Vidyalankar. T.Y. Diploma : Sem. VI [EJ/ET/EX/EN/DE/ED/EI] Advanced Communication System [ACS]
|
|
|
- Tyler Gordon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 T.Y. Diploma : Sem. VI [EJ/ET/EX/EN/DE/ED/EI] Advanced Communication System [ACS] Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any THREE of the following : [16] Q.1(a) (i) Write RADAR range equation and state their factor affecting maximum range [4] of RADAR. 1/4 P Ae S t R max = 4 π λ P min where R max = maximum range Ae = capture area of antenna P t = Transmitted power S = Effective surface area of target = signal wavelength p min = Minimum receivable power The factor affecting maximum range are as follows (i) Transmitted power (ii) Frequency (f) (iii) Target cross sectional area (s) (iv) Minimum received signal (p min) Q.1(a) (ii) Compare Between waveguide and Two wire transmission line. [4] [Any 4 points 1 marks each] Waveguide Two wire transmission line 1) It is a hollow metallic pipe which carry Two wire transmission line. It is conductor microwave energy. which carry electrical energy. ) Dielectric losses are less. Dielectric losses are more. 3) For analysis, wave theory is considered For analysis, circuit theory is considered 4) It can handle more power It can handle less power 5) Rectangular circular waveguides are available Twisted pair, co axial cable are available 6) Radiation, copper losses are less Radiation, copper losses are more. Q.1(a) (iii)state four advantages of geostationary satellite. [4] Advantages of geostationary satellite [4 points - 1 marks each] (i) Three satellites gives global coverage with the exception of the polar regions. (ii) It requires limited earth station tracking since the statlite remains fixed in its position with respect. (iii) The communication channel can be either broadcast or point to point. (iv) Continuous communication is possible (v) It is not necessary to rotate dish antenna on earth. Q.1(a) (iv) State splicing technologies used for optical fiber? Explain Fusion splicing in detail? i) Fusion Splicing ii) Mechanical Splicing Fusion Splicing [1 mark] [4] (a) (b) (c) 1
2 : T.Y. Diploma ACS The fusion splicing of single fiber involves the heating of two prepared fiber ends to their fusing points with the application of axial pressure between two optical fiber. It is essential that shipped fiber ends are adequately positioned and aligned in order to achieve good continuity at junction. Flame heating source such as microplasma torches are utilized & widely used heating source is electric are, which gives consistant, easily controlled, heat under field condition. This heat may weaken the fiber. Q.1(b) Attempt any One of the following : [6] Q.1(b) (i) What is dominant made? Explain How wave propagates through rectangular [6] waveguide? [definition 1 mark, diagram 1 mark, explanation 4 marks] Dominant mode: it is mode for which cut off wavelength maximum. Propagation of wave through the rectangular waveguide or parallel plane waveguide. In connection with transmission line, standing waves & reflections are produced if a line is terminated in a short ckt voltage is zero & a current is maximum at this termination. Rectangular waveguide has two pairs of walls & we shall considering their addition one pair at a time. In one pair, second short is added to ensure that it doesn t disturb the existing wave pattern. In above diagram three suitable positions for the second short circuit are indicated. Each of them is at a point of zero voltage on the line & each is located at a distance from the first short circuit that is a multiple of half wavelength s. Electromagnetic wave are reflected due to presence of one wall & will set up reflected pattern, that reflected pattern will be destroyed unless the second wall is placed three half wavelength away from first wall. When top & bottom walls are added to our parallel plane waveguide, the result is standard rectangular waveguide. The addition of these two wall do not affect any result. In practice however their presence is required to confine the wave. y z y b a x
3 Prelim Question Paper Solution Q.1(b) (ii) Explain the working principle and construction of PIN diode? Write two [6] applications? [working principle marks, construction marks, Two application marks] In Pin diode intrinsic larger is sandwiched between P & N region. GaAs is used in construction of PIN diode. It has narrow larger of P type semiconductor separated from an equally narrow n type material by thicker region of intrinsic material. Working : PIN diode acts as ordinary diode of frequency upto 100 MHZ. At this frequency it works as rectifier. At microwave frequencies the diode acts as a variable resistance. When a bias is varied on a PIN diode it s microwave resistance changes from 5 to 10 k when bias & It changes from 1 to 10 when bias is positive If diode is mounted across 50 co axial line, it will not significantly load the line when it is back biased, so that power flow will be unaffected When diode is forward biased, its resistance becomes very low. So that most of power is reflected and hardly any transmitted. Thus the diode is acting as a switch. Application: 1. Used for microwave power switching limiting. Used as a pulse modulator. Q. Attempt any Four of the following : [16] Q.(a) List two advantages and two applications of circular waveguide? [4] (i) Propagates both vertically and horizontally polarized wave in the same waveguide. (ii) Easy to manufacture and join together. Application: (i) Rotating joints in radars to connect the horn antenna feeding a paroboloid reflector. (ii) For short and medium distance broad band communication. Q.(b) Justify magnetron as on oscillator? [4] [diagram marks, Explanation marks] Klystren, TWT all are linear tubes. Magnetron are cross field tubes in which magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other. In cavity magnetron, there is interaction of e with a rotating electro magnetic field of constant angular velocity. These provides oscillations of very high peak power. Fig. (b) Cavity 3
4 : T.Y. Diploma ACS Construction: i) It consist of circular anode into which an even number of resonant cavities has been machined. The diameter of each cavity is equal to 1/ wavelength of desired operating frequency. Anode is usually made up of copper. It is connected to high positive d.c. voltage. ii) In the center of anode, called as interaction chamber, is a circular cathode that emits e s when heated. iii) The direction of e is modified by surrounding the tube with a strong magnetic field usually supplied by c permanent magnets. iv) 8 anode cavities are tightly coupled to each other, both operation is characterized by a combination of frequency and phrase of oscillation relative to adjacent cavity. v) Total phase shift around the ring of cavity is = 45 Working: Magnetron is having radial electric field and axial magnetic field. It magnetic field is absent, e travel straight from cathode to anode. Due to radical electric field force acting on it, as shown a. If magnetic field is increased slightly, it will exert a force bending the path of e as shown by b If the strength of magnetic field is mode sufficiently high if prevents e from reaching anode, shown by c anode current = 0 The magnetic field required to return e bact to cathode just touching the surface of anode is called as cut off magnetic field. If magnetic field is more than cut off field then e come back to cathode quite faster By property adjusting the anode voltage & the strength of magnetic field the e can be made to bend such that they rarely reach the anode and cause current flow in circular loops. In making their circular passes in the interaction chamber, the e excite the resonant cavities into oscillation. Therefore magnetron is an oscillator, not an amplifier Application: i) Pulsed magnetron commonly used in radarsys ii) Continuous wave magnetron are used for heating purpose in microwave oven. iii) Voltage tunable magnetrons are used in telemetry & in missile application. Q.(c) Describe the function of satellite earth station its block diagram. [4] [block diagram marks, Function marks] Function : The communication is established to satellite through earth station. The earth station can be located on the ship at the sea, or on the space craft or actually on earth. The location of earth station is decided depending upon the ease of control of satellite and the function of the satellite. The type of earth station depends upon the a) Function of the station. b) Type of service c) Frequency bands used d) Transmitters e) Reciver and f) Antenna characteristic. The four major subsystems of any earth station are receiver, antenna, transmits and tracking equipment Encoder Multiplexer Baseband Modulator UP converter High Power Amplifier User interface Antenna Demultiplexer Baseband Demodulator Decoder Down converter Low Noise Amplifier 4
