MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17435) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may vary but the examiner may try to assess the understanding level of the candidate. 3) The language errors such as grammatical, spelling errors should not be given more Importance (Not applicable for subject English and Communication Skills. 4) While assessing figures, examiner may give credit for principal components indicated in the figure. The figures drawn by candidate and model answer may vary. The examiner may give credit for any equivalent figure drawn. 5) Credits may be given step wise for numerical problems. In some cases, the assumed constant values may vary and there may be some difference in the candidate s answers and model answer. 6) In case of some questions credit may be given by judgement on part of examiner of relevant answer based on candidate s understanding. 7) For programming language papers, credit may be given to any other program based on equivalent concept. Sub Q.N. Answer Marking Scheme Q.1 Attempt any SIX of following 12 Marks 1 a)i) Define active transducer. Give two examples. 2 M Active transducer is transducers which do not required power supply for converting one 1 M form of energy to another. OR Active transducer is transducer which do not required power supply for converting nonelectrical quantity (like temperature, pressure, humidity etc.) into electrical quantity.e. g. Thermocouples, Piezoelectric transducer etc. 1 M ii) State the difference between absolute and secondary instruments. 2 M Absolute instrument:- The absolute instrument measures the measurement in terms of physical constants of the instruments. 1 M Examples Tangent Galvanometer, Rayleigh s current Balance. Secondary Instruments: These instruments are so constructed that the quantity being Measured can only be measured by observing the output indicated by the instrument. 1 M Examples voltmeter, ammeter. iii) State the role of delay line in CRO. 2 M The delay line is used in CRO to delay the signal for some time in the vertical sections. As horizontal channel consists of trigger circuit and time based generator. This causes more time to reach signal to horizontal plates than vertical plates. For synchronization of reaching input signal at same time to both the plates in CRT. 2 M Page 1
2 iv) Write the units of temperature. 2 M Several scales and units exist for measuring temperature, the most common 2 M being Celsius (denoted C; formerly called centigrade), Fahrenheit (denoted F), and, especially in science, Kelvin (denoted K). v) State any four applications of DSO. 2 M Any four application of DSO: It can be used to measure ac as well as dc voltages and currents. It can calculate the mean value, peak value, peak to peak value, duty cycle, etc. It can be used to measure frequency, time period, time interval between two signals, and phase for periodic as well as non-periodic signals. It is used to give the visual representation for a target of radar such as aero plane, ship etc. In medical fields, it is used to display cardiograms that are useful for diagnosis of heart of the patient. It can be used to determine the modulation characteristic and detect the standing waves in transmission lines. It can be used to observe the V- I Characteristics of diodes, transistors. It can be used to observe the B-H curves, P-V diagrams. It can be used to observe the radiation pattern generated by the transmitting antenna. In modern DSO it is possible to add, subtract the waveforms. ½ M each vi) Compare RF and AF type signal generator(any two) 2 M RF signal generator AF signal generator 1M for each point This type of signal generator is used to generate RF or radio frequency signals. RF signal generators use frequency synthesizers to provide the stability and accuracy needed This type of signal generator is used for audio applications. Signal generators such as these run over the audio range, typically from about 20 Hz to 20 khz and more. AF signal generator uses free running oscillators, although some used frequency locked loop techniques to improve stability. vii) State the need of transducer. 2 M A transducer is required to converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another.. Where electrical signals are converted to and from other physical quantities (energy, force, torque, light, motion, position, etc.). The process of converting one form of energy to another is known as transduction. Need- viii) State the principle of piezoelectric transducer. State its any one application. 2 M Principle of piezoelectric transducer: Certain solid materials (crystals) when deformed generate electric charges within them. This effect is reversible; i.e., if a charge is applied, then material mechanically deforms. OR Principal- 1M & Applicatio n-1m The transducers that work on the principle of piezoelectric effect to measure changes in Page 2
3 displacement, force, pressure, strain and acceleration converting them to Electric charge are termed as Piezoelectric Transducers. This transducer produces electric voltage When there is application of mechanical stress or forces along certain planes. Applications: These are used for the measurement of Displacement. Piezoelectric crystal is also used for measurement of force, pressure or acceleration. b) Attempt any TWO of following: 8 Marks i) Write the classification of transducers. Classify the following transducers 1)Thermistor 2)LVDT? Transducer classification (any four criteria) Primary & secondary transducer. Active & passive transducer. Analog & Digital transducer. Transducer & inverse transducer. Electrical &mechanical transducer Thermistor :- Passive Transducer LVDT :- Secondary transducer. ii) Define following: 1)Sensitivity 2)Accuracy Sensitivity: The ratio of change in the output of an instrument to the change in input. It is expressed in terms of milivolt, microvolt or tenth of a degree. 4 M Classificati on- 1M 1M 4 M for each define Accuracy: Accuracy refers to the closeness of a measured value to a standard or known value. iii) Draw and explain shunt resistor type DC ammeter. 4 M - Diagram & - Explanatio n Explanation:- Where,Rm=Internal resistance Rsh= Resistance of the shunt Im= Full scale deflection current Ish= Shunt current I=current to be measured Vshunt= Vmovement Page 3
4 IshRsh=ImRm and Rsh=ImRm/Ish Ish=I-Im The coil winding of basic movement is small & it is light in weight. So this coil enables small currents to pass through it. It is required to pass current range through coil then the construction become bulky. In order to avoid this resistor is connected in parallel with the basic movement. This resistor is called is shunt resistor. So major amount of current passes through it & a small current passes through the coil. Q 2 Attempt any FOUR of the following. 16 Marks a) Describe lissagous figure.how are used to determine phase and frequency. 4 M One of the quickest methods of determining frequency is by using Lissagous patterns produced on the Screen. This pattern results when sine waves are applied simultaneously to both pairs of the deflection plates. If one frequency is an integral multiple (harmonic) of the other, the pattern will be stationary and is called a Lissagous figure. Frequency measurement using Lissagous pattern: In this method of measurement a standard frequency is applied to one set of deflection plates of the CRT tube while the unknown frequency is simultaneously applied to the other set of plates. The resulting pattern depends on the integral & phase relationship between two frequencies. Describe- & phase-1m & Frequency -1M Keep frequency fh constant and vary frequency fv, noting that the pattern. Spins in alternate directions and change shape. The pattern will stand still whenever fv and fh are in an integral ratio. The fv = fh pattern stands still and is a single circle or ellipse. (As per fig a) Page 4
