(ans: Five rows and five columns accommodate 25 switch locations. )
|
|
|
- Brian Terry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 Sensors & Actuators 2.1 Problems Problem 2.1 (Music icon address What screen-row-column address would the controller assign to the music icon shown in Figure 2.10 if the icon is located on the third screen of 16 possible screens? (ans: Sixteen screens have 4-bit addresses from 0000 (first screen to 1111 (sixteenth screen. The third screen has address 0010, giving the music icon the screen-row-column address Problem 2.2 (Calculator switch array A scientific calculator has 50 keys for digits and logarithmic and trigonometric functions arranged in five rows and ten columns. Specify a binary address code to indicate what key was pressed. (ans: Five rows require a 3-bit code and ten columns a 4-bit code. Hence, each key has a 7 bit address. Problem 2.3 (Forming a touch screen switch array A touch screen array has a count of rows and columns that sums to 10. What is the structure of the array that accommodates the maximum number of keys? (ans: Five rows and five columns accommodate 25 switch locations. Problem 2.4 (Finger swipe along a switch array Extending Example 2.7, a linear switch array is 10 cm long and has a resolution R s =2switches/mm. A swipe motion is detected if the mid-point changes by more than 8 switches. If the sampling period T s =0.1 s, what is the minimum finger swipe speed along the linear array that indicates a swipe motion? (ans: δx m =8switches, R s =2switches/mm, and T s =0.1s, gives v min = δx m 8 switches = R s T s 2 switches/mm 0.1 s =40mm/s 9
2 10 CHAPTER 2. SENSORS & ACTUATORS Problem 2.5 (Multiple finger gesture Extending Example 2.8, a linear switch array is 10 cm long and has a resolution R s =2switches/mm, and sampling period T s =0.1 s. If P 1=20and P 2=40 and P 1 =22and P 2 =36is sensed as a gesture, what is the finger swipe speed? Is it widening or spreading? (ans: S = P 2 P 1=40 20 = 20 S 20 switches = R s 2 switches/mm =10mm S = P 2 P 1 =36 22 = 14 S 14 switches = R s 2 switches/mm =7mm Hence, the finger separation narrows. The widening separation speed is v F = S /R s S/R s T s = 7 mm 10 mm 0.1 s Equivalently, the finger narrowing separation speed is 30 mm/s. = 30 mm/s Problem 2.6 (Number of bits in a large color LED display A large color billboard is a two-dimensional array of pixels, with each pixel containing red, green and blue LEDs. (Single LED packages contain separate R, G, and B LEDs inside. Assuming that each LED is controlled to shine at one of 256 levels, how many bits are needed to specify a color image on the billboard? How many different colors can each 3-LED pixel display? (ans: Number of LEDs is = ( 3 million 256 levels are set by 8 bits (= 2 3, so the total number of bits per image equals , or 24 million bits. The number of colors that each 3-LED pixel can display equals 2 24 = = ( 16 million colors Problem 2.7 (Number of possible images in a large color LED display A large color billboard is a twodimensional array of pixels, with each pixel containing red, green and blue LEDs. Assuming that each LED is controlled to shine at one of 256 levels, what is the number of different images that can be displayed? Express answer as a power of 10. (ans: The number of colors each RGB pixel can display equals The number of different possible images that 10 6 pixels can display is = or 16 trillion images.
3 2.1. PROBLEMS 11 Problem 2.8 (Bit rate to generate a full-screen movie A video game displays images on your laptop monitor having a resolution of pixels. Each pixel contains a red, green, and blue LEDs, and each LED is controlled to shine at one of 256 levels. The game produces a new image on the screen 60 times per second. How many bits per second are being sent to your monitor while you are playing your game? Give answer in scientific notation (x.xx 10 y. (ans: Number of LEDs equals 1, 680 1, 050 3= LEDs/frame 256 levels per LED are set by 8 bits, so the total number of bits per frame equals 8 bits/led LEDs/frame = bits/frame At 60 frames per second, the bit rate equals 60 frames/s bits/frame = bits/s Problem 2.9 (Smartphone location from two range measurements This problem considers the location information using the range values measured by two antennas. Let antennas A1 and A2 be located 5 km apart. Determine the two possible locations for the smartphone relative to antenna A1 when the smartphone range from A1 is 3 km and from A2 is 3.5 km. (ans: Let A1 be at (0,0, and A2 at (5,0 km. Smartphone location is (x S,y S. Then, A1 range value R 1 =3gives x 2 S + y 2 S =9 A2 range value R 2 =3.5 gives (x S y 2 S =12.25 Equating both to y 2 S gives y 2 S =9 x 2 S =12.25 (x S 5 2 [= (x 2 S 10x S + 25] Canceling x 2 S and solving for x S yields x S = The two solutions for y S come from the A1 equation =2.175 km y S = ± 9 x 2 S = ± = ± = ±2.066 km
4 12 CHAPTER 2. SENSORS & ACTUATORS Problem 2.10 (Smartphone location region caused by range errors Sketch and determine the four points defining the region that contains your smartphone when the range measured from antenna A1 is (3 ± 0.1 km and that from A2 is (3.5 ± 0.1 km. (ans: Let A1 be at (0,0, and A2 at (5,0 km. Smartphone location is (x S,y S. Consider solutions due to positive (+ and negative ( errors with the fours cases (++, (+, ( +, (. First (++, A1 range value R 1 =3.1 and A2 range value R 2 =3.6 give x S++ = The two solutions for y S come from the A1 equation =2.17 km y S++ = ± = ±2.22 km For (+, A1 range value R 1 =3.1 and A2 range value R 2 =3.4 give x S+ = The two solutions for y S come from the A1 equation =2.31 km y S+ = ± = ±2.07 km For ( +, A1 range value R 1 =2.9 and A2 range value R 2 =3.6 give x S + = The two solutions for y S come from the A1 equation =2.05 km y S + = ± = ±2.06 km For (, A1 range value R 1 =2.9 and A2 range value R 2 =3.4 give x S = The two solutions for y S come from the A1 equation =2.19 km y S = ± = ±1.91 km Problem 2.11 (Pulse time for a bar code scan In Example 2.21, if a laser spot moves across the bar code at 10 m/s, and the width of the thinnest bar is 1 mm, what is the duration of the shortest pulse produced by the scanner? Give answer in μs (10 6 s. (ans: t = d v = 10 3 m 10 m/s =10 4 s = μs
5 2.1. PROBLEMS 13 Problem 2.12 (IR range sensor In an IR autofocus camera, the emitter and detector are separated by 1 cm and positioned 1 cm behind the lenses, which are modeled as pinholes. The light reflected from an object produces a spot 1 mm from the centerline of the detector pinhole. What is the range of the object from the camera in meters (m? (ans: With s =10 2 m, f =10 2 m, x =10 3 m gives r = sf x = 10 2 m 10 2 m 10 3 m =0.10 m Problem 2.13 (Digital IR range sensor In a digital IR autofocus camera, the emitter and detector are 1 cm apart and the detector array is 1 cm behind the lens. An IR detector element has near and far limits x F =0.01 mm and x N =0.02 mm that senses light reflected from an object located from r N to r F in range. Determine the values of r N and r F in m. (ans:s =10 2 m, f =10 2 m, x F =10 5 m gives s =10 2 m, f =10 2 m, x N = m gives r F = sf = 10 2 m 10 2 m x F 10 5 =10m m r N = sf x F = 10 2 m 10 2 m m =5m Problem 2.14 (Digital IR range sensor dimensions In a digital IR autofocus camera, the emitter and detector are 1 cm apart and the detector array is 1 cm behind the lens. What are the detector element s near and far limits (x F and x N that senses light reflected from an object located 1 m to 4 m away? Give answer in millimeters (mm. (ans:s =10 2 m, f =10 2 m, r F =4m gives x F = sf = 10 2 m 10 2 m = m = m =0.025 mm r F 4 m s =10 2 m, f =10 2 m, r N =1m gives x N = sf = 10 2 m 10 2 m =10 4 m = m =0.1mm r N 1 m
