A review on optical time division multiplexing (OTDM)
|
|
|
- Matthew Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Academic Research and Development ISSN: Impact Factor: RJIF Volume 3; Issue 1; January 2018; Page No A review on optical time division multiplexing (OTDM) Harkaran Singh Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, DAV. Institute of Engineering & Technology, Jalandhar, Punjab, India Abstract Electrical multiplexing has limited channel capacity as the Ethernet switches can only run at most 10 Gbps. To increase this channel capacity optical multiplexing is required. The OTDM path network has the ability for 100 Gbps Ethernet switching, however more modulators need to be equipped in the transmitters, and only connections from the source node to its downstream nodes in a super light path can be referred to be used. The recent advances in optical time division multiplexing (OTDM) shows the technique to be highly suited to the generation and transmission of high capacity data on a single optical carrier. This approach uses a single wavelength to carry capacities of at least 40 Gbps. Such systems are based on a clock frequency and tributary data rates which are easily accessible using electronic components. In this system or methodology the short optical pulses are used in a return-to-zero data transmission format with temporal interleaving to map a number of optical data channels into a single electronic clock cycle. It is an approach that can be used to achieve extremely high data-rate bit interleaved systems. This article summarizes the basic uses of optical time division multiplexing and outlines a possible methodology to evolve transport networks to encompass the potential that OTDM has to offer. Keywords: time division multiplexing, optical devices data communication multiplexing and de multiplexing light paths Introduction Optical time division multiplexing (OTDM) is a very powerful and scalable technique to investigate high-speed data transmission systems, related signal processing and monitoring technologies at serial data rates beyond the bandwidth limitation of (optic) electronics. The OTDM technique is basically compatible with modern multi-level quadrature-amplitude modulation (QAM) formats and digital coherent detection. In contrast to wavelength division multiplexing (WDM), only one wavelength (one/single color) of light is used in optical time division multiplexing. The operation principle of OTDM is as follows The different optical pulse streams called tributaries originating from the same laser (same central wavelength) are firstly separately encoded by electrically generated data signals. Due to the low duty cycle of their pulses the tributaries are serially bit interleaved in order to form the high speed serial OTDM data signal. At the receiver end, an ultrafast optical clock and data recovery extracts the individual time-domain tributaries, which are subsequently processed by conventional (optic) electronics [7]. The basic principle of this technology is to multiplex a number of low bit rate optical channels in time domain. The overall OTDM system can be viewed as three big blocks i.e. transmitter block, line system, and receiver block. The basic transmitter block consists of laser sources, modulators, channel alignment systems, and multiplexer. Further the line system contains optical amplifiers and transmission fibers. And the receiver block further has synchronization circuit and a channel demultiplexer. Channel allocation by time division multiplexing is dependent on the fundamental electrical data rate and the optical pulse width. With a fixed electrical clock we need to shorten the optical pulse width in order to multiplex more channels within the same clock period. In addition to it, the shortened pulse width can help reduce the crosstalk between channels because of more room left in bit slot. However, short optical pulses are subjected to heavy dispersion penalty as traveling distance increases. The use of transform-limited pulse and dispersion slope compensation technique can reduce the dispersion effect on OTDM. Transform-limited pulse has a property which reduces the optical spectral width for a given pulse width. This ensures the pulse broadening due to dispersion is minimized. Adding negative slope dispersion fiber can actually minimize the pulse broadening effect over a long distance. This is basically dependent on the choice of dispersion slope factor and length of the dispersion compensated fiber, which in turn depends on the fiber fabrication technology. Polarization mode dispersion is also a main concern as traveling distance increases over 100km.Accurate control on the channel alignment is also critical as transmission speed increases because more channels are multiplexed in a fix clock period. Any misalignment can cause a problem in the performance of the OTDM system because of crosstalk and dispersion. The use of electro-optic switching technique or all-optical switching technique can be used in demultiplexing at the receiver end. The electro-optic technique is great for transmission speed at less than 40 GB/s. It is more difficult to achieve for speed over 40Gb/s due to restraint on electrical drive power. All-optical switching is based on third order nonlinear effect of the optical fiber. Methodology The basic principle of OTDM is as follows: 520
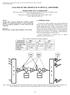
2 Optical time division multiplexing is more powerful optical multiplexing technique as it can combine multiple low bit rate channel in to single high bit rate channel in time basis. Each channel can be multiplexed in to multiplexer for given period of time. In OTDM, only one wavelength of light is used instead of different wavelength of light in WDM. Fig 1 The above figure shows the schematic block diagram of an optical time division multiplexing system. Description A Simple OTDM consists of the following three main stages 1. Transmitter 2. Inline system 3. Receiver The transmitter consists of optical source, modulator, channel alignment and multiplexer. Optical signal can be modulated using Return to Zero (RZ), Non Return to Zero (NRZ), Manchester and various length of fiber can be used for the channel alignment or for delay signal, the multiplexer is used to combine the various optical data stream. The line system consists of optical amplifier, add-drop multiplexer and transmission fiber. Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (SOA) and Erbium dropped fiber Amplifier (EDFA) is used for optical amplifier to amplify the optical signal in between into the network while the receiver consists of a demultiplexer and synchnoronous clock. The synchronous clock is used to extract framing pulse or clock signal. The demultiplexer is then used to separate out the multiplexed optical signal [7]. Figure shows the design of optical time division multiplexing. Fig 2 521
3 Literature Review The authors Cada, Habara, Tucker et al. in their study of Optical Time Division Multiplexing concluded that 1. A time-division optical multiplexer system, having a plurality of multiplexer elements the optical multiplexer elements comprising: A first optical waveguide for receiving and transmitting a first optical signal having a first optical carrier wavelength; A second optical waveguide for receiving and transmitting a second optical signal having a second optical carrier wavelength; and A third optical waveguide for alternately receiving the first and second optical signals and providing an optical output signal; Said first and second optical waveguides being joined together at a junction; said third optical waveguide being coupled to said junction by switchable filter means for alternately passing one of the first and second optical signals; where in: The plurality of multiplexer elements are arranged in a plurality of cascaded groups, each group having twice the elements of a following group; Inputs of the elements in each respective group are connected to outputs of the elements in a respective preceding group; The switchable filter means of the elements of a respective group are controlled in synchronism by respective control signals; and The switchable filter means of the elements in each respective group are controlled by a control signal having a frequency twice the frequency of a following group Fig 1: is a plan view of a multiplex element according to the invention; Fig 2: is a sectional view along line AB of the multiplex element of FIG. 1 according to the invention; Fig 3A and 3B: show possible band transitions of a filter with a multiple quantum well layer sequence; Fig 4A-4D: show the combining of the entering signal streams by an applied, sine-wave electrical field, to make one outgoing signal stream; Fig 5: shows an exemplary embodiment of a time-division multiplexer; and Fig 6: shows a transmission unit having a time-division multiplexer according to the invention [1] 2. An optical time-division multiplexer comprising: At least one multiplex element having inputs for receiving at least two optical signals, the signals having carriers of different wavelengths, the inputs being connected to an optical signal output via a junction, the element further having switchable filter means for switching the signals applied to the inputs to the signal output in alternation, wherein the multiplex element is controlled so that a switching time interval is shorter than a pulse duration of the input signals. 