5 When fv=2fh a two loop horizontal pattern is obtained. (As per fig b) To determine the frequency from any Lissagous figure, count the number of horizontal loops in the pattern, Divide it by the number of vertical loops and multiply this quantity by fh (known frequency). Fv = (fraction) fh Fraction= (No. Of loops touches to horizontal tangent) /(no of loops touches to vertical tangent) Phase measurement using Lissagous pattern: Explanation:- 1. The Phase measurement can be done by using Lissagous Figures. 2. The CRO is set to operate in X-Y mode, then the display obtained on the screen of a CRO is called as Lissagous pattern (Figure), when two sine waves of the same frequency are applied to the CRO.(one vertical and one horizontal Deflection plates). 3. Depending upon the phase shift between the two signals, the shape of the Lissagous figure will go on changing. 4. The Phase shift is given by ϴ= sin -1 (A/B) b) Draw and explain the working of electromagnetic flowmeter. 4 M Diagram- & Working Page 5
6 Working :- The operation of this type of flow meter is based on Faraday s law of electromagnetic Induction. The law state that whenever the conductor moves through a magnetic field, an e.m.f is induced in the conductor proportional to the relative velocity between the conductor & the magnetic field. It consists of a pipe, short section of which is subjected to a transverse magnetic field. The Conductive fluid is passed through this pipe. As fluid passes, its motion relative to field produces an e.m.f proportional to velocity according to Faraday s law. This output e.m.f is collected by the electrodes (kept at points of maximum potential Difference) and is given to external circuitry. c) Explain the seebeck and peltier effect.state its application. 4 M Seeback effect : Seeback effect states that whenever two dissimilar metals are connected together to form two junctions, out of which, one junction is subjected to high temperature and another junction is subjected to low temperature then e.m.f is induced proportional to the temperature difference between two junctions. Application: Seeback effect is used to measure the temperature difference between two objects. Peltier effect : Peltier effect state that two dissimilar metals closed loop, Id current forced to flow through the closed loop then one junction will be heated and other will become cool. Application: It can be used either for heating or for cooling, in practice the main application is cooling. It can also be used as a temperature controller that either heats or cools. d) Draw and explain half wave rectifier type AC voltmeter. 4 M Seebeck and peltier effect & applicatio n-1m for Each Diagram- & Explanatio n- Explanation: The circuit given in which the rectifying element (diode) is connected in series with Sinusoidal voltage source, PMMC, and multiplier resistor. The Function of Multiplier is to limit the current drawn by the PMMC to ovoid it from damage. The diode conducts during positive half cycle and does not conduct during negative half cycle. The average current through the meter will be given by the expression. Iav = Vav / 2R = 0.45 * [Vrms/R] Page 6
7 e) Describe the working of function generator wih suitable diagram. 4 M Diagram- & Working- OR Working: The frequency is controlled by varying the capacitor in LC or RC circuit. In this instrument the frequency is controlled by varying the magnitude of current which drives the integrator. The instrument produces sine, triangular and square waves with a frequency range of 0.01 Hz to 100 khz. The frequency controlled voltage regulates two current sources. The upper current source supplies constant current to the integrator whose output voltage increases linearly with time, according to the equation of the output signal voltage. An increase or decrease in the current increases or decreases the slope of the output voltage and hence controls the frequency. The voltage comparator multivibrator changes states at a pre- determined maximum level of the integrator output voltage. This change cuts off the upper current supply and switches on the lower current supply Page 7
8 The lower current source supplies a reverse current to the integrator, so that its output decreases linearly with time. When the output reaches a pre-determined minimum level, the voltage comparator again changes state and switches on the upper current source. The output of the integrator is a triangular waveform whose frequency is determined by the magnitude of the current supplied by the constant current sources. The comparator output delivers a square wave voltage of the same frequency. The resistance diode network alters the slope of the triangular wave as its amplitude changes and produces a sine wave with less than 1% distortion. f) Compare digital and analog instruments.(any four) 4 M Analog instrument Digital instruments 1M for Each point The instrument that displays analog signals is called as an analog instrument. The accuracy of analog instrument is less The resolution of analog of analog instrument is less The analog instrument require more power Examples PMMC instrument DC voltmeter,dc ammeter The instrument that displays digital signals is called as an digital instrument The accuracy of digital instruments is more The resolution of digital instruments is more. The digital instrument requires less power. Examples Logical analyzer, Digital analyzer, computer base instruments. Q. 3 Attempt any FOUR of the following. 16 Marks a) Describe the working of analog AC ammeter. 4 M Explanatio n-4m Explanation: 1. Shunt can be used with A.C ammeter to increase their range but cannot be used to decrease their range. 2. Most AC ammeter use a current transformer instead of shunts to change the scale values. This type of Ammeter is shown in the diagram Page 8
9 3. The primary of the transformer is connected in series with the load, and ammeter is connected to the secondary of the transformer. 4. The range of meter is changed by selecting different taps on secondary of transformer. The different taps on the transformer provides different turn s ratio between primary and secondary of the transformer. 5. The turn s ratio is the ratio of number of turns of wire on the primary as compared to the number of turns of wires in the secondary. b) Draw the block diagram of logic analyzer and explain its working. 4 M Digram- & Working- Explanation: 1. Logic analyzer used to analyze digital signals. Logic analyzer deals with digital domain. 2. This is basically multichannel oscilloscope. The probes connect the logical analyzer to system which is under test. The probes operates as voltage divides, the lowest possible s/w rate can be selected by dividing the i/p signal. 3. The different logic families i.e. TTL, CMOS, NMOS etc. have different threshold voltage. Hence adjustable threshold comparators are used. Each signal is connected to each line of logic analyzer. 4. The reference signal of each comparator is set to a voltage. The logic analyzer memory consists of a RAM. 5. The clock signals I.e, internal or external clock i/p is connected to memory on receiving Page 9
10 c) Draw LCR-Q meter.state its application. 4 M Diagram- & Applicatio n- 1M each Applications: (arks-consider Any 2 points) 1. In the Measurement of different parameters like inductance, capacitance, resistance, dissipation factor, quality factor, current, voltage, phase angle between the current and voltage, conductance, susceptance etc. quickly with very high precision. 2. Data collection and Automation is made easy with a wide variety of interfaces such as; USB, USB Host Port, RS-232 and GPIB interfaces, which are available on all of IET's LCR-Q meters. 3. They are highly used in industry. d) Explain how frequency and voltage measurement is done in CRO with suitable example. 4 M Page 10
11 Frequency and voltage measurem ent- for Each Example: Page 11
12 (OR) Can consider same type of example for DC Measurement. Frequency Measurement : The frequency can be measured accurately on CRO by two ways On calibrated ciao : In this method, the frequency can be found out indirectly. The signal whose frequency is to be measured is applied to the vertical input terminal and switch ON the sweep generator then count the number of division covered by one cycle of the signal on the screen. e) List the temperature range and material used for J,K,S,R thermocouple. 4 M 1M for Sr. No. Type of transducer Material used Temperature range in (degree. Celsius) Each Point 1 J Iron-Constantan -180 to K Chromel-Alumel -200 to S Platinum-Platinum/ 10% Rhodium 4 R Platinum-Platinum/ 13% Rhodium -0 to to Page 12
