O. Napoly LC02, SLAC, Feb. 5, Higher Order Modes Measurements
|
|
|
- Owen Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 O. Napoly LC02, SLAC, Feb. 5, 2002 Higher Order Modes Measurements with Beam at the TTF Linac
2 TTF Measurements A collective effort including most of Saclay, Orsay and DESY TTF physicists : S. Fartoukh, G. Devanz, C. Magne, M. Jablonka, H.W. Glock, N. Baboi, M. Huening, G. Kreps, M. Liepe, S. Schreiber, H. Weise, M. Wendt... 1) TTF Modules : HOMs below cut-off 2) Resonant Excitation : Experimental Methods 3) Results and Analysis for Dipole Passbands 4) Interpretation for the 3rd Dipole Passband
3 TTF : Superconducting Modules Five 8-cavity modules assembled, three modules tested in TTF linac
4 TTF : The 3 Measured Modules * * * * DESY * Cavities with high-q, MHz mode
5 Monopole HOMs Monopole HOMs (m=0, TM0xx ) have a major impact on power dissipation in the HOM coupler (~ 30 W/ module) They have a negligible influence on longitudinal dynamics : HOM induced multi-bunch energy spread , smaller than the spread induced by RF-stabilisation Transverse effect through tilted cavities not yet taken into account.
6 The Dipole Passbands The TDR Model * * * * propagating evanescent FM ω l / 2π [GHz] (measurement) Q l (measurement) (R/Q) l [Ω/cm 2 ] (simulation) 1 st dipole passband nd dipole passband rd dipole passband (measured since 1998 HOM experiments)
7 Emittance Growths : the TDR Situation With the list of HOMs from the TDR, both the single bunch and the multi bunch emittance growths are small: δε y /ε y < 4% 50 seeds Assumptions : - 1 MHz frequency spread mm RMS cavity misalignments - 1 st bunch steered through all quadrupole centres Emittance growth [%]
8 Emittance Growths : MHz mode 3rd passband GHz HOM ( R/Q = 23.5 Ω /cm 2, Q = 10 6, One mode / 8 cavities ) Multi-bunch emittance ε MB = mm mrd (on 50 seed average) Single-bunch emittance δε SB /ε 0 = 7 % (only one seed) 50 seeds Design emittance ε 0 Multi bunch emittance [µm]
9 TM011 : HOM Frequency Spread σ f [Hz] R/Q = 150 Ω # Mode
10 TE111 : HOM Frequency Spread σ f [Hz] R/Q = 15.6 Ω/cm 2 # Mode
11 TM110 : HOM Frequency Spread σ f [Hz] R/Q = 9 Ω/cm 2 # Mode
12 Resonant Excitation : Experimental Methods Resonance HOM / Beam by : 1. Cavity detuning : f HOM shifted to mf Beam harmonics f Beam < tuning range 1 MHz 2. Beam charge modulation f mod tuneable side-bands f HOM = m f Beam ± f mod Brilloin zone [0, f Beam ] as large as possible HOM 0.6 Modulated charge f mod f mod bunch harmonics sidebands Charge [nc] Bunch number m f b (m+1) f b
13 Dipole HOM excitation: Wake Potentials : W R/Q r 0m r 1m cos m(θ 0 θ HOM ) HOM Pick Up W R/Q r 0m r 1 m 1 m cos m(θ 0 θ HOM ) BPM TTF dogleg magnet operates only in x-plane : δx = ± 2cm monopole m = 0 : P HOM δx 0, δx BPM = 0 dipole m = 1 : P HOM δx 2, δx BPM δx quadrupole m = 2 : P HOM δx 4, δx BPM δx 3
14 High-Q HOM in the 3rd Passband HOM : f = GHz, Q = 10 6 measured with 216 MHz Injector #1 in Module 1, in off resonance BPM Signal on resonance 400 µs 216 MHz beam with 15 MHz modulation 125 µs beating due to 8 khz off resonance
15 High-Q HOM in the 3rd Passband Frequency f HOM,, damping Q and "m=1" are easily measured. Coupling R/Q is not: requires beam parameters and polarisation HOM at GHz HOM Pickup Signal Beam at 2.6 GHz Decay time Q = 10 6 frequency domain 35 µs beam time domain
16 High-Q HOM in the 3rd Passband HOM : f = GHz, Q = measured with 1 MHz Injector #2 in Module 2, in HOM Pick Up Signal = 2576 (1.3 GHz/1296) beam harmonics 20 bunches f HOM = MHz f tuner steps
17 Results and Analysis for the Dipole Passbands The 3 rd Dipole Passband : The 2585 MHz identified as the highest frequency HOM within the 3 rd dipole passband : NOT A SURPRISE! E field 2π mode at ~ GHz, synchronous with e beam R/Q = 24 Ω/cm 2, the highest dipole coupling. QUESTIONS : why the bad damping, Q > 10 5? why only in 2 out of 8 cavities?
18 Higher Order Dipole Passband : Q =
19 Goal : Prove or dis-prove the existence of long-lived HOMs, particularly in the 5 th dipole passband. Three Methods : ( f and Q measured with beam) 1. Measure R/Q from beam excitation in the BPM : no way, most BPM signals are triggered by quadrupole modes! 2. Identify the position of measured modes in the passband : very difficult, because the measured passband is a forest! 3. Measure R/Q from beam excitation in the HOM couplers : main unknowns are the polarisations Ki / HOM / x-plane
20 Quadrupole Q1 Dipole D5 Q = Powerful Quadrupole HOMs are co-excited
21 The 5 th dipole passband : module measurements are difficult to interpret. Cavity #1 Cavity #7
22 Benchmarking with 1887 MHz Q = R/Q = 0.16 Ω/cm 2, from URMEL Mode measured in all 8 cavities with N.A.
23 22 db SA from (cables + 10dB attenuator) fc2 fc8 = 22 KHz Assuming : cos(φ)=1 and Pext = P K1
24 The modes TM110-8 in (C1-C6,C8) are spread by about 300 khz, with mode in C7 about 3 MHz below! Off resonance cavity response Q = f = 5 khz
25 The loaded cavity 54 MHz Pn = U n 2 /(R/Q Q) The exponential decay of the empty cavity P = PN exp(-2t/τ) depends on number of bunches N The start of the decay can be a bit higher or much lower than the video signal
26 TM110-5 vs. TM MHz R/Q = 8.7 Ω/cm 2, Q = x BPM = 1.75 mm 1887 MHz R/Q = 0.16 Ω/cm 2, Q = x BPM = mm
27 MHz Prediction f-spread = 560 khz for polar #1 850 khz for polar #2
28 5 th Dipole Passband Trapped Mode Prediction for : f =3068 MHz, R/Q = 1.1 Ω/cm 2, Q = in cavity C7, as a function of the modulation frequency
29 Conclusions for Higher Passbands No signal (~ 0dBm= 1 mw) of strong HOM with low damping (R/Q 1 Ω/cm 2, Q 10 6 ) But, no decisive proof that such modes do not exist. Possible explanations for low power signal : ( ~ 40 dbm instead of ~ 0 dbm): R/Q 1 Ω/cm 2 Vertical polarisation HOM is harmless Signal is off resonance : f Q1 f D5 > 100 khz Last bunch generates low field across gap
30 Necessary Improvements Improve BPM resolution (complement with strip-line) Offset beam horizontally and vertically Check linearity for dipole modes Measure direct pick-up signal of HOM couplers dependence on offset dependence on coupler dependence on modulation frequency Measure HOM power for well understood monopole modes, and compare to prediction Vary number of bunches by one unit. A complete frequency scan will be very long
31 Interpretation of the 3 rd Dipole Passband Puzzle A recent (preliminary) calculation by M. Dohlus (DESY) might elucidate the problem of the 3 rd dipole passband. It combines S-parameter and MAFIA type of calculations, a method also developed at the U ty of Rostock. It is based on the real geometry of Input and HOM couplers.
