Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture On the Selection of Topics
|
|
|
- Warren McDaniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 4 (2000), No. 2, Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture On the Selection of Topics Claus Pütz Institute for Geometry and Applied Mathematics RWTH Aachen, D Aachen, Germany puetz@dg-ac.de Abstract. Descriptive Geometry (DG) is an applied mathematical discipline dealing with the practical performance of the process of representation as well as with the analysis and generation of objects in three-dimensional space by methods of drawing. Due to the decreasing share of DG in the curriculum of architectural studies it is no longer possible to teach DG even roughly to its full extent. As contribution to the development of a curriculum Descriptive Geometry for architects the geometrical topics actually used by professional architects as well as those which assist the student directly or indirectly in developing skills fundamental in the daily work of professional architects are explored. Key Words: Descriptive Geometry courses, architecture, selection of topics MSC 2000: 51N05 1. Introduction In order to determine the topics and methods of Descriptive Geometry (DG) which are in particular relevant for professional architects we will not only clarify the value of the various ways of projection for architectural drawings but also analyse the application of spatial objects in the architect s field of activity. 2. Selecting ways of projection The following aspects are relevant for selecting the type of projection: The predefinition of architectural objects by orthogonal projection, the ways of projection with realistic effects and the enhancement of the realistic effects by other means. ISSN /$ 2.50 c 2000 Heldermann Verlag
2 210 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture 2.1. Orthogonal projection Architects depend on drawings to develop projects, to locate problematical areas and to find solutions regarding design and construction. These solutions have to be secured and they provide the basis for all following phases of architectural planing and realisation. The drawing facilitates the thinking-process and enables the architect to communicate with all the other specialists involved in the process of building. DG represents an essential contribution to the predefinition of architectural designs by means of orthographic projection onto special image planes: ground plan (the image plane π 1 is horizontal), elevation (the image plane π 2 is vertical and parallel to a main plane of the object), side view and section (the image plane is vertical but not parallel to a main plane of the object). With these orthogonal projections all tasks of spatial geometry relevant to a professional architect can be solved by combination of only eleven basic tasks: 1. Determination of a fourth point of a plane, 2. intersection of a straight line and a plane, 3. intersection line of two planes, 4. determination of a line orthogonal to a plane,
3 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture determination of a plane orthogonal to a line, 6. rotating a point about a straight line, 7. true length of a line segment, 8. true size of the angle between a line and the image plane, 9. true size of the angle between a plane and the image plane, 10. true size of the angle between two intersecting lines, 11. true size and shape of a plane figure. Due to the great importance of this topic the aspects of orthogonal projection mentioned above should build the main part of teaching DG for students of architecture. From experience we know that these topics are for students the most difficult ones to understand. Once understood, the practising architect works with these methods everyday. Therefore most of them forget that they had to learn it once and that this was a hard job.
4 212 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture 2.2. Ways of projection with realistic effects Architects utilise realistic views significantly less than orthographic views. Realistic views are mainly used to show laymen the effect of the architectural design. For the architect it is important that these drawings come as near as possible to reality. The more the projective beams and the visual rays (of the observer) correspond, the better the realistic effect of a drawing. In most cases the oblique parallel projection is unfavourable, e.g. because the outline of a sphere is an ellipse. The orthographic parallel projection is beneficial; the outline of a sphere is a circle. The central projection is ideal because the projective beams and the visual rays can actually correspond; the outline of a sphere is a circle. But the effect of a central projection will be unfavourable when the observer looks from the wrong position: if the centre of the sphere is not on the main visual ray, the outline of a sphere is an ellipse or even an other conic. Regarding this, the four ways of projection with the most realistic results are determined: Axonometry The orthographic parallel projection onto an inclined image plane has especially good effects and is easy to draw. Birds-eye-view Even though the oblique parallel projection onto a horizontal image plane has disadvantages in regard of its realistic effects it should be taught because it is the easiest realistic drawing.
5 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture 213 Perspective The central projection onto a vertical image plane has the best realistic effect; with this perspective the architect can show his design in the most favourable way. Frontal perspective The central projection onto an image plane parallel to the elevation plane is a special case of the perspective: The object cannot be shown from every angle but the method of construction is easier.
6 214 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture These reflections imply that the birds-eye-view and the perspective are particularly important to architects and therefore should be taught in full detail. The axonometry and the frontal perspective are also suggested to be included in the curriculum. In order to present a concise and simple method of drawing views for architects, a composition procedure has been designed which works for all ways of projection, requires little effort and allows drawings of every object. The basis of the composition procedure consists of four steps: (a) birds-eye-view, (b) axonometry, (c) perspective, (d) frontal perspective. I. Choice of view: (a) (b) (c) (d)
7 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture 215 II. Determining the ground plan: (a) (b) (c) (d) III. Protracting the heights: (a) (b) (c) (d)
8 216 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture IV. Simplifications for the reproduction of parallel lines: (a) (b) (c) (d) Supplementary elements are developed which are able to reduce the effort in construction even more: V. Simplifications for the subdivision of lines, VI. simple reproduction of figures in vertical planes, VII. simple reproduction of figures in inclined planes, VIII. reconstruction of the parameters of a projection Enhancement of realistic effects The realistic effect of ground plans can be improved by including shadows; this technique is often also useful for elevations, axonometry and perspectives. The corresponding geometrical ideas should be part of the curriculum. The construction of shadows is possible by means of the eleven above mentioned basic tasks. Illustrations of reflections in architectural drawings are not really necessary. On the other hand there are some trivial special cases which are worth to mention in the mandatory course.
9 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture Selection of objects The following objects are to distinguish: Polyhedra, curved surfaces and the intersections of curved surfaces Polyhedra Polyhedra represent the spatial objects being most important to architects. Everybody will agree that the preponderant part of architecture is formed by prisms and cuboids whereas pyramids are rarely used and regular polyhedra are nearly never found. On the other hand there are a lot of general polyhedra in architecture. To handle polyhedra in drawings the architect must be able to master only the eleven above mentioned basic tasks. Some easement of labour can be achieved by using affinity or perspectivity when a prism or a pyramid is cut by a plane Curved surfaces Straight cylinders are often used as architectural elements; the advantage of straight cylinders is that they are formed by straight lines (beams) and circles of the same size, therefore the prefabrication is easy to plan. The straight cylinder is mostly positioned horizontally or vertically. Elliptical, parabolic and general cylinders are seldom used in architecture: The straight lines and the repetition of the same curves on the surface are advantageous, but the bending differs in each point of the curves. There are only few straight circular cones
10 218 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture in architecture (and nearly no general cones): Their disadvantage is that all straight lines intersect in one point and all the circles differ in their radius. To handle cylinders and cones in drawings the architect can fall back on the thorough elaborateness of prisms and pyramids. Furthermore ellipses, the construction of tangents and the development of the surfaces have to be dealt with. There is a limited number of spheres in architecture: Due to its double bending a sphere can be built as a shell and will carry a multiple of its own weight. But the fabrication of spheres is expensive. General surfaces of revolution are less suitable as parts of buildings: The meridians can be manufactured repeatedly in the same form, but the parallel circles on the surface differ in size. Most examples of surfaces of revolution in architecture are tori (rotated circles) or one-sheet hyperboloids of revolution (rotated straight lines).