13 f) Draw a neat labelled block diagram of dual trace CRO. 4 M - Diagram & - Lebelled Q. 4 Attempt any FOUR of following: 16 Marks a) Describe the working of video pattern generator. 4 M block diagram: Explanatio n-4m Explanation: A pattern generator provides video signals directly with RF modulation on standard TV channels for alignment, testing and servicing of TV receivers. The output signal is designed to produce simple geometric patterns like vertical and horizontal bars, checker board, cross hatch dots etc. an FM sound is also provided in pattern generators for aligning sound sections of the receiver. The generator employs two stable chains of multivibrator, Page 13
14 divider and pulse shaping circuits to produce a series of horizontal bars below the line frequency and vertical bars above the 15.6KHz. Vertical bars are used to check and set horizontal linearity. Similarly Horizontal bars are used to check and set vertical linearity Picture centering and aspect ratio is checked and set with cross hatched pattern by counting the number of squares on the vertical and horizontal sides of the screen. b) Draw block diagram of harmonic distortion analyzer. Explain its working. 4 M Block Diagram : Diagram- & Working- Explanation: The signal has very low distortion and this can be checked by reading its o/p distortion by connecting directly into analyser The signal from source is fed to the amplifier under test. This generates harmonics and original fundamental frequency. The original fundamental frequency is removed by notch filter. The switch is first placed in position 1 and total content of fundamental & harmonics (E T ) is measured. Then the switch is moved to position 2 to measure just the harmonics (E H ). The value of THD total harmonic distortion is then found THD = x 100 Explain the role of vertical deflection and horizontal system in CRO. c) Explain the role of vertical deflection and horizontal deflection between in CRO 4 M Explanation: Vertical Deflection System consists of Attenuator Network, Vertical amplifier. Attenuator reduces the amplitude of the signal before applying to the vertical amplifier. The main function of vertical amplifier is to determine the sensitivity and bandwidth (range of frequencies which can be produced accurately on CRT screen) of an oscilloscope (in terms of V/cm.) The gain of vertical amplifier determines the smallest signal that the oscilloscope can satisfactorily produce on CRT screen. The sensitivity of an oscilloscope is directly proportional to the gain of the vertical amplifier. Explanatio n- for horizontal deflection and for vertical deflection Page 14
15 Horizontal Deflection System consists of trigger circuit,sweep generator and horizontal amplifier. The horizontal (x) deflection plates are fed by a sweep voltage that provides a time base. The horizontal plates are supplied through an amplifier, but they can be fed directly when voltages are of sufficient magnitude. Block Diagram d) Draw the block diagram of pulse generator. State the difference between square wave generator and pulse generator. Block Diagram: 4 M Diagram:2 M & 1 mark each point(max. 2 point). The difference between square wave and pulse generator. Square Wave generator 1. Square wave generator produce square waveform. 2. Duty cycle is exactly equal to 50%. 3. Square wave generators are used where low, power, low frequency characteristics is to be investigated. For example Audio system. Pulse Wave generator 1. Pulse wave generator produce Pulse of different width. 2. Duty cycle is varied between 50-70%. 3.Pulse generator is used in comparatively higher power application Page 15
16 e) Draw neat circuit diagram of LVDT. State it s any four applications. 4 M Diagram: Diagram & ½ M for each Applicatio n Application of LVDT: 1. It is used for small displacement measurement i.e from fraction of mm to few cm. 2. It is used as secondary transducer to measure force, pressure, weight in electrical quantity. 3. It is used to measure the thickness of metal sheet roll. 4. It is used to measure tension in a cord. 5. LVDTs are commonly used for position feedback in servomechanisms, and for automated measurement in machine tools and many other industrial and scientific applications. f) Draw and explain the working of linear potentiometer. 4 M Diagram:2 Diagram M & Working:2 M Working: The potentiometer is also called as pots and it one of the most commonly used devices for measuring the displacement of the body. The potentiometer is the electrical type of transducer or sensor and it is of resistive type because it works on the principle of change of resistance of the wire with its length. The resistance of the wire is directly proportional to the length of the wire, thus as the length of the wire changes the resistance of the wire also changes to change the resistance one sliding contact is provided is called as wiper. The movement of this wiper is translator so called as linear potentiometer Page 16
17 Q.5 Attempt any FOUR of following: 16 Marks a) Describe how flow is measured using Doppler type ultrasonic flow meter. 4 M Explanation : 4M Note: Explanation: 4marks only describe is ask in question Doppler flow meters use a single-head sensor design allowing fast, simple mounting on the outside of pipes. The single-head transducer includes both transmit and receive piezo-electric crystals in the same housing. Doppler flow meters use the principal that sound waves will be returned to a transmitter at an altered frequency if reflectors in the liquid are in motion. This frequency shift is in direct proportion to the velocity of the liquid. It is precisely measured by the instrument to calculate the flow rate. So the liquid must contain gas bubbles or solids for the Doppler measurement to work. The fluid velocity can be expressed as v = c (f r - f t ) / 2 f t cosφ (1) where f r = received frequency f t = transmission frequency v = fluid flow velocity Φ = the relative angle between the transmitted ultrasonic beam and the fluid flow c = the velocity of sound in the fluid b) Draw the block diagram of spectrum analyzer. Explain its working. 4 M Working: Working:2 M & Block A spectrum analyser provides a calibrated graphical display on its CRT, with frequency on the horizontal axis and amplitude (voltage) on the vertical axis. Diagram Displayed as vertical lines against these co-ordinates are sinusoidal components of which the i/p signal is composed. The height represents the absolute magnitude and the horizontal location represents the frequency. Referring to the block diagram of the basic spectrum analyser, the saw tooth generator provides the saw tooth voltage which drives the horizontal axis element of the scope and this saw tooth voltage is the frequency controlled element of the voltage tuned oscillator. As the oscillator sweeps from f min to f max of its frequency band at a linear recurring rate, it beats with the frequency component of the input signal and Page 17
18 Diagram: produce an IF, whenever a frequency component is met during its sweep. The frequency component and voltage tuned oscillator frequency beats together to produce a difference frequency, i.e. IF. The IF corresponding to the component is amplified and detected if necessary and then applied to the vertical plates of the CRO producing a display of amplitude versus frequency. Spectrum analyzers are widely used in radar, oceanography and biomedical fields. c) Define signal generator. State the need of signal generator. 4 M A class of generators that are available as separate instruments to provide signals for general test purpose are usually designated as signal generators. Need of Signal Generators: Signal Generators provide various signal which are required for testing the electronic circuits, frequency response at transmitting and receiving stage. So the need is 1. The frequency of the signal should be known and stable. 2. The amplitude should be controllable from very small to relatively large values. 3. Finally, the signal should be distortion free. Define:1M & Need:3M d) Compare thermistor and RTD(Any four) 4 M Thermister RTD 1.Thermistor is made up of semiconductor Materials. 2.Semiconductor materials have Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) of resistance.hence, the resistance of a thermistor decreases with an increase in temperature and increases with a decrease in temperature. 3.The resistance temperature characteristics of thermistor are highly nonlinear. 4.It has large temperature coefficient of resistance i.e. thermistor highly sensitive to temperature compared to RTD. 5.It has low operating temperature range compared to RTD i.e., minus 100 to plus 300 C. 6.Size of thermistors are small. 7.They are not costlier 1. RTD is made up of metals. 2. Metals have Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) of resistance. Hence,the resistance of RTD increases with an increase in temperature and decreases with a decrease in temperature. 3. The resistance temperature characteristics of RTD's are linear. 4. It is less sensitive to temperature compared to thermistor. 5.It has-a wide operating temperature range i.e., minus 200 to plus 650 C. 6. RTD's are relatively larger in size. 7. They are costlier as compared to 1 M for Each point Page 18
