IE1206 Embedded Electronics
|
|
|
- Myles Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 E06 Embedded Electronics e e3 e4 e Ex Ex P-block Documentation, Seriecom, Pulse sensor,,, P, series and parallel K AB Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of program task Kirchhoffs laws Node analysis Two ports AD e5 Ex3 K AB Two port, AD, omparator/schmitt e6 e8 Ex6 e3 Ex4 Ex5 e0 e7 e9 e e Ex7 presentation wr. exam K3 AB3 Transients PWM Phasor PWM P AP/ND-sensor K4 AB4 Step-up, -oscillator -osc, D-motor, P PWM P-filter Trafo Guest lecturer presentation of program task Trafo, Ethernet contact
2 omplex phasors, -method X X omplex OHM s law for and. omplex OHM s law for Z. ] e[ ] m[ arctan arg( Z Z Z Z Z ϕ f π
3 Voltage divider, Transfer function Simple filters are often designed as a voltage dividers.a filter transfer function, H( or H(f, is the ratio between output voltage and input voltage. This ratio we get directly from the voltage divider formula! Z H ( Z Z Z Z Z
4 P HP BP BS P lowpass HP highpass BP bandpass BS bandstop BP and BS filters can be seen as different combination of P and HP filters.
5
6 Transfer function (4. a Set up an expression of f(,,,. b Set up the transfer function / the amount function and the phase function. c What filter type is the transfer function, P HP BP BS? d What break frequency has the transfer function?
7 Transfer function (4. Answer a
8 Transfer function (4.
9 Transfer function (4. arctan arg arctan 90 arg ( 4 Answer b /
10 Transfer function (4. Answer c P HP BP BS? { } 0 { } HP
11 Transfer function (4. f G π Answer d Break frequency? At the break frequency the numerator real part and imaginary part are equal.
12
13 Phasor - vector π f X X Z
14 Phasor chart for voltage divider (.8 The figure shows a voltage divider. t is connected to an A voltage source and it s output voltage is. At a some frequency the reactance of the inductor is X. Draw the phasor chart of this circuit with, and at this frequency. se as reference phase ( horizontal.
15 Phasor chart for voltage divider (.8 3
16 -calculation of the divided voltage 0 5 ( 6 ( ( 6 ( 4 X
17 Here are some more filters if time permits!
18 Filter (4.7 The figure shows a simple filter with two and one. a Derive the filter complex transfer function /. b At what angle frequency X will the amount function be Give an expresson for this frequency X with. / / c What value has the amount of the transfer function at very low frequencys, 0? What value has the phase function at very low frequencys? d What value has the amount of the transfer function at very high frequencys,? What value has the phase function at very high frequencys?? arg?? arg? 0?, (? d c b a X X
19 Filter (4.7 a ( 4( ( ( ( b X 0 arg c 0 arg 0,5 0 0 d
20
21 Filter if time (4.8 The figure shows a simple filter with and. a Derive the filter transfer function /. b At what angular frequency x will the denominator be purely imaginary? Give an expression of this frequency x with and. c What value has the amount function at this angular frequency, x? d What value has the phase function at this angular frequency, x? e Give an expression of the transfer function between / ( Note! You already have the transferfunction / from a? ( (? ( ( arg? ( (?,, (? ( ( e d c b a X X X X X
22 Filter if time (4.8 E b a 0 ( ( 90 arg arg 0 ( d c e (?
23
24 Voltage ratio N : N N dφ dt N dφ dt N N
25 urrent ratio 0 0 0, ( N N P P P N : N
26
27 Two values are missing? (5. For a transformer the following data was given: Primary Secondary N N V? 00? 9 A alculate the two values that are missing. and.
28 Two values are missing! (5. For a transformer the following data was given: Primary Secondary N N V 3A? 00 75V? 9 A alculate the two values that are missing. and. n N /N 600/00 3 n n
29 Two values are missing? (5. For a transformer the following data was given:. Primary Secondary N N? 30 V A 50? A alculate the two values that are missing. N and.
30 Two values are missing! (5. For a transformer the following data was given:. Primary Secondary N N? 30 V A 50 38V? A 900 alculate the two values that are missing. N and. n / / 6 N N n /n 30/6 38,3 V
31 Two values are missing? (5.3 For a transformer the following data was given: Primary Secondary N N V?? 7 V 9 A alculate the two values that are missing. and N.
32 Two values are missing! (5.3 For a transformer the following data was given: Primary Secondary N N V?? 7 V 9 A 5A 339 alculate the two values that are missing. and N. N 5, 77 N N N N N , 08 A
33
34 nductive coupling The coupling factor indicates how much of its flow a coil has in common with another coil? An ideal transformer has the coupling factor k (00% ± M is called mutal inductance k M Series connected coils Anti series connected coils TOT M TOT M Parallel connected coils Anti parallel connected coils M TOT M M TOT M
35 Mutal inductance (5.8 Three inductors, 6, 3 5 [H] are series connected. When inductors are close to each other the placement on the circuit board can be important. n the figure to the left a will inductors to have a portion of the magnetic lines in common. They then have the mutual inductances M 3, M 3, M 3 [H]. n the figure to the right b the inductors are mounted three dimensional so that there are no shared power magnetic lines. a alculate the total inductance for the arrangement in figure a. TOT? b alculate the total inductance for the arrangement in figure b. TOT?
