Filters. Signals are sequences of numbers. Simple algebraic operations on signals can perform useful functions: shifting multiplication addition
|
|
|
- Roy Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Filters Signals are sequences of numbers. Simple algebraic operations on signals can perform useful functions: shifting multiplication addition
2 Simple Example... Smooth points to better reveal trend X = [ ]
3 Smoothing Average each pair of adjacent points INPUT OUTPUT X = [ ] Y =[ ] plot (X,'o-') plot (Y,'o-') for k = 2:length(X) Y(k) = (X(k) + X(k-1)) / 2; end for k = 2:length(X) Y(k) =.5*X(k) +.5*X(k-1); end
4 Image Filtering Images are matrices, values specifies intensity (or RGB) of pixel Average adjacent intensities in rows and in columns Original Average adjacent pixels
5 Original Average adjacent pixels
6 Filtering Audio: buzz Original After two-point averaging 200 Hz pulse train 200 Hz pulse train Time in ms Time in ms
7 Pulse Train can be generated as a sum of phasors that are integer multiples of f0, each with equal amplitude.
8 Generating a pulse train Phasor function [signal, t] = make_buzz_phasor(srate, f0) t = 0:1/srate:.5; signal = zeros (1, length(t)); for freq = f0 : f0: srate/2 omega = 2*pi*freq; signal = signal + cos(omega*t); end Time function approach function [buzz, t] = make_buzz(srate, f0) dur =.5; totsamps = dur*srate; samps_per_cycle = fix((1/f0) * srate); buzz = (rem([0:totsamps], samps_per_cycle) == 0); t = (1:length (buzz))/srate;
9 Alternative Conceptualization of shift weight (multiply) add Averaging.5 * X = [ ].5 * X! = [ ].5*X = [ ].5*X!= [ ] Y = [ ]
10 Generalized Feedforward Filter (H) multiple of shifted versions of input (M) weighting coefficients associated with each (b) b is a vector of coefficients of length M, weighting the M shifted versions of the input Y(k) = b(1)* X(k) + b(2)* X(k-1) b(m)* X(k-(M-1)) In the averaging example, b=[.5.5] As M increases, signal gets smooth (if b>0)
11 Differencing Suppose b = [.5 -.5] This takes the difference between adjacent samples (which is the velocity) Opposite effect from smoothing--removes overall trend while emphasizing the noise plot (Y, 'o-') plot (X,'o-')
12 Differencing Images Original Difference
13 Differencing the buzz... Original After two-point difference 200 Hz pulse train 200 Hz pulse train Time in ms Time in ms
14 Frequency Response What happens if the input to an averaging filter is a phasor (sinusoid)? We know that it will be a sinusoid of the same frequency and amplitude as the input, but different amplitude and phase. Why? Filters delay, multiply and add. So the filter operation will sum the original sinusoid with others of the same frequency and different phases and amplitudes. We have already seen that the sum of sinusoids of the same frequency is itself a sinusoid, whose amplitude and phase can be determined from the amplitude and phase of the sinusoids being summed.
15 Frequency response of two point smoother Y (k) =.5X(k)+.5X(k 1) X(k) =e j k Y (k) =.5e j k +.5e j (k 1) Y (k) =.5e j k +.5e j k j Y (k) =.5e j k +.5e j k e j Means shift input by ω Y (k) =.5(1 + e j ) e j k Y (k) =.5(1 + e jw ) X(k) Y (k) X(k) =.5(1 + e j )=H( ) Transfer Function
16 Transfer Function H is complex number, function of ω: magnitude angle H( ) Arg(H( )) multiply the input phasor by H to get output phasor Y (k) =H( )X(k) abs(h) tells us the amplitude ratio output/input angle(h) tells us the phase shift of the output. Y (k) =H( ) X(k)e jarg(h( )) IF X(k) =e j k Y (k) =H( ) e j( k+arg(h( ))
17 To see what happens to the amplitude of a phasor of arbitrary frequency, we can plot the value of H(ω) for a set of ω values we choose. π radians/sample (=sampling rate/2) is the highest frequency that can be coded in a digital signal. Anything higher will be equivalent to a low frequency (its alias). Amplitude Response radians sample cycles 2 radians sr samples second
18 Phase Response To see what happens to the phase of a phasor of arbitrary frequency, we can plot the value of Arg(H(ω)) for a set of ω values we choose.
