Step by step procedure for NMR data acquisition
|
|
|
- George Dorsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Step by step procedure for NMR data acquisition Spectrometers The UTHSCSA 500, 600, and 700 MHz spectrometers are each equipped with 4 independent RF channels and are each operated by a Red Hat Linux workstation running the spectrometer control program, TopSpin. There is, however, one IMPORTANT difference of which you should be aware, which is that the 500 and 700 MHz spectrometers have newer consoles (so called Avance I) compared to the 600 MHz spectrometer (so called DRX console). The newer consoles allow one to run the latest version of the spectrometer control software (currently TopSpin 2.11), whereas the older console is only capable of being operated by an older version, TopSpin Thus, although many things are the same between the two versions of TopSpin, there are some important differences. The ones relevant to this data acquisition guide are indicated below. Note also that some of the commands and procedures will depend on the type of probe installed in the spectrometer, for example, whether the probe is equipped with single (Z) or triple-axis (X, Y,Z) gradients, whether automatic tuning and matching is available, and whether it s a high-sensitivity cryoprobe or not. A summary of all probes available for the UTHSCSA spectrometers are listed below: Spectrometer ProbeName RF Coils Gradient Coils ATM Cryo 500 TXI 1H, 13C, 15N X,Y,Z Yes No 500 QXI 1H, 13C, 15N, 31P X, Y, Z No No 600 TXI-Cryo 1H, 13C, 15N Z No Yes 600 QXI 1H, 13C, 15N, 31P X,Y,Z No No 700 TCI-Cryo 1H, 13C, 15N Z Yes Yes 700 TXI 1H, 13C, 15N X, Y, Z Yes No 700 QXI 1H, 13C, 15N, 31P X,Y,Z No No Starting TopSpin 1. First login as a user in the linux workstation. If you don't have an account please contact us to setup one for you. 2. Click the redhat icon, then BRUKER menu, and finally topspin2.1 (Av500 & Av700) or topspin1.3 (Av600). TopSpin window will appear.
2 Preparation for acquisition 1. Since some of the commands of TopSpin require a dataset, open a dataset first. You can do this by clicking the Browser menu from the left hand side panel and choosing appropriate data set. Currently, all the users' datasets are stored in /avance5004, / avance6003 and /avance7002 disks on the 500, 600 and 700 MHz spectrometers respectively. If these data directories are not displayed (as will be the case for a first time user), you can add them by right clicking and choosing Add new data dir... menu. To open a data set listed in the browser double click or right click and choose display (drag and drop has now been disabled). 2. Now the desired sample temperature can be set by typing edte at the command line. Wait for the sample temperature to reach the desired value before proceeding to the next step. Inserting Sample 1. NMR tube containing sample should be held in a plastic spinner (use the blue color spinner in 500 and 600 MHz spectrometers; use the white color spinner in 700 MHz spectrometer). Hold the sample by the top, place sample tube in the spinner and the spinner in the sample depth gauge. Push or pull the sample tube so that the depth of the sample above and below the center line of the sample depth gauge is equal. However, never exceed the lower limit (position of the adjustable white platform,
3 which should be at the line marked 5 mm 15mm) as this can damage the probe as well as the sample, as the sample will rest on the tip of the tube, not the spinner. This is important for all probes, but especially the cryoprobes installed on the 600 and 700MHz spectrometers. 2. Remove the black cap from the top of the magnet bore. Next, press the LIFT button in upper left portion of the BSMS keyboard. Wait for the airflow (hissing sound that can be heard). Then remove the depth gauge before inserting the sample and spinner into the magnet. Pressing the LIFT button will toggle the air flow off and will drop the sample tube gently to the magnet bore where it will be positioned at the top of the probe. Locking 3. Lock signal can be seen in the lock display window that can be opened by typing lockdisp at the command line. 4. Enter lock at the command line and select appropriate solvent from the pop up solvent table window (H20+D2O or CDCl3 etc) and wait for the lock finished message to appear at the bottom of the topspin window. After that Lock On/Off LED will light on the BSMS keyboard. DO NOT LOCK THE SPECROMETER USING ANY OTHER METHOD. If the spectrometer fails to lock, this may indicate that your sample does not include any deuterated solvent. Tuning and Matching the Probe The resonance frequency of the RF coils will vary depending on the content (particularly, the salt content) of the individual NMR sample. Thus, it's necessary to Tune the RF coil to the correct value to yield the correct resonant frequency for the magnet field strength you are using. This is done by inserting the sample in the probe and then by adjusting two variable capacitors, called tune and match on the probe such that the reflected radio frequency power is minimized at the proper frequency. Importantly, the higher frequency, the greater the degree to which the tuning of the RF coil will depend on the content of the particular sample. This in practical terms means that it is essentially always necessary to tune the RF coil for 1H, whereas it is less important for lower frequency nuclei, such as 13C and 15N. Thus, in terms of standard operating procedures, we recommend that you ALWAYS adjust the 1H tuning, whereas adjustment of 13C and 15N tuning should be considered optional (and in most cases, not necessary). 5. On probes equipped with automatic tuning and matching (ATM), this can be done
4 with the atmm command. Currently, the conventional TXI probe on the 500 and conventional TXI and TCI cryoprobe on the 700 include ATM. Open an existing dataset and then use the edc command to save it to a new name (such as tune1h). Now type rpar Tuneh and press enter. In the acquisition window type atmm and press enter. Click optimize at the top of the atmm menu bar and choose start. This will enable tuning and matching of the probe for the selected channel (1H in this case). Alternatively, do not click optimize and manually adjust with the displayed tuning and matching buttons. Repeat this process for the all the desired channels (You will have to setup separate experiments for this, for example using rpar Tunec and rpar Tunen to tune either the 13C or 15N channels, respectively). 6. On probes without ATM, open an existing dataset and then use the edc command to save to a new name (such as tuneh). Now, type rpar Tuneh and press enter. Then go to the acquisition window by clicking acqu in the current datset menu bar or simply type a at the command line. Now type wobb at the command line. Go to the magnet and look for various screws underneath. These are color coded such that they match the color on the plate of the probe where RF cables attach. On all probes, yellow corresponds to 1H, red corresponds to 15N, and blue corresponds to 13C. Adjust those screws using the tool (either attached to the probe by a flexible chain or a separate tool, which we usually keep next to the magnet on the top of the preamp) until you get good tuning and matching. After this type stop. To tune other nuclei, such as 13C and 15N open an existing dataset and then use the edc command to save to a new name (such as tunec or tunen). Now, type rpar Tunec or rpar Tunen and press enter. Then go to the acquisition window and type wobb at the command line and repeat the process as described above. Examples of Wobble Curves with Different Tuning and Matching bad matching and bad tuning bad matching and good tuning
5 good matching and bad tuning good matching and good tuning Importantly, when manually tuning the cryoprobe on the 600 (which will always be the case since it does not have an ATM device), you will need to type the command crpoff prior to initiating the tuning procedure; once the tuning procedure is done, you will need to type the command crpon (these commands switch the probe from the normal situation where it uses internal cold preamplifiers to the standard warm preamplifiers (which are needed for tuning) and then back again). Shimming Shimming is a process in which minor adjustments are made to the magnetic field until uniform magnetic field is achieved around the sample. This is difficult to do manually, but can be done using automatic procedures. Before shimming any sample, read a recent stored shimfile for the current probe by typing rsh and choosing an appropriate shim file from the list. On the 500 and 700 MHz spectrometers there are two automated procedures possible, named gradshim and topshim. Topshim is strongly recommended over Gradshim as it's a newer procedure with a number of improvements relative to Gradshim. On the 600 MHz spectrometer, only Gradshim is available and therefore will have to be used. 7. To run Topshim, type topshim 1h 1d (or, if you have a Shigemi tube, topshim 1h 1d shigemi). If your sample is 100% D2O or CDCl3 or any other deuterated solvent, then use topshim 2h 1d. This procedure is entirely automated and will adjust the shims along the Z-direction (these are the ones that vary most from sample to sample). Typically, TopShim is complete within a minute, although it can be shorter or longer than this depending on the initial homogeneity (generally, starting with poor shims will cause TopShim to take longer to converge). Once Topshim is complete, click on the autoshim button on the BSMS keypad, which will automatically optimize the most sensitive Z- and X/Y shims in a continuous manner. Users may wish to save the
