Photothermal Speckle Modulation for Materials Characterization*
|
|
|
- Violet Barber
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Photothermal Speckle Modulation for Materials Characterization* Alexander M. Stolyarov**, Ryan Sullenberger, David Crompton, Thomas Jeys, Brian G. Saar, William Herzog MIT Lincoln Laboratory, 244 Wood St. Lexington, MA **Corresponding author: Distribution A: Public Release Abstract We have developed a non-contact, photothermal materials characterization method based on visible-light speckle imaging. This technique is applied to remotely measure the infrared absorption spectra of materials and to discriminate materials based on their thermal conductivities. A wavelength-tunable ( µm), intensity-modulated, quantum cascade pump laser and a continuous-wave 532-nm probe laser illuminate a sample surface such that the two laser spots overlap. Surface absorption of the intensity- modulated pump laser induces a time-varying thermoelastic surface deformation, resulting in a time-varying 532-nm scattering speckle field from the surface. The speckle modulation amplitude, derived from a series of visible camera images, is found to correlate with the amplitude of the surface motion. By tuning the pump laser s wavelength over a molecular absorption feature, the amplitude spectrum of the speckle modulation is found to correlate to the IR absorption spectrum. As an example, we demonstrate this technique for spectroscopic identification of thin polymeric films. Furthermore, by adjusting the rate of modulation of the pump beam and measuring the associated modulation transfer to the visible speckle pattern, information about the This work is sponsored by the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering under Air Force Contract #FA C Opinions, interpretations, conclusions and recommendations are those of the author and are not necessarily endorsed by the United States Government.
2 thermal time constants of surface and sub-surface features can be revealed. Using this approach, we demonstrate the ability to distinguish between different materials (including metals, semiconductors, and insulators) based on differences in their thermal conductivities. Body of Paper When a diffuse surface or volume is illuminated by a laser beam, the coherent superposition of the scattered wavefronts results in a high contrast, random intensity pattern known as laser speckle [1]. While a nuisance for many coherent optical techniques such a laser radar and holography, the unique characteristics of laser speckle have enabled many applications, from blood flow imaging [2,3], to imaging through turbid media [4], to the extraction of remote speech [5] and many others [6]. Here we report on a new materials characterization technique based on speckle imaging, called photothermal speckle modulation (PSM). The approach involves measuring changes in the visible (532-nm) speckle pattern from a surface co-illuminated by a visible probe laser and an intensity-modulated long wave infrared (LWIR) pump laser ( µm). The absorption of the pump laser generates a time-varying thermoelastic surface motion, consequently leading to correlated fluctuations in the speckle pattern. Critically, inherent to PSM is the interferometric sensitivity on the intensity of each speckle lobe scattering diffusely from a surface, and therefore, this method is distinct from other pump-probe photothermal techniques [7-10] that primarily rely on measuring the deflection of a specular probe beam with position sensitive detectors. Potential applications of this technique are broad and include remote chemical sensing of bulk, thin film and powder materials, and non-contact characterization of surface and sub-surface thermal properties.
3 A schematic of the measurement scheme is illustrated in figure 1. A tunable ( µm) pump quantum cascade laser (QCL) and a visible (532-nm), single frequency probe laser are projected onto a sample under interrogation so that their laser spots overlap. Diffusively scattered probe light from the sample generates a speckle pattern which is imaged onto a visible CMOS camera. The absorption of the pump photons by the sample results in surface heating and subsequent thermoelastic deformation of the surface, both out-of-plane and in-plane, as depicted in figure 2. The pump laser power is intensity-modulated (fully on to fully off), while the probe beam is on continuously. Photothermally-induced surface deformations are excited at the frequency of the pump beam modulation, leading to speckle patterns that change in a periodic manner at the same frequency as the pump modulation. The pump modulation rate (typically 22 Hz or higher in our experiments) is selected to be faster than the time scale associated with natural speckle fluctuations due to, for example, vibrations or air currents, thus allowing high sensitivity lock-in detection at the modulation frequency. Moreover, in contrast to laser vibrometry techniques, which are only sensitive to out-of-plane surface motion, changes in the speckle pattern are effected by both the in-plane and out-of-plane surface deformations [6].
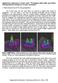
4 (a) IR laser (pump) visible laser speckle image sample visible camera visible laser (probe) IR on IR off (b) (c) y time FFT (magnitude) x Frequency (Hz) Fig. 1. PSM measurement scheme (a) (left) A tunable infrared laser (pump) and a 532-nm visible laser (probe) are projected onto the same location of a sample of interest such that their laser spots are coincident. A visible camera monitors changes in the visible laser speckle pattern as the sample s surface is periodically heated and cooled by the modulated infrared laser. (right) Illustration of the speckle pattern when pump laser is on (green) and off (black) (b) A series of speckle images are captured by the visible camera. (c) FFT spectra of each pixel through the image stack are averaged together, exposing the PSM signal which exists at the infrared modulation frequency. In a typical measurement, ~1 mw average pump power is amplitude-modulated with a 50% duty cycle and focused to ~ 0.6 mm (full width half maximum, FWHM) spot on the surface of interest while the ~1 mw probe beam illuminates a ~3 mm FWHM spot roughly concentric with the pump. In our experiments, the sample is positioned ~1.8
5 meters from the pump, probe, and CMOS camera. The focusing range, focal length, and F-stop of the camera s lens are set to 1.5 m, 160 mm, and f/4, respectively. The lens is intentionally set to focus ~0.3 m in front of Temp. (deg C) deformation (nm) (a) end 4.5 mid start Time (ms) out-of-plane in-plane 5 (b) 2 (c) radial position (mm) radial position (mm) Fig 2. Photothermal surface deformation simulations using NASTRAN for a single cycle of a 1 mw average power (50% duty cycle, spot size FWHM = 0.6 mm), 20 Hz pump excitation beam incident onto a PMMA block. a) peak surface temperature response transient b) normal to surface deformations of the surface at the start, middle and end of a heating cycle c) in-plane, or radial deformations. Deformations are shown as a function of distance from the center of the heating spot. the sample such that the average speckle lobe size is increased to approximately 5 pixels / speckle lobe. The CMOS camera records a stack of images which are processed to quantify the photothermal speckle modulation (PSM) signal. In a typical experiment,
6 20,000 images (frames) are collected at 500 frames per second, and each frame is 46 by 46 pixels (see figure 1b for an example speckle image stack). The magnitude of the PSM signal is obtained from this image stack using the following algorithm: first, a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is applied to each pixel in the image stack individually. Second, the FFT spectrum for each pixel is averaged over all the pixels resulting in a PSM spectrum for that image stack, as shown in figure 1c. As can be seen, the FFT spectrum contains a signal only at the pump modulation frequency (in this example, 22 Hz). By tuning the QCL s wavelength over a molecular absorption feature, the amplitude spectrum of the speckle modulation is found to correlate to the IR absorption spectrum. In addition to the absorption information, adjusting the rate of modulation of the pump beam and recording the associated modulation transfer to the probe beam, information about the thermal time constants of the surface can be discerned. This enables surface and even sub-surface materials discrimination based on differences in thermal conductivity. We demonstrate the spectroscopic materials characterization capabilities of this technique on thin films of several polymers (PMMA, Teflon AF, and PDMS), each having distinct absorption features in a wavelength range that overlaps the wavelength tuning range of our QCL. Each polymer was dissolved in a solution and applied onto a KBr substrate using standard spin-coating techniques. The samples were dried on a hot plate at 100 C for 5 minutes to remove any residual solvent. The absorption spectrum for each sample was obtained on a Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectrometer (Bruker VERTEX 70 with a Seagull TM reflection accessory) by measuring both the transmission (T) and reflection (R) of the sample. Since KBr is transparent in the IR, the sample absorption (A) can be expressed as: A = 1-T-R (1). The surface roughness on the film
