MAHARASHTRASTATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
|
|
|
- Janice West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MODEL ANSWER WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Electronic Instrumentation Subject Code:17435 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may vary but the examiner may try to assess the understanding level of the candidate. 3) The language errors such as grammatical, spelling errors should not be given more Importance (Not applicable for subject English and Communication Skills. 4) While assessing figures, examiner may give credit for principal components indicated in the figure. The figures drawn by candidate and model answer may vary. The examiner may give credit for anyequivalent figure drawn. 5) Credits may be given step wise for numerical problems. In some cases, the assumed constant values may vary and there may be some difference in the candidate s answers and model answer. 6) In case of some questions credit may be given by judgement on part of examiner of relevant answer based on candidate s understanding. 7) For programming language papers, credit may be given to any other program based on equivalent concept. Q. No. Sub Q.N. Answer Q.1 (A) Attempt any SIX : a) State two examples of absolute instruments and two examples of secondary instruments. Examples of Absolute Instruments: i) Tangent Galvanometer, ii) Absolute electrometer, and iii) Raleigh current balance. Examples of Secondary Instrument: i) Ammeter,ii) voltmeter, iii)ampere-hour meter, wattmeter. b) Compare active transducer and passive transducer on the basis of working principle and examples. Active Transducer 1.The active transducer does not use any external power source for producing the output 2.Additional source is not Require Passive transducer The passive transducer requires the additional energy source for working. 2. Additional source is Require Markin g Scheme 12- Total Marks each Any2 points each 3. Solar Cell Tachogenerator, Thermocouple, Photovoltaic cell 3. LVDT, Thermistor, Differential transformer, Photomultiplier tube, Page1
2 c) State the need of wave analyzer. Also give types of wave analyzer. Need of Wave analyzer: Mathematically any complex wave form is made up of a fundamental and its harmonics. It is often desired to measure the amplitude of each harmonic or fundamental individually. This can be performed by instruments called wave analyzer; this is the simplest form of analysis in the frequency domain. Types of Wave analyzer: Frequency Selective Wave Analyzer need ½ M types each Super heterodyne Wave Analyzer d) List any four applications of CRO. Applications of CRO: 1. Examination of Waveform 2. Voltage measurement 3. Current measurement 4. Modulation Index measurement 5. Time measurement 6. Phase measurement. Any 4 applicat ion ½ M each e) List advantages of digital instruments. Advantages of Digital Instruments: i) The digital instruments indicate the reading directly in decimal numbers. (ii) The reading may be carried to any number of significant figures by merely positioning the decimal point. (iii) The digital instrument requires smaller power. (iv) Its output is in digital form, so it is directly fed into the memory devices like the taperecorder, printers, floppy discs, and digital computer etc. (v)these instruments are free from observational errors, like a parallax and approximation errors. (vi) It has high resolution. Any 4 applicat ion ½ M each Page2
3 f) State any two important specifications of analog D.C. Voltmeter. i)range: in terms of voltage ii)movement type iii)accuracy iv)sensitivity v)operating temp Any 2 applicat ion each g) What is pt-100? Explain. Pt-100 is Resistance Temperature Detector. Pt Stands for Platinum material and 100 stands for 100Ωresistance at 0 0 centigrade. h) What is signal generator? Explain it s need. A signal generator is an electronic device that generates repeating or non-repeating electronic signals in either the analog or the digital domain. An oscillator (sine wave generator) is one of the most basic electronic instruments. Generation of signals (AF or RF) is an important fact of electronic trouble shooting & development. The signal generator is used to provide known test conditions for the performance & evolution of various electronic system & for replacing missing signals in the systems being analyzed for repair. Explain, Need - B) Attempt any TWO : 8 a) Describe with neat diagram the operation of R.F. signal generator. 4M diagra m Operation: The RF oscillator is formed by an LC tank circuit. It generates a stable carrier Frequency over any frequency range. The oscillator is an LC tank circuit, so the Operati on Page3
4 Frequency stability is limited. The frequency range is selected by connecting a switch to particular capacitor. The amplitude modulation is provided by an internal sine wave generator. It may also be provided by an external source. The modulation is done in a wide band amplifier. For modulation sine, square, Triangular wave or pulse may be used. The output of wideband amplifier is connected to attenuator. The required range of attenuation is selected and level of output signal can be controlled. The output meter is used to give an indicator of the output signal. b) Give examples of any two materials used and any two applications of piezo-electric transducer. Materials: 1) Natural Crystals- Quartz crystal, Rochelle salt 2) Synthetic Crystal-Barium Titanium Application: 1) Piezoelectric transducers also are used to generate ultrasonic vibrations for cleaning, atomizing liquids. 2) It is used to measure pressure 3) It is used in nonconventional energy source generation system. 4M Exampl e Applica tions c) Give-classification of flow measuring transducer. 4M Classifi cation- 4M ' Page4
5 Q 2 Attempt any FOUR : a) Describe different types and applications of thermistors. 4M Types : The bead form of the thermistor is smallest in shape, When bead is enclosed inside the solid glass rod to form probes. The disc shape is made by pressing material under high pressure with diameter range from 2.5 mm to 25mm. 16- Total Marks Types Descrip tion- Applications of NTC: For temperature measurement and control. Temperature compensation. Fluid flow measurement. Applications of PTC: Temperature sensing in electrical motors and transformers protection. Liquid level sensor. To protect solid state fuse against excess current. Applica tion- b) Describe any two specifications of analog d.c. ammeter. Draw the connection diagram of d.c. ammeter in electronics circuits. 4M Meter Ammeter connected in series in the circuit Face Size Function Backlighting Amperage Meter Current Shunt Type Weight Current 2.75in (69.85 mm) 0 to 25A 12V DC 24V DC 1mA at full scale Internal 0.25lb (0.11 kg) Any relevant Specific ation marks to be given Diagra m- Page5
6 c) Draw the block diagram of digital multimeter. Explain its working. 4M Explanation: Digital meters offer high accuracy has high input impedance and are small in size. The output available is electrical for interfacing with external equipment in addition to a visual read out. All digital meters employ some kind of analog to digital converter and have a visible readout display at the converter output. DMM is basically a dc voltmeter. A basic digital multimeter DMM is made up of several A/D converters, circuitry for counting and an attenuation circuit. Alternating current is converted in to a dc by employing rectifiers and filters. A basic block diagram of DMM is shown in the figure above The current to voltage converter shown in the block diagram can be implemented with the circuit shown in the following figure. Block diagra m - Explana tion - Page6