5 Prelim Question Paper Solution Explanation: The baseband signal is applied to the encoder. Encoder converts the format ready for modulation. The carrier is modulated by the encoded baseband signal. Ths modulated carrier is then upconverted to the uplink frequency of the satellite. The amplifier then amplifies this signal to high power level, ready for transmission. The signal is then passed through the polarization feed of the antenna. The signal received from the antenna is of different frequency (downlink frequency) and is very small in amplitude. This signal is amplified by the low noise amplifier. It is then down converted to intermediate frequency by the down converter. This signal is then demodulated and decoded to get baseband signal. These attitude data are satellites contration in space and tendency to shift, which can be sensed by infrared sensors. Based on those data, controlling torque may be generated by two methods Passive and Active. Passive attitude control is used for spin stabilization where the decrease in spin rate and shifting back to its correct N S orientation. Active attitude control is used with three axes stabilization, three momentum wheel on these axes controlling their speed of rotation based on the command signal reached form the controlling earth station. Q.(d) Describe Radiation losses in optical fiber cable [4] [two types Explaining 1 type marks, type marks] Whenever an optical fiber undergoes a bend of finite radius of curvature, radioactive losses accurs. There are two types of bends. Power lost Field distribution (1) Macroscopic bend Due to radiation () Microscopic bend Curved fiber The part of mode which is on the outside of bend is required to travel faster than that on inside so that wavefront perpendicular to direction of propagation is maintained. Hence part of mode in the cladding needs the travel faster than the velocity of light in that medium. As this is not possible, the energy associated with this part of mode. If is last through radiation Microbends Microbends are small scale fluctuations in radius of curvature of fiber axis. They are caused either by non uniformities in manufacturing of fiber or by non uniform in manufacturing of fiber or by non uniform lateral pressure created during called of fiber core Q.(e) Define with respect to satellite in detail. [4] (i) Numerical aperture (ii) Acceptance cone [1 mark each] (i) Numerical aperture Numerical aperture is measure of light collecting ability of fiber. It is independent of fiber core diameter. R Core Fig.: Power loss from higher-order modes Claddity 5
6 : T.Y. Diploma ACS By snell s law: n 0 sin 1 = n 1 sin π In ABC = - θ π n 0 sin 1 = nsin -f 1 n 0 sin 1 = n 1 cos = n 1 (1 sin ) 1/ For total internal reflection 1 = a & = c n sin c = (from critical angle definition) n 1/ n0 sin a = n -n 1 = N.A. (ii) Acceptance cone Acceptance cone is defined as the range of angles for rays to be propagated by total internal reflection within fiber core. Q.3 Attempt any four of the following : [16] Q.3(a) An air field rectangular waveguide of inside dimensions cm operates in [4] dominant mode TE 1, 0. Find cut off frequency, & phase velocity at frequency 3.59H [formula 1 mark & answer : 1 mark] Given: Dimensions cm a = 7 cm b = 3.5 cm m = 1 n = 0 c = m/s 1/ 1/ 1 mπ nπ 1 1 π 0 π Solution: i) f c = + = + π με a b π με π 0 = + π με 73.5 c π = π 7 = 1/ π π = f c =.148 GHZ 1/ 1/ 1 π = π με m π = π 7 = = / 1/ 1/ =
7 Phase velocity = c 1- fc / f 0 = Prelim Question Paper Solution / = = v p = m/s To provide monitoring function optical sensor systems are used in mobiles. & fiber optic communication is reliable for short as well as long distance communicate in minimum radies. Q.3(b) Explain Antenna scanning method s used in radar. [4] [diagram marks, explanation marks] Radar antennas are often made to scan given area of the surrounding space There are many scanning patterns depending on its application. 1) Horizontal Scanning Scans only in horizontal plane wherever the scanning in horizontal directional is required example ship is ship securing then horizontal scanning is performed. Nodding scan is an extension of this, the antenna is moved rapidly in elevation while it rotates more slowly in azimuth and scanning in both planes is obtained. This system can be used to scan limited sector. Noddi Axis of rotation Helical Scanning: In this the elevation of the antenna is raised slowly while it rotates more rapidly in azimuth. If a limited area of more or les circular shape is to be covered, then spiral scan may be used. Q.3(c) Give characteristics and classification of fiber. [4] [characteristics marks, classification marks] The char of light transmission thro a glass fiber depend on many factors. i) The composition of fiber ii) The amount & type of light introduced in fibers iii) The diameter & length of fiber. Composition of fiber determines the refractive index by the process called doping. Other material are introduced into material that after its index number. This process produces a single fiber core with core index n 1 & cladding index n Another chas. op fiber, which depend on its size, is it s mode of operation. Mode refers to mathematical & physical description of propagation of energy thro a medium no. of mode supported by single fiber can be 1 to 1,00,000 fibers can provide path for one light rays or may rays i.e. single mode or multimode. lobe 7
8 : T.Y. Diploma ACS Archive Index profile It describes the relation of multiple indices which exist in the core adding of particular fiber. There are major, indicates i) Step index ii) Graded index i) Step index The step index decribes an abrupt index change from core to cladding. Core & cladding both are having uniform refractive index. ii) Graded index With graded index, the highest index is at the center. This number gradually decreases until reaches the index no. of cladding. Three classifications of fiber(types) a) Multimode step index fiber b) Multimode graded index fiber. c) Single mode step index fiber. a) Multimode step index fiber. Has a core diameter from 100 to 970 m. With this large core diameter, there are many paths thro which light can travel multimode. Therefore, the light ray travelling the straight path through the center reaches the end before the other rays, which follow a zigzag path. the difference in the length of time it takes the various rays to exit the fiber is called modal dispersion. This form of a signal distortion which limits the bandwidth of fiber. b) Multimode graded index fiber. Because light rays travels more slowly than the light nearer the surface. Therefore, both light rays arrive at the exit point at almost the same time, thus reducing model dispersion. Graded index fiber has core diameter ranging from m & cladding diameter of 15 m. c) Single mode step index fiber. It is widely used in wide band communication with this fiber, a light ray can travel on only one path. Therefore, modal dispersion is zero. The core diameter of this fiber range from 5 m 10 m. 8
9 Prelim Question Paper Solution Q.3(d) Draw field pattern of circular waveguide. [4] [diagram 4 marks] Circular waveguide has different method of mode labeling because of circular cross section. Now, Here m = no of full wave intensity variations around the circumference. n = no of half wave intensity changes radially out from the center to the wall. TE, 1 mode is the dominant mode of circular wavelength. Advantages of Circular waveguide: 1. Circular waveguide are easier to manufacture than rectangular ones.. They are also easier to join together. Disadvantages: 1. Its cross section area is much bigger than that of a corresponding rectangular waveguide.. In circular waveguide plan of polarization of wave s travel changes through the waveguide. Waveguide components Flanges: When waveguide pieces or components are joined together, the coupling is done by means of flanges. Functions of Flanges 1. To ensure a smooth mechanical junction and suitable electrical characteristics.. Low external radiation and low internal reflection Q.3(e) Illustrate the block diagram of fiber optic communication system. [4] [block diagram marks, explanation marks] Information Source Optical detector Electrical Transmit Electrical Receive Optical Source Optical Fiber cable Destination Information source provide an signal to drive electrical stage which ultimately drives an optical source to give modulation of light wave carrier. Optical source which provides the electrical optical conversion may either semiconductor laser or LED. Optical carrier may be modulated using either analog or digital information signal. But analog modulation is less effective because it requires far higher signal to noise ratio at the receiver. Laser drive ckt directly modulate the intensity of mod semiconductor laser with encoded digital signal. Hence digital signal launched into FOC. Avalanche photodiode (APD) followed by front end amplifier & equalizer are wed to provides gain as well as linear signal processing & noise bandwidth reduction. Finally signal obtained is decoded to give original information 9
