arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 5 Oct 2016
|
|
|
- Colleen Dorsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TARGET: A Digitizing And Trigger ASIC For The Cherenkov Telescope Array arxiv:6.536v [astro-ph.im] 5 Oct 26 S. Funk, D. Jankowsky,a), H. Katagiri 2, M. Kraus,b), A. Okumura 3, H. Schoorlemmer 4, A. Shigenaka 2, H. Tajima 3, L. Tibaldo 4, G. Varner 5, A. Zink, J. Zorn 4 and the CTA consortium c) Erlangen Centre for Astroparticle Physics (ECAP), Erwin- Rommel-Str., D 958 Erlangen, Germany 2 College of Science, Ibaraki University, 2--, Bunkyo, Mito 3-852, Japan 3 Institute for Space-Earth Environmental Research, Nagoya University, Furo-cho, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya, Aichi , Japan 4 Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, P.O. Box 398, D 6929 Heidelberg, Germany 5 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Hawaii, 255 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA a) Corresponding author: david.jankowsky@fau.de b) Corresponding author: manuel.kraus@fau.de c) Full consortium author list at Abstract. The future ground-based gamma-ray observatory Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA) will feature multiple types of imaging atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes, each with thousands of pixels. To be affordable, camera concepts for these telescopes have to feature low cost per channel and at the same time meet the requirements for CTA in order to achieve the desired scientific goals. We present the concept of the TeV Array Readout Electronics with GSa/s sampling and Event Trigger (TARGET) Application Specific Circuit (ASIC), envisaged to be used in the cameras of various CTA telescopes, e.g. the Gamma-ray Cherenkov Telescope (GCT), a proposed 2-Mirror Small-Sized Telescope, and the Schwarzschild-Couder Telescope (SCT), a proposed Medium-Sized Telescope. In the latest version of this readout concept the sampling and trigger parts are split into dedicated ASICs, TARGET C and T5TEA, both providing 6 parallel input channels. TARGET C features a tunable sampling rate (usually GSa/s), a 6k sample deep buffer for each channel and on-demand digitization and transmission of waveforms with typical spans of ns. The trigger ASIC, T5TEA, provides 4 low voltage differential signal (LVDS) trigger outputs and can generate a pedestal voltage independently for each channel. Trigger signals are generated by T5TEA based on the analog sum of the input in four independent groups of four adjacent channels and compared to a threshold set by the user. Thus, T5TEA generates four LVDS trigger outputs, as well as 6 pedestal voltages fed to TARGET C independently for each channel. We show preliminary results of the characterization and testing of TARGET C and T5TEA. INTRODUCTION The TARGET application-specific-integrated circuit (ASIC) series has been designed and optimized specifically for the readout of Cherenkov cameras [], such as the GCT [2] (or see paper of L. Tibaldo et al. in these proceedings) and SCT [3] telescopes proposed for the Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA) [4]. CTA will feature a number of telescopes an order of magnitude higher than present arrays like H.E.S.S. or VERITAS and, therefore, the costs for the readout electronics are an important factor and should be reasonably low. Nevertheless, performance requirements given by the CTA consortium have to be met in order to reach the scientific goals aimed for. The proposed layout of the TARGET modules is capable of reading out 64 photodetector pixels and consists out of 8 TARGET ASICs and a companion field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and, thus, features a very limited number of components, making it both cheap and reliable. The key features of all generations of TARGET ASICs are a tunable sampling frequency GSa/s, a several µs deep analog buffer, a dynamic range bits, trigger with adjustable threshold, a continuous sampling and almost deadtime free operation as well as the possibility to record full waveforms.
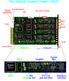
2 In order to minimize the crosstalk between the sampling and trigger paths, which occurred in former versions of TARGET, the two functions have been split into separate ASICs in the newest generation of TARGET ASICs, with the T5TEA ASIC for triggering and the TARGET C ASIC for sampling and digitization. This step significantly improves the trigger performance whilst retaining the charge resolution and dynamic range of TARGET 7 [5]. In this paper we give a short overview of the architecture of TARGET and present some measurements carried out to characterize the performance of the ASICs. We conclude with an outlook of future developments. TARGET C AND T5TEA ARCHITECTURE The main functional blocks of the ASICs are triggering (T5TEA), analog sampling and storage buffers, analog-todigital converters (ADC) for digitizing the signals (TARGET C) and internal digital-to-analog converters (DAC) for setting operation values (both). The sampling and storage of signals is done using switched capacitor arrays (SCAs) where the signal is connected sequentially to the capacitors via analog switches. The sampling array consists of two blocks with 32 cells (capacitors) operated in ping pong mode: while data sampling is performed by one block, the other block is buffered to the storage array. In contrast, the storage array consists of a larger number of cells (6348 per channel) to guarantee a large buffer depth ( 6 µs). Wilkinson ADCs are used for digitizing the analog signals in the storage array on demand. A Wilkinson ramp generator passes an adjustable ramp to all channels and simultaneously a 2 bit counter starts counting until the ramp signal crosses the analog voltage. The measured counts then correspond to the value of the applied signal. The digitization is initiated by a request from the FPGA based on external or internal (i.e. from T5TEA) signals. These features and other important ones (including performance results which will be explained in the following sections) for TARGET C and T5TEA are listed in Table. For comparison we also show the performance of previous generations of TARGET, namely TARGET 5 and TARGET 7. TABLE. Characteristics and performance of TARGET C + T5TEA compared to the former generations TARGET 5 and TARGET 7. Characteristics TARGET 5 TARGET 7 TARGET C + T5TEA Number of Channels Sampling frequency (Gsa/s) Size of storage array Digitization clock speed (MHz) Samples digitized simultaneously Trigger (sum of 4 channels) integrated integrated companion Performance Dynamic Range (V)..9.9 Integrated non linearity (mv) Charge linearity range (pe ) Charge resolution at pe 8% 4% 4% Charge resolution at > pe 2%.8%.8% Minimum trigger threshold (mv) Trigger noise (mv) 5 5 assuming 4 mv/pe For all the measurements presented in this paper a custom evaluation board was used. This board only contains the two ASICs, TARGET C and T5TEA, and all necessary components to control them, notably a FPGA. Figure shows a photograph of the evaluation board used for all the measurements.
3 FIGURE. Evaluation board with the T5TEA and TARGETC ASICs. This board was used for all measurements shown is this paper. CHARACTERIZATION OF TARGET C AND T5TEA TARGET C Sampling/Digitization Performance The TARGET C ASIC is, for the most part, identical to the sampling and digitization part of TARGET 7 with the exception of an increased digitization clock speed of 5 MHz allowing a faster digitization compared to TARGET 7 and the split off trigger path. The DC transfer functions and thus the achievable dynamic range, DC noise, and actual digitization time can be controlled with various ASIC parameters set on the fly via the companion FPGA. We tuned the transfer function parameters of TARGET C with the goal of a dynamic range comparable to TARGET 7 with a small integrated non linearity and a smooth transition to the saturated regime. Since the TARGET ASICs record the full waveform for every event a good charge reconstruction is also guaranteed in the saturated regime of the ASIC transfer function using waveform parameters like the rising or falling edge of the pulse. The measured transfer function of TARGET C is shown in Figure 2 and its dynamic range spans.9 V with a DC noise of mv. So, TARGET C shows the same performance as TARGET 7 as it is expected. The knowledge of the DC transfer function is used to convert the raw ADC counts from the digitizer into a voltage. Examples of calibrated sinusoids and a pulse equivalent to the FIGURE 2. Transfer function recorded with the onboard input to TARGET expected in the camera are shown in Fig- DAC at 5 MHz digitization speed. ure 3. The measured sinusoid yields a sampling frequency of.9986 ±.4 GSa/s which can be corrected to the expected value of GSa/s by further tuning. One of the most important performance figures of the TARGET readout electronics is its charge resolution. Here, we expect again a performance as good as in TARGET 7. The split of the sampling/digitization and trigger path might nevertheless have a positive impact on the performance of TARGET C. The charge resolution measurement shown in Figure 4 was performed using a simple integration method with a window of 6 ns and results in a resolution of 4 % at pe (assuming a conversion number of 4mV/pe). This is expected to fulfill the camera requirements. However, more complex methods using the full waveform information might yield an even better performance. In the final camera there will be additional noise contributions from the photodetectors and the amplifying/shaping circuits that will degrade the overall charge resolution with respect to TARGET alone.
