Chapter 13 THE SEVENTEENTH CENTURY IN EUROPE
|
|
|
- Robyn Mitchell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 13 THE SEVENTEENTH CENTURY IN EUROPE The key events of seventeenth century Europe were: the rise of the Dutch republic, the decline of Spain, and the Thirty Years War. After Holland gained its independence from Spain, its prosperity was founded on free enterprise at home and a world wide maritime trade. Throughout Europe there was a revolt against longestablished authority, especially in the field of science. Frances Bacon proposed an inductive approach to the physical sciences which was widely accepted by the end of the century. René Descartes freed Western philosophy from its dependence on Plato and Aristotle with a new theory of knowledge that led to the famous conclusion, I think, therefore I am. The visual arts, at first, did not keep up with these new thoughts; instead it coincided with the recovery of the Papacy from the Protestant Reformation. With the rise of academies for the arts came the growth of art collecting, both of old masters and contemporary works, making easel painting a prime importance. Key Terms: Caravaggism Baroque Learning Objectives: The blatant use of the arts and architecture by the French monarchy. The influence of Dutch art in England. The effects of the Protestant Reformation on the arts. The rise of still life and genre subject matter in Dutch painting. NEW BEGINNINGS IN ROME Caravaggio, Conversion of St. Paul (fig. 13.1) This painting does not use the usual symbolism of religious paintings. Page 129
2 Caravaggio approaches the subject of Paul s conversion by rejecting the idealism of the High Renaissance. Texture throughout the painting is rendered with illusionistic skill. As a means of attaining spiritual understanding Caravaggio relies on the senses instead of the intellect. This approach to painting was called Caravaggism and became a great influence throughout Europe in that the artists began to produce paintings of unidealized, boldly illuminated figures that were set against dark, mysterious backgrounds. Carracci, ceiling frescoes (fig. 13.2) Carracci broke away from the past as Caravaggio did. His ceiling frescoes are painted in a style inspired by Raphael and antique sculpture, and are evenly lit. Carracci rationalized Michelangelo s scheme in the Sistine Chapel and used skillful foreshortened figures. BAROQUE ART AND ARCHITECTURE The term Baroque was first used as a term of critical abuse coming from two words current in seventeenth century Italy: the Italian barocco referred to tortuous medieval pedantry and the Portuguese barrocco, which is a deformed pearl. Both words had to do with the deviation from a norm and to the eighteenth century theorists they applied to an art and architecture that appeared impure and irrational. Rubens and van Dyck Peter Paul Rubens age and social background set him apart from other artists. He was the son of a prominent lawyer and was given a Classical education. In 1609, Rubens was appointed court painter to the Habsburg regent of the Netherlands. Rubens, Rape of the Daughters of Leucippus fig. 13.4) Rubens robust sensuality and fertile imagination created a strong individual character in all of his works. This painting may have been inspired by Titian s Rape of Europa(fig ). The influence of Brueghel can also be seen in the background landscape. Page 130
3 Rubens introduced a new brand of female beauty: fullbreasted, broad-waisted, more of a woman than of a girl. The women in this painting are in complementary poses; one almost a mirror image of the other. Rubens rejected the traditional use of the pyramidal composition for a picture of intersecting diagonals with the twist and counter twist of the forms. Rubens, Landscape with Rainbow (fig. 13.8) Rubens made a fortune with his work and in 1635 bought a country estate whose surrounding country inspired a series of paintings. Though in the past Rubens had often sketched views of nature, it is only now that he depicts landscape for its own sake. A Flemish pride in land ownership may have prompted works such as this painting. van Dyck, Charles I with M. de St. Antoine (fig ) van Dyck was one of Rubens most notable assistant. Though he painted a variety of subject matters it was as a portrait painter that he excelled. Charles I is presented in the grand manner of Marcus Aurelius but is shown riding through a triumphal arch. van Dyck used a low viewpoint to create a sense of a divinely appointed monarchy. The Easel Painting in Italy Italian works of art were eagerly sought by collectors. Gentileschi, Judith Slaying Holofernes (fig ) Gentileschi was a follower of Caravaggio, but her canvases created a strong sense of violence not found in Caravaggio s work. In this painting, Judith is slowly carving off the head of Holofernes in vivid reconstruction of the story told in the Book of Judith. Gentileschi specialized in paintings depicting women in a dominant role. Some people attribute this to the fact that she was raped and that it was she who was tortured during the trial. Page 131
4 Reni, Atalanta and Hippomenes (fig ) Reni adopted Caravaggio s dramatic chiaroscuro for his dramatic figures. In this painting Reni composed the figures like an antique relief. The figures are posed as if in a ballet and the drapery is rendered like fluttering ribbons. Bernini Bernini regarded himself primarily as a sculptor yet he was also a gifted architect. He was a fast worker with a demonic drive and dominated the artistic scene in Rome for half a century. Bernini, Ecstasy of St. Teresa (fig ) This sculpture is the centerpiece of a chapel commissioned by Cardinal Federico Cornaro. Bernini responded to St. Teresa s writings and did not minimize the body s great share in the spiritual experience. St. Teresa is shown with physical abandon, having just received communion and her miraculous transformation at the moment of her death. Borromini Borromini had a great knowledge of ancient Roman architecture and his work made more of a intellectual than emotional appeal. He was a stone carver by trade and at first was employed as a decorative sculptor and draftsman. Borromini, S Agnese in Piazza Navona (figs ; 21) Borromini s use of intersecting equilateral triangles and circles created a very unusual hexagonal central space. The purpose of the church was to provide suitable space for the preaching of sermons to students and this freed Borromini from the usual Counter Reformation church plan. The dome is unprecedented in concept in that it is formed simply by the continuation of the walls upwards and inwards until they meet in the circle of light beneath the lantern. Poussin and Claude Two of the most distinguished painters in Rome during the mid-seventeenth century were Poussin and Claude Lorraine. Page 132
5 In 1628 Poussin was commissioned to do an important altarpiece in St. Peter s but it was not well received, after which he concentrated on relatively small paintings for cabinets of collectors. Claude had no Classical training but was trained as a pastry-cook before he went to Rome, where he learned to paint as an assistant to a decorative artist. The Classical Landscape was virtually his creation and the idea of landscape as one of the higher art forms was largely due to him. Poussin, The Holy Family on the Steps (fig ) This painting shows Poussin s work at its most stoical severity. Every element has both a symbolic meaning and a pictorial function in the simple balance of the composition. Lorraine, Landscape with the Father of Psyche sacrificing to Apollo (fig ) Lorraine s landscapes represent the pastoral world of a Classical Golden Age which was a recurring theme in European literature and art. His inspiration was the countryside around Rome. His principal innovation was in the treatment of light emanating from the horizon towards the spectator and was reflected by the water showing his avoidance of the blaze of noonday light in favor of the diffused glow of morning and early evening. Velazquéz After visiting Rome twice, Velazquéz began to work in a style that was influenced by Caravaggio. In 1623, Velazquéz entered into the service of the Spanish king Philip IV in whose art collection Velazquéz was exposed to the works by Venetian painters. Velazquéz, Las Meninas (fig ) This painting is regarded as Velazquéz supreme achievement. By the end of the seventeenth century this painting was regarded as a painting about painting. All of the figures within the painting are members of the royal household. The figures are presented in a haphazard arrangement making the composition come across like a snapshot and not a formal painting. Page 133
