170 Gbit/s transmission in an erbium-doped waveguide amplifier on silicon
|
|
|
- Marybeth Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 170 Gbit/s transmission in an erbium-doped waveguide amplifier on silicon Jonathan D. B. Bradley, 1, * Marcia Costa e Silva, 2 Mathilde Gay, 2 Laurent Bramerie, 2 Alfred Driessen, 1 Kerstin Wörhoff, 1 Jean-Claude Simon, 2 and Markus Pollnau 1 1 Integrated Optical Microsystems Group, MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology, University of Twente, P.O. Box 217, 7500 AE Enschede, The Netherlands 2 FOTON Laboratory, CNRS UMR 6082 / PERSYST Platform,University of Rennes 1 / ENSSAT, 6 Rue de Kerampont, BP Lannion Cedex, France *j.d.b.bradley@ewi.utwente.nl Abstract: Signal transmission experiments were performed at 170 Gbit/s in an integrated Al 2 O 3 :Er 3+ waveguide amplifier to investigate its potential application in high-speed photonic integrated circuits. Net internal gain of up to 11 db was measured for a continuous-wave 1532 nm signal under 1480 nm pumping, with a threshold pump power of 4 mw. A differential group delay of 2 ps between the TE and TM fundamental modes of the 5.7- cm-long amplifier was measured. When selecting a single polarization open eye diagrams and bit error rates equal to those of the transmission system without the amplifier were observed for a 1550 nm signal encoded with a 170 Gbit/s return-to-zero pseudo-random bit sequence Optical Society of America OCIS codes: ( ) Integrated optics devices; ( ) Integrated optics materials; ( ) Optical amplifiers; ( ) Rare-earth-doped materials. References and links 1. Y. Kang, H.-D. Liu, M. Morse, M. J. Paniccia, M. Zadka, S. Litski, G. Sarid, A. Pauchard, Y.-H. Kuo, H.-W. Chen, W. S. Zaoui, J. E. Bowers, A. Beling, D. C. McIntosh, X. Zheng, and J. C. Campbell, Monolithic germanium/silicon avalanche photodiodes with 340 GHz gain-bandwidth product, Nat. Photonics 3(1), (2008). 2. S. Ferber, R. Ludwig, C. Boerner, C. Schubert, C. Schmidt-Langhorst, M. Kroh, V. Marembert, and H. G. Weber, 160 Gbit/s DPSK transmission over 320 km fibre link with high long-term stability, Electron. Lett. 41(4), (2005). 3. L. H. Spiekman, Semiconductor optical amplifiers, in Optical Fiber Telecommunications Volume IVA, I. P. Kaminow and T. Li, eds. (Academic Press, 2002), pp T. Kitagawa, K. Hattori, K. Shuto, M. Yasu, M. Kobayashi, and M. Horiguchi, Amplification in erbium-doped silica-based planar lightwave circuits, Electron. Lett. 28(19), (1992). 5. D. R. Zimmerman, and L. H. Spiekman, Amplifiers for the masses: EDFA, EDWA, and SOA amplets for metro and access networks, J. Lightwave Technol. 22(1), (2004). 6. G. N. van den Hoven, R. J. I. M. Koper, A. Polman, C. van Dam, K. W. M. van Uffelen, and M. K. Smit, Net optical gain at 1.53 µm in Er-doped Al 2O 3 waveguides on silicon, Appl. Phys. Lett. 68(14), (1996). 7. J. D. B. Bradley, L. Agazzi, D. Geskus, F. Ay, K. Wörhoff, and M. Pollnau, Gain bandwidth of 80 nm and 2 db/cm peak gain in Al 2O 3:Er 3+ optical amplifiers on silicon, submitted. 8. G. Nykolak, M. Haner, P. C. Becker, J. Shmulovich, and Y. H. Wong, Systems evaluation of an Er 3+ -doped planar waveguide amplifier, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 5(10), (1993). 9. J.-M. P. Delavaux, S. Granlund, O. Mizuhara, L. D. Tzeng, D. Barbier, M. Rattay, F. St. Andre, and A. Kevorkian, Integrated optics erbium-ytterbium amplifier system in 10-Gb/s fiber transmission experiment, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 9(2), (1997). 10. J. Shmulovich, A. J. Bruce, G. Lenz, P. B. Hansen, T. N. Nielsen, D. J. Muehlner, G. A. Bogert, I. Brener, E. J. Laskowski, A. Paunescu, I. Ryazansky, D. C. Jacobson, and A. E. White, Integrated planar waveguide amplifier with 15 db net gain at 1550 nm, in Optical Fiber Communication Conference and the International Conference on Integrated Optics and Optical Fiber Communication, OSA Technical Digest (Optical Society of America, 1999), paper PD S. Demiguel, N. Sahri, M. Hartlaub, F. Blache, H. Gariah, S. Vuiye, D. Carpentier, D. Barbier, and J. C. Campbell, Low-cost photoreceiver integrating an EDWA and waveguide PIN photodiode for 40 Gbit/s applications, Electron. Lett. 43(1), (2007). 12. K. Wörhoff, J. D. B. Bradley, F. Ay, D. Geskus, T. Blauwendraat, and M. Pollnau, Reliable low-cost fabrication of low-loss Al 2O 3:Er 3+ waveguides with 5.4-dB optical gain, IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 45(5), (2009). (C) 2009 OSA 23 November 2009 / Vol. 17, No. 24 / OPTICS EXPRESS 22201
2 13. J. D. B. Bradley, F. Ay, K. Wörhoff, and M. Pollnau, Fabrication of low-loss channel waveguides in Al 2O 3 and Y 2O 3 layers by inductively coupled plasma reactive ion etching, Appl. Phys. B 89(2-3), (2007). 14. M. Thual, D. Malarde, B. Abhervé-Guégen, P. Rochard, and P. Chanclou, Truncated Gaussian beams through microlenses based on a graded-index section, Opt. Eng. 46(1), (2007). 15. Platform for test and Research on optical telecommunications SYSTems, M. Costa e Silva, H. Ramanitra, M. Gay, L. Bramerie, S. Lobo, M. Joindot, J. C. Simon, A. Shen, and G.-H. Duan, Wavelength tunability assessment of a 170 Gbit/s transmitter using a quantum dash Fabry Perot modelocked laser, to be presented at the 35 th European Conference on Optical Communication, Vienna, Austria, September, F. Lelarge, B. Dagens, J. Renaudier, R. Brenot, A. Accard, F. Dijk, D. Make, O. L. Gouezigou, J.-G. Provost, F. Poingt, J. Landreau, O. Drisse, E. Derouin, B. Rousseau, F. Pommereau, and G.-H. Duan, Recent advances on InAs/InP quantum dash based semiconductor lasers and optical amplifiers operating at 1.55 µm, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 13(1), (2007). 18. K. Wörhoff, B. J. Offrein, P. V. Lambeck, G. L. Bona, and A. Driessen, G. L. Bona, and A. Driessen, Birefringence compensation applying double-core waveguiding structures, IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 11(2), (1999). 1. Introduction One of the key driving forces behind integrated optics, and particularly silicon photonics, is the potential for higher data transmission rates compared to integrated electronic circuits [1]. Data rates as high as 160 Gbit/s have been demonstrated in long-haul optical fiber networks [2] and in the future transmission at this speed can also be expected at the chip level. In such integrated photonic circuits, several enabling elements would be required, including an amplifier to boost the optical signal at various stages. Semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs) are well established as packaged components. However fabrication of such devices is complex, requiring many processing steps, and for incorporation of a SOA between siliconbased passive components hybrid integration methods are required. In addition, due to their short carrier lifetimes of ~50 ps, when they are operated in the saturated or quasi-saturated gain regime SOAs exhibit transient gain suppression and recovery which is dependent on both the bit rate and the bit sequence [3]. This can result in cross-talk between different wavelength channels when amplifying wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) signals. Alternatively, planar erbium-doped waveguide amplifiers (EDWA) [4] offer a potential solution for amplification at high speed on a chip. Er-doped amplifiers with their long excited-state lifetime of ~10 ms and accordingly longer gain recovery time do not exhibit such transient channel cross-talk. EDWAs can be deposited directly on thermally oxidized silicon or other materials allowing all-optical signal enhancement with a straightforward process flow [5]. Furthermore, the widespread availability of compact, low-cost laser diode pump sources begins to make such devices more attractive. Compared to other EDWA materials, Al 2 O 3 :Er 3+ offers increased integration potential. Because of its relatively high refractive index contrast ( n 0.2 compared to the SiO 2 cladding), more compact waveguide cross-sections and thus higher pump intensities can be achieved, allowing higher integration density and reducing pump power requirements [6]. Recently we have demonstrated significantly improved continuous-wave gain with a wavelength range of 80 nm and 2 db/cm at the 1532 nm peak in this material [7]. In the past, transmission experiments at up to 10 Gbit/s using an EDWA have been carried out [8 10] and a packaged photoreceiver using an EDWA for 40 Gbit/s applications has also been reported [11]. In this letter we demonstrate amplification at 170 Gbit/s in an Al2O3:Er3 + EDWA deposited on thermally oxidized silicon. 