ModuLab XM ECS DUMMY CELL TEST
|
|
|
- Dominic Bruce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ModuLab XM ECS DUMMY CELL TEST
2 Why Run a Dummy Cell Test? Before beginning a dummy cell test, please ensure that the Solartron Analytical ModuLab XM ECS is connected and communicating with your PC. If you are unsure or need assistance with this, please refer to AMETEK / Solartron at: Additionally, it is imperative that the software and firmware corresponding to the Solartron Analytical ModuLab XM ECS, XM-Studio, be downloaded onto the connected PC. This can be found at: When working with the Solartron Analytical ModuLab XM ECS, as with all Solartron Analytical equipment, it is important to perform a dummy cell test to ensure that the apparatus is working properly. Running a dummy cell test with known parameters and expected results can help to determine whether a ModuLab XM ECS that is supplying questionable data requires repair or calibration. A properly working potentiostat/fra that outputs questionable data can indicate any of the following: Faulty ethernet connection Noise interference (could be from power outlet, or from pumps, heaters, etc.) Bad connection to the experiment (i.e.-something may have disconnected mid-experiment) Broken or corroded cables AC voltage level is set too low Insufficient integration time during the experiment Measurements taken outside the specified range of the apparatus Disqualifying the notion that the ModuLab XM ECS is responsible is a crucial step to determining the cause of erroneous data. Running a successful dummy cell test and obtaining experimental results that match expected results indicates that the potentiostat/fra is working correctly under the software configuration. The following is a guide which outlines the steps of performing two dummy cell experiments, cyclic voltammetry to test the PSTAT module that runs time domain (DC) tests, and impedance to test the FRA. Cyclic voltammetry, along with an outlined experiment will be discussed first in this document, followed by an overview of impedance and steps for taking this measurement. 1 P a g e
3 Background-Cyclic Voltammetry Each Solartron Analytical ModuLab XM ECS includes a test cell labeled ModuLab Test Cell that may be used for a DC test. (Figure 1). Figure 1 The dummy cell test can be performed with any predictable experiment. One of the easiest tests used to evaluate equipment using DC circuits is cyclic voltammetry. In cyclic voltammetry, the potential is ramped across the dummy cell. When the potential reaches a set value, it is ramped in the opposite direction. During this time, the system measures voltage and current through the dummy cell and outputs the data. Typically, this experiment is run for several cycles (Figure 2). Figure 2 Cyclic voltammetry is useful for a dummy cell test, due to the predictability of the cell behavior and ease of calculation. The following equation, also referred to as Ohm s Law, is used to approximate cell behavior, where V=potential, measured in volts; I=current, measured in amps; and R=resistance, measured in Ohms: V=IR Eqn 1 (Ohm s Law) 2 P a g e
4 Experimental Setup-Physical Equipment-Cyclic Voltammetry To set up a cyclic voltammetry experiment in XM Studio, connect BNC cables between the Solartron Analytical ModuLab XM ECS and the ModuLab Test Cell. Each cable should be connected to its corresponding position on the test cell using the appropriate color-coded cables (Figure 3). The potentiostat will apply a DC voltage to the counter electrode and will measure the current through the working electrode. Figure 3 3 P a g e
5 Experimental Setup & Run-Software-Cyclic Voltammetry Before beginning a new experiment, ensure that the ModuLab XM ECS is connected and communicating with the PC in use. For more information regarding connections and communications, please refer to the ModuLab XM ECS Connections/Communications document at Step 1: Select the Project Tab (Figure 4). Figure 4 Step 2: Click + Project, New Experiment. A list of modules that are present should display highlighted in green (Figure 5) Figure 5 Step 3: Click + New Experiment, then Setup (Figure 6). Select Pstat only from the Potentiostat configuration: drop down box. NOTE: When choosing from the Potentiostat configuration dropdown menu, FRA will not be listed even if it is present. The photo always shows the FRA to be present even if not fitted. For this cyclic voltammetry test, the FRA is not used. The actual components used within the chassis for the selected Potentiostat configuration is reflected in the photo that displays on the righthand portion of the software screen (Figure 6). MFRA MAT Figure 6 4 P a g e
6 Step 4: Right click on Setup. Select Add New, then Step (Figure 7). Figure 7 Step 5: The following menu will appear. Select DC Voltage Control (Figure 8). Figure 8 Step 6: A selection of experiments will open. Select Cyclic Voltammetry (Figure 9). Figure 9 5 P a g e
7 Step 7: The following screen will appear outlining a cyclic voltammetry experiment (Figure 10). Figure 10 Step 8: Under Scan Setup, change the 1 st vertex level to -8, and change the 2 nd vertex level to 8. Leave the remaining default parameters in place (Figure 11). Figure 11 6 P a g e
8 Step 9: Select Run (Figure 12). Figure 12 Step 10: A screen like that shown in Figure 13 will display which shows the connection setup. Select Run again. Figure 13 7 P a g e
9 Step 11: Using the default axes I versus current density, the screen will automatically show progress with a default graph as the experiment runs (Figure 14). Figure 14 Step 12: Use the drop-down box in the Axes section to change the axes to V vs. I and select Refresh (Figure 15). Figure 15 8 P a g e
10 Evaluating Data Step 13: Select the Fitting tab (Figure 16). Figure 16 Step 14: From the drop-down box, select Line, then click Run to obtain the line of best fit (Figure 17). Figure 17 9 P a g e
11 Step 15: The line of best fit will appear on the graph (Figure 18), and line fitting results will be displayed numerically (Figure 19). Figure 18 Figure P a g e