6 This painting demonstrates the painter s unique power to represent life as it takes place before our eyes. DUTCH PAINTING The Dutch revolt against the Spanish king started out to regain their ancient privileges and soon included the struggle for religious as well as civic liberties. After the defeat of the Spaniards many Protestant sects were tolerated in Holland as well as giving asylum to Jews fleeing Spain. The Dutch republic was defensive, rather than aggressive in foreign policy with an economy based on commerce, instead of agriculture. Bankers, merchants, and shippers made up the upper class and under their patronage secular painting flourished as never before and as nowhere else. The Dutch brought easel painting with its varied subject matters to its height and there was little if no demand for altarpiece or even grandiose architecture or sculpture. Hals Hals is regarded as the founder of the Dutch school of painting, specializing in portrait painting. In his portrait like paintings of people from contemporary life, Hals was free to study expression and character. Hals, The Merry Drinker (fig ) The subject is presented with a bibulously flushed face, twinkling eyes and seems to be surprised by the viewer. The brushwork is spontaneous and gives the impression of instantaneous life and the jagged outline suggests sudden movement. Much of the animated spark comes from the highlights added as the final touch to the work. Rembrandt From the beginning of his career Rembrandt incorporated the spiraling compositions of Rubens and the strong chiaroscuro of Caravaggio. Rembrandt would always assimilate outside influences into his work. Page 134
7 Rembrandt, The Night Watch (fig ) This is the traditional name of a painting that is really a group portrait of a militia company. Rembrandt presented this group as they leave their headquarters for a ceremonial parade enabling him to present an insignificant incident as a grand historical spectacle. Rembrandt wanted to create a thrilling atmosphere with the use of contrasts of light and shade, brilliant and drab color, a variety of poses, gestures and facial expressions. Rembrandt, Return of the Prodigal Son (fig ) The paintings done in Rembrandt s later years were intensely private. In this painting Rembrandt used somber colors which have an interior warmth. Rembrandt emphasizes the relationship between the father and the kneeling son by using a light that also catches the hands and face of the elder brother. Rembrandt does not use emotion or gestures but the meaning of the parable is visible in the image of humble repentance and tender fatherly forgiveness. Landscape After the founding of the Dutch republic a new way of representing the featureless Dutch local scene began to appear in paintings. The new representation of landscape was never meant for Biblical or mythological stories. Landscape paintings were rarely commissioned by individual patrons. Rather they were usually painted on speculation for a wide public, sold on the open market and bought by town dwelling merchants. It was believed that the Bible and nature were twin sources of divine understanding and the recurrence in paintings of the towers of medieval churches was a reminder of the Protestant origin and providential protection of the republic. Most of the landscape paintings were manifestation of contemporary scenes. van Goyen, View of Rhenen (fig ) van Goyen is regarded as one of the most gifted Dutch landscape painters. Page 135
8 This painting depicts shipping on the river, three men on a punt on a backwater in the foreground and foot travelers on the right. These elements and the use of medieval walls are absorbed into a vision of peace and harmony. As in many Dutch landscapes two-thirds of the canvas is devoted to the sky. van Ruisdael, Windmill at Wijk (fig ) van Ruisdael adopted a less restricted palette than van Goyen. In this painting, van Ruisdael exaggerated the size of the mill and has replaced the town wall with the figures of three women. He did include the church and gave prominence to the palings reinforcing the river bank and protected the land from floods. Still Life and Genre Nearly all of the Dutch artists at this time specialized in a particular subject matter and were sometimes even more selective like a still life painter restricting himself to a single class of objects. Scenes of ordinary everyday indoor life vied with landscape and still life for the favors of the Dutch art buying public. These small paintings with sharp detail represented the familiar world and were easily adapted for the living rooms of the middle class houses. Kalf, Still Life (fig ) Kalf was one of the most gifted still life painters of the seventeenth century who depicted luxury objects such as Turkish rugs and Chinese porcelain bowls with oranges and lemons. This painting demonstrated his illusionistic skill which enabled him to create sumptuous colors, textures, reflections and transparencies. Leysster, The Proposition (fig ) The realism of these paintings was not the main reason for their popularity, most if not all of them originally carried a moral message. Page 136
9 Many of them alluded to sexual transgression which was presented in such a manner that they offered the viewer the choice of merely enjoying the painting. Vermeer He also specialized in moralizing genre pictures but he produced very few paintings. Vermeer stands apart from other painters of his time on account of his extreme, sensitivity in the rendering of light. His method of capturing the sparkle of light in minute pearl like dots beyond the contours of objects is unique. Vermeer, The Art of Painting (fig ) The painter here is dressed in sixteenth century costume and the model is posed with the attributes of the Muse of History. The drapery resembles that used in official portraits and on the wall is a recently printed Dutch map of the Netherlands. ENGLAND AND FRANCE There was a close cultural link between the Dutch republic and England. English books were translated into Dutch but in the visual arts the influence was in the opposite direction. Dutch influence dominated the decorative arts and domestic architecture; a more Italian style was introduced for royal buildings by Inigo Jones. In France, the visual arts were enrolled, ordered, and paraded in the service of autocracy. No other art movement is more directly expressive of the political ambitions and achievements of a monarch than that for Louis XIV. Wren, St Paul s Cathedral (fig ) Wren turned to the Italian style when he was called upon to design this and 51 parish churches which had been destroyed by a fire in He studied engravings of Bramante s design for St Peter s in Rome before deciding on the final design. Page 137
10 Garden facade of the Palace of Versailles (fig ) The palace of Versailles was a manifestation of Louis XIV s determination to shine as the greatest ruler in Europe. The king s personal approval was needed for even minor decorative details, especially those having referring to him. Page 138
Irregular Pear or Stone
 BAROQUE ART Irregular Pear or Stone 16 th century Throughout Europe = religious tension - Protestants broke away from Roman Catholic Church. response to the Protestant Reformation, Catholic Church initiated
BAROQUE ART Irregular Pear or Stone 16 th century Throughout Europe = religious tension - Protestants broke away from Roman Catholic Church. response to the Protestant Reformation, Catholic Church initiated
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject www.xtremepapers.com ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2013 2
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject www.xtremepapers.com ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2013 2
Baroque. From the Portuguese word barocca pearl of irregular shape. Implies strangeness, irregularity, extravagance
 Baroque 1600-1750 Baroque From the Portuguese word barocca pearl of irregular shape. Implies strangeness, irregularity, extravagance The term baroque was not a complement it originally meant overdone too
Baroque 1600-1750 Baroque From the Portuguese word barocca pearl of irregular shape. Implies strangeness, irregularity, extravagance The term baroque was not a complement it originally meant overdone too
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2012 2 hours 15 minutes *2574265004*
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2012 2 hours 15 minutes *2574265004*
Ecstacy of Santa Teresa by Bernini
 Baroque Art Baroque Sculptures David by Bernini Bernini's David was completed when Bernini was 25. David is posed to release the rock. Captures the heroic moment not the heroic nature the other davids
Baroque Art Baroque Sculptures David by Bernini Bernini's David was completed when Bernini was 25. David is posed to release the rock. Captures the heroic moment not the heroic nature the other davids
Chapter 22 AP Art History
 Chapter 22 AP Art History Students will be able to Assess the impact of the Council of Trent s guidelines for the Counter-Reformation art of the Roman Catholic Church. Explore how the work of Bernini and
Chapter 22 AP Art History Students will be able to Assess the impact of the Council of Trent s guidelines for the Counter-Reformation art of the Roman Catholic Church. Explore how the work of Bernini and
If it s not Baroque, don t fix it! 17 century Art
 5 L s If it s not Baroque, don t fix it! th 17 century Art Look up (lots of painted ceilings) Light (chiaroscuro and tenebrism) Life (vanitas still lifes) Levels (meanings and symbolism) Lands (landscapes,
5 L s If it s not Baroque, don t fix it! th 17 century Art Look up (lots of painted ceilings) Light (chiaroscuro and tenebrism) Life (vanitas still lifes) Levels (meanings and symbolism) Lands (landscapes,
Essential Question: How did the Renaissance change art in Western Europe?