32 It predicts the correct passband pattern and HOM damping C46 measurement s12 vs. f Q vs. Φ Example of cavity with Saclay HOM couplers
33 It predicts: the correct pairing of polarisations, with high and low HOM damping the correct shape of s12 through HOM couplers K1-K2 s12 vs. f DESY --- Saclay
34 It predicts "module modes" extending over the entire module, in the case of homogeneous HOM coupler type.
35 It predicts a practical solution for reducing Q < 10 5 DESY type HOM coupler One coupler is "mirrored" Q vs. Φ Q vs. Φ
36 Polarisation pattern may not be completely understood Mode: GHz /cavity 7 Ampl. [a.u.] Hal Val -3-2,5-2 -1,5-1 -0,5 0 0,5 1 Steerer 7INJ1 [A] Example of S28 cavity (module 3) with DESY HOM couplers showing a vertically polarized HOM at MHz with Q = : vertical polarisation DESY coupler f (low Q) < f (high Q) Saclay coupler
37 Conclusions LESSONS HOM above cut-off may not be contained in a single cavity : single cavity R/Q is not relevant, because field pattern is changed module R/Q not useful for (m=1) modes because orbit not constant. Although used for f and Q, beam measurements MUST be used for measuring beam coupling R/Q and polarisation Φ. requires qualitative improvement in experimental set-up. CONCLUSIONS The puzzle of 3 rd dipole passband might be explained and cured. No evidence for dangerous HOM in the other passbands although high-q modes exists, especially in the 5 th passband
Superstructures; First Cold Test and Future Applications
 Superstructures; First Cold Test and Future Applications DESY: C. Albrecht, V. Ayvazyan, R. Bandelmann, T. Büttner, P. Castro, S. Choroba, J. Eschke, B. Faatz, A. Gössel, K. Honkavaara, B. Horst, J. Iversen,
Superstructures; First Cold Test and Future Applications DESY: C. Albrecht, V. Ayvazyan, R. Bandelmann, T. Büttner, P. Castro, S. Choroba, J. Eschke, B. Faatz, A. Gössel, K. Honkavaara, B. Horst, J. Iversen,
Using Higher Order Modes in the Superconducting TESLA Cavities for Diagnostics at DESY
 Using Higher Order Modes in the Superconducting TESLA Cavities for Diagnostics at FLASH @ DESY N. Baboi, DESY, Hamburg for the HOM team : S. Molloy 1, N. Baboi 2, N. Eddy 3, J. Frisch 1, L. Hendrickson
Using Higher Order Modes in the Superconducting TESLA Cavities for Diagnostics at FLASH @ DESY N. Baboi, DESY, Hamburg for the HOM team : S. Molloy 1, N. Baboi 2, N. Eddy 3, J. Frisch 1, L. Hendrickson
HOM Based Diagnostics at the TTF
 HOM Based Diagnostics at the TTF Nov 14, 2005 Josef Frisch, Nicoleta Baboi, Linda Hendrickson, Olaf Hensler, Douglas McCormick, Justin May, Olivier Napoly, Rita Paparella, Marc Ross, Claire Simon, Tonee
HOM Based Diagnostics at the TTF Nov 14, 2005 Josef Frisch, Nicoleta Baboi, Linda Hendrickson, Olaf Hensler, Douglas McCormick, Justin May, Olivier Napoly, Rita Paparella, Marc Ross, Claire Simon, Tonee
HIGHER ORDER MODES FOR BEAM DIAGNOSTICS IN THIRD HARMONIC 3.9 GHZ ACCELERATING MODULES *
 HIGHER ORDER MODES FOR BEAM DIAGNOSTICS IN THIRD HARMONIC 3.9 GHZ ACCELERATING MODULES * N. Baboi #, N. Eddy, T. Flisgen, H.-W. Glock, R. M. Jones, I. R. R. Shinton, and P. Zhang # # Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron
HIGHER ORDER MODES FOR BEAM DIAGNOSTICS IN THIRD HARMONIC 3.9 GHZ ACCELERATING MODULES * N. Baboi #, N. Eddy, T. Flisgen, H.-W. Glock, R. M. Jones, I. R. R. Shinton, and P. Zhang # # Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron
Test of two Nb superstructure prototypes
 SLAC-PUB-1413 Test of two Nb superstructure prototypes J. Sekutowicz, P. Castro, A. Gössel, G. Kreps, R. Lange, A. Matheisen, W.-D. Möller, H.-B. Peters, D. Proch, H. Schlarb, S. Schreiber, S. Simrock,
SLAC-PUB-1413 Test of two Nb superstructure prototypes J. Sekutowicz, P. Castro, A. Gössel, G. Kreps, R. Lange, A. Matheisen, W.-D. Möller, H.-B. Peters, D. Proch, H. Schlarb, S. Schreiber, S. Simrock,
Physics Requirements Document Document Title: SCRF 1.3 GHz Cryomodule Document Number: LCLSII-4.1-PR-0146-R0 Page 1 of 7
 Document Number: LCLSII-4.1-PR-0146-R0 Page 1 of 7 Document Approval: Originator: Tor Raubenheimer, Physics Support Lead Date Approved Approver: Marc Ross, Cryogenic System Manager Approver: Jose Chan,
Document Number: LCLSII-4.1-PR-0146-R0 Page 1 of 7 Document Approval: Originator: Tor Raubenheimer, Physics Support Lead Date Approved Approver: Marc Ross, Cryogenic System Manager Approver: Jose Chan,
The TESLA Linear Collider. Winfried Decking (DESY) for the TESLA Collaboration
 The TESLA Linear Collider Winfried Decking (DESY) for the TESLA Collaboration Outline Project Overview Highlights 2000/2001 Publication of the TDR Cavity R&D TTF Operation A0 and PITZ TESLA Beam Dynamics
The TESLA Linear Collider Winfried Decking (DESY) for the TESLA Collaboration Outline Project Overview Highlights 2000/2001 Publication of the TDR Cavity R&D TTF Operation A0 and PITZ TESLA Beam Dynamics
Diagnostics I M. Minty DESY
 Diagnostics I M. Minty DESY Introduction Beam Charge / Intensity Beam Position Summary Introduction Transverse Beam Emittance Longitudinal Beam Emittance Summary Diagnostics I Diagnostics II Synchrotron
Diagnostics I M. Minty DESY Introduction Beam Charge / Intensity Beam Position Summary Introduction Transverse Beam Emittance Longitudinal Beam Emittance Summary Diagnostics I Diagnostics II Synchrotron
PUBLICATION. HOM electronics and code to probe beam centring on 3.9 GHz cavities
 EuCARD-REP-2014-010 European Coordination for Accelerator Research and Development PUBLICATION HOM electronics and code to probe beam centring on 3.9 GHz cavities Zhang, P (DESY) 19 June 2014 The research
EuCARD-REP-2014-010 European Coordination for Accelerator Research and Development PUBLICATION HOM electronics and code to probe beam centring on 3.9 GHz cavities Zhang, P (DESY) 19 June 2014 The research
Resonant Excitation of High Order Modes in the 3.9 GHz Cavity of LCLS-II Linac
 Resonant Excitation of High Order Modes in the 3.9 GHz Cavity of LCLS-II Linac LCLS-II TN-16-05 9/12/2016 A. Lunin, T. Khabiboulline, N. Solyak, A. Sukhanov, V. Yakovlev April 10, 2017 LCLSII-TN-16-06
Resonant Excitation of High Order Modes in the 3.9 GHz Cavity of LCLS-II Linac LCLS-II TN-16-05 9/12/2016 A. Lunin, T. Khabiboulline, N. Solyak, A. Sukhanov, V. Yakovlev April 10, 2017 LCLSII-TN-16-06
Calibrating the Cavity Voltage. Presentation of an idea
 Calibrating the Cavity Voltage. Presentation of an idea Stefan Wilke, DESY MHF-e 21st ESLS rf meeting Kraków, 15th/16th nov 2017 Accelerators at DESY. linear and circular Page 2 Accelerators at DESY. linear
Calibrating the Cavity Voltage. Presentation of an idea Stefan Wilke, DESY MHF-e 21st ESLS rf meeting Kraków, 15th/16th nov 2017 Accelerators at DESY. linear and circular Page 2 Accelerators at DESY. linear
A Design of a 3rd Harmonic Cavity for the TTF 2 Photoinjector
 TESLA-FEL 2002-05 A Design of a 3rd Harmonic Cavity for the TTF 2 Photoinjector J. Sekutowicz, R. Wanzenberg DESY, Notkestr. 85, 22603 Hamburg, Germany W.F.O. Müller, T. Weiland TEMF, TU Darmstadt, Schloßgartenstr.