6 14 CHAPTER 2. SENSORS & ACTUATORS Problem 2.15 (Sonar ranging - range to TOF A sonar system operates in air up to a maximum range of 4 m. What is the maximum TOF? Give answer in ms (10 3 s? (ans: c = 343 m/s gives TOF max = 2r max c = 8 m =0.023 s =23ms 343 m/s Problem 2.16 (Sonar ranging - TOF to range A sonar system observes a TOF =10ms. What is the object range in meters (m? (ans: c = 343 m/s gives d = c TOF 2 = 343 m/s 10 2 s 2 =1.72 m Problem 2.17 (Sonar ranging resolution A sonar system experiences a jitter in the echo arrival time because of dynamic temperature variations in air, which limits the TOF resolution to ΔTOF = ±50μs. What is the corresponding sonar range resolution Δr in mm? (ans: c = 343 m/s gives Δd = c ΔTOF 2 = 343 m/s ± s 2 = ± m =8.58 mm Problem 2.18 (Radar ranging - range to TOF A radar system operates up to a maximum range of m. What is the maximum TOF? (ans: c = m/s gives TOF max = 2r max c = m m/s = s =0.667 μs Problem 2.19 (Radar ranging - TOF to range A radar system observes a TOF = 0.1 μs. What is the object range in meters (m? (ans: c = m/s gives r = c TOF 2 = m/s 10 7 s 2 =15m
7 2.1. PROBLEMS 15 Problem 2.20 (Radar ranging resolution A radar system is specified to have a range resolution of ±0.1m. What is the corresponding resolution in the radar TOF? (ans: c = m/s gives ΔTOF = 2Δr c = ± m m/s = ± s = ± s (± 0.67 ns
8 16 CHAPTER 2. SENSORS & ACTUATORS 2.2 Matlab Projects Project 2.1 (Acquire microphone speech signal Using the Matlab script in Example 16.9 as a guide, acquire speech data from the microphone on your laptop and display -sample and 1,000-sample waveforms. (ans: % Microphone_input & speaker output clear % clears workspace clf % clears figures recobj = audiorecorder(8000, 8, 1; % define ADC specs disp( Start speaking now % prompt speaker recordblocking(recobj, 2; % record for 2 sec disp( End of recording ; % indicate end play(recobj; % playback recording. myrecording = getaudiodata(recobj; % form data array nr = length(myrecording/2; % middle of array subplot(2,1,1,plot(myrecording(nr-50:nr+49; % Plot samplesfrom middle. grid on title( samples from myrecording xlabel( time (125 \mus/unit ylabel( amplitude subplot(2,1,2,plot(myrecording(nr-:nr+499; % Plot 0 samplesfrom middle. grid on title( 0 samples from myrecording xlabel( time (125 \mus/unit ylabel( amplitude 0.15 samples from myrecording amplitude (arb. units time (125 µs/unit samples from myrecording amplitude (arb. units time (125 µs/unit
9 2.2. MATLAB PROJECTS 17 Project 2.2 (Having fun with speech Write a Matlab program that plays acquired microphone speech normally and after a one second pause backwards, that is, in time-reversed order. (ans: clear % clears workspace recobj = audiorecorder(8000, 8, 1; % define ADC specs disp( Start speaking now % prompt speaker recordblocking(recobj, 2; % record for 2 sec disp( End of recording ; % indicate end play(recobj; % playback recording. myrecording = getaudiodata(recobj; % store data in array sound(myrecording,8000 % play the speech on the speaker revrecording = myrecording; for i=1:length(myrecording revrecording(length(myrecording+1-i = myrecording(i; end sound(revrecording,8000 % play the speech on the speaker Project 2.3 (Transform a jpeg image file into 3D matrix Using the Matlab script in Example as a guide, acquire a jpeg image file on your laptop, transform it into 3D matrix and display in image format. (ans: The Matlab function image( takes either a double-precision variable in range [0,1] or a uint8 (unsigned 8-bit variable in the range [0,255]. The image( function figures out the variable type. clear filename = input( enter filename, s ; filename = [filename.jpg ] Im = imread(filename; %Im is uint8 [0,255] subplot(1,2,1, image(im title( Original image R = zeros(size(im; % R is double R = double(im/255; % convert R to [0,1] subplot(1,2,2,image(r % R image title( Image from matrix Original image Image from matrix
10 18 CHAPTER 2. SENSORS & ACTUATORS Interesting addition: Matlab script that forms a random image. The Matlab function image( takes either a double-precision variable in range [0,1] or a uint8 (unsigned 8-bit variable in the range [0,255]. The image( function figures out the variable type. clear matrix= rand(,; % color intensities [0.1] [m n]=size(matrix; my_imager = zeros(m,n,3; %initialize the R image my_imageg = zeros(m,n,3; %initialize the G image my_imageb = zeros(m,n,3; %initialize the B image my_imagergb = zeros(m,n,3; %initialize the RGB image my_imager(:,:,1 = matrix; % R image subplot(2,2,1,image(my_imager % plot R image % plots square pixels title( Red image my_imageg(:,:,2 = matrix; % G image subplot(2,2,2,image(my_imageg % plot G image % plots square pixels title( Green image my_imageb(:,:,3 = matrix; % B image subplot(2,2,3,image(my_imageb % plot B image % plots square pixels title( Blue image my_imagergb(:,:,1 = matrix; % R component my_imagergb(:,:,2 = matrix; % G component my_imagergb(:,:,3 = matrix; % B component subplot(2,2,4,image(my_imagergb % plot RGB image % plots square pixels title( RGB image imwrite(my_imagergb, rand_image.jpg % save 10,000-pixel jpg Red image Green image Blue image RGB image
11 2.2. MATLAB PROJECTS 19 Project 2.4 (Transform Matlab color image The 3D matrix produced by a jpeg displays the x, y spacial location in the first two dimensions and the third dimension defining the red, blue, and green (RGB values at each spacial location. Modify an acquired jpeg image to display its R, G, and B components as separate images. (ans: clear filename = input( enter filename, s ; filename = [filename.jpg ] Im = imread(filename; %Im is uint8 [0,255] subplot(2,2,1, image(im R = zeros(size(im; % R is double R(:,:,1 = double(im(:,:,1/255; % convert R to [0,1] subplot(2,2,2,image(r % R image G = zeros(size(im; G(:,:,2 = double(im(:,:,2/255; subplot(2,2,3,image(g B = zeros(size(im; B(:,:,3 = double(im(:,:,3/255; subplot(2,2,4,image(b % G image % B image
12 20 CHAPTER 2. SENSORS & ACTUATORS Project 2.5 (Convert a color jpeg image into a gray-scale image Using the Matlab script in Example 16.12, generate a gray-scale image that is a 2D matrix of numbers that vary from 0 to 255. (ans: clear filename = input( enter filename, s ; filename = [filename.jpg ] A8 = imread(filename; % uint8 values [0,255] subplot(1,2,1,image(a8; % produces square pixels [R C D] = size(a8; % row, column and depth Gray = zeros(r,c; % form gray-scale image matrix for i=1:r for j = 1:C D = cast(a8(i,j,:, double ; % convert from uint8 to double for calcs Gray(i,j = sqrt(sum(d.ˆ2/3 ; % sqrt (sum of squares/3 = gray-level end end Gray = cast(floor(gray, uint8 ; % convert to 8-bit integer A(:,:,1 = Gray; % gray-scale image has equal RGB values A(:,:,2 = Gray; A(:,:,3 = Gray; subplot(1,2,2,image(a; % plot gray-scale image imwrite(a, gray_image.jpg % save gray-scale jpg
(ans: Five rows require a 3-bit code and ten columns a 4-bit code. Hence, each key has a 7 bit address.
