David Tipper. Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh
|
|
|
- Delilah King
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3G: UMTS overview David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh 2700 Slides 8 Subscriber base continues to grow 1 billion wireless subscribers in 2002 (surpassed Landline) Predict 3 billion by G Driving Factors 800 Billion Mobile Revenues %Voice, SMS 9.5%, All Other nonvoice 9.5% 2
2 3G Development 1986 ITU began studies of 3G as: Future Public Land Mobile Telecom. Systems (FPLMTS) 1997 changed to IMT-2000 (International Mobile Telecom. in Year 2000) ITU-R studying radio aspects, ITU-TT studying network aspects (signaling, services, numbering, quality of service, security, operations) IMT-2000 vision of 3G 1 global standard in 1 global frequency band to support wireless data service Spectrum: MHz and MHz worldwide Multiple radio environments (phone should switch seamlessly among cordless, cellular, satellite) Support for packet switching and asymmetric data rates Target data rates for 3G Vehicular: 144 kbps Pedestrian: 384 kbps Indoor office: Mbps roadmap to > 10Mbps late Suite of four standards approved after political fight 3 3G Requirements Seamless End to End Service with different data rates Satellite Global Suburban Urban In-Building Macro-cell Micro-cell Pico-cell up to 144 kbps up to 384 kbps up to 2Mbps 4
3 Third Generation Standards ITU approved suite of four 3G standards EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for Global Evolution) TDMA standard with advanced modulation and combined timeslots Provides unification of NA-TDMA and GSM Only meets some of the 3G requirements (2.75G?) UMTS (Universal Mobile Telephone Service) also called WCDMA (wideband CDMA) Dominant standard outside of US and leading standard for 3G worldwide Viewed as 3G migration path for GSM/GPRS/EDGE systems CDMA 2000 Also called (3X and cdma three): competes directly with W- CDMA up to 2 Mb/s Evolutionary path for IS-95 which is the dominant standard in the US TD-SCDMA : Stand alone standard developed in China 5 Evolution Path to 3G 2G systems IS-95 CDMA 2.5G systems CDMA x-RTT EDGE 3G systems CDMA xEVDO GSM GPRS UMTS (WCDMA) Telcom
4 3G Spectrum Allocations 7 Diverse 3G Spectrum Telcom
5 3G Spectrum Cost 9 Current status of 3G Two partnership projects to harmonize and standardize the two main 3G standards 3GPP that deals with the UMTS standard 3GPP2 that deals with the US cdma2000 proposal 3G spectrum allocated in over 100 countries spectrum not consistent throughout the world Deployments occurring slower than expected Service providers strapped for cash (spectrum expensive) Equipment delays Many carriers going went with 2.5 G first to build data market Subscribers (2Q 2008) 18% 3G, 82% 2G or 2.5G, 0.01% 1G ~30% 3G penetration rate in USA GSM /GPRS/EDGE/UMTS 88% of all mobiles worldwide 10
6 UMTS Universal Mobile Telecommunication Services Often Called GSM 3 UMTS is a complete system architecture As in GSM emphasis on standardized interfaces mix and match equipment from various vendors Simple evolution from GPRS allows one to reuse/upgrade some of the GPRS backhaul equipment Backward compatible handsets and signaling to support intermode and intersystem handoffs Intermode; TDD to FDD, FDD to TDD Intersystem: UMTS to GSM or UMTS to GPRS UMTS supports a variety of user data rates and both packet and circuit switched services System composed of three main subsystems 12 UMTS System Architecture USIM Node B Node B RNC MSC/VLR HLR GMSC PSTN ME Node B Node B RNC SGSN GGSN Internet UE UTRAN CN External Networks UE (User Equipment) that interfaces with the user UTRAN (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network) handles all radio related functionality WCDMA is radio interface standard here. CN (Core Network) is responsible for transport functions such as switching and routing calls and data, tracking users 13
7 UMTS System Architecture UE ME (Mobile Equipment) is the single or multimode terminal used for radio communication USIM (UMTS Subscriber Identity Module) is a smart card that holds the subscriber identity, subscribed services, authentication and encryption keys UTRAN Node B (equivalent to BTS in GSM/GPRS) performs the air interface processing (channel coding, rate adaptation, spreading, synchronization, power control). Can operate a group of antennas/radios RNC (Radio Network Controller) (equivalent to GSM BSC) Responsible for radio resource management and control of the Node Bs. Handoff decisions, congestion control, power control, encryption, admission control, protocol conversion, etc. 14 UTRAN architecture UE 1 Node B I ub RNS RNC: Radio Network Controller RNS: Radio Network Subsystem RNC CN UE 3 UE 2 Node B Node B Node B Node B I ub I ur RNC UTRAN contains several RNSs Node B can support FDD or TDD or both RNC is responsible for handover decisions requiring signalingto the UE Cell offers FDD or TDD I u RNS 15
8 UMTS System Architecture Core Networks (CN) HLR (Home Location Register) database located in the user s home system that stores the master copy of the user s service profile. The HLR also stores the UE location on the level of MSC and SGSN, 3G MSC / VLR Switch and database that serves the UE in its current location for Circuit Switched (CS) services. The MSC function is used to switch the CS transactions, and VLR function holds a copy of the visiting user s service profile, as well as more precise information on the UE s location within the serving system. 3G GMSC (Gateway MSC) Switch at the point where UMTS is connected to external CS networks. All incoming and outgoing CS connections go through GMSC. 3G SGSN (Serving GPRS Support Node) Similar to that of MSC / VLR but is used for Packet Switched (PS) services. The part of the network that is accessed via the SGSN is often referred to as the PS domain. Upgrade version of serving GPRS support node. 3G GGSN (Gateway GPRS Support Node) Functionality is close to that of GMSC but is in the relation to PS services. Upgraded version of gateway GPRS support Node 16 Core network The Core Network (CN) and the Interface I u are separated into two logical domains: Circuit Switched Domain (CSD) Circuit switched service including signaling Resource reservation at connection setup 3G versions of GSM components (MSC, GMSC, VLR, HLR) I u CS Packet Switched Domain (PSD) Handles all packet data services 3G versions of GPRS components (SGSN, GGSN) I u PS General approach of building on GSM/GPRS infrastructure,helps to saves $ and faster deployment 18
9 Core network: architecture BTS A bis BSS I u VLR BSC MSC GMSC PSTN Node BTSB I u CS AuC EIR HLR Node B I ub GR Node B RNC SGSN G n GGSN G i Node B RNS I u PS CN 19 GSM GPRS Evolution GSM GPRS Voice Mobile Switching Center Visitor Location register it Gateway MSC Core Network Home Location register Base Station Controller data PCU SGSN GGSN 20
10 GSM GPRS UMTS Evolution GSM GPRS UMTS Voice Mobile Switching Center Visitor Location Register Gateway MSC Radio Network Controller Core Network Home Location Register Radio Network Controller data 3G SGSN 3G GGSN 21 WCDMA Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) The air radio interface standard for UMTS Wideband direct sequence spread spectrum Variable orthogonal spreading for multiple access (OVSF) Three types of interface : FDD: separate uplink/downlink frequency bands with constant frequency offset between them TDD: uplink/downlink in same band but time-shares transmissions in each direction Dual mode :supports FDD and TDD Wide range of data rates due to CDMA with variable spreading, coding and modes Varying user bit rate is mapped to variable power and spreading Different services can be mixed on a single carrier for a user 22
11 WCDMA 5-MHz Channel (25 GSM channels) Each service provider can deploy multiple 5MHz carriers at same cell site Each 5 MHz shared by multiple subscribers using CDMA Maximum chip rate = 3.84 Mchips/sec Standard advantages of CDMA Soft handoff Frequency reuse cluster size of 1, Better quality in multipath environment RAKE receiver QPSK modulation 23 Scrambling and Channelization Channelization codes are orthogonal codes Separates transmissions from the same source Uplink: used to separate different physical channels from the same UE voice and data session Downlink: used to separate transmissions to different physical channels and different UEs UMTS uses orthogonal variable spreading codes Scrambling (pseudonoise scrambling) Applied on top of channelization spreading Separates transmissions from different sources Uplink effect: separate mobiles from each other Downlink effect: separate base stations from each other 24
12 Physical Layer: Spreading Spreading of the low-bandwidth data signal to produce the wideband CDMA signal consists of two steps: Channelization or spreading code to reach channel rate of 3.84 Mchips/s Scrambling to provide separation of transmissions 25 Channelization Spreading UMTS uses variable spreading and power levels to provide different user data rates. In FDD mode 10 msec frames are used The number of chips per bits is called the Spreading Factor (SF) and define the data service required for the user: T bit = SF x T chip For UMTS: Bit Rate x SF = 3.84 Mchips/s (Chip Rate) SF can change in every 10 msec frame Service Bearer Date Rate (kbps) SF Modulation Rate (Mchips/s) Speech Packet 64 kbps Packet 384 kbps
