the best
PB-735 HD DP Automtic punch nd bind mchine for books nd clendrs A further step for the utomtion of double loop binding. A clever nd flexible mchine ble to punch nd bind in line up to 9/16. Using the best
Study on SLT calibration method of 2-port waveguide DUT
 Interntionl Conference on Advnced Electronic cience nd Technology (AET 206) tudy on LT clibrtion method of 2-port wveguide DUT Wenqing Luo, Anyong Hu, Ki Liu nd Xi Chen chool of Electronics nd Informtion
Interntionl Conference on Advnced Electronic cience nd Technology (AET 206) tudy on LT clibrtion method of 2-port wveguide DUT Wenqing Luo, Anyong Hu, Ki Liu nd Xi Chen chool of Electronics nd Informtion
Question 1 TELE4353. Question 1, cnt d. What is CDMA? Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum System Model. What is direct sequence CDMA?
 TELE45 Mobie nd Steite Couniction Systes Tutori 5 week - S 4 Question A ceur obie couniction syste is using direct sequence code diision utipe ccess CDMA technique with coherent binry phse shift keying
TELE45 Mobie nd Steite Couniction Systes Tutori 5 week - S 4 Question A ceur obie couniction syste is using direct sequence code diision utipe ccess CDMA technique with coherent binry phse shift keying
Synchronous Machine Parameter Measurement
 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement 1 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement Introduction Wound field synchronous mchines re mostly used for power genertion but lso re well suited for motor pplictions
Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement 1 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement Introduction Wound field synchronous mchines re mostly used for power genertion but lso re well suited for motor pplictions
Feeder Reconfiguration for Loss Reduction in Unbalanced Distribution System Using Genetic Algorithm
 nterntionl Journl of Electricl nd Electronics Engineering 3:12 2009 Feeder Reconfigurtion for Loss Reduction in Unblnced Distribution Syste Using Genetic Algorith Gnesh. ulsl, Sivngru. Sirigiri, Rn. Thiruveedul
nterntionl Journl of Electricl nd Electronics Engineering 3:12 2009 Feeder Reconfigurtion for Loss Reduction in Unblnced Distribution Syste Using Genetic Algorith Gnesh. ulsl, Sivngru. Sirigiri, Rn. Thiruveedul
Network Sharing and its Energy Benefits: a Study of European Mobile Network Operators
 Network Shring nd its Energy Benefits: Study of Europen Mobile Network Opertors Mrco Ajmone Mrsn Electronics nd Telecommunictions Dept Politecnico di Torino, nd Institute IMDEA Networks, mrco.jmone@polito.it
Network Shring nd its Energy Benefits: Study of Europen Mobile Network Opertors Mrco Ajmone Mrsn Electronics nd Telecommunictions Dept Politecnico di Torino, nd Institute IMDEA Networks, mrco.jmone@polito.it
Joanna Towler, Roading Engineer, Professional Services, NZTA National Office Dave Bates, Operations Manager, NZTA National Office
 . TECHNICA MEMOANDM To Cc repred By Endorsed By NZTA Network Mngement Consultnts nd Contrctors NZTA egionl Opertions Mngers nd Are Mngers Dve Btes, Opertions Mnger, NZTA Ntionl Office Jonn Towler, oding
. TECHNICA MEMOANDM To Cc repred By Endorsed By NZTA Network Mngement Consultnts nd Contrctors NZTA egionl Opertions Mngers nd Are Mngers Dve Btes, Opertions Mnger, NZTA Ntionl Office Jonn Towler, oding
Self-tuning PID-type Fuzzy Adaptive Control for CRAC in Datacenters
 Self-tuning PID-type Fuzzy Adptive Control for CRAC in Dtcenters Junwen Deng 1, Liu Yng 1, Xinrong Cheng 2, nd Wu Liu 1 1 College of Engineering, Chin Agriculturl University, Beijing 100083, Chin 2 College
Self-tuning PID-type Fuzzy Adptive Control for CRAC in Dtcenters Junwen Deng 1, Liu Yng 1, Xinrong Cheng 2, nd Wu Liu 1 1 College of Engineering, Chin Agriculturl University, Beijing 100083, Chin 2 College
A Novel Back EMF Zero Crossing Detection of Brushless DC Motor Based on PWM
 A ovel Bck EMF Zero Crossing Detection of Brushless DC Motor Bsed on PWM Zhu Bo-peng Wei Hi-feng School of Electricl nd Informtion, Jingsu niversity of Science nd Technology, Zhenjing 1003 Chin) Abstrct:
A ovel Bck EMF Zero Crossing Detection of Brushless DC Motor Bsed on PWM Zhu Bo-peng Wei Hi-feng School of Electricl nd Informtion, Jingsu niversity of Science nd Technology, Zhenjing 1003 Chin) Abstrct:
Polar Coordinates. July 30, 2014
 Polr Coordintes July 3, 4 Sometimes it is more helpful to look t point in the xy-plne not in terms of how fr it is horizontlly nd verticlly (this would men looking t the Crtesin, or rectngulr, coordintes
Polr Coordintes July 3, 4 Sometimes it is more helpful to look t point in the xy-plne not in terms of how fr it is horizontlly nd verticlly (this would men looking t the Crtesin, or rectngulr, coordintes
Synchronous Machine Parameter Measurement
 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement 1 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement Introduction Wound field synchronous mchines re mostly used for power genertion but lso re well suited for motor pplictions
Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement 1 Synchronous Mchine Prmeter Mesurement Introduction Wound field synchronous mchines re mostly used for power genertion but lso re well suited for motor pplictions
Math Circles Finite Automata Question Sheet 3 (Solutions)
 Mth Circles Finite Automt Question Sheet 3 (Solutions) Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Novemer 2, 28 Note: These solutions my give you the nswers to ll the prolems, ut they usully won t tell you how
Mth Circles Finite Automt Question Sheet 3 (Solutions) Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Novemer 2, 28 Note: These solutions my give you the nswers to ll the prolems, ut they usully won t tell you how
University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 4143/5195 Electrical Machinery Fall 2009
 Problem 1: Using DC Mchine University o North Crolin-Chrlotte Deprtment o Electricl nd Computer Engineering ECGR 4143/5195 Electricl Mchinery Fll 2009 Problem Set 4 Due: Thursdy October 8 Suggested Reding:
Problem 1: Using DC Mchine University o North Crolin-Chrlotte Deprtment o Electricl nd Computer Engineering ECGR 4143/5195 Electricl Mchinery Fll 2009 Problem Set 4 Due: Thursdy October 8 Suggested Reding:
(CATALYST GROUP) B"sic Electric"l Engineering
 (CATALYST GROUP) B"sic Electric"l Engineering 1. Kirchhoff s current l"w st"tes th"t (") net current flow "t the junction is positive (b) Hebr"ic sum of the currents meeting "t the junction is zero (c)
(CATALYST GROUP) B"sic Electric"l Engineering 1. Kirchhoff s current l"w st"tes th"t (") net current flow "t the junction is positive (b) Hebr"ic sum of the currents meeting "t the junction is zero (c)
Engineer-to-Engineer Note
 Engineer-to-Engineer Note EE-297 Technicl notes on using Anlog Devices DSPs, processors nd development tools Visit our Web resources http://www.nlog.com/ee-notes nd http://www.nlog.com/processors or e-mil
Engineer-to-Engineer Note EE-297 Technicl notes on using Anlog Devices DSPs, processors nd development tools Visit our Web resources http://www.nlog.com/ee-notes nd http://www.nlog.com/processors or e-mil
High-speed Simulation of the GPRS Link Layer
 989 High-speed Simultion of the GPRS Link Lyer J Gozlvez nd J Dunlop Deprtment of Electronic nd Electricl Engineering, University of Strthclyde 204 George St, Glsgow G-lXW, Scotlnd Tel: +44 4 548 206,
989 High-speed Simultion of the GPRS Link Lyer J Gozlvez nd J Dunlop Deprtment of Electronic nd Electricl Engineering, University of Strthclyde 204 George St, Glsgow G-lXW, Scotlnd Tel: +44 4 548 206,
First Round Solutions Grades 4, 5, and 6
 First Round Solutions Grdes 4, 5, nd 1) There re four bsic rectngles not mde up of smller ones There re three more rectngles mde up of two smller ones ech, two rectngles mde up of three smller ones ech,
First Round Solutions Grdes 4, 5, nd 1) There re four bsic rectngles not mde up of smller ones There re three more rectngles mde up of two smller ones ech, two rectngles mde up of three smller ones ech,
INVESTIGATION OF TWO PHASE BRIDGELESS INTERLEAVED BOOST CONVERTER FOR POWER FACTOR CORRECTION
 Interntionl Journl of ecent Advnces in Enineerin & Technoloy (IJAET) INVETIGATION OF TWO PHAE BIGELE INTELEAVE BOOT CONVETE FO POWE FACTO COECTION 1 V.Nithin, 2 P.iv Priy, 3 N.iv unth, 4 r..eyezhi & 5
Interntionl Journl of ecent Advnces in Enineerin & Technoloy (IJAET) INVETIGATION OF TWO PHAE BIGELE INTELEAVE BOOT CONVETE FO POWE FACTO COECTION 1 V.Nithin, 2 P.iv Priy, 3 N.iv unth, 4 r..eyezhi & 5
CHAPTER 3 AMPLIFIER DESIGN TECHNIQUES
 CHAPTER 3 AMPLIFIER DEIGN TECHNIQUE 3.0 Introduction olid-stte microwve mplifiers ply n importnt role in communiction where it hs different pplictions, including low noise, high gin, nd high power mplifiers.
CHAPTER 3 AMPLIFIER DEIGN TECHNIQUE 3.0 Introduction olid-stte microwve mplifiers ply n importnt role in communiction where it hs different pplictions, including low noise, high gin, nd high power mplifiers.
A Channel Splitting Technique for Reducing Handoff Delay in Wireless Networks
 Interntionl Journl o Engineering Reserch & Technology (IJERT) A Chnnel Splitting Technique or Reducing Hndo ely in Wireless Networks Jeykumr. J #1, Venktesh. * 2, Vigneswri. G* 3, Nivethith. V *4 # 1 PG
Interntionl Journl o Engineering Reserch & Technology (IJERT) A Chnnel Splitting Technique or Reducing Hndo ely in Wireless Networks Jeykumr. J #1, Venktesh. * 2, Vigneswri. G* 3, Nivethith. V *4 # 1 PG
Dataflow Language Model. DataFlow Models. Applications of Dataflow. Dataflow Languages. Kahn process networks. A Kahn Process (1)
 The slides contin revisited mterils from: Peter Mrwedel, TU Dortmund Lothr Thiele, ETH Zurich Frnk Vhid, University of liforni, Riverside Dtflow Lnguge Model Drsticlly different wy of looking t computtion:
The slides contin revisited mterils from: Peter Mrwedel, TU Dortmund Lothr Thiele, ETH Zurich Frnk Vhid, University of liforni, Riverside Dtflow Lnguge Model Drsticlly different wy of looking t computtion:
Understanding Basic Analog Ideal Op Amps
 Appliction Report SLAA068A - April 2000 Understnding Bsic Anlog Idel Op Amps Ron Mncini Mixed Signl Products ABSTRACT This ppliction report develops the equtions for the idel opertionl mplifier (op mp).