12 Step 16: As the dummy cell being tested is valued at 9.6kΩ between RE1 and RE2, it is expected that this will be the value obtained from the experimental results. The gradient listed from the fitting results indicates the approximate value of the resistance, 9,514 Ω, or roughly 9.5 kω. Because the data from the experiment matches the expected/calculated results, it can be inferred that the equipment is in good working order. In this case, other causes for misinformation should be explored. 11 P a g e
13 Background-Impedance Each Solartron Analytical ModuLab XM ECS includes a test cell labeled ModuLab Test Cell. The test module contains a known resistor capacitor circuit as shown below (Figure 20). Figure 20 The dummy cell test can be performed using voltage controlled impedance. This is labeled Potentiostatic Impedance in the XM-Studio software that accompanies the ModuLab XM ECS. In a potentiostatic impedance test, the AC potential is constant across the dummy cell. During this time, the system measures AC current passing through the module and displays measurement results (Figure 21). Figure 21 A potentiostatic impedance test is useful for this dummy cell test due to the predictability of the cell behavior and ease of calculation. The following equation is used to approximate cell behavior, where V=potential, measured in volts; I=current, measured in amps; and Z=impedance, measured in Ohms: Z=V/I Eqn 2 12 P a g e
14 Experimental Setup-Physical Equipment-Impedance To set up a potentiostatic impedance test in XM Studio, connect BNC cables between the Solartron Analytical ModuLab XM ECS and the ModuLab Test Cell. Each cable should be connected to its corresponding position on the test cell using the appropriate color-coded cables (Figure 22). Figure 22 The potential that is selected within the software will be applied to the circuitry within the test module (Figure 23). Measurements will be taken between the reference electrodes, and the resulting current will be plotted against the voltage. Figure P a g e
15 Experimental Setup & Run-Software-Impedance Step 1: Follow steps 1-4 from the Experimental Setup & Run-Software-Cyclic Voltammetry section of this document. Step 2: The following menu will appear. Select Impedance Voltage Control (Figure 24). Figure 24 Step 3: A selection of experiments will open. Select Potentiostatic Impedance (Figure 25). Figure P a g e
16 Step 4: The following screen will appear outlining a potentiostatic impedance experiment (Figure 26). Figure 26 Step 5: Under Scan Setup Leave the DC level at 0V, and leave as vs Open circuit. Leave the default parameters in place and press Run (Figure 27). Figure P a g e
17 Step 6: Select Run (Figure 28). Figure 28 Step 7: A screen like that shown in Figure 29 will display which shows the connection setup. Select Run again. Figure P a g e
18 Step 8: The screen will automatically show progress with a default graph as the experiment runs. The Axes should be adjusted beneath the Axes tab using the drop-down box for each parameter. For this impedance experiment, it is beneficial to select a Bode graph with the parameters outlined below (Figure 30). Figure P a g e
19 Evaluating Data Step 9: The data presented in the Bode diagram (Figure 31) can be compared to the outlined circuit in Figure 23 to verify the functionality of the ModuLab XM ECS. The Bode diagram shows two areas with a negative one slope which indicate the presence of two capacitors. The Bode diagram also shows three regions with a slope of zero, which indicates the presence of three resistors. As the module s schematic consists of two capacitors and three resistors, the experimental results verify that the ModuLab XM ECS is in good working order. Figure P a g e
20 Step 10: Data from the experiment can also be verified by performing an equivalent circuit fit. Begin by selecting the Fitting tab (Figure 32). Figure 32 Step 11: From the drop-down box, select Equivalent circuit (Figure 33). Figure P a g e
21 Step 12: Using the menu in Figure 34, load the existing model (select Load, then C:\My Data\ModuLab\Fitting Models\). Alternatively, select each portion of the circuit tested and place it in the equivalent ciruit builder. Figure 34 Step 13: Input the anticipated values from the circuit tested as starting values for this fit. The values from the test module are shown in Figure 35. Figure P a g e
22 Step 14: Select Run. The fitting results will be displayed as shown in Figure 36 below. These should be an approximate match to the values input in step 13. The line of best fit will also display as shown in Figure 37. This should closely match the original experimental graph from Figure 31. If the line of best fit and the given values of the testing results nearly equal those from the test box, it can be inferred that the ModuLab XM ECS is in good working order. Figure P a g e
23 Figure P a g e
24 23 P a g e 0218RevB
Universal Dummy Cell 2. Operator's Manual
 Universal Dummy Cell 2 Operator's Manual Copyright 2003, Gamry Instruments, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. Revision 1.0 May 5, 2003 Copyrights and Trademarks UDC2 Universal Dummy Cell 2
Universal Dummy Cell 2 Operator's Manual Copyright 2003, Gamry Instruments, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. Revision 1.0 May 5, 2003 Copyrights and Trademarks UDC2 Universal Dummy Cell 2
Universal Dummy Cell 3. Operator's Manual
 Universal Dummy Cell 3 Operator's Manual Copyright 2005, Gamry Instruments, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. Revision 1.1 December 27, 2005 Copyrights and Trademarks UDC3 Universal Dummy
Universal Dummy Cell 3 Operator's Manual Copyright 2005, Gamry Instruments, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. Revision 1.1 December 27, 2005 Copyrights and Trademarks UDC3 Universal Dummy
OHM S LAW. Ohm s Law The relationship between potential difference (V) across a resistor of resistance (R) and the current (I) passing through it is
 OHM S LAW Objectives: a. To find the unknown resistance of an ohmic resistor b. To investigate the series and parallel combination of resistors c. To investigate the non-ohmic resistors Apparatus Required:
OHM S LAW Objectives: a. To find the unknown resistance of an ohmic resistor b. To investigate the series and parallel combination of resistors c. To investigate the non-ohmic resistors Apparatus Required:
NOVA FI20 and on-board integrator tutorial
 Version 1.11.0 NOVA FI20 and on-board integrator tutorial 1 The FI20 module The FI20 is an optional module for the Autolab PGSTAT 1. This module is a combined filter and analog integrator module. The non
Version 1.11.0 NOVA FI20 and on-board integrator tutorial 1 The FI20 module The FI20 is an optional module for the Autolab PGSTAT 1. This module is a combined filter and analog integrator module. The non
3. Apparatus/ Materials 1) Computer 2) Vernier board circuit
 Experiment 3 RLC Circuits 1. Introduction You have studied the behavior of capacitors and inductors in simple direct-current (DC) circuits. In alternating current (AC) circuits, these elements act somewhat
Experiment 3 RLC Circuits 1. Introduction You have studied the behavior of capacitors and inductors in simple direct-current (DC) circuits. In alternating current (AC) circuits, these elements act somewhat
Electric Circuit Experiments
 Electric Circuit Experiments 1. Using the resistor on the 5-resistor block, vary the potential difference across it in approximately equal increments for eight different values (i.e. use one to eight D-
Electric Circuit Experiments 1. Using the resistor on the 5-resistor block, vary the potential difference across it in approximately equal increments for eight different values (i.e. use one to eight D-
Ansoft Designer Tutorial ECE 584 October, 2004
 Ansoft Designer Tutorial ECE 584 October, 2004 This tutorial will serve as an introduction to the Ansoft Designer Microwave CAD package by stepping through a simple design problem. Please note that there
Ansoft Designer Tutorial ECE 584 October, 2004 This tutorial will serve as an introduction to the Ansoft Designer Microwave CAD package by stepping through a simple design problem. Please note that there
II. Experimental Procedure
 Ph 122 July 27, 2006 Ohm's Law http://www.physics.sfsu.edu/~manuals/ph122/ I. Theory In this lab we will make detailed measurements on one resistor to see if it obeys Ohm's law. We will also verify the
Ph 122 July 27, 2006 Ohm's Law http://www.physics.sfsu.edu/~manuals/ph122/ I. Theory In this lab we will make detailed measurements on one resistor to see if it obeys Ohm's law. We will also verify the
Setting up a Multi sine impedance measurement
 Setting up a Multi sine impedance measurement Case study: how do I setup a Multi Sine impedance measurement? 1 Single sine vs Multi sine Traditional electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements
Setting up a Multi sine impedance measurement Case study: how do I setup a Multi Sine impedance measurement? 1 Single sine vs Multi sine Traditional electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements
NOVA technical note #8 1. Case study: how to use cutoff conditions in a FRA frequency scan?
 NOVA technical note #8 1 Cutoffs in FRA 1 Case study: how to use cutoff conditions in a FRA frequency scan? One of the FAQ from NOVA users is: Can I use cutoffs during a FRA frequency scan? Using cutoffs
NOVA technical note #8 1 Cutoffs in FRA 1 Case study: how to use cutoff conditions in a FRA frequency scan? One of the FAQ from NOVA users is: Can I use cutoffs during a FRA frequency scan? Using cutoffs
Laboratory Battery Testing Systems for Cell Applications
 LBT Testing Data Sheet, Page 1 Laboratory Battery Testing Systems for Applications An Introduction to LBT The Laboratory Battery Testing series is Arbin s latest generation of testing equipment, derived
LBT Testing Data Sheet, Page 1 Laboratory Battery Testing Systems for Applications An Introduction to LBT The Laboratory Battery Testing series is Arbin s latest generation of testing equipment, derived
Mechatronics. Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2
 Mechatronics Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2 There is an electronics revolution taking place in the industrialized world. Electronics pervades all activities. Perhaps the most important
Mechatronics Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2 There is an electronics revolution taking place in the industrialized world. Electronics pervades all activities. Perhaps the most important
Compliance Voltage How Much is Enough?
 Introduction Compliance Voltage How Much is Enough? The compliance voltage of a potentiostat is the maximum voltage that the potentiostat can apply to the counter electrode in order to control the desired
Introduction Compliance Voltage How Much is Enough? The compliance voltage of a potentiostat is the maximum voltage that the potentiostat can apply to the counter electrode in order to control the desired
Chapter 1: DC circuit basics
 Chapter 1: DC circuit basics Overview Electrical circuit design depends first and foremost on understanding the basic quantities used for describing electricity: voltage, current, and power. In the simplest
Chapter 1: DC circuit basics Overview Electrical circuit design depends first and foremost on understanding the basic quantities used for describing electricity: voltage, current, and power. In the simplest
Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software
 Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software In this chapter, we introduce the use of analog circuit simulation software and circuit layout software. I. Introduction So far we have designed
Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software In this chapter, we introduce the use of analog circuit simulation software and circuit layout software. I. Introduction So far we have designed
Measuring Batteries using the Right Setup: Dual-cell CR2032 and Battery Holder
 Measuring Batteries using the Right Setup: Dual-cell CR2032 and 18650 Battery Holder Introduction Knowing the exact specifications when testing batteries or any other energy-storage device is crucial.
Measuring Batteries using the Right Setup: Dual-cell CR2032 and 18650 Battery Holder Introduction Knowing the exact specifications when testing batteries or any other energy-storage device is crucial.