7 Optional diagram For resistance measurement the meter includes a precision low current source that is applied across the unknown resistance again this gives a dc voltage which is digitised and read out as ohms. d) Draw the block diagram of DSO. List it s application. 4M Applications: The DSO is used to give the visual representation for a target of radar such as aeroplane, ship etc. The DSO can be used to check the faulty components in various circuits. It can be used in medical field. The DSO can be used to measure ac as well as dc voltages and current. It can be used to analyze TV waveforms. The digital storage oscilloscope (DSO) is used to observe the radiation pattern generated by the transmitting antenna oscilloscope. The DSO used to save signals, so that it can be compared to or processed. The DSO can be used to measure the inductance, capacitor. It can be used to measure frequency, time period, time interval between signals etc. Block Diagra m- any two Each Page7
8 It can be used to observe the V-I characteristics of diodes, transistors. e) Draw the block diagram of function generator. Explain. 4M Explanation A function generator produces different waveforms of adjustable frequency. The common output waveforms are the sine, square, triangular and saw tooth waves. The frequency may be adjusted from a fraction of a hertz to several hundred khz. The block diagram of a function generator is illustrated above. Usually the frequency is controlled by varying the capacitor in the LC or RC circuit. In this instrument the frequency is controlled by varying the magnitude of current which drives the integrator. This instrument produces sine triangular and square wave with a frequency range of 0.01 Hz to 100 khz. The frequency controlled voltage regulates two current sources. The upper current source supplies constant current to the integrator whose output voltage increases linearly with time according to the equation of the output signal voltage. An increase or decrease in the current increases or decreases the slope of the output voltage and hence controls the frequency. The voltage comparator multivibrator changes states at a pre-determined maximum level of the integrator output voltage. This change cuts off the upper current supply and switches on the lower current supply. The lower current source supplies a reverse current to the integrator so that its output decreases linearly with time. When the output reaches a pre-determined minimum level, the voltage comparator again changes state 7 switches on the upper current source. The output of the integrator is a triangular waveform whose frequency is determined Block- Explain - Page8
9 by the magnitude of the current supplied by the constant current sources. The comparator output delivers a square wave voltage of the same frequency. The resistance diode network alters the slope of the triangular wave as its amplitude changes and produces a sine wave with less than 1% distortion. f) Explain primary and secondary transducer with the help of suitable diagram. 4M Primary Transducer:- Primary transducers are detectors which sense a physical phenomenon.the transducer which directly comes in contact with measuring & acts as a sensor to sense or detect the physical quantity is called primary transducers. As shown in Fig the Bourdon tube comes in contact with input pressure directly hence it act as a primary transducer, which convert the pressure into proportional displacement of its free end. Secondary Transducer:- The displacement given by the Bourdon tube is now applied to the core of the LVDT to convert this displacement into proportional electrical quantity(voltage).hence the LVDT is called as secondary transducer. Primar y -1 M Seconda ry -1 M - Diagra m Q.3 Attempt any FOUR: List any four static characteristics and any four dynamic characteristics of electronic a) instruments. Static Characteristics: Accuracy the degree of exactness (closeness) of measurement compared to the expected 16- Total Marks 4M Static chara- Page9
10 (desired) value. Resolution the smallest change in a measurement variable to which an instrument will respond. Precision a measure of consistency or repeatability of measurement, i.e successive reading do not differ. Sensitivity ratio of change in the output (response) of instrument to a change of input or measured variable. Expected value the design value or the most probable value that expect to obtain. Error the deviation of the true value from the desired value. Dynamic Characteristics: Dynamic error-the difference between the true and measured value with no static error. Dynami c chara- b) Lag delay in the response of an instrument to changes in the measured variable. Fidelity the degree to which an instrument indicates the changes in the measured variable without dynamic error (faithful reproduction). A basic d Arsonval meter with an internal resistance of R m = 100Ω and full scale deflection current Im = 1mA is to be converted into d.c. voltmeter with the range of (0-10) V. Find the valve of series resistance. Given: Rm=100Ω Im= 1mA V=10V Rs = Rm = 100 =9900 Ω =9.9k Ω So the value of Rs=9.9k Ω 4M 4M c) Explain with neat block diagram of digital LCR meter. 4M Block Dia- Page10
11 Explain - Explanation: The above figure shows the typical LCR meter. It can give direct reading of the value of the component under measurement. It has switching arrangement for the purpose of the measurement of L,C and R. An internal oscillator generates an Ac signal of 1 KHz frequency. It is used for exciting bridge for Ac measurement. Provision is also given to excite the bridge with an external oscillator. The oscillator excites the bridge. The output from the bridge is fed to the detector amplifier through an emitter follower circuit. The amplified output from the amplifier is rectified using shunt diode and then fed to the meter. This enables the meter to always move in one direction for all Ac measurement. For DC resistance measurement separate provision is available to excite the bridge with DC voltage. For Ac or DC operation a selector switch is provided to the meter. To improve the range of the measurement multipliers are provided. High precision metal film resistors of good temperature stability are used in multiplier stage. The multiplier range is provided in decade steps. Any variation in the value multipleresistor either due to aging or temperature will affect the accuracy of measurement. d) Describe with neat sketch Lissajous pattern for phase measurement. 4M When two signals are applied simultaneously to an oscilloscope one to the horizontal channel and other to the vertical channel, the resulting pattern is a lissajous figure that shows a phase difference between the two signals. when two sinusoidal voltages of equal frequency which are in phase with each otherare applied to the horizontal and vertical deflection plates, the pattern appearing Describ e Patterns Page11
12 on the screen is a straight line as is clear from the figure below. i)if the Lissajous figure is a straight line with an inclination of with positive x-axis, then the phase difference between the two sinusoidal signals will be 0 0. That means, there is no phase difference between those two sinusoidal signals. ii) If the Lissajous figure is in circular shape, then the phase difference between the two sinusoidal signals will be or iii) the phase difference between the two sinusoidal signals by using formulae, when the Lissajous figures are of elliptical shape e) Draw the block diagram of pulse generator. 4M Page12