Appliction Report SLAA068A - April 2000 Understnding Bsic Anlog Idel Op Amps Ron Mncini Mixed Signl Products ABSTRACT This ppliction report develops the equtions for the idel opertionl mplifier (op mp).
Application of Wavelet De-noising in Vibration Torque Measurement
 IJCSI Interntionl Journl of Computer Science Issues, Vol. 9, Issue 5, No 3, September 01 www.ijcsi.org 9 Appliction of Wvelet De-noising in Vibrtion orque Mesurement Ho Zho 1 1 Jixing University, Jixing,
IJCSI Interntionl Journl of Computer Science Issues, Vol. 9, Issue 5, No 3, September 01 www.ijcsi.org 9 Appliction of Wvelet De-noising in Vibrtion orque Mesurement Ho Zho 1 1 Jixing University, Jixing,
5 I. T cu2. T use in modem computing systems, it is desirable to. A Comparison of Half-Bridge Resonant Converter Topologies
 74 EEE TRANSACTONS ON POER ELECTRONCS, VOL. 3, NO. 2, APRL 988 A Comprison of Hlf-Bridge Resonnt Converter Topologies Abstrct-The hlf-bridge series-resonnt, prllel-resonnt, nd combintion series-prllel
74 EEE TRANSACTONS ON POER ELECTRONCS, VOL. 3, NO. 2, APRL 988 A Comprison of Hlf-Bridge Resonnt Converter Topologies Abstrct-The hlf-bridge series-resonnt, prllel-resonnt, nd combintion series-prllel
Study on Application of a Human-Robot Collaborative System Using Hand-Guiding in a Production Line
 Study on Appliction of Humn-Robot Collbortive System Using Hnd-Guiding in Production Line FUJII Msku : Mnger, Control & Communiction Technology Deprment, Products Development Center, Corporte Reserch &
Study on Appliction of Humn-Robot Collbortive System Using Hnd-Guiding in Production Line FUJII Msku : Mnger, Control & Communiction Technology Deprment, Products Development Center, Corporte Reserch &
Domination and Independence on Square Chessboard
 Engineering nd Technology Journl Vol. 5, Prt, No. 1, 017 A.A. Omrn Deprtment of Mthemtics, College of Eduction for Pure Science, University of bylon, bylon, Irq pure.hmed.omrn@uobby lon.edu.iq Domintion
Engineering nd Technology Journl Vol. 5, Prt, No. 1, 017 A.A. Omrn Deprtment of Mthemtics, College of Eduction for Pure Science, University of bylon, bylon, Irq pure.hmed.omrn@uobby lon.edu.iq Domintion
9.4. ; 65. A family of curves has polar equations. ; 66. The astronomer Giovanni Cassini ( ) studied the family of curves with polar equations
 54 CHAPTER 9 PARAMETRIC EQUATINS AND PLAR CRDINATES 49. r, 5. r sin 3, 5 54 Find the points on the given curve where the tngent line is horizontl or verticl. 5. r 3 cos 5. r e 53. r cos 54. r sin 55. Show
54 CHAPTER 9 PARAMETRIC EQUATINS AND PLAR CRDINATES 49. r, 5. r sin 3, 5 54 Find the points on the given curve where the tngent line is horizontl or verticl. 5. r 3 cos 5. r e 53. r cos 54. r sin 55. Show
A Cluster-based TDMA System for Inter-Vehicle Communications *
 JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING 30, 213-231 (2014) A Cluster-bsed TDMA System for Inter-Vehicle Communictions * Deprtment of Electricl Engineering Ntionl Sun Yt-Sen University Kohsiung,
JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING 30, 213-231 (2014) A Cluster-bsed TDMA System for Inter-Vehicle Communictions * Deprtment of Electricl Engineering Ntionl Sun Yt-Sen University Kohsiung,
Temporal Secondary Access Opportunities for WLAN in Radar Bands
 The 4th Interntionl Symposium on Wireless Personl Multimedi Communictions WPMC'), Temporl Secondry Access Opportunities for WLAN in Rdr Bnds Miurel Tercero, Ki Won Sung, nd Jens Znder Wireless@KTH, Royl
The 4th Interntionl Symposium on Wireless Personl Multimedi Communictions WPMC'), Temporl Secondry Access Opportunities for WLAN in Rdr Bnds Miurel Tercero, Ki Won Sung, nd Jens Znder Wireless@KTH, Royl
Performance Comparison of Sliding Mode Control and Conventional PI Controller for Speed Control of Separately Excited Direct Current Motors
 Journl of Science nd Technology Vol. 13, No. 2 Engineering nd Computer Sciences (ECS) Performnce Comprison of Sliding Mode Control nd Conventionl PI Controller for Speed Control of Seprtely Excited Direct
Journl of Science nd Technology Vol. 13, No. 2 Engineering nd Computer Sciences (ECS) Performnce Comprison of Sliding Mode Control nd Conventionl PI Controller for Speed Control of Seprtely Excited Direct
Distributed two-hop proportional fair resource allocation in Long Term Evolution Advanced networks
 WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND MOBILE COMPUTING Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2016; 16:264 278 Published online 12 August 2014 in Wiley Online Librry (wileyonlinelibrry.com)..2517 RESEARCH ARTICLE Distributed
WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND MOBILE COMPUTING Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2016; 16:264 278 Published online 12 August 2014 in Wiley Online Librry (wileyonlinelibrry.com)..2517 RESEARCH ARTICLE Distributed
Kyushu Institute of Technology
 Title: Integrted Rescue Service Stellite (IRS-St) Primry Point of Contct (POC): Mohmed Ibrhim Co-uthors: Btsuren Amglnbt, Puline Fure, Kevin Chou Orgniztion:, 1-1 Sensui, Tobt, Kitkyushu 804-8550, Jpn
Title: Integrted Rescue Service Stellite (IRS-St) Primry Point of Contct (POC): Mohmed Ibrhim Co-uthors: Btsuren Amglnbt, Puline Fure, Kevin Chou Orgniztion:, 1-1 Sensui, Tobt, Kitkyushu 804-8550, Jpn
Fuzzy Logic Controller for Three Phase PWM AC-DC Converter
 Journl of Electrotechnology, Electricl Engineering nd Mngement (2017) Vol. 1, Number 1 Clusius Scientific Press, Cnd Fuzzy Logic Controller for Three Phse PWM AC-DC Converter Min Muhmmd Kml1,, Husn Ali2,b
Journl of Electrotechnology, Electricl Engineering nd Mngement (2017) Vol. 1, Number 1 Clusius Scientific Press, Cnd Fuzzy Logic Controller for Three Phse PWM AC-DC Converter Min Muhmmd Kml1,, Husn Ali2,b
Y9.ET1.3 Implementation of Secure Energy Management against Cyber/physical Attacks for FREEDM System
 Y9.ET1.3 Implementtion of Secure Energy ngement ginst Cyber/physicl Attcks for FREED System Project Leder: Fculty: Students: Dr. Bruce cillin Dr. o-yuen Chow Jie Dun 1. Project Gols Develop resilient cyber-physicl
Y9.ET1.3 Implementtion of Secure Energy ngement ginst Cyber/physicl Attcks for FREED System Project Leder: Fculty: Students: Dr. Bruce cillin Dr. o-yuen Chow Jie Dun 1. Project Gols Develop resilient cyber-physicl
A Multipath Routing Algorithm Based on Traffic Prediction in Wireless Mesh Networks
 Counictions n Network, 009,, 8-90 oi:0.436/cn.009.03 Publishe Online Noveber 009 (http://www.scirp.org/ournl/cn). A Multipth Routing Algorith Bse on Trffic Preiction in Wireless Mesh Networks Abstrct Zhiyun
Counictions n Network, 009,, 8-90 oi:0.436/cn.009.03 Publishe Online Noveber 009 (http://www.scirp.org/ournl/cn). A Multipth Routing Algorith Bse on Trffic Preiction in Wireless Mesh Networks Abstrct Zhiyun
Postprint. This is the accepted version of a paper presented at IEEE PES General Meeting.
 http://www.div-portl.org Postprint This is the ccepted version of pper presented t IEEE PES Generl Meeting. Cittion for the originl published pper: Mhmood, F., Hooshyr, H., Vnfretti, L. (217) Sensitivity
http://www.div-portl.org Postprint This is the ccepted version of pper presented t IEEE PES Generl Meeting. Cittion for the originl published pper: Mhmood, F., Hooshyr, H., Vnfretti, L. (217) Sensitivity
MATH 118 PROBLEM SET 6
 MATH 118 PROBLEM SET 6 WASEEM LUTFI, GABRIEL MATSON, AND AMY PIRCHER Section 1 #16: Show tht if is qudrtic residue modulo m, nd b 1 (mod m, then b is lso qudrtic residue Then rove tht the roduct of the
MATH 118 PROBLEM SET 6 WASEEM LUTFI, GABRIEL MATSON, AND AMY PIRCHER Section 1 #16: Show tht if is qudrtic residue modulo m, nd b 1 (mod m, then b is lso qudrtic residue Then rove tht the roduct of the
Simulation of Transformer Based Z-Source Inverter to Obtain High Voltage Boost Ability
 Interntionl Journl of cience, Engineering nd Technology Reserch (IJETR), olume 4, Issue 1, October 15 imultion of Trnsformer Bsed Z-ource Inverter to Obtin High oltge Boost Ability A.hnmugpriy 1, M.Ishwry
Interntionl Journl of cience, Engineering nd Technology Reserch (IJETR), olume 4, Issue 1, October 15 imultion of Trnsformer Bsed Z-ource Inverter to Obtin High oltge Boost Ability A.hnmugpriy 1, M.Ishwry
Pulse Width Modulated AC Voltage Controller Filter Design by Optimization Technique
 Fro the SelectedWorks of Innovtive Reserch Publictions IRP Indi Winter Noveber, 05 Pulse Width Modulted AC Voltge Controller Filter Design by Optiiztion Technique N. Murli, Dr.V. Blji Avilble t: https://works.bepress.co/irpindi/430/
Fro the SelectedWorks of Innovtive Reserch Publictions IRP Indi Winter Noveber, 05 Pulse Width Modulted AC Voltge Controller Filter Design by Optiiztion Technique N. Murli, Dr.V. Blji Avilble t: https://works.bepress.co/irpindi/430/
Section 2.2 PWM converter driven DC motor drives
 Section 2.2 PWM converter driven DC motor drives 2.2.1 Introduction Controlled power supply for electric drives re obtined mostly by converting the mins AC supply. Power electronic converter circuits employing