TESLA-FEL 2002-05 A Design of a 3rd Harmonic Cavity for the TTF 2 Photoinjector J. Sekutowicz, R. Wanzenberg DESY, Notkestr. 85, 22603 Hamburg, Germany W.F.O. Müller, T. Weiland TEMF, TU Darmstadt, Schloßgartenstr.
HOM/LOM Coupler Study for the ILC Crab Cavity*
 SLAC-PUB-1249 April 27 HOM/LOM Coupler Study for the ILC Crab Cavity* L. Xiao, Z. Li, K. Ko, SLAC, Menlo Park, CA9425, U.S.A Abstract The FNAL 9-cell 3.9GHz deflecting mode cavity designed for the CKM
SLAC-PUB-1249 April 27 HOM/LOM Coupler Study for the ILC Crab Cavity* L. Xiao, Z. Li, K. Ko, SLAC, Menlo Park, CA9425, U.S.A Abstract The FNAL 9-cell 3.9GHz deflecting mode cavity designed for the CKM
The HOM measurement of a TESLA cavity (Z84) for HOM-BPM and cavity alignment
 The HOM measurement of a TESLA cavity (Z84) for HOM-BPM and cavity alignment Ken.Watanabe:GUAS/AS (KEK) : presenter Hitoshi.Hayano, Shuichi.Noguchi, Eiji.Kako, Toshio.Shishido (KEK) Joint DESY and University
The HOM measurement of a TESLA cavity (Z84) for HOM-BPM and cavity alignment Ken.Watanabe:GUAS/AS (KEK) : presenter Hitoshi.Hayano, Shuichi.Noguchi, Eiji.Kako, Toshio.Shishido (KEK) Joint DESY and University
Main Injector Cavity Simulation and Optimization for Project X
 Main Injector Cavity Simulation and Optimization for Project X Liling Xiao Advanced Computations Group Beam Physics Department Accelerator Research Division Status Meeting, April 7, 2011 Outline Background
Main Injector Cavity Simulation and Optimization for Project X Liling Xiao Advanced Computations Group Beam Physics Department Accelerator Research Division Status Meeting, April 7, 2011 Outline Background
CERN EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH INVESTIGATION OF A RIDGE-LOADED WAVEGUIDE STRUCTURE FOR CLIC X-BAND CRAB CAVITY
 CERN EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CLIC Note 1003 INVESTIGATION OF A RIDGE-LOADED WAVEGUIDE STRUCTURE FOR CLIC X-BAND CRAB CAVITY V.F. Khan, R. Calaga and A. Grudiev CERN, Geneva, Switzerland.
CERN EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CLIC Note 1003 INVESTIGATION OF A RIDGE-LOADED WAVEGUIDE STRUCTURE FOR CLIC X-BAND CRAB CAVITY V.F. Khan, R. Calaga and A. Grudiev CERN, Geneva, Switzerland.
COUPLER DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE ILC CRAB CAVITY
 COUPLER DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE ILC CRAB CAVITY C. Beard 1), G. Burt 2), A. C. Dexter 2), P. Goudket 1), P. A. McIntosh 1), E. Wooldridge 1) 1) ASTeC, Daresbury laboratory, Warrington, Cheshire,
COUPLER DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE ILC CRAB CAVITY C. Beard 1), G. Burt 2), A. C. Dexter 2), P. Goudket 1), P. A. McIntosh 1), E. Wooldridge 1) 1) ASTeC, Daresbury laboratory, Warrington, Cheshire,
Beam Position Monitor with HOM couplers
 Beam Position Monitor with HOM couplers Masaru Sawamura and Ryoji Nagai Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) 2-4 Shirakata-Shirane, Tokai, Ibaraki 319-1195, Japan Corresponding author: Masaru
Beam Position Monitor with HOM couplers Masaru Sawamura and Ryoji Nagai Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) 2-4 Shirakata-Shirane, Tokai, Ibaraki 319-1195, Japan Corresponding author: Masaru
Demonstration of exponential growth and saturation at VUV wavelengths at the TESLA Test Facility Free-Electron Laser. P. Castro for the TTF-FEL team
 Demonstration of exponential growth and saturation at VUV wavelengths at the TESLA Test Facility Free-Electron Laser P. Castro for the TTF-FEL team 100 nm 1 Å FEL radiation TESLA Test Facility at DESY
Demonstration of exponential growth and saturation at VUV wavelengths at the TESLA Test Facility Free-Electron Laser P. Castro for the TTF-FEL team 100 nm 1 Å FEL radiation TESLA Test Facility at DESY
FAST RF KICKER DESIGN
 FAST RF KICKER DESIGN David Alesini LNF-INFN, Frascati, Rome, Italy ICFA Mini-Workshop on Deflecting/Crabbing Cavity Applications in Accelerators, Shanghai, April 23-25, 2008 FAST STRIPLINE INJECTION KICKERS
FAST RF KICKER DESIGN David Alesini LNF-INFN, Frascati, Rome, Italy ICFA Mini-Workshop on Deflecting/Crabbing Cavity Applications in Accelerators, Shanghai, April 23-25, 2008 FAST STRIPLINE INJECTION KICKERS
Performance of the TTF Photoinjector Laser System
 Performance of the TTF Photoinjector Laser System S. Schreiber, DESY Laser Issues for Electron Photoinjectors, October 23-25, 22, Stanford, California, USA & I. Will, A. Liero, W. Sandner, MBI Berlin Overview
Performance of the TTF Photoinjector Laser System S. Schreiber, DESY Laser Issues for Electron Photoinjectors, October 23-25, 22, Stanford, California, USA & I. Will, A. Liero, W. Sandner, MBI Berlin Overview
Detection of Beam Induced Dipole-Mode Signals in the SLC S-Band Structures* Abstract
 -. SLAC-PUB-79 June 1997 Detection of Beam nduced Dipole-Mode Signals in the SLC S-Band Structures* M. Seidel, C. Adolphsen, R. Assmann, D.H. Whittum Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University,
-. SLAC-PUB-79 June 1997 Detection of Beam nduced Dipole-Mode Signals in the SLC S-Band Structures* M. Seidel, C. Adolphsen, R. Assmann, D.H. Whittum Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University,
Cavity BPM With Dipole-Mode Selective Coupler
 Cavity BPM With Dipole-Mode Selective Coupler Zenghai Li Advanced Computations Department Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Presented at PAC23 Portland, Oregon. May 12-16, 23 Work supported by the U.S.
Cavity BPM With Dipole-Mode Selective Coupler Zenghai Li Advanced Computations Department Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Presented at PAC23 Portland, Oregon. May 12-16, 23 Work supported by the U.S.