7 resulting from the solvent drying step was sufficient to generate a speckle pattern, therefore no further surface modifications or sample preparation steps were performed. Figure 3 shows the PSM magnitude spectrum for each material plotted versus pump wavelength, showing excellent agreement with the material s absorption spectrum. PSM signal µm Teflon AF / KBr T - R PSM signal µm PMMA / KBr T - R PSM signal µm PDMS / KBr T - R Frequency (cm -1 ) Fig. 3. PSM for spectroscopic materials analysis. PSM spectra of (top) a 2 µm Teflon AF film on a KBr substrate, (middle) a 10.4 µm PMMA film on a KBr substrate, and (bottom) a 4.4 µm PDMS film on a KBr substrate. A modification of this technique can be leveraged to distinguish between classes of materials based on their thermal conductivities. Instead of varying the pump laser wavelength, the frequency of the pump beam can be tuned and the PSM signal can be analyzed as a function of pump modulation frequency. The photothermal response as a function of the pump excitation frequency can be understood by considering the step
8 response of the material to an incident heat load over a small spot. Initially, the thermoelastic response rises nearly linearly with time before leveling off to a quasi steady-state condition. This transient behavior is well described by Beck [11], and the apparent time constant can vary from a few milliseconds for materials with high conductivity to tens of milliseconds for materials for low conductivity. When the period of excitation is long relative to the time constant, changes in the period (and frequency) of excitation produce very small changes in the peak thermoelastic response. In this region, the photothermal response vs. frequency curve is relatively flat. When the period of excitation is small relative to the time constant, the photothermal response becomes nearly proportional to the period (and inversely proportional to frequency). The transition frequency between these two regimes depends on the time constant, which is determined by the material s conductivity, specific heat and density. For higher conductivity materials, this transition occurs at higher frequencies. We demonstrate the ability to distinguish between bulk materials based on this rationale. Bars (2 mm thick by 6 mm x 10 cm) of PMMA, aluminum, and stainless steel were used as targets. The QCL wavelength and flux was fixed at 7.85 µm and 5W/cm 2, respectively. The modulation frequency was tuned from 5 Hz through 200 Hz, while the PSM signal was analyzed for several frequencies in this range. Figure 4a shows the results of this experiment compared with simulations performed for these materials and experimental conditions using Finite Element Analysis (Nastran). As expected, aluminum (thermal conductivity of 200 W/mK) has a nearly flat response at low frequencies while PMMA (thermal conductivity of.2 W/mK) shows a 1/frequency dependence starting around 10 Hz. Note
9 that the response amplitude depends on a number of factors including: thermal expansion coefficient, specific heat, density and thermal conductivity. An intriguing feature of this technique is the ability to distinguish between subsurface properties of objects, for example, between different materials that have identical surface finishes. As a proof-of-principle demonstration, we applied a 4 µm layer of PMMA to two substrates that are IR-transmissive but have different thermal conductivities: Germanium (Ge) and Potassium Bromide (KBr). Pump light from the QCL was incident onto to each of the samples at the same fixed wavelength and average intensity (7.85 μm, 5 W/cm 2 ). The CMOS camera collected images at 500 frames per second with an exposure time of 0.19 milliseconds per frame. The pump light modulation frequency was tuned from 10 Hz through 200 Hz, and the PSM signal was analyzed for each frequency. The results of this experiment are displayed in Fig. 4b. For optically thin films, where the penetration depth of the pump beam is on the order of the film thickness, the photothermal surface response is still dominated by the thermal properties of the substrate, since it is the substrate which conducts most of the heat away from the surface film. Because the Ge substrate is a better thermal conductor than KBr, the PSM signal remains relatively flat to higher frequencies for Ge before it starts decreasing. Also, since the coefficient of thermal expansion is larger for KBr than for Ge, the overall signal strength is higher for KBr compared to Ge. Thus, although the surface materials for the two curves are the same (PMMA), the difference between the functional forms of the PSM signals as a function of IR pump light modulation frequency allows the two underlying substrates to be distinguished from each other due to their differing thermal conductivities.
10 PSM signal (a.u.) [markers] markers = experiment, curves = Nastran PMMA Stainless Steel Aluminum (a) PMMA / KBr PMMA / Ge 10 0 (b) Response (nm) [curves] Infrared Modulation Frequency (Hz) Fig. 4. Photothermal speckle modulation for thermal conductivity discrimination (a) Photothermal speckle modulation frequency responsivity data for (a) three different materials, and (b) thin PMMA films (~4 µm thick) deposited onto KBr and Ge substrates. In summary, we have developed a new non-contact, pump-probe materials characterization method based on visible-light speckle imaging. Using this technique, IR absorption spectra and thermoelastic time constants of materials can be evaluated by analyzing speckle-pattern modulations of the probe beam induced by surface absorption of an IR pump beam. The methods described here provide new opportunities for remote sensing and other materials characterization applications, including a range of nondestructive analysis, where material composition, subsurface features, and thermoelastic
11 properties are of interest and can be obtained remotely and with high sensitivity using the PSM approach. Acknowledgements This work is sponsored by the Assistant Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering under Air Force Contract #FA C Opinions, interpretations, conclusions and recommendations are those of the author and are not necessarily endorsed by the United States Government. References: [1] J.W. Goodman; Speckle Phenomena in Optics: Theory and Applications, Roberts and company Publishers (2007) [2] J.D. Briers, S. Webster; Laser Speckle Contrast Analysis (LASCA); A Nonscanning, Full-field Technique for Monitoring Capillary Blood Flow Jour. of Biom. Optics 1(2) [3] C. Regan, J.C. Ramirez-San-Juan, B. Choi; Photothermal laser speckle imaging Opt. Lett. 39 (17) [4] O. Katz, P. Heidmann, M. Fink, S. Gigan; Non-invasive single-shot imaging through scattering layers and around corners via speckle correlations Nat. Photon. 8, , 2014.
12 [5] Z. Zalevsky, Y. Beiderman, I. Margalit, S. Gingold, M. Teicher, V. Mico, J. Garcia; Simultaneous remote extraction of multiple speech sources and heart beats from secondary speckles pattern Opt. Express 17 (24) , [6] R.S. Sirohi; Speckle Metrology, Marcel Dekker, Inc., [7] S. Ameri, E. A. Ash, V. Neuman, C. R. Petts; Photo-displacement Imaging Electronics Letters 17, (10) 337, [8] M. A. Olmstead, N.M. Amer, S. Kohn; Photothermal Displacement Spectrscopy: An Optical Probe for Solids and Surfaces Appl. Phys. A 32, , [9] A.C. Boccara and D. Fournier; Sensitive photothermal deflection technique for measuring absorption in optically thin media Opt. Lett. 5 (9) 377, [10] R.H. Farahi, A. Passian, L. Tetard, and T. Thundat, Pump-probe photothermal spectroscopy using quantum cascade lasers J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys , [11] J. V. Beck, Large time solutions for temperatures in a semi-infinite body with a disk heat source Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer Vol. 24, , 1981.