 Essential Question: How did the Renaissance change art in Western Europe? Warm-Up Question: Define these terms: Renaissance Humanism Classicism Why did the Renaissance begin in Italy? What factors led
Essential Question: How did the Renaissance change art in Western Europe? Warm-Up Question: Define these terms: Renaissance Humanism Classicism Why did the Renaissance begin in Italy? What factors led
Triumph of Divine Providence Pietro da Cortona
 Triumph of Divine Providence Pietro da Cortona 1633-1639 Baroque Architecture and Art Defining the Baroque A reaction against the symmetry and balanced style of the Renaissance Incorporates more MOTION
Triumph of Divine Providence Pietro da Cortona 1633-1639 Baroque Architecture and Art Defining the Baroque A reaction against the symmetry and balanced style of the Renaissance Incorporates more MOTION
TEENAGE MUTANT NINJA ARTISTS
 MICHELANGELO LEONARDO TEENAGE MUTANT NINJA ARTISTS RAPHAEL DONATELLO 14 Leonardo da Vinci Mona Lisa 15 In addition of painting and sculpture Leonardo kept notebooks with plans and diagrams of numerous
MICHELANGELO LEONARDO TEENAGE MUTANT NINJA ARTISTS RAPHAEL DONATELLO 14 Leonardo da Vinci Mona Lisa 15 In addition of painting and sculpture Leonardo kept notebooks with plans and diagrams of numerous
Writing about Art: Asking Questions
 WRITING ACROSS THE CURRICULUM Writing about Art: Asking Questions Any work of art provokes a response in the viewer. Your task as writer is to define and discuss the choices and techniques the artist has
WRITING ACROSS THE CURRICULUM Writing about Art: Asking Questions Any work of art provokes a response in the viewer. Your task as writer is to define and discuss the choices and techniques the artist has
The Renaissance It had long since come to my attention that people of accomplishment rarely sat back and let things happen to them.
 The Renaissance 1350-1600 It had long since come to my attention that people of accomplishment rarely sat back and let things happen to them. They went out and happened to things Leonardo da Vinci A Return
The Renaissance 1350-1600 It had long since come to my attention that people of accomplishment rarely sat back and let things happen to them. They went out and happened to things Leonardo da Vinci A Return
HOA5. General Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Level Examination. HISTORY OF ART Unit 5 Historical Study (1) Time allowed: 2 hours
 General Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Level Examination HISTORY OF ART Unit 5 Historical Study (1) HOA5 Tuesday 12 June 2007 9.00 am to 11.00 am For this paper you must have: a 16-page lined
General Certificate of Education June 2007 Advanced Level Examination HISTORY OF ART Unit 5 Historical Study (1) HOA5 Tuesday 12 June 2007 9.00 am to 11.00 am For this paper you must have: a 16-page lined
(D) sfumato (C) Greek temple architecture
 1. All of the following are humanistic traits in the above statue by Michelangelo EXCEPT (A) use of marble (B) contrapposto stance (C) free-standing sculpture (D) sfumato (E) glorification of the human
1. All of the following are humanistic traits in the above statue by Michelangelo EXCEPT (A) use of marble (B) contrapposto stance (C) free-standing sculpture (D) sfumato (E) glorification of the human
Silk Road. Used for trade between the Chinese and Romans from CE 1 to 200 CE
 Renaissance Silk Road Used for trade between the Chinese and Romans from CE 1 to 200 CE After fall of Rome and fall of Han Dynasty, Silk Road was dangerous to travel on 1200 s when Mongols gained control
Renaissance Silk Road Used for trade between the Chinese and Romans from CE 1 to 200 CE After fall of Rome and fall of Han Dynasty, Silk Road was dangerous to travel on 1200 s when Mongols gained control
Chapter 22 AP Art History
 Chapter 22 AP Art History Students will be able to Assess the impact of the Council of Trent s guidelines for the Counter-Reformation art of the Roman Catholic Church. Explore how the work of Bernini and
Chapter 22 AP Art History Students will be able to Assess the impact of the Council of Trent s guidelines for the Counter-Reformation art of the Roman Catholic Church. Explore how the work of Bernini and
ART HISTORY (PRINCIPAL) 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics For Examination from 2016
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Pre-U Certifi cate www.xtremepapers.com ART HISTORY (PRINCIPAL) 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 2 hours 15 minutes
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Pre-U Certifi cate www.xtremepapers.com ART HISTORY (PRINCIPAL) 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics For Examination from 2016 SPECIMEN PAPER 2 hours 15 minutes
Oman College of Management & Technology
 Oman College of Management & Technology COURSE NAME: HISTORY OF INTERIOR DESIGN PROPOSED BY: DR.MOHAMED ALNEJEM SEMESTER: FIRST 2015/2016 CHAPTER (5): -The Renaissance in Italy -Baroque and Rococo in Italy
Oman College of Management & Technology COURSE NAME: HISTORY OF INTERIOR DESIGN PROPOSED BY: DR.MOHAMED ALNEJEM SEMESTER: FIRST 2015/2016 CHAPTER (5): -The Renaissance in Italy -Baroque and Rococo in Italy
A History of Portraiture. Studio Art with Mrs. Mendola
 A History of Portraiture Studio Art with Mrs. Mendola What Is A Portrait? A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expression
A History of Portraiture Studio Art with Mrs. Mendola What Is A Portrait? A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expression
Introduction to The Renaissance. Marshall High School Western Civilization II Mr. Cline Unit Two AB
 Introduction to The Renaissance Marshall High School Western Civilization II Mr. Cline Unit Two AB Introduction to Renaissance Art Now we will look at probably what for most people defines this age; Renaissance
Introduction to The Renaissance Marshall High School Western Civilization II Mr. Cline Unit Two AB Introduction to Renaissance Art Now we will look at probably what for most people defines this age; Renaissance
The setting is elaborately classical - though the composition recalls iconographical precedents of Medieval Times. The Annunciation by Donatello
 Artist: Donatello St. George Zuccone The St. George is widely regarded as a tribute to the classical heroes of antiquity. His features are strong and masculine, yet delicate and youthful, as Florentines
Artist: Donatello St. George Zuccone The St. George is widely regarded as a tribute to the classical heroes of antiquity. His features are strong and masculine, yet delicate and youthful, as Florentines
What changed during the Middle Ages that gave rise to the Renaissance? Trade & Cities? Government? Religion? Human Potential?
