Improving Transmission Line Performance using Transient Based Adaptive SPAR
|
|
|
- Merryl Holmes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
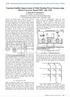
1 Proceedings of the 14 th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON ), Cairo University, Egypt, December 19-21, 2, Paper ID 249. Improving Transmission Line Performance using Transient Based Adaptive SPAR O. E. Gouda*, D. K. Ibrahim D. H. Helmi, D. M. Khalifa* G. M. Amer* Department of Electrical Power Egyptian Electricity Transmission Engineering Company. Higher Institute of Technology Cairo University Banha University Cairo, Egypt Cairo, Egypt Banha, Egypt * *dr_ghada11@hotmail.com Abstract - Adaptive SPAR offers many advantages over conventional techniques. In the case of transient faults, the arcing extinction time can be accurately determined and in the case of a permanent fault, breaker reclosure can be avoided. This paper describes, in some detail, the design of a new Adaptive SPAR technique that extracts high frequencies transients, from the CVT. The main case of study in this paper is the High Dam / Nagh Hamady, Nagh Hamady /Assuit kv double circuit transmission system in the Egyptian network. Fault scenario cases representing different fault locations, inception angles, actual representation to secondary arc characteristics, and with/without shunt reactor existence were extracted from simulation work, and then verified through real field records in that system. The outcome of this study indicates that the proposed technique can be used as an effective means of achieving an adaptive single pole auto reclosure scheme. Index Terms - Transmission lines, Single Pole Auto Reclosure, Adaptive, Dead Time, Transient Fault, Permanent Fault. I. INTRODUCTION Operation of transmission networks faces a lot of obstacles regarding the trip/close decision on each line and its consequences on the stability of the network [1, 2]. A successful Automatic close back-in decision (Auto Reclose) to a line can maintain the reliability of the network by restoring power supply and obtain a secure decision by avoiding the attempt to close onto fault. Also, Auto Reclosing (AR) Dead Time affects the stability of the transmission line and therefore the whole network. According to statistics shown in [3] Arcing faults represents of the transmission faults. Most of these faults are transient faults that may extinguish by tripping the line. These faults may occur due to moisture in the early morning or polluted insulators, which are common conditions in the Egyptian environment [4]. Therefore, AR is supposed to be a necessary application in order to improve reliability to important transmission lines. Single pole Auto Reclosing (SPAR) algorithms can be programmed either in an individual device or implemented as a function in a numerical relay. Traditional SPAR Algorithms perform their main function successfully; which is to reclose the faulty phase after specific predefine dead time, regardless the fault situation (extinguished or not) [, 6]. Usually, this dead time is a fixed interval [7], and it can reflect the time margin for a phase to separate from the three phase line without losing stability in the system. It's obvious, that stability margin can be increased as much as the dead time reduced. The optimum solution to this problem is to adapt the dead time according to the information captured from the voltage and current signals associated with the faulty phase after tripping. Adaptive dead time schemes were developed in literature in order to reduce the dead time using different techniques involving neural network [8, 9], fuzzy logic [], zero sequence voltage [11], and power of high frequency components in current signals [12]. In this paper, a new SPAR algorithm is developed, where dead time is adapted according to the fault extinguishing information. The proposed SPAR performs several functions, first it can discriminate between natures of faults, and secondly it can detect the instant of fault extinguished. Discrimination between faults nature is important to decide closing or blocking decisions, while fault extinguishing detection is essential to ensure the instant of reclosing decision. Hence, the faulty phase will stay out of service for the least essential time required and then reclosed back-in to service without unsuccessful AR attempt (i.e. close onto fault ). If permanent fault is detected, the other healthy phases will be tripped and the proposed SPAR will be blocked for further later closing attempts. Algorithms used in this SPAR depend on the harmonic distortion analysis of the voltage waveform at the faulty line end terminal in order to perform the first function. The second function is accomplished using transient waveforms based fault detection / location technique. The algorithms are discussed in details and the Egyptian kv network is used for testing of the algorithms. Different fault scenarios where subjected to the algorithms, in which different fault locations, inception angles, actual representation to secondary arc characteristics and with/without shunt reactor existence were extracted from simulation work, and then verified through real field records in that system. II. TRANSIENT BASED SPAR ALGORITHMS After the fault been detected, classified, and located through protection devices, a single phase tripping order is issued to circuit breaker. In this instant, three scenarios can be expected regarding fault existence after breaker tripping action. The 614
2 first scenario is the extinguishing of the fault instantaneously by the trip decision, and no secondary arc exists but the oscillation due to shunt reactor starts, if any. The first scenario represents the transient fault type. The second scenario is the existences of fault after tripping decision, which extinguishing instant appears within specific time period (i.e. fixed dead time). The second scenario represents the long duration transient fault type. The third scenario, is the existence of secondary arc for specific time period (i.e. fixed dead time), without the extinguishing instant occurrence. The third scenario represents the permanent fault type and any closing attempt to it will be unsuccessful. The new SPAR algorithms have to perform two sub- routines in order to reach successful reclose attempt. The first subroutine is to distinguish between existence and absence of secondary arc. The second sub routine is to search for arc extinguish in case of secondary arc existence. The flow chart shown in figure (1) describes the proposed SPAR algorithms with details about its inputs, expected functions, and implemented routines. First: The analog inputs to the algorithms will be the secondary voltage from the instrument transformers installed on the line under study and the transient voltage signals from the communication tap of the coupling capacitive voltage transformer (CCVT) [13]. The transmission protection devices should supply the algorithms with information, which is phase selection. The digital inputs to the algorithms will be provided from the circuit breaker regarding trip decision. Second: the inputs will be in processing successive windows of data. The information regarding the protection data, the secondary voltage from one end terminal will be fed to the first sub routine in order to differentiate between existence and non existence of secondary arc. This sub routine will accomplish "Condition#1" status. In this sub routine, the voltage inputs from both line ends processed using Discreet Fourier Transform (DFT) in order to compute fundamentals and odd harmonic components. The computed frequency components of voltage from one line end will be used to calculate a discrimination quantity. Since, it's well known that arcing faults voltages has a high percentage of harmonics, and after studying the voltage signal of several fault scenarios, it was found that the percentage of odd harmonics in ranges of (3,, 7, 9) are more obvious. Therefore, a good method of measuring the harmonics of secondary arc and separate it from the shunt reactor oscillation will be through using Total Harmonic Distortion Percentage "THD " [14]. ( ) 2 ( V F n ) n = 3,,7,9 THD = (1) V (1) F V ( F n ) : Amplitude of (n) harmonic component of faulted line sending end voltage. V ( 1) F : Amplitude of fundamental frequency component of faulted line sending end voltage. Fig. 1 Proposed SPAR algorithms flow chart. The calculated THD amplitude, from the faulty phase sending end voltage (Shunt reactor location); can be used to determine the secondary arc existence when exceeding specific threshold. But due to the existence of different threshold with the variation of system conditions related to shunt reactors existence/ non existence, another expression will be derived from the first, which is difference of THD between faulty phase and other two healthy phases. THD _ diff = ( THD_ p1) ((( THD_ p2) + ( THD_ p3)) / 2) (2) THD _ p1, Circuit Breaker (Trip) Protection (Phase Selection) No Transient Fault Action: Close No Permanent Fault Action: Block THD _ p 2 CCVT (Secondary Voltage Signal) 1st Sub Routine Condition # 1 Yes Cond. 1> ε 1 t < DT Yes AND Gate THD _ p 3 Data Window Long Transient Fault Action: Close CCVT (Transient Voltage Signals) 2nd Sub Routine Condition # 2 Cond. 2> ε 2 : It is the Total Harmonic Distortion percentage for the faulty phase and the other two healthy phases, respectively. THD _ diff : It is absolute difference in Total Harmonic Distortion percentage between he faulty phase and the other two healthy phases. 61
