LOI progress report INTRODUCTION
|
|
|
- Blanche Reeves
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LOI-5 LOI progress report Summary of Experiments from August 4th through 22nd, 2008 November 10, 2008 INTRODUCTION Waveform distortions of the LOI system were investigated using a liquid resistor in place of the ferrite-loaded RF cavity (fig. 1). The liquid resistor (LR) can be modelled simply by a known shunt resistance with some stray capacitance across it, while the ferrite cavity shows more complicated structure. The new configuration also enabled high-power measurements of output impedance by changing the LR resistance. As for waveform distortions [1], we first suspected the coupling of the triode feedback coil and the triode anode choke, because these coils are placed closely in parallel. The feedback coil was then re-arranged at a right angle to the anode choke. However, the waveforms were almost the same as in the parallel arrangement. In the meantime, high frequency oscillations (50~65MHz) were also observed in the driver and the output stages. Measures such as a swamping resistor at the triode grid input, and increase of the grid bias resistance of the tetrode were tried. There were, however, no significant improvements or changes. The voltage gain, which is defined by the ratio of the LR voltage to the triode grid-input voltage, was measured for a right-angle arrangement. The result shows quite different features from the previous ones [2]. Output impedance was measured for five resistance values of LR between 4.8~1.17Kohms. Further measurements toward the lower values will be performed when more copper sulfate becomes available. In the following sections are reported, experimental setup in section 1, LR impedance measurements in section 2, RF waveforms under various conditions in section 3, voltage gain in a final stage in section 4, output impedance in section 5, faults and remedies in section 6, and discussions and conclusions in section 7. Table of the actual stage of this experiment is attached in the appendix. Figure 1: Liquid resistor in place of the ferrite-loaded RF cavity, which is seen at the left-hand side. 1
2 1. Experimental setup The LOI high power drive system (LOI HPD) is shown in Fig. 2, where the LR was installed in place of the ferrite cavity in this experiment. In order to keep the temperature rise of the LR as low as possible, the RF ON-period was limited by short grid-switching pulses of 1msec duration. These pulses are generated in the LOI timing system in Fig. 3, and are fed to the triode grid switcher and the tetrode G1 supply. The pulses are delayed from the Bend-field minimum by 0 ~ 8.8msec to scan a whole frequency range (Fig. 4). The plate voltages and grid bias voltages were the same as in ref. [1], while the current threshold of the Buck Regulator (BR) output was set to 30A-peak: potentiometer dial is 6.0 [3]. Fig. 5 shows the BR output voltage and current, and the tetrode output current in a switched mode. The experimental conditions were summarized in Table 1. Table 1 Experimental conditions load liquid resistor (solution of CuSO 4 ) repetition rate 50Hz class of operation grid switching class A for final triode and driver tetrode ON: 1msec duration at any delay time from the ISIS 50Hz clock OFF: other period than above duty factor 5% RF frequency 2.6 MHz (t = 0msec)~ 6.2 MHz (t = 10msec) ISIS Bend Field (50Hz) arbitrary units ISIS 50Hz delay 1 msec grid-switching pulse ISIS 50Hz sec Figure 4: Timing of grid-switching pulse for RF generation. Delay time is adjusted by the CP8865 digital delay module in fig. 3. Figure 5: Signals in a switching mode: from top, BR voltage (2kV/V), BR current (35A/V), and tetrode supply current (10A/10mV). 2
3 Figure 2: LOI HPD with Liquid Resistor STEP START COMMON EARTH PLATE August 23, 2008 YI DRIVER G1-300V,10A switching output DRIVER G2 1.4KV,10A DRIVER ANODE 5KV,40A CROWBAR BUCK REGULATOR 16KV, 25A T/R SET 13µ A 50mV 50A RF AMP 6x5M 10K V 5000p 3KV 5000p 3KV 4x4000p 15KV 2x1500p 20KV 300W Solid State Amp. 55dB Amplitude modulation RF-law 69p APN input voltage.54µ 1023p.54 µ 1K dB atten. (50ohm) (40x into 50ohms) 3.2µ 53µ 50 5A BURLE K 116µ 4V 1,650A HEATER TRANSFORMER 12n 1.3A 150n 1K 10 12n 12µ 220p EEV BW1643J2 38n 110 GRID -650V switching 5A output 9A 0.4µ 118µ 14V 555A HEATER TRANSFORMER 96n 55.4 µ 1.5K 0.2µ 0.4µ A grid voltage (120 x) 50mV 30A Pearson 310 Output CT (0.1v/2amps into 50ohms) Analog output (25mV/div into 50ohms) LR voltage P6015 (1000 x) 3 APN LIQUID RESISTOR (LR) Tektronics 465B CuSO4 solution
4 ISIS 50Hz (crate 48) Buffer Fanout TTL Buffer Fanout TTL for any trigger for any trigger CP8865 Digital Delay TTL Level Adapter NIM Fan IN/OUT NIM Dual Gate Generator delay, width ISIS 2nd Har HPRF System 4 Diag.->Hall 2, Channel 8 Carrier AM IN Amplitude Modulator Level Adapter TTL HP8012B Pulse Generator delay rise-, fall-time width amplitude 50Hz, 100Hz compensation 300W Solid-state Amp. Trigger Triode Grid Switcher BIAS -200V. INPUT A Tetrode G1 Supply INPUT B Figure 3: LOI timing system for grid switching and triggers 9/2/2008, YI
5 2. LR impedance measurements The resistive part of the LR was measured by two methods: one is to use the bridge impedance meter at 10kHz, and the other a resistive divider method at 1kHz. The latter method assumes the stray capacitance across the LR is negligible at 1KHz. Results agree well with each other as shown in Table 2 and Fig.6. However, the stray capacitance and the capacitance between the LOI chassis and the coupling bar of the LR and triode are important for experiments in the RF frequency range. These capacitances were measured by the Hewlett-Packard HP4195A network/impedance analyser, resulting in 9.5pF and 39.7pF, respectively. The impedance seen looking into the LR at the location of Pearson CT was also measured by the voltage and current monitors of the LR. With the solution conductance 4,437uS, the measurement shows 860ohms at 2.73MHz, while the calculation is 812±30ohms. The calculation error comes from the uncertainty of the LR resistance. The LR impedances by the two methods agree within 10% error. Table 2 LR resistance measurements conductance of LR [kω] Dummy LR*[kΩ] CuSO 4 solution [µs] divider method divider method bridge method , ~4.14 1, , ~1.54 3, , *) Dummy LR is located just outside the LOI area, which has the same structure with LR and is connected in series for the CuSO 4 flow. 6 5 resistance [Kohms] conductance [us] Figure 6: LR resistance measured by two methods. Square(divider method for dummy LR), triangle(bridge method for dummy LR) and red circle(divider method for LR). 5
6 delay = 0 msec 1 msec 2 msec 3 msec 4 msec 5 msec 6 msce 7 msec 8 msec 8.8 msec 0.2 msec/div delay = 0msec, 2.69MHz delay = 1msec, 2.94MHz delay = 2msec, 3.42MHz delay = 3msec, 4.03MHz delay = 4msec, 4.72MHz 0.2 usec/div 0.2 usec/div 0.2 usec/div 0.2 usec/div 0.1 usec/div delay = 5msec, 5.38MHz delay = 6msec, 5.43MHz delay = 7msec, 5.75MHz delay = 8msec, 6.10MHz delay = 8.8msec, 6.10MHz 0.1 usec/div 0.1 usec/div 0.1 usec/div 0.1 usec/div 0.1 usec/div Figure 7: RF envelopes and waveforms with LR resistance of 4.8kohms (August 18, 2008). Waveforms are taken at the beginning of each 1msec-duration. From top to bottom line in each screen, LR voltage (10kV/div), LR input current (10A/div), grid input voltage (240V/div) and grid input current (20A/div). APN 50ohm-output was kept 2volts-peak.