Energy Recovering Linac Issues
 Energy Recovering Linac Issues L. Merminga Jefferson Lab EIC Accelerator Workshop Brookhaven National Laboratory February 26-27, 2002 Outline Energy Recovery RF Stability in Recirculating, Energy Recovering
Energy Recovering Linac Issues L. Merminga Jefferson Lab EIC Accelerator Workshop Brookhaven National Laboratory February 26-27, 2002 Outline Energy Recovery RF Stability in Recirculating, Energy Recovering
3.9 GHz Deflecting Mode Cavity
 3.9 GHz Deflecting Mode Cavity Timothy W. Koeth July 12, 2005 History of 3.9 GHz DMC Cavity Simulations The Other Modes concern and modeling R/Q Wake Field Simulations Design: OM couplers Testing: Vertical
3.9 GHz Deflecting Mode Cavity Timothy W. Koeth July 12, 2005 History of 3.9 GHz DMC Cavity Simulations The Other Modes concern and modeling R/Q Wake Field Simulations Design: OM couplers Testing: Vertical
Design of S-band re-entrant cavity BPM
 Nuclear Science and Techniques 20 (2009) 133 139 Design of S-band re-entrant cavity BPM LUO Qing SUN Baogen * HE Duohui National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, School of Nuclear Science and Technology,
Nuclear Science and Techniques 20 (2009) 133 139 Design of S-band re-entrant cavity BPM LUO Qing SUN Baogen * HE Duohui National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, School of Nuclear Science and Technology,
Electron Cloud Studies in the Fermilab Main Injector using Microwave Transmission
 Electron Cloud Studies in the Fermilab Main Injector using Microwave Transmission J. Charles Thangaraj on behalf of E-cloud team @ Fermilab (B. Zwaska, C. Tan, N. Eddy,..) p ω c ω ω Microwave measurement
Electron Cloud Studies in the Fermilab Main Injector using Microwave Transmission J. Charles Thangaraj on behalf of E-cloud team @ Fermilab (B. Zwaska, C. Tan, N. Eddy,..) p ω c ω ω Microwave measurement
NanoBPM tests in the ATF extraction line
 NLC - The Next Linear Collider Project NanoBPM tests in the ATF extraction line Calibrate movers (tilters) and BPM s Understand and test dynamic range and resolution June 2003 Marc Ross What are the uses
NLC - The Next Linear Collider Project NanoBPM tests in the ATF extraction line Calibrate movers (tilters) and BPM s Understand and test dynamic range and resolution June 2003 Marc Ross What are the uses
Bunch-by-Bunch Broadband Feedback for the ESRF
 Bunch-by-Bunch Broadband Feedback for the ESRF ESLS RF meeting / Aarhus 21-09-2005 J. Jacob, E. Plouviez, J.-M. Koch, G. Naylor, V. Serrière Goal: Active damping of longitudinal and transverse multibunch
Bunch-by-Bunch Broadband Feedback for the ESRF ESLS RF meeting / Aarhus 21-09-2005 J. Jacob, E. Plouviez, J.-M. Koch, G. Naylor, V. Serrière Goal: Active damping of longitudinal and transverse multibunch
Dark current Monitor for the European XFEL D. Lipka, W. Kleen, J. Lund-Nielsen, D. Nölle, S. Vilcins, V. Vogel; DESY Hamburg
 Dark current Monitor for the European XFEL D. Lipka, W. Kleen, J. Lund-Nielsen, D. Nölle, S. Vilcins, V. Vogel; DESY Hamburg Content 2 Dark current Principle of detecting weakly charged bunches with resonator
Dark current Monitor for the European XFEL D. Lipka, W. Kleen, J. Lund-Nielsen, D. Nölle, S. Vilcins, V. Vogel; DESY Hamburg Content 2 Dark current Principle of detecting weakly charged bunches with resonator
Dark Current Kicker Studies at FLASH
 Dark Current Kicker Studies at FLASH F. Obier, J. Wortmann, S. Schreiber, W. Decking, K. Flöttmann FLASH Seminar, DESY, 02 Feb 2010 History of the dark current kicker 2005 Vertical kicker was installed
Dark Current Kicker Studies at FLASH F. Obier, J. Wortmann, S. Schreiber, W. Decking, K. Flöttmann FLASH Seminar, DESY, 02 Feb 2010 History of the dark current kicker 2005 Vertical kicker was installed
THIRD HARMONIC CAVITY MODAL ANALYSIS
 THIRD HARMONIC CAVITY MODAL ANALYSIS B. Szczesny, I.R.R. Shinton, R.M. Jones, Cockcroft Institute of Accelerator Science and Technology, Daresbury, UK School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester,
THIRD HARMONIC CAVITY MODAL ANALYSIS B. Szczesny, I.R.R. Shinton, R.M. Jones, Cockcroft Institute of Accelerator Science and Technology, Daresbury, UK School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester,
STATUS OF THE ILC CRAB CAVITY DEVELOPMENT
 STATUS OF THE ILC CRAB CAVITY DEVELOPMENT SLAC-PUB-4645 G. Burt, A. Dexter, Cockcroft Institute, Lancaster University, LA 4YR, UK C. Beard, P. Goudket, P. McIntosh, ASTeC, STFC, Daresbury laboratories,
STATUS OF THE ILC CRAB CAVITY DEVELOPMENT SLAC-PUB-4645 G. Burt, A. Dexter, Cockcroft Institute, Lancaster University, LA 4YR, UK C. Beard, P. Goudket, P. McIntosh, ASTeC, STFC, Daresbury laboratories,
RF Design of Normal Conducting Deflecting Cavity
 RF Design of Normal Conducting Deflecting Cavity Valery Dolgashev (SLAC), Geoff Waldschmidt, Ali Nassiri (Argonne National Laboratory, Advanced Photon Source) 48th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop
RF Design of Normal Conducting Deflecting Cavity Valery Dolgashev (SLAC), Geoff Waldschmidt, Ali Nassiri (Argonne National Laboratory, Advanced Photon Source) 48th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop
A prototype S-band BPM system for the ILC energy spectrometer
 EUROTeV-Report-2008-072 A prototype S-band BPM system for the ILC energy spectrometer A. Lyapin, B. Maiheu, D. Attree, M. Wing, S. Boogert, G. Boorman, M. Slater, D. Ward January 12, 2009 Abstract This
EUROTeV-Report-2008-072 A prototype S-band BPM system for the ILC energy spectrometer A. Lyapin, B. Maiheu, D. Attree, M. Wing, S. Boogert, G. Boorman, M. Slater, D. Ward January 12, 2009 Abstract This
The HOMSC2018 Workshop in Cornell A Brief Summary
 The HOMSC2018 Workshop in Cornell A Brief Summary Nicoleta Baboi, DESY DESY-TEMF Meeting DESY, Hamburg, 15 Nov. 2018 Overview http://indico.classe.cornell.edu/event/185/overview Page 2 Scientific Program
The HOMSC2018 Workshop in Cornell A Brief Summary Nicoleta Baboi, DESY DESY-TEMF Meeting DESY, Hamburg, 15 Nov. 2018 Overview http://indico.classe.cornell.edu/event/185/overview Page 2 Scientific Program
3 rd Harmonic Cavity at ELETTRA
 3 rd Harmonic Cavity at ELETTRA G.Penco, M.Svandrlik FERMI @ Elettra G.O.F. RF UPGRADE BOOSTER Big Projects Started FINALLY at ELETTRA during 25 Experiments with 3HC concluded in December 24 Now activities
3 rd Harmonic Cavity at ELETTRA G.Penco, M.Svandrlik FERMI @ Elettra G.O.F. RF UPGRADE BOOSTER Big Projects Started FINALLY at ELETTRA during 25 Experiments with 3HC concluded in December 24 Now activities
The impedance budget of the CERN Proton Synchrotron (PS)
 The impedance budget of the CERN Proton Synchrotron (PS) Serena Persichelli CERN Hadron Synchrotron Collective effects University of Rome La Sapienza serena.persichelli@cern.ch Why do we study the beam
The impedance budget of the CERN Proton Synchrotron (PS) Serena Persichelli CERN Hadron Synchrotron Collective effects University of Rome La Sapienza serena.persichelli@cern.ch Why do we study the beam
OVERVIEW OF RECENT TRENDS AND DEVELOPMENTS FOR BPM SYSTEMS
 OVERVIEW OF RECENT TRENDS AND DEVELOPMENTS FOR BPM SYSTEMS Manfred Wendt Fermilab Assembled with great help of the colleagues from the beam instrumentation community! Contents Introduction BPM Pickup Broadband
OVERVIEW OF RECENT TRENDS AND DEVELOPMENTS FOR BPM SYSTEMS Manfred Wendt Fermilab Assembled with great help of the colleagues from the beam instrumentation community! Contents Introduction BPM Pickup Broadband
