Avances en Mezcladores: Circuitos Subarmonicos y sus Aplicaciones
|
|
|
- Ami Walsh
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Avances en Mezcladores: Circuitos Subarmonicos y sus Aplicaciones Carlos E. Saavedra, Ph.D. Profesor Asociado y Coordinador de Postgrado Electrical and Computer Engineering Queen s University CANADA
2 Plan de la charla Porque los mezcladores subarmonicos? Mezcladores subharmonicos (SHM) en CMOS Análisis del SHM basado en la celda de Gilbert-Cell Avances recientes: el SHM con multiplicación x4 Multiplicadores de frequencia usando SHM s Conclusión
3 Gigahertz Integrated Circuits Group Líder del grupo y diseñador en jefe: Profesor Carlos Saavedra Estudiantes de doctorado Ahmed El-Gabaly, Jiangtao Xu Maestria: Min Wang, Shan He Pregrado Greg Reynen, Jeet Mondal, Kevin Greig
4 Infraestructura Experimental Probe Station 50 GHz Vector Network Analyzer 44 GHz Spectrum Analyzer with Noise Fig. measurement capability 40 GHz Signal Generators (Anritsu) Digital Sampling Oscilloscopes
5 Subharmonic Mixers the big picture Output signal frequency is the sum and difference of one input frequency and a multiple of the other input frequency. Internally multiplies f LO Downconversion IF f LO f RF f RF 2f LO f RF + 2f LO 2x SHM n=2 4x SHM n=4 5
6 Terahertz Receiver for Radio Astronomy
7 Diode-based Subharmonic Mixers Schottky diodes are often used in THz systems due to their speed The mixers are cooled to 4 Kelvin to minimize their internal noise Waveguide structures are preferred due to their low loss Mixers using SIS junctions are also employed
8 Diode SHM analysis The currents are: and Summation at node vp: Taylor series expansion: one of the multiplication terms is:
9 SHM s in Superheterodyne Receivers The LO frequency is reduced by flo /n Oscillator phase-noise is much better at lower frequencies than at higher ones. At 3 GHz one could use an FBAR resonator and get a XTAL oscillator performance levels
10 Direct-Conversion (zero IF) Receivers LO self-mixing in a fundamental mixer cause serious interference problems at baseband in direct-conversion receivers 10
11 LO self-mixing in zero-if receivers using a fundamental mixer: A 1 2 LO A cos( w LO A FT LO baseband signal t) A A FT LO cos( w A FT LO t) = cos(2w LO t) A LO cos( w t) using a x2 Subharmonic mixer: A LO LO 1 cos( w LOt) AFT cos(2w LOt) = ALO AFT cos( wlot) + 2 self-mixing products are not at baseband 1 2 A LO A FT cos(3w LO t)
12 CMOS SHM Design Considerations SHM s based on the Gilbert cell have conversion gain, even at high multiplication factors High port-to-port isolation is easily achieved using a differential circuit topology In contrast to diode-based SHM s, diplexers are not needed to feed the RF and LO signals to the mixer These attributes, however, come at the cost of DC power consumption and lower P1dB and IIP3 relative to diodebased SHM s.
13 x2 SHM using a Gilbert Cell [3-5] Standard Gilbert Cell x2 LO multiplication
14 x2 SHM Operation Details v LO 0 = ALO sin( wlot) v LO 180 = ALO sin( wlot -p ) Using the relationship, v = v 2 2 LO0 LO180
15 Modeling the Conversion Gain Converge the two transistors in the X2 doubler network into a single equivalent transistor The drive signal of the equivalent transistor is, v LOeq µ cos( 2w LO t) Analyze the resulting mixer circuit as a classic Gilbert-Cell mixer to obtain a a closed-form expression for conversion gain.
16 Modeling the Conversion Gain cont d For more modeling details see Ref. [6]
17 CMOS x2 SHM Power Performance Conversion Gain ~ 8 db P1dB,out = - 9 dbm OIP3 = 0 dbm
18 RF input match Port Isolations Broadband input match obtained using an active balun at the RF port
19 x2 SHM Chip Microphotograph RF frequency LO frequency IF frequency DC Power 2.1 GHz 1 GHz 100 MHz 36 mw 2 Chip Size 0.42 mm incl. pads mixer core input/output active baluns
20 Recent Advances: X4 Subharmonic Mixer B. R. Jackson and C. E. Saavedra, A CMOS Ku Band 4X Subharmonic Mixer, IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, Vol. 43, No. 6, pp , June 2008.
21 The LO Multiplication Core - modeling Left-half of the core Model this as a smaller circuit The current at 4fLO i T 1 æ ö» µ ncoxwesat ALOç + sin(2w LOt) + cos( 4w LOt) 2 è ø
22 The LO phases in the multiplication core Octet-phase LO signal used to generate the 4fLO signal
23 Creating a differential at signal at 4ωLO: v LO ( t) = A LO æ sinçw è LO n = 0, 1, 2, 3,,7 2p ö t + n = A 8 ø LO æ sinçw è LO t + n p ö 4 ø At the frequency, ω, the phases are: 0, π/4, π/2, 3π/4, 7π/4 At the frequency, 4ω, the phases are: 0, π, 0, π, v 4 ( w t np ) LO ( t) = vd + it Zind µ sin 4 LO + n = 0, 1, 2, 3,,7
24 LO Octet Phase Generation Create a set of quadrature signals using a method of your choice Generate the π/4 vector: add a 0 and a π/2 vector using an active summing junction. Repeat for the other 3 vectors. For equalizing the loading effects
25 Fully integrated x4 SHP Mixer I/O circuitry RF active balun
26 Fully integrated x4 SHP Mixer I/O circuitry IF output stage: differential to single-ended conversion
27 x4 SHM Power Performance LO power = 10 dbm Conversion Gain: 6 db à best reported to date for a x4 SHP mixer P1dB,out : -7 dbm RF = 12.1 GHz, LO = 3.0 GHz, IF = 100 MHz
28 Spectral Response
29 Intermodulation Distortion Measurements Two-tones: 12.1 GHz and GHz OIP3 = + 5 dbm OIP2 = + 24 dbm Using passive baluns will improve these values
30 LO Self-Mixing Performance How to evaluate LO self-mixing behavior: 1) Measure the DC level at the IF port with no RF and LO input signals: 2) Measure the DC level at the IF with an LO signal applied and no RF input signal: 3) LO Self-Mixing is thus: Self -Mixing V DC1 V = V -V DC1 DC 2 LO input signal used: GHz à Vrms = 707 mv Measured self-mixing voltage at the IF port: 4.2 mv à 44 db rejection V DC 2
31 CMOS Subharmonic Mixers and Applications Ku Band x4 SHM Chip RF frequency 12.1 GHz LO frequency 3 GHz IF frequency 100 MHz Noise Figure 15 db (DSB) Chip Size 0.72 mm incl. pads DC Power 5 mw (mixer core) mw (full chip)
32 Frequency Multiplication with SHM s odd-order frequency multipliers can be conveniently designed Frequency Tripler with Fundamental Signal Cancellation No output filtering needed B. R. Jackson, F. Mazzilli and C. E. Saavedra, A Frequency Tripler using a Subharmonic Mixer and Fundamental Cancellation, IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, Vol. 57, No. 5, pp , May 2009.
33 Frequency Tripler Design x2 Subharmonic Mixer The feedforward path: Phase Shifter & Amplifier
34 Effect of Phase and Amplitude Mismatch in the Fundamental Cancellation Process The phase and amplitude of the fundamental signal have to be tuned for maximum signal cancellation at the output.