13 Diagram: Block Dia-4M f) Draw the block diagram of Instrumentation system. Explain the function of each block. 4M Diagram: Block dia- Explanation: Primary sensing & Transduction Element: It is a detector which responds to physical phenomenon or a change in physical equipment. And transduction element transforms output of sensing element in electrical signal or in compatible signal. The compatible or electrical signal is the processed by intermediate means or signal condition unit as per requirement of output devices. So as Data get conditioned, filtered and stabled here at this stage. Data transition Element: The data after conditioning has to be conveyed to the intelligent system so as either can be monitored or recorded, or displayed.this is the function of transmission element which transfer this data in appropriate format. Data presentation Element: this is the final stage og the system. It consists of either pointer-scale, or digital display, or recorder or printer. Explain - Page13
14 Q.4 A) Attempt any FOUR : a) With neat sketch, explain working principle and construction of PMMC. 4M Diagram:- 16- Total Marks Skech- Construction:- The moving coil is wound with many turns of copper wire. The coil is mounted on a rectangular aluminum former which is pivoted on jeweled bearings. The coils move freely in the field of a permanent magnet. Working Principle:- When current passes through the coil a deflecting torque is produced. This deflecting torque is produced due to interaction between magnetic field produced by permanent magnet and magnetic field produced by moving coil. Due to this torque the coil deflects and this deflection is proportional to the current flowing through the coil. The pointer attached to the coil indicated the magnitude of quantity being measured. The another torque is developed by the hair spring known as controlling torque. This torque help to stabilize the pointer. The pointer becomes stable at equilibrium, this is possible only when the controlling torque becomes equal to the deflecting torque. Constru ction-- Workin g Principl e- b) Draw the block diagram of digital frequency meter. Explain the function of each block. 4M Block dia- Diagram:- Page14
15 Functio n- Working:- Amplifier -: The signal whose frequency is measured is first amplified. The output of amplifier is applied to the Schmitt trigger. Schmitt trigger: Schmitt trigger converted the signal in to square wave having fast rise and fall times. The square wave is then differentiate and clipped. Each pulse is proportional to each cycle of unknown signal. Start stop gate- The output from Schmitt trigger is applied to start and stop gate, when the gate is open input pulse are allowed to pass through it. A counter will count these pulse. When gate is closed input pulse are not allowed to pass through the gate. The counter will now stop counting. Counter and display- The number of pulse during the period gate is open and counted by the counter. If this interval between start and stop condition id known. The frequency of unknown signal is measured. F=N/t F= unknown frequency N= number of counts displayed by counter. t= time interval between start and stop condition of the gate. c) Draw the block diagram of dual beam dual trace oscilloscope 4M Diagram: Block dia-4m Page15
16 d) Describe with neat block diagram operation of spectrum analyzer. 4M Diagram:- Blockdi a- Working: Referring to the block diagram of the basic spectrum analyzer, the saw tooth generator provides the saw tooth voltage which drives the horizontal axis element of the scope and this saw tooth voltage is the frequency controlled element of the voltage tuned oscillator. As the oscillator sweeps from f min to f max of its frequency band at a linear recurring rate, it beats with the frequency component of the input signal and produce an IF, whenever a frequency component is met during its sweep. The frequency component and voltage tuned oscillator frequency beats together to produce a difference frequency, i.e. IF. The IF corresponding to the component is amplified and detected if necessary and then applied to the vertical plates of the CRO producing a display of amplitude versus frequency. Spectrum analyzers are widely used in radar, oceanography and biomedical fields. Operati on- Page16
17 e) Illustrate the working of RVDT as a displacement transducer. 4M Diagram:- Diagra m- Working of RVDT :- It is similar to the LVDT except that its core is cam shaped and may be rotated between the windings by means of a shaft. Workin g- At primary null position of the core, the output voltage of secondary windings S 1 and S 2 are equal and in opposition. Therefore, the net output is zero. Any angular displacement voltage output. The grater this angular displacement, the grater will be the differential output. Hence the response of the transducer is linear. The amount of angular displacement and its direction is proportional to the magnitude and phase of the output voltage of the transducer. f) Give the classification of thermocouples based on material used and temperature range. Classification of Thermocouple:- 4M Type Material Temperature ranges J type Iron-constant c to c K type Chromel Alumel c to c T type Copper Constant c to c R type Pt(87%) Rh(13) c to c Platinum Any 4 = 1 M each S type Pt (90%) Rh(10%)-Pt c to c Page17
18 E type Chromel- constant c to c Q.5 Attempt any FOUR : 16- Total Marks a) Explain with neat diagram the operation of single beam dual trace oscilloscope. 4M Diagram: Diagra m- Working: A mode control system (s1) enables the electronic switch to operate in two modes Alternate and chop mode and x-y mode. Alternate mode: When the switch (s1) is in alternate position, the electronic switch feeds each signal alternatively to the vertical amplifier. Operati on- Page18
19 The electronic switch alternately connects the main vertical amplifier to channels A and B and adds a different dc component to each signal This dc component directs the beam alternately to the upper or lower half of the screen. The switching takes place at the start of each new sweep of the sweep generator. The switching rate of the electronic switch rate,so that the CRT spot traces the channel A signal on one sweep and the succeeding sweep. The sweep trigger signal is available from channels A or B and the trigger pick-off takes place before the electronic switch. This arrangement maintains the correct phase relationship between signal A and B. Chop mode: When the switch (s1) is in the chop mode position, the electronic switch is free running at the rate of KHz, entirely independent of the frequency of the sweep generator.the switch successively connects small segments of A and B waveforms to the main vertical amplifier at a relatively fast chopping rate of 500 KHz. e.g. 1 MS segments of each waveform are to the CRT display. If the chopping rate is slow, the continuity of the display is lost and it is better to use the alternate mode of operation. X-Y mode: In the x-y mode operation the sweep generator is disconnected and channel B is connected to the horizontal amplifier. Since both preamplifiers are identical and have the same delay time, accurate x-y measurements can be made. b) Describe with neat block diagram the operation of frequency selective wave analyzer. 4M Block dia- Diagram:- Page19