3. The optical time-division multiplexer of claim 2, wherein the pulse duration of the optical input signals is less than 50 ps. 4. The optical time-division multiplexer of claim 2, wherein for each multiplex element, the at least two optical signals are two digital optical signals, a switching signal period is equal to the input signals' pulse duration during multiplexing, and a pulse duration of the output of the multiplexer is halved during multiplexing. 5. The optical time-division multiplexer of claim 2, wherein the switchable filter means is disposed between the junction and the signal output. 6. The optical time-division multiplexer of claim 2, wherein the input signals to be multiplexed are digital signals, and the switchable filter means is controlled by a periodic alternating voltage of frequency f=1/t, where T represents the duration of one bit-clock period of the input signals to be multiplexed. 7. The optical time-division multiplexer of claim 2, wherein the multiplex element has two signal inputs for receiving respective signals, the respective signals each having a different respective carrier wavelength, and wherein the switchable filter means alternatingly blocks a respective one of the carrier wavelengths. 8. The optical time-division multiplexer of claim 2, wherein 522
4 a plurality of multiplex elements are disposed in a cascade, and wherein one signal output of each multiplex element is connected to one signal input of a following multiplex element. 9. The optical time-division multiplexer of claim 2, further comprising a plurality of optical wave guides for transmitting the optical signals, wherein the optical waveguides are planar optical wave guides. 10. The optical time-division multiplexer of claim 2, wherein the switchable filter means has a multiple-quantum-well structure, and has a pass band switchable by the application of an electrical field. 11. The optical time-division multiplexer of claim 2, further comprising optical wave guides for transmitting the optical signals, the optical waveguides substantially comprising semiconductor layers. 12. An optical transmitter having an optical time-division multiplexer of claim 2, wherein individual integrated semiconductor elements are provided [2]. 13. An optical multiplexer element comprising: A first optical waveguide for receiving and transmitting a first optical signal having a first optical carrier wavelength; a second optical waveguide for receiving and transmitting a second optical signal having a second optical carrier wavelength; and a third optical waveguide for alternately receiving the first and second optical signals and providing an optical output signal; and Switchable filter means for alternately passing one of the first and second optical signals; wherein said first and second optical waveguides are joined together at a junction, and wherein said third optical waveguide is coupled to said junction by said switchable filter means for alternately passing one of the first and second optical signals, wherein the multiplexer element is controlled so that a switching time interval is shorter than a pulse duration of the first and second optical signals. 14. The optical multiplexer element according to claim 13, wherein said optical multiplexer, including said first, second and third optical waveguides, said junction, and said switchable filter means, is formed as an integrated optics layer structure on a substrate. 15. The optical multiplexer element according to claim 14, wherein at least said switchable filter means is formed as a multiple-quantum-well layer sequence, said switchable filter means including electrodes encompassing the multiple-quantum-well layer sequence, for connection to an external source of control signals whereby the alternate passing of the first and second optical signals by said switchable filter means is controlled [3]. 16. The optical multiplexer element according to claim 14, wherein at least said first, second and third optical waveguides are formed of layers of at least one of PLZT, LiNbO 3, and optical polymers. 17. An optical multiplexer system, having a plurality of multiplexer elements according to claim 13, wherein the plurality of multiplexer elements are arranged in a plurality of groups, outputs of the multiplexer elements of one group being connected to inputs of the multiplexer elements of a succeeding group. 18. A time-division optical multiplexer system, having a plurality of multiplexer elements according to claim 13, wherein: The plurality of multiplexer elements are arranged in three cascaded groups, a first group having four elements, a second group having two elements, and a third group having one element; Inputs of the element in the third group are connected to outputs of the elements in the second group, and inputs of the elements in the second group are connected to outputs of the elements in the first group; The switchable filter means of the elements of a respective group are controlled in synchronism by respective control signals; The switchable filter means of the elements in the first group are controlled by a control signal having a first frequency, the switchable filter means of the elements in the second group are controlled by a control signal having a frequency twice the first frequency, and the switchable filter means of the element in the third group are controlled by a control signal having a frequency four times the first frequency [4]. Channel allocation by time division multiplexing is dependent on the fundamental electrical data rate and the optical pulse width. With fixed electrical clock, one must shorten the optical pulse width in order to multiplex more channels within the clock period. In addition, the shortened pulse width can help reduce the crosstalk between channels because of more room left in bit slot. However, short optical pulses are subjected to heavy dispersion penalty as traveling distance increases. The use of transform-limited pulse and dispersion slope compensation technique can reduce the dispersion effect on OTDM. Transform-limited pulse has the property that minimizes the optical spectral width for a given pulse width. This ensures the pulse broadening due to dispersion is minimized. Adding negative slope dispersion fiber can actually reduce the pulse broadening effect over long distance. This is dependent on the choice of dispersion slope factor and length of the dispersion compensated fiber, which in turn depends on the fiber fabrication technology. Polarization mode dispersion is also a main concern as traveling distance increases over 100km. Accurate control on the channel alignment is also critical as transmission speed increases because more channels are multiplexed in a fix clock period. Any misalignment can affect the performance of the OTDM system because of crosstalk and dispersion. Electro-optic switching technique or all-optical switching technique can achieve de multiplexing at receiver end. The electro-optic technique is great for transmission speed at less than 40 Gb/s. It is more difficult to achieve for speed over 40Gb/s due to restraint on electrical drive power. All-optical switching is based on third order non-linear effect of the optical fiber. It is highly suitable for ultra-fast speed transmission because the non-linear response is in fs range. It is also allowing add/drop of an individual channel or a number of channels, which is great feature for network operation. Although, the all-optical switch is very bulky and expensive to made. Nevertheless, successful de- multiplexing can only be accomplished with accurate timing extraction. The timing jitter from the extraction circuit can directly affect the BER 523