3 If "THD_diff" didn't exceed specific threshold ( ε 1) then "Condition#1" not specified, and fault is transient, and no arcing exist. Therefore, Closing Decision can be accomplished instantaneously. If "THD_diff" increases than specific threshold ( ε 1) then "Condition#1" is satisfied, and secondary arcing exist. Therefore, another subroutine will work in parallel with the 1st subroutine to search for the arc extinguishing instant. The transient input signal will fed to the 2nd subroutine, in order to search for arc extinguishing moment. The transient signal can detect any transient disturbance within the line length and locate its position according to the following equation [1]. L ( tb ta) v x = (3) 2 x : It is the distance to fault from the sending end of the line. L : It is the line length. tb, ta : It is the time detected where the transient signals at terminal b and a respectively, exceeds specific threshold. v : It is the wave propagation velocity of the line. If the signal exceeds specific threshold ( ε 2 ), while the location ' x ' exist within the line length, therefore, transient disturbance occurs and arc is extinguished. At this result, "Condition#2" is satisfied. Hence, significance of secondary arc existence and long duration transient fault extinguishing is presented. Closing decision may be issued afterwards instantaneously. If "Condition#1" exist for specific time period which represents allowed dead time, and "Condition#2" not satisfied, therefore, permanent fault exists. Permanent fault status requires tripping the other healthy phases, and blocking decision to any further closing attempts to the SPAR. The maximum allowed dead time is related to a stability study regarding the line and determining the maximum time period that the line may operate with two healthy phases only without loosing system stability. Setting the thresholds ( ε 1), ( ε 2 ), and maximum allowed dead time must be done according to each study separately. It may differ between simulated cases and recorded fault scenarios due to load conditions or environmental effects. III. SPAR TESTING REALISTIC NETWORK For the purpose of testing the new SPAR algorithms, a simulation case study is represented using Egyptian kv transmission network data. The line under study lies between High Dam Substation and Nag Hamady substation. The line is double circuit configuration with 146 miles in length. The line has a shunt reactor permanently installed to it from the High Dam Busbar direction only. Schematic diagram for the system under study is shown in figure (2). Fig. 2 Egyptian kv network. Table I Fault Scenarios used for testing the SPAR. Case D Ph Rec In feed Ex Instant A Yes Normal 1 A No Normal 1 B No Normal 1 B Yes Normal 1 A No Normal 2 67 B Yes Weak C No Weak 2 67 A Yes Normal 3 - B No Normal 3 - C Yes Weak 3 - D: Refers to the distance in length percentage between the sending end and the fault point on the line. Ph: Refers to the Faulty phase. Rec: Refers to the Existence status of reactor. (1, 2, 3): Refers to the type of fault (Transient, Long duration Transient, and permanent respectively). Ex. Instant: Refers to the fault extinguishing instant in seconds, if fault recorded starts at the trip time. Arcing faults in this study is represented with primary and secondary arc algorithms programmed to the ATP software through the ATP models language [16]. The primary and secondary arcing models are extracted from an experimental study done in [17]. Although both arcs are simulated in fault representation, but in this study, which occur after the breaker tripping action, secondary arc will be our main concern. In order to show the importance of the study, comprehensive fault scenarios will be represented to test the SPAR. The fault scenarios will include different fault types (i.e. transient, long duration transient, permanent), existence of reactor status, different fault locations (i.e. -- ) of the line length and different (extinction times of long duration transient 616
4 fault). Finally, a validation process is presented in this study, where the SPAR is tested against real fault record on the same line. IV. USING ADAPTIVE SPAR ALGORITHMS In order to reach valid thresholds for all fault scenarios discussed above, a comprehensive study for voltage and transient signals corresponding to different fault types and system conditions is done. Figures (3, 6) shows the sending end voltage signal for cases 1 and 3 respectively, while figures (4, ) shows the sending end transient voltage signals for cases 1 and 3 respectively. Cases 1 and 3, represent transient fault, where only two disturbances occurs on transient signals, the first occurs at.1 seconds, which represent the primary arc initiation time, and protection devices should deal with this type of fault to trigger the breaker control circuit to produce trip decision, which appears at the instant.2 seconds as the 2nd disturbance. It's obvious from the transient signals that no transient signals appear afterwards, and also the shunt reactor oscillation is shown after tripping instantaneously. That's all is a significance of the fault final extinguishing and the system is balanced. SPAR close decision must not be issued after the trip time instant instantaneously, in order to leave some delay time before closing, in order to let the severe discharge due to breaker tripping period to end first. Close Action will depend on circuit breaker characteristics, and system conditions, which are in our case, the close will happen after.1 seconds ( cycles) Fig. Transient Voltage signal for transient fault on Phase "B", located at apart from line sending end, with reactor absence Fig. 3 Sending End secondary Voltage for transient fault on Phase "A", located at apart from line sending end, with reactor existence. 1. x Fig. 4 Transient Voltage signal for transient fault on Phase "A", located at apart from line sending end, with reactor existence Fig. 6 Sending End secondary Voltage for transient fault on Phase "B", located at apart from line sending end, with reactor absence. Case 7 show a long duration transient fault type, where the transient signal, and the sending end secondary voltage signal are shown in figures (7, 8), respectively. As shown in figure (7), the signal starts at.2 seconds (i.e. after the breaker trip action by msec), and a third disturbance appears with high magnitude at.67 seconds from the start of the simulation time. Hence, long duration transient fault occurs, where secondary arc exist and extinguished at the 3rd disturbance time. Figures (9, ) show the transient signals and sending end secondary voltage for case, which represent permanent fault (i.e. extinguishing moment will occur after the maximum allowed dead time). This fault type need a SPAR block action after the maximum allowed dead time ending in order to maintain stability for the line. In the kv Egyptian network, the maximum allowed dead time for SPAR is milliseconds (4 cycles) but in the simulation cases a smaller time period is used (37 msec or 19 cycles) in order to give a clear representation to the test results. 617
5 Fig. 7 Transient Voltage signal for long duration transient fault on Phase "C", located at apart from line sending end, with reactor absence Fig. Sending End secondary Voltage for Permanent fault on Phase "C", located at apart from line sending end, with reactor existence Case1 Case3 Case7 Case - THD Fig. 8 Sending End sending Voltage for long duration transient fault on Phase "C", located at apart from line sending end, with reactor absence. The MATLAB [18] is used to program the proposed SPAR algorithms and testing the cases. Figures (11), shows the Total Harmonic Distortion percentage (THD ) for all the cases 1,3,7,9, and. THD results didn't exceed 11 for transient faults while it increases in secondary arc gradually till extinguish instant reaching 46 then it falls again to the transient fault values. It's obvious that the first condition threshold will be Data Window (.*Cycle ) Fig. 11 SPAR THD results. Table II SPAR Condition 1 and 2 results for all simulation cases. Case Condition # 1 Occurrence time (MDW) Condition # 2 Occurrence time (MDW) Start End Start End (48) End (48) End (48) End Fig. 9 Transient Voltage signal for Permanent fault on Phase "C", located at apart from line sending end, with reactor existence. Table (II) shows conditions 1 and 2 for all the simulated cases described in table (I). Each condition is specified by its start time and end time of the condition by the moving data window number, which is illustrated in figure (11). 618
6 Case Table III SPAR Functions results for all simulation cases. SPAR Action Time Fault Adaptive DT duration Table (III) show the results for the fault type, SPAR action, and SPAR action time, respectively, for all the simulated cases described in table (I). Action 1, 2 is presenting close and block respectively. Fault type 1, 2, and 3 is representing transient, long duration transient and permanent fault respectively. As shown in figures the cases are well identified to their fault types and correct SPAR actions and the time where the action is taken is recognized in milliseconds. Table (III), shows the SPAR action type and proposed time in milliseconds, which starting from the simulation start time. The breaker trip at 2 milliseconds after the simulation start time, and the SPAR algorithms starts after milliseconds from the trip order, So, if the transient fault conditions is specified, therefore, the SPAR will give a close within 16 milliseconds and the total adaptive dead time as shown in table will be 26 milliseconds from the trip order. Long duration transient faults, will have a close when it reaches it's extinguish condition as shown in cases, 6, and 7. Permanent faults will give a block decision after the corresponding fault type conditions satisfied and passed the maximum allowed dead time of the system, which is this simulation cases is 37 milliseconds from the start of algorithms work or 47 milliseconds from the trip order. V. ALGORITHMS TESTING ON REAL FIELD RECORDS Validation through the field record is required in order to check the feasibility of the new SPAR algorithms with the main problem. Fault occurred at phase "B", at the middle of the line, when the reactor is existed and the in feed is in its normal conditions. Figures (12, 13) shows the transient signal and the secondary voltage signal for a real fault record occurred on the same line under study. Due to the absence of the CVT communication transient waveforms in this fault record, the transient voltage signal is captured from filtering the sending end secondary voltage signal using Butterworth high pass filter with a cut-off frequency of Hz. It's obvious from the record that the fault type is transient, and a perfect action after the breaker tripping, will be a SPAR close decision. As shown in figure (14), the total harmonic distortion percentage didn't exceed 18, and both conditions (1 and 2) didn't exist. The proposed SPAR decision was a close decision, and the fault type was transient as shown in figure. As shown in table (IV) detects the time for the close action which is 3 milliseconds after the record start time. The breaker trip at 13 milliseconds after the record start time, and the SPAR algorithms starts after milliseconds from the trip order, So, if the transient fault conditions is specified, therefore, the SPAR will give a close within 6 milliseconds and the total adaptive dead time as shown in table will be 26 milliseconds from the trip order. Transient Voltage Signal (V) Fig. 12 Transient Voltage signal (recorded case) for Transient fault on Phase "B", located at apart from line sending end, with reactor existence Fig. 13 Sending End Primary Voltage signal (recorded case) for Transient fault on Phase "B", located at apart from line sending end, with reactor existence. THD, Condition 1, Condition Data Window (.*Cycle ) THD Condition 1 Condition 2 Fig. 14 SPAR THD, Condition 1, and Condition 2 results. Table IV 619