35 Frequency Tripler Design cont d subtractor output buffer From the SHP Mixer From the feedforward circuit
36 Output Spectrum Input Freq. Input power Output Freq. Conv. Gain Fund. Reject. 1 GHz -10 dbm 3 GHz 3 db 30 db
37 Power Performance High suppression of the fundamental and other harmonics achieved without on-chip or off-chip filtering.
38 Noise Performance The minimum phasenoise degradation in a multiplier is: 20 log( n) = db for n = 3. In this work, the degradation is: 9.69 db
39 Frequency Tripler Demonstration Chip Input freq. 1 GHz Output freq. 3 GHz Fund. Reject. 30 db Chip Size 0.80 mm incl. pads DC Power 68 mw (full chip) 2
40 Conclusion In general, transistor-based SHM s can yield good levels of conv. gain: less than a fundamental Gilbert-Cell but higher than a diode SHM Excellent LO-to-RF and LO-to-IF isolation obtained due to the internal multiplication of the LO signal. By balancing gain and linearity requirements, the P1dB and IP3 points can be optimized in a CMOS SHM Novel circuit concepts can be realized by using SHM s such as odd-order multipliers
41 Acknowledgements Graduate students: Brad Jackson (PhD) Francesco Mazzilli (MSc) Funding Organizations: CMC Microsystems (IC fabrication grants) Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) Ontario Ministry of Training, Colleges and Universities
42 About the speaker: Carlos Saavedra received the Ph.D. and M.Sc. degrees from Cornell University and the B.Sc. degree from the University of Virginia. From he was with Millitech Corporation and in the year 2000 he joined Queen s University where he is now Associate Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the Coordinator of Graduate Studies. Prof. Saavedra is a member of the Technical Program Committee of the IEEE RFIC Symposium and serves as a reviewer for several journals, including the IEEE T-MTT, IEEE MWCL, IEEE TCAS-II and Electronics Letters. He is a Senior Member of the IEEE.
43 References 1. T. H. Teo, W. G. Yeoh, Low-Power Short-Range Radio CMOS Subharmonic RF Front-End Using CG-CS LNA, IEEE Trans. Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, Vol. 55, No. 7, pp , July R. H. Kodkani and L. E. Larson, A 24 GHz CMOS Passive Subharmonic Mixer/Downconverter for Zero-IF Applications, IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory and Tech., Vol. 56, No. 5, pp , May Z. Zhaofeng, L. Tsui, C. Zhiheng and J. Lau, A CMOS Self-Mixing-Free Front-End for Direct Conversion Applications, IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp , Sydney, Australia, May K. Nimmagadda and G. Rebeiz, A 1.9 GHz Double-Balanced Subharmonic Mixer for Direct Conversion Receivers, IEEE RFIC Symposium, pp , B. R. Jackson and C. E. Saavedra, A CMOS Subharmonic Mixer with Active Input and Output Baluns, Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, Vol. 48, No. 12, pp , December B. R. Jackson, F. Mazzilli and C. E. Saavedra, A Frequency Tripler using a Subharmonic Mixer and Fundamental Cancellation, IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, Vol. 57, No. 5, pp , May B. R. Jackson and C. E. Saavedra, A CMOS Ku Band 4X Subharmonic Mixer, IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, Vol. 43, No. 6, pp , June 2008.
Frequency Multipliers Design Techniques and Applications
 Frequency Multipliers Design Techniques and Applications Carlos E. Saavedra Associate Professor Electrical and Computer Engineering Queen s University Kingston, Ontario CANADA Outline Introduction applications
Frequency Multipliers Design Techniques and Applications Carlos E. Saavedra Associate Professor Electrical and Computer Engineering Queen s University Kingston, Ontario CANADA Outline Introduction applications
A Volterra Series Approach for the Design of Low-Voltage CG-CS Active Baluns
 A Volterra Series Approach for the Design of Low-Voltage CG-CS Active Baluns Shan He and Carlos E. Saavedra Gigahertz Integrated Circuits Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Queen s
A Volterra Series Approach for the Design of Low-Voltage CG-CS Active Baluns Shan He and Carlos E. Saavedra Gigahertz Integrated Circuits Group Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Queen s
Intermodulation Distortion Mitigation in Microwave Amplifiers and Frequency Converters
 Intermodulation Distortion Mitigation in Microwave Amplifiers and Frequency Converters Carlos Saavedra Professor of Electrical Engineering Queen s University Kingston, Ontario K7L 3N6 30 January 2017 Outline
Intermodulation Distortion Mitigation in Microwave Amplifiers and Frequency Converters Carlos Saavedra Professor of Electrical Engineering Queen s University Kingston, Ontario K7L 3N6 30 January 2017 Outline
AS WITH other active RF circuits, the intermodulation distortion
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 61, NO. 1, JANUARY 2013 177 Design of a Low-Voltage and Low-Distortion Mixer Through Volterra-Series Analysis Shan He and Carlos E. Saavedra,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 61, NO. 1, JANUARY 2013 177 Design of a Low-Voltage and Low-Distortion Mixer Through Volterra-Series Analysis Shan He and Carlos E. Saavedra,
RFIC DESIGN ELEN 351 Lecture 7: Mixer Design
 RFIC DESIGN ELEN 351 Lecture 7: Mixer Design Dr. Allen Sweet Copy Right 2003 ELEN 351 1 Mixer Specifications Conversion Gain / Loss (Gain defined as the ratio of power at the I freq to the power at the
RFIC DESIGN ELEN 351 Lecture 7: Mixer Design Dr. Allen Sweet Copy Right 2003 ELEN 351 1 Mixer Specifications Conversion Gain / Loss (Gain defined as the ratio of power at the I freq to the power at the
LF to 4 GHz High Linearity Y-Mixer ADL5350
 LF to GHz High Linearity Y-Mixer ADL535 FEATURES Broadband radio frequency (RF), intermediate frequency (IF), and local oscillator (LO) ports Conversion loss:. db Noise figure:.5 db High input IP3: 25
LF to GHz High Linearity Y-Mixer ADL535 FEATURES Broadband radio frequency (RF), intermediate frequency (IF), and local oscillator (LO) ports Conversion loss:. db Noise figure:.5 db High input IP3: 25
A 3 8 GHz Broadband Low Power Mixer
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 3, 8 361 A 3 8 GHz Broadband Low Power Mixer Chih-Hau Chen and Christina F. Jou Institute of Communication Engineering, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan Abstract
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 3, 8 361 A 3 8 GHz Broadband Low Power Mixer Chih-Hau Chen and Christina F. Jou Institute of Communication Engineering, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan Abstract
QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A 40MHZ TO 900MHZ DIRECT CONVERSION QUADRATURE DEMODULATOR
 DESCRIPTION QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A LT5517 Demonstration circuit 678A is a 40MHz to 900MHz Direct Conversion Quadrature Demodulator featuring the LT5517. The LT 5517 is a direct
DESCRIPTION QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A LT5517 Demonstration circuit 678A is a 40MHz to 900MHz Direct Conversion Quadrature Demodulator featuring the LT5517. The LT 5517 is a direct
Advanced RFIC Design ELEN359A, Lecture 3: Gilbert Cell Mixers. Instructor: Dr. Allen A Sweet
 Advanced RFIC Design ELEN359A, Lecture 3: Gilbert Cell Mixers Instructor: Dr. Allen A Sweet All of Design is the Art and Science of Navigating Tradeoffs Science gives us the tools to understand what nature,
Advanced RFIC Design ELEN359A, Lecture 3: Gilbert Cell Mixers Instructor: Dr. Allen A Sweet All of Design is the Art and Science of Navigating Tradeoffs Science gives us the tools to understand what nature,
Mixer. General Considerations V RF VLO. Noise. nonlinear, R ON
 007/Nov/7 Mixer General Considerations LO S M F F LO L Noise ( a) nonlinearity (b) Figure 6.5 (a) Simple switch used as mixer (b) implementation of switch with an NMOS device. espect to espect to It is
007/Nov/7 Mixer General Considerations LO S M F F LO L Noise ( a) nonlinearity (b) Figure 6.5 (a) Simple switch used as mixer (b) implementation of switch with an NMOS device. espect to espect to It is
A 24-GHz Quadrature Receiver Front-end in 90-nm CMOS
 A 24GHz Quadrature Receiver Frontend in 90nm CMOS Törmänen, Markus; Sjöland, Henrik Published in: Proc. 2009 IEEE Asia Pacific Microwave Conference Published: 20090101 Link to publication Citation for
A 24GHz Quadrature Receiver Frontend in 90nm CMOS Törmänen, Markus; Sjöland, Henrik Published in: Proc. 2009 IEEE Asia Pacific Microwave Conference Published: 20090101 Link to publication Citation for
Updates on THz Amplifiers and Transceiver Architecture
 Updates on THz Amplifiers and Transceiver Architecture Sanggeun Jeon, Young-Chai Ko, Moonil Kim, Jae-Sung Rieh, Jun Heo, Sangheon Pack, and Chulhee Kang School of Electrical Engineering Korea University
Updates on THz Amplifiers and Transceiver Architecture Sanggeun Jeon, Young-Chai Ko, Moonil Kim, Jae-Sung Rieh, Jun Heo, Sangheon Pack, and Chulhee Kang School of Electrical Engineering Korea University
MIXERS AND their local oscillators are often designed
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 58, NO. 8, AUGUST 2011 1705 A Low-Noise Self-Oscillating Mixer Using a Balanced VCO Load Stanley S. K. Ho, Member, IEEE, and Carlos E.