NOVA also supports multiple BA modules. Please refer to the MultiBA tutorial for more information. 2
 Version 1.11.0 NOVA Bipotentiostat tutorial 1 The BA, BIPOT & ARRAY module The BA, BIPOT and ARRAY are optional modules that provide one additional working electrode, WE(2) 1. Depending on the type of
Version 1.11.0 NOVA Bipotentiostat tutorial 1 The BA, BIPOT & ARRAY module The BA, BIPOT and ARRAY are optional modules that provide one additional working electrode, WE(2) 1. Depending on the type of
ECE 220 Laboratory 3 Thevenin Equivalent Circuits, Constant Current Source, and Inverting Amplifier
 ECE 220 Laboratory 3 Thevenin Equivalent Circuits, Constant Current Source, and Inverting Amplifier Michael W. Marcellin The first portion of this document describes preparatory work to be completed in
ECE 220 Laboratory 3 Thevenin Equivalent Circuits, Constant Current Source, and Inverting Amplifier Michael W. Marcellin The first portion of this document describes preparatory work to be completed in
RESISTANCE & OHM S LAW (PART I
 RESISTANCE & OHM S LAW (PART I and II) Objectives: To understand the relationship between potential and current in a resistor and to verify Ohm s Law. To understand the relationship between potential and
RESISTANCE & OHM S LAW (PART I and II) Objectives: To understand the relationship between potential and current in a resistor and to verify Ohm s Law. To understand the relationship between potential and
DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW
 July 15, 2008 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law 1 Name Date Partners DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action
July 15, 2008 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law 1 Name Date Partners DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action
NOVA. Getting started
 NOVA Getting started Table of contents Introduction... 7 The philosophy of Nova... 8 1 Nova installation... 11 1.1 Requirements... 11 1.2 Software installation... 11 1.2.1.NET 4.0 framework installation...
NOVA Getting started Table of contents Introduction... 7 The philosophy of Nova... 8 1 Nova installation... 11 1.1 Requirements... 11 1.2 Software installation... 11 1.2.1.NET 4.0 framework installation...
NOVA. Getting started
 NOVA Getting started NOVA Getting started 3 Table of contents The philosophy of Nova... 8 1 Nova installation... 11 1.1 Requirements... 11 1.2 Software installation... 11 1.2.1.NET framework installation...
NOVA Getting started NOVA Getting started 3 Table of contents The philosophy of Nova... 8 1 Nova installation... 11 1.1 Requirements... 11 1.2 Software installation... 11 1.2.1.NET framework installation...
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1. See suggested breadboard configuration on following page!
 ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response
 ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
Introduction PNP C NPN C
 Introduction JT Transistors: A JT (or any transistor) can be used either as a switch with positions of on or off, or an amplifier that controls its output at all levels in between the extreme on or off
Introduction JT Transistors: A JT (or any transistor) can be used either as a switch with positions of on or off, or an amplifier that controls its output at all levels in between the extreme on or off
Figure AC circuit to be analyzed.
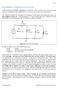 7.2(1) MULTISIM DEMO 7.2: INTRODUCTION TO AC ANALYSIS In this section, we ll introduce AC Analysis in Multisim. This is perhaps one of the most useful Analyses that Multisim offers, and we ll use it in
7.2(1) MULTISIM DEMO 7.2: INTRODUCTION TO AC ANALYSIS In this section, we ll introduce AC Analysis in Multisim. This is perhaps one of the most useful Analyses that Multisim offers, and we ll use it in
Experiment 2 Determining the Capacitive Reactance of a Capacitor in an AC Circuit
 Experiment 2 Determining the apacitive eactance of a apacitor in an A ircuit - Objects of the experiments: a- Investigating the voltage and the current at a capacitor in an A circuit b- Observing the phase
Experiment 2 Determining the apacitive eactance of a apacitor in an A ircuit - Objects of the experiments: a- Investigating the voltage and the current at a capacitor in an A circuit b- Observing the phase
Chapter 1: DC circuit basics
 Chapter 1: DC circuit basics Overview Electrical circuit design depends first and foremost on understanding the basic quantities used for describing electricity: Voltage, current, and power. In the simplest
Chapter 1: DC circuit basics Overview Electrical circuit design depends first and foremost on understanding the basic quantities used for describing electricity: Voltage, current, and power. In the simplest
Electric Currents 2 D V. (1)
 Name: Date: Electric Currents 2. A battery is connected in series with a resistor R. The battery transfers 2 000 C of charge completely round the circuit. During this process, 2 500 J of energy is dissipated
Name: Date: Electric Currents 2. A battery is connected in series with a resistor R. The battery transfers 2 000 C of charge completely round the circuit. During this process, 2 500 J of energy is dissipated
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics
 ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1
 EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1 PURPOSE: To verify the validity of Thevenin and maximum power transfer theorems. To demonstrate the linear
EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1 PURPOSE: To verify the validity of Thevenin and maximum power transfer theorems. To demonstrate the linear
Electricity Transition Questions Applied General in Science
 Electricity Transition Questions Applied General in Science Marks: 62 marks Pass = 30% Comments: Merit = 45% Distinction = 65% Name: Teacher: MDS Date: Q1. (a) Draw one line from each circuit symbol to
Electricity Transition Questions Applied General in Science Marks: 62 marks Pass = 30% Comments: Merit = 45% Distinction = 65% Name: Teacher: MDS Date: Q1. (a) Draw one line from each circuit symbol to
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit
 Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
P a g e 1 ST985. TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual. Analog Arts Inc.
