GATE 2003 Instrumentation Engineering
|
|
|
- Randell Miller
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GATE 2003 Instrumentation Engineering Q Carry One Mark Each 1. A large number of 230 Ω resistors are obtained by combining 120 Ω resistors with a standard deviation of 4.0 Ω and 110 Ω resistors with a standard deviation of 3.0 Ω.The standard deviation of the 230 Ω resistors thus formed will be (A) 3.5Ω (B) 5.0Ω (C) 7.0Ω (D) 12.0Ω 2. A 3 ½ digit multimeter has an accuracy specification of (± 0.5% of reading ±5 counts). If the meter reads 2.00 ma on a full scale of 20 ma, the worst-case error in the reading is (A) 0.5% (C) 3.0% (B) 2.5% (D) 5.5% 3. Which one of the following is a derived unit (NOT a basic unit) in SI system? (A) Candela (C) Kelvin (B) Coulomb (D) mol. 4. A shaft encoder attached to a dc motor has a sensitivity of 500 pulses per revolution. A frequency meter connected to the output of the encoder indicates the frequency to be 5500 Hz. The speed of the motor in RPM is (A) 110 (B) 220 (C) 550 (D) A Pirani gage sensor is used to measure pressure of the order of (A) 10MPa (C) 100Pa (B) 1 MPa (D) 1Pa 6. Which of the following flow meters has the lowest pressure drop for a given range of flow? (A) Orifice meter (C) Flow Nozzle (B) Venturi meter (D) Rotameter Page : 1
2 7. Different types of transducers and signal conditioning circuits are given below. Match the transducer with the appropriate signal conditioning circuit commonly used with it. P Thermocouple 1 DC Bridge Q Strain gage 2 Phase sensitive detector R Piezoelectric sensor 3 Charge amplifier S L.V.D.T. 4 Cold junction compensation 5 Instrumentation amplifier (A) P 2, Q 3, R 5, S 1 (B) P 1, Q 5, R 2, S 3 (C) P 4, Q 1, R 2, S 5 (D) P 4, Q 1, R 3, S 2 8. An integrator circuit is shown in Fig. Q.8 The opamp is of type 741 and has an input offset current i os of 1 µa.c is 1 µf and R is 1M Ω. If the input V i is a 1 khz square wave of 1 V peak to peak, the out put V 0, under steady state condition, will be C V i Vi R i OS V 0 Fig. Q. 8 (A) a square wave of 1 V peak to peak (B) a triangular wave of 1 V peak to peak (C) positive supply voltage V cc (D) negative supply voltage V cc 9. The out put of an opamp whose input is a 2.5 MHz square wave is shown in Fig. Q. 9. The slew rate of the opamp is 4V 4V (A) 0.8 V/μs (B) 8.0 V/ μs 0.4µS Fig. Q. 9 (C) 20.0 V/ μs (D) 40.0 V/ μs Page : 2
3 10. The opamp and the 1 ma current source in the circuit of Fig. Q.10 are ideal. The out put of the opamp is 1.5KΩ 1.0KΩ 1mA Output 5 V (A) 1.5 ma (B) 1.5 V Fig. Q. 10 (C) 7.5V (D) 1.5V 11. Introducing a schottky diode between the base and collector of the output transistor in a TTL circuit (A) increases the speed of operation by inhibiting saturation (B) decreases the speed of operation by inhibiting saturation (C) increases the FAN OUT by enabling saturation (D) increases the speed of operation by enabling saturation 12. The Karnaugh map for a four variable Boolean function is given in Fig. Q.12. The correct Boolean sum of product is (A) PQRS Q S (B) PQRS QS Fig. Q. 12 (C) PQRQS (D) PQRS Q 13. Two 4-bit 2 s complement numbers 1011 and 0110 are added. The result expressed in 4-bit 2 s complement notation is (A) 0001 (B) 0010 (C) 1101 (D) cannot be expressed in 4-bit 2 s complement Page : 3
4 14. The input output characteristics of a Schmitt trigger is given in Fig. Q. 14. The noise margin of the Schmitt trigger is 5V V 1 V 3 V V i Fig. Q. 14 (A) 1 V (B) 2 V (C) 3 V (D) 4 V 15. Some of the pins of an 8085 CPU and their functions are listed below. Identify the correct answer that matches the pins to their respective functions P RST Selects IO of memory Q HOLD 2 Demultiplexes the address and data bus R IO M 3 Is a vectored interrupt S ALE 4 Facilitates direct memory access 5 Is a clock 6 Selects BCD mode of operation (A) P 3, Q 2, R 1, S 4 (B) P 4, Q 1, R 5, S 3 (C) P 3, Q 4, R 1, S 2 (D) P 2, Q 3, R 6, S A real function f(t) has a Fourier transform F(ω). The Fourier transform of [f(t) f(t)] is (A) zero (C) real and odd (B) real (D) imaginary 17. A system of equations represented by AX = 0, where X is a column vector of unknowns and A is a matrix containing coefficients, has a nontrivial solutions when A is (A) nonsingular (C) symmetric (B) singular (D) Hermetian 18. A sinusoidal signal of frequency 1 khz is used to produce an FM signal with a modulation index β = 5. The bandwidth (where 98% of power is contained) of the FM signal is (A) 2 khz (C) 6 khz (B) 3 khz (D) 12 khz Page : 4
5 19. Given x[n] =, the energy of the signal given by x[n] is (A) (B) πω (C) Infinite (D) 2πω 20. The current coil of a 200V, 5A, electrodynamometer type LPF wattmeter carries a current of 2 cos (100πt) A. The voltage across the pressure coil is sin (100πt) V. the meter will indicate (A) 0W (C) 200 W (B) 100W (D) 400W 21. The clock frequency of a timer counter is 10 MHz. the timer counter is used in the period mode and the input to the timer counter is a square wave of frequency 2 khz. The display of the timer counter will show a value (A) 200 (B) 2000 (C) 5000 (D) The insulation level for a 5 A full scale rectifier type ammeter is specified as 2.5 kv. It is then safe to use the meter with a potential difference of upto 2.5 kv between (A) the terminals of the meter (C) both the terminals and the case (B) case and the ground (D) one of the terminals and the ground 23. An oscilloscope screen displays a line inclined at 45. Its Y-input is a sine wave of frequency f then the X-input should be (A) sine wave of frequency f and 0 phase shift with the Y-input (B) sine wave of frequency f and 45 phase shift with the Y-input (C) sine wave of frequency f and 90 phase shift with the Y-input (D) saw-tooth wave of frequency f 24. In a synchro pair, the control transmitter excites the three stator windings of the control transformer. The stator winding voltages will have (A) equal magnitudes but different phases (B) different magnitudes and different phases (C) equal magnitudes and phases (D) different magnitudes but equal phases Page : 5
6 25. The steady state error for the feedback control system shown in Fig. Q.25 when subjected to a unit step input is r K p K 1 sτ c Fig. Q.25 (A) zero 1 (B) (1 KK P ) (C) KK p ( 1 KK P ) (D) infinite 26. A three-stack variable reluctance stepper motor has 12 numbers of rotor and stator teeth on each stack. The resolution of angular rotation for the stepper motor, assuming no. two stacks are excited simultaneously, is (A) 10 (B) 15 (C) 20 (D) In the feedback scheme shown in Fig. Q. 27, the time-constant of the closed loop system will be r A 1 sτ β C (A) A (B) (1 A, ) (C) (D) ( 1 A ) Fig. Q. 27 Page : 6
