Part 10: Transducers
|
|
|
- Lillian Copeland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Part 10: Transducers 10.1: Classification of Transducers An instrument may be defined as a device or a system which is designed to maintain a functional relationship between prescribed properties of physical variables and must include ways and means of communication to a human observer. Generalized Measurement System Primary sensing The quantity under measurement makes its first contact with the primary sensing of a measurement system Quantity to be measured Primary sensing Variable conversion Variable manipulatio n Data transmissio n Variable presentatio n Variable conversion Variable manipulation Data preserving The output of the primary sensing is converted to some other suitable form for the instrument to perform desired function The function of this is to manipulate the signal presented to it preserving the original nature of the signal. This conveys the information about the quantity under measurement to the personnel handling the instrument or the system for monitoring, control & analysis purposes. We can define Transducer as a device which, accurately transforms energy from one form to another. Another name for Transducer is PICK UP. Classification of Transducers The transducers can be classified as: (i) Based upon transduction principle (ii) Primary and secondary transducers (iii) Passive and active transducers (iv) Analog and digital transducers (v) Transducers and inverse transducers (i) Based upon Transduction Principle The transducers can be classified on the basis of principle of transduction as resistive, inductive, capacitive etc., depending upon how they convert the input quantity into resistance, inductance or capacitance respectively. (ii) Primary and Secondary Transducers The first transducer which converts physical phenomenon into displacement, pressure, velocity etc. which is to be accepted by next stage is known as Primary Transducer. : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: Page 240
2 The output of the primary transducer is converted subsequently into a usable output by a device called Secondary Transducer (iii) Passive and Active Transducers Passive transducers: They derive the power required for transduction from an auxillary power source. Eg: Resistive, inductive and capacitive transducers. Active transducers: They do not require an auxillary power source to produce their output. They are also known as self generating type since they develop their own voltage or current output. Eg: piezoelectric, photovoltaic etc (iv) Analog and digital Transducers Analog transducers: These Transducers convert the input quantity into an analog output which is a continuous function of time. Eg: LVDT, thermocouple etc. Digital Transducers: These transducers convert the input quantity into an electrical output which is in the form of pulses. (v) Transducers & Inverse Transducers Transducer: A transducer can be broadly defined as a device which converts a non electrical quantity into an electrical quantity. Example: L.V.D.T, Resistive and Capacitive Transducers as well. Inverse transducer: An inverse transducer is defined as a device which converts an electrical quantity into a non electrical quantity. NOTE: Generally a Inverse Transducer is a output transducer. Example: Indicating Instruments, Pen Recorders, Oscilloscope. 1. Input Characteristics 1.A Type of Input and operating Range 1. The type of input, which can be any physical quantity, is generally determined in advanced a physical quantity may be measured through use of a number of transducers. 2. However the choice of a particular transducer that is selected for the purpose, depends upon the useful range of selected quantity over which the transducer can be used. 1.B Loading Effects 1. The transducer, that is selected for a particular application should ideally extract no force, power or energy from the quantity under measurement in order that the latter is measured accurately. 2. Ideally a transducer should have no loading effect on the input quantity being measured. : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: Page 241
3 2. Transfer Characteristics 2.A Transfer Function 1. The transfer function of a transducer defines a relationship between the input quantity and the output. 2. The Sensitivity of a transducer is defined as the differential Quotient, S 3. The Scale Factor is defined as the inverse of Sensitivity, 2.B Error The errors in transducers occur because they do not follow, in many situations the input output relationship given by q f(q ). Any deviation from above mentioned relationship results in errors. 3. Output Characteristics 3.A Type of Electrical Output The types of outputs which may be available from the transducers may be a voltage, current, impedance or a time function of these amplitudes. 3.B Output Impedance The output impedance instrumentation is loaded. of a transducer determines to the extent the subsequent stages of Constant Voltage Source If the output Impedance is low compared to the forward Impedance of the System, then the transducer has the characteristics of a constant voltage Source. Provided the output of the transducer is a voltage. Constant Current Source If the forward Impedance is High as compared with the output impedance of the transducer, it then behaves as a Constant Current Source. : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: Page 242
4 10.2: Resistive Transducers Introduction It is generally seen that methods which involve the measurement of change in resistance are preferred to those employing other principles. This is because both alternating as well as direct currents and voltage are suitable for resistance measurements. Effect 1. Change in length 2. Change in length and area of cross section 3. Change in resistivity Potentiometer As a primary transducer Linear and angular displacements, thickness High pressure strain Temperature Temperature, pressure, weight, force, fluid flow rate, viscosity, velocity, acceleration and altitude of vehicles in space All the above quantities except velocity and altitude Thermal conductivity, gas composition, fluid flow rate, wind velocity and direction, low pressure and vacuum and infrared radiation 1. A resistance potentiometer, or simply a POT (a resistive potentiometer used for the purpose of voltage division is called a POT) consists of a resistive provided with a sliding contact. This sliding contact is called a wiper. 2. The resistive of the POT may be excited by either d.c. or a.c. voltage. The POT is a Passive Transducer since it requires an external power source for its operation. Analysis i Output device meter e x wiper x e Let e i and e 0 input and output voltages respectively x t total length of translational pot : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: Page 243