4 Amplitude [mv] 6 4 Amplitude [mv] htemp Entries 96 Mean 36.5 Mean y RMS 2.7 RMS y Time [ns] Time [ns] (a) Calibrated data recorded with the TARGET evaluation board for injected 5 MHz sinusoids. (b) Calibrated data for an 35 mv injected pulse with a FWHM width of ns. The width is equivalent to the expected input from the camera. FIGURE 3. Sinusoid and pulse injected with a function generator. The pulse events were recorded with a trigger rate of khz. Charge Resolution TARGETC Charge resolution [fraction] 2 2 Input amplitude [mv] FIGURE 4. TARGET C charge resolution for injected function generator pulses. The resolution was determined as ratio of the standard deviation of the reconstructed charge and the mean value. With the expected conversion number of 4mV/pe the TARGET C performance is equal or even better than TARGET 7. T5TEA Trigger Performance The trigger ASIC T5TEA can be controlled by various parameters but the two most important ones, which have the largest impact on the trigger performance, are PMTref4 and Thresh. Thresh sets the reference voltage for the comparator with which the amplitude of the input signal is compared and, therefore, directly sets the threshold of the trigger ASIC. On the other hand PMTref4 controls the reference voltage for the summing amplifier which performs the analog sum of the four input signals of one trigger group and is able to shift the signal closer to the comparator threshold of Thresh. All parameters are controlled by a 2 bit digital-to-analog converter and have an operating voltage range of to 2.5 V. For all trigger measurements pulses with varying amplitudes, a full width at half maximum of ns with rise times of 5.4 ns and a frequency of khz were applied to one channel. The number of occurring trigger signals of one group in a certain time window can be counted by the FPGA. It should be noted that for all trigger measurements sampling of TARGET C was enabled which leads to a larger noise but reflects the environment of normal operations. The efficiency of the trigger can be calculated as ɛ = N trigger /N pulses, where N trigger is the number of trigger signals measured by the FPGA and N pulses the number of injected pulses by the function generator. To investigate the general performance of the trigger ASIC one can apply signals with varying amplitudes for a given parameter combination of PMTref4 and Thresh. The trigger efficiency ɛ as a function of the input amplitude A is shown in Figure 5. Here, a Gaussian error function, also called efficiency curve,
5 f (A; µ, σ) = 2 ( ( )) A µ + erf 2σ was fitted to the data points. The fit parameters µ corresponds to the threshold of 5% trigger efficiency and σ to the width of the rising edge, called noise. Here, PMTref4 was set to 98 DAC and Thresh was adjusted to result in the lowest threshold µ. With our current evaluation board design and these settings we get a lowest threshold of 8 mv (2 pe) and a corresponding noise of mv (/4 pe) which meets the desired camera performance (assuming a conversion number of 4 mv/pe) and represents a significant improvement in comparison to the TARGET 5 [6] and TARGET 7 [5] performance. The response to varying Thresh can be best seen in Figure 6 where the trigger rate was measured as a function of the set threshold. Pulses with a constant amplitude of mvpp were applied to one channel and Thresh was varied to change the threshold of the trigger ASIC. In this figure one can recognize different domains: on the right side the trigger rate rises to khz (corresponding to % trigger () Trigger Efficiency µ = (7.33 ±.3) mv σ = (.84 ±.4) mv Pulse Amplitude [mv] FIGURE 5. Efficiency curve of T5TEA. The black data points show the calculated trigger efficiency as a function of the applied signal amplitude. The red curve is the best-fit Gaussian error function. efficiency) at mv (Thresh: 25 DAC) and stays constant until the threshold crosses the baseline of the signal and begins to trigger at random fluctuations ( baseline noise ) at mv (Thresh 3 DAC), which causes the large trigger rate (peak on the left). Also a scan in the parameter space of PMTref4 and Thresh was performed: for each combination of the two parameters an efficiency curve was measured and the threshold and noise were determined. The results of the scan are shown in Figure 7. The outcome is comparable to the former measurements: over the measured range of PMTref4 we get lowest thresholds of < mv (2.5 pe) and over the whole range of PMTref4 and Thresh we get a noise of < 2 mv (.5 pe), while the noise increases with larger thresholds. The visible fluctuations of the noise are caused by statistical fluctuations. It shows that thresholds between 2.5 pe and 4 pe can be set to.5 pe precision. Thus, the desired performance of the trigger ASIC T5TEA is met even at this early stage of our board design. Trigger rate [ Hz] Threshold [mv] FIGURE 6. Trigger rate of T5TEA as a function of the set threshold (Thresh). Signal offset (PMTref4) Mean threshold [mv] Signal offset (PMTref4) Noise [mv] (a) Trigger threshold Thresh (b) Noise Thresh FIGURE 7. Scan through the PMTref4 - Thresh space. Shown are the results which were determined by measuring efficiency curves. The white areas correspond to a not working trigger (right) and too large thresholds (values > 5 mv, left).
6 OUTLOOK Since the presented measurements do not represent final results, further improvements are expected: on the one hand by tuning all available parameters and on the other hand by improving the design of the evaluation boards and camera modules. Figure 8 shows an efficiency curve measured with a debugged and optimized design of our evaluation board where the termination resistors were changed and bypassing capacitors were added. These improvements lowered the threshold to 3 mv (3/4 pe) and the noise to.6 mv (.5 pe). Currently ongoing investigations address the whole readout chain with SiPM, buffer and shaper board and an evaluation board. The next steps in the near future include production and testing of complete TARGET modules and the production of an entire camera, called CHEC-S, which will be used in the prototype GCT telescope. Trigger Efficiency µ = (2.82 ±.8) mv σ = (.55 ±.24) mv Pulse Amplitude [mv] FIGURE 8. Efficiency curve of T5TEA measured with the newest design of the evaluation board. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We gratefully acknowledge support from the agencies and organizations under Funding Agencies at www. cta-observatory.org. REFERENCES [] L. Tibaldo, J. A. Vandenbroucke, A. M. Albert, S. Funk, T. Kawashima, M. Kraus, A. Okumura, L. Sapozhnikov, H. Tajima, G. S. Varner, T. Wu, A. Zink, and f. t. CTA consortium, ArXiv e-prints August (25), arxiv: [astro-ph.im]. [2] A. M. Brown, A. Abchiche, D. Allan, J. P. Amans, T. P. Armstrong, A. Balzer, D. Berge, C. Boisson, J.-J. Bousquet, M. Bryan, G. Buchholtz, P. M. Chadwick, H. Costantini, G. Cotter, M. K. Daniel, A. De Franco, F. De Frondat, J.-L. Dournaux, D. Dumas, G. Fasola, S. Funk, J. Gironnet, J. A. Graham, T. Greenshaw, O. Hervet, N. Hidaka, J. A. Hinton, J.-M. Huet, I. Jegouzo, T. Jogler, M. Kraus, J. S. Lapington, P. Laporte, J. Lefaucheur, S. Markoff, T. Melse, L. Mohrmann, P. Molyneux, S. J. Nolan, A. Okumura, J. P. Osborne, R. D. Parsons, S. Rosen, D. Ross, G. Rowell, Y. Sato, F. Sayede, J. Schmoll, H. Schoorlemmer, M. Servillat, H. Sol, V. Stamatescu, M. Stephan, R. Stuik, J. Sykes, H. Tajima, J. Thornhill, L. Tibaldo, C. Trichard, J. Vink, J. J. Watson, R. White, N. Yamane, A. Zech, A. Zink, and J. Zorn, ArXiv e-prints August (26), arxiv: [astro-ph.im]. [3] A. N. Otte, J. Biteau, H. Dickinson, S. Funk, T. Jogler, C. A. Johnson, P. Karn, K. Meagher, H. Naoya, T. Nguyen, A. Okumura, M. Santander, L. Sapozhnikov, A. Stier, H. Tajima, L. Tibaldo, J. Vandenbroucke, S. Wakely, A. Weinstein, D. A. Williams, and f. t. CTA Consortium, ArXiv e-prints September (25), arxiv: [astro-ph.im]. [4] B. S. Acharya, M. Actis, T. Aghajani, G. Agnetta, J. Aguilar, F. Aharonian, M. Ajello, A. Akhperjanian, M. Alcubierre, J. Aleksić, and et al., Astroparticle Physics 43, 3 8March (23). [5] L. Tibaldo, J. A. Vandenbroucke, A. M. Albert, S. Funk, T. Kawashima, M. Kraus, A. Okumura, L. Sapozhnikov, H. Tajima, G. S. Varner, T. Wu, A. Zink, and f. t. CTA consortium, ArXiv e-prints August (25), arxiv: [astro-ph.im]. [6] A. Albert, S. Funk, T. Kawashima, M. Murphy, A. Okumura, R. Quagliani, L. Sapozhnikov, H. Tajima, L. Tibaldo, J. Vandenbroucke, G. Varner, and T. Wu, ArXiv e-prints July (26), arxiv: [astroph.im].