10 : T.Y. Diploma ACS Q.3(f) Describe working principle of OTDR with its Block diagram? [4] Block diagram of OTDR The main block of reflector meter are the generator of the testing impulse and detection system of the backscattered signal. An optical time domain reflectometer is used in fiber optics to measure the time and intensity of light reflected. It is used as a trouble shooting device to find fault, splices and bends in fiber optic cables, with an eye toward identifying light locs. A light pulse is launched into the fiber in forward direction from laser using either a directional coupler or beam splitter. Coupler makes possible to couple optical excitation power into the tested fiber and simultaneously to deviate the backscattered power to optical receiver. The backscattered light is deflected using an avalanche photodiode. O/P of photodiode drives integrator improves the received signal to noise ratio by giving an nonthematic average over a no. of measurement taken at one point within a fiber. Then signal is fed to log. amplifier and average measurements for successive points with the fiber are plotted. Q.4 Attempt any TWO : [16] Q.4(a) Draw block dia of MTI radar and explain its operation? [4] [4 marks] Mixer f o + f c f o STALO COHO Amplifier f o f o + f c If amplifier Phase detector Antenna f o f c f c f c f c Subtractor circuit Amplifier 1 Delay line Radar display MTI Fig. 1: Block diagram of MTI Radar 10
11 Prelim Question Paper Solution Principle: [4 marks] When it is desired to remove clutter due to stationary target & an MTI rader is employed. The basic principle of MTI radar is to compare a set of received echoes with those received during previous sweep & cancelling out those whose phase has remain unchanged. Moving targets will give change of phase & are not cancelled. The cullers due to stationery target both man made & natural are removed from displays this allows easier detection of moving targets. Block diagram description It shows two mixes mixer. Generates transmitters frequency which is obtained by sum frequency produced by two OSC r The STALO (stable Local OSC r producing f O ) & COHO (coherent OSC r producing f C ). The transmitted frequency drives multi cavity klyston amplifier, which act as an o/p tube This amplifier provides the desired amplification for providing a high power pulse when modulator switches it ON. This Tx r pulse is the o/p via the duplexes. Echo pulse from target is received by MT 1 radar antenna. If echo is due to moving target the echo pulse undergoes a dopples frequency shift. The received echo pulse then pass through mixes 1 of receiver which heterodynes the received signal of frequency (f O + f C ) with o/p of STALO at f O & produces a difference frequency f C at it s o/p Two mixes 1 & are identical in all respect except that mixes produces different frequency where as mixes 1 produces a sum frequency. This different frequency signal is further amplified by an, If amplifier & given to phase sensitive detector. This detector compares IF signal with reference signal from COHO OSC r. Frequency produced by COHO is same as IF frequency & called as coherent frequency. The detector provides an o/p depending up phase difference between two signal. Since all the received signal pulses will have a phase different compared with transmitted pulses. Thus phase detector gives o/p for fixed target & moving target. Doppler frequency shift causes this variation in phase difference. A change of half cycle in Doppler frequency shift would cause an o/p of opposite polarity in the phase detector. The o/p of phase detector therefore will have an o/p that has different magnitude. Q.4(b) Illustrate the block dia of satellite subsystem [4] Solar panels [4 marks] Receiver Antenna subsystem Communication antenna Freq. X lator i/ps from onboard sensors Charger and batteries X mitter Telemetry tracking and control subsystem Power subsystem Communication subsystem Regulators protection and conditioning DC to all subsystems Control signals to all subsystems Telemetry antenna Fig. AKM DC/DC convertor DC/AC convertor DC to AC to special subsystem Attitude control subsystem Propulsion subsystem Jet thruster 11
12 : T.Y. Diploma ACS Satellite subsystem consist of i) Power Subsystem ii) Communication iii) Telemetry tracking & command iv) Altitude control v) Antenna subsystem i) Power Subsystem : Provides power to cell subsystem. All solar panels are pointed towards the sun generous many kilowatts DC power. DC power is used to charge batteries which provides DC current to components when solar panels are not properly positioned DC to DC converter is used to reuse the level of voltages because some component like TWT requires high DC voltage. ii) Communication Subsystem : It consist of Receiver frequency x 10r and transmitter and are designed to operate at separate frequencies. Transponders shares common antenna subsystem which receivers up link frequency amplifies then again translate them in frequency & after amplification retransmits as a downlink frequency. iii) Telemetry tracking & command : This subsystem is responsible for monitoring on board conditions like temp and battery voltages. After monitoring it sends data back to earth station for analysis. According to result analysis ground station issues the order to satellite by transmitting a signal to command subsystem. The command subsystem control the function of satellite like firing and jet thrusters. iv) Altitude control : It provides stabilization in orbit and senses the changes in orientation of satellite with built in jet thruster it makes the necessary correction to attitude of satellite. Population of satellite: It uses AKM to put the satellite into final orbit. v) Antenna subsystem : It consist of one or more antennas used for receiving signal from ground station and for transmitting information back to earth station. Q.4(c) Draw constructional sketch of TWT and explain its working, state its application. [4] [Construction diagram 3 marks, Explanation 3 marks, application marks] It consist of thin conduction helical coil. This coil is placed inside the glass tube. Cathode is used to emit e beam. A magnetic focusing field is provided to prevent the beam from spreading & guide it. By using i/p waveguide, RF signal is applied to helix similarly at o/p end o/p waveguide is used. Collector is having high positive voltage, placed at the o/p end of helix. So e beam get accelerated to the collector. The RF signal comes out from o/p end of helix. Working: 1. Electron beam passes through the center or axis of helix. The microwave signal to be amplified is applied to the end of helix near the cathode & o/p is taken from end of helix near collector.. The purpose of helix is to provide a path for the RF signal that will slow down its propagation. The propagation of RF along the helix is made approximately equal to velocity of e beam from cathode to collector. 1
13 Prelim Question Paper Solution 3. Cathode emits e beam RF field is weak at the i/p of helix which is due to the i/p signal. The electric field produced by the helix cause e to be speeded up & slowed down. This produces velocity modulation, which causes buncing of e s 4. At a point at which axial field is zero e velocity is unaffected. 5. A point where axial field is positive, e coming against it is accelerated & tries to catch up e which encounter the RF axial field. 6. A point where axial field is positive the e gets velocity modulated. 7. The density modulated e beam is in step with electromagnetic wave travelling down the helix, the e bunches induces voltage into helix which reinforce the voltage already present there 8. This result is that strength of electromagnetic field on helix increases as wave travel down the tube towards the collector. 9. At the end signal is considerably amplified. Coaxial cables are used to extract energy from the helix. Application 1. In broadband microwave Rx r as a low noise RF amplifier.. As a repeater amplifier in wideband communication cables & coaxial cables. 3. It is used as power 0/8 tube in communication. 4. GaAs semiconductor is having two band valance band & conduction band. Bandgap between them is called as forbidden gap. i) Central vally : It consist of conduction e it is above 1.43 ev from valance band. ii) Satalite valley: It is at higher energy level than central valley. At room temperature, when applied electric field intensity is flow then all the e are present in lower valley when electric field intensity is increased more photons are generated they strike e because of collision energy is transferred to e their kinetic energy increases. e shifts in the upward direction. This is called as electron transfer If more electric field is applied e moves towards satellite valley, Mass of e increase with further increases in electric field energy e gets increases but the velocity will reduce, and current will also reduce. Q.5 Attempt any four of the following : [16] Q.5(a) Compare between LED and LASER [4] [4 points 1 mark each] Parameter LED LASER Principle of operation Spontaneous emission Stimulated emission Spectral width Broad Narrow Data rate Low Very High Transmission Distance Smaller Greater Temp. Sensitivity Less More Coupling efficiency Very low High Compatible fibers Multimode step index Single mode step index Noise More less 13