Ultra-sensitive, room-temperature THz detector using nonlinear parametric upconversion
 15 th Coherent Laser Radar Conference Ultra-sensitive, room-temperature THz detector using nonlinear parametric upconversion M. Jalal Khan Jerry C. Chen Z-L Liau Sumanth Kaushik Ph: 781-981-4169 Ph: 781-981-3728
15 th Coherent Laser Radar Conference Ultra-sensitive, room-temperature THz detector using nonlinear parametric upconversion M. Jalal Khan Jerry C. Chen Z-L Liau Sumanth Kaushik Ph: 781-981-4169 Ph: 781-981-3728
Laser Speckle Reducer LSR-3000 Series
 Datasheet: LSR-3000 Series Update: 06.08.2012 Copyright 2012 Optotune Laser Speckle Reducer LSR-3000 Series Speckle noise from a laser-based system is reduced by dynamically diffusing the laser beam. A
Datasheet: LSR-3000 Series Update: 06.08.2012 Copyright 2012 Optotune Laser Speckle Reducer LSR-3000 Series Speckle noise from a laser-based system is reduced by dynamically diffusing the laser beam. A
Tunable wideband infrared detector array for global space awareness
 Tunable wideband infrared detector array for global space awareness Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Sergio R. Restaino 1, Scott W. Teare 2, Sanjay Krishna 3, Mike Lenz 3, J.S. Brown 3, S.J. Lee 3, Christopher C.
Tunable wideband infrared detector array for global space awareness Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Sergio R. Restaino 1, Scott W. Teare 2, Sanjay Krishna 3, Mike Lenz 3, J.S. Brown 3, S.J. Lee 3, Christopher C.
NEW LASER ULTRASONIC INTERFEROMETER FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS B.Pouet and S.Breugnot Bossa Nova Technologies; Venice, CA, USA
 NEW LASER ULTRASONIC INTERFEROMETER FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS B.Pouet and S.Breugnot Bossa Nova Technologies; Venice, CA, USA Abstract: A novel interferometric scheme for detection of ultrasound is presented.
NEW LASER ULTRASONIC INTERFEROMETER FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS B.Pouet and S.Breugnot Bossa Nova Technologies; Venice, CA, USA Abstract: A novel interferometric scheme for detection of ultrasound is presented.
Characterization of Surface Structures using THz Radar Techniques with Spatial Beam Filtering and Out-of-Focus Detection
 ECNDT 2006 - Tu.2.8.3 Characterization of Surface Structures using THz Radar Techniques with Spatial Beam Filtering and Out-of-Focus Detection Torsten LÖFFLER, Bernd HILS, Hartmut G. ROSKOS, Phys. Inst.
ECNDT 2006 - Tu.2.8.3 Characterization of Surface Structures using THz Radar Techniques with Spatial Beam Filtering and Out-of-Focus Detection Torsten LÖFFLER, Bernd HILS, Hartmut G. ROSKOS, Phys. Inst.
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter
 Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA
 Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA Abstract: Speckle interferometry (SI) has become a complete technique over the past couple of years and is widely used in many branches of
Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA Abstract: Speckle interferometry (SI) has become a complete technique over the past couple of years and is widely used in many branches of
THE INFLUENCE OF THE RADIATION SOURCE PARAMETERS ON THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL SPECKLE CORRELATION METHOD
 THE INFLUENCE OF THE RADIATION SOURCE PARAMETERS ON THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL SPECKLE CORRELATION METHOD Lin Li 1*, Fedor Gubarev 1,2 1 National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, 634050, Tomsk, Russia
THE INFLUENCE OF THE RADIATION SOURCE PARAMETERS ON THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL SPECKLE CORRELATION METHOD Lin Li 1*, Fedor Gubarev 1,2 1 National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, 634050, Tomsk, Russia
Thermal management and thermal properties of high-brightness diode lasers
 Thermal management and thermal properties of high-brightness diode lasers Jens W. Tomm Max-Born-Institut für Nichtlineare Optik und Kurzzeitspektroskopie Berlin Max-Born-Str. 2 A, D-12489 Berlin, Germany
Thermal management and thermal properties of high-brightness diode lasers Jens W. Tomm Max-Born-Institut für Nichtlineare Optik und Kurzzeitspektroskopie Berlin Max-Born-Str. 2 A, D-12489 Berlin, Germany
Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
Instruction manual and data sheet ipca h
 1/15 instruction manual ipca-21-05-1000-800-h Instruction manual and data sheet ipca-21-05-1000-800-h Broad area interdigital photoconductive THz antenna with microlens array and hyperhemispherical silicon
1/15 instruction manual ipca-21-05-1000-800-h Instruction manual and data sheet ipca-21-05-1000-800-h Broad area interdigital photoconductive THz antenna with microlens array and hyperhemispherical silicon
Section 2: Lithography. Jaeger Chapter 2 Litho Reader. The lithographic process
 Section 2: Lithography Jaeger Chapter 2 Litho Reader The lithographic process Photolithographic Process (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Substrate covered with silicon dioxide barrier layer Positive photoresist
Section 2: Lithography Jaeger Chapter 2 Litho Reader The lithographic process Photolithographic Process (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Substrate covered with silicon dioxide barrier layer Positive photoresist
STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC
 STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION D. F ei, X. R. Zhang, C. M. Gan, and S. Y. Zhang Lab of Modern Acoustics and Institute of Acoustics Nanjing University, Nanjing,
STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION D. F ei, X. R. Zhang, C. M. Gan, and S. Y. Zhang Lab of Modern Acoustics and Institute of Acoustics Nanjing University, Nanjing,
Section 2: Lithography. Jaeger Chapter 2 Litho Reader. EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-1
 Section 2: Lithography Jaeger Chapter 2 Litho Reader EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-1 The lithographic process EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-2 Photolithographic Process (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Substrate covered
Section 2: Lithography Jaeger Chapter 2 Litho Reader EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-1 The lithographic process EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-2 Photolithographic Process (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Substrate covered
Infrared wire grid polarizers: metrology, modeling, and laser damage threshold
 Infrared wire grid polarizers: metrology, modeling, and laser damage threshold Matthew George, Bin Wang, Jonathon Bergquist, Rumyana Petrova, Eric Gardner Moxtek Inc. Calcon 2013 Wire Grid Polarizer (WGP)
Infrared wire grid polarizers: metrology, modeling, and laser damage threshold Matthew George, Bin Wang, Jonathon Bergquist, Rumyana Petrova, Eric Gardner Moxtek Inc. Calcon 2013 Wire Grid Polarizer (WGP)
Section 2: Lithography. Jaeger Chapter 2. EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-1
 Section 2: Lithography Jaeger Chapter 2 EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-1 The lithographic process EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-2 Photolithographic Process (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Substrate covered with silicon
Section 2: Lithography Jaeger Chapter 2 EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-1 The lithographic process EE143 Ali Javey Slide 5-2 Photolithographic Process (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Substrate covered with silicon
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/2/e1700324/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Photocarrier generation from interlayer charge-transfer transitions in WS2-graphene heterostructures Long Yuan, Ting-Fung
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/2/e1700324/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Photocarrier generation from interlayer charge-transfer transitions in WS2-graphene heterostructures Long Yuan, Ting-Fung
Novel laser power sensor improves process control
 Novel laser power sensor improves process control A dramatic technological advancement from Coherent has yielded a completely new type of fast response power detector. The high response speed is particularly
Novel laser power sensor improves process control A dramatic technological advancement from Coherent has yielded a completely new type of fast response power detector. The high response speed is particularly
Applications of Steady-state Multichannel Spectroscopy in the Visible and NIR Spectral Region
 Feature Article JY Division I nformation Optical Spectroscopy Applications of Steady-state Multichannel Spectroscopy in the Visible and NIR Spectral Region Raymond Pini, Salvatore Atzeni Abstract Multichannel
Feature Article JY Division I nformation Optical Spectroscopy Applications of Steady-state Multichannel Spectroscopy in the Visible and NIR Spectral Region Raymond Pini, Salvatore Atzeni Abstract Multichannel
capabilities Infrared Contact us for a Stock or Custom Quote Today!