19 as compared to RTD. 8.They have high self resistance. Thus, they require shielding cables to minimize interference problems. 9.Thermistors also provide an accuracy of ± 0.01 C. 10.They are widely used for dynamic temperature measurement. thermistor. 8. They have low self resistance. 9. RTD's provide high degree of accuracy and long term stability. 10. They are used in laboratory and industrial applications. e) Draw the circuit for 2 wire and 3 wire system of RTD. 4 M Diagram for 2 wire system of RTD Each Diagram:2 M Diagram for 3 wire system of RTD f) Describe the working of capacitive transducer. State its two applications. 4 M Working:3 Describe the working of capacitive transducer. State its two application. Diagram with Working: The capacitive Transducer is worked on the principle of change of capacitance which caused by i) change in overlapping area, ii) change in the distance d between the plates and iii) change in dielectric constant. This changes causes by the physical variables like displacement, force and pressure and change in dielectric constant caused by the change in media like liquid, gas level. C= єa/d = є r є 0 A/d M & Application: 1/2 M Page 19
20 Application: i) It is used for the measurement of force and pressure. ii) It is used for measurement of humidity in gases. iii) It is used for measurement of volume, density liquid level, weight etc. (consider Any other relevant application) Q.6 Attempt any FOUR of following: 16 Marks a) State any four applications of digital multimeter. 4 M Applications of digital multimeter: i) Voltage measurement. ii)current Measurement. iii)resistance Measurement. iv) Time and frequency measurement. v) Component testing by means of forward and reverse voltage, resistance. vi) Continuity test of circuits. (consider any four application) 1M to each point b) Draw the block diagram of digital voltmeter and explain its working. 4 M Diagram: (Consider any type of DVM- Digital ramp type voltmeter/integrated type DVM/Dual Slope type/successive approximation type) Diagram: & Working: Working: Ramp Type DVM The operating principle is to measure the time that a linear ramp takes to change the input level to the ground level or vice-versa. This time period is measured with an electronic time interval counter and the count is displayed as a number of digits on display. The ramp may be positive or negative. In this case a negative ramp has been selected. At the start of the measurement a ramp voltage is initiated [counter is reset to 0 & sample rate multivibrator gives a pulse which initiates the ramp generator ] Page 20
21 The ramp generator is continuously compared with the voltage that is being measured. At the instant these two voltages become equal the input comparator generates start pulse which opens a gate. The ramp continues until the second comparator circuit senses that the ramp has reached zero value. The ground comparator compares the ramp with the ground, when the ramp voltage equals zero the ground comparator generates stop pulse. This pulse closes the gate. The time duration of the gate opening is proportional to the input voltage value. In the time interval between the start and stop pulses the gate opens and the oscillator circuit drives the counter. The magnitude of the count indicates the, magnitude of the input voltage which is displayed by the read out. Therefore the voltage is converted into time and the time count represents the magnitude of the voltage. c) Draw block diagram of DSO and explain its working. 4 M Diagram: Diagram: & Working: OR Page 21
22 Working: A digital oscilloscope digitizes the input signal so that all subsequent signals are digitized. A conventional CRT is used and storage occurs in electronic digital memory fig above shows a block diagram of a basic digital storage oscilloscope. The input signal is digitized and stored in memory in digital form.in this state it is capable of being analyzed to produce a variety of different information. To view the display on the CRT the data from memory is reconstructed in analog form. Digitizing occurs by taking a sample of the input waveform at periodic intervals. In order to ensure that no information is lost sampling theory states that the sampling rate must be at least twice as fast as the highest frequency in i/p signal. Many different i/p channels are used with digital storage oscilloscopes. however if all these channels share a common store, through a multiplexer, then the memory available to each channels is reduced Oscilloscopes with up to 40 channels are commercially obtainable with a storage capability of dots Several oscilloscopes also have a floppy disc storage capability to allow nonvolatile storage of waveforms which can be later recalled into the oscilloscope and manipulated. d) Define four dynamic characteristics of instruments. 4 M 1 Mark for 1. Speed of response: It is defined as rapidity with which a measurement system responds to changes in the measured quantity. 2. Measuring Lag: It is the retardation or delay in response of the measurement system to the changes in the measured quantity. 3. Fidelity: It is defined as degree to which a measurement system indicates changes in the measured quantity without any dynamic error. 4. Dynamic Error: It is the difference between true value of quantity (under measurement)changing with time. each characteristic s definition e) Explain working of multirange voltmeter with neat diagram using PMMC meter movement. Diagram: 4 M Diagram: & Working: Multirange voltmeter OR Page 22
23 Explanation: A PMMC Movement is converted into multirange DC Voltmeter by connecting 2 or more (series resistance ) multiplier in series with the PMMC meter. The multiplier value is calculated by R S = (V/Im)-Rm= (m-1)rm The multiplier resistance is limits current flowing through meter to avoid meter from damage. Selection of different value of multiplier is done by selector switch or potential divider arrangement is used. f) List and explain different types of errors. 4 M Errors are classified as 1)Gross Error, 2)Systematic Errori)Instrumental Error, ii)observational error, iii)environmental error, 3)Random Error 1)Gross Error: It is the human mistakes in reading instruments and recording and calculating measurement results. It is caused by experimenter carelessness or equipment failure. It may be due to the person s bad habit of not properly remembering data at the time of taking down reading, writing and calculating, and then presenting the wrong data at a later time. This may be the reason for gross errors in the reported data, and such errors may end up in calculation of the final results, thus deviating results. 2)Systematic Error: Systematic errors are of three types. i)instrumental error-these errors arise due to three main reason i)due to inherent shortcomings in the instrument,ii)due to misuse of Instruments and iii)due to loading effects of instruments. ii)environmental Error: These are due to conditions external to the measuring device including conditions in the area surrounding the instrument. These may be the effects of temperature, pressure, humidity, dust, vibrations or external magnetic or electrostatic field. iii)observational Error: These are human factors involved in measurement. No two persons the same situation in exactly the same way. Error caused due to this is called Parallax error. 3) Random Error: The error due to multitude of small factors which change or fluctuate from one measurement to another. These errors are randomly occurred so called as random errors. listing of error: 2marks, explanation: 2marks Page 23