11 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture 219 General surfaces generated by the translating a curve don t supply the architect with solutions for his tasks. The only exception is the hyperbolic paraboloid: On its surface there are two cohorts of straight lines, therefore form boards can be used for its fabrication. Furthermore two cohorts of parables are on the surface which opportunely divert the forces. So great spans with small construction heights are possible. Building parts generated by a screwing motion can almost only found at spiral staircases and ramps. All the surfaces treated until now can relatively easily be generated by a movement of a curve. Of course there are other surfaces which can be relevant for solving architectural tasks. As they do not follow simple geometrical laws and their construction is very complicated to handle. These surfaces are not part of the curriculum of DG. On the other hand it should be noticed that only those parts of buildings are to produce easily and economically, which are easy to draw. If the architect still intends to use a general surface, he has to use a model or a computer specialist.
12 220 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture Recapitulating it can be argued, that straight cylinders are most frequently used as architectural elements among curved surfaces; therefore students of architecture should be taught the necessary knowledge of cylinders thoroughly. General cylinders, straight circle cones and spheres can be dealt with in a straighter way. Some other surfaces (e.g. hyperbolic paraboloid and spiral surfaces) can only be touched briefly in a mandatory DG course and should be dealt with in an advanced and optional course. The remaining surfaces are of no significance for architecture Intersections of curved surfaces As mentioned above, curved surface are rarely used in architecture; even more infrequently these surface are positioned in a way, that they intersect.
13 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture 221 Most of these rare cases are built by intersecting straight cylinders. Combining two cylinders in certain cases the line of intersection lays in a plane. These cases are easier to handle and cheaper to build than curved lines. Intersections of curved surfaces are very rare in architecture and can therefore be neglected in the curriculum. However, since even two straight circle cylinders can intersect in a curved line, students of architecture should be taught the basic principles dealing with intersections, e.g. the methods of auxiliary planes to find points of intersection, and the method of tangential planes to find the tangents of the curved line. 4. Conclusion This selection of topics in a DG course enables students of architecture to solve geometrical tasks which occur in their future jobs. Furthermore they are able to efficiently acquaint themselves with the skills to solve special geometrical problems if they occur in practice. The results of this work can be used for developing a curriculum for teaching architecture at university and they represent the basis to tie the teaching of Descriptive Geometry to other subjects within the study of architecture.
14 222 C. Pütz: Descriptive Geometry Courses for Students of Architecture References [1] C. Pütz: Untersuchungen zur Auswahl der Lehrinhalte des Faches Darstellende Geometrie für die Hochschulausbildung zum Architekten. PhD thesis 1990, RWTH Aachen, Germany. Received August 1, 2000; final form November 15, 2000
Multi-View Drawing Review
 Multi-View Drawing Review Sacramento City College EDT 300/ENGR 306 EDT 300 / ENGR 306 - Chapter 5 1 Objectives Identify and select the various views of an object. Determine the number of views needed to
Multi-View Drawing Review Sacramento City College EDT 300/ENGR 306 EDT 300 / ENGR 306 - Chapter 5 1 Objectives Identify and select the various views of an object. Determine the number of views needed to
Appendix. Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2016 A.Y. Brailov, Engineering Graphics, DOI /
 Appendix See Figs. A.1, A.2, A.3, A.4, A.5, A.6, A.7, A.8, A.9, A.10, A.11, A.12, A.13, A.14, A.15, A.16, A.17, A.18, A.19, A.20, A.21, A.22, A.23, A.24, A.25, A.26, A.27, A.28, A.29, A.30, A.31, A.32,
Appendix See Figs. A.1, A.2, A.3, A.4, A.5, A.6, A.7, A.8, A.9, A.10, A.11, A.12, A.13, A.14, A.15, A.16, A.17, A.18, A.19, A.20, A.21, A.22, A.23, A.24, A.25, A.26, A.27, A.28, A.29, A.30, A.31, A.32,
1 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION SECTION I: INTRODUCTION TO ISOMETRIC PROJECTION
 1 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION SECTION I: INTRODUCTION TO ISOMETRIC PROJECTION Orthographic projection shows drawings of an object in a two-dimensional format, with views given in plan, elevation and end elevation
1 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION SECTION I: INTRODUCTION TO ISOMETRIC PROJECTION Orthographic projection shows drawings of an object in a two-dimensional format, with views given in plan, elevation and end elevation
Technical Drawing Paper 1 - Higher Level (Plane and Solid Geometry)
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission 2008. M81 Leaving Certificate Examination 2008 Technical Drawing Paper 1 - Higher Level (Plane and Solid Geometry) (200 Marks) Friday 13 June
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission 2008. M81 Leaving Certificate Examination 2008 Technical Drawing Paper 1 - Higher Level (Plane and Solid Geometry) (200 Marks) Friday 13 June
Copyrighted Material. Copyrighted Material. Copyrighted. Copyrighted. Material
 Engineering Graphics ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION People who work with drawings develop the ability to look at lines on paper or on a computer screen and "see" the shapes of the objects the lines represent.
Engineering Graphics ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION People who work with drawings develop the ability to look at lines on paper or on a computer screen and "see" the shapes of the objects the lines represent.
APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY PART A Answer ANY Two questions. 10 marks each.