 Infrared capabilities o 65+ Stock Components Available for Immediate Delivery o Design Expertise in SWIR, Mid-Wave, and Long-Wave Assemblies o Flat, Spherical, and Aspherical Manufacturing Expertise Edmund
Infrared capabilities o 65+ Stock Components Available for Immediate Delivery o Design Expertise in SWIR, Mid-Wave, and Long-Wave Assemblies o Flat, Spherical, and Aspherical Manufacturing Expertise Edmund
LASER GENERATION AND DETECTION OF SURFACE ACOUSTIC WAVES
 LASER GENERATION AND DETECTION OF SURFACE ACOUSTIC WAVES USING GAS-COUPLED LASER ACOUSTIC DETECTION INTRODUCTION Yuqiao Yang, James N. Caron, and James B. Mehl Department of Physics and Astronomy University
LASER GENERATION AND DETECTION OF SURFACE ACOUSTIC WAVES USING GAS-COUPLED LASER ACOUSTIC DETECTION INTRODUCTION Yuqiao Yang, James N. Caron, and James B. Mehl Department of Physics and Astronomy University
Exposure schedule for multiplexing holograms in photopolymer films
 Exposure schedule for multiplexing holograms in photopolymer films Allen Pu, MEMBER SPIE Kevin Curtis,* MEMBER SPIE Demetri Psaltis, MEMBER SPIE California Institute of Technology 136-93 Caltech Pasadena,
Exposure schedule for multiplexing holograms in photopolymer films Allen Pu, MEMBER SPIE Kevin Curtis,* MEMBER SPIE Demetri Psaltis, MEMBER SPIE California Institute of Technology 136-93 Caltech Pasadena,
Project Staff: Feng Zhang, Prof. Jianfeng Dai (Lanzhou Univ. of Tech.), Prof. Todd Hasting (Univ. Kentucky), Prof. Henry I. Smith
 3. Spatial-Phase-Locked Electron-Beam Lithography Sponsors: No external sponsor Project Staff: Feng Zhang, Prof. Jianfeng Dai (Lanzhou Univ. of Tech.), Prof. Todd Hasting (Univ. Kentucky), Prof. Henry
3. Spatial-Phase-Locked Electron-Beam Lithography Sponsors: No external sponsor Project Staff: Feng Zhang, Prof. Jianfeng Dai (Lanzhou Univ. of Tech.), Prof. Todd Hasting (Univ. Kentucky), Prof. Henry
Individually ventilated cages microclimate monitoring using photoacoustic spectroscopy
 Individually ventilated cages microclimate monitoring using photoacoustic spectroscopy Jean-Philippe Besson*, Marcel Gyger**, Stéphane Schilt *, Luc Thévenaz *, * Nanophotonics and Metrology Laboratory
Individually ventilated cages microclimate monitoring using photoacoustic spectroscopy Jean-Philippe Besson*, Marcel Gyger**, Stéphane Schilt *, Luc Thévenaz *, * Nanophotonics and Metrology Laboratory
A Narrow-Band Tunable Diode Laser System with Grating Feedback
 A Narrow-Band Tunable Diode Laser System with Grating Feedback S.P. Spirydovich Draft Abstract The description of diode laser was presented. The tuning laser system was built and aligned. The free run
A Narrow-Band Tunable Diode Laser System with Grating Feedback S.P. Spirydovich Draft Abstract The description of diode laser was presented. The tuning laser system was built and aligned. The free run
Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities
 Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities M. T. Rakher*, S. Strauf, Y. Choi, N.G. Stolz, K.J. Hennessey, H. Kim, A. Badolato, L.A. Coldren, E.L. Hu, P.M. Petroff, D. Bouwmeester University
Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities M. T. Rakher*, S. Strauf, Y. Choi, N.G. Stolz, K.J. Hennessey, H. Kim, A. Badolato, L.A. Coldren, E.L. Hu, P.M. Petroff, D. Bouwmeester University
Surface-Emitting Single-Mode Quantum Cascade Lasers
 Surface-Emitting Single-Mode Quantum Cascade Lasers M. Austerer, C. Pflügl, W. Schrenk, S. Golka, G. Strasser Zentrum für Mikro- und Nanostrukturen, Technische Universität Wien, Floragasse 7, A-1040 Wien
Surface-Emitting Single-Mode Quantum Cascade Lasers M. Austerer, C. Pflügl, W. Schrenk, S. Golka, G. Strasser Zentrum für Mikro- und Nanostrukturen, Technische Universität Wien, Floragasse 7, A-1040 Wien
Remote Sensing for Transparent Fluid Pressure by Laser Speckle
 American Journal of Science and Technology 2017; 4(5): 91-96 http://www.aascit.org/journal/ajst ISSN: 2375-3846 Remote Sensing for Transparent Fluid Pressure by Laser Speckle Sabah Mohammed Hadi 1, *,
American Journal of Science and Technology 2017; 4(5): 91-96 http://www.aascit.org/journal/ajst ISSN: 2375-3846 Remote Sensing for Transparent Fluid Pressure by Laser Speckle Sabah Mohammed Hadi 1, *,
The FTNIR Myths... Misinformation or Truth
 The FTNIR Myths... Misinformation or Truth Recently we have heard from potential customers that they have been told that FTNIR instruments are inferior to dispersive or monochromator based NIR instruments.
The FTNIR Myths... Misinformation or Truth Recently we have heard from potential customers that they have been told that FTNIR instruments are inferior to dispersive or monochromator based NIR instruments.
plasmonic nanoblock pair
 Nanostructured potential of optical trapping using a plasmonic nanoblock pair Yoshito Tanaka, Shogo Kaneda and Keiji Sasaki* Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 1-2,
Nanostructured potential of optical trapping using a plasmonic nanoblock pair Yoshito Tanaka, Shogo Kaneda and Keiji Sasaki* Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 1-2,
DetectionofMicrostrctureofRoughnessbyOpticalMethod
 Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Chemical Engineering Volume 1 Issue Version 1.0 Year 01 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA)
Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Chemical Engineering Volume 1 Issue Version 1.0 Year 01 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA)
Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 12, Number 3, 2009, 308 316 Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals Daniela DRAGOMAN 1, Adrian DINESCU 2, Raluca MÜLLER2, Cristian KUSKO 2, Alex.
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 12, Number 3, 2009, 308 316 Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals Daniela DRAGOMAN 1, Adrian DINESCU 2, Raluca MÜLLER2, Cristian KUSKO 2, Alex.