36 Mutal inductance (5.8 [ ] [ ] H b H a M M M M M M TOT TOT
37
IE1206 Embedded Electronics
 IE06 Embedded Electronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I,, R, P, serial and parallel KC LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs laws Node
IE06 Embedded Electronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I,, R, P, serial and parallel KC LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs laws Node
IE1206 Embedded Electronics
 IE06 Embedded Electronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex PI-block Documentation, Serial com Pulse sensors I,,, P, series and parallel K LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs laws Node
IE06 Embedded Electronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex PI-block Documentation, Serial com Pulse sensors I,,, P, series and parallel K LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs laws Node
IE1206 Embedded Electronics
 E06 Embedded Electronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex PC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors,, R, P, serial and parallel KC LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs laws ode analysis
E06 Embedded Electronics Le Le3 Le4 Le Ex Ex PC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors,, R, P, serial and parallel KC LAB Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs laws ode analysis
IE1206 Embedded Electronics
 IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le1 Le3 Le4 Le2 Ex1 Ex2 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, serial and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulsesensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs
IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le1 Le3 Le4 Le2 Ex1 Ex2 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, serial and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulsesensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Currents. March 23, 2014 Chapter 30 1
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Currents March 23, 2014 Chapter 30 1 Driven LC Circuit! The voltage V can be thought of as the projection of the vertical axis of the phasor V m representing the time-varying
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Currents March 23, 2014 Chapter 30 1 Driven LC Circuit! The voltage V can be thought of as the projection of the vertical axis of the phasor V m representing the time-varying
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits 30-7 AC Circuits with AC Source Resistors, capacitors, and inductors have different phase relationships between current and voltage
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits 30-7 AC Circuits with AC Source Resistors, capacitors, and inductors have different phase relationships between current and voltage
Chapter 6: Alternating Current
 hapter 6: Alternating urrent 6. Alternating urrent.o 6.. Define alternating current (A) An alternating current (A) is the electrical current which varies periodically with time in direction and magnitude.
hapter 6: Alternating urrent 6. Alternating urrent.o 6.. Define alternating current (A) An alternating current (A) is the electrical current which varies periodically with time in direction and magnitude.
Alternating current circuits- Series RLC circuits
 FISI30 Física Universitaria II Professor J.. ersosimo hapter 8 Alternating current circuits- Series circuits 8- Introduction A loop rotated in a magnetic field produces a sinusoidal voltage and current.
FISI30 Física Universitaria II Professor J.. ersosimo hapter 8 Alternating current circuits- Series circuits 8- Introduction A loop rotated in a magnetic field produces a sinusoidal voltage and current.
An induced emf is the negative of a changing magnetic field. Similarly, a self-induced emf would be found by
 This is a study guide for Exam 4. You are expected to understand and be able to answer mathematical questions on the following topics. Chapter 32 Self-Induction and Induction While a battery creates an
This is a study guide for Exam 4. You are expected to understand and be able to answer mathematical questions on the following topics. Chapter 32 Self-Induction and Induction While a battery creates an
Chapter 33. Alternating Current Circuits
 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits Alternating Current Circuits Electrical appliances in the house use alternating current (AC) circuits. If an AC source applies an alternating voltage to a series
Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits Alternating Current Circuits Electrical appliances in the house use alternating current (AC) circuits. If an AC source applies an alternating voltage to a series
Exam 3 Review Session
 Exam 3 Review Session I will hold a review for Exam 3 which covers Chapters 27, 28, 29 and 30, on Wednesday November 7 th at 7:15pm in MPHY 205. Exam 3 will be given in class on Thursday, November 8 th.
Exam 3 Review Session I will hold a review for Exam 3 which covers Chapters 27, 28, 29 and 30, on Wednesday November 7 th at 7:15pm in MPHY 205. Exam 3 will be given in class on Thursday, November 8 th.
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 2 = 1 LC. Review ( ) Review (2) Review (3) e! Rt. cos "t + # ( ) q = q max. Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 30 U E
 Review hysics for Scientists & Engineers Spring Semester 005 Lecture 30! If we have a single loop RLC circuit, the charge in the circuit as a function of time is given by! Where q = q max e! Rt L cos "t
Review hysics for Scientists & Engineers Spring Semester 005 Lecture 30! If we have a single loop RLC circuit, the charge in the circuit as a function of time is given by! Where q = q max e! Rt L cos "t
Look over Chapter 31 sections 1-4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11 Examples 1-8. Look over Chapter 21 sections Examples PHYS 2212 PHYS 1112
 PHYS 2212 Look over Chapter 31 sections 1-4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11 Examples 1-8 PHYS 1112 Look over Chapter 21 sections 11-14 Examples 16-18 Good Things To Know 1) How AC generators work. 2) How to find the
PHYS 2212 Look over Chapter 31 sections 1-4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11 Examples 1-8 PHYS 1112 Look over Chapter 21 sections 11-14 Examples 16-18 Good Things To Know 1) How AC generators work. 2) How to find the
CHAPTER 9. Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 CHAPTER 9 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 9.1 The Sinusoidal Source A sinusoidal voltage source (independent or dependent) produces a voltage that varies sinusoidally with time. A sinusoidal current source
CHAPTER 9 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 9.1 The Sinusoidal Source A sinusoidal voltage source (independent or dependent) produces a voltage that varies sinusoidally with time. A sinusoidal current source