Q.1 a) Attempt any SIX of the following: 12M. (i) Give comparison between active transducer and passive transducer. Ans:- (Any Two) 1M each
 Page 1 of 26 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written
Page 1 of 26 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer
 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code : 17317 Page No: 1 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code : 17317 Page No: 1 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
1. A) Attempt any six of the following: [12M]
![1. A) Attempt any six of the following: [12M] 1. A) Attempt any six of the following: [12M]](/thumbs/95/125538661.jpg) Subject Code: 17435 Model Answer Page 1 of 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17435 Model Answer Page 1 of 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model
Table of Contents...2. About the Tutorial...6. Audience...6. Prerequisites...6. Copyright & Disclaimer EMI INTRODUCTION Voltmeter...
 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION
 SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17317 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17317 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
UNIT 2. Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator. Ans. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) MODEL ANSWER
 MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Electronic Instruments and Measurements Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Electronic Instruments and Measurements Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17317) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17317) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Rayat Shikshan Sanstha s Karmaveer Bhaurao Patil Polytechnic, Satara. Sub: Electrical Engineering Assignment No: 1
 Assignment No: 1 1) Define Precision and Dead zone 2) Define 1) Speed of response 2) Lag 3) Fidelity 4)dynamic error 3) Define Standard and State its classification 4) What is Calibration & State its necessity
Assignment No: 1 1) Define Precision and Dead zone 2) Define 1) Speed of response 2) Lag 3) Fidelity 4)dynamic error 3) Define Standard and State its classification 4) What is Calibration & State its necessity
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) SUMMER 2013 EXAMINATION
 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 2013 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 12117 Model Answer Page No: 1 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 2013 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 12117 Model Answer Page No: 1 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
b) State the types of standards of measurement. 2M
 MODEL ANSWER WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Electronic Instruments & Measurements Subject Code: 17317 I m p o r t a n t I n s t r u c t i o n s t o e x a m i n e r s : 1) The answers should be examined
MODEL ANSWER WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Electronic Instruments & Measurements Subject Code: 17317 I m p o r t a n t I n s t r u c t i o n s t o e x a m i n e r s : 1) The answers should be examined
UNIT-3. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
Synchronous Machines Study Material
 Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY
 SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY-621105. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EI 1306-MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY-621105. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EI 1306-MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION
5. Transducers Definition and General Concept of Transducer Classification of Transducers
 5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
Definitions. Spectrum Analyzer
 SIGNAL ANALYZERS Spectrum Analyzer Definitions A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure
SIGNAL ANALYZERS Spectrum Analyzer Definitions A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure
EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION
 EE6352 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT V ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS Digital Voltmeter (DVM) It is a device used for measuring the magnitude of DC voltages. AC voltages can be measured
EE6352 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT V ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS Digital Voltmeter (DVM) It is a device used for measuring the magnitude of DC voltages. AC voltages can be measured
MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION. Part A
 MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A 1. Define Standard deviation. 2. Why calibration of instrument is important? 3. What are the different calibration methodologies?
MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A 1. Define Standard deviation. 2. Why calibration of instrument is important? 3. What are the different calibration methodologies?
DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 Department of Technical Education DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Third Semester ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION Contact Hours/Week : 04 Contact Hours/Semester :
Department of Technical Education DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Third Semester ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION Contact Hours/Week : 04 Contact Hours/Semester :
MAHARASHTRASTATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 MODEL ANSWER WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Electronic Instrumentation 17435 4 Subject Code:17435 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
MODEL ANSWER WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Electronic Instrumentation 17435 4 Subject Code:17435 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
Electronic Instrumentation & Automation. ET-7th semester. By : Rahul Sharma ET & TC Deptt. RCET, Bhilai
 Electronic Instrumentation & Automation ET-7th semester By : Rahul Sharma ET & TC Deptt. RCET, Bhilai UNIT: III Voltage and Current Measurements Digital Voltmeters: Non-Integrating type, Integrating Type,
Electronic Instrumentation & Automation ET-7th semester By : Rahul Sharma ET & TC Deptt. RCET, Bhilai UNIT: III Voltage and Current Measurements Digital Voltmeters: Non-Integrating type, Integrating Type,
State the application of negative feedback and positive feedback (one in each case)
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM. Course Title: Electronics Instruments and Measurement (Code: )
 GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM Course Title: Electronics Instruments and Measurement (Code: 3341104) Diploma Programme in which this course is offered Electronics
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM Course Title: Electronics Instruments and Measurement (Code: 3341104) Diploma Programme in which this course is offered Electronics
Bhoj Reddy Engineering College for Women, Hyderabad Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Electrical and Electronics Instrumentation
 Bhoj Reddy Engineering College for Women, Hyderabad Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Electrical and Electronics Instrumentation Academic Year: 2016-17 III B Tech II Semester Branch:
Bhoj Reddy Engineering College for Women, Hyderabad Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Electrical and Electronics Instrumentation Academic Year: 2016-17 III B Tech II Semester Branch:
ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS
 ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS Digital Voltmeter (DVM) Used to measure the ac and dc voltages and displays the result in digital form. Types: Ramp type DVM Integrating type DVM Potentiometric type DVM
ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS Digital Voltmeter (DVM) Used to measure the ac and dc voltages and displays the result in digital form. Types: Ramp type DVM Integrating type DVM Potentiometric type DVM
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) MODEL ANSWER
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
9/28/2010. Chapter , The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
IT.MLD900 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER. Signal Conditioning
 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation UNIT What are the basic performance characteristics of a system?