 Chapter 2 Edited with the trial version of Foxit Advanced PDF Editor Sensors & Actuators 2.1 Problems Problem 2.1 (Music icon address What screen-row-column address would the controller assign to the music
Chapter 2 Edited with the trial version of Foxit Advanced PDF Editor Sensors & Actuators 2.1 Problems Problem 2.1 (Music icon address What screen-row-column address would the controller assign to the music
(ans: Five rows and five columns accommodate 25 switch locations. ) 8 switches = 40 mm/s 2 switches/mm 0.1 s
 Chapter Sensors & Actuators.1 Problems Problem.1 (Music icon address What screen-row-column address would the controller assign to the music icon shown in Figure.10 if the icon is located on the third
Chapter Sensors & Actuators.1 Problems Problem.1 (Music icon address What screen-row-column address would the controller assign to the music icon shown in Figure.10 if the icon is located on the third
University of Bahrain
 University of Bahrain College of Engineering Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Experiment 5 EEG 453 Multimedia Audio processing Objectives This experiment demonstrates different Audio processing
University of Bahrain College of Engineering Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Experiment 5 EEG 453 Multimedia Audio processing Objectives This experiment demonstrates different Audio processing
Matlab for CS6320 Beginners
 Matlab for CS6320 Beginners Basics: Starting Matlab o CADE Lab remote access o Student version on your own computer Change the Current Folder to the directory where your programs, images, etc. will be
Matlab for CS6320 Beginners Basics: Starting Matlab o CADE Lab remote access o Student version on your own computer Change the Current Folder to the directory where your programs, images, etc. will be
GE U111 HTT&TL, Lab 1: The Speed of Sound in Air, Acoustic Distance Measurement & Basic Concepts in MATLAB
 GE U111 HTT&TL, Lab 1: The Speed of Sound in Air, Acoustic Distance Measurement & Basic Concepts in MATLAB Contents 1 Preview: Programming & Experiments Goals 2 2 Homework Assignment 3 3 Measuring The
GE U111 HTT&TL, Lab 1: The Speed of Sound in Air, Acoustic Distance Measurement & Basic Concepts in MATLAB Contents 1 Preview: Programming & Experiments Goals 2 2 Homework Assignment 3 3 Measuring The
Play with image files 2-dimensional array matrix
 Previous class: Play with sound files Practice working with vectors Now: Play with image files 2-dimensional array matrix A picture as a matrix 2-dimensional array 1458-by-2084 150 149 152 153 152 155
Previous class: Play with sound files Practice working with vectors Now: Play with image files 2-dimensional array matrix A picture as a matrix 2-dimensional array 1458-by-2084 150 149 152 153 152 155
Brief Introduction to Vision and Images
 Brief Introduction to Vision and Images Charles S. Tritt, Ph.D. January 24, 2012 Version 1.1 Structure of the Retina There is only one kind of rod. Rods are very sensitive and used mainly in dim light.
Brief Introduction to Vision and Images Charles S. Tritt, Ph.D. January 24, 2012 Version 1.1 Structure of the Retina There is only one kind of rod. Rods are very sensitive and used mainly in dim light.
MATLAB Image Processing Toolbox
 MATLAB Image Processing Toolbox Copyright: Mathworks 1998. The following is taken from the Matlab Image Processing Toolbox users guide. A complete online manual is availabe in the PDF form (about 5MB).
MATLAB Image Processing Toolbox Copyright: Mathworks 1998. The following is taken from the Matlab Image Processing Toolbox users guide. A complete online manual is availabe in the PDF form (about 5MB).
Chapter 8. Representing Multimedia Digitally
 Chapter 8 Representing Multimedia Digitally Learning Objectives Explain how RGB color is represented in bytes Explain the difference between bits and binary numbers Change an RGB color by binary addition
Chapter 8 Representing Multimedia Digitally Learning Objectives Explain how RGB color is represented in bytes Explain the difference between bits and binary numbers Change an RGB color by binary addition
Experiment 8: Sampling
 Prepared By: 1 Experiment 8: Sampling Objective The objective of this Lab is to understand concepts and observe the effects of periodically sampling a continuous signal at different sampling rates, changing
Prepared By: 1 Experiment 8: Sampling Objective The objective of this Lab is to understand concepts and observe the effects of periodically sampling a continuous signal at different sampling rates, changing
Experiment 1 Introduction to MATLAB and Simulink
 Experiment 1 Introduction to MATLAB and Simulink INTRODUCTION MATLAB s Simulink is a powerful modeling tool capable of simulating complex digital communications systems under realistic conditions. It includes
Experiment 1 Introduction to MATLAB and Simulink INTRODUCTION MATLAB s Simulink is a powerful modeling tool capable of simulating complex digital communications systems under realistic conditions. It includes
Image processing in MATLAB. Linguaggio Programmazione Matlab-Simulink (2017/2018)
 Image processing in MATLAB Linguaggio Programmazione Matlab-Simulink (2017/2018) Images in MATLAB MATLAB can import/export several image formats BMP (Microsoft Windows Bitmap) GIF (Graphics Interchange
Image processing in MATLAB Linguaggio Programmazione Matlab-Simulink (2017/2018) Images in MATLAB MATLAB can import/export several image formats BMP (Microsoft Windows Bitmap) GIF (Graphics Interchange
A PROPOSED ALGORITHM FOR DIGITAL WATERMARKING
 A PROPOSED ALGORITHM FOR DIGITAL WATERMARKING Dr. Mohammed F. Al-Hunaity dr_alhunaity@bau.edu.jo Meran M. Al-Hadidi Merohadidi77@gmail.com Dr.Belal A. Ayyoub belal_ayyoub@ hotmail.com Abstract: This paper
A PROPOSED ALGORITHM FOR DIGITAL WATERMARKING Dr. Mohammed F. Al-Hunaity dr_alhunaity@bau.edu.jo Meran M. Al-Hadidi Merohadidi77@gmail.com Dr.Belal A. Ayyoub belal_ayyoub@ hotmail.com Abstract: This paper
Introduction to DSP ECE-S352 Fall Quarter 2000 Matlab Project 1
 Objective: Introduction to DSP ECE-S352 Fall Quarter 2000 Matlab Project 1 This Matlab Project is an extension of the basic correlation theory presented in the course. It shows a practical application
Objective: Introduction to DSP ECE-S352 Fall Quarter 2000 Matlab Project 1 This Matlab Project is an extension of the basic correlation theory presented in the course. It shows a practical application
CIS581: Computer Vision and Computational Photography Homework: Cameras and Convolution Due: Sept. 14, 2017 at 3:00 pm
 CIS58: Computer Vision and Computational Photography Homework: Cameras and Convolution Due: Sept. 4, 207 at 3:00 pm Instructions This is an individual assignment. Individual means each student must hand
CIS58: Computer Vision and Computational Photography Homework: Cameras and Convolution Due: Sept. 4, 207 at 3:00 pm Instructions This is an individual assignment. Individual means each student must hand
Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon )
 ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
6.098/6.882 Computational Photography 1. Problem Set 1. Assigned: Feb 9, 2006 Due: Feb 23, 2006
 6.098/6.882 Computational Photography 1 Problem Set 1 Assigned: Feb 9, 2006 Due: Feb 23, 2006 Note The problems marked with 6.882 only are for the students who register for 6.882. (Of course, students
6.098/6.882 Computational Photography 1 Problem Set 1 Assigned: Feb 9, 2006 Due: Feb 23, 2006 Note The problems marked with 6.882 only are for the students who register for 6.882. (Of course, students
Colorado School of Mines. Computer Vision. Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science.
 Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Sensors and Image Formation Imaging sensors and models of image formation Coordinate systems Digital
Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Sensors and Image Formation Imaging sensors and models of image formation Coordinate systems Digital
Some Basic Concepts of Remote Sensing. Lecture 2 August 31, 2005
 Some Basic Concepts of Remote Sensing Lecture 2 August 31, 2005 What is remote sensing Remote Sensing: remote sensing is science of acquiring, processing, and interpreting images and related data that
Some Basic Concepts of Remote Sensing Lecture 2 August 31, 2005 What is remote sensing Remote Sensing: remote sensing is science of acquiring, processing, and interpreting images and related data that
k y 2k y,max k x 2k x,max
 EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2012 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Assignment 5 Due Feb 26, 2012 1. Finish reading Nishimura Ch. 5. 2. For the 16 turn spiral trajectory, plotted below, what is the a) Spatial resolution,
EE225E/BIOE265 Spring 2012 Principles of MRI Miki Lustig Assignment 5 Due Feb 26, 2012 1. Finish reading Nishimura Ch. 5. 2. For the 16 turn spiral trajectory, plotted below, what is the a) Spatial resolution,
Assignment: Light, Cameras, and Image Formation
 Assignment: Light, Cameras, and Image Formation Erik G. Learned-Miller February 11, 2014 1 Problem 1. Linearity. (10 points) Alice has a chandelier with 5 light bulbs sockets. Currently, she has 5 100-watt
Assignment: Light, Cameras, and Image Formation Erik G. Learned-Miller February 11, 2014 1 Problem 1. Linearity. (10 points) Alice has a chandelier with 5 light bulbs sockets. Currently, she has 5 100-watt
Digital Imaging Rochester Institute of Technology
 Digital Imaging 1999 Rochester Institute of Technology So Far... camera AgX film processing image AgX photographic film captures image formed by the optical elements (lens). Unfortunately, the processing
Digital Imaging 1999 Rochester Institute of Technology So Far... camera AgX film processing image AgX photographic film captures image formed by the optical elements (lens). Unfortunately, the processing
Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing
 Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing MATLAB for Image Processing Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 4- Matlab introduction Basic MATLAB commands MATLAB windows Reading images Displaying images image() colormap()
Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing MATLAB for Image Processing Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 4- Matlab introduction Basic MATLAB commands MATLAB windows Reading images Displaying images image() colormap()
CS 445 HW#2 Solutions
 1. Text problem 3.1 CS 445 HW#2 Solutions (a) General form: problem figure,. For the condition shown in the Solving for K yields Then, (b) General form: the problem figure, as in (a) so For the condition
1. Text problem 3.1 CS 445 HW#2 Solutions (a) General form: problem figure,. For the condition shown in the Solving for K yields Then, (b) General form: the problem figure, as in (a) so For the condition
ECE 5650/4650 MATLAB Project 1
 This project is to be treated as a take-home exam, meaning each student is to due his/her own work. The project due date is 4:30 PM Tuesday, October 18, 2011. To work the project you will need access to
This project is to be treated as a take-home exam, meaning each student is to due his/her own work. The project due date is 4:30 PM Tuesday, October 18, 2011. To work the project you will need access to
Lab 1. Basic Image Processing Algorithms Fall 2017
 Lab 1 Basic Image Processing Algorithms Fall 2017 Lab practices - Wednesdays 8:15-10:00, room 219: excercise leaders: Csaba Benedek, Balázs Nagy instructor: Péter Bogdány 8:15-10:00, room 220: excercise
Lab 1 Basic Image Processing Algorithms Fall 2017 Lab practices - Wednesdays 8:15-10:00, room 219: excercise leaders: Csaba Benedek, Balázs Nagy instructor: Péter Bogdány 8:15-10:00, room 220: excercise
5.1 Image Files and Formats
 5 IMAGE GRAPHICS IN THIS CHAPTER 5.1 IMAGE FILES AND FORMATS 5.2 IMAGE I/O 5.3 IMAGE TYPES AND PROPERTIES 5.1 Image Files and Formats With digital cameras and scanners available at ridiculously low prices,
5 IMAGE GRAPHICS IN THIS CHAPTER 5.1 IMAGE FILES AND FORMATS 5.2 IMAGE I/O 5.3 IMAGE TYPES AND PROPERTIES 5.1 Image Files and Formats With digital cameras and scanners available at ridiculously low prices,
Commercial Scanners and Science
 Commercial Scanners and Science Specs vs Reality Ian Shelton - DDO Bob Simcoe - Harvard 4/28/2008 RJS Starting with Pixels Photosensitive area on the CCD chip This pixel would often be called a 4um pixel
Commercial Scanners and Science Specs vs Reality Ian Shelton - DDO Bob Simcoe - Harvard 4/28/2008 RJS Starting with Pixels Photosensitive area on the CCD chip This pixel would often be called a 4um pixel
Chapter 5: Signal conversion
 Chapter 5: Signal conversion Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to: explain the need for signal conversion between analogue and digital form in communications and microprocessors
Chapter 5: Signal conversion Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to: explain the need for signal conversion between analogue and digital form in communications and microprocessors
Acoustic resolution. photoacoustic Doppler velocimetry. in blood-mimicking fluids. Supplementary Information
 Acoustic resolution photoacoustic Doppler velocimetry in blood-mimicking fluids Joanna Brunker 1, *, Paul Beard 1 Supplementary Information 1 Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University
Acoustic resolution photoacoustic Doppler velocimetry in blood-mimicking fluids Joanna Brunker 1, *, Paul Beard 1 Supplementary Information 1 Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University
Putting It All Together: Computer Architecture and the Digital Camera
 461 Putting It All Together: Computer Architecture and the Digital Camera This book covers many topics in circuit analysis and design, so it is only natural to wonder how they all fit together and how