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 58, NO. 8, AUGUST 2011 1705 A Low-Noise Self-Oscillating Mixer Using a Balanced VCO Load Stanley S. K. Ho, Member, IEEE, and Carlos E.
Low-Power RF Integrated Circuit Design Techniques for Short-Range Wireless Connectivity
 Low-Power RF Integrated Circuit Design Techniques for Short-Range Wireless Connectivity Marvin Onabajo Assistant Professor Analog and Mixed-Signal Integrated Circuits (AMSIC) Research Laboratory Dept.
Low-Power RF Integrated Circuit Design Techniques for Short-Range Wireless Connectivity Marvin Onabajo Assistant Professor Analog and Mixed-Signal Integrated Circuits (AMSIC) Research Laboratory Dept.
Evaluating and Optimizing Tradeoffs in CMOS RFIC Upconversion Mixer Design. by Dr. Stephen Long University of California, Santa Barbara
 Evaluating and Optimizing Tradeoffs in CMOS RFIC Upconversion Mixer Design by Dr. Stephen Long University of California, Santa Barbara It is not easy to design an RFIC mixer. Different, sometimes conflicting,
Evaluating and Optimizing Tradeoffs in CMOS RFIC Upconversion Mixer Design by Dr. Stephen Long University of California, Santa Barbara It is not easy to design an RFIC mixer. Different, sometimes conflicting,
LOW NOISE GHZ RECEIVERS USING SINGLE-DIODE HARMONIC MIXERS
 First International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 399 LOW NOISE 500-700 GHZ RECEIVERS USING SINGLE-DIODE HARMONIC MIXERS Neal R. Erickson Millitech Corp. P.O. Box 109 S. Deerfield, MA 01373
First International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 399 LOW NOISE 500-700 GHZ RECEIVERS USING SINGLE-DIODE HARMONIC MIXERS Neal R. Erickson Millitech Corp. P.O. Box 109 S. Deerfield, MA 01373
The Schottky Diode Mixer. Application Note 995
 The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
Full 360 Vector-Sum Phase-Shifter for Microwave System Applications You Zheng, Member, IEEE, and Carlos E. Saavedra, Senior Member, IEEE
 752 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 57, NO. 4, APRIL 2010 Full 360 Vector-Sum Phase-Shifter for Microwave System Applications You Zheng, Member, IEEE, and Carlos E. Saavedra,
752 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 57, NO. 4, APRIL 2010 Full 360 Vector-Sum Phase-Shifter for Microwave System Applications You Zheng, Member, IEEE, and Carlos E. Saavedra,
A 1.6-to-3.2/4.8 GHz Dual Modulus Injection-Locked Frequency Multiplier in
 RTU1D-2 LAICS A 1.6-to-3.2/4.8 GHz Dual Modulus Injection-Locked Frequency Multiplier in 0.18µm CMOS L. Zhang, D. Karasiewicz, B. Ciftcioglu and H. Wu Laboratory for Advanced Integrated Circuits and Systems
RTU1D-2 LAICS A 1.6-to-3.2/4.8 GHz Dual Modulus Injection-Locked Frequency Multiplier in 0.18µm CMOS L. Zhang, D. Karasiewicz, B. Ciftcioglu and H. Wu Laboratory for Advanced Integrated Circuits and Systems
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
Design and Simulation of 5GHz Down-Conversion Self-Oscillating Mixer
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(12): 2595-2599, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Design and Simulation of 5GHz Down-Conversion Self-Oscillating Mixer 1 Alishir Moradikordalivand, 2 Sepideh Ebrahimi
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(12): 2595-2599, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Design and Simulation of 5GHz Down-Conversion Self-Oscillating Mixer 1 Alishir Moradikordalivand, 2 Sepideh Ebrahimi
95GHz Receiver with Fundamental Frequency VCO and Static Frequency Divider in 65nm Digital CMOS
 95GHz Receiver with Fundamental Frequency VCO and Static Frequency Divider in 65nm Digital CMOS Ekaterina Laskin, Mehdi Khanpour, Ricardo Aroca, Keith W. Tang, Patrice Garcia 1, Sorin P. Voinigescu University
95GHz Receiver with Fundamental Frequency VCO and Static Frequency Divider in 65nm Digital CMOS Ekaterina Laskin, Mehdi Khanpour, Ricardo Aroca, Keith W. Tang, Patrice Garcia 1, Sorin P. Voinigescu University
Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS. EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez. April 15, 2004
 Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez April 15, 2004 The University of Texas at El Paso Dr Tim S. Yao ABSTRACT Two circuits satisfying the
Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez April 15, 2004 The University of Texas at El Paso Dr Tim S. Yao ABSTRACT Two circuits satisfying the
Analog and RF circuit techniques in nanometer CMOS
 Analog and RF circuit techniques in nanometer CMOS Bram Nauta University of Twente The Netherlands http://icd.ewi.utwente.nl b.nauta@utwente.nl UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE. Outline Introduction Balun-LNA-Mixer
Analog and RF circuit techniques in nanometer CMOS Bram Nauta University of Twente The Netherlands http://icd.ewi.utwente.nl b.nauta@utwente.nl UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE. Outline Introduction Balun-LNA-Mixer
Direct-Conversion I-Q Modulator Simulation by Andy Howard, Applications Engineer Agilent EEsof EDA
 Direct-Conversion I-Q Modulator Simulation by Andy Howard, Applications Engineer Agilent EEsof EDA Introduction This article covers an Agilent EEsof ADS example that shows the simulation of a directconversion,
Direct-Conversion I-Q Modulator Simulation by Andy Howard, Applications Engineer Agilent EEsof EDA Introduction This article covers an Agilent EEsof ADS example that shows the simulation of a directconversion,
CMOS RFIC Design for Direct Conversion Receivers. Zhaofeng ZHANG Supervisor: Dr. Jack Lau
 CMOS RFIC Design for Direct Conversion Receivers Zhaofeng ZHANG Supervisor: Dr. Jack Lau Outline of Presentation Background Introduction Thesis Contributions Design Issues and Solutions A Direct Conversion