 UNIT-1 1. What are the basic performance characteristics of a system? Ans: STATIC CHARACTE RISTICS The static characteristics of an instrument are, in general, considered for instruments which are used
UNIT-1 1. What are the basic performance characteristics of a system? Ans: STATIC CHARACTE RISTICS The static characteristics of an instrument are, in general, considered for instruments which are used
FMCET UNIT I - INTRODUCTION
 UNIT I - INTRODUCTION 1. Write the main static characteristics? (April/may 2008) The main static characteristics are: Accuracy Sensitivity Reproducibility Drift Static error Dead zone Resolution Precision
UNIT I - INTRODUCTION 1. Write the main static characteristics? (April/may 2008) The main static characteristics are: Accuracy Sensitivity Reproducibility Drift Static error Dead zone Resolution Precision
Summer 2015 Examination
 Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
4. Digital Measurement of Electrical Quantities
 4.1. Concept of Digital Systems Concept A digital system is a combination of devices designed for manipulating physical quantities or information represented in digital from, i.e. they can take only discrete
4.1. Concept of Digital Systems Concept A digital system is a combination of devices designed for manipulating physical quantities or information represented in digital from, i.e. they can take only discrete
Introduction to Measurement Systems
 MFE 3004 Mechatronics I Measurement Systems Dr Conrad Pace Page 4.1 Introduction to Measurement Systems Role of Measurement Systems Detection receive an external stimulus (ex. Displacement) Selection measurement
MFE 3004 Mechatronics I Measurement Systems Dr Conrad Pace Page 4.1 Introduction to Measurement Systems Role of Measurement Systems Detection receive an external stimulus (ex. Displacement) Selection measurement
Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation. 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance?
 UNIT -6 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance? Ans: Maxwell's bridge, shown in Fig. 1.1, measures an unknown inductance in of standard arm offers
UNIT -6 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance? Ans: Maxwell's bridge, shown in Fig. 1.1, measures an unknown inductance in of standard arm offers
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER EI6601 Modern Electronic Instrumentation Regulation
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER EI6601 Modern Electronic Instrumentation Regulation
 VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
PART A. 1. List the types of DC Motors. Give any difference between them. BTL 1 Remembering
 UNIT I DC MACHINES Three phase circuits, a review. Construction of DC machines Theory of operation of DC generators Characteristics of DC generators Operating principle of DC motors Types of DC motors
UNIT I DC MACHINES Three phase circuits, a review. Construction of DC machines Theory of operation of DC generators Characteristics of DC generators Operating principle of DC motors Types of DC motors
Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405]
![Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405] Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405]](/thumbs/95/124646158.jpg) UNIT-1 1. Discuss liquid in glass thermometers? 2. Write a short note on strain gauges. 3. Mention the various temperature scales and relation between them. 4. An experiment is conducted to calibrate a
UNIT-1 1. Discuss liquid in glass thermometers? 2. Write a short note on strain gauges. 3. Mention the various temperature scales and relation between them. 4. An experiment is conducted to calibrate a
Test No. 1. Introduction to Scope Measurements. Report History. University of Applied Sciences Hamburg. Last chance!! EEL2 No 1
 University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No. Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No. Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION
 Subject Code:173 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The
Subject Code:173 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The
DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING. Test No. 1. Introduction to Scope Measurements. 1. Correction. Term Correction. Term...
 2. Correction. Correction Report University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No.
2. Correction. Correction Report University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) UNIT I
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : EMI(16EC416) Year & Sem: III B.Tech & I Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : EMI(16EC416) Year & Sem: III B.Tech & I Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech
SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: / N
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Acknowledgments Introduction
 Acknowledgments Introduction xiii xi 1 Electronic meters 1 1.1 Digital meters 2 1.2 Nondigital (analog) meters 6 1.3 Differential meters 14 1.4 Digital meter displays and ranges 16 1.5 Nondigital meter
Acknowledgments Introduction xiii xi 1 Electronic meters 1 1.1 Digital meters 2 1.2 Nondigital (analog) meters 6 1.3 Differential meters 14 1.4 Digital meter displays and ranges 16 1.5 Nondigital meter
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17213 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17213 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Communication Circuit Lab Manual
 German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements
 Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks)
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. UNIT III TUNED AMPLIFIERS PART A (2 Marks) 1. What is meant by tuned amplifiers? Tuned amplifiers are amplifiers that are designed to reject a certain
MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Linear Integrated Circuit Subject Code:
 MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Linear Integrated Circuit Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Linear Integrated Circuit Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS NEWS RESULTS FORUMS UNIT 8
 UNIT 8 (a) Interfacing resistive transducers to electronic circuits. Introduction to data acquisition systems. 2 Hours (b) Display Devices and Signal Generators: X-Y recorders. Nixie tubes. LCD and LED
UNIT 8 (a) Interfacing resistive transducers to electronic circuits. Introduction to data acquisition systems. 2 Hours (b) Display Devices and Signal Generators: X-Y recorders. Nixie tubes. LCD and LED
Downloaded from Downloaded from
 IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION- 2002 SUBJECT: BEG232EC, Instrumentation Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks.
IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION- 2002 SUBJECT: BEG232EC, Instrumentation Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks.
Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date:
 PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date: 1 2330A Current and Voltage 2 2330B Controlling Current
PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date: 1 2330A Current and Voltage 2 2330B Controlling Current
Scheme Q.1 Attempt any SIX of following: 12-Total Marks a) Draw symbol NPN and PNP transistor. 2 M Ans: Symbol Of NPN and PNP BJT (1M each)
 Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17319) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17319) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
DEPT: II EEE EE6404-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENTATION 2MARK: UNIT-1. An instrument is a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity.