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Aug 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Aug 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Aug 2016](/thumbs/89/97826994.jpg) The GCT camera for the Cherenkov Telescope Array arxiv:1608.03420v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Aug 2016 A.M. Brown a, A. Abchiche b, D. Allan a, J.-P. Amans c, T.P. Armstrong a, A. Balzer d, D.Berge d, C. Boisson
The GCT camera for the Cherenkov Telescope Array arxiv:1608.03420v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Aug 2016 A.M. Brown a, A. Abchiche b, D. Allan a, J.-P. Amans c, T.P. Armstrong a, A. Balzer d, D.Berge d, C. Boisson
Temperature dependent aspects of the Compact High Energy Camera (CHEC-S) Front-End Electronic (FEE) calibration
 Temperature dependent aspects of the Compact High Energy Camera (CHEC-S) Front-End Electronic (FEE) calibration Master s Thesis in Physics Presented by Johannes Schäfer 12.3.219 Erlangen Centre for Astroparticle
Temperature dependent aspects of the Compact High Energy Camera (CHEC-S) Front-End Electronic (FEE) calibration Master s Thesis in Physics Presented by Johannes Schäfer 12.3.219 Erlangen Centre for Astroparticle
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Sep 2017
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Sep 2017 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Sep 2017](/thumbs/78/78708328.jpg) A Compact High Energy Camera (CHEC) for the Gamma-ray Cherenkov Telescope of the Cherenkov Telescope Array arxiv:1709.05799v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Sep 2017 R. White Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, P.O.
A Compact High Energy Camera (CHEC) for the Gamma-ray Cherenkov Telescope of the Cherenkov Telescope Array arxiv:1709.05799v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Sep 2017 R. White Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, P.O.
TARGET: A multi-channel digitizer chip for very-high-energy gamma-ray telescopes
 SLAC-PUB-14202 TARGET: A multi-channel digitizer chip for very-high-energy gamma-ray telescopes K. Bechtol a,, S. Funk a, A. Okumura c,a,, L. L. Ruckman b, A. Simons a, H. Tajima a, J. Vandenbroucke a,,
SLAC-PUB-14202 TARGET: A multi-channel digitizer chip for very-high-energy gamma-ray telescopes K. Bechtol a,, S. Funk a, A. Okumura c,a,, L. L. Ruckman b, A. Simons a, H. Tajima a, J. Vandenbroucke a,,
A 4 Channel Waveform Sampling ASIC in 130 nm CMOS
 A 4 Channel Waveform Sampling ASIC in 130 nm CMOS E. Oberla, H. Grabas, J.F. Genat, H. Frisch Enrico Fermi Institute, University of Chicago K. Nishimura, G. Varner University of Hawai I Large Area Picosecond
A 4 Channel Waveform Sampling ASIC in 130 nm CMOS E. Oberla, H. Grabas, J.F. Genat, H. Frisch Enrico Fermi Institute, University of Chicago K. Nishimura, G. Varner University of Hawai I Large Area Picosecond
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Oct 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Oct 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Oct 2016](/thumbs/80/80514322.jpg) Techniques And Results For The Calibration Of The MST Prototype For The Cherenkov Telescope Array arxiv:1610.03347v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Oct 2016 L. Oakes 1,a), M. Garczarczyk 2, S. Kaphle 1, M. Mayer 1,
Techniques And Results For The Calibration Of The MST Prototype For The Cherenkov Telescope Array arxiv:1610.03347v1 [astro-ph.im] 11 Oct 2016 L. Oakes 1,a), M. Garczarczyk 2, S. Kaphle 1, M. Mayer 1,
A 4-Channel Fast Waveform Sampling ASIC in 130 nm CMOS
 A 4-Channel Fast Waveform Sampling ASIC in 130 nm CMOS E. Oberla, H. Grabas, M. Bogdan, J.F. Genat, H. Frisch Enrico Fermi Institute, University of Chicago K. Nishimura, G. Varner University of Hawai I
A 4-Channel Fast Waveform Sampling ASIC in 130 nm CMOS E. Oberla, H. Grabas, M. Bogdan, J.F. Genat, H. Frisch Enrico Fermi Institute, University of Chicago K. Nishimura, G. Varner University of Hawai I
SAM (Swift Analogue Memory): a new GHz sampling ASIC for the HESS-II Front-End Electronics.
 SAM (Swift Analogue Memory): a new GHz sampling ASIC for the HESS-II Front-End Electronics. E. Delagnes 1, Y. Degerli 1, P. Goret 1, P. Nayman 2, F. Toussenel 2, P. Vincent 2 1 DAPNIA, CEA/Saclay 2 IN2P3/LPNHE
SAM (Swift Analogue Memory): a new GHz sampling ASIC for the HESS-II Front-End Electronics. E. Delagnes 1, Y. Degerli 1, P. Goret 1, P. Nayman 2, F. Toussenel 2, P. Vincent 2 1 DAPNIA, CEA/Saclay 2 IN2P3/LPNHE
A Prototype Amplifier-Discriminator Chip for the GLAST Silicon-Strip Tracker
 A Prototype Amplifier-Discriminator Chip for the GLAST Silicon-Strip Tracker Robert P. Johnson Pavel Poplevin Hartmut Sadrozinski Ned Spencer Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics The GLAST Project
A Prototype Amplifier-Discriminator Chip for the GLAST Silicon-Strip Tracker Robert P. Johnson Pavel Poplevin Hartmut Sadrozinski Ned Spencer Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics The GLAST Project
PARISROC, a Photomultiplier Array Integrated Read Out Chip
 PARISROC, a Photomultiplier Array Integrated Read Out Chip S. Conforti Di Lorenzo a, J.E. Campagne b, F. Dulucq a, C. de La Taille a, G. Martin-Chassard a, M. El Berni a, W. Wei c a OMEGA/LAL/IN2P3, centre
PARISROC, a Photomultiplier Array Integrated Read Out Chip S. Conforti Di Lorenzo a, J.E. Campagne b, F. Dulucq a, C. de La Taille a, G. Martin-Chassard a, M. El Berni a, W. Wei c a OMEGA/LAL/IN2P3, centre
A Fast Waveform-Digitizing ASICbased DAQ for a Position & Time Sensing Large-Area Photo-Detector System
 A Fast Waveform-Digitizing ASICbased DAQ for a Position & Time Sensing Large-Area Photo-Detector System Eric Oberla on behalf of the LAPPD collaboration PHOTODET 2012 12-June-2012 Outline LAPPD overview:
A Fast Waveform-Digitizing ASICbased DAQ for a Position & Time Sensing Large-Area Photo-Detector System Eric Oberla on behalf of the LAPPD collaboration PHOTODET 2012 12-June-2012 Outline LAPPD overview:
SPACIROC3: A Front-End Readout ASIC for JEM- EUSO cosmic ray observatory
 : A Front-End Readout ASIC for JEM- EUSO cosmic ray observatory Sylvie Blin-Bondil a1, Pierre Barrillon b, Sylvie Dagoret-Campagne b, Frederic Dulucq a, Christophe de La Taille a, Hiroko Miyamoto b, Camille
: A Front-End Readout ASIC for JEM- EUSO cosmic ray observatory Sylvie Blin-Bondil a1, Pierre Barrillon b, Sylvie Dagoret-Campagne b, Frederic Dulucq a, Christophe de La Taille a, Hiroko Miyamoto b, Camille
A 130nm CMOS Evaluation Digitizer Chip for Silicon Strips readout at the ILC
 A 130nm CMOS Evaluation Digitizer Chip for Silicon Strips readout at the ILC Jean-Francois Genat Thanh Hung Pham on behalf of W. Da Silva 1, J. David 1, M. Dhellot 1, D. Fougeron 2, R. Hermel 2, J-F. Huppert
A 130nm CMOS Evaluation Digitizer Chip for Silicon Strips readout at the ILC Jean-Francois Genat Thanh Hung Pham on behalf of W. Da Silva 1, J. David 1, M. Dhellot 1, D. Fougeron 2, R. Hermel 2, J-F. Huppert
High Speed Analog CMOS Pipeline System for the Recording of Fast Signals from Cherenkov Telescopes
 High Speed Analog COS Pipeline System for the Recording of Fast Signals from Cherenkov Telescopes CRISTIAN CHIŢU ; and WERNER HOFANN ASIC Labor Universität Heidelberg Schröderstr.90, D-690Heidelberg ax-planck-institut
High Speed Analog COS Pipeline System for the Recording of Fast Signals from Cherenkov Telescopes CRISTIAN CHIŢU ; and WERNER HOFANN ASIC Labor Universität Heidelberg Schröderstr.90, D-690Heidelberg ax-planck-institut
Noise Characteristics Of The KPiX ASIC Readout Chip
 Noise Characteristics Of The KPiX ASIC Readout Chip Cabrillo College Stanford Linear Accelerator Center What Is The ILC The International Linear Collider is an e- e+ collider Will operate at 500GeV with
Noise Characteristics Of The KPiX ASIC Readout Chip Cabrillo College Stanford Linear Accelerator Center What Is The ILC The International Linear Collider is an e- e+ collider Will operate at 500GeV with
A correlation-based timing calibration and diagnostic technique for fast digitizing ASICs