19 Code for plotting amplitude, phase response % AVERAGE2PTS_RESP % Louis Goldstein % 31 March 1996 % Use MATLAB to sketch magnitude and phase of H(w) for the simple average2pts filter. % % Set up a vector of test frequencies to plot, from % zero to the Nyquist frequency % Frequencies are represented in radians per sample nfreqs = 100; w = 0:pi/nfreqs:pi-(pi/nfreqs); % %Compute a vector of H values, one for each value of w. H =.5 * (1 + exp(-j*w)); % % Plot the Amplitude of H as a function of frequency: figure (1) plot (w/pi,abs(h),'or') xlabel ('Frequency in fractions of pi, the Nyquist frequency') ylabel ('Amplitude') % % Plot the phase of H as a function of frequency figure(2) plot (w/pi,angle(h)*180/pi, 'or') xlabel ('Frequency in fractions of pi, the Nyquist frequency') ylabel ('Phase shift in degrees')
20 Distributivity of Filters Filters are distributive. So H is a linear filter (feedforward, but also feedback) If: X H Y W H Z Then: X+W H Y+Z
21 Filtering more complex signals Any periodic signal can be decomposed into a sum of phasors (X(ω)), each of which has its amplitude and phase (Fourier Theorem). The amplitude spectrum of the input shows the amplitudes of all the phasors that compose it. We can determine the filter output of a complex signal by summing the filter outputs of all the phasors that compose it. The resulting amplitudes will be shown in the amplitude spectrum of the output.
22 H(ω) Buzz input spectrum (f0 = 200 Hz) output spectrum
ECE 2713 Homework 7 DUE: 05/1/2018, 11:59 PM
 Spring 2018 What to Turn In: ECE 2713 Homework 7 DUE: 05/1/2018, 11:59 PM Dr. Havlicek Submit your solution for this assignment electronically on Canvas by uploading a file to ECE-2713-001 > Assignments
Spring 2018 What to Turn In: ECE 2713 Homework 7 DUE: 05/1/2018, 11:59 PM Dr. Havlicek Submit your solution for this assignment electronically on Canvas by uploading a file to ECE-2713-001 > Assignments
Basic Signals and Systems
 Chapter 2 Basic Signals and Systems A large part of this chapter is taken from: C.S. Burrus, J.H. McClellan, A.V. Oppenheim, T.W. Parks, R.W. Schafer, and H. W. Schüssler: Computer-based exercises for
Chapter 2 Basic Signals and Systems A large part of this chapter is taken from: C.S. Burrus, J.H. McClellan, A.V. Oppenheim, T.W. Parks, R.W. Schafer, and H. W. Schüssler: Computer-based exercises for
ECE 2713 Homework Matlab code:
 ECE 7 Homework 7 Spring 8 Dr. Havlicek. Matlab code: -------------------------------------------------------- P - Create and plot the signal x_[n] as a function of n. - Compute the DFT X_[k]. Plot the
ECE 7 Homework 7 Spring 8 Dr. Havlicek. Matlab code: -------------------------------------------------------- P - Create and plot the signal x_[n] as a function of n. - Compute the DFT X_[k]. Plot the
Digital Video and Audio Processing. Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises
 Digital Video and Audio Processing Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises Rudolf Mester Institut für Angewandte Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main 6th November 2002 Chapter
Digital Video and Audio Processing Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises Rudolf Mester Institut für Angewandte Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main 6th November 2002 Chapter
EEO 401 Digital Signal Processing Prof. Mark Fowler
 EEO 41 Digital Signal Processing Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #17.5 MATLAB Examples Reading Assignment: MATLAB Tutorial on Course Webpage 1/24 Folder Navigation Current folder name here Type commands here