13 WCDMA Variable Spreading The channelization codes are Orthogonal Variable Spreading Factor codes that preserves the orthogonality between a user s different physical channels. The OVSF codes can be defined using a code tree. In the code tree the channelization codes are uniquely described as C CH,SF,k where SF is the Spreading Factor of the code and k is the code number, 0 <= k <= SF 1 C CH,4,0 = C CH,2,0 = 1 1 C CH,4,1 = C CH,1,0 = 1 C CH,4,2 = C CH,2,1 = 1 1 C CH,4,3 = SF = 1 SF 2 SF = 4 SF between 4 and 512 on DL between 4 and 256 on UL 28 Scrambling and Channelization Codes Usage Length Number of codes Code family Spreading Channelization code Uplink: Separation of physical data and control channels from same terminal Downlink: Separation of downlink connections of different users within one cell chips ( s) Downlink also 512 chips Number of codes under one scrambling code = spreading factor Orthogonal Variable Spreading Factor (OVSF) Yes, increases transmission bandwidth Scrambling code Uplink: Separation of terminals Downlink: Separation of sectors (cells) Uplink: 10 ms chips or 66.7 s = 256 chips Downlink: 10 ms = chips Uplink: Several millions Downlink: 512 Long: Gold code Short: Extended S(2) family No, it does not affect transmission bandwidth 29
14 WCDMA QPSK Modulator 30 Turbocodes Used in 3G cellular (UMTS) standard TurboCode: Concatenation of codes with interleaving - followed by an iterative algorithm for decoding Instead of counting differences in bit positions, distance probabilities are used pick max probability to decode word Iterative decoding allows one to tradeoff delay vs. accuracy 31
15 Concatenated Code System Data Outer Code Encoder Inner Code Encoder Modulator R= K/N code r=k/n Overall Code rate = Rr Concatenation makes coding more powerful Turbocodes adds an interleaving step Radio Chan nnel Source Decoder Inner Code Decoder Demod -ulator 32 WCDMA Forward Error Control Convolutional Coding: for voice and control info ½ rate and 1/3 rate codes with constraint length 8 Block Interleave over 10, 20, 40, or 80 ms Turbo Coding for data and some control info Two parallel rate 1/3 convolutional codes constraint length 3 with interleaving block length bits Iterative decoding to improve BER in poor channel environments. 34
16 Turbocode Performance 36 WCDMA Parameters Channel bandwidth 5.MHz Downlink RF channel structure Chip rate Frame length Handover Direct spread spectrum QPSK modulation 3.84 Mcps 10ms/20ms (optional TDD mode) Softer handover, soft handover and interfrequency handover 37
17 UMTS FDD frame structure Radio frame 10 ms µs µs Time slot Pilot TFCI FBI TPC 2560 chips, 10 bits Data 2560 chips, 10*2 k bits (k = 0...6) uplink DPCCH uplink DPDCH µs Data 1 TPC TFCI Data 2 Pilot downlink DPCH FBI: Feedback Information DPDCH DPCCH DPDCHDPCCH TPC: Transmit Power Control 2560 chips, 10*2 k bits (k = 0...7) Slot structure NOT for user separation but synchronisation for periodic functions! TFCI: Transport Format Combination Indicator DPCCH: Dedicated Physical Control Channel DPDCH: Dedicated Physical Data Channel DPCH: Dedicated Physical Channel 38 UMTS Data rate adjusted every 10 msec by variable spreading and power 39
18 UMTS Protocol Stack User Plane Radio Link Control (RLC) Presents a reliable channel to higher layers by retransmitting erroneous packets Medium Access Control (MAC) Channel access, multiplexing traffic streams, scheduling priority flows Physical Layer Measurements, power control algorithms Control Plane Radio Resource Control (RRC) Connection and QoS management Radio Resource Management (RRM) Algorithms for admission control, handovers 41 UMTS protocol stacks (user plane) Circuit Switched Domain Uses same protocols as GSM Packet Switched Domain Builds on GPRS Stack UE U u UTRAN I u PS 3G G n apps. & protocols SGSN IP, PPP, IP tunnel PDCP PDCP GTP GTP GTP RRM/RLC RRM/RLCUDP/IP UDP/IP UDP/IP MAC MAC AAL5 AAL5 L2 radio radio ATM ATM L1 3G GGSN IP, PPP, GTP UDP/IP L2 L1 43
19 RLC Functions Segmentation and reassembly Concatenation Padding Transfer of user data Error correction In-sequence delivery Duplicate detection Flow control Sequence number check (UM) Protocol error detection and recovery Ciphering Suspend/resume function for data transfer 44 MAC Functions Mapping of logical channels onto transport channels Selection of transport format for each transport channel Priority handling between data flows of one MS Priority handling between MSs by means of dynamic scheduling Identification of MSs on common transport channels Multiplexing/demultiplexing of higher layer PDUs into/from transport blocks to/from the physical layer Traffic volume monitoring Dynamic transport channel type switching Ciphering Access service class selection for RACH transmissions 47
20 MAC: Logical Channels Builds on GSM/GPRS structure Control channels: Broadcast control channel (BCCH) Paging control channel (PCCH) Dedicated control channel (DCCH) Common control channel (CCCH) random access channel (RACH) Traffic channels: Dedicated traffic channel (DTCH) Common traffic channel (CTCH) (broadcast or multi-cast traffic) Control and traffic channels are per UMTS frequency channel (5MHz channel) in fashion similar to cdmaone 48 MAC Entities MAC-b handles the following transport channels: broadcast channel (BCH) MAC-c/sh handles the following transport channels: paging channel (PCH) forward access channel (FACH) random access channel (RACH) common packet channel (UL CPCH). The CPCH exists only in FDD mode. downlink shared channel (DSCH) MAC-d handles the following transport channels: dedicated transport channels (DCH) 49
21 Physical Channels Primary Common Control Physical Channel (PCCPCH) Secondary Common Control Physical Channel (SCCPCH) Physical Random Access Channel (PRACH) (RACH in MAC layer) Dedicated Physical Data Channel (DPDCH) Physical Downlink Shared Channel (PDSCH) Physical Common Packet Channel (PCPCH) Synchronization Channel (SCH) Common Pilot Channel (CPICH) Acquisition Indicator Channel (AICH) Paging Indication Channel (PICH) CPCH Status Indication Channel (CSICH) Collision Detection/Channel Assignment Indicator Channel (CD/CA- ICH) 51 Physical Channels Physical Random Access Channel (PRACH) 52
22 Physical Channels Dedicated Uplink Physical Channel 53 Physical Channels Physical Common Packet Channel (PCPCH) Uplink packet transmission P0 P1 Pj Pj Message Part 4096 chips 0 or 8 slots N*10 msec Access Preamble Control Part Collision Detection Preamble Data part 54
23 UMTS Architecture: Control Plane GMM / SM / SMS GMM / SM / SMS Relay RRC RRC RANAP RANAP RLC RLC SCCP SCCP MAC L1 MS Uu MAC Signalling Bearer AAL5 L1 ATM RNS Iu-Ps Signalling Bearer AAL5 ATM 3G SGSN [2] 56 RRC: Functions and Signaling Procedures Broadcast of information related to the non-access stratum (Core Network) Broadcast of information related to the access stratum Establishment, maintenance and release of an RRC connection between the UE and UTRAN Establishment, reconfiguration and release of Radio Bearers Assignment, reconfiguration and release of radio resources for the RRC connection RRC connection mobility functions Control of requested QoS UE measurement reporting and control of the reporting Outer loop power control Control of ciphering Paging Initial cell selection and cell re-selection Arbitration of radio resources on uplink DCH Timing advance (TDD mode) 57
24 UMTS Diversity UMTS DS- CDMA support multi-path diversity Note can tolerate a wider range of multi-path delay spread than IS- 95 due to greater spreading UMTS supports macro-diversity. it Allows UE to transmit the same signal via 2 or more cells, in order to counteract interference problems. When macro-diversity is used, and when 2 cells are belonging to 2 Node Bs, that are belonging to 2 different RNCs, these RNCs have a specific functionality: Serving RNC (SRNC): The SRNC is in charge of the radio connection between the UE and UTRAN. Drift RNC (DRNC): A RNC, that supports the SRNC with radio resources when the connection between the UTRAN and the UE needs to use cell(s) controlled by this RNC, is referred to a Drift RNC. Telcom Power Control In order to maximize the cell capacity, it has to equalize the received power per bit of all mobile stations at all times. Open loop power control The initial power control is Open Loop. The MS (UE) estimates the power level based on the received level of the pilot from the BTS (Node B). If no response is received the MS waits a defined time and retransmits with a higher power level. The MS continues to do this until it receives a response. MS Access 1 with estimated power MS Access 2 with increased power MS (UE)... MS Access n with increased power BTS (Node B) Response with power control 59