 . Physics Procedia (212) 1 8 Physics Procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia TIPP 211 - Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 211 A correlation-based timing calibration and diagnostic technique
. Physics Procedia (212) 1 8 Physics Procedia www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia TIPP 211 - Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 211 A correlation-based timing calibration and diagnostic technique
MAROC: Multi-Anode ReadOut Chip for MaPMTs
 Author manuscript, published in "2006 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference, and 15th International Room 2006 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Temperature Record Semiconductor
Author manuscript, published in "2006 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference, and 15th International Room 2006 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Temperature Record Semiconductor
CATIROC a multichannel front-end ASIC to read out the SPMT system of the JUNO experiment
 CATIROC a multichannel front-end ASIC to read out the SPMT system of the JUNO experiment Dr. Selma Conforti (OMEGA/IN2P3/CNRS) OMEGA microelectronics group Ecole Polytechnique & CNRS IN2P3 http://omega.in2p3.fr
CATIROC a multichannel front-end ASIC to read out the SPMT system of the JUNO experiment Dr. Selma Conforti (OMEGA/IN2P3/CNRS) OMEGA microelectronics group Ecole Polytechnique & CNRS IN2P3 http://omega.in2p3.fr
KLauS4: A Multi-Channel SiPM Charge Readout ASIC in 0.18 µm UMC CMOS Technology
 1 KLauS: A Multi-Channel SiPM Charge Readout ASIC in 0.18 µm UMC CMOS Technology Z. Yuan, K. Briggl, H. Chen, Y. Munwes, W. Shen, V. Stankova, and H.-C. Schultz-Coulon Kirchhoff Institut für Physik, Heidelberg
1 KLauS: A Multi-Channel SiPM Charge Readout ASIC in 0.18 µm UMC CMOS Technology Z. Yuan, K. Briggl, H. Chen, Y. Munwes, W. Shen, V. Stankova, and H.-C. Schultz-Coulon Kirchhoff Institut für Physik, Heidelberg
PoS(PhotoDet 2012)030
 NECTAR: New Electronics for the Cherenkov Telescope Array a, J. Bolmont a, P. Corona a, E. Delagnes b, D. Dzahini c, F. Feinstein d, D. Gascon e, J.-F. Glicenstein b, P. Nayman a, F. Rarbi c, M. Ribó e,
NECTAR: New Electronics for the Cherenkov Telescope Array a, J. Bolmont a, P. Corona a, E. Delagnes b, D. Dzahini c, F. Feinstein d, D. Gascon e, J.-F. Glicenstein b, P. Nayman a, F. Rarbi c, M. Ribó e,
PARISROC, a Photomultiplier Array Integrated Read Out Chip.
 PARISROC, a Photomultiplier Array Integrated Read Out Chip. S. Conforti Di Lorenzo*, J.E.Campagne, F. Dulucq*, C. de La Taille*, G. Martin-Chassard*, M. El Berni. LAL/IN2P3, Laboratoire de l Accélérateur
PARISROC, a Photomultiplier Array Integrated Read Out Chip. S. Conforti Di Lorenzo*, J.E.Campagne, F. Dulucq*, C. de La Taille*, G. Martin-Chassard*, M. El Berni. LAL/IN2P3, Laboratoire de l Accélérateur
Institute for Particle and Nuclear Studies, High Energy Accelerator Research Organization 1-1 Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan
 1, Hiroaki Aihara, Masako Iwasaki University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan E-mail: chojyuro@gmail.com Manobu Tanaka Institute for Particle and Nuclear Studies, High Energy Accelerator
1, Hiroaki Aihara, Masako Iwasaki University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan E-mail: chojyuro@gmail.com Manobu Tanaka Institute for Particle and Nuclear Studies, High Energy Accelerator
Development of a 20 GS/s Sampling Chip in 130nm CMOS Technology
 Development of a 20 GS/s Sampling Chip in 130nm CMOS Technology 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Orlando, Florida, October 28 th 2009 Jean-Francois Genat On behalf of Mircea Bogdan 1, Henry J. Frisch
Development of a 20 GS/s Sampling Chip in 130nm CMOS Technology 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Orlando, Florida, October 28 th 2009 Jean-Francois Genat On behalf of Mircea Bogdan 1, Henry J. Frisch
PoS(TWEPP-17)025. ASICs and Readout System for a multi Mpixel single photon UV imaging detector capable of space applications
 ASICs and Readout System for a multi Mpixel single photon UV imaging detector capable of space applications Andrej Seljak a, Gary S. Varner a, John Vallerga b, Rick Raffanti c, Vihtori Virta a, Camden
ASICs and Readout System for a multi Mpixel single photon UV imaging detector capable of space applications Andrej Seljak a, Gary S. Varner a, John Vallerga b, Rick Raffanti c, Vihtori Virta a, Camden
The Trigger System of the MEG Experiment
 The Trigger System of the MEG Experiment On behalf of D. Nicolò F. Morsani S. Galeotti M. Grassi Marco Grassi INFN - Pisa Lecce - 23 Sep. 2003 1 COBRA magnet Background Rate Evaluation Drift Chambers Target
The Trigger System of the MEG Experiment On behalf of D. Nicolò F. Morsani S. Galeotti M. Grassi Marco Grassi INFN - Pisa Lecce - 23 Sep. 2003 1 COBRA magnet Background Rate Evaluation Drift Chambers Target
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Nov 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Nov 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Nov 2014](/thumbs/72/66682521.jpg) Measurements and tests on FBK silicon sensors with an optimized electronic design for a CTA camera arxiv:1411.5241v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Nov 214 G. Ambrosi (1), M. Ambrosio (2), C. Aramo (2), E. Bissaldi
Measurements and tests on FBK silicon sensors with an optimized electronic design for a CTA camera arxiv:1411.5241v1 [astro-ph.im] 19 Nov 214 G. Ambrosi (1), M. Ambrosio (2), C. Aramo (2), E. Bissaldi
A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors
 A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors L.L.Jones a, P.Seller a, I.Lazarus b, P.Coleman-Smith b a STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, OX11 0QX, UK b STFC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington WA4 4AD, UK
A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors L.L.Jones a, P.Seller a, I.Lazarus b, P.Coleman-Smith b a STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, OX11 0QX, UK b STFC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington WA4 4AD, UK
ANITA ROSS Trigger/Digitizer/DAQ. Gary S. Varner University of Hawai, i, Manoa ANITA Collaboration JPL March 2004
 ANITA ROSS Trigger/Digitizer/DAQ Gary S. Varner University of Hawai, i, Manoa ANITA Collaboration Meeting @ JPL March 2004 Overview System overview Reiterate, with ROSS simplifications ROSS trigger descope
ANITA ROSS Trigger/Digitizer/DAQ Gary S. Varner University of Hawai, i, Manoa ANITA Collaboration Meeting @ JPL March 2004 Overview System overview Reiterate, with ROSS simplifications ROSS trigger descope
Final Results from the APV25 Production Wafer Testing
 Final Results from the APV Production Wafer Testing M.Raymond a, R.Bainbridge a, M.French b, G.Hall a, P. Barrillon a a Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, London, UK b Rutherford Appleton Laboratory,
Final Results from the APV Production Wafer Testing M.Raymond a, R.Bainbridge a, M.French b, G.Hall a, P. Barrillon a a Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, London, UK b Rutherford Appleton Laboratory,
Characterization and performance of the ASIC (CITIROC) front-end of the ASTRI camera arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 May 2015
![Characterization and performance of the ASIC (CITIROC) front-end of the ASTRI camera arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 May 2015 Characterization and performance of the ASIC (CITIROC) front-end of the ASTRI camera arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 May 2015](/thumbs/93/113917105.jpg) Characterization and performance of the ASIC (CITIROC) front-end of the ASTRI camera arxiv:1506.00264v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 May 2015 D. Impiombato a,, S. Giarrusso a, T. Mineo a, O. Catalano a, C. Gargano
Characterization and performance of the ASIC (CITIROC) front-end of the ASTRI camera arxiv:1506.00264v1 [physics.ins-det] 31 May 2015 D. Impiombato a,, S. Giarrusso a, T. Mineo a, O. Catalano a, C. Gargano
Picosecond time measurement using ultra fast analog memories.
