DR. - ING. ARTUR SEIBT Lagergasse 2/6 A 1030 Wien (Vienna) Austria
|
|
|
- Jasper Godfrey Daniels
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DR. - ING. ARTUR SEIBT Lagergasse 2/6 A 1030 Wien (Vienna) Austria Tel Fax GSM A GSM D dr.seibt@aon.at Fachartikel, erscheint in "Bodo's Power Nov. 14" " The Nichols Chart - the superior practical tool for design and test of the stability of feedback amplifiers and control systems like SMPS." Zwischenüberschrift: "Comprehensive articles and books about feedback loop design and test abound, Bode Plots and Nyquist Diagrams, both highly impractical, are discussed at great length and recommended, while the superior Nichols Chart is hardly ever mentioned."
2 2 This article was triggered by the article "Three stability assessment methods every engineer should know about" in "Bodo's Power, July 2014, p. 50. The statements of the author about the shortcomings of the Bode Plots are to the point. The purpose of this article is to present the Nichols Chart, invented by the American engineer Nathaniel Nichols in 1947, as the superior practical method. It overcomes the disadvantages of the other methods and can be used without knowledge of Function Theory and Complex Variables. Its application does not require special instruments nor software, the results are obvious, easy to interpret und directly applicable to the design and test of feedback systems. 1. Stability, wild oscillations, the necessity of tests. Feedback amplifiers and control systems can oscillate if the time delay between the input and feedback signals becomes too great. For practical applications it is necessary to know the kind and degree of static and dynamic stability. The former is obtained by measuring Nichols Charts (or equivalent, however less practical, plots), the latter by testing the transient response. A word of caution: by no means will wild oscillations always be apparent! If the output voltages of a SMPS or other voltage regulator seem to be all right on a voltmeter, this is no proof of proper function or acceptable stability. Many SMPS oscillate in the application without that this is detected because the average output voltages remain constant. Also, an audio amplifier may seem to function while oscillating far above the audio band. Examples of other causes of oscillations: the negative input resistance of SMPS can produce oscillations which have nothing to do with the regulation loop; the negative input impedance of circuits like emitter followers may cause oscillations in the hundreds of MHz, active components such as power mosfet's may also oscillate in the hundred MHz region. In all these cases some parasitic inductance is enough. The use of a scope is required, but not all scopes are capable of detecting hf oscillations, also passive probes exhibit very low input impedances at high frequencies which can damp oscillations so far that they stop when the probe is connected! In practice, wild oscillations of SMPS will show up on the scope and mostly also acoustically, because the bandwidth of the loops is predominantly in the audio range, the sound will be emitted by the ferrite cores and some ceramic capacitors. The test with the scope is only negative, i.e. if there are oscillations, the circuit is unstable, but if none are visible, this will be no proof of stability; the circuit may be on the verge of instability, and a small change of load, temperature or input voltage can suffice. Especially awkward are oscillations which occur only when a circuit is actually driven. Example: an amplifier may seem stable at rest, but when it is driven e.g. by a sine wave signal, oscillations will appear during portions of the waveform. Transient tests by load steps from electronic loads which apply periodic steps are too mild and can not uncover hidden problems. It is necessary to apply stochastic steps, both in amplitude and time. The decay transients will often superimpose which overdrives the loop amplifier; the result are sudden very high and long excursions of the output voltage, far in excess of the excursions caused by periodic loads! Sensitive loads like microcomputers dislike excessive supply voltage deviations and may malfunction. Another example are "dc" motor loads; dc motors draw high ac currents, much to the surprise of many engineers who only designed for the average current. Not only must the demand by the positive peak currents be met, the negative peak currents must also be accepted by the SMPS, this can lead to the outbreak of oscillations or even a temporary interruption of the regulation loop. Textbooks generally talk about the design and test of "the" stability plot. In the real world the static and dynamic stability depend on: 1. Component tolerances, temperature and long term behaviour, 2. The load, 3. Often also the input voltage. Consequently, a professional design requires that a set of stability plots is compiled and transient tests performed for several temperature and load combinations - at least!
3 3 1. The design engineer has to design in and verify a sufficient stability margin, taking into account the tolerances and temperature dependencies of all vital components. Example: electrolytic capacitors are notorious troublemakers: their tolerances of typ to + 50 % are only valid when new and at 20 degr. C, the capacitance value depends strongly on temperature and decreases sharply at low temperatures, with time, it will be reduced by loss of electrolyte. The ESR, mostly important for stability, drops with increasing temperature and rises with age. This can result in an amplifier or SMPS being stable at 20 degr. C and starting to oscillate after warming up. The manufacturers guarantee only a maximum ESR. Thus SMPS may suddenly oscillate in production after a batch of "better" capacitors was installed. Due to the exponential dependence of life on the internal temperature, electrolytics constitute the main cause of SMPS failures resp. cause the onset of oscillations with age. 2. Between light and high load several parameters of SMPS change, ripple increases which can overdrive the loop amplifier and cause nonlinear behaviour, rarely understood. Inductive components may approach saturation. 3. The influence of the input voltage depends on the circuit configuration chosen. Examples: With the simple buck regulator the influence is greatest, with a flyback using current-mode control it is least. For completeness, it should be mentioned that wild oscillations vary all over the map: from mild oscillations which do not interfere with the delivery of power to destructive ones which, once initiated, destroy the SMPS immediately. Therefore weak oscillations should always be regarded as a warning sign, and the SMPS taken out of service, because they can build up to destruction, and many SMPS components can burn and emit obnoxious gases. 2. Theory and Practice. Starting with Strecker 1931, Nyquist 1932 and Dr. Bode's famous book 1945, the ground work of feedback and linear control systems theory was laid by the 60's. These texts, typically covering several hundred pages, request the readers' knowledge of higher mathematics. There are basically two approaches to stability prediction: Some methods assume that the system response can be described by a set of equations, stability is then analysed by purely mathematical methods. These methods ignore the complexity of the real world, assuming that practical circuits comply with equations. The mathematical treatment ignores amplitudes, dynamic ranges, nonlinearities, overdrive, limiting, the properties of semiconductors, passive components, parasitic components, to name a few. In the case of SMPS ripple and its effects are disregarded, and the fact that all SMPS are sampling systems and its implications are seldomly mentioned. If transfer functions are not available, Nyquist, Bode or Nichols plots can be obtained and graphed from frequency response data gained from measurements of the real system. Dr. Bode was a mathematician at the Bell Labs with an astounding understanding of electronics engineering. He realized that real-world electronics systems and their components are far from ideal, also, that complex numbers are a mathematical construct useful for describing electrical phenomena, but that in the real world there are neither imaginary components nor measuring results, hence that all plots in the complex plane are impractical. He was first to introduce a representation in engineering units, the pair of "Bode plots" in which the results of amplitude or gain and phase measurements are entered directly in db and degrees. His plots can be used without reference to or knowledge of Function Theory and Complex Variables.