5 performance of the OTDM system [5]. After studying this Optical Multiplex Techniques I, conclude that channel capacity will be increased and we transmit more data thorough single fiber. Till date in Commercial application we can Transmit 1Tb/s through single fiber. Berlin s Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute in collaboration with the Technical University of Denmark in Copenhagen have succeeded in generating a serial data rate of 10.2 Terabit per second and transmitting it over a 29 km long fiber optic link. Further, Increased Data rate by using Combination of OTDM + WDM optically Multiplexing Techniques. After studying this Optical Multiplex Techniques I, conclude that channel capacity will be increased and we transmit more data thorough single fiber. till date in Commercial application we can Transmit 1Tb/s through single fiber. Berlin s Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute in collaboration with the Technical University of Denmark in Copenhagen have succeeded in generating a serial data rate of 10.2 Terabit per second and transmitting it over a 29 km long fiber optic link. Further, Increased Data rate by using Combination of OTDM + WDM optically Multiplexing Techniques [6]. Different optical pulse streams, called tributaries, originating from the same laser (same central wavelength), are separately encoded by electrically generated data signals. Due to the low duty cycle of their pulses (1.5 ps at 10 GHz) the tributaries are serially bit interleaved in order to form the high speed serial OTDM data signal. At the receiver end, an ultra-fast optical clock and data recovery extracts the individual time-domain tributaries, which are subsequently processed by conventional (opto) electronics. References 1. Cada, et al., Two-Wavelength Optical Switching in a GaAs Multiple Quantum Well Directional Coupler, Applied Physics Letters. 1990; 56(21): Habara, et al., Optical Switching Networks Using Tree- Structured Waveguide Optical Switches, Electronics and Communications in Japan. 1987; 7(11): Tucker, et al., Optical Time-Division Multiplexing For Very High Bit-Rate Transmission, Journal of Lightwave Technology. 1988; 11: Jeffrey Huang. 5. Raj Hakani, Nirma University. 6. Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, HHI. 7. IEEE Magazine, Journal of Lightwave Technology, 1988, 6(11). 524
Performance Analysis of Optical Time Division Multiplexing Using RZ Pulse Generator
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 10, October 2015,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 10, October 2015,
SHF Communication Technologies AG
 SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 12277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 10 Fax ++49 30 / 753 10 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz
SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 12277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 10 Fax ++49 30 / 753 10 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz
Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 3, ISSUE 06 34 Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System Meenakshi,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY ENHANCEMENTS AND EMERGING ENGINEERING RESEARCH, VOL 3, ISSUE 06 34 Comparative Analysis Of Different Dispersion Compensation Techniques On 40 Gbps Dwdm System Meenakshi,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 93 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 93 (016 ) 647 654 6th International Conference On Advances In Computing & Communications, ICACC 016, 6-8 September 016,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 93 (016 ) 647 654 6th International Conference On Advances In Computing & Communications, ICACC 016, 6-8 September 016,
Implementing of High Capacity Tbps DWDM System Optical Network
 , pp. 211-218 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijfgcn.2016.9.6.20 Implementing of High Capacity Tbps DWDM System Optical Network Daleep Singh Sekhon *, Harmandar Kaur Deptt.of ECE, GNDU Regional Campus, Jalandhar,Punjab,India
, pp. 211-218 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijfgcn.2016.9.6.20 Implementing of High Capacity Tbps DWDM System Optical Network Daleep Singh Sekhon *, Harmandar Kaur Deptt.of ECE, GNDU Regional Campus, Jalandhar,Punjab,India
Kuldeep Kaur #1, Gurpreet Bharti *2
 Performance Evaluation of Hybrid Optical Amplifier in Different Bands for DWDM System Kuldeep Kaur #1, Gurpreet Bharti *2 #1 M Tech Student, E.C.E. Department, YCOE, Talwandi Sabo, Punjabi University,
Performance Evaluation of Hybrid Optical Amplifier in Different Bands for DWDM System Kuldeep Kaur #1, Gurpreet Bharti *2 #1 M Tech Student, E.C.E. Department, YCOE, Talwandi Sabo, Punjabi University,
Simulative Analysis of 40 Gbps DWDM System Using Combination of Hybrid Modulators and Optical Filters for Suppression of Four-Wave Mixing
 Vol.9, No.7 (2016), pp.213-220 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsip.2016.9.7.18 Simulative Analysis of 40 Gbps DWDM System Using Combination of Hybrid Modulators and Optical Filters for Suppression of Four-Wave
Vol.9, No.7 (2016), pp.213-220 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijsip.2016.9.7.18 Simulative Analysis of 40 Gbps DWDM System Using Combination of Hybrid Modulators and Optical Filters for Suppression of Four-Wave
ANALYSIS OF DWDM SYSTEM USING DIFFERENT MODULATION AND COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE AT DIFFERENT BIT RATES
 ANALYSIS OF DWDM SYSTEM USING DIFFERENT MODULATION AND COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE AT DIFFERENT BIT RATES MEENAKSHI SHARMA 1,NAVPREET KAUR 2 1 MTech Scholar,Deptt. Of ECE,IET Bhaddal,Punjab 2 Assistant Professor,Deptt.
ANALYSIS OF DWDM SYSTEM USING DIFFERENT MODULATION AND COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE AT DIFFERENT BIT RATES MEENAKSHI SHARMA 1,NAVPREET KAUR 2 1 MTech Scholar,Deptt. Of ECE,IET Bhaddal,Punjab 2 Assistant Professor,Deptt.
Performance Analysis Of Hybrid Optical OFDM System With High Order Dispersion Compensation
 Performance Analysis Of Hybrid Optical OFDM System With High Order Dispersion Compensation Manpreet Singh Student, University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India. Abstract Orthogonal
Performance Analysis Of Hybrid Optical OFDM System With High Order Dispersion Compensation Manpreet Singh Student, University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India. Abstract Orthogonal
Implementation and analysis of 2 Tbps MDRZ DWDM system at ultra narrow channel spacing
 Implementation and analysis of 2 Tbps MDRZ DWDM system at ultra narrow channel spacing 1 Ragini Sharma, 2 Kamaldeep Kaur 1 Student, 2 Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering BBSBEC, Fatehgarh
Implementation and analysis of 2 Tbps MDRZ DWDM system at ultra narrow channel spacing 1 Ragini Sharma, 2 Kamaldeep Kaur 1 Student, 2 Assistant Professor Department of Electrical Engineering BBSBEC, Fatehgarh
Photoneco white papers: Single-modulator RZ-DQPSK transmitter Description of the prior art
 Photoneco white papers: Single-modulator RZ-DQPSK transmitter Description of the prior art Optical fiber systems in their infancy used to waste bandwidth both in the optical and in the electrical domain
Photoneco white papers: Single-modulator RZ-DQPSK transmitter Description of the prior art Optical fiber systems in their infancy used to waste bandwidth both in the optical and in the electrical domain
REDUCTION OF CROSSTALK IN WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXED FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 77, 367 378, 2007 REDUCTION OF CROSSTALK IN WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXED FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS R. Tripathi Northern India Engineering College
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 77, 367 378, 2007 REDUCTION OF CROSSTALK IN WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXED FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS R. Tripathi Northern India Engineering College
40Gb/s Optical Transmission System Testbed
 The University of Kansas Technical Report 40Gb/s Optical Transmission System Testbed Ron Hui, Sen Zhang, Ashvini Ganesh, Chris Allen and Ken Demarest ITTC-FY2004-TR-22738-01 January 2004 Sponsor: Sprint