FIRST MEASUREMENTS FROM A NEW BROADBAND VIBROTHERMOGRAPHY MEASUREMENT SYSTEM
 FIRST MEASUREMENTS FROM A NEW BROADBAND VIBROTHERMOGRAPHY MEASUREMENT SYSTEM Stephen D. Holland 1 Center for NDE and Aerospace Eng Dept, Iowa State Univ, Ames, Iowa 50011 ABSTRACT. We report on the construction
FIRST MEASUREMENTS FROM A NEW BROADBAND VIBROTHERMOGRAPHY MEASUREMENT SYSTEM Stephen D. Holland 1 Center for NDE and Aerospace Eng Dept, Iowa State Univ, Ames, Iowa 50011 ABSTRACT. We report on the construction
Design and characterization of 1.1 micron pixel image sensor with high near infrared quantum efficiency
 Design and characterization of 1.1 micron pixel image sensor with high near infrared quantum efficiency Zach M. Beiley Andras Pattantyus-Abraham Erin Hanelt Bo Chen Andrey Kuznetsov Naveen Kolli Edward
Design and characterization of 1.1 micron pixel image sensor with high near infrared quantum efficiency Zach M. Beiley Andras Pattantyus-Abraham Erin Hanelt Bo Chen Andrey Kuznetsov Naveen Kolli Edward
March 31, 2003 Single-photon Detection at 1.55 µm with InGaAs APDs and via Frequency Upconversion Marius A. Albota and Franco N.C.
 March 31, 2003 Single-photon Detection at 1.55 µm with InGaAs APDs and via Frequency Upconversion Marius A. Albota and Franco N.C. Wong Quantum and Optical Communications Group MIT Funded by: ARO MURI,
March 31, 2003 Single-photon Detection at 1.55 µm with InGaAs APDs and via Frequency Upconversion Marius A. Albota and Franco N.C. Wong Quantum and Optical Communications Group MIT Funded by: ARO MURI,
Micro-sensors - what happens when you make "classical" devices "small": MEMS devices and integrated bolometric IR detectors
 Micro-sensors - what happens when you make "classical" devices "small": MEMS devices and integrated bolometric IR detectors Dean P. Neikirk 1 MURI bio-ir sensors kick-off 6/16/98 Where are the targets
Micro-sensors - what happens when you make "classical" devices "small": MEMS devices and integrated bolometric IR detectors Dean P. Neikirk 1 MURI bio-ir sensors kick-off 6/16/98 Where are the targets
PhE102-VASE. PHE102 Variable Angle Spectroscopic Ellipsometer. Angstrom Advanced Inc. Angstrom Advanced. Angstrom Advanced
 Angstrom Advanced PhE102-VASE PHE102 Variable Angle Spectroscopic Ellipsometer Angstrom Advanced Instruments for Thin Film and Semiconductor Applications sales@angstromadvanced.com www.angstromadvanced.com
Angstrom Advanced PhE102-VASE PHE102 Variable Angle Spectroscopic Ellipsometer Angstrom Advanced Instruments for Thin Film and Semiconductor Applications sales@angstromadvanced.com www.angstromadvanced.com
Absentee layer. A layer of dielectric material, transparent in the transmission region of
 Glossary of Terms A Absentee layer. A layer of dielectric material, transparent in the transmission region of the filter, due to a phase thickness of 180. Absorption curve, absorption spectrum. The relative
Glossary of Terms A Absentee layer. A layer of dielectric material, transparent in the transmission region of the filter, due to a phase thickness of 180. Absorption curve, absorption spectrum. The relative
Supplementary Figure 1 Reflective and refractive behaviors of light with normal
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Reflective and refractive behaviors of light with normal incidence in a three layer system. E 1 and E r are the complex amplitudes of the incident wave and
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Reflective and refractive behaviors of light with normal incidence in a three layer system. E 1 and E r are the complex amplitudes of the incident wave and
Development and Applications of a Sample Compartment FTIR Microscope
 Application Note Development and Applications of a Sample Since the early to mid-1940 s, scientists using infrared spectroscopy have been trying to obtain spectral data from ever smaller samples. Starting
Application Note Development and Applications of a Sample Since the early to mid-1940 s, scientists using infrared spectroscopy have been trying to obtain spectral data from ever smaller samples. Starting
Lecture 18: Photodetectors
 Lecture 18: Photodetectors Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Photodetector principle 2 3 Photoconductor 4 4 Photodiodes 6 4.1 Heterojunction photodiode.................... 8 4.2 Metal-semiconductor photodiode................
Lecture 18: Photodetectors Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Photodetector principle 2 3 Photoconductor 4 4 Photodiodes 6 4.1 Heterojunction photodiode.................... 8 4.2 Metal-semiconductor photodiode................
Spatially Resolved Backscatter Ceilometer
 Spatially Resolved Backscatter Ceilometer Design Team Hiba Fareed, Nicholas Paradiso, Evan Perillo, Michael Tahan Design Advisor Prof. Gregory Kowalski Sponsor, Spectral Sciences Inc. Steve Richstmeier,
Spatially Resolved Backscatter Ceilometer Design Team Hiba Fareed, Nicholas Paradiso, Evan Perillo, Michael Tahan Design Advisor Prof. Gregory Kowalski Sponsor, Spectral Sciences Inc. Steve Richstmeier,
Material analysis by infrared mapping: A case study using a multilayer
 Material analysis by infrared mapping: A case study using a multilayer paint sample Application Note Author Dr. Jonah Kirkwood, Dr. John Wilson and Dr. Mustafa Kansiz Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction
Material analysis by infrared mapping: A case study using a multilayer paint sample Application Note Author Dr. Jonah Kirkwood, Dr. John Wilson and Dr. Mustafa Kansiz Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit
 Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit Purpose 1. To understand the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction of light at a single slit and at a circular aperture; 2. To learn how to measure
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit Purpose 1. To understand the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction of light at a single slit and at a circular aperture; 2. To learn how to measure
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication
 InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
Terahertz spectroscopy measurements
 0 Terahertz spectroscopy measurements For general medicine and pharmacy students author: József Orbán, PhD. teaching facility: Univerity of Pécs, Medical School Department of Biophysics research facility:
0 Terahertz spectroscopy measurements For general medicine and pharmacy students author: József Orbán, PhD. teaching facility: Univerity of Pécs, Medical School Department of Biophysics research facility:
EE143 Fall 2016 Microfabrication Technologies. Lecture 3: Lithography Reading: Jaeger, Chap. 2
 EE143 Fall 2016 Microfabrication Technologies Lecture 3: Lithography Reading: Jaeger, Chap. 2 Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1-1 The lithographic process 1-2 1 Photolithographic
EE143 Fall 2016 Microfabrication Technologies Lecture 3: Lithography Reading: Jaeger, Chap. 2 Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1-1 The lithographic process 1-2 1 Photolithographic
2. Pulsed Acoustic Microscopy and Picosecond Ultrasonics
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Picosecond Ultrasonic Microscopy of Semiconductor Nanostructures Thomas J GRIMSLEY