 Picosecond time measurement using ultra fast analog memories. Dominique Breton a, Eric Delagnes b, Jihane Maalmi a acnrs/in2p3/lal-orsay, bcea/dsm/irfu breton@lal.in2p3.fr Abstract The currently existing
Picosecond time measurement using ultra fast analog memories. Dominique Breton a, Eric Delagnes b, Jihane Maalmi a acnrs/in2p3/lal-orsay, bcea/dsm/irfu breton@lal.in2p3.fr Abstract The currently existing
Performance of 8-stage Multianode Photomultipliers
 Performance of 8-stage Multianode Photomultipliers Introduction requirements by LHCb MaPMT characteristics System integration Test beam and Lab results Conclusions MaPMT Beetle1.2 9 th Topical Seminar
Performance of 8-stage Multianode Photomultipliers Introduction requirements by LHCb MaPMT characteristics System integration Test beam and Lab results Conclusions MaPMT Beetle1.2 9 th Topical Seminar
CALICE AHCAL overview
 International Workshop on the High Energy Circular Electron-Positron Collider in 2018 CALICE AHCAL overview Yong Liu (IHEP), on behalf of the CALICE collaboration Nov. 13, 2018 CALICE-AHCAL Progress, CEPC
International Workshop on the High Energy Circular Electron-Positron Collider in 2018 CALICE AHCAL overview Yong Liu (IHEP), on behalf of the CALICE collaboration Nov. 13, 2018 CALICE-AHCAL Progress, CEPC
ADC Measurements PARISROC Chip. Selma Conforti Di Lorenzo OMEGA/LAL Orsay
 ADC Measurements PARISROC Chip Selma Conforti Di Lorenzo OMEGA/LAL Orsay PARISROC ADC Measurements Ecole Microélectronique_11/16 octobre 2009 conforti@lal.in2p3.fr 2 TEST BOARD TEST BENCH ASIC FPGA USB
ADC Measurements PARISROC Chip Selma Conforti Di Lorenzo OMEGA/LAL Orsay PARISROC ADC Measurements Ecole Microélectronique_11/16 octobre 2009 conforti@lal.in2p3.fr 2 TEST BOARD TEST BENCH ASIC FPGA USB
SDG2122X SDG2082X SDG2042X
 Key Features SDG2122X SDG2082X SDG2042X Dual-channel, 120MHz maximum bandwidth, 20Vpp maximum High-performance sampling system with 1.2GSa/s sampling rate and 16-bit vertical resolution. No detail in your
Key Features SDG2122X SDG2082X SDG2042X Dual-channel, 120MHz maximum bandwidth, 20Vpp maximum High-performance sampling system with 1.2GSa/s sampling rate and 16-bit vertical resolution. No detail in your
PoS(PD07)026. Compact, Low-power and Precision Timing Photodetector Readout. Gary S. Varner. Larry L. Ruckman. Jochen Schwiening, Jaroslav Va vra
 Compact, Low-power and Precision Timing Photodetector Readout Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University of Hawaii E-mail: varner@phys.hawaii.edu Larry L. Ruckman Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University
Compact, Low-power and Precision Timing Photodetector Readout Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University of Hawaii E-mail: varner@phys.hawaii.edu Larry L. Ruckman Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, University
Timing Measurement in the CALICE Analogue Hadronic Calorimeter.
 Timing Measurement in the CALICE Analogue Hadronic Calorimeter. AHCAL Main Meeting Motivation SPS CERN Testbeam setup Timing Calibration Results and Conclusion Eldwan Brianne Hamburg 16/12/16 Motivation
Timing Measurement in the CALICE Analogue Hadronic Calorimeter. AHCAL Main Meeting Motivation SPS CERN Testbeam setup Timing Calibration Results and Conclusion Eldwan Brianne Hamburg 16/12/16 Motivation
Analogue to Digital Conversion
 Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Analogue to Digital Conversion
 Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
User s Manual for Integrator Long Pulse ILP8 22AUG2016
 User s Manual for Integrator Long Pulse ILP8 22AUG2016 Contents Specifications... 3 Packing List... 4 System Description... 5 RJ45 Channel Mapping... 8 Customization... 9 Channel-by-Channel Custom RC Times...
User s Manual for Integrator Long Pulse ILP8 22AUG2016 Contents Specifications... 3 Packing List... 4 System Description... 5 RJ45 Channel Mapping... 8 Customization... 9 Channel-by-Channel Custom RC Times...
Implementation of High Precision Time to Digital Converters in FPGA Devices
 Implementation of High Precision Time to Digital Converters in FPGA Devices Tobias Harion () Implementation of HPTDCs in FPGAs January 22, 2010 1 / 27 Contents: 1 Methods for time interval measurements
Implementation of High Precision Time to Digital Converters in FPGA Devices Tobias Harion () Implementation of HPTDCs in FPGAs January 22, 2010 1 / 27 Contents: 1 Methods for time interval measurements
A Low-Power 6-b Integrating-Pipeline Hybrid Analog-to-Digital Converter
 A Low-Power 6-b Integrating-Pipeline Hybrid Analog-to-Digital Converter Quentin Diduck, Martin Margala * Electrical and Computer Engineering Department 526 Computer Studies Bldg., PO Box 270231 University
A Low-Power 6-b Integrating-Pipeline Hybrid Analog-to-Digital Converter Quentin Diduck, Martin Margala * Electrical and Computer Engineering Department 526 Computer Studies Bldg., PO Box 270231 University
Evaluation of the performance of the Time over Threshold technique for the digitization of the signal of KM3NeT
 Evaluation of the performance of the Time over Threshold technique for the digitization of the signal of KM3NeT G. Bourlis, A. Leisos, A. Tsirigotis, S.E. Tzamarias Physics Laboratory Hellenic Open University
Evaluation of the performance of the Time over Threshold technique for the digitization of the signal of KM3NeT G. Bourlis, A. Leisos, A. Tsirigotis, S.E. Tzamarias Physics Laboratory Hellenic Open University
1 A1 PROs. Ver0.1 Ai9943. Complete 10-bit, 25MHz CCD Signal Processor. Features. General Description. Applications. Functional Block Diagram
 1 A1 PROs A1 PROs Ver0.1 Ai9943 Complete 10-bit, 25MHz CCD Signal Processor General Description The Ai9943 is a complete analog signal processor for CCD applications. It features a 25 MHz single-channel
1 A1 PROs A1 PROs Ver0.1 Ai9943 Complete 10-bit, 25MHz CCD Signal Processor General Description The Ai9943 is a complete analog signal processor for CCD applications. It features a 25 MHz single-channel
The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip
 The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip D.C. Christian, dcc@fnal.gov Fermilab, POBox 500 Batavia, IL 60510, USA 1 Introduction The most striking feature of BTeV, a dedicated b physics experiment
The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip D.C. Christian, dcc@fnal.gov Fermilab, POBox 500 Batavia, IL 60510, USA 1 Introduction The most striking feature of BTeV, a dedicated b physics experiment
Front-End and Readout Electronics for Silicon Trackers at the ILC
 2005 International Linear Collider Workshop - Stanford, U.S.A. Front-End and Readout Electronics for Silicon Trackers at the ILC M. Dhellot, J-F. Genat, H. Lebbolo, T-H. Pham, and A. Savoy Navarro LPNHE
2005 International Linear Collider Workshop - Stanford, U.S.A. Front-End and Readout Electronics for Silicon Trackers at the ILC M. Dhellot, J-F. Genat, H. Lebbolo, T-H. Pham, and A. Savoy Navarro LPNHE
Analogue Sum ASIC for L1 Trigger Decision in Cherenkov Telescope Cameras
 Analogue Sum ASIC for L1 Trigger Decision in Cherenkov Telescope Cameras Joan Abel Barrio a, Oscar Blanch b, Joan Boix b, Eric Delagnes c, Carlos Delgado d, Lluís Freixas Coromina d*, David Gascón e, Fabrice
Analogue Sum ASIC for L1 Trigger Decision in Cherenkov Telescope Cameras Joan Abel Barrio a, Oscar Blanch b, Joan Boix b, Eric Delagnes c, Carlos Delgado d, Lluís Freixas Coromina d*, David Gascón e, Fabrice