The University of Kansas Technical Report 40Gb/s Optical Transmission System Testbed Ron Hui, Sen Zhang, Ashvini Ganesh, Chris Allen and Ken Demarest ITTC-FY2004-TR-22738-01 January 2004 Sponsor: Sprint
Phase Modulator for Higher Order Dispersion Compensation in Optical OFDM System
 Phase Modulator for Higher Order Dispersion Compensation in Optical OFDM System Manpreet Singh 1, Karamjit Kaur 2 Student, University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India 1. Assistant
Phase Modulator for Higher Order Dispersion Compensation in Optical OFDM System Manpreet Singh 1, Karamjit Kaur 2 Student, University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala, India 1. Assistant
Performance Comparison of Pre-, Post-, and Symmetrical Dispersion Compensation for 96 x 40 Gb/s DWDM System using DCF
 Performance Comparison of Pre-, Post-, and Symmetrical Dispersion Compensation for 96 x 40 Gb/s DWDM System using Sabina #1, Manpreet Kaur *2 # M.Tech(Scholar) & Department of Electronics & Communication
Performance Comparison of Pre-, Post-, and Symmetrical Dispersion Compensation for 96 x 40 Gb/s DWDM System using Sabina #1, Manpreet Kaur *2 # M.Tech(Scholar) & Department of Electronics & Communication
Optical Complex Spectrum Analyzer (OCSA)
 Optical Complex Spectrum Analyzer (OCSA) First version 24/11/2005 Last Update 05/06/2013 Distribution in the UK & Ireland Characterisation, Measurement & Analysis Lambda Photometrics Limited Lambda House
Optical Complex Spectrum Analyzer (OCSA) First version 24/11/2005 Last Update 05/06/2013 Distribution in the UK & Ireland Characterisation, Measurement & Analysis Lambda Photometrics Limited Lambda House
All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration
 1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks
 363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
OPTICAL NETWORKS. Building Blocks. A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005
 OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
1.6 Tbps High Speed Long Reach DWDM System by incorporating Modified Duobinary Modulation Scheme
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet 1.6
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347-5161 2014 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet 1.6
Performance Analysis of WDM RoF-EPON Link with and without DCF and FBG
 Optics and Photonics Journal, 2013, 3, 163-168 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2013.32027 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/opj) Performance Analysis of WDM RoF-EPON Link with and
Optics and Photonics Journal, 2013, 3, 163-168 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2013.32027 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/opj) Performance Analysis of WDM RoF-EPON Link with and
Performance Measures of DWDM System under the Impact of Four Wave Mixing
 Performance Measures of DWDM System under the Impact of Four Wave Mixing S. Esther Jenifa 1, K. Gokulakrishnan 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Regional Center, Anna
Performance Measures of DWDM System under the Impact of Four Wave Mixing S. Esther Jenifa 1, K. Gokulakrishnan 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Regional Center, Anna
Design of Ultra High Capacity DWDM System with Different Modulation Formats
 Design of Ultra High Capacity DWDM System with Different Modulation Formats A. Nandhini 1, K. Gokulakrishnan 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Regional Center, Anna
Design of Ultra High Capacity DWDM System with Different Modulation Formats A. Nandhini 1, K. Gokulakrishnan 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Regional Center, Anna
Comparative Analysis of Various Optimization Methodologies for WDM System using OptiSystem
 Comparative Analysis of Various Optimization Methodologies for WDM System using OptiSystem Koushik Mukherjee * Department of Electronics and Communication, Dublin Institute of Technology, Ireland E-mail:
Comparative Analysis of Various Optimization Methodologies for WDM System using OptiSystem Koushik Mukherjee * Department of Electronics and Communication, Dublin Institute of Technology, Ireland E-mail:
Global Consumer Internet Traffic
 Evolving Optical Transport Networks to 100G Lambdas and Beyond Gaylord Hart Infinera Abstract The cable industry is beginning to migrate to 100G core optical transport waves, which greatly improve fiber
Evolving Optical Transport Networks to 100G Lambdas and Beyond Gaylord Hart Infinera Abstract The cable industry is beginning to migrate to 100G core optical transport waves, which greatly improve fiber
Chapter 3 Metro Network Simulation
 Chapter 3 Metro Network Simulation 3.1 Photonic Simulation Tools Simulation of photonic system has become a necessity due to the complex interactions within and between components. Tools have evolved from
Chapter 3 Metro Network Simulation 3.1 Photonic Simulation Tools Simulation of photonic system has become a necessity due to the complex interactions within and between components. Tools have evolved from
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems
 Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT OF 32 CHANNEL LONG HAUL DWDM SOLITON LINK USING ELECTRONIC DISPERSION COMPENSATION
 International Journal of Electronics, Communication & Instrumentation Engineering Research and Development (IJECIERD) ISSN 2249-684X Vol. 2 Issue 4 Dec - 2012 11-16 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT
International Journal of Electronics, Communication & Instrumentation Engineering Research and Development (IJECIERD) ISSN 2249-684X Vol. 2 Issue 4 Dec - 2012 11-16 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENT
Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates
 Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates Simarpreet Kaur Gill 1, Gurinder Kaur 2 1Mtech Student, ECE Department, Rayat- Bahra University,
Performance Evaluation of 32 Channel DWDM System Using Dispersion Compensation Unit at Different Bit Rates Simarpreet Kaur Gill 1, Gurinder Kaur 2 1Mtech Student, ECE Department, Rayat- Bahra University,
Prabhjeet Singh a, Narwant Singh b, Amandeep Singh c
 ISSN : 2250-3021 Investigation of DWDM System for Different Modulation Formats Prabhjeet Singh a, Narwant Singh b, Amandeep Singh c a B.G.I.E.T. Sangrur, India b G.N.D.E.C. Ludhiana, India c R.I.E.T, Ropar,
ISSN : 2250-3021 Investigation of DWDM System for Different Modulation Formats Prabhjeet Singh a, Narwant Singh b, Amandeep Singh c a B.G.I.E.T. Sangrur, India b G.N.D.E.C. Ludhiana, India c R.I.E.T, Ropar,
Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p.
 Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Performance Analysis of Chromatic Dispersion Compensation of a Chirped Fiber Grating on a Differential Phase-shift-keyed Transmission
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 13, No. 1, March 2009, pp. 107-111 DOI: 10.3807/JOSK.2009.13.1.107 Performance Analysis of Chromatic Dispersion Compensation of a Chirped Fiber Grating on a
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 13, No. 1, March 2009, pp. 107-111 DOI: 10.3807/JOSK.2009.13.1.107 Performance Analysis of Chromatic Dispersion Compensation of a Chirped Fiber Grating on a
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING. FINAL EXAMINATION, April 2017 DURATION: 2.5 hours
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING ECE4691-111 S - FINAL EXAMINATION, April 2017 DURATION: 2.5 hours Optical Communication and Networks Calculator Type: 2 Exam Type: X Examiner:
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING ECE4691-111 S - FINAL EXAMINATION, April 2017 DURATION: 2.5 hours Optical Communication and Networks Calculator Type: 2 Exam Type: X Examiner:
Next-Generation Optical Fiber Network Communication
 Next-Generation Optical Fiber Network Communication Naveen Panwar; Pankaj Kumar & manupanwar46@gmail.com & chandra.pankaj30@gmail.com ABSTRACT: In all over the world, much higher order off modulation formats
Next-Generation Optical Fiber Network Communication Naveen Panwar; Pankaj Kumar & manupanwar46@gmail.com & chandra.pankaj30@gmail.com ABSTRACT: In all over the world, much higher order off modulation formats
from ocean to cloud THE FUTURE IS NOW - MAXIMIZING SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY AND CAPACITY USING MODERN COHERENT TRANSPONDER TECHNIQUES