EEO 41 Digital Signal Processing Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #17.5 MATLAB Examples Reading Assignment: MATLAB Tutorial on Course Webpage 1/24 Folder Navigation Current folder name here Type commands here
CS 591 S1 Midterm Exam Solution
 Name: CS 591 S1 Midterm Exam Solution Spring 2016 You must complete 3 of problems 1 4, and then problem 5 is mandatory. Each problem is worth 25 points. Please leave blank, or draw an X through, or write
Name: CS 591 S1 Midterm Exam Solution Spring 2016 You must complete 3 of problems 1 4, and then problem 5 is mandatory. Each problem is worth 25 points. Please leave blank, or draw an X through, or write
The Formula for Sinusoidal Signals
 The Formula for I The general formula for a sinusoidal signal is x(t) =A cos(2pft + f). I A, f, and f are parameters that characterize the sinusoidal sinal. I A - Amplitude: determines the height of the
The Formula for I The general formula for a sinusoidal signal is x(t) =A cos(2pft + f). I A, f, and f are parameters that characterize the sinusoidal sinal. I A - Amplitude: determines the height of the
Sampling and Reconstruction of Analog Signals
 Sampling and Reconstruction of Analog Signals Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to convert an analog signal to a discrete-time sequence via sampling (ii) Ability to construct an analog signal
Sampling and Reconstruction of Analog Signals Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to convert an analog signal to a discrete-time sequence via sampling (ii) Ability to construct an analog signal
Digital Signal Processing Fourier Analysis of Continuous-Time Signals with the Discrete Fourier Transform
 Digital Signal Processing Fourier Analysis of Continuous-Time Signals with the Discrete Fourier Transform D. Richard Brown III D. Richard Brown III 1 / 11 Fourier Analysis of CT Signals with the DFT Scenario:
Digital Signal Processing Fourier Analysis of Continuous-Time Signals with the Discrete Fourier Transform D. Richard Brown III D. Richard Brown III 1 / 11 Fourier Analysis of CT Signals with the DFT Scenario:
Syllabus Cosines Sampled Signals. Lecture 1: Cosines. ECE 401: Signal and Image Analysis. University of Illinois 1/19/2017
 Lecture 1: Cosines ECE 401: Signal and Image Analysis University of Illinois 1/19/2017 1 Syllabus 2 Cosines 3 Sampled Signals Outline 1 Syllabus 2 Cosines 3 Sampled Signals Who should take this course?
Lecture 1: Cosines ECE 401: Signal and Image Analysis University of Illinois 1/19/2017 1 Syllabus 2 Cosines 3 Sampled Signals Outline 1 Syllabus 2 Cosines 3 Sampled Signals Who should take this course?
1 Introduction and Overview
 DSP First, 2e Lab S-0: Complex Exponentials Adding Sinusoids Signal Processing First Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification: The
DSP First, 2e Lab S-0: Complex Exponentials Adding Sinusoids Signal Processing First Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification: The
DSP First. Laboratory Exercise #2. Introduction to Complex Exponentials
 DSP First Laboratory Exercise #2 Introduction to Complex Exponentials The goal of this laboratory is gain familiarity with complex numbers and their use in representing sinusoidal signals as complex exponentials.
DSP First Laboratory Exercise #2 Introduction to Complex Exponentials The goal of this laboratory is gain familiarity with complex numbers and their use in representing sinusoidal signals as complex exponentials.