7 28. A grating that has 1200 lines/mm is irradiated with a narrow beam of white light at an incident angle of 25 to the grating normal. The first order peak observed at an angle of 15 belongs to the wavelength (A) nm (B) nm (C) nm (D) nm 29. A light beam is incident normally on a glass-air interface. The glass has a refractive index Air is assumed to be of refractive index 1.0. The Fresnel, intensity reflection coefficient is (A) 0.53 (C) (B) 0.25 (D) A light source is formed by putting a pinhole to let in sunlight. The above light source has (A) NO spatial-or temporal coherence (B) NO spatial coherence but has temporal cohenrece (C) spatial coherence but NO temporal coherence (D) quasi-monochromaticity Q Carry One Mark Each 31. An RTD is assumed to be represented in the range 0 C to 100 o C by a linear model as R 0 ( T ) R T where T is the temperature in o C. R O = 100 with a variation of RTD is 2. The true model of the 7 2 R T R0 ( T 6 10 T ) Two worst-case error magnitude in the resistance value that will be introduced, if the linear model is used over a range of 0 to 100 o C, is (A) 2 (C) 3.0 (B) 2.8 (D) 3.4 Page : 7
8 32. Measurement of large external radius is possible with the help of an angle piece and a screw gage as shown in Fig. Q.32. The radius R can be expressed from the measurement of H and as θ H R H sin (A) 1 sin H cos (B) 1 cos (C) (D) 33. Koster s modification of Michelson interferometer is used to determine the thickness of a gage G. The gage G is placed on the mirror M 2 as shown in Fig. Q. 33(a). The field-of-view observed through the lens L is shown in Fig. Q.33. (b). The fractional-fringe shift e, as shown in Fig. Q. 33 (b), is measured to be 0.15 when the wavelength of light used is 0.63 m. A quick check with a micrometer shows that the gage length is approximately 100 m. Then an accurate estimate of gage length, in m, is Fig. Q. 32 Page : 8
9 Quasi monochromatic light L M 1 Eye (A) (B) G M 2 Fig. Q. 33(a) (C) (D) e Fig. Q. 33(b) 34. A temperature-measuring instrument is modeled as a first order system with a time constant of 5s. The sensor of the instrument is placed inside an oil bath whose temperature has a sinusoidal variation with amplitude of 10 o C and a period of 20s around an average temperature of 200 o C. The sinusoidal component at the output of the instrument will have amplitude. (A) 0 o C (B) 5.37 o C (C) 8.57 o C (D) 10 o C Data given below should be used for answering questions Q.35 and Q.36 The table provides the thermo-emf sensitivity of five materials with reference to platinum around 273K Material Constantan Nickel Copper Iron Nichrome Sensitivity (μvk ) The thermocouple pair that gives the maximum sensitivity around 273 K is (A) Platinum Constantan (C) Nickel Constantan (B) Nichrome Constantan (D) Copper - Nickel 36. Two copper-constantan thermocouples are connected such that the two constantan wires are joined together. The two copper wires are connected to the input of a low noise chopper stabilized differential amplifier having a gain of One of the thermocouple junctions is immersed in a flask containing ice and water in equal proportion. The other thermocouple is at a temperature T. If the output of the amplifier is V, the temperature T is (A) 205 o C (B) o C (C) o C (D) 50 o C Page : 9
10 37. An N-type semiconductor strain gage has a nominal resistance of 1000 and gage factor of 100. The resistance of the gage, when a compressive strain of 100 m /m is applied, is (A) 900 (B) 990 (C) 1010 (D) A signal conditioning circuit suitable for a push-pull type capacitive transducer is given in Fig. Q.38. The output V 0 is E E ~ ~ C C C- C Vo Fig. Q. 38 (A) V = E (B) V = E (C) V = E (D) V = E 39. A Piezoelectric transducer with a sensitivity of 2.0p C/N having a capacitance of 1600 pf and a leakage resistance of is connected to a charge amplifier as shown in Fig. Q.39. If a force of 0.1 sin 10 t N is applied to the transducer, the output-amplitude of the charge amplifier is 10 8 Ω 1 nf Output Fig. Q. 39 (A) mv (B) mv (C) mv (D) mv Page : 10
11 40. In a seismic acceleration sensor, with a displacement transducer as the secondary element, decreasing the mass while maintaining all other parameters of the sensor unchanged will (A) reduce both natural frequency and steady-state sensitivity (B) increase both natural frequency and steady-state sensitivity (C) increase natural frequency but reduce steady-state sensitivity (D) increase natural frequency without affecting steady-state sensitivity 41. For a steady flow of liquid, the float of the rotameter will remain in a particular position when (A) drag force is balanced by the weight of the float and buoyancy force (B) weight of the float is balanced by the drag force and buoyancy force (C) buoyancy force is balanced by the drag force and weight of the float (D) drag force and buoyancy together is slightly greater than the weight of the float 42. A photo-detector circuit is given in the Figure. The photo-diode has an active area of 10-2 cm 2 and sensitivity of 0.55 A/W. When light of intensity 10 m W/cm 2 falls on the photo-diode, the output V 0 is 100 kω Light V 0 Fig. Q. 42 (A) 10.1 V (B) 5.5 V (C) 5.5 V (D) 10.1 V 43. A forward-biased silicion diode when carrying negligible current, has a voltage drop of 0.64 V. When the current is 1A it dissipates 1 W. The ON-resistance of the diode is (A) 0.36 (C) 0.72 (B) 0.64 (D) 1.0 Page : 11
12 44. A transistor amplifier circuit is shown in the Figure.The quiescent collector current, rounded off to first decimal, is V i C V CC = 24V 560KΩ 4.7KΩ C V 0 β = 100, V BE = 0.7V C = 0.1 µf (A) 2.6 ma (B) 2.3 ma Fig. Q. 44 (C) 2.1 ma (D) 2.0 ma 45. The opamp used in the inverting amplifier shown in Fig. Q.45 has an equivalent input offset voltage V ios of 5mV. The output offset voltage is 560KΩ V i 10KΩ V ios V 0 10KΩ Fig. Q. 45 (A) 5 mv (B) 280 mv (C) 285 mv (D) 560 mv Page : 12
13 46. A resistance R T of a resistive transducer is modeled as R( 1 Kx), where K is the constant of transformation and x the input quantity being sensed. The resistor is connected to an ideal, opamp signal conditioning circuit of Fig. Q. 46. The value of R is 100, K is and x is 75. The output V 0 is R T 4V 100Ω 12KΩ R T - V 0 12KΩ Fig. Q. 46 (A) 400 mv (B) 4 mv (C) 300 mv (D) 600 mv 47. In the circuit in the Figure, the opamps used are ideal. The output V 0 is V 1 =1V 10KΩ 10KΩ V 0 V 2 =2V 10KΩ 10KΩ 2KΩ 1KΩ Fig. Q. 47 (A) 3.0 V (B) 1.5 V (C) 1.0 V (D) 0.5V Page : 13