20 Operation:- The wave analyzer consist of a very a narrow pass-band filter section can be tuned to a particular frequency. The complex wave to be analyzed is passed through an adjustable attenuator which serves as a range multimeter and permits a large range of signal amplitudes to be analyzed without loading the amplifier. The output of the attenuator is then fed to a selective amplifier, which amplifies the selected frequency. The driver amplifier applies the attenuated input signal to a high Q active filter. This high-q filter is a low pass filter which allows the frequency which is selected to pass and reject all others. The magnitude of the selected frequency is indicated by the meter and the filter section identifies the frequency of the component. The capacitors are used for range changing and the potentiometer is used to change the frequency within the selected pass-band, hence this wave analyzer is also called a frequency selective voltmeter. The selected signal output from the final amplifier stage is applied to the meter circuit & un-tuned buffer amplifier. The main function of the buffer amplifier is to drive output devices. c) Describe construction and working of capacitive transducer with suitable diagram. 4M Operati on- Page20
21 Diagram: Diagra m- Construction: It consists of two plates, one fixed and the other free to move as the displacement is applied on it. Working: The movable plate works as a cantilever plat, decreasing the distance between the two plate. Due to this decrease in distance the capacitance of a capacitor increases. The air between the two plates works as a dielectric medium. The capacitance of an air dielectric capacitor does not vary linearly with change in distance between the plates.for the linearity can be the closely approximated by keeping the change in the distance small or by having a medium of high dielectric constant in the space between the two plates.this type of capacitive transducer may be used to measure displacements. Constr uction- Workin g- d) Describe the working of electromagnetic flow meter with suitable diagram. 4M Diagrame:- Diagra m- Working :- The operation of this type of flowmeter is based on Faraday s law of electromagnetic induction. The law state that whenever the conductor moves through a magnetic field, Workin g- Page21
22 an emf is induced in the conductor proportional to the relative velocity between the conductor & the magnetic field.it consists of a pipe, short section of which is subjected to a transverse magnetic field. The conductive fluid is passed through this pipe. As fluid passes, its motion relative to field produces an emf proportional to velocity according to Faraday s law.this output emf is collected by the electrodes (kept at points of maximum potential difference) and is given to external circuitry. e) Define unit. Give two examples of each of base unit, supplementary unit and derived units. 4M Unit:- The result of a measurement of a physical quantity must be defined both in kind and magnitude. The standard measure of each kind of physical quantity is called a Unit. Base Unit:(any two) Length, Mass, Time, Intensity of electric current, Thermodynamic Temperature, Luminous intensity, Amount of substance Supplementary unit: (any two) Plane angle, Solid angle Derived units: (any two) Area, Volume, Frequency, Density, Velocity, Acceleration, Force, Pressure, Viscosity, Power, Resistance, capacitance, Inductance, Work, Energy, Quantity of heat f) What are requirements of shunt resistance in ammeter? 4M The coil winding of basic movement is small & it is light in weight. So this coil enables small currents to pass through it. It is required to pass current range through coil then the construction become bulky. In order to avoid this resistor is connected in parallel with the basic movement. 4M This resistor is called is shunt resistor. So major amount of current passes through it & a small current passes through the coil. Q.6 Attempt any FOUR: a) Define error. List source of error in measurement system. 4M Definition of Error:- An error is the deviation of the true value from the desired value. Sources of error:- Gross Errors:- The gross error occurs due to the human mistakes in reading or using the 16- Total Marks Definat ion Page22
23 b) instruments. Systematic errors:- These are sub divided as :- Instrumental errors :- These errors occurs due to inherent shortcomings in the instruments, misuse of instruments and loading effects of the instruments Observational error:- These are due to carelessness of the operator Environmental error:- This include condition in the area surrounding the instrument such as the effect of changes in temperature, humidity, barometric pressure or magnetic or electrostatic field. Random error:- These are due to unknown causes and occur even when all the systematic errors have been accounted for. Compare analog instruments and digital instruments on the basis of accuracy, resolution, working principle and examples List- 4M Analog instruments Digital instruments Any 4 Accuracy is less Accuracy is more points Resolution is less Resolution is more Displays analog signal Displays digital signal each Examples: PMMC instruments, DC Examples: Logic analyzer, digital voltmeter, DC ammeter analyzer c) Draw neat and labeled diagram of internal structure of CRT. 4M Diagram: diag. labelin g d) Describe working principle of Logic Analyzer with neat diagram. 4M Diagram:- Working Principle:- Page23
24 A block diagram of a typical logical analyzer. It has a data gathering unit information processing and storage unit and a display unit. The data gathering unit has A pod slots for carrying data from the digital system under test to the logic analyzer. A key pad used for entering commands. Information processing storage unit:- Records all the data from data gathering unit with respect to clock signal. This clock signal determines whether the data is high or low w.r.t defined threshold voltages. This info stored in memory available for detailing to display unit. The display unit is a cathode ray tube (CRT) that displays the command menu for the operator and also displays the output data. e) List any eight front panel controls of CRO. 4M Front panel controls of CRO (any eight) 1. POWER ON 2. INTENSITY 3.FOCUS 4. TIME BASE 5.TIME BASE VARIABLE 6. HOLD-OFF 7. POSITION/x5 8.LEVEL 9. AUTO/NORM 10. INT/EXT ½ M 11. LINE 12.TV 13. CH1/CH / 15. HF Rej 16. ac/dc 17. each SWP/X-Y , 1KHz 19. Positions 20.ac/dc/gnd 21. EXT-TRIG 22.INPUT BNC CH1/Y (CH2/X) 23.TRACE 24.CH1/CH2 ATTENUATOR f) Define the term temperature and flow. State their units. 4M Temperature:-It is the degree or intensity of heat present in a substance or object. Units of Temperature: Celsius or centigrade ( C) Fahrenheit ( F) Kelvin ( K). Flow:-Flow is defined as fluid in motion. Flow may be of Gas or Liquids. Units of Flow: (any two) Tonnes/hour Kg/minute litres/hour litres/minute m3/hour Nm3/hour (any two) - Page24
25 Page25
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer
 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code : 17317 Page No: 1 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code : 17317 Page No: 1 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
Q.1 a) Attempt any SIX of the following: 12M. (i) Give comparison between active transducer and passive transducer. Ans:- (Any Two) 1M each
 Page 1 of 26 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written
Page 1 of 26 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written
Table of Contents...2. About the Tutorial...6. Audience...6. Prerequisites...6. Copyright & Disclaimer EMI INTRODUCTION Voltmeter...