6 current shim set for future use; this may be done by typing wsh and by supplying a descriptive filename. NOTE, it is possible to use TopShim to shim in X, Y, and Z directions simultaneously, using topshim 3d 1h. NOTE, however, this will only work on probes with triple-axis gradient coils. which includes all of the UTHSCSA probes, except for the 600 and 700 MHZ cyroprobes (which are equipped only with Z-gradient pulsed field gradient coils). 8. To run Gradshim type gradshim. The first time gradshim is run there is a setup process. Agree with the setup process and click "seen" to ignore all the error messages. For both 3D and 1D buttons (top of window) enter your username in the User field and enter /opt/topspinx.x/ in the disk field. Create an iteration control file (the following is for 1D shimming). <edit> <iteration control> <new> Give the file a name, ie 1D_5steps Add the following 5 steps: step 1, lowz, size=18 step 2, midz, size=18 step 3, midz, size=18 step 4, highz, size=18 step 5, highz, size=18 <save> The size is the length of the sample chamber. The units don't exactly correspond to mm, but 18 is a good entry for an 18 mm chamber. If these sizes are set too high, the procedure may fail to converge on a homogeneously shimmed field. Thereafter, your iteration control file should be selected by default, but if not, select it from the list. The * button expands the list of available iteration control files. <Start gradient shimming> It should say that it will do 5 iterations. But, sometimes program exits after 1 iteration. If so, choosing the iteration control file from the list again will solve this problem. A plot will be displayed of the frequency (as a measure of the field) over vertical coordinates with 0 at the center of the sample. The size you have selected is in a different color. The field is homogeneous when the central
7 colored part of the plot is vertical. You may have to repeat gradshim to get the field homogeneous. First delete the previous plot window, else the new lines will be added to the old ones. If the line has a hook on one end that can't be straightened, or appears to be unstable in its effort to converge on a vertical line, your sample chamber may not be centered properly. 9. Wait for the message setsh finished to appear at the bottom of the topspin main window. This message indicates that gradshim is finished. Setting up experiments 1. You need to create a new dataset before starting any experiment. To do this open an existing dataset as described in the Step 1 of Preparation for acquisition. Now type edc from the command line. In the edc display window which will pop up, type all the necessary parameters like Name, Expno, Dir and User etc and then press OK. This will take you to the new dataset you have created. 2. Next determine the 90 degree proton pulse at high power. To do this on the 500 and 700 MHz spectrometer (running TopSpin 2.11),issue the command pulsecal and wait. Calibrated pulselengths for a hard pulse and a soft pulse will be shown in a new window. Note down these values. The automated procedure, pulsecal is only available in the newer version of TopSpin. Thus, the following manual procedure will have to be used on the 600. This procedure can also be run on 500 & 700 and may be desirable if one suspects the values determined by the pulsecal procedure are not accurate. To manually calibrate the 1H pulse we use a one pulse experiment. To use this, create a new experiment (calib1h for example) using edc command, and then type rpar calib1h on the command line. The intensity of the resulting solvent peak will be maximum when the pulse length is exactly 90 degree and the signal intensity will be minimum (null signal) when the pulse length is equal to multiples of 180 degree (180, 360, 540, 720 etc). But, in practice, due to radiation damping the solvent signal won't be null for 180 degree pulse if your sample is in 90%H2O/10%D2O. Only, 360 degree pulse gives the null signal. So, finding out the 360 degree pulse is widely recommended. Open the calib1h dataset and set pl1 (power level for the hard 90 degree) as -3 db (in 500 MHz & 600 MHz spectrometers) or +2.5 db (in 700 MHz spectrometer). Set p1 as 1u and then type zgefp. Type apk (automatic phase correction) to phase the spectrum. Zoom in around the water signal using the mouse and the type dpl1 at the at the command
8 line. Now type popt at the command line and press enter. A window will pop up. Enter the STARTVAL, ENDVAL and INC parameters for the parameter p1 (90 degree hard proton pulse). For example, enter 30 usec, 36 usec and 0.4 usec for STARTVAL, ENDVAL and INC fields respectively. Then click the start optimize button. After popt is finished you can see that solvent signal intensity will be plotted as a function of p1 value. Find out the p1 value corresponding to 360 degree (p1 value at which you see a null). From that value 90 degree pulse can be calculated. Readjust the STARTVAL, ENDVAL, and INC values if you don't see any NULL. Since all multiples of 360 degree pulses (720, 1080 degrees etc) give you a null signal (see the sine wave diagram), beginners sometimes get confused in choosing the correct null. This is especially true when you have high salt sample. So, use the following tip to avoid this confusion. Calculate the 90 degree pulse from the value you got for 360 degree pulse. In the calib1h experiment set p1 to 90 degree pulse. Acquire the signal (zg followed by efp or zgefp). Type apk to phase correct it. The signal should be a maximum. Now set p1 to 360 degree pulse. Acquire the signal (do not phase correct the signal). You should see a null signal. Finally, set p1 to 270 degree pulse. Acquire the signal (Again, do not phase correct it). Now you should see a signal with negative maximum. If you don't see the signal intensities as explained above then it is likely that you are seeing a wrong null and pulse length calibrated for 90 degree is wrong. 3. To setup your experiment of interest, use edc to create a new data set and then use rpar to read a standard parameter set for the experiment. If you wish to run 1D proton spectrum then choose PROTON or any other suitable standard parameter set from the list and click OK. Similarly, if you wish to run a 2D heteronuclear experiment like HSQC, then choose a parameter set like HSQCETF3GPSI from the list and click OK. This step will ensure that all the necessary standard parameters are copied for the
9 experiment. Please note that the standard parameter sets are named according to a standard coding method (see the Pulprog.info in the /opt/topspinx.x/exp/stan/nmr/lists /pp/ directory for a detailed explanation of the coding system). 4. Type edasp and check that the routings are OK. A typical routing setup for the UTHSCSA spectrometers is shown below. Loading standard parameter sets will ensure the correct edasp settings for you. Nevertheless, it is still a good idea to check the edasp settings before you start any NMR experiment. 5. Issue the command getprosol 1H <pulselength> <power>. Substitute the values of the proton hard pulse length and power level you got from step 2 above (for example, getprosol 1H ) here. All the other 1H pulses and their power levels (as well as pulse times and power levels for other nuclei) will be calculated and stored in the current dataset. 6. Now you have to set the carrier positions for each of the dimensions of your experiment. These parameters determine the center of the spectrum in ppm and are set by typing the commands o1p, o2p, and o3p. Common center positions in ppm for the different nuclei are listed in the table below:
10 1H H2O H amide C Calpha C Ca/Cb Center C Carbonyl N amide As an example, if you wanted to setup a 3D HNCA experiment, you would type o1p 4.706, o2p 53.5, and 03p Although these values should work for most proteins, it may be desirable to optimize them (particularly, 15N carrier position for example) for your individual protein. 7. After setting the center, you have to set the desired spectral width in units of ppm. You can set these values by issuing eda command or clicking AcquPars menu. In the eda window look for SW[PPM] parameter. If you do not see that then click the width menu in the left hand side panel. Set the correct values for ALL dimensions. Typical values for common experiments are listed in the table below: Experiment 1D 1H: 1D 13C: 2D H-N HSQC: 3D HNCA: 3D HNCO: 3D CBCA(CO)NH: 3D HNCACB: etc Sweep Width/Spectral Width 16ppm 200ppm 1H 16ppm, 15N 28 ppm 1H 16ppm, 15N 28 ppm, 13C 24 ppm 1H 16ppm, 15N 28 ppm, 13C 12 ppm 1H 16ppm, 15N 28 ppm, 13C 60 ppm 1H 16ppm, 15N 28 ppm, 13C 60 ppm 8. Change the number of sample points (TD) in each dimension if you are not satisfied with the default values set by rpar command. Typically, TD is set to 16, 32 or 64k for standard 1D experiments. In the multidimensional experiments TD for direct dimension (usually proton) is set for 1k or 2k. Follow the table to get some idea about the TD set for indirectly detected dimension. Experiment Indirect dimension TD 2D-15N HSQC 15N D-13C HSQC 13C D-13C HSQC 13C determined by the (Constant time version) decremental delay 3D HNCA 15N 64
11 3D HNCA 13C D CBCA(CO)NH 15N 64 3D CBCA(CO)NH 13C D HCCH-TOCSY 1H D HCCH-TOCSY 13C D 15N NOESY 1H D 15N NOESY 15N D 13C NOESY 1H D 13C NOESY 13C Graphical Representation of Acquisition Parameters 9. Change the number of scans (NS) & dummy scans (DS) if you need to. Increasing the NS will improve the quality (Signal-to-Noise ratio) of the spectrum. But, the total experiment time will also be increased. Typical 1D experiments can have NS of 1k or 2k. But, typical 2D experiments will be completed in an hour if you set the NS to 8 and TD to 360. But if you set NS to 32 then the same experiment will take 4 hrs to complete. So, increase the number of scans only if needed. Also, note that NS should ideally be an integral number of the longest phase cycle in the pulse program. For example, if the longest phase cycle of the pulseprogram is 8 then you should set NS to integral multiples 8. Use the command expt to determine the total time needed to
12 complete the experiment. During dummy scans, the actual experiment will be run but no data will be acquired. This will help sample to reach a steady state or equilibrium. For DS default value set by the rpar command should be sufficient. 10. The receiver gain is set by the parameter rg. Receiver gain is a very important parameter to match the amplitude of the fid to the dynamic range of the digitizer. If the FID is clipped at the top or bottom of the display then rg should be reduced. If the gain is too low and not utilizing a suitable (25-40 %) part of the dynamic range of the digitizer, it should be increased. Typically, the receiver gain is set automatically by the rga command. Effect of clipped fid as a result of RG set too high 11.Type zg to start the acquisition. You should see an FID in the acquisition window as shown below
13 FID (time domain signal) If you have acquired an fid (time domain data) then you type efp to see the the frequency domain spectrum. The efp applies exponential window function to the time domain data and then Fourier transforms the data followed by phase correction using the values PHC0 (zero order) and PHC1(first order). If the spectrum is not phased correctly then you can give apk command to do the automatic phase correction.