 P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
Experiment P-10 Ohm's Law
 1 Experiment P-10 Ohm's Law Objectives To study the relationship between the voltage applied to a given resistor and the intensity of the current running through it. Modules and Sensors PC + NeuLog application
1 Experiment P-10 Ohm's Law Objectives To study the relationship between the voltage applied to a given resistor and the intensity of the current running through it. Modules and Sensors PC + NeuLog application
EC-3: Capacitors and RC-Decay
 Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. You must use complete sentences and clearly explain your reasoning to receive full credit. EC-3, Part I: Do not do
Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. You must use complete sentences and clearly explain your reasoning to receive full credit. EC-3, Part I: Do not do
Experiment A3 Electronics I Procedure
 Experiment A3 Electronics I Procedure Deliverables: Checked lab notebook, Brief technical memo Overview Most of the transducers used in modern engineering applications are electronic, meaning they convert
Experiment A3 Electronics I Procedure Deliverables: Checked lab notebook, Brief technical memo Overview Most of the transducers used in modern engineering applications are electronic, meaning they convert
173 Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Goals Experimental Apparatus Background Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
 Goals 173 Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy XXGoals To learn the effect of placing capacitors and resistors in series and parallel To model electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data XXExperimental
Goals 173 Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy XXGoals To learn the effect of placing capacitors and resistors in series and parallel To model electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data XXExperimental
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters
 BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
Equivalent Circuit Determination of Quartz Crystals
 Page 1 of 11 Equivalent Circuit Determination of Quartz Crystals By Stephan Synkule & Florian Hämmerle 2010 Omicron Lab V1.1 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com
Page 1 of 11 Equivalent Circuit Determination of Quartz Crystals By Stephan Synkule & Florian Hämmerle 2010 Omicron Lab V1.1 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com
NOVA. Booster Tutorial. Version
 NOVA Booster Tutorial Version 1.11.0 1 The Booster10A and Booster20A The Booster10A and Booster20A are additional modules that can be interfaced with the PGSTAT128N, 30, 302, 302N, 100 and 100N. The boosters
NOVA Booster Tutorial Version 1.11.0 1 The Booster10A and Booster20A The Booster10A and Booster20A are additional modules that can be interfaced with the PGSTAT128N, 30, 302, 302N, 100 and 100N. The boosters
Precision Linear Battery Testing
 Precision Linear Battery Testing Index Linear Battery Testing for Cell Applications +/- 5V, 0-5V with current ranges from 200mA to 10A...P1 Linear Battery Testing for High Cell Applications 0-5V with current
Precision Linear Battery Testing Index Linear Battery Testing for Cell Applications +/- 5V, 0-5V with current ranges from 200mA to 10A...P1 Linear Battery Testing for High Cell Applications 0-5V with current
2. BAND-PASS NOISE MEASUREMENTS
 2. BAND-PASS NOISE MEASUREMENTS 2.1 Object The objectives of this experiment are to use the Dynamic Signal Analyzer or DSA to measure the spectral density of a noise signal, to design a second-order band-pass
2. BAND-PASS NOISE MEASUREMENTS 2.1 Object The objectives of this experiment are to use the Dynamic Signal Analyzer or DSA to measure the spectral density of a noise signal, to design a second-order band-pass
LABORATORY 3 v3 CIRCUIT ELEMENTS
 University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Leon Chua LABORATORY 3 v3 CIRCUIT ELEMENTS The purpose of this laboratory is to familiarize
University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Leon Chua LABORATORY 3 v3 CIRCUIT ELEMENTS The purpose of this laboratory is to familiarize
High Precision Coulombic Efficiency Testing
 Revision: 02 Why Does Precision Matter? High Precision Coulombic Efficiency Testing Measurement precision is more critical for long-term testing and long-term projections than control accuracy alone. Most
Revision: 02 Why Does Precision Matter? High Precision Coulombic Efficiency Testing Measurement precision is more critical for long-term testing and long-term projections than control accuracy alone. Most
Lab 4 OHM S LAW AND KIRCHHOFF S CIRCUIT RULES
 57 Name Date Partners Lab 4 OHM S LAW AND KIRCHHOFF S CIRCUIT RULES AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in a circuit.
57 Name Date Partners Lab 4 OHM S LAW AND KIRCHHOFF S CIRCUIT RULES AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in a circuit.
The cutoff framework in NOVA provides three degrees of freedom:
 Version 1.11.0 NOVA Cutoff tutorial 1 Cutoffs Cutoffs are convenient tools that can be used to control the experimental conditions, in order to prevent or to react on specific situations, for example when
Version 1.11.0 NOVA Cutoff tutorial 1 Cutoffs Cutoffs are convenient tools that can be used to control the experimental conditions, in order to prevent or to react on specific situations, for example when
Lab 3 DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW
 43 Name Date Partners Lab 3 DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS + - VOLTS OBJECTIVES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in a circuit. To understand
43 Name Date Partners Lab 3 DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS + - VOLTS OBJECTIVES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in a circuit. To understand
Each individual is to report on the design, simulations, construction, and testing according to the reporting guidelines attached.
 EE 352 Design Project Spring 2015 FM Receiver Revision 0, 03-02-15 Interim report due: Friday April 3, 2015, 5:00PM Project Demonstrations: April 28, 29, 30 during normal lab section times Final report
EE 352 Design Project Spring 2015 FM Receiver Revision 0, 03-02-15 Interim report due: Friday April 3, 2015, 5:00PM Project Demonstrations: April 28, 29, 30 during normal lab section times Final report
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit
 LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
UNIVERSITY OF UTAH ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
 UNIVERSITY OF UTAH ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ECE 3110 LAB EXPERIMENT NO. 4 CLASS AB POWER OUTPUT STAGE Objective: In this laboratory exercise you will build and characterize a class AB power output
UNIVERSITY OF UTAH ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ECE 3110 LAB EXPERIMENT NO. 4 CLASS AB POWER OUTPUT STAGE Objective: In this laboratory exercise you will build and characterize a class AB power output
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION
 Objectives: ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION The primary goal of this laboratory is to study the operation and limitations of several commonly used pieces of instrumentation:
Objectives: ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION The primary goal of this laboratory is to study the operation and limitations of several commonly used pieces of instrumentation:
Using ir compensation
 Case study: how to use the ir compensation option in NOVA? 1 What is the ir drop Using ir compensation Potentiostats are instruments that are designed to control the potential of the working electrode
Case study: how to use the ir compensation option in NOVA? 1 What is the ir drop Using ir compensation Potentiostats are instruments that are designed to control the potential of the working electrode
Experiment 2. Ohm s Law. Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current.