14 : T.Y. Diploma ACS Q.5(b) Explain the function of magic Tee in detail. [4] Collinear arms E-arm Port 3 Port A magic tee is a combination of E plane Tee & H plane tee. Tee & H plane tee. The various properties of magic tee are as follows: 1) If waves of equal amplitude & p same phase are fed into P 1 & P the o/p will zero at P 3 & additive at P 4. ) If a wave fed into P 4 i.e. H arm it will be equally divided between P 1 & P with a equal amplitude & same phase & will not appear at P 3. 3) If a wave is fed into P 3 it will produce an o/p of equal magnitude & opposite phase at P 1 & P & o/p at P 4 is zero. 4) If a wave fed into P & P of equal amplitude & out of phase then o/p at the P 3 will be maximum & at P 4 will be zero. 5) If a wave is fed into one co linear arm i.e. at P 1 or P it will not appear at P or P 1 because E arm causes phase delay while H arm cause phase advance. Q.5(c) With neat sketch describe the operation of GUNN diode. [4] Construction: Gold alloy cathode Heat sink Active n layer Port 1 H-arm Port 4 n + substrate Anode gold wire 8 m 5 m Cathode The Gunn diode is not a diode, It is a thin piece of N type GaAs or I n P semiconductor. Working: If a relatively small d.c. voltage is placed across a thin slice of GaAs, such as shown in fig that forms a special registor. The formed resistance is negative resistance i.e. over some voltage ranges an increase in voltage result in decrease in current and vice versa, just the opposite of ohm s law predicts for linear resistance. When it is so biased that, the time it takes for electrons to flow across the material is such that the current will be 180 out of phase with applied voltage. 14
15 Prelim Question Paper Solution If the Gunn diode is so biased and connected to a cavity that is resonant near the e transit time, it result in oscillation. The Gunn diode, therefore is used primarily as a microwave oscillation. Feature: Gunn diode are avaible to oscillate at frequency upto 50GHz In the lower microwave range, power o/p upto several watts are possible The thickness of semiconductor, determines the frequency of oscillation. Application: The high power Gunn diodes are used in variety of low power transmitter applications. Gunn diode oscillators use in police radar, CW Doppler radar, burglar alarms and aircrafts. Q.5(d) Write short note on : [4] 1) Foot print ) Station Keeping 1) Foot print The satellite downlink antenna transmits signals (beam) towards the earth in a particular patterns called footprint. The footprint of a stalite is the earth area that the satellite can receive from or transmits to. The earths coverage area increase with beam width & beam width decreases with increases in height. ) Station Keeping Control signals that are to be generated ground to keep satellite in position is known as station keeping. Gravitational forces causes orbital drift of satellite, so the orbit of satellite must be periodically adjusted. Most satellite contain small rockets or thus jets for keeping satellite in proper orbit. Process of firing the rocket under ground control to maintain or adjust orbit is referred as station keeping. Q.5(e) Calculate N.A and acceptance angle of fiber having refractive index of core = 1.40 [4] and cladding = 136 [Formula 1 mark, answer 1 mark] Given: n 1 = 1.40 n = 136 Calculate i) N. A. ii) a Ans: Formula: N. A. = h h = = = N. A. = Q.6 Attempt any four of the following : [16] Q.6(a) Explain function of : i) Circulator ii) Isolator [4] i) Circulator Symbol of circulator 15
16 : T.Y. Diploma ACS Circulator is a four port device. It has a particular property that each terminal is connected to next clockwise terminal, i.e. port 1 is connected port & not to the port 3 & port 4. Circulators are used in parametric amplifiers, tunnel diode amplifier & duplexer in radar. ii) Isolator It provides very small attenuation for transmission. Isolator make use of 45 twisted rectangular waveguide. It is a two port device. In microwave generators the output amplitude & frequency tends to fluctuate with changes in load. Fluctuation occurs due o mismatch of generator output to load. That result reflected wave from load. These reflected waves causes the instability of amplitude & frequency of microwave generator. If the isolator is inserted between generator & load then the generator is coupled to load with zero attenuation and reflection. TE 1, mode Port 1 Top View Resistive Card Circular Waveguide The basic behavior of wave in circular waveguide is the same as in rectangular guides. Since circular waveguide have a different geometry and same different cup plication minor modifications are required in all the parameters and definition evolved evolved for rectangular waveguide. 1) The formula for cut off wavelength is different because of different geometry, and it is given by πr 0 = kr Where r = radius (internal) of waveguide kr = constant 16
17 Prelim Question Paper Solution Q.6(b) Illustrate how telemetry, tracking and command system used in satellite [4] communication? [block dia m, explanation m] Command Telemetry Command Subystem Tracking System Computer Controller Telemetry Receiver Processor These systems are partly on the satellite and partly at the control earth station. They support the function of space craft management Telemetry: It collects data from all sensors on the satellite and send to the controlling earth sation. The sighting device is used to maintain space craft attitude are also monitored by telemetry. At the earth station using computer, telemetry data is monitored and decoded. Tracking: By using velocity and acceleration sensors an spacecraft the orbital position of satellite can be defect from earth sation. For accurate and precise result no of earth station can be used. Command: Command is the set of instruction of controlling earth station for the spacecraft. During the time of launching, command signal can control firing of moter When the satellite has reached proper orbit solar panel deployment and action of spinner operation start after getting a command signal. Command signal can also be used to make changes in attitude. Main & Auxiliary propulsion subsystem : Most satellite contains propulsion subsystem in addition with attitude control subsystem It is used AKM to put the satellite into final orbit. By using rockets that could be change the orbit of a satellite, or remove the satellite form orbit. This subsystem is also operated by command control subsystem. Modes can exit in to but in TM on such zero subscript mode will not exist because magnetic field exist on both X and y axis. TE, TM 1, TM 1 such mode exist. TE 10 is the dominant mode for TE TM 11 is the dominant mode f 0 TM where cut off wavelength has maximum value. Physical dimensions of waveguide decides the dominant mode of propogation. 17
18 : T.Y. Diploma ACS Q.6(c) List display methods used in RADAR & Explain A scope displays method in detail. [4] [List 1 mark, diagram 1 mark, explanation marks] A Scope display It is a deflection modulation of a cathode ray tube screen. A sweep waveform is applied to horizontal deflection plate of a CRT. & moves the beam slowly form left to right. The playback period is rapid. In absence of any received signal the displays is simply horizontal straight line. The demodulated receiver o/p is applied to vertical deflection plates & causes the deflection of a beam from horizontal line. The horizontal deflection sawtooth waveform is sync.with transmitted pulse so that the width of CRT screen corresponds to time interval between successive pulse. Displacement from left hand side of CRT corresponds to range of target. The 1 st blip due to transmitted pulse is a reference pulse, then comes various strong blips, dut to reflections from ground near by objects of each which is here called ground clutter. The height of each blip corresponds to strength of returned echoes while its distance form P reference blip is a measure of range equally into P 1 & P in phase & with the same amplitude. 3 1 Q.6(d) Draw schematic of LASER and describe its working principle with transition [4] process involved in LASER process Metal P-type n-type 18
19 Prelim Question Paper Solution This is the construction of semiconductor LASER LASER operates on the principle of stimulate emission. There are basically three steps : i) Absorption ii) spontaneous emission iv) stimulated emission Absorption: under normal condition e stays at the lower energy level i.e. ground state E 1. If the photon of (E E 1 ) energy id incident on this e then e absorbs this energy and goes 10 the higher energy level E. Spontaneous emission, after absorption process the e present at the higher energy level. If no incident light provided externally there stays at this stage for shorter time (other falls down) to the lower level emitting a photon with energy E E 1. Stimulated emission: Because of this process, light amplification takes place. Before occurance of spontaneous emission, if the incident photon is allowed to strike to excited e then there is no chance for this atom to go to further higher energy level. Hence atom leaves it s higher position and then emits two photon while going to lower energy level. Q.6(e) State advantage of fiber optic commination [4] [Any 8 points, points 1 marks] 1) Large Band Width: to H ) Small Size and Weitht: Diameter is in m 3) Electrical Isolation: Fiber made from glass & fiber create no arcing, shortcircuit electrically hazardous area. 4) Immunity to interference & cross talk : Fibers are dielectric waveguide. Hence it is free from EMI and RFI. Hence immune to interference and cross talk 5) Signal Security: Light doesn t radiate significant. Hence proved high degree of signal security. 6) Low transmission loss: Losses are low upto 0.4 db & low attenuation losses. 7) Aexibility: We can provide bent to fiber upto small radii or twisted without damage. 8) System Reliability : Less repeater are required hence in creasing the reliability and reduction the cost. 19
Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat.
 Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat. Scattering: The changes in direction of light confined within an OF, occurring due to imperfection in
Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat. Scattering: The changes in direction of light confined within an OF, occurring due to imperfection in
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17656 16117 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Assume suitable data, if necessary. (4) Use of Non-programmable Electronic
17656 16117 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Answer each next main Question on a new page. (3) Assume suitable data, if necessary. (4) Use of Non-programmable Electronic
Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications by Stuart M. Wentworth Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
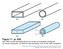 Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
T.Y. Diploma : Sem. VI [EJ/ET/EX/EN/DE/ED/EI] Advanced Communication System
![T.Y. Diploma : Sem. VI [EJ/ET/EX/EN/DE/ED/EI] Advanced Communication System T.Y. Diploma : Sem. VI [EJ/ET/EX/EN/DE/ED/EI] Advanced Communication System](/thumbs/93/111288895.jpg) T.Y. Diploma : Sem. VI [EJ/ET/EX/EN/DE/ED/EI] Advanced Communication System Time : 3 Hrs.] MSBTE Specimen Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any THREE of the following : [12] Q.1(a) (i)
T.Y. Diploma : Sem. VI [EJ/ET/EX/EN/DE/ED/EI] Advanced Communication System Time : 3 Hrs.] MSBTE Specimen Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any THREE of the following : [12] Q.1(a) (i)
MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) LAB MANUAL VI SEMESTER
 1 MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) LAB MANUAL VI SEMESTER RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDERGARH)123029 Department Of Electronics and Communication
1 MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) LAB MANUAL VI SEMESTER RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDERGARH)123029 Department Of Electronics and Communication
3. (a) Derive an expression for the Hull cut off condition for cylindrical magnetron oscillator. (b) Write short notes on 8 cavity magnetron [8+8]
![3. (a) Derive an expression for the Hull cut off condition for cylindrical magnetron oscillator. (b) Write short notes on 8 cavity magnetron [8+8] 3. (a) Derive an expression for the Hull cut off condition for cylindrical magnetron oscillator. (b) Write short notes on 8 cavity magnetron [8+8]](/thumbs/73/68588725.jpg) Code No: RR320404 Set No. 1 1. (a) Compare Drift space bunching and Reflector bunching with the help of Applegate diagrams. (b) A reflex Klystron operates at the peak of n=1 or 3 / 4 mode. The dc power
Code No: RR320404 Set No. 1 1. (a) Compare Drift space bunching and Reflector bunching with the help of Applegate diagrams. (b) A reflex Klystron operates at the peak of n=1 or 3 / 4 mode. The dc power
EC 1402 Microwave Engineering
 SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY-621105. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC 1402 Microwave Engineering
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR,TRICHY-621105. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC 1402 Microwave Engineering
is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic
 is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. The
is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending light through an optical fiber. The light forms an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. The
Satellite Sub-systems
 Satellite Sub-systems Although the main purpose of communication satellites is to provide communication services, meaning that the communication sub-system is the most important sub-system of a communication
Satellite Sub-systems Although the main purpose of communication satellites is to provide communication services, meaning that the communication sub-system is the most important sub-system of a communication
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB VIVA QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB VIVA QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Why can t conventional tubes be used at microwave frequencies? Conventional tubes can t be used at microwave frequencies because of transit time effect.
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB VIVA QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Why can t conventional tubes be used at microwave frequencies? Conventional tubes can t be used at microwave frequencies because of transit time effect.
Optical Fiber Communication
 A Seminar report On Optical Fiber Communication Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of Mechanical SUBMITTED TO: www.studymafia.org SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org
A Seminar report On Optical Fiber Communication Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of degree Of Mechanical SUBMITTED TO: www.studymafia.org SUBMITTED BY: www.studymafia.org
R.K.YADAV. 2. Explain with suitable sketch the operation of two-cavity Klystron amplifier. explain the concept of velocity and current modulations.
 Question Bank DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION SUBJECT- MICROWAVE ENGINEERING(EEC-603) Unit-III 1. What are the high frequency limitations of conventional tubes? Explain clearly. 2. Explain
Question Bank DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION SUBJECT- MICROWAVE ENGINEERING(EEC-603) Unit-III 1. What are the high frequency limitations of conventional tubes? Explain clearly. 2. Explain
MICROWAVE MICROWAVE TRAINING BENCH COMPONENT SPECIFICATIONS:
 Microwave section consists of Basic Microwave Training Bench, Advance Microwave Training Bench and Microwave Communication Training System. Microwave Training System is used to study all the concepts of
Microwave section consists of Basic Microwave Training Bench, Advance Microwave Training Bench and Microwave Communication Training System. Microwave Training System is used to study all the concepts of
COM 46: ADVANCED COMMUNICATIONS jfm 07 FIBER OPTICS
 FIBER OPTICS Fiber optics is a unique transmission medium. It has some unique advantages over conventional communication media, such as copper wire, microwave or coaxial cables. The major advantage is
FIBER OPTICS Fiber optics is a unique transmission medium. It has some unique advantages over conventional communication media, such as copper wire, microwave or coaxial cables. The major advantage is
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS
 UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
Fiber Optic Communications Communication Systems
 INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
Magnetron. Physical construction of a magnetron
 anode block interaction space cathode filament leads Magnetron The magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube that works as self-excited microwave oscillator. Crossed electron and magnetic fields are used
anode block interaction space cathode filament leads Magnetron The magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube that works as self-excited microwave oscillator. Crossed electron and magnetic fields are used
B ==================================== C
 Satellite Space Segment Communication Frequencies Frequency Band (GHz) Band Uplink Crosslink Downlink Bandwidth ==================================== C 5.9-6.4 3.7 4.2 0.5 X 7.9-8.4 7.25-7.7575 0.5 Ku 14-14.5
Satellite Space Segment Communication Frequencies Frequency Band (GHz) Band Uplink Crosslink Downlink Bandwidth ==================================== C 5.9-6.4 3.7 4.2 0.5 X 7.9-8.4 7.25-7.7575 0.5 Ku 14-14.5
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad 500014. Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SUB: MICROWAVE ENGINEERING SECTION: ECE IV A & B NAME OF THE FACULTY: S RAVI KUMAR,T.SUDHEER
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad 500014. Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SUB: MICROWAVE ENGINEERING SECTION: ECE IV A & B NAME OF THE FACULTY: S RAVI KUMAR,T.SUDHEER
SATELLITE SUBSYSTEMS. Networks and Communication Department. Dr. Marwah Ahmed
 1 SATELLITE SUBSYSTEMS Networks and Communication Department Dr. Marwah Ahmed Outlines Attitude and Orbit Control System (AOCS) Telemetry, Tracking, Command and Monitoring (TTC & M) Power System Communication
1 SATELLITE SUBSYSTEMS Networks and Communication Department Dr. Marwah Ahmed Outlines Attitude and Orbit Control System (AOCS) Telemetry, Tracking, Command and Monitoring (TTC & M) Power System Communication
Know how Pulsed Doppler radar works and how it s able to determine target velocity. Know how the Moving Target Indicator (MTI) determines target
 Moving Target Indicator 1 Objectives Know how Pulsed Doppler radar works and how it s able to determine target velocity. Know how the Moving Target Indicator (MTI) determines target velocity. Be able to
Moving Target Indicator 1 Objectives Know how Pulsed Doppler radar works and how it s able to determine target velocity. Know how the Moving Target Indicator (MTI) determines target velocity. Be able to
2. The Basic principle of optical fibre (Or) Working principle of optical fibre (or) Total internal reflection
 Introduction Fibre optics deals with the light propagation through thin glass fibres. Fibre optics plays an important role in the field of communication to transmit voice, television and digital data signals
Introduction Fibre optics deals with the light propagation through thin glass fibres. Fibre optics plays an important role in the field of communication to transmit voice, television and digital data signals
The absorption of the light may be intrinsic or extrinsic
 Attenuation Fiber Attenuation Types 1- Material Absorption losses 2- Intrinsic Absorption 3- Extrinsic Absorption 4- Scattering losses (Linear and nonlinear) 5- Bending Losses (Micro & Macro) Material
Attenuation Fiber Attenuation Types 1- Material Absorption losses 2- Intrinsic Absorption 3- Extrinsic Absorption 4- Scattering losses (Linear and nonlinear) 5- Bending Losses (Micro & Macro) Material
Optodevice Data Book ODE I. Rev.9 Mar Opnext Japan, Inc.