7 delay = 0 msec 1 msec 2 msec 3 msec 4 msec 5 msec 6 msce 7 msec 8 msec 8.8 msec 0.2 msec/div delay = 0msec, 2.72MHz delay = 1msec, 2.97MHz delay = 2msec, 3.44MHz delay = 3msec, 4.13MHz delay = 4msec, 4.82MHz 0.2 usec/div 0.2 usec/div 0.2 usec/div 0.2 usec/div 0.1 usec/div delay = 5msec, 5.20MHz delay = 6msec, 5.64MHz delay = 7msec, 5.86MHz delay = 8msec, 5.89MHz delay = 8.8msec, 6.13MHz 0.1 usec/div 0.1 usec/div 0.1 usec/div 0.1 usec/div 0.1 usec/div Figure 8: RF envelopes and waveforms with LR resistance of 1.17kohms (August 22, 2008). Waveforms are taken at the beginning of each 1msec-duration. From top to bottom line in each screen, LR voltage (10kV/div), LR input current (10A/div), grid input voltage (240V/div) and grid input current (20A/div). APN 50ohm-output was kept 1.6volts-peak.
8 3. RF waveforms High power experiments were carried out under various conditions to investigate the waveform distortions and the onset of high frequency components (50~65MHz). The conditions were, (1) different arrangements of the feedback coil and the anode choke, (2) installation of the swamping resistor (3.4ohms) at the triode grid input, (3) increase of the grid bias resistance of the tetrode from the present 2Kohms to 1Kohms, and (4) lowering the LR impedance. However, there were no significant changes/improvements in waveforms for cases (1)~(3). Typical RF envelopes and waveforms are shown in Fig.7, where the right-angle arrangement in (1) is applied and the LR resistance is 4.82Kohms. The 50ohm-output of an all-pass-network (APN) of the tetrode looks fine sinusoidal, and is kept as 2volts-peak through the experiments. In the figure, RF envelope indicates some resonance at delay = 2msec (between 3.4 and 4.0MHz). And, a large second-harmonic component appears at 4.72MHz (delay = 4msec), although there is no such component in the grid input voltage. High frequency deformations can clearly be seen in both the grid input and LR voltages at frequencies above 5.4MHz (delay = 5msec). For comparison, waveforms with lower LR resistance of 1.17Kohms are shown in Fig. 8. Slight changes between them are observed. Especially, a second-harmonic component almost disappeared at 4.815MHz (delay = 4msec) for the latter case. The reason(s) of these deformations are not clear yet. However, it may be probable that some parasitic resonances at the driver and/or final stage are excited by even a small amount of high frequency component at the APN input. 4. Voltage gain in a final stage Voltage gain in a final stage is defined by the ratio of the LR voltage to the grid input voltage. The data were sampled from the pictures in Fig. 7 to calculate the gain. The results are shown in Fig. 9 with the TopSpice calculations for the model LOI system [2]. Although they agree relatively well below 3MHz, they differ by a factor of more than 3 at higher frequencies. These discrepancies are, however, very surprising, because in February, 2003, Oki showed a good agreement for the experiments at KEK. His data is attached in the appendix. It is then reasonable to think the LOI parameters have changed since then. More speculations are given in section Triode anode output/grid inp frequency [MHz] Figure 9: Voltage gain of the final triode. Dots are for measurements and solid-line for calculations 8
9 5. Output impedance In the previous output impedance measurements, the HP4195A probe was directly connected to the output end of the final triode[2]. In this report, the voltage gain in section 4 was measured in high power conditions by changing the LR resistance, since the gain has strong dependence upon the output impedance. The LR voltage is 7kV-peak or higher, and the frequency is 2.7MHz. The results are shown in Fig. 10. The TopSpice calculations are also shown for the model LOI system and the cases where 250 and 2,500ohms resistors are artificially added at the output of the final triode. As seen in the figure, measured data are scattered around calculations. Measurements will be continued to a lower resistance value when more copper sulfate becomes available. Gain LOI design: Z0 Measurements Output Impedance: Z0 +250ohms Output Impedance: Z0 + 2Kohms LR resistance, Kohms Figure 10: Voltage gain variation with LR resistance. Measurements are at 2.7MHz for the resistance between 4.82 and 1.17Kohms. TopSpice calculations are also shown for comparison (see in the text). 6. Faults and remedies Faults and incomplete interlocks were found during the experiments. Remedies or temporary measures are summarized below. (1) Grid-switcher parts were found to be broken (August 6): IGBT(1RG4PH20K), trim pot at the emitter of Transistor(Q1) and zenor(d1). > All replaced. (2) No interlock available from the tetrode chiller. >New temperature sensor (60 C) attached to the water pipe flange at the water manifold (August 7). Chiller flow-interlock disabled at TB6(49,50) (August 5). (3) Grid-switcher fan was shorted (August 17). >Disconnected from the AC line. Need to replace with a new one. (4) AC lead of a triode heater supply was blown at the fuse box (August 21). >Should be replaced with a larger-size lead. (5) flow interlock of the LR at the cavity was disabled at the TB7(65,66) (August 21). 9
10 7. Discussions and conclusions In this experiment, reasons of the waveform deformation could not be found. Adversely, gain curve showed quite different features from the previous measurements in We think the reason is that circuit parameters have been changed since the final design and test experiments of the LOI in February, The circuit elements that have been changed are the anode chokes for both tubes. We purchased new anode chokes for use at ISIS, because the former chokes had poor current capacities. These new chokes are now installed in the present LOI HPD. So, it may be possible that the new chokes have brought undesired resonances into the driver and final stages and have produced the waveform distortions and gain change. Especially for the gain, parameter changes of triode such as amplification factor and/or plate resistance will also be another possibility. In the forthcoming LOI experiments, characteristic survey of each anode choke and examination of the triode gain without feedback loop should be performed. Further actions are highly required as soon as possible. Last but not least: as for output impedance measurements, it seems quicker to use low-impedance solid resistors for resistance below a few hundred ohms. (YI) References: [1] LOI status report LOI-2, September 24, [2] T Oki, et al., NIM A 565 (2006) [3] D Horan and M Middendorf, "Buck regulator upgrades", 12th collaboration meeting, January 18, 2008, 10