 Experiment 2 Ohm s Law 2.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 2 Ohm s Law 2.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 2 Electric Circuit Fundamentals
 Experiment 2 Electric Circuit Fundamentals Introduction This experiment has two parts. Each part will have to be carried out using the Multisim Electronics Workbench software. The experiment will then
Experiment 2 Electric Circuit Fundamentals Introduction This experiment has two parts. Each part will have to be carried out using the Multisim Electronics Workbench software. The experiment will then
Transmission Lines and TDR
 Transmission Lines and TDR Overview This is the procedure for lab 2b. This is a one- week lab. The prelab should be done BEFORE going to the lab session. In this lab, pulse propagation down transmission
Transmission Lines and TDR Overview This is the procedure for lab 2b. This is a one- week lab. The prelab should be done BEFORE going to the lab session. In this lab, pulse propagation down transmission
MicroLab 500-series Getting Started
 MicroLab 500-series Getting Started 2 Contents CHAPTER 1: Getting Started Connecting the Hardware....6 Installing the USB driver......6 Installing the Software.....8 Starting a new Experiment...8 CHAPTER
MicroLab 500-series Getting Started 2 Contents CHAPTER 1: Getting Started Connecting the Hardware....6 Installing the USB driver......6 Installing the Software.....8 Starting a new Experiment...8 CHAPTER
Equivalent Circuit Determination of Quartz Crystals
 Equivalent Circuit Determination of Quartz Crystals By Stephan Synkule & Florian Hämmerle 2017 by OMICRON Lab V2.1 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical
Equivalent Circuit Determination of Quartz Crystals By Stephan Synkule & Florian Hämmerle 2017 by OMICRON Lab V2.1 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3)
 Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Rowan University Freshman Clinic I Lab Project 2 The Operational Amplifier (Op Amp)
 Rowan University Freshman Clinic I Lab Project 2 The Operational Amplifier (Op Amp) Objectives Become familiar with an Operational Amplifier (Op Amp) electronic device and it operation Learn several basic
Rowan University Freshman Clinic I Lab Project 2 The Operational Amplifier (Op Amp) Objectives Become familiar with an Operational Amplifier (Op Amp) electronic device and it operation Learn several basic
Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters
 BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
Experiment 1 Alternating Current with Coil and Ohmic Resistors
 Experiment Alternating Current with Coil and Ohmic esistors - Objects of the experiment - Determining the total impedance and the phase shift in a series connection of a coil and a resistor. - Determining
Experiment Alternating Current with Coil and Ohmic esistors - Objects of the experiment - Determining the total impedance and the phase shift in a series connection of a coil and a resistor. - Determining
ECE4902 Lab 5 Simulation. Simulation. Export data for use in other software tools (e.g. MATLAB or excel) to compare measured data with simulation
 ECE4902 Lab 5 Simulation Simulation Export data for use in other software tools (e.g. MATLAB or excel) to compare measured data with simulation Be sure to have your lab data available from Lab 5, Common
ECE4902 Lab 5 Simulation Simulation Export data for use in other software tools (e.g. MATLAB or excel) to compare measured data with simulation Be sure to have your lab data available from Lab 5, Common
ECE Lab #4 OpAmp Circuits with Negative Feedback and Positive Feedback
 ECE 214 Lab #4 OpAmp Circuits with Negative Feedback and Positive Feedback 20 February 2018 Introduction: The TL082 Operational Amplifier (OpAmp) and the Texas Instruments Analog System Lab Kit Pro evaluation
ECE 214 Lab #4 OpAmp Circuits with Negative Feedback and Positive Feedback 20 February 2018 Introduction: The TL082 Operational Amplifier (OpAmp) and the Texas Instruments Analog System Lab Kit Pro evaluation
LABORATORY 3 v1 CIRCUIT ELEMENTS
 University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 3 v1 CIRCUIT ELEMENTS The purpose of this laboratory is to familiarize
University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 3 v1 CIRCUIT ELEMENTS The purpose of this laboratory is to familiarize
Building a Microcontroller based potentiostat: A Inexpensive and. versatile platform for teaching electrochemistry and instrumentation.
 Supporting Information for Building a Microcontroller based potentiostat: A Inexpensive and versatile platform for teaching electrochemistry and instrumentation. Gabriel N. Meloni* Instituto de Química
Supporting Information for Building a Microcontroller based potentiostat: A Inexpensive and versatile platform for teaching electrochemistry and instrumentation. Gabriel N. Meloni* Instituto de Química
LABORATORY 5 v3 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 5 v3 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER Integrated operational amplifiers opamps
University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 5 v3 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER Integrated operational amplifiers opamps
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope
 EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
ECE 2274 Lab 1 (Intro)
 ECE 2274 Lab 1 (Intro) Richard Dumene: Spring 2018 Revised: Richard Cooper: Spring 2018 Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) The purpose of this lab course is to familiarize you with high-end lab equipment, and train
ECE 2274 Lab 1 (Intro) Richard Dumene: Spring 2018 Revised: Richard Cooper: Spring 2018 Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) The purpose of this lab course is to familiarize you with high-end lab equipment, and train
PHYS 1402 General Physics II Experiment 5: Ohm s Law
 PHYS 1402 General Physics II Experiment 5: Ohm s Law Student Name Objective: To investigate the relationship between current and resistance for ordinary conductors known as ohmic conductors. Theory: For
PHYS 1402 General Physics II Experiment 5: Ohm s Law Student Name Objective: To investigate the relationship between current and resistance for ordinary conductors known as ohmic conductors. Theory: For
Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance
 E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
RLC Software User s Manual
 RLC Software User s Manual Venable Instruments 4201 S. Congress, Suite 201 Austin, TX 78745 512-837-2888 www.venable.biz Introduction The RLC software allows you to measure the frequency response of RLC
RLC Software User s Manual Venable Instruments 4201 S. Congress, Suite 201 Austin, TX 78745 512-837-2888 www.venable.biz Introduction The RLC software allows you to measure the frequency response of RLC
The Oscilloscope. Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift ( ) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope.