Section 2.2 PWM converter driven DC motor drives 2.2.1 Introduction Controlled power supply for electric drives re obtined mostly by converting the mins AC supply. Power electronic converter circuits employing
Electronic Circuits I - Tutorial 03 Diode Applications I
 Electronic Circuits I - Tutoril 03 Diode Applictions I -1 / 9 - T & F # Question 1 A diode cn conduct current in two directions with equl ese. F 2 When reverse-bised, diode idelly ppers s short. F 3 A
Electronic Circuits I - Tutoril 03 Diode Applictions I -1 / 9 - T & F # Question 1 A diode cn conduct current in two directions with equl ese. F 2 When reverse-bised, diode idelly ppers s short. F 3 A
EET 438a Automatic Control Systems Technology Laboratory 5 Control of a Separately Excited DC Machine
 EE 438 Automtic Control Systems echnology bortory 5 Control of Seprtely Excited DC Mchine Objective: Apply proportionl controller to n electromechnicl system nd observe the effects tht feedbck control
EE 438 Automtic Control Systems echnology bortory 5 Control of Seprtely Excited DC Mchine Objective: Apply proportionl controller to n electromechnicl system nd observe the effects tht feedbck control
Three-Phase Synchronous Machines The synchronous machine can be used to operate as: 1. Synchronous motors 2. Synchronous generators (Alternator)
 Three-Phse Synchronous Mchines The synchronous mchine cn be used to operte s: 1. Synchronous motors 2. Synchronous genertors (Alterntor) Synchronous genertor is lso referred to s lterntor since it genertes
Three-Phse Synchronous Mchines The synchronous mchine cn be used to operte s: 1. Synchronous motors 2. Synchronous genertors (Alterntor) Synchronous genertor is lso referred to s lterntor since it genertes
Mixed CMOS PTL Adders
 Anis do XXVI Congresso d SBC WCOMPA l I Workshop de Computção e Aplicções 14 20 de julho de 2006 Cmpo Grnde, MS Mixed CMOS PTL Adders Déor Mott, Reginldo d N. Tvres Engenhri em Sistems Digitis Universidde
Anis do XXVI Congresso d SBC WCOMPA l I Workshop de Computção e Aplicções 14 20 de julho de 2006 Cmpo Grnde, MS Mixed CMOS PTL Adders Déor Mott, Reginldo d N. Tvres Engenhri em Sistems Digitis Universidde
Free Space Optical Communication System against Channel Fading
 Free Spce Opticl Communiction System ginst Chnnel Fding Prem.S 1, A.Elngovn 1 ME- 1 Applied Electronics, Aruni Engineering College, Tiruvnnmli, Tmil Ndu-6663, Indi Assistnt Professor of ECE Deprtment,
Free Spce Opticl Communiction System ginst Chnnel Fding Prem.S 1, A.Elngovn 1 ME- 1 Applied Electronics, Aruni Engineering College, Tiruvnnmli, Tmil Ndu-6663, Indi Assistnt Professor of ECE Deprtment,
DYE SOLUBILITY IN SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE FLUID
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Yer 2015, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 1311-1315 1311 DYE SOLUBILITY IN SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE FLUID by Jun YAN, Li-Jiu ZHENG *, Bing DU, Yong-Fng QIAN, nd Fng YE Lioning Provincil Key Lbortory
THERMAL SCIENCE, Yer 2015, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 1311-1315 1311 DYE SOLUBILITY IN SUPERCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE FLUID by Jun YAN, Li-Jiu ZHENG *, Bing DU, Yong-Fng QIAN, nd Fng YE Lioning Provincil Key Lbortory
April 9, 2000 DIS chapter 10 CHAPTER 3 : INTEGRATED PROCESSOR-LEVEL ARCHITECTURES FOR REAL-TIME DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING
 April 9, 2000 DIS chpter 0 CHAPTE 3 : INTEGATED POCESSO-LEVEL ACHITECTUES FO EAL-TIME DIGITAL SIGNAL POCESSING April 9, 2000 DIS chpter 3.. INTODUCTION The purpose of this chpter is twofold. Firstly, bsic
April 9, 2000 DIS chpter 0 CHAPTE 3 : INTEGATED POCESSO-LEVEL ACHITECTUES FO EAL-TIME DIGITAL SIGNAL POCESSING April 9, 2000 DIS chpter 3.. INTODUCTION The purpose of this chpter is twofold. Firstly, bsic
MEASURE THE CHARACTERISTIC CURVES RELEVANT TO AN NPN TRANSISTOR
 Electricity Electronics Bipolr Trnsistors MEASURE THE HARATERISTI URVES RELEVANT TO AN NPN TRANSISTOR Mesure the input chrcteristic, i.e. the bse current IB s function of the bse emitter voltge UBE. Mesure
Electricity Electronics Bipolr Trnsistors MEASURE THE HARATERISTI URVES RELEVANT TO AN NPN TRANSISTOR Mesure the input chrcteristic, i.e. the bse current IB s function of the bse emitter voltge UBE. Mesure
Lecture 20. Intro to line integrals. Dan Nichols MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts.