READOUT TECHNIQUES FOR DRIFT AND LOW FREQUENCY NOISE REJECTION IN INFRARED ARRAYS
 READOUT TECHNIQUES FOR DRIFT AND LOW FREQUENCY NOISE REJECTION IN INFRARED ARRAYS Finger 1, G, Dorn 1, R.J 1, Hoffman, A.W. 2, Mehrgan, H. 1, Meyer, M. 1, Moorwood A.F.M. 1 and Stegmeier, J. 1 1) European
READOUT TECHNIQUES FOR DRIFT AND LOW FREQUENCY NOISE REJECTION IN INFRARED ARRAYS Finger 1, G, Dorn 1, R.J 1, Hoffman, A.W. 2, Mehrgan, H. 1, Meyer, M. 1, Moorwood A.F.M. 1 and Stegmeier, J. 1 1) European
Datasheet RS Pro Arbitrary Waveform Generator 40MHz RS Stock Number : ENGLISH
 Datasheet RS Pro Arbitrary Waveform Generator 40MHz RS Stock Number : 123-6460 ENGLISH SDG2122X SDG2082X SDG2042X Overview SIGLENT s SDG2000X is a series of dual-channel function/arbitrary waveform generators
Datasheet RS Pro Arbitrary Waveform Generator 40MHz RS Stock Number : 123-6460 ENGLISH SDG2122X SDG2082X SDG2042X Overview SIGLENT s SDG2000X is a series of dual-channel function/arbitrary waveform generators
FlexDDS-NG DUAL. Dual-Channel 400 MHz Agile Waveform Generator
 FlexDDS-NG DUAL Dual-Channel 400 MHz Agile Waveform Generator Excellent signal quality Rapid parameter changes Phase-continuous sweeps High speed analog modulation Wieserlabs UG www.wieserlabs.com FlexDDS-NG
FlexDDS-NG DUAL Dual-Channel 400 MHz Agile Waveform Generator Excellent signal quality Rapid parameter changes Phase-continuous sweeps High speed analog modulation Wieserlabs UG www.wieserlabs.com FlexDDS-NG
Preliminary simulation study of the front-end electronics for the central detector PMTs
 Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 1-27 (Draft) Preliminary simulation study of the front-end electronics for the central detector PMTs A. F. Barbosa Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Fsicas - CBPF, e-mail:
Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 1-27 (Draft) Preliminary simulation study of the front-end electronics for the central detector PMTs A. F. Barbosa Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Fsicas - CBPF, e-mail:
Analog Peak Detector and Derandomizer
 Analog Peak Detector and Derandomizer G. De Geronimo, A. Kandasamy, P. O Connor Brookhaven National Laboratory IEEE Nuclear Sciences Symposium, San Diego November 7, 2001 Multichannel Readout Alternatives
Analog Peak Detector and Derandomizer G. De Geronimo, A. Kandasamy, P. O Connor Brookhaven National Laboratory IEEE Nuclear Sciences Symposium, San Diego November 7, 2001 Multichannel Readout Alternatives
Pixel hybrid photon detectors
 Pixel hybrid photon detectors for the LHCb-RICH system Ken Wyllie On behalf of the LHCb-RICH group CERN, Geneva, Switzerland 1 Outline of the talk Introduction The LHCb detector The RICH 2 counter Overall
Pixel hybrid photon detectors for the LHCb-RICH system Ken Wyllie On behalf of the LHCb-RICH group CERN, Geneva, Switzerland 1 Outline of the talk Introduction The LHCb detector The RICH 2 counter Overall
MAROC: Multi-Anode ReadOut Chip for MaPMTs
 MAROC: Multi-Anode ReadOut Chip for MaPMTs P. Barrillon, S. Blin, M. Bouchel, T. Caceres, C. De La Taille, G. Martin, P. Puzo, N. Seguin-Moreau To cite this version: P. Barrillon, S. Blin, M. Bouchel,
MAROC: Multi-Anode ReadOut Chip for MaPMTs P. Barrillon, S. Blin, M. Bouchel, T. Caceres, C. De La Taille, G. Martin, P. Puzo, N. Seguin-Moreau To cite this version: P. Barrillon, S. Blin, M. Bouchel,
Digitization of PMT signals with FADCs: comparison of simulation and measurement
 Digitization of PMT signals with FADCs: comparison of simulation and measurement Arno Gadola General, 10. 12.05.2010 Outline Summary of previous presentations Impact of sampling rate Verification of simulation
Digitization of PMT signals with FADCs: comparison of simulation and measurement Arno Gadola General, 10. 12.05.2010 Outline Summary of previous presentations Impact of sampling rate Verification of simulation
SPEAR BTS Toroid Calibration
 SPEAR BTS Toroid Calibration J. Sebek April 3, 2012 Abstract The Booster to SPEAR (BTS) transport line contains several toroids used for measuring the charge that is injected into SPEAR. One of these toroids
SPEAR BTS Toroid Calibration J. Sebek April 3, 2012 Abstract The Booster to SPEAR (BTS) transport line contains several toroids used for measuring the charge that is injected into SPEAR. One of these toroids
The behavior of the FastADC in time domain
 August 29, 2000 The behavior of the FastADC in time domain F. Tonisch 1. General remarks The 8-channel FastADC was developed for use with the readout electronic of the Waveguide Beam Position Monitors
August 29, 2000 The behavior of the FastADC in time domain F. Tonisch 1. General remarks The 8-channel FastADC was developed for use with the readout electronic of the Waveguide Beam Position Monitors
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
Pulse Shape Analysis for a New Pixel Readout Chip
 Abstract Pulse Shape Analysis for a New Pixel Readout Chip James Kingston University of California, Berkeley Supervisors: Daniel Pitzl and Paul Schuetze September 7, 2017 1 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...
Abstract Pulse Shape Analysis for a New Pixel Readout Chip James Kingston University of California, Berkeley Supervisors: Daniel Pitzl and Paul Schuetze September 7, 2017 1 Table of Contents 1 Introduction...
Ultra fast single photon counting chip
 Ultra fast single photon counting chip P. Grybos, P. Kmon, P. Maj, R. Szczygiel Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Automatics, Computer Science and Biomedical Engineering AGH University of Science and
Ultra fast single photon counting chip P. Grybos, P. Kmon, P. Maj, R. Szczygiel Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Automatics, Computer Science and Biomedical Engineering AGH University of Science and
SalSA Readout: GEISER & Digitizers. Gary S. Varner Univ. of Hawaii February 2005
 SalSA Readout: GEISER & Digitizers Gary S. Varner Univ. of Hawaii February 2005 Outline Transient Recording Have explored 3 techniques through prototype measurement stage For more than a year have been
SalSA Readout: GEISER & Digitizers Gary S. Varner Univ. of Hawaii February 2005 Outline Transient Recording Have explored 3 techniques through prototype measurement stage For more than a year have been
astro-ph/ Nov 1996
 Analog Optical Transmission of Fast Photomultiplier Pulses Over Distances of 2 km A. Karle, T. Mikolajski, S. Cichos, S. Hundertmark, D. Pandel, C. Spiering, O. Streicher, T. Thon, C. Wiebusch, R. Wischnewski
Analog Optical Transmission of Fast Photomultiplier Pulses Over Distances of 2 km A. Karle, T. Mikolajski, S. Cichos, S. Hundertmark, D. Pandel, C. Spiering, O. Streicher, T. Thon, C. Wiebusch, R. Wischnewski
Towards an ADC for the Liquid Argon Electronics Upgrade
 1 Towards an ADC for the Liquid Argon Electronics Upgrade Gustaaf Brooijmans Upgrade Workshop, November 10, 2009 2 Current LAr FEB Existing FEB (radiation tolerant for LHC, but slhc?) Limits L1 latency
1 Towards an ADC for the Liquid Argon Electronics Upgrade Gustaaf Brooijmans Upgrade Workshop, November 10, 2009 2 Current LAr FEB Existing FEB (radiation tolerant for LHC, but slhc?) Limits L1 latency
Development of a sampling ASIC for fast detector signals
 Development of a sampling ASIC for fast detector signals Hervé Grabas Work done in collaboration with Henry Frisch, Jean-François Genat, Eric Oberla, Gary Varner, Eric Delagnes, Dominique Breton. Signal