 Western I. Europe The emerged Renaissance from the Middle Ages during an era known as the Renaissance From 1300 to 1600, Western Europe experienced a rebirth in trade, learning, & Greco-Roman ideas During
Western I. Europe The emerged Renaissance from the Middle Ages during an era known as the Renaissance From 1300 to 1600, Western Europe experienced a rebirth in trade, learning, & Greco-Roman ideas During
Section 1. Objectives
 Objectives Describe the characteristics of the Renaissance and understand why it began in Italy. Identify Renaissance artists and explain how new ideas affected the arts of the period. Understand how writers
Objectives Describe the characteristics of the Renaissance and understand why it began in Italy. Identify Renaissance artists and explain how new ideas affected the arts of the period. Understand how writers
What Is A Portrait? The intent is to display the likeness, personality, and even the mood of the person.
 What Is A Portrait? A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expression is predominant. The intent is to display the likeness,
What Is A Portrait? A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expression is predominant. The intent is to display the likeness,
Artist: Rembrandt van Rijn Title: The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp Medium: Oil on canvas Size: 5'3¾" X 7'1¼" (1.6 X 2.
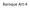 Baroque Art-4 Artist: Rembrandt van Rijn Title: The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp Medium: Oil on canvas Size: 5'3¾" X 7'1¼" (1.6 X 2.1 m) Date: 1632 Revered as one of the greatest artist of all time
Baroque Art-4 Artist: Rembrandt van Rijn Title: The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp Medium: Oil on canvas Size: 5'3¾" X 7'1¼" (1.6 X 2.1 m) Date: 1632 Revered as one of the greatest artist of all time
The Renaissance in Europe Ideas and Art of the Renaissance
 The Renaissance in Europe 1350-1600 Ideas and Art of the Renaissance How can ideas be reflected in art, sculpture, and architecture? How can art influence culture? Essential Questions Ceiling of the Sistine
The Renaissance in Europe 1350-1600 Ideas and Art of the Renaissance How can ideas be reflected in art, sculpture, and architecture? How can art influence culture? Essential Questions Ceiling of the Sistine
Red, Yellow, and Blue are the Primary Colors, in varying combinations they make up the entire spectrum of visual light.!
 Art 1 Semester Test Review Red, Yellow, and Blue are the Primary Colors, in varying combinations they make up the entire spectrum of visual light. Secondary colors are Green, Violet, and Orange, they are
Art 1 Semester Test Review Red, Yellow, and Blue are the Primary Colors, in varying combinations they make up the entire spectrum of visual light. Secondary colors are Green, Violet, and Orange, they are
Spain s Empire and European Absolutism. Chapter 21, Section 1
 Spain s Empire and European Absolutism Chapter 21, Section 1 Section Opener During a time of religious and economic instability, Philip II rules Spain with a strong hand. Philip II of Spain May 21 1527
Spain s Empire and European Absolutism Chapter 21, Section 1 Section Opener During a time of religious and economic instability, Philip II rules Spain with a strong hand. Philip II of Spain May 21 1527
On lined paper put Art history #3, your name, order # and Period
 Art History #3 On lined paper put Art history #3, your name, order # and Period 1. What was Vermeer s Subject matter 2. What was Vermeer s most famous painting? 3. Rococo was characterized by themes. 4.
Art History #3 On lined paper put Art history #3, your name, order # and Period 1. What was Vermeer s Subject matter 2. What was Vermeer s most famous painting? 3. Rococo was characterized by themes. 4.
The Pursuit of Reality
 The Pursuit of Reality The Artemision Bronze / Venus de Milo Classical Hellenistic Greek Sculpture. Greek sculpture is a steady progression towards greater naturalism and realism, but is idealised and
The Pursuit of Reality The Artemision Bronze / Venus de Milo Classical Hellenistic Greek Sculpture. Greek sculpture is a steady progression towards greater naturalism and realism, but is idealised and
The Martyrdom of Saint Matthew by Caravaggio. The Elevation of the Cross by Peter Paul Rubens
 The Martyrdom of Saint Matthew by Caravaggio Painted in 1599-1600, this piece uses strong contrasts of light and dark, chiaroscuro, to provide drama, as well as the hugely exaggerated positions and emotions
The Martyrdom of Saint Matthew by Caravaggio Painted in 1599-1600, this piece uses strong contrasts of light and dark, chiaroscuro, to provide drama, as well as the hugely exaggerated positions and emotions
Art of the Renaissance
 Art of the Renaissance Changes in Art & Learning The rise of Humanism can be seen in paintings created by Renaissance artists. During the Medieval period, art and learning were centered on the church and
Art of the Renaissance Changes in Art & Learning The rise of Humanism can be seen in paintings created by Renaissance artists. During the Medieval period, art and learning were centered on the church and
Art Glossary Studio Art Course
 Art Glossary Studio Art Course Abstract: not realistic, though often based on an actual subject. Accent: a distinctive feature, such as a color or shape, added to bring interest to a composition. Advertisement:
Art Glossary Studio Art Course Abstract: not realistic, though often based on an actual subject. Accent: a distinctive feature, such as a color or shape, added to bring interest to a composition. Advertisement:
Unit 1: Renaissance and Ming Dynasty
 Unit 1: Renaissance and Ming Dynasty Day 3 Starter Jan 11th and 12th Draw a picture of a landscape on the paper attached to the bottom of your desk Renaissance Architecture 1. Revival of Greek and Roman
Unit 1: Renaissance and Ming Dynasty Day 3 Starter Jan 11th and 12th Draw a picture of a landscape on the paper attached to the bottom of your desk Renaissance Architecture 1. Revival of Greek and Roman
Renaissance Art - (fill in the time range above)
 Name Class Renaissance Art - (fill in the time range above) 1) Renaissance meaning refers to a revival of the arts. 2) It began in Italy around and spread throughout lasting until the. 3) Renaissance artists
Name Class Renaissance Art - (fill in the time range above) 1) Renaissance meaning refers to a revival of the arts. 2) It began in Italy around and spread throughout lasting until the. 3) Renaissance artists
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject
 www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject *3066672515* ART HISTORY 9799/03 Paper 3 Thematic Topics May/June
www.xtremepapers.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject *3066672515* ART HISTORY 9799/03 Paper 3 Thematic Topics May/June
ESSAY PROMPT: Discuss how Renaissance ideas are expressed in the Italian art of the period, referring to specific works and artists.