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCE. BEng (HONS)/MEng BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING. BEng (HONS) MEDICAL ENGINEERING
 LH29 SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCE BEng (HONS)/MEng BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING BEng (HONS) MEDICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 MODULE NO: BME4004 Date: Wednesday 18 May 2016 Time:
LH29 SCHOOL OF SPORT AND BIOMEDICAL SCIENCE BEng (HONS)/MEng BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING BEng (HONS) MEDICAL ENGINEERING SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 MODULE NO: BME4004 Date: Wednesday 18 May 2016 Time:
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 19 Chapter 29 sec. 1,2,5 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Series and Parallel R and L Resistors and inductors in series: R series = R 1 + R 2 L series = L
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 19 Chapter 29 sec. 1,2,5 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Series and Parallel R and L Resistors and inductors in series: R series = R 1 + R 2 L series = L
Chapter 31 Alternating Current
 Chapter 31 Alternating Current In this chapter we will learn how resistors, inductors, and capacitors behave in circuits with sinusoidally vary voltages and currents. We will define the relationship between
Chapter 31 Alternating Current In this chapter we will learn how resistors, inductors, and capacitors behave in circuits with sinusoidally vary voltages and currents. We will define the relationship between
LECTURE 19. Alternating Current Generators (DEMO)
 ETURE 9 A Generators A ircuits Start by considering simple circuits with one element (R,, or ) in addition to the driving emf. It will lead to Oscillations and Driven R circuits Alternating urrent Generators
ETURE 9 A Generators A ircuits Start by considering simple circuits with one element (R,, or ) in addition to the driving emf. It will lead to Oscillations and Driven R circuits Alternating urrent Generators
Alternating Current. Slide 1 / 69. Slide 2 / 69. Slide 3 / 69. Topics to be covered. Sources of Alternating EMF. Sources of alternating EMF
 Slide 1 / 69 lternating urrent Sources of alternating EMF Transformers ircuits and Impedance Topics to be covered Slide 2 / 69 LR Series ircuits Resonance in ircuit Oscillations Sources of lternating EMF
Slide 1 / 69 lternating urrent Sources of alternating EMF Transformers ircuits and Impedance Topics to be covered Slide 2 / 69 LR Series ircuits Resonance in ircuit Oscillations Sources of lternating EMF
Alternating Current. Slide 2 / 69. Slide 1 / 69. Slide 3 / 69. Slide 4 / 69. Slide 6 / 69. Slide 5 / 69. Topics to be covered
 Slide 1 / 69 lternating urrent Sources of alternating EMF ircuits and Impedance Slide 2 / 69 Topics to be covered LR Series ircuits Resonance in ircuit Oscillations Slide 3 / 69 Sources of lternating EMF
Slide 1 / 69 lternating urrent Sources of alternating EMF ircuits and Impedance Slide 2 / 69 Topics to be covered LR Series ircuits Resonance in ircuit Oscillations Slide 3 / 69 Sources of lternating EMF
Chapter 31. Alternating Current. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow
 Chapter 31 Alternating Current PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 31 Looking forward at How
Chapter 31 Alternating Current PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 31 Looking forward at How
ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL ENGINEERING SCIENCE C103 TUTORIAL 18 ALTERNATING CURRENT
 ENGINEERING OUNIL ERTIFIATE LEVEL ENGINEERING SIENE 03 TUTORIAL 8 ALTERNATING URRENT On completion of this tutorial you should be able to do the following. Explain alternating current. Explain Root Mean
ENGINEERING OUNIL ERTIFIATE LEVEL ENGINEERING SIENE 03 TUTORIAL 8 ALTERNATING URRENT On completion of this tutorial you should be able to do the following. Explain alternating current. Explain Root Mean
Coil in the AC circuit
 Coil in the AC circuit LEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, parallel connection, series connection, a. c. impedance, phase displacement, vector diagram Principle The impedance and phase displacement
Coil in the AC circuit LEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, parallel connection, series connection, a. c. impedance, phase displacement, vector diagram Principle The impedance and phase displacement
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment)
 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment) 1. In an A.C. circuit A ; the current leads the voltage by 30 0 and in circuit B, the current lags behind the voltage by 30 0. What is the
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment) 1. In an A.C. circuit A ; the current leads the voltage by 30 0 and in circuit B, the current lags behind the voltage by 30 0. What is the
PHYS 1444 Section 501 Lecture #20
 PHYS 1444 Section 501 Lecture #0 Monday, Apr. 17, 006 Transformer Generalized Faraday s Law Inductance Mutual Inductance Self Inductance Inductor Energy Stored in the Magnetic Field 1 Announcements Quiz
PHYS 1444 Section 501 Lecture #0 Monday, Apr. 17, 006 Transformer Generalized Faraday s Law Inductance Mutual Inductance Self Inductance Inductor Energy Stored in the Magnetic Field 1 Announcements Quiz
Worksheet for Exploration 31.1: Amplitude, Frequency and Phase Shift
 Worksheet for Exploration 31.1: Amplitude, Frequency and Phase Shift We characterize the voltage (or current) in AC circuits in terms of the amplitude, frequency (period) and phase. The sinusoidal voltage
Worksheet for Exploration 31.1: Amplitude, Frequency and Phase Shift We characterize the voltage (or current) in AC circuits in terms of the amplitude, frequency (period) and phase. The sinusoidal voltage
Chapter 11. Alternating Current
 Unit-2 ECE131 BEEE Chapter 11 Alternating Current Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe how an AC voltage is produced with an AC generator (alternator) Define alternation,
Unit-2 ECE131 BEEE Chapter 11 Alternating Current Objectives After completing this chapter, you will be able to: Describe how an AC voltage is produced with an AC generator (alternator) Define alternation,
EE42: Running Checklist of Electronics Terms Dick White
 EE42: Running Checklist of Electronics Terms 14.02.05 Dick White Terms are listed roughly in order of their introduction. Most definitions can be found in your text. Terms2 TERM Charge, current, voltage,
EE42: Running Checklist of Electronics Terms 14.02.05 Dick White Terms are listed roughly in order of their introduction. Most definitions can be found in your text. Terms2 TERM Charge, current, voltage,
Goals. Introduction. To understand the use of root mean square (rms) voltages and currents.
 Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
Goals. Introduction. To understand the use of root mean square (rms) voltages and currents.
 Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS ETC104 AC CIRCUITS. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Ronald S. Krive. Revised Date: October 2007 by Dennis Eimer
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS ETC104 AC CIRCUITS 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Ronald S. Krive Revised Date: October 2007 by Dennis Eimer Division of Technology Dr. John Keck, Dean Ms. Brenda Russell,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS ETC104 AC CIRCUITS 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Ronald S. Krive Revised Date: October 2007 by Dennis Eimer Division of Technology Dr. John Keck, Dean Ms. Brenda Russell,
ECE215 Lecture 7 Date:
 Lecture 7 Date: 29.08.2016 AC Circuits: Impedance and Admittance, Kirchoff s Laws, Phase Shifter, AC bridge Impedance and Admittance we know: we express Ohm s law in phasor form: where Z is a frequency-dependent
Lecture 7 Date: 29.08.2016 AC Circuits: Impedance and Admittance, Kirchoff s Laws, Phase Shifter, AC bridge Impedance and Admittance we know: we express Ohm s law in phasor form: where Z is a frequency-dependent
CHAPTER 6 Frequency Response, Bode. Plots, and Resonance
 CHAPTER 6 Frequency Response, Bode Plots, and Resonance CHAPTER 6 Frequency Response, Bode Plots, and Resonance 1. State the fundamental concepts of Fourier analysis. 2. Determine the output of a filter
CHAPTER 6 Frequency Response, Bode Plots, and Resonance CHAPTER 6 Frequency Response, Bode Plots, and Resonance 1. State the fundamental concepts of Fourier analysis. 2. Determine the output of a filter
Exercise 9: inductor-resistor-capacitor (LRC) circuits
 Exercise 9: inductor-resistor-capacitor (LRC) circuits Purpose: to study the relationship of the phase and resonance on capacitor and inductor reactance in a circuit driven by an AC signal. Introduction
Exercise 9: inductor-resistor-capacitor (LRC) circuits Purpose: to study the relationship of the phase and resonance on capacitor and inductor reactance in a circuit driven by an AC signal. Introduction
Circuit Systems with MATLAB and PSpice
 Circuit Systems with MATLAB and PSpice Won Y. Yang and Seung C. Lee Chung-Ang University, South Korea BICENTENNIAL 9 I CE NTE NNIAL John Wiley & Sons(Asia) Pte Ltd Contents Preface Limits of Liability
Circuit Systems with MATLAB and PSpice Won Y. Yang and Seung C. Lee Chung-Ang University, South Korea BICENTENNIAL 9 I CE NTE NNIAL John Wiley & Sons(Asia) Pte Ltd Contents Preface Limits of Liability
Chapter 6: Alternating Current. An alternating current is an current that reverses its direction at regular intervals.
 Chapter 6: Alternating Current An alternating current is an current that reverses its direction at regular intervals. Overview Alternating Current Phasor Diagram Sinusoidal Waveform A.C. Through a Resistor
Chapter 6: Alternating Current An alternating current is an current that reverses its direction at regular intervals. Overview Alternating Current Phasor Diagram Sinusoidal Waveform A.C. Through a Resistor
PHYS 1441 Section 001 Lecture #22 Wednesday, Nov. 29, 2017
 PHYS 1441 Section 001 Lecture #22 Chapter 29:EM Induction & Faraday s Law Transformer Electric Field Due to Changing Magnetic Flux Chapter 30: Inductance Mutual and Self Inductance Energy Stored in Magnetic
PHYS 1441 Section 001 Lecture #22 Chapter 29:EM Induction & Faraday s Law Transformer Electric Field Due to Changing Magnetic Flux Chapter 30: Inductance Mutual and Self Inductance Energy Stored in Magnetic
Lecture # 3 Circuit Configurations
 CPEN 206 Linear Circuits Lecture # 3 Circuit Configurations Dr. Godfrey A. Mills Email: gmills@ug.edu.gh Phone: 0269073163 February 15, 2016 Course TA David S. Tamakloe CPEN 206 Lecture 3 2015_2016 1 Circuit
CPEN 206 Linear Circuits Lecture # 3 Circuit Configurations Dr. Godfrey A. Mills Email: gmills@ug.edu.gh Phone: 0269073163 February 15, 2016 Course TA David S. Tamakloe CPEN 206 Lecture 3 2015_2016 1 Circuit
not to be republished NCERT ALTERNATING CURRENT Chapter Seven MCQ 1
 hapter Seven ALTERNATING URRENT MQ 1 7.1 If the rms current in a 50 Hz ac circuit is 5 A, the value of the current 1/300 seconds after its value becomes zero is (a) 5 2 A (b) 5 3/2 A (c) 5/6 A (d) 5/ 2
hapter Seven ALTERNATING URRENT MQ 1 7.1 If the rms current in a 50 Hz ac circuit is 5 A, the value of the current 1/300 seconds after its value becomes zero is (a) 5 2 A (b) 5 3/2 A (c) 5/6 A (d) 5/ 2
AC Circuits. "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert ( )
 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
Electric Circuits II Magnetically Coupled Circuits. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Circuits II Magnetically Coupled Circuits Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Mutual Inductance 2 Dot Convention 3 Analyze Circuits Involving Mutual Inductance 4 Energy in a Coupled Circuit
Electric Circuits II Magnetically Coupled Circuits Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Mutual Inductance 2 Dot Convention 3 Analyze Circuits Involving Mutual Inductance 4 Energy in a Coupled Circuit
Electrical Circuits (2)
 Electrical Circuits (2) Lecture 1 Intro. & Review Dr.Eng. Basem ElHalawany Course Info Title Electric Circuits (2) Lecturer: Lecturer Webpage: Teaching Assistant (TA) Course Webpage References Software
Electrical Circuits (2) Lecture 1 Intro. & Review Dr.Eng. Basem ElHalawany Course Info Title Electric Circuits (2) Lecturer: Lecturer Webpage: Teaching Assistant (TA) Course Webpage References Software
Alternating Current. Asist. Prof. Dr. Aytaç Gören Asist. Prof. Dr. Levent Çetin
 Asist. Prof. Dr. Aytaç Gören Asist. Prof. Dr. Levent Çetin 30.10.2012 Contents Alternating Voltage Phase Phasor Representation of AC Behaviors of Basic Circuit Components under AC Resistance, Reactance
Asist. Prof. Dr. Aytaç Gören Asist. Prof. Dr. Levent Çetin 30.10.2012 Contents Alternating Voltage Phase Phasor Representation of AC Behaviors of Basic Circuit Components under AC Resistance, Reactance
Electronics and Instrumentation ENGR-4300 Spring 2004 Section Experiment 5 Introduction to AC Steady State
 Experiment 5 Introduction to C Steady State Purpose: This experiment addresses combinations of resistors, capacitors and inductors driven by sinusoidal voltage sources. In addition to the usual simulation
Experiment 5 Introduction to C Steady State Purpose: This experiment addresses combinations of resistors, capacitors and inductors driven by sinusoidal voltage sources. In addition to the usual simulation
EE202 Circuit Theory II , Spring
 EE202 Circuit Theory II 2018-2019, Spring I. Introduction & Review of Circuit Theory I (3 Hrs.) Introduction II. Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis (Chapter 9 of Nilsson - 9 Hrs.) (by Y.Kalkan) The Sinusoidal
EE202 Circuit Theory II 2018-2019, Spring I. Introduction & Review of Circuit Theory I (3 Hrs.) Introduction II. Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis (Chapter 9 of Nilsson - 9 Hrs.) (by Y.Kalkan) The Sinusoidal
ωc ωc sin(wt 90o ) (for a capacitance) (4)
 Physics'241'Signal'Processing:'Lab'3' Sinusoidal esponse of, L ircuits In the previous lab, we studied the behavior of series combinations of and L circuits with input square and triangular waveforms.