Development of a sampling ASIC for fast detector signals Hervé Grabas Work done in collaboration with Henry Frisch, Jean-François Genat, Eric Oberla, Gary Varner, Eric Delagnes, Dominique Breton. Signal
PoS(ICRC2017)800. Development of a strategy for calibrating the novel SiPM camera of the SST-1M telescope proposed for the Cherenkov Telescope Array
 Development of a strategy for calibrating the novel SiPM camera of the SST-1M telescope proposed for the Cherenkov Telescope Array I. Al Samarai a, a, F. Cadoux a, V. Coco a, D. della Volpe a, Y. Favre
Development of a strategy for calibrating the novel SiPM camera of the SST-1M telescope proposed for the Cherenkov Telescope Array I. Al Samarai a, a, F. Cadoux a, V. Coco a, D. della Volpe a, Y. Favre
A DSP IMPLEMENTED DIGITAL FM MULTIPLEXING SYSTEM
 A DSP IMPLEMENTED DIGITAL FM MULTIPLEXING SYSTEM Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Rosenthal, Glenn K. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
A DSP IMPLEMENTED DIGITAL FM MULTIPLEXING SYSTEM Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Rosenthal, Glenn K. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
Traditional analog QDC chain and Digital Pulse Processing [1]
![Traditional analog QDC chain and Digital Pulse Processing [1] Traditional analog QDC chain and Digital Pulse Processing [1]](/thumbs/75/72878980.jpg) Giuliano Mini Viareggio April 22, 2010 Introduction The aim of this paper is to compare the energy resolution of two gamma ray spectroscopy setups based on two different acquisition chains; the first chain
Giuliano Mini Viareggio April 22, 2010 Introduction The aim of this paper is to compare the energy resolution of two gamma ray spectroscopy setups based on two different acquisition chains; the first chain
The Fermilab Short Baseline Program and Detectors
 Detector SBND and NNN 2016, 3-5 November 2016, IHEP Beijing November 3, 2016 1 / 34 Outline Detector SBND 1 2 3 Detector 4 SBND 5 6 2 / 34 3 detectors in the neutrino beam from the 8GeV Booster (E peak
Detector SBND and NNN 2016, 3-5 November 2016, IHEP Beijing November 3, 2016 1 / 34 Outline Detector SBND 1 2 3 Detector 4 SBND 5 6 2 / 34 3 detectors in the neutrino beam from the 8GeV Booster (E peak
SV2C 28 Gbps, 8 Lane SerDes Tester
 SV2C 28 Gbps, 8 Lane SerDes Tester Data Sheet SV2C Personalized SerDes Tester Data Sheet Revision: 1.0 2015-03-19 Revision Revision History Date 1.0 Document release. March 19, 2015 The information in
SV2C 28 Gbps, 8 Lane SerDes Tester Data Sheet SV2C Personalized SerDes Tester Data Sheet Revision: 1.0 2015-03-19 Revision Revision History Date 1.0 Document release. March 19, 2015 The information in
Electronic Readout System for Belle II Imaging Time of Propagation Detector
 Electronic Readout System for Belle II Imaging Time of Propagation Detector Dmitri Kotchetkov University of Hawaii at Manoa for Belle II itop Detector Group March 3, 2017 Barrel Particle Identification
Electronic Readout System for Belle II Imaging Time of Propagation Detector Dmitri Kotchetkov University of Hawaii at Manoa for Belle II itop Detector Group March 3, 2017 Barrel Particle Identification
Application Note #5 Direct Digital Synthesis Impact on Function Generator Design
 Impact on Function Generator Design Introduction Function generators have been around for a long while. Over time, these instruments have accumulated a long list of features. Starting with just a few knobs
Impact on Function Generator Design Introduction Function generators have been around for a long while. Over time, these instruments have accumulated a long list of features. Starting with just a few knobs
A radiation tolerant, low-power cryogenic capable CCD readout system:
 A radiation tolerant, low-power cryogenic capable CCD readout system: Enabling focal-plane mounted CCD read-out for ground or space applications with a pair of ASICs. Overview What do we want to read out
A radiation tolerant, low-power cryogenic capable CCD readout system: Enabling focal-plane mounted CCD read-out for ground or space applications with a pair of ASICs. Overview What do we want to read out
Power Meter PW3335. Ken Sakai Engineering Division 4, Engineering Department. Power Meter PW3335
 1 Abstract The is a power meter that can measure direct input of 60 mv to 1000 V and 10 μa to 30 A with a high degree of accuracy. To enable it to measure targets ranging from standby power to operating
1 Abstract The is a power meter that can measure direct input of 60 mv to 1000 V and 10 μa to 30 A with a high degree of accuracy. To enable it to measure targets ranging from standby power to operating
PACS codes: Qx, Nc, Kv, v Keywords: Digital data acquisition, segmented HPGe detectors, clock and trigger distribution
 Clock and Trigger Synchronization between Several Chassis of Digital Data Acquisition Modules W. Hennig, H. Tan, M. Walby, P. Grudberg, A. Fallu-Labruyere, W.K. Warburton, XIA LLC, 31057 Genstar Road,
Clock and Trigger Synchronization between Several Chassis of Digital Data Acquisition Modules W. Hennig, H. Tan, M. Walby, P. Grudberg, A. Fallu-Labruyere, W.K. Warburton, XIA LLC, 31057 Genstar Road,
Study of the ALICE Time of Flight Readout System - AFRO
 Study of the ALICE Time of Flight Readout System - AFRO Abstract The ALICE Time of Flight Detector system comprises about 176.000 channels and covers an area of more than 100 m 2. The timing resolution
Study of the ALICE Time of Flight Readout System - AFRO Abstract The ALICE Time of Flight Detector system comprises about 176.000 channels and covers an area of more than 100 m 2. The timing resolution
G0CWA ANALOG AF/MF SIGNAL GENERATOR APRIL 2013
 G0CWA ANALOG AF/MF SIGNAL GENERATOR APRIL 2013 INTRODUCTION Hi here is my design for a simple easily customizable signal generator generating variable levels of sin, triangular and square wave signals
G0CWA ANALOG AF/MF SIGNAL GENERATOR APRIL 2013 INTRODUCTION Hi here is my design for a simple easily customizable signal generator generating variable levels of sin, triangular and square wave signals
Total Absorption Dual Readout Calorimetry R&D
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 37 (2012 ) 309 316 TIPP 2011 - Technology and Instrumentation for Particle Physics 2011 Total Absorption Dual Readout Calorimetry R&D B. Bilki
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 37 (2012 ) 309 316 TIPP 2011 - Technology and Instrumentation for Particle Physics 2011 Total Absorption Dual Readout Calorimetry R&D B. Bilki
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Experiment 10 Sampling and Reconstruction In this experiment we shall learn how an analog signal can be sampled in the time domain and then how the same samples can be used to reconstruct the original
Experiment 10 Sampling and Reconstruction In this experiment we shall learn how an analog signal can be sampled in the time domain and then how the same samples can be used to reconstruct the original
Chapter 13: Comparators
 Chapter 13: Comparators So far, we have used op amps in their normal, linear mode, where they follow the op amp Golden Rules (no input current to either input, no voltage difference between the inputs).
Chapter 13: Comparators So far, we have used op amps in their normal, linear mode, where they follow the op amp Golden Rules (no input current to either input, no voltage difference between the inputs).