5 x i displacement of wiper from its zero position R p total resistance of potentiometer Quick Refresher Guide Transducers R m resistance of a meter or a recording monitoring the output be R m R Lleft over resistance Resistance per unit length The total resistance seen by the source is: R (1-K)+ Current, i e /R The output voltage under load condition is: e i( ) X Error output voltage under load output voltage under no load e K -e [ ] % error -e [ ] Power Rating of Potentiometers 1. The potentiometers, are designed with a definite power rating which is related directly to their heat dissipating capacity. 2. Since, Power ei, the maximum input excitation voltage that can be used is, e P volts : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: Page 244
6 Linearity and Sensitivity of POTs 1. In order to achieve a good linearity, the resistance of potentiometer, should be as low as possible when using a meter for reading the output voltage which has a fixed value of input resistance. 2. In order to get a high sensitivity the output voltage e, Should be high which in turn requires a high input voltage e. 3. The resistance of the potentiometer, cannot be made low because if we do so the power dissipation goes up with the result that we have to make the input voltage small to keep the power dissipation to the acceptable level. This results in lower sensitivity. 4. Thus linearity and sensitivity are therefore two conflicting requirements. If is made small, the linearity improves, but a lower value requires a lower input voltage e in order to keep down the power dissipation and a lower value of e results in a lower value of output voltage e resulting in lower sensitivity. Materials used for Potentiometers 1. The materials used for POTs may be classified as wire wound and Non wire wound. a. Wire wound POTs Platinum, Nickel, Chromium, Copper and some other precious resistance s. b. Non wire wound POTs These are also called as continuous POTs and have improved resolution and life. Cermet, Hot Moulded Carbon, Carbon film, Thin metal films are used. Strain Gauge If a metal conductor is stretched or compressed its resistance changes on account of the fact that both length and diameter of conductor changes. Also there is a change in the value of resistivity of the conductor when it is strained and this property is called piezo resistive effect. Therefore, resistance strain gauges are also known as piezo resistive gauges. Theory of Strain Gauges Let us consider a strain gauge made of circular wire. The wire has the dimensions, Length L Area A Diameter D before being strained. The material of the wire has a resistivity. esistance of unstrained gauge, R L/A. : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: Page 245
Sensors (Transducer) Introduction By Sintayehu Challa
 Sensors (Transducer) Introduction What are Sensors? Basically the quantities to be measured are Non-Electrical quantities such as temperature, pressure,displacement,humidity, fluid flow, speed etc, but
Sensors (Transducer) Introduction What are Sensors? Basically the quantities to be measured are Non-Electrical quantities such as temperature, pressure,displacement,humidity, fluid flow, speed etc, but
5. Transducers Definition and General Concept of Transducer Classification of Transducers
 5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
Introduction. ELCT903, Sensor Technology Electronics and Electrical Engineering Department 1. Dr.-Eng. Hisham El-Sherif
 Introduction In automation industry every mechatronic system has some sensors to measure the status of the process variables. The analogy between the human controlled system and a computer controlled system
Introduction In automation industry every mechatronic system has some sensors to measure the status of the process variables. The analogy between the human controlled system and a computer controlled system
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements
 Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
Sensors. Chapter 3. Storey: Electrical & Electronic Systems Pearson Education Limited 2004 OHT 3.1
 Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
Synchronous Machines Study Material
 Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER
 VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
EE T55 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION
 EE T55 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT V: TRANSDUCERS Temperature transducers-rtd, thermistor, Thermocouple-Displacement transducer-inductive, capacitive, LVDT, Pressure transducer Bourdon tube,
EE T55 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT V: TRANSDUCERS Temperature transducers-rtd, thermistor, Thermocouple-Displacement transducer-inductive, capacitive, LVDT, Pressure transducer Bourdon tube,
Length and Position Measurement
 Length and Position Measurement Primary standards were once based on the length of a bar of metal at a given temperature. The present standard is: 1 meter = distance traveled by light in a vacuum in 3.335641
Length and Position Measurement Primary standards were once based on the length of a bar of metal at a given temperature. The present standard is: 1 meter = distance traveled by light in a vacuum in 3.335641
MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION. Part A
 MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A 1. Define Standard deviation. 2. Why calibration of instrument is important? 3. What are the different calibration methodologies?
MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A 1. Define Standard deviation. 2. Why calibration of instrument is important? 3. What are the different calibration methodologies?
Downloaded from Downloaded from
 IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION- 2002 SUBJECT: BEG232EC, Instrumentation Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks.
IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION- 2002 SUBJECT: BEG232EC, Instrumentation Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks.