Topic. Filters, Reverberation & Convolution THEY ARE ALL ONE
 Topic Filters, Reverberation & Convolution THEY ARE ALL ONE What is reverberation? Reverberation is made of echoes Echoes are delayed copies of the original sound In the physical world these are caused
Topic Filters, Reverberation & Convolution THEY ARE ALL ONE What is reverberation? Reverberation is made of echoes Echoes are delayed copies of the original sound In the physical world these are caused
Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon )
 ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
Here are some of Matlab s complex number operators: conj Complex conjugate abs Magnitude. Angle (or phase) in radians
 Lab #2: Complex Exponentials Adding Sinusoids Warm-Up/Pre-Lab (section 2): You may do these warm-up exercises at the start of the lab period, or you may do them in advance before coming to the lab. You
Lab #2: Complex Exponentials Adding Sinusoids Warm-Up/Pre-Lab (section 2): You may do these warm-up exercises at the start of the lab period, or you may do them in advance before coming to the lab. You
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis
 ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Prof. Paris Last updated: October 9, 2007 Part I Spectrum Representation of Signals Lecture: Sums of Sinusoids (of different frequency) Introduction Sum of Sinusoidal
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Prof. Paris Last updated: October 9, 2007 Part I Spectrum Representation of Signals Lecture: Sums of Sinusoids (of different frequency) Introduction Sum of Sinusoidal
Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals
 Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/1 1 Review of Complex Numbers Using Euler s famous formula for the complex exponential The
Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/1 1 Review of Complex Numbers Using Euler s famous formula for the complex exponential The
Lecture 3, Multirate Signal Processing
 Lecture 3, Multirate Signal Processing Frequency Response If we have coefficients of an Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter h, or in general the impulse response, its frequency response becomes (using
Lecture 3, Multirate Signal Processing Frequency Response If we have coefficients of an Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter h, or in general the impulse response, its frequency response becomes (using
Topic 2. Signal Processing Review. (Some slides are adapted from Bryan Pardo s course slides on Machine Perception of Music)
 Topic 2 Signal Processing Review (Some slides are adapted from Bryan Pardo s course slides on Machine Perception of Music) Recording Sound Mechanical Vibration Pressure Waves Motion->Voltage Transducer
Topic 2 Signal Processing Review (Some slides are adapted from Bryan Pardo s course slides on Machine Perception of Music) Recording Sound Mechanical Vibration Pressure Waves Motion->Voltage Transducer
Concordia University. Discrete-Time Signal Processing. Lab Manual (ELEC442) Dr. Wei-Ping Zhu
 Concordia University Discrete-Time Signal Processing Lab Manual (ELEC442) Course Instructor: Dr. Wei-Ping Zhu Fall 2012 Lab 1: Linear Constant Coefficient Difference Equations (LCCDE) Objective In this
Concordia University Discrete-Time Signal Processing Lab Manual (ELEC442) Course Instructor: Dr. Wei-Ping Zhu Fall 2012 Lab 1: Linear Constant Coefficient Difference Equations (LCCDE) Objective In this
Armstrong Atlantic State University Engineering Studies MATLAB Marina Sound Processing Primer
 Armstrong Atlantic State University Engineering Studies MATLAB Marina Sound Processing Primer Prerequisites The Sound Processing Primer assumes knowledge of the MATLAB IDE, MATLAB help, arithmetic operations,
Armstrong Atlantic State University Engineering Studies MATLAB Marina Sound Processing Primer Prerequisites The Sound Processing Primer assumes knowledge of the MATLAB IDE, MATLAB help, arithmetic operations,
Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation
 Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/15 1 Time-Frequency Spectrum We have seen that a wide range of interesting waveforms can be synthesized
Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/15 1 Time-Frequency Spectrum We have seen that a wide range of interesting waveforms can be synthesized
Synthesis: From Frequency to Time-Domain
 Synthesis: From Frequency to Time-Domain I Synthesis is a straightforward process; it is a lot like following a recipe. I Ingredients are given by the spectrum X (f )={(X 0, 0), (X 1, f 1 ), (X 1, f 1),...,