Instruction for Operating the Bruker Avance III 800 MHz NMR Spectrometers in UTMB
 Instruction for Operating the Bruker Avance III 800 MHz NMR Spectrometers in UTMB Written by Tianzhi Wang, date: February 8, 2013. No food, no drink in NMR room and no internet in NMR host computer except
Instruction for Operating the Bruker Avance III 800 MHz NMR Spectrometers in UTMB Written by Tianzhi Wang, date: February 8, 2013. No food, no drink in NMR room and no internet in NMR host computer except
User manual Bruker DPX200 NMR spectrometer
 User manual Bruker DPX200 NMR spectrometer Insert the NMR tube in the spinner in such a way that the bottom of the tube reaches the grey disc at the bottom of the spinnerholder. Make sure that the NMR
User manual Bruker DPX200 NMR spectrometer Insert the NMR tube in the spinner in such a way that the bottom of the tube reaches the grey disc at the bottom of the spinnerholder. Make sure that the NMR
NMR spectrometer usage at the BioNMR facility ETH Zürich
 NMR spectrometer usage at the BioNMR facility ETH Zürich Accounts 2 Safety precautions: strong magnetic fields 2 Parts of an NMR spectrometer 3 NMR data storage 3 Start topspin software 3 Initial steps
NMR spectrometer usage at the BioNMR facility ETH Zürich Accounts 2 Safety precautions: strong magnetic fields 2 Parts of an NMR spectrometer 3 NMR data storage 3 Start topspin software 3 Initial steps
NMR Spectrometer Operation: xwinnmr
 NMR Spectrometer Operation: xwinnmr Dr. Robert Peterson Facility Manager NMR Technology Center UCLA-DOE Institute for Genomics and Proteomics UCLA Dept. of Chemistry and Biochemistry Overview This is a
NMR Spectrometer Operation: xwinnmr Dr. Robert Peterson Facility Manager NMR Technology Center UCLA-DOE Institute for Genomics and Proteomics UCLA Dept. of Chemistry and Biochemistry Overview This is a
400 MHz spectrometer user manual
 400 MHz spectrometer user manual january 2017 Sandrine Denis-Quanquin 1. THE NMR SPECTROMETER... 3 2. MANUAL MODE / AUTOMATION... 4 2.1 SAMPLE CHANGER... 4 2.2 MANUAL MODE... 4 2.3 AUTOMATION... 4 3. PRELIMINARY
400 MHz spectrometer user manual january 2017 Sandrine Denis-Quanquin 1. THE NMR SPECTROMETER... 3 2. MANUAL MODE / AUTOMATION... 4 2.1 SAMPLE CHANGER... 4 2.2 MANUAL MODE... 4 2.3 AUTOMATION... 4 3. PRELIMINARY
H Micro-Imaging. Tuning and Matching. i. Open any 1H data set and type wobb.
 - 1-1 H Micro-Imaging The NMR-specific properties of the objects are visualized as multidimensional images. Translational motion can be observed and spectroscopic information can be spatially resolved.
- 1-1 H Micro-Imaging The NMR-specific properties of the objects are visualized as multidimensional images. Translational motion can be observed and spectroscopic information can be spatially resolved.
HMBC 17. Goto. Introduction AVANCE User s Guide Bruker 185
 Chapter HMBC 17 Introduction 17.1 Goto Heteronuclear Multiple Bond Correlation spectroscopy is a modified version of HMQC suitable for determining long-range 1 H- 13 C connectivity. This is useful in determining
Chapter HMBC 17 Introduction 17.1 Goto Heteronuclear Multiple Bond Correlation spectroscopy is a modified version of HMQC suitable for determining long-range 1 H- 13 C connectivity. This is useful in determining
1D Transient NOE on the Bruker DRX-500 and DRX-600
 1D Transient NOE on the Bruker DRX-500 and DRX-600 Reference: Stott, K., Stonehouse, J., Keeler, T.L. and Shaka, A.J., J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117 (14), pp. 4199-4200. At thermal equilibrium in a strong
1D Transient NOE on the Bruker DRX-500 and DRX-600 Reference: Stott, K., Stonehouse, J., Keeler, T.L. and Shaka, A.J., J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117 (14), pp. 4199-4200. At thermal equilibrium in a strong
Two Dimensional Homonuclear Correlation Spectroscopy
 Two Dimensional Homonuclear Correlation Spectroscopy Gradient COSY William D. Wheeler, Ph.D. Department of Chemistry University of Wyoming April 16, 1999 Revised September 22, 1999 2 INTRODUCTION Correlation
Two Dimensional Homonuclear Correlation Spectroscopy Gradient COSY William D. Wheeler, Ph.D. Department of Chemistry University of Wyoming April 16, 1999 Revised September 22, 1999 2 INTRODUCTION Correlation
Two Dimensional Heteronuclear Correlation Spectroscopy
 Two Dimensional Heteronuclear Correlation Spectroscopy Gradient HMQC William D. Wheeler, Ph.D. Department of Chemistry University of Wyoming Revised September 7, 2006 2 INTRODUCTION Correlation Spectroscopy
Two Dimensional Heteronuclear Correlation Spectroscopy Gradient HMQC William D. Wheeler, Ph.D. Department of Chemistry University of Wyoming Revised September 7, 2006 2 INTRODUCTION Correlation Spectroscopy
TopSpin Guide Book. Basic NMR Experiments User Manual. Innovation with Integrity. Version 002 NMR
 TopSpin Guide Book Basic NMR Experiments User Manual Version 002 Innovation with Integrity NMR Copyright by Bruker Corporation All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
TopSpin Guide Book Basic NMR Experiments User Manual Version 002 Innovation with Integrity NMR Copyright by Bruker Corporation All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
Two Dimensional Homonuclear Correlation Spectroscopy
 Two Dimensional Homonuclear Correlation Spectroscopy DQF-COSY William D. Wheeler, Ph.D. Department of Chemistry University of Wyoming September 23, 1999 2 INTRODUCTION Correlation Spectroscopy Correlation
Two Dimensional Homonuclear Correlation Spectroscopy DQF-COSY William D. Wheeler, Ph.D. Department of Chemistry University of Wyoming September 23, 1999 2 INTRODUCTION Correlation Spectroscopy Correlation
An NMR Caveman s Guide to Quickly Acquiring Spectroscopic Data By Brian Sparling
 An NMR Caveman s Guide to Quickly Acquiring Spectroscopic Data By Brian Sparling Disclaimer: this guide is meant to be a quick, routine means of obtaining characterization data for unknown compounds in
An NMR Caveman s Guide to Quickly Acquiring Spectroscopic Data By Brian Sparling Disclaimer: this guide is meant to be a quick, routine means of obtaining characterization data for unknown compounds in
Exercise at the Spectrometer
 Exercise at the Spectrometer General The script is written for Bruker spectrometers. The color code means, red for all commands and green for parameters in the TopSpin commando line. The script gives additional
Exercise at the Spectrometer General The script is written for Bruker spectrometers. The color code means, red for all commands and green for parameters in the TopSpin commando line. The script gives additional
Student Name: Date Completed: Supervisor:
 2 NMR Training for the 600 MHz NMR with Chempack INOVA 600 Tests and Assignment Certification Student Name: 600-Test #1: The student will be given a written test administered by Dr. Lee. This test will
2 NMR Training for the 600 MHz NMR with Chempack INOVA 600 Tests and Assignment Certification Student Name: 600-Test #1: The student will be given a written test administered by Dr. Lee. This test will
Recording EPR Spectra using ER 4102ST Resonator
 Recording EPR Spectra using ER 4102ST Resonator This protocol gives step-by-step instructions for recording an EPR spectrum using the high sensitivity Bruker SHQE cavity (assuming the SHQE is already in