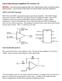
4 Although more practical than Nyquist, the Bode Plots suffer from the division into two separate plots. It is obvious whether a system is stable or not, but it is far from easy to read from the pair of plots which changes to a circuit or system have to be made to stabilize it or to improve the margins, nor are critical frequencies obvious. 3. The Nichols Chart. 4 Nichols recognized the shortcomings of the Nyquist and Bode plots and performed the logical step further. It is hard to understand why Bode Plots are strongly advertised in most textbooks while the superior Nichols Chart is rarely mentioned. It is derived from the Nyquist plot by conformal mapping into rectangular real coordinates. It combines the advantages of the Nyquist plot and the Bode plot pair. The frequency is the parameter along the curve from right to left. The list of advantages is impressive: 1. The whole information is concentrated in one curve as in the Nyquist plot, but on a real rectanguar coordinate system with db and degree axes as in the Bode plots, so that measurement results can be entered directly; no calculations necessary, no knowledge of higher mathematics. 2. Every full revolution of the Nyquist plot is mapped onto another 360 degree wide half plane in parallel to the vertical axis such that it can be extended on the left as needed. Nyquist plots of complicated circuits are almost impossible to interpret, in the Nichols representation the interwoven Nyquist curve is so to speak unfolded into the left half planes and easy to interpret. 3. Gain and phase margins can be read directly, and, like in the Nyquist plot, the closest distances to the critical frequencies. Necessary changes to the circuit in order to stabilize or improve stability margins are immediately and clearly obvious. 4. Due to the logarithmic vertical scale any gain change just needs a vertical shift. 5. Nichols Charts are powerful tools for determining closed loop response from open loop measurements. On the other hand, open loop measurements are often impossible because the gain and the offset drift of the amplifier may be so high that no input signal can be applied without saturating it. In such cases Nichols Charts can be used to convert closed loop measurements to open loop responses. Open loop measurements are entered into the rectangular grid, a second grid of contour lines for gain and phase is overlaid from which the closed loop response can be read; closed loop gain is obtained from the gain contour which the curve touches, and the phase from the phase contour which it intersects. Fig. 1: Example of a Nichols Plot, showing how the gain and phase margins can be directly read from the diagram: the phase margin is the distance from the intersection of the curve with the 0 db axis and the critical degree point, here 35 degrees. The gain margin is the vertical distance between the degree - point and the intersection between a vertical line through the degree - point and the curve, here 15 db. The frequency is the parameter along the curve from right to left. The minimum distance between the degr. point and the curve indicates the critical frequency.
5 5 Fig. 2: The Nichols Chart with closed loop gain and phase contour lines overlaid on the rectangular coordinate system for the open loop response. Further information about the Nichols Chart can be found in older literature. 4. Some remarks on design and test of SMPS. Design of feedback circuits It is not the purpose of this article, but it should be emphasized that the design and test of a SMPS loop is a fairly simple task and requires only a minute fraction of the whole design time, this is also true for nested loops as they are used e.g. in current-mode control. Too many texts exaggerate and inflate the task. The simple mathematical models rarely reflect the real world. The assumption of linear operation, e.g., is bold, disregarding the facts that SMPS are sampling systems and that there are such ugly phenomena as hf ripple, magnetic and capacitive interference, coupling due to poor e.c. board layout, nonlinear, voltage- and temperature-dependent properties of components etc. It does not make sense to even think about loop design before the whole circuit design and layout has been perfected so much that all such influences on the loop have been minimized! Example: the disastrous effects of hf ripple on the loop amplifier are seldomly recognized; most are of the simple lf LM 224 op amp type. Such amplifiers can not digest 100 KHz+ ripple and saturate already at very low levels which results in highly nonlinear behaviour. This is aggravated by any lead compensation because this boasts high frequencies. As the ripple is load-dependent, loop behaviour may be acceptable at low load, but goes out of
6 6 control at high load. By and large it can be said from decades of experience: if a loop proves difficult to stabilize, something is very wrong in the whole design and layout which should be remedied instead of trying more complicated "loop compensations". The gist of it is: there is no way around testing and obtaining the Nichols Charts for all important modes of operation resp. loads and at a minimum of 3 typical temperatures. The proof of the pudding is the transient behaviour for various (stochastic) load steps. As the latter is simpler and takes the least time, it is practical to first design for an optimum transient performance and then measure the Nichols Charts. There is another good reason for this procedure: it is difficult to predict the transient performance from the Nichols (or other) Charts which can cause time-consuming iterations. It should be noted that the static and dynamic performance of a well designed SMPS is excellent and hardly inferior to that of a linear regulator - despite so many statements of the contrary. 5. Some measuring problems. Quite often, with amplifiers, it is necessary to measure amplitude and phase far into the MHz range, although the frequency range of interest is only audio, because it is necessary to get the curve in the vicinity of the critical point. SMPS are sampling systems with an optimum operating frequency range between 100 and 250 KHz, the bandwidth of the control loop has to stay well below half the clock frequency. As mentioned, loop amplifiers are mostly of the lf LM 224 type, the undistorted output amplitude decreases fast with increasing frequency; it is safe to assume that the available swing decreases along with the frequency response. The input test signal must be accordingly reduced, otherwise the amplifier will saturate, the measurement be grossly in error! This a dangerous pitfall. The signal-to-noise ratio will become poor, noise, flicker, SMPS ripple, hf interference will crop up. Standard ac voltage measuring instruments are wideband and will - depending on their measuring principle - measure the interference as well. Filters would improve the amplitude measurement but upset the phase. Gain - Phase - Meters or Network Analyzers will accept signals with a fairly poor S/N ratio, but it is best to always check the signals with a scope! When the S/N ratio becomes really poor, the scope remains the last resort for performing such measurements, because even if the picture is corrupted by noise, flicker, hf etc., it is still possible to see the signal and to estimate the amplitude. For measuring phase never use XY plots but the two-channel mode with triggering from one channel. Phase is nothing else but time difference and can be measured with high resolution by overdriving the inputs, mark the zero crossings and selecting faster time base settings. And the time difference can still be estimated even if interference is present!