 Required OSNR (db/0.1nm RBW) @ 10-dB Q-factor THE FUTURE IS NOW - MAXIMIZING SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY AND CAPACITY USING MODERN COHERENT TRANSPONDER TECHNIQUES Neal S. Bergano, Georg Mohs, and Alexei Pilipetskii
Required OSNR (db/0.1nm RBW) @ 10-dB Q-factor THE FUTURE IS NOW - MAXIMIZING SPECTRAL EFFICIENCY AND CAPACITY USING MODERN COHERENT TRANSPONDER TECHNIQUES Neal S. Bergano, Georg Mohs, and Alexei Pilipetskii
Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise
 Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise Ben Wu, * Zhenxing Wang, Bhavin J. Shastri, Matthew P. Chang, Nicholas A. Frost, and Paul R. Prucnal
Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise Ben Wu, * Zhenxing Wang, Bhavin J. Shastri, Matthew P. Chang, Nicholas A. Frost, and Paul R. Prucnal
All-Optical Signal Processing. Technologies for Network. Applications. Prof. Paul Prucnal. Department of Electrical Engineering PRINCETON UNIVERSITY
 All-Optical Signal Processing Technologies for Network Applications Prof. Paul Prucnal Department of Electrical Engineering PRINCETON UNIVERSITY Globecom Access 06 Business Forum Advanced Technologies
All-Optical Signal Processing Technologies for Network Applications Prof. Paul Prucnal Department of Electrical Engineering PRINCETON UNIVERSITY Globecom Access 06 Business Forum Advanced Technologies
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor
 Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
Dynamic gain-tilt compensation using electronic variable optical attenuators and a thin film filter spectral tilt monitor P. S. Chan, C. Y. Chow, and H. K. Tsang Department of Electronic Engineering, The
Design and Performance Analysis of Optical Transmission System
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 04, Issue 05 (May. 2014), V3 PP 22-26 www.iosrjen.org Design and Performance Analysis of Optical Transmission System
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 Vol. 04, Issue 05 (May. 2014), V3 PP 22-26 www.iosrjen.org Design and Performance Analysis of Optical Transmission System
100 Gb/s Optical Time-Division Multiplexed Networks
 2086 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2002 100 Gb/s Optical Time-Division Multiplexed Networks Scott A. Hamilton, Member, IEEE, Bryan S. Robinson, Student Member, IEEE, Thomas
2086 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2002 100 Gb/s Optical Time-Division Multiplexed Networks Scott A. Hamilton, Member, IEEE, Bryan S. Robinson, Student Member, IEEE, Thomas
Performance Analysis of Dispersion Compensation using FBG and DCF in WDM Systems
 Performance Analysis of Dispersion using FBG and DCF in WDM Systems Ranjana Rao 1 Dr. Suresh Kumar 2 1 M. Tech Scholar, ECE Deptt UIET MDU Rohtak, Haryana, India 2 Assistant Professor, ECE Deptt, UIET
Performance Analysis of Dispersion using FBG and DCF in WDM Systems Ranjana Rao 1 Dr. Suresh Kumar 2 1 M. Tech Scholar, ECE Deptt UIET MDU Rohtak, Haryana, India 2 Assistant Professor, ECE Deptt, UIET
Implementation of Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing FBG
 AUSTRALIAN JOURNAL OF BASIC AND APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN:1991-8178 EISSN: 2309-8414 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Implementation of Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Network with FBG 1 J. Sharmila
AUSTRALIAN JOURNAL OF BASIC AND APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN:1991-8178 EISSN: 2309-8414 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Implementation of Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Network with FBG 1 J. Sharmila
Performance Investigation of RAMAN-EDFA HOA for DWDM System (Received 17 September, 2016 Accepted 02 October, 2016)
 Performance Investigation of RAMAN-EDFA HOA for DWDM System (Received 17 September, 2016 Accepted 02 October, 2016) ABSTRACT Neha Thakral Research Scholar, DAVIET, Jalandhar nthakral9@gmail.com Earlier
Performance Investigation of RAMAN-EDFA HOA for DWDM System (Received 17 September, 2016 Accepted 02 October, 2016) ABSTRACT Neha Thakral Research Scholar, DAVIET, Jalandhar nthakral9@gmail.com Earlier
Single- versus Dual-Carrier Transmission for Installed Submarine Cable Upgrades
 Single- versus Dual-Carrier Transmission for Installed Submarine Cable Upgrades L. Molle, M. Nölle, C. Schubert (Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, HHI) W. Wong, S. Webb, J. Schwartz (Xtera Communications)
Single- versus Dual-Carrier Transmission for Installed Submarine Cable Upgrades L. Molle, M. Nölle, C. Schubert (Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, HHI) W. Wong, S. Webb, J. Schwartz (Xtera Communications)
Study the Effects and Compensation of Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) at Different Bit Rates
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN: 2250-3021 Volume 2, Issue 7(July 2012), PP 32-40 Study the Effects and Compensation of Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) at Different Bit Rates Kapil Kashyap
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) ISSN: 2250-3021 Volume 2, Issue 7(July 2012), PP 32-40 Study the Effects and Compensation of Polarization Mode Dispersion (PMD) at Different Bit Rates Kapil Kashyap
ANALYSIS OF FWM POWER AND EFFICIENCY IN DWDM SYSTEMS BASED ON CHROMATIC DISPERSION AND CHANNEL SPACING
 ANALYSIS OF FWM POWER AND EFFICIENCY IN DWDM SYSTEMS BASED ON CHROMATIC DISPERSION AND CHANNEL SPACING S Sugumaran 1, Manu Agarwal 2, P Arulmozhivarman 3 School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University,
ANALYSIS OF FWM POWER AND EFFICIENCY IN DWDM SYSTEMS BASED ON CHROMATIC DISPERSION AND CHANNEL SPACING S Sugumaran 1, Manu Agarwal 2, P Arulmozhivarman 3 School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University,
Performance of Optical Encoder and Optical Multiplexer Using Mach-Zehnder Switching
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Performance of Optical Encoder and Optical Multiplexer Using Mach-Zehnder Switching Abhishek Raj 1, A.K. Jaiswal 2, Mukesh Kumar 3, Rohini Saxena 4, Neelesh Agrawal 5 1 PG
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Performance of Optical Encoder and Optical Multiplexer Using Mach-Zehnder Switching Abhishek Raj 1, A.K. Jaiswal 2, Mukesh Kumar 3, Rohini Saxena 4, Neelesh Agrawal 5 1 PG
Design and Modeling of For Optical SDM Transmission Systems Enabling FMF with 14 Spatial and Polarized Modes
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-6, Issue-1, pp-134-139 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Design and Modeling of For Optical SDM Transmission
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-6, Issue-1, pp-134-139 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access Design and Modeling of For Optical SDM Transmission
Comparison of Advance Data Modulation Formats in 4 10Gbps WDM Optical Communication System using YDFA, EDFA and Raman Amplifier
 Comparison of Advance Data Modulation Formats in 4 10Gbps WDM Optical Communication System using YDFA, EDFA and Raman Amplifier Simranjeet Singh Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
Comparison of Advance Data Modulation Formats in 4 10Gbps WDM Optical Communication System using YDFA, EDFA and Raman Amplifier Simranjeet Singh Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
40Gb/s & 100Gb/s Transport in the WAN Dr. Olga Vassilieva Fujitsu Laboratories of America, Inc. Richardson, Texas
 40Gb/s & 100Gb/s Transport in the WAN Dr. Olga Vassilieva Fujitsu Laboratories of America, Inc. Richardson, Texas All Rights Reserved, 2007 Fujitsu Laboratories of America, Inc. Outline Introduction Challenges
40Gb/s & 100Gb/s Transport in the WAN Dr. Olga Vassilieva Fujitsu Laboratories of America, Inc. Richardson, Texas All Rights Reserved, 2007 Fujitsu Laboratories of America, Inc. Outline Introduction Challenges
[Jain* et al., 5(6): June, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116
![[Jain* et al., 5(6): June, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116 [Jain* et al., 5(6): June, 2016] ISSN: IC Value: 3.00 Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/82/86006432.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY ELIMINATING FOUR WAVE MIXING WITH DYNAMIC CHANNEL SHUFFLING IN DWDM OPTICAL NETWORK Alisha Jain*, Harpreet Kaur * Student, Deptt.
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY ELIMINATING FOUR WAVE MIXING WITH DYNAMIC CHANNEL SHUFFLING IN DWDM OPTICAL NETWORK Alisha Jain*, Harpreet Kaur * Student, Deptt.