461 Putting It All Together: Computer Architecture and the Digital Camera This book covers many topics in circuit analysis and design, so it is only natural to wonder how they all fit together and how
Summer Solutions Common Core Mathematics 4. Common Core. Mathematics. Help Pages
 4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
THREE DIMENSIONAL FLASH LADAR FOCAL PLANES AND TIME DEPENDENT IMAGING
 THREE DIMENSIONAL FLASH LADAR FOCAL PLANES AND TIME DEPENDENT IMAGING ROGER STETTNER, HOWARD BAILEY AND STEVEN SILVERMAN Advanced Scientific Concepts, Inc. 305 E. Haley St. Santa Barbara, CA 93103 ASC@advancedscientificconcepts.com
THREE DIMENSIONAL FLASH LADAR FOCAL PLANES AND TIME DEPENDENT IMAGING ROGER STETTNER, HOWARD BAILEY AND STEVEN SILVERMAN Advanced Scientific Concepts, Inc. 305 E. Haley St. Santa Barbara, CA 93103 ASC@advancedscientificconcepts.com
TRIANGULATION-BASED light projection is a typical
 246 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 1, JANUARY 2004 A 120 110 Position Sensor With the Capability of Sensitive and Selective Light Detection in Wide Dynamic Range for Robust Active Range
246 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 1, JANUARY 2004 A 120 110 Position Sensor With the Capability of Sensitive and Selective Light Detection in Wide Dynamic Range for Robust Active Range
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2015 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2015 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Lab S-3: Beamforming with Phasors. N r k. is the time shift applied to r k
 DSP First, 2e Signal Processing First Lab S-3: Beamforming with Phasors Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification: The Exercise section
DSP First, 2e Signal Processing First Lab S-3: Beamforming with Phasors Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification: The Exercise section
COURSE ECE-411 IMAGE PROCESSING. Er. DEEPAK SHARMA Asstt. Prof., ECE department. MMEC, MM University, Mullana.
 COURSE ECE-411 IMAGE PROCESSING Er. DEEPAK SHARMA Asstt. Prof., ECE department. MMEC, MM University, Mullana. Why Image Processing? For Human Perception To make images more beautiful or understandable
COURSE ECE-411 IMAGE PROCESSING Er. DEEPAK SHARMA Asstt. Prof., ECE department. MMEC, MM University, Mullana. Why Image Processing? For Human Perception To make images more beautiful or understandable
Previous Lecture: Today s Lecture: Announcements: 2-d array examples. Image processing
 Previous Lecture: 2-d array examples Today s Lecture: Image processing Announcements: Discussion this week in Upson B7 lab Prelim 1 to be returned at of lecture. Unclaimed papers (and those on which student
Previous Lecture: 2-d array examples Today s Lecture: Image processing Announcements: Discussion this week in Upson B7 lab Prelim 1 to be returned at of lecture. Unclaimed papers (and those on which student
Motion illusion, rotating snakes
 Motion illusion, rotating snakes Previous classes Computer vision overview Mathematics of pinhole camera Sensors and light Recap: projection X t x K R 1 1 0 0 0 1 33 32 31 23 22 21 13 12 11 0 0 z y x t
Motion illusion, rotating snakes Previous classes Computer vision overview Mathematics of pinhole camera Sensors and light Recap: projection X t x K R 1 1 0 0 0 1 33 32 31 23 22 21 13 12 11 0 0 z y x t
Active Stereo Vision. COMP 4102A Winter 2014 Gerhard Roth Version 1
 Active Stereo Vision COMP 4102A Winter 2014 Gerhard Roth Version 1 Why active sensors? Project our own texture using light (usually laser) This simplifies correspondence problem (much easier) Pluses Can
Active Stereo Vision COMP 4102A Winter 2014 Gerhard Roth Version 1 Why active sensors? Project our own texture using light (usually laser) This simplifies correspondence problem (much easier) Pluses Can
Infrared Illumination for Time-of-Flight Applications
 WHITE PAPER Infrared Illumination for Time-of-Flight Applications The 3D capabilities of Time-of-Flight (TOF) cameras open up new opportunities for a number of applications. One of the challenges of TOF
WHITE PAPER Infrared Illumination for Time-of-Flight Applications The 3D capabilities of Time-of-Flight (TOF) cameras open up new opportunities for a number of applications. One of the challenges of TOF
PLazeR. a planar laser rangefinder. Robert Ying (ry2242) Derek Xingzhou He (xh2187) Peiqian Li (pl2521) Minh Trang Nguyen (mnn2108)
 PLazeR a planar laser rangefinder Robert Ying (ry2242) Derek Xingzhou He (xh2187) Peiqian Li (pl2521) Minh Trang Nguyen (mnn2108) Overview & Motivation Detecting the distance between a sensor and objects
PLazeR a planar laser rangefinder Robert Ying (ry2242) Derek Xingzhou He (xh2187) Peiqian Li (pl2521) Minh Trang Nguyen (mnn2108) Overview & Motivation Detecting the distance between a sensor and objects
DSP First Lab 06: Digital Images: A/D and D/A
 DSP First Lab 06: Digital Images: A/D and D/A Pre-Lab and Warm-Up: You should read at least the Pre-Lab and Warm-up sections of this lab assignment and go over all exercises in the Pre-Lab section before
DSP First Lab 06: Digital Images: A/D and D/A Pre-Lab and Warm-Up: You should read at least the Pre-Lab and Warm-up sections of this lab assignment and go over all exercises in the Pre-Lab section before
EEE 187: Robotics. Summary 11: Sensors used in Robotics
 1 EEE 187: Robotics Summary 11: Sensors used in Robotics Fig. 1. Sensors are needed to obtain internal quantities such as joint angle and external information such as location in maze Sensors are used
1 EEE 187: Robotics Summary 11: Sensors used in Robotics Fig. 1. Sensors are needed to obtain internal quantities such as joint angle and external information such as location in maze Sensors are used
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2016 Textbook http://szeliski.org/book/ General Comments Prerequisites Linear algebra!!!
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2016 Textbook http://szeliski.org/book/ General Comments Prerequisites Linear algebra!!!