7 7
Testing Power Sources for Stability
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, oscillator, power source, stability testing, feedback loop, error amplifier compensation, impedance, output voltage, transfer function, gain crossover, bode
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, oscillator, power source, stability testing, feedback loop, error amplifier compensation, impedance, output voltage, transfer function, gain crossover, bode
Positive Feedback and Oscillators
 Physics 3330 Experiment #5 Fall 2011 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
Physics 3330 Experiment #5 Fall 2011 Positive Feedback and Oscillators Purpose In this experiment we will study how spontaneous oscillations may be caused by positive feedback. You will construct an active
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
Specify Gain and Phase Margins on All Your Loops
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, power supply, gain and phase margins, feedback loop, open-loop gain, output capacitance, stability margins, oscillator, power electronics circuits, voltmeter,
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, power supply, gain and phase margins, feedback loop, open-loop gain, output capacitance, stability margins, oscillator, power electronics circuits, voltmeter,
Linear Regulators: Theory of Operation and Compensation
 Linear Regulators: Theory of Operation and Compensation Introduction The explosive proliferation of battery powered equipment in the past decade has created unique requirements for a voltage regulator
Linear Regulators: Theory of Operation and Compensation Introduction The explosive proliferation of battery powered equipment in the past decade has created unique requirements for a voltage regulator
Constant Current Control for DC-DC Converters
 Constant Current Control for DC-DC Converters Introduction...1 Theory of Operation...1 Power Limitations...1 Voltage Loop Stability...2 Current Loop Compensation...3 Current Control Example...5 Battery
Constant Current Control for DC-DC Converters Introduction...1 Theory of Operation...1 Power Limitations...1 Voltage Loop Stability...2 Current Loop Compensation...3 Current Control Example...5 Battery
9 Feedback and Control
 9 Feedback and Control Due date: Tuesday, October 20 (midnight) Reading: none An important application of analog electronics, particularly in physics research, is the servomechanical control system. Here
9 Feedback and Control Due date: Tuesday, October 20 (midnight) Reading: none An important application of analog electronics, particularly in physics research, is the servomechanical control system. Here
Measuring LDOs requires more bandwidth than you think
 Measuring LDOs requires more bandwidth than you think by Bernhard Baumgartner, OMICRON Lab, and Steve Sandler and Charles Hymowitz, AEi Systems, Los Angeles, Calif. Most electronic systems contain at least
Measuring LDOs requires more bandwidth than you think by Bernhard Baumgartner, OMICRON Lab, and Steve Sandler and Charles Hymowitz, AEi Systems, Los Angeles, Calif. Most electronic systems contain at least
Chapter 13: Comparators
 Chapter 13: Comparators So far, we have used op amps in their normal, linear mode, where they follow the op amp Golden Rules (no input current to either input, no voltage difference between the inputs).
Chapter 13: Comparators So far, we have used op amps in their normal, linear mode, where they follow the op amp Golden Rules (no input current to either input, no voltage difference between the inputs).
LFR: flexible, clip-around current probe for use in power measurements
 LFR: flexible, clip-around current probe for use in power measurements These technical notes should be read in conjunction with the LFR short-form datasheet. Power Electronic Measurements Ltd Nottingham
LFR: flexible, clip-around current probe for use in power measurements These technical notes should be read in conjunction with the LFR short-form datasheet. Power Electronic Measurements Ltd Nottingham
E Typical Application and Component Selection AN 0179 Jan 25, 2017
 1 Typical Application and Component Selection 1.1 Step-down Converter and Control System Understanding buck converter and control scheme is essential for proper dimensioning of external components. E522.41
1 Typical Application and Component Selection 1.1 Step-down Converter and Control System Understanding buck converter and control scheme is essential for proper dimensioning of external components. E522.41
LDO Regulator Stability Using Ceramic Output Capacitors
 LDO Regulator Stability Using Ceramic Output Capacitors Introduction Ultra-low ESR capacitors such as ceramics are highly desirable because they can support fast-changing load transients and also bypass
LDO Regulator Stability Using Ceramic Output Capacitors Introduction Ultra-low ESR capacitors such as ceramics are highly desirable because they can support fast-changing load transients and also bypass
BUCK Converter Control Cookbook
 BUCK Converter Control Cookbook Zach Zhang, Alpha & Omega Semiconductor, Inc. A Buck converter consists of the power stage and feedback control circuit. The power stage includes power switch and output
BUCK Converter Control Cookbook Zach Zhang, Alpha & Omega Semiconductor, Inc. A Buck converter consists of the power stage and feedback control circuit. The power stage includes power switch and output
Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Lesson Four Lesson Five PREVIEW COPY
 Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
HAMEG EMI measurement tools
 HAMEG EMI measurement tools Whoever sells an electric or electronic instrument or apparatus within the EWR must conform to the European Union Directives on Electromagnetic Compatibility, EMC. This applies
HAMEG EMI measurement tools Whoever sells an electric or electronic instrument or apparatus within the EWR must conform to the European Union Directives on Electromagnetic Compatibility, EMC. This applies
ECEN 474/704 Lab 5: Frequency Response of Inverting Amplifiers
 ECEN 474/704 Lab 5: Frequency Response of Inverting Amplifiers Objective Design, simulate and layout various inverting amplifiers. Introduction Inverting amplifiers are fundamental building blocks of electronic
ECEN 474/704 Lab 5: Frequency Response of Inverting Amplifiers Objective Design, simulate and layout various inverting amplifiers. Introduction Inverting amplifiers are fundamental building blocks of electronic
Testing and Stabilizing Feedback Loops in Today s Power Supplies
 Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, open loop transfer function, voltage loop gain, error amplifier,
Keywords Venable, frequency response analyzer, impedance, injection transformer, oscillator, feedback loop, Bode Plot, power supply design, open loop transfer function, voltage loop gain, error amplifier,
Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06)
 Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
When input, output and feedback voltages are all symmetric bipolar signals with respect to ground, no biasing is required.
 1 When input, output and feedback voltages are all symmetric bipolar signals with respect to ground, no biasing is required. More frequently, one of the items in this slide will be the case and biasing
1 When input, output and feedback voltages are all symmetric bipolar signals with respect to ground, no biasing is required. More frequently, one of the items in this slide will be the case and biasing
PURPOSE: NOTE: Be sure to record ALL results in your laboratory notebook.