25 Power Control Closed loop power control When communication is established, power is controlled by the Closed Loop Power Control. BTS sends power control bits To MS (UE) (1500 times/sec) RNC sets SIR target for service MS (UE) MS transmits (Tx) RNC calculates BLER for Tx Continues poser control BTS (Node B) RNC sends new SIR target RNC Inner Loop Outer Loop 60 Power Control The RNC sets the target BLER (Block Error Rate) level for the service. RNC derives SIR (Signal to Interference Ratio) target from BLER, and sends it to the BTS. Uplink RNC performs frequent estimations of the received SIR and compares it to a target SIR. If measured SIR is higher than the target SIR, the base station will command the MS to lower the power: If it is too low, it will command the mobile station to increase its power: The measured-command-react cycle is executed a rate of 1500 times per second (1.5 KHz) for each mobile station (Inner Loop). The RNC calculates the SIR target once every 10 ms (or more depending on services) and adjusts the SIR target (Outer Loop). Downlink, same closed-loop power control technique is used but the motivation is different: it is desirable to provide a marginal amount of additional power to mobile stations at the cell edge, as they suffer increased adjacent cell interference. 61
26 QoS Classes/Services Traffic class Conversational Streaming Interactive Background Characteristics Preserve time relation (variation) between information entities of the stream Conversational pattern (stringent and low delay) Asymmetric applications More tolerant to jitter than conversational class. Use of buffer to smooth out jitter Request response pattern Preserve data integrity Destination is not expecting the data within a certain time Preserve data integrity Application examples Voice, video telephony, video games Streaming multimedia Web browsing, network games Background download of e- mail, electronic postcard 62 Conversational Classes Speech service Speech codec in UMTS employs a Adaptive Multi-rate (AMR) technique. The multi-rate speech coder is a single integrated speech codec with eight source rates: (GSM-EFR), 10.2, 7.95, 7.40, 6.70, 5.90, 5.15, 4.75 kbps and 0 kbps. The AMR bit rates are controlled by the radio access network and not depend on the speech activity. For interoperability with existing cellular networks, some modes are the same as in existing cellular networks: 12.2 kbps = GSM EFR codec 7.4 kbps = North American TDMA speech codec 6.7 kbps = Japanese PDC The AMR speech coder is capable of switching its rate every 20 ms speech frame upon command. Telcom
27 Admission Control Accepts or rejects requests to establish a radio access bearer Located at the RNC Estimates the load increase that the establishment of the radio access bearer would cause to the radio network Check is applied separately for uplink and downlink directions Radio access bearer will be accepted if admission control admits both uplink and downlink Example: Wideband power-based admission control Telcom Handover in UMTS 1 Comm. Tower Comm. Tower Node B Comm. Tower Comm. Tower 2 Soft handoff When stay on same frequency in adjacent sectors or cells Node B 4 iu 3 BTS RNS Core Network Telcom
28 Types of UMTS Handoffs 1. Intra RNC: between Node B s or sector of same Node B s attached to same RNC 2. Inter RNC: between Node B s attached to different RNC s, can be rerouted between RNC s locally if link, or rerouted by 3GMSC/SGSN, if RNC s in same service area 3. Inter 3GMSC/SGSN between Node B s attached to different 4. Inter System Handoff between Node B and BTS along with a change of mode (WCDMA, GSM), (WCDMA, GPRS) Note types 1,2, and 3 can be a Soft/Softer or Hard handoff, whereas, type 4 is always a Hard handoff Telcom Location Management Three types of location updating 1. Location Area (LA)- zone registration as in GSM, plus can require periodic registration of users 2. Routing Areas (RA) zone registration as in GPRS for packet based services 3. UTRAN Registration Areas (URA) zone registration for certain types of services Telcom
29 UMTS Security UMTS Security Functions Main security elements from GSM Authentication of subscribers using challenge/response Subscriber identity confidentiality (TMSI) SIM card (call USIM) Authentication of user to USIM by use of a PIN Radio interface encryption UMTS enhancements/new features Mutual authentication to protect against false base stations New encrpytion/key generation/authentication algorithms with greater security Encryption extended farther back into wired network (prevents eavesdropping on microwave relays) Telcom UMTS Security Architecture Telcom
30 UMTS Security UMTS authenticates and encrypts circuit switched and packet switched connections separately (even from same MS) AUC and USIM have 128 bit shared secret data When authentication requested AUC generates a vector of 128 bit integrity keys (IK) using algorithm f4 with a 128 bit random number input RAND Authetication challenge is created using algorithm f9 with inputs: Integrity Key Direction of transmission (up or downlink) 32 bit random number: FRESH Hyperframe count (32 bits) prevents replay attacks Only RAND and FRESH and the correct response are transmitted over the air Telcom UMTS Security Telcom 2700 Security architecture at AUC 75
31 UMTS Security After authentication encryption provided using algorithm f8, with inputs 128 bit cipher key CK, Hyperframe count (32 bits), direction, etc. CK is created by algorithm f3 using 128 bit random number RAND and 128 bit shared secret data of USIM/AUC The encryption algorithms allow for future improvement User specifies protocol version (algorithm used) in set up message along with times for length of using IKs Currently Kasumi algorithm or Advanced Encryption Standard are used for f8 and f9 May eventually move to using IP level encryption and authentication Telcom UMTS Versions Telcom
32 HIGH SPEED DOWLINK PACKET ACCESS (HSDPA) HSDPA 3.5G system upgrade of UMTS Standardised in 3GPP Release 5 Objective is to support delay-tolerant l t services in low mobility scenarios with with enhanced resource efficiency and service quality support for background, interactive and (to some extent) streaming services low mobility enable downlink peak rates of 8-10 Mbits/s >> 3G requirements lower resource consumption per transferred delay-tolerant bit 79 HIGH SPEED DOWLINK PACKET ACCESS HSDPA upgrade of UMTS similar to EDGE upgrade of GPRS completely backwards compatible no new spectrum needed d reuse existing infrastructure and 5MHz channels primarily software and minor hardware upgrades coexistence of HSDPA- and non-hsdpa-enabled terminals coexistence of HSDPA- and non-hsdpa-enabled NODE-Bs data flows on HS-DSCH moving from non-hsdpa-cell to HSDPA-cell are automatically switched to a supported transport channel, e.g. DCH gradual hot-spot-based network upgrades possible cost-effective 80
33 HSDPA Architecture UE channel quality indicator NODEB RNC shared channel Upgrade UMTS downlink channels to a HS version: higher-order modulation: QPSK and 16-QAM fast link adaptation: adaptive modulation and coding fast channel-aware scheduling: centered at the Node B fast hybrid ARQ on downlink: combines FEC and selective ARQ reduced TTI of 2 ms: to facilitate better tracking of channel variations HS channels typically transmits at relatively fixed power 81 NEW PHYSICAL CHANNELS PHYSICAL CHANNELS HS-PDSCH downlink SF 16 data only (up to 15 streams to a user) HS-SCCH(s) downlink MAC-hs signalling, H-ARQ,etc. HS-DPCCH uplink SF 256 CQI, (N)ACK 82
34 PHYSICAL LAYER PROCESSING Physical Layer Processing information bit sequence CRC Turbo encoding rate matching interleaving modulation (series parallel) mapping on code tree spreading modulation complex scrambling other channels gain ADAPTIVE 84 ADAPTIVE MODULATION AND CODING LINK ADAPTATION: channel-dependent AMC typically more efficient for services that tolerate short-term data rate variations with only power-controlled channels, it is difficult to exploit all resoures AMC can exploit resources better, at the cost of transfer rate jitter Fixed spreading factor SF but variable number of streams and bits per channel symbol MODULATION SPREADING FACTOR TURBO CODE RATE BITS/ BLOCK/CODE DATA RATE (15 CODES) 16 1/ Mbps QPSK 16 1/ Mbps 16 3/ Mbps 16-QAM /2 3/ Mbps 10.8 Mbps 85
35 HSDPA Upgrades Infrastructure NODE-B a new MAC sublayer (MAC-hs) is standardised and needs to be implemented in the NODE-B depending on the legacy NODE-B capabilities, this update may be done via remote software downloads or may possibly require hardware upgrades as well RNC is largely maintains the UMTS Release 99 functionality a software-only upgrade is required, e.g. to enable assignment of data flows to the HS-DSCH (~ channel switching) no substantial impact on the CORE network is expected New Mobile Terminals Support physical interface, higher data rates and H-ARQ HSDPA deployments began 2006 in Europe, Canada, etc. Over 100 deployments 87 HSUPA High Speed Uplink Packet Access Similar to HSDPA advanced coding and modulation techniques with hybrid ARQ to improve data rate on uplink channel in UMTS Now called Enhanced Uplink (EUL) (3GPP) Data rates from.73mbps 5.76Mbps, 11.5Mbps being tested Uses new Enhanced versions of Signaling and physical channels Focus of UMTS now on IP in the backhaul 88