Recording EPR Spectra using ER 4102ST Resonator This protocol gives step-by-step instructions for recording an EPR spectrum using the high sensitivity Bruker SHQE cavity (assuming the SHQE is already in
NMR Basics. Lecture 2
 NMR Basics Lecture 2 Continuous wave (CW) vs. FT NMR There are two ways of tuning a piano: - key by key and recording each sound (or frequency). - or, kind of brutal, is to hit with a sledgehammer and
NMR Basics Lecture 2 Continuous wave (CW) vs. FT NMR There are two ways of tuning a piano: - key by key and recording each sound (or frequency). - or, kind of brutal, is to hit with a sledgehammer and
NMR Hardware 06/06/2017. Outline. Instrumentation: Magnet. Increasing magnetic field increases Sensitivity, by power of 3/2 Dispersion, linearly
 NMR Hardware Outline Magnet Lock Shims Gradient Probe Signal generation and transmitters Receiver and digitizer Variable temperature system Solids hardware Instrumentation: Magnet Often the most impressive
NMR Hardware Outline Magnet Lock Shims Gradient Probe Signal generation and transmitters Receiver and digitizer Variable temperature system Solids hardware Instrumentation: Magnet Often the most impressive
Your first NMR measurement
 Your first NMR measurement Introduction Select 10mM water in D2O as NMR sample. The NMR spectrum of such sample consists of only two signals: the water signal and the peak of the reference (TSP). Follow
Your first NMR measurement Introduction Select 10mM water in D2O as NMR sample. The NMR spectrum of such sample consists of only two signals: the water signal and the peak of the reference (TSP). Follow
KJM D-SELECTIVE NMR Experiments on the AVIIIHD-800. Version 1.0. Topspin 3.5 Windows 7
 KJM 9250 1D-SELECTIVE NMR Experiments on the AVIIIHD-800 Version 1.0 Topspin 3.5 Windows 7 Professor Emeritus Alistair Lawrence Wilkins, University of Waikato, New Zealand. January 2018 1D-SELECTIVE NMR
KJM 9250 1D-SELECTIVE NMR Experiments on the AVIIIHD-800 Version 1.0 Topspin 3.5 Windows 7 Professor Emeritus Alistair Lawrence Wilkins, University of Waikato, New Zealand. January 2018 1D-SELECTIVE NMR
KJM D-SELECTIVE NMR Experiments on the AVI-600 and AVII-600. Version 1.0. Topspin 3.5 Windows 7 Topspin 1.3 Windows XP
 KJM 9250 1D-SELECTIVE NMR Experiments on the AVI-600 and AVII-600 Version 1.0 Topspin 3.5 Windows 7 Topspin 1.3 Windows XP Professor Emeritus Alistair Lawrence Wilkins, University of Waikato, New Zealand.
KJM 9250 1D-SELECTIVE NMR Experiments on the AVI-600 and AVII-600 Version 1.0 Topspin 3.5 Windows 7 Topspin 1.3 Windows XP Professor Emeritus Alistair Lawrence Wilkins, University of Waikato, New Zealand.
Pulsed-Field Gradient NMR Diffusion Measurement Protocol
 Pulsed-Field Gradient NMR Diffusion Measurement Protocol Advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy Facility National High Magnetic Field Laboratory University of Florida, Gainesville, FL. Contents
Pulsed-Field Gradient NMR Diffusion Measurement Protocol Advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy Facility National High Magnetic Field Laboratory University of Florida, Gainesville, FL. Contents
8 COSY. 8.1 Introduction. 8.2 Magnitude COSY
 8 COSY 8.1 Introduction COSY (COrrelation SpectroscopY) is a homonuclear 2D technique that is used to correlate the chemical shifts of 1 H nuclei which are J-coupled to one another. In this chapter, two
8 COSY 8.1 Introduction COSY (COrrelation SpectroscopY) is a homonuclear 2D technique that is used to correlate the chemical shifts of 1 H nuclei which are J-coupled to one another. In this chapter, two
PINMRF. Varian 300 MHz NMR Spectrometers User Guide for Advanced 1D and Basic 2D NMR Experiments
 PINMRF Varian 300 MHz NMR Spectrometers User Guide for Advanced 1D and Basic 2D NMR Experiments INCLUDING: Inova-300-1 w/ 5mm 4-nucleus probe 365 WTHR Inova-300-2 w/ 5mm 4-nucleus probe 4100 BRWN Table
PINMRF Varian 300 MHz NMR Spectrometers User Guide for Advanced 1D and Basic 2D NMR Experiments INCLUDING: Inova-300-1 w/ 5mm 4-nucleus probe 365 WTHR Inova-300-2 w/ 5mm 4-nucleus probe 4100 BRWN Table
Chapter 1. 1 The NMR Spectrometer. 1.1 Components of an NMR Spectrometer The Magnet
 Chapter 1 1 The NMR Spectrometer 1.1 Components of an NMR Spectrometer 1.1.1 The Magnet In most current NMR spectrometers the magnetic field is generated by a superconducting magnet (Fig. 1.1). The first
Chapter 1 1 The NMR Spectrometer 1.1 Components of an NMR Spectrometer 1.1.1 The Magnet In most current NMR spectrometers the magnetic field is generated by a superconducting magnet (Fig. 1.1). The first
The Agilent OneNMR Probe
 The Agilent OneNMR Probe Technical Overview Introduction The Agilent OneNMR probe represents a new class of NMR probes. This technology is the most signifi cant advance in solution-state probes in over
The Agilent OneNMR Probe Technical Overview Introduction The Agilent OneNMR probe represents a new class of NMR probes. This technology is the most signifi cant advance in solution-state probes in over
Implementing ultrafast 2D NMR experiments on a Bruker Avance Spectrometer
 Implementing ultrafast 2D NMR experiments on a Bruker Avance Spectrometer Laetitia Rouger, Benoît Charrier, Serge Akoka, Patrick Giraudeau EBSI group CEISAM laboratory http://www.sciences.univ-nantes.fr/ceisam/en_ebsi1.php
Implementing ultrafast 2D NMR experiments on a Bruker Avance Spectrometer Laetitia Rouger, Benoît Charrier, Serge Akoka, Patrick Giraudeau EBSI group CEISAM laboratory http://www.sciences.univ-nantes.fr/ceisam/en_ebsi1.php
Open acqi window if the button has been lost. autolocking routine, alock= y for autolocking, alock= n for typical manual locking
 Glossary of Common NMR Commands and Terms aa acqi ai alock aph array at points (np) axis='p' axis= pd BPsvf bc bs cd directory abort acquisition, hard stop Open acqi window if the button has been lost
Glossary of Common NMR Commands and Terms aa acqi ai alock aph array at points (np) axis='p' axis= pd BPsvf bc bs cd directory abort acquisition, hard stop Open acqi window if the button has been lost
Gradients. Effects of B0 gradients on transverse magnetisation Similar to figure 10 of Sattler review Progr. NMR 34 (1999), 93
 Gradients 1. What are gradients? Modern high-resolution NMR probes contain -besides the RF coils - additional coils that can be fed a DC current. The coils are built so that a pulse (~1 ms long) of DC
Gradients 1. What are gradients? Modern high-resolution NMR probes contain -besides the RF coils - additional coils that can be fed a DC current. The coils are built so that a pulse (~1 ms long) of DC
Instructions for 1 H-, 13 C-, 19 F-, and 31 P-Spectra on the Varian Mercury-Vx-300
 1 Instructions for 1 H-, 13 C-, 19 F-, and 31 P-Spectra on the Varian Mercury-Vx-300 Please note: Under no circumstances move the magnet or the automatic sampler table. Do not attempt to use the auto sampler
1 Instructions for 1 H-, 13 C-, 19 F-, and 31 P-Spectra on the Varian Mercury-Vx-300 Please note: Under no circumstances move the magnet or the automatic sampler table. Do not attempt to use the auto sampler
Program. short intro the hardware locking and shimming 1D proton setup presaturation spectra
 Program short intro the hardware locking and shimming 1D proton setup presaturation spectra 13 C spectra, DEPT processing of 1D file transfer and backup 2D homonuclear + 2D processing 2D heteronuclear