 EE4902 Lab 9 CMOS OP-AMP PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to measure the closed-loop performance of an op-amp designed from individual MOSFETs. This op-amp, shown in Fig. 9-1, combines all of the major
EE4902 Lab 9 CMOS OP-AMP PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to measure the closed-loop performance of an op-amp designed from individual MOSFETs. This op-amp, shown in Fig. 9-1, combines all of the major
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF FEEDBACK CONTROLLERS FOR A DC BUCK-BOOST CONVERTER
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF FEEDBACK CONTROLLERS FOR A DC BUCK-BOOST CONVERTER Murdoch University: The Murdoch School of Engineering & Information Technology Author: Jason Chan Supervisors: Martina Calais &
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF FEEDBACK CONTROLLERS FOR A DC BUCK-BOOST CONVERTER Murdoch University: The Murdoch School of Engineering & Information Technology Author: Jason Chan Supervisors: Martina Calais &
ETIN25 Analogue IC Design. Laboratory Manual Lab 2
 Department of Electrical and Information Technology LTH ETIN25 Analogue IC Design Laboratory Manual Lab 2 Jonas Lindstrand Martin Liliebladh Markus Törmänen September 2011 Laboratory 2: Design and Simulation
Department of Electrical and Information Technology LTH ETIN25 Analogue IC Design Laboratory Manual Lab 2 Jonas Lindstrand Martin Liliebladh Markus Törmänen September 2011 Laboratory 2: Design and Simulation
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5)
 Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers
 Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers Introduction Isolated converters are required to provide electrical isolation between two interrelated systems. Isolation between the power source and
Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers Introduction Isolated converters are required to provide electrical isolation between two interrelated systems. Isolation between the power source and
Chapter 2 Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion
 09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007
 BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007 1. An open loop control system has its (a) control action independent of the output or desired quantity (b) controlling action, depending upon
BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007 1. An open loop control system has its (a) control action independent of the output or desired quantity (b) controlling action, depending upon
STATION NUMBER: LAB SECTION: Filters. LAB 6: Filters ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 43/100 INTRODUCTION TO MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUITS
 Lab 6: Filters YOUR EE43/100 NAME: Spring 2013 YOUR PARTNER S NAME: YOUR SID: YOUR PARTNER S SID: STATION NUMBER: LAB SECTION: Filters LAB 6: Filters Pre- Lab GSI Sign- Off: Pre- Lab: /40 Lab: /60 Total:
Lab 6: Filters YOUR EE43/100 NAME: Spring 2013 YOUR PARTNER S NAME: YOUR SID: YOUR PARTNER S SID: STATION NUMBER: LAB SECTION: Filters LAB 6: Filters Pre- Lab GSI Sign- Off: Pre- Lab: /40 Lab: /60 Total:
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
note application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise by David Owen
 application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise note by David Owen The stability of an RF source is often a critical parameter for many applications. Performance varies considerably with
application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise note by David Owen The stability of an RF source is often a critical parameter for many applications. Performance varies considerably with
Power supplies are one of the last holdouts of true. The Purpose of Loop Gain DESIGNER SERIES
 DESIGNER SERIES Power supplies are one of the last holdouts of true analog feedback in electronics. For various reasons, including cost, noise, protection, and speed, they have remained this way in the
DESIGNER SERIES Power supplies are one of the last holdouts of true analog feedback in electronics. For various reasons, including cost, noise, protection, and speed, they have remained this way in the
Chapter 10 Feedback ECE 3120 Microelectronics II Dr. Suketu Naik
 1 Chapter 10 Feedback Operational Amplifier Circuit Components 2 1. Ch 7: Current Mirrors and Biasing 2. Ch 9: Frequency Response 3. Ch 8: Active-Loaded Differential Pair 4. Ch 10: Feedback 5. Ch 11: Output
1 Chapter 10 Feedback Operational Amplifier Circuit Components 2 1. Ch 7: Current Mirrors and Biasing 2. Ch 9: Frequency Response 3. Ch 8: Active-Loaded Differential Pair 4. Ch 10: Feedback 5. Ch 11: Output
Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization
 Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied to the
Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied to the
Op Amp Booster Designs
 Op Amp Booster Designs Although modern integrated circuit operational amplifiers ease linear circuit design, IC processing limits amplifier output power. Many applications, however, require substantially
Op Amp Booster Designs Although modern integrated circuit operational amplifiers ease linear circuit design, IC processing limits amplifier output power. Many applications, however, require substantially
Application Note 323. Flex Power Modules. Input Filter Design - 3E POL Regulators
 Application Note 323 Flex Power Modules Input Filter Design - 3E POL Regulators Introduction The design of the input capacitor is critical for proper operation of the 3E POL regulators and also to minimize
Application Note 323 Flex Power Modules Input Filter Design - 3E POL Regulators Introduction The design of the input capacitor is critical for proper operation of the 3E POL regulators and also to minimize
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1. See suggested breadboard configuration on following page!
 ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter
 Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter 3.1 Introduction DC/DC Converter efficiently converts unregulated DC voltage to a regulated DC voltage with better efficiency and high power density.
Chapter 3 : Closed Loop Current Mode DC\DC Boost Converter 3.1 Introduction DC/DC Converter efficiently converts unregulated DC voltage to a regulated DC voltage with better efficiency and high power density.
Microelectronic Circuits II. Ch 9 : Feedback
 Microelectronic Circuits II Ch 9 : Feedback 9.9 Determining the Loop Gain 9.0 The Stability problem 9. Effect on Feedback on the Amplifier Poles 9.2 Stability study using Bode plots 9.3 Frequency Compensation
Microelectronic Circuits II Ch 9 : Feedback 9.9 Determining the Loop Gain 9.0 The Stability problem 9. Effect on Feedback on the Amplifier Poles 9.2 Stability study using Bode plots 9.3 Frequency Compensation
AN726. Vishay Siliconix AN726 Design High Frequency, Higher Power Converters With Si9166
 AN726 Design High Frequency, Higher Power Converters With Si9166 by Kin Shum INTRODUCTION The Si9166 is a controller IC designed for dc-to-dc conversion applications with 2.7- to 6- input voltage. Like
AN726 Design High Frequency, Higher Power Converters With Si9166 by Kin Shum INTRODUCTION The Si9166 is a controller IC designed for dc-to-dc conversion applications with 2.7- to 6- input voltage. Like
Designing low-frequency decoupling using SIMPLIS
 Designing low-frequency decoupling using SIMPLIS K. Covi Traditional approach to sizing decoupling Determine effective ESR required Parallel electrolytic caps until ESR = ΔV/ΔI where ΔV = desired voltage
Designing low-frequency decoupling using SIMPLIS K. Covi Traditional approach to sizing decoupling Determine effective ESR required Parallel electrolytic caps until ESR = ΔV/ΔI where ΔV = desired voltage
Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers
 Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers INTRODUCTION Isolated converters are required to provide electrical isolation between two interrelated systems. Isolation between the power source and
Design of Isolated Converters Using Simple Switchers INTRODUCTION Isolated converters are required to provide electrical isolation between two interrelated systems. Isolation between the power source and
University of Utah Electrical Engineering Department ECE 2100 Experiment No. 2 Linear Operational Amplifier Circuits II
 University of Utah Electrical Engineering Department ECE 2100 Experiment No. 2 Linear Operational Amplifier Circuits II Minimum required points = 51 Grade base, 100% = 85 points Recommend parts should
University of Utah Electrical Engineering Department ECE 2100 Experiment No. 2 Linear Operational Amplifier Circuits II Minimum required points = 51 Grade base, 100% = 85 points Recommend parts should
Chapter 10 Switching DC Power Supplies
 Chapter 10 Switching One of the most important applications of power electronics 10-1 Linear Power Supplies Very poor efficiency and large weight and size 10-2 Switching DC Power Supply: Block Diagram
Chapter 10 Switching One of the most important applications of power electronics 10-1 Linear Power Supplies Very poor efficiency and large weight and size 10-2 Switching DC Power Supply: Block Diagram
Half bridge converter. DC balance with current signal injection
 Runo Nielsen page of 569 Tommerup telephone : +45 64 76 email : runo.nielsen@tdcadsl.dk December Control methods in pulse width modulated converters The half bridge converter has been around for many years.