Mechatronics System Design - Sensors
 Mechatronics System Design - Sensors Aim of this class 1. The functional role of the sensor? 2. Displacement, velocity and visual sensors? 3. An integrated example-smart car with visual and displacement
Mechatronics System Design - Sensors Aim of this class 1. The functional role of the sensor? 2. Displacement, velocity and visual sensors? 3. An integrated example-smart car with visual and displacement
 VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
Introduction to Measurement Systems
 MFE 3004 Mechatronics I Measurement Systems Dr Conrad Pace Page 4.1 Introduction to Measurement Systems Role of Measurement Systems Detection receive an external stimulus (ex. Displacement) Selection measurement
MFE 3004 Mechatronics I Measurement Systems Dr Conrad Pace Page 4.1 Introduction to Measurement Systems Role of Measurement Systems Detection receive an external stimulus (ex. Displacement) Selection measurement
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems INDUCTIVE SENSORS (Chapter 3.4, 7.3) 3 Inductive sensors 4 Inductive
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems INDUCTIVE SENSORS (Chapter 3.4, 7.3) 3 Inductive sensors 4 Inductive
IV B. Tech. II Sem (13EE432A) ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS. (Elective - II)
 COURSE OBJECTIVES: Students will be able to (13EE432A) ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS (Elective - II) 1. Memorize modelling of loads and their characteristics 2. Understand design of substations 3. Compare
COURSE OBJECTIVES: Students will be able to (13EE432A) ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS (Elective - II) 1. Memorize modelling of loads and their characteristics 2. Understand design of substations 3. Compare
Advanced Measurements
 Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture 3: Position, Displacement, and Level Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty
Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture 3: Position, Displacement, and Level Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty
Electronic Systems - B1 23/04/ /04/ SisElnB DDC. Chapter 2
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS. Introduction. B1 - Sensors and actuators. Introduction
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Load Cells, LVDTs and Thermocouples
 Load Cells, LVDTs and Thermocouples Introduction Load cells are utilized in nearly every electronic weighing system while LVDTs are used to measure the displacement of a moving object. Thermocouples have
Load Cells, LVDTs and Thermocouples Introduction Load cells are utilized in nearly every electronic weighing system while LVDTs are used to measure the displacement of a moving object. Thermocouples have
PART A. 1. List the types of DC Motors. Give any difference between them. BTL 1 Remembering
 UNIT I DC MACHINES Three phase circuits, a review. Construction of DC machines Theory of operation of DC generators Characteristics of DC generators Operating principle of DC motors Types of DC motors
UNIT I DC MACHINES Three phase circuits, a review. Construction of DC machines Theory of operation of DC generators Characteristics of DC generators Operating principle of DC motors Types of DC motors
Electronic component
 Electronic component Electronic component: An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. 2 TYPES OF
Electronic component Electronic component: An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. 2 TYPES OF
FMCET UNIT I - INTRODUCTION
 UNIT I - INTRODUCTION 1. Write the main static characteristics? (April/may 2008) The main static characteristics are: Accuracy Sensitivity Reproducibility Drift Static error Dead zone Resolution Precision
UNIT I - INTRODUCTION 1. Write the main static characteristics? (April/may 2008) The main static characteristics are: Accuracy Sensitivity Reproducibility Drift Static error Dead zone Resolution Precision
An Instrumentation System
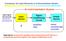 Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Position Sensors. The Potentiometer.
 Position Sensors In this tutorial we will look at a variety of devices which are classed as Input Devices and are therefore called "Sensors" and in particular those sensors which are Positional in nature
Position Sensors In this tutorial we will look at a variety of devices which are classed as Input Devices and are therefore called "Sensors" and in particular those sensors which are Positional in nature
Ultrasonic. Advantages
 Ultrasonic Advantages Non-Contact: Nothing touches the target object Measures Distance: The distance to the target is measured, not just its presence Long and Short Range: Objects can be sensed from 2
Ultrasonic Advantages Non-Contact: Nothing touches the target object Measures Distance: The distance to the target is measured, not just its presence Long and Short Range: Objects can be sensed from 2
1. A transducer converts
 1. A transducer converts a. temperature to resistance b. force into current c. position into voltage d. one form of energy to another 2. Whose of the following transducers the output is a change in resistance?
1. A transducer converts a. temperature to resistance b. force into current c. position into voltage d. one form of energy to another 2. Whose of the following transducers the output is a change in resistance?
Continuous Sensors Accuracy Resolution Repeatability Linearity Precision Range
 Continuous Sensors A sensor element measures a process variable: flow rate, temperature, pressure, level, ph, density, composition, etc. Much of the time, the measurement is inferred from a second variable:
Continuous Sensors A sensor element measures a process variable: flow rate, temperature, pressure, level, ph, density, composition, etc. Much of the time, the measurement is inferred from a second variable:
Course of Instrumentation. and Measurement. National School of Engineers of Tunis ENIT. Karim Bourouni. Dipl.Dr-Ing.
 1 Course of Instrumentation and Measurement Karim Bourouni National School of Engineers of Tunis ENIT Dipl.Dr-Ing. (R.U. Energetic of Buildings and Solar Systems) Industrial Engineering Department 2 Plan
1 Course of Instrumentation and Measurement Karim Bourouni National School of Engineers of Tunis ENIT Dipl.Dr-Ing. (R.U. Energetic of Buildings and Solar Systems) Industrial Engineering Department 2 Plan
MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation. Data Acquisition
 MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Data Acquisition Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Sampling Concepts 1 f s t Sampling Rate f s 2 f m or
MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Data Acquisition Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Sampling Concepts 1 f s t Sampling Rate f s 2 f m or
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 527 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 527 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
Bhoj Reddy Engineering College for Women, Hyderabad Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Electrical and Electronics Instrumentation
 Bhoj Reddy Engineering College for Women, Hyderabad Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Electrical and Electronics Instrumentation Academic Year: 2016-17 III B Tech II Semester Branch:
Bhoj Reddy Engineering College for Women, Hyderabad Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Electrical and Electronics Instrumentation Academic Year: 2016-17 III B Tech II Semester Branch:
DEPT: II EEE EE6404-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENTATION 2MARK: UNIT-1. An instrument is a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity.