14 48. For an ECG amplifier, the input signals is 100μV corrupted by a common mode noise of 5mV. The output of the amplifier contains 50mV of signal and mv of noise. The CMRR of the amplifier is (A) 40 db (B) 60dB (C) 80dB (D) 100dB 49. A 50 W power amplifier has a rated output of 30V r.m.s and a voltage gain of 40 db. It is connected to 40 W loudspeaker having an internal resistance of 10Ω. Determine the maximum input voltage that can be given to the power amplifier so that neither the power amplifier nor the loudspeaker is overloaded. (A) 40 V (B) 20 V (C) 0.4 V (D) 0.2 V 50. The circuit shown in Fig. Q.50 is that of a waveform generator. Assuming ideal devices, and ± 12 V supply, the output V is a 10 kω 12 V V 0 1µF 10 kω 500 Ω 12 V 10 kω 6 V 6 V Fig. Q.50 (A) triangular wave of period 120 ms and amplitude ± 6V (B) square wave of period 60 ms and amplitude ± 6V (C) square wave of period 120 ms and amplitude ± 6V (D) square wave of period 60 ms and amplitude ± 12V Page : 14
15 51. The logic circuit of Fig.Q.51 is a A B Y Fig.Q.51 (A) half adder (B) XOR (C) equality detector (D) full adder 52. The correct cyclic sequence of the outputs (Q 0 Q 1 ) for the JK master slave flip-flop circuit shown in Fig. Q. 52 when the input clock is applied is J 0 Q 0 J 1 Q 1 Clock C 1 C 1 Y K 0 Q 0 K 1 Q Fig.Q.52 (A) 00, 01, 10, 11, 00, 01. (B) 00, 10, 01, 00, 10, 01,. (C) 00, 01, 10, 00, 01, 10,. (D) 00, 11, 00, 11, 00, 11,. Page : 15
16 53. For the CMOS analog switch shown in Fig.Q.53, the positive supply is V DD and the negative. supply is V EE The input V i is bipolar. The switch will be ON and V 0 will be equal to V i provided. V 1 V i V 0 V 2 Fig. Q. 53 (A) V 1 = V 2 = V DD (B) V 1 = V 2 = V EE (C) V 1 = V DD and V 2 = V EE (D) V 1 = V EE and V 2 = V DD 54. A 2-to-1 digital multiplexer having a switching delay of 1μs is connected as shown in Fig. Q.54. The output of the multiplexer is tied to its own select input S. The input which gets selected when S = 0 is tied to 1 and the input that gets selected when S = 1 is tied to 0.The output V 0 will be 2 To 1 MUX 1 0 S = 0 S = 1 S Fig. Q. 54 V 0 (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) pulse train of frequency 0.5 MH Z (D) pulse train of frequency 1.0 MH Z Page : 16
17 55. The square wave C 1 shown in Fig. Q.55 is given to the clock input of a 4-bit binary up/down counter whose UP/ DN input is fed with the pulse train P u. The counter is a negative edge triggered one. The counter starts with 0000 and will reach 0000 again at the C 1 P U Fig.Q.55 (A) 15 th clock pulse (B) 16 th clock pulse (C) 44 th clock pulse (D) 48 th clock pulse Data given below should be used for answering questions Q. 56 and Q. 57 In a dual slope ADC, the reference voltage is 100 mv and the first integration period is set as 50 ms. The input resistor of the integrator is 100 kω and the integrating capacitor F. 56. For an input voltage of 120 mv, the second integration (de-integration) period will be (A) 50ms (C) 100 ms (B) 60ms (D) 120ms 57. If the input of 120 mv is corrupted by power supply interference at 50 Hz having peak amplitude of 3 mv, the worst case error introduced by the interference in the reading is (A) 0% (C) 3% (B) 1% (D) % Page : 17
18 58. A ROM is interfaced to an 8085 CPU as indicated in Fig. Q.58. The address range occupied by the ROM is From 8085 CPU A 0 to A 12 D 0 to D 7 ROM From 8085 RD CPU RD IO/M 13 A CS Fig.Q.58 (A) FFF (B) FFF (C) FFF (D) FFF 59. In an 8085 system containing 8KB of ROM and 8KB of RAM, the ROM is selected when A 15 is 0 and the RAM is selected when A15 is 1. A13 and A14 are unused. The CPU executes the following program Prog1 MV1 A,00H STA 8080H DCR A STA C080H RET The content of memory location 8080 H after the execution of the RETURN instruction is (A) FFH (B) FEH (C) 01H (D) 00H 60. A linear time invariant system with system function H(z) =1z -1 z -2 is given an input signal sampled at 18 khz. The frequency of the analog sinusoid which CANNOT pass through the system is (A) khz (C) 12 khz (B) 6 khz (D) khz 61. A discrete time system with input(x[n]) output (y[n]) relation y[n] = x[n]2x[n1] x[n2] is a good approximation to a (A) high-pass filter (B) band stop filter blocking ω (C) low- pass filter (D) band pass filter passing ω < Page : 18
19 62. The scheme shown in Fig. Q. 62 is used for the generation of wideband FM from a narrow band FM. The multiplier box multiplies the input frequency by the factor shown. The input x(t) is a narrow band FM signal of carrier 100 khz and frequency deviation of 25Hz. The local oscillator frequency in khz and the multiplication constant m to achieve an output y(t)with a carrier of 2.0 MHz and a frequency deviation of 1.0 khz are respectively: x(t) x 5 Mixer x m y(t) ~ Fig. Q. 62 Local oscillator (A) 750,4 (B) 1000,4 (C) 750,8 (D) 1000,8 63. Given h[n] = [1,2,2], f[n] is obtained by convolving h[n] with itself and g[n] by correlating h[n] with itself. Which one of the following statements is true? (A) f[n] is causal and its maximum value is 9 (B) f[n] is non-causal and its maximum value is 8 (C) g[n] is causal and its maximum value is 9 (D) g[n] is non- causal and its maximum value is Bilinear transformation avoids the problem of aliasing encountered with the use of impulseinvariance through (A) mapping the entire imaginary axis of the s-plane onto the unit circle in the z-plane (B) pre- filtering the input signal to impose bank limitedness (C) mapping zeros of the left half of the s-plane inside the unit circle in the z-plane (D) up sampling the input signal so that the bandwidth is reduced Page : 19
20 65. A linear phase FIR system with impulse response real has a zero at z = e. The largest set of remaining zeros that can be obtained from the above information is (A) e, e, e (B) e, e, e (C) 2e, 2e, e (D) 2e, e 66. Given x = [a, b, c, d] as the input, linear time invariant system produces an output y = [x, x, x, x, < repeated N times>]. The impulse response of the system is (A) δ[n 4i] (C) u[n] u[n N 1] (B) u[n] u[n N] (D) δ[n i] 67. The sequence x[n] whose z transform is X(z) = e 112 is (A)! u[n] (B)! u[n] (C) (-1)! u[n] (D) ( )! u[n 1] 68. Direct form implementation of the FIR structure shown in Fig. Q.68 (a) is also implemented in Fig. Q.68 (b) in lattice form. The coefficients k 1 and k 2 are respectively Input x(n) Z -1 Z -1 Input x(n) Output y(n) Output y(n) Z -1 Z -1 k 1 k 1 k 2 k 2 Fig. Q. 68(a) (A) and (B) and Fig. Q. 68(b) (C) and (D) and Page : 20