 ESSAY PROMPT: Discuss how Renaissance ideas are expressed in the Italian art of the period, referring to specific works and artists. Which ideas characterized the Italian Renaissance as both a rebirth
ESSAY PROMPT: Discuss how Renaissance ideas are expressed in the Italian art of the period, referring to specific works and artists. Which ideas characterized the Italian Renaissance as both a rebirth
The revival of classical Greek & Roman painting, sculpture, and architecture
 1780-1820 The revival of classical Greek & Roman painting, sculpture, and architecture The late 18 th and early 19 th centuries were a time of quick and drastic change in Western society: Revolutions;
1780-1820 The revival of classical Greek & Roman painting, sculpture, and architecture The late 18 th and early 19 th centuries were a time of quick and drastic change in Western society: Revolutions;
Rococo. The Century of Louis XV
 Rococo The Century of Louis XV 1700-1800 1 The Marquise de Pompadour became the mistress of Louis XV, king of France, in 1745. François Boucher painted this portrait, which hangs in the Louvre museum in
Rococo The Century of Louis XV 1700-1800 1 The Marquise de Pompadour became the mistress of Louis XV, king of France, in 1745. François Boucher painted this portrait, which hangs in the Louvre museum in
The Renaissance. Time of Rebirth ( )
 The Renaissance Time of Rebirth (1300-1600) The Middle Ages: Early Middle Ages (476 800) Heavy Roman influence Various ethnic groups High Middle Ages (800 1300) Development of feudal society 3 tiered caste
The Renaissance Time of Rebirth (1300-1600) The Middle Ages: Early Middle Ages (476 800) Heavy Roman influence Various ethnic groups High Middle Ages (800 1300) Development of feudal society 3 tiered caste
Mr. Cline Marshall High School Western Civilization II Unit TwoEA. The Northern Renaissance
 Mr. Cline Marshall High School Western Civilization II Unit TwoEA The Northern Renaissance Italy was the birthplace of the Renaissance, where ruins of ancient Rome stood in almost every city. This link
Mr. Cline Marshall High School Western Civilization II Unit TwoEA The Northern Renaissance Italy was the birthplace of the Renaissance, where ruins of ancient Rome stood in almost every city. This link
Read pages Answer HW4 questions on device When finished, do CW6 p357 Vocab
 Read pages 350-356 Answer HW4 questions on device When finished, do CW6 p357 Vocab Renaissance Ideas Spread to Northern Europe Monarchs in England and in France (such as Francis I who hired Italian architects
Read pages 350-356 Answer HW4 questions on device When finished, do CW6 p357 Vocab Renaissance Ideas Spread to Northern Europe Monarchs in England and in France (such as Francis I who hired Italian architects
In the fifteenth century, Italy was not the unified country we know today. At that time the boot-shaped peninsula was divided into many small
 The Renaissance The Renaissance occurred between 1400 A.D. and 1600 A.D. It began in the city states of Italy. Renaissance means "rebirth" in French. The art of this period reflected back to the classical
The Renaissance The Renaissance occurred between 1400 A.D. and 1600 A.D. It began in the city states of Italy. Renaissance means "rebirth" in French. The art of this period reflected back to the classical
RENAISSANCE ARCHITECTURE
 RENAISSANCE ARCHITECTURE The clarity and precise geometry of central perspective mirrors the interest of Italian Renaissance artists and architects for Classical Roman examples. The Renaissance revival
RENAISSANCE ARCHITECTURE The clarity and precise geometry of central perspective mirrors the interest of Italian Renaissance artists and architects for Classical Roman examples. The Renaissance revival
Explain how the printing revolution shaped European society. Describe the themes that northern European artists, humanists, and writers explored.
 Objectives Explain how the printing revolution shaped European society. Describe the themes that northern European artists, humanists, and writers explored. Terms and People Johann Gutenberg in 1455, printed
Objectives Explain how the printing revolution shaped European society. Describe the themes that northern European artists, humanists, and writers explored. Terms and People Johann Gutenberg in 1455, printed
THE AGE OF THE REFORMATION SIXTEENTH-CENTURY ART IN NORTHERN EUROPE AND SPAIN
 23 THE AGE OF THE REFORMATION SIXTEENTH-CENTURY ART IN NORTHERN EUROPE AND SPAIN TEXT PAGES 662 687 THE PROTESTANT REFORMATION 1 Who was Martin Luther and what was his goal when he posted his ninety-five
23 THE AGE OF THE REFORMATION SIXTEENTH-CENTURY ART IN NORTHERN EUROPE AND SPAIN TEXT PAGES 662 687 THE PROTESTANT REFORMATION 1 Who was Martin Luther and what was his goal when he posted his ninety-five
Year Course Programme High Renaissance to Baroque
 Year Course Programme 2016 17 High Renaissance to Baroque 1500 1720 Wednesdays, 21 September 2016 12 July 2017 (over 3 terms) 11.10 15.30 (Each term includes optional gallery talks, commencing at 10.00
Year Course Programme 2016 17 High Renaissance to Baroque 1500 1720 Wednesdays, 21 September 2016 12 July 2017 (over 3 terms) 11.10 15.30 (Each term includes optional gallery talks, commencing at 10.00
Chapter Living History. A statue of King David from a medieval cathedral
 Chapter 3 Sculptors are artists who make statues using stone, metal or wood. In the Middle Ages, sculptors worked in the great Gothic churches that we read about on page 141. They carved the statues of
Chapter 3 Sculptors are artists who make statues using stone, metal or wood. In the Middle Ages, sculptors worked in the great Gothic churches that we read about on page 141. They carved the statues of
The Renaissance Outcome: The Renaissance in Italy
 The Renaissance Outcome: The Renaissance in Italy Constructive Response Question 1.Summarize the Renaissance and identify why it started in Italy. What will we learn? 1. What is the Renaissance? 2. Why
The Renaissance Outcome: The Renaissance in Italy Constructive Response Question 1.Summarize the Renaissance and identify why it started in Italy. What will we learn? 1. What is the Renaissance? 2. Why
Ch. 18 Renaissance through the Baroque
 Ch. 18 Renaissance through the Baroque Renaissance Period is birth of Humanism and the belief in the individual. This is seen in the artwork and the way that the human figure is represented. The European
Ch. 18 Renaissance through the Baroque Renaissance Period is birth of Humanism and the belief in the individual. This is seen in the artwork and the way that the human figure is represented. The European
Western Civilization. Art Discussion, Oct. 31, 2011 Group 1
 Western Civilization Art Discussion, Oct. 31, 2011 Group 1 CATHOLIC BAROQUE Bernini, The Ecstasy of St. Teresa. 1645-52 What is happening to St. Teresa in this sculpture? What is Teresa s emotional response?