Third Harmonic Cavity Status
 Third Harmonic Cavity Status General parameters Cavity design Main coupler calculation HOM analysis and HOM coupler design Lorentz Forces and Stress analysis Summary General parameters Third harmonic cavity
Third Harmonic Cavity Status General parameters Cavity design Main coupler calculation HOM analysis and HOM coupler design Lorentz Forces and Stress analysis Summary General parameters Third harmonic cavity
Cavity BPMs for the NLC
 SLAC-PUB-9211 May 2002 Cavity BPMs for the NLC Ronald Johnson, Zenghai Li, Takashi Naito, Jeffrey Rifkin, Stephen Smith, and Vernon Smith Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, 2575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo
SLAC-PUB-9211 May 2002 Cavity BPMs for the NLC Ronald Johnson, Zenghai Li, Takashi Naito, Jeffrey Rifkin, Stephen Smith, and Vernon Smith Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, 2575 Sand Hill Road, Menlo
Feedback Requirements for SASE FELS. Henrik Loos, SLAC IPAC 2010, Kyoto, Japan
 Feedback Requirements for SASE FELS Henrik Loos, SLAC, Kyoto, Japan 1 1 Henrik Loos Outline Stability requirements for SASE FELs Diagnostics for beam parameters Transverse: Beam position monitors Longitudinal:
Feedback Requirements for SASE FELS Henrik Loos, SLAC, Kyoto, Japan 1 1 Henrik Loos Outline Stability requirements for SASE FELs Diagnostics for beam parameters Transverse: Beam position monitors Longitudinal:
New apparatus for precise synchronous phase shift measurements in storage rings 1
 New apparatus for precise synchronous phase shift measurements in storage rings 1 Boris Podobedov and Robert Siemann Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94309 Measuring
New apparatus for precise synchronous phase shift measurements in storage rings 1 Boris Podobedov and Robert Siemann Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94309 Measuring
SOLEIL Libera Performance
 SOLEIL Libera Performance Libera Workshop 24/25 September 2007 on behalf of the SOLEIL BPM team BPM system: MAC2 requirements, Feb. 2002 closed orbit Correction number of BPMs 120 instead of 112 single
SOLEIL Libera Performance Libera Workshop 24/25 September 2007 on behalf of the SOLEIL BPM team BPM system: MAC2 requirements, Feb. 2002 closed orbit Correction number of BPMs 120 instead of 112 single
FLASH at DESY. FLASH. Free-Electron Laser in Hamburg. The first soft X-ray FEL operating two undulator beamlines simultaneously
 FLASH at DESY The first soft X-ray FEL operating two undulator beamlines simultaneously Katja Honkavaara, DESY for the FLASH team FEL Conference 2014, Basel 25-29 August, 2014 First Lasing FLASH2 > First
FLASH at DESY The first soft X-ray FEL operating two undulator beamlines simultaneously Katja Honkavaara, DESY for the FLASH team FEL Conference 2014, Basel 25-29 August, 2014 First Lasing FLASH2 > First
Snowmass WG5: Superconducting Cavities and Couplers (Draft August 12, 2005 Rong-Li Geng) Topic 1: Cavity Shape
 Snowmass WG5: Superconducting Cavities and Couplers (Draft August 12, 2005 Rong-Li Geng) Topic 1: Cavity Shape Overview The cavity shape determines the fundamental mode as well as the higher order modes
Snowmass WG5: Superconducting Cavities and Couplers (Draft August 12, 2005 Rong-Li Geng) Topic 1: Cavity Shape Overview The cavity shape determines the fundamental mode as well as the higher order modes
Cavity-type Beam Position Monitors for the SASE FEL at the TESLA Test Facility
 TESLA-FEL 2003-03 Cavity-type Beam Position Monitors for the SASE FEL at the TESLA Test Facility R. Lorenz 1, S. Sabah 2,H.J.Schreiber 3, H. Waldmann 3 1 Westdeutscher Rundfunk, 50600 Köln 2 VI-TELEFILTER
TESLA-FEL 2003-03 Cavity-type Beam Position Monitors for the SASE FEL at the TESLA Test Facility R. Lorenz 1, S. Sabah 2,H.J.Schreiber 3, H. Waldmann 3 1 Westdeutscher Rundfunk, 50600 Köln 2 VI-TELEFILTER
BPMs with Precise Alignment for TTF2
 BPMs with Precise Alignment for TTF2 D. Noelle, G. Priebe, M. Wendt, and M. Werner Deutsches Elektronen Synchrotron DESY, Notkestr. 85, D-22603 Hamburg, Germany Abstract. Design and technology of the new,
BPMs with Precise Alignment for TTF2 D. Noelle, G. Priebe, M. Wendt, and M. Werner Deutsches Elektronen Synchrotron DESY, Notkestr. 85, D-22603 Hamburg, Germany Abstract. Design and technology of the new,
Next Linear Collider Beam Position Monitors
 NLC - The Project Beam Position Monitors Steve Smith SLAC October 23, 2002 What s novel, extreme, or challenging? Push resolution frontier Novel cavity BPM design for high resolution, stability Push well
NLC - The Project Beam Position Monitors Steve Smith SLAC October 23, 2002 What s novel, extreme, or challenging? Push resolution frontier Novel cavity BPM design for high resolution, stability Push well
SIMULATION OF : H.O.M DAMPED CAVITIES
 E.S.L.S Radio Frequency Meeting Aarhus, DENMARK Sept 2005 SIMULATION OF : H.O.M DAMPED CAVITIES Grenoble - FRANCE TARGET OF SIMULATIONS AT E.S.R.F DEVELOPPING A PROTOTYPE OF NORMAL CONDUCTING CAVITY (at
E.S.L.S Radio Frequency Meeting Aarhus, DENMARK Sept 2005 SIMULATION OF : H.O.M DAMPED CAVITIES Grenoble - FRANCE TARGET OF SIMULATIONS AT E.S.R.F DEVELOPPING A PROTOTYPE OF NORMAL CONDUCTING CAVITY (at
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS
 UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS SCHOOL OF COMPUTER & COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING EKT 341 LABORATORY MODULE LAB 2 Antenna Characteristic 1 Measurement of Radiation Pattern, Gain, VSWR, input impedance and reflection
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS SCHOOL OF COMPUTER & COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING EKT 341 LABORATORY MODULE LAB 2 Antenna Characteristic 1 Measurement of Radiation Pattern, Gain, VSWR, input impedance and reflection
H. Weise, Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron, Hamburg, Germany for the XFEL Group
 7+(7(6/$;)(/352-(&7 H. Weise, Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron, Hamburg, Germany for the XFEL Group $EVWUDFW The overall layout of the X-Ray FEL to be built in international collaboration at DESY will
7+(7(6/$;)(/352-(&7 H. Weise, Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron, Hamburg, Germany for the XFEL Group $EVWUDFW The overall layout of the X-Ray FEL to be built in international collaboration at DESY will
Precision RF Beam Position Monitors for Measuring Beam Position and Tilt Progress Report
 Precision RF Beam Position Monitors for Measuring Beam Position and Tilt Progress Report UC Berkeley Senior Personnel Yury G. Kolomensky Collaborating Institutions Stanford Linear Accelerator Center: Marc
Precision RF Beam Position Monitors for Measuring Beam Position and Tilt Progress Report UC Berkeley Senior Personnel Yury G. Kolomensky Collaborating Institutions Stanford Linear Accelerator Center: Marc
Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA
 d e Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Accelerator & Fusion Research Division I # RECEIVED Presented at the International Workshop on Collective Effects and Impedance for B-Factories,
d e Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Accelerator & Fusion Research Division I # RECEIVED Presented at the International Workshop on Collective Effects and Impedance for B-Factories,
High Precision THIRD HARMONIC SC Cavity Alignment/Diagnostics/BPM with HOM Measurements Roger M. Jones Univ. of Manchester/ Cockcroft Inst.
