Baroque. Premise. Timeline: Overview/History [CHP. 17 THE BAROQUE STYLE IN WESTERN EUROPE] P AGE 1
|
|
|
- Robyn King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 [CHP. 17 THE BAROQUE STYLE IN WESTERN EUROPE] P AGE 1 Baroque The Baroque era began in Rome, and then spread to the rest of Europe It included the 17 th and most of the 18 th centuries. In general, it took all the innovations of the Renaissance and combined them with the drama of Mannerism. Having learned all the Renaissance techniques, Baroque artists could represent the human form convincingly from any angle, they could portray the most complex forms in perfect perspective, and could reproduce almost anything in the seen world realistically The main differences between the Baroque and Renaissance art are that Renaissance art is rational and static, while Baroque art is emotional and dynamic It s useful to recall and compare Michelangelo s David and Bernini s David to draw the distinction. Baroque took on a different character in each of its major geographic locations. But in general, we could say that Baroque art is characterized by strong emotion and energy; dramatic lighting, scale and balance In essence, it was a great deal more intense, and more theatrical than the art of the Renaissance. The major artists of the Italian Baroque were the Painter Caravaggio, and the sculptor Bernini The most renowned artist of the Flemish Baroque was Peter Paul Rubens. The three great masters of the Dutch Baroque were Hals, Rembrandt, and Vermeer Finally, Velasquez was the most gifted artist of the Spanish Baroque. Premise Encompasses the period between 1600 and 1750 (17th and most of the 18th centuries) Began in Rome, then spread to the rest of Europe. In general, it took all the innovations of the Renaissance and combined them with the drama of Mannerism. In its efforts to counter the Reformation, the Roman Catholic Church encouraged visual forms that appealed to the senses and excited religious feeling. Artists portrayed miracles with drama and realism. The central theme of Baroque art and literature is the conflict between reason with passion. Idealism of the High Renaissance gave way to Baroque realism and an art that is often look ornate, dynamic, with greater color saturation and more contrast between light and shadow; by comparison Renaissance styles look relatively static. The Baroque diversity in subject matter and style is most apparent in Dutch art which includes a style of art that might be characterized as Realist art, focusing on the atmospheric effects of dramatic shadow and lighting. Timeline: 1543 to 1565 Council of Trent Papacy of Paul V (Borghese) 1609 Galileo invents telescope 1620 Francis Bacon writes Novum Organum Papacy of Urban VIII (Barberini) 1637 Descartes writes Discourse on Method Papacy of Innocent X (Pamphili) Newton ( ) Overview/History Baroque encompasses the period between 1600 and 1750 (17th and most of the 18th centuries) began in Rome, then spread to the rest of Europe In general, it took all the innovations of the Renaissance and combined them with the drama of Mannerism. Having learned all the Renaissance techniques, Baroque artists could represent the human form convincingly from any angle, they could portray the most complex forms in perfect perspective, and could reproduce almost anything in the seen world realistically. The main differences between the Baroque and Renaissance art are that Renaissance art is rational and static, while Baroque art is emotional and dynamic characterized by strong emotion and energy; dramatic lighting, scale and balance. In essence, Baroque art was a great deal more intense, and more theatrical than the art of the Renaissance.
2 [CHP. 17 THE BAROQUE STYLE IN WESTERN EUROPE] P AGE 2 Baroque took on a different character in each of its major geographic locations. The Baroque style is often subdivided into an aristocratic and a bourgeois (middle class) style. Both styles emphasize portraiture. Other principal themes include episodes from classical mythology (aristocratic style) and stories from the Bible and genre scenes (bourgeois style). In the later Rococo style, subject matter is devoted almost exclusively to earthy parables on the vicissitudes of amatory love. Major artists of the regions: Italian Baroque: Caravaggio and Bernini Flemish Baroque: Peter Paul Rubens. Dutch Baroque: Hals, Rembrandt, and Vermeer Spanish Baroque: Velasquez Diversity in subject matter and style: era when subjects such as the everyday activities of people, the landscape, and still life became acceptable themes for artists to depict. The central theme THEME of Baroque art and literature is the conflict between reason with passion. Idealism of the High Renaissance gave way to Baroque realism and an art that is often look ornate, dynamic, with greater color saturation and more contrast between light and shadow; by comparison Renaissance styles look relatively static. The Baroque diversity in subject matter and style is most apparent in Dutch art which includes a style of art that might be characterized as Realist art, focusing on the atmospheric effects of dramatic shadow and lighting. Variety of Baroque styles, including classicism (Common traits of 17th & 18th centuries) 1. spacious and dynamic 2. brilliant and colorful 3. theatrical and passionate 4. sensual and ecstatic 5. opulent and extravagant 6. versatile and virtuoso 7. embrace viewer Caravaggio and St. Peter s Baroque Artistic Characteristics / Devices Written program (like telling a story) everything has meaning Breathtaking Movement Naturalism breaks into viewers space heightened emotionalism exaltation light, dancing, chiaroscuro (strong), symbol of God spotlight, just appears, window The real moment in action Immediacy Psychological self portrait inwardness mystery of individual Visual game Las Meninas Genre everyday objects, subject matter, people, activities (domestic) Drama Rembrandt s group portraits, Light Tensions between:... light and dark real and unreal illusion and reality concave and convex certainty and uncertainty passion and intellectual earthly and heavenly naturalism and classicism classicism and romanticism
3 [CHP. 17 THE BAROQUE STYLE IN WESTERN EUROPE] P AGE 3 religious and non religious sensual, passion and prof. math & fancy love and creation Christianity and empire (Charles) BAROQUE IN ITALY Sculpture and Architecture Bernini St. Peter's Colonnade, Rome, begun 1656 collonade was created for growing numbers who visit the St. Peter's Basilica Baldacchino, St. Peter's, Rome, , gilded bronze, 95' high was created to create a more human scale in the interior of St. Peter's The Ecstacy of St. Teresa, created inside St. Peter's David, 1623, marble, lifesize a more dynamic and literal version compared to Michelangelo and Donatello Painting Baroque painting had many of the same attributes that Baroque sculpture and architecture had: theatrics, sexual innuendo, and violent subjects. Giovanni Pietro Bellori was an influential Baroque art critic who fervently believed that "ideal" and Classical forms were more desirable than naturalistic or "more realistic" images. Annibale Carracci( ) ideal and Classical a favorite of Bellori because of his use of "ideal" forms. The Virgin Appearing to St. Luke and St. Catherine, 1592, Oil on canvas Carravaggio ( ) naturalistic and "real" Italian painter who influenced most of the painters of his time through his use of great contrasts and theatrical lighting was a murderer (condottieri) and had a violent nature in works are characteristic dark backgrounds and bright highlights called tenebroso also uses many diagonals which makes a composition more active The Calling of Saint Matthew, , Oil on canvas Judith Beheading Holofernes, c. 1598, Oil on canvas The Conversion of Saint Paul, , Oil on canvas Artemisia Gentileschi ( ) a master female artist from the Baroque era did Biblical and mythological subjects which portrayed violent themes Judith Beheading Holofernes, 1620, Oil on canvas Italian Baroque Caravaggio ( ) Bernini Northern Europe Baroque Flemish Baroque (Flanders) Peter Paul Rubens ( ) wealthy trader, diplomat, and artist from Flanders