Program short intro the hardware locking and shimming 1D proton setup presaturation spectra 13 C spectra, DEPT processing of 1D file transfer and backup 2D homonuclear + 2D processing 2D heteronuclear
KJM Version 1.0. Topspin 3.5 Windows 7 Topspin 1.3 Windows XP
 KJM 9250 1 H NMR spectra on the AVI-600 and AVII-600 Version 1.0 Topspin 3.5 Windows 7 Topspin 1.3 Windows XP Professor Emeritus Alistair Lawrence Wilkins, University of Waikato, New Zealand. January 2018
KJM 9250 1 H NMR spectra on the AVI-600 and AVII-600 Version 1.0 Topspin 3.5 Windows 7 Topspin 1.3 Windows XP Professor Emeritus Alistair Lawrence Wilkins, University of Waikato, New Zealand. January 2018
6.S02 MRI Lab Acquire MR signals. 2.1 Free Induction decay (FID)
 6.S02 MRI Lab 1 2. Acquire MR signals Connecting to the scanner Connect to VMware on the Lab Macs. Download and extract the following zip file in the MRI Lab dropbox folder: https://www.dropbox.com/s/ga8ga4a0sxwe62e/mit_download.zip
6.S02 MRI Lab 1 2. Acquire MR signals Connecting to the scanner Connect to VMware on the Lab Macs. Download and extract the following zip file in the MRI Lab dropbox folder: https://www.dropbox.com/s/ga8ga4a0sxwe62e/mit_download.zip
Laboratory Experiments for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy May 6, 2004
 CONTENTS 1 Contents Laboratory Experiments for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy May 6, 2004 1 Introduction 3 2 Safety 3 2.1 High Magnetic Fields......................................... 3 2.1.1
CONTENTS 1 Contents Laboratory Experiments for Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy May 6, 2004 1 Introduction 3 2 Safety 3 2.1 High Magnetic Fields......................................... 3 2.1.1
If the magnetic field is larger, more energy is required to excite a given nucleus.
 1 2 If an NMR-active nucleus such as 1 H or 13 C is put into a magnet field, then it will come into resonance if it is irradiated with rf at the correct frequency. The correct frequency depends mainly
1 2 If an NMR-active nucleus such as 1 H or 13 C is put into a magnet field, then it will come into resonance if it is irradiated with rf at the correct frequency. The correct frequency depends mainly
SpinCore RadioProcessor LabVIEW Extensions
 NMR Interface User's Manual SpinCore Technologies, Inc. http:// Congratulations and thank you for choosing a design from SpinCore Technologies, Inc. We appreciate your business! At SpinCore we try to fully
NMR Interface User's Manual SpinCore Technologies, Inc. http:// Congratulations and thank you for choosing a design from SpinCore Technologies, Inc. We appreciate your business! At SpinCore we try to fully
Lab 8 6.S02 Spring 2013 MRI Projection Imaging
 1. Spin Echos 1.1 Find f0, TX amplitudes, and shim settings In order to acquire spin echos, we first need to find the appropriate scanner settings using the FID GUI. This was all done last week, but these
1. Spin Echos 1.1 Find f0, TX amplitudes, and shim settings In order to acquire spin echos, we first need to find the appropriate scanner settings using the FID GUI. This was all done last week, but these
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2008 ISSN 1434 193X SUPPORTING INFORMATION Title: Structural Elucidation with NMR Spectroscopy: Practical Strategies for Organic
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2008 ISSN 1434 193X SUPPORTING INFORMATION Title: Structural Elucidation with NMR Spectroscopy: Practical Strategies for Organic
Standard Operating Procedure
 Standard Operating Procedure Nanosurf Atomic Force Microscopy Operation Facility NCCRD Nanotechnology Center for Collaborative Research and Development Department of Chemistry and Engineering Physics The
Standard Operating Procedure Nanosurf Atomic Force Microscopy Operation Facility NCCRD Nanotechnology Center for Collaborative Research and Development Department of Chemistry and Engineering Physics The
2015 Spin echoes and projection imaging
 1. Spin Echoes 1.1 Find f0, transmit amplitudes, and shim settings In order to acquire spin echoes, we first need to find the appropriate scanner settings using the FID GUI. This was all done last week,
1. Spin Echoes 1.1 Find f0, transmit amplitudes, and shim settings In order to acquire spin echoes, we first need to find the appropriate scanner settings using the FID GUI. This was all done last week,
Recording EPR spectra using the Loop Gap Resonator (LGR)
 Recording EPR spectra using the Loop Gap Resonator (LGR) This protocol gives step-by-step instructions for recording EPR spectra of spin labeled proteins (Nitroxide label like MTSSL) using the LGR assuming
Recording EPR spectra using the Loop Gap Resonator (LGR) This protocol gives step-by-step instructions for recording EPR spectra of spin labeled proteins (Nitroxide label like MTSSL) using the LGR assuming
Ultrahigh-resolution Total Correlation NMR Spectroscopy
 Ultrahigh-resolution Total Correlation NMR Spectroscopy Supporting Information Mohammadali Foroozandeh, Ralph W. Adams, Mathias Nilsson and Gareth A. Morris* All experimental spectra were recorded at a
Ultrahigh-resolution Total Correlation NMR Spectroscopy Supporting Information Mohammadali Foroozandeh, Ralph W. Adams, Mathias Nilsson and Gareth A. Morris* All experimental spectra were recorded at a
Fast Methods for Small Molecules
 Fast Methods for Small Molecules Technical Overview Throughput is a key concern in many NMR laboratories, and using faster methods is one way to increase it. Traditionally, multidimensional NMR requires
Fast Methods for Small Molecules Technical Overview Throughput is a key concern in many NMR laboratories, and using faster methods is one way to increase it. Traditionally, multidimensional NMR requires
CRL MASS SPECTROMETRY FACILITY INSTRUMENT USER MANUAL MALDI MICRO. Operating Instructions. Basement Spec Lab:
 CRL MASS SPECTROMETRY FACILITY INSTRUMENT USER MANUAL MALDI MICRO Operating Instructions Basement Spec Lab: 00.097 crs Page of 2 This is a guide to using the MALDI Micro for those who have received training.
CRL MASS SPECTROMETRY FACILITY INSTRUMENT USER MANUAL MALDI MICRO Operating Instructions Basement Spec Lab: 00.097 crs Page of 2 This is a guide to using the MALDI Micro for those who have received training.
Eclipse+ NMR Training Guide
 Eclipse+ NMR Training Guide Version 4.3.4 ECLIPSE+ NMR Training Guide Revision 20050617 Copyright 2005 by JEOL USA, Inc. Analytical Instruments Division 11 Dearborn Road Peabody, MA 01960 (978) 535-5900
Eclipse+ NMR Training Guide Version 4.3.4 ECLIPSE+ NMR Training Guide Revision 20050617 Copyright 2005 by JEOL USA, Inc. Analytical Instruments Division 11 Dearborn Road Peabody, MA 01960 (978) 535-5900
Operating Procedures for MICROCT1 Nikon XTH 225 ST
 Operating Procedures for MICROCT1 Nikon XTH 225 ST Ensuring System is Ready (go through to ensure all windows and tasks below have been completed either by you or someone else prior to mounting and scanning
Operating Procedures for MICROCT1 Nikon XTH 225 ST Ensuring System is Ready (go through to ensure all windows and tasks below have been completed either by you or someone else prior to mounting and scanning
Instruction manual for T3DS software. Tool for THz Time-Domain Spectroscopy. Release 4.0
 Instruction manual for T3DS software Release 4.0 Table of contents 0. Setup... 3 1. Start-up... 5 2. Input parameters and delay line control... 6 3. Slow scan measurement... 8 4. Fast scan measurement...