 High Precision THIRD HARMONIC SC Cavity Alignment/Diagnostics/BPM with HOM Measurements Roger M. Jones Univ. of Manchester/ Cockcroft Inst. EuCARD WP10.5 Task leader on HOM Distribution (inc. 3 sub-tasks)
High Precision THIRD HARMONIC SC Cavity Alignment/Diagnostics/BPM with HOM Measurements Roger M. Jones Univ. of Manchester/ Cockcroft Inst. EuCARD WP10.5 Task leader on HOM Distribution (inc. 3 sub-tasks)
Third Harmonic Superconducting passive cavities in ELETTRA and SLS
 RF superconductivity application to synchrotron radiation light sources Third Harmonic Superconducting passive cavities in ELETTRA and SLS 2 cryomodules (one per machine) with 2 Nb/Cu cavities at 1.5 GHz
RF superconductivity application to synchrotron radiation light sources Third Harmonic Superconducting passive cavities in ELETTRA and SLS 2 cryomodules (one per machine) with 2 Nb/Cu cavities at 1.5 GHz
Photograph of the rectangular waveguide components
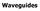 Waveguides Photograph of the rectangular waveguide components BACKGROUND A transmission line can be used to guide EM energy from one point (generator) to another (load). A transmission line can support
Waveguides Photograph of the rectangular waveguide components BACKGROUND A transmission line can be used to guide EM energy from one point (generator) to another (load). A transmission line can support
SwissFEL Design and Status
 SwissFEL Design and Status Hans H. Braun Mini Workshop on Compact X ray Free electron Lasers Eastern Forum of Science and Technology Shanghai July 19, 2010 SwissFEL, the next large facility at PSI SwissFEL
SwissFEL Design and Status Hans H. Braun Mini Workshop on Compact X ray Free electron Lasers Eastern Forum of Science and Technology Shanghai July 19, 2010 SwissFEL, the next large facility at PSI SwissFEL
Project X Cavity RF and mechanical design. T. Khabiboulline, FNAL/TD/SRF
 Project X Cavity RF and mechanical design T. Khabiboulline, FNAL/TD/SRF TTC meeting on CW-SRF, 2013 Project X Cavity RF and mechanical design T 1 High ß Low ß 0.5 HWR SSR1 SSR2 0 1 10 100 1 10 3 1 10 4
Project X Cavity RF and mechanical design T. Khabiboulline, FNAL/TD/SRF TTC meeting on CW-SRF, 2013 Project X Cavity RF and mechanical design T 1 High ß Low ß 0.5 HWR SSR1 SSR2 0 1 10 100 1 10 3 1 10 4
Nonintercepting Diagnostics for Transverse Beam Properties: from Rings to ERLs
 Nonintercepting Diagnostics for Transverse Beam Properties: from Rings to ERLs Alex H. Lumpkin Accelerator Operations Division Advanced Photon Source Presented at Jefferson National Accelerator Laboratory
Nonintercepting Diagnostics for Transverse Beam Properties: from Rings to ERLs Alex H. Lumpkin Accelerator Operations Division Advanced Photon Source Presented at Jefferson National Accelerator Laboratory
Influences of a Beam-Pipe Discontinuity on the Signals of a Nearby Beam Position Monitor (BPM)
 Internal Report DESY M 1-2 May 21 Influences of a Beam-Pipe Discontinuity on the Signals of a Nearby Beam Position Monitor (BPM) A.K. Bandyopadhyay, A. Joestingmeier, A.S. Omar, R. Wanzenberg Deutsches
Internal Report DESY M 1-2 May 21 Influences of a Beam-Pipe Discontinuity on the Signals of a Nearby Beam Position Monitor (BPM) A.K. Bandyopadhyay, A. Joestingmeier, A.S. Omar, R. Wanzenberg Deutsches
MEASURES TO REDUCE THE IMPEDANCE OF PARASITIC RESONANT MODES IN THE DAΦNE VACUUM CHAMBER
 Frascati Physics Series Vol. X (1998), pp. 371-378 14 th Advanced ICFA Beam Dynamics Workshop, Frascati, Oct. 20-25, 1997 MEASURES TO REDUCE THE IMPEDANCE OF PARASITIC RESONANT MODES IN THE DAΦNE VACUUM
Frascati Physics Series Vol. X (1998), pp. 371-378 14 th Advanced ICFA Beam Dynamics Workshop, Frascati, Oct. 20-25, 1997 MEASURES TO REDUCE THE IMPEDANCE OF PARASITIC RESONANT MODES IN THE DAΦNE VACUUM
Automatic phase calibration for RF cavities using beam-loading signals. Jonathan Edelen LLRF 2017 Workshop (Barcelona) 18 Oct 2017
 Automatic phase calibration for RF cavities using beam-loading signals Jonathan Edelen LLRF 2017 Workshop (Barcelona) 18 Oct 2017 Introduction How do we meet 10-4 energy stability for PIP-II? 2 11/9/2017
Automatic phase calibration for RF cavities using beam-loading signals Jonathan Edelen LLRF 2017 Workshop (Barcelona) 18 Oct 2017 Introduction How do we meet 10-4 energy stability for PIP-II? 2 11/9/2017
MAX II RF system 100 MHz technology Lars Malmgren 10th ESLS RF Meeting Dortmund September 27-28, 2006
 MAX II RF system 1 MHz technology Lars Malmgren 1th ESLS RF Meeting Dortmund September 27-28, 26 Facts and figures MAX-II Frequency [MHz] Harmonic number No of cavity cells No of transmitters Cell radius
MAX II RF system 1 MHz technology Lars Malmgren 1th ESLS RF Meeting Dortmund September 27-28, 26 Facts and figures MAX-II Frequency [MHz] Harmonic number No of cavity cells No of transmitters Cell radius
CAVITY BPM DESIGNS, RELATED ELECTRONICS AND MEASURED PERFORMANCES
 TUOC2 Proceedings of DIPAC9, Basel, Switzerland CAVITY BPM DESIGNS, ELATED ELECTONICS AND MEASUED PEFOMANCES D. Lipka, DESY, Hamburg, Germany Abstract Future accelerators like the International Linear
TUOC2 Proceedings of DIPAC9, Basel, Switzerland CAVITY BPM DESIGNS, ELATED ELECTONICS AND MEASUED PEFOMANCES D. Lipka, DESY, Hamburg, Germany Abstract Future accelerators like the International Linear
Beam Position Monitors: Detector Principle and Signal Estimation. Peter Forck. Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung GSI, Darmstadt, Germany
 Outline: Beam Position Monitors: Detector Principle and Signal Estimation Peter Forck Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung GSI, Darmstadt, Germany General discussion on BPM features and specification
Outline: Beam Position Monitors: Detector Principle and Signal Estimation Peter Forck Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung GSI, Darmstadt, Germany General discussion on BPM features and specification
ERL Prototype at BNL. Work supported by Brookhaven Science Associates, LLC under Contract No. DE-AC02-98CH10886 with the U.S. Department of Energy.