Western Civilization Art Discussion, Oct. 31, 2011 Group 1 CATHOLIC BAROQUE Bernini, The Ecstasy of St. Teresa. 1645-52 What is happening to St. Teresa in this sculpture? What is Teresa s emotional response?
Art History Final Exam Review Mrs. Milewski
 Art History Final Exam Review Mrs. Milewski 1. Identify which art theory is demonstrated by this painting 2. Which art movement focused on medieval romances, gothic horror stories and gothic revival architecture?
Art History Final Exam Review Mrs. Milewski 1. Identify which art theory is demonstrated by this painting 2. Which art movement focused on medieval romances, gothic horror stories and gothic revival architecture?
What was the Renaissance?
 The Renaissance What was the Renaissance? What was the Renaissance, and where did it begin? Began mostly in Italy, and spread to Northern Europe Why Italy? Urban Societies Major Trading Centers Centrally
The Renaissance What was the Renaissance? What was the Renaissance, and where did it begin? Began mostly in Italy, and spread to Northern Europe Why Italy? Urban Societies Major Trading Centers Centrally
1. Setting the Stage. Madonna and Child in Glory. Enlarge. 2. The Renaissance Connection
 1. Setting the Stage The Middle Ages (a period of European history from the third through 13th centuries), art and learning were centered on the church and religion. But at the start of the 14th century,
1. Setting the Stage The Middle Ages (a period of European history from the third through 13th centuries), art and learning were centered on the church and religion. But at the start of the 14th century,
Content Area 3 Part 3 Renaissance & Baroque One Pagers. AP ARTH C. Montenegro
 Content Area 3 Part 3 Renaissance & Baroque One Pagers AP ARTH C. Montenegro Attached you will find the following: Explanations and considerations when filling out the One Pagers, Table of Main Themes,
Content Area 3 Part 3 Renaissance & Baroque One Pagers AP ARTH C. Montenegro Attached you will find the following: Explanations and considerations when filling out the One Pagers, Table of Main Themes,
The Division of Art: Specialization and the Dutch. There are many things which make the Golden Age of Dutch Art fascinating to
 Marcus Shera Professor Angela Ho HNRS 122 11/29/16 The Division of Art: Specialization and the Dutch There are many things which make the Golden Age of Dutch Art fascinating to both art historians and
Marcus Shera Professor Angela Ho HNRS 122 11/29/16 The Division of Art: Specialization and the Dutch There are many things which make the Golden Age of Dutch Art fascinating to both art historians and
Thirty-Minute Essay Questions from Earlier AP Exams
 Thirty-Minute Essay Questions from Earlier AP Exams A: In most parts of the world, public sculpture is a common and accepted sight. Identify three works of public sculpture whose effects are different
Thirty-Minute Essay Questions from Earlier AP Exams A: In most parts of the world, public sculpture is a common and accepted sight. Identify three works of public sculpture whose effects are different
Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance
 Ch. 1-1 Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Essential Question: Why did the Renaissance start in Italy? Italy s Advantage Classical and Worldly Values The Renaissance Revolutionizes Art Renaissance Writers
Ch. 1-1 Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Essential Question: Why did the Renaissance start in Italy? Italy s Advantage Classical and Worldly Values The Renaissance Revolutionizes Art Renaissance Writers
! Exploring!Abraham!Bloemaert s! Transition!into!the!Baroque!! Geoffrey!Matthews!
 ! Exploring!Abraham!Bloemaert s! Transition!into!the!Baroque!! Geoffrey!Matthews!! Exploring Abraham Bloemaert s Transition into the Baroque Geoffrey Matthews Professor Kelley Helmstruter Di Dio Art History
! Exploring!Abraham!Bloemaert s! Transition!into!the!Baroque!! Geoffrey!Matthews!! Exploring Abraham Bloemaert s Transition into the Baroque Geoffrey Matthews Professor Kelley Helmstruter Di Dio Art History
Chapter Art of the 16 th Century
 Chapter 18-5 Art of the 16 th Century France Artist: Parmigianino Title: Madonna with the Long Neck Medium: Oil on wood panel Size: 7'1" X 4'4" (2.16 X 1.32 m) Date: 1534 40 Painted with softened facial
Chapter 18-5 Art of the 16 th Century France Artist: Parmigianino Title: Madonna with the Long Neck Medium: Oil on wood panel Size: 7'1" X 4'4" (2.16 X 1.32 m) Date: 1534 40 Painted with softened facial
Essential Question: What changes in Europe led to the Renaissance?
 Essential Question: What changes in Europe led to the Renaissance? Examine the diagram above and then answer the following questions. 1. In this Renaissance plant which root grows straight up? Which roots
Essential Question: What changes in Europe led to the Renaissance? Examine the diagram above and then answer the following questions. 1. In this Renaissance plant which root grows straight up? Which roots
What Was the Renaissance?
 THE RENAISSANCE What Was the Renaissance? It was a change in thinking about the world and the place people occupy in it A new philosophy called HUMANISM came to dominate people s thinking Humanism emphasizes
THE RENAISSANCE What Was the Renaissance? It was a change in thinking about the world and the place people occupy in it A new philosophy called HUMANISM came to dominate people s thinking Humanism emphasizes
Northern Renaissance
 Northern Renaissance Northern Renaissance Objective: Explain the causes and effects of the Northern Renaissance and its impact upon history. Identify major literary and artistic figures, and explain the
Northern Renaissance Northern Renaissance Objective: Explain the causes and effects of the Northern Renaissance and its impact upon history. Identify major literary and artistic figures, and explain the
 Art Appreciation Activity Points % of Total Discuss 60 5% Exam 60 5% Final Exam 100 8% Journal 90 7% Practice 220 18% Quiz 360 29% Test (CST) 180 14% Test (TST) 180 14% Total Points for the Course : 1250
Art Appreciation Activity Points % of Total Discuss 60 5% Exam 60 5% Final Exam 100 8% Journal 90 7% Practice 220 18% Quiz 360 29% Test (CST) 180 14% Test (TST) 180 14% Total Points for the Course : 1250
Learning Academy YEAR COURSE. Wednesdays, 26 September July 2019 (over 3 terms)
 Learning Academy H I G H R E N A I S S A N C E T O B A R O Q U E 1500 1720 Wednesdays, 26 September 2018 10 July 2019 (over 3 terms) (Each term includes optional gallery talks, commencing at 10.00 and
Learning Academy H I G H R E N A I S S A N C E T O B A R O Q U E 1500 1720 Wednesdays, 26 September 2018 10 July 2019 (over 3 terms) (Each term includes optional gallery talks, commencing at 10.00 and
Art Appreciation UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO PAINTING LESSON 1: BROAD STROKES: PRINCIPLES OF PAINTING
 Core Art Appreciation Art Appreciation is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn
Core Art Appreciation Art Appreciation is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn
This is an introduction to Italian Art - The Renaissance
 This is an introduction to Italian Art - The Renaissance I am Mr. Lanni, Art Teacher at Columbia Middle School. I will lead you through this presentation which highlights a few artists from this period.