4 [CHP. 17 THE BAROQUE STYLE IN WESTERN EUROPE] P AGE 4 influential in art because he bucked trends and worked in a painterly fashion (the brush strokes were active and easily recognized in the painting. The Garden of Love, c , Oil on canvas Rape of the Daughters 0f Leucippus c.1635, oil on canvas, 6.5'x 8' active painting with sensual overtones mythological subject at the time of the Reformation soft, painterly look Dutch Baroque The Netherlands Rembrandt van Rijn ( ) conveyed character and drama through his use of dark and light Self Portraits conveyed these ideas of character in light and shadow they are also a chronicle of a person's life, because he did them each year Rembrandt was an excellent printmaker. He used a process called etching. This is a process that involves scratching into a metal plate, which has been covered with an acid resistant coating, then dipping the plate in acid until it mars the surface of the plate. The plate is then washed, ink is pushed into the grooves left by the acid, and finally it is printed on paper. The Little Children Being Brought to Jesus ("The 100 Guilder Print"), Completed , Etching and drypoint, 1st state The company of Frans Banning Cock preparing to march out, known as the Nightwatch, 1642, Oil on canvas Abraham and Isaac, 1634, Oil on canvas Jan Vermeer ( ) master of light and perspective. works were technically correct to the finest detail Dutch banker and mapmaker View of Delft, c , Oil on canvas The Art of Painting, c , Oil on canvas Woman Holding a Water Pitcher c , oil on canvas, 16"x 15" exceptional perspective, convincing 3 D space dramatic lighting high detail Hals Dutch Baroque Spanish Baroque Diego Velasquez ( ) court painter for Philip IV of Spain Las Meninas, 1656, Oil on canvas "Maids of Honor" (English translation) is a view into the artist's studio and the Royal family's lives. Innocent X, c France Nicholas Poussin used Classical subject matter allegorical painter (he used a picture of mythological scenes to convey ideas about Christianity) allegories are intended to convey an idea through analogy and metaphor. saw a connection between art and music Most painters of the 17th and 18th Centuries allied themselves with either the Rubenists (bright vibrant color, painterliness, and exuberant brushwork) or the Poussinists (classical, idealist, and used a limited palette). The Rape of the Sabine Women, , Oil on canvas
5 [CHP. 17 THE BAROQUE STYLE IN WESTERN EUROPE] P AGE 5 Landscape with the Funeral of Phocion, 1648, Oil on canvas Phocion was a Greek who was executed because he would not conceal the truth. It is a comment on the Stoic nature of Phocion and reflects this in its sharp detail and calm. Part 5: Unit Exam Essay Questions Define the Baroque style of art. What were its visual characteristics? Name two artists whose works exemplify Baroque art. Discuss the artistic contributions of Rembrandt. Use examples of his paintings to illustrate your answer. Using examples in your text compare Baroque and Renaissance pictorial style. Compare Bernini's David to Michelangelo's David, showing how they illustrate the Baroque and Renaissance styles respectively. Define the Baroque style of art. What were its visual characteristics? Name two artists whose works exemplify Baroque art and use their work to help describe the Baroque stylistic period. Discuss the artistic contributions of Rembrandt. Use examples of his paintings to illustrate your answer. Discuss the political developments of the 17th century in western Europe. How did they affect the arts? Using examples in your text, compare Baroque and Renaissance pictorial style. Explain the iconography of Bernini's Pluto and Proserpina. What myth is it based on, and how is it reflected in the sculpture's style? Describe the Baroque, Renaissance, and Gothic elements of St. Paul's Cathedral in London. Compare Bernini's David to Michelangelo's David, analyzing how they exemplify the Baroque and Renaissance styles respectively. Compare Caravaggiois tenebrism with Leonardo's chiaroscuro, using the examples in your textbook. Discuss the role of women in the arts from Antiquity through the seventeenth century. Cite examples from your textbook. Discuss the political developments of the 17th century in Western Europe. How did they affect the arts? Using examples in your text, compare Baroque and Renaissance pictorial style. Explain the iconography of Bernini's Pluto and Proserpina. What is it based on, and how is it reflected in the style? Describe the Baroque, Renaissance and Gothic elements of St. Paul's Cathedral in London. Compare Bernini's David to Michelangelo's David, showing how they illustrate the Baroque and Renaissance styles respectively. Compare Caravaggio's tenebrism with Leonardo's chiaroscuro, using the examples in your textbook. Discuss the role of women in the arts from Antiquity through the seventeenth century. Cite examples from your textbook Chapter Outline (AAT4) THE BAROQUE STYLE IN WESTERN EUROPE, 17th CENTURY Age of Absolutism: Louis XIV of France; Philip IV of Spain; Charles I of England Heliocentrism and advances in science: Kepler; Copernicus; Galileo; Newton Thirty Years' War ( ) Treaty of Westphalia (1648) Dutch East India Company; the rise of capitalism Charles I of England executed (1649) Oliver Cromwell ( ) Witch craze in Europe and New England Lives of the Artists: Bellori; van Mander, The Painter's Book New Saint Peter's completed Great Fire of London (1666) Wren builds Saint Paul's, the first Protestant cathedral, in London Urban VIII (papacy ) New genres in painting: landscape; vanitas; still life Italian artists: Bernini; Borromini; Caravaggio; Gentileschi; the Carracci; Pietro da Cortona; Gaulli Flanders: Rubens; van Dyck Dutch Republic: Rembrandt; Hals; Leyster; Vermeer; Ruisdael; Oosterwyck; Etching and drypoint France: The Louvre The Court of Versailles: LeBrun; Tuby; Le Vau; Perrault; Le Nôtre, Hardouin Mansart French Academy founded (1648) Poussin: theory of artistic modes
6 [CHP. 17 THE BAROQUE STYLE IN WESTERN EUROPE] P AGE 6 Lorrain: pastoral landscape Spain: Cotán; Zurburán; Velázquez Define or identify the following terms: Academy (a) the gymnasium near Athens where Plato taught; (b) from the eighteenth century, the cultural and artistic establishment and the standards that they represent. aedicule asymmetrical baldacchino balustrade burr calligraphy camera obscura cantilever château chattra clerestory drypoint etching etching ground foreshortening gable (or pitched) roof impasto mausoleum, mausolea minaret miniature obelisk podium rectilinear section silhouette state stupa stylus tenebrism travertine (a) a small building used as a shrine; (b) a niche designed to hold a statue. Both types are formed by two columns or pilasters supporting a gable or pediment. characterized by asymmetry, or lack of balance, in the arrangement of parts or components. a canopy or canopylike structure above an altar or throne. a series of balusters, or upright pillars, supporting a rail (as along the edge of a balcony or bridge). in etching, the rough ridge left projecting above the surface of an engraved plate where the design has been incised. handwriting designed to be beautiful; calligraphic writing or drawing can be expressive as well as beautiful. a dark enclosure or box into which light is admitted through a small hole, enabling images to be projected onto a wall or screen placed opposite that hole; the forerunner of the photographic camera. a long, low architectural support that enables a cantilevered element such as an eave or a cornice to project horizontally without vertical support at the far end. French word for a castle or large country house. a royal parasol crowning the dome (an.d.a) of a Buddhist stupa, symbolically honoring the Buddha. the upper part of the main outer wall of a building (especially a church), located above an adjoining roof and admitting light through a row of windows. an engraving in which the image is scratched directly into the surface of a metal plate with a pointed instrument. (a) a printmaking process in which an impression is taken from a metal plate on which the image has been etched, or eaten away by acid; (b) a print produced by such a process. a resinous, acid resistant substance used to cover a copper plate before an image is etched on it. the use of perspective to represent a single object extending back in space at an angle to the picture plane. a roof formed by the intersection of two planes sloping down from a central beam. the thick application of paint, usually oil or acrylic, to a canvas or panel. an elaborate tomb (named for Mausolos, a fourth century b.c. ruler commemorated by a magnificent tomb at Halikarnassos). a tall, slender tower attached to a mosque, from which the muezzin calls the Muslim faithful to prayer. a representation executed on a much smaller scale than the original object. a tall, four sided stone, usually monolithic, that tapers toward the top and is capped by a pyramidion. (a) the masonry forming the base of a temple; (b) a raised platform or pedestal. consisting of, bounded by, or moving in, a straight line or lines. a diagrammatic representation of a building intersected by a vertical plane. the outline of an object, usually filled in with black or some other uniform color. one of the successive printed stages of a print, distinguished from other stages by the greater or lesser amount of work carried out on the image. in Buddhist architecture, a dome shaped or rounded structure made of brick, earth, or stone, containing the relic of a Buddha or other honored individual. a pointed instrument used in antiquity for writing on clay, wax, papyrus, and parchment; a pointed metal instrument used to scratch an image on the plate used to produce an etching. a style of painting used by Caravaggio and his followers in which most objects are in shadow, while a few are brightly illuminated. a hard limestone used as a building material by the Etruscans and Romans.