Synthesis: From Frequency to Time-Domain I Synthesis is a straightforward process; it is a lot like following a recipe. I Ingredients are given by the spectrum X (f )={(X 0, 0), (X 1, f 1 ), (X 1, f 1),...,
Frequency Division Multiplexing Spring 2011 Lecture #14. Sinusoids and LTI Systems. Periodic Sequences. x[n] = x[n + N]
![Frequency Division Multiplexing Spring 2011 Lecture #14. Sinusoids and LTI Systems. Periodic Sequences. x[n] = x[n + N] Frequency Division Multiplexing Spring 2011 Lecture #14. Sinusoids and LTI Systems. Periodic Sequences. x[n] = x[n + N]](/thumbs/88/116022205.jpg) Frequency Division Multiplexing 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture #4 complex exponentials discrete-time Fourier series spectral coefficients band-limited signals To engineer the sharing of a channel through frequency
Frequency Division Multiplexing 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture #4 complex exponentials discrete-time Fourier series spectral coefficients band-limited signals To engineer the sharing of a channel through frequency
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering. EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series
 THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series 1. Objective The goal of this laboratory exercise is to
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series 1. Objective The goal of this laboratory exercise is to
THE CITADEL THE MILITARY COLLEGE OF SOUTH CAROLINA. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. ELEC 423 Digital Signal Processing
 THE CITADEL THE MILITARY COLLEGE OF SOUTH CAROLINA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ELEC 423 Digital Signal Processing Project 2 Due date: November 12 th, 2013 I) Introduction In ELEC
THE CITADEL THE MILITARY COLLEGE OF SOUTH CAROLINA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ELEC 423 Digital Signal Processing Project 2 Due date: November 12 th, 2013 I) Introduction In ELEC
DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing
 DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing 2 nd Year Electronics Lab IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Table of Contents Equipment... 2 Aims... 2 Objectives... 2 Recommended Textbooks... 3 Recommended
DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing 2 nd Year Electronics Lab IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Table of Contents Equipment... 2 Aims... 2 Objectives... 2 Recommended Textbooks... 3 Recommended
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 31 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #19 C-T Systems: Frequency-Domain Analysis of Systems Reading Assignment: Section 5.2 of Kamen and Heck 1/17 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show
EECE 31 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #19 C-T Systems: Frequency-Domain Analysis of Systems Reading Assignment: Section 5.2 of Kamen and Heck 1/17 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show
ECE 3793 Matlab Project 4
 ECE 3793 Matlab Project 4 Spring 2017 Dr. Havlicek DUE: 5/3/2017, 11:59 PM What to Turn In: Make one file that contains your solution for this assignment. It can be an MS WORD file or a PDF file. For Problem
ECE 3793 Matlab Project 4 Spring 2017 Dr. Havlicek DUE: 5/3/2017, 11:59 PM What to Turn In: Make one file that contains your solution for this assignment. It can be an MS WORD file or a PDF file. For Problem
FFT analysis in practice
 FFT analysis in practice Perception & Multimedia Computing Lecture 13 Rebecca Fiebrink Lecturer, Department of Computing Goldsmiths, University of London 1 Last Week Review of complex numbers: rectangular
FFT analysis in practice Perception & Multimedia Computing Lecture 13 Rebecca Fiebrink Lecturer, Department of Computing Goldsmiths, University of London 1 Last Week Review of complex numbers: rectangular
ECE 2713 Design Project Solution
 ECE 2713 Design Project Solution Spring 218 Dr. Havlicek 1. (a) Matlab code: ---------------------------------------------------------- P1a Make a 2 second digital audio signal that contains a pure cosine
ECE 2713 Design Project Solution Spring 218 Dr. Havlicek 1. (a) Matlab code: ---------------------------------------------------------- P1a Make a 2 second digital audio signal that contains a pure cosine
END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time.