 Optodevice Data Book ODE-408-001I Rev.9 Mar. 2003 Opnext Japan, Inc. Section 1 Operating Principles 1.1 Operating Principles of Laser Diodes (LDs) and Infrared Emitting Diodes (IREDs) 1.1.1 Emitting Principles
Optodevice Data Book ODE-408-001I Rev.9 Mar. 2003 Opnext Japan, Inc. Section 1 Operating Principles 1.1 Operating Principles of Laser Diodes (LDs) and Infrared Emitting Diodes (IREDs) 1.1.1 Emitting Principles
Chapter 18: Fiber Optic and Laser Technology
 Chapter 18: Fiber Optic and Laser Technology Chapter 18 Objectives At the conclusion of this chapter, the reader will be able to: Describe the construction of fiber optic cable. Describe the propagation
Chapter 18: Fiber Optic and Laser Technology Chapter 18 Objectives At the conclusion of this chapter, the reader will be able to: Describe the construction of fiber optic cable. Describe the propagation
LE/ESSE Payload Design
 LE/ESSE4360 - Payload Design 4.3 Communications Satellite Payload - Hardware Elements Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Dr. Jinjun Shan, Professor of Space Engineering Department of Earth and Space Science
LE/ESSE4360 - Payload Design 4.3 Communications Satellite Payload - Hardware Elements Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Dr. Jinjun Shan, Professor of Space Engineering Department of Earth and Space Science
1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems
 OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-I : OPTICAL FIBERS STRUCTURE: 1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems The operating range of optical fiber system term and the characteristics of the four key components of
OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-I : OPTICAL FIBERS STRUCTURE: 1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems The operating range of optical fiber system term and the characteristics of the four key components of
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) Winter 15 EXAMINATIONS
 Winter 15 EXAMINATIONS Subject Code: 17656 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the answer scheme. 2) The
Winter 15 EXAMINATIONS Subject Code: 17656 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the answer scheme. 2) The
Introduction to Fiber Optics
 Introduction to Fiber Optics Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior Milestones in Electrical Communication 1838 Samuel F.B. Morse
Introduction to Fiber Optics Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior Milestones in Electrical Communication 1838 Samuel F.B. Morse
KULLIYYAH OF ENGINEERING
 KULLIYYAH OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION LABORATORY (ECE 4103) EXPERIMENT NO 3 RADIATION PATTERN AND GAIN CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DISH (PARABOLIC)
KULLIYYAH OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION LABORATORY (ECE 4103) EXPERIMENT NO 3 RADIATION PATTERN AND GAIN CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DISH (PARABOLIC)
Elements of Optical Networking
 Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
UNIT Write short notes on travelling wave antenna? Ans: Travelling Wave Antenna
 UNIT 4 1. Write short notes on travelling wave antenna? Travelling Wave Antenna Travelling wave or non-resonant or aperiodic antennas are those antennas in which there is no reflected wave i.e., standing
UNIT 4 1. Write short notes on travelling wave antenna? Travelling Wave Antenna Travelling wave or non-resonant or aperiodic antennas are those antennas in which there is no reflected wave i.e., standing
CHAPTER -15. Communication Systems
 CHAPTER -15 Communication Systems COMMUNICATION Communication is the act of transmission and reception of information. COMMUNICATION SYSTEM: A system comprises of transmitter, communication channel and
CHAPTER -15 Communication Systems COMMUNICATION Communication is the act of transmission and reception of information. COMMUNICATION SYSTEM: A system comprises of transmitter, communication channel and
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME & CODE: EC2403 & RF AND MICROWAVE ENGINEERING UNIT I
 FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai -625 020 An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai -625 020 An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Photonics and Fiber Optics
 1 UNIT V Photonics and Fiber Optics Part-A 1. What is laser? LASER is the acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. The absorption and emission of light by materials has been
1 UNIT V Photonics and Fiber Optics Part-A 1. What is laser? LASER is the acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. The absorption and emission of light by materials has been
Fiberoptic and Waveguide Sensors
 Fiberoptic and Waveguide Sensors Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mecahnical Engineering University of Washington Optical sensors Advantages: -immune from electromagnetic field interference (EMI) - extreme
Fiberoptic and Waveguide Sensors Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mecahnical Engineering University of Washington Optical sensors Advantages: -immune from electromagnetic field interference (EMI) - extreme
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR. By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Third Edition by J.
 PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
REVERBERATION CHAMBER FOR EMI TESTING
 1 REVERBERATION CHAMBER FOR EMI TESTING INTRODUCTION EMI Testing 1. Whether a product is intended for military, industrial, commercial or residential use, while it must perform its intended function in
1 REVERBERATION CHAMBER FOR EMI TESTING INTRODUCTION EMI Testing 1. Whether a product is intended for military, industrial, commercial or residential use, while it must perform its intended function in
Module IV, Lecture 2 DNP experiments and hardware
 Module IV, Lecture 2 DNP experiments and hardware tunnel diodes, Gunn diodes, magnetrons, traveling-wave tubes, klystrons, gyrotrons Dr Ilya Kuprov, University of Southampton, 2013 (for all lecture notes
Module IV, Lecture 2 DNP experiments and hardware tunnel diodes, Gunn diodes, magnetrons, traveling-wave tubes, klystrons, gyrotrons Dr Ilya Kuprov, University of Southampton, 2013 (for all lecture notes
Intensity Modulation. Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington. W. Wang
 Intensity Modulation Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Why Intensity Modulation Simple optical setup Broadband or mono-chormatic light source Less sensitive but
Intensity Modulation Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Why Intensity Modulation Simple optical setup Broadband or mono-chormatic light source Less sensitive but
Telecommunication Wiring Questions
 Telecommunication Wiring Questions 1. is the process of modifying a carrier frequency in rhythm to the audio frequency. A, Modulation B. Amplitude C. Change of phase D. Interference 2. is the property
Telecommunication Wiring Questions 1. is the process of modifying a carrier frequency in rhythm to the audio frequency. A, Modulation B. Amplitude C. Change of phase D. Interference 2. is the property
DEPARTMENT OF CSE QUESTION BANK
 DEPARTMENT OF CSE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: CS6304 SUBJECT NAME: ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Part-A UNIT-I ANALOG COMMUNICATION 1.Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics
DEPARTMENT OF CSE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE: CS6304 SUBJECT NAME: ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Part-A UNIT-I ANALOG COMMUNICATION 1.Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber
 Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic wave Ray Theory Light
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic wave Ray Theory Light
UNIT Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion?
 UNIT 3 1. Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion? Ans: The dispersion of the transmitted optical signal causes distortion for both digital and analog transmission along optical fibers.
UNIT 3 1. Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion? Ans: The dispersion of the transmitted optical signal causes distortion for both digital and analog transmission along optical fibers.
Lab 12 Microwave Optics.
 b Lab 12 Microwave Optics. CAUTION: The output power of the microwave transmitter is well below standard safety levels. Nevertheless, do not look directly into the microwave horn at close range when the
b Lab 12 Microwave Optics. CAUTION: The output power of the microwave transmitter is well below standard safety levels. Nevertheless, do not look directly into the microwave horn at close range when the
TOPIC 2 WAVEGUIDE AND COMPONENTS
 TOPIC 2 WAVEGUIDE AND COMPONENTS COURSE LEARNING OUTCOME (CLO) CLO1 Explain clearly the generation of microwave, the effects of microwave radiation and the propagation of electromagnetic in a waveguide
TOPIC 2 WAVEGUIDE AND COMPONENTS COURSE LEARNING OUTCOME (CLO) CLO1 Explain clearly the generation of microwave, the effects of microwave radiation and the propagation of electromagnetic in a waveguide
MAHAVEER INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY. Microwave and Digital Communications Lab. Department Of Electronics and Communication Engineering
 MAHAVEER INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Microwave and Digital Communications Lab Department Of Electronics and Communication Engineering MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB List of Experiments: 1.Reflex Klystron
MAHAVEER INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Microwave and Digital Communications Lab Department Of Electronics and Communication Engineering MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB List of Experiments: 1.Reflex Klystron
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
Transmission Media. Beulah A L/CSE. 2 July 2008 Transmission Media Beulah A. 1
 Transmission Media Beulah A L/CSE 2 July 2008 Transmission Media Beulah A. 1 Guided Transmission Media Magnetic Media A tape can hold 7 gigabytes. A box can hold about 1000 tapes. Assume a box can be delivered
Transmission Media Beulah A L/CSE 2 July 2008 Transmission Media Beulah A. 1 Guided Transmission Media Magnetic Media A tape can hold 7 gigabytes. A box can hold about 1000 tapes. Assume a box can be delivered
Chapter 3 Solution to Problems
 Chapter 3 Solution to Problems 1. The telemetry system of a geostationary communications satellite samples 100 sensors on the spacecraft in sequence. Each sample is transmitted to earth as an eight-bit
Chapter 3 Solution to Problems 1. The telemetry system of a geostationary communications satellite samples 100 sensors on the spacecraft in sequence. Each sample is transmitted to earth as an eight-bit
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Chapter 1 Introduction National Sun Yat-sen University Table of Contents Elements of a Digital Communication System Communication Channels and Their Wire-line
Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Chapter 1 Introduction National Sun Yat-sen University Table of Contents Elements of a Digital Communication System Communication Channels and Their Wire-line
In an unmagnetized piece of iron, the atoms are arranged in domains. In each domain the atoms are aligned, but the domains themselves are random.