7 vanitas [CHP. 17 THE BAROQUE STYLE IN WESTERN EUROPE] P AGE 7 a category of painting, often a still life, the theme of which is the transitory nature of earthly things and the inevitability of death. France Georges de La Tour, St. Joseph the Carpenter, c.1645 Louis Le Nain, Family of Country People, c.1640, oil on canvas Jacques Callot, The Hanging Tree from Miseries of War, 1621, etching Nicholas Poussin, Abduction of the Sabine Women, c , oil on canvas Nicholas Poussin, Burial of Phocion, 1648, oil on canvas Claude Perrault, Louis Le Vau, and Charles Le Brun, east facade of the Louvre, Paris, Louis Le Vau and Jules Hardouin Mansart, Palace of Versailles, Versailles, France, b.1669 Hall of Mirrors (Galerie des Glaces), Palace of Versailles André Le Nôtre, gardens of the Palace of Versailles England Christopher Wren, new St. Paul s Cathedral, London, Other topics to consider: Explain the iconography of Bernini's Pluto and Proserpina. What is it based on, and how is it reflected in the style? Describe the Baroque, Renaissance and Gothic elements of St. Paul's Cathedral in London. Summary Baroque art is not single style, nor is it the contribution of any single center. It is: o truly international variety of expressions o differences in Baroque styles were no longer regional on a provincial basis. o artists of many different personalities and persuasions. The achievements of the Renaissance had brought about the ability of artists to depict the visual world as they chose. In many instances, Baroque artists chose to crete art that was the theatrical or dramatic moment. Styles of the past were also beginning to be seen as historically significant. the experience of the senses was also to be exploited. Artists frequently worked for long periods in lands far from their homes. Graphic arts, easily transported, brought replicas of the great works of leading masters to opposite ends of the world. The ravages of political and religious wars still continued. Baroque artists and their patrons began to use art as a form of social consciousness raising
If it s not Baroque, don t fix it! 17 century Art
 5 L s If it s not Baroque, don t fix it! th 17 century Art Look up (lots of painted ceilings) Light (chiaroscuro and tenebrism) Life (vanitas still lifes) Levels (meanings and symbolism) Lands (landscapes,
5 L s If it s not Baroque, don t fix it! th 17 century Art Look up (lots of painted ceilings) Light (chiaroscuro and tenebrism) Life (vanitas still lifes) Levels (meanings and symbolism) Lands (landscapes,
Irregular Pear or Stone
 BAROQUE ART Irregular Pear or Stone 16 th century Throughout Europe = religious tension - Protestants broke away from Roman Catholic Church. response to the Protestant Reformation, Catholic Church initiated
BAROQUE ART Irregular Pear or Stone 16 th century Throughout Europe = religious tension - Protestants broke away from Roman Catholic Church. response to the Protestant Reformation, Catholic Church initiated
Gardner s Art Through the Ages, 13e. Chapter 25 Northern Europe, 1600 to 1700
 Gardner s Art Through the Ages, 13e Chapter 25 Northern Europe, 1600 to 1700 1 Europe in the 17 th Century 2 Goals Recognize the distinctive characteristics of the Baroque style Understand the diversity
Gardner s Art Through the Ages, 13e Chapter 25 Northern Europe, 1600 to 1700 1 Europe in the 17 th Century 2 Goals Recognize the distinctive characteristics of the Baroque style Understand the diversity
Ecstacy of Santa Teresa by Bernini
 Baroque Art Baroque Sculptures David by Bernini Bernini's David was completed when Bernini was 25. David is posed to release the rock. Captures the heroic moment not the heroic nature the other davids
Baroque Art Baroque Sculptures David by Bernini Bernini's David was completed when Bernini was 25. David is posed to release the rock. Captures the heroic moment not the heroic nature the other davids
Triumph of Divine Providence Pietro da Cortona
 Triumph of Divine Providence Pietro da Cortona 1633-1639 Baroque Architecture and Art Defining the Baroque A reaction against the symmetry and balanced style of the Renaissance Incorporates more MOTION
Triumph of Divine Providence Pietro da Cortona 1633-1639 Baroque Architecture and Art Defining the Baroque A reaction against the symmetry and balanced style of the Renaissance Incorporates more MOTION
Baroque. From the Portuguese word barocca pearl of irregular shape. Implies strangeness, irregularity, extravagance
 Baroque 1600-1750 Baroque From the Portuguese word barocca pearl of irregular shape. Implies strangeness, irregularity, extravagance The term baroque was not a complement it originally meant overdone too
Baroque 1600-1750 Baroque From the Portuguese word barocca pearl of irregular shape. Implies strangeness, irregularity, extravagance The term baroque was not a complement it originally meant overdone too
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2012 2 hours 15 minutes *2574265004*
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2012 2 hours 15 minutes *2574265004*
(D) sfumato (C) Greek temple architecture
 1. All of the following are humanistic traits in the above statue by Michelangelo EXCEPT (A) use of marble (B) contrapposto stance (C) free-standing sculpture (D) sfumato (E) glorification of the human
1. All of the following are humanistic traits in the above statue by Michelangelo EXCEPT (A) use of marble (B) contrapposto stance (C) free-standing sculpture (D) sfumato (E) glorification of the human
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject www.xtremepapers.com ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2013 2
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject www.xtremepapers.com ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2013 2
Chapter 22 AP Art History
 Chapter 22 AP Art History Students will be able to Assess the impact of the Council of Trent s guidelines for the Counter-Reformation art of the Roman Catholic Church. Explore how the work of Bernini and
Chapter 22 AP Art History Students will be able to Assess the impact of the Council of Trent s guidelines for the Counter-Reformation art of the Roman Catholic Church. Explore how the work of Bernini and
The Martyrdom of Saint Matthew by Caravaggio. The Elevation of the Cross by Peter Paul Rubens
 The Martyrdom of Saint Matthew by Caravaggio Painted in 1599-1600, this piece uses strong contrasts of light and dark, chiaroscuro, to provide drama, as well as the hugely exaggerated positions and emotions
The Martyrdom of Saint Matthew by Caravaggio Painted in 1599-1600, this piece uses strong contrasts of light and dark, chiaroscuro, to provide drama, as well as the hugely exaggerated positions and emotions
Essential Question: How did the Renaissance change art in Western Europe?
 Essential Question: How did the Renaissance change art in Western Europe? Warm-Up Question: Define these terms: Renaissance Humanism Classicism Why did the Renaissance begin in Italy? What factors led
Essential Question: How did the Renaissance change art in Western Europe? Warm-Up Question: Define these terms: Renaissance Humanism Classicism Why did the Renaissance begin in Italy? What factors led
ART HISTORY (PRINCIPAL) 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics For Examination from 2016
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Pre-U Certifi cate www.xtremepapers.com ART HISTORY (PRINCIPAL) 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 2 hours 15 minutes
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Pre-U Certifi cate www.xtremepapers.com ART HISTORY (PRINCIPAL) 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 2 hours 15 minutes
What Is A Portrait? The intent is to display the likeness, personality, and even the mood of the person.