CMOS RFIC Design for Direct Conversion Receivers Zhaofeng ZHANG Supervisor: Dr. Jack Lau Outline of Presentation Background Introduction Thesis Contributions Design Issues and Solutions A Direct Conversion
Digitally Assisted Radio-Frequency Integrated Circuits
 Digitally Assisted Radio-Frequency Integrated Circuits by David Stewart A thesis submitted to the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering in conformity with the requirements for the degree of
Digitally Assisted Radio-Frequency Integrated Circuits by David Stewart A thesis submitted to the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering in conformity with the requirements for the degree of
HIGHLY INTEGRATED MINIATURE-SIZED SINGLE SIDEBAND SUBHARMONIC KA-BAND UP-CONVERTER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 18, 145 154, 2010 HIGHLY INTEGRATED MINIATURE-SIZED SINGLE SIDEBAND SUBHARMONIC KA-BAND UP-CONVERTER P.-K. Singh, S. Basu, W.-C. Chien, and Y.-H. Wang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 18, 145 154, 2010 HIGHLY INTEGRATED MINIATURE-SIZED SINGLE SIDEBAND SUBHARMONIC KA-BAND UP-CONVERTER P.-K. Singh, S. Basu, W.-C. Chien, and Y.-H. Wang
THERE is continued interest in finding new methods
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 64, NO. 7, JULY 2016 2113 Variable 360 Vector-Sum Phase Shifter With Coarse and Fine Vector Scaling Mohammad-Mahdi Mohsenpour, Member, IEEE, and
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 64, NO. 7, JULY 2016 2113 Variable 360 Vector-Sum Phase Shifter With Coarse and Fine Vector Scaling Mohammad-Mahdi Mohsenpour, Member, IEEE, and
A n I/Q modulator is frequently used in
 A Simplified Subharmonic I/Q Modulator This passive vector modulator uses opposite polarity diode pairs for frequency doubling to extend the range of operation By Ian Doyle M/A-COM Eurotec Operations A
A Simplified Subharmonic I/Q Modulator This passive vector modulator uses opposite polarity diode pairs for frequency doubling to extend the range of operation By Ian Doyle M/A-COM Eurotec Operations A
1 MHz 6 GHz RF Mixer with built in PLL Synthesizer
 Windfreak Technologies Preliminary Data Sheet v0.1a MixNV Active Mixer v1.4a $499.00US 1 MHz 6 GHz RF Mixer with built in PLL Synthesizer Features Open source Labveiw GUI software control via USB Run hardware
Windfreak Technologies Preliminary Data Sheet v0.1a MixNV Active Mixer v1.4a $499.00US 1 MHz 6 GHz RF Mixer with built in PLL Synthesizer Features Open source Labveiw GUI software control via USB Run hardware
A High Gain and Improved Linearity 5.7GHz CMOS LNA with Inductive Source Degeneration Topology
 A High Gain and Improved Linearity 5.7GHz CMOS LNA with Inductive Source Degeneration Topology Ch. Anandini 1, Ram Kumar 2, F. A. Talukdar 3 1,2,3 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering,
A High Gain and Improved Linearity 5.7GHz CMOS LNA with Inductive Source Degeneration Topology Ch. Anandini 1, Ram Kumar 2, F. A. Talukdar 3 1,2,3 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering,
A 5 GHz CMOS Low Power Down-conversion Mixer for Wireless LAN Applications
 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on CIRCUITS, SYSTES, ELECTRONICS, CONTROL & SIGNAL PROCESSING, Dallas, USA, November 1-, 2006 26 A 5 GHz COS Low Power Down-conversion ixer for Wireless LAN Applications
Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on CIRCUITS, SYSTES, ELECTRONICS, CONTROL & SIGNAL PROCESSING, Dallas, USA, November 1-, 2006 26 A 5 GHz COS Low Power Down-conversion ixer for Wireless LAN Applications
WIDE-BAND HIGH ISOLATION SUBHARMONICALLY PUMPED RESISTIVE MIXER WITH ACTIVE QUASI- CIRCULATOR
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 18, 135 143, 2010 WIDE-BAND HIGH ISOLATION SUBHARMONICALLY PUMPED RESISTIVE MIXER WITH ACTIVE QUASI- CIRCULATOR W. C. Chien, C.-M. Lin, C.-H. Liu, S.-H.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 18, 135 143, 2010 WIDE-BAND HIGH ISOLATION SUBHARMONICALLY PUMPED RESISTIVE MIXER WITH ACTIVE QUASI- CIRCULATOR W. C. Chien, C.-M. Lin, C.-H. Liu, S.-H.
TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers
 TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Overview 2 Razavi: Chapter 6.1-6.3, pp. 343-398. Lee: Chapter 13. 6.1 Mixers general
TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Overview 2 Razavi: Chapter 6.1-6.3, pp. 343-398. Lee: Chapter 13. 6.1 Mixers general
A FIXED-TUNED 400 GHz SUBHARIVIONIC MIXER
 A FIXED-TUNED 400 GHz SUBHARIVIONIC MIXER USING PLANAR SCHOTTKY DIODES Jeffrey L. Hesler% Kai Hui, Song He, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical Engineering University of Virginia Charlottesville,
A FIXED-TUNED 400 GHz SUBHARIVIONIC MIXER USING PLANAR SCHOTTKY DIODES Jeffrey L. Hesler% Kai Hui, Song He, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical Engineering University of Virginia Charlottesville,
Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU)
 Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEÜ) 64 (2010) 978 -- 982 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU) journal homepage: www.elsevier.de/aeue LETTER Linearization technique using
Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEÜ) 64 (2010) 978 -- 982 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Int. J. Electron. Commun. (AEU) journal homepage: www.elsevier.de/aeue LETTER Linearization technique using
LINEARITY IMPROVEMENT OF CASCODE CMOS LNA USING A DIODE CONNECTED NMOS TRANSISTOR WITH A PARALLEL RC CIRCUIT
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 17, 29 38, 2010 LINEARITY IMPROVEMENT OF CASCODE CMOS LNA USING A DIODE CONNECTED NMOS TRANSISTOR WITH A PARALLEL RC CIRCUIT C.-P. Chang, W.-C. Chien, C.-C.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 17, 29 38, 2010 LINEARITY IMPROVEMENT OF CASCODE CMOS LNA USING A DIODE CONNECTED NMOS TRANSISTOR WITH A PARALLEL RC CIRCUIT C.-P. Chang, W.-C. Chien, C.-C.