36 3GPP IP Reference Architecture PSTN Legacy (2G) mobile networks Applications & services PSTN gateway Gateway CSCF HSS HLR Other 3GPP PLMN GGSN GGSN SGSN Internet/ IP networks RNS RNC RNS Node B Node B Radio access network The 3GPP IP reference architecture all traffic IP - with QoS Classes 89 UMTS UMTS is most popular 3G technology Upgrade path from GPRS/EDGE primarily in air interface to WCDMA standard Now called 3GSM WCDMA variable power/spreading cdma Provides standard benefits of cdma technology (frequency reuse factor 1, soft handoff, etc.) Deployed throughout the world Upgrade path to HSPDA and HSUPA and all IP in the core defined - over 62.5 million HSPA users 90
David Tipper. Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh
 3G: UMTS overview David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh 2700 Slides 12 Subscriber base continues to grow 1 billion wireless subscribers
3G: UMTS overview David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh 2700 Slides 12 Subscriber base continues to grow 1 billion wireless subscribers
CHAPTER 2 WCDMA NETWORK
 CHAPTER 2 WCDMA NETWORK 2.1 INTRODUCTION WCDMA is a third generation mobile communication system that uses CDMA technology over a wide frequency band to provide high-speed multimedia and efficient voice
CHAPTER 2 WCDMA NETWORK 2.1 INTRODUCTION WCDMA is a third generation mobile communication system that uses CDMA technology over a wide frequency band to provide high-speed multimedia and efficient voice
TELE4652 Mobile and Satellite Communications
 Mobile and Satellite Communications Lecture 12 UMTS W-CDMA UMTS W-CDMA The 3G global cellular standard set to supersede GSM Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS) Slow on the uptake by mid-2008
Mobile and Satellite Communications Lecture 12 UMTS W-CDMA UMTS W-CDMA The 3G global cellular standard set to supersede GSM Universal Mobile Telecommunication System (UMTS) Slow on the uptake by mid-2008
Lecture overview. UMTS concept UTRA FDD TDD
 Lecture overview 3G UMTS concept UTRA FDD TDD 3 rd Generation of Mobile Systems Goal to create a global system enabling global roaming International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT-2000) requirements: Throughput
Lecture overview 3G UMTS concept UTRA FDD TDD 3 rd Generation of Mobile Systems Goal to create a global system enabling global roaming International Mobile Telecommunications (IMT-2000) requirements: Throughput
IMT IMT-2000 stands for IMT: International Mobile Communications 2000: the frequency range of 2000 MHz and the year 2000
 IMT-2000 IMT-2000 stands for IMT: International Mobile Communications 2000: the frequency range of 2000 MHz and the year 2000 In total, 17 proposals for different IMT-2000 standards were submitted by regional
IMT-2000 IMT-2000 stands for IMT: International Mobile Communications 2000: the frequency range of 2000 MHz and the year 2000 In total, 17 proposals for different IMT-2000 standards were submitted by regional
Content. WCDMA BASICS HSDPA In general HSUPA
 HSPA essentials Content WCDMA BASICS HSDPA In general HSUPA WCDMA Network Architecture USIM card Affected elements for HSPA GSM/WCDMA mobile Uu GSM/WCDMA mobile WCDMA mobile Uu Uu BTS BTS RAN Iub Iub RNC
HSPA essentials Content WCDMA BASICS HSDPA In general HSUPA WCDMA Network Architecture USIM card Affected elements for HSPA GSM/WCDMA mobile Uu GSM/WCDMA mobile WCDMA mobile Uu Uu BTS BTS RAN Iub Iub RNC
Mobilné systémy 3. generácie UMTS
 Mobilné systémy 3. generácie UMTS Ing. Matúš Turcsány, PhD. turcsany@ktl.elf.stuba.sk KTL FEI STU 2009 Prehľad prednášok UMTS HSDPA, EUL HSPA evolution LTE LTE-Advanced Nasadené technológie GSM worldwide
Mobilné systémy 3. generácie UMTS Ing. Matúš Turcsány, PhD. turcsany@ktl.elf.stuba.sk KTL FEI STU 2009 Prehľad prednášok UMTS HSDPA, EUL HSPA evolution LTE LTE-Advanced Nasadené technológie GSM worldwide
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part VI: WCDMA Basics. Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 24.1.
 Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part VI: WCDMA Basics Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 24.1.2008 Outline Network elements Physical layer Radio resource management
Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part VI: WCDMA Basics Jyri Hämäläinen, Communications and Networking Department, TKK, 24.1.2008 Outline Network elements Physical layer Radio resource management
1. Introduction to WCDMA. 1.1 Summary of the Main Parameters in WCDMA 1.2 Power Control 1.3 Softer and Soft Handovers
 UMTS WCDMA / HSPA 1. Introduction to WCDMA 1.1 Summary of the Main Parameters in WCDMA 1.2 Power Control 1.3 Softer and Soft Handovers IMT-2000 International Mobile Telecommunications 3G Frequency Allocation
UMTS WCDMA / HSPA 1. Introduction to WCDMA 1.1 Summary of the Main Parameters in WCDMA 1.2 Power Control 1.3 Softer and Soft Handovers IMT-2000 International Mobile Telecommunications 3G Frequency Allocation
RF Lecture Series Modulation Fundamentals Introduction to WCDMA
 RF Lecture Series Modulation Fundamentals Introduction to WCDMA Jeff Brenner Verigy Austin, TX 1. Introduction Second generation (2G) mobile communication standards were developed to provide higher bandwidth
RF Lecture Series Modulation Fundamentals Introduction to WCDMA Jeff Brenner Verigy Austin, TX 1. Introduction Second generation (2G) mobile communication standards were developed to provide higher bandwidth
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 9 UMTS. Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone
 Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 9 UMTS Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone 3GPP standards evolution 2G 3G 4G GSM GPRS EDGE UMTS TD-SCDMA HSDPA TDMA FDMA CDMA OFDMA
Politecnico di Milano Facoltà di Ingegneria dell Informazione MRN 9 UMTS Mobile Radio Networks Prof. Antonio Capone 3GPP standards evolution 2G 3G 4G GSM GPRS EDGE UMTS TD-SCDMA HSDPA TDMA FDMA CDMA OFDMA
Communication Networks Chapter 9: UMTS
 Communication Networks Chapter 9: UMTS o IMT-2000 o UMTS Architecture o UTRAN Architecture o UMTS Mobility Support o UMTS Development UMTS and IMT-2000 Proposals for IMT-2000 (International Mobile Telecommunications)
Communication Networks Chapter 9: UMTS o IMT-2000 o UMTS Architecture o UTRAN Architecture o UMTS Mobility Support o UMTS Development UMTS and IMT-2000 Proposals for IMT-2000 (International Mobile Telecommunications)
UMTS: Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
 Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks UMTS: Universal Mobile Telecommunications System Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander
Department of Computer Science Institute for System Architecture, Chair for Computer Networks UMTS: Universal Mobile Telecommunications System Mobile Communication and Mobile Computing Prof. Dr. Alexander
Mobile Communications II Chapter 5: UMTS
 Mobile Communications II Chapter 5: UMTS Universal Mobile Communication System Overview/Standardisations Architecture Data services HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) UMTS Goal to create an Universal Personal
Mobile Communications II Chapter 5: UMTS Universal Mobile Communication System Overview/Standardisations Architecture Data services HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) UMTS Goal to create an Universal Personal
Lauri Pirttiaho, NMP/Oulu
 Contents: General about radio communications systems 3GPP WCDMA L1, the physical layer structure Transmitting and receiving Channels Codings Procedures Not included: Lauri Pirttiaho, NMP/Oulu diversity
Contents: General about radio communications systems 3GPP WCDMA L1, the physical layer structure Transmitting and receiving Channels Codings Procedures Not included: Lauri Pirttiaho, NMP/Oulu diversity
References. What is UMTS? UMTS Architecture
 1 References 2 Material Related to LTE comes from 3GPP LTE: System Overview, Product Development and Test Challenges, Agilent Technologies Application Note, 2008. IEEE Communications Magazine, February
1 References 2 Material Related to LTE comes from 3GPP LTE: System Overview, Product Development and Test Challenges, Agilent Technologies Application Note, 2008. IEEE Communications Magazine, February
HSPA & HSPA+ Introduction
 HSPA & HSPA+ Introduction www.huawei.com Objectives Upon completion of this course, you will be able to: Understand the basic principle and features of HSPA and HSPA+ Page1 Contents 1. HSPA & HSPA+ Overview
HSPA & HSPA+ Introduction www.huawei.com Objectives Upon completion of this course, you will be able to: Understand the basic principle and features of HSPA and HSPA+ Page1 Contents 1. HSPA & HSPA+ Overview
Le L c e t c ur u e e UMTS T S Uni n ve v r e sa s l a M ob o i b le e Te T l e ec e o c m. o Sy S s y t s em e I.