 What Is A Portrait? A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expression is predominant. The intent is to display the likeness,
What Is A Portrait? A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expression is predominant. The intent is to display the likeness,
Italian Baroque. Monday, March 02, Art History Semester 2 Page 1
 Art History Semester 2 Page 1 Italian Baroque Monday, March 02, 2015 11:36 PM General info: 1600-1750 Characteristics: Action, passion, and healthy eaters Counter Reformation over Catholic Church strong
Art History Semester 2 Page 1 Italian Baroque Monday, March 02, 2015 11:36 PM General info: 1600-1750 Characteristics: Action, passion, and healthy eaters Counter Reformation over Catholic Church strong
Oman College of Management & Technology
 Oman College of Management & Technology COURSE NAME: HISTORY OF INTERIOR DESIGN PROPOSED BY: DR.MOHAMED ALNEJEM SEMESTER: FIRST 2015/2016 CHAPTER (5): -The Renaissance in Italy -Baroque and Rococo in Italy
Oman College of Management & Technology COURSE NAME: HISTORY OF INTERIOR DESIGN PROPOSED BY: DR.MOHAMED ALNEJEM SEMESTER: FIRST 2015/2016 CHAPTER (5): -The Renaissance in Italy -Baroque and Rococo in Italy
1. Setting the Stage. Madonna and Child in Glory. Enlarge. 2. The Renaissance Connection
 1. Setting the Stage The Middle Ages (a period of European history from the third through 13th centuries), art and learning were centered on the church and religion. But at the start of the 14th century,
1. Setting the Stage The Middle Ages (a period of European history from the third through 13th centuries), art and learning were centered on the church and religion. But at the start of the 14th century,
Explain how the printing revolution shaped European society. Describe the themes that northern European artists, humanists, and writers explored.
 Objectives Explain how the printing revolution shaped European society. Describe the themes that northern European artists, humanists, and writers explored. Terms and People Johann Gutenberg in 1455, printed
Objectives Explain how the printing revolution shaped European society. Describe the themes that northern European artists, humanists, and writers explored. Terms and People Johann Gutenberg in 1455, printed
Art Appreciation UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO PAINTING LESSON 1: BROAD STROKES: PRINCIPLES OF PAINTING
 Core Art Appreciation Art Appreciation is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn
Core Art Appreciation Art Appreciation is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn
Your name Period # What was the purpose of art in Ancient Egyptian culture? What were the rules about representing humans in Ancient Egyptian art?
 Review questions for art history portion of the final exam, Art 1 Your name Period # What was the purpose of art in Ancient Egyptian culture? What were the rules about representing humans in Ancient Egyptian
Review questions for art history portion of the final exam, Art 1 Your name Period # What was the purpose of art in Ancient Egyptian culture? What were the rules about representing humans in Ancient Egyptian
Introduction to Art History
 Core is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn how to critique and compare works
Core is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn how to critique and compare works
TEENAGE MUTANT NINJA ARTISTS
 MICHELANGELO LEONARDO TEENAGE MUTANT NINJA ARTISTS RAPHAEL DONATELLO 14 Leonardo da Vinci Mona Lisa 15 In addition of painting and sculpture Leonardo kept notebooks with plans and diagrams of numerous
MICHELANGELO LEONARDO TEENAGE MUTANT NINJA ARTISTS RAPHAEL DONATELLO 14 Leonardo da Vinci Mona Lisa 15 In addition of painting and sculpture Leonardo kept notebooks with plans and diagrams of numerous
Is the link to Caravaggio's style to Zurbaran and Velázquez. Tenebrism. Martyr of St. Bartholomew
 Baroque Art-3 Hapsburg Spain Artist: Jusepe de Ribera Title: Martyrdom of Saint Bartholomew Medium: Oil on canvas Size: 41¼ X 44⅞" (1.05 X 1.14 m) Date: 1634 Known as Little Spaniard Is the link to Caravaggio's
Baroque Art-3 Hapsburg Spain Artist: Jusepe de Ribera Title: Martyrdom of Saint Bartholomew Medium: Oil on canvas Size: 41¼ X 44⅞" (1.05 X 1.14 m) Date: 1634 Known as Little Spaniard Is the link to Caravaggio's
Art Appreciation UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO PAINTING. Core
 Core is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn how to critique and compare works
Core is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn how to critique and compare works
26/10/2017. Baroque Painting. Key Notions. Timeline. Or, an Enlightened Darkness St. Lawrence, 10/26/2017
 1492 Columbus reaches the West Indies 1498 Savonarola executed 1520 Death of Raphael 1521 Luther excommunicated 1601-02 Caravaggio s Incredulity 1633 Galileo forced to recant 1648 Independence of Dutch
1492 Columbus reaches the West Indies 1498 Savonarola executed 1520 Death of Raphael 1521 Luther excommunicated 1601-02 Caravaggio s Incredulity 1633 Galileo forced to recant 1648 Independence of Dutch
Chapter 22 AP Art History
 Chapter 22 AP Art History Students will be able to Assess the impact of the Council of Trent s guidelines for the Counter-Reformation art of the Roman Catholic Church. Explore how the work of Bernini and
Chapter 22 AP Art History Students will be able to Assess the impact of the Council of Trent s guidelines for the Counter-Reformation art of the Roman Catholic Church. Explore how the work of Bernini and
A History of Portraiture. Studio Art with Mrs. Mendola
 A History of Portraiture Studio Art with Mrs. Mendola What Is A Portrait? A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expression
A History of Portraiture Studio Art with Mrs. Mendola What Is A Portrait? A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expression
What changed during the Middle Ages that gave rise to the Renaissance? Trade & Cities? Government? Religion? Human Potential?