This is an introduction to Italian Art - The Renaissance I am Mr. Lanni, Art Teacher at Columbia Middle School. I will lead you through this presentation which highlights a few artists from this period.
Warmup. What is her name? Mona Lisa. Painted by Leonardo da Vinci in 1503
 Warmup What is her name? Mona Lisa Painted by Leonardo da Vinci in 1503 Agenda Renaissance PowerPoint with notes Mirror Writing activity Test December 13 th Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Setting
Warmup What is her name? Mona Lisa Painted by Leonardo da Vinci in 1503 Agenda Renaissance PowerPoint with notes Mirror Writing activity Test December 13 th Italy: Birthplace of the Renaissance Setting
Mathew is the figure with the beard He sits among a group of men in a tavern coun<ng tax money he was a Roman tax collector As Jesus enters
 1 2 3 4 Mathew is the figure with the beard He sits among a group of men in a tavern coun
1 2 3 4 Mathew is the figure with the beard He sits among a group of men in a tavern coun
7th Chapter 11 Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following describes one effect of Marco Polo s journey to China? a. Marco Polo became the
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following describes one effect of Marco Polo s journey to China? a. Marco Polo became the
 Thanks so much for purchasing this product! Interactive Notebooks are an amazing way to get your students engaged and active in their learning! The graphic organizers and foldables in this resource are
Thanks so much for purchasing this product! Interactive Notebooks are an amazing way to get your students engaged and active in their learning! The graphic organizers and foldables in this resource are
State of the Arts: Pre-Raphaelites
 State of the Arts: Pre-Raphaelites This curriculum is based on the Pre-Raphaelite portion of the first program. Please prepare yourself by watching the entire program before showing it to your students.
State of the Arts: Pre-Raphaelites This curriculum is based on the Pre-Raphaelite portion of the first program. Please prepare yourself by watching the entire program before showing it to your students.
ARH 1210: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present
 ARH 1210: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions
ARH 1210: History of Western Art: Renaissance to the Present General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions
Introduction to Art History
 Core is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn how to critique and compare works
Core is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn how to critique and compare works
Name: What does the term Renaissance refer to? What was the basis for the Italian Renaissance?
 Name: Chapter 13: European Society in the Age of the Renaissance AP Euro ~ Mr. Nielsen Complete the graphic organizers as you read Chapter 13. DO NOT SIMPLY HUNT FOR THE ANSWERS AS DOING SO WILL LEAVE
Name: Chapter 13: European Society in the Age of the Renaissance AP Euro ~ Mr. Nielsen Complete the graphic organizers as you read Chapter 13. DO NOT SIMPLY HUNT FOR THE ANSWERS AS DOING SO WILL LEAVE
Characteristics of the Renaissance Examples Activity
 Example Characteristics of the Renaissance Examples Activity Greek and/or Roman Influence Humanism Emphasis on the Individual Celebration of Secular Achievements 1. Brunelleschi s Dome 2. Brief Biography
Example Characteristics of the Renaissance Examples Activity Greek and/or Roman Influence Humanism Emphasis on the Individual Celebration of Secular Achievements 1. Brunelleschi s Dome 2. Brief Biography
Art Appreciation UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO PAINTING. Core
 Core is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn how to critique and compare works
Core is a survey of the history of Western visual arts, with a primary focus on painting. Students begin with an introduction to the basic principles of painting and learn how to critique and compare works
Other Artists. Raffaello Sanzio, became known as Raphael. Renowned painter, accomplished architect
 Other Artists Raphael Raffaello Sanzio, became known as Raphael Renowned painter, accomplished architect Most famous work, The School of Athens, fresco painting made on fresh, moist plaster Also well known
Other Artists Raphael Raffaello Sanzio, became known as Raphael Renowned painter, accomplished architect Most famous work, The School of Athens, fresco painting made on fresh, moist plaster Also well known
WARM-UP. What would you create? Why?
 WARM-UP You are a 35 year old adult. You ve been working your whole life, doing okay, but usually too busy to enjoy life during the weekdays. Suddenly, a wealthy citizen from Austin offers you a paycheck
WARM-UP You are a 35 year old adult. You ve been working your whole life, doing okay, but usually too busy to enjoy life during the weekdays. Suddenly, a wealthy citizen from Austin offers you a paycheck
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2010 2 hours 15 minutes * 7002
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject ART HISTORY 9799/02 Paper 2 Historical Topics May/June 2010 2 hours 15 minutes * 7002
The use of perspective allowed artists to Vernacular
 Journal 02-25-19 Journal A The use of perspective allowed artists to A. apply layers of paint to create color variations B. create the appearance of three dimensions in their paintings C. copyright their
Journal 02-25-19 Journal A The use of perspective allowed artists to A. apply layers of paint to create color variations B. create the appearance of three dimensions in their paintings C. copyright their
The Northern Renaissance, an introduction
 The Northern Renaissance, an introduction Albrecht Dürer, Adam and Eve, 1504, engraving, fourth state, 25.1 x 20 cm (The Metropolitan Museum of Art) The word Renaissance is generally defined as the rebirth
The Northern Renaissance, an introduction Albrecht Dürer, Adam and Eve, 1504, engraving, fourth state, 25.1 x 20 cm (The Metropolitan Museum of Art) The word Renaissance is generally defined as the rebirth
A P A R T H I S T O R Y AP Long Essay Questions
 Long Essay Questions Religious Spaces (1998) Many cultures designate spaces or create structures for religious devotion. Choose two specific examples, each from a different culture. At least one culture
Long Essay Questions Religious Spaces (1998) Many cultures designate spaces or create structures for religious devotion. Choose two specific examples, each from a different culture. At least one culture
7/8 World History. Week 26. The Renaissance
 7/8 World History Week 26 The Renaissance Tuesday Do Now Thinking back through all the past societies you've studied, what are some of the reasons that a society enters a golden age or period of prosperity?
7/8 World History Week 26 The Renaissance Tuesday Do Now Thinking back through all the past societies you've studied, what are some of the reasons that a society enters a golden age or period of prosperity?
1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning ( )
 1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning (1300-1600) After suffering through wars, destruction, and the plague of the Middle Ages, people wanted to celebrate life and the human spirit.