 END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS 2005 Unit: Day and Time: Time Allowed: ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time. Total Number of Questions:
END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS 2005 Unit: Day and Time: Time Allowed: ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time. Total Number of Questions:
Project I: Phase Tracking and Baud Timing Correction Systems
 Project I: Phase Tracking and Baud Timing Correction Systems ECES 631, Prof. John MacLaren Walsh, Ph. D. 1 Purpose In this lab you will encounter the utility of the fundamental Fourier and z-transform
Project I: Phase Tracking and Baud Timing Correction Systems ECES 631, Prof. John MacLaren Walsh, Ph. D. 1 Purpose In this lab you will encounter the utility of the fundamental Fourier and z-transform
Lab 4 Fourier Series and the Gibbs Phenomenon
 Lab 4 Fourier Series and the Gibbs Phenomenon EE 235: Continuous-Time Linear Systems Department of Electrical Engineering University of Washington This work 1 was written by Amittai Axelrod, Jayson Bowen,
Lab 4 Fourier Series and the Gibbs Phenomenon EE 235: Continuous-Time Linear Systems Department of Electrical Engineering University of Washington This work 1 was written by Amittai Axelrod, Jayson Bowen,
George Mason University ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Spring 2017
 Assigned: March 7, 017 Due Date: Week of April 10, 017 George Mason University ECE 01: Introduction to Signal Analysis Spring 017 Laboratory Project #7 Due Date Your lab report must be submitted on blackboard
Assigned: March 7, 017 Due Date: Week of April 10, 017 George Mason University ECE 01: Introduction to Signal Analysis Spring 017 Laboratory Project #7 Due Date Your lab report must be submitted on blackboard
Digital Signal Processing Lecture 1 - Introduction
 Digital Signal Processing - Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville August 20, 2015 Overview 1 2 3 4 Basic building blocks in DSP Frequency analysis Sampling Filtering
Digital Signal Processing - Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville August 20, 2015 Overview 1 2 3 4 Basic building blocks in DSP Frequency analysis Sampling Filtering
Additive Synthesis OBJECTIVES BACKGROUND
 Additive Synthesis SIGNALS & SYSTEMS IN MUSIC CREATED BY P. MEASE, 2011 OBJECTIVES In this lab, you will construct your very first synthesizer using only pure sinusoids! This will give you firsthand experience
Additive Synthesis SIGNALS & SYSTEMS IN MUSIC CREATED BY P. MEASE, 2011 OBJECTIVES In this lab, you will construct your very first synthesizer using only pure sinusoids! This will give you firsthand experience
Fourier Signal Analysis
 Part 1B Experimental Engineering Integrated Coursework Location: Baker Building South Wing Mechanics Lab Experiment A4 Signal Processing Fourier Signal Analysis Please bring the lab sheet from 1A experiment
Part 1B Experimental Engineering Integrated Coursework Location: Baker Building South Wing Mechanics Lab Experiment A4 Signal Processing Fourier Signal Analysis Please bring the lab sheet from 1A experiment
Signal Processing First Lab 02: Introduction to Complex Exponentials Multipath. x(t) = A cos(ωt + φ) = Re{Ae jφ e jωt }
 Signal Processing First Lab 02: Introduction to Complex Exponentials Multipath Pre-Lab and Warm-Up: You should read at least the Pre-Lab and Warm-up sections of this lab assignment and go over all exercises
Signal Processing First Lab 02: Introduction to Complex Exponentials Multipath Pre-Lab and Warm-Up: You should read at least the Pre-Lab and Warm-up sections of this lab assignment and go over all exercises
Lecture Schedule: Week Date Lecture Title
 http://elec3004.org Sampling & More 2014 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at The University of Queensland Lecture Schedule: Week Date Lecture Title 1 2-Mar Introduction 3-Mar
http://elec3004.org Sampling & More 2014 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at The University of Queensland Lecture Schedule: Week Date Lecture Title 1 2-Mar Introduction 3-Mar
ELT COMMUNICATION THEORY