 Western I. Europe The emerged Renaissance from the Middle Ages during an era known as the Renaissance From 1300 to 1600, Western Europe experienced a rebirth in trade, learning, & Greco-Roman ideas During
Western I. Europe The emerged Renaissance from the Middle Ages during an era known as the Renaissance From 1300 to 1600, Western Europe experienced a rebirth in trade, learning, & Greco-Roman ideas During
 Art Appreciation Activity Points % of Total Discuss 60 5% Exam 60 5% Final Exam 100 8% Journal 90 7% Practice 220 18% Quiz 360 29% Test (CST) 180 14% Test (TST) 180 14% Total Points for the Course : 1250
Art Appreciation Activity Points % of Total Discuss 60 5% Exam 60 5% Final Exam 100 8% Journal 90 7% Practice 220 18% Quiz 360 29% Test (CST) 180 14% Test (TST) 180 14% Total Points for the Course : 1250
HOA5. General Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Level Examination. HISTORY OF ART Unit 5 Historical Study (1) Time allowed: 2 hours
 General Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Level Examination HISTORY OF ART Unit 5 Historical Study (1) HOA5 Tuesday 12 June 2007 9.00 am to 11.00 am For this paper you must have: a 16-page lined
General Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Level Examination HISTORY OF ART Unit 5 Historical Study (1) HOA5 Tuesday 12 June 2007 9.00 am to 11.00 am For this paper you must have: a 16-page lined
ART HISTORY AND CRITICISM (AHIS)
 Art History and Criticism (AHIS) 1 ART HISTORY AND CRITICISM (AHIS) AHIS 101 Cave Paintings to Cathedrals Description: Survey of the history of western art from the earliest times to the end of the Medieval
Art History and Criticism (AHIS) 1 ART HISTORY AND CRITICISM (AHIS) AHIS 101 Cave Paintings to Cathedrals Description: Survey of the history of western art from the earliest times to the end of the Medieval
The Pursuit of Reality
 The Pursuit of Reality The Artemision Bronze / Venus de Milo Classical Hellenistic Greek Sculpture. Greek sculpture is a steady progression towards greater naturalism and realism, but is idealised and
The Pursuit of Reality The Artemision Bronze / Venus de Milo Classical Hellenistic Greek Sculpture. Greek sculpture is a steady progression towards greater naturalism and realism, but is idealised and
Writing about Art: Asking Questions
 WRITING ACROSS THE CURRICULUM Writing about Art: Asking Questions Any work of art provokes a response in the viewer. Your task as writer is to define and discuss the choices and techniques the artist has
WRITING ACROSS THE CURRICULUM Writing about Art: Asking Questions Any work of art provokes a response in the viewer. Your task as writer is to define and discuss the choices and techniques the artist has
Section 1. Objectives
 Objectives Describe the characteristics of the Renaissance and understand why it began in Italy. Identify Renaissance artists and explain how new ideas affected the arts of the period. Understand how writers
Objectives Describe the characteristics of the Renaissance and understand why it began in Italy. Identify Renaissance artists and explain how new ideas affected the arts of the period. Understand how writers
Read pages Answer HW4 questions on device When finished, do CW6 p357 Vocab
 Read pages 350-356 Answer HW4 questions on device When finished, do CW6 p357 Vocab Renaissance Ideas Spread to Northern Europe Monarchs in England and in France (such as Francis I who hired Italian architects
Read pages 350-356 Answer HW4 questions on device When finished, do CW6 p357 Vocab Renaissance Ideas Spread to Northern Europe Monarchs in England and in France (such as Francis I who hired Italian architects
Silk Road. Used for trade between the Chinese and Romans from CE 1 to 200 CE
 Renaissance Silk Road Used for trade between the Chinese and Romans from CE 1 to 200 CE After fall of Rome and fall of Han Dynasty, Silk Road was dangerous to travel on 1200 s when Mongols gained control
Renaissance Silk Road Used for trade between the Chinese and Romans from CE 1 to 200 CE After fall of Rome and fall of Han Dynasty, Silk Road was dangerous to travel on 1200 s when Mongols gained control
Warmup. What is her name? Mona Lisa. Painted by Leonardo da Vinci in 1503
 Warmup What is her name? Mona Lisa Painted by Leonardo da Vinci in 1503 Agenda Renaissance PowerPoint with notes Mirror Writing activity Test December 13 th Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Setting
Warmup What is her name? Mona Lisa Painted by Leonardo da Vinci in 1503 Agenda Renaissance PowerPoint with notes Mirror Writing activity Test December 13 th Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Setting
Content Area 3 Part 3 Renaissance & Baroque One Pagers. AP ARTH C. Montenegro
 Content Area 3 Part 3 Renaissance & Baroque One Pagers AP ARTH C. Montenegro Attached you will find the following: Explanations and considerations when filling out the One Pagers, Table of Main Themes,
Content Area 3 Part 3 Renaissance & Baroque One Pagers AP ARTH C. Montenegro Attached you will find the following: Explanations and considerations when filling out the One Pagers, Table of Main Themes,
Rococo. The Century of Louis XV
 Rococo The Century of Louis XV 1700-1800 1 The Marquise de Pompadour became the mistress of Louis XV, king of France, in 1745. François Boucher painted this portrait, which hangs in the Louvre museum in
Rococo The Century of Louis XV 1700-1800 1 The Marquise de Pompadour became the mistress of Louis XV, king of France, in 1745. François Boucher painted this portrait, which hangs in the Louvre museum in
29/10/2018. Dutch Painting. Monday, October 29, 2018 Course Outline. Key Notions. The Netherlands. The 4 genres of Dutch painting.
 Dutch Painting Or, Expertise in Artistic Technique Monday, October 29, 2018 Course Outline The Netherlands The 4 genres of Dutch painting Vermeer Key Notions -Genre scene -Merry company -Still life -Vanitas
Dutch Painting Or, Expertise in Artistic Technique Monday, October 29, 2018 Course Outline The Netherlands The 4 genres of Dutch painting Vermeer Key Notions -Genre scene -Merry company -Still life -Vanitas
Introduction to The Renaissance. Marshall High School Western Civilization II Mr. Cline Unit Two AB
 Introduction to The Renaissance Marshall High School Western Civilization II Mr. Cline Unit Two AB Introduction to Renaissance Art Now we will look at probably what for most people defines this age; Renaissance
Introduction to The Renaissance Marshall High School Western Civilization II Mr. Cline Unit Two AB Introduction to Renaissance Art Now we will look at probably what for most people defines this age; Renaissance
The Renaissance It had long since come to my attention that people of accomplishment rarely sat back and let things happen to them.
 The Renaissance 1350-1600 It had long since come to my attention that people of accomplishment rarely sat back and let things happen to them. They went out and happened to things Leonardo da Vinci A Return
The Renaissance 1350-1600 It had long since come to my attention that people of accomplishment rarely sat back and let things happen to them. They went out and happened to things Leonardo da Vinci A Return
8. Identify the artists, patron and style. What was its intended function and patron. Limbourg Bros, Duke of Berry, International Gothic, prayer book
 1. Name the architect of the dome of this building. Name the building. Explain one innovation he used to either lighten the weight of the dome or strengthen it. Brunelleschi, Florence Cathedral, Il Duomo,
1. Name the architect of the dome of this building. Name the building. Explain one innovation he used to either lighten the weight of the dome or strengthen it. Brunelleschi, Florence Cathedral, Il Duomo,
The Renaissance in Europe Ideas and Art of the Renaissance
 The Renaissance in Europe 1350-1600 Ideas and Art of the Renaissance How can ideas be reflected in art, sculpture, and architecture? How can art influence culture? Essential Questions Ceiling of the Sistine
The Renaissance in Europe 1350-1600 Ideas and Art of the Renaissance How can ideas be reflected in art, sculpture, and architecture? How can art influence culture? Essential Questions Ceiling of the Sistine
The Northern Renaissance. By: Salomón Castillo, Nicolás Esquivel, Franklin Figueroa, Nicole Peng, Sebastián Samayoa, Patricia Venegas
 The Northern Renaissance By: Salomón Castillo, Nicolás Esquivel, Franklin Figueroa, Nicole Peng, Sebastián Samayoa, Patricia Venegas Northern Renaissance Begins The Northern Renaissance describes the Renaissance
The Northern Renaissance By: Salomón Castillo, Nicolás Esquivel, Franklin Figueroa, Nicole Peng, Sebastián Samayoa, Patricia Venegas Northern Renaissance Begins The Northern Renaissance describes the Renaissance
Artist: Rembrandt van Rijn Title: The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp Medium: Oil on canvas Size: 5'3¾" X 7'1¼" (1.6 X 2.
 Baroque Art-4 Artist: Rembrandt van Rijn Title: The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp Medium: Oil on canvas Size: 5'3¾" X 7'1¼" (1.6 X 2.1 m) Date: 1632 Revered as one of the greatest artist of all time
Baroque Art-4 Artist: Rembrandt van Rijn Title: The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp Medium: Oil on canvas Size: 5'3¾" X 7'1¼" (1.6 X 2.1 m) Date: 1632 Revered as one of the greatest artist of all time
Progetto in rete Reading Circles for CLIL History of Art Liceo Artistico M.Preti- A. Frangipane - Reggio Calabria
 Name: Researching resources about Baroque Art and Gian Lorenzo Bernini (working in groups) Ex 1.aReading activity: Baroque Art (Pearson resources and online resources) (work in pairs) Ex 1.b First watch
Name: Researching resources about Baroque Art and Gian Lorenzo Bernini (working in groups) Ex 1.aReading activity: Baroque Art (Pearson resources and online resources) (work in pairs) Ex 1.b First watch
Summer School Duccio to Degas: Introducing Western European art
 Summer School Duccio to Degas: Introducing Western European art 1250 1925 Monday 25 Friday 29 September, 4pm Monday 25 September Early altarpieces We begin with an introduction to ways of looking at paintings
Summer School Duccio to Degas: Introducing Western European art 1250 1925 Monday 25 Friday 29 September, 4pm Monday 25 September Early altarpieces We begin with an introduction to ways of looking at paintings
1. Which major architectural structure was completed during the 15th century and why was its completion important to the people of Florence?