Runo Nielsen page of 569 Tommerup telephone : +45 64 76 email : runo.nielsen@tdcadsl.dk December Control methods in pulse width modulated converters The half bridge converter has been around for many years.
Ensuring Clean Power for RF and Digital Applications
 SSC12-IX-4 Ensuring Clean Power for RF and Digital Applications Tom Boehler and Steven Sandler AEi Systems Los Angeles, CA, 90045; 310-216-1144 TomBoehler@aeng.com Steve@aeng.com ABSTRACT Power supply
SSC12-IX-4 Ensuring Clean Power for RF and Digital Applications Tom Boehler and Steven Sandler AEi Systems Los Angeles, CA, 90045; 310-216-1144 TomBoehler@aeng.com Steve@aeng.com ABSTRACT Power supply
While the Riso circuit is both simple to implement and design it has a big disadvantage in precision circuits. The voltage drop from Riso is
 Hello, and welcome to part six of the TI Precision Labs on op amp stability. This lecture will describe the Riso with dual feedback stability compensation method. From 5: The previous videos discussed
Hello, and welcome to part six of the TI Precision Labs on op amp stability. This lecture will describe the Riso with dual feedback stability compensation method. From 5: The previous videos discussed
Filters And Waveform Shaping
 Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
Electric Circuit Fall 2016 Pingqiang Zhou LABORATORY 7. RC Oscillator. Guide. The Waveform Generator Lab Guide
 LABORATORY 7 RC Oscillator Guide 1. Objective The Waveform Generator Lab Guide In this lab you will first learn to analyze negative resistance converter, and then on the basis of it, you will learn to
LABORATORY 7 RC Oscillator Guide 1. Objective The Waveform Generator Lab Guide In this lab you will first learn to analyze negative resistance converter, and then on the basis of it, you will learn to
THE K FACTOR: A NEW MATHEMATICAL TOOL FOR STABILITY ANALYSIS AND SYNTHESIS
 Reference Reading #4 THE K FACTOR: A NEW MATHEMATICAL TOOL FOR STABILITY ANALYSIS AND SYNTHESIS H. Dean Venable Venable Industries, Inc. 2120 W. Braker Lane, Suite M Austin, TX 78758 info@venableind.com
Reference Reading #4 THE K FACTOR: A NEW MATHEMATICAL TOOL FOR STABILITY ANALYSIS AND SYNTHESIS H. Dean Venable Venable Industries, Inc. 2120 W. Braker Lane, Suite M Austin, TX 78758 info@venableind.com
Impact of the Output Capacitor Selection on Switching DCDC Noise Performance
 Impact of the Output Capacitor Selection on Switching DCDC Noise Performance I. Introduction Most peripheries in portable electronics today tend to systematically employ high efficiency Switched Mode Power
Impact of the Output Capacitor Selection on Switching DCDC Noise Performance I. Introduction Most peripheries in portable electronics today tend to systematically employ high efficiency Switched Mode Power
Chapter 4: AC Circuits and Passive Filters
 Chapter 4: AC Circuits and Passive Filters Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to: use V-t, I-t and P-t graphs for resistive loads describe the relationship between rms and peak
Chapter 4: AC Circuits and Passive Filters Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to: use V-t, I-t and P-t graphs for resistive loads describe the relationship between rms and peak
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits
 Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Four-Channel Sample-and-Hold Amplifier AD684
 a FEATURES Four Matched Sample-and-Hold Amplifiers Independent Inputs, Outputs and Control Pins 500 ns Hold Mode Settling 1 s Maximum Acquisition Time to 0.01% Low Droop Rate: 0.01 V/ s Internal Hold Capacitors
a FEATURES Four Matched Sample-and-Hold Amplifiers Independent Inputs, Outputs and Control Pins 500 ns Hold Mode Settling 1 s Maximum Acquisition Time to 0.01% Low Droop Rate: 0.01 V/ s Internal Hold Capacitors
Exercise 3 Operational Amplifiers and feedback circuits
 LAB EXERCISE 3 Page 1 of 19 Exercise 3 Operational Amplifiers and feedback circuits 1. Introduction Goal of the exercise The goals of this exercise are: Analyze the behavior of Op Amp circuits with feedback.
LAB EXERCISE 3 Page 1 of 19 Exercise 3 Operational Amplifiers and feedback circuits 1. Introduction Goal of the exercise The goals of this exercise are: Analyze the behavior of Op Amp circuits with feedback.
EE320L Electronics I. Laboratory. Laboratory Exercise #2. Basic Op-Amp Circuits. Angsuman Roy. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #2 Basic Op-Amp Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of
EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #2 Basic Op-Amp Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of
Pole, zero and Bode plot
 Pole, zero and Bode plot EC04 305 Lecture notes YESAREKEY December 12, 2007 Authored by: Ramesh.K Pole, zero and Bode plot EC04 305 Lecture notes A rational transfer function H (S) can be expressed as
Pole, zero and Bode plot EC04 305 Lecture notes YESAREKEY December 12, 2007 Authored by: Ramesh.K Pole, zero and Bode plot EC04 305 Lecture notes A rational transfer function H (S) can be expressed as
Laboratory 6. Lab 6. Operational Amplifier Circuits. Required Components: op amp 2 1k resistor 4 10k resistors 1 100k resistor 1 0.