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Picosecond Ultrasonic Microscopy of Semiconductor Nanostructures Thomas J GRIMSLEY
Supplementary information to Nature article: Wavelength-scalable hollow optical fibres with large photonic band gaps for CO 2 laser transmission
 Supplementary information to Nature article: Wavelength-scalable hollow optical fibres with large photonic band gaps for CO 2 laser transmission I. Modal characteristics of CO 2 laser guiding fibres Due
Supplementary information to Nature article: Wavelength-scalable hollow optical fibres with large photonic band gaps for CO 2 laser transmission I. Modal characteristics of CO 2 laser guiding fibres Due
The on-line detection of moisture and coatings by means of thermal waves. by R. Huttner and E. Schollmeyer
 The on-line detection of moisture and coatings by means of thermal waves moist by R. Huttner and E. Schollmeyer Oeutsches Texfilforschungszentrum Nord-West e. V., Institut an der Universitat Ouisburg Gesamthochschule,
The on-line detection of moisture and coatings by means of thermal waves moist by R. Huttner and E. Schollmeyer Oeutsches Texfilforschungszentrum Nord-West e. V., Institut an der Universitat Ouisburg Gesamthochschule,
3550 Aberdeen Ave SE, Kirtland AFB, NM 87117, USA ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 Beam Combination of Multiple Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers via Volume Bragg Gratings Chunte A. Lu* a, William P. Roach a, Genesh Balakrishnan b, Alexander R. Albrecht b, Jerome V. Moloney
Beam Combination of Multiple Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers via Volume Bragg Gratings Chunte A. Lu* a, William P. Roach a, Genesh Balakrishnan b, Alexander R. Albrecht b, Jerome V. Moloney
Imaging obscured subsurface inhomogeneity using laser speckle
 Imaging obscured subsurface inhomogeneity using laser speckle Ralph Nothdurft, Gang Yao Department of Biological Engineering, University of Missouri-Columbia, Columbia, MO 65211 renothdurft@mizzou.edu,
Imaging obscured subsurface inhomogeneity using laser speckle Ralph Nothdurft, Gang Yao Department of Biological Engineering, University of Missouri-Columbia, Columbia, MO 65211 renothdurft@mizzou.edu,
SURFACE ANALYSIS STUDY OF LASER MARKING OF ALUMINUM
 SURFACE ANALYSIS STUDY OF LASER MARKING OF ALUMINUM Julie Maltais 1, Vincent Brochu 1, Clément Frayssinous 2, Réal Vallée 3, Xavier Godmaire 4 and Alex Fraser 5 1. Summer intern 4. President 5. Chief technology
SURFACE ANALYSIS STUDY OF LASER MARKING OF ALUMINUM Julie Maltais 1, Vincent Brochu 1, Clément Frayssinous 2, Réal Vallée 3, Xavier Godmaire 4 and Alex Fraser 5 1. Summer intern 4. President 5. Chief technology
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin
 Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
LightGage Frequency Scanning Technology
 Corning Tropel Metrology Instruments LightGage Frequency Scanning Technology Thomas J. Dunn 6 October 007 Introduction Presentation Outline Introduction Review of Conventional Interferometry FSI Technology
Corning Tropel Metrology Instruments LightGage Frequency Scanning Technology Thomas J. Dunn 6 October 007 Introduction Presentation Outline Introduction Review of Conventional Interferometry FSI Technology
INFRARED ANALYSIS OF SINGLE AND MULTILAYER FILMS IN THE PRODUCTION AREA
 INFRARED ANALYSIS OF SINGLE AND MULTILAYER FILMS IN THE PRODUCTION AREA Sandy Rintoul Wilks Enterprise, Inc. South Norwalk, CT Scott Cobranchi Sealed Air Corporation Duncan, SC Nina Tani Sealed Air Corporation
INFRARED ANALYSIS OF SINGLE AND MULTILAYER FILMS IN THE PRODUCTION AREA Sandy Rintoul Wilks Enterprise, Inc. South Norwalk, CT Scott Cobranchi Sealed Air Corporation Duncan, SC Nina Tani Sealed Air Corporation
Chemical Imaging. Whiskbroom Imaging. Staring Imaging. Pushbroom Imaging. Whiskbroom. Staring. Pushbroom
 Chemical Imaging Whiskbroom Chemical Imaging (CI) combines different technologies like optical microscopy, digital imaging and molecular spectroscopy in combination with multivariate data analysis methods.
Chemical Imaging Whiskbroom Chemical Imaging (CI) combines different technologies like optical microscopy, digital imaging and molecular spectroscopy in combination with multivariate data analysis methods.
COMPOSITE MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES TESTING BY ELECTRONIC HOLOGRAPHY
 COMPOSITE MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES TESTING BY ELECTRONIC HOLOGRAPHY Dan N. Borza 1 1 Laboratoire de Mécanique de Rouen, Institut National des Sciences Appliquées de Rouen Place Blondel, BP 08, Mont-Saint-Aignan,
COMPOSITE MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES TESTING BY ELECTRONIC HOLOGRAPHY Dan N. Borza 1 1 Laboratoire de Mécanique de Rouen, Institut National des Sciences Appliquées de Rouen Place Blondel, BP 08, Mont-Saint-Aignan,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information Real-space imaging of transient carrier dynamics by nanoscale pump-probe microscopy Yasuhiko Terada, Shoji Yoshida, Osamu Takeuchi, and Hidemi Shigekawa*
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information Real-space imaging of transient carrier dynamics by nanoscale pump-probe microscopy Yasuhiko Terada, Shoji Yoshida, Osamu Takeuchi, and Hidemi Shigekawa*
Hamidreza Karbasi, P. Eng., PhD Conestoga College ITAL Oct. 7, 2010
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2010 Boston Presented by: Hamidreza Karbasi, P. Eng., PhD Conestoga College ITAL Oct. 7, 2010 Creating and Building Sustainable Environments Outline Background Objectives
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2010 Boston Presented by: Hamidreza Karbasi, P. Eng., PhD Conestoga College ITAL Oct. 7, 2010 Creating and Building Sustainable Environments Outline Background Objectives
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings
 A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
A STUDY ON THE VIBRATION CHARACTERISTICS OF CFRP COMPOSITE MATERIALS USING TIME- AVERAGE ESPI
 A STUDY ON THE VIBRATION CHARACTERISTICS OF CFRP COMPOSITE MATERIALS USING TIME- AVERAGE ESPI Authors: K.-M. Hong, Y.-J. Kang, S.-J. Kim, A. Kim, I.-Y. Choi, J.-H. Park, C.-W. Cho DOI: 10.12684/alt.1.66
A STUDY ON THE VIBRATION CHARACTERISTICS OF CFRP COMPOSITE MATERIALS USING TIME- AVERAGE ESPI Authors: K.-M. Hong, Y.-J. Kang, S.-J. Kim, A. Kim, I.-Y. Choi, J.-H. Park, C.-W. Cho DOI: 10.12684/alt.1.66
EFFECT OF SURFACE COATINGS ON GENERATION OF LASER BASED ULTRASOUND
 EFFECT OF SURFACE COATINGS ON GENERATION OF LASER BASED ULTRASOUND V.V. Shah, K. Balasubramaniam and J.P. Singh+ Department of Aerospace Engineering and Mechanics +Diagnostic Instrumentation and Analysis
EFFECT OF SURFACE COATINGS ON GENERATION OF LASER BASED ULTRASOUND V.V. Shah, K. Balasubramaniam and J.P. Singh+ Department of Aerospace Engineering and Mechanics +Diagnostic Instrumentation and Analysis
UNMATCHED OUTPUT POWER AND TUNING RANGE
 ARGOS MODEL 2400 SF SERIES TUNABLE SINGLE-FREQUENCY MID-INFRARED SPECTROSCOPIC SOURCE UNMATCHED OUTPUT POWER AND TUNING RANGE One of Lockheed Martin s innovative laser solutions, Argos TM Model 2400 is