 Lecture 12 UMTS Universal Mobile Telecom. System What is UMTS? UMTS stands for Universal Mobile Telecommunication System It is a part of the ITU IMT-2000 vision of a global family of 3G mobile communication
Lecture 12 UMTS Universal Mobile Telecom. System What is UMTS? UMTS stands for Universal Mobile Telecommunication System It is a part of the ITU IMT-2000 vision of a global family of 3G mobile communication
Index. API 218 APL 47 Application testing 301 Automatic Gain Control See AGC. 3GPP 18, 208, 312 3GPP specifications 47, 48, 57, 208, 220, 243, 273
 Index 3GPP 18, 208, 312 3GPP specifications 47, 48, 57, 208, 220, 243, 273 AC 21, 237, 242, 263 Acquisition Indicator 217 Active set 240, 250, 285 Adjacent power leakage See APL Admission Control See AC
Index 3GPP 18, 208, 312 3GPP specifications 47, 48, 57, 208, 220, 243, 273 AC 21, 237, 242, 263 Acquisition Indicator 217 Active set 240, 250, 285 Adjacent power leakage See APL Admission Control See AC
ICT 5305 Mobile Communications. Lecture - 6 April Dr. Hossen Asiful Mustafa
 ICT 5305 Mobile Communications Lecture - 6 April 2016 Dr. Hossen Asiful Mustafa 4 types of handover 1 2 3 4 MS MS MS MS BTS BTS BTS BTS BSC BSC BSC MSC MSC Handover decision receive level BTS old receive
ICT 5305 Mobile Communications Lecture - 6 April 2016 Dr. Hossen Asiful Mustafa 4 types of handover 1 2 3 4 MS MS MS MS BTS BTS BTS BTS BSC BSC BSC MSC MSC Handover decision receive level BTS old receive
Part 7. B3G and 4G Systems
 Part 7. B3G and 4G Systems p. 1 Roadmap HSDPA HSUPA HSPA+ LTE AIE IMT-Advanced (4G) p. 2 HSPA Standardization 3GPP Rel'99: does not manage the radio spectrum efficiently when dealing with bursty traffic
Part 7. B3G and 4G Systems p. 1 Roadmap HSDPA HSUPA HSPA+ LTE AIE IMT-Advanced (4G) p. 2 HSPA Standardization 3GPP Rel'99: does not manage the radio spectrum efficiently when dealing with bursty traffic
Macro Diversity Combining Optimisation in HSPA Flat Architecture
 HELSINKI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Faculty of Electronics, Communication and Automation Department of Communications and Networking Macro Diversity Combining Optimisation in HSPA Flat Architecture Petri
HELSINKI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Faculty of Electronics, Communication and Automation Department of Communications and Networking Macro Diversity Combining Optimisation in HSPA Flat Architecture Petri
Background: Cellular network technology
 Background: Cellular network technology Overview 1G: Analog voice (no global standard ) 2G: Digital voice (again GSM vs. CDMA) 3G: Digital voice and data Again... UMTS (WCDMA) vs. CDMA2000 (both CDMA-based)
Background: Cellular network technology Overview 1G: Analog voice (no global standard ) 2G: Digital voice (again GSM vs. CDMA) 3G: Digital voice and data Again... UMTS (WCDMA) vs. CDMA2000 (both CDMA-based)
Mobile Comms. Systems. Radio Interface
 Radio Interface Multiple Access Techniques MuAT (1/23) The transmission of bidirectional information in duplex systems (uplink - UL - and downlink - DL - channels) can be done by dividing in: frequency:
Radio Interface Multiple Access Techniques MuAT (1/23) The transmission of bidirectional information in duplex systems (uplink - UL - and downlink - DL - channels) can be done by dividing in: frequency:
High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA)
 High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) HSDPA Background & Basics Principles: Adaptive Modulation, Coding, HARQ Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Resource Management: Fast Scheduling, Mobility Performance
High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) HSDPA Background & Basics Principles: Adaptive Modulation, Coding, HARQ Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Resource Management: Fast Scheduling, Mobility Performance
LTE systems: overview
 LTE systems: overview Luca Reggiani LTE overview 1 Outline 1. Standard status 2. Signal structure 3. Signal generation 4. Physical layer procedures 5. System architecture 6. References LTE overview 2 Standard
LTE systems: overview Luca Reggiani LTE overview 1 Outline 1. Standard status 2. Signal structure 3. Signal generation 4. Physical layer procedures 5. System architecture 6. References LTE overview 2 Standard
UMR UTC/CNRS Cellular Networks
 UMR UTC/CNRS 7253 www.hds.utc.fr Cellular Networks Enrico NATALIZIO enrico.natalizio@hds.utc.fr 1 Cellular networks - history Radio communication was invented by Nikola Tesla and Guglielmo Marconi: in
UMR UTC/CNRS 7253 www.hds.utc.fr Cellular Networks Enrico NATALIZIO enrico.natalizio@hds.utc.fr 1 Cellular networks - history Radio communication was invented by Nikola Tesla and Guglielmo Marconi: in
Outline / Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 18: Cellular: 1G, 2G, and 3G. Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS)
 Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 18: Cellular: 1G, 2G, and 3G 1G: AMPS 2G: GSM 2.5G: EDGE, CDMA 3G: WCDMA Peter Steenkiste Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17
Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 18: Cellular: 1G, 2G, and 3G 1G: AMPS 2G: GSM 2.5G: EDGE, CDMA 3G: WCDMA Peter Steenkiste Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17
Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel (EDCH) High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA)
 Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel (EDCH) High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA) EDCH Background & Basics Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Resource Management: Scheduling, Handover Performance Results Background
Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel (EDCH) High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA) EDCH Background & Basics Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Resource Management: Scheduling, Handover Performance Results Background
RADIO LINK ASPECT OF GSM
 RADIO LINK ASPECT OF GSM The GSM spectral allocation is 25 MHz for base transmission (935 960 MHz) and 25 MHz for mobile transmission With each 200 KHz bandwidth, total number of channel provided is 125
RADIO LINK ASPECT OF GSM The GSM spectral allocation is 25 MHz for base transmission (935 960 MHz) and 25 MHz for mobile transmission With each 200 KHz bandwidth, total number of channel provided is 125
CHAPTER 13 CELLULAR WIRELESS NETWORKS
 CHAPTER 13 CELLULAR WIRELESS NETWORKS These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial
CHAPTER 13 CELLULAR WIRELESS NETWORKS These slides are made available to faculty in PowerPoint form. Slides can be freely added, modified, and deleted to suit student needs. They represent substantial
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei 1393
 Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 GSM 2 GSM Architecture Frequency Band and Channels Frames in GSM Interfaces, Planes, and Layers of GSM Handoff Short Message Service (SMS) 3 subscribers
Mohammad Hossein Manshaei manshaei@gmail.com 1393 GSM 2 GSM Architecture Frequency Band and Channels Frames in GSM Interfaces, Planes, and Layers of GSM Handoff Short Message Service (SMS) 3 subscribers
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1. GSM and UMTS
 Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
Mobile Network Evolution Part 1 GSM and UMTS GSM Cell layout Architecture Call setup Mobility management Security GPRS Architecture Protocols QoS EDGE UMTS Architecture Integrated Communication Systems
WCDMA System Overview
 Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. WCDMA System Overview Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Table of Contents Background and Standardization of WCDMA WCDMA
Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. WCDMA System Overview Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Table of Contents Background and Standardization of WCDMA WCDMA
CS 6956 Wireless & Mobile Networks April 1 st 2015
 CS 6956 Wireless & Mobile Networks April 1 st 2015 The SIM Card Certain phones contain SIM lock and thus work only with the SIM card of a certain operator. However, this is not a GSM restriction introduced
CS 6956 Wireless & Mobile Networks April 1 st 2015 The SIM Card Certain phones contain SIM lock and thus work only with the SIM card of a certain operator. However, this is not a GSM restriction introduced
University of Twente. Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science (EEMCS) WCDMA Enhanced Uplink performance evaluation
 University of Twente Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science (EEMCS) WCDMA Enhanced Uplink performance evaluation Camilo Orejuela Mesa Master of Science in Telematics Thesis
University of Twente Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics and Computer Science (EEMCS) WCDMA Enhanced Uplink performance evaluation Camilo Orejuela Mesa Master of Science in Telematics Thesis
Chapter 5 3G Wireless Systems. Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar.
 Chapter 5 3G Wireless Systems Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar. Upgrade paths for 2G Technologies 2G IS-95 GSM- IS-136 & PDC 2.5G IS-95B HSCSD GPRS EDGE Cdma2000-1xRTT W-CDMA 3G Cdma2000-1xEV,DV,DO EDGE Cdma2000-3xRTT
Chapter 5 3G Wireless Systems Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar. Upgrade paths for 2G Technologies 2G IS-95 GSM- IS-136 & PDC 2.5G IS-95B HSCSD GPRS EDGE Cdma2000-1xRTT W-CDMA 3G Cdma2000-1xEV,DV,DO EDGE Cdma2000-3xRTT
WCDMA FDD Mode Transmitter. Dr. Chih-Peng Li ( 李 )
 WCDMA FDD Mode Transmitter Dr. Chih-Peng Li ( 李 ) Table of Contents Traditional Sequential ASIC Design Flow Introduction to WCDMA Transmitter Specifications WCDMA Network Architecture Physical Layer General
WCDMA FDD Mode Transmitter Dr. Chih-Peng Li ( 李 ) Table of Contents Traditional Sequential ASIC Design Flow Introduction to WCDMA Transmitter Specifications WCDMA Network Architecture Physical Layer General
IMT-2000/UMTS delivering full BWA
 IMT-2000/UMTS delivering full BWA Rémi THOMAS Directeur du projet réseau UMTS d Orange France Agenda 3G and IMT 2000 Family UMTS phase 1 principles From GSM to GSM/UMTS Key Technical Characteristics of
IMT-2000/UMTS delivering full BWA Rémi THOMAS Directeur du projet réseau UMTS d Orange France Agenda 3G and IMT 2000 Family UMTS phase 1 principles From GSM to GSM/UMTS Key Technical Characteristics of
Agilent Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations
 Agilent Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations Application Note 1355 DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder Conv. coder Rate matching Rate
Agilent Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations Application Note 1355 DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder Conv. coder Rate matching Rate
UMTS Radio Access Network Physical Layer. Fabrizio Tomatis
 UMTS Radio Access Network Physical Layer Fabrizio Tomatis Agenda 3G Standardization process 3GPP standardization committee ITU and frequency planning Physical layer principles Mapping of transport channels
UMTS Radio Access Network Physical Layer Fabrizio Tomatis Agenda 3G Standardization process 3GPP standardization committee ITU and frequency planning Physical layer principles Mapping of transport channels
17 Third generation mobile communication systems
 17 Third generation mobile communication systems 17.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous chapters we presented examples of existing mobile communication systems. Among the second generation systems there are
17 Third generation mobile communication systems 17.1 INTRODUCTION In the previous chapters we presented examples of existing mobile communication systems. Among the second generation systems there are
IS-95 /CdmaOne Standard. By Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar.