 Laboratory 6 Operational Amplifier Circuits Required Components: 1 741 op amp 2 1k resistor 4 10k resistors 1 100k resistor 1 0.1 F capacitor 6.1 Objectives The operational amplifier is one of the most
Laboratory 6 Operational Amplifier Circuits Required Components: 1 741 op amp 2 1k resistor 4 10k resistors 1 100k resistor 1 0.1 F capacitor 6.1 Objectives The operational amplifier is one of the most
CHAPTER 9 FEEDBACK. NTUEE Electronics L.H. Lu 9-1
 CHAPTER 9 FEEDBACK Chapter Outline 9.1 The General Feedback Structure 9.2 Some Properties of Negative Feedback 9.3 The Four Basic Feedback Topologies 9.4 The Feedback Voltage Amplifier (Series-Shunt) 9.5
CHAPTER 9 FEEDBACK Chapter Outline 9.1 The General Feedback Structure 9.2 Some Properties of Negative Feedback 9.3 The Four Basic Feedback Topologies 9.4 The Feedback Voltage Amplifier (Series-Shunt) 9.5
Lab 10: Oscillators (version 1.1)
 Lab 10: Oscillators (version 1.1) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive equipment.
Lab 10: Oscillators (version 1.1) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive equipment.
Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL. Andrea M. Zanchettin, PhD Winter Semester, Linear control systems design Part 1
 Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL Andrea M. Zanchettin, PhD Winter Semester, 2018 Linear control systems design Part 1 Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 2 Step responses Assume
Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 1 AUTOMATIC CONTROL Andrea M. Zanchettin, PhD Winter Semester, 2018 Linear control systems design Part 1 Andrea Zanchettin Automatic Control 2 Step responses Assume
Constant Current Control for DC-DC Converters
 APPLICATION NOTE AN:211 Constant Current Control for DC-DC Converters Contents Page Introduction 1 Theory of Operation 1 Power Limitations 2 Voltage Loop Stability 2 Current Control Example 7 Component
APPLICATION NOTE AN:211 Constant Current Control for DC-DC Converters Contents Page Introduction 1 Theory of Operation 1 Power Limitations 2 Voltage Loop Stability 2 Current Control Example 7 Component
LM148/LM248/LM348 Quad 741 Op Amps
 Quad 741 Op Amps General Description The LM148 series is a true quad 741. It consists of four independent, high gain, internally compensated, low power operational amplifiers which have been designed to
Quad 741 Op Amps General Description The LM148 series is a true quad 741. It consists of four independent, high gain, internally compensated, low power operational amplifiers which have been designed to
Glossary + - A BNC plug that shorts the inner wire in a coax cable to the outer shield through a
 50Ω Terminator AC Active Alligator Clip Back Bias Base Battery Bias + - Bipolar Transistor BJT Black Box BNC BNC Cable A BNC plug that shorts the inner wire in a coax cable to the outer shield through
50Ω Terminator AC Active Alligator Clip Back Bias Base Battery Bias + - Bipolar Transistor BJT Black Box BNC BNC Cable A BNC plug that shorts the inner wire in a coax cable to the outer shield through
LINEAR MODELING OF A SELF-OSCILLATING PWM CONTROL LOOP
 Carl Sawtell June 2012 LINEAR MODELING OF A SELF-OSCILLATING PWM CONTROL LOOP There are well established methods of creating linearized versions of PWM control loops to analyze stability and to create
Carl Sawtell June 2012 LINEAR MODELING OF A SELF-OSCILLATING PWM CONTROL LOOP There are well established methods of creating linearized versions of PWM control loops to analyze stability and to create
Field Effect Transistors
 Field Effect Transistors Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors (FETs). We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct a common-source amplifier stage,
Field Effect Transistors Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors (FETs). We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct a common-source amplifier stage,
Designing a Multi-Phase Asynchronous Buck Regulator Using the LM2639
 Designing a Multi-Phase Asynchronous Buck Regulator Using the LM2639 Overview The LM2639 provides a unique solution to high current, low voltage DC/DC power supplies such as those for fast microprocessors.
Designing a Multi-Phase Asynchronous Buck Regulator Using the LM2639 Overview The LM2639 provides a unique solution to high current, low voltage DC/DC power supplies such as those for fast microprocessors.
Emitter base bias. Collector base bias Active Forward Reverse Saturation forward Forward Cut off Reverse Reverse Inverse Reverse Forward
 SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS-2 [Transistor, constructional characteristics, biasing of transistors, transistor configuration, transistor as an amplifier, transistor as a switch, transistor as an oscillator] Transistor
SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS-2 [Transistor, constructional characteristics, biasing of transistors, transistor configuration, transistor as an amplifier, transistor as a switch, transistor as an oscillator] Transistor
CHAPTER 6 INPUT VOLATGE REGULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF NON-LINEAR DYNAMICS IN PV SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 6 INPUT VOLATGE REGULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF NON-LINEAR DYNAMICS IN PV SYSTEM 6. INTRODUCTION The DC-DC Cuk converter is used as an interface between the PV array and the load,
CHAPTER 6 INPUT VOLATGE REGULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF NON-LINEAR DYNAMICS IN PV SYSTEM 6. INTRODUCTION The DC-DC Cuk converter is used as an interface between the PV array and the load,
Understanding, measuring, and reducing output noise in DC/DC switching regulators
 Understanding, measuring, and reducing output noise in DC/DC switching regulators Practical tips for output noise reduction Katelyn Wiggenhorn, Applications Engineer, Buck Switching Regulators Robert Blattner,
Understanding, measuring, and reducing output noise in DC/DC switching regulators Practical tips for output noise reduction Katelyn Wiggenhorn, Applications Engineer, Buck Switching Regulators Robert Blattner,
ECE 363 FINAL (F16) 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts)
 ECE 363 FINAL (F16) NAME: 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts) You are asked to design a high-side switch for a remotely operated fuel pump. You decide to use the IRF9520 power
ECE 363 FINAL (F16) NAME: 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts) You are asked to design a high-side switch for a remotely operated fuel pump. You decide to use the IRF9520 power
The measurement of loop gain in feedback seismometers Brett M. Nordgren April 9, 1999 Rev.