Volterra. VT1115MF Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Controller. Partial Circuit Analysis
 Volterra VT1115MF Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Controller Partial Circuit Analysis For questions, comments, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs concerning semiconductor
Volterra VT1115MF Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Controller Partial Circuit Analysis For questions, comments, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs concerning semiconductor
Buffered LABRADOR (BLAB3) Design Review. Gary S. Varner 4 NOV 09
 Buffered LABRADOR (BLAB3) Design Review Gary S. Varner 4 NOV 09 Baseline confirmation Goals for today Ice Radio Sampler (IRS) as sampling/storage array basis High rate/long latency architecture Review
Buffered LABRADOR (BLAB3) Design Review Gary S. Varner 4 NOV 09 Baseline confirmation Goals for today Ice Radio Sampler (IRS) as sampling/storage array basis High rate/long latency architecture Review
A novel method based solely on FPGA units enabling measurement of time and charge of analog signals in Positron Emission Tomography
 A novel method based solely on FPGA units enabling measurement of time and charge of analog signals in Positron Emission Tomography M. Pałka 1, T. Bednarski 1, P. Białas 1, E. Czerwiński 1, Ł. Kapłon 1,2,
A novel method based solely on FPGA units enabling measurement of time and charge of analog signals in Positron Emission Tomography M. Pałka 1, T. Bednarski 1, P. Białas 1, E. Czerwiński 1, Ł. Kapłon 1,2,
Electronic Instrumentation for Radiation Detection Systems
 Electronic Instrumentation for Radiation Detection Systems January 23, 2018 Joshua W. Cates, Ph.D. and Craig S. Levin, Ph.D. Course Outline Lecture Overview Brief Review of Radiation Detectors Detector
Electronic Instrumentation for Radiation Detection Systems January 23, 2018 Joshua W. Cates, Ph.D. and Craig S. Levin, Ph.D. Course Outline Lecture Overview Brief Review of Radiation Detectors Detector
TRANSMISSION OF RADIOMETER DATA FROM THE SYNCHRONOUS METEOROLOGICAL SATELLITE
 TRANSMISSION OF RADIOMETER DATA FROM THE SYNCHRONOUS METEOROLOGICAL SATELLITE Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Davies, Richard S. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International
TRANSMISSION OF RADIOMETER DATA FROM THE SYNCHRONOUS METEOROLOGICAL SATELLITE Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Davies, Richard S. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International
Nyquist filter FIFO. Amplifier. Impedance matching. 40 MHz sampling ADC. DACs for gain and offset FPGA. clock distribution (not yet implemented)
 The Digital Gamma Finder (DGF) Firewire clock distribution (not yet implemented) DSP One of four channels Inputs Camac for 4 channels 2 cm System FPGA Digital part Analog part FIFO Amplifier Nyquist filter
The Digital Gamma Finder (DGF) Firewire clock distribution (not yet implemented) DSP One of four channels Inputs Camac for 4 channels 2 cm System FPGA Digital part Analog part FIFO Amplifier Nyquist filter
The Medipix3 Prototype, a Pixel Readout Chip Working in Single Photon Counting Mode with Improved Spectrometric Performance
 26 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record NM1-6 The Medipix3 Prototype, a Pixel Readout Chip Working in Single Photon Counting Mode with Improved Spectrometric Performance R. Ballabriga, M. Campbell,
26 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record NM1-6 The Medipix3 Prototype, a Pixel Readout Chip Working in Single Photon Counting Mode with Improved Spectrometric Performance R. Ballabriga, M. Campbell,
E. Delagnes 1 H. Grabas 1 D. Breton 2 J Maalmi 2
 REACHING A FEW PS PRECISION WITH THE 16-CHANNEL DIGITIZER AND TIMESTAMPER SAMPIC ASIC E. Delagnes 1 H. Grabas 1 D. Breton 2 J Maalmi 2 1 CEA/IRFU Saclay 2 CNRS/IN2P3/LAL Orsay This work has been funded
REACHING A FEW PS PRECISION WITH THE 16-CHANNEL DIGITIZER AND TIMESTAMPER SAMPIC ASIC E. Delagnes 1 H. Grabas 1 D. Breton 2 J Maalmi 2 1 CEA/IRFU Saclay 2 CNRS/IN2P3/LAL Orsay This work has been funded
Characterizing the Noise Performance of the KPiX ASIC. Readout Chip. Jerome Kyrias Carman
 Characterizing the Noise Performance of the KPiX ASIC Readout Chip Jerome Kyrias Carman Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI) Cabrillo College Stanford Linear Accelerator
Characterizing the Noise Performance of the KPiX ASIC Readout Chip Jerome Kyrias Carman Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI) Cabrillo College Stanford Linear Accelerator
3. The Trigger System. 51
 3. The Trigger System. 51 3.2.1.6 Array trigger and clock board In order to analize properly the images taken by the readout systems, it is very important to know with high accuracy when the samples were
3. The Trigger System. 51 3.2.1.6 Array trigger and clock board In order to analize properly the images taken by the readout systems, it is very important to know with high accuracy when the samples were
ANITA-Lite Trigger Object (ALTO Rev. B) User s Manual
 ANITA-Lite Trigger Object (ALTO Rev. B) User s Manual Gary S. Varner, David Ridley, James Kennedy and Mary Felix Contact: varner@phys.hawaii.edu Instrumentation Development Laboratory Department of Physics
ANITA-Lite Trigger Object (ALTO Rev. B) User s Manual Gary S. Varner, David Ridley, James Kennedy and Mary Felix Contact: varner@phys.hawaii.edu Instrumentation Development Laboratory Department of Physics
Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project
 Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 012-2009 (Draft) Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project H. P. Lima Jr, A. F. Barbosa, R. G. Gama Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas - CBPF L. F. G. Gonzalez
Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 012-2009 (Draft) Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project H. P. Lima Jr, A. F. Barbosa, R. G. Gama Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas - CBPF L. F. G. Gonzalez
The Medium Size Telescopes of the Cherenkov Telescope Array
 The Medium Size Telescopes of the Cherenkov Telescope Array G. Pühlhofer 1,a) and the CTA Consortium 2 arxiv:1610.02899v1 [astro-ph.im] 10 Oct 2016 1 Institut für Astronomie und Astrophysik, Eberhard Karls
The Medium Size Telescopes of the Cherenkov Telescope Array G. Pühlhofer 1,a) and the CTA Consortium 2 arxiv:1610.02899v1 [astro-ph.im] 10 Oct 2016 1 Institut für Astronomie und Astrophysik, Eberhard Karls
MASE: Multiplexed Analog Shaped Electronics
 MASE: Multiplexed Analog Shaped Electronics C. Metelko, A. Alexander, J. Poehlman, S. Hudan, R.T. desouza Outline 1. Needs 2. Problems with existing Technology 3. Design Specifications 4. Overview of the
MASE: Multiplexed Analog Shaped Electronics C. Metelko, A. Alexander, J. Poehlman, S. Hudan, R.T. desouza Outline 1. Needs 2. Problems with existing Technology 3. Design Specifications 4. Overview of the
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 5 Sep 2011
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 5 Sep 2011 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 5 Sep 2011](/thumbs/87/96509672.jpg) Concept and status of the CALICE analog hadron calorimeter engineering prototype arxiv:1109.0927v1 [physics.ins-det] 5 Sep 2011 Abstract Mark Terwort on behalf of the CALICE collaboration DESY, Notkestrasse
Concept and status of the CALICE analog hadron calorimeter engineering prototype arxiv:1109.0927v1 [physics.ins-det] 5 Sep 2011 Abstract Mark Terwort on behalf of the CALICE collaboration DESY, Notkestrasse
An ASIC dedicated to the RPCs front-end. of the dimuon arm trigger in the ALICE experiment.
 An ASIC dedicated to the RPCs front-end of the dimuon arm trigger in the ALICE experiment. L. Royer, G. Bohner, J. Lecoq for the ALICE collaboration Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire de Clermont-Ferrand
An ASIC dedicated to the RPCs front-end of the dimuon arm trigger in the ALICE experiment. L. Royer, G. Bohner, J. Lecoq for the ALICE collaboration Laboratoire de Physique Corpusculaire de Clermont-Ferrand
PASA Production Acceptance Test
 PASA Production Acceptance Test Uwe Bonnes, Helmut Oeschler, Simon Lang Institut für Kernphysik, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Germany Luciano Musa CERN, Geneva, CH-1211 Switzerland Lennart Österman
PASA Production Acceptance Test Uwe Bonnes, Helmut Oeschler, Simon Lang Institut für Kernphysik, Technische Universität Darmstadt, Germany Luciano Musa CERN, Geneva, CH-1211 Switzerland Lennart Österman
User s Manual for Integrator Short Pulse ISP16 10JUN2016
 User s Manual for Integrator Short Pulse ISP16 10JUN2016 Specifications Exceeding any of the Maximum Ratings and/or failing to follow any of the Warnings and/or Operating Instructions may result in damage
User s Manual for Integrator Short Pulse ISP16 10JUN2016 Specifications Exceeding any of the Maximum Ratings and/or failing to follow any of the Warnings and/or Operating Instructions may result in damage
Agilent 33220A Function Generator Tutorial
 Contents UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE105 Lab Experiments Agilent 33220A Function Generator Tutorial 1 Introduction
Contents UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE105 Lab Experiments Agilent 33220A Function Generator Tutorial 1 Introduction
Contraints for radio-transient detection (From informations gained with CODALEMA)
 Contraints for radio-transient detection (From informations gained with CODALEMA) Possible targets Astroparticles EAS Charged primary (CODALEMA) Neutrino? Gamma? («à la HESS») Astrophysics Solar burst,
Contraints for radio-transient detection (From informations gained with CODALEMA) Possible targets Astroparticles EAS Charged primary (CODALEMA) Neutrino? Gamma? («à la HESS») Astrophysics Solar burst,
arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.im] 17 Jan 2017
![arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.im] 17 Jan 2017 arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.im] 17 Jan 2017](/thumbs/81/83201239.jpg) A novel analog power supply for gain control of the Multi-Pixel Photon Counter (MPPC) Zhengwei Li a,, Congzhan Liu a, Yupeng Xu a, Bo Yan a,b, Yanguo Li a, Xuefeng Lu a, Xufang Li a, Shuo Zhang a,b, Zhi
A novel analog power supply for gain control of the Multi-Pixel Photon Counter (MPPC) Zhengwei Li a,, Congzhan Liu a, Yupeng Xu a, Bo Yan a,b, Yanguo Li a, Xuefeng Lu a, Xufang Li a, Shuo Zhang a,b, Zhi