Instruction manual for T3DS software Release 4.0 Table of contents 0. Setup... 3 1. Start-up... 5 2. Input parameters and delay line control... 6 3. Slow scan measurement... 8 4. Fast scan measurement...
Laboratory Experiment #1 Introduction to Spectral Analysis
 J.B.Francis College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department 22-403 Laboratory Experiment #1 Introduction to Spectral Analysis Introduction The quantification of electrical energy can be accomplished
J.B.Francis College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department 22-403 Laboratory Experiment #1 Introduction to Spectral Analysis Introduction The quantification of electrical energy can be accomplished
7 Equipments. Spectrometers
 7 Equipments Spectrometers There are three spectrometers located in the NMR laboratory: Varian UNITYplus 500 MHz (NMR500), Varian UNITYplus 500 MHz (Nightmare) and Varian INOVA 600 MHz. All spectrometers
7 Equipments Spectrometers There are three spectrometers located in the NMR laboratory: Varian UNITYplus 500 MHz (NMR500), Varian UNITYplus 500 MHz (Nightmare) and Varian INOVA 600 MHz. All spectrometers
Engineering 3821 Fall Pspice TUTORIAL 1. Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill
 Engineering 3821 Fall 2003 Pspice TUTORIAL 1 Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill 2 INTRODUCTION The PSpice program is a member of the SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit
Engineering 3821 Fall 2003 Pspice TUTORIAL 1 Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill 2 INTRODUCTION The PSpice program is a member of the SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit
Ansoft Designer Tutorial ECE 584 October, 2004
 Ansoft Designer Tutorial ECE 584 October, 2004 This tutorial will serve as an introduction to the Ansoft Designer Microwave CAD package by stepping through a simple design problem. Please note that there
Ansoft Designer Tutorial ECE 584 October, 2004 This tutorial will serve as an introduction to the Ansoft Designer Microwave CAD package by stepping through a simple design problem. Please note that there
Bruker Dimension Icon AFM Quick User s Guide
 Bruker Dimension Icon AFM Quick User s Guide March 3, 2015 GLA Contacts Jingjing Jiang (jjiang2@caltech.edu 626-616-6357) Xinghao Zhou (xzzhou@caltech.edu 626-375-0855) Bruker Tech Support (AFMSupport@bruker-nano.com
Bruker Dimension Icon AFM Quick User s Guide March 3, 2015 GLA Contacts Jingjing Jiang (jjiang2@caltech.edu 626-616-6357) Xinghao Zhou (xzzhou@caltech.edu 626-375-0855) Bruker Tech Support (AFMSupport@bruker-nano.com
(N)MR Imaging. Lab Course Script. FMP PhD Autumn School. Location: C81, MRI Lab B0.03 (basement) Instructor: Leif Schröder. Date: November 3rd, 2010
 (N)MR Imaging Lab Course Script FMP PhD Autumn School Location: C81, MRI Lab B0.03 (basement) Instructor: Leif Schröder Date: November 3rd, 2010 1 Purpose: Understanding the basic principles of MR imaging
(N)MR Imaging Lab Course Script FMP PhD Autumn School Location: C81, MRI Lab B0.03 (basement) Instructor: Leif Schröder Date: November 3rd, 2010 1 Purpose: Understanding the basic principles of MR imaging
Brightness and Contrast Control Reference Guide
 innovation Series Scanners Brightness and Contrast Control Reference Guide A-61506 Part No. 9E3722 CAT No. 137 0337 Using the Brightness and Contrast Control This Reference Guide provides information and
innovation Series Scanners Brightness and Contrast Control Reference Guide A-61506 Part No. 9E3722 CAT No. 137 0337 Using the Brightness and Contrast Control This Reference Guide provides information and
The University of Texas at Austin Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Facility. Bruker EMX+ CW EPR Spectrometer
 The University of Texas at Austin Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Facility Bruker EMX+ CW EPR Spectrometer Contents: General Notes...2 Turning on the Instrument...2 Collecting a Spectrum...3 Turning off
The University of Texas at Austin Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Facility Bruker EMX+ CW EPR Spectrometer Contents: General Notes...2 Turning on the Instrument...2 Collecting a Spectrum...3 Turning off
Bruker Dimension Icon AFM Quick User s Guide
 Bruker Dimension Icon AFM Quick User s Guide August 8 2014 GLA Contacts Jingjing Jiang (jjiang2@caltech.edu 626-616-6357) Xinghao Zhou (xzzhou@caltech.edu 626-375-0855) Bruker Tech Support (AFMSupport@bruker-nano.com
Bruker Dimension Icon AFM Quick User s Guide August 8 2014 GLA Contacts Jingjing Jiang (jjiang2@caltech.edu 626-616-6357) Xinghao Zhou (xzzhou@caltech.edu 626-375-0855) Bruker Tech Support (AFMSupport@bruker-nano.com
Temps can range -130 to +120 C. See instructions below (part I). Such data can also be acquired on Athena and the AVANCE-360.
 Flourine-19 Experiments on Varian Spectrometers updated: 2010 May 12 The difficulty with 19 F experiments involving decoupling (or 2D heterocorrelation) is the close proximity of the 19 F resonant frequency
Flourine-19 Experiments on Varian Spectrometers updated: 2010 May 12 The difficulty with 19 F experiments involving decoupling (or 2D heterocorrelation) is the close proximity of the 19 F resonant frequency
P a g e 1 ST985. TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual. Analog Arts Inc.
 P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
SDI. Table of Contents
 NMSC-2 User Manual 2 Table of Contents Introduction........ 4 Hardware Installation.... 5 NMSC Power On.. 8 Overview... 9 FFT Measurement Screen.. 10 FFT Setup..... 11 FFT Detector..... 14 FFT Calibration.....
NMSC-2 User Manual 2 Table of Contents Introduction........ 4 Hardware Installation.... 5 NMSC Power On.. 8 Overview... 9 FFT Measurement Screen.. 10 FFT Setup..... 11 FFT Detector..... 14 FFT Calibration.....
EENG-201 Experiment # 4: Function Generator, Oscilloscope
 EENG-201 Experiment # 4: Function Generator, Oscilloscope I. Objectives Upon completion of this experiment, the student should be able to 1. To become familiar with the use of a function generator. 2.
EENG-201 Experiment # 4: Function Generator, Oscilloscope I. Objectives Upon completion of this experiment, the student should be able to 1. To become familiar with the use of a function generator. 2.