 DEPT: II EEE 2MARK: UNIT-1 1. Define instrument. An instrument is a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity. 2. What are the types of instruments? a. Mechanical instrument b. Electrical
DEPT: II EEE 2MARK: UNIT-1 1. Define instrument. An instrument is a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity. 2. What are the types of instruments? a. Mechanical instrument b. Electrical
PVA Sensor Specifications
 Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Sensors 24.1 Sections 8.2-8.5 Position, Velocity, and Acceleration (PVA) Sensors PVA Sensor Specifications Good website to start your search for sensor specifications:
Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Sensors 24.1 Sections 8.2-8.5 Position, Velocity, and Acceleration (PVA) Sensors PVA Sensor Specifications Good website to start your search for sensor specifications:
Introduction to Internet of Things Prof. Sudip Misra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Internet of Things Prof. Sudip Misra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 03 Sensing So, we have already understood the basics
Introduction to Internet of Things Prof. Sudip Misra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 03 Sensing So, we have already understood the basics
Think About Control Fundamentals Training. Terminology Control. Eko Harsono Control Fundamental
 Think About Control Fundamentals Training Terminology Control Eko Harsono eko.harsononus@gmail.com; 1 Contents Topics: Slide No: Process Control Terminology 3-10 Control Principles 11-18 Basic Control
Think About Control Fundamentals Training Terminology Control Eko Harsono eko.harsononus@gmail.com; 1 Contents Topics: Slide No: Process Control Terminology 3-10 Control Principles 11-18 Basic Control
DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 Department of Technical Education DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Third Semester ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION Contact Hours/Week : 04 Contact Hours/Semester :
Department of Technical Education DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Third Semester ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION Contact Hours/Week : 04 Contact Hours/Semester :
Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Third Semester. Electrical and Electronics Engineering
 Question Paper Code : 31391 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2013. Third Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 2201/EE 33/EI 1202/10133 EE 302/080280016 MEASUREMENTS AND
Question Paper Code : 31391 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2013. Third Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 2201/EE 33/EI 1202/10133 EE 302/080280016 MEASUREMENTS AND
Sensors and Transducers
 Sensors and Transducers Transducers-Transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form of energy. Electrical transducers are those which convert one form of energy into electrical
Sensors and Transducers Transducers-Transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form of energy. Electrical transducers are those which convert one form of energy into electrical
STRAIN, FORCE, PRESSURE, AND FLOW MEASUREMENTS
 SECTION 4 STRAIN,, PRESSURE, AND FLOW MEASUREMENTS Walt Kester STRAIN GAGES The most popular electrical elements used in force measurements include the resistance strain gage, the semiconductor strain
SECTION 4 STRAIN,, PRESSURE, AND FLOW MEASUREMENTS Walt Kester STRAIN GAGES The most popular electrical elements used in force measurements include the resistance strain gage, the semiconductor strain
DSC Lab 2: Force and Displacement Measurement Page 1
 DSC Lab 2: Force and Displacement Measurement Page 1 Overview of Laboratory on Force and Displacement Measurement This lab course introduces concepts in force and motion measurement using strain-gauge
DSC Lab 2: Force and Displacement Measurement Page 1 Overview of Laboratory on Force and Displacement Measurement This lab course introduces concepts in force and motion measurement using strain-gauge
Lab 2A: Introduction to Sensing and Data Acquisition
 Lab 2A: Introduction to Sensing and Data Acquisition Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin June 12, 2014 1 Lab 2A 2 Sensors 3 DAQ 4 Experimentation
Lab 2A: Introduction to Sensing and Data Acquisition Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin June 12, 2014 1 Lab 2A 2 Sensors 3 DAQ 4 Experimentation
5. The Different Types of Resistors
 5. The Different Types of Resistors Resistors ( R ), are the most fundamental and commonly used of all the electronic components, to the point where they are almost taken for granted. There are many different
5. The Different Types of Resistors Resistors ( R ), are the most fundamental and commonly used of all the electronic components, to the point where they are almost taken for granted. There are many different
WIRELESS MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS
 WIRELESS MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS REAL-TIME WIRELESS DATA TRANSFER ROD STRAIN PRESSURE OIL FLOW FRICTION TEMPERATURE PISTON TEMPERATURE RING PRESSURE RING MOTION PIN MOTION STRAIN FRICTION We custom build real-time
WIRELESS MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS REAL-TIME WIRELESS DATA TRANSFER ROD STRAIN PRESSURE OIL FLOW FRICTION TEMPERATURE PISTON TEMPERATURE RING PRESSURE RING MOTION PIN MOTION STRAIN FRICTION We custom build real-time
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM. Course Title: Electronics Instruments and Measurement (Code: )
 GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM Course Title: Electronics Instruments and Measurement (Code: 3341104) Diploma Programme in which this course is offered Electronics
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM Course Title: Electronics Instruments and Measurement (Code: 3341104) Diploma Programme in which this course is offered Electronics
Sensors & Actuators. Transduction principles Sensors & Actuators - H.Sarmento
 Sensors & Actuators Transduction principles 2014-2015 Sensors & Actuators - H.Sarmento Outline Resistive transduction. Photoconductive transduction (resistive). Capacitive transduction. Inductive transduction.
Sensors & Actuators Transduction principles 2014-2015 Sensors & Actuators - H.Sarmento Outline Resistive transduction. Photoconductive transduction (resistive). Capacitive transduction. Inductive transduction.