11 Appendix 1 Voltage gain of the final triode was measured and reported internally in February, 2003 by T Oki. The load was then the KEK PS ferrite-loaded cavity, the shunt impedance of which was assumed to be 2Kohms. The following figure is taken from ref.2. See text in section 4. Figure caption: voltage gain in the swept-frequency mode (box) and in the fixed-frequency mode (triangle). The dashed line shows the analytical calculations [2]. 11
12 under construction Appendix 2 will be completed in November, 2008 completed
LOI Progress Report -- Summary of Experiment in January
 LOI Progress Report -- Summary of Experiment in January 2010 -- LOI-7 February 18, 2010 1. Introduction Following the previous experiments in October, 2009, a new method to improve the RF waveform distortions
LOI Progress Report -- Summary of Experiment in January 2010 -- LOI-7 February 18, 2010 1. Introduction Following the previous experiments in October, 2009, a new method to improve the RF waveform distortions
Summary LOI Developments
 The 8th Collaboration Meeting on the 2nd Harmonic RF System July 4, 2003, ISIS Summary LOI Developments 1996 through 2003 1. Introduction why the Low Output Impedance? 2. History of the scheme (1) cathode
The 8th Collaboration Meeting on the 2nd Harmonic RF System July 4, 2003, ISIS Summary LOI Developments 1996 through 2003 1. Introduction why the Low Output Impedance? 2. History of the scheme (1) cathode
Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06)
 Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization
 Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied to the
Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied to the
Common-Source Amplifiers
 Lab 2: Common-Source Amplifiers Introduction The common-source stage is the most basic amplifier stage encountered in CMOS analog circuits. Because of its very high input impedance, moderate-to-high gain,
Lab 2: Common-Source Amplifiers Introduction The common-source stage is the most basic amplifier stage encountered in CMOS analog circuits. Because of its very high input impedance, moderate-to-high gain,
Department of Physics and Astronomy
 Report 201 /07 201., R. Wedberg, K. Gajewski Department of Physics and Astronomy P.O. Box 516 SE 751 20 Uppsala Sweden Papers in the FREIA Report Series are published on internet in PDF- formats. Download
Report 201 /07 201., R. Wedberg, K. Gajewski Department of Physics and Astronomy P.O. Box 516 SE 751 20 Uppsala Sweden Papers in the FREIA Report Series are published on internet in PDF- formats. Download
1. General Instructions 2 2. Safety 2 3. Lamp Starting Test Instrument LSTI 5 3
 1. General Instructions 2 2. Safety 2 3. Lamp Starting Test Instrument LSTI 5 3 3.1. Components and Connections of the Front Panel (Fig. 1) 5 3.2. Connection of the Rear Panel (Fig. 2) 7 3.3. Operation
1. General Instructions 2 2. Safety 2 3. Lamp Starting Test Instrument LSTI 5 3 3.1. Components and Connections of the Front Panel (Fig. 1) 5 3.2. Connection of the Rear Panel (Fig. 2) 7 3.3. Operation
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS AND SYSTEM DESCRIPTION FOR THE. ISO-STIM 01D STIMULUS ISOLATION UNIT ±100 V / ±10 ma, bipolar output
 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS AND SYSTEM DESCRIPTION FOR THE ISO-STIM 01D STIMULUS ISOLATION UNIT ±100 V / ±10 ma, bipolar output VERSION 4.0 npi 2014 npi electronic GmbH, Bauhofring 16, D-71732 Tamm, Germany
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS AND SYSTEM DESCRIPTION FOR THE ISO-STIM 01D STIMULUS ISOLATION UNIT ±100 V / ±10 ma, bipolar output VERSION 4.0 npi 2014 npi electronic GmbH, Bauhofring 16, D-71732 Tamm, Germany
1. High Frequency Performance
 1. High Frequency Performance 1.1. High frequency (-3dB) bandwidth The CWT behaviour at frequencies approaching and exceeding its specified (-3dB) bandwidth is very complicated. It is related to the distributed
1. High Frequency Performance 1.1. High frequency (-3dB) bandwidth The CWT behaviour at frequencies approaching and exceeding its specified (-3dB) bandwidth is very complicated. It is related to the distributed
Arbitrary/Function Waveform Generators 4075B Series
 Data Sheet Arbitrary/Function Waveform Generators Point-by-Point Signal Integrity The Arbitrary/Function Waveform Generators are versatile high-performance single- and dual-channel arbitrary waveform generators
Data Sheet Arbitrary/Function Waveform Generators Point-by-Point Signal Integrity The Arbitrary/Function Waveform Generators are versatile high-performance single- and dual-channel arbitrary waveform generators
Memo. 1 Summary. 1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Experiments. 1.3 Conclusion
 Topic: Tested: Date: Author: High frequency oscillations measured with high bandwidth current sensors at low current Pearson 2878 and SDN-414 shunts with different resistance values 2014 April 11 th Martin
Topic: Tested: Date: Author: High frequency oscillations measured with high bandwidth current sensors at low current Pearson 2878 and SDN-414 shunts with different resistance values 2014 April 11 th Martin
Physics 120 Lab 6 (2018) - Field Effect Transistors: Ohmic Region
 Physics 120 Lab 6 (2018) - Field Effect Transistors: Ohmic Region The field effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device can be used in two extreme ways as an active element in a circuit. One is
Physics 120 Lab 6 (2018) - Field Effect Transistors: Ohmic Region The field effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device can be used in two extreme ways as an active element in a circuit. One is
Common-source Amplifiers
 Lab 1: Common-source Amplifiers Introduction The common-source amplifier is one of the basic amplifiers in CMOS analog circuits. Because of its very high input impedance, relatively high gain, low noise,
Lab 1: Common-source Amplifiers Introduction The common-source amplifier is one of the basic amplifiers in CMOS analog circuits. Because of its very high input impedance, relatively high gain, low noise,
Capacitive Touch Sensing Tone Generator. Corey Cleveland and Eric Ponce
 Capacitive Touch Sensing Tone Generator Corey Cleveland and Eric Ponce Table of Contents Introduction Capacitive Sensing Overview Reference Oscillator Capacitive Grid Phase Detector Signal Transformer
Capacitive Touch Sensing Tone Generator Corey Cleveland and Eric Ponce Table of Contents Introduction Capacitive Sensing Overview Reference Oscillator Capacitive Grid Phase Detector Signal Transformer
Report of the British Rife Group. Presented to the International Rife Technology Conference. Las Vegas March 2002.