7 Recorded Fault Case SPAR Function "Fault ", "Action", "Action Time" results. SPAR Action Time Fault The agreement between the tasks goals and the algorithms results, prove the feasibility of the proposed SPAR to be used in any fault case or system condition. Thresholds and dead time must be provided after a load flow, short circuit and transient stability studies to the line under study before SPAR installation. It's preferred to monitor and capture data through high resolution and using higher sampling rate devices (i.e. fault recorders, PMU's) in order to reach the specific goals accurately. VI. CONCLUSIONS Adaptive DT duration This paper proposes new algorithms for Adaptive SPAR technique that extracts high frequencies transients, and secondary voltage waveform from the CVT. The new Adaptive SPAR can differentiate between permanent and transient faults during the dead time period. The system can then, adapt itself to reduce the dead time and reclose in case of transient faults, or trip the other two phases and blocking the circuit breaker in case of permanent faults, respectively. The used transient signals from CVT proves the fault extinguishing detection process, since its well known by the high accuracy and speed in detection and location of transient disturbance within the line, without been affected with the common instrument transformer problems (i.e. Saturation, and Ferro Resonance). The use of THD as a discriminator between the existence and non existence of the arcing phenomena helps to improve the SPAR decision by differentiating between fault arcing phenomena and other harmonics oscillation due to shunt reactor existence within the line under study. While traditional protection relays may easily mal-operate due to the oscillations resulted from reactor existence, the proposed adaptive SPAR succeeded to overcome this phenomena and successful achieve its main tasks. The new SPAR algorithms presented in this paper reduces the dead time according to each fault case, and differentiate between fault types in order to reach successful SPAR decisions, in order to improve transmission system stability during operation process. [3] Y.G. Paithankar, S.R. Bhide, "Fundamentals of Power System Protection ", Prentice-Hall of India Private Limited, New Delhi, 23. [4] M. Khalifa, A. El-Morshedy, O. E. Gouda, S. E. D. Habib, "A new monitor for pollution on power line insulators. II. Simulated field tests", IEE Proceedings C Generation, Transmission and Distribution, Volume 13, Issue 1, Jan 1988 P [] "REXA 1, User s Guide", Link: [6] "LFAA 1, 2", Link: [7] S. P. Ahn, C. H. Kim, R.K. Aggarwal, A. T. Johns, An alternative approach to adaptive single pole auto-reclosing in high voltage transmission systems based on variable dead time control, IEEE Transaction on Power Delivery, Vol. 16, No. 4, pp , October 21. [8] M. Jannati, B. Vahidi, S.H. Hosseinian, H.R. Baghaee, A new adaptive single phase auto-reclosure scheme for EHV transmission lines, Proceedings of 12th International Middle- East Power System Conference, (MEPCON 28), Egypt, pp , March 28. [9] M.A. El-Hadidy, D.H. Moustafa, A.S. Attia, Using neurowavelet technique for adaptive single phase autoreclosure of transmission lines, Proceedings of the 39th International Universities Power Engineering Conference, (UPEC 24), UK, Vol. 1, pp , September 24. [] X. Lin, P. Liu, Method of distinguishing between instant and permanent fault of transmission lines based on fuzzy decision, IEEE Catalog No. 98EX137, pp. 4-46, [11] S. Jamali, A. Parham, "One Terminal Digital Algorithm for Adaptive Single Pole Auto-Reclosing Based on Zero Sequence Voltage", Iranian Journal of Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Vol. 4, 78 No. 3, July 28. [12] Z. Q. Bo, R. K. Aggarwal, A. T. Johns, A novel technique to distinguish between transient and permanent fault based on detection of current transients, Proceeding of 4th International Conference on Advances in Power System Control and Management, APSCOM-97, Hong Kong, pp , November [13] F. S. Carvalho, S. Carneiro Jr., Transient conditions in CCVTs outputs and their effects on the detection of traveling waves, Electric Power Systems Research, Vol. 76, No. 8, pp , May 26. [14] H. Khorashadi-Zadeh, Zuyi Li, "A Novel PMU-Based Transmission Line Protection Scheme Design", 39th North American Power Symposium (NAPS '7), pp , 27. [1] Z.Q. Bo, M.A. Redfern, G.C. Weller, "Positional protection of transmission line using fault generated high frequency transient signals", IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, Vol. 1, No. 3, pp , Jul 2. [16] L. Dube, MODELS in ATP, Language Manual, It's available on: [17] A.T. Johns, R.K. Aggarwal, Y.H. Song, "Improved techniques for modelling fault arcs on faulted EHV transmission systems," IEE Proceedings Generation, Transmission and Distribution, Vol. 141, No. 2, pp , [18] The MathWorks Inc., Using MATLAB, 27. REFERENCES [1] F. Calero, D. Hou "Practical Considerations for Single-Pole-Trip Line-Protection Schemes", SEL Technical Paper 6184, Link: [2] IEEE Guide for Automatic Reclosing of Line Circuit Breakers for AC Distribution and Transmission Lines, IEEE Standard C
Neutral Reactor Optimization in order to Reduce Arc Extinction Time during Three-Phase Tripping
 Neutral Reactor Optimization in order to Reduce Arc Extinction Time during Three-Phase Tripping P. Mestas, M. C. Tavares Abstract. The optimization of the grounding neutral reactor is a common practice
Neutral Reactor Optimization in order to Reduce Arc Extinction Time during Three-Phase Tripping P. Mestas, M. C. Tavares Abstract. The optimization of the grounding neutral reactor is a common practice
Harmonic Analysis of a High Speed Automatic Reclosing on a 400 kv Overhead Transmission Line
 Harmonic Analysis of a High Speed Automatic Reclosing on a 400 kv Overhead Transmission Line ANGELA IAGAR, SORIN IOAN DEACONU, CORINA DANIELA CUNTAN, IOAN BACIU Department of Electrotechnical Engineering
Harmonic Analysis of a High Speed Automatic Reclosing on a 400 kv Overhead Transmission Line ANGELA IAGAR, SORIN IOAN DEACONU, CORINA DANIELA CUNTAN, IOAN BACIU Department of Electrotechnical Engineering
A Novel Fuzzy Neural Network Based Distance Relaying Scheme
 902 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 15, NO. 3, JULY 2000 A Novel Fuzzy Neural Network Based Distance Relaying Scheme P. K. Dash, A. K. Pradhan, and G. Panda Abstract This paper presents a new
902 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 15, NO. 3, JULY 2000 A Novel Fuzzy Neural Network Based Distance Relaying Scheme P. K. Dash, A. K. Pradhan, and G. Panda Abstract This paper presents a new
An Ellipse Technique Based Relay For Extra High Voltage Transmission Lines Protection
 Proceedings of the 14th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON 10), Cairo University, Egypt, December 19-21, 2010, Paper ID 162. An Ellipse Technique Based Relay For Extra High Voltage
Proceedings of the 14th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON 10), Cairo University, Egypt, December 19-21, 2010, Paper ID 162. An Ellipse Technique Based Relay For Extra High Voltage
Adaptive Autoreclosure to Increase System Stability and Reduce Stress to Circuit Breakers
 Adaptive Autoreclosure to Increase System Stability and Reduce Stress to Circuit Breakers 70 th Annual Conference for Protective Relay Engineers Siemens AG 2017 All rights reserved. siemens.com/energy-management
Adaptive Autoreclosure to Increase System Stability and Reduce Stress to Circuit Breakers 70 th Annual Conference for Protective Relay Engineers Siemens AG 2017 All rights reserved. siemens.com/energy-management
Keywords: Transformer, differential protection, fuzzy rules, inrush current. 1. Conventional Protection Scheme For Power Transformer
 Vol. 3 Issue 2, February-2014, pp: (69-75), Impact Factor: 1.252, Available online at: www.erpublications.com Modeling and Simulation of Modern Digital Differential Protection Scheme of Power Transformer
Vol. 3 Issue 2, February-2014, pp: (69-75), Impact Factor: 1.252, Available online at: www.erpublications.com Modeling and Simulation of Modern Digital Differential Protection Scheme of Power Transformer
Adaptive Autoreclosure to Increase System Stability and Reduce Stress to Circuit Breakers
 Adaptive Autoreclosure to Increase System Stability and Reduce Stress to Circuit Breakers Jörg Blumschein 1), Yilmaz Yelgin 1), Andrea udwig 2) 1) Siemens AG, Energy Management Division 2) 50Hertz Transmission
Adaptive Autoreclosure to Increase System Stability and Reduce Stress to Circuit Breakers Jörg Blumschein 1), Yilmaz Yelgin 1), Andrea udwig 2) 1) Siemens AG, Energy Management Division 2) 50Hertz Transmission
Symmetrical Components in Analysis of Switching Event and Fault Condition for Overcurrent Protection in Electrical Machines
 Symmetrical Components in Analysis of Switching Event and Fault Condition for Overcurrent Protection in Electrical Machines Dhanashree Kotkar 1, N. B. Wagh 2 1 M.Tech.Research Scholar, PEPS, SDCOE, Wardha(M.S.),India
Symmetrical Components in Analysis of Switching Event and Fault Condition for Overcurrent Protection in Electrical Machines Dhanashree Kotkar 1, N. B. Wagh 2 1 M.Tech.Research Scholar, PEPS, SDCOE, Wardha(M.S.),India
Feature Extraction of Magnetizing Inrush Currents in Transformers by Discrete Wavelet Transform
 Feature Extraction of Magnetizing Inrush Currents in Transformers by Discrete Wavelet Transform Patil Bhushan Prataprao 1, M. Mujtahid Ansari 2, and S. R. Parasakar 3 1 Dept of Electrical Engg., R.C.P.I.T.
Feature Extraction of Magnetizing Inrush Currents in Transformers by Discrete Wavelet Transform Patil Bhushan Prataprao 1, M. Mujtahid Ansari 2, and S. R. Parasakar 3 1 Dept of Electrical Engg., R.C.P.I.T.