 Art 111: Short Answer/Essay Questions Exam #2 20-30 of these questions will appear on the exam either as slide identification questions or as a list of questions for you to answer. Answers to these questions
Art 111: Short Answer/Essay Questions Exam #2 20-30 of these questions will appear on the exam either as slide identification questions or as a list of questions for you to answer. Answers to these questions
An introduction to the Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century
 An introduction to the Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century Share Tweet Email Albrecht Dürer, Self-Portrait, 1500 (Alte Pinakothek, Munich) https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/renaissance-reformation/northern-renaissance1/beginners-guide-northern-renaissance/a/an-introduction-to-the-northern-ren...
An introduction to the Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century Share Tweet Email Albrecht Dürer, Self-Portrait, 1500 (Alte Pinakothek, Munich) https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/renaissance-reformation/northern-renaissance1/beginners-guide-northern-renaissance/a/an-introduction-to-the-northern-ren...
1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning ( )
 1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning (1300-1600) After suffering through wars, destruction, and the plague of the Middle Ages, people wanted to celebrate life and the human spirit.
1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning (1300-1600) After suffering through wars, destruction, and the plague of the Middle Ages, people wanted to celebrate life and the human spirit.
All of Catholic Europe was involved in the regenerative energy of the Baroque, called the Counter Reformation. It was led by Rome and the head of the
 Chapter 11 All of Catholic Europe was involved in the regenerative energy of the Baroque, called the Counter Reformation. It was led by Rome and the head of the Roman Catholic church, the Pope. This effort
Chapter 11 All of Catholic Europe was involved in the regenerative energy of the Baroque, called the Counter Reformation. It was led by Rome and the head of the Roman Catholic church, the Pope. This effort
ARH 1210: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present
 ARH 1210: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions
ARH 1210: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions
Art Glossary Studio Art Course
 Art Glossary Studio Art Course Abstract: not realistic, though often based on an actual subject. Accent: a distinctive feature, such as a color or shape, added to bring interest to a composition. Advertisement:
Art Glossary Studio Art Course Abstract: not realistic, though often based on an actual subject. Accent: a distinctive feature, such as a color or shape, added to bring interest to a composition. Advertisement:
20/03/ Tectonic/atectonic -Tenebrism. Baroque Painting. Friday, March 20, 2015 Course Outline. Key Notions
 Baroque Painting Or, an Enlightened Darkness St. Lawrence, 3/20/2015 Friday, March 20, 2015 Course Outline Protestantism Caravaggio Velazquez Rubens Classical Vs. Baroque Key Notions -Tectonic/atectonic
Baroque Painting Or, an Enlightened Darkness St. Lawrence, 3/20/2015 Friday, March 20, 2015 Course Outline Protestantism Caravaggio Velazquez Rubens Classical Vs. Baroque Key Notions -Tectonic/atectonic
Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance
 Ch. 1-1 Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Essential Question: Why did the Renaissance start in Italy? Italy s Advantage Classical and Worldly Values The Renaissance Revolutionizes Art Renaissance Writers
Ch. 1-1 Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Essential Question: Why did the Renaissance start in Italy? Italy s Advantage Classical and Worldly Values The Renaissance Revolutionizes Art Renaissance Writers
The Renaissance Outcome: The Renaissance in Italy
 The Renaissance Outcome: The Renaissance in Italy Constructive Response Question 1.Summarize the Renaissance and identify why it started in Italy. What will we learn? 1. What is the Renaissance? 2. Why
The Renaissance Outcome: The Renaissance in Italy Constructive Response Question 1.Summarize the Renaissance and identify why it started in Italy. What will we learn? 1. What is the Renaissance? 2. Why
M.LiT Tour by Irene Koo. Title: The Beauty and Vanity of Portraiture European and 21 st Century. Description: Location:
 M.LiT Tour by Irene Koo Title: The Beauty and Vanity of Portraiture European and 21 st Century Description: Location: Intro: Hello, Welcome to the Virginia Museum of Fine Arts. My name is Irene Koo. Our
M.LiT Tour by Irene Koo Title: The Beauty and Vanity of Portraiture European and 21 st Century Description: Location: Intro: Hello, Welcome to the Virginia Museum of Fine Arts. My name is Irene Koo. Our
Mary Cassatt Impressionism
 Mary Cassatt 1844-1926 Impressionism In the vertical art storage rack you will find the following reproduction and posters: Large reproduction: Susan on a Balcony Holding a Dog (1883) Posters: The Art
Mary Cassatt 1844-1926 Impressionism In the vertical art storage rack you will find the following reproduction and posters: Large reproduction: Susan on a Balcony Holding a Dog (1883) Posters: The Art
THE AGE OF THE REFORMATION SIXTEENTH-CENTURY ART IN NORTHERN EUROPE AND SPAIN
 23 THE AGE OF THE REFORMATION SIXTEENTH-CENTURY ART IN NORTHERN EUROPE AND SPAIN TEXT PAGES 662 687 THE PROTESTANT REFORMATION 1 Who was Martin Luther and what was his goal when he posted his ninety-five
23 THE AGE OF THE REFORMATION SIXTEENTH-CENTURY ART IN NORTHERN EUROPE AND SPAIN TEXT PAGES 662 687 THE PROTESTANT REFORMATION 1 Who was Martin Luther and what was his goal when he posted his ninety-five
ART HISTORY (ARTH) Art History Major. Sequencing of Courses. Interdisciplinary Study. Language Study. Study Abroad and Internships.
 Art History (ARTH) 1 ART HISTORY (ARTH) Art History majors graduate from Bucknell with a thorough grounding in the history of art, highly developed critical thinking skills, and a global cultural awareness
Art History (ARTH) 1 ART HISTORY (ARTH) Art History majors graduate from Bucknell with a thorough grounding in the history of art, highly developed critical thinking skills, and a global cultural awareness
Greenwich Visual Arts Objectives The History of Art (Shapers) High School
 The (Shapers) Media, Techniques and Processes 1. Uses pencils with a variety of techniques that show a range of values (*1a) 2. Uses slab construction to build a Greek vase out of clay (*1a, 4b, 4c) 3.
The (Shapers) Media, Techniques and Processes 1. Uses pencils with a variety of techniques that show a range of values (*1a) 2. Uses slab construction to build a Greek vase out of clay (*1a, 4b, 4c) 3.