 ERL Prototype at BNL Ilan Ben-Zvi, for the Superconducting Accelerator and Electron Cooling group, Collider-Accelerator Department Brookhaven National Laboratory & Center for Accelerator Science and Education
ERL Prototype at BNL Ilan Ben-Zvi, for the Superconducting Accelerator and Electron Cooling group, Collider-Accelerator Department Brookhaven National Laboratory & Center for Accelerator Science and Education
Booster High-level RF Frequency Tracking Improvement Via the Bias-Curve Optimization
 FERMILAB-TM-227-AD Booster High-level RF Frequency Tracking Improvement Via the Bias-Curve Optimization Xi Yang Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory Box 5, Batavia IL 651 Abstract It is important to improve
FERMILAB-TM-227-AD Booster High-level RF Frequency Tracking Improvement Via the Bias-Curve Optimization Xi Yang Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory Box 5, Batavia IL 651 Abstract It is important to improve
Longitudinal bunch shape Overview of processing electronics for Beam Position Monitor (BPM) Measurements:
 Pick-Ups for bunched Beams The image current at the beam pipe is monitored on a high frequency basis i.e. the ac-part given by the bunched beam. Beam Position Monitor BPM equals Pick-Up PU Most frequent
Pick-Ups for bunched Beams The image current at the beam pipe is monitored on a high frequency basis i.e. the ac-part given by the bunched beam. Beam Position Monitor BPM equals Pick-Up PU Most frequent
A 3 GHz SRF reduced-β Cavity for the S-DALINAC
 A 3 GHz SRF reduced-β Cavity for the S-DALINAC D. Bazyl*, W.F.O. Müller, H. De Gersem Gefördert durch die DFG im Rahmen des GRK 2128 20.11.2018 M.Sc. Dmitry Bazyl TU Darmstadt TEMF Upgrade of the Capture
A 3 GHz SRF reduced-β Cavity for the S-DALINAC D. Bazyl*, W.F.O. Müller, H. De Gersem Gefördert durch die DFG im Rahmen des GRK 2128 20.11.2018 M.Sc. Dmitry Bazyl TU Darmstadt TEMF Upgrade of the Capture
Low-Level RF. S. Simrock, DESY. MAC mtg, May 05 Stefan Simrock DESY
 Low-Level RF S. Simrock, DESY Outline Scope of LLRF System Work Breakdown for XFEL LLRF Design for the VUV-FEL Cost, Personpower and Schedule RF Systems for XFEL RF Gun Injector 3rd harmonic cavity Main
Low-Level RF S. Simrock, DESY Outline Scope of LLRF System Work Breakdown for XFEL LLRF Design for the VUV-FEL Cost, Personpower and Schedule RF Systems for XFEL RF Gun Injector 3rd harmonic cavity Main
EC6503 Transmission Lines and WaveguidesV Semester Question Bank
 UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
High Order Modes Survey and Mitigation of the CEBAF C100 Cryomodules
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia (2015) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia ICFA mini Workshop on High Order Modes in Superconducting Cavities, HOMSC14 High
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Physics Procedia (2015) 000 000 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia ICFA mini Workshop on High Order Modes in Superconducting Cavities, HOMSC14 High
SRF EXPERIENCE WITH THE CORNELL HIGH-CURRENT ERL INJECTOR PROTOTYPE
 SRF EXPERIENCE WITH THE CORNELL HIGH-CURRENT ERL INJECTOR PROTOTYPE M. Liepe, S. Belomestnykh, E. Chojnacki, Z. Conway, V. Medjidzade, H. Padamsee, P. Quigley, J. Sears, V. Shemelin, V. Veshcherevich,
SRF EXPERIENCE WITH THE CORNELL HIGH-CURRENT ERL INJECTOR PROTOTYPE M. Liepe, S. Belomestnykh, E. Chojnacki, Z. Conway, V. Medjidzade, H. Padamsee, P. Quigley, J. Sears, V. Shemelin, V. Veshcherevich,
Using a TE011 Cavity to Measure the Magnetic Momentum of a Magnetized Beam. Jiquan Guo
 Using a TE011 Cavity to Measure the Magnetic Momentum of a Magnetized Beam Jiquan Guo Acknowledgements This work is a part of JLab LDRD Generation and Characterization of Magnetized Bunched Electron Beam
Using a TE011 Cavity to Measure the Magnetic Momentum of a Magnetized Beam Jiquan Guo Acknowledgements This work is a part of JLab LDRD Generation and Characterization of Magnetized Bunched Electron Beam
5.5 SNS Superconducting Linac
 JP0150514 ICANS - XV 15 th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources November 6-9, 2000 Tsukuba, Japan Ronald M. Sundelin Jefferson Lab* 5.5 SNS Superconducting Linac 12000
JP0150514 ICANS - XV 15 th Meeting of the International Collaboration on Advanced Neutron Sources November 6-9, 2000 Tsukuba, Japan Ronald M. Sundelin Jefferson Lab* 5.5 SNS Superconducting Linac 12000
DESIGN AND BEAM DYNAMICS STUDIES OF A MULTI-ION LINAC INJECTOR FOR THE JLEIC ION COMPLEX
 DESIGN AND BEAM DYNAMICS STUDIES OF A MULTI-ION LINAC INJECTOR FOR THE JLEIC ION COMPLEX Speaker: P.N. Ostroumov Contributors: A. Plastun, B. Mustapha and Z. Conway HB2016, July 7, 2016, Malmö, Sweden
DESIGN AND BEAM DYNAMICS STUDIES OF A MULTI-ION LINAC INJECTOR FOR THE JLEIC ION COMPLEX Speaker: P.N. Ostroumov Contributors: A. Plastun, B. Mustapha and Z. Conway HB2016, July 7, 2016, Malmö, Sweden
Status of the HOM Damped Cavity Project
 Status of the HOM Damped Cavity Project E. Weihreter / BESSY for the HOM Damped Cavity Collaboration BESSY, Daresbury Lab, DELTA, MaxLab, NTHU Project funded by the EC under contract HPRI-CT-1999-50011
Status of the HOM Damped Cavity Project E. Weihreter / BESSY for the HOM Damped Cavity Collaboration BESSY, Daresbury Lab, DELTA, MaxLab, NTHU Project funded by the EC under contract HPRI-CT-1999-50011
Beam Infrared Detection with Resolution in Time
 Excellence in Detectors and Instrumentation Technologies Beam Infrared Detection with Resolution in Time Alessandro Drago INFN - Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, Italy October 20-29, 2015 Introduction
Excellence in Detectors and Instrumentation Technologies Beam Infrared Detection with Resolution in Time Alessandro Drago INFN - Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, Italy October 20-29, 2015 Introduction
Fundamental mode rejection in SOLEIL dipole HOM couplers
 Fundamental mode rejection in SOLEIL dipole HOM couplers G. Devanz, DSM/DAPNIA/SACM, CEA/Saclay, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette 14th June 2004 1 Introduction The SOLEIL superconducting accelerating cavity is a heavily
Fundamental mode rejection in SOLEIL dipole HOM couplers G. Devanz, DSM/DAPNIA/SACM, CEA/Saclay, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette 14th June 2004 1 Introduction The SOLEIL superconducting accelerating cavity is a heavily
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT
 CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
Proceedings of the Fifth Workshop on RF Superconductivity, DESY, Hamburg, Germany. E. Haebel. A. Mosnier. Centre dbtudes de Saclay, France
 Large or Small Iris Aperture in SC multicell cavities? E. Haebel CERN, Geneva, Switzerland A. Mosnier Centre dbtudes de Saclay, France 1. Introduction As the cost of the superconducting linear accelerator,
Large or Small Iris Aperture in SC multicell cavities? E. Haebel CERN, Geneva, Switzerland A. Mosnier Centre dbtudes de Saclay, France 1. Introduction As the cost of the superconducting linear accelerator,
EuroTeV High Bandwidth Wall Current Monitor. Alessandro D Elia AB-BI-PI 1-1 -
 EU contract number RII3-CT-2003-506395 CARE/ELAN Document-2007-012 EuroTeV High Bandwidth Wall Current Monitor Alessandro D Elia AB-BI-PI 1-1 - EU contract number RII3-CT-2003-506395 CARE/ELAN Document-2007-012
EU contract number RII3-CT-2003-506395 CARE/ELAN Document-2007-012 EuroTeV High Bandwidth Wall Current Monitor Alessandro D Elia AB-BI-PI 1-1 - EU contract number RII3-CT-2003-506395 CARE/ELAN Document-2007-012
What s going on? FLASH Seminar Many People s work presented by D.Nölle, MDI,
 ; FLASH What s going on? Report on Diagnostic Activities at FLASH FLASH Seminar 11.11.08 Many People s work presented by D.Nölle, MDI, 9-2579 1 Topics FLASH BPMs Revision of the Stripline BPM Electronics
; FLASH What s going on? Report on Diagnostic Activities at FLASH FLASH Seminar 11.11.08 Many People s work presented by D.Nölle, MDI, 9-2579 1 Topics FLASH BPMs Revision of the Stripline BPM Electronics
REVIEW ON SUPERCONDUCTING RF GUNS
 REVIEW ON SUPERCONDUCTING RF GUNS D. Janssen #, A. Arnold, H. Büttig, U. Lehnert, P. Michel, P. Murcek, C. Schneider, R. Schurig, F. Staufenbiel, J. Teichert, R. Xiang, Forschungszentrum Rossendorf, Germany.
REVIEW ON SUPERCONDUCTING RF GUNS D. Janssen #, A. Arnold, H. Büttig, U. Lehnert, P. Michel, P. Murcek, C. Schneider, R. Schurig, F. Staufenbiel, J. Teichert, R. Xiang, Forschungszentrum Rossendorf, Germany.