Improving Current and Voltage Transformers Accuracy Using Artificial Neural Network
 Improving Current and Voltage Transformers Accuracy Using Artificial Neural Network Haidar Samet 1, Farshid Nasrfard Jahromi 1, Arash Dehghani 1, and Afsaneh Narimani 2 1 Shiraz University 2 Foolad Technic
Improving Current and Voltage Transformers Accuracy Using Artificial Neural Network Haidar Samet 1, Farshid Nasrfard Jahromi 1, Arash Dehghani 1, and Afsaneh Narimani 2 1 Shiraz University 2 Foolad Technic
MODEL POWER SYSTEM TESTING GUIDE October 25, 2006
 October 25, 2006 Document name Category MODEL POWER SYSTEM TESTING GUIDE ( ) Regional Reliability Standard ( ) Regional Criteria ( ) Policy ( ) Guideline ( x ) Report or other ( ) Charter Document date
October 25, 2006 Document name Category MODEL POWER SYSTEM TESTING GUIDE ( ) Regional Reliability Standard ( ) Regional Criteria ( ) Policy ( ) Guideline ( x ) Report or other ( ) Charter Document date
A NEW DIFFERENTIAL PROTECTION ALGORITHM BASED ON RISING RATE VARIATION OF SECOND HARMONIC CURRENT *
 Iranian Journal of Science & Technology, Transaction B, Engineering, Vol. 30, No. B6, pp 643-654 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 2006 Shiraz University A NEW DIFFERENTIAL PROTECTION ALGORITHM
Iranian Journal of Science & Technology, Transaction B, Engineering, Vol. 30, No. B6, pp 643-654 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 2006 Shiraz University A NEW DIFFERENTIAL PROTECTION ALGORITHM
Considering Characteristics of Arc on Travelling Wave Fault Location Algorithm for the Transmission Lines without Using Line Parameters
 Considering Characteristics of Arc on Travelling Wave Fault Location Algorithm for the Transmission Lines without Using Line Parameters M. Bashir mohsenbashir@ieee.org I. Niazy ismail_niazy@ieee.org J.
Considering Characteristics of Arc on Travelling Wave Fault Location Algorithm for the Transmission Lines without Using Line Parameters M. Bashir mohsenbashir@ieee.org I. Niazy ismail_niazy@ieee.org J.
USING SUPERIMPOSED PRINCIPLES (DELTA) IN PROTECTION TECHNIQUES IN AN INCREASINGLY CHALLENGING POWER NETWORK
 USING SUPERIMPOSED PRINCIPLES (DELTA) IN PROTECTION TECHNIQUES IN AN INCREASINGLY CHALLENGING POWER NETWORK P Horton, S Swain patricia.horton@ge.com, simon.swain@ge.com UK INTRODUCTION Superimposed techniques
USING SUPERIMPOSED PRINCIPLES (DELTA) IN PROTECTION TECHNIQUES IN AN INCREASINGLY CHALLENGING POWER NETWORK P Horton, S Swain patricia.horton@ge.com, simon.swain@ge.com UK INTRODUCTION Superimposed techniques
Negative-Sequence Based Scheme For Fault Protection in Twin Power Transformer
 Negative-Sequence Based Scheme For Fault Protection in Twin Power Transformer Ms. Kanchan S.Patil PG, Student kanchanpatil2893@gmail.com Prof.Ajit P. Chaudhari Associate Professor ajitpc73@rediffmail.com
Negative-Sequence Based Scheme For Fault Protection in Twin Power Transformer Ms. Kanchan S.Patil PG, Student kanchanpatil2893@gmail.com Prof.Ajit P. Chaudhari Associate Professor ajitpc73@rediffmail.com
Voltage Sags Evaluating Methods, Power Quality and Voltage Sags Assessment regarding Voltage Dip Immunity of Equipment
 s Evaluating Methods, Power Quality and s Assessment regarding Voltage Dip Immunity of Equipment ANTON BELÁŇ, MARTIN LIŠKA, BORIS CINTULA, ŽANETA ELESCHOVÁ Institute of Power and Applied Electrical Engineering
s Evaluating Methods, Power Quality and s Assessment regarding Voltage Dip Immunity of Equipment ANTON BELÁŇ, MARTIN LIŠKA, BORIS CINTULA, ŽANETA ELESCHOVÁ Institute of Power and Applied Electrical Engineering
Hybrid Anti-Islanding Algorithm for Utility Interconnection of Distributed Generation
 Hybrid Anti-Islanding Algorithm for Utility Interconnection of Distributed Generation Maher G. M. Abdolrasol maher_photo@yahoo.com Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of Malaya Lembah Pantai, 50603
Hybrid Anti-Islanding Algorithm for Utility Interconnection of Distributed Generation Maher G. M. Abdolrasol maher_photo@yahoo.com Dept. of Electrical Engineering University of Malaya Lembah Pantai, 50603
Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on SIMULATION, MODELING AND OPTIMIZATION, Corfu, Greece, August 17-19, 2005 (pp )
 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on SIMULATION, MODELING AND OPTIMIZATION, Corfu, Greece, August 7-9, 5 (pp567-57) Power differential relay for three phase transformer B.BAHMANI Marvdasht Islamic
Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on SIMULATION, MODELING AND OPTIMIZATION, Corfu, Greece, August 7-9, 5 (pp567-57) Power differential relay for three phase transformer B.BAHMANI Marvdasht Islamic
Wavelet Based Fault Detection, Classification in Transmission System with TCSC Controllers
 ISSN: 2248-9622, Vol. 5, Issue 8, (Part - 3) August 215, pp.25-29 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Wavelet Based Fault Detection, Classification in Transmission System with TCSC Controllers 1 G.Satyanarayana,
ISSN: 2248-9622, Vol. 5, Issue 8, (Part - 3) August 215, pp.25-29 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Wavelet Based Fault Detection, Classification in Transmission System with TCSC Controllers 1 G.Satyanarayana,
Comparison of Wavelet Transform and Fourier Transform based methods of Phasor Estimation for Numerical Relaying
 Comparison of Wavelet Transform and Fourier Transform based methods of Phasor Estimation for Numerical Relaying V.S.Kale S.R.Bhide P.P.Bedekar Department of Electrical Engineering, VNIT Nagpur, India Abstract
Comparison of Wavelet Transform and Fourier Transform based methods of Phasor Estimation for Numerical Relaying V.S.Kale S.R.Bhide P.P.Bedekar Department of Electrical Engineering, VNIT Nagpur, India Abstract
CHAPTER 5 POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BY USING POWER ACTIVE FILTERS
 86 CHAPTER 5 POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BY USING POWER ACTIVE FILTERS 5.1 POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT This chapter deals with the harmonic elimination in Power System by adopting various methods. Due to the
86 CHAPTER 5 POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BY USING POWER ACTIVE FILTERS 5.1 POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT This chapter deals with the harmonic elimination in Power System by adopting various methods. Due to the
EARTH-FAULT ANALYSIS OF THE MEDIUM VOLTAGE NETWORK GROUNDED WITH LOW VALUE RESISTANCE
 EARH-FAUL ANALYSIS OF HE MEDIUM VOLAGE NEWORK GROUNDED WIH LOW VALUE RESISANCE Zoran Ristanovic EPS - JP Eletrovojvodina Bul. Oslobodjenja 100, Novi Sad(Yugoslavia) el: 381 1 7 64 - Fax: 381 1 3 668 -
EARH-FAUL ANALYSIS OF HE MEDIUM VOLAGE NEWORK GROUNDED WIH LOW VALUE RESISANCE Zoran Ristanovic EPS - JP Eletrovojvodina Bul. Oslobodjenja 100, Novi Sad(Yugoslavia) el: 381 1 7 64 - Fax: 381 1 3 668 -
Keywords: Wavelet packet transform (WPT), Differential Protection, Inrush current, CT saturation.
 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Differential Protection of Three Phase Power Transformer Using Wavelet Packet Transform Jitendra Singh Chandra*, Amit Goswami
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Differential Protection of Three Phase Power Transformer Using Wavelet Packet Transform Jitendra Singh Chandra*, Amit Goswami
PROTECTION SIGNALLING
 PROTECTION SIGNALLING 1 Directional Comparison Distance Protection Schemes The importance of transmission system integrity necessitates high-speed fault clearing times and highspeed auto reclosing to avoid
PROTECTION SIGNALLING 1 Directional Comparison Distance Protection Schemes The importance of transmission system integrity necessitates high-speed fault clearing times and highspeed auto reclosing to avoid
Distance Relay Response to Transformer Energization: Problems and Solutions
 1 Distance Relay Response to Transformer Energization: Problems and Solutions Joe Mooney, P.E. and Satish Samineni, Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories Abstract Modern distance relays use various filtering
1 Distance Relay Response to Transformer Energization: Problems and Solutions Joe Mooney, P.E. and Satish Samineni, Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories Abstract Modern distance relays use various filtering
SAFETY ASPECTS AND NOVEL TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS FOR EARTH FAULT MANAGEMENT IN MV ELECTRICITY DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS
 SAFETY ASPECTS AND NOVEL TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS FOR EARTH FAULT MANAGEMENT IN MV ELECTRICITY DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS A. Nikander*, P. Järventausta* *Tampere University of Technology, Finland, ari.nikander@tut.fi,
SAFETY ASPECTS AND NOVEL TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS FOR EARTH FAULT MANAGEMENT IN MV ELECTRICITY DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS A. Nikander*, P. Järventausta* *Tampere University of Technology, Finland, ari.nikander@tut.fi,
Earth Fault Protection
 Earth Fault Protection Course No: E03-038 Credit: 3 PDH Velimir Lackovic, Char. Eng. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774
Earth Fault Protection Course No: E03-038 Credit: 3 PDH Velimir Lackovic, Char. Eng. Continuing Education and Development, Inc. 9 Greyridge Farm Court Stony Point, NY 10980 P: (877) 322-5800 F: (877) 322-4774
A New Fault Detection Tool for Single Phasing of a Three Phase Induction Motor. S.H.Haggag, Ali M. El-Rifaie,and Hala M.