2. Al 2 O 3 :Er 3+ channel waveguide gain A 5.7-cm-long reactively co-sputtered Er-doped aluminum oxide (Al 2 O 3 :Er 3+ ) straight channel waveguide amplifier was fabricated on a thermally oxidized silicon substrate. The fabrication procedure has been reported elsewhere [12, 13]. The cross-sectional dimensions of the ridge-type channel waveguide were 0.9 µm 4.0 µm with an etch depth of approximately 50 nm. The uncladded waveguide was single mode at wavelengths of 1480 nm and above. The doping concentration, uniform throughout the Al 2 O 3 :Er 3+ core layer, was cm 3 [7]. (C) 2009 OSA 23 November 2009 / Vol. 17, No. 24 / OPTICS EXPRESS 22202
3 Prior to transmission experiments, the continuous-wave small-signal gain of the amplifier was measured at 1532 nm (the 4 I 13/2 4 I 15/2 Er transition gain peak) and 1550 nm (the wavelength at which transmission experiments were performed). Pump light from a 1480 nm Raman laser source and signal light at 1532 nm or 1550 nm from a tunable laser were combined using a WDM fiber multiplexer (MUX) and coupled to and from the chip via lensed fibers [14]. Both microlensed fibers have a mode-field diameter of 2.9 µm at 1/e 2 of the intensity profile. This mode-field diameter appears to be a good compromise to the asymmetry of the waveguide. At the output, the residual pump light and amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) were filtered using a 0.25 nm tunable bandpass filter and the signal power was measured with an optical power meter. Both co- and counter-propagating pump cases were investigated. The internal net small signal gain was calculated by subtracting the total propagation loss from the measured signal enhancement with pump on and pump off. The total small-signal propagation loss was calculated at each wavelength using the known background loss of 0.13 db/cm, calculated confinement of the signal light within the Al 2 O 3 :Er 3+ waveguide core (85%) and measured 4 I 15/2 4 I 13/2 absorption crosssections [7]. The residual pump light and ASE were measured by shifting the bandpass filter 2 nm from the signal wavelength and determined to be negligible (> 20 db lower than the amplified signal). The resulting gain vs. pump power curves are shown in Fig. 1. The average gain for both TE- and TM-polarized signal light is shown, since similar signal enhancement was measured for each polarization (± 0.2 db). In the co-propagating case, up to 11 db total internal net gain at 1532 nm was measured for a launched pump power of 63 mw, while 6.6 db gain was measured at 1550 nm. The threshold launched pump power for internal net gain was 4 mw and 3 mw at 1532 nm and 1550 nm, respectively. For a launched pump power of 65 mw constant internal net gain was measured when varying the launched signal power from 1 µw to 1 mw, demonstrating unsaturated gain for launched signal powers in this range. While high internal net gain was demonstrated, external fiber-chip-fiber net gain was not obtained, because the amplifier was designed for on-chip amplification, hence achieving low fiber-chip coupling loss was not considered in the design. However, with improved lensed fibers and appropriate waveguide design fiber-chip coupling losses on the order of 1 db/facet are predicted, thus principally also allowing for fiber-chip-fiber net gain. Furthermore, in a longer amplifier internal net gain of more than 20 db is expected across the entire C-band wavelength range ( nm) [7]. The net internal gain measured at 1550 nm using a counter-propagating pump setup and the 170 Gbit/s modulated signal is also shown in Fig. 1. A higher threshold pump power is observed for counter-propagating pumping as compared to the co-propagating pump measurement. The difference in the two curves is probably due to a difference in pump coupling efficiency between the two lensed fibers. Net gain of up to 6.3 db at 1550 nm was achieved in the counter-propagating setup when the launched pump power was increased to 110 mw. (C) 2009 OSA 23 November 2009 / Vol. 17, No. 24 / OPTICS EXPRESS 22203
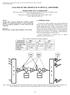
4 Fig. 1. Internal net small signal gain at 1532 nm and 1550 nm (for co-propagating pumping and counter-propagating pumping with 170 Gbit/s signal) as a function of launched 1480 nm pump power Gbit/s transmission measurements Transmission experiments were performed at a bit rate of 170 Gbit/s on the Platform for test and Research on optical telecommunications SYSTems (PERSYST) [15]. The experimental setup is depicted schematically in Fig. 2. The transmitter was composed of a 42.5 GHz optical clock generated from a filtered and chirp-compensated quantum dash Fabry-Perot modelocked laser source at 1550 nm [16, 17]. Following this, a LiNbO 3 Mach-Zehnder Interferometer (MZI) was modulated electronically by a pattern generator, specified for up to bit sequences, to obtain a 42.5 Gbit/s return-to-zero pseudo-random bit sequence (PRBS). The transmitter ended with an optical time division multiplexing (OTDM) bit rate multiplier consisting of two stages. In each stage the signal was split into two channels with one channel delayed, after which the two signals were recombined. In this manner four delayed versions of the 42.5 Gbit/s signal were multiplexed, resulting in a 170 Gbit/s data stream consisting of pulses with a full width at half maximum (FWHM) of 1.5 ps. An erbiumdoped fiber amplifier (EDFA) was then used to boost the signal followed by an optical attenuator and polarization controller to adjust the amount of power and the polarization of the signal light coupled to the device, respectively. An optical isolator was used to eliminate any back-scattered pump or signal light. The 1550 nm 170 Gbit/s signal was coupled to and from the chip via the microlensed fibers nm pump light from a Raman pump laser source was coupled to the chip in a counter-propagating approach using a fiber multiplexer (MUX). A reverse-pumping scheme was selected because it simplified the transmission setup by eliminating the need for filtering of residual pump light in front of the receiver. The transmitted signal was amplified by an EDFA before entering the receiver part of the setup. The first part of the receiver was an electro-optical loop which optically demultiplexed the 170 Gbit/s data stream to 42.5 Gbit/s and recovered the 42.5 Gbit/s optical clock [16]. The loop was composed of an electro-absorption modulator (EAM), an optical delay line, an electrical clock recovery and a high finesse electrical band-pass filter, and was used to select and transmit one of the four multiplexed 42.5 Gbit/s signal pulse trains. Following this, the signal light was detected by a 42.5 Gbit/s electrical time division demultiplexing receiver (ETDM). An optical sampling oscilloscope (with 1 ps resolution) was used for visualization. (C) 2009 OSA 23 November 2009 / Vol. 17, No. 24 / OPTICS EXPRESS 22204