1.1 The Renaissance: a rebirth or revival of art and learning (1300-1600) After suffering through wars, destruction, and the plague of the Middle Ages, people wanted to celebrate life and the human spirit.
April 16, 2014 The Renaissance and it s Famous People
 April 16, 2014 The Renaissance and it s Famous People Homework: Michelangelo: The Italian Sculptor & Painter Lived: 1475 1564 From: Florence, Italy Personality/Training: Bad temper, ambitious, & religious,
April 16, 2014 The Renaissance and it s Famous People Homework: Michelangelo: The Italian Sculptor & Painter Lived: 1475 1564 From: Florence, Italy Personality/Training: Bad temper, ambitious, & religious,
The use of perspective allowed artists to Vernacular
 Journal 02-26-18 Journal A The use of perspective allowed artists to A. apply layers of paint to create color variations B. create the appearance of three dimensions in their paintings C. copyright their
Journal 02-26-18 Journal A The use of perspective allowed artists to A. apply layers of paint to create color variations B. create the appearance of three dimensions in their paintings C. copyright their
Line Line Characteristic of Line are: Width Length Direction Focus Feeling Types of Line: Outlines Contour Lines Gesture Lines Sketch Lines
 Line Line: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with a pointed tool or implied by the edges
Line Line: An element of art that is used to define shape, contours, and outlines, also to suggest mass and volume. It may be a continuous mark made on a surface with a pointed tool or implied by the edges
Visual Art. Forms of Art - Watercolor 187 words. Forms of Art - African Sculpture 201 words. Forms of Art - Abstract Art 233 words
 ARTICLE-A-DAY Visual Art 7 Articles Check articles you have read: Forms of Art - Watercolor 187 words Forms of Art - African Sculpture 201 words Forms of Art - Abstract Art 233 words Forms of Art - Landscape
ARTICLE-A-DAY Visual Art 7 Articles Check articles you have read: Forms of Art - Watercolor 187 words Forms of Art - African Sculpture 201 words Forms of Art - Abstract Art 233 words Forms of Art - Landscape
Art of the Italian Renaissance
 Art of the Italian Renaissance A time of great change for art and architecture I want to thank a fellow teacher, Susan M. Pojer of Horace Greeley High School in Chappaqua, New York who created a PowerPoint
Art of the Italian Renaissance A time of great change for art and architecture I want to thank a fellow teacher, Susan M. Pojer of Horace Greeley High School in Chappaqua, New York who created a PowerPoint
Rivaled Poussin in fame His figures tell no drama9c story, point out no moral, praise no hero, celebrate no saint His figure merely provide an excuse
 1 2 3 4 Rivaled Poussin in fame His figures tell no drama9c story, point out no moral, praise no hero, celebrate no saint His figure merely provide an excuse to paint the radiant landscape For French landscape
1 2 3 4 Rivaled Poussin in fame His figures tell no drama9c story, point out no moral, praise no hero, celebrate no saint His figure merely provide an excuse to paint the radiant landscape For French landscape
Rigaud, Louis XIV. Essay by Tessa Fleming. Share Tweet . Hyacinthe Rigaud, Louis XIV, 1701, oil on canvas, 9 2 x 6 3. Musée du Louvre, Paris
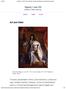 Rigaud, Louis XIV Essay by Tessa Fleming. Share Tweet Email Art and State Hyacinthe Rigaud, Louis XIV, 1701, oil on canvas, 9 2 x 6 3. Musée du Louvre, Paris The early seventeenth century was marked by
Rigaud, Louis XIV Essay by Tessa Fleming. Share Tweet Email Art and State Hyacinthe Rigaud, Louis XIV, 1701, oil on canvas, 9 2 x 6 3. Musée du Louvre, Paris The early seventeenth century was marked by
Art Glossary Western Art History
 Art Glossary Western Art History Abstract: not realistic, though often based on an actual subject. Abstract Concept: an idea that does not take a visible form, such as justice, truth. Aesthetics: the study
Art Glossary Western Art History Abstract: not realistic, though often based on an actual subject. Abstract Concept: an idea that does not take a visible form, such as justice, truth. Aesthetics: the study
GOTHIC ART. Teacher Ms. Isabel 1
 GOTHIC ART Teacher Ms. Isabel 1 Gothic Art:Features The Gothic style first appeared in the 12th century in the area around Paris. In architecture, Gothic buildings employed a variety of new techniques
GOTHIC ART Teacher Ms. Isabel 1 Gothic Art:Features The Gothic style first appeared in the 12th century in the area around Paris. In architecture, Gothic buildings employed a variety of new techniques
Your name Period # What was the purpose of art in Ancient Egyptian culture? What were the rules about representing humans in Ancient Egyptian art?
 Review questions for art history portion of the final exam, Art 1 Your name Period # What was the purpose of art in Ancient Egyptian culture? What were the rules about representing humans in Ancient Egyptian
Review questions for art history portion of the final exam, Art 1 Your name Period # What was the purpose of art in Ancient Egyptian culture? What were the rules about representing humans in Ancient Egyptian
Artists: Michelangelo
 Artists: Michelangelo By Biography.com Editors and A+E Networks, adapted by Newsela staff on 08.08.16 Word Count 851 Level 1060L A portrait of Michelangelo by Jacopino del Conte. Wikimedia Commons Synopsis:
Artists: Michelangelo By Biography.com Editors and A+E Networks, adapted by Newsela staff on 08.08.16 Word Count 851 Level 1060L A portrait of Michelangelo by Jacopino del Conte. Wikimedia Commons Synopsis:
Chapter 13.2: The Northern Renaissance
 Chapter 13.2: The Northern Renaissance Ch.13.2 Essential Questions: What were the origins and characteristics of the Northern Renaissance? What was the impact of the Renaissance on German and Flemish painters?
Chapter 13.2: The Northern Renaissance Ch.13.2 Essential Questions: What were the origins and characteristics of the Northern Renaissance? What was the impact of the Renaissance on German and Flemish painters?
The Renaissance. Europe 1300s 1600s
 The Renaissance Europe 1300s 1600s The word Renaissance = rebirth The Renaissance was the period of rebirth and creativity that followed Europe s Middle Ages It was a rebirth of interest in classical (Greek
The Renaissance Europe 1300s 1600s The word Renaissance = rebirth The Renaissance was the period of rebirth and creativity that followed Europe s Middle Ages It was a rebirth of interest in classical (Greek
An introduction to the Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century
 An introduction to the Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century Share Tweet Email Albrecht Dürer, Self-Portrait, 1500 (Alte Pinakothek, Munich) https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/renaissance-reformation/northern-renaissance1/beginners-guide-northern-renaissance/a/an-introduction-to-the-northern-ren...
An introduction to the Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century Share Tweet Email Albrecht Dürer, Self-Portrait, 1500 (Alte Pinakothek, Munich) https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/renaissance-reformation/northern-renaissance1/beginners-guide-northern-renaissance/a/an-introduction-to-the-northern-ren...