21 69. The output resistance across the terminals 1 and 2 of the DC bridge in Fig. Q.69 is 4V 20KΩ 25KΩ 1 V o 2 30KΩ 25KΩ Fig. Q. 69 (A) 12.5 kω (B) 24.5 kω (C) 25.0 kω (D) 100 kω 70. For the bridge circuit in Fig. Q.70, the voltages are V 1 V 2 ~ ~ Vd R = 100Ω Z x Fig. Q. 70 V 1 = 2 cos 1000 t V, V 2 = 2cos (1000 t 45 ) and V d = 0. The value of R = 100 Ω Then Z x will be (A) 100 Ω resistor in series with 100 mh inductor (B) 100 Ω resistor in series with 100 µf capacitor (C) 100 Ω resistance in parallel with 100 mh inductor (D) 100 Ω resistance in parallel with 100 µf capacitor Page : 21
22 71. An oscilloscope is powered from 230 V mains having a nominal frequency of nearly 50 Hz. The triggering mode of the oscilloscope is set to LINE. A square wave from a function generator is fed to the Y input and a stable display (properly triggered) is obtained when the frequency of the function generator is 297 Hz. The actual frequency of the power supply is (A) 50 Hz (B) 49.5 Hz (C) 49.0 Hz (D) 48.5 Hz 72. The primary of a 200/1 A, 5 VA, 0.8 PF current transformer (CT) carries 100 A. The secondary current is A. The ratio error of the CT is (A) 1.0 % (B) 0.5% (C) 0.5% (D) 1.0% 73. A very low-loss coil tested with a Q-meter and the distributed (self) capacitance of the coil is found to be 820 pf. Resonance occurred at an angular frequency ω of 10 6 rad./s with a capacitance of 9.18 nf. The inductance of the coil is (A) 100pH (C) 100 nh (B) 100µH (D) 100mH 74. A potentiometer circuit is shown in Fig. Q. 74. The jockey of the potentiometer is kept exactly at the mid-point and the ammeter reads the current, I, as 0.2 ma. When V x is reversed the ammeter reads 3.8 ma. The internal resistance of the ammeter and the unknown potential V x are respectively 2 V 1800 Ω Ammeter I V x Fig.Q.74 (A) 500 Ω, 1.1 V (B) 50 Ω, 1.1 V (C) 500 Ω, 0.9 V (D) 50 Ω, 0.9 V Page : 22
23 75. The 5 V Zener diode in Fig. Q. 75 is ideal and the ammeter (A), of full-scale 1 ma, has an internal resistance of 100 Ω. The circuit shown, with terminal 1 positive, R m = 100 Ω 1 A V z = 5 V R s = 900 Ω 2 Fig. Q. 75 (A) 0 1 VDC voltmeter (B) 0 1 ma DC ammeter A 76. The transfer function of a system is 2 2 s input is A (A) 2 (B) 0 (C) 0 6 V DC voltmeter (D) 0 5 V AC voltmeter. The steady-state gain of the system to a unit-step (C) (D) not possible to be determined 77. The closed loop control system shown in Fig. Q.77 has τ > 0. The system will remain stable for all τ in the range R(S) τ 1 s 5 C(S) S(S 1) (A) τ 1 < 0.5 (B) 0.5 < τ 1 <1.0 Fig. Q. 77 (C) τ 1 <1.0 (D) τ 1 >1.0 Page : 23
24 78. In Fig. Q.78, K 1 and K 2 are proportional controllers. For the control system to remain stable, the upper limits of K 1 and K 2 are x(t) K 2 K 1 1 S 1 8 (S 2)(S 4) y(t) Fig. Q. 77 (A), (B) 1, (C), 10 (D) 10,1 79. The response of a system to a unit impulse is y(t) = e ( ). Which one of the following is the correct statement about the system? (A) The system is nonlinear (B) The system is unstable in open loop (C) The steady-state gain of the system for a unit input is 0.2 (D) The steady-state gain of the system for a unit step input is A PID controller has the transfer function 2 with the unit of time expressed in minutes. s The parameters proportional band and reset time for the above controller are respectively (A) 200% and 0.4 min. (C) 200% and 5 min. (B) 50% and 0.4 min. (D) 50% and min. 81. For a dynamic system, various matrices for a state space model are give by A, [10]. 2 3 B 1 andc The system poles are located at (A) 2, 1 (C) 3, 1 (B) 2, 3 (D) 1,0 82. The transfer function of a system is given by ( ) angle between the output and the input will be (A) (B) 45 =. ( ). If x (t) is 0.5 sin t, then the phase (C) (D) 90 Page : 24
25 83. The transfer function of a second order band-pas filter, having a centre frequency of 1000 rad/s selectivity of 100 and a gain of 0 db at the centre frequency, is 10s 100s (A) (C) s 10s 10 s 100s 10 s 100s (B) (D) s s 10 s 100s 10 Data given below should be used for answering questions Q. 84 and Q The root locus plot for a system, with transfer function, is shown in Fig Q.84. A s( s 1)( s 2) unity feedback proportional control system is built using this system. 84. The maximum possible controller gain, for which the unity feedback system is stable, is approximately - 2J X X -2-1 X J FIG Q 84 (A) 6.0 (B) 3.0 (C) 0.4 (D) The maximum possible controller gain, for which the unity feedback system exhibits a nonoscillatory response to a unit step input, is (A) 6.0 (B) 3.0 (C) 0.4 (D) 0.2 Page : 25
26 86. An ultrasonic beam of frequency 1 MHz and intensity 0.5 W/cm 2 passes through a layer of soft tissue of thickness t with an attenuation coefficient of 1.18 cm -1. The ratio of output to input power is 1/e 2. The thickness of the tissue is (A) 1 cm (B) cm (C) cm (D) cm 87. The refractive indices of the core and cladding of an optical fibre are 1.46 and respectively. The diameter of the core is 4 µm. When operated at a wavelength of 1.31 µm, the fiber functions as a (A) single-mode fibre with a numerical aperture of 0.1 (B) multimode fibre with a numerical aperture of 0.15 (C) single-mode fibre with a numerical aperture of 0.12 (D) ten-mode fibre with a numerical aperture of A cardiac output measurement set-up uses the thermo-dilution principle. The change in the output temperature is 7 C for 5.60 litres per minute of cardiac output with an integration time of 10 s. For a second measurement, with all other parameters remaining unchanged, the change in the temperature is 10 C with an integration time of 20 s. The cardiac output in litres per minute for this will be (A) 5.60 (B) 4.21 (C) 3.92 (D) X-rays emitted from a molybdenum target at 35 kv have wavelength edges K a = 70.9 pm and K β = 63.2 pm. These X-rays are passed through a zirconia filter of K-edge 68.9 pm. The output of the filter contains primarily X-rays of wavelengths (A) 63.2 pm (B) 70.9 pm (C) Both 63.2 pm and 70.9 pm (D) Neither 63.2 pm not 70.9 pm 90. A quasi-monochromatic light source with average central wavelength of 630 nm has a spectral width of 10GHz. The coherence length of the source is (A) 3µm (B) 3mm (C) 3cm (D) 3m. Page : 26