 DEPT: II EEE 2MARK: UNIT-1 1. Define instrument. An instrument is a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity. 2. What are the types of instruments? a. Mechanical instrument b. Electrical
DEPT: II EEE 2MARK: UNIT-1 1. Define instrument. An instrument is a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity. 2. What are the types of instruments? a. Mechanical instrument b. Electrical
AC LAB ECE-D ecestudy.wordpress.com
 PART B EXPERIMENT NO: 1 AIM: PULSE AMPLITUDE MODULATION (PAM) & DEMODULATION DATE: To study Pulse Amplitude modulation and demodulation process with relevant waveforms. APPARATUS: 1. Pulse amplitude modulation
PART B EXPERIMENT NO: 1 AIM: PULSE AMPLITUDE MODULATION (PAM) & DEMODULATION DATE: To study Pulse Amplitude modulation and demodulation process with relevant waveforms. APPARATUS: 1. Pulse amplitude modulation
Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Third Semester. Electrical and Electronics Engineering
 Question Paper Code : 31391 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2013. Third Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 2201/EE 33/EI 1202/10133 EE 302/080280016 MEASUREMENTS AND
Question Paper Code : 31391 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2013. Third Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 2201/EE 33/EI 1202/10133 EE 302/080280016 MEASUREMENTS AND
Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months
 PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Laboratory Experiment 1. Function Generator and Oscilloscope
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Laboratory Experiment 1 Function Generator and Oscilloscope The purpose of this first laboratory assignment is to acquaint you with the function generator
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Laboratory Experiment 1 Function Generator and Oscilloscope The purpose of this first laboratory assignment is to acquaint you with the function generator
IV B. Tech. II Sem (13EE432A) ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS. (Elective - II)
 COURSE OBJECTIVES: Students will be able to (13EE432A) ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS (Elective - II) 1. Memorize modelling of loads and their characteristics 2. Understand design of substations 3. Compare
COURSE OBJECTIVES: Students will be able to (13EE432A) ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS (Elective - II) 1. Memorize modelling of loads and their characteristics 2. Understand design of substations 3. Compare
Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE
 Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
INDEX IEC:
 60050-300 IEC:2001 173 INDEX A absolute absolute error... 311-01-05 (absolute) frequency deviation... 314-08-07 accessory accessory (of a measuring instrument)... 312-03-01 accessory of limited interchangeability...
60050-300 IEC:2001 173 INDEX A absolute absolute error... 311-01-05 (absolute) frequency deviation... 314-08-07 accessory accessory (of a measuring instrument)... 312-03-01 accessory of limited interchangeability...
Sine waves by far the most important form of alternating quantity important properties are shown below
 AC DC METERS 1 Sine waves by far the most important form of alternating quantity important properties are shown below 2 Average value of a sine wave average value over one (or more) cycles is clearly zero
AC DC METERS 1 Sine waves by far the most important form of alternating quantity important properties are shown below 2 Average value of a sine wave average value over one (or more) cycles is clearly zero
Basic Electronics Learning by doing Prof. T.S. Natarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Basic Electronics Learning by doing Prof. T.S. Natarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 38 Unit junction Transistor (UJT) (Characteristics, UJT Relaxation oscillator,
Basic Electronics Learning by doing Prof. T.S. Natarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 38 Unit junction Transistor (UJT) (Characteristics, UJT Relaxation oscillator,
Introduction. In the frequency domain, complex signals are separated into their frequency components, and the level at each frequency is displayed
 SPECTRUM ANALYZER Introduction A spectrum analyzer measures the amplitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument The spectrum analyzer is to the frequency
SPECTRUM ANALYZER Introduction A spectrum analyzer measures the amplitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument The spectrum analyzer is to the frequency
Sonic Distance Sensors
 Sonic Distance Sensors Introduction - Sound is transmitted through the propagation of pressure in the air. - The speed of sound in the air is normally 331m/sec at 0 o C. - Two of the important characteristics
Sonic Distance Sensors Introduction - Sound is transmitted through the propagation of pressure in the air. - The speed of sound in the air is normally 331m/sec at 0 o C. - Two of the important characteristics
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17215 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17215 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Wireless Communication
 Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
SYLLABUS MODULE 1: Measurement and Error: Definitions, Accuracy and Precision, Significant Figures, Types of Error, Statistical Analysis, Probability
 SYLLABUS MODULE 1: Measurement and Error: Definitions, Accuracy and Precision, Significant Figures, Types of Error, Statistical Analysis, Probability of Errors, Limiting Errors. Relevant problems. Ammeters:
SYLLABUS MODULE 1: Measurement and Error: Definitions, Accuracy and Precision, Significant Figures, Types of Error, Statistical Analysis, Probability of Errors, Limiting Errors. Relevant problems. Ammeters:
Exam Booklet. Pulse Circuits
 Exam Booklet Pulse Circuits Pulse Circuits STUDY ASSIGNMENT This booklet contains two examinations for the six lessons entitled Pulse Circuits. The material is intended to provide the last training sought
Exam Booklet Pulse Circuits Pulse Circuits STUDY ASSIGNMENT This booklet contains two examinations for the six lessons entitled Pulse Circuits. The material is intended to provide the last training sought
DE59 ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTATION & MEASUREMENT 2012
 Q.2 a. Define the terms: Ans. (i) Accuracy: It is the closeness with which an instrument reading approaches the true value of the quantity being measured. Accuracy (in percent) =100 - %ε r (ii) (iii) (iv)
Q.2 a. Define the terms: Ans. (i) Accuracy: It is the closeness with which an instrument reading approaches the true value of the quantity being measured. Accuracy (in percent) =100 - %ε r (ii) (iii) (iv)
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS
 CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #2 Title: Function Generators and Oscilloscopes Suggested Equipment:
 RUTGERS UNIVERSITY The State University of New Jersey School of Engineering Department Of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #2 Title:
RUTGERS UNIVERSITY The State University of New Jersey School of Engineering Department Of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #2 Title:
Test No. 2. Advanced Scope Measurements. History. University of Applied Sciences Hamburg. Last chance!! EEL2 No 2
 University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L1: in charge of the report Test No. 2 Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L1: in charge of the report Test No. 2 Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS
 M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS M.D. SINGH Formerly Principal Sagar Institute of Technology and Research Bhopal J.G. JOSHI Lecturer Department of Electronics and Telecommunication
M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS M.D. SINGH Formerly Principal Sagar Institute of Technology and Research Bhopal J.G. JOSHI Lecturer Department of Electronics and Telecommunication
TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: Coil Losses:
 TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: To amplify the selective range of frequencies, the resistive load R C is replaced by a tuned circuit. The tuned circuit is capable of amplifying a signal over a narrow
TUNED AMPLIFIERS 5.1 Introduction: To amplify the selective range of frequencies, the resistive load R C is replaced by a tuned circuit. The tuned circuit is capable of amplifying a signal over a narrow
An Instrumentation System