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering 013 Vol II,, July 3-5, 013, London, U.K. A New Fault Detection Tool for Single Phasing of a Three Phase Induction Motor S.H.Haggag, Ali M. El-Rifaie,and
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering 013 Vol II,, July 3-5, 013, London, U.K. A New Fault Detection Tool for Single Phasing of a Three Phase Induction Motor S.H.Haggag, Ali M. El-Rifaie,and
Ferroresonance Signal Analysis with Wavelet Transform on 500 kv Transmission Lines Capacitive Voltage Transformers
 Signal Analysis with Wavelet Transform on 500 kv Transmission Lines Capacitive Voltage Transformers I Gusti Ngurah Satriyadi Hernanda, I Made Yulistya Negara, Adi Soeprijanto, Dimas Anton Asfani, Mochammad
Signal Analysis with Wavelet Transform on 500 kv Transmission Lines Capacitive Voltage Transformers I Gusti Ngurah Satriyadi Hernanda, I Made Yulistya Negara, Adi Soeprijanto, Dimas Anton Asfani, Mochammad
Evaluating the activation of auto recloser relays in power distribution grid of Masjed Soleiman City
 EUROPEAN ACADEMC RESEARCH Vol. V, ssue 2/ May 2016 SSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org mpact Factor: 3.4546 (UF) DRJ Value: 5.9 (B+) Evaluating the activation of auto recloser relays in power distribution
EUROPEAN ACADEMC RESEARCH Vol. V, ssue 2/ May 2016 SSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org mpact Factor: 3.4546 (UF) DRJ Value: 5.9 (B+) Evaluating the activation of auto recloser relays in power distribution
UNIT-4 POWER QUALITY MONITORING
 UNIT-4 POWER QUALITY MONITORING Terms and Definitions Spectrum analyzer Swept heterodyne technique FFT (or) digital technique tracking generator harmonic analyzer An instrument used for the analysis and
UNIT-4 POWER QUALITY MONITORING Terms and Definitions Spectrum analyzer Swept heterodyne technique FFT (or) digital technique tracking generator harmonic analyzer An instrument used for the analysis and
A New Subsynchronous Oscillation (SSO) Relay for Renewable Generation and Series Compensated Transmission Systems
 21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2015 Grid of the Future Symposium A New Subsynchronous Oscillation (SSO) Relay for Renewable Generation and Series Compensated
21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2015 Grid of the Future Symposium A New Subsynchronous Oscillation (SSO) Relay for Renewable Generation and Series Compensated
Swinburne Research Bank
 Swinburne Research Bank http://researchbank.swinburne.edu.au Tashakori, A., & Ektesabi, M. (2013). A simple fault tolerant control system for Hall Effect sensors failure of BLDC motor. Originally published
Swinburne Research Bank http://researchbank.swinburne.edu.au Tashakori, A., & Ektesabi, M. (2013). A simple fault tolerant control system for Hall Effect sensors failure of BLDC motor. Originally published
RESEARCH ON CLASSIFICATION OF VOLTAGE SAG SOURCES BASED ON RECORDED EVENTS
 24 th International Conference on Electricity Distribution Glasgow, 2-5 June 27 Paper 97 RESEARCH ON CLASSIFICATION OF VOLTAGE SAG SOURCES BASED ON RECORDED EVENTS Pengfei WEI Yonghai XU Yapen WU Chenyi
24 th International Conference on Electricity Distribution Glasgow, 2-5 June 27 Paper 97 RESEARCH ON CLASSIFICATION OF VOLTAGE SAG SOURCES BASED ON RECORDED EVENTS Pengfei WEI Yonghai XU Yapen WU Chenyi
Capacitive Voltage Substations Ferroresonance Prevention Using Power Electronic Devices
 Capacitive Voltage Substations Ferroresonance Prevention Using Power Electronic Devices M. Sanaye-Pasand, R. Aghazadeh Applied Electromagnetics Research Excellence Center, Electrical & Computer Engineering
Capacitive Voltage Substations Ferroresonance Prevention Using Power Electronic Devices M. Sanaye-Pasand, R. Aghazadeh Applied Electromagnetics Research Excellence Center, Electrical & Computer Engineering
Chapter -3 ANALYSIS OF HVDC SYSTEM MODEL. Basically the HVDC transmission consists in the basic case of two
 Chapter -3 ANALYSIS OF HVDC SYSTEM MODEL Basically the HVDC transmission consists in the basic case of two convertor stations which are connected to each other by a transmission link consisting of an overhead
Chapter -3 ANALYSIS OF HVDC SYSTEM MODEL Basically the HVDC transmission consists in the basic case of two convertor stations which are connected to each other by a transmission link consisting of an overhead
Busbars and lines are important elements
 CHAPTER CHAPTER 23 Protection of Busbars and Lines 23.1 Busbar Protection 23.2 Protection of Lines 23.3 Time-Graded Overcurrent Protection 23.4 Differential Pilot-Wire Protection 23.5 Distance Protection
CHAPTER CHAPTER 23 Protection of Busbars and Lines 23.1 Busbar Protection 23.2 Protection of Lines 23.3 Time-Graded Overcurrent Protection 23.4 Differential Pilot-Wire Protection 23.5 Distance Protection
Fault Location Technique for UHV Lines Using Wavelet Transform
 International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 77-88 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Fault Location Technique for UHV Lines
International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 77-88 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Fault Location Technique for UHV Lines
[Nayak, 3(2): February, 2014] ISSN: Impact Factor: 1.852
![[Nayak, 3(2): February, 2014] ISSN: Impact Factor: 1.852 [Nayak, 3(2): February, 2014] ISSN: Impact Factor: 1.852](/thumbs/96/128468304.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Classification of Transmission Line Faults Using Wavelet Transformer B. Lakshmana Nayak M.TECH(APS), AMIE, Associate Professor,
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Classification of Transmission Line Faults Using Wavelet Transformer B. Lakshmana Nayak M.TECH(APS), AMIE, Associate Professor,
Detection and Classification of One Conductor Open Faults in Parallel Transmission Line using Artificial Neural Network
 Detection and Classification of One Conductor Open Faults in Parallel Transmission Line using Artificial Neural Network A.M. Abdel-Aziz B. M. Hasaneen A. A. Dawood Electrical Power and Machines Eng. Dept.
Detection and Classification of One Conductor Open Faults in Parallel Transmission Line using Artificial Neural Network A.M. Abdel-Aziz B. M. Hasaneen A. A. Dawood Electrical Power and Machines Eng. Dept.
International Journal of Digital Application & Contemporary research Website: (Volume 2, Issue 10, May 2014)
 Digital Differential Protection of Power Transformer Gitanjali Kashyap M. Tech. Scholar, Dr. C. V. Raman Institute of Science and technology, Chhattisgarh (India) alisha88.ele@gmail.com Dharmendra Kumar
Digital Differential Protection of Power Transformer Gitanjali Kashyap M. Tech. Scholar, Dr. C. V. Raman Institute of Science and technology, Chhattisgarh (India) alisha88.ele@gmail.com Dharmendra Kumar
AORC Technical meeting 2014
 http : //www.cigre.org B4-112 AORC Technical meeting 214 HVDC Circuit Breakers for HVDC Grid Applications K. Tahata, S. Ka, S. Tokoyoda, K. Kamei, K. Kikuchi, D. Yoshida, Y. Kono, R. Yamamoto, H. Ito Mitsubishi
http : //www.cigre.org B4-112 AORC Technical meeting 214 HVDC Circuit Breakers for HVDC Grid Applications K. Tahata, S. Ka, S. Tokoyoda, K. Kamei, K. Kikuchi, D. Yoshida, Y. Kono, R. Yamamoto, H. Ito Mitsubishi
POWER TRANSFORMER PROTECTION USING ANN, FUZZY SYSTEM AND CLARKE S TRANSFORM
 POWER TRANSFORMER PROTECTION USING ANN, FUZZY SYSTEM AND CLARKE S TRANSFORM 1 VIJAY KUMAR SAHU, 2 ANIL P. VAIDYA 1,2 Pg Student, Professor E-mail: 1 vijay25051991@gmail.com, 2 anil.vaidya@walchandsangli.ac.in
POWER TRANSFORMER PROTECTION USING ANN, FUZZY SYSTEM AND CLARKE S TRANSFORM 1 VIJAY KUMAR SAHU, 2 ANIL P. VAIDYA 1,2 Pg Student, Professor E-mail: 1 vijay25051991@gmail.com, 2 anil.vaidya@walchandsangli.ac.in
OCCURRENCE OF DELAYED CURRENT ZERO CROSSING DUE TO LINE REACTIVE OVERCOMPENSATION LT CAMPINAS FERNAO DIAS 500 kv.