April 16, 2014 The Renaissance and it s Famous People
 April 16, 2014 The Renaissance and it s Famous People Homework: Michelangelo: The Italian Sculptor & Painter Lived: 1475 1564 From: Florence, Italy Personality/Training: Bad temper, ambitious, & religious,
April 16, 2014 The Renaissance and it s Famous People Homework: Michelangelo: The Italian Sculptor & Painter Lived: 1475 1564 From: Florence, Italy Personality/Training: Bad temper, ambitious, & religious,
Mr. Cline Marshall High School Western Civilization II Unit TwoEA. The Northern Renaissance
 Mr. Cline Marshall High School Western Civilization II Unit TwoEA The Northern Renaissance Italy was the birthplace of the Renaissance, where ruins of ancient Rome stood in almost every city. This link
Mr. Cline Marshall High School Western Civilization II Unit TwoEA The Northern Renaissance Italy was the birthplace of the Renaissance, where ruins of ancient Rome stood in almost every city. This link
30/03/2017. Dutch Painting. Thursday, March 30, 2017 Course Outline. The Netherlands. The 4 genres of Dutch painting. Vermeer
 Dutch Painting Or, Expertise in artistic technique St. Lawrence, 3/30/2017 Thursday, March 30, 2017 Course Outline The Netherlands The 4 genres of Dutch painting Vermeer 1 1601-02 Caravaggio s Incredulity
Dutch Painting Or, Expertise in artistic technique St. Lawrence, 3/30/2017 Thursday, March 30, 2017 Course Outline The Netherlands The 4 genres of Dutch painting Vermeer 1 1601-02 Caravaggio s Incredulity
Chapter 1 Sections 1 & 2 Pgs /action/yt/watch?videoid=4mgspiaibju
 Chapter 1 Sections 1 & 2 Pgs 48-60 http://www.cleanvideosearch.com/media /action/yt/watch?videoid=4mgspiaibju All the world is full of knowing men, of most learned schoolmasters, and vast libraries; and
Chapter 1 Sections 1 & 2 Pgs 48-60 http://www.cleanvideosearch.com/media /action/yt/watch?videoid=4mgspiaibju All the world is full of knowing men, of most learned schoolmasters, and vast libraries; and
Visual Analysis: How Gauguin s Vision after the Sermon (1888) Deviates from Conventions in 19th-Century French Painting Soryn Mouton/ Bedarida/ HTA
 Visual Analysis: How Gauguin s Vision after the Sermon (1888) Deviates from Conventions in 19th-Century French Painting Soryn Mouton/ Bedarida/ HTA 1/ 9-30-15 Paul Gauguin, in his 1888 work titled Vision
Visual Analysis: How Gauguin s Vision after the Sermon (1888) Deviates from Conventions in 19th-Century French Painting Soryn Mouton/ Bedarida/ HTA 1/ 9-30-15 Paul Gauguin, in his 1888 work titled Vision
WHAT WAS ROMANESQUE ART LIKE?
 ROMANESQUE ART WHAT WAS ROMANESQUE ART LIKE? Romanesque: It s a new style of art, called so, because it is reminiscent of Roman art (But it has got nothing to do with Roman art) What was the romanesque
ROMANESQUE ART WHAT WAS ROMANESQUE ART LIKE? Romanesque: It s a new style of art, called so, because it is reminiscent of Roman art (But it has got nothing to do with Roman art) What was the romanesque
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2010 2 hours 15 minutes * 7002
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2010 2 hours 15 minutes * 7002
Chapter 18 The Age of Faith
 Chapter 18 The Age of Faith Just after the spread of Christianity By the year 250, 60 percent of Asia Minor had converted to Christianity In 313, the Roman Emperor Constantine legalized the practice of
Chapter 18 The Age of Faith Just after the spread of Christianity By the year 250, 60 percent of Asia Minor had converted to Christianity In 313, the Roman Emperor Constantine legalized the practice of
HAA. HAA 0010 INTRODUCTION TO WORLD ART 3 cr. HAA 0030 INTRODUCTION TO MODERN ART 3 cr. HAA 0090 INTRODUCTION TO CONTEMPORARY ART 3 cr.
 HAA HAA 0010 INTRODUCTION TO WORLD ART 3 cr. Intended to introduce the student to major monuments of western art from Egypt to the 20th century, and to demonstrate the tools of analysis with which one
HAA HAA 0010 INTRODUCTION TO WORLD ART 3 cr. Intended to introduce the student to major monuments of western art from Egypt to the 20th century, and to demonstrate the tools of analysis with which one
Welcome to Art 1H. Honors Ancient & Medieval Art
 Welcome to Art 1H Honors Ancient & Medieval Art Introduction What is Art History? Not the book or proper academic definition, but you (the student s) definition What is Art History? The academic discipline
Welcome to Art 1H Honors Ancient & Medieval Art Introduction What is Art History? Not the book or proper academic definition, but you (the student s) definition What is Art History? The academic discipline
BREATHITT HIGH SCHOOL Arts and Humanities: Discovering Art History
 BREATHITT HIGH SCHOOL Arts and Humanities: Discovering Art History Units: I. Part One: The World and Work of the Artist Lesson 1: Learning About Art I can explain how there is no single definitive definition
BREATHITT HIGH SCHOOL Arts and Humanities: Discovering Art History Units: I. Part One: The World and Work of the Artist Lesson 1: Learning About Art I can explain how there is no single definitive definition
Atmospheric Perspective (Aerial Perspective) Quality of the atmosphere between viewer and objects changes the appearance of objects.
 Light and Color Atmospheric Perspective (Aerial Perspective) Quality of the atmosphere between viewer and objects changes the appearance of objects. Foreground = clarity, precision, contrast Background
Light and Color Atmospheric Perspective (Aerial Perspective) Quality of the atmosphere between viewer and objects changes the appearance of objects. Foreground = clarity, precision, contrast Background
Year Course Programme High Renaissance to Baroque
 Year Course Programme 2016 17 High Renaissance to Baroque 1500 1720 Wednesdays, 21 September 2016 12 July 2017 (over 3 terms) 11.10 15.30 (Each term includes optional gallery talks, commencing at 10.00
Year Course Programme 2016 17 High Renaissance to Baroque 1500 1720 Wednesdays, 21 September 2016 12 July 2017 (over 3 terms) 11.10 15.30 (Each term includes optional gallery talks, commencing at 10.00
The Renaissance. Time of Rebirth ( )
 The Renaissance Time of Rebirth (1300-1600) The Middle Ages: Early Middle Ages (476 800) Heavy Roman influence Various ethnic groups High Middle Ages (800 1300) Development of feudal society 3 tiered caste
The Renaissance Time of Rebirth (1300-1600) The Middle Ages: Early Middle Ages (476 800) Heavy Roman influence Various ethnic groups High Middle Ages (800 1300) Development of feudal society 3 tiered caste
ARH 012: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present
 ARH 012: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions
ARH 012: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions
7th Chapter 11 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following describes one effect of Marco Polo s journey to China? a. Marco Polo became the
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following describes one effect of Marco Polo s journey to China? a. Marco Polo became the
Welcome to Art 6H. Art & Aesthetics
 Welcome to Art 6H Art & Aesthetics Aesthetics - Beauty Aesthetics is a branch of philosophy that examines the nature of art and our experience of it. It developed in England as philosophers grouped together
Welcome to Art 6H Art & Aesthetics Aesthetics - Beauty Aesthetics is a branch of philosophy that examines the nature of art and our experience of it. It developed in England as philosophers grouped together
ARH 012: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present
 ARH 012: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present General Information: Term: 2019 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions
ARH 012: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present General Information: Term: 2019 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions
Characteristics of the Renaissance Examples Activity
 Example Characteristics of the Renaissance Examples Activity Greek and/or Roman Influence Humanism Emphasis on the Individual Celebration of Secular Achievements 1. Brunelleschi s Dome 2. Brief Biography
Example Characteristics of the Renaissance Examples Activity Greek and/or Roman Influence Humanism Emphasis on the Individual Celebration of Secular Achievements 1. Brunelleschi s Dome 2. Brief Biography
2. A painting of fruit, flowers or insects is called. 3. Paintings made from millions of tiny coloured dots are typical of the style.