 The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
Ohm s Law and Electrical Circuits
 Ohm s Law and Electrical Circuits INTRODUCTION In this experiment, you will measure the current-voltage characteristics of a resistor and check to see if the resistor satisfies Ohm s law. In the process
Ohm s Law and Electrical Circuits INTRODUCTION In this experiment, you will measure the current-voltage characteristics of a resistor and check to see if the resistor satisfies Ohm s law. In the process
BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement. Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements.
 BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement Learning Objectives: Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements. Supplies and Components: Breadboard
BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement Learning Objectives: Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements. Supplies and Components: Breadboard
I-V, C-V and AC Impedance Techniques and Characterizations of Photovoltaic Cells
 I-V, C-V and AC Impedance Techniques and Characterizations of Photovoltaic Cells John Harper 1, Xin-dong Wang 2 1 AMETEK Advanced Measurement Technology, Southwood Business Park, Hampshire,GU14 NR,United
I-V, C-V and AC Impedance Techniques and Characterizations of Photovoltaic Cells John Harper 1, Xin-dong Wang 2 1 AMETEK Advanced Measurement Technology, Southwood Business Park, Hampshire,GU14 NR,United
Experiment 3. Ohm s Law. Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current.
 Experiment 3 Ohm s Law 3.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 3 Ohm s Law 3.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
User s Manual for Integrator Short Pulse ISP16 10JUN2016
 User s Manual for Integrator Short Pulse ISP16 10JUN2016 Specifications Exceeding any of the Maximum Ratings and/or failing to follow any of the Warnings and/or Operating Instructions may result in damage
User s Manual for Integrator Short Pulse ISP16 10JUN2016 Specifications Exceeding any of the Maximum Ratings and/or failing to follow any of the Warnings and/or Operating Instructions may result in damage
Experiment P49: Transistor Lab 2 Current Gain: The NPN Emitter-Follower Amplifier (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P49-1 Experiment P49: Transistor Lab 2 Current Gain: The NPN Emitter-Follower Amplifier (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P49-1 Experiment P49: Transistor Lab 2 Current Gain: The NPN Emitter-Follower Amplifier (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh
VOLTAGE. User Guide ACCESSORIES. External Sensor DT140. for MicroLog EC600 and EC V ±0.05V ±3% (before calibration)
 External Sensor VOLTAGE DT140 Range: Resolution: Accuracy: Input impedance: Calibration: OV protection: 0-10V ±0.05V ±3% (before calibration) 3MΩ 2 calibration points ±30V ACCESSORIES User Guide for MicroLog
External Sensor VOLTAGE DT140 Range: Resolution: Accuracy: Input impedance: Calibration: OV protection: 0-10V ±0.05V ±3% (before calibration) 3MΩ 2 calibration points ±30V ACCESSORIES User Guide for MicroLog
LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will measure the I-V characteristics of the rectifier and Zener diodes, in both forward and reverse-bias mode, as well as learn what mechanisms
LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will measure the I-V characteristics of the rectifier and Zener diodes, in both forward and reverse-bias mode, as well as learn what mechanisms
Calibration Coefficients and Thermistor Selection
 Calibration Coefficients and Thermistor Selection March, 2017 Page 1 ABSTRACT Calibration coefficients for thermistors are determined by the Steinhart-Hart equation for a given thermistor, temperature
Calibration Coefficients and Thermistor Selection March, 2017 Page 1 ABSTRACT Calibration coefficients for thermistors are determined by the Steinhart-Hart equation for a given thermistor, temperature
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 Experiment 10: LR and Undriven LRC Circuits
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.0 Spring 005 Experiment 10: LR and Undriven LRC Circuits OBJECTIVES 1. To determine the inductance L and internal resistance R L of a coil,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.0 Spring 005 Experiment 10: LR and Undriven LRC Circuits OBJECTIVES 1. To determine the inductance L and internal resistance R L of a coil,
EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE
 EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE Appending 4 in your Textbook contains a short tutorial on PSPICE. Additional information, tutorials and a demo version of PSPICE can be found at the manufacturer
EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE Appending 4 in your Textbook contains a short tutorial on PSPICE. Additional information, tutorials and a demo version of PSPICE can be found at the manufacturer
Experiment P-24 Circuits and Series Resistance
 1 Experiment P-24 Circuits and Series Resistance Objectives To study the relationship between the voltage applied to a given resistor and the intensity of the current running through it. Modules and Sensors
1 Experiment P-24 Circuits and Series Resistance Objectives To study the relationship between the voltage applied to a given resistor and the intensity of the current running through it. Modules and Sensors
Unit 4: Principles of Electrical and Electronic Engineering. LO1: Understand fundamental electrical principles Maximum power transfer
 Unit 4: Principles of Electrical and Electronic Engineering LO1: Understand fundamental electrical principles Maximum power transfer Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions should accompany
Unit 4: Principles of Electrical and Electronic Engineering LO1: Understand fundamental electrical principles Maximum power transfer Instructions and answers for teachers These instructions should accompany
DC/DC Converter Stability Measurement
 Strongly supported by By Stephan Synkule, Lukas Heinzle & Florian Hämmerle 2018 by OMICRON Lab V3.3 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical support.