<#)*,$+0"$#)* ?">& B"$"')*+0"$#)* ?">&? F. S. Blair March 24, Analog and Digital Signals
 S. Blair March 24, 2008 8 1.5. Analog and Digital Signals
S. Blair March 24, 2008 8 1.5. Analog and Digital Signals
Picosecond Pulses for Test & Measurement
 Picosecond Pulses for Test & Measurement White Paper PN 200-0100-00 Revision 1.1 September 2003 Calmar Optcom, Inc www.calamropt.com Overview Calmar s picosecond laser sources are actively mode-locked
Picosecond Pulses for Test & Measurement White Paper PN 200-0100-00 Revision 1.1 September 2003 Calmar Optcom, Inc www.calamropt.com Overview Calmar s picosecond laser sources are actively mode-locked
A Comparison and Outline of Tolerances in Performing Optical Time Division Multiplexing using Electro-Absorption Modulators
 A Comparison and Outline of Tolerances in Performing Optical Time Division Multiplexing using Electro-Absorption Modulators by Mark Owsiak A thesis submitted to the Department of Electrical and Computer
A Comparison and Outline of Tolerances in Performing Optical Time Division Multiplexing using Electro-Absorption Modulators by Mark Owsiak A thesis submitted to the Department of Electrical and Computer
Free Space Optical Communication System under all weather conditions using DWDM
 Free Space Optical Communication System under all weather conditions using DWDM 1 Vivek Takhi, 2 Simranjit Singh 1, 2 Department of ECE, Punjabi University, Patiala, India Abstract: In this paper, the
Free Space Optical Communication System under all weather conditions using DWDM 1 Vivek Takhi, 2 Simranjit Singh 1, 2 Department of ECE, Punjabi University, Patiala, India Abstract: In this paper, the
Wavelength Interleaving Based Dispersion Tolerant RoF System with Double Sideband Carrier Suppression
 Wavelength Interleaving Based Dispersion Tolerant RoF System with Double Sideband Carrier Suppression Hilal Ahmad Sheikh 1, Anurag Sharma 2 1 (Dept. of Electronics & Communication, CTITR, Jalandhar, India)
Wavelength Interleaving Based Dispersion Tolerant RoF System with Double Sideband Carrier Suppression Hilal Ahmad Sheikh 1, Anurag Sharma 2 1 (Dept. of Electronics & Communication, CTITR, Jalandhar, India)
from ocean to cloud Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, Heinrich-Hertz-Institut, Einsteinufer 37, D-10587, Berlin, Germany
 Single- versus Dual-Carrier Transmission for Installed Submarine Cable Upgrades Lutz Molle, Markus Nölle, Colja Schubert (Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, Heinrich-Hertz-Institut), Wai Wong,
Single- versus Dual-Carrier Transmission for Installed Submarine Cable Upgrades Lutz Molle, Markus Nölle, Colja Schubert (Fraunhofer Institute for Telecommunications, Heinrich-Hertz-Institut), Wai Wong,
Enhancing Optical Network Capacity using DWDM System and Dispersion Compansating Technique
 ISSN (Print) : 2320 3765 ISSN (Online): 2278 8875 International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Vol. 6, Issue 12, December 2017 Enhancing Optical
ISSN (Print) : 2320 3765 ISSN (Online): 2278 8875 International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Vol. 6, Issue 12, December 2017 Enhancing Optical
SHF Communication Technologies AG
 SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23D 12277 Berlin Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 10 Fax ++49 30 / 753 10 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.de Web: http://www.shf.de Datasheet SHF 46215 B Optical
SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23D 12277 Berlin Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 10 Fax ++49 30 / 753 10 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.de Web: http://www.shf.de Datasheet SHF 46215 B Optical
Simulation of Pre & Post Compensation Techniques for 16 Channels DWDM Optical Network using CSRZ & DRZ Formats
 Simulation of Pre & Post Compensation Techniques for 16 Channels DWDM Optical Network using CSRZ & DRZ Formats Richa Arya 1, Malti Rani 2 1 M. Tech, Computer Science Department, Punjab Technical University,
Simulation of Pre & Post Compensation Techniques for 16 Channels DWDM Optical Network using CSRZ & DRZ Formats Richa Arya 1, Malti Rani 2 1 M. Tech, Computer Science Department, Punjab Technical University,
Design And Analysis Of Ultra High Capacity DWDM System With And Without Square Root Module For Different Modulation Formats
 Volume 8, No. 5, May June 2017 International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at www.ijarcs.info ISSN No. 0976-5697 Design And Analysis Of Ultra High Capacity
Volume 8, No. 5, May June 2017 International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at www.ijarcs.info ISSN No. 0976-5697 Design And Analysis Of Ultra High Capacity
Peter J. Winzer Bell Labs, Alcatel-Lucent. Special thanks to: R.-J. Essiambre, A. Gnauck, G. Raybon, C. Doerr
 Optically-routed long-haul networks Peter J. Winzer Bell Labs, Alcatel-Lucent Special thanks to: R.-J. Essiambre, A. Gnauck, G. Raybon, C. Doerr Outline Need and drivers for transport capacity Spectral
Optically-routed long-haul networks Peter J. Winzer Bell Labs, Alcatel-Lucent Special thanks to: R.-J. Essiambre, A. Gnauck, G. Raybon, C. Doerr Outline Need and drivers for transport capacity Spectral
Ultra High Capacity Wavelength Division Multiplexed Optical Wireless Communication System
 Ultra High Capacity Wavelength Division Multiplexed Optical Wireless Communication System 1 Meenakshi, 2 Gurinder Singh 1 Student, 2 Assistant Professor 1 Electronics and communication, 1 Ludhiana College
Ultra High Capacity Wavelength Division Multiplexed Optical Wireless Communication System 1 Meenakshi, 2 Gurinder Singh 1 Student, 2 Assistant Professor 1 Electronics and communication, 1 Ludhiana College
Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET
 Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET 1 Outlines of the Class Principles of WDM DWDM, CWDM, Bidirectional WDM Components of WDM AWG, filter Problems with WDM Four-wave mixing Stimulated Brillouin scattering WDM Network
Dr. Monir Hossen ECE, KUET 1 Outlines of the Class Principles of WDM DWDM, CWDM, Bidirectional WDM Components of WDM AWG, filter Problems with WDM Four-wave mixing Stimulated Brillouin scattering WDM Network
COMPARISON OF PRE, POST AND SYMMETRICAL DISPERSION COMPENSATION SCHEME WITH 10 GB/S NRZ LINK FOR SCM SYSTEM
 COMPARISON OF PRE, POST AND SYMMETRICAL DISPERSION COMPENSATION SCHEME WITH 10 GB/S NRZ LINK FOR SCM SYSTEM RUCHI AGARWAL 1 & VIVEKANAND MISHRA 1, Electronics and communication Engineering, Sardar Vallabhbhai
COMPARISON OF PRE, POST AND SYMMETRICAL DISPERSION COMPENSATION SCHEME WITH 10 GB/S NRZ LINK FOR SCM SYSTEM RUCHI AGARWAL 1 & VIVEKANAND MISHRA 1, Electronics and communication Engineering, Sardar Vallabhbhai
Wavelength Multiplexing. The Target
 The Target Design a MAN* like fiber network for high data transmission rates. The network is partial below sea level and difficult to install and to maintain. Such a fiber network demands an optimized
The Target Design a MAN* like fiber network for high data transmission rates. The network is partial below sea level and difficult to install and to maintain. Such a fiber network demands an optimized
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES
 COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES Encoding Coding is the process of embedding clocks into a given data stream and producing a signal that can be transmitted over a selected medium.
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES Encoding Coding is the process of embedding clocks into a given data stream and producing a signal that can be transmitted over a selected medium.