 OCCURRENCE OF DELAYED CURRENT ZERO CROSSING DUE TO LINE REACTIVE OVERCOMPENSATION LT CAMPINAS FERNAO DIAS 500 kv. Ricardo André Gonçalves 1 / 17 1 - INTRODUCRION Studies conducted on several 500 kv compensated
OCCURRENCE OF DELAYED CURRENT ZERO CROSSING DUE TO LINE REACTIVE OVERCOMPENSATION LT CAMPINAS FERNAO DIAS 500 kv. Ricardo André Gonçalves 1 / 17 1 - INTRODUCRION Studies conducted on several 500 kv compensated
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) Using Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
 Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) Using Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) Dr. Hamdy Ashour Arab Academy for Science &Technology Department of Electrical & Computer Control Engineering P.O. 1029 Miami,
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) Using Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) Dr. Hamdy Ashour Arab Academy for Science &Technology Department of Electrical & Computer Control Engineering P.O. 1029 Miami,
Smart Busbar Protection Based ANFIS Technique for Substations and Power Plants
 Smart Busbar Protection Based ANFIS Technique for Substations and Power Plants 1 Mohamed A. Ali, 2 Sayed A. Ward, 3 Mohamed S. Elkhalafy 123 Faculty of Engineering Shoubra, Benha University Email: 1 mohamed.mohamed02@feng.bu.edu.eg,
Smart Busbar Protection Based ANFIS Technique for Substations and Power Plants 1 Mohamed A. Ali, 2 Sayed A. Ward, 3 Mohamed S. Elkhalafy 123 Faculty of Engineering Shoubra, Benha University Email: 1 mohamed.mohamed02@feng.bu.edu.eg,
ISSN: Page 298
 Sizing Current Transformers Rating To Enhance Digital Relay Operations Using Advanced Saturation Voltage Model *J.O. Aibangbee 1 and S.O. Onohaebi 2 *Department of Electrical &Computer Engineering, Bells
Sizing Current Transformers Rating To Enhance Digital Relay Operations Using Advanced Saturation Voltage Model *J.O. Aibangbee 1 and S.O. Onohaebi 2 *Department of Electrical &Computer Engineering, Bells
Delayed Current Zero Crossing Phenomena during Switching of Shunt-Compensated Lines
 Delayed Current Zero Crossing Phenomena during Switching of Shunt-Compensated Lines David K Olson Xcel Energy Minneapolis, MN Paul Nyombi Xcel Energy Minneapolis, MN Pratap G Mysore Pratap Consulting Services,
Delayed Current Zero Crossing Phenomena during Switching of Shunt-Compensated Lines David K Olson Xcel Energy Minneapolis, MN Paul Nyombi Xcel Energy Minneapolis, MN Pratap G Mysore Pratap Consulting Services,
Accurate Current Measurement Transducer for Relaying Purpose
 Accurate Current Measurement Transducer for Relaying Purpose Ashish S. Paramane 1, Dr.P.K.Katti 2 Department of Electrical Engineering Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, Lonere, Maharashtra
Accurate Current Measurement Transducer for Relaying Purpose Ashish S. Paramane 1, Dr.P.K.Katti 2 Department of Electrical Engineering Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, Lonere, Maharashtra
PQ for Industrial Benchmarking with various methods to improve. Tushar Mogre.
 General PQ: Power Quality has multiple issues involved. Thus, need to have some benchmarking standards. Very little is spoken about the LT supply installation within an industry. There is need to understand
General PQ: Power Quality has multiple issues involved. Thus, need to have some benchmarking standards. Very little is spoken about the LT supply installation within an industry. There is need to understand
Tab 2 Voltage Stresses Switching Transients
 Tab 2 Voltage Stresses Switching Transients Distribution System Engineering Course Unit 10 2017 Industry, Inc. All rights reserved. Transient Overvoltages Decay with time, usually within one or two cycles
Tab 2 Voltage Stresses Switching Transients Distribution System Engineering Course Unit 10 2017 Industry, Inc. All rights reserved. Transient Overvoltages Decay with time, usually within one or two cycles
S1-3: New and re-discovered theories and practices in relay protection
 (Cheboksary, September 9-13, 27) S1-3: New and re-discovered theories and practices in relay protection Practical experience from multiterminal line differential protection installations Z. GAJIĆ, I. BRNČIĆ,
(Cheboksary, September 9-13, 27) S1-3: New and re-discovered theories and practices in relay protection Practical experience from multiterminal line differential protection installations Z. GAJIĆ, I. BRNČIĆ,
Application of Fuzzy Logic Controller in UPFC to Mitigate THD in Power System
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 9, Issue 8 (January 2014), PP. 25-33 Application of Fuzzy Logic Controller in UPFC
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 9, Issue 8 (January 2014), PP. 25-33 Application of Fuzzy Logic Controller in UPFC
FAULT DETECTION, CLASSIFICATION AND LOCATION ON AN UNDERGROUND CABLE NETWORK USING WAVELET TRANSFORM
 90 FAULT DETECTION, CLASSIFICATION AND LOCATION ON AN UNDERGROUND CABLE NETWORK USING WAVELET TRANSFORM Hashim Hizam, Jasronita Jasni, Mohd Zainal Abidin Ab Kadir, Wan Fatinhamamah Wan Ahmad Department
90 FAULT DETECTION, CLASSIFICATION AND LOCATION ON AN UNDERGROUND CABLE NETWORK USING WAVELET TRANSFORM Hashim Hizam, Jasronita Jasni, Mohd Zainal Abidin Ab Kadir, Wan Fatinhamamah Wan Ahmad Department
Relay Protection of EHV Shunt Reactors Based on the Traveling Wave Principle
 Relay Protection of EHV Shunt Reactors Based on the Traveling Wave Principle Jules Esztergalyos, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract--The measuring technique described in this paper is based on Electro Magnetic
Relay Protection of EHV Shunt Reactors Based on the Traveling Wave Principle Jules Esztergalyos, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract--The measuring technique described in this paper is based on Electro Magnetic
SERIES (OPEN CONDUCTOR) FAULT DISTANCE LOCATION IN THREE PHASE TRANSMISSION LINE USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK
 1067 SERIES (OPEN CONDUCTOR) FAULT DISTANCE LOCATION IN THREE PHASE TRANSMISSION LINE USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK A Nareshkumar 1 1 Assistant professor, Department of Electrical Engineering Institute
1067 SERIES (OPEN CONDUCTOR) FAULT DISTANCE LOCATION IN THREE PHASE TRANSMISSION LINE USING ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK A Nareshkumar 1 1 Assistant professor, Department of Electrical Engineering Institute
Module 2 : Current and Voltage Transformers. Lecture 8 : Introduction to VT. Objectives. 8.1 Voltage Transformers 8.1.1Role of Tuning Reactor
 Module 2 : Current and Voltage Transformers Lecture 8 : Introduction to VT Objectives In this lecture we will learn the following: Derive the equivalent circuit of a CCVT. Application of CCVT in power
Module 2 : Current and Voltage Transformers Lecture 8 : Introduction to VT Objectives In this lecture we will learn the following: Derive the equivalent circuit of a CCVT. Application of CCVT in power
A C. Wallner Siemens AG Berlin, (Germany)
 21, rue d'artois, F-75008 Paris http://www.cigre.org A3-115 Session 2004 CIGRÉ A Algorithm for the Three-Pole Controlled Auto-Reclosing of Shunt Compensated Transmission Lines with a Optimization for the
21, rue d'artois, F-75008 Paris http://www.cigre.org A3-115 Session 2004 CIGRÉ A Algorithm for the Three-Pole Controlled Auto-Reclosing of Shunt Compensated Transmission Lines with a Optimization for the
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT SOLUTIONS OF FAULTED PHASE EARTHING TECHNIQUE FOR AN EARTH FAULT CURRENT LIMITATION
 EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT SOLUTIONS OF FAULTED PHASE EARTHING TECHNIQUE FOR AN EARTH FAULT CURRENT LIMITATION David TOPOLANEK Petr TOMAN Michal PTACEK Jaromir DVORAK Brno University of Technology - Czech
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT SOLUTIONS OF FAULTED PHASE EARTHING TECHNIQUE FOR AN EARTH FAULT CURRENT LIMITATION David TOPOLANEK Petr TOMAN Michal PTACEK Jaromir DVORAK Brno University of Technology - Czech
Improvement of Power System Distribution Quality Due to Using Dc-Converter Loads and Electric Arc Furnaces. H.A. Khalik, M. A. Aziz, and E. Farouk.