ARGOS MODEL 2400 SF SERIES TUNABLE SINGLE-FREQUENCY MID-INFRARED SPECTROSCOPIC SOURCE UNMATCHED OUTPUT POWER AND TUNING RANGE One of Lockheed Martin s innovative laser solutions, Argos TM Model 2400 is
The KrF alternative for fast ignition inertial fusion
 The KrF alternative for fast ignition inertial fusion IstvánB Földes 1, Sándor Szatmári 2 Students: A. Barna, R. Dajka, B. Gilicze, Zs. Kovács 1 Wigner Research Centre of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences,
The KrF alternative for fast ignition inertial fusion IstvánB Földes 1, Sándor Szatmári 2 Students: A. Barna, R. Dajka, B. Gilicze, Zs. Kovács 1 Wigner Research Centre of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences,
Supplementary information for Stretchable photonic crystal cavity with
 Supplementary information for Stretchable photonic crystal cavity with wide frequency tunability Chun L. Yu, 1,, Hyunwoo Kim, 1, Nathalie de Leon, 1,2 Ian W. Frank, 3 Jacob T. Robinson, 1,! Murray McCutcheon,
Supplementary information for Stretchable photonic crystal cavity with wide frequency tunability Chun L. Yu, 1,, Hyunwoo Kim, 1, Nathalie de Leon, 1,2 Ian W. Frank, 3 Jacob T. Robinson, 1,! Murray McCutcheon,
Lithography. 3 rd. lecture: introduction. Prof. Yosi Shacham-Diamand. Fall 2004
 Lithography 3 rd lecture: introduction Prof. Yosi Shacham-Diamand Fall 2004 1 List of content Fundamental principles Characteristics parameters Exposure systems 2 Fundamental principles Aerial Image Exposure
Lithography 3 rd lecture: introduction Prof. Yosi Shacham-Diamand Fall 2004 1 List of content Fundamental principles Characteristics parameters Exposure systems 2 Fundamental principles Aerial Image Exposure
Properties of a Detector
 Properties of a Detector Quantum Efficiency fraction of photons detected wavelength and spatially dependent Dynamic Range difference between lowest and highest measurable flux Linearity detection rate
Properties of a Detector Quantum Efficiency fraction of photons detected wavelength and spatially dependent Dynamic Range difference between lowest and highest measurable flux Linearity detection rate
RECENTLY, using near-field scanning optical
 1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging. Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging
 Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Improving the Collection Efficiency of Raman Scattering
 PERFORMANCE Unparalleled signal-to-noise ratio with diffraction-limited spectral and imaging resolution Deep-cooled CCD with excelon sensor technology Aberration-free optical design for uniform high resolution
PERFORMANCE Unparalleled signal-to-noise ratio with diffraction-limited spectral and imaging resolution Deep-cooled CCD with excelon sensor technology Aberration-free optical design for uniform high resolution
Polarization Gratings for Non-mechanical Beam Steering Applications
 Polarization Gratings for Non-mechanical Beam Steering Applications Boulder Nonlinear Systems, Inc. 450 Courtney Way Lafayette, CO 80026 USA 303-604-0077 sales@bnonlinear.com www.bnonlinear.com Polarization
Polarization Gratings for Non-mechanical Beam Steering Applications Boulder Nonlinear Systems, Inc. 450 Courtney Way Lafayette, CO 80026 USA 303-604-0077 sales@bnonlinear.com www.bnonlinear.com Polarization
Title: Laser marking with graded contrast micro crack inside transparent material using UV ns pulse
 Cover Page Title: Laser marking with graded contrast micro crack inside transparent material using UV ns pulse laser Authors: Futoshi MATSUI*(1,2), Masaaki ASHIHARA(1), Mitsuyasu MATSUO (1), Sakae KAWATO(2),
Cover Page Title: Laser marking with graded contrast micro crack inside transparent material using UV ns pulse laser Authors: Futoshi MATSUI*(1,2), Masaaki ASHIHARA(1), Mitsuyasu MATSUO (1), Sakae KAWATO(2),
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3000 cm 1
 Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter
 8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
You won t be able to measure the incident power precisely. The readout of the power would be lower than the real incident power.
 1. a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and describe these terms: i. dynamic range ii. linear dynamic range iii. sensitivity iv. responsivity b) Imagine you are using an optical
1. a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and describe these terms: i. dynamic range ii. linear dynamic range iii. sensitivity iv. responsivity b) Imagine you are using an optical
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication
 InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
Instructions for the Experiment
 Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
Instructions for the Experiment Excitonic States in Atomically Thin Semiconductors 1. Introduction Alongside with electrical measurements, optical measurements are an indispensable tool for the study of
M. N. Trainer and P. J. Freud. Application Note. SL-AN-05 Revision D. Provided By: Microtrac, Inc. Particle Size Measuring Instrumentation
 High-Concentration Submicron Particle Size Distribution by Dynamic Light Scattering: Power spectrum development with heterodyne technology advances biotechnology and nanotechnology measurements M. N. Trainer
High-Concentration Submicron Particle Size Distribution by Dynamic Light Scattering: Power spectrum development with heterodyne technology advances biotechnology and nanotechnology measurements M. N. Trainer
Technical Explanation for Displacement Sensors and Measurement Sensors
 Technical Explanation for Sensors and Measurement Sensors CSM_e_LineWidth_TG_E_2_1 Introduction What Is a Sensor? A Sensor is a device that measures the distance between the sensor and an object by detecting
Technical Explanation for Sensors and Measurement Sensors CSM_e_LineWidth_TG_E_2_1 Introduction What Is a Sensor? A Sensor is a device that measures the distance between the sensor and an object by detecting
Composite Thermal Damage Measurement with Handheld FTIR. April 9, 2013 Brian D. Flinn, Ashley Tracey, and Tucker Howie University of Washington
 Composite Thermal Damage Measurement with Handheld FTIR April 9, 2013 Brian D. Flinn, Ashley Tracey, and Tucker Howie University of Washington Composite Thermal Damage Measurement with Handheld FTIR Motivation
Composite Thermal Damage Measurement with Handheld FTIR April 9, 2013 Brian D. Flinn, Ashley Tracey, and Tucker Howie University of Washington Composite Thermal Damage Measurement with Handheld FTIR Motivation
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #3 is due today No class Monday, Feb 26 Pre-record
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements Homework #3 is due today No class Monday, Feb 26 Pre-record
attosnom I: Topography and Force Images NANOSCOPY APPLICATION NOTE M06 RELATED PRODUCTS G
 APPLICATION NOTE M06 attosnom I: Topography and Force Images Scanning near-field optical microscopy is the outstanding technique to simultaneously measure the topography and the optical contrast of a sample.
APPLICATION NOTE M06 attosnom I: Topography and Force Images Scanning near-field optical microscopy is the outstanding technique to simultaneously measure the topography and the optical contrast of a sample.