π code 0 Changchun,130000,China Key Laboratory of National Defense.Changchun,130000,China Keywords:DPSK; CSRZ; atmospheric channel
 4th International Conference on Computer, Mechatronics, Control and Electronic Engineering (ICCMCEE 2015) Differential phase shift keying in the research on the effects of type pattern of space optical
4th International Conference on Computer, Mechatronics, Control and Electronic Engineering (ICCMCEE 2015) Differential phase shift keying in the research on the effects of type pattern of space optical
Eye-Diagram-Based Evaluation of RZ and NRZ Modulation Methods in a 10-Gb/s Single-Channel and a 160-Gb/s WDM Optical Networks
 International Journal of Optics and Applications 2017, 7(2): 31-36 DOI: 10.5923/j.optics.20170702.01 Eye-Diagram-Based Evaluation of RZ and NRZ Modulation Methods in a 10-Gb/s Single-Channel and a 160-Gb/s
International Journal of Optics and Applications 2017, 7(2): 31-36 DOI: 10.5923/j.optics.20170702.01 Eye-Diagram-Based Evaluation of RZ and NRZ Modulation Methods in a 10-Gb/s Single-Channel and a 160-Gb/s
Thursday, April 17, 2008, 6:28:40
 Wavelength Division Multiplexing By: Gurudatha Pai K gurudatha@gmail.com Thursday, April 17, 2008, 6:28:40 Overview Introduction Popular Multiplexing Techniques Optical Networking WDM An Analogy of Multiplexing
Wavelength Division Multiplexing By: Gurudatha Pai K gurudatha@gmail.com Thursday, April 17, 2008, 6:28:40 Overview Introduction Popular Multiplexing Techniques Optical Networking WDM An Analogy of Multiplexing
ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS
 MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
MANDEEP SINGH AND S K RAGHUWANSHI: ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS DOI: 10.1917/ijct.013.0106 ANALYSIS OF THE CROSSTALK IN OPTICAL AMPLIFIERS Mandeep Singh 1 and S. K. Raghuwanshi 1 Department
Performance Analysis Of An Ultra High Capacity 1 Tbps DWDM-RoF System For Very Narrow Channel Spacing
 Performance Analysis Of An Ultra High Capacity 1 Tbps DWDM-RoF System For Very Narrow Channel Spacing Viyoma Sarup* and Amit Gupta Chandigarh University Punjab, India *viyoma123@gmail.com Abstract A RoF
Performance Analysis Of An Ultra High Capacity 1 Tbps DWDM-RoF System For Very Narrow Channel Spacing Viyoma Sarup* and Amit Gupta Chandigarh University Punjab, India *viyoma123@gmail.com Abstract A RoF
A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs
 A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs Yue Tian, Qingjiang Chang, and Yikai Su * State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department
A WDM passive optical network enabling multicasting with color-free ONUs Yue Tian, Qingjiang Chang, and Yikai Su * State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Department
SIMULATIVE INVESTIGATION OF SINGLE-TONE ROF SYSTEM USING VARIOUS DUOBINARY MODULATION FORMATS
 SIMULATIVE INVESTIGATION OF SINGLE-TONE ROF SYSTEM USING VARIOUS DUOBINARY MODULATION FORMATS Namita Kathpal 1 and Amit Kumar Garg 2 1,2 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Deenbandhu
SIMULATIVE INVESTIGATION OF SINGLE-TONE ROF SYSTEM USING VARIOUS DUOBINARY MODULATION FORMATS Namita Kathpal 1 and Amit Kumar Garg 2 1,2 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Deenbandhu
Increasing input power dynamic range of SOA by shifting the transparent wavelength of tunable optical filter
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 27, 2018 Increasing input power dynamic range of SOA by shifting the transparent wavelength of tunable optical filter Yu, Jianjun; Jeppesen, Palle Published in: Journal
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Oct 27, 2018 Increasing input power dynamic range of SOA by shifting the transparent wavelength of tunable optical filter Yu, Jianjun; Jeppesen, Palle Published in: Journal
Project: IEEE P Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks N
 Project: IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks N (WPANs( WPANs) Title: [VLC PHY Considerations] Date Submitted: [09 September 2008] Source: [Sang-Kyu Lim, Kang Tae-Gyu, Dae Ho
Project: IEEE P802.15 Working Group for Wireless Personal Area Networks N (WPANs( WPANs) Title: [VLC PHY Considerations] Date Submitted: [09 September 2008] Source: [Sang-Kyu Lim, Kang Tae-Gyu, Dae Ho
Multi-user, 10 Gb/s spectrally. coded O-CDMA system with hybrid chip and slot-level timing coordination
 Multi-user, 10 Gb/s spectrally phase coded O-CDMA system with hybrid chip and slot-level timing coordination Zhi Jiang, 1a) D. S. Seo, 1,2 D. E. Leaird, 1 A. M. Weiner, 1 R. V. Roussev, 3 C. Langrock,
Multi-user, 10 Gb/s spectrally phase coded O-CDMA system with hybrid chip and slot-level timing coordination Zhi Jiang, 1a) D. S. Seo, 1,2 D. E. Leaird, 1 A. M. Weiner, 1 R. V. Roussev, 3 C. Langrock,
International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering
 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: Performance Analysis of WDM/SCM System Using EDFA Mukesh Kumar
ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: Performance Analysis of WDM/SCM System Using EDFA Mukesh Kumar
BER Evaluation of FSO Link with Hybrid Amplifier for Different Duty Cycles of RZ Pulse in Different Conditions of Rainfall
 I.J. Wireless and Microwave Technologies, 2017, 1, 1-12 Published Online January 2017 in MECS(http://www.mecs-press.net) DOI: 10.5815/ijwmt.2017.01.01 Available online at http://www.mecs-press.net/ijwmt
I.J. Wireless and Microwave Technologies, 2017, 1, 1-12 Published Online January 2017 in MECS(http://www.mecs-press.net) DOI: 10.5815/ijwmt.2017.01.01 Available online at http://www.mecs-press.net/ijwmt
Performance of A Multicast DWDM Network Applied to the Yemen Universities Network using Quality Check Algorithm
 Performance of A Multicast DWDM Network Applied to the Yemen Universities Network using Quality Check Algorithm Khaled O. Basulaim, Samah Ali Al-Azani Dept. of Information Technology Faculty of Engineering,
Performance of A Multicast DWDM Network Applied to the Yemen Universities Network using Quality Check Algorithm Khaled O. Basulaim, Samah Ali Al-Azani Dept. of Information Technology Faculty of Engineering,
Optical Transport Tutorial
 Optical Transport Tutorial 4 February 2015 2015 OpticalCloudInfra Proprietary 1 Content Optical Transport Basics Assessment of Optical Communication Quality Bit Error Rate and Q Factor Wavelength Division
Optical Transport Tutorial 4 February 2015 2015 OpticalCloudInfra Proprietary 1 Content Optical Transport Basics Assessment of Optical Communication Quality Bit Error Rate and Q Factor Wavelength Division
32-Channel DWDM System Design and Simulation by Using EDFA with DCF and Raman Amplifiers
 2012 International Conference on Information and Computer Networks (ICICN 2012) IPCSIT vol. 27 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore 32-Channel DWDM System Design and Simulation by Using EDFA with DCF
2012 International Conference on Information and Computer Networks (ICICN 2012) IPCSIT vol. 27 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore 32-Channel DWDM System Design and Simulation by Using EDFA with DCF
Electronically switchable Bragg gratings provide versatility
 Page 1 of 5 Electronically switchable Bragg gratings provide versatility Recent advances in ESBGs make them an optimal technological fabric for WDM components. ALLAN ASHMEAD, DigiLens Inc. The migration
Page 1 of 5 Electronically switchable Bragg gratings provide versatility Recent advances in ESBGs make them an optimal technological fabric for WDM components. ALLAN ASHMEAD, DigiLens Inc. The migration
Performance Analysis of Inter-satellite
 ABHIYANTRIKI An International Journal of Engineering & Technology (A Peer Reviewed & Indexed Journal) Vol. 4, No. 4 (April, 2017) http://www.aijet.in/ eissn: 2394-627X Performance Analysis of Inter-satellite
ABHIYANTRIKI An International Journal of Engineering & Technology (A Peer Reviewed & Indexed Journal) Vol. 4, No. 4 (April, 2017) http://www.aijet.in/ eissn: 2394-627X Performance Analysis of Inter-satellite
Improved Analysis of Hybrid Optical Amplifier in CWDM System
 Improved Analysis of Hybrid Optical Amplifier in CWDM System 1 Bandana Mallick, 2 Reeta Kumari, 3 Anirban Mukherjee, 4 Kunwar Parakram 1. Asst Proffesor in Dept. of ECE, GIET Gunupur 2, 3,4. Student in
Improved Analysis of Hybrid Optical Amplifier in CWDM System 1 Bandana Mallick, 2 Reeta Kumari, 3 Anirban Mukherjee, 4 Kunwar Parakram 1. Asst Proffesor in Dept. of ECE, GIET Gunupur 2, 3,4. Student in
Coherent Optical OFDM System or Long-Haul Transmission
 Coherent Optical OFDM System or Long-Haul Transmission Simarjit Singh Saini Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Guru Nanak Dev University, Regional Campus, Gurdaspur, Punjab, India
Coherent Optical OFDM System or Long-Haul Transmission Simarjit Singh Saini Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Guru Nanak Dev University, Regional Campus, Gurdaspur, Punjab, India
MULTIPLE-ACCESS techniques are required to meet
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 1, JANUARY 2005 143 Four-User, 2.5-Gb/s, Spectrally Coded OCDMA System Demonstration Using Low-Power Nonlinear Processing Z. Jiang, Student Member, IEEE, D.