Special Lecture Series Biosensors and Instrumentation
 !1 Special Lecture Series Biosensors and Instrumentation Lecture 6: Micromechanical Sensors 1 This is the first part of the material on micromechanical sensors which deals with piezoresistive and piezoelectric
!1 Special Lecture Series Biosensors and Instrumentation Lecture 6: Micromechanical Sensors 1 This is the first part of the material on micromechanical sensors which deals with piezoresistive and piezoelectric
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Electrical and Electronics Instrumentation Course Code
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Electrical and Electronics Instrumentation Course Code
HTS PARTIAL CORE TRANSFORMER- FAULT CURRENT LIMITER
 EEA CONFERENCE & EXHIBITION 2013, 19-21 JUNE, AUCKLAND HTS PARTIAL CORE TRANSFORMER- FAULT CURRENT LIMITER JIT KUMAR SHAM*, UNIVERSITY OF CANTERBURY, CHRISTCHURCH, NEW ZEALAND PROF. PAT BODGER, UNIVERSITY
EEA CONFERENCE & EXHIBITION 2013, 19-21 JUNE, AUCKLAND HTS PARTIAL CORE TRANSFORMER- FAULT CURRENT LIMITER JIT KUMAR SHAM*, UNIVERSITY OF CANTERBURY, CHRISTCHURCH, NEW ZEALAND PROF. PAT BODGER, UNIVERSITY
Resistance and Ohm s Law R V I. 1 ohm = 1 volt ampere
 Resistance and Ohm s Law If you maintain an electric potential difference, or voltage V, across any conductor, an electric current occurs. In general, the magnitude of the current depends on the potential
Resistance and Ohm s Law If you maintain an electric potential difference, or voltage V, across any conductor, an electric current occurs. In general, the magnitude of the current depends on the potential
REQUIRED SKILLS AND KNOWLEDGE UEENEEE104A. Topic and Description NIDA Lesson CARD #
 REQUIRED SKILLS AND KNOWLEDGE UEENEEE104A KS01-EE104A Direct current circuits T1 Topic and Description NIDA Lesson CARD # Basic electrical concepts encompassing: electrotechnology industry static and current
REQUIRED SKILLS AND KNOWLEDGE UEENEEE104A KS01-EE104A Direct current circuits T1 Topic and Description NIDA Lesson CARD # Basic electrical concepts encompassing: electrotechnology industry static and current
Solution for Electrical and Electronic Measurements
 Q.1) Solution for Electrical and Electronic Measurements May 2016 Index a). 2 b). 2 c). 3-4 d). 5-6 e).. 6 Q.2) a). 7-11 b). 11-16 Q.3) a). 17-20 b). 21-22 Q.4) a). 23-25 b). 25-27 Q.5) a). N.A b). 28-31
Q.1) Solution for Electrical and Electronic Measurements May 2016 Index a). 2 b). 2 c). 3-4 d). 5-6 e).. 6 Q.2) a). 7-11 b). 11-16 Q.3) a). 17-20 b). 21-22 Q.4) a). 23-25 b). 25-27 Q.5) a). N.A b). 28-31
Sensors DR. GYURCSEK ISTVÁN
 DR. GYURCSEK ISTVÁN Sensors Sources and additional materials (recommended) Lambert Miklós: Szenzorok elmélet (ISBN 978-963-874001-1-3) Bp. 2009 Jacob Fraden: Handbook of Modern Sensors (ISBN 978-1-4419-6465-6)
DR. GYURCSEK ISTVÁN Sensors Sources and additional materials (recommended) Lambert Miklós: Szenzorok elmélet (ISBN 978-963-874001-1-3) Bp. 2009 Jacob Fraden: Handbook of Modern Sensors (ISBN 978-1-4419-6465-6)
1. Explain in detail the constructional details and working of DC motor.
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
The units of vibration depend on the vibrational parameter, as follows:
 Vibration Measurement Vibration Definition Basically, vibration is oscillating motion of a particle or body about a fixed reference point. Such motion may be simple harmonic (sinusoidal) or complex (non-sinusoidal).
Vibration Measurement Vibration Definition Basically, vibration is oscillating motion of a particle or body about a fixed reference point. Such motion may be simple harmonic (sinusoidal) or complex (non-sinusoidal).
Q.1 a) Attempt any SIX of the following: 12M. (i) Give comparison between active transducer and passive transducer. Ans:- (Any Two) 1M each
 Page 1 of 26 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written
Page 1 of 26 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written
LAB ASSIGNMENT No. 1 Characteristics of IC Temperature Sensor (LM 335)
 LAB ASSIGNMENT No. 1 Characteristics of IC Temperature Sensor (LM 335) Equipment Required: ST2302with power supply cord Multi Meter Connecting cords Connection diagram: Temperature Transducers: The most
LAB ASSIGNMENT No. 1 Characteristics of IC Temperature Sensor (LM 335) Equipment Required: ST2302with power supply cord Multi Meter Connecting cords Connection diagram: Temperature Transducers: The most
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 145L: Electronic Transducer Laboratory FINAL EXAMINATION Fall 2013 You have three hours to
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 145L: Electronic Transducer Laboratory FINAL EXAMINATION Fall 2013 You have three hours to
Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation. 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance?