A 900MHz / 1.8GHz CMOS Receiver for Dual Band Applications*
 FA 8.2: S. Wu, B. Razavi A 900MHz / 1.8GHz CMOS Receiver for Dual Band Applications* University of California, Los Angeles, CA This dual-band CMOS receiver for GSM and DCS1800 applications incorporates
FA 8.2: S. Wu, B. Razavi A 900MHz / 1.8GHz CMOS Receiver for Dual Band Applications* University of California, Los Angeles, CA This dual-band CMOS receiver for GSM and DCS1800 applications incorporates
Highly linear common-gate mixer employing intrinsic second and third order distortion cancellation
 Highly linear common-gate mixer employing intrinsic second and third order distortion cancellation Mahdi Parvizi a), and Abdolreza Nabavi b) Microelectronics Laboratory, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran
Highly linear common-gate mixer employing intrinsic second and third order distortion cancellation Mahdi Parvizi a), and Abdolreza Nabavi b) Microelectronics Laboratory, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran
Millimeter- and Submillimeter-Wave Planar Varactor Sideband Generators
 Millimeter- and Submillimeter-Wave Planar Varactor Sideband Generators Haiyong Xu, Gerhard S. Schoenthal, Robert M. Weikle, Jeffrey L. Hesler, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical and Computer
Millimeter- and Submillimeter-Wave Planar Varactor Sideband Generators Haiyong Xu, Gerhard S. Schoenthal, Robert M. Weikle, Jeffrey L. Hesler, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical and Computer
INTEGRATED COMPACT BROAD KA-BAND SUB-HA- RMONIC SINGLE SIDEBAND UP-CONVERTER MMIC
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 8, 179 194, 2009 INTEGRATED COMPACT BROAD KA-BAND SUB-HA- RMONIC SINGLE SIDEBAND UP-CONVERTER MMIC P. K. Singh, S. Basu, and Y.-H. Wang Department of Electrical
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 8, 179 194, 2009 INTEGRATED COMPACT BROAD KA-BAND SUB-HA- RMONIC SINGLE SIDEBAND UP-CONVERTER MMIC P. K. Singh, S. Basu, and Y.-H. Wang Department of Electrical
RF Mixers. Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, A down-conversion system. An up-conversion system
 RF Mixers Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul RF Mixers are 3-port active or passive devices. They are designed to yield both, a sum and a difference frequency at a single output port
RF Mixers Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul RF Mixers are 3-port active or passive devices. They are designed to yield both, a sum and a difference frequency at a single output port
A Passive X-Band Double Balanced Mixer Utilizing Diode Connected SiGe HBTs
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.d on: Nov 29, 218 A Passive X-Band Double Balanced Mixer Utilizing Diode Connected SiGe HBTs Michaelsen, Rasmus Schandorph; Johansen, Tom Keinice; Tamborg, Kjeld; Zhurbeno, Vitaliy
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.d on: Nov 29, 218 A Passive X-Band Double Balanced Mixer Utilizing Diode Connected SiGe HBTs Michaelsen, Rasmus Schandorph; Johansen, Tom Keinice; Tamborg, Kjeld; Zhurbeno, Vitaliy
SP 22.3: A 12mW Wide Dynamic Range CMOS Front-End for a Portable GPS Receiver
 SP 22.3: A 12mW Wide Dynamic Range CMOS Front-End for a Portable GPS Receiver Arvin R. Shahani, Derek K. Shaeffer, Thomas H. Lee Stanford University, Stanford, CA At submicron channel lengths, CMOS is
SP 22.3: A 12mW Wide Dynamic Range CMOS Front-End for a Portable GPS Receiver Arvin R. Shahani, Derek K. Shaeffer, Thomas H. Lee Stanford University, Stanford, CA At submicron channel lengths, CMOS is
A COMPACT WIDEBAND MATCHING 0.18-µM CMOS UWB LOW-NOISE AMPLIFIER USING ACTIVE FEED- BACK TECHNIQUE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 16, 161 169, 2010 A COMPACT WIDEBAND MATCHING 0.18-µM CMOS UWB LOW-NOISE AMPLIFIER USING ACTIVE FEED- BACK TECHNIQUE J.-Y. Li, W.-J. Lin, and M.-P. Houng Department
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 16, 161 169, 2010 A COMPACT WIDEBAND MATCHING 0.18-µM CMOS UWB LOW-NOISE AMPLIFIER USING ACTIVE FEED- BACK TECHNIQUE J.-Y. Li, W.-J. Lin, and M.-P. Houng Department
Passive GaAs MMIC IQ Mixer. Green Status. Refer to our website for a list of definitions for terminology presented in this table.
 Passive GaAs MMIC IQ Mixer MMIQ-1037H 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description MMIQ-1037H is a high linearity, passive GaAs MMIC IQ mixer. This is an ultra-broadband mixer spanning 10 to 37 GHz on the
Passive GaAs MMIC IQ Mixer MMIQ-1037H 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description MMIQ-1037H is a high linearity, passive GaAs MMIC IQ mixer. This is an ultra-broadband mixer spanning 10 to 37 GHz on the
ACTIVE MIXERS based on the Gilbert cell configuration
 1126 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 58, NO. 5, MAY 2010 A CMOS Broadband Low-Noise Mixer With Noise Cancellation Stanley S. K. Ho, Member, IEEE, and Carlos E. Saavedra, Senior
1126 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 58, NO. 5, MAY 2010 A CMOS Broadband Low-Noise Mixer With Noise Cancellation Stanley S. K. Ho, Member, IEEE, and Carlos E. Saavedra, Senior
RF transmitter with Cartesian feedback
 UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN EECS 522 FINAL PROJECT: RF TRANSMITTER WITH CARTESIAN FEEDBACK 1 RF transmitter with Cartesian feedback Alexandra Holbel, Fu-Pang Hsu, and Chunyang Zhai, University of Michigan Abstract
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN EECS 522 FINAL PROJECT: RF TRANSMITTER WITH CARTESIAN FEEDBACK 1 RF transmitter with Cartesian feedback Alexandra Holbel, Fu-Pang Hsu, and Chunyang Zhai, University of Michigan Abstract
Self Calibrated Image Reject Mixer
 Self Calibrated Image Reject Mixer Project name: Self Calibrated Image Reject Mixer. Design number: 6313. Design password: Student names: Mostafa Elmala. Area: mm X mm. Technology: Technology is SCN4ME_SUBM,
Self Calibrated Image Reject Mixer Project name: Self Calibrated Image Reject Mixer. Design number: 6313. Design password: Student names: Mostafa Elmala. Area: mm X mm. Technology: Technology is SCN4ME_SUBM,
Low Distortion Mixer AD831
 Low Distortion Mixer AD831 FEATURES Doubly Balanced Mixer Low Distortion +24 dbm Third Order Intercept (IP3) +1 dbm 1 db Compression Point Low LO Drive Required: 1 dbm Bandwidth 5 MHz RF and LO Input Bandwidths
Low Distortion Mixer AD831 FEATURES Doubly Balanced Mixer Low Distortion +24 dbm Third Order Intercept (IP3) +1 dbm 1 db Compression Point Low LO Drive Required: 1 dbm Bandwidth 5 MHz RF and LO Input Bandwidths
CMOS 120 GHz Phase-Locked Loops Based on Two Different VCO Topologies
 JOURNAL OF ELECTROMAGNETIC ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE, VOL. 17, NO. 2, 98~104, APR. 2017 http://dx.doi.org/10.5515/jkiees.2017.17.2.98 ISSN 2234-8395 (Online) ISSN 2234-8409 (Print) CMOS 120 GHz Phase-Locked
JOURNAL OF ELECTROMAGNETIC ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE, VOL. 17, NO. 2, 98~104, APR. 2017 http://dx.doi.org/10.5515/jkiees.2017.17.2.98 ISSN 2234-8395 (Online) ISSN 2234-8409 (Print) CMOS 120 GHz Phase-Locked
Design of A Wideband Active Differential Balun by HMIC