 Introduction The measurement of loop gain in feedback seismometers Brett M. Nordgren http://bnordgren.org/contactb.html April 9, 1999 Rev. October 5, 2004 In reading the messages coming through PSN-L,
Introduction The measurement of loop gain in feedback seismometers Brett M. Nordgren http://bnordgren.org/contactb.html April 9, 1999 Rev. October 5, 2004 In reading the messages coming through PSN-L,
A New Concept of Power Quality Monitoring
 A New Concept of Power Quality Monitoring Victor Anunciada 1, Hugo Ribeiro 2 1 Instituto de Telecomunicações, Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisboa, Portugal, avaa@lx.it.pt 2 Instituto de Telecomunicações,
A New Concept of Power Quality Monitoring Victor Anunciada 1, Hugo Ribeiro 2 1 Instituto de Telecomunicações, Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisboa, Portugal, avaa@lx.it.pt 2 Instituto de Telecomunicações,
LM6118/LM6218 Fast Settling Dual Operational Amplifiers
 Fast Settling Dual Operational Amplifiers General Description The LM6118/LM6218 are monolithic fast-settling unity-gain-compensated dual operational amplifiers with ±20 ma output drive capability. The
Fast Settling Dual Operational Amplifiers General Description The LM6118/LM6218 are monolithic fast-settling unity-gain-compensated dual operational amplifiers with ±20 ma output drive capability. The
Features MIC2193BM. Si9803 ( 2) 6.3V ( 2) VDD OUTP COMP OUTN. Si9804 ( 2) Adjustable Output Synchronous Buck Converter
 MIC2193 4kHz SO-8 Synchronous Buck Control IC General Description s MIC2193 is a high efficiency, PWM synchronous buck control IC housed in the SO-8 package. Its 2.9V to 14V input voltage range allows
MIC2193 4kHz SO-8 Synchronous Buck Control IC General Description s MIC2193 is a high efficiency, PWM synchronous buck control IC housed in the SO-8 package. Its 2.9V to 14V input voltage range allows
55:041 Electronic Circuits The University of Iowa Fall Exam 3. Question 1 Unless stated otherwise, each question below is 1 point.
 Exam 3 Name: Score /65 Question 1 Unless stated otherwise, each question below is 1 point. 1. An engineer designs a class-ab amplifier to deliver 2 W (sinusoidal) signal power to an resistive load. Ignoring
Exam 3 Name: Score /65 Question 1 Unless stated otherwise, each question below is 1 point. 1. An engineer designs a class-ab amplifier to deliver 2 W (sinusoidal) signal power to an resistive load. Ignoring
KH103 Fast Settling, High Current Wideband Op Amp
 KH103 Fast Settling, High Current Wideband Op Amp Features 80MHz full-power bandwidth (20V pp, 100Ω) 200mA output current 0.4% settling in 10ns 6000V/µs slew rate 4ns rise and fall times (20V) Direct replacement
KH103 Fast Settling, High Current Wideband Op Amp Features 80MHz full-power bandwidth (20V pp, 100Ω) 200mA output current 0.4% settling in 10ns 6000V/µs slew rate 4ns rise and fall times (20V) Direct replacement
DC/DC Converter Stability Measurement
 Strongly supported by By Stephan Synkule, Lukas Heinzle & Florian Hämmerle 2018 by OMICRON Lab V3.3 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical support.
Strongly supported by By Stephan Synkule, Lukas Heinzle & Florian Hämmerle 2018 by OMICRON Lab V3.3 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical support.
Oscillators. An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier.
 Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
DC/DC Converter Stability Measurement
 Strongly supported by By Stephan Synkule, Lukas Heinzle & Florian Hämmerle 214 by OMICRON Lab V2.1 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical support.
Strongly supported by By Stephan Synkule, Lukas Heinzle & Florian Hämmerle 214 by OMICRON Lab V2.1 Visit www.omicron-lab.com for more information. Contact support@omicron-lab.com for technical support.
Summer 2015 Examination
 Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
UNIT I. Operational Amplifiers
 UNIT I Operational Amplifiers Operational Amplifier: The operational amplifier is a direct-coupled high gain amplifier. It is a versatile multi-terminal device that can be used to amplify dc as well as
UNIT I Operational Amplifiers Operational Amplifier: The operational amplifier is a direct-coupled high gain amplifier. It is a versatile multi-terminal device that can be used to amplify dc as well as
2. There are many circuit simulators available today, here are just few of them. They have different flavors (mostly SPICE-based), platforms,
 1. 2. There are many circuit simulators available today, here are just few of them. They have different flavors (mostly SPICE-based), platforms, complexity, performance, capabilities, and of course price.
1. 2. There are many circuit simulators available today, here are just few of them. They have different flavors (mostly SPICE-based), platforms, complexity, performance, capabilities, and of course price.
University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 Electrical Engineering Design II Fall 2013
 Exercise 1: PWM Modulator University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 Electrical Engineering Design II Fall 2013 Lab 3: Power-System Components and
Exercise 1: PWM Modulator University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 Electrical Engineering Design II Fall 2013 Lab 3: Power-System Components and
ENEE307 Lab 7 MOS Transistors 2: Small Signal Amplifiers and Digital Circuits
 ENEE307 Lab 7 MOS Transistors 2: Small Signal Amplifiers and Digital Circuits In this lab, we will be looking at ac signals with MOSFET circuits and digital electronics. The experiments will be performed
ENEE307 Lab 7 MOS Transistors 2: Small Signal Amplifiers and Digital Circuits In this lab, we will be looking at ac signals with MOSFET circuits and digital electronics. The experiments will be performed
Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Copyright 2004 by Oxford University Press, Inc.