 UNIT -6 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance? Ans: Maxwell's bridge, shown in Fig. 1.1, measures an unknown inductance in of standard arm offers
UNIT -6 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance? Ans: Maxwell's bridge, shown in Fig. 1.1, measures an unknown inductance in of standard arm offers
Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405]
![Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405] Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405]](/thumbs/95/124646158.jpg) UNIT-1 1. Discuss liquid in glass thermometers? 2. Write a short note on strain gauges. 3. Mention the various temperature scales and relation between them. 4. An experiment is conducted to calibrate a
UNIT-1 1. Discuss liquid in glass thermometers? 2. Write a short note on strain gauges. 3. Mention the various temperature scales and relation between them. 4. An experiment is conducted to calibrate a
MEAS Silicon MEMS Piezoresistive Accelerometer and its Benefits
 MEAS Silicon MEMS Piezoresistive Accelerometer and its Benefits Piezoresistive Accelerometers 1. Bonded Strain Gage type (Gages bonded to metal seismic mass using epoxy) Undamped circa 1950 s Fluid (oil)
MEAS Silicon MEMS Piezoresistive Accelerometer and its Benefits Piezoresistive Accelerometers 1. Bonded Strain Gage type (Gages bonded to metal seismic mass using epoxy) Undamped circa 1950 s Fluid (oil)
IT.MLD900 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER. Signal Conditioning
 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS LECTURE-2 ELECTRONIC DEVICES -1 RESISTOR, IDEAL SOURCE VOLTAGE & CAPACITOR
 BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS LECTURE-2 ELECTRONIC DEVICES -1 RESISTOR, IDEAL SOURCE VOLTAGE & CAPACITOR In the last lecture we saw the importance of learning about
BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS LECTURE-2 ELECTRONIC DEVICES -1 RESISTOR, IDEAL SOURCE VOLTAGE & CAPACITOR In the last lecture we saw the importance of learning about
Workshop 1 Measurement techniques and sensors
 The University of British Columbia GEOG 309 / Andreas Christen January 31, 2008 Workshop 1 Measurement techniques and sensors Goals 1 Use components and a multi-meter to understand measurement principles
The University of British Columbia GEOG 309 / Andreas Christen January 31, 2008 Workshop 1 Measurement techniques and sensors Goals 1 Use components and a multi-meter to understand measurement principles
UNIT 10 INTRODUCTION TO TRANSDUCERS AND SENSORS
 UNIT 10 INTRODUCTION TO TRANSDUCERS AND SENSORS Structure 10.1 Introduction Objectives 10.2 Active and Passive Sensors 10.3 Basic Requirements of a Sensor/Transducer 10.4 Discrete Event Sensors 10.4.1
UNIT 10 INTRODUCTION TO TRANSDUCERS AND SENSORS Structure 10.1 Introduction Objectives 10.2 Active and Passive Sensors 10.3 Basic Requirements of a Sensor/Transducer 10.4 Discrete Event Sensors 10.4.1
CURRENT ELECTRICITY. 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour Ans: c
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour 2. Electric pressure is also called (a) resistance (b) power (c) voltage (d) energy 3. The substances which
CURRENT ELECTRICITY 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour 2. Electric pressure is also called (a) resistance (b) power (c) voltage (d) energy 3. The substances which
System Inputs, Physical Modeling, and Time & Frequency Domains
 System Inputs, Physical Modeling, and Time & Frequency Domains There are three topics that require more discussion at this point of our study. They are: Classification of System Inputs, Physical Modeling,
System Inputs, Physical Modeling, and Time & Frequency Domains There are three topics that require more discussion at this point of our study. They are: Classification of System Inputs, Physical Modeling,
Fig 1 Microphone transducer types
 Microphones Microphones are the most critical element in the recording chain. Every sound not created purely electronically must be transduced through a microphone in order to be recorded. There is a bewildering
Microphones Microphones are the most critical element in the recording chain. Every sound not created purely electronically must be transduced through a microphone in order to be recorded. There is a bewildering
Course Plan Overview January 2015
 Course Plan Overview January 2015 Page- 1 Impedance: Traditional electrical sense - as generalized resistance: Simple & Complex!! In the mechanical sense, or in a general sense with regard to other domains
Course Plan Overview January 2015 Page- 1 Impedance: Traditional electrical sense - as generalized resistance: Simple & Complex!! In the mechanical sense, or in a general sense with regard to other domains
Lecture 5. In The Name of Allah. Instrumentation. Dr. Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 In The Name of Allah Instrumentation Dr. Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Position Sensors Topics to be covered include: v v v v v v Introduction Resistive Displacement
In The Name of Allah Instrumentation Dr. Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Position Sensors Topics to be covered include: v v v v v v Introduction Resistive Displacement
Measurement and Instrumentation
 Measurement and Instrumentation Theory and Application Alan S. Morris Reza Langari ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Academic
Measurement and Instrumentation Theory and Application Alan S. Morris Reza Langari ELSEVIER AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Academic
ni.com Sensor Measurement Fundamentals Series
 Sensor Measurement Fundamentals Series Introduction to Data Acquisition Basics and Terminology Litkei Márton District Sales Manager National Instruments What Is Data Acquisition (DAQ)? 3 Why Measure? Engineers
Sensor Measurement Fundamentals Series Introduction to Data Acquisition Basics and Terminology Litkei Márton District Sales Manager National Instruments What Is Data Acquisition (DAQ)? 3 Why Measure? Engineers
Lecture 5. In The Name of Allah. Instrumentation. Dr. Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad
 In The Name of Allah Instrumentation Dr. Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Position Sensors Topics to be covered include: v v v v v v Introduction Resistive Displacement