5 Fig. 2. Experimental setup for 170 Gbit/s transmission measurements. In initial transmission experiments with a randomly polarized signal it was observed that two polarization modes were present. In order to investigate the polarization dependence of the amplifier, the differential group delay (DGD) between the fundamental TE and TM modes in the pumped and unpumped EDWA was measured using a continuous tunable laser source and a DGD analyzer. In both cases the DGD was found to be approximately 2 ps corresponding to a waveguide birefringence of ~7 x The impact of DGD on the 170 Gbit/s signal was also clearly observed in the eye diagram as shown in Fig. 3, by varying the polarization controller state. In Fig. 3(a) the input polarization controller state was adjusted such that both modes propagated with almost equal intensity, while in Fig. 3(b) one mode was more strongly excited, and in Fig. 3(c) almost a single polarization mode was excited. The two overlayed pulse trains corresponding to the fundamental TE and TM modes are visible in each image. This polarization dependence should not affect the system when used in a transmitter in a photonic integrated circuit, for instance, even though it would affect signal quality in an in-line use of the device. However, by careful design of the waveguides the birefringence can be largely reduced [18] so that polarization-independent amplification even at these bit rates can be obtained. For all bit error rate (BER) measurements a single polarization state was selected by adjusting the polarization controller on one fundamental mode. Typical eye diagrams without the EDWA and with the EDWA and a single polarization are shown in Figs. 4(a) and 4(b), respectively. The eye pattern is open and the pulse FWHM is 2 ps in both cases. (C) 2009 OSA 23 November 2009 / Vol. 17, No. 24 / OPTICS EXPRESS 22205
6 Fig. 3. Transmission eye diagrams for different polarization states of the 170 Gbit/s signal coupled to the EDWA. In each image two overlayed pulse trains are visible as a result of differential group delay between the fundamental TE and TM polarized modes supported by the EDWA. The input signal polarization state was adjusted such that in (a) both modes propagated with almost equal intensity, (b) one mode was more strongly excited, and (c) almost a single polarization mode was excited. (C) 2009 OSA 23 November 2009 / Vol. 17, No. 24 / OPTICS EXPRESS 22206
7 Fig. 4. Transmission eye diagrams at 170 Gbit/s (a) without EDWA and (b) with EDWA and a launched signal power of 0.5 mw and counter-propagating pump power of 65 mw. In order to determine the compatibility of the device in a telecommunication application, BER assessments were performed on the device. The BER was measured as a function of the input power on the ETDM 42.5 Gbit/s receiver for 0.5 mw and 0.1 mw of signal power and a pump power of 65 mw launched into the EDWA. A reference was measured with the same input power in EDFA 2 as with the EDWA included in order to take into account the fiber-tofiber losses (~10 db when pumped) of the EDWA. The results are shown in Fig. 5. For each input signal power, the curve with the EDWA is superposed with the reference, showing that when the polarization state is properly adjusted, the EDWA does not add any penalty to the system. A minimum launched signal power of 0.1 mw was investigated in this setup in order to ensure sufficient power reached the receiver. However, based on the negligible ASE in the small-signal gain measurements and with improved coupling losses, no penalties can also be expected in the EDWA for launched signal powers in the 1-10 µw range. (C) 2009 OSA 23 November 2009 / Vol. 17, No. 24 / OPTICS EXPRESS 22207
8 4. Conclusions Fig Gbit/s BER measurements for different launched signal powers P s and a launched pump power of 65 mw as a function of the input power at the 42.5 Gbit/s receiver. A reference measurement with EDWA removed and identical optical power launched into the receiver is also shown. Net internal gain of up to 11 db at 1532 nm and data transmission at 170 Gbit/s at 1550 nm have been demonstrated in an integrated Al 2 O 3 :Er 3+ amplifier when pumping at 1480 nm. Despite a DGD of 2 ps between the two guided polarization modes of the amplifier, no BER power penalty was observed at 170 Gbit/s by injecting the signal in a single fundamental polarization state. The ability to amplify signals at high data rates, when combined with straightforward fabrication techniques and the possibility to integrate with various materials, confirm such amplifiers as potential components in future high-speed photonic integrated circuits. Acknowledgments We would like to thank the Centre Commun Lannionais d Optique of CNRS Foton for the fabrication of the microlensed fibers. This work was supported by funding through the European Union's Sixth Framework Programme (Specific Targeted Research Project PI- OXIDE, contract no ) and the European FP6 Network of Excellence epixnet High Speed Characterisation Platform. (C) 2009 OSA 23 November 2009 / Vol. 17, No. 24 / OPTICS EXPRESS 22208
Monolithic integration of erbium-doped amplifiers with silicon waveguides
 Monolithic integration of erbium-doped amplifiers with silicon waveguides Laura Agazzi, 1* Jonathan D. B. Bradley, 1 Feridun Ay, 1 Gunther Roelkens, 2 Roel Baets, 2 Kerstin Wörhoff, 1 and Markus Pollnau
Monolithic integration of erbium-doped amplifiers with silicon waveguides Laura Agazzi, 1* Jonathan D. B. Bradley, 1 Feridun Ay, 1 Gunther Roelkens, 2 Roel Baets, 2 Kerstin Wörhoff, 1 and Markus Pollnau
A silicon avalanche photodetector fabricated with standard CMOS technology with over 1 THz gain-bandwidth product
 A silicon avalanche photodetector fabricated with standard CMOS technology with over 1 THz gain-bandwidth product Myung-Jae Lee and Woo-Young Choi* Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering,
A silicon avalanche photodetector fabricated with standard CMOS technology with over 1 THz gain-bandwidth product Myung-Jae Lee and Woo-Young Choi* Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering,
Mitigation of Mode Partition Noise in Quantum-dash Fabry-Perot Mode-locked Lasers using Manchester Encoding
 Mitigation of Mode Partition Noise in Quantum-dash Fabry-Perot Mode-locked Lasers using Manchester Encoding Mohamed Chaibi*, Laurent Bramerie, Sébastien Lobo, Christophe Peucheret *chaibi@enssat.fr FOTON
Mitigation of Mode Partition Noise in Quantum-dash Fabry-Perot Mode-locked Lasers using Manchester Encoding Mohamed Chaibi*, Laurent Bramerie, Sébastien Lobo, Christophe Peucheret *chaibi@enssat.fr FOTON
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique
 S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
Chapter 8. Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM) Part II: Amplifiers
 Chapter 8 Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM) Part II: Amplifiers Introduction Traditionally, when setting up an optical link, one formulates a power budget and adds repeaters when the path loss exceeds
Chapter 8 Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (WDM) Part II: Amplifiers Introduction Traditionally, when setting up an optical link, one formulates a power budget and adds repeaters when the path loss exceeds
Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University
 Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Last Lecture Topics Course introduction Ray optics & optical
Photonics Group Department of Micro- and Nanosciences Aalto University Optical Amplifiers Photonics and Integrated Optics (ELEC-E3240) Zhipei Sun Last Lecture Topics Course introduction Ray optics & optical
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber
 Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
Elements of Optical Networking
 Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Optical Fibre Amplifiers Continued
 1 Optical Fibre Amplifiers Continued Stavros Iezekiel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Cyprus ECE 445 Lecture 09 Fall Semester 2016 2 ERBIUM-DOPED FIBRE AMPLIFIERS BASIC
1 Optical Fibre Amplifiers Continued Stavros Iezekiel Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Cyprus ECE 445 Lecture 09 Fall Semester 2016 2 ERBIUM-DOPED FIBRE AMPLIFIERS BASIC
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems
 Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
The Report of Gain Performance Characteristics of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA)
 The Report of Gain Performance Characteristics of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) Masruri Masruri (186520) 22/05/2008 1 Laboratory Setup The laboratory setup using in this laboratory experiment
The Report of Gain Performance Characteristics of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) Masruri Masruri (186520) 22/05/2008 1 Laboratory Setup The laboratory setup using in this laboratory experiment
An integrated recirculating optical buffer
 An integrated recirculating optical buffer Hyundai Park, John P. Mack, Daniel J. Blumenthal, and John E. Bowers* University of California, Santa Barbara, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
An integrated recirculating optical buffer Hyundai Park, John P. Mack, Daniel J. Blumenthal, and John E. Bowers* University of California, Santa Barbara, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion
 Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
All-optical logic based on silicon micro-ring resonators
 All-optical logic based on silicon micro-ring resonators Qianfan Xu and Michal Lipson School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University 411 Phillips Hall, Ithaca, NY 14853 lipson@ece.cornell.edu
All-optical logic based on silicon micro-ring resonators Qianfan Xu and Michal Lipson School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University 411 Phillips Hall, Ithaca, NY 14853 lipson@ece.cornell.edu
Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators. by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings
 Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings Paper no: 1471 S. Y. Set, H. Geiger, R. I. Laming, M. J. Cole and L. Reekie Optoelectronics Research
Optimisation of DSF and SOA based Phase Conjugators by Incorporating Noise-Suppressing Fibre Gratings Paper no: 1471 S. Y. Set, H. Geiger, R. I. Laming, M. J. Cole and L. Reekie Optoelectronics Research
32-Channel DWDM System Design and Simulation by Using EDFA with DCF and Raman Amplifiers
 2012 International Conference on Information and Computer Networks (ICICN 2012) IPCSIT vol. 27 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore 32-Channel DWDM System Design and Simulation by Using EDFA with DCF
2012 International Conference on Information and Computer Networks (ICICN 2012) IPCSIT vol. 27 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore 32-Channel DWDM System Design and Simulation by Using EDFA with DCF
Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF
 Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF Koji Ieda a), Kenji Kurokawa, Katsusuke Tajima, and Kazuhide Nakajima NTT Access Network Service Systems Laboratories, NTT Corporation, 1 7 1 Hanabatake,
Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF Koji Ieda a), Kenji Kurokawa, Katsusuke Tajima, and Kazuhide Nakajima NTT Access Network Service Systems Laboratories, NTT Corporation, 1 7 1 Hanabatake,
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements HW #5 is assigned (due April 9) April 9 th class will be in
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements HW #5 is assigned (due April 9) April 9 th class will be in
Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p.
 Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
40 Gb/s NRZ-DQPSK data wavelength conversion with amplitude regeneration using four-wave mixing in a quantum dash semiconductor optical amplifier
 Front. Optoelectron. DOI 10.1007/s12200-016-0628-x RESEARCH ARTICLE 40 Gb/s NRZ-DQPSK data wavelength conversion with amplitude regeneration using four-wave mixing in a quantum dash semiconductor optical
Front. Optoelectron. DOI 10.1007/s12200-016-0628-x RESEARCH ARTICLE 40 Gb/s NRZ-DQPSK data wavelength conversion with amplitude regeneration using four-wave mixing in a quantum dash semiconductor optical
All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration
 1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
Active mode-locking of miniature fiber Fabry-Perot laser (FFPL) in a ring cavity
 Active mode-locking of miniature fiber Fabry-Perot laser (FFPL) in a ring cavity Shinji Yamashita (1)(2) and Kevin Hsu (3) (1) Dept. of Frontier Informatics, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences The University
Active mode-locking of miniature fiber Fabry-Perot laser (FFPL) in a ring cavity Shinji Yamashita (1)(2) and Kevin Hsu (3) (1) Dept. of Frontier Informatics, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences The University
Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window
 Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2,3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer and Communications Research Laboratories,
Optical fiber-fault surveillance for passive optical networks in S-band operation window Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2,3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer and Communications Research Laboratories,
Lecture 9 External Modulators and Detectors
 Optical Fibres and Telecommunications Lecture 9 External Modulators and Detectors Introduction Where are we? A look at some real laser diodes. External modulators Mach-Zender Electro-absorption modulators
Optical Fibres and Telecommunications Lecture 9 External Modulators and Detectors Introduction Where are we? A look at some real laser diodes. External modulators Mach-Zender Electro-absorption modulators
Chapter 12: Optical Amplifiers: Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs)
 Chapter 12: Optical Amplifiers: Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs) Prof. Dr. Yaocheng SHI ( 时尧成 ) yaocheng@zju.edu.cn http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/yaocheng 1 Traditional Optical Communication System Loss
Chapter 12: Optical Amplifiers: Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFAs) Prof. Dr. Yaocheng SHI ( 时尧成 ) yaocheng@zju.edu.cn http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/yaocheng 1 Traditional Optical Communication System Loss
SOA-BASED NOISE SUPPRESSION IN SPECTRUM-SLICED PONs: IMPACT OF BIT-RATE AND SOA GAIN RECOVERY TIME
 SOA-BASED NOISE SUPPRESSION IN SPECTRUM-SLICED PONs: IMPACT OF BIT-RATE AND SOA GAIN RECOVERY TIME Francesco Vacondio, Walid Mathlouthi, Pascal Lemieux, Leslie Ann Rusch Centre d optique photonique et
SOA-BASED NOISE SUPPRESSION IN SPECTRUM-SLICED PONs: IMPACT OF BIT-RATE AND SOA GAIN RECOVERY TIME Francesco Vacondio, Walid Mathlouthi, Pascal Lemieux, Leslie Ann Rusch Centre d optique photonique et