 Design of A Wideband Active Differential Balun by HMIC Chaoyi Li 1, a and Xiaofei Guo 2, b 1School of Electronics Engineering, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing 400065, China;
Design of A Wideband Active Differential Balun by HMIC Chaoyi Li 1, a and Xiaofei Guo 2, b 1School of Electronics Engineering, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Chongqing 400065, China;
55-65GHz Single Side Band Mixer. GaAs Monolithic Microwave IC
 55-65GHz Single Side Band Mixer GaAs Monolithic Microwave IC Description The CHM1298 is a multifunction chip (MFC) which integrates a LO buffer amplifier and a sub-harmonically balanced diode mixer for
55-65GHz Single Side Band Mixer GaAs Monolithic Microwave IC Description The CHM1298 is a multifunction chip (MFC) which integrates a LO buffer amplifier and a sub-harmonically balanced diode mixer for
Receiver Architecture
 Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
CHAPTER 3 CMOS LOW NOISE AMPLIFIERS
 46 CHAPTER 3 CMOS LOW NOISE AMPLIFIERS 3.1 INTRODUCTION The Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) plays an important role in the receiver design. LNA serves as the first block in the RF receiver. It is a critical
46 CHAPTER 3 CMOS LOW NOISE AMPLIFIERS 3.1 INTRODUCTION The Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) plays an important role in the receiver design. LNA serves as the first block in the RF receiver. It is a critical
ACMOS RF up/down converter would allow a considerable
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 32, NO. 7, JULY 1997 1151 Low Voltage Performance of a Microwave CMOS Gilbert Cell Mixer P. J. Sullivan, B. A. Xavier, and W. H. Ku Abstract This paper demonstrates
IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 32, NO. 7, JULY 1997 1151 Low Voltage Performance of a Microwave CMOS Gilbert Cell Mixer P. J. Sullivan, B. A. Xavier, and W. H. Ku Abstract This paper demonstrates
Passive Device Characterization for 60-GHz CMOS Power Amplifiers
 Passive Device Characterization for 60-GHz CMOS Power Amplifiers Kenichi Okada, Kota Matsushita, Naoki Takayama, Shogo Ito, Ning Li, and Akira Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 2009/4/20 Motivation
Passive Device Characterization for 60-GHz CMOS Power Amplifiers Kenichi Okada, Kota Matsushita, Naoki Takayama, Shogo Ito, Ning Li, and Akira Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 2009/4/20 Motivation
Chapter 6. Case Study: 2.4-GHz Direct Conversion Receiver. 6.1 Receiver Front-End Design
 Chapter 6 Case Study: 2.4-GHz Direct Conversion Receiver The chapter presents a 0.25-µm CMOS receiver front-end designed for 2.4-GHz direct conversion RF transceiver and demonstrates the necessity and
Chapter 6 Case Study: 2.4-GHz Direct Conversion Receiver The chapter presents a 0.25-µm CMOS receiver front-end designed for 2.4-GHz direct conversion RF transceiver and demonstrates the necessity and
PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET IQ DEMODULATOR FOR DIGITAL VIDEO/DATA RECEIVER. Vcc (I) GND (I) VAGC GND (RF) RF IN RF IN GND (RF) Vcc (RF) GND (Q) Vcc (Q)
 PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET FEATURES DESCRIPTION IQ DEMODULATOR FOR DIGITAL VIDEO/DATA RECEIVER ON CHIP 9 PHASE SHIFTER IQ PHASE AND AMPLITUDE BALANCE: Amplitude Balance: ±.5 db Phase Balance: ± 2. LOW DISTORTION:
PRELIMINARY DATA SHEET FEATURES DESCRIPTION IQ DEMODULATOR FOR DIGITAL VIDEO/DATA RECEIVER ON CHIP 9 PHASE SHIFTER IQ PHASE AND AMPLITUDE BALANCE: Amplitude Balance: ±.5 db Phase Balance: ± 2. LOW DISTORTION:
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based and Shooting Method Based RF Simulation
 SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based and Shooting Method Based RF Simulation Silvaco Overview SSRF Attributes Harmonic balance approach to solve system of equations in frequency domain Well suited for
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based and Shooting Method Based RF Simulation Silvaco Overview SSRF Attributes Harmonic balance approach to solve system of equations in frequency domain Well suited for
A NOVEL BIASED ANTI-PARALLEL SCHOTTKY DIODE STRUCTURE FOR SUBHARMONIC
 Page 342 A NOVEL BIASED ANTI-PARALLEL SCHOTTKY DIODE STRUCTURE FOR SUBHARMONIC Trong-Huang Lee', Chen-Yu Chi", Jack R. East', Gabriel M. Rebeiz', and George I. Haddad" let Propulsion Laboratory California
Page 342 A NOVEL BIASED ANTI-PARALLEL SCHOTTKY DIODE STRUCTURE FOR SUBHARMONIC Trong-Huang Lee', Chen-Yu Chi", Jack R. East', Gabriel M. Rebeiz', and George I. Haddad" let Propulsion Laboratory California
65-GHz Receiver in SiGe BiCMOS Using Monolithic Inductors and Transformers
 65-GHz Receiver in SiGe BiCMOS Using Monolithic Inductors and Transformers Michael Gordon, Terry Yao, Sorin P. Voinigescu University of Toronto March 10 2006, UBC, Vancouver Outline Motivation mm-wave
65-GHz Receiver in SiGe BiCMOS Using Monolithic Inductors and Transformers Michael Gordon, Terry Yao, Sorin P. Voinigescu University of Toronto March 10 2006, UBC, Vancouver Outline Motivation mm-wave
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator. Advanced RF Circuit Simulation
 SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator Advanced RF Circuit Simulation SmartSpice RF Overview Uses harmonic balance approach to solve system equations in frequency domain Well suited for RF and
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator Advanced RF Circuit Simulation SmartSpice RF Overview Uses harmonic balance approach to solve system equations in frequency domain Well suited for RF and
Full Duplex CMOS Transceiver with On-Chip Self-Interference Cancelation. Seyyed Amir Ayati
 Full Duplex CMOS Transceiver with On-Chip Self-Interference Cancelation by Seyyed Amir Ayati A Dissertation Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy Approved
Full Duplex CMOS Transceiver with On-Chip Self-Interference Cancelation by Seyyed Amir Ayati A Dissertation Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Doctor of Philosophy Approved
IC design for wireless system
 IC design for wireless system Lecture 6 Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Ahmed.madian@guc.edu.eg 1 outlines Introduction to mixers Mixer metrics Mixer topologies Mixer performance analysis Mixer design issues Dr. Ahmed
IC design for wireless system Lecture 6 Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Ahmed.madian@guc.edu.eg 1 outlines Introduction to mixers Mixer metrics Mixer topologies Mixer performance analysis Mixer design issues Dr. Ahmed
Wide-Band Two-Stage GaAs LNA for Radio Astronomy
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 56, 119 124, 215 Wide-Band Two-Stage GaAs LNA for Radio Astronomy Jim Kulyk 1,GeWu 2, Leonid Belostotski 2, *, and James W. Haslett 2 Abstract This paper presents
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 56, 119 124, 215 Wide-Band Two-Stage GaAs LNA for Radio Astronomy Jim Kulyk 1,GeWu 2, Leonid Belostotski 2, *, and James W. Haslett 2 Abstract This paper presents
A 38 TO 44 GHz SUB-HARMONIC BALANCED HBT MIXER WITH INTEGRATED MINIATURE SPIRAL TYPE MARCHAND BALUN
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 135, 317 330, 2013 A 38 TO 44 GHz SUB-HARMONIC BALANCED HBT MIXER WITH INTEGRATED MINIATURE SPIRAL TYPE MARCHAND BALUN Tom K. Johansen 1, * and Viktor Krozer