 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
5. Transducers Definition and General Concept of Transducer Classification of Transducers
 5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
b) State the types of standards of measurement. 2M
 MODEL ANSWER WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Electronic Instruments & Measurements Subject Code: 17317 I m p o r t a n t I n s t r u c t i o n s t o e x a m i n e r s : 1) The answers should be examined
MODEL ANSWER WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Electronic Instruments & Measurements Subject Code: 17317 I m p o r t a n t I n s t r u c t i o n s t o e x a m i n e r s : 1) The answers should be examined
UNIT-3. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION
 SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17317 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
SUMMER 15 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17317 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
1. A) Attempt any six of the following: [12M]
![1. A) Attempt any six of the following: [12M] 1. A) Attempt any six of the following: [12M]](/thumbs/95/125538661.jpg) Subject Code: 17435 Model Answer Page 1 of 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17435 Model Answer Page 1 of 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the Model answer scheme. 2) The model
UNIT 2. Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator. Ans. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
Rayat Shikshan Sanstha s Karmaveer Bhaurao Patil Polytechnic, Satara. Sub: Electrical Engineering Assignment No: 1
 Assignment No: 1 1) Define Precision and Dead zone 2) Define 1) Speed of response 2) Lag 3) Fidelity 4)dynamic error 3) Define Standard and State its classification 4) What is Calibration & State its necessity
Assignment No: 1 1) Define Precision and Dead zone 2) Define 1) Speed of response 2) Lag 3) Fidelity 4)dynamic error 3) Define Standard and State its classification 4) What is Calibration & State its necessity
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) MODEL ANSWER
 MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Electronic Instruments and Measurements Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Electronic Instruments and Measurements Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
Synchronous Machines Study Material
 Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) SUMMER 2013 EXAMINATION
 MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 2013 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 12117 Model Answer Page No: 1 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC 27001 2005 Certified) SUMMER 2013 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 12117 Model Answer Page No: 1 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17435) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17435) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17317) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17317) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Bhoj Reddy Engineering College for Women, Hyderabad Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Electrical and Electronics Instrumentation
 Bhoj Reddy Engineering College for Women, Hyderabad Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Electrical and Electronics Instrumentation Academic Year: 2016-17 III B Tech II Semester Branch:
Bhoj Reddy Engineering College for Women, Hyderabad Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Electrical and Electronics Instrumentation Academic Year: 2016-17 III B Tech II Semester Branch:
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY
 SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY-621105. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EI 1306-MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY-621105. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EI 1306-MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION
Definitions. Spectrum Analyzer
 SIGNAL ANALYZERS Spectrum Analyzer Definitions A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure
SIGNAL ANALYZERS Spectrum Analyzer Definitions A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure
DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 Department of Technical Education DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Third Semester ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION Contact Hours/Week : 04 Contact Hours/Semester :
Department of Technical Education DIPLOMA COURSE IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Third Semester ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION Contact Hours/Week : 04 Contact Hours/Semester :
PART A. 1. List the types of DC Motors. Give any difference between them. BTL 1 Remembering
 UNIT I DC MACHINES Three phase circuits, a review. Construction of DC machines Theory of operation of DC generators Characteristics of DC generators Operating principle of DC motors Types of DC motors
UNIT I DC MACHINES Three phase circuits, a review. Construction of DC machines Theory of operation of DC generators Characteristics of DC generators Operating principle of DC motors Types of DC motors
Sine waves by far the most important form of alternating quantity important properties are shown below
 AC DC METERS 1 Sine waves by far the most important form of alternating quantity important properties are shown below 2 Average value of a sine wave average value over one (or more) cycles is clearly zero
AC DC METERS 1 Sine waves by far the most important form of alternating quantity important properties are shown below 2 Average value of a sine wave average value over one (or more) cycles is clearly zero
 VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) UNIT I
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : EMI(16EC416) Year & Sem: III B.Tech & I Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : EMI(16EC416) Year & Sem: III B.Tech & I Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech
4. Digital Measurement of Electrical Quantities
 4.1. Concept of Digital Systems Concept A digital system is a combination of devices designed for manipulating physical quantities or information represented in digital from, i.e. they can take only discrete
4.1. Concept of Digital Systems Concept A digital system is a combination of devices designed for manipulating physical quantities or information represented in digital from, i.e. they can take only discrete
MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION. Part A
 MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A 1. Define Standard deviation. 2. Why calibration of instrument is important? 3. What are the different calibration methodologies?
MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A 1. Define Standard deviation. 2. Why calibration of instrument is important? 3. What are the different calibration methodologies?