Q d d f - QdOTa3 6. Stanford Linear Acceleratori Center, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94309
 SLAC-PUB-7349 November 1996 Q d d f - QdOTa3 6 -- /oz- Numerical Modeling of Bearn-Environment nteractions in the PEP-1 B-Factory C-K Ng, K KO, Z Li and X E Lin Stanford Linear Acceleratori Center, Stanford
SLAC-PUB-7349 November 1996 Q d d f - QdOTa3 6 -- /oz- Numerical Modeling of Bearn-Environment nteractions in the PEP-1 B-Factory C-K Ng, K KO, Z Li and X E Lin Stanford Linear Acceleratori Center, Stanford
Numerical Simulation of &hepep-i1 Beam Position Monitor*
 SLACPUB957006 September 1995 Numerical Simulation of &hepepi1 Beam Position Monitor* N. Kurita D. Martin C.K. Ng S. Smith Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University Stanford CA 94309USA and
SLACPUB957006 September 1995 Numerical Simulation of &hepepi1 Beam Position Monitor* N. Kurita D. Martin C.K. Ng S. Smith Stanford Linear Accelerator Center Stanford University Stanford CA 94309USA and
NEW OPPORTUNITIES IN VACUUM ELECTRONICS USING PHOTONIC BAND GAP STRUCTURES
 NEW OPPORTUNITIES IN VACUUM ELECTRONICS USING PHOTONIC BAND GAP STRUCTURES J. R. Sirigiri, C. Chen, M. A. Shapiro, E. I. Smirnova, and R. J. Temkin Plasma Science and Fusion Center Massachusetts Institute
NEW OPPORTUNITIES IN VACUUM ELECTRONICS USING PHOTONIC BAND GAP STRUCTURES J. R. Sirigiri, C. Chen, M. A. Shapiro, E. I. Smirnova, and R. J. Temkin Plasma Science and Fusion Center Massachusetts Institute
A HIGHER HARMONIC CAVITY AT 800 MHz FOR HL-LHC
 A HIGHER HARMONIC CAVITY AT 800 MHz FOR HL-LHC T. Roggen, P. Baudrenghien, R. Calaga, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract A superconducting 800 MHz second harmonic system is proposed for HL-LHC. It serves
A HIGHER HARMONIC CAVITY AT 800 MHz FOR HL-LHC T. Roggen, P. Baudrenghien, R. Calaga, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract A superconducting 800 MHz second harmonic system is proposed for HL-LHC. It serves
CHALLENGES IN ILC SCRF TECHNOLOGY *
 CHALLENGES IN ILC SCRF TECHNOLOGY * Detlef Reschke #, DESY, D-22603 Hamburg, Germany Abstract With a baseline operating gradient of 31,5 MV/m at a Q-value of 10 10 the superconducting nine-cell cavities
CHALLENGES IN ILC SCRF TECHNOLOGY * Detlef Reschke #, DESY, D-22603 Hamburg, Germany Abstract With a baseline operating gradient of 31,5 MV/m at a Q-value of 10 10 the superconducting nine-cell cavities
High acceleration gradient. Critical applications: Linear colliders e.g. ILC X-ray FELs e.g. DESY XFEL
 High acceleration gradient Critical applications: Linear colliders e.g. ILC X-ray FELs e.g. DESY XFEL Critical points The physical limitation of a SC resonator is given by the requirement that the RF magnetic
High acceleration gradient Critical applications: Linear colliders e.g. ILC X-ray FELs e.g. DESY XFEL Critical points The physical limitation of a SC resonator is given by the requirement that the RF magnetic
HOM Couplers at DESY Jacek Sekutowicz** 2000 Hamburg 52, West-Germany
 ntroduction HOM Couplers at DESY Jacek Sekutowicz** DESY, MHF, NotkestraBe 85 2000 Hamburg 52, West-Germany UiMEL computation and beadpull measurements showed that a 4-cell, 500 MHz HERA cavity has five
ntroduction HOM Couplers at DESY Jacek Sekutowicz** DESY, MHF, NotkestraBe 85 2000 Hamburg 52, West-Germany UiMEL computation and beadpull measurements showed that a 4-cell, 500 MHz HERA cavity has five
Status of the 1.5 GeV Synchrotron Light Source DELTA and Related Accelerator Physics Activities
 Status of the 1.5 GeV Synchrotron Light Source and Related Accelerator Physics Activities 2006 RuPAC, September 10-14, Novosibirsk Thomas Weis for the machine and accelerator physics group Dortmund University
Status of the 1.5 GeV Synchrotron Light Source and Related Accelerator Physics Activities 2006 RuPAC, September 10-14, Novosibirsk Thomas Weis for the machine and accelerator physics group Dortmund University
LCLS Injector Diagnostics. Henrik Loos. Diagnostics overview Transverse Beam Properties Longitudinal Beam Properties
 Diagnostics overview Transverse Beam Properties Longitudinal Beam Properties LCLS Diagnostics Tasks Charge Toroids (Gun, Inj, BC, Und) Faraday cups (Gun & Inj) Trajectory & energy Stripline BPMs (Gun,
Diagnostics overview Transverse Beam Properties Longitudinal Beam Properties LCLS Diagnostics Tasks Charge Toroids (Gun, Inj, BC, Und) Faraday cups (Gun & Inj) Trajectory & energy Stripline BPMs (Gun,
CHARACTERIZATION OF BUTTON AND STRIPLINE BEAM POSITION MONITORS AT FLASH. Summer Student Programme 2007 DESY- Hamburg.
 CHARACTERIZATION OF BUTTON AND STRIPLINE BEAM POSITION MONITORS AT FLASH Summer Student Programme 2007 DESY- Hamburg Yeşim Cenger Ankara University, Turkey E-mail: ycenger@eng.ankara.edu.tr supervisor
CHARACTERIZATION OF BUTTON AND STRIPLINE BEAM POSITION MONITORS AT FLASH Summer Student Programme 2007 DESY- Hamburg Yeşim Cenger Ankara University, Turkey E-mail: ycenger@eng.ankara.edu.tr supervisor
Design considerations for the RF phase reference distribution system for X-ray FEL and TESLA
 Design considerations for the RF phase reference distribution system for X-ray FEL and TESLA Krzysztof Czuba *a, Henning C. Weddig #b a Institute of Electronic Systems, Warsaw University of Technology,
Design considerations for the RF phase reference distribution system for X-ray FEL and TESLA Krzysztof Czuba *a, Henning C. Weddig #b a Institute of Electronic Systems, Warsaw University of Technology,
RF Cavity Design. Erk Jensen CERN BE/RF. CERN Accelerator School Accelerator Physics (Intermediate level) Darmstadt 2009
 RF Cavity Design Erk Jensen CERN BE/RF CERN Accelerator School Accelerator Physics (Intermediate level) Darmstadt 009 CAS Darmstadt '09 RF Cavity Design 1 Overview DC versus RF Basic equations: Lorentz
RF Cavity Design Erk Jensen CERN BE/RF CERN Accelerator School Accelerator Physics (Intermediate level) Darmstadt 009 CAS Darmstadt '09 RF Cavity Design 1 Overview DC versus RF Basic equations: Lorentz
A HIGH EFFICIENCY 17GHz TW CHOPPERTRON
 1 SLAC 07 A HIGH EFFICIENCY 17GHz TW CHOPPERTRON J. Haimson and B. Mecklenburg Work performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy SBIR Grant No.DE-FG02-06ER84468 2 SLAC 07 Figure 1. Centerline
1 SLAC 07 A HIGH EFFICIENCY 17GHz TW CHOPPERTRON J. Haimson and B. Mecklenburg Work performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy SBIR Grant No.DE-FG02-06ER84468 2 SLAC 07 Figure 1. Centerline
REVIEW OF FAST BEAM CHOPPING F. Caspers CERN AB-RF-FB
 F. Caspers CERN AB-RF-FB Introduction Review of several fast chopping systems ESS-RAL LANL-SNS JAERI CERN-SPL Discussion Conclusion 1 Introduction Beam choppers are typically used for β = v/c values between
F. Caspers CERN AB-RF-FB Introduction Review of several fast chopping systems ESS-RAL LANL-SNS JAERI CERN-SPL Discussion Conclusion 1 Introduction Beam choppers are typically used for β = v/c values between
Experiment 12: Microwaves
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 OBJECTIVES Experiment 12: Microwaves To observe the polarization and angular dependence of radiation from a microwave generator
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 OBJECTIVES Experiment 12: Microwaves To observe the polarization and angular dependence of radiation from a microwave generator