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 135, 317 330, 2013 A 38 TO 44 GHz SUB-HARMONIC BALANCED HBT MIXER WITH INTEGRATED MINIATURE SPIRAL TYPE MARCHAND BALUN Tom K. Johansen 1, * and Viktor Krozer
Above 200 GHz On-Chip CMOS Frequency Generation, Transmission and Receiving
 Above 200 GHz On-Chip CMOS Frequency Generation, Transmission and Receiving Bassam Khamaisi and Eran Socher Department of Physical Electronics Faculty of Engineering Tel-Aviv University Outline Background
Above 200 GHz On-Chip CMOS Frequency Generation, Transmission and Receiving Bassam Khamaisi and Eran Socher Department of Physical Electronics Faculty of Engineering Tel-Aviv University Outline Background
Integrated receivers for mid-band SKA. Suzy Jackson Engineer, Australia Telescope National Facility
 Integrated receivers for mid-band SKA Suzy Jackson Engineer, Australia Telescope National Facility ASKAP/SKA Special Technical Brief 23 rd October, 2009 Talk overview Mid band SKA receiver challenges ASKAP
Integrated receivers for mid-band SKA Suzy Jackson Engineer, Australia Telescope National Facility ASKAP/SKA Special Technical Brief 23 rd October, 2009 Talk overview Mid band SKA receiver challenges ASKAP
DOUBLE-SIDEBAND MIXER CIRCUITS
 DOUBLE-SIDEBAND MIXER CIRCUITS SBW SERIES Waveguide, SMA / SBB SERIES DC Biasable, Low Power DB, DM SERIES General Purpose SBE SERIES Even Harmonic (1/2 ) TB, TBR SERIES Best Spurs, Overlap / W Y W Y Z
DOUBLE-SIDEBAND MIXER CIRCUITS SBW SERIES Waveguide, SMA / SBB SERIES DC Biasable, Low Power DB, DM SERIES General Purpose SBE SERIES Even Harmonic (1/2 ) TB, TBR SERIES Best Spurs, Overlap / W Y W Y Z
1. Device Overview. Low LO Drive Passive GaAs MMIC IQ Mixer
 Low LO Drive Passive GaAs MMIC IQ Mixer MMIQ-1040L 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description MMIQ-1040L is a low LO drive, passive GaAs MMIC IQ mixer that operates down to an unrivaled +3 dbm LO drive
Low LO Drive Passive GaAs MMIC IQ Mixer MMIQ-1040L 1. Device Overview 1.1 General Description MMIQ-1040L is a low LO drive, passive GaAs MMIC IQ mixer that operates down to an unrivaled +3 dbm LO drive
Efficiently simulating a direct-conversion I-Q modulator
 Efficiently simulating a direct-conversion I-Q modulator Andy Howard Applications Engineer Agilent Eesof EDA Overview An I-Q or vector modulator is a commonly used integrated circuit in communication systems.
Efficiently simulating a direct-conversion I-Q modulator Andy Howard Applications Engineer Agilent Eesof EDA Overview An I-Q or vector modulator is a commonly used integrated circuit in communication systems.
Session 3. CMOS RF IC Design Principles
 Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
IN SUBMICROMETER CMOS nodes with reduced power
 464 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 64, NO. 1, DECEMBER 016 Method to Improve the Linearity of Active Commutating Mixers Using Dynamic Current Injection Mohammad-Mahdi Mohsenpour,
464 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 64, NO. 1, DECEMBER 016 Method to Improve the Linearity of Active Commutating Mixers Using Dynamic Current Injection Mohammad-Mahdi Mohsenpour,
A 200 GHz Broadband, Fixed-Tuned, Planar Doubler
 A 200 GHz Broadband, Fixed-Tuned, Planar Doubler David W. Porterfield Virginia Millimeter Wave, Inc. 706 Forest St., Suite D Charlottesville, VA 22903 Abstract - A 100/200 GHz planar balanced frequency
A 200 GHz Broadband, Fixed-Tuned, Planar Doubler David W. Porterfield Virginia Millimeter Wave, Inc. 706 Forest St., Suite D Charlottesville, VA 22903 Abstract - A 100/200 GHz planar balanced frequency
A GHz MONOLITHIC GILBERT CELL MIXER. Andrew Dearn and Liam Devlin* Introduction
 A 40 45 GHz MONOLITHIC GILBERT CELL MIXER Andrew Dearn and Liam Devlin* Introduction Millimetre-wave mixers are commonly realised using hybrid fabrication techniques, with diodes as the nonlinear mixing
A 40 45 GHz MONOLITHIC GILBERT CELL MIXER Andrew Dearn and Liam Devlin* Introduction Millimetre-wave mixers are commonly realised using hybrid fabrication techniques, with diodes as the nonlinear mixing
i 1 i 2 LOmod 3 RF OUT 4 RF OUT 5 IF 6 IF 7 ENABLE 8 YYWW
 Vector Modulator/Mixer Technical Data HPMX-27 Features 5 MHz to 4 GHz Overall Operating Frequency Range 4-4 MHz LOmod range 2.7-5.5 V Operation (3 V, 25 ma) Differential High Impedance i, q Inputs On-Chip
Vector Modulator/Mixer Technical Data HPMX-27 Features 5 MHz to 4 GHz Overall Operating Frequency Range 4-4 MHz LOmod range 2.7-5.5 V Operation (3 V, 25 ma) Differential High Impedance i, q Inputs On-Chip
Dr.-Ing. Ulrich L. Rohde
 Dr.-Ing. Ulrich L. Rohde Noise in Oscillators with Active Inductors Presented to the Faculty 3 : Mechanical engineering, Electrical engineering and industrial engineering, Brandenburg University of Technology
Dr.-Ing. Ulrich L. Rohde Noise in Oscillators with Active Inductors Presented to the Faculty 3 : Mechanical engineering, Electrical engineering and industrial engineering, Brandenburg University of Technology
SYSTEM LEVEL ANALYSIS OF A DIRECT-CONVERSION WIMAX RECEIVER AT 5.3 GHZ AND CORRESPONDING MIXER DESIGN
 SYSTEM LEVEL ANALYSIS OF A DIRECT-CONVERSION WIMAX RECEIVER AT 5.3 GHZ AND CORRESPONDING MIXER DESIGN A. ANTONOPOULOS, N. MAVREDAKIS, N. MAKRIS, M. BUCHER TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CRETE, GREECE KEYWORDS:
SYSTEM LEVEL ANALYSIS OF A DIRECT-CONVERSION WIMAX RECEIVER AT 5.3 GHZ AND CORRESPONDING MIXER DESIGN A. ANTONOPOULOS, N. MAVREDAKIS, N. MAKRIS, M. BUCHER TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF CRETE, GREECE KEYWORDS:
Introduction to Receivers
 Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
An Oscillator and a Mixer for 140-GHz Heterodyne Receiver Front-End based on SiGe HBT Technology
 JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.15, NO.1, FEBRUARY, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2015.15.1.029 An Oscillator and a Mixer for 140-GHz Heterodyne Receiver Front-End based on SiGe
JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.15, NO.1, FEBRUARY, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2015.15.1.029 An Oscillator and a Mixer for 140-GHz Heterodyne Receiver Front-End based on SiGe
WITH THE exploding growth of the wireless communication
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 60, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2012 387 0.6 3-GHz Wideband Receiver RF Front-End With a Feedforward Noise and Distortion Cancellation Resistive-Feedback
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 60, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2012 387 0.6 3-GHz Wideband Receiver RF Front-End With a Feedforward Noise and Distortion Cancellation Resistive-Feedback
Wideband Tunable RF Filters for Channel Selection in Crowded Spectral Bands
 Wideband Tunable RF Filters for Channel Selection in Crowded Spectral Bands Sanghoon Park, Ki-Jin Kim, Kwang-Ho Ahn, Hyeon-Woo Lee Abstract It is very effective way to utilize a very wide tunable filter
Wideband Tunable RF Filters for Channel Selection in Crowded Spectral Bands Sanghoon Park, Ki-Jin Kim, Kwang-Ho Ahn, Hyeon-Woo Lee Abstract It is very effective way to utilize a very wide tunable filter
A 3rd- and 5th-order intermodulation products generator for predistortion of base-station HPAs