EE ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION
 EE6352 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT V ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS Digital Voltmeter (DVM) It is a device used for measuring the magnitude of DC voltages. AC voltages can be measured
EE6352 - ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT V ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS Digital Voltmeter (DVM) It is a device used for measuring the magnitude of DC voltages. AC voltages can be measured
Electronic Instrumentation & Automation. ET-7th semester. By : Rahul Sharma ET & TC Deptt. RCET, Bhilai
 Electronic Instrumentation & Automation ET-7th semester By : Rahul Sharma ET & TC Deptt. RCET, Bhilai UNIT: III Voltage and Current Measurements Digital Voltmeters: Non-Integrating type, Integrating Type,
Electronic Instrumentation & Automation ET-7th semester By : Rahul Sharma ET & TC Deptt. RCET, Bhilai UNIT: III Voltage and Current Measurements Digital Voltmeters: Non-Integrating type, Integrating Type,
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) MODEL ANSWER
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17215 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17215 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Summer 2015 Examination
 Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER EI6601 Modern Electronic Instrumentation Regulation
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER EI6601 Modern Electronic Instrumentation Regulation
9/28/2010. Chapter , The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
INDEX IEC:
 60050-300 IEC:2001 173 INDEX A absolute absolute error... 311-01-05 (absolute) frequency deviation... 314-08-07 accessory accessory (of a measuring instrument)... 312-03-01 accessory of limited interchangeability...
60050-300 IEC:2001 173 INDEX A absolute absolute error... 311-01-05 (absolute) frequency deviation... 314-08-07 accessory accessory (of a measuring instrument)... 312-03-01 accessory of limited interchangeability...
Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405]
![Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405] Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405]](/thumbs/95/124646158.jpg) UNIT-1 1. Discuss liquid in glass thermometers? 2. Write a short note on strain gauges. 3. Mention the various temperature scales and relation between them. 4. An experiment is conducted to calibrate a
UNIT-1 1. Discuss liquid in glass thermometers? 2. Write a short note on strain gauges. 3. Mention the various temperature scales and relation between them. 4. An experiment is conducted to calibrate a
State the application of negative feedback and positive feedback (one in each case)
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
IT.MLD900 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER. Signal Conditioning
 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS
 RAE-Lessons by 4S7VJ 1 CHAPTER-7 RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS MEASURMENTS By 4S7VJ 7.1 TEST EQUIPMENT & MEASUREMENTS Correct operation of amateur radio equipment involves measurements to ensure optimum
RAE-Lessons by 4S7VJ 1 CHAPTER-7 RADIO AMATEUR EXAM GENERAL CLASS MEASURMENTS By 4S7VJ 7.1 TEST EQUIPMENT & MEASUREMENTS Correct operation of amateur radio equipment involves measurements to ensure optimum
Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE
 Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
IV B. Tech. II Sem (13EE432A) ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS. (Elective - II)
 COURSE OBJECTIVES: Students will be able to (13EE432A) ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS (Elective - II) 1. Memorize modelling of loads and their characteristics 2. Understand design of substations 3. Compare
COURSE OBJECTIVES: Students will be able to (13EE432A) ELECTRICAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS (Elective - II) 1. Memorize modelling of loads and their characteristics 2. Understand design of substations 3. Compare
Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation UNIT What are the basic performance characteristics of a system?
 UNIT-1 1. What are the basic performance characteristics of a system? Ans: STATIC CHARACTE RISTICS The static characteristics of an instrument are, in general, considered for instruments which are used
UNIT-1 1. What are the basic performance characteristics of a system? Ans: STATIC CHARACTE RISTICS The static characteristics of an instrument are, in general, considered for instruments which are used
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment)
 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment) 1. In an A.C. circuit A ; the current leads the voltage by 30 0 and in circuit B, the current lags behind the voltage by 30 0. What is the
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment) 1. In an A.C. circuit A ; the current leads the voltage by 30 0 and in circuit B, the current lags behind the voltage by 30 0. What is the
Contents. Acknowledgments. About the Author
 Contents Figures Tables Preface xi vii xiii Acknowledgments About the Author xv xvii Chapter 1. Basic Mathematics 1 Addition 1 Subtraction 2 Multiplication 2 Division 3 Exponents 3 Equations 5 Subscripts
Contents Figures Tables Preface xi vii xiii Acknowledgments About the Author xv xvii Chapter 1. Basic Mathematics 1 Addition 1 Subtraction 2 Multiplication 2 Division 3 Exponents 3 Equations 5 Subscripts
FMCET UNIT I - INTRODUCTION
 UNIT I - INTRODUCTION 1. Write the main static characteristics? (April/may 2008) The main static characteristics are: Accuracy Sensitivity Reproducibility Drift Static error Dead zone Resolution Precision
UNIT I - INTRODUCTION 1. Write the main static characteristics? (April/may 2008) The main static characteristics are: Accuracy Sensitivity Reproducibility Drift Static error Dead zone Resolution Precision
Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation. 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance?
 UNIT -6 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance? Ans: Maxwell's bridge, shown in Fig. 1.1, measures an unknown inductance in of standard arm offers
UNIT -6 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance? Ans: Maxwell's bridge, shown in Fig. 1.1, measures an unknown inductance in of standard arm offers
Electronic Systems - B1 23/04/ /04/ SisElnB DDC. Chapter 2
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS. Introduction. B1 - Sensors and actuators. Introduction
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Wireless Communication
 Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering Code : A30203 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering Code : A30203 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch
Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Third Semester. Electrical and Electronics Engineering
 Question Paper Code : 31391 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2013. Third Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 2201/EE 33/EI 1202/10133 EE 302/080280016 MEASUREMENTS AND
Question Paper Code : 31391 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2013. Third Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 2201/EE 33/EI 1202/10133 EE 302/080280016 MEASUREMENTS AND
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad
 Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A40203
Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A40203
Part 10: Transducers
 Part 10: Transducers 10.1: Classification of Transducers An instrument may be defined as a device or a system which is designed to maintain a functional relationship between prescribed properties of physical
Part 10: Transducers 10.1: Classification of Transducers An instrument may be defined as a device or a system which is designed to maintain a functional relationship between prescribed properties of physical
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit
 Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 210 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 210 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR
An Instrumentation System
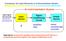 Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Acknowledgments Introduction
 Acknowledgments Introduction xiii xi 1 Electronic meters 1 1.1 Digital meters 2 1.2 Nondigital (analog) meters 6 1.3 Differential meters 14 1.4 Digital meter displays and ranges 16 1.5 Nondigital meter
Acknowledgments Introduction xiii xi 1 Electronic meters 1 1.1 Digital meters 2 1.2 Nondigital (analog) meters 6 1.3 Differential meters 14 1.4 Digital meter displays and ranges 16 1.5 Nondigital meter
UNIT II MEASUREMENT OF POWER & ENERGY
 UNIT II MEASUREMENT OF POWER & ENERGY Dynamometer type wattmeter works on a very simple principle which is stated as "when any current carrying conductor is placed inside a magnetic field, it experiences
UNIT II MEASUREMENT OF POWER & ENERGY Dynamometer type wattmeter works on a very simple principle which is stated as "when any current carrying conductor is placed inside a magnetic field, it experiences
1. (a) Determine the value of Resistance R and current in each branch when the total current taken by the curcuit in figure 1a is 6 Amps.