RGB COLORS. Connecting with Computer Science cs.ubc.ca/~hoos/cpsc101
 RGB COLORS Clicker Question How many numbers are commonly used to specify the colour of a pixel? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 or more 2 Yellow = R + G? Combining red and green makes yellow Taught in elementary
RGB COLORS Clicker Question How many numbers are commonly used to specify the colour of a pixel? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 or more 2 Yellow = R + G? Combining red and green makes yellow Taught in elementary
SECTION I - CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL IMAGING PROCESSING CONCEPTS
 RADT 3463 - COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT 3463 Computerized Imaging 1 SECTION I - CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL IMAGING PROCESSING CONCEPTS RADT 3463 COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT
RADT 3463 - COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT 3463 Computerized Imaging 1 SECTION I - CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL IMAGING PROCESSING CONCEPTS RADT 3463 COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Model 765 Fast Rise Time Pulse Generator
 Fast Rise Time Pulse Generator Features of the 765: 70 ps Rise (Tr) and Fall (Tf) Times +/- 5.0 Volts pk-pk Delay and Width Resolution of 10 ps Narrow Widths (300 ps) Jitter < 25 ps Complete Channel Multiplex
Fast Rise Time Pulse Generator Features of the 765: 70 ps Rise (Tr) and Fall (Tf) Times +/- 5.0 Volts pk-pk Delay and Width Resolution of 10 ps Narrow Widths (300 ps) Jitter < 25 ps Complete Channel Multiplex
Determining MTF with a Slant Edge Target ABSTRACT AND INTRODUCTION
 Determining MTF with a Slant Edge Target Douglas A. Kerr Issue 2 October 13, 2010 ABSTRACT AND INTRODUCTION The modulation transfer function (MTF) of a photographic lens tells us how effectively the lens
Determining MTF with a Slant Edge Target Douglas A. Kerr Issue 2 October 13, 2010 ABSTRACT AND INTRODUCTION The modulation transfer function (MTF) of a photographic lens tells us how effectively the lens
CHAPTER -15. Communication Systems
 CHAPTER -15 Communication Systems COMMUNICATION Communication is the act of transmission and reception of information. COMMUNICATION SYSTEM: A system comprises of transmitter, communication channel and
CHAPTER -15 Communication Systems COMMUNICATION Communication is the act of transmission and reception of information. COMMUNICATION SYSTEM: A system comprises of transmitter, communication channel and
New Features Guide. Version 2.00
 New Features Guide Version 2.00 Features added or changed as a result of firmware updates may no longer match the descriptions in the documentation supplied with this product. Visit our website for information
New Features Guide Version 2.00 Features added or changed as a result of firmware updates may no longer match the descriptions in the documentation supplied with this product. Visit our website for information
Lab S-2: Direction Finding: Time-Difference or Phase Difference
 DSP First, 2e Signal Processing First Lab S-2: Direction Finding: Time-Difference or Phase Difference Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification:
DSP First, 2e Signal Processing First Lab S-2: Direction Finding: Time-Difference or Phase Difference Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification:
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering. EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series
 THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series 1. Objective The goal of this laboratory exercise is to
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series 1. Objective The goal of this laboratory exercise is to
Lecture 1: Introduction to Matlab Programming
 What is Matlab? Lecture 1: Introduction to Matlab Programming Math 490 Prof. Todd Wittman The Citadel Matlab stands for. Matlab is a programming language optimized for linear algebra operations. It is
What is Matlab? Lecture 1: Introduction to Matlab Programming Math 490 Prof. Todd Wittman The Citadel Matlab stands for. Matlab is a programming language optimized for linear algebra operations. It is
Lab 8: Introduction to the e-puck Robot
 Lab 8: Introduction to the e-puck Robot This laboratory requires the following equipment: C development tools (gcc, make, etc.) C30 programming tools for the e-puck robot The development tree which is
Lab 8: Introduction to the e-puck Robot This laboratory requires the following equipment: C development tools (gcc, make, etc.) C30 programming tools for the e-puck robot The development tree which is
Today s Menu. Near Infrared Sensors
 Today s Menu Near Infrared Sensors CdS Cells Programming Simple Behaviors 1 Near-Infrared Sensors Infrared (IR) Sensors > Near-infrared proximity sensors are called IRs for short. These devices are insensitive
Today s Menu Near Infrared Sensors CdS Cells Programming Simple Behaviors 1 Near-Infrared Sensors Infrared (IR) Sensors > Near-infrared proximity sensors are called IRs for short. These devices are insensitive
CS/NEUR125 Brains, Minds, and Machines. Due: Wednesday, February 8
 CS/NEUR125 Brains, Minds, and Machines Lab 2: Human Face Recognition and Holistic Processing Due: Wednesday, February 8 This lab explores our ability to recognize familiar and unfamiliar faces, and the
CS/NEUR125 Brains, Minds, and Machines Lab 2: Human Face Recognition and Holistic Processing Due: Wednesday, February 8 This lab explores our ability to recognize familiar and unfamiliar faces, and the
4th Grade Mathematics Mathematics CC
 Course Description In Grade 4, instructional time should focus on five critical areas: (1) attaining fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing understanding of dividing to find quotients
Course Description In Grade 4, instructional time should focus on five critical areas: (1) attaining fluency with multi-digit multiplication, and developing understanding of dividing to find quotients
Set No.1. Code No: R
 Set No.1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Regular Examinations, November -2008 RADAR SYSTEMS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any
Set No.1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Regular Examinations, November -2008 RADAR SYSTEMS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any
Introduction to Color Theory
 Systems & Biomedical Engineering Department SBE 306B: Computer Systems III (Computer Graphics) Dr. Ayman Eldeib Spring 2018 Introduction to With colors you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a
Systems & Biomedical Engineering Department SBE 306B: Computer Systems III (Computer Graphics) Dr. Ayman Eldeib Spring 2018 Introduction to With colors you can set a mood, attract attention, or make a
Capturing Light in man and machine
 Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Capturing Light in man and machine CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2014 Etymology PHOTOGRAPHY light drawing / writing Image Formation Digital Camera
Exercise 1-4. The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION OF FUNDAMENTALS
 Exercise 1-4 The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the different parameters in the radar equation, and with the interaction between these
Exercise 1-4 The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the different parameters in the radar equation, and with the interaction between these
Measuring Distance Using Sound
 Measuring Distance Using Sound Distance can be measured in various ways: directly, using a ruler or measuring tape, or indirectly, using radio or sound waves. The indirect method measures another variable
Measuring Distance Using Sound Distance can be measured in various ways: directly, using a ruler or measuring tape, or indirectly, using radio or sound waves. The indirect method measures another variable
Filters. Signals are sequences of numbers. Simple algebraic operations on signals can perform useful functions: shifting multiplication addition
 Filters Signals are sequences of numbers. Simple algebraic operations on signals can perform useful functions: shifting multiplication addition Simple Example... Smooth points to better reveal trend X