 BBC Learning English Quiznet Appreciating art 1. An artist often paints a picture onto. a) a paintbrush b) an easel c) a canvas d) a palette 2. A painting of fruit, flowers or insects is called. a) a still-life
BBC Learning English Quiznet Appreciating art 1. An artist often paints a picture onto. a) a paintbrush b) an easel c) a canvas d) a palette 2. A painting of fruit, flowers or insects is called. a) a still-life
Thirty-Minute Essay Questions from Earlier AP Exams
 Thirty-Minute Essay Questions from Earlier AP Exams A: In most parts of the world, public sculpture is a common and accepted sight. Identify three works of public sculpture whose effects are different
Thirty-Minute Essay Questions from Earlier AP Exams A: In most parts of the world, public sculpture is a common and accepted sight. Identify three works of public sculpture whose effects are different
Rigaud, Louis XIV. Essay by Tessa Fleming. Share Tweet . Hyacinthe Rigaud, Louis XIV, 1701, oil on canvas, 9 2 x 6 3. Musée du Louvre, Paris
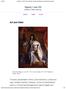 Rigaud, Louis XIV Essay by Tessa Fleming. Share Tweet Email Art and State Hyacinthe Rigaud, Louis XIV, 1701, oil on canvas, 9 2 x 6 3. Musée du Louvre, Paris The early seventeenth century was marked by
Rigaud, Louis XIV Essay by Tessa Fleming. Share Tweet Email Art and State Hyacinthe Rigaud, Louis XIV, 1701, oil on canvas, 9 2 x 6 3. Musée du Louvre, Paris The early seventeenth century was marked by
Chapter 13 THE SEVENTEENTH CENTURY IN EUROPE
 Chapter 13 THE SEVENTEENTH CENTURY IN EUROPE The key events of seventeenth century Europe were: the rise of the Dutch republic, the decline of Spain, and the Thirty Years War. After Holland gained its
Chapter 13 THE SEVENTEENTH CENTURY IN EUROPE The key events of seventeenth century Europe were: the rise of the Dutch republic, the decline of Spain, and the Thirty Years War. After Holland gained its
2-Point Perspective. Lettering with Depth!
 2-Point Perspective Lettering with Depth! Introduction to Perspective The Renaissance (1400-1600) was a great rebirth of European learning and discovery. It ended 1000 years of superstition and ignorance
2-Point Perspective Lettering with Depth! Introduction to Perspective The Renaissance (1400-1600) was a great rebirth of European learning and discovery. It ended 1000 years of superstition and ignorance
General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June History of Art
 General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2012 History of Art HART3 Unit 3 Investigation and Interpretation (1) Friday 1 June 2012 1.30 pm to 3.00 pm For this paper you must have:
General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2012 History of Art HART3 Unit 3 Investigation and Interpretation (1) Friday 1 June 2012 1.30 pm to 3.00 pm For this paper you must have:
2002 AP ART HISTORY SLIDE-BASED MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
 2002 AP ART HISTORY SLIDE-BASED MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1 SECTION I Part A Time 16 minutes Directions: Questions 1-30 are divided into sets of questions based on slides. In these sets, each of the questions
2002 AP ART HISTORY SLIDE-BASED MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1 SECTION I Part A Time 16 minutes Directions: Questions 1-30 are divided into sets of questions based on slides. In these sets, each of the questions
Art 232: History of Western Art II
 Art 232: History of Western Art II Professor Ellen Daugherty Rhodes College, Spring 2005 414 Clough, Ext. 3663 417 Clough, MWF 1:00-1:50 daughertye@rhodes.edu CRN: 20120 Office Hours: Thursday 1:30-4:30
Art 232: History of Western Art II Professor Ellen Daugherty Rhodes College, Spring 2005 414 Clough, Ext. 3663 417 Clough, MWF 1:00-1:50 daughertye@rhodes.edu CRN: 20120 Office Hours: Thursday 1:30-4:30
Review for Art History Exam #1. Lesson 1: The Renaissance Lesson 2: The Northern Renaissance
 Review for Art History Exam #1 Lesson 1: The Renaissance Lesson 2: The Northern Renaissance REVIEW QUESTION #1: What is the title of this sculpture & who is the sculptor? J Donatello s David Donatello
Review for Art History Exam #1 Lesson 1: The Renaissance Lesson 2: The Northern Renaissance REVIEW QUESTION #1: What is the title of this sculpture & who is the sculptor? J Donatello s David Donatello
LIBERAL ARTS COLLEGE
 LIBERAL ARTS COLLEGE 2018-2019 LBCL 295/A: THE HISTORY OF ART Section A: Monday and Wednesday, 13:15-14:30 Instructor: Mark Russell Email: mark.russell@concordia.ca Office Hours: Rm. 304 - M/W, 14:45-15:45
LIBERAL ARTS COLLEGE 2018-2019 LBCL 295/A: THE HISTORY OF ART Section A: Monday and Wednesday, 13:15-14:30 Instructor: Mark Russell Email: mark.russell@concordia.ca Office Hours: Rm. 304 - M/W, 14:45-15:45
Mark your answers on the gradecam sheet with a #2 pencil. Mark answer very black.
 2 nd Semester Final-Arts and Humanities 10 th Grade Mark your answers on the gradecam sheet with a #2 pencil. Mark answer very black. Multiple Choice Choose the best answer. 1. The circular chart used
2 nd Semester Final-Arts and Humanities 10 th Grade Mark your answers on the gradecam sheet with a #2 pencil. Mark answer very black. Multiple Choice Choose the best answer. 1. The circular chart used
John The Baptist (Classic Portraits) By F. B. Meyer
 John The Baptist (Classic Portraits) By F. B. Meyer A summary of Chapter 5, Sections 3 4 in James Joyce's A Portrait of the Artist as He distractedly muses on the fact that John the Baptist lived on locusts
John The Baptist (Classic Portraits) By F. B. Meyer A summary of Chapter 5, Sections 3 4 in James Joyce's A Portrait of the Artist as He distractedly muses on the fact that John the Baptist lived on locusts
ARH 012: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present
 ARH 012: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions
ARH 012: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions
03/11/2016. Dutch Painting. Thursday, November 3, 2016 Course Outline. The Netherlands. The 4 genres of Dutch painting. Vermeer
 Dutch Painting Or, Expertise in artistic technique St. Lawrence, 11/3/2016 Thursday, November 3, 2016 Course Outline The Netherlands The 4 genres of Dutch painting Vermeer 1 1601-02 Caravaggio s Incredulity
Dutch Painting Or, Expertise in artistic technique St. Lawrence, 11/3/2016 Thursday, November 3, 2016 Course Outline The Netherlands The 4 genres of Dutch painting Vermeer 1 1601-02 Caravaggio s Incredulity
On lined paper put Art history #3, your name, order # and Period
 Art History #3 On lined paper put Art history #3, your name, order # and Period 1. What was Vermeer s Subject matter 2. What was Vermeer s most famous painting? 3. Rococo was characterized by themes. 4.
Art History #3 On lined paper put Art history #3, your name, order # and Period 1. What was Vermeer s Subject matter 2. What was Vermeer s most famous painting? 3. Rococo was characterized by themes. 4.
Leonardo Da Vinci ITALY FRANCE
 Leonardo Da Vinci ITALY FRANCE INTRODUCTION Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519), a Florentine artist, one of the great masters of the High Renaissance, is celebrated as a painter, sculptor, architect, engineer,
Leonardo Da Vinci ITALY FRANCE INTRODUCTION Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519), a Florentine artist, one of the great masters of the High Renaissance, is celebrated as a painter, sculptor, architect, engineer,
The Renaissance. Europe 1300s 1600s
 The Renaissance Europe 1300s 1600s The word Renaissance = rebirth The Renaissance was the period of rebirth and creativity that followed Europe s Middle Ages It was a rebirth of interest in classical (Greek
The Renaissance Europe 1300s 1600s The word Renaissance = rebirth The Renaissance was the period of rebirth and creativity that followed Europe s Middle Ages It was a rebirth of interest in classical (Greek
Ar#sts, Movements, and Styles in Western Art
 Ar#sts, Movements, and Styles in Western Art Classical Greek Art Great emphasis on statues. Emphasized the human form in more natural poses. The idea was to create a statue in the perfect human form. Discus
Ar#sts, Movements, and Styles in Western Art Classical Greek Art Great emphasis on statues. Emphasized the human form in more natural poses. The idea was to create a statue in the perfect human form. Discus