All-optical AND gate with improved extinction ratio using signal induced nonlinearities in a bulk semiconductor optical amplifier
 All-optical AND gate with improved extinction ratio using signal induced nonlinearities in a bulk semiconductor optical amplifier L. Q. Guo, and M. J. Connelly Optical Communications Research Group, Department
All-optical AND gate with improved extinction ratio using signal induced nonlinearities in a bulk semiconductor optical amplifier L. Q. Guo, and M. J. Connelly Optical Communications Research Group, Department
An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources and a Novel Bidirectional Reach Extender
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 15, No. 3, September 2011, pp. 222-226 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2011.15.3.222 An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 15, No. 3, September 2011, pp. 222-226 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.3807/josk.2011.15.3.222 An Amplified WDM-PON Using Broadband Light Source Seeded Optical Sources
All-optical clock division at 40 GHz using a semiconductor amplifier. nonlinear interferometer
 All-optical clock division at 40 GHz using a semiconductor amplifier nonlinear interferometer R. J. Manning, I. D. Phillips, A. D. Ellis, A. E. Kelly, A. J. Poustie, K.J. Blow BT Laboratories, Martlesham
All-optical clock division at 40 GHz using a semiconductor amplifier nonlinear interferometer R. J. Manning, I. D. Phillips, A. D. Ellis, A. E. Kelly, A. J. Poustie, K.J. Blow BT Laboratories, Martlesham
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs
 A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs Yue Tian, Qingjiang Chang, and Yikai Su * State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department
A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs Yue Tian, Qingjiang Chang, and Yikai Su * State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department
A HIGH SPEED WDM PON FOR DOWNSTREAM DPSK ASK SIGNALS AND UPSTREAM OOK SIGNAL WITH BROADCAST CAPABILTY
 A HIGH SPEED WDM PON FOR DOWNSTREAM DPSK ASK SIGNALS AND UPSTREAM OOK SIGNAL WITH BROADCAST CAPABILTY 1 AAMIR KHAN, 2 ANITA CHOPRA 1 Department of Information Technology, Suresh Gyan Vihar University,
A HIGH SPEED WDM PON FOR DOWNSTREAM DPSK ASK SIGNALS AND UPSTREAM OOK SIGNAL WITH BROADCAST CAPABILTY 1 AAMIR KHAN, 2 ANITA CHOPRA 1 Department of Information Technology, Suresh Gyan Vihar University,
Investigation of Performance Analysis of EDFA Amplifier. Using Different Pump Wavelengths and Powers
 Investigation of Performance Analysis of EDFA Amplifier Using Different Pump Wavelengths and Powers Ramandeep Kaur, Parkirti, Rajandeep Singh ABSTRACT In this paper, an investigation of the performance
Investigation of Performance Analysis of EDFA Amplifier Using Different Pump Wavelengths and Powers Ramandeep Kaur, Parkirti, Rajandeep Singh ABSTRACT In this paper, an investigation of the performance
ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS
 MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
EDFA WDM Optical Network using GFF
 EDFA WDM Optical Network using GFF Shweta Bharti M. Tech, Digital Communication, (Govt. Women Engg. College, Ajmer), Rajasthan, India ABSTRACT This paper describes the model and simulation of EDFA WDM
EDFA WDM Optical Network using GFF Shweta Bharti M. Tech, Digital Communication, (Govt. Women Engg. College, Ajmer), Rajasthan, India ABSTRACT This paper describes the model and simulation of EDFA WDM
A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation
 A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer & Communications Research Laboratories,
A broadband fiber ring laser technique with stable and tunable signal-frequency operation Chien-Hung Yeh 1 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Transmission System Department, Computer & Communications Research Laboratories,
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication
 InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise
 Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise Ben Wu, * Zhenxing Wang, Bhavin J. Shastri, Matthew P. Chang, Nicholas A. Frost, and Paul R. Prucnal
Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise Ben Wu, * Zhenxing Wang, Bhavin J. Shastri, Matthew P. Chang, Nicholas A. Frost, and Paul R. Prucnal
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers
 Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. 4.1 Introduction
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Introduction In this chapter focus are given more on WDM system. The results which are obtained mainly from the simulation work are presented. In simulation analysis, the study will
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Introduction In this chapter focus are given more on WDM system. The results which are obtained mainly from the simulation work are presented. In simulation analysis, the study will
Performance Analysis of Optical Time Division Multiplexing Using RZ Pulse Generator
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 10, October 2015,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 10, October 2015,
DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M.
 DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M. Published in: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium of the IEEE Photonics
DBR based passively mode-locked 1.5m semiconductor laser with 9 nm tuning range Moskalenko, V.; Williams, K.A.; Bente, E.A.J.M. Published in: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium of the IEEE Photonics
Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration
 22 Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration Jun-Hyuk Seo, and Woo-Young Choi Department of Electrical and
22 Gigabit Transmission in 60-GHz-Band Using Optical Frequency Up-Conversion by Semiconductor Optical Amplifier and Photodiode Configuration Jun-Hyuk Seo, and Woo-Young Choi Department of Electrical and
Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers with Low Noise Figure
 Hideaki Hasegawa *, Masaki Funabashi *, Kazuomi Maruyama *, Kazuaki Kiyota *, and Noriyuki Yokouchi * In the multilevel phase modulation which is expected to provide the nextgeneration modulation format
Hideaki Hasegawa *, Masaki Funabashi *, Kazuomi Maruyama *, Kazuaki Kiyota *, and Noriyuki Yokouchi * In the multilevel phase modulation which is expected to provide the nextgeneration modulation format
Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode
 Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode Chien Hung Yeh, 1* Fu Yuan Shih, 2 Chia Hsuan Wang, 3 Chi Wai Chow, 3 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Information and Communications
Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode Chien Hung Yeh, 1* Fu Yuan Shih, 2 Chia Hsuan Wang, 3 Chi Wai Chow, 3 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Information and Communications
arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 19 May 2014
![arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 19 May 2014 arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 19 May 2014](/thumbs/91/106837035.jpg) 1 arxiv:1405.4742v1 [physics.optics] 19 May 2014 1 Experimental investigation of relaxation oscillations resonance in mode-locked Fabry-Perot semiconductor lasers V. Roncin*, J. Poëtte, J-F. Hayau, P.
1 arxiv:1405.4742v1 [physics.optics] 19 May 2014 1 Experimental investigation of relaxation oscillations resonance in mode-locked Fabry-Perot semiconductor lasers V. Roncin*, J. Poëtte, J-F. Hayau, P.