 IS-95 /CdmaOne Standard By Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar. CDMA Classification of CDMA Systems CDMA SYSTEMS CDMA one CDMA 2000 IS95 IS95B JSTD 008 Narrow Band Wide Band CDMA Multiple Access in CDMA: Each user is assigned
IS-95 /CdmaOne Standard By Mrs.M.R.Kuveskar. CDMA Classification of CDMA Systems CDMA SYSTEMS CDMA one CDMA 2000 IS95 IS95B JSTD 008 Narrow Band Wide Band CDMA Multiple Access in CDMA: Each user is assigned
CDMA & WCDMA (UMTS) AIR INTERFACE. ECE 2526-WIRELESS & CELLULAR COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Monday, June 25, 2018
 CDMA & WCDMA (UMTS) AIR INTERFACE ECE 2526-WIRELESS & CELLULAR COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Monday, June 25, 2018 SPREAD SPECTRUM OPTIONS (1) Fast Frequency Hopping (FFSH) Advantages: Has higher anti-jamming
CDMA & WCDMA (UMTS) AIR INTERFACE ECE 2526-WIRELESS & CELLULAR COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Monday, June 25, 2018 SPREAD SPECTRUM OPTIONS (1) Fast Frequency Hopping (FFSH) Advantages: Has higher anti-jamming
EDCH Background & Basics. Principles: scheduling, handover Performance Results
 Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel (EDCH) High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA) EDCH Background & Basics Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Principles: scheduling, handover Performance Results Background E-DCH
Enhanced Uplink Dedicated Channel (EDCH) High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA) EDCH Background & Basics Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Principles: scheduling, handover Performance Results Background E-DCH
MOBILE COMPUTING 4/8/18. Basic Call. Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN. CSE 40814/60814 Spring Transit. switch. Transit. Transit.
 MOBILE COMPUTING CSE 40814/60814 Spring 2018 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
MOBILE COMPUTING CSE 40814/60814 Spring 2018 Public Switched Telephone Network - PSTN Transit switch Transit switch Long distance network Transit switch Local switch Outgoing call Incoming call Local switch
Long Term Evolution (LTE)
 1 Lecture 13 LTE 2 Long Term Evolution (LTE) Material Related to LTE comes from 3GPP LTE: System Overview, Product Development and Test Challenges, Agilent Technologies Application Note, 2008. IEEE Communications
1 Lecture 13 LTE 2 Long Term Evolution (LTE) Material Related to LTE comes from 3GPP LTE: System Overview, Product Development and Test Challenges, Agilent Technologies Application Note, 2008. IEEE Communications
A NEW EFFICIENT HANDOVER ALGORITHM FOR MBMS ENABLED 3G MOBILE CELLULAR NETWORKS UNIVERSITY OF CYPRUS
 Master s Thesis A NEW EFFICIENT HANDOVER ALGORITHM FOR MBMS ENABLED 3G MOBILE CELLULAR NETWORKS Christopher Christophorou UNIVERSITY OF CYPRUS DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE December 2005 UNIVERSITY OF
Master s Thesis A NEW EFFICIENT HANDOVER ALGORITHM FOR MBMS ENABLED 3G MOBILE CELLULAR NETWORKS Christopher Christophorou UNIVERSITY OF CYPRUS DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE December 2005 UNIVERSITY OF
Introduction. Air Interface. LTE and UMTS Terminology and Concepts
 LTE and UMTS Terminology and Concepts By Chris Reece, Subject Matter Expert - 8/2009 UMTS and LTE networks are surprisingly similar in many respects, but the terms, labels and acronyms they use are very
LTE and UMTS Terminology and Concepts By Chris Reece, Subject Matter Expert - 8/2009 UMTS and LTE networks are surprisingly similar in many respects, but the terms, labels and acronyms they use are very
HSDPA Background & Basics Principles: Adaptive Modulation, Coding, HARQ Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Principles: Fast scheduling, Mobility
 High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) HSDPA Background & Basics Principles: Adaptive Modulation, Coding, HARQ Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Principles: Fast scheduling, Mobility Performance Results
High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) HSDPA Background & Basics Principles: Adaptive Modulation, Coding, HARQ Channels/ UTRAN Architecture Principles: Fast scheduling, Mobility Performance Results
Developing Mobile Applications
 Developing Mobile Applications GSM networks 1 carriers GSM 900 MHz 890-915 MHz 935-960 MHz up down 200 KHz 200 KHz 25 MHz 25 MHz 2 frequency reuse A D K B J L C H E G I F A 3 Reuse patterns 4/12 4 base
Developing Mobile Applications GSM networks 1 carriers GSM 900 MHz 890-915 MHz 935-960 MHz up down 200 KHz 200 KHz 25 MHz 25 MHz 2 frequency reuse A D K B J L C H E G I F A 3 Reuse patterns 4/12 4 base
GSM and WCDMA RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15. Lecture no: Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology
 RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15 Lecture no: 11 GSM and WCDMA Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2015-05-12 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Contents (Brief) history of mobile
RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15 Lecture no: 11 GSM and WCDMA Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 2015-05-12 Ove Edfors - ETIN15 1 Contents (Brief) history of mobile
CHAPTER 7 ROLE OF ADAPTIVE MULTIRATE ON WCDMA CAPACITY ENHANCEMENT
 CHAPTER 7 ROLE OF ADAPTIVE MULTIRATE ON WCDMA CAPACITY ENHANCEMENT 7.1 INTRODUCTION Originally developed to be used in GSM by the Europe Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), the AMR speech codec
CHAPTER 7 ROLE OF ADAPTIVE MULTIRATE ON WCDMA CAPACITY ENHANCEMENT 7.1 INTRODUCTION Originally developed to be used in GSM by the Europe Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), the AMR speech codec
RFCD 202: Introduction to W-CDMA
 RFCD 202: Introduction to W-CDMA Technical data is subject to change Copyright@2003 Agilent Technologies Printed on Dec. 4, 2002 5988-8504ENA This paper examines the core concepts of one operating mode
RFCD 202: Introduction to W-CDMA Technical data is subject to change Copyright@2003 Agilent Technologies Printed on Dec. 4, 2002 5988-8504ENA This paper examines the core concepts of one operating mode
WCDMA and cdma The Radio Interfaces for Future Mobile Multimedia Communications - Part II
 WCDMA and cdma2000 - The Radio Interfaces for Future Mobile Multimedia Communications - Part II Emre A. Yavuz 6.0 WCDMA The WCDMA scheme has been developed as a joint effort between ETSI and ARIB during
WCDMA and cdma2000 - The Radio Interfaces for Future Mobile Multimedia Communications - Part II Emre A. Yavuz 6.0 WCDMA The WCDMA scheme has been developed as a joint effort between ETSI and ARIB during
Chapter 8: GSM & CDAMA Systems
 Chapter 8: GSM & CDAMA Systems Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Second Generation (Digital) Cellular System Operated in 900 MHz band GSM is also operated in 1800 MHz band and this version of
Chapter 8: GSM & CDAMA Systems Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) Second Generation (Digital) Cellular System Operated in 900 MHz band GSM is also operated in 1800 MHz band and this version of
RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15. Lecture no: GSM and WCDMA. Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology
 RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15 Lecture no: 11 GSM and WCDMA Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 1 Contents (Brief) history of mobile telephony Global System for
RADIO SYSTEMS ETIN15 Lecture no: 11 GSM and WCDMA Ove Edfors, Department of Electrical and Information Technology Ove.Edfors@eit.lth.se 1 Contents (Brief) history of mobile telephony Global System for
ETSI TS V6.2.0 ( )
 TS 25 2 V6.2. (24-9) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Physical channels and mapping of transport channels onto physical channels (FDD) (3GPP TS 25.2 version 6.2.
TS 25 2 V6.2. (24-9) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Physical channels and mapping of transport channels onto physical channels (FDD) (3GPP TS 25.2 version 6.2.