Physics'241'Signal'Processing:'Lab'3' Sinusoidal esponse of, L ircuits In the previous lab, we studied the behavior of series combinations of and L circuits with input square and triangular waveforms.
Chapter 8. Chapter 9. Chapter 6. Chapter 10. Chapter 11. Chapter 7
 5.5 Series and Parallel Combinations of 246 Complex Impedances 5.6 Steady-State AC Node-Voltage 247 Analysis 5.7 AC Power Calculations 256 5.8 Using Power Triangles 258 5.9 Power-Factor Correction 261
5.5 Series and Parallel Combinations of 246 Complex Impedances 5.6 Steady-State AC Node-Voltage 247 Analysis 5.7 AC Power Calculations 256 5.8 Using Power Triangles 258 5.9 Power-Factor Correction 261
Lecture XII: Ideal filters
 BME 171: Signals and Systems Duke University October 29, 2008 This lecture Plan for the lecture: 1 LTI systems with sinusoidal inputs 2 Analog filtering frequency-domain description: passband, stopband
BME 171: Signals and Systems Duke University October 29, 2008 This lecture Plan for the lecture: 1 LTI systems with sinusoidal inputs 2 Analog filtering frequency-domain description: passband, stopband
Lecture Outline Chapter 24. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 24 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 24 Alternating-Current Circuits Units of Chapter 24 Alternating Voltages and Currents Capacitors in AC Circuits RC Circuits Inductors
Lecture Outline Chapter 24 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 24 Alternating-Current Circuits Units of Chapter 24 Alternating Voltages and Currents Capacitors in AC Circuits RC Circuits Inductors
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems INDUCTIVE SENSORS (Chapter 3.4, 7.3) 3 Inductive sensors 4 Inductive
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems INDUCTIVE SENSORS (Chapter 3.4, 7.3) 3 Inductive sensors 4 Inductive
Physics 132 Quiz # 23
 Name (please (please print) print) Physics 132 Quiz # 23 I. I. The The current in in an an ac ac circuit is is represented by by a phasor.the value of of the the current at at some time time t t is is
Name (please (please print) print) Physics 132 Quiz # 23 I. I. The The current in in an an ac ac circuit is is represented by by a phasor.the value of of the the current at at some time time t t is is
1. If the flux associated with a coil varies at the rate of 1 weber/min,the induced emf is
 1. f the flux associated with a coil varies at the rate of 1 weber/min,the induced emf is 1 1. 1V 2. V 60 3. 60V 4. Zero 2. Lenz s law is the consequence of the law of conservation of 1. Charge 2. Mass
1. f the flux associated with a coil varies at the rate of 1 weber/min,the induced emf is 1 1. 1V 2. V 60 3. 60V 4. Zero 2. Lenz s law is the consequence of the law of conservation of 1. Charge 2. Mass
Chapter 13 Magnetically Coupled Circuits. Chapter Objectives:
 Chapter 13 Magnetically Coupled Circuits Chapter Objectives: Understand magnetically coupled circuits. Learn the concept of mutual inductance. Be able to determine energy in a coupled circuit. Learn how
Chapter 13 Magnetically Coupled Circuits Chapter Objectives: Understand magnetically coupled circuits. Learn the concept of mutual inductance. Be able to determine energy in a coupled circuit. Learn how
Two-Port Networks and Filters
 Two-Port Networks and Filters Filters By combining resistors capacitors and inductors in special ways you can design networks that are capable of passing certain frequencies of signals while rejecting
Two-Port Networks and Filters Filters By combining resistors capacitors and inductors in special ways you can design networks that are capable of passing certain frequencies of signals while rejecting
Experiment 9: AC circuits
 Experiment 9: AC circuits Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Introduction Last week (RC circuit): This week:
Experiment 9: AC circuits Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Introduction Last week (RC circuit): This week:
I(A) FIGURE 1 - Current vs. Time graph
 ab 7 A ircuits What You Need To Know: The Physics All of the circuit labs you ve been dealing with in this lab course have been using direct current or D. D implies that the current has a constant value
ab 7 A ircuits What You Need To Know: The Physics All of the circuit labs you ve been dealing with in this lab course have been using direct current or D. D implies that the current has a constant value
Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits
 Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits Aim: To obtain the characteristics of series and parallel resonant circuits. Apparatus required: Decade resistance box, Decade inductance box, Decade capacitance box
Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits Aim: To obtain the characteristics of series and parallel resonant circuits. Apparatus required: Decade resistance box, Decade inductance box, Decade capacitance box
Chapter 24. Alternating Current Circuits
 Chapter 24 Alternating Current Circuits Objective of Lecture Generators and Motors Inductance RL Circuits (resistance and inductance) Transformers AC REMINDER: WORK ON THE EXAMPLES Read physics in perspective
Chapter 24 Alternating Current Circuits Objective of Lecture Generators and Motors Inductance RL Circuits (resistance and inductance) Transformers AC REMINDER: WORK ON THE EXAMPLES Read physics in perspective
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
 CSEE 4620 Homework 3 Fall 2018 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 1. THE PRIMARY MAGNET Magnetic resonance imaging requires a very strong static magnetic field to align the nuclei. Modern MRI scanners require
CSEE 4620 Homework 3 Fall 2018 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 1. THE PRIMARY MAGNET Magnetic resonance imaging requires a very strong static magnetic field to align the nuclei. Modern MRI scanners require
PHYSICS WORKSHEET CLASS : XII. Topic: Alternating current
 PHYSICS WORKSHEET CLASS : XII Topic: Alternating current 1. What is mean by root mean square value of alternating current? 2. Distinguish between the terms effective value and peak value of an alternating