 Lecture 2 Intro to line integrls Dn Nichols nichols@mth.umss.edu MATH 233, Spring 218 University of Msschusetts April 12, 218 (2) onservtive vector fields We wnt to determine if F P (x, y), Q(x, y) is
Lecture 2 Intro to line integrls Dn Nichols nichols@mth.umss.edu MATH 233, Spring 218 University of Msschusetts April 12, 218 (2) onservtive vector fields We wnt to determine if F P (x, y), Q(x, y) is
Information-Coupled Turbo Codes for LTE Systems
 Informtion-Coupled Turbo Codes for LTE Systems Lei Yng, Yixun Xie, Xiowei Wu, Jinhong Yun, Xingqing Cheng nd Lei Wn rxiv:709.06774v [cs.it] 20 Sep 207 Abstrct We propose new clss of informtion-coupled
Informtion-Coupled Turbo Codes for LTE Systems Lei Yng, Yixun Xie, Xiowei Wu, Jinhong Yun, Xingqing Cheng nd Lei Wn rxiv:709.06774v [cs.it] 20 Sep 207 Abstrct We propose new clss of informtion-coupled
Design and Modeling of Substrate Integrated Waveguide based Antenna to Study the Effect of Different Dielectric Materials
 Design nd Modeling of Substrte Integrted Wveguide bsed Antenn to Study the Effect of Different Dielectric Mterils Jgmeet Kour 1, Gurpdm Singh 1, Sndeep Ary 2 1Deprtment of Electronics nd Communiction Engineering,
Design nd Modeling of Substrte Integrted Wveguide bsed Antenn to Study the Effect of Different Dielectric Mterils Jgmeet Kour 1, Gurpdm Singh 1, Sndeep Ary 2 1Deprtment of Electronics nd Communiction Engineering,
LECTURE 9: QUADRATIC RESIDUES AND THE LAW OF QUADRATIC RECIPROCITY
 LECTURE 9: QUADRATIC RESIDUES AND THE LAW OF QUADRATIC RECIPROCITY 1. Bsic roerties of qudrtic residues We now investigte residues with secil roerties of lgebric tye. Definition 1.1. (i) When (, m) 1 nd
LECTURE 9: QUADRATIC RESIDUES AND THE LAW OF QUADRATIC RECIPROCITY 1. Bsic roerties of qudrtic residues We now investigte residues with secil roerties of lgebric tye. Definition 1.1. (i) When (, m) 1 nd
Educating High School Students in Process Simulation and Control with a Simulink-Based Controller Design for Microbial Fuel Cells
 Educting High School Students in Process Siultion nd Control with Siulink-Bsed Controller Design for Microbil Fuel Cells Cleent Ekputr nd Zuyi (Jcky) Hung Gret Vlley High School/Villnov University Abstrct
Educting High School Students in Process Siultion nd Control with Siulink-Bsed Controller Design for Microbil Fuel Cells Cleent Ekputr nd Zuyi (Jcky) Hung Gret Vlley High School/Villnov University Abstrct
Module 9. DC Machines. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 9 DC Mchines Version EE IIT, Khrgpur esson 40 osses, Efficiency nd Testing of D.C. Mchines Version EE IIT, Khrgpur Contents 40 osses, efficiency nd testing of D.C. mchines (esson-40) 4 40.1 Gols
Module 9 DC Mchines Version EE IIT, Khrgpur esson 40 osses, Efficiency nd Testing of D.C. Mchines Version EE IIT, Khrgpur Contents 40 osses, efficiency nd testing of D.C. mchines (esson-40) 4 40.1 Gols
BP-P2P: Belief Propagation-Based Trust and Reputation Management for P2P Networks
 1 9th Annul IEEE Communictions Society Conference on Sensor, Mesh nd Ad Hoc Communictions nd Networs (SECON) BP-PP: Belief Propgtion-Bsed Trust nd Reputtion Mngement for PP Networs Ermn Aydy School of
1 9th Annul IEEE Communictions Society Conference on Sensor, Mesh nd Ad Hoc Communictions nd Networs (SECON) BP-PP: Belief Propgtion-Bsed Trust nd Reputtion Mngement for PP Networs Ermn Aydy School of
Math 116 Calculus II
 Mth 6 Clculus II Contents 7 Additionl topics in Integrtion 7. Integrtion by prts..................................... 7.4 Numericl Integrtion.................................... 7 7.5 Improper Integrl......................................
Mth 6 Clculus II Contents 7 Additionl topics in Integrtion 7. Integrtion by prts..................................... 7.4 Numericl Integrtion.................................... 7 7.5 Improper Integrl......................................