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 1, JANUARY 2005 143 Four-User, 2.5-Gb/s, Spectrally Coded OCDMA System Demonstration Using Low-Power Nonlinear Processing Z. Jiang, Student Member, IEEE, D.
To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks
 289 To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks Areet Aulakh 1, Kulwinder Singh Malhi 2 1 Student, M.Tech, ECE department, Punjabi University,
289 To investigate effects of extinction ratio on SOA based wavelength Converters for all Optical Networks Areet Aulakh 1, Kulwinder Singh Malhi 2 1 Student, M.Tech, ECE department, Punjabi University,
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES
 ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BY AENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2016 March 10(3): pages 76-82 Open Access Journal Design and Performance
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BY AENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2016 March 10(3): pages 76-82 Open Access Journal Design and Performance
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Optik 119 (2008)
 Optik 119 (28) 39 314 Optik Optics www.elsevier.de/ijleo Timing jitter dependence on data format for ideal dispersion compensated 1 Gbps optical communication systems Manjit Singh a, Ajay K. Sharma b,,
Optik 119 (28) 39 314 Optik Optics www.elsevier.de/ijleo Timing jitter dependence on data format for ideal dispersion compensated 1 Gbps optical communication systems Manjit Singh a, Ajay K. Sharma b,,
RZ BASED DISPERSION COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE IN DWDM SYSTEM FOR BROADBAND SPECTRUM
 RZ BASED DISPERSION COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE IN DWDM SYSTEM FOR BROADBAND SPECTRUM Prof. Muthumani 1, Mr. Ayyanar 2 1 Professor and HOD, 2 UG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
RZ BASED DISPERSION COMPENSATION TECHNIQUE IN DWDM SYSTEM FOR BROADBAND SPECTRUM Prof. Muthumani 1, Mr. Ayyanar 2 1 Professor and HOD, 2 UG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
Elements of Optical Networking
 Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Polarization Mode Dispersion compensation in WDM system using dispersion compensating fibre
 Polarization Mode Dispersion compensation in WDM system using dispersion compensating fibre AMANDEEP KAUR (Assist. Prof.) ECE department GIMET Amritsar Abstract: In this paper, the polarization mode dispersion
Polarization Mode Dispersion compensation in WDM system using dispersion compensating fibre AMANDEEP KAUR (Assist. Prof.) ECE department GIMET Amritsar Abstract: In this paper, the polarization mode dispersion
Performance Evaluation using M-QAM Modulated Optical OFDM Signals
 Proc. of Int. Conf. on Recent Trends in Information, Telecommunication and Computing, ITC Performance Evaluation using M-QAM Modulated Optical OFDM Signals Harsimran Jit Kaur 1 and Dr.M. L. Singh 2 1 Chitkara
Proc. of Int. Conf. on Recent Trends in Information, Telecommunication and Computing, ITC Performance Evaluation using M-QAM Modulated Optical OFDM Signals Harsimran Jit Kaur 1 and Dr.M. L. Singh 2 1 Chitkara
Emerging Subsea Networks
 EVALUATION OF NONLINEAR IMPAIRMENT FROM NARROW- BAND UNPOLARIZED IDLERS IN COHERENT TRANSMISSION ON DISPERSION-MANAGED SUBMARINE CABLE SYSTEMS Masashi Binkai, Keisuke Matsuda, Tsuyoshi Yoshida, Naoki Suzuki,
EVALUATION OF NONLINEAR IMPAIRMENT FROM NARROW- BAND UNPOLARIZED IDLERS IN COHERENT TRANSMISSION ON DISPERSION-MANAGED SUBMARINE CABLE SYSTEMS Masashi Binkai, Keisuke Matsuda, Tsuyoshi Yoshida, Naoki Suzuki,
Investigation of Influence of Mixed
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5755/j01.eie.23.2.18003 ELEKTRONIKA IR ELEKTROTECHNIKA, ISSN 1392-1215, VOL. 23, NO. 2, 2017 Investigation of Influence of Mixed Configurations on Performance of WDM-PON Inna Kurbatska
http://dx.doi.org/10.5755/j01.eie.23.2.18003 ELEKTRONIKA IR ELEKTROTECHNIKA, ISSN 1392-1215, VOL. 23, NO. 2, 2017 Investigation of Influence of Mixed Configurations on Performance of WDM-PON Inna Kurbatska
6. has units of bits/second. a. Throughput b. Propagation speed c. Propagation time d. (b)or(c)
 King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Information Technology Department First Semester 1436/1437 IT224: Networks 1 Sheet# 10 (chapter 3-4-5) Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Before
King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Information Technology Department First Semester 1436/1437 IT224: Networks 1 Sheet# 10 (chapter 3-4-5) Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Before
Multiplexing. Chapter 8. Frequency Division Multiplexing Diagram. Frequency Division Multiplexing. Multiplexing
 Multiplexing Chapter 8 Multiplexing Frequency Division Multiplexing FDM Useful bandwidth of medium exceeds required bandwidth of channel Each signal is modulated to a different carrier frequency Carrier
Multiplexing Chapter 8 Multiplexing Frequency Division Multiplexing FDM Useful bandwidth of medium exceeds required bandwidth of channel Each signal is modulated to a different carrier frequency Carrier
Analysis of four channel CWDM Transceiver Modules based on Extinction Ratio and with the use of EDFA
 Analysis of four channel CWDM Transceiver Modules based on Extinction Ratio and with the use of EDFA P.P. Hema [1], Prof. A.Sangeetha [2] School of Electronics Engineering [SENSE], VIT University, Vellore
Analysis of four channel CWDM Transceiver Modules based on Extinction Ratio and with the use of EDFA P.P. Hema [1], Prof. A.Sangeetha [2] School of Electronics Engineering [SENSE], VIT University, Vellore
Ultra-high-speed optical signal processing of serial data signals
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Ultra-high-speed optical signal processing of serial data signals Clausen, Anders; Mulvad, Hans Christian Hansen; Palushani, Evarist; Galili, Michael; Hu,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Ultra-high-speed optical signal processing of serial data signals Clausen, Anders; Mulvad, Hans Christian Hansen; Palushani, Evarist; Galili, Michael; Hu,