DESIGN TEMPLATE ISSUES ANALYSIS FOR ROBUST DESIGN OUTPUT. performance, yield, reliability
 DESIGN TEMPLATE ISSUES performance, yield, reliability ANALYSIS FOR ROBUST DESIGN properties, figure-of-merit thermodynamics, kinetics, process margins process control OUTPUT models, options Optical Amplification
DESIGN TEMPLATE ISSUES performance, yield, reliability ANALYSIS FOR ROBUST DESIGN properties, figure-of-merit thermodynamics, kinetics, process margins process control OUTPUT models, options Optical Amplification
High-Power Semiconductor Laser Amplifier for Free-Space Communication Systems
 64 Annual report 1998, Dept. of Optoelectronics, University of Ulm High-Power Semiconductor Laser Amplifier for Free-Space Communication Systems G. Jost High-power semiconductor laser amplifiers are interesting
64 Annual report 1998, Dept. of Optoelectronics, University of Ulm High-Power Semiconductor Laser Amplifier for Free-Space Communication Systems G. Jost High-power semiconductor laser amplifiers are interesting
Performance of Optical Encoder and Optical Multiplexer Using Mach-Zehnder Switching
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Performance of Optical Encoder and Optical Multiplexer Using Mach-Zehnder Switching Abhishek Raj 1, A.K. Jaiswal 2, Mukesh Kumar 3, Rohini Saxena 4, Neelesh Agrawal 5 1 PG
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Performance of Optical Encoder and Optical Multiplexer Using Mach-Zehnder Switching Abhishek Raj 1, A.K. Jaiswal 2, Mukesh Kumar 3, Rohini Saxena 4, Neelesh Agrawal 5 1 PG
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor
 Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
Resonant normal-incidence separate-absorptioncharge-multiplication. photodiodes
 Resonant normal-incidence separate-absorptioncharge-multiplication Ge/Si avalanche photodiodes Daoxin Dai 1*, Hui-Wen Chen 1, John E. Bowers 1 Yimin Kang 2, Mike Morse 2, Mario J. Paniccia 2 1 University
Resonant normal-incidence separate-absorptioncharge-multiplication Ge/Si avalanche photodiodes Daoxin Dai 1*, Hui-Wen Chen 1, John E. Bowers 1 Yimin Kang 2, Mike Morse 2, Mario J. Paniccia 2 1 University
Dispersion engineered As 2 S 3 planar waveguides for broadband four-wave mixing based wavelength conversion of 40 Gb/s signals
 Dispersion engineered As 2 S 3 planar waveguides for broadband four-wave mixing based wavelength conversion of 40 Gb/s signals Feng Luan, 1 Mark D. Pelusi, 1 Michael R.E. Lamont, 1 Duk-Yong Choi, 2 Steve
Dispersion engineered As 2 S 3 planar waveguides for broadband four-wave mixing based wavelength conversion of 40 Gb/s signals Feng Luan, 1 Mark D. Pelusi, 1 Michael R.E. Lamont, 1 Duk-Yong Choi, 2 Steve
New pumping scheme for high gain and low noise figure in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier
 New pumping scheme for high gain and low noise figure in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier V. Sinivasagam, 1,3a) Mustafa A. G. Abushagur, 1,2 K. Dimyati, 3 and F. Tumiran 1 1 Photronix (M) Sdn. Bhd., G05,
New pumping scheme for high gain and low noise figure in an erbium-doped fiber amplifier V. Sinivasagam, 1,3a) Mustafa A. G. Abushagur, 1,2 K. Dimyati, 3 and F. Tumiran 1 1 Photronix (M) Sdn. Bhd., G05,
CSO/CTB PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT BY USING FABRY-PEROT ETALON AT THE RECEIVING SITE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 107 113, 2009 CSO/CTB PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT BY USING FABRY-PEROT ETALON AT THE RECEIVING SITE S.-J. Tzeng, H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, K.-H. Chang,and C.-H.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 6, 107 113, 2009 CSO/CTB PERFORMANCE IMPROVEMENT BY USING FABRY-PEROT ETALON AT THE RECEIVING SITE S.-J. Tzeng, H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, K.-H. Chang,and C.-H.
Optical Fiber Amplifiers. Scott Freese. Physics May 2008
 Optical Fiber Amplifiers Scott Freese Physics 262 2 May 2008 Partner: Jared Maxson Abstract The primary goal of this experiment was to gain an understanding of the basic components of an Erbium doped fiber
Optical Fiber Amplifiers Scott Freese Physics 262 2 May 2008 Partner: Jared Maxson Abstract The primary goal of this experiment was to gain an understanding of the basic components of an Erbium doped fiber
Simulation of All-Optical XOR, AND, OR gate in Single Format by Using Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers
 Simulation of All-Optical XOR, AND, OR gate in Single Format by Using Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers Chang Wan Son* a,b, Sang Hun Kim a, Young Min Jhon a, Young Tae Byun a, Seok Lee a, Deok Ha Woo a,
Simulation of All-Optical XOR, AND, OR gate in Single Format by Using Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers Chang Wan Son* a,b, Sang Hun Kim a, Young Min Jhon a, Young Tae Byun a, Seok Lee a, Deok Ha Woo a,
Gain bandwidth of 80 nm and 2 db/cm peak gain in Al 2 O 3 :Er 3+ optical amplifiers on silicon
 Bradley et al. Vol. 27, No. 2/ February 2010/ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 187 Gain bandwidth of 80 nm and 2 db/cm peak gain in Al 2 O 3 :Er 3+ optical amplifiers on silicon J. D. B. Bradley,* L. Agazzi, D. Geskus,
Bradley et al. Vol. 27, No. 2/ February 2010/ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 187 Gain bandwidth of 80 nm and 2 db/cm peak gain in Al 2 O 3 :Er 3+ optical amplifiers on silicon J. D. B. Bradley,* L. Agazzi, D. Geskus,
Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source
 JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. X, NO. XX, XXXX XXX 1 Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source Jérôme Vasseur, Jianjun Yu Senior Member,
JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. X, NO. XX, XXXX XXX 1 Downstream Transmission in a WDM-PON System Using a Multiwavelength SOA-Based Fiber Ring Laser Source Jérôme Vasseur, Jianjun Yu Senior Member,
All-optical logic gates using a semiconductor optical amplifier assisted by an optical filter
 All-optical logic gates using a semiconductor optical amplifier assisted by an optical filter Z. Li, Y. Liu, S. Zhang, H. Ju, H. de Waardt, G.D. Khoe H.J.S. Dorren and D. Lenstra Abstract: A simple all-optical
All-optical logic gates using a semiconductor optical amplifier assisted by an optical filter Z. Li, Y. Liu, S. Zhang, H. Ju, H. de Waardt, G.D. Khoe H.J.S. Dorren and D. Lenstra Abstract: A simple all-optical
Spatial Investigation of Transverse Mode Turn-On Dynamics in VCSELs
 Spatial Investigation of Transverse Mode Turn-On Dynamics in VCSELs Safwat W.Z. Mahmoud Data transmission experiments with single-mode as well as multimode 85 nm VCSELs are carried out from a near-field
Spatial Investigation of Transverse Mode Turn-On Dynamics in VCSELs Safwat W.Z. Mahmoud Data transmission experiments with single-mode as well as multimode 85 nm VCSELs are carried out from a near-field
Fiberoptic Communication Systems By Dr. M H Zaidi. Optical Amplifiers
 Optical Amplifiers Optical Amplifiers Optical signal propagating in fiber suffers attenuation Optical power level of a signal must be periodically conditioned Optical amplifiers are a key component in
Optical Amplifiers Optical Amplifiers Optical signal propagating in fiber suffers attenuation Optical power level of a signal must be periodically conditioned Optical amplifiers are a key component in
Channel wavelength selectable singleõdualwavelength erbium-doped fiber ring laser
 Channel wavelength selectable singleõdualwavelength erbium-doped fiber ring laser Tong Liu Yeng Chai Soh Qijie Wang Nanyang Technological University School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang
Channel wavelength selectable singleõdualwavelength erbium-doped fiber ring laser Tong Liu Yeng Chai Soh Qijie Wang Nanyang Technological University School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) phase stabilization. (a) DC output of the MZI with and without phase stabilization. (b) Performance of MZI stabilization
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) phase stabilization. (a) DC output of the MZI with and without phase stabilization. (b) Performance of MZI stabilization
Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides
 Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides Ozdal Boyraz, Tejaswi Indukuri, and Bahram Jalali University of California, Los Angeles Department of Electrical Engineering, Los
Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides Ozdal Boyraz, Tejaswi Indukuri, and Bahram Jalali University of California, Los Angeles Department of Electrical Engineering, Los
International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research)
 International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational
International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational
All-Optical Clock Division Using Period-one Oscillation of Optically Injected Semiconductor Laser
 International Conference on Logistics Engineering, Management and Computer Science (LEMCS 2014) All-Optical Clock Division Using Period-one Oscillation of Optically Injected Semiconductor Laser Shengxiao
International Conference on Logistics Engineering, Management and Computer Science (LEMCS 2014) All-Optical Clock Division Using Period-one Oscillation of Optically Injected Semiconductor Laser Shengxiao
Ultra High Speed All Optical Demultiplexing based on Two Photon Absorption. in a Laser Diode. Glasnevin, Dublin 9, IRELAND
 Ultra High Speed All Optical Demultiplexing based on Two Photon Absorption in a Laser Diode B.C. Thomsen 1, L.P Barry 2, J.M. Dudley 1, and J.D. Harvey 1 1. Department of Physics, University of Auckland,
Ultra High Speed All Optical Demultiplexing based on Two Photon Absorption in a Laser Diode B.C. Thomsen 1, L.P Barry 2, J.M. Dudley 1, and J.D. Harvey 1 1. Department of Physics, University of Auckland,
Suppression of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering
 Suppression of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering 42 2 5 W i de l y T u n a b l e L a s e r T ra n s m i t te r www.lumentum.com Technical Note Introduction This technical note discusses the phenomenon and
Suppression of Stimulated Brillouin Scattering 42 2 5 W i de l y T u n a b l e L a s e r T ra n s m i t te r www.lumentum.com Technical Note Introduction This technical note discusses the phenomenon and
PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF TWO-CHANNEL DISPERSION SUPPORTED TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS USING SINGLE AND DOUBLE-CAVITY FABRY-PEROT FILTERS AS DEMULTIPLEXERS
 PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF TWO-CHANNEL DISPERSION SUPPORTED TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS USING SINGLE AND DOUBLE-CAVITY FABRY-PEROT FILTERS AS DEMULTIPLEXERS Mário M. Freire Department of Mathematics and Information
PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF TWO-CHANNEL DISPERSION SUPPORTED TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS USING SINGLE AND DOUBLE-CAVITY FABRY-PEROT FILTERS AS DEMULTIPLEXERS Mário M. Freire Department of Mathematics and Information
Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized Optical Signals in WDM System
 The Quarterly Journal of Optoelectronical Nanostructures Islamic Azad University Spring 2016 / Vol. 1, No.1 Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized
The Quarterly Journal of Optoelectronical Nanostructures Islamic Azad University Spring 2016 / Vol. 1, No.1 Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide
 Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 9 18, 29 CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER H. Ahmad, M. Z. Zulkifli, S. F. Norizan,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 9 18, 29 CONTROLLABLE WAVELENGTH CHANNELS FOR MULTIWAVELENGTH BRILLOUIN BISMUTH/ERBIUM BAS-ED FIBER LASER H. Ahmad, M. Z. Zulkifli, S. F. Norizan,
Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks
 363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
OPTICAL NETWORKS. Building Blocks. A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005
 OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices
 644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
10 Gb/s transmission over 5 km at 850 nm using single-mode photonic crystal fiber, single-mode VCSEL, and Si-APD
 10 Gb/s transmission over 5 km at 850 nm using single-mode photonic crystal fiber, single-mode VCSEL, and Si-APD Hideaki Hasegawa a), Yosuke Oikawa, Masato Yoshida, Toshihiko Hirooka, and Masataka Nakazawa
10 Gb/s transmission over 5 km at 850 nm using single-mode photonic crystal fiber, single-mode VCSEL, and Si-APD Hideaki Hasegawa a), Yosuke Oikawa, Masato Yoshida, Toshihiko Hirooka, and Masataka Nakazawa
Setup of the four-wavelength Doppler lidar system with feedback controlled pulse shaping
 Setup of the four-wavelength Doppler lidar system with feedback controlled pulse shaping Albert Töws and Alfred Kurtz Cologne University of Applied Sciences Steinmüllerallee 1, 51643 Gummersbach, Germany
Setup of the four-wavelength Doppler lidar system with feedback controlled pulse shaping Albert Töws and Alfred Kurtz Cologne University of Applied Sciences Steinmüllerallee 1, 51643 Gummersbach, Germany
Heterogeneously Integrated Microwave Signal Generators with Narrow- Linewidth Lasers
 Heterogeneously Integrated Microwave Signal Generators with Narrow- Linewidth Lasers John E. Bowers, Jared Hulme, Tin Komljenovic, Mike Davenport and Chong Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Heterogeneously Integrated Microwave Signal Generators with Narrow- Linewidth Lasers John E. Bowers, Jared Hulme, Tin Komljenovic, Mike Davenport and Chong Zhang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Improved Analysis of Hybrid Optical Amplifier in CWDM System
 Improved Analysis of Hybrid Optical Amplifier in CWDM System 1 Bandana Mallick, 2 Reeta Kumari, 3 Anirban Mukherjee, 4 Kunwar Parakram 1. Asst Proffesor in Dept. of ECE, GIET Gunupur 2, 3,4. Student in
Improved Analysis of Hybrid Optical Amplifier in CWDM System 1 Bandana Mallick, 2 Reeta Kumari, 3 Anirban Mukherjee, 4 Kunwar Parakram 1. Asst Proffesor in Dept. of ECE, GIET Gunupur 2, 3,4. Student in
RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 7, 25 33, 2009 RADIO-OVER-FIBER TRANSPORT SYSTEMS BASED ON DFB LD WITH MAIN AND 1 SIDE MODES INJECTION-LOCKED TECHNIQUE H.-H. Lu, C.-Y. Li, C.-H. Lee,
Introduction and concepts Types of devices
 ECE 6323 Introduction and concepts Types of devices Passive splitters, combiners, couplers Wavelength-based devices for DWDM Modulator/demodulator (amplitude and phase), compensator (dispersion) Others:
ECE 6323 Introduction and concepts Types of devices Passive splitters, combiners, couplers Wavelength-based devices for DWDM Modulator/demodulator (amplitude and phase), compensator (dispersion) Others:
International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering
 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: Performance Analysis of WDM/SCM System Using EDFA Mukesh Kumar
ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: Performance Analysis of WDM/SCM System Using EDFA Mukesh Kumar
Colorless Components for WDM-based Optical Access Networks
 Colorless Components for WDM-based Optical Access Networks Quoc Thai Nguyen, Gwenaëlle Girault, Olivier Vaudel, Laurent Bramerie, Pascal Besnard, Alexandre Shen, Guang-Hua Duan, Christophe Kazmierski,
Colorless Components for WDM-based Optical Access Networks Quoc Thai Nguyen, Gwenaëlle Girault, Olivier Vaudel, Laurent Bramerie, Pascal Besnard, Alexandre Shen, Guang-Hua Duan, Christophe Kazmierski,
Performance analysis of Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier at different pumping configurations
 Performance analysis of Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier at different pumping configurations Mayur Date M.E. Scholar Department of Electronics and Communication Ujjain Engineering College, Ujjain (M.P.) datemayur3@gmail.com
Performance analysis of Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier at different pumping configurations Mayur Date M.E. Scholar Department of Electronics and Communication Ujjain Engineering College, Ujjain (M.P.) datemayur3@gmail.com
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER
 CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
Optical Communications and Networks - Review and Evolution (OPTI 500) Massoud Karbassian
 Optical Communications and Networks - Review and Evolution (OPTI 500) Massoud Karbassian m.karbassian@arizona.edu Contents Optical Communications: Review Optical Communications and Photonics Why Photonics?