 Feedback 1 Figure 8.1 General structure of the feedback amplifier. This is a signal-flow diagram, and the quantities x represent either voltage or current signals. 2 Figure E8.1 3 Figure 8.2 Illustrating
Feedback 1 Figure 8.1 General structure of the feedback amplifier. This is a signal-flow diagram, and the quantities x represent either voltage or current signals. 2 Figure E8.1 3 Figure 8.2 Illustrating
400 MHz Passive High-Voltage Probe R&S RT-ZH
 Manual 400 MHz Passive High-Voltage Probe R&S RT-ZH11 1409.7737.02 Printed in Germany Test and Measurment Manufacturer ROHDE & SCHWARZ For comprehensive information about Rohde and Schwarz, please visit
Manual 400 MHz Passive High-Voltage Probe R&S RT-ZH11 1409.7737.02 Printed in Germany Test and Measurment Manufacturer ROHDE & SCHWARZ For comprehensive information about Rohde and Schwarz, please visit
EE301 Electronics I , Fall
 EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
PKT 512A-RO High Impedance Passive Cable Divider
 PKT 512A-RO High Impedance Passive Cable Divider Instruction Manual Copyright 2011 PMK GmbH All rights reserved. Information in this publication supersedes that in all previously published material. Specifications
PKT 512A-RO High Impedance Passive Cable Divider Instruction Manual Copyright 2011 PMK GmbH All rights reserved. Information in this publication supersedes that in all previously published material. Specifications
Laboratory 9. Required Components: Objectives. Optional Components: Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x 741 op-amp 2x 1k resistors 4x 10k resistors 1x l00k resistor 1x 0.1F capacitor Optional Components:
Laboratory 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x 741 op-amp 2x 1k resistors 4x 10k resistors 1x l00k resistor 1x 0.1F capacitor Optional Components:
AVERAGE CURRENT MODE CONTROL IN POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTERS ANALOG VERSUS DIGITAL. K. D. Purton * and R. P. Lisner**
 AVERAGE CURRENT MODE CONTROL IN POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTERS ANALOG VERSUS DIGITAL Abstract K. D. Purton * and R. P. Lisner** *Department of Electrical and Computer System Engineering, Monash University,
AVERAGE CURRENT MODE CONTROL IN POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTERS ANALOG VERSUS DIGITAL Abstract K. D. Purton * and R. P. Lisner** *Department of Electrical and Computer System Engineering, Monash University,
DATASHEET HS-1145RH. Features. Applications. Ordering Information. Pinout
 DATASHEET HS-45RH Radiation Hardened, High Speed, Low Power, Current Feedback Video Operational Amplifier with Output Disable FN4227 Rev 2. February 4, 25 The HS-45RH is a high speed, low power current
DATASHEET HS-45RH Radiation Hardened, High Speed, Low Power, Current Feedback Video Operational Amplifier with Output Disable FN4227 Rev 2. February 4, 25 The HS-45RH is a high speed, low power current
Dr Ian R. Manchester
 Week Content Notes 1 Introduction 2 Frequency Domain Modelling 3 Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 Block Diagrams 5 Feedback System Characteristics Assign 1 Due 6 Root Locus 7 Root Locus 2 Assign
Week Content Notes 1 Introduction 2 Frequency Domain Modelling 3 Transient Performance and the s-plane 4 Block Diagrams 5 Feedback System Characteristics Assign 1 Due 6 Root Locus 7 Root Locus 2 Assign
JFET 101, a Tutorial Look at the Junction Field Effect Transistor 8May 2007, edit 2April2016, Wes Hayward, w7zoi
 JFET 101, a Tutorial Look at the Junction Field Effect Transistor 8May 2007, edit 2April2016, Wes Hayward, w7zoi FETs are popular among experimenters, but they are not as universally understood as the
JFET 101, a Tutorial Look at the Junction Field Effect Transistor 8May 2007, edit 2April2016, Wes Hayward, w7zoi FETs are popular among experimenters, but they are not as universally understood as the
Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems
 Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems Introduction The two major problems that the modern power systems are facing are voltage and angle stabilities. There are various approaches to overcome
Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems Introduction The two major problems that the modern power systems are facing are voltage and angle stabilities. There are various approaches to overcome
GLOSSARY. A connector used to T together two BNC coax cables and a BNC jack. The transfer function vs. frequency plotted on Log Log axis.
 GLOSSARY 50ΩTerminator AC Active Alligator Clip Back Bias Base Battery Bias + - Bipolar Transistor BJT Black Box BNC BNC Cable A BNC plug that shorts the inner wire in a coax cable to the outer shield
GLOSSARY 50ΩTerminator AC Active Alligator Clip Back Bias Base Battery Bias + - Bipolar Transistor BJT Black Box BNC BNC Cable A BNC plug that shorts the inner wire in a coax cable to the outer shield
University of California at Berkeley Donald A. Glaser Physics 111A Instrumentation Laboratory
 Published on Instrumentation LAB (http://instrumentationlab.berkeley.edu) Home > Lab Assignments > Digital Labs > Digital Circuits II Digital Circuits II Submitted by Nate.Physics on Tue, 07/08/2014-13:57
Published on Instrumentation LAB (http://instrumentationlab.berkeley.edu) Home > Lab Assignments > Digital Labs > Digital Circuits II Digital Circuits II Submitted by Nate.Physics on Tue, 07/08/2014-13:57
Vishay Siliconix AN724 Designing A High-Frequency, Self-Resonant Reset Forward DC/DC For Telecom Using Si9118/9 PWM/PSM Controller.
 AN724 Designing A High-Frequency, Self-Resonant Reset Forward DC/DC For Telecom Using Si9118/9 PWM/PSM Controller by Thong Huynh FEATURES Fixed Telecom Input Voltage Range: 30 V to 80 V 5-V Output Voltage,
AN724 Designing A High-Frequency, Self-Resonant Reset Forward DC/DC For Telecom Using Si9118/9 PWM/PSM Controller by Thong Huynh FEATURES Fixed Telecom Input Voltage Range: 30 V to 80 V 5-V Output Voltage,
Practical Testing Techniques For Modern Control Loops
 VENABLE TECHNICAL PAPER # 16 Practical Testing Techniques For Modern Control Loops Abstract: New power supply designs are becoming harder to measure for gain margin and phase margin. This measurement is
VENABLE TECHNICAL PAPER # 16 Practical Testing Techniques For Modern Control Loops Abstract: New power supply designs are becoming harder to measure for gain margin and phase margin. This measurement is
Input Stage Concerns. APPLICATION NOTE 656 Design Trade-Offs for Single-Supply Op Amps
 Maxim/Dallas > App Notes > AMPLIFIER AND COMPARATOR CIRCUITS Keywords: single-supply, op amps, amplifiers, design, trade-offs, operational amplifiers Apr 03, 2000 APPLICATION NOTE 656 Design Trade-Offs
Maxim/Dallas > App Notes > AMPLIFIER AND COMPARATOR CIRCUITS Keywords: single-supply, op amps, amplifiers, design, trade-offs, operational amplifiers Apr 03, 2000 APPLICATION NOTE 656 Design Trade-Offs
Low Cost, General Purpose High Speed JFET Amplifier AD825
 a FEATURES High Speed 41 MHz, 3 db Bandwidth 125 V/ s Slew Rate 8 ns Settling Time Input Bias Current of 2 pa and Noise Current of 1 fa/ Hz Input Voltage Noise of 12 nv/ Hz Fully Specified Power Supplies:
a FEATURES High Speed 41 MHz, 3 db Bandwidth 125 V/ s Slew Rate 8 ns Settling Time Input Bias Current of 2 pa and Noise Current of 1 fa/ Hz Input Voltage Noise of 12 nv/ Hz Fully Specified Power Supplies:
1 TRANSISTOR CIRCUITS
 FM TRANSMITTERS The first group of circuits we will discuss are FM TRANSMITTERS. They can be called SPY TRANSMITTERS, FM BUGS, or a number of other interesting names. They all do the same thing. They transmit
FM TRANSMITTERS The first group of circuits we will discuss are FM TRANSMITTERS. They can be called SPY TRANSMITTERS, FM BUGS, or a number of other interesting names. They all do the same thing. They transmit