 Code No: 07A3EC01 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production
Code No: 07A3EC01 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2008 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING ( Common to Civil Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production
DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING. Test No. 1. Introduction to Scope Measurements. 1. Correction. Term Correction. Term...
 2. Correction. Correction Report University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No.
2. Correction. Correction Report University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No.
1. Explain in detail the constructional details and working of DC motor.
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
Exam Booklet. Pulse Circuits
 Exam Booklet Pulse Circuits Pulse Circuits STUDY ASSIGNMENT This booklet contains two examinations for the six lessons entitled Pulse Circuits. The material is intended to provide the last training sought
Exam Booklet Pulse Circuits Pulse Circuits STUDY ASSIGNMENT This booklet contains two examinations for the six lessons entitled Pulse Circuits. The material is intended to provide the last training sought
ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS
 ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS Digital Voltmeter (DVM) Used to measure the ac and dc voltages and displays the result in digital form. Types: Ramp type DVM Integrating type DVM Potentiometric type DVM
ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS Digital Voltmeter (DVM) Used to measure the ac and dc voltages and displays the result in digital form. Types: Ramp type DVM Integrating type DVM Potentiometric type DVM
DE59 ELECTRONIC INSTRUMENTATION & MEASUREMENT 2012
 Q.2 a. Define the terms: Ans. (i) Accuracy: It is the closeness with which an instrument reading approaches the true value of the quantity being measured. Accuracy (in percent) =100 - %ε r (ii) (iii) (iv)
Q.2 a. Define the terms: Ans. (i) Accuracy: It is the closeness with which an instrument reading approaches the true value of the quantity being measured. Accuracy (in percent) =100 - %ε r (ii) (iii) (iv)
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
Test No. 1. Introduction to Scope Measurements. Report History. University of Applied Sciences Hamburg. Last chance!! EEL2 No 1
 University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No. Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L: in charge of the report Test No. Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS NEWS RESULTS FORUMS UNIT 8
 UNIT 8 (a) Interfacing resistive transducers to electronic circuits. Introduction to data acquisition systems. 2 Hours (b) Display Devices and Signal Generators: X-Y recorders. Nixie tubes. LCD and LED
UNIT 8 (a) Interfacing resistive transducers to electronic circuits. Introduction to data acquisition systems. 2 Hours (b) Display Devices and Signal Generators: X-Y recorders. Nixie tubes. LCD and LED
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. Subject Code: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 Subject Code: 17215 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Subject Code: 17215 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Maltase cross tube. D. Senthilkumar P a g e 1
 Thermionic Emission Maltase cross tube Definition: The emission of electrons when a metal is heated to a high temperature Explanation: In metals, there exist free electrons which are able to move around
Thermionic Emission Maltase cross tube Definition: The emission of electrons when a metal is heated to a high temperature Explanation: In metals, there exist free electrons which are able to move around
EE T55 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION
 EE T55 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT V: TRANSDUCERS Temperature transducers-rtd, thermistor, Thermocouple-Displacement transducer-inductive, capacitive, LVDT, Pressure transducer Bourdon tube,
EE T55 MEASUREMENTS AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT V: TRANSDUCERS Temperature transducers-rtd, thermistor, Thermocouple-Displacement transducer-inductive, capacitive, LVDT, Pressure transducer Bourdon tube,
ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICITY
 INTRODUCTION ELECTRONICS ND ELECTRICITY The science of Electronics and Electricity makes a very important contribution to our everyday existence. Electricity is concerned with the generation, transmission
INTRODUCTION ELECTRONICS ND ELECTRICITY The science of Electronics and Electricity makes a very important contribution to our everyday existence. Electricity is concerned with the generation, transmission
Sensors. Chapter 3. Storey: Electrical & Electronic Systems Pearson Education Limited 2004 OHT 3.1
 Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
Name Date: Course number: MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START EXPERIMENT 10. Electronic Circuits
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE)
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Suject : Electrical & Electronic Measurements(16EE224) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Suject : Electrical & Electronic Measurements(16EE224) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech
Communication Circuit Lab Manual
 German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS. Faculty: 1.Shaik.Jakeer Hussain 2.P.Sandeep patil 3.P.Ramesh Babu
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Faculty: 1.Shaik.Jakeer Hussain 2.P.Sandeep patil 3.P.Ramesh Babu UNIT-I ELECTRON DYNAMICS AND CRO: Motion of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields. Simple problems
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Faculty: 1.Shaik.Jakeer Hussain 2.P.Sandeep patil 3.P.Ramesh Babu UNIT-I ELECTRON DYNAMICS AND CRO: Motion of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields. Simple problems
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17213 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17213 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR. By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Third Edition by J.
 PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06)
 Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS)
 Name Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A30203 : II B.
Name Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : A30203 : II B.
A 11/89. Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model SF-8616 and 8617 COILS SET. Copyright November 1989 $15.
 Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model SF-8616 and 8617 012-03800A 11/89 COILS SET Copyright November 1989 $15.00 How to Use This Manual The best way to learn to use the
Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model SF-8616 and 8617 012-03800A 11/89 COILS SET Copyright November 1989 $15.00 How to Use This Manual The best way to learn to use the
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS
 CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
DEPT: II EEE EE6404-MEASUREMENT & INSTRUMENTATION 2MARK: UNIT-1. An instrument is a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity.