Chapter 2: Global System for Mobile Communication
 Chapter 2: Global System for Mobile Communication (22 Marks) Introduction- GSM services and features, GSM architecture, GSM channel types, Example of GSM Call: GSM to PSTN call, PSTN to GSM call. GSM frame
Chapter 2: Global System for Mobile Communication (22 Marks) Introduction- GSM services and features, GSM architecture, GSM channel types, Example of GSM Call: GSM to PSTN call, PSTN to GSM call. GSM frame
Md. Firoz Hossain Abu Shadat Mohammad Sohab
 Mathematical Modelling of Call Admission Control in WCDMA Network Md. Firoz Hossain Abu Shadat Mohammad Sohab This thesis is presented as part of Degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering With
Mathematical Modelling of Call Admission Control in WCDMA Network Md. Firoz Hossain Abu Shadat Mohammad Sohab This thesis is presented as part of Degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering With
Keysight Technologies Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations (Including Femtocells)
 Keysight Technologies Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations (Including Femtocells) Application Note DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder
Keysight Technologies Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Transceiver Stations (Including Femtocells) Application Note DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder
3G Technologies. Outline. WCDMA, TD-(S)CDMA and cdma2000 Janne Kurjenniemi. Background. 3G technologies WCDMA TD-(S)CDMA. cdma2000
 3G Technologies WCDMA, TD-(S)CDMA and cdma2000 Janne Kurjenniemi 1 Magister Solutions 2006-11-02 / JKu Outline Background Why new radio access Frequency allocation Spread spectrum 3G technologies WCDMA
3G Technologies WCDMA, TD-(S)CDMA and cdma2000 Janne Kurjenniemi 1 Magister Solutions 2006-11-02 / JKu Outline Background Why new radio access Frequency allocation Spread spectrum 3G technologies WCDMA
APPLICATION PROGRAMMING: MOBILE COMPUTING [ INEA00112W ] Marek Piasecki PhD Wireless Telecommunication
![APPLICATION PROGRAMMING: MOBILE COMPUTING [ INEA00112W ] Marek Piasecki PhD Wireless Telecommunication APPLICATION PROGRAMMING: MOBILE COMPUTING [ INEA00112W ] Marek Piasecki PhD Wireless Telecommunication](/thumbs/82/86735605.jpg) APPLICATION PROGRAMMING: MOBILE COMPUTING [ INEA00112W ] Marek Piasecki PhD Wireless Telecommunication (W6/2013) What is Wireless Communication? Transmitting/receiving voice and data using electromagnetic
APPLICATION PROGRAMMING: MOBILE COMPUTING [ INEA00112W ] Marek Piasecki PhD Wireless Telecommunication (W6/2013) What is Wireless Communication? Transmitting/receiving voice and data using electromagnetic
Multi-User Communication
 Multi-User Communication Lecture 10 WCDMA Overview slide 1 Objective Introduce WCDMA from a systems perspective, but with a focus on lower layers (FDD mode) WCDMA Release 99 giving you, hopefully a technology
Multi-User Communication Lecture 10 WCDMA Overview slide 1 Objective Introduce WCDMA from a systems perspective, but with a focus on lower layers (FDD mode) WCDMA Release 99 giving you, hopefully a technology
IMT-2000 members UTRA-TDD and UTRA-FDD
 IMT-2000 members UTRA-TDD and UTRA-FDD Dr. Christian Menzel, SIEMENS AG christian.menzel@icn.siemens.de Author Siemens AG, Munich Siemens AG 2000 IMT-2000_UTRA_TDD_FDD_1 UTRA (FDD + TDD)! IMT-2000 and
IMT-2000 members UTRA-TDD and UTRA-FDD Dr. Christian Menzel, SIEMENS AG christian.menzel@icn.siemens.de Author Siemens AG, Munich Siemens AG 2000 IMT-2000_UTRA_TDD_FDD_1 UTRA (FDD + TDD)! IMT-2000 and
An Introduction to Wireless Technologies Part 2. F. Ricci
 An Introduction to Wireless Technologies Part 2 F. Ricci Content Medium access control (MAC): FDMA = Frequency Division Multiple Access TDMA = Time Division Multiple Access CDMA = Code Division Multiple
An Introduction to Wireless Technologies Part 2 F. Ricci Content Medium access control (MAC): FDMA = Frequency Division Multiple Access TDMA = Time Division Multiple Access CDMA = Code Division Multiple
Chapter 5 Acknowledgment:
 Chapter 5 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. Manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
Chapter 5 Acknowledgment: This material is based on the slides formatted by Dr Sunilkumar S. Manvi and Dr Mahabaleshwar S. Kakkasageri, the authors of the textbook: Wireless and Mobile Networks, concepts
ETSI SMG#24 TDoc SMG 903 / 97. December 15-19, 1997 Source: SMG2. Concept Group Alpha - Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA: System Description Summary
 ETSI SMG#24 TDoc SMG 903 / 97 Madrid, Spain Agenda item 4.1: UTRA December 15-19, 1997 Source: SMG2 Concept Group Alpha - Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA: System Description Summary Concept Group Alpha -
ETSI SMG#24 TDoc SMG 903 / 97 Madrid, Spain Agenda item 4.1: UTRA December 15-19, 1997 Source: SMG2 Concept Group Alpha - Wideband Direct-Sequence CDMA: System Description Summary Concept Group Alpha -
Chapter 7 GSM: Pan-European Digital Cellular System. Prof. Jang-Ping Sheu
 Chapter 7 GSM: Pan-European Digital Cellular System Prof. Jang-Ping Sheu Background and Goals GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) Beginning from 1982 European standard Full roaming in Europe
Chapter 7 GSM: Pan-European Digital Cellular System Prof. Jang-Ping Sheu Background and Goals GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) Beginning from 1982 European standard Full roaming in Europe
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing. Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
 CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Cellular Networks: 2.5G and 3G 2.5G Data services over 2G networks GSM: High-speed
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Cellular Networks: 2.5G and 3G 2.5G Data services over 2G networks GSM: High-speed
3G TECHNOLOGY WHICH CAN PROVIDE AUGMENTED DATA TRANSFER RATES FOR GSM STANDARTS AND THE MODULATION TECHNIQUES
 3G TECHNOLOGY WHICH CAN PROVIDE AUGMENTED DATA TRANSFER RATES FOR GSM STANDARTS AND THE MODULATION TECHNIQUES Mustafa ALKAN Ejder ORUÇ Nur ERZEN Özgür GENÇ malkan@tk.gov.tr eoruc@tk.gov.tr nerzen@tk.gov.tr
3G TECHNOLOGY WHICH CAN PROVIDE AUGMENTED DATA TRANSFER RATES FOR GSM STANDARTS AND THE MODULATION TECHNIQUES Mustafa ALKAN Ejder ORUÇ Nur ERZEN Özgür GENÇ malkan@tk.gov.tr eoruc@tk.gov.tr nerzen@tk.gov.tr
UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN)
 UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) UTRAN Architecture and Protocols UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (UTRA) UTRAN Procedures (see separate presentation) Important References Books: Kaaranen, Ahtiainen,
UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN) UTRAN Architecture and Protocols UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (UTRA) UTRAN Procedures (see separate presentation) Important References Books: Kaaranen, Ahtiainen,
Radio Network Controller for HSDPA. Abstract
 HSDPA Radio Network Controller for HSDPA HSDPA High Speed Downlink Packet AccessW-CDMA 14.4 Mbps RNCHSDPA HSDPA Abstract High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) technology provides a maximum data transfer
HSDPA Radio Network Controller for HSDPA HSDPA High Speed Downlink Packet AccessW-CDMA 14.4 Mbps RNCHSDPA HSDPA Abstract High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) technology provides a maximum data transfer
HSDPA SYSTEM SIMULATION
 Thesis Number: MEE05:30 HSDPA SYSTEM SIMULATION Nguyen Kim Cuong Khan Muhammad Sohaib This thesis is presented as part of Degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering Blekinge Institute of Technology
Thesis Number: MEE05:30 HSDPA SYSTEM SIMULATION Nguyen Kim Cuong Khan Muhammad Sohaib This thesis is presented as part of Degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering Blekinge Institute of Technology
LTE (Long Term Evolution)
 LTE (Long Term Evolution) Assoc. Prof. Peter H J Chong, PhD (UBC) School of EEE Nanyang Technological University Office: +65 6790 4437 E-mail: ehjchong@ntu.edu.sg 2 Outline Introduction SAE (System Architecture
LTE (Long Term Evolution) Assoc. Prof. Peter H J Chong, PhD (UBC) School of EEE Nanyang Technological University Office: +65 6790 4437 E-mail: ehjchong@ntu.edu.sg 2 Outline Introduction SAE (System Architecture
Channelisation Codes (2)
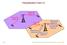 Channelisation Codes (2) Scram. #0 +Chan. #1 Scram. #0 +Chan. #0 Scram. #1 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #1 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #1 +Chan. #1 R.Scram. #0 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #0 +Chan. #1 p. 51 Channelisation Codes (3)
Channelisation Codes (2) Scram. #0 +Chan. #1 Scram. #0 +Chan. #0 Scram. #1 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #1 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #1 +Chan. #1 R.Scram. #0 +Chan. #0 R.Scram. #0 +Chan. #1 p. 51 Channelisation Codes (3)
Contents. UMTS Radio Access Network (UTRAN) UTRAN Architecture. Refresher: Some concepts. UTRAN Bearer Architecture.