 Report of the British Rife Group Presented to the International Rife Technology Conference. Las Vegas March 2002. Introduction. I came away from the last Rife conference with a sense of excitement, tinged
Report of the British Rife Group Presented to the International Rife Technology Conference. Las Vegas March 2002. Introduction. I came away from the last Rife conference with a sense of excitement, tinged
CONVERTING 1524 SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY DESIGNS TO THE SG1524B
 LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS PS-5 CONVERTING 1524 SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY DESIGNS TO THE SG1524B Stan Dendinger Manager, Advanced Product Development Silicon General, Inc. INTRODUCTION Many power control
LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS PS-5 CONVERTING 1524 SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY DESIGNS TO THE SG1524B Stan Dendinger Manager, Advanced Product Development Silicon General, Inc. INTRODUCTION Many power control
User Manual Rev. 1502
 User Manual Rev. 1502 LDP-AV D06 101/17 / V03 / IF / picolas/manual-ldp-av_d06-n20 PicoLAS GmbH Company for Innovative Power Electronics and Laser Technology Table of Contents LDP-AV D06... 1 Table of
User Manual Rev. 1502 LDP-AV D06 101/17 / V03 / IF / picolas/manual-ldp-av_d06-n20 PicoLAS GmbH Company for Innovative Power Electronics and Laser Technology Table of Contents LDP-AV D06... 1 Table of
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
Experiment 8 Frequency Response
 Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
Current-mode PWM controller
 DESCRIPTION The is available in an 8-Pin mini-dip the necessary features to implement off-line, fixed-frequency current-mode control schemes with a minimal external parts count. This technique results
DESCRIPTION The is available in an 8-Pin mini-dip the necessary features to implement off-line, fixed-frequency current-mode control schemes with a minimal external parts count. This technique results
Low Power. Video Op Amp with Disable AD810 REV. A. Closed-Loop Gain and Phase vs. Frequency, G = +2, R L = 150, R F = 715 Ω
 CLOSED-LOOP db SHIFT Degrees DIFFERENTIAL % DIFFERENTIAL Degrees a FEATURES High Speed MHz Bandwidth ( db, G = +) MHz Bandwidth ( db, G = +) V/ s Slew Rate ns Settling Time to.% ( = V Step) Ideal for Video
CLOSED-LOOP db SHIFT Degrees DIFFERENTIAL % DIFFERENTIAL Degrees a FEATURES High Speed MHz Bandwidth ( db, G = +) MHz Bandwidth ( db, G = +) V/ s Slew Rate ns Settling Time to.% ( = V Step) Ideal for Video
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
EFRATOM LPRO-101 Repair reference guide By Fred de Vries, PE1FBO, Revision 2, August 2008, PE1FBO. LPRO repair reference guide 1
 EFRATOM LPRO-101 Repair reference guide By Fred de Vries, PE1FBO, 2008 Revision 2, August 2008, PE1FBO LPRO repair reference guide 1 Contents Brief specs...4 Rubidium lamp...4 Temperature controlled assemblies...5
EFRATOM LPRO-101 Repair reference guide By Fred de Vries, PE1FBO, 2008 Revision 2, August 2008, PE1FBO LPRO repair reference guide 1 Contents Brief specs...4 Rubidium lamp...4 Temperature controlled assemblies...5
Basic Harris DX Transmitter Tutorial
 BASIC DX TUTORIAL Basic Harris DX Transmitter Tutorial Basic DX Theory The Harris DX Transmitters series, introduced in 1986, have proven to be the most efficient method of Amplitude Modulation at medium
BASIC DX TUTORIAL Basic Harris DX Transmitter Tutorial Basic DX Theory The Harris DX Transmitters series, introduced in 1986, have proven to be the most efficient method of Amplitude Modulation at medium
6. HARDWARE PROTOTYPE AND EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
 6. HARDWARE PROTOTYPE AND EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS Laboratory based hardware prototype is developed for the z-source inverter based conversion set up in line with control system designed, simulated and discussed
6. HARDWARE PROTOTYPE AND EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS Laboratory based hardware prototype is developed for the z-source inverter based conversion set up in line with control system designed, simulated and discussed
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators
 Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
8121 Power Tube. Linear Beam Power Tube
 8121 Power Tube Linear Beam Power Tube Coaxial-Electrode Structure Ceramic-Metal Seals Full Ratings up to 500 MHz Forced-Air Cooled 170 Watts PEP Output at 30 MHz 235 Watts CW Output at 470 MHz The BURLE
8121 Power Tube Linear Beam Power Tube Coaxial-Electrode Structure Ceramic-Metal Seals Full Ratings up to 500 MHz Forced-Air Cooled 170 Watts PEP Output at 30 MHz 235 Watts CW Output at 470 MHz The BURLE
8072 Power Tube. VHF Linear Amplifier Tube. Coaxial-Electrode Structure Ceramic-Metal Seals Full Input to 500 MHz Conduction Cooled
 8072 Power Tube VHF Linear Amplifier Tube Coaxial-Electrode Structure Ceramic-Metal Seals Full Input to 500 MHz Conduction Cooled The BURLE 8072 is a small, conduction cooled beam power tube designed for
8072 Power Tube VHF Linear Amplifier Tube Coaxial-Electrode Structure Ceramic-Metal Seals Full Input to 500 MHz Conduction Cooled The BURLE 8072 is a small, conduction cooled beam power tube designed for
LM1203 RGB Video Amplifier System
 LM1203 RGB Video Amplifier System General Description The LM1203 is a wideband video amplifier system intended for high resolution RGB color monitor applications In addition to three matched video amplifiers
LM1203 RGB Video Amplifier System General Description The LM1203 is a wideband video amplifier system intended for high resolution RGB color monitor applications In addition to three matched video amplifiers
EFRATOM LPRO 101 Repair reference guide By Fred de Vries, PE1FBO Revision 7, January LPRO repair reference guide 1
 EFRATOM LPRO 101 Repair reference guide By Fred de Vries, PE1FBO Revision 7, January 2011 1 Contents Contents... 2 Connections on unit... 3 Typical operating parameters... 4 Rubidium lamp... 4 Temperature
EFRATOM LPRO 101 Repair reference guide By Fred de Vries, PE1FBO Revision 7, January 2011 1 Contents Contents... 2 Connections on unit... 3 Typical operating parameters... 4 Rubidium lamp... 4 Temperature
User Manual LDP-AV D06-N20. máåçi^p=dãäe= `çãé~åó=ñçê=fååçî~íáîé=mçïéê=bäéåíêçåáåë=~åç=i~ëéê=qéåüåçäçöó= = h~áëéêëíê~ëëé=nmm= RONPQ=eÉêòçÖÉåê~íÜ= =
 User Manual LDP-AV D06-N20 máåçi^p=dãäe= `çãé~åó=ñçê=fååçî~íáîé=mçïéê=bäéåíêçåáåë=~åç=i~ëéê=qéåüåçäçöó= = h~áëéêëíê~ëëé=nmm= RONPQ=eÉêòçÖÉåê~íÜ= = müçåéw= HQV=EMF=OQMTJRSP=RUJM= c~ñw= = HQV=EMF=OQMTJRSP=RUJOV=
User Manual LDP-AV D06-N20 máåçi^p=dãäe= `çãé~åó=ñçê=fååçî~íáîé=mçïéê=bäéåíêçåáåë=~åç=i~ëéê=qéåüåçäçöó= = h~áëéêëíê~ëëé=nmm= RONPQ=eÉêòçÖÉåê~íÜ= = müçåéw= HQV=EMF=OQMTJRSP=RUJM= c~ñw= = HQV=EMF=OQMTJRSP=RUJOV=
Retuning of FMIT #3 from 70.0 MHZ to 78.0 MHZ Charley Schwartz 10/28/02 DRAFT
 Retuning of FMIT #3 from 70.0 MHZ to 78.0 MHZ Charley Schwartz 10/28/02 DRAFT This document serves two purposes, an entry into the engineering records of the process and data accumulated during the tuning
Retuning of FMIT #3 from 70.0 MHZ to 78.0 MHZ Charley Schwartz 10/28/02 DRAFT This document serves two purposes, an entry into the engineering records of the process and data accumulated during the tuning
DLVP A OPERATOR S MANUAL