Improving synchronized transfers in public transit networks using real-time tactics
 Improving synchronized trnsfers in public trnsit networks using rel-time tctics Zhongjun Wu 1,2,3, Grhm Currie 3, Wei Wng 1,2 1 Jingsu Key Lbortory of Urbn ITS, Si Pi Lou 2#, Nnjing, 210096, Chin 2 School
Improving synchronized trnsfers in public trnsit networks using rel-time tctics Zhongjun Wu 1,2,3, Grhm Currie 3, Wei Wng 1,2 1 Jingsu Key Lbortory of Urbn ITS, Si Pi Lou 2#, Nnjing, 210096, Chin 2 School
Chapter 6. Direct Current Motors
 Chter 6 Direct Current Motors DC Motors A DC Motor Arture (rotor) long with the couttor Constructionl Fetures of DC Motors A 4-Pole DC Motor Couttor long with the rture on the rotor Slient-oles on the
Chter 6 Direct Current Motors DC Motors A DC Motor Arture (rotor) long with the couttor Constructionl Fetures of DC Motors A 4-Pole DC Motor Couttor long with the rture on the rotor Slient-oles on the
Soft switched DC-DC PWM Converters
 Soft switched DC-DC PWM Converters Mr.M. Prthp Rju (), Dr. A. Jy Lkshmi () Abstrct This pper presents n upgrded soft switching technique- zero current trnsition (ZCT), which gives better turn off chrcteristics
Soft switched DC-DC PWM Converters Mr.M. Prthp Rju (), Dr. A. Jy Lkshmi () Abstrct This pper presents n upgrded soft switching technique- zero current trnsition (ZCT), which gives better turn off chrcteristics
Three-Phase NPC Inverter Using Three-Phase Coupled Inductor
 ThreePhse NPC Inverter Using ThreePhse Coupled Inductor Romeu Husmnn 1, Rodrigo d Silv 2 nd Ivo Brbi 2 1 Deprtment of Electricl nd Telecommuniction Engineering, University of Blumenu FURB Blumenu SC Brzil,
ThreePhse NPC Inverter Using ThreePhse Coupled Inductor Romeu Husmnn 1, Rodrigo d Silv 2 nd Ivo Brbi 2 1 Deprtment of Electricl nd Telecommuniction Engineering, University of Blumenu FURB Blumenu SC Brzil,
EXIT CHARTS FOR TURBO RECEIVERS IN MIMO SYSTEMS
 EXIT CHATS FO TUBO ECEIVES IN MIMO SYSTEMS Césr Hermosill Universidd Técnic Federico Snt Mrí Vlpríso, Chile hermosil@inrs-telecomuquebecc Leszek Szczeciński Institut Ntionl de l echerche Scientifique-EMT
EXIT CHATS FO TUBO ECEIVES IN MIMO SYSTEMS Césr Hermosill Universidd Técnic Federico Snt Mrí Vlpríso, Chile hermosil@inrs-telecomuquebecc Leszek Szczeciński Institut Ntionl de l echerche Scientifique-EMT
Synchronous Generator Line Synchronization
 Synchronous Genertor Line Synchroniztion 1 Synchronous Genertor Line Synchroniztion Introduction One issue in power genertion is synchronous genertor strting. Typiclly, synchronous genertor is connected
Synchronous Genertor Line Synchroniztion 1 Synchronous Genertor Line Synchroniztion Introduction One issue in power genertion is synchronous genertor strting. Typiclly, synchronous genertor is connected
CSI-SF: Estimating Wireless Channel State Using CSI Sampling & Fusion
 CSI-SF: Estimting Wireless Chnnel Stte Using CSI Smpling & Fusion Riccrdo Crepldi, Jeongkeun Lee, Rul Etkin, Sung-Ju Lee, Robin Krvets University of Illinois t Urbn-Chmpign Hewlett-Pckrd Lbortories Emil:{rcrepl,rhk}@illinoisedu,
CSI-SF: Estimting Wireless Chnnel Stte Using CSI Smpling & Fusion Riccrdo Crepldi, Jeongkeun Lee, Rul Etkin, Sung-Ju Lee, Robin Krvets University of Illinois t Urbn-Chmpign Hewlett-Pckrd Lbortories Emil:{rcrepl,rhk}@illinoisedu,
Eliminating Non-Determinism During Test of High-Speed Source Synchronous Differential Buses
 Eliminting Non-Determinism During of High-Speed Source Synchronous Differentil Buses Abstrct The t-speed functionl testing of deep sub-micron devices equipped with high-speed I/O ports nd the synchronous
Eliminting Non-Determinism During of High-Speed Source Synchronous Differentil Buses Abstrct The t-speed functionl testing of deep sub-micron devices equipped with high-speed I/O ports nd the synchronous
BP-P2P: Belief Propagation-Based Trust and Reputation Management for P2P Networks
 BP-PP: Belief Propgtion-Bsed Trust nd Reputtion Mngement for PP Networs Ermn Aydy School of Electricl nd Comp. Eng. Georgi Institute of Technology Atlnt, GA 333, USA Emil: eydy@gtech.edu Frmrz Feri School
BP-PP: Belief Propgtion-Bsed Trust nd Reputtion Mngement for PP Networs Ermn Aydy School of Electricl nd Comp. Eng. Georgi Institute of Technology Atlnt, GA 333, USA Emil: eydy@gtech.edu Frmrz Feri School
High Speed On-Chip Interconnects: Trade offs in Passive Termination
 High Speed On-Chip Interconnects: Trde offs in Pssive Termintion Rj Prihr University of Rochester, NY, USA prihr@ece.rochester.edu Abstrct In this pper, severl pssive termintion schemes for high speed