 Contents UMTS Radio Access Network (UTRAN) T-110.498 UMTS Networks Chapter 4 Päivi Savola 4.2.2003 UTRAN Architecture Base Station Radio Network Controller Radio Resource Management, QoS Control Functions
Contents UMTS Radio Access Network (UTRAN) T-110.498 UMTS Networks Chapter 4 Päivi Savola 4.2.2003 UTRAN Architecture Base Station Radio Network Controller Radio Resource Management, QoS Control Functions
UTRAN Radio Resource Management
 UTRAN Radio Resource Management BTS 3 BTS 1 UE BTS 2 Introduction Handover Control Soft/Softer Handover Inter Frequency Handover Power Control Closed Loop Power Control Open Loop Power Control Interference
UTRAN Radio Resource Management BTS 3 BTS 1 UE BTS 2 Introduction Handover Control Soft/Softer Handover Inter Frequency Handover Power Control Closed Loop Power Control Open Loop Power Control Interference
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture. Outline. Introduction. Cont. Chapter 1: Introduction
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 1: Introduction Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Sep. 2006 Outline Introduction
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 1: Introduction Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Sep. 2006 Outline Introduction
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
 Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 1: Introduction Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Sep. 2006 1 Outline Introduction
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture Chapter 1: Introduction Prof. Yuh-Shyan Chen Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taipei University Sep. 2006 1 Outline Introduction
WCDMA UMTS Radio Access for Third Generation Mobile Communications Third Edition
 WCDMA UMTS Radio Access for Third Generation Mobile Communications Third Edition Edited by Harri Holma and Antti Toskala Both of Nokia, Finland John Wiley & Sons, Ltd Contents Preface Acknowledgements
WCDMA UMTS Radio Access for Third Generation Mobile Communications Third Edition Edited by Harri Holma and Antti Toskala Both of Nokia, Finland John Wiley & Sons, Ltd Contents Preface Acknowledgements
UTRAN Radio Resource Management
 UTRAN Radio Resource Management BTS 3 Introduction Handover Control Soft/Softer Handover Inter Frequency Handover Power Control UE BTS 2 Closed Loop Power Control Open Loop Power Control Interference Management
UTRAN Radio Resource Management BTS 3 Introduction Handover Control Soft/Softer Handover Inter Frequency Handover Power Control UE BTS 2 Closed Loop Power Control Open Loop Power Control Interference Management
Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Stations
 Agilent Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Stations Application Note 1355 DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder Conv. coder Rate matching Rate matching Interleaver
Agilent Designing and Testing 3GPP W-CDMA Base Stations Application Note 1355 DTCH data bits DCCH data bits Add CRC & tail bits Add CRC & tail bits Conv. coder Conv. coder Rate matching Rate matching Interleaver
LTE Aida Botonjić. Aida Botonjić Tieto 1
 LTE Aida Botonjić Aida Botonjić Tieto 1 Why LTE? Applications: Interactive gaming DVD quality video Data download/upload Targets: High data rates at high speed Low latency Packet optimized radio access
LTE Aida Botonjić Aida Botonjić Tieto 1 Why LTE? Applications: Interactive gaming DVD quality video Data download/upload Targets: High data rates at high speed Low latency Packet optimized radio access
ETSI TS V7.1.0 ( )
 TS 125 308 V7.1.0 (2006-12) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA); Overall description; Stage 2 (3GPP TS 25.308 version 7.1.0
TS 125 308 V7.1.0 (2006-12) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA); Overall description; Stage 2 (3GPP TS 25.308 version 7.1.0
A Simulation Tool for Third Generation CDMA Systems Presentation to IEEE Sarnoff Symposium
 A Simulation Tool for Third Generation CDMA Systems Presentation to IEEE Sarnoff Symposium March 22, 2000 Fakhrul Alam, William Tranter, Brian Woerner Mobile and Portable Radio Research Group () e-mail:
A Simulation Tool for Third Generation CDMA Systems Presentation to IEEE Sarnoff Symposium March 22, 2000 Fakhrul Alam, William Tranter, Brian Woerner Mobile and Portable Radio Research Group () e-mail:
Specific Systems Cellular. Part 1 #12
 Specific Systems Cellular Part 1 #12 Victor S. Frost Dan F. Servey Distinguished Professor Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Kansas 2335 Irving Hill Dr. Lawrence, Kansas 66045 Phone:
Specific Systems Cellular Part 1 #12 Victor S. Frost Dan F. Servey Distinguished Professor Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Kansas 2335 Irving Hill Dr. Lawrence, Kansas 66045 Phone:
Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. part 1: General considerations. Agenda
 Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. part 1: General considerations Agenda Mobile Networks Standards Network Architectures Call Set Up Network Roll Out Site Equipment Distributed
Dimensioning, configuration and deployment of Radio Access Networks. part 1: General considerations Agenda Mobile Networks Standards Network Architectures Call Set Up Network Roll Out Site Equipment Distributed
Communication Systems GSM
 Communication Systems GSM Computer Science Organization I. Data and voice communication in IP networks II. Security issues in networking III. Digital telephony networks and voice over IP 2 last to final
Communication Systems GSM Computer Science Organization I. Data and voice communication in IP networks II. Security issues in networking III. Digital telephony networks and voice over IP 2 last to final
UTRAN Radio Resource Management
 UTRAN Radio Resource Management BTS 3 BTS 1 UE BTS 2 Introduction Handover Control Soft/Softer Handover Inter Frequency Handover Power Control Closed Loop Power Control Open Loop Power Control Interference
UTRAN Radio Resource Management BTS 3 BTS 1 UE BTS 2 Introduction Handover Control Soft/Softer Handover Inter Frequency Handover Power Control Closed Loop Power Control Open Loop Power Control Interference
ETSI TS V ( )
 TS 125 302 V3.11.0 (2001-12) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Services provided by the physical layer (3GPP TS 25.302 version 3.11.0 Release 1999) 1 TS 125 302
TS 125 302 V3.11.0 (2001-12) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); Services provided by the physical layer (3GPP TS 25.302 version 3.11.0 Release 1999) 1 TS 125 302
Enhanced High-Speed Packet Access HSPA+ Background: HSPA Evolution Higher Data Rates Signaling Improvements Architecture Evolution/ Home NodeB
 Enhanced High-Speed Packet Access HSPA+ Background: HSPA Evolution Higher Data Rates Signaling Improvements Architecture Evolution/ Home NodeB HSPA+ (HSPA Evolution) Background For operators deploying
Enhanced High-Speed Packet Access HSPA+ Background: HSPA Evolution Higher Data Rates Signaling Improvements Architecture Evolution/ Home NodeB HSPA+ (HSPA Evolution) Background For operators deploying
Satellite Digital Multimedia Broadcast system for Public Protection Disaster Recovery mission
 Satellite Digital Multimedia Broadcast system for Public Protection Disaster Recovery mission B. Martin (beatrice.martin@space.alcatel.fr) MG. Françon*, C. Nussli*, JD. Gayrard*, N. Chuberre* Alcatel Space
Satellite Digital Multimedia Broadcast system for Public Protection Disaster Recovery mission B. Martin (beatrice.martin@space.alcatel.fr) MG. Françon*, C. Nussli*, JD. Gayrard*, N. Chuberre* Alcatel Space
Enhanced High-Speed Packet Access HSPA+ Background: HSPA Evolution Higher Data Rates Signaling Improvements Architecture Evolution/ Home NodeB
 Enhanced High-Speed Packet Access HSPA+ Background: HSPA Evolution Higher Data Rates Signaling Improvements Architecture Evolution/ Home NodeB HSPA+ The evolution of UMTS HSPA Corresponding to UMTS Release
Enhanced High-Speed Packet Access HSPA+ Background: HSPA Evolution Higher Data Rates Signaling Improvements Architecture Evolution/ Home NodeB HSPA+ The evolution of UMTS HSPA Corresponding to UMTS Release
Vocoder RNS RNC. Node B. Node B UE2. Figure 1. Synchronisation issues model.
 TSG-RAN Working Group 2 (Radio layer 2 and Radio layer 3) TSGR2#2(99) 90 Stockholm 8 th to 11 th March 1999 Agenda Item: 8.7 Source: Title: Nokia UTRAN Synchronisation Document for: FYI [This contribution
TSG-RAN Working Group 2 (Radio layer 2 and Radio layer 3) TSGR2#2(99) 90 Stockholm 8 th to 11 th March 1999 Agenda Item: 8.7 Source: Title: Nokia UTRAN Synchronisation Document for: FYI [This contribution
3GPP: Evolution of Air Interface and IP Network for IMT-Advanced. Francois COURAU TSG RAN Chairman Alcatel-Lucent
 3GPP: Evolution of Air Interface and IP Network for IMT-Advanced Francois COURAU TSG RAN Chairman Alcatel-Lucent 1 Introduction Reminder of LTE SAE Requirement Key architecture of SAE and its impact Key
3GPP: Evolution of Air Interface and IP Network for IMT-Advanced Francois COURAU TSG RAN Chairman Alcatel-Lucent 1 Introduction Reminder of LTE SAE Requirement Key architecture of SAE and its impact Key
Page 1. Problems with 1G Systems. Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs) EEC173B/ECS152C, Spring Cellular Wireless Network
 EEC173B/ECS152C, Spring 2009 Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs) Cellular Wireless Network Architecture and Protocols Applying concepts learned in first two weeks: Frequency planning, channel allocation
EEC173B/ECS152C, Spring 2009 Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANs) Cellular Wireless Network Architecture and Protocols Applying concepts learned in first two weeks: Frequency planning, channel allocation
ETSI TS V4.2.0 ( )
 TS 125 401 V4.2.0 (2001-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); UTRAN Overall Description (3GPP TS 25.401 version 4.2.0 Release 4) 1 TS 125 401 V4.2.0 (2001-09) Reference
TS 125 401 V4.2.0 (2001-09) Technical Specification Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); UTRAN Overall Description (3GPP TS 25.401 version 4.2.0 Release 4) 1 TS 125 401 V4.2.0 (2001-09) Reference
2G Mobile Communication Systems
 2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
2G Mobile Communication Systems 2G Review: GSM Services Architecture Protocols Call setup Mobility management Security HSCSD GPRS EDGE References Jochen Schiller: Mobile Communications (German and English),
BASIC CONCEPTS OF HSPA
 284 23-3087 Uen Rev A BASIC CONCEPTS OF HSPA February 2007 White Paper HSPA is a vital part of WCDMA evolution and provides improved end-user experience as well as cost-efficient mobile/wireless broadband.
284 23-3087 Uen Rev A BASIC CONCEPTS OF HSPA February 2007 White Paper HSPA is a vital part of WCDMA evolution and provides improved end-user experience as well as cost-efficient mobile/wireless broadband.