 4/7 Properties of the Magnetic Force 1. Perpendicular to the field and velocity. 2. If the velocity and field are parallel, the force is zero. 3. Roughly (field and vel perp), the force is the product
4/7 Properties of the Magnetic Force 1. Perpendicular to the field and velocity. 2. If the velocity and field are parallel, the force is zero. 3. Roughly (field and vel perp), the force is the product
Optical fibre. Principle and applications
 Optical fibre Principle and applications Circa 2500 B.C. Earliest known glass Roman times-glass drawn into fibers Venice Decorative Flowers made of glass fibers 1609-Galileo uses optical telescope 1626-Snell
Optical fibre Principle and applications Circa 2500 B.C. Earliest known glass Roman times-glass drawn into fibers Venice Decorative Flowers made of glass fibers 1609-Galileo uses optical telescope 1626-Snell
RADAR CHAPTER 3 RADAR
 RADAR CHAPTER 3 RADAR RDF becomes Radar 1. As World War II approached, scientists and the military were keen to find a method of detecting aircraft outside the normal range of eyes and ears. They found
RADAR CHAPTER 3 RADAR RDF becomes Radar 1. As World War II approached, scientists and the military were keen to find a method of detecting aircraft outside the normal range of eyes and ears. They found
Optical systems have carrier frequencies of ~100 THz. This corresponds to wavelengths from µm.
 Introduction A communication system transmits information form one place to another. This could be from one building to another or across the ocean(s). Many systems use an EM carrier wave to transmit information.
Introduction A communication system transmits information form one place to another. This could be from one building to another or across the ocean(s). Many systems use an EM carrier wave to transmit information.
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL BANK Name : MICROWAVE ENGINEERING Code : A70442 Class : IV B. Tech I
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL BANK Name : MICROWAVE ENGINEERING Code : A70442 Class : IV B. Tech I
Optical Fiber Technology. Photonic Network By Dr. M H Zaidi
 Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
UNIT What is splicing? Explain about fusion splicing? Ans: Splicing
 UNIT 4 1. What is splicing? Explain about fusion splicing? Ans: Splicing A permanent joint formed between two individual optical fibers in the field is known as splicing. The fiber splicing is used to
UNIT 4 1. What is splicing? Explain about fusion splicing? Ans: Splicing A permanent joint formed between two individual optical fibers in the field is known as splicing. The fiber splicing is used to
VIVA-VOCE QUESTIONS MICROWAVE LAB
 VIVA-VOCE QUESTIONS MICROWAVE LAB DAWAR PARUL EXPERIMENT NO.-2 1) How are wavelength measured? 2) How do you measure wavelength in a compression wave? 3) What is the units of measure for wavelength? 4)
VIVA-VOCE QUESTIONS MICROWAVE LAB DAWAR PARUL EXPERIMENT NO.-2 1) How are wavelength measured? 2) How do you measure wavelength in a compression wave? 3) What is the units of measure for wavelength? 4)
EC Transmission Lines And Waveguides
 EC6503 - Transmission Lines And Waveguides UNIT I - TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines - General Solution, Physical Significance of the Equations 1. Define Characteristic
EC6503 - Transmission Lines And Waveguides UNIT I - TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines - General Solution, Physical Significance of the Equations 1. Define Characteristic
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications 7 th Edition. Chapter 4 Transmission Media
 William Stallings Data and Computer Communications 7 th Edition Chapter 4 Transmission Media Overview Guided - wire Unguided - wireless Characteristics and quality determined by medium and signal For guided,
William Stallings Data and Computer Communications 7 th Edition Chapter 4 Transmission Media Overview Guided - wire Unguided - wireless Characteristics and quality determined by medium and signal For guided,
SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF TCE COURSE PLAN
 SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF TCE COURSE PLAN Course Code : TE1018 Course Title : Microwave Radio And Optical Fiber
SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF TCE COURSE PLAN Course Code : TE1018 Course Title : Microwave Radio And Optical Fiber
(Refer Slide Time: 2:45)
 Millimeter Wave Technology. Professor Minal Kanti Mandal. Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Lecture-01. Introduction to Millimeter-Wave
Millimeter Wave Technology. Professor Minal Kanti Mandal. Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Lecture-01. Introduction to Millimeter-Wave
INTRODUCTION. Basic operating principle Tracking radars Techniques of target detection Examples of monopulse radar systems
 Tracking Radar H.P INTRODUCTION Basic operating principle Tracking radars Techniques of target detection Examples of monopulse radar systems 2 RADAR FUNCTIONS NORMAL RADAR FUNCTIONS 1. Range (from pulse
Tracking Radar H.P INTRODUCTION Basic operating principle Tracking radars Techniques of target detection Examples of monopulse radar systems 2 RADAR FUNCTIONS NORMAL RADAR FUNCTIONS 1. Range (from pulse
Microwave Optics. Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX. January 16, 2014
 Microwave Optics Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX January 16, 2014 1 Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Visible light has
Microwave Optics Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX January 16, 2014 1 Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Visible light has
Experiment-4 Study of the characteristics of the Klystron tube
 Experiment-4 Study of the characteristics of the Klystron tube OBJECTIVE To study the characteristics of the reflex Klystron tube and to determine the its electronic tuning range EQUIPMENTS Klystron power
Experiment-4 Study of the characteristics of the Klystron tube OBJECTIVE To study the characteristics of the reflex Klystron tube and to determine the its electronic tuning range EQUIPMENTS Klystron power
Optical behavior. Reading assignment. Topic 10
 Reading assignment Optical behavior Topic 10 Askeland and Phule, The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4 th Ed.,Ch. 0. Shackelford, Materials Science for Engineers, 6 th Ed., Ch. 16. Chung, Composite
Reading assignment Optical behavior Topic 10 Askeland and Phule, The Science and Engineering of Materials, 4 th Ed.,Ch. 0. Shackelford, Materials Science for Engineers, 6 th Ed., Ch. 16. Chung, Composite
Projects in microwave theory 2009
 Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2009 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
Electrical and information technology Projects in microwave theory 2009 Write a short report on the project that includes a short abstract, an introduction, a theory section, a section on the results and
21. (i) Briefly explain the evolution of fiber optic system (ii) Compare the configuration of different types of fibers. or 22. (b)(i) Derive modal eq
 Unit-1 Part-A FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai - 625 020. [An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution] DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND
Unit-1 Part-A FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai - 625 020. [An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution] DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND
Exercise 1-3. Radar Antennas EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION OF FUNDAMENTALS. Antenna types
 Exercise 1-3 Radar Antennas EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the role of the antenna in a radar system. You will also be familiar with the intrinsic characteristics
Exercise 1-3 Radar Antennas EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the role of the antenna in a radar system. You will also be familiar with the intrinsic characteristics
. From the above data, determine the network is symmetric or not.
 Velammal College of Engineering and Technology, Madurai Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Question Bank Subject Name: EC2353 Antennas And Wave Propagation Faculty: Mrs G VShirley
Velammal College of Engineering and Technology, Madurai Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Question Bank Subject Name: EC2353 Antennas And Wave Propagation Faculty: Mrs G VShirley
Experiment 19. Microwave Optics 1
 Experiment 19 Microwave Optics 1 1. Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Using a three centimeter microwave wavelength transforms the scale of the experiment. Microns
Experiment 19 Microwave Optics 1 1. Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Using a three centimeter microwave wavelength transforms the scale of the experiment. Microns
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber. Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab
 Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Travelling Wave, Broadband, and Frequency Independent Antennas. EE-4382/ Antenna Engineering
 Travelling Wave, Broadband, and Frequency Independent Antennas EE-4382/5306 - Antenna Engineering Outline Traveling Wave Antennas Introduction Traveling Wave Antennas: Long Wire, V Antenna, Rhombic Antenna
Travelling Wave, Broadband, and Frequency Independent Antennas EE-4382/5306 - Antenna Engineering Outline Traveling Wave Antennas Introduction Traveling Wave Antennas: Long Wire, V Antenna, Rhombic Antenna
Navy Electricity and Electronics Training Series
 NONRESIDENT TRAINING COURSE Navy Electricity and Electronics Training Series Module 11 Microwave Principles NAVEDTRA 14183 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
NONRESIDENT TRAINING COURSE Navy Electricity and Electronics Training Series Module 11 Microwave Principles NAVEDTRA 14183 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-II. Unit- I MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS
 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-II Unit- I MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS 1. Explain microwave power measurement. 2. Why we can not use ordinary diode and transistor in microwave detection and microwave amplification? 3.