 DLVP-50-300-3000A OPERATOR S MANUAL DYNALOAD DIVISION 36 NEWBURGH RD. HACKETTSTOWN, NJ 07840 PHONE (908) 850-5088 FAX (908) 908-0679 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...3 SPECIFICATIONS...5 MODE SELECTOR
DLVP-50-300-3000A OPERATOR S MANUAL DYNALOAD DIVISION 36 NEWBURGH RD. HACKETTSTOWN, NJ 07840 PHONE (908) 850-5088 FAX (908) 908-0679 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...3 SPECIFICATIONS...5 MODE SELECTOR
Design and performance of LLRF system for CSNS/RCS *
 Design and performance of LLRF system for CSNS/RCS * LI Xiao 1) SUN Hong LONG Wei ZHAO Fa-Cheng ZHANG Chun-Lin Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China Abstract:
Design and performance of LLRF system for CSNS/RCS * LI Xiao 1) SUN Hong LONG Wei ZHAO Fa-Cheng ZHANG Chun-Lin Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China Abstract:
ML4818 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller
 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
HOME ASSIGNMENT. Figure.Q3
 HOME ASSIGNMENT 1. For the differential amplifier circuit shown below in figure.q1, let I=1 ma, V CC =5V, v CM = -2V, R C =3kΩ and β=100. Assume that the BJTs have v BE =0.7 V at i C =1 ma. Find the voltage
HOME ASSIGNMENT 1. For the differential amplifier circuit shown below in figure.q1, let I=1 ma, V CC =5V, v CM = -2V, R C =3kΩ and β=100. Assume that the BJTs have v BE =0.7 V at i C =1 ma. Find the voltage
Measurement and Analysis for Switchmode Power Design
 Measurement and Analysis for Switchmode Power Design Switched Mode Power Supply Measurements AC Input Power measurements Safe operating area Harmonics and compliance Efficiency Switching Transistor Losses
Measurement and Analysis for Switchmode Power Design Switched Mode Power Supply Measurements AC Input Power measurements Safe operating area Harmonics and compliance Efficiency Switching Transistor Losses
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS
 CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
ANALOG ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (CODE: EEE - 228)
 ANALOG ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (CODE: EEE - 228) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ANIL NEERUKONDA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCES (Affiliated to AU, Approved by AICTE
ANALOG ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (CODE: EEE - 228) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ANIL NEERUKONDA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCES (Affiliated to AU, Approved by AICTE
MQH0XX-YYDS3-ZZZ-2S. High Power 2 Channel RF Driver: For 2 Acousto-optic Q-Switches. Description: Key Features: Applications:
 High Power 2 Channel RF Driver: For 2 Acousto-optic Q-Switches MQH0XX-YYDS3-ZZZ-2S Former Model Number: 390XX-YYDSZZZ-2CH-A Description: The MQH0XX-YYDS3-ZZZ-2S is a High Power RF Driver with two RF outputs
High Power 2 Channel RF Driver: For 2 Acousto-optic Q-Switches MQH0XX-YYDS3-ZZZ-2S Former Model Number: 390XX-YYDSZZZ-2CH-A Description: The MQH0XX-YYDS3-ZZZ-2S is a High Power RF Driver with two RF outputs
electrical noise and interference, environmental changes, instrument resolution, or uncertainties in the measurement process itself.
 MUST 382 / EELE 491 Spring 2014 Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements Electrical laboratory work depends upon various devices to supply power to a circuit, to generate controlled input signals, and for
MUST 382 / EELE 491 Spring 2014 Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements Electrical laboratory work depends upon various devices to supply power to a circuit, to generate controlled input signals, and for
ARN-21D Solid State Modulator - A/A mode
 ARN-D Solid State Modulator - A/A mode Power Requirements for the solid state air-to-air modulator shall not exceed the following under any combination of normal operating conditions: 0.5 Ampere @ volts
ARN-D Solid State Modulator - A/A mode Power Requirements for the solid state air-to-air modulator shall not exceed the following under any combination of normal operating conditions: 0.5 Ampere @ volts
Model 305 Synchronous Countdown System
 Model 305 Synchronous Countdown System Introduction: The Model 305 pre-settable countdown electronics is a high-speed synchronous divider that generates an electronic trigger pulse, locked in time with
Model 305 Synchronous Countdown System Introduction: The Model 305 pre-settable countdown electronics is a high-speed synchronous divider that generates an electronic trigger pulse, locked in time with
EXHIBIT 3 : FCC (c) (TEST DATA) AND FCC (MEASUREMENT PROCEDURES) INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMITTER MEASUREMENTS, Part 2.
 EXHIBIT 3 : FCC 2.1033(c) (TEST DATA) AND FCC 2.1041 (MEASUREMENT PROCEDURES) INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMITTER MEASUREMENTS, Part 2.1033(c)(14) Exhibits 4 through 9 on the following pages present the required
EXHIBIT 3 : FCC 2.1033(c) (TEST DATA) AND FCC 2.1041 (MEASUREMENT PROCEDURES) INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMITTER MEASUREMENTS, Part 2.1033(c)(14) Exhibits 4 through 9 on the following pages present the required
Technical Bulletin Switch Mode PS Principles Page 1 of 5
 Technical Bulletin Switch Mode PS Principles Page 1 of 5 Switch Mode PS Principles By G8MNY (Updated Dec 06) (8 Bit ASCII Graphics use code page 437 or 850) There are 2 types, they work slightly differently
Technical Bulletin Switch Mode PS Principles Page 1 of 5 Switch Mode PS Principles By G8MNY (Updated Dec 06) (8 Bit ASCII Graphics use code page 437 or 850) There are 2 types, they work slightly differently
8791 Power Tube. Linear Beam Power Amplifier Tube
 8791 Power Tube Linear Beam Power Amplifier Tube Ruggedized, Reliable 80 Watt Average-Noise-Power Output with White Noise Loading 250 Watt Power Output in VHF-Linear Translator Service 500 Watt PEP Output
8791 Power Tube Linear Beam Power Amplifier Tube Ruggedized, Reliable 80 Watt Average-Noise-Power Output with White Noise Loading 250 Watt Power Output in VHF-Linear Translator Service 500 Watt PEP Output
TOE 7704 to TOE 7711 A
 Synthesizers/function generators with sweep, trigger, AM and frequency counter Special features 1 mhz to 44 MHz Sweep, trigger, gate Variable symmetry Digital display of frequency, sweep, AC, DC Amplitude
Synthesizers/function generators with sweep, trigger, AM and frequency counter Special features 1 mhz to 44 MHz Sweep, trigger, gate Variable symmetry Digital display of frequency, sweep, AC, DC Amplitude
E84 Lab 3: Transistor
 E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. AN109 Microprocessor-compatible DACs Dec
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1988 Dec DAC products are designed to convert a digital code to an analog signal. Since a common source of digital signals is the data bus of a microprocessor, DAC circuits that are
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1988 Dec DAC products are designed to convert a digital code to an analog signal. Since a common source of digital signals is the data bus of a microprocessor, DAC circuits that are
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
PreLab 6 PWM Design for H-bridge Driver (due Oct 23)
 GOAL PreLab 6 PWM Design for H-bridge Driver (due Oct 23) The overall goal of Lab6 is to demonstrate a DC motor controller that can adjust speed and direction. You will design the PWM waveform and digital
GOAL PreLab 6 PWM Design for H-bridge Driver (due Oct 23) The overall goal of Lab6 is to demonstrate a DC motor controller that can adjust speed and direction. You will design the PWM waveform and digital
Calsytech, # 38 North Mada Street Nandambakkam, Chennai, Tamil Nadu. Discipline Electro-Technical Calibration Issue Date
 Last Amended on 23.11.2016 Page 1 of 7 SOURCE 1. DC VOLTAGE $ 1mV to 10 mv 10 mv to100 mv 100 mv to1000 V 0.43% to 0.05% 0.05% to 0.01% 0.01% to 0.004% Calibrator, Calibrator by DC VOLTAGE 1mV to 20 mv
Last Amended on 23.11.2016 Page 1 of 7 SOURCE 1. DC VOLTAGE $ 1mV to 10 mv 10 mv to100 mv 100 mv to1000 V 0.43% to 0.05% 0.05% to 0.01% 0.01% to 0.004% Calibrator, Calibrator by DC VOLTAGE 1mV to 20 mv
audionet AMP 1 V2 User s Manual Stereo - Amplifier
 audionet AMP 1 V2 Stereo - Amplifier User s Manual 1 2 Contents 1 Preface... 4 1.1 Included... 5 1.2 Transport... 5 2 Overview control elements... 6 2.1 Front panel... 6 3 Overview connections... 7 3.1
audionet AMP 1 V2 Stereo - Amplifier User s Manual 1 2 Contents 1 Preface... 4 1.1 Included... 5 1.2 Transport... 5 2 Overview control elements... 6 2.1 Front panel... 6 3 Overview connections... 7 3.1
Analog Circuit II Laboratory ( EC 409) EC 409 Analog Electronics Lab - II
 Analog Circuit II Laboratory ( EC 409) Subject Subject Title L T P Contact Credit Full Code Hours / Unit# Marks EC 409 Analog Electronics Lab - II 0 0 2 2 1 100 Course Outcomes:- After successful completion
Analog Circuit II Laboratory ( EC 409) Subject Subject Title L T P Contact Credit Full Code Hours / Unit# Marks EC 409 Analog Electronics Lab - II 0 0 2 2 1 100 Course Outcomes:- After successful completion
Agilent 8360B Series Synthesized Swept Signal Generators 8360L Series Synthesized Swept CW Generators Data Sheet
 Agilent 8360B Series Synthesized Swept Signal Generators 8360L Series Synthesized Swept CW Generators Data Sheet 10 MHz to 110 GHz Specifications apply after full user calibration, and in coupled attenuator
Agilent 8360B Series Synthesized Swept Signal Generators 8360L Series Synthesized Swept CW Generators Data Sheet 10 MHz to 110 GHz Specifications apply after full user calibration, and in coupled attenuator
Chino Scientific Instruments Manufacturing
 DIGITAL MICRO OHM METER Chino s made DIGITAL MICRO OHM METER is a compact high reliability 3 ½ digit instrument suitable for measurement of resistivity of copper wires from 70 SWG to 50 SWG resistance
DIGITAL MICRO OHM METER Chino s made DIGITAL MICRO OHM METER is a compact high reliability 3 ½ digit instrument suitable for measurement of resistivity of copper wires from 70 SWG to 50 SWG resistance
Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT Real Time Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Monitoring System Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Guilherme K. Kolotelo, Rogers G. Reichert Cambridge, MA
Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT Real Time Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Monitoring System Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Guilherme K. Kolotelo, Rogers G. Reichert Cambridge, MA
Intermittent Beam Kicker Systems for Møller Measurement in G 0 Back Angle Experiments at 80 μa Beam. C. Yan. Abstract
 Jlab-TN-06-002 Intermittent Beam Kicker Systems for Møller Measurement in G 0 Back Angle Experiments at 80 μa Beam C. Yan Abstract Two identical fast beam kicker systems (FWHM ~ 2 μs) were installed at
Jlab-TN-06-002 Intermittent Beam Kicker Systems for Møller Measurement in G 0 Back Angle Experiments at 80 μa Beam C. Yan Abstract Two identical fast beam kicker systems (FWHM ~ 2 μs) were installed at
LSI/CSI LS7560N LS7561N BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR CONTROLLER
 LSI/CSI LS7560N LS7561N LSI Computer Systems, Inc. 15 Walt Whitman Road, Melville, NY 747 (631) 71-0400 FAX (631) 71-0405 UL A3800 BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR CONTROLLER April 01 FEATURES Open loop motor control
LSI/CSI LS7560N LS7561N LSI Computer Systems, Inc. 15 Walt Whitman Road, Melville, NY 747 (631) 71-0400 FAX (631) 71-0405 UL A3800 BRUSHLESS DC MOTOR CONTROLLER April 01 FEATURES Open loop motor control
CHAPTER 6. Motor Driver
 CHAPTER 6 Motor Driver In this lab, we will construct the circuitry that your robot uses to drive its motors. However, before testing the motor circuit we will begin by making sure that you are able to
CHAPTER 6 Motor Driver In this lab, we will construct the circuitry that your robot uses to drive its motors. However, before testing the motor circuit we will begin by making sure that you are able to
MULT SWP X1K K VERN START FREQ DURATION AMPLITUDE 0 TTL OUT RAMP
 Signal Generators This document is a quick reference guide to the operation of the signal generators available in the laboratories. Major functions will be covered, but some features such as their sweep
Signal Generators This document is a quick reference guide to the operation of the signal generators available in the laboratories. Major functions will be covered, but some features such as their sweep
OPERATING MANUAL CAVITY DUMPER / PULSE PICKER DRIVER MODEL NUMBER: 643ZZ.ZZZ-SYN-Y-X
 OPERATING MANUAL CAVITY DUMPER / PULSE PICKER DRIVER MODEL NUMBER: Where: X is the division factors for the pulse rate. Y is the multiplier of the reference input frequency 3ZZ.ZZZ is the output RF frequency
OPERATING MANUAL CAVITY DUMPER / PULSE PICKER DRIVER MODEL NUMBER: Where: X is the division factors for the pulse rate. Y is the multiplier of the reference input frequency 3ZZ.ZZZ is the output RF frequency
Electronics I. laboratory measurement guide
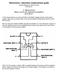 Electronics I. laboratory measurement guide Andras Meszaros, Mark Horvath 2015.02.01. 5. Measurement Basic circuits with operational amplifiers 2015.02.01. In this measurement you will need both controllable
Electronics I. laboratory measurement guide Andras Meszaros, Mark Horvath 2015.02.01. 5. Measurement Basic circuits with operational amplifiers 2015.02.01. In this measurement you will need both controllable
SixPac Series of SCR AC Controller and DC Converters
 SixPac Series of SCR AC Controller and DC Converters Complete Series of SCR Three-Phase Power Control Units Features Include: Compact, rugged construction Applications include: Windmill Converters Motor
SixPac Series of SCR AC Controller and DC Converters Complete Series of SCR Three-Phase Power Control Units Features Include: Compact, rugged construction Applications include: Windmill Converters Motor
Copyright 2014, R. Eckweiler & OCARC, Inc. Page 1 of 6
 HOM rev. new Heathkit of the Month: by Bob Eckweiler, AF6C Heathkit of the Month #59 - IG-72 Audio Generator TEST EQUIPMENT Heathkit IG-72 Audio Generator. Introduction: The IG-72 Audio Oscillator is a
HOM rev. new Heathkit of the Month: by Bob Eckweiler, AF6C Heathkit of the Month #59 - IG-72 Audio Generator TEST EQUIPMENT Heathkit IG-72 Audio Generator. Introduction: The IG-72 Audio Oscillator is a
PLL Synchronizer User s Manual / Version 1.0.6
 PLL Synchronizer User s Manual / Version 1.0.6 AccTec B.V. Den Dolech 2 5612 AZ Eindhoven The Netherlands phone +31 (0) 40-2474321 / 4048 e-mail AccTecBV@tue.nl Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Technical
PLL Synchronizer User s Manual / Version 1.0.6 AccTec B.V. Den Dolech 2 5612 AZ Eindhoven The Netherlands phone +31 (0) 40-2474321 / 4048 e-mail AccTecBV@tue.nl Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Technical
RF Power Amplifier (RFPA) Designing a 'Output Tank Circuit'
 RF Power Amplifier (RFPA) Designing a 'Output Tank Circuit' By Larry E. Gugle K4RFE, RF Design, Manufacture, Test & Service Engineer (Retired) Figure-1 Output 'Tank' Circuit Network in Low-Pass Filter
RF Power Amplifier (RFPA) Designing a 'Output Tank Circuit' By Larry E. Gugle K4RFE, RF Design, Manufacture, Test & Service Engineer (Retired) Figure-1 Output 'Tank' Circuit Network in Low-Pass Filter
CEM3378/3379 Voltage Controlled Signal Processors
 CEM3378/3379 Voltage Controlled Signal Processors The CEM3378 and CEM3379 contain general purpose audio signal processing blocks which are completely separate from each other. These devices are useful
CEM3378/3379 Voltage Controlled Signal Processors The CEM3378 and CEM3379 contain general purpose audio signal processing blocks which are completely separate from each other. These devices are useful
Dual, Current Feedback Low Power Op Amp AD812
 a FEATURES Two Video Amplifiers in One -Lead SOIC Package Optimized for Driving Cables in Video Systems Excellent Video Specifications (R L = ): Gain Flatness. db to MHz.% Differential Gain Error. Differential
a FEATURES Two Video Amplifiers in One -Lead SOIC Package Optimized for Driving Cables in Video Systems Excellent Video Specifications (R L = ): Gain Flatness. db to MHz.% Differential Gain Error. Differential
1 TRANSISTOR CIRCUITS
 FM TRANSMITTERS The first group of circuits we will discuss are FM TRANSMITTERS. They can be called SPY TRANSMITTERS, FM BUGS, or a number of other interesting names. They all do the same thing. They transmit
FM TRANSMITTERS The first group of circuits we will discuss are FM TRANSMITTERS. They can be called SPY TRANSMITTERS, FM BUGS, or a number of other interesting names. They all do the same thing. They transmit
Negative-Feedback Tone Control
 Negative-Feedback Tone Control Independent Variation of Bass and Treble Without Switches By P. J. BAXANDALL B.Sc.(Eng.) T he circuit to be described is the outcome of a prolonged investigation of tone-control
Negative-Feedback Tone Control Independent Variation of Bass and Treble Without Switches By P. J. BAXANDALL B.Sc.(Eng.) T he circuit to be described is the outcome of a prolonged investigation of tone-control
Op Amp Booster Designs
 Op Amp Booster Designs Although modern integrated circuit operational amplifiers ease linear circuit design, IC processing limits amplifier output power. Many applications, however, require substantially
Op Amp Booster Designs Although modern integrated circuit operational amplifiers ease linear circuit design, IC processing limits amplifier output power. Many applications, however, require substantially
Copyright 2016, R. Eckweiler & OCARC, Inc. Page 1 of 7
 Heathkit of the Month: by Bob Eckweiler, AF6C ELECTRONIC TEST EQUIPMENT Heathkit IM-38 AC Vacuum Tube Voltmeter (VTVM). Introduction: Back in March of 2013 Heathkit of the Month #47 discussed the Heathkit
Heathkit of the Month: by Bob Eckweiler, AF6C ELECTRONIC TEST EQUIPMENT Heathkit IM-38 AC Vacuum Tube Voltmeter (VTVM). Introduction: Back in March of 2013 Heathkit of the Month #47 discussed the Heathkit
A 100-Watt Transmitter Using a Pair of VT1625s
 12/16/2007 6:00 PM VT1625 100 Watt Transmitter A 100-Watt Transmitter Using a Pair of VT1625s FIG. 10.6 A 100-watt transmitter for five bands, using salvaged TV power transformer and surplus 1625 amplifier
12/16/2007 6:00 PM VT1625 100 Watt Transmitter A 100-Watt Transmitter Using a Pair of VT1625s FIG. 10.6 A 100-watt transmitter for five bands, using salvaged TV power transformer and surplus 1625 amplifier
Model 176 and 178 DC Amplifiers
 Model 176 and 178 DC mplifiers Features*! Drifts to 100 MΩ! CMR: 120 db @! Gain Linearity of ±.005% *The key features of this amplifier series, listed above, do not necessarily apply
Model 176 and 178 DC mplifiers Features*! Drifts to 100 MΩ! CMR: 120 db @! Gain Linearity of ±.005% *The key features of this amplifier series, listed above, do not necessarily apply
PE Electrical Machine / Power Electronics. Power Electronics Training System. ufeatures. } List of Experiments
 Electrical Machine / Power Electronics PE-5000 Power Electronics Training System The PE-5000 Power Electronics Training System consists of 28 experimental modules, a three-phase squirrel cage motor, load,
Electrical Machine / Power Electronics PE-5000 Power Electronics Training System The PE-5000 Power Electronics Training System consists of 28 experimental modules, a three-phase squirrel cage motor, load,
TRT HV System Simulations
 April 9, 2001 TRT HV System Simulations R. Van Berg - University of Pennsylvania A preliminary model of a TRT HV system has been assembled in order to understand the limits of sensitivity for Distributor
April 9, 2001 TRT HV System Simulations R. Van Berg - University of Pennsylvania A preliminary model of a TRT HV system has been assembled in order to understand the limits of sensitivity for Distributor
CEM3389 Voltage Controlled Signal Processor
 CEM3389 Voltage Controlled Signal Processor The CEM3389 is a general purpose audio signal processing device intended for use in multichannel systems. Included on-chip are a wide-range four-pole lowpass
CEM3389 Voltage Controlled Signal Processor The CEM3389 is a general purpose audio signal processing device intended for use in multichannel systems. Included on-chip are a wide-range four-pole lowpass
RF Generators. Requirements:
 Requirements: RF Generators to deliver a requested forward power (adjustable) level into an RF system power level is adjusted manually, or power level is controlled by a digital or analog input signal
Requirements: RF Generators to deliver a requested forward power (adjustable) level into an RF system power level is adjusted manually, or power level is controlled by a digital or analog input signal
Multiple Instrument Station Module
 Multiple Instrument Station Module Digital Storage Oscilloscope Vertical Channels Sampling rate Bandwidth Coupling Input impedance Vertical sensitivity Vertical resolution Max. input voltage Horizontal
Multiple Instrument Station Module Digital Storage Oscilloscope Vertical Channels Sampling rate Bandwidth Coupling Input impedance Vertical sensitivity Vertical resolution Max. input voltage Horizontal
An Electronic Watt-Watt-Hour Meter
 An Electronic Watt-Watt-Hour Meter The continued emphasis on energy conservation has forced designers to consider the power consumption and efficiency of their products. While equipment for the industrial
An Electronic Watt-Watt-Hour Meter The continued emphasis on energy conservation has forced designers to consider the power consumption and efficiency of their products. While equipment for the industrial
FAN4146 Ground Fault Interrupter
 Features For Two-Wire ALCI and RCD Applications Precision Sense Amplifier and Bandgap Reference Built-in AC Rectifier Direct DC Coupled to Sense Coil Built-in Noise Filter Low-Voltage SCR Disable SCR Gate
Features For Two-Wire ALCI and RCD Applications Precision Sense Amplifier and Bandgap Reference Built-in AC Rectifier Direct DC Coupled to Sense Coil Built-in Noise Filter Low-Voltage SCR Disable SCR Gate
Calibration Techniques for the Home Lab
 Calibration Techniques for the Home Lab Jacques Audet VE2AZX jacaudet@videotron.ca Web: ve2azx.net September 2018 ve2azx.net 1 Summary - Using a reference multimeter as a calibrator for less accurate instruments.