In The Name of Allah Instrumentation Dr. Ali Karimpour Associate Professor Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Position Sensors Topics to be covered include: v v v v v v Introduction Resistive Displacement
Industrial Sensors. Proximity Mechanical Optical Inductive/Capacitive. Position/Velocity Potentiometer LVDT Encoders Tachogenerator
 Proximity Mechanical Optical Inductive/Capacitive Position/Velocity Potentiometer LVDT Encoders Tachogenerator Force/Pressure Vibration/acceleration Industrial Sensors 1 Definitions Accuracy: The agreement
Proximity Mechanical Optical Inductive/Capacitive Position/Velocity Potentiometer LVDT Encoders Tachogenerator Force/Pressure Vibration/acceleration Industrial Sensors 1 Definitions Accuracy: The agreement
PDu150CL Ultra low Noise 150V Piezo Driver with Strain Gauge Feedback
 PDu15CL Ultra low Noise 15V Piezo Driver with Strain auge Feedback The PDu15CL combines a miniature high voltage power supply, precision strain conditioning circuit, feedback controller, and ultra low
PDu15CL Ultra low Noise 15V Piezo Driver with Strain auge Feedback The PDu15CL combines a miniature high voltage power supply, precision strain conditioning circuit, feedback controller, and ultra low
Quantity available (A) Quantity required (R) Sl. No. Deficiency (R - A) Description of Equipment
 . 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (R 203) Semester II EE62 Electric Circuits Laboratory Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (20 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (R 203) Semester II EE62 Electric Circuits Laboratory Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (20 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
electronics for computer engineering (Sensor) by KrisMT Computer Engineering, ICT, University of Phayao
 305222 electronics for computer engineering (Sensor) by KrisMT Computer Engineering, ICT, University of Phayao ห วข อ Sensor =? Each type of sensor Technology Interpolation Sensor =? is a device that measures
305222 electronics for computer engineering (Sensor) by KrisMT Computer Engineering, ICT, University of Phayao ห วข อ Sensor =? Each type of sensor Technology Interpolation Sensor =? is a device that measures
AC bridge circuits. A balanced bridge shows a null, or minimum reading, on the indicator.
 AC bridge circuits As we saw with DC measurement circuits, the circuit configuration known as a bridge can be a very useful way to measure unknown values of resistance. This is true with AC as well, and
AC bridge circuits As we saw with DC measurement circuits, the circuit configuration known as a bridge can be a very useful way to measure unknown values of resistance. This is true with AC as well, and
Measurement Techniques
 Measurement Techniques Anders Sjöström Juan Negreira Montero Department of Construction Sciences. Division of Engineering Acoustics. Lund University Disposition Introduction Errors in Measurements Signals
Measurement Techniques Anders Sjöström Juan Negreira Montero Department of Construction Sciences. Division of Engineering Acoustics. Lund University Disposition Introduction Errors in Measurements Signals
TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION. Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service
 Code No.207 TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Code No.207 TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Sensors for Mechatronics
 Sensors for Mechatronics Paul P.L Regtien Hertgelo The Netherlands AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK' OXFORD ELSEVIER PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Contents Preface xi
Sensors for Mechatronics Paul P.L Regtien Hertgelo The Netherlands AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK' OXFORD ELSEVIER PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY TOKYO Contents Preface xi
CAH CARD. user leaflet. 1 of 15. Copyright Issue 12.1 January 2015
 CAH CARD user leaflet 1 of 15 INTRODUCTION The function of the card is to energise a transducer (LVDT, Half-Bridge or Full-Bridge) with a stable a.c. waveform and to convert the output of the transducer
CAH CARD user leaflet 1 of 15 INTRODUCTION The function of the card is to energise a transducer (LVDT, Half-Bridge or Full-Bridge) with a stable a.c. waveform and to convert the output of the transducer
Industrial Instrumentation Prof. Alok Barua Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Kharagpur
 Industrial Instrumentation Prof. Alok Barua Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Kharagpur Lecture - 6 Torque Measurement Good afternoon! This is lesson 6 of Industrial
Industrial Instrumentation Prof. Alok Barua Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Kharagpur Lecture - 6 Torque Measurement Good afternoon! This is lesson 6 of Industrial
Instrumentation (ch. 4 in Lecture notes)
 TMR7 Experimental methods in Marine Hydrodynamics week 35 Instrumentation (ch. 4 in Lecture notes) Measurement systems short introduction Measurement using strain gauges Calibration Data acquisition Different
TMR7 Experimental methods in Marine Hydrodynamics week 35 Instrumentation (ch. 4 in Lecture notes) Measurement systems short introduction Measurement using strain gauges Calibration Data acquisition Different
Inductive Analog-Sensors
 SENSOREN FÜR AUTOMATION Inductive Analog-Sensors Item group 260 Non-contacting measurement of distance and position -Distance -Displacement -Position -Edge guiding -Concentricity -Centering -Sorting -Counting
SENSOREN FÜR AUTOMATION Inductive Analog-Sensors Item group 260 Non-contacting measurement of distance and position -Distance -Displacement -Position -Edge guiding -Concentricity -Centering -Sorting -Counting
Signal Conditioning Fundamentals for PC-Based Data Acquisition Systems
 Application Note 048 Signal Conditioning Fundamentals for PC-Based Data Acquisition Systems Introduction PC-based data acquisition (DAQ) systems and plugin boards are used in a very wide range of applications
Application Note 048 Signal Conditioning Fundamentals for PC-Based Data Acquisition Systems Introduction PC-based data acquisition (DAQ) systems and plugin boards are used in a very wide range of applications
LVDT. Inductive Position Transducer. SL Series. Key-Features:
 LVDT Inductive Position Transducer SL Series Key-Features: Content: - Measurement ranges 10...600 mm - External, or cable electronics with cable break detection - Linearity up to ±0.10 % of full scale
LVDT Inductive Position Transducer SL Series Key-Features: Content: - Measurement ranges 10...600 mm - External, or cable electronics with cable break detection - Linearity up to ±0.10 % of full scale
Sensors & transducers
 Sensors & transducers Prof. H. Arya DEPT. OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING IIT BOMBAY Sensors Sensors - A device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon. Sensors are also
Sensors & transducers Prof. H. Arya DEPT. OF AEROSPACE ENGINEERING IIT BOMBAY Sensors Sensors - A device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon. Sensors are also
B.E. Sem.VII [ETRX] Basics of VLSI
![B.E. Sem.VII [ETRX] Basics of VLSI B.E. Sem.VII [ETRX] Basics of VLSI](/thumbs/87/95047122.jpg) B.E. Sem.VII [ETRX] Basics of VLSI 1. Physics of FET NMOS, PMOS, enhancement and depletion mode transistor, MOSFET, threshold voltage, flatband condition, threshold adjustment, linear and saturated operation,
B.E. Sem.VII [ETRX] Basics of VLSI 1. Physics of FET NMOS, PMOS, enhancement and depletion mode transistor, MOSFET, threshold voltage, flatband condition, threshold adjustment, linear and saturated operation,
PDu150CL Ultra-low Noise 150V Piezo Driver with Strain Gauge Feedback
 PDu1CL Ultra-low Noise 1V Piezo Driver with Strain auge Feedback The PDu1CL combines a miniature high-voltage power supply, precision strain conditioning circuit, feedback controller, and ultra-low noise
PDu1CL Ultra-low Noise 1V Piezo Driver with Strain auge Feedback The PDu1CL combines a miniature high-voltage power supply, precision strain conditioning circuit, feedback controller, and ultra-low noise
Radio Frequency Electronics
 Radio Frequency Electronics Preliminaries IV Born 22 February 1857, died 1 January 1894 Physicist Proved conclusively EM waves (theorized by Maxwell ), exist. Hz names in his honor. Created the field of
Radio Frequency Electronics Preliminaries IV Born 22 February 1857, died 1 January 1894 Physicist Proved conclusively EM waves (theorized by Maxwell ), exist. Hz names in his honor. Created the field of
NIRMA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT EE101: Elements of Electrical Engineering DC CIRCUIT
 NIRMA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT EE101: Elements of Electrical Engineering DC CIRCUIT Learning Objective: Resistance, Effect of temperature on resistance, temperature
NIRMA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT EE101: Elements of Electrical Engineering DC CIRCUIT Learning Objective: Resistance, Effect of temperature on resistance, temperature
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) Summer 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: 1/22
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: / Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Summer 5 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 754 Model Answer Page No: / Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
Power systems Protection course
 Al-Balqa Applied University Power systems Protection course Department of Electrical Energy Engineering 1 Part 5 Relays 2 3 Relay Is a device which receive a signal from the power system thought CT and
Al-Balqa Applied University Power systems Protection course Department of Electrical Energy Engineering 1 Part 5 Relays 2 3 Relay Is a device which receive a signal from the power system thought CT and
Advanced Measurements
 Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture 5: Displacement measurement Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering
Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture 5: Displacement measurement Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering
Eddy Current Testing (ET) Technique
 Research Group Eddy Current Testing (ET) Technique Professor Pedro Vilaça * * Contacts: Address: Puumiehenkuja 3 (room 202), 02150 Espoo, Finland pedro.vilaca@aalto.fi October 2017 Contents Historical
Research Group Eddy Current Testing (ET) Technique Professor Pedro Vilaça * * Contacts: Address: Puumiehenkuja 3 (room 202), 02150 Espoo, Finland pedro.vilaca@aalto.fi October 2017 Contents Historical
1. The coulomb is a unit of. A. charge B. voltage C. energy D. capacitance E. current. 2. The following is not true about voltage:
 BioE 1310 - Review 1 - DC 1/16/2017 Instructions: On the Answer Sheet, enter your 2-digit ID number (with a leading 0 if needed) in the boxes of the ID section. Fill in the corresponding numbered circles.
BioE 1310 - Review 1 - DC 1/16/2017 Instructions: On the Answer Sheet, enter your 2-digit ID number (with a leading 0 if needed) in the boxes of the ID section. Fill in the corresponding numbered circles.
H01C RESISTORS. Definition statement. References. Limiting references CPC - H01C
 H01C RESISTORS Definition statement This place covers: Passive two-terminal electrical components per se that implement electrical resistance as a circuit element, thereby enabling typically a direct proportion
H01C RESISTORS Definition statement This place covers: Passive two-terminal electrical components per se that implement electrical resistance as a circuit element, thereby enabling typically a direct proportion
 4.2 SHORT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1. What is meant by cell? The basic living unit of the body is cell. The function of organs and other structure of the body is understood by cell organization. 2. Give the
4.2 SHORT QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1. What is meant by cell? The basic living unit of the body is cell. The function of organs and other structure of the body is understood by cell organization. 2. Give the
Sonic Distance Sensors
 Sonic Distance Sensors Introduction - Sound is transmitted through the propagation of pressure in the air. - The speed of sound in the air is normally 331m/sec at 0 o C. - Two of the important characteristics
Sonic Distance Sensors Introduction - Sound is transmitted through the propagation of pressure in the air. - The speed of sound in the air is normally 331m/sec at 0 o C. - Two of the important characteristics