Optical Communications and Networks - Review and Evolution (OPTI 500) Massoud Karbassian m.karbassian@arizona.edu Contents Optical Communications: Review Optical Communications and Photonics Why Photonics?
Lecture 15 Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and OTDR
 Lecture 15 Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and OTDR Introduction Where are we? Using semiconductors as amplifiers. Amplifier geometry Cross talk Polarisation dependence Gain clamping Real amplifier performance
Lecture 15 Semiconductor Optical Amplifiers and OTDR Introduction Where are we? Using semiconductors as amplifiers. Amplifier geometry Cross talk Polarisation dependence Gain clamping Real amplifier performance
Analysis of four channel CWDM Transceiver Modules based on Extinction Ratio and with the use of EDFA
 Analysis of four channel CWDM Transceiver Modules based on Extinction Ratio and with the use of EDFA P.P. Hema [1], Prof. A.Sangeetha [2] School of Electronics Engineering [SENSE], VIT University, Vellore
Analysis of four channel CWDM Transceiver Modules based on Extinction Ratio and with the use of EDFA P.P. Hema [1], Prof. A.Sangeetha [2] School of Electronics Engineering [SENSE], VIT University, Vellore
Public Progress Report 2
 Embedded Resonant and ModulablE Self- Tuning Laser Cavity for Next Generation Access Network Transmitter ERMES Public Progress Report 2 Project Project acronym: ERMES Project full title: Embedded Resonant
Embedded Resonant and ModulablE Self- Tuning Laser Cavity for Next Generation Access Network Transmitter ERMES Public Progress Report 2 Project Project acronym: ERMES Project full title: Embedded Resonant
Performance Analysis of SOA-MZI based All-Optical AND & XOR Gate
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Utkarsh
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Utkarsh
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis
 EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis Narruvala Lokesh, kranthi Kumar Katam,Prof. Jabeena A Vellore Institute of Technology VIT University, Vellore, India Abstract : Optical network that apply wavelength division
EDFA-WDM Optical Network Analysis Narruvala Lokesh, kranthi Kumar Katam,Prof. Jabeena A Vellore Institute of Technology VIT University, Vellore, India Abstract : Optical network that apply wavelength division
High bit-rate combined FSK/IM modulated optical signal generation by using GCSR tunable laser sources
 High bit-rate combined FSK/IM modulated optical signal generation by using GCSR tunable laser sources J. J. Vegas Olmos, I. Tafur Monroy, A. M. J. Koonen COBRA Research Institute, Eindhoven University
High bit-rate combined FSK/IM modulated optical signal generation by using GCSR tunable laser sources J. J. Vegas Olmos, I. Tafur Monroy, A. M. J. Koonen COBRA Research Institute, Eindhoven University
IBM T. J. Watson Research Center IBM Corporation
 Broadband Silicon Photonic Switch Integrated with CMOS Drive Electronics B. G. Lee, J. Van Campenhout, A. V. Rylyakov, C. L. Schow, W. M. J. Green, S. Assefa, M. Yang, F. E. Doany, C. V. Jahnes, R. A.
Broadband Silicon Photonic Switch Integrated with CMOS Drive Electronics B. G. Lee, J. Van Campenhout, A. V. Rylyakov, C. L. Schow, W. M. J. Green, S. Assefa, M. Yang, F. E. Doany, C. V. Jahnes, R. A.
A review on optical time division multiplexing (OTDM)
 International Journal of Academic Research and Development ISSN: 2455-4197 Impact Factor: RJIF 5.22 www.academicsjournal.com Volume 3; Issue 1; January 2018; Page No. 520-524 A review on optical time division
International Journal of Academic Research and Development ISSN: 2455-4197 Impact Factor: RJIF 5.22 www.academicsjournal.com Volume 3; Issue 1; January 2018; Page No. 520-524 A review on optical time division
Performance Investigation of RAMAN-EDFA HOA for DWDM System (Received 17 September, 2016 Accepted 02 October, 2016)
 Performance Investigation of RAMAN-EDFA HOA for DWDM System (Received 17 September, 2016 Accepted 02 October, 2016) ABSTRACT Neha Thakral Research Scholar, DAVIET, Jalandhar nthakral9@gmail.com Earlier
Performance Investigation of RAMAN-EDFA HOA for DWDM System (Received 17 September, 2016 Accepted 02 October, 2016) ABSTRACT Neha Thakral Research Scholar, DAVIET, Jalandhar nthakral9@gmail.com Earlier
SIMULATIVE INVESTIGATION OF SINGLE-TONE ROF SYSTEM USING VARIOUS DUOBINARY MODULATION FORMATS
 SIMULATIVE INVESTIGATION OF SINGLE-TONE ROF SYSTEM USING VARIOUS DUOBINARY MODULATION FORMATS Namita Kathpal 1 and Amit Kumar Garg 2 1,2 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Deenbandhu
SIMULATIVE INVESTIGATION OF SINGLE-TONE ROF SYSTEM USING VARIOUS DUOBINARY MODULATION FORMATS Namita Kathpal 1 and Amit Kumar Garg 2 1,2 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Deenbandhu
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE C AND L BAND ERBIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS (C,L-EDFAs)
 DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE C AND L BAND ERBIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS (C,L-EDFAs) Ahmet Altuncu Arif Başgümüş Burçin Uzunca Ekim Haznedaroğlu e-mail: altuncu@dumlupinar.edu.tr e-mail:
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE C AND L BAND ERBIUM DOPED FIBER AMPLIFIERS (C,L-EDFAs) Ahmet Altuncu Arif Başgümüş Burçin Uzunca Ekim Haznedaroğlu e-mail: altuncu@dumlupinar.edu.tr e-mail:
S Optical Networks Course Lecture 2: Essential Building Blocks
 S-72.3340 Optical Networks Course Lecture 2: Essential Building Blocks Edward Mutafungwa Communications Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, P. O. Box 2300, FIN-02015 TKK, Finland Tel: +358 9
S-72.3340 Optical Networks Course Lecture 2: Essential Building Blocks Edward Mutafungwa Communications Laboratory, Helsinki University of Technology, P. O. Box 2300, FIN-02015 TKK, Finland Tel: +358 9
Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA
 Optics Communications 252 (2005) 127 131 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA Peng-Chun Peng a, *, Kai-Ming Feng b, Wei-Ren
Optics Communications 252 (2005) 127 131 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Long-distance fiber grating sensor system using a fiber ring laser with EDWA and SOA Peng-Chun Peng a, *, Kai-Ming Feng b, Wei-Ren
Performance Analysis of Gb/s DWDM Metropolitan Area Network using SMF-28 and MetroCor Optical Fibres
 Research Cell: An International Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN: 2229-6913 Issue Sept 2011, Vol. 4 11 Performance Analysis of 32 2.5 Gb/s DWDM Metropolitan Area Network using SMF-28 and MetroCor Optical
Research Cell: An International Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN: 2229-6913 Issue Sept 2011, Vol. 4 11 Performance Analysis of 32 2.5 Gb/s DWDM Metropolitan Area Network using SMF-28 and MetroCor Optical