Strongly supported by By Stephan Synkule, Lukas Heinzle & Florian Hämmerle 2018 by OMICRON Lab V3.3 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical support.
Effects of Incident Optical Power on the Effective Reverse Bias Voltage of Photodiodes This Lab Fact demonstrates how the effective reverse bias
 Effects of Incident Optical Power on the Effective Reverse Bias Voltage of Photodiodes This Lab Fact demonstrates how the effective reverse bias voltage on a photodiode can vary as a function of the incident
Effects of Incident Optical Power on the Effective Reverse Bias Voltage of Photodiodes This Lab Fact demonstrates how the effective reverse bias voltage on a photodiode can vary as a function of the incident
Low Value Impedance Measurement using the Voltage / Current Method
 Low Value Impedance Measurement using the Voltage / Current Method By Florian Hämmerle & Tobias Schuster 2017 Omicron Lab V2.2 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com
Low Value Impedance Measurement using the Voltage / Current Method By Florian Hämmerle & Tobias Schuster 2017 Omicron Lab V2.2 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com
Lab. 1: Simple Linear Circuit Analysis
 Lab. 1: Simple Linear Circuit Analysis Philippe Piot (February 9th, 27) 1. Ohm's Law The circuit shown in Figure 1 was built with resistance R=1 and then 1 kω. For these two values of the resistance, the
Lab. 1: Simple Linear Circuit Analysis Philippe Piot (February 9th, 27) 1. Ohm's Law The circuit shown in Figure 1 was built with resistance R=1 and then 1 kω. For these two values of the resistance, the
DC Circuits, Ohm's Law and Multimeters Physics 246
 DC Circuits, Ohm's Law and Multimeters Physics 246 Theory: In this lab we will learn the use of multimeters, verify Ohm s law, and study series and parallel combinations of resistors and capacitors. For
DC Circuits, Ohm's Law and Multimeters Physics 246 Theory: In this lab we will learn the use of multimeters, verify Ohm s law, and study series and parallel combinations of resistors and capacitors. For
Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst
 Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst Lab Summary In this lab you will build two active filters on a breadboard, using an op-amp, resistors, and capacitors, and take data for the magnitude
Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst Lab Summary In this lab you will build two active filters on a breadboard, using an op-amp, resistors, and capacitors, and take data for the magnitude
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013
 Signature Name (print, please) Lab section # Lab partner s name (if any) Date(s) lab was performed ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013 In this lab we will demonstrate basic
Signature Name (print, please) Lab section # Lab partner s name (if any) Date(s) lab was performed ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013 In this lab we will demonstrate basic
Experiment #3: Experimenting with Resistor Circuits
 Name/NetID: Experiment #3: Experimenting with Resistor Circuits Laboratory Outline During the semester, the lecture will provide some of the mathematical underpinnings of circuit theory. The laboratory
Name/NetID: Experiment #3: Experimenting with Resistor Circuits Laboratory Outline During the semester, the lecture will provide some of the mathematical underpinnings of circuit theory. The laboratory
General Department PHYSICS LABORATORY APHY 112 EXPERIMENT 2: OHMS LAW. Student s name... Course Semester. Year.Reg.No
 General Department PHYSICS LABORATORY APHY 112 EXPERIMENT 2: OHMS LAW Student s name... Course Semester. Year.Reg.No FREDERICK UNIVERSITY 1 EXPERIMENT 3 OHMS LAW Equipment needed Equipment needed Circuits
General Department PHYSICS LABORATORY APHY 112 EXPERIMENT 2: OHMS LAW Student s name... Course Semester. Year.Reg.No FREDERICK UNIVERSITY 1 EXPERIMENT 3 OHMS LAW Equipment needed Equipment needed Circuits
Performing Cyclic Voltammetry Measurements Using Model 2450-EC or 2460-EC Electrochemistry Lab System
 Performing Cyclic Voltammetry Measurements Using Model 2450-EC or 2460-EC Electrochemistry Lab System Application Note Chemical engineers, chemists, and other scientists use electrical measurement techniques
Performing Cyclic Voltammetry Measurements Using Model 2450-EC or 2460-EC Electrochemistry Lab System Application Note Chemical engineers, chemists, and other scientists use electrical measurement techniques
Chapter 8: Field Effect Transistors
 Chapter 8: Field Effect Transistors Transistors are different from the basic electronic elements in that they have three terminals. Consequently, we need more parameters to describe their behavior than
Chapter 8: Field Effect Transistors Transistors are different from the basic electronic elements in that they have three terminals. Consequently, we need more parameters to describe their behavior than
Lab 2: Capacitors. Integrator and Differentiator Circuits
 Lab 2: Capacitors Topics: Differentiator Integrator Low-Pass Filter High-Pass Filter Band-Pass Filter Integrator and Differentiator Circuits The simple RC circuits that you built in a previous section
Lab 2: Capacitors Topics: Differentiator Integrator Low-Pass Filter High-Pass Filter Band-Pass Filter Integrator and Differentiator Circuits The simple RC circuits that you built in a previous section
Filter Design, Active Filters & Review. EGR 220, Chapter 14.7, December 14, 2017
 Filter Design, Active Filters & Review EGR 220, Chapter 14.7, 14.11 December 14, 2017 Overview ² Passive filters (no op amps) ² Design examples ² Active filters (use op amps) ² Course review 2 Example:
Filter Design, Active Filters & Review EGR 220, Chapter 14.7, 14.11 December 14, 2017 Overview ² Passive filters (no op amps) ² Design examples ² Active filters (use op amps) ² Course review 2 Example:
