RLC Software User s Manual
|
|
|
- Deborah Carson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RLC Software User s Manual Venable Instruments 4201 S. Congress, Suite 201 Austin, TX
2 Introduction The RLC software allows you to measure the frequency response of RLC circuits using one of the Venable Instruments frequency response analyzers (FRA). You can calibrate your RLC box, run measurements through a range of frequencies, build a theoretical model based on the empirical data, and generate reports. The RLC software is controlled mainly through the RLC Control Panel, which has four components: Setup, Measurement, Model, and Report. Installation 1. Insert the NI driver CD from National Instruments and install the driver for your GPIB-USB interface. 2. To test the interface, plug your GPIB-USB to an USB port on your computer (leave the GPIB connector unplugged). 3. In order to check that the driver was installed properly, launch the Getting Started Wizard application from the National Instruments/NI program group. Click on Verify your hardware and software installation. The application should report that the NI troubleshooting wizard was successfully completed. Hit OK and then exit the application. 4. Plug the GPIB connector to the back of your Venable analyzer. 5. Insert the RLC installation CD and install the software. Please read the following section on how to activate the RLC application. Software Activation The RLC software is protected against illegal copying and use. In order to run, first it must be activated. There are three ways to activate your RLC software: If you have an Internet connection, you may use the "Electronic Registration" button to validate your serial number. This is the fastest and easiest method. If you don't have an Internet connection but you have access, you can send your site code along with your name, company name, address, phone number, and Venable frequency response analyzer serial number (on the back of the instrument) to authorize@venable.biz. Your site code is shown when you select "Show site code" from the "License" menu. Otherwise, you can call Venable Instruments with your site code.
3 Setup Tab The Setup tab consists of two sections: hardware, and default plot. In the hardware section, there are four parameters to define: Analyzer: currently the supported FRAs are the Venable models 350, 3120, 3215, and GPIB interface: if there are more than one GPIB interfaces connected to the computer, this field identifies the interface that is used with the current FRA. GPIB address: the address of the FRA. Reference resistor: this is the value, in Ohms, of the resistor used inside the RLC box to measure current. The Venable RLC boxes use 100 Ohm reference resistors. Figure 1. Setup window In the default plot section you can choose the type of plot that will be used whenever you create a new document. Possible options are Impedance plot and Nyquist plot. If the Automatically use the default type option is checked, you won t be prompted for a plot type every time that you create a new one. Measurement Tab Before measurements can be taken, the system must be calibrated. The purpose of the calibration process is to quantify the parasitic components that are present
4 in the RLC box. With an estimation of the values of these parasitic elements, the actual measurements of RLC circuits can be corrected to improve accuracy. The parasitic components are usually modeled as two elements: one in series (of inductive nature), and one in parallel (of capacitive nature). Figure 2. Parasitic model The calibration process consists of two steps: an open-circuit sweep, and a closed-circuit sweep. Once the calibration process starts, the RLC software will prompt you to first open and then close the circuit in order to take the respective measurements. Open Circuit Sweep When the circuit is open, the impedance of the parallel parasitic element can be calculated (the impedance of the series element is so much smaller that its effect is negligible in the calculation). Figure 3. Open circuit model
5 Closed Circuit Sweep After the open-circuit sweep is complete, a closed-circuit sweep is run. In this case, the parallel element can be removed from the equation, and the impedance of the series element can be calculated. Figure 4. Closed circuit model After the open-circuit and closed-circuit sweeps are complete, you can save the calibration data for future use. That way, it is not necessary to re-calibrate before every session of measurements. 1.E E+04 Open_imp 70 1.E Impedance [Ohm] 1.E+02 1.E+01 1.E+00 1.E-01 Closed_phase Open_phase Phase [ ] 1.E Closed_imp 1.E E+03 1.E+04 1.E+05 1.E+06 1.E+07 Frequency [Hz] Figure 5. Example of open and closed circuit impedance and phase plots Once the calibration is done, the system is ready to measure RLC circuits. After sweeping through the frequency range, the software will automatically correct the raw data and create another plot with the tag w/o parasitics. This plot is the result of subtracting the series and parallel parasitic elements from the raw data.
6 1.E Imp with parasitics 70 Imp w/o parasitics 50 Impedance [Ohm] 1.E+00 Phase with parasitics Phase w/o parasitics Phase [ ] E E+03 1.E+04 1.E+05 1.E+06 1.E+07 Frequency [Hz] Figure 6. Uncorrected and corrected plots The parameters related to measurements are in the FRA Settings section: Single point or sweep: a single point measurement is done at a specified frequency. A sweep is a series of measurements taken throughout a range of frequencies, from the start frequency to the stop frequency, and with a resolution of 10 steps per decade. Start and stop frequencies: they define the first and last points in the sweep. In the case of a single point setup, only the start frequency is relevant. Integration time: specifies the length of time over which each sample is taken. There are four possible settings: 10 s, 2.5 s, 0.33 s, and 0.05 s. A slower setting will take longer to run but will produce more precise results. A/C and D/C voltages: they specify the injection voltages. Input coupling: specifies whether the input coupling is A/C or D/C. Limit maximum phase change between data points: without this option, the software will always take 10 data points per frequency decade, regardless of the results. A possible problem arises when a sweep involves a resonant point, where the impedance changes abruptly from one frequency to the next. In this case, you can use this feature to mitigate the problem. If, for example, you set the maximum phase change at 20, the software will adapt its frequency interval so that no two points will be more than 20 apart in phase.
7 Figure 7. The Measurement tab Modeling Tab The modeling tab is used to create a theoretical model out of the circuit that was measured. You can choose the component type and the data set to model. The available component types are different combinations of a resistor, a capacitor, and an inductor, arranged in parallel or in series. After selecting the component type and data set, the calculated theoretical values for R, L, and C are displayed on the window. You can also override the values of R, L, and C by typing different values in the respective controls. You can create a plot that will represent the theoretical RLC circuit based on the values shown. If you wish to create a model with more than three components, you could create multiple models and combine them in series or in parallel using the math functions. The theoretical values of the circuit components are calculated by attempting to fit the model to the measured data. In the case of components in series, the maximum or minimum values of susceptance (for capacitive or inductive circuits, respectively) are used to calculate the capacitance or inductance. In the case of components in parallel, the maximum or minimum values of reactance (for inductive or capacitive circuits, respectively) are used. In order to more accurately calculate the theoretical model, it is better to sweep through a wide frequency range.
8 Figure 8. The modeling tab 1.E Impedance [Ohm] 1.E Phase [ ] E E+02 1.E+03 1.E+04 1.E+05 1.E+06 Frequency [Hz] Imp_sw eep Imp_model Phase_sw eep Phase_model Figure 9. Example of a measured RC circuit and its derived model
9 Reporting Tab The RLC application can generate reports in PDF format. The reports include a chart with uncorrected and corrected data, modeling information, and optionally a chart with the open and closed circuit calibration data, and a text version of all the plots in tabular format. Figure 10. Reporting tab Working with Documents, Views, and Data Sets The RLC application can contain multiple documents. A document is a collection of one or more data sets (plots). The data contained in a document is shown to you through a view window. There are four different types of views: Impedance: impedance magnitude and phase versus frequency. Gain: gain magnitude and phase versus frequency. Nyquist: resistance versus reactance. Text: impedance magnitude and phase versus frequency. When the application starts, it creates an empty document and shows an impedance view for that document. You can create new documents and open and save existing documents.
10 Manipulating Data Set Properties A data set is a collection of data points obtained by running a sweep through a range of frequencies. A document can contain multiple data sets. To select a data set, simply click any part of the curve with the mouse pointer, or use the up and down keys to cycle through the collection of data sets. The properties of a data set can be viewed and edited by selecting Data Set Properties from the View menu. The Data Set Properties dialog shows the current data set number, name, type, and description. You can specify whether the data set should be visible, and whether the description should be shown on the screen. The colors are also editable. The voltage node, current node, and scale factor determine how the impedance is calculated, according to the formula shown on the dialog. For acquired data, the voltage node is by default channel #2, the current node is channel #1, and the scale factor is the negative of the reference resistor (defined in the Setup tab). Figure 11. Data set properties Manipulating Graph Properties The properties related to a graph (view) can be edited by selecting the Graph Properties from the View menu.
11 Figure 12. Graph settings This window allows you to select the plot type, change the grid color, select whether the graph title and legend are shown, and define the scaling parameters. Working with Slide Bars Slide bars are useful for tracking and displaying data values at a specific frequency, represented by a vertical line, and a description box. To create a slide bar, select Add Slide Bar from the View menu. More than one slide bar may be opened at one time, either from the same or different data sets. Add Slide Bar is not available in a text display window. The bar can be dragged using the mouse pointer (except in Nyquist plots, where only the Left or Right keys may be used), and the box will show the data at the selected frequency. The frequency can also be typed in, and the line will move to that frequency. The information shown on the slide bar window is frequency, impedance magnitude and phase, and calculated values for R and L or C for the equivalent RL or RC circuit. The Equivalent Circuit button determines whether the equivalent circuit is series or parallel. Figure 13. Slidebar example
12 You can use the left or right keys to move the slide bar between data points taken by the analyzer. The shift+left or shift+right key combinations find the 0 degree, +/-90 degree, or the +/-180 degree phase points if they exist. The ctrl+left or ctrl+right key combinations find the 0 db crossing point if it exists. Math Operations The RLC application can apply math functions to one or two data sets. To do this, select the Math Menu item from the Actions menu. Figure 14. Math menu The possible operations are: add, subtract, multiply, divide, add in parallel, subtract in parallel, invert, negate, and create transfer function. The create transfer function operation divides two plots and shows the result in a new gain/phase view. Table 1. Math functions Operation Name Function Application Add Z = Z 1 + Z 2 Cascading filters Subtract Z = Z 1 - Z 2 Removing series parasitic Multiply Z = Z 1 x Z 2 Combining gain stages Divide Z = Z 1 / Z 2 Add in parallel Z = (Z 1 x Z 2 ) / (Z 1 + Z 2 ) Combining filters Subtract in parallel Z = (Z 1 x Z 2 ) / (Z 1 - Z 2 ) Removing parallel parasitic Invert Y = 1 / Z 1 Impedance to admittance Negate Z = -Z phase shift Create transfer function Z = Z 1 / (Z 1 + Z 2 ) Filter attenuation
13 Appendix - The RLC Box The Venable FRA models 350, 3120, 3215, and 3225 have custom RLC boxes that plug directly into the analyzer in order to minimize parasitics. The following is a schematic of the circuit used in the Venable RLC boxes. Figure 15. RLC Box Schematic
Smart Measurement Solutions. Bode 100. User Manual
 Smart Measurement Solutions Bode 100 User Manual Bode 100 User Manual Bode 100 User Manual Article Number VESD0661 - Manual Version: Bode100.AE.4 OMICRON Lab 2010. All rights reserved. This User Manual
Smart Measurement Solutions Bode 100 User Manual Bode 100 User Manual Bode 100 User Manual Article Number VESD0661 - Manual Version: Bode100.AE.4 OMICRON Lab 2010. All rights reserved. This User Manual
Bode 100. User Manual
 Bode 100 User Manual Bode 100 User Manual Article Number VESD0661 - Manual Version: Bode100.AE.3 OMICRON Lab 2008. All rights reserved. This User Manual is a publication of OMICRON electronics GmbH. This
Bode 100 User Manual Bode 100 User Manual Article Number VESD0661 - Manual Version: Bode100.AE.3 OMICRON Lab 2008. All rights reserved. This User Manual is a publication of OMICRON electronics GmbH. This
Ansoft Designer Tutorial ECE 584 October, 2004
 Ansoft Designer Tutorial ECE 584 October, 2004 This tutorial will serve as an introduction to the Ansoft Designer Microwave CAD package by stepping through a simple design problem. Please note that there
Ansoft Designer Tutorial ECE 584 October, 2004 This tutorial will serve as an introduction to the Ansoft Designer Microwave CAD package by stepping through a simple design problem. Please note that there
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department. EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab
 University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE OBJECTIVE This experiment
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE OBJECTIVE This experiment
Figure Main frame of IMNLab.
 IMNLab Tutorial This Tutorial guides the user to go through the design procedure of a wideband impedance match network for a real circuit by using IMNLab. Wideband gain block TQP3M97 evaluation kit from
IMNLab Tutorial This Tutorial guides the user to go through the design procedure of a wideband impedance match network for a real circuit by using IMNLab. Wideband gain block TQP3M97 evaluation kit from
Core Technology Group Application Note 1 AN-1
 Measuring the Impedance of Inductors and Transformers. John F. Iannuzzi Introduction In many cases it is necessary to characterize the impedance of inductors and transformers. For instance, power supply
Measuring the Impedance of Inductors and Transformers. John F. Iannuzzi Introduction In many cases it is necessary to characterize the impedance of inductors and transformers. For instance, power supply
USING THE VENABLE WINDOWS SOFTWARE VERSION 4
 USING THE VENABLE WINDOWS SOFTWARE VERSION 4 FOR MODELS 3215/3225/3235 Venable Instruments 4201 S. Congress, Suite 201 Austin, TX 78745 512-837-2888 www.venable.biz TABLE OF CONTENTS TOPICS PAGE System
USING THE VENABLE WINDOWS SOFTWARE VERSION 4 FOR MODELS 3215/3225/3235 Venable Instruments 4201 S. Congress, Suite 201 Austin, TX 78745 512-837-2888 www.venable.biz TABLE OF CONTENTS TOPICS PAGE System
Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance
 Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
Lab #5 Steady State Power Analysis
 Lab #5 Steady State Power Analysis Steady state power analysis refers to the power analysis of circuits that have one or more sinusoid stimuli. This lab covers the concepts of RMS voltage, maximum power
Lab #5 Steady State Power Analysis Steady state power analysis refers to the power analysis of circuits that have one or more sinusoid stimuli. This lab covers the concepts of RMS voltage, maximum power
AC Circuits INTRODUCTION DISCUSSION OF PRINCIPLES. Resistance in an AC Circuit
 AC Circuits INTRODUCTION The study of alternating current 1 (AC) in physics is very important as it has practical applications in our daily lives. As the name implies, the current and voltage change directions
AC Circuits INTRODUCTION The study of alternating current 1 (AC) in physics is very important as it has practical applications in our daily lives. As the name implies, the current and voltage change directions
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis
 ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
USING THE VENABLE WINDOWS SOFTWARE VERSION 5.5
 USING THE VENABLE WINDOWS SOFTWARE VERSION 5.5 FOR MODELS 350a/350b/220/250/3120/3215/3225/3235/HP3577 and Series 43xx/51xx/63xx/74xx/88xx/350c Venable Instruments 8656 SH 71 West, Bldg. E Cuesta Centre
USING THE VENABLE WINDOWS SOFTWARE VERSION 5.5 FOR MODELS 350a/350b/220/250/3120/3215/3225/3235/HP3577 and Series 43xx/51xx/63xx/74xx/88xx/350c Venable Instruments 8656 SH 71 West, Bldg. E Cuesta Centre
Figure AC circuit to be analyzed.
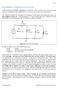 7.2(1) MULTISIM DEMO 7.2: INTRODUCTION TO AC ANALYSIS In this section, we ll introduce AC Analysis in Multisim. This is perhaps one of the most useful Analyses that Multisim offers, and we ll use it in
7.2(1) MULTISIM DEMO 7.2: INTRODUCTION TO AC ANALYSIS In this section, we ll introduce AC Analysis in Multisim. This is perhaps one of the most useful Analyses that Multisim offers, and we ll use it in
An Introductory Guide to Circuit Simulation using NI Multisim 12
 School of Engineering and Technology An Introductory Guide to Circuit Simulation using NI Multisim 12 This booklet belongs to: This document provides a brief overview and introductory tutorial for circuit
School of Engineering and Technology An Introductory Guide to Circuit Simulation using NI Multisim 12 This booklet belongs to: This document provides a brief overview and introductory tutorial for circuit
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit
 LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
A Walk Through the MSA Software Vector Network Analyzer Reflection Mode 12/12/09
 A Walk Through the MSA Software Vector Network Analyzer Reflection Mode 12/12/09 This document is intended to familiarize you with the basic features of the MSA and its software, operating as a Vector
A Walk Through the MSA Software Vector Network Analyzer Reflection Mode 12/12/09 This document is intended to familiarize you with the basic features of the MSA and its software, operating as a Vector
AA-35 ZOOM. RigExpert. User s manual. Antenna and cable analyzer
 AA-35 ZOOM Antenna and cable analyzer RigExpert User s manual . Table of contents Introduction Operating the AA-35 ZOOM First time use Main menu Multifunctional keys Connecting to your antenna SWR chart
AA-35 ZOOM Antenna and cable analyzer RigExpert User s manual . Table of contents Introduction Operating the AA-35 ZOOM First time use Main menu Multifunctional keys Connecting to your antenna SWR chart
Equivalent Circuit Determination of Quartz Crystals
 Page 1 of 11 Equivalent Circuit Determination of Quartz Crystals By Stephan Synkule & Florian Hämmerle 2010 Omicron Lab V1.1 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com
Page 1 of 11 Equivalent Circuit Determination of Quartz Crystals By Stephan Synkule & Florian Hämmerle 2010 Omicron Lab V1.1 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope
 EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
Impedance Transformation with Transmission Lines
 Impedance Transformation with Transmission Lines Software Installation and Operation Manual Don Cochran WAØJOW 21826 Gardner Rd. Spring Hill, KS 66083 (913) 856-4075 Manual Revision 1 Page 1 Table of Contents
Impedance Transformation with Transmission Lines Software Installation and Operation Manual Don Cochran WAØJOW 21826 Gardner Rd. Spring Hill, KS 66083 (913) 856-4075 Manual Revision 1 Page 1 Table of Contents
Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance
 E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
MicroLab 500-series Getting Started
 MicroLab 500-series Getting Started 2 Contents CHAPTER 1: Getting Started Connecting the Hardware....6 Installing the USB driver......6 Installing the Software.....8 Starting a new Experiment...8 CHAPTER
MicroLab 500-series Getting Started 2 Contents CHAPTER 1: Getting Started Connecting the Hardware....6 Installing the USB driver......6 Installing the Software.....8 Starting a new Experiment...8 CHAPTER
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
Resonant Frequency of the LRC Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor)
 72 Resonant Frequency of the LRC Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Equipment List Qty Items Part Numbers 1 PASCO 750 Interface 1 Voltage Sensor CI-6503 1 AC/DC Electronics Laboratory EM-8656 2 Banana
72 Resonant Frequency of the LRC Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Equipment List Qty Items Part Numbers 1 PASCO 750 Interface 1 Voltage Sensor CI-6503 1 AC/DC Electronics Laboratory EM-8656 2 Banana
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit
 Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
Activity P52: LRC Circuit (Voltage Sensor)
 Activity P52: LRC Circuit (Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) AC circuits P52 LRC Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity) Equipment Needed Qty
Activity P52: LRC Circuit (Voltage Sensor) Concept DataStudio ScienceWorkshop (Mac) ScienceWorkshop (Win) AC circuits P52 LRC Circuit.DS (See end of activity) (See end of activity) Equipment Needed Qty
AC System Monitoring Device
 AC System Monitoring Device Andrew Jarrett Project Adviser: Professor Steven D.Gutschlag Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering May 11, 2016 ABSTRACT This document covers the design of a device
AC System Monitoring Device Andrew Jarrett Project Adviser: Professor Steven D.Gutschlag Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering May 11, 2016 ABSTRACT This document covers the design of a device
Name Date: Course number: MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START EXPERIMENT 10. Electronic Circuits
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
Measure Low Value Impedance Current Shunt Impedance
 Measure Low Value Impedance Current Shunt Impedance By Florian Hämmerle 2017 Omicron Lab V2.0 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical support. Page
Measure Low Value Impedance Current Shunt Impedance By Florian Hämmerle 2017 Omicron Lab V2.0 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical support. Page
Using the V5.x Integrator
 Using the V5.x Integrator This document explains how to produce the Bode plots for an electromagnetic guitar pickup using the V5.x Integrator. Equipment: Test coil 50-100 turns of 26 AWG coated copper
Using the V5.x Integrator This document explains how to produce the Bode plots for an electromagnetic guitar pickup using the V5.x Integrator. Equipment: Test coil 50-100 turns of 26 AWG coated copper
Experiment Guide: RC/RLC Filters and LabVIEW
 Description and ackground Experiment Guide: RC/RLC Filters and LabIEW In this lab you will (a) manipulate instruments manually to determine the input-output characteristics of an RC filter, and then (b)
Description and ackground Experiment Guide: RC/RLC Filters and LabIEW In this lab you will (a) manipulate instruments manually to determine the input-output characteristics of an RC filter, and then (b)
INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE
 AC Filters & Resonance 167 Name Date Partners INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven
AC Filters & Resonance 167 Name Date Partners INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven
SAMPLE: EXPERIMENT 2 Series RLC Circuit / Bode Plot
 SAMPLE: EXPERIMENT 2 Series RLC Circuit / Bode Plot ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- This experiment is an excerpt from: Electric Experiments
SAMPLE: EXPERIMENT 2 Series RLC Circuit / Bode Plot ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- This experiment is an excerpt from: Electric Experiments
RigExpert AA-170 Antenna Analyzer (0.1 to 170 MHz) User s manual
 RigExpert AA-170 Antenna Analyzer (0.1 to 170 MHz) User s manual Table of contents 1. Description... 3 2. Specifications... 4 3. Precautions... 5 4. Operation... 6 4.1. Preparation for use... 6 4.2. Turning
RigExpert AA-170 Antenna Analyzer (0.1 to 170 MHz) User s manual Table of contents 1. Description... 3 2. Specifications... 4 3. Precautions... 5 4. Operation... 6 4.1. Preparation for use... 6 4.2. Turning
Core Technology Group Application Note 6 AN-6
 Characterization of an RLC Low pass Filter John F. Iannuzzi Introduction Inductor-capacitor low pass filters are utilized in systems such as audio amplifiers, speaker crossover circuits and switching power
Characterization of an RLC Low pass Filter John F. Iannuzzi Introduction Inductor-capacitor low pass filters are utilized in systems such as audio amplifiers, speaker crossover circuits and switching power
AC Measurements with the Agilent 54622D Oscilloscope
 AC Measurements with the Agilent 54622D Oscilloscope Objectives: At the end of this experiment you will be able to do the following: 1. Correctly configure the 54622D for measurement of voltages. 2. Perform
AC Measurements with the Agilent 54622D Oscilloscope Objectives: At the end of this experiment you will be able to do the following: 1. Correctly configure the 54622D for measurement of voltages. 2. Perform
Engineering 3821 Fall Pspice TUTORIAL 1. Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill
 Engineering 3821 Fall 2003 Pspice TUTORIAL 1 Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill 2 INTRODUCTION The PSpice program is a member of the SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit
Engineering 3821 Fall 2003 Pspice TUTORIAL 1 Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill 2 INTRODUCTION The PSpice program is a member of the SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited
 Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 10 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS USING PSPICE
 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 10 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS USING PSPICE Objective: To learn to use a circuit simulator package for plotting the response of a circuit in the time domain. Preliminary: Revise laboratory 8 to
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 10 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS USING PSPICE Objective: To learn to use a circuit simulator package for plotting the response of a circuit in the time domain. Preliminary: Revise laboratory 8 to
Use of the LTI Viewer and MUX Block in Simulink
 Use of the LTI Viewer and MUX Block in Simulink INTRODUCTION The Input-Output ports in Simulink can be used in a model to access the LTI Viewer. This enables the user to display information about the magnitude
Use of the LTI Viewer and MUX Block in Simulink INTRODUCTION The Input-Output ports in Simulink can be used in a model to access the LTI Viewer. This enables the user to display information about the magnitude
Lab 10 - INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE
 159 Name Date Partners Lab 10 - INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven by AC signals
159 Name Date Partners Lab 10 - INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven by AC signals
IVCAD VNA Base Load Pull with Active/Hybrid Tuning. Getting Started v3.5
 IVCAD VNA Base Load Pull with Active/Hybrid Tuning Getting Started v3.5 1 Setting and Configuration Block Diagram... 3 1.1 VNA setup... 5 1.2 RF source setup... 6 1.3 Power meter setup... 7 1.4 Source
IVCAD VNA Base Load Pull with Active/Hybrid Tuning Getting Started v3.5 1 Setting and Configuration Block Diagram... 3 1.1 VNA setup... 5 1.2 RF source setup... 6 1.3 Power meter setup... 7 1.4 Source
A Walk Through the MSA Software Vector Network Analyzer Transmission Mode 12/18/09
 A Walk Through the MSA Software Vector Network Analyzer Transmission Mode 12/18/09 This document is intended to familiarize you with the basic features of the MSA and its software, operating as a Vector
A Walk Through the MSA Software Vector Network Analyzer Transmission Mode 12/18/09 This document is intended to familiarize you with the basic features of the MSA and its software, operating as a Vector
 RC_Circuits RC Circuits Lab Q1 Open the Logger Pro program RC_RL_Circuits via the Logger Launcher icon on your desktop. RC Circuits Lab Part1 Part 1: Measuring Voltage and Current in an RC Circuit 1. 2.
RC_Circuits RC Circuits Lab Q1 Open the Logger Pro program RC_RL_Circuits via the Logger Launcher icon on your desktop. RC Circuits Lab Part1 Part 1: Measuring Voltage and Current in an RC Circuit 1. 2.
Experiment P45: LRC Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
 PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P45-1 Experiment P45: (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file circuits 30 m 700 P45 P45_LRCC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED
PASCO scientific Vol. 2 Physics Lab Manual: P45-1 Experiment P45: (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file circuits 30 m 700 P45 P45_LRCC.SWS EQUIPMENT NEEDED
Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software
 Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software In this chapter, we introduce the use of analog circuit simulation software and circuit layout software. I. Introduction So far we have designed
Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software In this chapter, we introduce the use of analog circuit simulation software and circuit layout software. I. Introduction So far we have designed
RLC Frequency Response
 1. Introduction RLC Frequency Response The student will analyze the frequency response of an RLC circuit excited by a sinusoid. Amplitude and phase shift of circuit components will be analyzed at different
1. Introduction RLC Frequency Response The student will analyze the frequency response of an RLC circuit excited by a sinusoid. Amplitude and phase shift of circuit components will be analyzed at different
Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks
 OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
Getting Started with Qucs
 Getting Started with Qucs Graham Edge University of Toronto After downloading Qucs, installing it, and running for the first time you should see a window that looks something like this: The large yellow
Getting Started with Qucs Graham Edge University of Toronto After downloading Qucs, installing it, and running for the first time you should see a window that looks something like this: The large yellow
Introduction to PSpice
 Electric Circuit I Lab Manual 4 Session # 5 Introduction to PSpice 1 PART A INTRODUCTION TO PSPICE Objective: The objective of this experiment is to be familiar with Pspice (learn how to connect circuits,
Electric Circuit I Lab Manual 4 Session # 5 Introduction to PSpice 1 PART A INTRODUCTION TO PSPICE Objective: The objective of this experiment is to be familiar with Pspice (learn how to connect circuits,
Quick Start Guide for the PULSE PROFILING APPLICATION
 Quick Start Guide for the PULSE PROFILING APPLICATION MODEL LB480A Revision: Preliminary 02/05/09 1 1. Introduction This document provides information to install and quickly start using your PowerSensor+.
Quick Start Guide for the PULSE PROFILING APPLICATION MODEL LB480A Revision: Preliminary 02/05/09 1 1. Introduction This document provides information to install and quickly start using your PowerSensor+.
DC and AC Circuits. Objective. Theory. 1. Direct Current (DC) R-C Circuit
 [International Campus Lab] Objective Determine the behavior of resistors, capacitors, and inductors in DC and AC circuits. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young
[International Campus Lab] Objective Determine the behavior of resistors, capacitors, and inductors in DC and AC circuits. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young
3. Apparatus/ Materials 1) Computer 2) Vernier board circuit
 Experiment 3 RLC Circuits 1. Introduction You have studied the behavior of capacitors and inductors in simple direct-current (DC) circuits. In alternating current (AC) circuits, these elements act somewhat
Experiment 3 RLC Circuits 1. Introduction You have studied the behavior of capacitors and inductors in simple direct-current (DC) circuits. In alternating current (AC) circuits, these elements act somewhat
v(t) = V p sin(2π ft +φ) = V p cos(2π ft +φ + π 2 )
 1 Let us revisit sine and cosine waves. A sine wave can be completely defined with three parameters Vp, the peak voltage (or amplitude), its frequency w in radians/second or f in cycles/second (Hz), and
1 Let us revisit sine and cosine waves. A sine wave can be completely defined with three parameters Vp, the peak voltage (or amplitude), its frequency w in radians/second or f in cycles/second (Hz), and
PXIe Contents CALIBRATION PROCEDURE
 CALIBRATION PROCEDURE PXIe-5632 This document contains the verification and adjustment procedures for the PXIe-5632 Vector Network Analyzer. Refer to ni.com/calibration for more information about calibration
CALIBRATION PROCEDURE PXIe-5632 This document contains the verification and adjustment procedures for the PXIe-5632 Vector Network Analyzer. Refer to ni.com/calibration for more information about calibration
1. Hand Calculations (in a manner suitable for submission) For the circuit in Fig. 1 with f = 7.2 khz and a source vin () t 1.
 Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits
 Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits
 Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits Aim: To obtain the characteristics of series and parallel resonant circuits. Apparatus required: Decade resistance box, Decade inductance box, Decade capacitance box
Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits Aim: To obtain the characteristics of series and parallel resonant circuits. Apparatus required: Decade resistance box, Decade inductance box, Decade capacitance box
Frequency Response Analyzers for Stability Analysis and Power Electronics Performance Testing
 Frequency Response Analyzers for Stability Analysis and Power Electronics Performance Testing Product Features Since 1979, Venable Instruments has been focused on one goal: bringing the most versatile,
Frequency Response Analyzers for Stability Analysis and Power Electronics Performance Testing Product Features Since 1979, Venable Instruments has been focused on one goal: bringing the most versatile,
EECS40 RLC Lab guide
 EECS40 RLC Lab guide Introduction Second-Order Circuits Second order circuits have both inductor and capacitor components, which produce one or more resonant frequencies, ω0. In general, a differential
EECS40 RLC Lab guide Introduction Second-Order Circuits Second order circuits have both inductor and capacitor components, which produce one or more resonant frequencies, ω0. In general, a differential
Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits
 Name- Surname: ID: Department: Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits Objective In this exercise, the DC steady state response of simple RL and RC circuits is examined. The transient behavior of RC circuits
Name- Surname: ID: Department: Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits Objective In this exercise, the DC steady state response of simple RL and RC circuits is examined. The transient behavior of RC circuits
ECE 201 LAB 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPICE/PSPICE
 Version 1.1 1 of 33 BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Resistive Circuits EXPECTED KNOWLEDGE ECE 201 LAB 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPICE/PSPICE Ohm's Law: v = ir Node Voltage and Mesh Current Methods of Circuit
Version 1.1 1 of 33 BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Resistive Circuits EXPECTED KNOWLEDGE ECE 201 LAB 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPICE/PSPICE Ohm's Law: v = ir Node Voltage and Mesh Current Methods of Circuit
Experiment 2: Electronic Enhancement of S/N and Boxcar Filtering
 Experiment 2: Electronic Enhancement of S/N and Boxcar Filtering Synopsis: A simple waveform generator will apply a triangular voltage ramp through an R/C circuit. A storage digital oscilloscope, or an
Experiment 2: Electronic Enhancement of S/N and Boxcar Filtering Synopsis: A simple waveform generator will apply a triangular voltage ramp through an R/C circuit. A storage digital oscilloscope, or an
( ). (9.3) 9. EXPERIMENT E9: THE RLC CIRCUIT OBJECTIVES
 9. EXPERIMENT E9: THE RLC CIRCUIT OBJECTIVES In this experiment, you will measure the electric current, voltage, reactance, impedance, and understand the resonance phenomenon in an alternating-current
9. EXPERIMENT E9: THE RLC CIRCUIT OBJECTIVES In this experiment, you will measure the electric current, voltage, reactance, impedance, and understand the resonance phenomenon in an alternating-current
ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits
 ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Observe and calculate the response of first-order low pass and high pass filters. Gain
ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Observe and calculate the response of first-order low pass and high pass filters. Gain
Experiment Number 2. Revised: Summer 2013 PLECS RC, RL, and RLC Simulations
 Preface: Experiment Number 2 Revised: Summer 2013 PLECS RC, RL, and RLC Simulations Preliminary exercises are to be done and submitted individually Laboratory simulation exercises are to be done individually
Preface: Experiment Number 2 Revised: Summer 2013 PLECS RC, RL, and RLC Simulations Preliminary exercises are to be done and submitted individually Laboratory simulation exercises are to be done individually
MultiSim and Analog Discovery 2 Manual
 MultiSim and Analog Discovery 2 Manual 1 MultiSim 1.1 Running Windows Programs Using Mac Obtain free Microsoft Windows from: http://software.tamu.edu Set up a Windows partition on your Mac: https://support.apple.com/en-us/ht204009
MultiSim and Analog Discovery 2 Manual 1 MultiSim 1.1 Running Windows Programs Using Mac Obtain free Microsoft Windows from: http://software.tamu.edu Set up a Windows partition on your Mac: https://support.apple.com/en-us/ht204009
Exercise 1: Series RLC Circuits
 RLC Circuits AC 2 Fundamentals Exercise 1: Series RLC Circuits EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to analyze series RLC circuits by using calculations and measurements.
RLC Circuits AC 2 Fundamentals Exercise 1: Series RLC Circuits EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to analyze series RLC circuits by using calculations and measurements.
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3)
 Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
ET1210: Module 5 Inductance and Resonance
 Part 1 Inductors Theory: When current flows through a coil of wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire. This electromagnetic field accompanies any moving electric charge and is proportional to
Part 1 Inductors Theory: When current flows through a coil of wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire. This electromagnetic field accompanies any moving electric charge and is proportional to
Microwave Circuit Design: Lab 5
 1. Introduction Microwave Circuit Design: Lab 5 This lab investigates how trade-offs between gain and noise figure affect the design of an amplifier. 2. Design Specifications IMN OMN 50 ohm source Low
1. Introduction Microwave Circuit Design: Lab 5 This lab investigates how trade-offs between gain and noise figure affect the design of an amplifier. 2. Design Specifications IMN OMN 50 ohm source Low
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
P a g e 1 ST985. TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual. Analog Arts Inc.
 P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
Fig. 1. NI Elvis System
 Lab 2: Introduction to I Elvis Environment. Objectives: The purpose of this laboratory is to provide an introduction to the NI Elvis design and prototyping environment. Basic operations provided by Elvis
Lab 2: Introduction to I Elvis Environment. Objectives: The purpose of this laboratory is to provide an introduction to the NI Elvis design and prototyping environment. Basic operations provided by Elvis
Manual CBT current preamplifier PA1 and CBT Reader software Version 1.5
 Manual CBT current preamplifier PA1 and CBT Reader software Version 1.5 Aivon Oy Tietotie 3, FI-02150 Finland tel. +358-400-265501 email: info@aivon.fi Updates to this manual found at: www.aivon.fi This
Manual CBT current preamplifier PA1 and CBT Reader software Version 1.5 Aivon Oy Tietotie 3, FI-02150 Finland tel. +358-400-265501 email: info@aivon.fi Updates to this manual found at: www.aivon.fi This
PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC R, RC, and RL Circuits
 Purpose PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC, C, and L Circuits For a given frequency, doubling of the applied voltage to resistors, capacitors, and inductors doubles the current. Hence, each of these
Purpose PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC, C, and L Circuits For a given frequency, doubling of the applied voltage to resistors, capacitors, and inductors doubles the current. Hence, each of these
Solving Simple AC Circuits Using Circuit Impedance Calculation
 Exercise 4-1 Solving Simple AC Circuits Using Circuit Impedance Calculation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to resolve simple parallel and series ac circuits
Exercise 4-1 Solving Simple AC Circuits Using Circuit Impedance Calculation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to resolve simple parallel and series ac circuits
SIMULATIONS OF LCC RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY. Modified in Spring 2006
 SIMULATIONS OF LCC RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified in Spring 2006 Page 1 of 27 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the LCC circuit using MATLAB and CAPTURE
SIMULATIONS OF LCC RESONANT CIRCUIT POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified in Spring 2006 Page 1 of 27 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the LCC circuit using MATLAB and CAPTURE
Exponential Waveforms
 ENGR 210 Lab 9 Exponential Waveforms Purpose: To measure the step response of circuits containing dynamic elements such as capacitors. Equipment Required: 1 - HP 54xxx Oscilloscope 1 - HP 33120A Function
ENGR 210 Lab 9 Exponential Waveforms Purpose: To measure the step response of circuits containing dynamic elements such as capacitors. Equipment Required: 1 - HP 54xxx Oscilloscope 1 - HP 33120A Function
CHAPTER 14. Introduction to Frequency Selective Circuits
 CHAPTER 14 Introduction to Frequency Selective Circuits Frequency-selective circuits Varying source frequency on circuit voltages and currents. The result of this analysis is the frequency response of
CHAPTER 14 Introduction to Frequency Selective Circuits Frequency-selective circuits Varying source frequency on circuit voltages and currents. The result of this analysis is the frequency response of
Appendix 3 - Using A Spreadsheet for Data Analysis
 105 Linear Regression - an Overview Appendix 3 - Using A Spreadsheet for Data Analysis Scientists often choose to seek linear relationships, because they are easiest to understand and to analyze. But,
105 Linear Regression - an Overview Appendix 3 - Using A Spreadsheet for Data Analysis Scientists often choose to seek linear relationships, because they are easiest to understand and to analyze. But,
Lab 3: RC Circuits. Construct circuit 2 in EveryCircuit. Set values for the capacitor and resistor to match those in figure 2 and set the frequency to
 Lab 3: RC Circuits Prelab Deriving equations for the output voltage of the voltage dividers you constructed in lab 2 was fairly simple. Now we want to derive an equation for the output voltage of a circuit
Lab 3: RC Circuits Prelab Deriving equations for the output voltage of the voltage dividers you constructed in lab 2 was fairly simple. Now we want to derive an equation for the output voltage of a circuit
M. Conner Name: AP Physics C: RC Circuits Lab
 M. Conner Name: Date: Period: Equipment: breadboard jumper wires one 1 k, one 4.7 k, and one 5.6 k resistors one 1000 F, one 2200 F, and one 470 F capacitor one small alligator clip wire variable power
M. Conner Name: Date: Period: Equipment: breadboard jumper wires one 1 k, one 4.7 k, and one 5.6 k resistors one 1000 F, one 2200 F, and one 470 F capacitor one small alligator clip wire variable power
Experiment 2 Determining the Capacitive Reactance of a Capacitor in an AC Circuit
 Experiment 2 Determining the apacitive eactance of a apacitor in an A ircuit - Objects of the experiments: a- Investigating the voltage and the current at a capacitor in an A circuit b- Observing the phase
Experiment 2 Determining the apacitive eactance of a apacitor in an A ircuit - Objects of the experiments: a- Investigating the voltage and the current at a capacitor in an A circuit b- Observing the phase
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION
 Objectives: ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION The primary goal of this laboratory is to study the operation and limitations of several commonly used pieces of instrumentation:
Objectives: ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION The primary goal of this laboratory is to study the operation and limitations of several commonly used pieces of instrumentation:
LT Spice Getting Started Very Quickly. First Get the Latest Software!
 LT Spice Getting Started Very Quickly First Get the Latest Software! 1. After installing LT Spice, run it and check to make sure you have the latest version with respect to the latest version available
LT Spice Getting Started Very Quickly First Get the Latest Software! 1. After installing LT Spice, run it and check to make sure you have the latest version with respect to the latest version available
LAB EXERCISE 3 FET Amplifier Design and Linear Analysis
 ADS 2012 Workspaces and Simulation Tools (v.1 Oct 2012) LAB EXERCISE 3 FET Amplifier Design and Linear Analysis Topics: More schematic capture, DC and AC simulation, more on libraries and cells, using
ADS 2012 Workspaces and Simulation Tools (v.1 Oct 2012) LAB EXERCISE 3 FET Amplifier Design and Linear Analysis Topics: More schematic capture, DC and AC simulation, more on libraries and cells, using
NI Elvis Virtual Instrumentation And Prototyping Board
 NI Elvis Virtual Instrumentation And Prototyping Board Objectives: a) Become familiar with NI Elvis hardware ( breadboard ) and software b) Learn resistor color codes c) Learn how to use Digital Multimeter
NI Elvis Virtual Instrumentation And Prototyping Board Objectives: a) Become familiar with NI Elvis hardware ( breadboard ) and software b) Learn resistor color codes c) Learn how to use Digital Multimeter
Resonance. Resonance curve.
 Resonance This chapter will introduce the very important resonant (or tuned) circuit, which is fundamental to the operation of a wide variety of electrical and electronic systems in use today. The resonant
Resonance This chapter will introduce the very important resonant (or tuned) circuit, which is fundamental to the operation of a wide variety of electrical and electronic systems in use today. The resonant
Lab 9 Frequency Domain
 Lab 9 Frequency Domain 1 Components Required Resistors Capacitors Function Generator Multimeter Oscilloscope 2 Filter Design Filters are electric components that allow applying different operations to
Lab 9 Frequency Domain 1 Components Required Resistors Capacitors Function Generator Multimeter Oscilloscope 2 Filter Design Filters are electric components that allow applying different operations to
Laboratory 1: Motion in One Dimension
 Phys 131L Spring 2018 Laboratory 1: Motion in One Dimension Classical physics describes the motion of objects with the fundamental goal of tracking the position of an object as time passes. The simplest
Phys 131L Spring 2018 Laboratory 1: Motion in One Dimension Classical physics describes the motion of objects with the fundamental goal of tracking the position of an object as time passes. The simplest
Advanced Lab LAB 6: Signal Acquisition & Spectrum Analysis Using VirtualBench DSA Equipment: Objectives:
 Advanced Lab LAB 6: Signal Acquisition & Spectrum Analysis Using VirtualBench DSA Equipment: Pentium PC with National Instruments PCI-MIO-16E-4 data-acquisition board (12-bit resolution; software-controlled
Advanced Lab LAB 6: Signal Acquisition & Spectrum Analysis Using VirtualBench DSA Equipment: Pentium PC with National Instruments PCI-MIO-16E-4 data-acquisition board (12-bit resolution; software-controlled
PSM Soft. Features and Functions January PC Software Guide. Getting connected and Communication
 PSM Soft PC Software Guide Features and Functions January 2010 The PSM series Phase Sensitive Multimeters provide a wide range of exceptionally accurate and versatile instrumentation in one unique package.
PSM Soft PC Software Guide Features and Functions January 2010 The PSM series Phase Sensitive Multimeters provide a wide range of exceptionally accurate and versatile instrumentation in one unique package.
Handbook. Antenna Rotator Controller
 Handbook Controller 3S design GmbH 2. Südwieke 231 26817 Rhauderfehn Germany www.3sdesign.de Tel. +49-4952-921950 Contents I Table of content Part I 1 1 Operating... 1 2 Installation... 2 1 1 1.1 Operating
Handbook Controller 3S design GmbH 2. Südwieke 231 26817 Rhauderfehn Germany www.3sdesign.de Tel. +49-4952-921950 Contents I Table of content Part I 1 1 Operating... 1 2 Installation... 2 1 1 1.1 Operating
Crystal Characterisation with the TrewMac TE3001 Analyser
 Crystal Characterisation with the TrewMac TE300 Analyser The TrewMac TE300 Analyser is an excellent tool for the measurement and characterization of quartz crystals and resonators. With Hz resolution,
Crystal Characterisation with the TrewMac TE300 Analyser The TrewMac TE300 Analyser is an excellent tool for the measurement and characterization of quartz crystals and resonators. With Hz resolution,
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 29: ALTERNATING CURRENT.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALTERNATING VOLTAGES AND CURRENTS BEFORE, we only considered DIRECT CURRENTS, currents that only move in - NOW we consider ALTERNATING CURRENTS, currents that move in Alternating
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALTERNATING VOLTAGES AND CURRENTS BEFORE, we only considered DIRECT CURRENTS, currents that only move in - NOW we consider ALTERNATING CURRENTS, currents that move in Alternating
Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015
 ECE214: Electrical Circuits Laboratory Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015 1 Introduction In this lab you will investigate the magnitude and phase shift that occurs in an RC circuit
ECE214: Electrical Circuits Laboratory Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015 1 Introduction In this lab you will investigate the magnitude and phase shift that occurs in an RC circuit
EXPERIMENT 8: LRC CIRCUITS
 EXPERIMENT 8: LRC CIRCUITS Equipment List S 1 BK Precision 4011 or 4011A 5 MHz Function Generator OS BK 2120B Dual Channel Oscilloscope V 1 BK 388B Multimeter L 1 Leeds & Northrup #1532 100 mh Inductor
EXPERIMENT 8: LRC CIRCUITS Equipment List S 1 BK Precision 4011 or 4011A 5 MHz Function Generator OS BK 2120B Dual Channel Oscilloscope V 1 BK 388B Multimeter L 1 Leeds & Northrup #1532 100 mh Inductor
Instruction Manual. Model USB Wattmeter
 Instruction Manual Model 81041 USB Wattmeter TABLE OF CONTENTS Specifications and Leading Particulars. 2 General Description 1. Purpose and Application 3 2. Description. 3 3. Theory of Operation... 4
Instruction Manual Model 81041 USB Wattmeter TABLE OF CONTENTS Specifications and Leading Particulars. 2 General Description 1. Purpose and Application 3 2. Description. 3 3. Theory of Operation... 4
The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance
 Purpose Theory The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance a. To study the behavior of a series RLC circuit in an AC current. b. To measure the values of the L and C using the impedance method. c. To study the
Purpose Theory The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance a. To study the behavior of a series RLC circuit in an AC current. b. To measure the values of the L and C using the impedance method. c. To study the