 B B2B111 Pages: 2 Reg. No. Name: SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2017 Max.Marks:50 Course Code: BE110 Duration:3Hours Answer ANY Two questions. 10 marks each. 1. A line AB 100 mm long and
B B2B111 Pages: 2 Reg. No. Name: SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2017 Max.Marks:50 Course Code: BE110 Duration:3Hours Answer ANY Two questions. 10 marks each. 1. A line AB 100 mm long and
technical drawing
 technical drawing school of art, design and architecture nust spring 2011 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q6mk9hpxwvo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bnu2gb7w4qs Objective abstraction - axonometric view
technical drawing school of art, design and architecture nust spring 2011 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q6mk9hpxwvo http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bnu2gb7w4qs Objective abstraction - axonometric view
JUNIOR CERTIFICATE 2009 MARKING SCHEME TECHNICAL GRAPHICS HIGHER LEVEL
 . JUNIOR CERTIFICATE 2009 MARKING SCHEME TECHNICAL GRAPHICS HIGHER LEVEL Sections A and B Section A any ten questions from this section Q1 12 Four diagrams, 3 marks for each correct label. Q2 12 2 marks
. JUNIOR CERTIFICATE 2009 MARKING SCHEME TECHNICAL GRAPHICS HIGHER LEVEL Sections A and B Section A any ten questions from this section Q1 12 Four diagrams, 3 marks for each correct label. Q2 12 2 marks
Multiviews and Auxiliary Views
 Multiviews and Auxiliary Views Multiviews and Auxiliary Views Objectives Explain orthographic and multiview projection. Identifying the six principal views. Apply standard line practices to multiviews
Multiviews and Auxiliary Views Multiviews and Auxiliary Views Objectives Explain orthographic and multiview projection. Identifying the six principal views. Apply standard line practices to multiviews
ENGINEERING DRAWING IM 09 AND GRAPHICAL COMMUNICATION
 IM SYLLABUS (2014) ENGINEERING DRAWING IM 09 AND GRAPHICAL COMMUNICATION SYLLABUS Engineering Drawing and Graphical Communication IM 09 (Available in September) Syllabus 1 Paper (3 hours) Aims The aims
IM SYLLABUS (2014) ENGINEERING DRAWING IM 09 AND GRAPHICAL COMMUNICATION SYLLABUS Engineering Drawing and Graphical Communication IM 09 (Available in September) Syllabus 1 Paper (3 hours) Aims The aims
Period: Date Lesson 2: Common 3-Dimensional Shapes and Their Cross- Sections
 : Common 3-Dimensional Shapes and Their Cross- Sections Learning Target: I can understand the definitions of a general prism and a cylinder and the distinction between a cross-section and a slice. Warm
: Common 3-Dimensional Shapes and Their Cross- Sections Learning Target: I can understand the definitions of a general prism and a cylinder and the distinction between a cross-section and a slice. Warm
UNIT 5a STANDARD ORTHOGRAPHIC VIEW DRAWINGS
 UNIT 5a STANDARD ORTHOGRAPHIC VIEW DRAWINGS 5.1 Introduction Orthographic views are 2D images of a 3D object obtained by viewing it from different orthogonal directions. Six principal views are possible
UNIT 5a STANDARD ORTHOGRAPHIC VIEW DRAWINGS 5.1 Introduction Orthographic views are 2D images of a 3D object obtained by viewing it from different orthogonal directions. Six principal views are possible
Tapered or Conical Tee
 TRADE OF Industrial Insulation PHASE 2 Module 2 Geometry & Pattern Development UNIT: 9 Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Michael Kelly SOLAS 2014 Table of Contents Unit Objective...
TRADE OF Industrial Insulation PHASE 2 Module 2 Geometry & Pattern Development UNIT: 9 Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Michael Kelly SOLAS 2014 Table of Contents Unit Objective...
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS
 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS Course Structure Units Topics Marks Unit I Plane Geometry 16 1 Lines, angles and rectilinear figures 2 Circles and tangents 3 Special curves: ellipse, parabola, involute, cycloid.
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS Course Structure Units Topics Marks Unit I Plane Geometry 16 1 Lines, angles and rectilinear figures 2 Circles and tangents 3 Special curves: ellipse, parabola, involute, cycloid.
Chapter 1 Overview of an Engineering Drawing
 Chapter 1 Overview of an Engineering Drawing TOPICS Graphics language Engineering drawing Projection methods Orthographic projection Drawing standards TOPICS Traditional Drawing Tools Lettering Freehand
Chapter 1 Overview of an Engineering Drawing TOPICS Graphics language Engineering drawing Projection methods Orthographic projection Drawing standards TOPICS Traditional Drawing Tools Lettering Freehand
ORDINARY LEVEL PAST PAPERS
 ORDINARY LEVEL PAST PAPERS UNEB S4 1982 SECTION I PLANE GEOMETRY 1. (a) Construct a diagonal scale of 40mm to 10mm to read up to 20mm by 0.02mm. (b) Indicate on your scale the following readings. (i) 14.8mm.
ORDINARY LEVEL PAST PAPERS UNEB S4 1982 SECTION I PLANE GEOMETRY 1. (a) Construct a diagonal scale of 40mm to 10mm to read up to 20mm by 0.02mm. (b) Indicate on your scale the following readings. (i) 14.8mm.
CHAPTER 01 PRESENTATION OF TECHNICAL DRAWING. Prepared by: Sio Sreymean
 CHAPTER 01 PRESENTATION OF TECHNICAL DRAWING Prepared by: Sio Sreymean 2015-2016 Why do we need to study this subject? Effectiveness of Graphics Language 1. Try to write a description of this object. 2.
CHAPTER 01 PRESENTATION OF TECHNICAL DRAWING Prepared by: Sio Sreymean 2015-2016 Why do we need to study this subject? Effectiveness of Graphics Language 1. Try to write a description of this object. 2.
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER III ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER III ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70 Note: (i) Attempt all the questions. (ii) Use both sides of the drawing sheet, if necessary. (iii) All dimensions
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER III ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70 Note: (i) Attempt all the questions. (ii) Use both sides of the drawing sheet, if necessary. (iii) All dimensions
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS. Ms. Sicola
 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS Ms. Sicola Objectives List the six principal views of projection Sketch the top, front and right-side views of an object with normal, inclined, and oblique surfaces Objectives
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONS Ms. Sicola Objectives List the six principal views of projection Sketch the top, front and right-side views of an object with normal, inclined, and oblique surfaces Objectives
Geometry. ELG HS.G.14: Visualize relationships between two-dimensional and three-dimensional objects.