 DEPT: II EEE 2MARK: UNIT-1 1. Define instrument. An instrument is a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity. 2. What are the types of instruments? a. Mechanical instrument b. Electrical
DEPT: II EEE 2MARK: UNIT-1 1. Define instrument. An instrument is a device for determining the value or magnitude of a quantity. 2. What are the types of instruments? a. Mechanical instrument b. Electrical
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER
 VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization
 Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied to the
Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied to the
Sensors (Transducer) Introduction By Sintayehu Challa
 Sensors (Transducer) Introduction What are Sensors? Basically the quantities to be measured are Non-Electrical quantities such as temperature, pressure,displacement,humidity, fluid flow, speed etc, but
Sensors (Transducer) Introduction What are Sensors? Basically the quantities to be measured are Non-Electrical quantities such as temperature, pressure,displacement,humidity, fluid flow, speed etc, but
Position Sensors. The Potentiometer.
 Position Sensors In this tutorial we will look at a variety of devices which are classed as Input Devices and are therefore called "Sensors" and in particular those sensors which are Positional in nature
Position Sensors In this tutorial we will look at a variety of devices which are classed as Input Devices and are therefore called "Sensors" and in particular those sensors which are Positional in nature
Lecture 36 Measurements of High Voltages (cont) (Refer Slide Time: 00:14)
 Advances in UHV Transmission and Distribution Prof. B Subba Reddy Department of High Voltage Engg (Electrical Engineering) Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture 36 Measurements of High Voltages
Advances in UHV Transmission and Distribution Prof. B Subba Reddy Department of High Voltage Engg (Electrical Engineering) Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture 36 Measurements of High Voltages
Continuous Sensors Accuracy Resolution Repeatability Linearity Precision Range
 Continuous Sensors A sensor element measures a process variable: flow rate, temperature, pressure, level, ph, density, composition, etc. Much of the time, the measurement is inferred from a second variable:
Continuous Sensors A sensor element measures a process variable: flow rate, temperature, pressure, level, ph, density, composition, etc. Much of the time, the measurement is inferred from a second variable:
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are primarily conceptual questions designed to see whether you understand the main concepts of the chapter. 1. The four areas in Figure 20.34 are in a magnetic field.
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are primarily conceptual questions designed to see whether you understand the main concepts of the chapter. 1. The four areas in Figure 20.34 are in a magnetic field.
Analog Multimeter. household devices.
 1 Analog Multimeter A multimeter or a multitester, a.k.a.vom (volt-ohmmilliammeter), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter
1 Analog Multimeter A multimeter or a multitester, a.k.a.vom (volt-ohmmilliammeter), is an electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions in one unit. A typical multimeter
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM. Unit Objectives. Unit Objectives 2/29/2012
 SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
SECTION 3 BASIC AUTOMATIC CONTROLS UNIT 12 BASIC ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM Unit Objectives Describe the structure of an atom. Identify atoms with a positive charge and atoms with a negative charge. Explain
070 ELECTRONICS WORKS EXAMINATION STRUCTURE
 070 ELECTRONICS WORKS EXAMINATION STRUCTURE The trade will be examined under the following components or subject grouping: Electronic Devices and Circuit, Radio Communication and Television. EXAMINATION
070 ELECTRONICS WORKS EXAMINATION STRUCTURE The trade will be examined under the following components or subject grouping: Electronic Devices and Circuit, Radio Communication and Television. EXAMINATION
Scheme Q.1 Attempt any SIX of following: 12-Total Marks a) Draw symbol NPN and PNP transistor. 2 M Ans: Symbol Of NPN and PNP BJT (1M each)
 Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17319) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Q. No. WINTER 16 EXAMINATION (Subject Code: 17319) Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Oscilloscope Measurements
 PC1143 Physics III Oscilloscope Measurements 1 Purpose Investigate the fundamental principles and practical operation of the oscilloscope using signals from a signal generator. Measure sine and other waveform
PC1143 Physics III Oscilloscope Measurements 1 Purpose Investigate the fundamental principles and practical operation of the oscilloscope using signals from a signal generator. Measure sine and other waveform
TEST EQUIPMENT AND MEASUREMENTS
 Reading 39 Ron Bertrand VK2DQ http://www.radioelectronicschool.com SSB MEASUREMENTS Why use a two-tone test signal? TEST EQUIPMENT AND MEASUREMENTS The two-tone test signal is the standard modulating signal
Reading 39 Ron Bertrand VK2DQ http://www.radioelectronicschool.com SSB MEASUREMENTS Why use a two-tone test signal? TEST EQUIPMENT AND MEASUREMENTS The two-tone test signal is the standard modulating signal
DIRECTORATE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION DIPLOMA IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING II YEAR M SCHEME III SEMESTER.
 DIRECTORATE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION DIPLOMA IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING II YEAR M SCHEME III SEMESTER 2015-2016 onwards ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND INSTRUMENTATION CURRICULAM DEVELOPMENT CENTRE
DIRECTORATE OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION DIPLOMA IN ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING II YEAR M SCHEME III SEMESTER 2015-2016 onwards ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND INSTRUMENTATION CURRICULAM DEVELOPMENT CENTRE
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Test No. 2. Advanced Scope Measurements. History. University of Applied Sciences Hamburg. Last chance!! EEL2 No 2
 University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L1: in charge of the report Test No. 2 Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L1: in charge of the report Test No. 2 Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements
 Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM. Course Title: Electronics Instruments and Measurement (Code: )
 GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM Course Title: Electronics Instruments and Measurement (Code: 3341104) Diploma Programme in which this course is offered Electronics
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, AHMEDABAD, GUJARAT COURSE CURRICULUM Course Title: Electronics Instruments and Measurement (Code: 3341104) Diploma Programme in which this course is offered Electronics
TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION. Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service
 Code No.207 TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Code No.207 TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Chapter 11. Alternating Current
 Unit-2 ECE131 BEEE Chapter 11 Alternating Current Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe how an AC voltage is produced with an AC generator (alternator) Define alternation,
Unit-2 ECE131 BEEE Chapter 11 Alternating Current Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe how an AC voltage is produced with an AC generator (alternator) Define alternation,