SigCal32 User s Guide Version 3.0
 SigCal User s Guide . . SigCal32 User s Guide Version 3.0 Copyright 1999 TDT. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical,
SigCal User s Guide . . SigCal32 User s Guide Version 3.0 Copyright 1999 TDT. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical,
CryoProbe RF ELECTRONICS
 CryoProbe RF ELECTRONICS Technical Manual Version 3 Bruker BioSpin The information in this manual may be altered without notice. Bruker BioSpin accepts no responsibility for actions taken as a result of
CryoProbe RF ELECTRONICS Technical Manual Version 3 Bruker BioSpin The information in this manual may be altered without notice. Bruker BioSpin accepts no responsibility for actions taken as a result of
MicroLab 500-series Getting Started
 MicroLab 500-series Getting Started 2 Contents CHAPTER 1: Getting Started Connecting the Hardware....6 Installing the USB driver......6 Installing the Software.....8 Starting a new Experiment...8 CHAPTER
MicroLab 500-series Getting Started 2 Contents CHAPTER 1: Getting Started Connecting the Hardware....6 Installing the USB driver......6 Installing the Software.....8 Starting a new Experiment...8 CHAPTER
Figure 1 The Raith 150 TWO
 RAITH 150 TWO SOP Figure 1 The Raith 150 TWO LOCATION: Raith 150 TWO room, Lithography area, NanoFab PRIMARY TRAINER: SECONDARY TRAINER: 1. OVERVIEW The Raith 150 TWO is an ultra high resolution, low voltage
RAITH 150 TWO SOP Figure 1 The Raith 150 TWO LOCATION: Raith 150 TWO room, Lithography area, NanoFab PRIMARY TRAINER: SECONDARY TRAINER: 1. OVERVIEW The Raith 150 TWO is an ultra high resolution, low voltage
LLS - Introduction to Equipment
 Published on Advanced Lab (http://experimentationlab.berkeley.edu) Home > LLS - Introduction to Equipment LLS - Introduction to Equipment All pages in this lab 1. Low Light Signal Measurements [1] 2. Introduction
Published on Advanced Lab (http://experimentationlab.berkeley.edu) Home > LLS - Introduction to Equipment LLS - Introduction to Equipment All pages in this lab 1. Low Light Signal Measurements [1] 2. Introduction
Fire CR Calibration Guide
 1 Fire CR Calibration Guide This reference guide will guide you through the steps to complete the calibration for the Fire CR.. Getting Started: 1. Click on the Opal Icon on the Desktop. Figure 1 2. Once
1 Fire CR Calibration Guide This reference guide will guide you through the steps to complete the calibration for the Fire CR.. Getting Started: 1. Click on the Opal Icon on the Desktop. Figure 1 2. Once
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer (600MHz)
 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer (600MHz) Specifications: State of the art analytical 600 MHz Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer with Multi Nuclear Liquid and Solid CP-MAS Probes. I. Spectrometer
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer (600MHz) Specifications: State of the art analytical 600 MHz Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer with Multi Nuclear Liquid and Solid CP-MAS Probes. I. Spectrometer
The oscilloscope and RC filters
 (ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 4 The oscilloscope and C filters The objective of this experiment is to familiarize the student with the workstation
(ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 4 The oscilloscope and C filters The objective of this experiment is to familiarize the student with the workstation
TV SIGNAL LEVEL METER USER MANUAL
 TV SIGNAL LEVEL METER USER MANUAL - 0 - 1. Overview (1) (1) RF input (2) (3) A D E B C (2) Speaker (3) LCD display (4) Charger indicator (5) RS232 communication port (6) DC-IN port F G A. The battery icon
TV SIGNAL LEVEL METER USER MANUAL - 0 - 1. Overview (1) (1) RF input (2) (3) A D E B C (2) Speaker (3) LCD display (4) Charger indicator (5) RS232 communication port (6) DC-IN port F G A. The battery icon
LTSpice Basic Tutorial
 Index: I. Opening LTSpice II. Drawing the circuit A. Making Sure You Have a GND B. Getting the Parts C. Placing the Parts D. Connecting the Circuit E. Changing the Name of the Part F. Changing the Value
Index: I. Opening LTSpice II. Drawing the circuit A. Making Sure You Have a GND B. Getting the Parts C. Placing the Parts D. Connecting the Circuit E. Changing the Name of the Part F. Changing the Value
VnmrJ Liquids NMR User Guide. Varian NMR Spectrometer Systems with VnmrJ Software Pub. No , Rev. A0604
 VnmrJ Liquids NMR User Guide Varian NMR Spectrometer Systems with VnmrJ Software Pub. No. 01-999250-00, Rev. A0604 VnmrJ Liquids NMR User Guide Varian NMR Spectrometer Systems with VnmrJ Software Pub.
VnmrJ Liquids NMR User Guide Varian NMR Spectrometer Systems with VnmrJ Software Pub. No. 01-999250-00, Rev. A0604 VnmrJ Liquids NMR User Guide Varian NMR Spectrometer Systems with VnmrJ Software Pub.
Figure AC circuit to be analyzed.
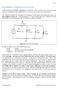 7.2(1) MULTISIM DEMO 7.2: INTRODUCTION TO AC ANALYSIS In this section, we ll introduce AC Analysis in Multisim. This is perhaps one of the most useful Analyses that Multisim offers, and we ll use it in
7.2(1) MULTISIM DEMO 7.2: INTRODUCTION TO AC ANALYSIS In this section, we ll introduce AC Analysis in Multisim. This is perhaps one of the most useful Analyses that Multisim offers, and we ll use it in
PHY3902 PHY3904. Nuclear magnetic resonance Laboratory Protocol
 PHY3902 PHY3904 Nuclear magnetic resonance Laboratory Protocol PHY3902 PHY3904 Nuclear magnetic resonance Laboratory Protocol GETTING STARTED You might be tempted now to put a sample in the probe and try
PHY3902 PHY3904 Nuclear magnetic resonance Laboratory Protocol PHY3902 PHY3904 Nuclear magnetic resonance Laboratory Protocol GETTING STARTED You might be tempted now to put a sample in the probe and try
Alibre Design Tutorial: Loft, Extrude, & Revolve Cut Loft-Tube-1
 Alibre Design Tutorial: Loft, Extrude, & Revolve Cut Loft-Tube-1 Part Tutorial Exercise 5: Loft-Tube-1 [Complete] In this Exercise, We will set System Parameters first, then part options. Then, in sketch
Alibre Design Tutorial: Loft, Extrude, & Revolve Cut Loft-Tube-1 Part Tutorial Exercise 5: Loft-Tube-1 [Complete] In this Exercise, We will set System Parameters first, then part options. Then, in sketch
Principios Básicos de RMN en sólidos destinado a usuarios. Gustavo Monti. Fa.M.A.F. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba Argentina
 Principios Básicos de RMN en sólidos destinado a usuarios Gustavo Monti Fa.M.A.F. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba Argentina magnet 1 2 4 5 6 computer 3 Block diagrama of a traditional NMR spectrometer.
Principios Básicos de RMN en sólidos destinado a usuarios Gustavo Monti Fa.M.A.F. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba Argentina magnet 1 2 4 5 6 computer 3 Block diagrama of a traditional NMR spectrometer.
Acceptance Solid State NMR Test Procedure. for Avance NMR Systems
 Acceptance Solid State NMR Test Procedure for Avance NMR Systems Manual P/N B92999 Acceptance Solid State NMR Test Procedures for AVANCE systems Index: 04 Number: B92999 Page: 1 (42) 1. Purpose 2. Area
Acceptance Solid State NMR Test Procedure for Avance NMR Systems Manual P/N B92999 Acceptance Solid State NMR Test Procedures for AVANCE systems Index: 04 Number: B92999 Page: 1 (42) 1. Purpose 2. Area
SigCalRP User s Guide
 SigCalRP User s Guide . . Version 4.2 Copyright 1997 TDT. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose
SigCalRP User s Guide . . Version 4.2 Copyright 1997 TDT. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose
Table 1. Placing the Sensor in the Sensor Cradle. Step Instruction Illustration
 Table 1. Placing the Sensor in the Sensor Cradle Step Instruction Illustration 1. A. Check "U-shaped" Positioner. The number pointing towards the Sensor (1 or 2) must correspond with the Sensor's size.
Table 1. Placing the Sensor in the Sensor Cradle Step Instruction Illustration 1. A. Check "U-shaped" Positioner. The number pointing towards the Sensor (1 or 2) must correspond with the Sensor's size.
Introduction to Simulink Assignment Companion Document
 Introduction to Simulink Assignment Companion Document Implementing a DSB-SC AM Modulator in Simulink The purpose of this exercise is to explore SIMULINK by implementing a DSB-SC AM modulator. DSB-SC AM
Introduction to Simulink Assignment Companion Document Implementing a DSB-SC AM Modulator in Simulink The purpose of this exercise is to explore SIMULINK by implementing a DSB-SC AM modulator. DSB-SC AM
Guide to Varian Spectrometers running VnmrJ
 Guide to Varian Spectrometers running VnmrJ David N.M. Jones Department of Pharmacology and Program in Biomolecular Structure University of Colorado Denver and Health Sciences Center All original material
Guide to Varian Spectrometers running VnmrJ David N.M. Jones Department of Pharmacology and Program in Biomolecular Structure University of Colorado Denver and Health Sciences Center All original material
ADI-100 Interrupter. Operator s Manual. 526 S. Seminole Bartlesville, OK /
 ADI-100 Interrupter Operator s Manual 526 S. Seminole Bartlesville, OK 74003 918/336-1221 www.sescocp.com ADI - 100 Interrupter FEATURES Clock Accuracy 100% during GPS lock Clock Drift 30 µsec per degree
ADI-100 Interrupter Operator s Manual 526 S. Seminole Bartlesville, OK 74003 918/336-1221 www.sescocp.com ADI - 100 Interrupter FEATURES Clock Accuracy 100% during GPS lock Clock Drift 30 µsec per degree
Chem 203 December 15, Final Exam Part II Problem 3 of 3 (30 points)
 Name: Chem 203 December 15, 2012 Final Exam Part II Problem 3 of 3 (30 points) Select and submit TWO OUT OF THE THREE PROBLEMS FROM PART II for grading. Do not submit three problems. If you wish to unstaple
Name: Chem 203 December 15, 2012 Final Exam Part II Problem 3 of 3 (30 points) Select and submit TWO OUT OF THE THREE PROBLEMS FROM PART II for grading. Do not submit three problems. If you wish to unstaple
Experiment 2: Electronic Enhancement of S/N and Boxcar Filtering
 Experiment 2: Electronic Enhancement of S/N and Boxcar Filtering Synopsis: A simple waveform generator will apply a triangular voltage ramp through an R/C circuit. A storage digital oscilloscope, or an
Experiment 2: Electronic Enhancement of S/N and Boxcar Filtering Synopsis: A simple waveform generator will apply a triangular voltage ramp through an R/C circuit. A storage digital oscilloscope, or an
BRUKER BSMS. BSMS User Manual. Version 002
 BRUKER BSMS BSMS User Manual Version 002 The information in this manual may be altered without notice. Bruker accepts no responsibility for actions taken as a result of use of this manual. Bruker accepts
BRUKER BSMS BSMS User Manual Version 002 The information in this manual may be altered without notice. Bruker accepts no responsibility for actions taken as a result of use of this manual. Bruker accepts
Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015
 ECE214: Electrical Circuits Laboratory Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015 1 Introduction In this lab you will investigate the magnitude and phase shift that occurs in an RC circuit
ECE214: Electrical Circuits Laboratory Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015 1 Introduction In this lab you will investigate the magnitude and phase shift that occurs in an RC circuit
DS-0321 FFT Analysis Software
 DS-0321 FFT Analysis Software Operation manual Damping factor measurement using Hilbert transform ONO SOKKI CO., LTD. The DS-0321 FFT Analysis software has the Hilbert operation function. A time envelope
DS-0321 FFT Analysis Software Operation manual Damping factor measurement using Hilbert transform ONO SOKKI CO., LTD. The DS-0321 FFT Analysis software has the Hilbert operation function. A time envelope
EPR spectrometer & components
 EPR spectrometer & components Water lines µ wave bridge 293.2 VC41 Gas Flow Controller Temperature Controller Vacuum pump for cryostat on left hand side water chiller HASKRIS EMX EPR Spectrometer EMX Magnet
EPR spectrometer & components Water lines µ wave bridge 293.2 VC41 Gas Flow Controller Temperature Controller Vacuum pump for cryostat on left hand side water chiller HASKRIS EMX EPR Spectrometer EMX Magnet
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss AxioZoom V16 Stereo Microscope
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss AxioZoom V16 Stereo Microscope ZEN 2012 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 If you require fluorescence imaging,
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss AxioZoom V16 Stereo Microscope ZEN 2012 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 If you require fluorescence imaging,
Module 1 Experimental Procedures. Experiment 1. What s in the Spectrometer?
 Module 1 Experimental Procedures Experiment 1. What s in the Spectrometer? Identify elements of the spectrometer shown in Fig. 9 in the open spectrometer unit and identify the path of the light. Experiment
Module 1 Experimental Procedures Experiment 1. What s in the Spectrometer? Identify elements of the spectrometer shown in Fig. 9 in the open spectrometer unit and identify the path of the light. Experiment
Contents STARTUP MICROSCOPE CONTROLS CAMERA CONTROLS SOFTWARE CONTROLS EXPOSURE AND CONTRAST MONOCHROME IMAGE HANDLING
 Operations Guide Contents STARTUP MICROSCOPE CONTROLS CAMERA CONTROLS SOFTWARE CONTROLS EXPOSURE AND CONTRAST MONOCHROME IMAGE HANDLING Nikon Eclipse 90i Operations Guide STARTUP Startup Powering Up Fluorescence
Operations Guide Contents STARTUP MICROSCOPE CONTROLS CAMERA CONTROLS SOFTWARE CONTROLS EXPOSURE AND CONTRAST MONOCHROME IMAGE HANDLING Nikon Eclipse 90i Operations Guide STARTUP Startup Powering Up Fluorescence
Free vibration of cantilever beam FREE VIBRATION OF CANTILEVER BEAM PROCEDURE
 FREE VIBRATION OF CANTILEVER BEAM PROCEDURE AIM Determine the damped natural frequency, logarithmic decrement and damping ratio of a given system from the free vibration response Calculate the mass of
FREE VIBRATION OF CANTILEVER BEAM PROCEDURE AIM Determine the damped natural frequency, logarithmic decrement and damping ratio of a given system from the free vibration response Calculate the mass of
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3)
 Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
NMR Spectrometer Hardware
 NMR Spectrometer Hardware Manoj Naik NMR Facility, TIFR Workshop on NMR & its applications TIFR, Mumbai November 23, 2009 Principle of NMR ω = γ B Nuclear Magnetic Resonance A Simplified 6 0 MHz NMR Spectrometer
NMR Spectrometer Hardware Manoj Naik NMR Facility, TIFR Workshop on NMR & its applications TIFR, Mumbai November 23, 2009 Principle of NMR ω = γ B Nuclear Magnetic Resonance A Simplified 6 0 MHz NMR Spectrometer
Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software
 Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software In this chapter, we introduce the use of analog circuit simulation software and circuit layout software. I. Introduction So far we have designed
Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software In this chapter, we introduce the use of analog circuit simulation software and circuit layout software. I. Introduction So far we have designed
ENSC327 Communication Systems Fall 2011 Assignment #1 Due Wednesday, Sept. 28, 4:00 pm
 ENSC327 Communication Systems Fall 2011 Assignment #1 Due Wednesday, Sept. 28, 4:00 pm All problem numbers below refer to those in Haykin & Moher s book. 1. (FT) Problem 2.20. 2. (Convolution) Problem
ENSC327 Communication Systems Fall 2011 Assignment #1 Due Wednesday, Sept. 28, 4:00 pm All problem numbers below refer to those in Haykin & Moher s book. 1. (FT) Problem 2.20. 2. (Convolution) Problem
The ideal K-12 science microscope solution. User Guide. for use with the Nova5000
 The ideal K-12 science microscope solution User Guide for use with the Nova5000 NovaScope User Guide Information in this document is subject to change without notice. 2009 Fourier Systems Ltd. All rights
The ideal K-12 science microscope solution User Guide for use with the Nova5000 NovaScope User Guide Information in this document is subject to change without notice. 2009 Fourier Systems Ltd. All rights
UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL. FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS REV1
 UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 - REV1 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 3 3.1. Display
UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 - REV1 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 3 3.1. Display
Lab Reference Manual. ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits. Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 Lab Reference Manual ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Contents 1. Circuit Analysis in PSpice 3 1.1 Transient and DC Analysis 3 1.2 Measuring
Lab Reference Manual ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Contents 1. Circuit Analysis in PSpice 3 1.1 Transient and DC Analysis 3 1.2 Measuring
Avance GRASP. Installation/User Manual BRUKER. Version
 Avance GRASP Installation/User Manual Version 002 BRUKER The information in this manual may be altered without notice. BRUKER accepts no responsibility for actions taken as a result of use of this manual.
Avance GRASP Installation/User Manual Version 002 BRUKER The information in this manual may be altered without notice. BRUKER accepts no responsibility for actions taken as a result of use of this manual.
AutoTest for VnmrJ. Varian NMR Spectrometer Systems Pub. No , Rev. A0604
 AutoTest for VnmrJ Varian NMR Spectrometer Systems Pub. No. 01-999247-00, Rev. A0604 AutoTest for VnmrJ Varian NMR Spectrometer Systems Pub. No. 01-999247-00, Rev. A0604 AutoTest for VnmrJ Varian NMR Spectrometer
AutoTest for VnmrJ Varian NMR Spectrometer Systems Pub. No. 01-999247-00, Rev. A0604 AutoTest for VnmrJ Varian NMR Spectrometer Systems Pub. No. 01-999247-00, Rev. A0604 AutoTest for VnmrJ Varian NMR Spectrometer