Filters Signals are sequences of numbers. Simple algebraic operations on signals can perform useful functions: shifting multiplication addition Simple Example... Smooth points to better reveal trend X
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET ETN3046 ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS TRIMESTER 1 (2018/2019) ADC2 Digital Carrier Modulation
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET ETN3046 ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS TRIMESTER 1 (2018/2019) ADC2 Digital Carrier Modulation TC Chuah (2018 July) Page 1 ADC2 Digital Carrier Modulation with MATLAB
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET ETN3046 ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS TRIMESTER 1 (2018/2019) ADC2 Digital Carrier Modulation TC Chuah (2018 July) Page 1 ADC2 Digital Carrier Modulation with MATLAB
HCS / ACN 6389 Speech Perception Lab
 HCS / ACN 6389 Speech Perception Lab Course Requirements Matlab problems & lab assignments (40%) Oral presentations (10%) Term project paper (50%) Dr. Peter Assmann Fall 2017 2 Term project: important
HCS / ACN 6389 Speech Perception Lab Course Requirements Matlab problems & lab assignments (40%) Oral presentations (10%) Term project paper (50%) Dr. Peter Assmann Fall 2017 2 Term project: important
ELEC MatLab Introductory Lab. Performed: Monday January 20 th Submitted: Monday January 27 th 2014
 ELEC 1908 MatLab Introductory Lab Performed: Monday January 20 th 2014 Submitted: Monday January 27 th 2014 Performed By Name, Student # Name, Student # Teaching Assistant Svetlana Demptchenko Introduction
ELEC 1908 MatLab Introductory Lab Performed: Monday January 20 th 2014 Submitted: Monday January 27 th 2014 Performed By Name, Student # Name, Student # Teaching Assistant Svetlana Demptchenko Introduction
Previous Lecture: Today s Lecture: Announcements: 2-d array examples. Working with images
 Previous Lecture: 2-d array examples Today s Lecture: Working with images Announcements: Discussion this week in the UP B7 computer lab Prelim 1 to be returned at of lecture. Unclaimed papers (and those
Previous Lecture: 2-d array examples Today s Lecture: Working with images Announcements: Discussion this week in the UP B7 computer lab Prelim 1 to be returned at of lecture. Unclaimed papers (and those
Vishay s TSDP Receiver Series for Infrared Data Communications
 VISHAY SEMICONDUCTORS www.vishay.com Infrared Remote Control Receivers By John Fisher The TSDP series devices described in this application note are suitable for receiving low-speed infrared data communications
VISHAY SEMICONDUCTORS www.vishay.com Infrared Remote Control Receivers By John Fisher The TSDP series devices described in this application note are suitable for receiving low-speed infrared data communications
EP375 Computational Physics
 EP375 Computational Physics Topic 13 IMAGE PROCESSING Department of Engineering Physics University of Gaziantep Apr 2016 Sayfa 1 Content 1. Introduction 2. Nature of Image 3. Image Types / Colors 4. Reading,
EP375 Computational Physics Topic 13 IMAGE PROCESSING Department of Engineering Physics University of Gaziantep Apr 2016 Sayfa 1 Content 1. Introduction 2. Nature of Image 3. Image Types / Colors 4. Reading,
EE/GP140-The Earth From Space- Winter 2008 Handout #16 Lab Exercise #3
 EE/GP140-The Earth From Space- Winter 2008 Handout #16 Lab Exercise #3 Topic 1: Color Combination. We will see how all colors can be produced by combining red, green, and blue in different proportions.
EE/GP140-The Earth From Space- Winter 2008 Handout #16 Lab Exercise #3 Topic 1: Color Combination. We will see how all colors can be produced by combining red, green, and blue in different proportions.
CSC 170 Introduction to Computers and Their Applications. Lecture #3 Digital Graphics and Video Basics. Bitmap Basics
 CSC 170 Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture #3 Digital Graphics and Video Basics Bitmap Basics As digital devices gained the ability to display images, two types of computer graphics
CSC 170 Introduction to Computers and Their Applications Lecture #3 Digital Graphics and Video Basics Bitmap Basics As digital devices gained the ability to display images, two types of computer graphics
4.5.1 Mirroring Gain/Offset Registers GPIO CMV Snapshot Control... 14
 Thank you for choosing the MityCAM-C8000 from Critical Link. The MityCAM-C8000 MityViewer Quick Start Guide will guide you through the software installation process and the steps to acquire your first
Thank you for choosing the MityCAM-C8000 from Critical Link. The MityCAM-C8000 MityViewer Quick Start Guide will guide you through the software installation process and the steps to acquire your first
Physics. Waves and Radiation Homework Exercises. National 4 & 5. Clackmannanshire Physics Network 0914
 Physics National 4 & 5 Waves and Radiation ----- 0914 Summary Homework 1: Homework 2: Homework 3: Homework 4: Homework 5: Homework 6: Homework 7: Waves I -Wave definitions - Speed, distance, time calculations
Physics National 4 & 5 Waves and Radiation ----- 0914 Summary Homework 1: Homework 2: Homework 3: Homework 4: Homework 5: Homework 6: Homework 7: Waves I -Wave definitions - Speed, distance, time calculations
Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing
 Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ Digital Image Fundamentals 2 Digital Image Fundamentals
Image and Multidimensional Signal Processing Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ Digital Image Fundamentals 2 Digital Image Fundamentals
Development of intelligent systems
 Development of intelligent systems (RInS) Robot sensors Danijel Skočaj University of Ljubljana Faculty of Computer and Information Science Academic year: 2017/18 Development of intelligent systems Robotic
Development of intelligent systems (RInS) Robot sensors Danijel Skočaj University of Ljubljana Faculty of Computer and Information Science Academic year: 2017/18 Development of intelligent systems Robotic
1. Explain how Doppler direction is identified with FMCW radar. Fig Block diagram of FM-CW radar. f b (up) = f r - f d. f b (down) = f r + f d
 1. Explain how Doppler direction is identified with FMCW radar. A block diagram illustrating the principle of the FM-CW radar is shown in Fig. 4.1.1 A portion of the transmitter signal acts as the reference
1. Explain how Doppler direction is identified with FMCW radar. A block diagram illustrating the principle of the FM-CW radar is shown in Fig. 4.1.1 A portion of the transmitter signal acts as the reference
MATLAB: SIGNAL PROCESSING
 MATLAB: SIGNAL PROCESSING - 1 - P a g e CONTENT Chapter No. Title Page No. Chapter 1 Introduction 3 Chapter 2 Arithmetic Operations 4-6 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Calculations 7-9 Chapter 4 Matrices 10-13
MATLAB: SIGNAL PROCESSING - 1 - P a g e CONTENT Chapter No. Title Page No. Chapter 1 Introduction 3 Chapter 2 Arithmetic Operations 4-6 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Calculations 7-9 Chapter 4 Matrices 10-13
Winston C Hall Tuner Photography
 D4s Custom Banks Settings Shooting and Custom Setting Menus Created by: Winston C Hall Tuner Photography 714 D4s Shooting and Custom Settings Banks This guide is an outline of my recommendations for the
D4s Custom Banks Settings Shooting and Custom Setting Menus Created by: Winston C Hall Tuner Photography 714 D4s Shooting and Custom Settings Banks This guide is an outline of my recommendations for the
Q A bitmap file contains the binary on the left below. 1 is white and 0 is black. Colour in each of the squares. What is the letter that is reve
 R 25 Images and Pixels - Reading Images need to be stored and processed using binary. The simplest image format is for an image to be stored as a bitmap image. Bitmap images are made up of picture elements
R 25 Images and Pixels - Reading Images need to be stored and processed using binary. The simplest image format is for an image to be stored as a bitmap image. Bitmap images are made up of picture elements
Solution Set #2