Calibration Techniques for the Home Lab Jacques Audet VE2AZX jacaudet@videotron.ca Web: ve2azx.net September 2018 ve2azx.net 1 Summary - Using a reference multimeter as a calibrator for less accurate instruments.
Introduction to ixblue RF drivers and amplifiers for optical modulators
 Introduction to ixblue RF drivers and amplifiers for optical modulators Introduction : ixblue designs, produces and commercializes optical modulators intended for a variety of applications including :
Introduction to ixblue RF drivers and amplifiers for optical modulators Introduction : ixblue designs, produces and commercializes optical modulators intended for a variety of applications including :
Computer-Based Project on VLSI Design Co 3/8
 Computer-Based Project on VLSI Design Co 3/8 This pamphlet describes a laboratory activity based on a former third year EIST experiment. Its purpose is the measurement of the switching speed of some CMOS
Computer-Based Project on VLSI Design Co 3/8 This pamphlet describes a laboratory activity based on a former third year EIST experiment. Its purpose is the measurement of the switching speed of some CMOS
UNIT 2. Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator. Ans. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION
 168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
Harald Klingbeil GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH. Contents
 CERN Accelerator School Ferrite Cavities Harald Klingbeil GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH Contents Usage of Ferrite Cavities Magnetic properties, hysteresis Simplified ferrite cavity
CERN Accelerator School Ferrite Cavities Harald Klingbeil GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung GmbH Contents Usage of Ferrite Cavities Magnetic properties, hysteresis Simplified ferrite cavity
Switched-mode power supply control circuit
 DESCRIPTION The /SE6 is a control circuit for use in switched-mode power supplies. It contains an internal temperature- compensated supply, PWM, sawtooth oscillator, overcurrent sense latch, and output
DESCRIPTION The /SE6 is a control circuit for use in switched-mode power supplies. It contains an internal temperature- compensated supply, PWM, sawtooth oscillator, overcurrent sense latch, and output
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators
 Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
MHz 58 db 1 KW RF Amplifier (EDA 00097)
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN A&B DEPARTMENT AB-Note-2004-029 RF 0.2-10 58 1 KW RF Amplifier (EDA 00097) M. Paoluzzi 25 th March 2004 Geneva, Switzerland 1 1. DESCRIPTION 1.1. GENERAL
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN A&B DEPARTMENT AB-Note-2004-029 RF 0.2-10 58 1 KW RF Amplifier (EDA 00097) M. Paoluzzi 25 th March 2004 Geneva, Switzerland 1 1. DESCRIPTION 1.1. GENERAL
WESTREX RA-1712 PHOTOGRAPHIC SOUND RECORD ELECTRONICS
 INTRODUCTION The RA-1712 solid state Record Electronics is an integrated system for recording photographic sound tracks on a Westrex photographic sound recorder. It accepts a 600Ω input signal level from
INTRODUCTION The RA-1712 solid state Record Electronics is an integrated system for recording photographic sound tracks on a Westrex photographic sound recorder. It accepts a 600Ω input signal level from
DRG-SC Series Signal Conditioners
 DRG-SC Series Signal Conditioners DRG-SC Series 245 Basic unit Models Available for Thermocouples, RTDs, DC Voltage and Current, Frequency, Strain Gage Bridge, AC Voltage and Current Field Configurable
DRG-SC Series Signal Conditioners DRG-SC Series 245 Basic unit Models Available for Thermocouples, RTDs, DC Voltage and Current, Frequency, Strain Gage Bridge, AC Voltage and Current Field Configurable
Interactive Tone Generator with Capacitive Touch. Corey Cleveland and Eric Ponce. Project Proposal
 Interactive Tone Generator with Capacitive Touch Corey Cleveland and Eric Ponce Project Proposal Overview Capacitance is defined as the ability for an object to store charge. All objects have this ability,
Interactive Tone Generator with Capacitive Touch Corey Cleveland and Eric Ponce Project Proposal Overview Capacitance is defined as the ability for an object to store charge. All objects have this ability,
Improved Second Source to the EL2020 ADEL2020
 Improved Second Source to the EL ADEL FEATURES Ideal for Video Applications.% Differential Gain. Differential Phase. db Bandwidth to 5 MHz (G = +) High Speed 9 MHz Bandwidth ( db) 5 V/ s Slew Rate ns Settling
Improved Second Source to the EL ADEL FEATURES Ideal for Video Applications.% Differential Gain. Differential Phase. db Bandwidth to 5 MHz (G = +) High Speed 9 MHz Bandwidth ( db) 5 V/ s Slew Rate ns Settling
Concepts to be Reviewed
 Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 3 Operational Amplifiers, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Reviewed Operational
Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 3 Operational Amplifiers, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Reviewed Operational
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS
 UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS ANALOG ELECTRONICS II EMT 212 2009/2010 EXPERIMENT # 3 OP-AMP (OSCILLATORS) 1 1. OBJECTIVE: 1.1 To demonstrate the Wien bridge oscillator 1.2 To demonstrate the RC phase-shift
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS ANALOG ELECTRONICS II EMT 212 2009/2010 EXPERIMENT # 3 OP-AMP (OSCILLATORS) 1 1. OBJECTIVE: 1.1 To demonstrate the Wien bridge oscillator 1.2 To demonstrate the RC phase-shift
Applications of the LM392 Comparator Op Amp IC
 Applications of the LM392 Comparator Op Amp IC The LM339 quad comparator and the LM324 op amp are among the most widely used linear ICs today. The combination of low cost, single or dual supply operation
Applications of the LM392 Comparator Op Amp IC The LM339 quad comparator and the LM324 op amp are among the most widely used linear ICs today. The combination of low cost, single or dual supply operation
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