 Vertical Progression: 7 th Grade 8 th Grade Geometry 7.G.A Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. o 7.G.A.3 Describe the two-dimensional figures
Vertical Progression: 7 th Grade 8 th Grade Geometry 7.G.A Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. o 7.G.A.3 Describe the two-dimensional figures
There will be a course blackboard which will be mirrored on website:
 48-175 Descriptive Geometry Spring Semester 9 units Lectures: UT (CMB 1030) 1.30:2.50 Recitations: TBD Instructor: Ramesh Krishnamurti CMB 1176 ramesh@cmu.edu There will be a course blackboard which will
48-175 Descriptive Geometry Spring Semester 9 units Lectures: UT (CMB 1030) 1.30:2.50 Recitations: TBD Instructor: Ramesh Krishnamurti CMB 1176 ramesh@cmu.edu There will be a course blackboard which will
Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 Marks)
 1 L.85A Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2011 Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 Marks) Time: 3 Hours This examination is divided into three sections: SECTION A SECTION B SECTION
1 L.85A Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2011 Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 Marks) Time: 3 Hours This examination is divided into three sections: SECTION A SECTION B SECTION
Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 Marks)
 M.85A ªM.858 Leaving Certificate Examination, 2009 Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 Marks) Time: 3 Hours This examination is divided into three sections: SECTION A SECTION B SECTION
M.85A ªM.858 Leaving Certificate Examination, 2009 Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 Marks) Time: 3 Hours This examination is divided into three sections: SECTION A SECTION B SECTION
Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching
 Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching Contents Freehand sketching techniques Pictorial projections - Axonometric - Oblique Isometric projection vs isometric sketch Isometric sketch from an orthographic views Isometric
Chapter 5 Pictorial sketching Contents Freehand sketching techniques Pictorial projections - Axonometric - Oblique Isometric projection vs isometric sketch Isometric sketch from an orthographic views Isometric
DESIGN & COMMUNICATION GRAPHICS
 photograph of three balls is shown. ll three are in mutual contact and rest on the horizontal plane. The centres of the two larger ones lie in a line which is parallel to the vertical plane. The drawing
photograph of three balls is shown. ll three are in mutual contact and rest on the horizontal plane. The centres of the two larger ones lie in a line which is parallel to the vertical plane. The drawing
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION
 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION C H A P T E R S I X OBJECTIVES 1. Recognize and the symbol for third-angle projection. 2. List the six principal views of projection. 3. Understand which views show depth in a drawing
ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION C H A P T E R S I X OBJECTIVES 1. Recognize and the symbol for third-angle projection. 2. List the six principal views of projection. 3. Understand which views show depth in a drawing
A Concise Introduction to Engineering Graphics
 A Concise Introduction to Engineering Graphics Fourth Edition Including Worksheet Series A Timothy J. Sexton, Professor Department of Industrial Technology Ohio University BONUS Book on CD: TECHNICAL GRAPHICS
A Concise Introduction to Engineering Graphics Fourth Edition Including Worksheet Series A Timothy J. Sexton, Professor Department of Industrial Technology Ohio University BONUS Book on CD: TECHNICAL GRAPHICS
Chapter 5 SECTIONS OF SOLIDS 5.1 INTRODUCTION
 Chapter 5 SECTIONS OF SOLIDS 5.1 INTRODUCTION We have studied about the orthographic projections in which a 3 dimensional object is detailed in 2-dimension. These objects are simple. In engineering most
Chapter 5 SECTIONS OF SOLIDS 5.1 INTRODUCTION We have studied about the orthographic projections in which a 3 dimensional object is detailed in 2-dimension. These objects are simple. In engineering most
4. Draw the development of the lateral surface of the part P of the cylinder whose front view is shown in figure 4. All dimensions are in cm.
 Code No: Z0122 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Bio-Medical Engineering, Mechatronics,
Code No: Z0122 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Bio-Medical Engineering, Mechatronics,
Engineering Graphics. Practical Book. Government Engineering College Bhuj (Kutch - Gujarat) Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Engineering Graphics Practical Book ASHISH J. MODI Department of Mechanical Engineering Government Engineering College Bhuj 370 001 (Kutch - Gujarat) SYLLABUS (AS PER GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY,
Engineering Graphics Practical Book ASHISH J. MODI Department of Mechanical Engineering Government Engineering College Bhuj 370 001 (Kutch - Gujarat) SYLLABUS (AS PER GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY,
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS 1E9
 Lecture 3 Monday, 15 December 2014 1 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS 1E9 Lecture 3: Isometric Projections Lecture 3 Monday, 15 December 2014 2 What is ISOMETRIC? It is a method of producing pictorial view of an object
Lecture 3 Monday, 15 December 2014 1 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS 1E9 Lecture 3: Isometric Projections Lecture 3 Monday, 15 December 2014 2 What is ISOMETRIC? It is a method of producing pictorial view of an object
Engineering Graphics, Class 13 Descriptive Geometry. Mohammad I. Kilani. Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan
 Engineering Graphics, Class 13 Descriptive Geometry Mohammad I. Kilani Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan Projecting a line into other views Given the front and right side projections
Engineering Graphics, Class 13 Descriptive Geometry Mohammad I. Kilani Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan Projecting a line into other views Given the front and right side projections
Chapter 4 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION
 Chapter 4 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION 4.1 INTRODUCTION We, the human beings are gifted with power to think. The thoughts are to be shared. You will appreciate that different ways and means are available to
Chapter 4 ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION 4.1 INTRODUCTION We, the human beings are gifted with power to think. The thoughts are to be shared. You will appreciate that different ways and means are available to
Isometric Drawing Chapter 26
 Isometric Drawing Chapter 26 Sacramento City College EDT 310 EDT 310 - Chapter 26 - Isometric Drawing 1 Drawing Types Pictorial Drawing types: Perspective Orthographic Isometric Oblique Pictorial - like
Isometric Drawing Chapter 26 Sacramento City College EDT 310 EDT 310 - Chapter 26 - Isometric Drawing 1 Drawing Types Pictorial Drawing types: Perspective Orthographic Isometric Oblique Pictorial - like
Section 5. Graphic techniques for portfolio presentation
 Graphics techniques 117 Section 5 Graphic techniques for portfolio presentation A general knowledge of some basic graphic techniques is needed by all Technology students in order that the presentation
Graphics techniques 117 Section 5 Graphic techniques for portfolio presentation A general knowledge of some basic graphic techniques is needed by all Technology students in order that the presentation
CENTRAL PROJECTION OF HELIX
 PERIODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. ARCHITECTURE VOL. 35, NOS. 1-2, PP. 79-89 (1991) CENTRAL PROJECTION OF HELIX M. SZOBOSZLAI Department of Descriptive Geometry, Faculty of Architecture Technical University,
PERIODICA POLYTECHNICA SER. ARCHITECTURE VOL. 35, NOS. 1-2, PP. 79-89 (1991) CENTRAL PROJECTION OF HELIX M. SZOBOSZLAI Department of Descriptive Geometry, Faculty of Architecture Technical University,
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN EXAMINATION GUIDELINES GRADE 12
 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN EXAMINATION GUIDELINES GRADE 12 2014 These guidelines consist of 10 pages. Engineering Graphics and Design 2 DBE/2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 1. Introduction 3 2. Assessment
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN EXAMINATION GUIDELINES GRADE 12 2014 These guidelines consist of 10 pages. Engineering Graphics and Design 2 DBE/2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 1. Introduction 3 2. Assessment
Multiview Drawing. Definition: Graphical representation of a 3- dimensional object on one plane (sheet of paper) using two or more views.
 Multiview Drawing Definition: Graphical representation of a 3- dimensional object on one plane (sheet of paper) using two or more views. Multiview Drawing Another name for multiview drawing is orthographic
Multiview Drawing Definition: Graphical representation of a 3- dimensional object on one plane (sheet of paper) using two or more views. Multiview Drawing Another name for multiview drawing is orthographic
Contents. Notes on the use of this publication
 Contents Preface xxiii Scope Notes on the use of this publication xxv xxvi 1 Layout of drawings 1 1.1 General 1 1.2 Drawing sheets 1 1.3 Title block 2 1.4 Borders and frames 2 1.5 Drawing formats 2 1.6
Contents Preface xxiii Scope Notes on the use of this publication xxv xxvi 1 Layout of drawings 1 1.1 General 1 1.2 Drawing sheets 1 1.3 Title block 2 1.4 Borders and frames 2 1.5 Drawing formats 2 1.6
Bridge Course On Engineering Drawing for Mechanical Engineers
 G. PULLAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY Accredited by NAAC with A Grade of UGC, Approved by AICTE, New Delhi Permanently Affiliated to JNTUA, Ananthapuramu (Recognized by UGC under 2(f) and 12(B)
G. PULLAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY Accredited by NAAC with A Grade of UGC, Approved by AICTE, New Delhi Permanently Affiliated to JNTUA, Ananthapuramu (Recognized by UGC under 2(f) and 12(B)
ENGINEERING DRAWING I
 INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGINEERING DRAWING I [TUTORIAL SHEETS] 1 CONTENTS Sheet No. 1: Technical Lettering 3 Sheet No. 2: Plane Geometrical Construction 5 Sheet No.
INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ENGINEERING DRAWING I [TUTORIAL SHEETS] 1 CONTENTS Sheet No. 1: Technical Lettering 3 Sheet No. 2: Plane Geometrical Construction 5 Sheet No.
Unit-5 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION
 Unit-5 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION Importance Points in Isometric: 1. For drawing the isometric, the object must be viewed such that either the front -right or the left edges becomes nearest. 2. All vertical
Unit-5 ISOMETRIC PROJECTION Importance Points in Isometric: 1. For drawing the isometric, the object must be viewed such that either the front -right or the left edges becomes nearest. 2. All vertical
Leaving Certificate 2014
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate 2014 Marking Scheme Design and Communication Graphics Higher Level Note to teachers and students on the use of published
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate 2014 Marking Scheme Design and Communication Graphics Higher Level Note to teachers and students on the use of published
Classical Viewing. Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico
 Classical Viewing Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Introduce the classical views Compare and contrast image
Classical Viewing Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Introduce the classical views Compare and contrast image
A Universal Geometrical Method for Reconstruction of Gothic Vaults
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 12 (2008), No. 1, 81 86. A Universal Geometrical Method for Reconstruction of Gothic Vaults Anna Kulig, Krystyna Romaniak Samodzielny Zakład Geometrii Wykreślnej
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 12 (2008), No. 1, 81 86. A Universal Geometrical Method for Reconstruction of Gothic Vaults Anna Kulig, Krystyna Romaniak Samodzielny Zakład Geometrii Wykreślnej
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS
 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS CLASS - XII (046) DESIGN OF THE QUESTION PAPER Time : 3 Hrs Max. Marks : 70 The weightage of the distribution of marks over different contents of the question paper shall be as follows:
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS CLASS - XII (046) DESIGN OF THE QUESTION PAPER Time : 3 Hrs Max. Marks : 70 The weightage of the distribution of marks over different contents of the question paper shall be as follows:
Design & Communication Graphics Ordinary Level Section A (60 Marks)
 M.84A ªM.844 Leaving Certificate Examination, 2009 Design & Communication Graphics Ordinary Level Section A (60 Marks) Time: 3 Hours This examination is divided into three sections: SECTION A SECTION B
M.84A ªM.844 Leaving Certificate Examination, 2009 Design & Communication Graphics Ordinary Level Section A (60 Marks) Time: 3 Hours This examination is divided into three sections: SECTION A SECTION B
Learning Outcomes. Students should be able to: Demonstrate an understanding of the planes of reference
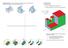 Orthographic projection is a means of representing a three-dimensional (3D) object in two dimensions (2D). It is the projection by parallel rays onto a plane at right angles to the rays. Demonstrate an
Orthographic projection is a means of representing a three-dimensional (3D) object in two dimensions (2D). It is the projection by parallel rays onto a plane at right angles to the rays. Demonstrate an
Graphical Communication
 Chapter 9 Graphical Communication mmm Becoming a fully competent engineer is a long yet rewarding process that requires the acquisition of many diverse skills and a wide body of knowledge. Learning most
Chapter 9 Graphical Communication mmm Becoming a fully competent engineer is a long yet rewarding process that requires the acquisition of many diverse skills and a wide body of knowledge. Learning most
SOME PHASES OF DESCRIPTIVE
 540 w. H. ROEVER [Nov.-Dec, SOME PHASES OF DESCRIPTIVE BY W. H. ROEVER GEOMETRY* The purpose of this paper is to recall those phases of descriptive geometry which are involved in the construction of adequate
540 w. H. ROEVER [Nov.-Dec, SOME PHASES OF DESCRIPTIVE BY W. H. ROEVER GEOMETRY* The purpose of this paper is to recall those phases of descriptive geometry which are involved in the construction of adequate
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan. Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1. Description: Unit C - Sketching - Test 2.
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1 Description: Unit C - Sketching - Test 2 Form: 501 1. The most often used combination of views includes the:
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Rowan Assessment: 9_12 T and I IC61 - Drafting I Test 1 Description: Unit C - Sketching - Test 2 Form: 501 1. The most often used combination of views includes the:
1.6. QUADRIC SURFACES 53. Figure 1.18: Parabola y = 2x 2. Figure 1.19: Parabola x = 2y 2
 1.6. QUADRIC SURFACES 53 Figure 1.18: Parabola y = 2 1.6 Quadric Surfaces Figure 1.19: Parabola x = 2y 2 1.6.1 Brief review of Conic Sections You may need to review conic sections for this to make more
1.6. QUADRIC SURFACES 53 Figure 1.18: Parabola y = 2 1.6 Quadric Surfaces Figure 1.19: Parabola x = 2y 2 1.6.1 Brief review of Conic Sections You may need to review conic sections for this to make more
Design & Communication Graphics
 L.84/85 Design & Communication Graphics Marking Scheme Ordinary Pg. 3 Higher Pg. 12 2013 L.84/85_MS 1/20 2013 L.84/85_MS 2/20 SECTION A - Core - Answer Any Three of the questions on this A3 sheet A-1.
L.84/85 Design & Communication Graphics Marking Scheme Ordinary Pg. 3 Higher Pg. 12 2013 L.84/85_MS 1/20 2013 L.84/85_MS 2/20 SECTION A - Core - Answer Any Three of the questions on this A3 sheet A-1.
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission. Leaving Certificate Marking Scheme. Design and Communication Graphics.
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate 2016 Marking Scheme Design and Communication Graphics Higher Level Note to teachers and students on the use of published
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate 2016 Marking Scheme Design and Communication Graphics Higher Level Note to teachers and students on the use of published
Design and Communication Graphics
 Design and Communication Graphics Scheme of Work 2014-2015 Ballyhaunis Community School Mission statement The DCG department aspires to provide a safe, stimulating environment where all students can develop
Design and Communication Graphics Scheme of Work 2014-2015 Ballyhaunis Community School Mission statement The DCG department aspires to provide a safe, stimulating environment where all students can develop
DWG 002. Blueprint Reading. Geometric Terminology Orthographic Projection. Instructor Guide
 DWG 002 Blueprint Reading Geometric Terminology Orthographic Projection Instructor Guide Introduction Module Purpose The purpose of the Blueprint Reading modules is to introduce students to production
DWG 002 Blueprint Reading Geometric Terminology Orthographic Projection Instructor Guide Introduction Module Purpose The purpose of the Blueprint Reading modules is to introduce students to production
Industrial Insulation PHASE 2 Module 2 Geometry & Pattern Development UNIT: 11 Valves & Flanges
 TRADE OF Industrial Insulation PHASE 2 Module 2 Geometry & Pattern Development UNIT: 11 Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Michael Kelly SOLAS 2014 Table of Contents Unit Objective...
TRADE OF Industrial Insulation PHASE 2 Module 2 Geometry & Pattern Development UNIT: 11 Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Michael Kelly SOLAS 2014 Table of Contents Unit Objective...
Exploring 3D in Flash
 1 Exploring 3D in Flash We live in a three-dimensional world. Objects and spaces have width, height, and depth. Various specialized immersive technologies such as special helmets, gloves, and 3D monitors
1 Exploring 3D in Flash We live in a three-dimensional world. Objects and spaces have width, height, and depth. Various specialized immersive technologies such as special helmets, gloves, and 3D monitors
GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION Advanced Higher
 GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION Advanced Higher Second edition published April 2000 NOTE OF CHANGES TO ADVANCED HIGHER ARRANGEMENTS SECOND EDITION PUBLISHED APRIL 2000 COURSE TITLE: Graphic Communication (Advanced
GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION Advanced Higher Second edition published April 2000 NOTE OF CHANGES TO ADVANCED HIGHER ARRANGEMENTS SECOND EDITION PUBLISHED APRIL 2000 COURSE TITLE: Graphic Communication (Advanced
CE 100 Civil Engineering Drawing Sessional (Lab Manual)
 CE 100 Civil Engineering Drawing Sessional (Lab Manual) Department of Civil Engineering Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology November, 2017 1 Preface This course is designed to provide civil
CE 100 Civil Engineering Drawing Sessional (Lab Manual) Department of Civil Engineering Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology November, 2017 1 Preface This course is designed to provide civil
Philadelphia University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department
 Philadelphia University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Basics of Engineering Drawing Manual Done by:- Eng. Laith R.I. Batarseh Eng. Hanan Khamis 2017 1 Table of contents SUBJECT
Philadelphia University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Basics of Engineering Drawing Manual Done by:- Eng. Laith R.I. Batarseh Eng. Hanan Khamis 2017 1 Table of contents SUBJECT
Volumes of Revolution
 Connecting Geometry to Advanced Placement* Mathematics A Resource and Strategy Guide Updated: 0/7/ Volumes of Revolution Objective: Students will visualize the volume of a geometric solid generated by
Connecting Geometry to Advanced Placement* Mathematics A Resource and Strategy Guide Updated: 0/7/ Volumes of Revolution Objective: Students will visualize the volume of a geometric solid generated by
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS 1.0 Introduction Engineering Graphics Drawing as an art Artist Graphic design Engineering graphics engineering drawing
 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS 1.0 Introduction Engineering is the profession in which the knowledge of mathematics and science gained by study, experience and practice is applied with good judgment to develop a
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS 1.0 Introduction Engineering is the profession in which the knowledge of mathematics and science gained by study, experience and practice is applied with good judgment to develop a
Orthographic Projection 1
 Orthographic Projection 1 What Is Orthographic Projection? Basically it is a way a representing a 3D object on a piece of paper. This means we make the object becomes 2D. The difference between Orthographic
Orthographic Projection 1 What Is Orthographic Projection? Basically it is a way a representing a 3D object on a piece of paper. This means we make the object becomes 2D. The difference between Orthographic
6. Draw the isometric view of a cone 40 mm diameter and axis 55 mm long when its axis is horizontal. Draw isometric scale. [16]
![6. Draw the isometric view of a cone 40 mm diameter and axis 55 mm long when its axis is horizontal. Draw isometric scale. [16] 6. Draw the isometric view of a cone 40 mm diameter and axis 55 mm long when its axis is horizontal. Draw isometric scale. [16]](/thumbs/85/92603403.jpg) Code No: R05010107 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2007 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Metallurgy & Material Technology,
Code No: R05010107 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2007 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Metallurgy & Material Technology,
ENGINEERING DRAWING LECTURE 4
 ENGINEERING DRAWING LECTURE 4 Conventions Convention or Code: The representation of any matter by some sign or mark on the drawing is known as convention or code. The convention make the drawing simple
ENGINEERING DRAWING LECTURE 4 Conventions Convention or Code: The representation of any matter by some sign or mark on the drawing is known as convention or code. The convention make the drawing simple
Leaving Certificate 201
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate 201 Marking Scheme Design and Communication Graphics Ordinary Level Note to teachers and students on the use of published
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate 201 Marking Scheme Design and Communication Graphics Ordinary Level Note to teachers and students on the use of published
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (Code No. 046)
 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (Code No. 046) CLASS XI-XII The subject of 'Engineering Graphics' has become an indispensable tool for Engineers, Technocrats, Architects, Draftsmen, Surveyors, Designers and many
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (Code No. 046) CLASS XI-XII The subject of 'Engineering Graphics' has become an indispensable tool for Engineers, Technocrats, Architects, Draftsmen, Surveyors, Designers and many
Technology Education Grades Drafting I
 Technology Education Grades 9-12 Drafting I 46 Grade Level: 9, 10, 11, 12 Technology Education, Grades 9-12 Drafting I Prerequisite: None Drafting I is an elective course which provides students the opportunity
Technology Education Grades 9-12 Drafting I 46 Grade Level: 9, 10, 11, 12 Technology Education, Grades 9-12 Drafting I Prerequisite: None Drafting I is an elective course which provides students the opportunity
ENGINEERING DRAWING. 1. Set squares are used to draw different angles. What is the angel a formed by the 45⁰ set square? Give a brief answer.
 ENGINEERING DRAWING 1. Set squares are used to draw different angles. What is the angel a formed by the 45⁰ set square? Give a brief answer. 2. Which is the correct method of hatching a plane surface?
ENGINEERING DRAWING 1. Set squares are used to draw different angles. What is the angel a formed by the 45⁰ set square? Give a brief answer. 2. Which is the correct method of hatching a plane surface?
Chapter 2: Dimensioning Basic Topics Advanced Topics Exercises
 Chapter 2: Dimensioning Basic Topics Advanced Topics Exercises Dimensioning: Basic Topics Summary 2-1) Detailed Drawings 2-2) Learning to Dimension 2-3) Dimension Appearance and Techniques. 2-4) Dimensioning
Chapter 2: Dimensioning Basic Topics Advanced Topics Exercises Dimensioning: Basic Topics Summary 2-1) Detailed Drawings 2-2) Learning to Dimension 2-3) Dimension Appearance and Techniques. 2-4) Dimensioning
UNIT I PLANE CURVES AND FREE HAND SKETCHING CONIC SECTIONS
 UNIT I PLANE CURVES AND FREE HAND SKETCHING CONIC SECTIONS Definition: The sections obtained by the intersection of a right circular cone by a cutting plane in different positions are called conic sections
UNIT I PLANE CURVES AND FREE HAND SKETCHING CONIC SECTIONS Definition: The sections obtained by the intersection of a right circular cone by a cutting plane in different positions are called conic sections
Module 1G: Creating a Circle-Based Cylindrical Sheet-metal Lateral Piece with an Overlaying Lateral Edge Seam And Dove-Tail Seams on the Top Edge
 Inventor (10) Module 1G: 1G- 1 Module 1G: Creating a Circle-Based Cylindrical Sheet-metal Lateral Piece with an Overlaying Lateral Edge Seam And Dove-Tail Seams on the Top Edge In Module 1A, we have explored
Inventor (10) Module 1G: 1G- 1 Module 1G: Creating a Circle-Based Cylindrical Sheet-metal Lateral Piece with an Overlaying Lateral Edge Seam And Dove-Tail Seams on the Top Edge In Module 1A, we have explored
COURSE TITLE: ENGINEERING DRAWING 2 GRADES LENGTH: FULL YEAR SCHOOLS: RUTHERFORD HIGH SCHOOL RUTHERFORD, NEW JERSEY DATE:
 COURSE TITLE: ENGINEERING DRAWING 2 GRADES 10-12 LENGTH: FULL YEAR SCHOOLS: RUTHERFORD HIGH SCHOOL RUTHERFORD, NEW JERSEY DATE: SPRING 2015 Engineering Drawing 2-2 Rutherford High School Rutherford, NJ
COURSE TITLE: ENGINEERING DRAWING 2 GRADES 10-12 LENGTH: FULL YEAR SCHOOLS: RUTHERFORD HIGH SCHOOL RUTHERFORD, NEW JERSEY DATE: SPRING 2015 Engineering Drawing 2-2 Rutherford High School Rutherford, NJ
A Concise Introduction to Engineering Graphics
 Concise Introduction to Engineering Graphics ourth Edition Including Worksheet Series imothy J. Sexton, Professor Department of Industrial echnology Ohio University ONUS ook on CD: ECHNICL GRPHICS Meyers,
Concise Introduction to Engineering Graphics ourth Edition Including Worksheet Series imothy J. Sexton, Professor Department of Industrial echnology Ohio University ONUS ook on CD: ECHNICL GRPHICS Meyers,
Structures. Program Details + Learning Standards Alignments: Learning By Design in Massachusetts
 How do buildings and bridges stand up? How are our bodies and buildings alike? Who designed our built our structures, and why? K-8 students will answer these questions when LBD:MA brings a wealth of hands-on
How do buildings and bridges stand up? How are our bodies and buildings alike? Who designed our built our structures, and why? K-8 students will answer these questions when LBD:MA brings a wealth of hands-on
Module 1H: Creating an Ellipse-Based Cylindrical Sheet-metal Lateral Piece
 Inventor (10) Module 1H: 1H- 1 Module 1H: Creating an Ellipse-Based Cylindrical Sheet-metal Lateral Piece In this Module, we will learn how to create an ellipse-based cylindrical sheetmetal lateral piece
Inventor (10) Module 1H: 1H- 1 Module 1H: Creating an Ellipse-Based Cylindrical Sheet-metal Lateral Piece In this Module, we will learn how to create an ellipse-based cylindrical sheetmetal lateral piece
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 marks)
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission 2011. M81A Leaving Certificate Examination, 2011 Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 marks) Friday, 17 June Afternoon,
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission 2011. M81A Leaving Certificate Examination, 2011 Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 marks) Friday, 17 June Afternoon,
AUXILIARY VIEWS C H A P T E R N I N E
 AUXILIARY VIEWS C H A P T E R N I N E Giesecke, Hill, Spencer, Dygdon, Novak, Lockhart, Goodman 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Create an auxiliary view from orthographic views. 2. Draw folding lines or reference-plane
AUXILIARY VIEWS C H A P T E R N I N E Giesecke, Hill, Spencer, Dygdon, Novak, Lockhart, Goodman 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Create an auxiliary view from orthographic views. 2. Draw folding lines or reference-plane
PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS ADVANCED MECHANICAL DRAWING CID 1220
 PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS ADVANCED MECHANICAL DRAWING CID 1220 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 4.0 Laboratory Hours: 3.0 Date Revised: Fall 00 NOTE: This course is not
PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS ADVANCED MECHANICAL DRAWING CID 1220 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 4.0 Laboratory Hours: 3.0 Date Revised: Fall 00 NOTE: This course is not
Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 marks)
 1 L.85A Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2012 Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 marks) Time: 3 Hours This examination is divided into three sections: SECTION A SECTION B SECTION
1 L.85A Pre-Leaving Certificate Examination, 2012 Design & Communication Graphics Higher Level Section A (60 marks) Time: 3 Hours This examination is divided into three sections: SECTION A SECTION B SECTION
CDT: DESIGN AND COMMUNICATION
 CDT: DESIGN AND COMMUNICATION Paper 7048/01 Structured Key message Whilst many excellent answers were seen, the following were considered to be areas where improvement could be made: the correct positioning
CDT: DESIGN AND COMMUNICATION Paper 7048/01 Structured Key message Whilst many excellent answers were seen, the following were considered to be areas where improvement could be made: the correct positioning
David Anderson. Gill & Macmillan
 One Volume Edition David nderson 3 and 4 Online Worksheets Ideal as homework exercises Will save students time as the problems are already set up on the page Worksheets are referenced in the text The material
One Volume Edition David nderson 3 and 4 Online Worksheets Ideal as homework exercises Will save students time as the problems are already set up on the page Worksheets are referenced in the text The material
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS ESSENTIALS. (A Text and Lecture Aid) Second Edition. Kirstie Plantenberg University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS
 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS ESSENTIALS (A Text and Lecture Aid) Second Edition Kirstie Plantenberg University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS ESSENTIALS (A Text and Lecture Aid) Second Edition Kirstie Plantenberg University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
11/12/2015 CHAPTER 7. Axonometric Drawings (cont.) Axonometric Drawings (cont.) Isometric Projections (cont.) 1) Axonometric Drawings
 CHAPTER 7 1) Axonometric Drawings 1) Introduction Isometric & Oblique Projection Axonometric projection is a parallel projection technique used to create a pictorial drawing of an object by rotating the
CHAPTER 7 1) Axonometric Drawings 1) Introduction Isometric & Oblique Projection Axonometric projection is a parallel projection technique used to create a pictorial drawing of an object by rotating the
Trade of Metal Fabrication. Module 5: Pipe Fabrication Unit 6: Pipe Development Unequal Diameter 'T' Piece Phase 2
 Trade of Metal Fabrication Module 5: Pipe Fabrication Unit 6: Pipe Development Unequal Diameter 'T' Piece Phase 2 Table of Contents List of Figures... 4 List of Tables... 4 Document Release History...