 05-78-0 Solution Set #. For the sampling function shown, analyze to determine its characteristics, e.g., the associated Nyquist sampling frequency (if any), whether a function sampled with s [x; x] may
05-78-0 Solution Set #. For the sampling function shown, analyze to determine its characteristics, e.g., the associated Nyquist sampling frequency (if any), whether a function sampled with s [x; x] may
Lab 1: First Order CT Systems, Blockdiagrams, Introduction
 ECEN 3300 Linear Systems Spring 2010 1-18-10 P. Mathys Lab 1: First Order CT Systems, Blockdiagrams, Introduction to Simulink 1 Introduction Many continuous time (CT) systems of practical interest can
ECEN 3300 Linear Systems Spring 2010 1-18-10 P. Mathys Lab 1: First Order CT Systems, Blockdiagrams, Introduction to Simulink 1 Introduction Many continuous time (CT) systems of practical interest can
1 Introduction 2 Principle of operation
 Published in IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation Received on 13th January 2009 Revised on 17th March 2009 ISSN 1751-8784 New waveform design for magnetron-based marine radar N. Levanon Department of Electrical
Published in IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation Received on 13th January 2009 Revised on 17th March 2009 ISSN 1751-8784 New waveform design for magnetron-based marine radar N. Levanon Department of Electrical
Introduction to Computer Vision
 Introduction to Computer Vision CS / ECE 181B Thursday, April 1, 2004 Course Details HW #0 and HW #1 are available. Course web site http://www.ece.ucsb.edu/~manj/cs181b Syllabus, schedule, lecture notes,
Introduction to Computer Vision CS / ECE 181B Thursday, April 1, 2004 Course Details HW #0 and HW #1 are available. Course web site http://www.ece.ucsb.edu/~manj/cs181b Syllabus, schedule, lecture notes,
Vixar High Power Array Technology
 Vixar High Power Array Technology I. Introduction VCSELs arrays emitting power ranging from 50mW to 10W have emerged as an important technology for applications within the consumer, industrial, automotive
Vixar High Power Array Technology I. Introduction VCSELs arrays emitting power ranging from 50mW to 10W have emerged as an important technology for applications within the consumer, industrial, automotive
Lab P-8: Digital Images: A/D and D/A
 DSP First, 2e Signal Processing First Lab P-8: Digital Images: A/D and D/A Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification: The Warm-up section
DSP First, 2e Signal Processing First Lab P-8: Digital Images: A/D and D/A Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification: The Warm-up section
Waitlist. We ll let you know as soon as we can. Biggest issue is TAs
 Bela Borsodi Bela Borsodi Waitlist We ll let you know as soon as we can. Biggest issue is TAs CS 143 James Hays Many materials, courseworks, based from him + previous TA staff serious thanks! Textbook
Bela Borsodi Bela Borsodi Waitlist We ll let you know as soon as we can. Biggest issue is TAs CS 143 James Hays Many materials, courseworks, based from him + previous TA staff serious thanks! Textbook
GESTURE RECOGNITION SOLUTION FOR PRESENTATION CONTROL
 GESTURE RECOGNITION SOLUTION FOR PRESENTATION CONTROL Darko Martinovikj Nevena Ackovska Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering Skopje, R. Macedonia ABSTRACT Despite the fact that there are different
GESTURE RECOGNITION SOLUTION FOR PRESENTATION CONTROL Darko Martinovikj Nevena Ackovska Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering Skopje, R. Macedonia ABSTRACT Despite the fact that there are different
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
Dust reduction filter. Live View
 E P2 Art Filters, Multi Exposure, Multi aspect Tiltable, high contrast and high resolution electronic viewfinder* Accessory Port High Speed 12.3 Megapixel Live MOS sensor High performance built in Real
E P2 Art Filters, Multi Exposure, Multi aspect Tiltable, high contrast and high resolution electronic viewfinder* Accessory Port High Speed 12.3 Megapixel Live MOS sensor High performance built in Real
Images and Graphics. 4. Images and Graphics - Copyright Denis Hamelin - Ryerson University
 Images and Graphics Images and Graphics Graphics and images are non-textual information that can be displayed and printed. Graphics (vector graphics) are an assemblage of lines, curves or circles with
Images and Graphics Images and Graphics Graphics and images are non-textual information that can be displayed and printed. Graphics (vector graphics) are an assemblage of lines, curves or circles with
Oversubscription. Sorry, not fixed yet. We ll let you know as soon as we can.
 Bela Borsodi Bela Borsodi Oversubscription Sorry, not fixed yet. We ll let you know as soon as we can. CS 143 James Hays Continuing his course many materials, courseworks, based from him + previous staff
Bela Borsodi Bela Borsodi Oversubscription Sorry, not fixed yet. We ll let you know as soon as we can. CS 143 James Hays Continuing his course many materials, courseworks, based from him + previous staff
Lane Detection in Automotive
 Lane Detection in Automotive Contents Introduction... 2 Image Processing... 2 Reading an image... 3 RGB to Gray... 3 Mean and Gaussian filtering... 5 Defining our Region of Interest... 6 BirdsEyeView Transformation...
Lane Detection in Automotive Contents Introduction... 2 Image Processing... 2 Reading an image... 3 RGB to Gray... 3 Mean and Gaussian filtering... 5 Defining our Region of Interest... 6 BirdsEyeView Transformation...
ABC Math Student Copy
 Page 1 of 17 Physics Week 9(Sem. 2) Name Chapter Summary Waves and Sound Cont d 2 Principle of Linear Superposition Sound is a pressure wave. Often two or more sound waves are present at the same place
Page 1 of 17 Physics Week 9(Sem. 2) Name Chapter Summary Waves and Sound Cont d 2 Principle of Linear Superposition Sound is a pressure wave. Often two or more sound waves are present at the same place
CS101 Lecture 12: Digital Images. What You ll Learn Today
 CS101 Lecture 12: Digital Images Sampling and Quantizing Using bits to Represent Colors and Images Aaron Stevens (azs@bu.edu) 20 February 2013 What You ll Learn Today What is digital information? How to
CS101 Lecture 12: Digital Images Sampling and Quantizing Using bits to Represent Colors and Images Aaron Stevens (azs@bu.edu) 20 February 2013 What You ll Learn Today What is digital information? How to
IMAGE FORMATION. Light source properties. Sensor characteristics Surface. Surface reflectance properties. Optics
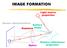 IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
Digitizing Color. Place Value in a Decimal Number. Place Value in a Binary Number. Chapter 11: Light, Sound, Magic: Representing Multimedia Digitally
 Chapter 11: Light, Sound, Magic: Representing Multimedia Digitally Fluency with Information Technology Third Edition by Lawrence Snyder Digitizing Color RGB Colors: Binary Representation Giving the intensities
Chapter 11: Light, Sound, Magic: Representing Multimedia Digitally Fluency with Information Technology Third Edition by Lawrence Snyder Digitizing Color RGB Colors: Binary Representation Giving the intensities
DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHY. Digital radiography is a film-less technology used to record radiographic images.
 DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHY Digital radiography is a film-less technology used to record radiographic images. 1 The purpose of digital imaging is to generate images that can be used in the diagnosis and assessment
DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHY Digital radiography is a film-less technology used to record radiographic images. 1 The purpose of digital imaging is to generate images that can be used in the diagnosis and assessment
High Dynamic Range Images
 High Dynamic Range Images TNM078 Image Based Rendering Jonas Unger 2004, V1.2 1 Introduction When examining the world around us, it becomes apparent that the lighting conditions in many scenes cover a
High Dynamic Range Images TNM078 Image Based Rendering Jonas Unger 2004, V1.2 1 Introduction When examining the world around us, it becomes apparent that the lighting conditions in many scenes cover a