4 Cold junction compensation 5 Instrumentation amplifier
 Q. to Q.5 carry one mark each Q. A large number of 3 resistors are obtained by combining resistors with a standard deviation of 4. and resistors with a standard deviation of 3. The standard deviation of
Q. to Q.5 carry one mark each Q. A large number of 3 resistors are obtained by combining resistors with a standard deviation of 4. and resistors with a standard deviation of 3. The standard deviation of
IN Branch GATE Paper 1999 SECTION A
 SECTION A 1. This question contains 30 sub-questions of multiple choice type. Each sub-question has only one correct answer. 1.1 is (A) 0 (B) 1.1 (C) 0.5 (D) 1 1.2. For the waveform V(t)=2+cos (ωt+ ) the
SECTION A 1. This question contains 30 sub-questions of multiple choice type. Each sub-question has only one correct answer. 1.1 is (A) 0 (B) 1.1 (C) 0.5 (D) 1 1.2. For the waveform V(t)=2+cos (ωt+ ) the
GATE 2008 Instrumentation Engineering
 GATE 2008 Instrumentation Engineering Q. 1 Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Given y = x 2x 10, the value of is equal to (A) 0 (B) 4 (C) 12 (D) 13 2. lim is (A) Indeterminate (B) 0 (C) 1 (D) 3. The power supplied
GATE 2008 Instrumentation Engineering Q. 1 Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Given y = x 2x 10, the value of is equal to (A) 0 (B) 4 (C) 12 (D) 13 2. lim is (A) Indeterminate (B) 0 (C) 1 (D) 3. The power supplied
GATE SOLVED PAPER - IN
 YEAR 202 ONE MARK Q. The i-v characteristics of the diode in the circuit given below are : v -. A v 0.7 V i 500 07 $ = * 0 A, v < 0.7 V The current in the circuit is (A) 0 ma (C) 6.67 ma (B) 9.3 ma (D)
YEAR 202 ONE MARK Q. The i-v characteristics of the diode in the circuit given below are : v -. A v 0.7 V i 500 07 $ = * 0 A, v < 0.7 V The current in the circuit is (A) 0 ma (C) 6.67 ma (B) 9.3 ma (D)
Electronics Eingineering
 Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering
 GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering Q. Q20 carry one mark each.. If z = x jy, where x and y are real, the value of e is (A) (C) e (B) e x y (D) e 2. The value of origin, is (A) 0 (B) 2πj dz, where the
GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering Q. Q20 carry one mark each.. If z = x jy, where x and y are real, the value of e is (A) (C) e (B) e x y (D) e 2. The value of origin, is (A) 0 (B) 2πj dz, where the
INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING - IN. , where the contour is the unit circle traversed clockwise, is.
 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Let be an matrix with rank (0 < < ). Then = 0 has independent solutions, where is (A) r (B) n (C) (D) + Q.2 The value of 1, where the contour is the unit circle traversed
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Let be an matrix with rank (0 < < ). Then = 0 has independent solutions, where is (A) r (B) n (C) (D) + Q.2 The value of 1, where the contour is the unit circle traversed
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
ML4818 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller
 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2013 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
Ñ dz, where the contour of integration is a simple closed
 . to.0 Carry Mark Each INGate - 009 IN: INSTUMENTATION ENGINEEING If z = x+jy, where x and y are real. The value of jz e is (A) (B) e x y (C) y e (D) e y The value of curve around the origin, is (A) 0
. to.0 Carry Mark Each INGate - 009 IN: INSTUMENTATION ENGINEEING If z = x+jy, where x and y are real. The value of jz e is (A) (B) e x y (C) y e (D) e y The value of curve around the origin, is (A) 0
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus
 UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL
 ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
Summer 2015 Examination
 Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering
 Q. No. 1 20 Carry One Mark Each GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering 1. The pressure coil of a dynamometer type wattmeter is (A) highly inductive (B) highly resistive (C) purely resistive (D) purely inductive
Q. No. 1 20 Carry One Mark Each GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering 1. The pressure coil of a dynamometer type wattmeter is (A) highly inductive (B) highly resistive (C) purely resistive (D) purely inductive
LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers
 LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13600 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers each with
LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13600 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers each with
GATE 2000 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 1 P a g e INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INTEGRATED CIRCUITS APPLICATIONS Code
1 P a g e INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INTEGRATED CIRCUITS APPLICATIONS Code
5. Transducers Definition and General Concept of Transducer Classification of Transducers
 5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Figure 1.1 Mechatronic system components (p. 3)
 Figure 1.1 Mechatronic system components (p. 3) Example 1.2 Measurement System Digital Thermometer (p. 5) Figure 2.2 Electric circuit terminology (p. 13) Table 2.2 Resistor color band codes (p. 18) Figure
Figure 1.1 Mechatronic system components (p. 3) Example 1.2 Measurement System Digital Thermometer (p. 5) Figure 2.2 Electric circuit terminology (p. 13) Table 2.2 Resistor color band codes (p. 18) Figure
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER PREPARED BY, PROF. CHIRAG H. RAVAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR NIRMA UNIVRSITY
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER PREPARED BY, PROF. CHIRAG H. RAVAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR NIRMA UNIVRSITY INTRODUCTION Op-Amp means Operational Amplifier. Operational stands for mathematical operation like addition,
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER PREPARED BY, PROF. CHIRAG H. RAVAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR NIRMA UNIVRSITY INTRODUCTION Op-Amp means Operational Amplifier. Operational stands for mathematical operation like addition,
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Dimensions in inches (mm) .268 (6.81).255 (6.48) .390 (9.91).379 (9.63) .045 (1.14).030 (.76) 4 Typ. Figure 1. Typical application circuit.
 LINEAR OPTOCOUPLER FEATURES Couples AC and DC signals.% Servo Linearity Wide Bandwidth, > KHz High Gain Stability, ±.%/C Low Input-Output Capacitance Low Power Consumption, < mw Isolation Test Voltage,
LINEAR OPTOCOUPLER FEATURES Couples AC and DC signals.% Servo Linearity Wide Bandwidth, > KHz High Gain Stability, ±.%/C Low Input-Output Capacitance Low Power Consumption, < mw Isolation Test Voltage,
Interface Electronic Circuits
 Lecture (5) Interface Electronic Circuits Part: 1 Prof. Kasim M. Al-Aubidy Philadelphia University-Jordan AMSS-MSc Prof. Kasim Al-Aubidy 1 Interface Circuits: An interface circuit is a signal conditioning
Lecture (5) Interface Electronic Circuits Part: 1 Prof. Kasim M. Al-Aubidy Philadelphia University-Jordan AMSS-MSc Prof. Kasim Al-Aubidy 1 Interface Circuits: An interface circuit is a signal conditioning
R & D Electronics DIGITAL IC TRAINER. Model : DE-150. Feature: Object: Specification:
 DIGITAL IC TRAINER Model : DE-150 Object: To Study the Operation of Digital Logic ICs TTL and CMOS. To Study the All Gates, Flip-Flops, Counters etc. To Study the both the basic and advance digital electronics
DIGITAL IC TRAINER Model : DE-150 Object: To Study the Operation of Digital Logic ICs TTL and CMOS. To Study the All Gates, Flip-Flops, Counters etc. To Study the both the basic and advance digital electronics
Dimensions in inches (mm) .021 (0.527).035 (0.889) .016 (.406).020 (.508 ) .280 (7.112).330 (8.382) Figure 1. Typical application circuit.
 IL Linear Optocoupler Dimensions in inches (mm) FEATURES Couples AC and DC signals.% Servo Linearity Wide Bandwidth, > khz High Gain Stability, ±.%/C Low Input-Output Capacitance Low Power Consumption,
IL Linear Optocoupler Dimensions in inches (mm) FEATURES Couples AC and DC signals.% Servo Linearity Wide Bandwidth, > khz High Gain Stability, ±.%/C Low Input-Output Capacitance Low Power Consumption,
TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION. Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service
 Code No.207 TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Code No.207 TAMIL NADU PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION Post of Principal / Assistant Director (Training) Included in the Tamil Nadu Employment and Training Service Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
Downloaded from Downloaded from
 IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION- 2002 SUBJECT: BEG232EC, Instrumentation Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks.
IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION- 2002 SUBJECT: BEG232EC, Instrumentation Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks.
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS BASIC ELECTRONICS
 PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS QUESTION BANK BASIC ELECTRONICS Sub Code: 17ELN15 / 17ELN25 IA Marks: 20 Hrs/ Week: 04 Exam Marks: 80 Total Hours: 50 Exam Hours: 03 Name of Faculty: Mr. Udoshi Basavaraj Module
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS QUESTION BANK BASIC ELECTRONICS Sub Code: 17ELN15 / 17ELN25 IA Marks: 20 Hrs/ Week: 04 Exam Marks: 80 Total Hours: 50 Exam Hours: 03 Name of Faculty: Mr. Udoshi Basavaraj Module
Homework Assignment 03
 Homework Assignment 03 Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 points each unless otherwise noted. 1. Two 0.68 μf capacitors are connected in series across a 10 khz sine wave signal source. The total capacitive reactance
Homework Assignment 03 Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 points each unless otherwise noted. 1. Two 0.68 μf capacitors are connected in series across a 10 khz sine wave signal source. The total capacitive reactance
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
Homework Assignment 06
 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 06 1. True or false: when transforming a circuit s diagram to a diagram of its small-signal model, we replace dc constant current sources
Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 06 1. True or false: when transforming a circuit s diagram to a diagram of its small-signal model, we replace dc constant current sources
Electronic Systems - B1 23/04/ /04/ SisElnB DDC. Chapter 2
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS. Introduction. B1 - Sensors and actuators. Introduction
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
HIGH LOW Astable multivibrators HIGH LOW 1:1
 1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER
 DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a switch-mode (chopper), constant-current driver with two channels: one for each winding of a two-phase stepper motor. is equipped with a Disable input
DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a switch-mode (chopper), constant-current driver with two channels: one for each winding of a two-phase stepper motor. is equipped with a Disable input
PowerAmp Design. PowerAmp Design PAD20 COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE OP AMP
 PowerAmp Design Rev C KEY FEATURES LOW COST HIGH VOLTAGE 150 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 5A 40 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 80 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY INTEGRATED HEAT SINK AND FAN SMALL SIZE 40mm SQUARE RoHS
PowerAmp Design Rev C KEY FEATURES LOW COST HIGH VOLTAGE 150 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 5A 40 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 80 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY INTEGRATED HEAT SINK AND FAN SMALL SIZE 40mm SQUARE RoHS
Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405]
![Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405] Question Bank SENSORS AND INSTRUMENTATION [EE-305/405]](/thumbs/95/124646158.jpg) UNIT-1 1. Discuss liquid in glass thermometers? 2. Write a short note on strain gauges. 3. Mention the various temperature scales and relation between them. 4. An experiment is conducted to calibrate a
UNIT-1 1. Discuss liquid in glass thermometers? 2. Write a short note on strain gauges. 3. Mention the various temperature scales and relation between them. 4. An experiment is conducted to calibrate a
Quantity available (A) Quantity required (R) Sl. No. Deficiency (R - A) Description of Equipment
 . 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (R 203) Semester II EE62 Electric Circuits Laboratory Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (20 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (R 203) Semester II EE62 Electric Circuits Laboratory Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (20 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
NJM3777 DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIVER NJM3777E3(SOP24)
 DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The NJM3777 is a switch-mode (chopper), constant-current driver with two channels: one for each winding of a two-phase stepper motor. The NJM3777 is equipped
DUAL STEPPER MOTOR DRIER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The NJM3777 is a switch-mode (chopper), constant-current driver with two channels: one for each winding of a two-phase stepper motor. The NJM3777 is equipped
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
Developer Techniques Sessions
 1 Developer Techniques Sessions Physical Measurements and Signal Processing Control Systems Logging and Networking 2 Abstract This session covers the technologies and configuration of a physical measurement
1 Developer Techniques Sessions Physical Measurements and Signal Processing Control Systems Logging and Networking 2 Abstract This session covers the technologies and configuration of a physical measurement
IT.MLD900 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER. Signal Conditioning
 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
PRODUCT CATALOG TRAINER KITS FOR ENGINEERING DEGREE COURSES MICROTECH INDUSTRIES
 PRODUCT CATALOG TRAINER KITS FOR ENGINEERING DEGREE COURSES µ MICROTECH INDUSTRIES 14A/ 1G, ULTADANGA ROAD GOPAL BHAVAN KOLKATA 700 004 Phone : (033) 3296 9273, Cell : 98312 63293 E- mail : hkg@cal3.vsnl.net.in
PRODUCT CATALOG TRAINER KITS FOR ENGINEERING DEGREE COURSES µ MICROTECH INDUSTRIES 14A/ 1G, ULTADANGA ROAD GOPAL BHAVAN KOLKATA 700 004 Phone : (033) 3296 9273, Cell : 98312 63293 E- mail : hkg@cal3.vsnl.net.in
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A
 Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
Downloaded From JNTU World. B.Tech II Year II Semester (R09) Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER
 Downloaded From Code: 9A02403 B.Tech II Year II Semester () Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER Answer any FIVE questions 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages
Downloaded From Code: 9A02403 B.Tech II Year II Semester () Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER Answer any FIVE questions 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages
UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency
 UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency Jamie E. Reinhold December 15, 2011 Abstract The design, simulation and layout of a UMAINE ECE Morse code Read Only Memory and transmitter
UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency Jamie E. Reinhold December 15, 2011 Abstract The design, simulation and layout of a UMAINE ECE Morse code Read Only Memory and transmitter
SG2525A SG3525A REGULATING PULSE WIDTH MODULATORS
 SG2525A SG3525A REGULATING PULSE WIDTH MODULATORS 8 TO 35 V OPERATION 5.1 V REFERENCE TRIMMED TO ± 1 % 100 Hz TO 500 KHz OSCILLATOR RANGE SEPARATE OSCILLATOR SYNC TERMINAL ADJUSTABLE DEADTIME CONTROL INTERNAL
SG2525A SG3525A REGULATING PULSE WIDTH MODULATORS 8 TO 35 V OPERATION 5.1 V REFERENCE TRIMMED TO ± 1 % 100 Hz TO 500 KHz OSCILLATOR RANGE SEPARATE OSCILLATOR SYNC TERMINAL ADJUSTABLE DEADTIME CONTROL INTERNAL
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS
 R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER V PHYSICS PAPER VI (A) ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT I: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER V PHYSICS PAPER VI (A) ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT I: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the:
 Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION
 Subject Code:173 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The
Subject Code:173 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The
Subject-wise Tests Tests will be activated at 06:00 pm on scheduled day
 Subject Name EE-01 Control Systems EE-02 Systems and Signal Processing EE-03 Analog and Digital Electronics EE-04 Engineering Mathematics and Numerical Analysis EE-05 Electric Circuits and Fields EE-06
Subject Name EE-01 Control Systems EE-02 Systems and Signal Processing EE-03 Analog and Digital Electronics EE-04 Engineering Mathematics and Numerical Analysis EE-05 Electric Circuits and Fields EE-06
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2004
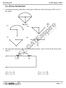 Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
Electrical Materials may be referred to a metal, dielectrics,electrical insulators or conductors,paramagnetic materials and many other.
 Electrical Engineering Paper-1 Syllabus : This part is for both objective and conventional types papers : 1) EM Theory- The electromagnetic force is said to be one of the fundamental interactions in nature
Electrical Engineering Paper-1 Syllabus : This part is for both objective and conventional types papers : 1) EM Theory- The electromagnetic force is said to be one of the fundamental interactions in nature
multivibrator; Introduction to silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs).
 Appendix The experiments of which details are given in this book are based largely on a set of 'modules' specially designed by Dr. K.J. Close. These 'modules' are now made and marketed by Irwin-Desman
Appendix The experiments of which details are given in this book are based largely on a set of 'modules' specially designed by Dr. K.J. Close. These 'modules' are now made and marketed by Irwin-Desman
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS. Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi
 EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
EE301 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS CHAPTER 2 : OSCILLATORS Lecturer : Engr. Muhammad Muizz Bin Mohd Nawawi 2.1 INTRODUCTION An electronic circuit which is designed to generate a periodic waveform continuously at
Preface... iii. Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1
 Table of Contents Preface... iii Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure of an Atom... 2 1.3 Classification of Solid Materials on the Basis of Conductivity... 2 1.4 Atomic
Table of Contents Preface... iii Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure of an Atom... 2 1.3 Classification of Solid Materials on the Basis of Conductivity... 2 1.4 Atomic
Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP Task Grid
 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Describe OSHA safety regulations. 102 Identify, select, and demonstrate proper hand tool use for electronics work. 103 Recognize the types and usages of fire extinguishers.
Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Describe OSHA safety regulations. 102 Identify, select, and demonstrate proper hand tool use for electronics work. 103 Recognize the types and usages of fire extinguishers.
LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers
 LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13700 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers, each with
LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13700 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers, each with
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. AN1221 Switched-mode drives for DC motors. Author: Lester J. Hadley, Jr.
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Author: Lester J. Hadley, Jr. 1988 Dec Author: Lester J. Hadley, Jr. ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to demonstrate the use of integrated switched-mode controllers, generally
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Author: Lester J. Hadley, Jr. 1988 Dec Author: Lester J. Hadley, Jr. ABSTRACT The purpose of this paper is to demonstrate the use of integrated switched-mode controllers, generally
Model 176 and 178 DC Amplifiers
 Model 176 and 178 DC mplifiers Features*! Drifts to 100 MΩ! CMR: 120 db @! Gain Linearity of ±.005% *The key features of this amplifier series, listed above, do not necessarily apply
Model 176 and 178 DC mplifiers Features*! Drifts to 100 MΩ! CMR: 120 db @! Gain Linearity of ±.005% *The key features of this amplifier series, listed above, do not necessarily apply
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2002 SECTION A (75 MARKS )
 SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
Contents. Acknowledgments. About the Author
 Contents Figures Tables Preface xi vii xiii Acknowledgments About the Author xv xvii Chapter 1. Basic Mathematics 1 Addition 1 Subtraction 2 Multiplication 2 Division 3 Exponents 3 Equations 5 Subscripts
Contents Figures Tables Preface xi vii xiii Acknowledgments About the Author xv xvii Chapter 1. Basic Mathematics 1 Addition 1 Subtraction 2 Multiplication 2 Division 3 Exponents 3 Equations 5 Subscripts
PowerAmp Design. PowerAmp Design PAD117A RAIL TO RAIL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 PowerAmp Design RAIL TO RAIL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER Rev J KEY FEATURES LOW COST RAIL TO RAIL INPUT & OUTPUT SINGLE SUPPLY OPERATION HIGH VOLTAGE 100 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 15A 250 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY
PowerAmp Design RAIL TO RAIL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER Rev J KEY FEATURES LOW COST RAIL TO RAIL INPUT & OUTPUT SINGLE SUPPLY OPERATION HIGH VOLTAGE 100 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 15A 250 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY
PAPER-II (Subjective)
 PAPER-II (Subjective) 1.(A) Choose and write the correct answer from among the four options given in each case for (a) to (j) below: (a) Improved commutation in d.c machines cannot be achieved by (i) Use
PAPER-II (Subjective) 1.(A) Choose and write the correct answer from among the four options given in each case for (a) to (j) below: (a) Improved commutation in d.c machines cannot be achieved by (i) Use
MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation. Data Acquisition
 MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Data Acquisition Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Sampling Concepts 1 f s t Sampling Rate f s 2 f m or
MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Data Acquisition Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Sampling Concepts 1 f s t Sampling Rate f s 2 f m or
Micropower, Single-Supply, Rail-to-Rail, Precision Instrumentation Amplifiers MAX4194 MAX4197
 General Description The is a variable-gain precision instrumentation amplifier that combines Rail-to-Rail single-supply operation, outstanding precision specifications, and a high gain bandwidth. This
General Description The is a variable-gain precision instrumentation amplifier that combines Rail-to-Rail single-supply operation, outstanding precision specifications, and a high gain bandwidth. This
Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques. Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur
 Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Data Conversion Circuits 2 Digital systems are being used
Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Data Conversion Circuits 2 Digital systems are being used
UNIT 1 MULTI STAGE AMPLIFIES
 UNIT 1 MULTI STAGE AMPLIFIES 1. a) Derive the equation for the overall voltage gain of a multistage amplifier in terms of the individual voltage gains. b) what are the multi-stage amplifiers? 2. Describe
UNIT 1 MULTI STAGE AMPLIFIES 1. a) Derive the equation for the overall voltage gain of a multistage amplifier in terms of the individual voltage gains. b) what are the multi-stage amplifiers? 2. Describe
MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION. Part A
 MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A 1. Define Standard deviation. 2. Why calibration of instrument is important? 3. What are the different calibration methodologies?
MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A 1. Define Standard deviation. 2. Why calibration of instrument is important? 3. What are the different calibration methodologies?
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET
 Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: REV. NO. : REV. DATE : PAGE:
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: REV. NO. : REV. DATE : PAGE:
EE Branch GATE Paper 2006
 Q. 1 Q. 20 carry one mark each 1. The following is true (A) A finite signal is always bounded (B) A bounded signal always possesses finite energy (C) A bounded signal is always zero outside the interval
Q. 1 Q. 20 carry one mark each 1. The following is true (A) A finite signal is always bounded (B) A bounded signal always possesses finite energy (C) A bounded signal is always zero outside the interval
Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date:
 PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date: 1 2330A Current and Voltage 2 2330B Controlling Current
PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date: 1 2330A Current and Voltage 2 2330B Controlling Current
Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab. Facebook: Twitter:
 Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab www.vidyathiplus.in Facebook: www.facebook.com/vidyarthiplus Twitter: www.twitter.com/vidyarthiplus Copyright 2011-2015 Vidyarthiplus.in (VP Group) Page 1 CIRCUIT
Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab www.vidyathiplus.in Facebook: www.facebook.com/vidyarthiplus Twitter: www.twitter.com/vidyarthiplus Copyright 2011-2015 Vidyarthiplus.in (VP Group) Page 1 CIRCUIT
ECE Branch GATE Paper (C) exp ( t ) sin (25t) (B) 4cos (20t + 3) + 2 sin (710t)
 Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Kompally, Secunderabad-500014. Branch Year&Sem Subject Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering : III B. Tech I Semester : IC Applications OBJECTIVES QUESTION
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Kompally, Secunderabad-500014. Branch Year&Sem Subject Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering : III B. Tech I Semester : IC Applications OBJECTIVES QUESTION
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3.
 Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
PowerAmp Design. PowerAmp Design PAD112 HIGH VOLTAGE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 PowerAmp Design Rev C KEY FEATURES LOW COST HIGH VOLTAGE 150 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 5 AMPS 50 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 100 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY INTEGRATED HEAT SINK AND FAN COMPATIBLE WITH PAD123
PowerAmp Design Rev C KEY FEATURES LOW COST HIGH VOLTAGE 150 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 5 AMPS 50 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 100 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY INTEGRATED HEAT SINK AND FAN COMPATIBLE WITH PAD123
Single Supply, Rail to Rail Low Power FET-Input Op Amp AD820
 a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from + V to + V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load
a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from + V to + V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 Some useful data:
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
i Intelligent Digitize Emulated Achievement Lab
 Electronics Circuits Equipment Intelligent Digitize Emulated Achievement Lab intelligent digitize emulated achievement lab is a digitized-based training system, which utilizes integrated Hardware Platform,
Electronics Circuits Equipment Intelligent Digitize Emulated Achievement Lab intelligent digitize emulated achievement lab is a digitized-based training system, which utilizes integrated Hardware Platform,
LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers
 LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13700 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers, each with
LM13700 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13700 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers, each with
GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? (A) Fig. Q.1
GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? (A) Fig. Q.1
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers. Final Examination.
 Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2002 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2002 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Oscillators. An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier.
 Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007
 BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007 1. An open loop control system has its (a) control action independent of the output or desired quantity (b) controlling action, depending upon
BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007 1. An open loop control system has its (a) control action independent of the output or desired quantity (b) controlling action, depending upon
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
IN Branch GATE Paper 2001 SECTION A
 SETION A 1. This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-questions (1.1 1.25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub questions, four possible answers (A, B, and D) are given, out of which only one is correct.
SETION A 1. This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-questions (1.1 1.25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub questions, four possible answers (A, B, and D) are given, out of which only one is correct.
MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Linear Integrated Circuit Subject Code:
 MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Linear Integrated Circuit Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
MODEL ANSWER SUMMER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Title: Linear Integrated Circuit Subject Code: Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
OBSOLETE. High Performance, BiFET Operational Amplifiers AD542/AD544/AD547 REV. B
 a FEATURES Ultralow Drift: 1 V/ C (AD547L) Low Offset Voltage: 0.25 mv (AD547L) Low Input Bias Currents: 25 pa max Low Quiescent Current: 1.5 ma Low Noise: 2 V p-p High Open Loop Gain: 110 db High Slew
a FEATURES Ultralow Drift: 1 V/ C (AD547L) Low Offset Voltage: 0.25 mv (AD547L) Low Input Bias Currents: 25 pa max Low Quiescent Current: 1.5 ma Low Noise: 2 V p-p High Open Loop Gain: 110 db High Slew
Concepts to be Reviewed
 Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 3 Operational Amplifiers, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Reviewed Operational
Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 3 Operational Amplifiers, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Reviewed Operational
Gechstudentszone.wordpress.com
 8.1 Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) UNIT 8: Operational Amplifier An operational amplifier ("op-amp") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended
8.1 Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) UNIT 8: Operational Amplifier An operational amplifier ("op-amp") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended
EE Branch GATE Paper 2001 SECTION A (TOTAL MARKS = 75)
 SECTION A (TOTAL MARKS = 75) 1. This question consists of 25 (TWENTY-FIVE) sub-questions (1.1-1.25) of ONE mark each. (25 1 = 25 ) 1.1 In a series RLC circuit at resonance, the magnitude of the voltage
SECTION A (TOTAL MARKS = 75) 1. This question consists of 25 (TWENTY-FIVE) sub-questions (1.1-1.25) of ONE mark each. (25 1 = 25 ) 1.1 In a series RLC circuit at resonance, the magnitude of the voltage