PHYSICS WORKSHEET CLASS : XII Topic: Alternating current 1. What is mean by root mean square value of alternating current? 2. Distinguish between the terms effective value and peak value of an alternating
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 11 Electricity and Magnetism AC circuits and EM waves Resonance in a Series RLC circuit Transformers Maxwell, Hertz and EM waves Electromagnetic Waves 6/18/2007 http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 11 Electricity and Magnetism AC circuits and EM waves Resonance in a Series RLC circuit Transformers Maxwell, Hertz and EM waves Electromagnetic Waves 6/18/2007 http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/2140website/main.htm
Physics Jonathan Dowling. Lecture 35: MON 16 NOV Electrical Oscillations, LC Circuits, Alternating Current II
 hysics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 35: MON 16 NOV Electrical Oscillations, LC Circuits, Alternating Current II Damped LCR Oscillator Ideal LC circuit without resistance: oscillations go on forever; ω
hysics 2113 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 35: MON 16 NOV Electrical Oscillations, LC Circuits, Alternating Current II Damped LCR Oscillator Ideal LC circuit without resistance: oscillations go on forever; ω
Review: Lecture 9. Instantaneous and Average Power. Effective or RMS Value. Apparent Power and Power Factor. Complex Power. Conservation of AC Power
 Review: Lecture 9 Instantaneous and Average Power p( t) VmI m cos ( v i ) VmI m cos ( t v i ) Maximum Average Power Transfer Z L R L jx Effective or RMS Value I rms I m L R P * TH Apparent Power and Power
Review: Lecture 9 Instantaneous and Average Power p( t) VmI m cos ( v i ) VmI m cos ( t v i ) Maximum Average Power Transfer Z L R L jx Effective or RMS Value I rms I m L R P * TH Apparent Power and Power
2015 ELECTRICAL SCIENCE
 Summer 2015 ELECTRICAL SCIENCE TIME: THREE HOURS Maximum Marks : 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from GROUP A, ANY TWO from GROUP B and from GROUP C. All parts of a question (a,b,etc) should
Summer 2015 ELECTRICAL SCIENCE TIME: THREE HOURS Maximum Marks : 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from GROUP A, ANY TWO from GROUP B and from GROUP C. All parts of a question (a,b,etc) should
LCR CIRCUITS Institute of Lifelong Learning, University of Delhi
 L UTS nstitute of Lifelong Learning, University of Delhi L UTS PHYSS (LAB MANUAL) nstitute of Lifelong Learning, University of Delhi PHYSS (LAB MANUAL) L UTS ntroduction ircuits containing an inductor
L UTS nstitute of Lifelong Learning, University of Delhi L UTS PHYSS (LAB MANUAL) nstitute of Lifelong Learning, University of Delhi PHYSS (LAB MANUAL) L UTS ntroduction ircuits containing an inductor
EE 221 Circuits II. Chapter 13 Magnetically Coupled Circuits
 EE Circuits II Chapter 3 Magnetically Coupled Circuits Magnetically Coupled Circuits 3. What is a transformer? 3. Mutual Inductance 3.3 Energy in a Coupled Circuit 3.4 inear Transformers 3.5 Ideal Transformers
EE Circuits II Chapter 3 Magnetically Coupled Circuits Magnetically Coupled Circuits 3. What is a transformer? 3. Mutual Inductance 3.3 Energy in a Coupled Circuit 3.4 inear Transformers 3.5 Ideal Transformers
Lecture 4 - Three-phase circuits, transformer and transient analysis of RLC circuits. Figure 4.1
 Lecture 4 - Three-phase circuits, transformer and transient analysis of RLC circuits Power supply to sizeable power converters are often from three-phase AC source. A balanced three-phase source consists
Lecture 4 - Three-phase circuits, transformer and transient analysis of RLC circuits Power supply to sizeable power converters are often from three-phase AC source. A balanced three-phase source consists
Unit-4. Magnetic Circuits
 Unit-4 Magnetic Circuits Topics to be Discussed Magnetic Coupling. Coefficient of Coupling (k). Sign of Mutual Voltage. Dot Convention. September 9, 0 Magnetic Circuits Magnetically Coupled Circuits A
Unit-4 Magnetic Circuits Topics to be Discussed Magnetic Coupling. Coefficient of Coupling (k). Sign of Mutual Voltage. Dot Convention. September 9, 0 Magnetic Circuits Magnetically Coupled Circuits A
RC circuit. Recall the series RC circuit.
 RC circuit Recall the series RC circuit. If C is discharged and then a constant voltage V is suddenly applied, the charge on, and voltage across, C is initially zero. The charge ultimately reaches the
RC circuit Recall the series RC circuit. If C is discharged and then a constant voltage V is suddenly applied, the charge on, and voltage across, C is initially zero. The charge ultimately reaches the
EEE3441 Electrical Machines Department of Electrical Engineering. Lecture. Basic Operating Principles of Transformers
 Department of Electrical Engineering Lecture Basic Operating Principles of Transformers In this Lecture Basic operating principles of following transformers are introduced Single-phase Transformers Three-phase
Department of Electrical Engineering Lecture Basic Operating Principles of Transformers In this Lecture Basic operating principles of following transformers are introduced Single-phase Transformers Three-phase
LC Resonant Circuits Dr. Roger King June Introduction
 LC Resonant Circuits Dr. Roger King June 01 Introduction Second-order systems are important in a wide range of applications including transformerless impedance-matching networks, frequency-selective networks,
LC Resonant Circuits Dr. Roger King June 01 Introduction Second-order systems are important in a wide range of applications including transformerless impedance-matching networks, frequency-selective networks,
IE1206 Embedded Electronics
 IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le1 Le3 Le4 Le2 Ex1 Ex2 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, serial and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs
IE1206 Embedded Electronics Le1 Le3 Le4 Le2 Ex1 Ex2 PIC-block Documentation, Seriecom Pulse sensors I, U, R, P, serial and parallel KC1 LAB1 Pulse sensors, Menu program Start of programing task Kirchhoffs
Bakiss Hiyana binti Abu Bakar JKE, POLISAS BHAB
 1 Bakiss Hiyana binti Abu Bakar JKE, POLISAS 1. Explain AC circuit concept and their analysis using AC circuit law. 2. Apply the knowledge of AC circuit in solving problem related to AC electrical circuit.
1 Bakiss Hiyana binti Abu Bakar JKE, POLISAS 1. Explain AC circuit concept and their analysis using AC circuit law. 2. Apply the knowledge of AC circuit in solving problem related to AC electrical circuit.
Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3
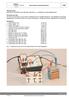 Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, Maxwell s equations, a.c. impedance, phase displacement. Principle and task The coil is connected in a circuit with a
Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, Maxwell s equations, a.c. impedance, phase displacement. Principle and task The coil is connected in a circuit with a
Chapter 33. Alternating Current Circuits
 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits C HAP T E O UTLI N E 33 1 AC Sources 33 2 esistors in an AC Circuit 33 3 Inductors in an AC Circuit 33 4 Capacitors in an AC Circuit 33 5 The L Series Circuit 33
Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits C HAP T E O UTLI N E 33 1 AC Sources 33 2 esistors in an AC Circuit 33 3 Inductors in an AC Circuit 33 4 Capacitors in an AC Circuit 33 5 The L Series Circuit 33
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 CONTINUOUS INTERNAL EVALUATION TEST -1 Date : 27/2/2018 Marks:60 Subject & Code : Basic Electrical Engineering, 17ELE25 Section: A,B,C,D,E Time : 8:30 am 11:30 a.m Name of faculty: Mrs. Dhanashree Bhate,
CONTINUOUS INTERNAL EVALUATION TEST -1 Date : 27/2/2018 Marks:60 Subject & Code : Basic Electrical Engineering, 17ELE25 Section: A,B,C,D,E Time : 8:30 am 11:30 a.m Name of faculty: Mrs. Dhanashree Bhate,
RLC Circuits. Centre College. Physics 230 Lab 8
 ircuits entre ollege Phsics 230 ab 8 1 Preliminaries Objective To stud the electrical characteristics of an alternating current circuit containing a resistor, inductor, and capacitor. Equipment Oscilloscope,
ircuits entre ollege Phsics 230 ab 8 1 Preliminaries Objective To stud the electrical characteristics of an alternating current circuit containing a resistor, inductor, and capacitor. Equipment Oscilloscope,
ELEN 140 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS II Winter 2013
 ELEN 140 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS II Winter 2013 Professor: Stephen O Loughlin Prerequisite: ELEN 130 Office: C234B Co-requisite: none Office Ph: (250) 762-5445 ext 4376 Lecture: 3.0 hrs/week Email: soloughlin@okanagan.bc.ca
ELEN 140 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS II Winter 2013 Professor: Stephen O Loughlin Prerequisite: ELEN 130 Office: C234B Co-requisite: none Office Ph: (250) 762-5445 ext 4376 Lecture: 3.0 hrs/week Email: soloughlin@okanagan.bc.ca
QUESTION BANK ETE (17331) CM/IF. Chapter1: DC Circuits
 QUESTION BANK ETE (17331) CM/IF Chapter1: DC Circuits Q1. State & explain Ohms law. Also explain concept of series & parallel circuit with the help of diagram. 3M Q2. Find the value of resistor in fig.
QUESTION BANK ETE (17331) CM/IF Chapter1: DC Circuits Q1. State & explain Ohms law. Also explain concept of series & parallel circuit with the help of diagram. 3M Q2. Find the value of resistor in fig.
AC Circuit. What is alternating current? What is an AC circuit?
 Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 1. Alternating Current 2. Resistor in an AC circuit 3. Capacitor in an AC circuit 4. Inductor in an AC circuit 5. RLC series circuit 6.
Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves 1. Alternating Current 2. Resistor in an AC circuit 3. Capacitor in an AC circuit 4. Inductor in an AC circuit 5. RLC series circuit 6.
AC Circuits INTRODUCTION DISCUSSION OF PRINCIPLES. Resistance in an AC Circuit
 AC Circuits INTRODUCTION The study of alternating current 1 (AC) in physics is very important as it has practical applications in our daily lives. As the name implies, the current and voltage change directions
AC Circuits INTRODUCTION The study of alternating current 1 (AC) in physics is very important as it has practical applications in our daily lives. As the name implies, the current and voltage change directions
Spring 2000 EE361: MIDTERM EXAM 1
 NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: Spring 2000 EE361: MIDTERM EXAM 1 This exam is open book and closed notes. Assume f=60 hz and use the constant µ o =4π 10-7 wherever necessary. Be sure to show all work clearly. 1.
NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: Spring 2000 EE361: MIDTERM EXAM 1 This exam is open book and closed notes. Assume f=60 hz and use the constant µ o =4π 10-7 wherever necessary. Be sure to show all work clearly. 1.