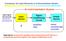 Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
FYSP1110/K1 (FYSP110/K1) USE OF AN OSCILLOSCOPE
 FYSP1110/K1 (FYSP110/K1) USE OF AN OSCILLOSCOPE 1 Introduction In this exercise you will get basic knowledge about how to use an oscilloscope. You ll also measure properties of components, which you are
FYSP1110/K1 (FYSP110/K1) USE OF AN OSCILLOSCOPE 1 Introduction In this exercise you will get basic knowledge about how to use an oscilloscope. You ll also measure properties of components, which you are
Draw in the space below a possible arrangement for the resistor and capacitor. encapsulated components
 1). An encapsulated component is known to consist of a resistor and a capacitor. It has two input terminals and two output terminals. A 5V, 1kHz square wave signal is connected to the input terminals and
1). An encapsulated component is known to consist of a resistor and a capacitor. It has two input terminals and two output terminals. A 5V, 1kHz square wave signal is connected to the input terminals and
Part 10: Transducers
 Part 10: Transducers 10.1: Classification of Transducers An instrument may be defined as a device or a system which is designed to maintain a functional relationship between prescribed properties of physical
Part 10: Transducers 10.1: Classification of Transducers An instrument may be defined as a device or a system which is designed to maintain a functional relationship between prescribed properties of physical
HAMEG Programmable Measuring Instruments Series 8100
 HAMEG Programmable Measuring Instruments Series 8100 HAMEG Programmable Measuring Instruments Series 8100 are ideally suited for test installations in production and automated tests in laboratories. They
HAMEG Programmable Measuring Instruments Series 8100 HAMEG Programmable Measuring Instruments Series 8100 are ideally suited for test installations in production and automated tests in laboratories. They
Using Circuits, Signals and Instruments
 Using Circuits, Signals and Instruments To be ignorant of one s ignorance is the malady of the ignorant. A. B. Alcott (1799-1888) Some knowledge of electrical and electronic technology is essential for
Using Circuits, Signals and Instruments To be ignorant of one s ignorance is the malady of the ignorant. A. B. Alcott (1799-1888) Some knowledge of electrical and electronic technology is essential for
Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Lesson Four Lesson Five PREVIEW COPY
 Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
Laboratory 3 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 3 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) The Oscilloscope Required Components: 1 10 resistor 2 100 resistors 2 lk resistors 1 2k resistor 2 4.7M resistors 1 0.F capacitor 1 0.1 F capacitor 1 1.0uF
Laboratory 3 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) The Oscilloscope Required Components: 1 10 resistor 2 100 resistors 2 lk resistors 1 2k resistor 2 4.7M resistors 1 0.F capacitor 1 0.1 F capacitor 1 1.0uF
1. Explain in detail the constructional details and working of DC motor.
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS
 BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS LECTURE-12 TRANSISTOR BIASING Emitter Current Bias Thermal Stability (RC Coupled Amplifier) Hello everybody! In our series of lectures
BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS LECTURE-12 TRANSISTOR BIASING Emitter Current Bias Thermal Stability (RC Coupled Amplifier) Hello everybody! In our series of lectures
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment)
 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment) 1. In an A.C. circuit A ; the current leads the voltage by 30 0 and in circuit B, the current lags behind the voltage by 30 0. What is the
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment) 1. In an A.C. circuit A ; the current leads the voltage by 30 0 and in circuit B, the current lags behind the voltage by 30 0. What is the
Contents. Acknowledgments. About the Author
 Contents Figures Tables Preface xi vii xiii Acknowledgments About the Author xv xvii Chapter 1. Basic Mathematics 1 Addition 1 Subtraction 2 Multiplication 2 Division 3 Exponents 3 Equations 5 Subscripts
Contents Figures Tables Preface xi vii xiii Acknowledgments About the Author xv xvii Chapter 1. Basic Mathematics 1 Addition 1 Subtraction 2 Multiplication 2 Division 3 Exponents 3 Equations 5 Subscripts
Electronic Instrumentation
 June - 0 Third Semester B.E. Degree Examination Time: 3 hrs. Max. Marks: 00 Note:. Answer any FIVE full questions, selecting at least TWO questions from each part. PAT - A. (a) De ne the following terms:
June - 0 Third Semester B.E. Degree Examination Time: 3 hrs. Max. Marks: 00 Note:. Answer any FIVE full questions, selecting at least TWO questions from each part. PAT - A. (a) De ne the following terms:
EXPERIMENT 1 PRELIMINARY MATERIAL
 EXPERIMENT 1 PRELIMINARY MATERIAL BREADBOARD A solderless breadboard, like the basic model in Figure 1, consists of a series of square holes, and those columns of holes are connected to each other via
EXPERIMENT 1 PRELIMINARY MATERIAL BREADBOARD A solderless breadboard, like the basic model in Figure 1, consists of a series of square holes, and those columns of holes are connected to each other via
09-2 EE 4770 Lecture Transparency. Formatted 12:49, 19 February 1998 from lsli
 09-1 09-1 Displacement and Proximity Displacement transducers measure the location of an object. Proximity transducers determine when an object is near. Criteria Used in Selection of Transducer How much
09-1 09-1 Displacement and Proximity Displacement transducers measure the location of an object. Proximity transducers determine when an object is near. Criteria Used in Selection of Transducer How much
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad
 Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A40203
Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A40203
P a g e 1 ST985. TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual. Analog Arts Inc.
 P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
BE Assignment. (1) Explain Active component and Passive component in Detail. (1) Explain practical voltage source and ideal voltage source.
 BE Assignment chapter-1 (1) Explain Active component and Passive component in Detail. (1) Explain practical voltage source and ideal voltage source. (2) Explain practical current source and ideal current
BE Assignment chapter-1 (1) Explain Active component and Passive component in Detail. (1) Explain practical voltage source and ideal voltage source. (2) Explain practical current source and ideal current
Name Date: Course number: MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START EXPERIMENT 10. Electronic Circuits
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM
 Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
4/30/2012. General Class Element 3 Course Presentation. Practical Circuits. Practical Circuits. Subelement G7. 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups
 General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G7 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3 Radio Wave Propagation
General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G7 2 Exam Questions, 2 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3 Radio Wave Propagation
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. Subject Code: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 Subject Code: 17215 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Subject Code: 17215 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL. B.Tech V Semester [ ] (Branch: ETE)
![Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL. B.Tech V Semester [ ] (Branch: ETE) Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL. B.Tech V Semester [ ] (Branch: ETE)](/thumbs/86/93078052.jpg) Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL SUBJECT:-DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM [BTEC-501] B.Tech V Semester [2013-14] (Branch: ETE) KCT COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH., FATEHGARH PUNJAB TECHNICAL
Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL SUBJECT:-DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM [BTEC-501] B.Tech V Semester [2013-14] (Branch: ETE) KCT COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH., FATEHGARH PUNJAB TECHNICAL
Goals. Introduction. To understand the use of root mean square (rms) voltages and currents.
 Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