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and
 Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Mercury Cadmium Telluride Detectors
 Mercury Cadmium Telluride Detectors ISO 9001 Certified J15 Mercury Cadmium Telluride Detectors (2 to 26 µm) General HgCdTe is a ternary semiconductor compound which exhibits a wavelength cutoff proportional
Mercury Cadmium Telluride Detectors ISO 9001 Certified J15 Mercury Cadmium Telluride Detectors (2 to 26 µm) General HgCdTe is a ternary semiconductor compound which exhibits a wavelength cutoff proportional
Infrared Illumination for Time-of-Flight Applications
 WHITE PAPER Infrared Illumination for Time-of-Flight Applications The 3D capabilities of Time-of-Flight (TOF) cameras open up new opportunities for a number of applications. One of the challenges of TOF
WHITE PAPER Infrared Illumination for Time-of-Flight Applications The 3D capabilities of Time-of-Flight (TOF) cameras open up new opportunities for a number of applications. One of the challenges of TOF
Ultra-stable flashlamp-pumped laser *
 SLAC-PUB-10290 September 2002 Ultra-stable flashlamp-pumped laser * A. Brachmann, J. Clendenin, T.Galetto, T. Maruyama, J.Sodja, J. Turner, M. Woods Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, 2575 Sand Hill Rd.,
SLAC-PUB-10290 September 2002 Ultra-stable flashlamp-pumped laser * A. Brachmann, J. Clendenin, T.Galetto, T. Maruyama, J.Sodja, J. Turner, M. Woods Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, 2575 Sand Hill Rd.,
Novel Beam Diagnostics Improve Laser Additive Manufacturing
 A Coherent Whitepaper November 17, 2016 Novel Beam Diagnostics Improve Laser Additive Manufacturing Laser additive manufacturing (LAM) is rapidly becoming an important method for the fabrication of both
A Coherent Whitepaper November 17, 2016 Novel Beam Diagnostics Improve Laser Additive Manufacturing Laser additive manufacturing (LAM) is rapidly becoming an important method for the fabrication of both
Grating-waveguide structures and their applications in high-power laser systems
 Grating-waveguide structures and their applications in high-power laser systems Marwan Abdou Ahmed*, Martin Rumpel, Tom Dietrich, Stefan Piehler, Benjamin Dannecker, Michael Eckerle, and Thomas Graf Institut
Grating-waveguide structures and their applications in high-power laser systems Marwan Abdou Ahmed*, Martin Rumpel, Tom Dietrich, Stefan Piehler, Benjamin Dannecker, Michael Eckerle, and Thomas Graf Institut
Nd:YSO resonator array Transmission spectrum (a. u.) Supplementary Figure 1. An array of nano-beam resonators fabricated in Nd:YSO.
 a Nd:YSO resonator array µm Transmission spectrum (a. u.) b 4 F3/2-4I9/2 25 2 5 5 875 88 λ(nm) 885 Supplementary Figure. An array of nano-beam resonators fabricated in Nd:YSO. (a) Scanning electron microscope
a Nd:YSO resonator array µm Transmission spectrum (a. u.) b 4 F3/2-4I9/2 25 2 5 5 875 88 λ(nm) 885 Supplementary Figure. An array of nano-beam resonators fabricated in Nd:YSO. (a) Scanning electron microscope
Novel Beam Diagnostics Improve Laser Additive Manufacturing
 White Paper Novel Beam Diagnostics Improve Laser Additive Manufacturing Laser additive manufacturing (LAM) is rapidly becoming an important method for the fabrication of both prototype and production metal
White Paper Novel Beam Diagnostics Improve Laser Additive Manufacturing Laser additive manufacturing (LAM) is rapidly becoming an important method for the fabrication of both prototype and production metal
Bias errors in PIV: the pixel locking effect revisited.
 Bias errors in PIV: the pixel locking effect revisited. E.F.J. Overmars 1, N.G.W. Warncke, C. Poelma and J. Westerweel 1: Laboratory for Aero & Hydrodynamics, University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands,
Bias errors in PIV: the pixel locking effect revisited. E.F.J. Overmars 1, N.G.W. Warncke, C. Poelma and J. Westerweel 1: Laboratory for Aero & Hydrodynamics, University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands,
photolithographic techniques (1). Molybdenum electrodes (50 nm thick) are deposited by
 Supporting online material Materials and Methods Single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) devices are fabricated using standard photolithographic techniques (1). Molybdenum electrodes (50 nm thick) are deposited
Supporting online material Materials and Methods Single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) devices are fabricated using standard photolithographic techniques (1). Molybdenum electrodes (50 nm thick) are deposited
NanoSpective, Inc Progress Drive Suite 137 Orlando, Florida
 TEM Techniques Summary The TEM is an analytical instrument in which a thin membrane (typically < 100nm) is placed in the path of an energetic and highly coherent beam of electrons. Typical operating voltages
TEM Techniques Summary The TEM is an analytical instrument in which a thin membrane (typically < 100nm) is placed in the path of an energetic and highly coherent beam of electrons. Typical operating voltages
SENSOR+TEST Conference SENSOR 2009 Proceedings II
 B8.4 Optical 3D Measurement of Micro Structures Ettemeyer, Andreas; Marxer, Michael; Keferstein, Claus NTB Interstaatliche Hochschule für Technik Buchs Werdenbergstr. 4, 8471 Buchs, Switzerland Introduction
B8.4 Optical 3D Measurement of Micro Structures Ettemeyer, Andreas; Marxer, Michael; Keferstein, Claus NTB Interstaatliche Hochschule für Technik Buchs Werdenbergstr. 4, 8471 Buchs, Switzerland Introduction
Laser Telemetric System (Metrology)
 Laser Telemetric System (Metrology) Laser telemetric system is a non-contact gauge that measures with a collimated laser beam (Refer Fig. 10.26). It measure at the rate of 150 scans per second. It basically
Laser Telemetric System (Metrology) Laser telemetric system is a non-contact gauge that measures with a collimated laser beam (Refer Fig. 10.26). It measure at the rate of 150 scans per second. It basically
A Laser-Based Thin-Film Growth Monitor
 TECHNOLOGY by Charles Taylor, Darryl Barlett, Eric Chason, and Jerry Floro A Laser-Based Thin-Film Growth Monitor The Multi-beam Optical Sensor (MOS) was developed jointly by k-space Associates (Ann Arbor,
TECHNOLOGY by Charles Taylor, Darryl Barlett, Eric Chason, and Jerry Floro A Laser-Based Thin-Film Growth Monitor The Multi-beam Optical Sensor (MOS) was developed jointly by k-space Associates (Ann Arbor,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Transfer printing stacked nanomembrane lasers on silicon Hongjun Yang 1,3, Deyin Zhao 1, Santhad Chuwongin 1, Jung-Hun Seo 2, Weiquan Yang 1, Yichen Shuai 1, Jesper Berggren 4, Mattias Hammar 4, Zhenqiang
Transfer printing stacked nanomembrane lasers on silicon Hongjun Yang 1,3, Deyin Zhao 1, Santhad Chuwongin 1, Jung-Hun Seo 2, Weiquan Yang 1, Yichen Shuai 1, Jesper Berggren 4, Mattias Hammar 4, Zhenqiang
Radial Coupling Method for Orthogonal Concentration within Planar Micro-Optic Solar Collectors
 Radial Coupling Method for Orthogonal Concentration within Planar Micro-Optic Solar Collectors Jason H. Karp, Eric J. Tremblay and Joseph E. Ford Photonics Systems Integration Lab University of California
Radial Coupling Method for Orthogonal Concentration within Planar Micro-Optic Solar Collectors Jason H. Karp, Eric J. Tremblay and Joseph E. Ford Photonics Systems Integration Lab University of California
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 Investigation of silver-only and silver / TOPAS coated hollow glass waveguides for visible and NIR laser delivery Jeffrey E. Melzer* a and James A. Harrington a a Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering,
Investigation of silver-only and silver / TOPAS coated hollow glass waveguides for visible and NIR laser delivery Jeffrey E. Melzer* a and James A. Harrington a a Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering,