 , 2011;4(12) Improvement of Power System Distribution Quality Due to Using Dc-Converter Loads and Electric Arc Furnaces H.A. Khalik, M. A. Aziz, and E. Farouk. Electrical power and Machines Engineering
, 2011;4(12) Improvement of Power System Distribution Quality Due to Using Dc-Converter Loads and Electric Arc Furnaces H.A. Khalik, M. A. Aziz, and E. Farouk. Electrical power and Machines Engineering
Journal of Engineering Technology
 A novel mitigation algorithm for switch open-fault in parallel inverter topology fed induction motor drive M. Dilip *a, S. F. Kodad *b B. Sarvesh *c a Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
A novel mitigation algorithm for switch open-fault in parallel inverter topology fed induction motor drive M. Dilip *a, S. F. Kodad *b B. Sarvesh *c a Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
Application of Wavelet Transform in Power System Analysis and Protection
 Application of Wavelet Transform in Power System Analysis and Protection Neha S. Dudhe PG Scholar Shri Sai College of Engineering & Technology, Bhadrawati-Chandrapur, India Abstract This paper gives a
Application of Wavelet Transform in Power System Analysis and Protection Neha S. Dudhe PG Scholar Shri Sai College of Engineering & Technology, Bhadrawati-Chandrapur, India Abstract This paper gives a
ANALYSIS OF A FLASHOVER OPERATION ON TWO 138KV TRANSMISSION LINES
 ANALYSIS OF A FLASHOVER OPERATION ON TWO 138KV TRANSMISSION LINES Authors: Joe Perez, P.E.: SynchroGrid, College Station, Texas Hung Ming Chou, SynchroGrid, College Station, Texas Mike McMillan, Bryan
ANALYSIS OF A FLASHOVER OPERATION ON TWO 138KV TRANSMISSION LINES Authors: Joe Perez, P.E.: SynchroGrid, College Station, Texas Hung Ming Chou, SynchroGrid, College Station, Texas Mike McMillan, Bryan
Intermittent transient earth fault protection
 Intermittent transient earth fault protection The directional intermittent transient earth fault protection is used to detect short intermittent transient faults in compensated cable networks (figure 3).
Intermittent transient earth fault protection The directional intermittent transient earth fault protection is used to detect short intermittent transient faults in compensated cable networks (figure 3).
Discrimination between Inrush and Fault Current in Power Transformer by using Fuzzy Logic
 Discrimination between Inrush and Fault Current in Power Transformer by using Fuzzy Logic Abdussalam 1, Mohammad Naseem 2, Akhaque Ahmad Khan 3 1 Department of Instrumentation & Control Engineering, Integral
Discrimination between Inrush and Fault Current in Power Transformer by using Fuzzy Logic Abdussalam 1, Mohammad Naseem 2, Akhaque Ahmad Khan 3 1 Department of Instrumentation & Control Engineering, Integral
A New Adaptive PMU Based Protection Scheme for Transposed/Untransposed Parallel Transmission Lines
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 17, NO. 2, APRIL 2002 395 A New Adaptive PMU Based Protection Scheme for Transposed/Untransposed Parallel Transmission Lines Ching-Shan Chen, Student Member, IEEE,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 17, NO. 2, APRIL 2002 395 A New Adaptive PMU Based Protection Scheme for Transposed/Untransposed Parallel Transmission Lines Ching-Shan Chen, Student Member, IEEE,
A Methodology for the Efficient Application of Controlled Switching to Current Interruption Cases in High-Voltage Networks
 A Methodology for the Efficient Application of Controlled Switching to Current Interruption Cases in High-Voltage Networks C. D. TSIREKIS Hellenic Transmission System Operator Kastoros 72, Piraeus GREECE
A Methodology for the Efficient Application of Controlled Switching to Current Interruption Cases in High-Voltage Networks C. D. TSIREKIS Hellenic Transmission System Operator Kastoros 72, Piraeus GREECE
Poornima G P. IJECS Volume 3 Issue 6 June, 2014 Page No Page 6453
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 3 Issue 6 June, 2014 Page No. 6453-6457 Role of Fault Current Limiter in Power System Network Poornima G P.1,
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN:2319-7242 Volume 3 Issue 6 June, 2014 Page No. 6453-6457 Role of Fault Current Limiter in Power System Network Poornima G P.1,
Protection from Voltage Sags and Swells by Using FACTS Controller
 Protection from Voltage Sags and Swells by Using FACTS Controller M.R.Mohanraj 1, V.P.Suresh 2, G.Syed Zabiyullah 3 Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Excel College
Protection from Voltage Sags and Swells by Using FACTS Controller M.R.Mohanraj 1, V.P.Suresh 2, G.Syed Zabiyullah 3 Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Excel College
Detection, localization, and classification of power quality disturbances using discrete wavelet transform technique
 From the SelectedWorks of Tarek Ibrahim ElShennawy 2003 Detection, localization, and classification of power quality disturbances using discrete wavelet transform technique Tarek Ibrahim ElShennawy, Dr.
From the SelectedWorks of Tarek Ibrahim ElShennawy 2003 Detection, localization, and classification of power quality disturbances using discrete wavelet transform technique Tarek Ibrahim ElShennawy, Dr.
A New Adaptive High Speed Distance Protection Scheme for Power Transmission Lines
 A New Adaptive High Speed Distance Protection Scheme for Power Transmission Lines M.M. Saha, T. Einarsson, S. Lidström ABB AB, Substation Automation Products, Sweden Keywords: Adaptive distance protection,
A New Adaptive High Speed Distance Protection Scheme for Power Transmission Lines M.M. Saha, T. Einarsson, S. Lidström ABB AB, Substation Automation Products, Sweden Keywords: Adaptive distance protection,
An Enhanced Symmetrical Fault Detection during Power Swing/Angular Instability using Park s Transformation
 Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Vol., No., April 6, pp. 3 ~ 3 DOI:.59/ijeecs.v.i.pp3-3 3 An Enhanced Symmetrical Fault Detection during Power Swing/Angular Instability
Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Vol., No., April 6, pp. 3 ~ 3 DOI:.59/ijeecs.v.i.pp3-3 3 An Enhanced Symmetrical Fault Detection during Power Swing/Angular Instability
Microcontroller Based Protective Relay Testing System
 Microcontroller Based Protective Relay Testing System ABDERRAHMANE OUADI, HAMID BENTARZI, MAHFOUD CHAFAI, and ABDELKADER ZITOUNI Signals and Systems Laboratory (SiSyLAB) IGEE, Boumerdes University E-mail:
Microcontroller Based Protective Relay Testing System ABDERRAHMANE OUADI, HAMID BENTARZI, MAHFOUD CHAFAI, and ABDELKADER ZITOUNI Signals and Systems Laboratory (SiSyLAB) IGEE, Boumerdes University E-mail:
Texas Reliability Entity Event Analysis. Event: May 8, 2011 Loss of Multiple Elements Category 1a Event
 Texas Reliability Entity Event Analysis Event: May 8, 2011 Loss of Multiple Elements Category 1a Event Texas Reliability Entity July 2011 Page 1 of 10 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 I. Event
Texas Reliability Entity Event Analysis Event: May 8, 2011 Loss of Multiple Elements Category 1a Event Texas Reliability Entity July 2011 Page 1 of 10 Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 I. Event
MAINTENANCE MANUAL 1B170K17 FOUR SHOT AUTO RECLOSE RELAY
 Sheet 1 of 9 MAINTENANCE MANUAL 1B170K17 FOUR SHOT AUTO RECLOSE RELAY The Maintenance Manual is to be read in conunction with Product/Test Manual Sheet 2 of 9 INDEX 1. FULL DESCRIPTION OF OPERATION 1.1
Sheet 1 of 9 MAINTENANCE MANUAL 1B170K17 FOUR SHOT AUTO RECLOSE RELAY The Maintenance Manual is to be read in conunction with Product/Test Manual Sheet 2 of 9 INDEX 1. FULL DESCRIPTION OF OPERATION 1.1
Online Diagnosis and Monitoring for Power Distribution System
 Energy and Power Engineering, 1,, 59-53 http://dx.doi.org/1.3/epe.1. Published Online November 1 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/epe) Online Diagnosis and Monitoring for Power Distribution System Atef Almashaqbeh,
Energy and Power Engineering, 1,, 59-53 http://dx.doi.org/1.3/epe.1. Published Online November 1 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/epe) Online Diagnosis and Monitoring for Power Distribution System Atef Almashaqbeh,
CHAPTER 4 POWER QUALITY AND VAR COMPENSATION IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
 84 CHAPTER 4 POWER QUALITY AND VAR COMPENSATION IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS 4.1 INTRODUCTION Now a days, the growth of digital economy implies a widespread use of electronic equipment not only in the industrial
84 CHAPTER 4 POWER QUALITY AND VAR COMPENSATION IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS 4.1 INTRODUCTION Now a days, the growth of digital economy implies a widespread use of electronic equipment not only in the industrial
Centralized busbar differential and breaker failure protection function
 Centralized busbar differential and breaker failure protection function Budapest, December 2015 Centralized busbar differential and breaker failure protection function Protecta provides two different types
Centralized busbar differential and breaker failure protection function Budapest, December 2015 Centralized busbar differential and breaker failure protection function Protecta provides two different types
A DYNAMIC VOLTAGE RESTORER (DVR) BASED MITIGATION SCHEME FOR VOLTAGE SAG AND SWELL
 A DYNAMIC VOLTAGE RESTORER (DVR) BASED MITIGATION SCHEME FOR VOLTAGE SAG AND SWELL Saravanan.R 1, Hariharan.M 2 1 PG Scholar, Department OF ECE, 2 PG Scholar, Department of ECE 1, 2 Sri Krishna College
A DYNAMIC VOLTAGE RESTORER (DVR) BASED MITIGATION SCHEME FOR VOLTAGE SAG AND SWELL Saravanan.R 1, Hariharan.M 2 1 PG Scholar, Department OF ECE, 2 PG Scholar, Department of ECE 1, 2 Sri Krishna College