High Speed On-Chip Interconnects: Trde offs in Pssive Termintion Rj Prihr University of Rochester, NY, USA prihr@ece.rochester.edu Abstrct In this pper, severl pssive termintion schemes for high speed
Innovative plate solutions for flexographic printing. nyloflex printing plates
 Innovtive plte solutions for flexogrphic printing nyloflex printing pltes nyloflex Printing Pltes Unique nd comprehensive expertise in flexogrphic printing Printing pltes from Flint Group to meet every
Innovtive plte solutions for flexogrphic printing nyloflex printing pltes nyloflex Printing Pltes Unique nd comprehensive expertise in flexogrphic printing Printing pltes from Flint Group to meet every
Distance dependent Call Blocking Probability, and Area Erlang Efficiency of Cellular Networks
 Distnce dependent Cll Blocking Probbility, nd Are Erlng Efficiency of Cellulr Networks Subhendu Btbyl 1, Suvr Sekhr Ds 1,2 1 G.S.Snyl School of Telecommuniction, Indin Institute of Technology Khrgpur,
Distnce dependent Cll Blocking Probbility, nd Are Erlng Efficiency of Cellulr Networks Subhendu Btbyl 1, Suvr Sekhr Ds 1,2 1 G.S.Snyl School of Telecommuniction, Indin Institute of Technology Khrgpur,
DESIGN OF CONTINUOUS LAG COMPENSATORS
 DESIGN OF CONTINUOUS LAG COMPENSATORS J. Pulusová, L. Körösi, M. Dúbrvská Institute of Robotics nd Cybernetics, Slovk University of Technology, Fculty of Electricl Engineering nd Informtion Technology
DESIGN OF CONTINUOUS LAG COMPENSATORS J. Pulusová, L. Körösi, M. Dúbrvská Institute of Robotics nd Cybernetics, Slovk University of Technology, Fculty of Electricl Engineering nd Informtion Technology
Kirchhoff s Rules. Kirchhoff s Laws. Kirchhoff s Rules. Kirchhoff s Laws. Practice. Understanding SPH4UW. Kirchhoff s Voltage Rule (KVR):
 SPH4UW Kirchhoff s ules Kirchhoff s oltge ule (K): Sum of voltge drops round loop is zero. Kirchhoff s Lws Kirchhoff s Current ule (KC): Current going in equls current coming out. Kirchhoff s ules etween
SPH4UW Kirchhoff s ules Kirchhoff s oltge ule (K): Sum of voltge drops round loop is zero. Kirchhoff s Lws Kirchhoff s Current ule (KC): Current going in equls current coming out. Kirchhoff s ules etween
SYNCHROPHASOR MEASUREMENT USING SUBSTATION INTELLIGENT ELECTRONIC DEVICES: ALGORITHMS AND TEST METHODOLOGY. A Dissertation JINFENG REN
 SYNCHROPHASOR MEASUREMENT USING SUBSTATION INTELLIGENT ELECTRONIC DEVICES: ALGORITHMS AND TEST METHODOLOGY A Disserttion by JINFENG REN Subitted to the Office of Grdute Studies of Texs A&M University in
SYNCHROPHASOR MEASUREMENT USING SUBSTATION INTELLIGENT ELECTRONIC DEVICES: ALGORITHMS AND TEST METHODOLOGY A Disserttion by JINFENG REN Subitted to the Office of Grdute Studies of Texs A&M University in
Engineer-to-Engineer Note
 Engineer-to-Engineer Note EE-236 Technicl notes on using Anlog Devices DSPs, processors nd development tools Contct our technicl support t dsp.support@nlog.com nd t dsptools.support@nlog.com Or visit our
Engineer-to-Engineer Note EE-236 Technicl notes on using Anlog Devices DSPs, processors nd development tools Contct our technicl support t dsp.support@nlog.com nd t dsptools.support@nlog.com Or visit our
On the Prediction of EPON Traffic Using Polynomial Fitting in Optical Network Units
 On the Prediction of EP Trffic Using Polynomil Fitting in Opticl Networ Units I. Mmounis (1),(3), K. Yinnopoulos (2), G. Ppdimitriou (4), E. Vrvrigos (1),(3) (1) Computer Technology Institute nd Press
On the Prediction of EP Trffic Using Polynomil Fitting in Opticl Networ Units I. Mmounis (1),(3), K. Yinnopoulos (2), G. Ppdimitriou (4), E. Vrvrigos (1),(3) (1) Computer Technology Institute nd Press
Analog computation of wavelet transform coefficients in real-time Moreira-Tamayo, O.; Pineda de Gyvez, J.
 Anlog computtion of wvelet trnsform coefficients in rel-time Moreir-Tmyo, O.; Pined de Gyvez, J. Published in: IEEE Trnsctions on Circuits nd Systems. I, Fundmentl Theory nd Applictions DOI: 0.09/8.558443
Anlog computtion of wvelet trnsform coefficients in rel-time Moreir-Tmyo, O.; Pined de Gyvez, J. Published in: IEEE Trnsctions on Circuits nd Systems. I, Fundmentl Theory nd Applictions DOI: 0.09/8.558443
A New Stochastic Inner Product Core Design for Digital FIR Filters
 MATEC Web of Conferences, (7) DOI:./ mtecconf/7 CSCC 7 A New Stochstic Inner Product Core Design for Digitl FIR Filters Ming Ming Wong,, M. L. Dennis Wong, Cishen Zhng, nd Ismt Hijzin Fculty of Engineering,
MATEC Web of Conferences, (7) DOI:./ mtecconf/7 CSCC 7 A New Stochstic Inner Product Core Design for Digitl FIR Filters Ming Ming Wong,, M. L. Dennis Wong, Cishen Zhng, nd Ismt Hijzin Fculty of Engineering,