Trade of Metal Fabrication Module 5: Pipe Fabrication Unit 6: Pipe Development Unequal Diameter 'T' Piece Phase 2 Table of Contents List of Figures... 4 List of Tables... 4 Document Release History...
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (XI-XII) (Code No. 046)
 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (XI-XII) (Code No. 046) The subject of 'Engineering Graphics' has become an indispensable tool for Engineers, Technocrats, Architects, Draftsmen, Surveyors, Designers and many other
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (XI-XII) (Code No. 046) The subject of 'Engineering Graphics' has become an indispensable tool for Engineers, Technocrats, Architects, Draftsmen, Surveyors, Designers and many other
Auxiliary Elevations and Plans
 Chapter 18 uxiliary Elevations and Plans uxiliary Elevations The pictorial view of the thatched cottage shown below indicates how the front elevation is: (i) Obtained from a viewing direction looking in
Chapter 18 uxiliary Elevations and Plans uxiliary Elevations The pictorial view of the thatched cottage shown below indicates how the front elevation is: (i) Obtained from a viewing direction looking in
Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12. Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the. Externally set task 2017
 Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12 Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the Externally set task 2017 This document is an extract from the Mathematics Essentials General Course Year 12 syllabus,
Mathematics Essential General Course Year 12 Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the Externally set task 2017 This document is an extract from the Mathematics Essentials General Course Year 12 syllabus,
ENGINEERING DRAWING. UNIT III - Part A
 DEVELOPMENT OF SURFACES: ENGINEERING DRAWING UNIT III - Part A 1. What is meant by development of surfaces? 2. Development of surfaces of an object is also known as flat pattern of the object. (True/ False)
DEVELOPMENT OF SURFACES: ENGINEERING DRAWING UNIT III - Part A 1. What is meant by development of surfaces? 2. Development of surfaces of an object is also known as flat pattern of the object. (True/ False)
Engineering Graphics, Class 8 Orthographic Projection. Mohammad I. Kilani. Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan
 Engineering Graphics, Class 8 Orthographic Projection Mohammad I. Kilani Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan Multi view drawings Multi view drawings provide accurate shape descriptions
Engineering Graphics, Class 8 Orthographic Projection Mohammad I. Kilani Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan Multi view drawings Multi view drawings provide accurate shape descriptions
Grade 7 Mathematics Item Specifications Florida Standards Assessments
 Assessment Limit MAFS7.G.1 Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including
Assessment Limit MAFS7.G.1 Draw, construct, and describe geometrical figures and describe the relationships between them. MAFS.7.G.1.1 Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046)
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70 Note: (i) Attempt all the questions. (ii) Use both sides of the drawing sheet, if necessary. (iii) All dimensions
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II ENGINEERING GRAPHICS (046) Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 70 Note: (i) Attempt all the questions. (ii) Use both sides of the drawing sheet, if necessary. (iii) All dimensions
FOUR CONIC SECTIONS. Sections of a Cone
 Conic Sections FOUR CONIC SECTIONS 1 Sections of a Cone The circle, ellipse, parabola and hyperbola are known as conic sections Circle Ellipse Parabola Hyperbola All four curves are obtained by slicing
Conic Sections FOUR CONIC SECTIONS 1 Sections of a Cone The circle, ellipse, parabola and hyperbola are known as conic sections Circle Ellipse Parabola Hyperbola All four curves are obtained by slicing
ENGINEERING AND DESIGN
 ENGINEERING AND DESIGN EXAMINATION GUIDELINES GRADE 12 2017 These guidelines consist of 10 pages. Engineering Graphics and Design 2 DBE/2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. ASSESSMENT IN GRADE
ENGINEERING AND DESIGN EXAMINATION GUIDELINES GRADE 12 2017 These guidelines consist of 10 pages. Engineering Graphics and Design 2 DBE/2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. ASSESSMENT IN GRADE
Mechanical Engineering Drawing
 Mechanical Engineering Drawing MECH 211 LECTURE 3 Contents of the lecture Shape description Shape generation Sectional views Auxiliary views Shape description Geometric shapes are seen according to view
Mechanical Engineering Drawing MECH 211 LECTURE 3 Contents of the lecture Shape description Shape generation Sectional views Auxiliary views Shape description Geometric shapes are seen according to view
Describing an Angle Bracket
 Basics of Drafting Describing an Angle Bracket Orthographic Projection Orthographic drawings represent three dimensional objects in three separate views arranged in a standard manner. Orthographic Views
Basics of Drafting Describing an Angle Bracket Orthographic Projection Orthographic drawings represent three dimensional objects in three separate views arranged in a standard manner. Orthographic Views
GOVERNMENT POLYTECHNIC, VALSAD MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ASSIGNMENT SUB: MECHANICAL DRAFTING (C321901) TERM:172
 GOVERNMENT POLYTECHNIC, VALSAD MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ASSIGNMENT SUB: MECHANICAL DRAFTING (C321901) TERM:172 1) When all the dimension are placed above the dimension line, it is called (a) Aligned
GOVERNMENT POLYTECHNIC, VALSAD MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ASSIGNMENT SUB: MECHANICAL DRAFTING (C321901) TERM:172 1) When all the dimension are placed above the dimension line, it is called (a) Aligned
GE 6152 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS
 GE 6152 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS UNIT - 4 DEVELOPMENT OF SURFACES Development of lateral surfaces of simple and truncated solids prisms, pyramids, cylinders and cones - Development of lateral surfaces of solids
GE 6152 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS UNIT - 4 DEVELOPMENT OF SURFACES Development of lateral surfaces of simple and truncated solids prisms, pyramids, cylinders and cones - Development of lateral surfaces of solids