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING-II Unit- I MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS 1. Explain microwave power measurement. 2. Why we can not use ordinary diode and transistor in microwave detection and microwave amplification? 3.
CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
 43 CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This work begins with design of reflectarrays with conventional patches as unit cells for operation at Ku Band in
43 CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This work begins with design of reflectarrays with conventional patches as unit cells for operation at Ku Band in
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNIACTION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNIACTION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Antennas and Wave Propagation (AWP) Course Code : A50418 Class :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNIACTION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : Antennas and Wave Propagation (AWP) Course Code : A50418 Class :
SYLLABUS Optical Fiber Communication
 SYLLABUS Optical Fiber Communication Subject Code : IA Marks : 25 No. of Lecture Hrs/Week : 04 Exam Hours : 03 Total no. of Lecture Hrs. : 52 Exam Marks : 100 UNIT - 1 PART - A OVERVIEW OF OPTICAL FIBER
SYLLABUS Optical Fiber Communication Subject Code : IA Marks : 25 No. of Lecture Hrs/Week : 04 Exam Hours : 03 Total no. of Lecture Hrs. : 52 Exam Marks : 100 UNIT - 1 PART - A OVERVIEW OF OPTICAL FIBER
MICROWAVE AND RADAR ENGINEERING (EE 322 F) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS. S.NO. NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT Page No.
 LIST OF EXPERIMENTS S.NO. NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT Page No. 1 To study wave guide components. 1-3 2 To study the characteristics of Gunn oscillator &Gun diode as 4-6 modulated source. 3 Study of wave guide
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS S.NO. NAME OF THE EXPERIMENT Page No. 1 To study wave guide components. 1-3 2 To study the characteristics of Gunn oscillator &Gun diode as 4-6 modulated source. 3 Study of wave guide
Chapter-1: Introduction
 Chapter-1: Introduction The purpose of a Communication System is to transport an information bearing signal from a source to a user destination via a communication channel. MODEL OF A COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
Chapter-1: Introduction The purpose of a Communication System is to transport an information bearing signal from a source to a user destination via a communication channel. MODEL OF A COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
Chapter 3 OPTICAL SOURCES AND DETECTORS
 Chapter 3 OPTICAL SOURCES AND DETECTORS 3. Optical sources and Detectors 3.1 Introduction: The success of light wave communications and optical fiber sensors is due to the result of two technological breakthroughs.
Chapter 3 OPTICAL SOURCES AND DETECTORS 3. Optical sources and Detectors 3.1 Introduction: The success of light wave communications and optical fiber sensors is due to the result of two technological breakthroughs.
Chapter 4: Practical Communication Systems. 18/09/2016 Nurul/DEE 3413/Practical Com System 1
 Chapter 4: Practical Communication Systems 18/09/2016 Nurul/DEE 3413/Practical Com System 1 Outline Fibre Optic Communication System Telephone System Radio Communication System Satellite Communication
Chapter 4: Practical Communication Systems 18/09/2016 Nurul/DEE 3413/Practical Com System 1 Outline Fibre Optic Communication System Telephone System Radio Communication System Satellite Communication
Basic concepts. Optical Sources (b) Optical Sources (a) Requirements for light sources (b) Requirements for light sources (a)
 Optical Sources (a) Optical Sources (b) The main light sources used with fibre optic systems are: Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) Semiconductor lasers (diode lasers) Fibre laser and other compact solid-state
Optical Sources (a) Optical Sources (b) The main light sources used with fibre optic systems are: Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) Semiconductor lasers (diode lasers) Fibre laser and other compact solid-state
Final Examination. 22 April 2013, 9:30 12:00. Examiner: Prof. Sean V. Hum. All non-programmable electronic calculators are allowed.
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 422H1S RADIO AND MICROWAVE WIRELESS SYSTEMS Final Examination
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 422H1S RADIO AND MICROWAVE WIRELESS SYSTEMS Final Examination
YOUNGS MODULUS BY UNIFORM & NON UNIFORM BENDING OF A BEAM
 YOUNGS MODULUS BY UNIFORM & NON UNIFORM BENDING OF A BEAM RECTANGULAR BEAM PLACED OVER TWO KNIFE EDGES & DISTANCE BETWEEN KNIFE EDGES IS KEPT CONSTANT AS l= 50cm UNIFORM WEIGHT HANGERS ARE SUSPENDED WITH
YOUNGS MODULUS BY UNIFORM & NON UNIFORM BENDING OF A BEAM RECTANGULAR BEAM PLACED OVER TWO KNIFE EDGES & DISTANCE BETWEEN KNIFE EDGES IS KEPT CONSTANT AS l= 50cm UNIFORM WEIGHT HANGERS ARE SUSPENDED WITH
Exercise 1-4. The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION OF FUNDAMENTALS
 Exercise 1-4 The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the different parameters in the radar equation, and with the interaction between these
Exercise 1-4 The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the different parameters in the radar equation, and with the interaction between these
Faraday Rotators and Isolators
 Faraday Rotators and I. Introduction The negative effects of optical feedback on laser oscillators and laser diodes have long been known. Problems include frequency instability, relaxation oscillations,
Faraday Rotators and I. Introduction The negative effects of optical feedback on laser oscillators and laser diodes have long been known. Problems include frequency instability, relaxation oscillations,
Fiber Optics IV - Testing
 PDHonline Course E311 (3 PDH) Fiber Optics IV - Testing Instructor: Lee Layton, PE 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org
PDHonline Course E311 (3 PDH) Fiber Optics IV - Testing Instructor: Lee Layton, PE 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org
Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks))
 Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks)) Lesson 3... Transmission Media, Part 1 Abstract The successful transmission of data depends principally on two factors: the quality of the signal being transmitted
Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks)) Lesson 3... Transmission Media, Part 1 Abstract The successful transmission of data depends principally on two factors: the quality of the signal being transmitted
ELEC4604. RF Electronics. Experiment 2
 ELEC4604 RF Electronics Experiment MICROWAVE MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES 1. Introduction and Objectives In designing the RF front end of a microwave communication system it is important to appreciate that the
ELEC4604 RF Electronics Experiment MICROWAVE MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES 1. Introduction and Objectives In designing the RF front end of a microwave communication system it is important to appreciate that the
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 4 Transmission Media
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 4 Transmission Media Ninth Edition by William Stallings Data and Computer Communications, Ninth Edition by William Stallings, (c) Pearson Education - Prentice Hall,
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 4 Transmission Media Ninth Edition by William Stallings Data and Computer Communications, Ninth Edition by William Stallings, (c) Pearson Education - Prentice Hall,
LESSON PLAN. LESSON PLAN DURATION : - 15 weeks (from JULY 2018 to NOVEMBER 2018)
 LESSON PLAN NAME OF THE FACULTY DISCIPLINE SEMESTER SUBJECT : - HIMANSHU YADAV : - ECE : - FIFTH : - MICROWAVE ENGG LESSON PLAN DURATION : - 15 weeks (from JULY 2018 to NOVEMBER 2018) WORK LOAD (LECTURE/PRACTICAL)
LESSON PLAN NAME OF THE FACULTY DISCIPLINE SEMESTER SUBJECT : - HIMANSHU YADAV : - ECE : - FIFTH : - MICROWAVE ENGG LESSON PLAN DURATION : - 15 weeks (from JULY 2018 to NOVEMBER 2018) WORK LOAD (LECTURE/PRACTICAL)
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
UNIT-1. Basic signal processing operations in digital communication
 UNIT-1 Lecture-1 Basic signal processing operations in digital communication The three basic elements of every communication systems are Transmitter, Receiver and Channel. The Overall purpose of this system
UNIT-1 Lecture-1 Basic signal processing operations in digital communication The three basic elements of every communication systems are Transmitter, Receiver and Channel. The Overall purpose of this system
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: Signature:
 Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
CHAPTER - 6 PIN DIODE CONTROL CIRCUITS FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER - 6 PIN DIODE CONTROL CIRCUITS FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS 2 NOTES 3 INTRODUCTION PIN DIODE CONTROL CIRCUITS FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS Chapter 6 discusses PIN Control Circuits
CHAPTER - 6 PIN DIODE CONTROL CIRCUITS FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS 2 NOTES 3 INTRODUCTION PIN DIODE CONTROL CIRCUITS FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS Chapter 6 discusses PIN Control Circuits