 Title A 3rd- and 5th-order intermodulation products generator for predistortion of base-station HPAs Author(s) Sun, XL; Cheung, SW; Yuk, TI Citation The 200 International Conference on Advanced Technologies
Title A 3rd- and 5th-order intermodulation products generator for predistortion of base-station HPAs Author(s) Sun, XL; Cheung, SW; Yuk, TI Citation The 200 International Conference on Advanced Technologies
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent
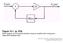 Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Low Flicker Noise Current-Folded Mixer
 Chapter 4 Low Flicker Noise Current-Folded Mixer The chapter presents a current-folded mixer achieving low 1/f noise for low power direct conversion receivers. Section 4.1 introduces the necessity of low
Chapter 4 Low Flicker Noise Current-Folded Mixer The chapter presents a current-folded mixer achieving low 1/f noise for low power direct conversion receivers. Section 4.1 introduces the necessity of low
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 20 / WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORKING / PAPER 20.2
 ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 20 / WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORKING / PAPER 20.2 20.2 A Digitally Calibrated 5.15-5.825GHz Transceiver for 802.11a Wireless LANs in 0.18µm CMOS I. Bouras 1, S. Bouras 1, T. Georgantas
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 20 / WIRELESS LOCAL AREA NETWORKING / PAPER 20.2 20.2 A Digitally Calibrated 5.15-5.825GHz Transceiver for 802.11a Wireless LANs in 0.18µm CMOS I. Bouras 1, S. Bouras 1, T. Georgantas
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY
 Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
RFIC DESIGN EXAMPLE: MIXER
 APPENDIX RFI DESIGN EXAMPLE: MIXER The design of radio frequency integrated circuits (RFIs) is relatively complicated, involving many steps as mentioned in hapter 15, from the design of constituent circuit
APPENDIX RFI DESIGN EXAMPLE: MIXER The design of radio frequency integrated circuits (RFIs) is relatively complicated, involving many steps as mentioned in hapter 15, from the design of constituent circuit
THE LINEARIZATION TECHNIQUE FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS SYSTEMS WITH THE INJECTION OF THE SECOND HARMONICS
 THE LINEARIZATION TECHNIQUE FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS SYSTEMS WITH THE INJECTION OF THE SECOND HARMONICS N. Males-Ilic#, B. Milovanovic*, D. Budimir# #Wireless Communications Research Group, Department
THE LINEARIZATION TECHNIQUE FOR MULTICHANNEL WIRELESS SYSTEMS WITH THE INJECTION OF THE SECOND HARMONICS N. Males-Ilic#, B. Milovanovic*, D. Budimir# #Wireless Communications Research Group, Department
Technical Article A DIRECT QUADRATURE MODULATOR IC FOR 0.9 TO 2.5 GHZ WIRELESS SYSTEMS
 Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 3.5GHz Downconverter Mixers with Selectable LO Doubler. PART MAX2683EUE MAX2684EUE *Exposed pad TOP VIEW IFOUT+ IFOUT-
 -; Rev ; / EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE.GHz Downconverter Mixers General Description The MAX/MAX are super-high-performance, low-cost downconverter mixers intended for wireless local loop (WLL) and digital
-; Rev ; / EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE.GHz Downconverter Mixers General Description The MAX/MAX are super-high-performance, low-cost downconverter mixers intended for wireless local loop (WLL) and digital
Low Distortion Mixer AD831
 a FEATURES Doubly-Balanced Mixer Low Distortion +2 dbm Third Order Intercept (IP3) + dbm 1 db Compression Point Low LO Drive Required: dbm Bandwidth MHz RF and LO Input Bandwidths 2 MHz Differential Current
a FEATURES Doubly-Balanced Mixer Low Distortion +2 dbm Third Order Intercept (IP3) + dbm 1 db Compression Point Low LO Drive Required: dbm Bandwidth MHz RF and LO Input Bandwidths 2 MHz Differential Current
DESIGN ANALYSIS AND COMPARATIVE STUDY OF RF RECEIVER FRONT-ENDS IN 0.18-µM CMOS
 International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Research Vol.1, Issue 1 (2011) 41-56 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., DESIGN ANALYSIS AND COMPARATIVE STUDY OF RF RECEIVER FRONT-ENDS IN 0.18-µM CMOS M.
International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Research Vol.1, Issue 1 (2011) 41-56 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., DESIGN ANALYSIS AND COMPARATIVE STUDY OF RF RECEIVER FRONT-ENDS IN 0.18-µM CMOS M.
A low-if 2.4 GHz Integrated RF Receiver for Bluetooth Applications Lai Jiang a, Shaohua Liu b, Hang Yu c and Yan Li d
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-06-27 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 329, pp 416-420 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.329.416 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A low-if 2.4 GHz Integrated
Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-06-27 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 329, pp 416-420 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.329.416 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A low-if 2.4 GHz Integrated
Berkeley. Mixers: An Overview. Prof. Ali M. Niknejad. U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2014 by Ali M. Niknejad
 Berkeley Mixers: An Overview Prof. Ali M. U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2014 by Ali M. Mixers Information PSD Mixer f c The Mixer is a critical component in communication circuits. It translates information
Berkeley Mixers: An Overview Prof. Ali M. U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2014 by Ali M. Mixers Information PSD Mixer f c The Mixer is a critical component in communication circuits. It translates information
Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance
 Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance Mixer Terms Defined Statistical Processing Applied to Mixers Today's stringent demands for precise electronic systems place a heavy burden
Understanding Mixers Terms Defined, and Measuring Performance Mixer Terms Defined Statistical Processing Applied to Mixers Today's stringent demands for precise electronic systems place a heavy burden
White Paper. A High Performance, GHz MMIC Frequency Multiplier with Low Input Drive Power and High Output Power. I.
 A High Performance, 2-42 GHz MMIC Frequency Multiplier with Low Input Drive Power and High Output Power White Paper By: ushil Kumar and Henrik Morkner I. Introduction Frequency multipliers are essential
A High Performance, 2-42 GHz MMIC Frequency Multiplier with Low Input Drive Power and High Output Power White Paper By: ushil Kumar and Henrik Morkner I. Introduction Frequency multipliers are essential
CMOS Design of Wideband Inductor-Less LNA
 IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 8, Issue 3, Ver. I (May.-June. 2018), PP 25-30 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 www.iosrjournals.org CMOS Design of Wideband Inductor-Less
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 8, Issue 3, Ver. I (May.-June. 2018), PP 25-30 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 www.iosrjournals.org CMOS Design of Wideband Inductor-Less