SYSTEM-WIDE disturbances in power systems are a challenging
 270 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 25, NO. 1, JANUARY 2010 A Novel Back Up Wide Area Protection Technique for Power Transmission Grids Using Phasor Measurement Unit M. M. Eissa, Senior Member,
270 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 25, NO. 1, JANUARY 2010 A Novel Back Up Wide Area Protection Technique for Power Transmission Grids Using Phasor Measurement Unit M. M. Eissa, Senior Member,
Detection and localization of internal turn-to-turn short circuits in transformer windings by means of negative sequence analysis
 No. E-14-AAA-0000 Detection and localization of internal turn-to-turn short circuits in transformer windings by means of negative sequence analysis Malihe Abi, Mohammad Mirzaie Faculty of Electrical and
No. E-14-AAA-0000 Detection and localization of internal turn-to-turn short circuits in transformer windings by means of negative sequence analysis Malihe Abi, Mohammad Mirzaie Faculty of Electrical and
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "Technology Enabling Modernization
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "Technology Enabling Modernization
Fault Location Using Sparse Wide Area Measurements
 319 Study Committee B5 Colloquium October 19-24, 2009 Jeju Island, Korea Fault Location Using Sparse Wide Area Measurements KEZUNOVIC, M., DUTTA, P. (Texas A & M University, USA) Summary Transmission line
319 Study Committee B5 Colloquium October 19-24, 2009 Jeju Island, Korea Fault Location Using Sparse Wide Area Measurements KEZUNOVIC, M., DUTTA, P. (Texas A & M University, USA) Summary Transmission line
High Voltage DC Transmission 2
 High Voltage DC Transmission 2 1.0 Introduction Interconnecting HVDC within an AC system requires conversion from AC to DC and inversion from DC to AC. We refer to the circuits which provide conversion
High Voltage DC Transmission 2 1.0 Introduction Interconnecting HVDC within an AC system requires conversion from AC to DC and inversion from DC to AC. We refer to the circuits which provide conversion
Analysis of Switching Transients of an EHV Transmission Line Consisting of Mixed Power Cable and Overhead Line Sections
 Analysis of Switching Transients of an EHV Transmission Line Consisting of Mixed Power Cable and Overhead Line Sections M. Kizilcay, K. Teichmann, S. Papenheim, P. Malicki Abstract -- Within the scope
Analysis of Switching Transients of an EHV Transmission Line Consisting of Mixed Power Cable and Overhead Line Sections M. Kizilcay, K. Teichmann, S. Papenheim, P. Malicki Abstract -- Within the scope
Shortcomings of the Low impedance Restricted Earth Fault function as applied to an Auto Transformer. Anura Perera, Paul Keller
 Shortcomings of the Low impedance Restricted Earth Fault function as applied to an Auto Transformer Anura Perera, Paul Keller System Operator - Eskom Transmission Introduction During the design phase of
Shortcomings of the Low impedance Restricted Earth Fault function as applied to an Auto Transformer Anura Perera, Paul Keller System Operator - Eskom Transmission Introduction During the design phase of
A Pyrotechnic Fault Current Limiter Model for Transient Calculations in Industrial Power Systems
 A Pyrotechnic Fault Current Limiter Model for Transient Calculations in Industrial Power Systems T. C. Dias, B. D. Bonatto, J. M. C. Filho Abstract-- Isolated industrial power systems or with high selfgeneration,
A Pyrotechnic Fault Current Limiter Model for Transient Calculations in Industrial Power Systems T. C. Dias, B. D. Bonatto, J. M. C. Filho Abstract-- Isolated industrial power systems or with high selfgeneration,
VALIDATION THROUGH REAL TIME SIMULATION OF A CONTROL AND PROTECTION SYSTEM APPLIED TO A RESONANT EARTHED NEUTRAL NETWORK
 VALIDATION THROUGH REAL TIME SIMULATION OF A CONTROL AND PROTECTION SYSTEM APPLIED TO A RESONANT EARTHED NEUTRAL NETWORK Eduardo MARTÍNEZ eduardo_martinez@fcirce.es Samuel BORROY sborroy@fcirce.es Laura
VALIDATION THROUGH REAL TIME SIMULATION OF A CONTROL AND PROTECTION SYSTEM APPLIED TO A RESONANT EARTHED NEUTRAL NETWORK Eduardo MARTÍNEZ eduardo_martinez@fcirce.es Samuel BORROY sborroy@fcirce.es Laura
Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter Based UPFC with ANN
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
Power Transmission of AC-DC Supply in a Single Composite Conductor
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 2 Issue 03 August 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Power Transmission of AC-DC Supply in a Single Composite Conductor P.
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 2 Issue 03 August 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Power Transmission of AC-DC Supply in a Single Composite Conductor P.
Modelling of Phasor Measurement Unit and Phasor Data Realisation with 2 Bus System
 Intl J Engg Sci Adv Research 05 Sep;(3):79-83 ling of Phasor Measurement Unit and Phasor Data Realisation with Bus System Chakrapani Mishra Department of Electrical Engineering FET, Rama University, Kanpur,
Intl J Engg Sci Adv Research 05 Sep;(3):79-83 ling of Phasor Measurement Unit and Phasor Data Realisation with Bus System Chakrapani Mishra Department of Electrical Engineering FET, Rama University, Kanpur,
A NEW DIRECTIONAL OVER CURRENT RELAYING SCHEME FOR DISTRIBUTION FEEDERS IN THE PRESENCE OF DG
 A NEW DIRECTIONAL OVER CURRENT RELAYING SCHEME FOR DISTRIBUTION FEEDERS IN THE PRESENCE OF DG CHAPTER 3 3.1 INTRODUCTION In plain radial feeders, the non-directional relays are used as they operate when
A NEW DIRECTIONAL OVER CURRENT RELAYING SCHEME FOR DISTRIBUTION FEEDERS IN THE PRESENCE OF DG CHAPTER 3 3.1 INTRODUCTION In plain radial feeders, the non-directional relays are used as they operate when
AN ANN BASED FAULT DETECTION ON ALTERNATOR
 AN ANN BASED FAULT DETECTION ON ALTERNATOR Suraj J. Dhon 1, Sarang V. Bhonde 2 1 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) 2 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) ABSTRACT: Synchronous
AN ANN BASED FAULT DETECTION ON ALTERNATOR Suraj J. Dhon 1, Sarang V. Bhonde 2 1 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) 2 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) ABSTRACT: Synchronous
FAULT CLASSIFICATION FOR DISTANCE PROTECTION
 FAULT CLASSIFICATION FOR DISTANCE PROTECTION Magnus Akke, Member IEEE ABB Automation Technology Products AB SE-7 59 Västerås, Sweden E-mail: magnus.akke@se.abb.com Abstract: This paper presents an overview
FAULT CLASSIFICATION FOR DISTANCE PROTECTION Magnus Akke, Member IEEE ABB Automation Technology Products AB SE-7 59 Västerås, Sweden E-mail: magnus.akke@se.abb.com Abstract: This paper presents an overview
Decriminition between Magnetising Inrush from Interturn Fault Current in Transformer: Hilbert Transform Approach
 SSRG International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (SSRG-IJEEE) volume 1 Issue 10 Dec 014 Decriminition between Magnetising Inrush from Interturn Fault Current in Transformer: Hilbert
SSRG International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (SSRG-IJEEE) volume 1 Issue 10 Dec 014 Decriminition between Magnetising Inrush from Interturn Fault Current in Transformer: Hilbert
A Versatile Control Scheme for UPQC for Power Quality Improvement using fuzzy controller
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 04, Issue 09 (September. 2014), V3 PP 11-20 www.iosrjen.org A Versatile Control Scheme for UPQC for Power Quality Improvement
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 04, Issue 09 (September. 2014), V3 PP 11-20 www.iosrjen.org A Versatile Control Scheme for UPQC for Power Quality Improvement
Power Quality and Digital Protection Relays
 Power Quality and Digital Protection Relays I. Zamora 1, A.J. Mazón 2, V. Valverde, E. Torres, A. Dyśko (*) Department of Electrical Engineering - University of the Basque Country Alda. Urquijo s/n, 48013
Power Quality and Digital Protection Relays I. Zamora 1, A.J. Mazón 2, V. Valverde, E. Torres, A. Dyśko (*) Department of Electrical Engineering - University of the Basque Country Alda. Urquijo s/n, 48013
UProtection Requirements. Ufor a Large scale Wind Park. Shyam Musunuri Siemens Energy
 UProtection Requirements Ufor a Large scale Wind Park Shyam Musunuri Siemens Energy Abstract: In the past wind power plants typically had a small power rating when compared to the strength of the connected
UProtection Requirements Ufor a Large scale Wind Park Shyam Musunuri Siemens Energy Abstract: In the past wind power plants typically had a small power rating when compared to the strength of the connected
Selection of Mother Wavelet for Processing of Power Quality Disturbance Signals using Energy for Wavelet Packet Decomposition
 Volume 114 No. 9 217, 313-323 ISSN: 1311-88 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Selection of Mother Wavelet for Processing of Power Quality Disturbance
Volume 114 No. 9 217, 313-323 ISSN: 1311-88 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Selection of Mother Wavelet for Processing of Power Quality Disturbance
Power Quality Basics. Presented by. Scott Peele PE
 Power Quality Basics Presented by Scott Peele PE PQ Basics Terms and Definitions Surge, Sag, Swell, Momentary, etc. Measurements Causes of Events Possible Mitigation PQ Tool Questions Power Quality Measurement
Power Quality Basics Presented by Scott Peele PE PQ Basics Terms and Definitions Surge, Sag, Swell, Momentary, etc. Measurements Causes of Events Possible Mitigation PQ Tool Questions Power Quality Measurement