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING I-YEAR/II-SEMESTER- EEE&ECE EE6201- CIRCUIT THEORY Two Marks with Answers PREPARED BY: Mr.A.Thirukkumaran,
VETRI VINAYAHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING I-YEAR/II-SEMESTER- EEE&ECE EE6201- CIRCUIT THEORY Two Marks with Answers PREPARED BY: Mr.A.Thirukkumaran,
Electric Transformer. Specifically, for each coil: Since the rate of change in flux through single loop of each coil are approximately the same,
 Electric Transformer Safety and Equipment Computer with PASCO 850 Universal Interface and PASCO Capstone Coils Set 3 Double Banana Cables PASCO Voltage Sensor (DIN to Banana cable with slip-on Alligator
Electric Transformer Safety and Equipment Computer with PASCO 850 Universal Interface and PASCO Capstone Coils Set 3 Double Banana Cables PASCO Voltage Sensor (DIN to Banana cable with slip-on Alligator
TRANSFORMER OPERATION
 Chapter 3 TRANSFORMER OPERATION 1 A transformer is a static device (no moving parts) used to transfer energy from one AC circuit to another. This transfer of energy may involve an increase or decrease
Chapter 3 TRANSFORMER OPERATION 1 A transformer is a static device (no moving parts) used to transfer energy from one AC circuit to another. This transfer of energy may involve an increase or decrease
V.S.B ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING I EEE-II Semester all subjects 2 & 16 marks QB
 V.S.B ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING I EEE-II Semester all subjects 2 & 16 marks QB Sl.No Subject Name Page No. 1 Circuit Theory 2 1 UNIT-I CIRCUIT THEORY TWO
V.S.B ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING I EEE-II Semester all subjects 2 & 16 marks QB Sl.No Subject Name Page No. 1 Circuit Theory 2 1 UNIT-I CIRCUIT THEORY TWO
Experiment 9 AC Circuits
 Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
Inductance. Chapter 30. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman. Lectures by Wayne Anderson
 Chapter 30 Inductance PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 30 To learn how current in one coil
Chapter 30 Inductance PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 30 To learn how current in one coil
EE2003 Circuit Theory Chapter 13 Magnetically Coupled Circuits
 EE003 Circuit Theory Chapter 3 Magnetically Coupled Circuits Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Magnetically Coupled Circuit Chapter 3 3. What is
EE003 Circuit Theory Chapter 3 Magnetically Coupled Circuits Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Magnetically Coupled Circuit Chapter 3 3. What is
Hours / 100 Marks Seat No.
 17323 14115 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full marks. (4) Assume
17323 14115 3 Hours / 100 Seat No. Instructions (1) All Questions are Compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full marks. (4) Assume
UNIT 1 CIRCUIT ANALYSIS 1 What is a graph of a network? When all the elements in a network is replaced by lines with circles or dots at both ends.
 UNIT 1 CIRCUIT ANALYSIS 1 What is a graph of a network? When all the elements in a network is replaced by lines with circles or dots at both ends. 2 What is tree of a network? It is an interconnected open
UNIT 1 CIRCUIT ANALYSIS 1 What is a graph of a network? When all the elements in a network is replaced by lines with circles or dots at both ends. 2 What is tree of a network? It is an interconnected open
Experiment 1 Alternating Current with Coil and Ohmic Resistors
 Experiment Alternating Current with Coil and Ohmic esistors - Objects of the experiment - Determining the total impedance and the phase shift in a series connection of a coil and a resistor. - Determining
Experiment Alternating Current with Coil and Ohmic esistors - Objects of the experiment - Determining the total impedance and the phase shift in a series connection of a coil and a resistor. - Determining
The power transformer
 ELEC0014 - Introduction to power and energy systems The power transformer Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct November 2017 1 / 35 Power transformers are used: to transmit
ELEC0014 - Introduction to power and energy systems The power transformer Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct November 2017 1 / 35 Power transformers are used: to transmit
, ,54 A
 AEB5EN2 Ground fault Example Power line 22 kv has the partial capacity to the ground 4,3.0 F/km. Decide whether ground fault currents compensation is required if the line length is 30 km. We calculate
AEB5EN2 Ground fault Example Power line 22 kv has the partial capacity to the ground 4,3.0 F/km. Decide whether ground fault currents compensation is required if the line length is 30 km. We calculate
13 th Asian Physics Olympiad India Experimental Competition Wednesday, 2 nd May 2012
 13 th Asian Physics Olympiad India Experimental Competition Wednesday, nd May 01 Please first read the following instructions carefully: 1. The time available is ½ hours for each of the two experimental
13 th Asian Physics Olympiad India Experimental Competition Wednesday, nd May 01 Please first read the following instructions carefully: 1. The time available is ½ hours for each of the two experimental
TEP. RLC Circuit with Cobra3
 RLC Circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Tuned circuit, series-tuned circuit, parallel-tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, capacitor, coil, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width,impedance,
RLC Circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Tuned circuit, series-tuned circuit, parallel-tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, capacitor, coil, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width,impedance,
ALTERNATING CURRENT CIRCUITS
 CHAPTE 23 ALTENATNG CUENT CCUTS CONCEPTUAL QUESTONS 1. EASONNG AND SOLUTON A light bulb and a parallel plate capacitor (including a dielectric material between the plates) are connected in series to the
CHAPTE 23 ALTENATNG CUENT CCUTS CONCEPTUAL QUESTONS 1. EASONNG AND SOLUTON A light bulb and a parallel plate capacitor (including a dielectric material between the plates) are connected in series to the
NZQA registered unit standard version 4 Page 1 of 6. Demonstrate knowledge of alternating current (a.c.) theory
 Page 1 of 6 Title Demonstrate knowledge of alternating current (a.c.) theory Level 4 Credits 7 Purpose This unit standard covers knowledge of basic a.c. theory for electricians and related trades. People
Page 1 of 6 Title Demonstrate knowledge of alternating current (a.c.) theory Level 4 Credits 7 Purpose This unit standard covers knowledge of basic a.c. theory for electricians and related trades. People
Impedance, Resonance, and Filters. Al Penney VO1NO
 Impedance, Resonance, and Filters A Quick Review Before discussing Impedance, we must first understand capacitive and inductive reactance. Reactance Reactance is the opposition to the flow of Alternating
Impedance, Resonance, and Filters A Quick Review Before discussing Impedance, we must first understand capacitive and inductive reactance. Reactance Reactance is the opposition to the flow of Alternating
Real-time Math Function of DL850 ScopeCorder
 Real-time Math Function of DL850 ScopeCorder Etsurou Nakayama *1 Chiaki Yamamoto *1 In recent years, energy-saving instruments including inverters have been actively developed. Researchers in R&D sections
Real-time Math Function of DL850 ScopeCorder Etsurou Nakayama *1 Chiaki Yamamoto *1 In recent years, energy-saving instruments including inverters have been actively developed. Researchers in R&D sections