 ELT 41307 COMMUNICATION THEORY Matlab Exercise #1 Sampling, Fourier transform, Spectral illustrations, and Linear filtering 1 SAMPLING The modeled signals and systems in this course are mostly analog (continuous
ELT 41307 COMMUNICATION THEORY Matlab Exercise #1 Sampling, Fourier transform, Spectral illustrations, and Linear filtering 1 SAMPLING The modeled signals and systems in this course are mostly analog (continuous
Subtractive Synthesis. Describing a Filter. Filters. CMPT 468: Subtractive Synthesis
 Subtractive Synthesis CMPT 468: Subtractive Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University November, 23 Additive synthesis involves building the sound by
Subtractive Synthesis CMPT 468: Subtractive Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University November, 23 Additive synthesis involves building the sound by
EECS 216 Winter 2008 Lab 2: FM Detector Part I: Intro & Pre-lab Assignment
 EECS 216 Winter 2008 Lab 2: Part I: Intro & Pre-lab Assignment c Kim Winick 2008 1 Introduction In the first few weeks of EECS 216, you learned how to determine the response of an LTI system by convolving
EECS 216 Winter 2008 Lab 2: Part I: Intro & Pre-lab Assignment c Kim Winick 2008 1 Introduction In the first few weeks of EECS 216, you learned how to determine the response of an LTI system by convolving
Signal Processing. Naureen Ghani. December 9, 2017
 Signal Processing Naureen Ghani December 9, 27 Introduction Signal processing is used to enhance signal components in noisy measurements. It is especially important in analyzing time-series data in neuroscience.
Signal Processing Naureen Ghani December 9, 27 Introduction Signal processing is used to enhance signal components in noisy measurements. It is especially important in analyzing time-series data in neuroscience.
1. In the command window, type "help conv" and press [enter]. Read the information displayed.
![1. In the command window, type help conv and press [enter]. Read the information displayed. 1. In the command window, type help conv and press [enter]. Read the information displayed.](/thumbs/82/86785923.jpg) ECE 317 Experiment 0 The purpose of this experiment is to understand how to represent signals in MATLAB, perform the convolution of signals, and study some simple LTI systems. Please answer all questions
ECE 317 Experiment 0 The purpose of this experiment is to understand how to represent signals in MATLAB, perform the convolution of signals, and study some simple LTI systems. Please answer all questions
Circuit Analysis-II. Circuit Analysis-II Lecture # 2 Wednesday 28 th Mar, 18
 Circuit Analysis-II Angular Measurement Angular Measurement of a Sine Wave ü As we already know that a sinusoidal voltage can be produced by an ac generator. ü As the windings on the rotor of the ac generator
Circuit Analysis-II Angular Measurement Angular Measurement of a Sine Wave ü As we already know that a sinusoidal voltage can be produced by an ac generator. ü As the windings on the rotor of the ac generator
Signal Processing First Lab 02: Introduction to Complex Exponentials Direction Finding. x(t) = A cos(ωt + φ) = Re{Ae jφ e jωt }
 Signal Processing First Lab 02: Introduction to Complex Exponentials Direction Finding Pre-Lab and Warm-Up: You should read at least the Pre-Lab and Warm-up sections of this lab assignment and go over
Signal Processing First Lab 02: Introduction to Complex Exponentials Direction Finding Pre-Lab and Warm-Up: You should read at least the Pre-Lab and Warm-up sections of this lab assignment and go over
Final Exam Practice Questions for Music 421, with Solutions
 Final Exam Practice Questions for Music 4, with Solutions Elementary Fourier Relationships. For the window w = [/,,/ ], what is (a) the dc magnitude of the window transform? + (b) the magnitude at half
Final Exam Practice Questions for Music 4, with Solutions Elementary Fourier Relationships. For the window w = [/,,/ ], what is (a) the dc magnitude of the window transform? + (b) the magnitude at half
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL and COMPUTER ENGINEERING. ECE 2025 Fall 1999 Lab #7: Frequency Response & Bandpass Filters
 GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL and COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2025 Fall 1999 Lab #7: Frequency Response & Bandpass Filters Date: 12 18 Oct 1999 This is the official Lab #7 description;
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL and COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2025 Fall 1999 Lab #7: Frequency Response & Bandpass Filters Date: 12 18 Oct 1999 This is the official Lab #7 description;
Signal Processing. Introduction
 Signal Processing 0 Introduction One of the premiere uses of MATLAB is in the analysis of signal processing and control systems. In this chapter we consider signal processing. The final chapter of the
Signal Processing 0 Introduction One of the premiere uses of MATLAB is in the analysis of signal processing and control systems. In this chapter we consider signal processing. The final chapter of the
Waveshaping Synthesis. Indexing. Waveshaper. CMPT 468: Waveshaping Synthesis
 Waveshaping Synthesis CMPT 468: Waveshaping Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University October 8, 23 In waveshaping, it is possible to change the spectrum
Waveshaping Synthesis CMPT 468: Waveshaping Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University October 8, 23 In waveshaping, it is possible to change the spectrum
AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE
 July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
y(n)= Aa n u(n)+bu(n) b m sin(2πmt)= b 1 sin(2πt)+b 2 sin(4πt)+b 3 sin(6πt)+ m=1 x(t)= x = 2 ( b b b b
 Exam 1 February 3, 006 Each subquestion is worth 10 points. 1. Consider a periodic sawtooth waveform x(t) with period T 0 = 1 sec shown below: (c) x(n)= u(n). In this case, show that the output has the
Exam 1 February 3, 006 Each subquestion is worth 10 points. 1. Consider a periodic sawtooth waveform x(t) with period T 0 = 1 sec shown below: (c) x(n)= u(n). In this case, show that the output has the
Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 7, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau
 Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 7, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau (Also see: Lecture ADSP, Slides 06) In discrete, digital signal we use the normalized frequency, T = / f s =: it is without a
Multirate Signal Processing Lecture 7, Sampling Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau (Also see: Lecture ADSP, Slides 06) In discrete, digital signal we use the normalized frequency, T = / f s =: it is without a
Sampling and aliasing Amplitude modulation
 Sampling and aliasing Amplitude modulation Signals and codes (SK) Department of Transport Telematics Faculty of Transportation Sciences, CTU in Prague Exercise 3 Exercise content Aliasing Computing aliases
Sampling and aliasing Amplitude modulation Signals and codes (SK) Department of Transport Telematics Faculty of Transportation Sciences, CTU in Prague Exercise 3 Exercise content Aliasing Computing aliases
Assignment 7: Tube Resonances
 Linguistics 582 Basics of Digital Signal Processing Reading: Assignment 7: Tube Resonances Stevens, K. (1989). On the quantal nature of speech. Journal of Phonetics, 17, 3-45. Read pp. 3-20. ONLY. Johnson,
Linguistics 582 Basics of Digital Signal Processing Reading: Assignment 7: Tube Resonances Stevens, K. (1989). On the quantal nature of speech. Journal of Phonetics, 17, 3-45. Read pp. 3-20. ONLY. Johnson,
Discrete-Time Signal Processing (DTSP) v14
 EE 392 Laboratory 5-1 Discrete-Time Signal Processing (DTSP) v14 Safety - Voltages used here are less than 15 V and normally do not present a risk of shock. Objective: To study impulse response and the
EE 392 Laboratory 5-1 Discrete-Time Signal Processing (DTSP) v14 Safety - Voltages used here are less than 15 V and normally do not present a risk of shock. Objective: To study impulse response and the
ELEC MatLab Introductory Lab. Performed: Monday January 20 th Submitted: Monday January 27 th 2014
 ELEC 1908 MatLab Introductory Lab Performed: Monday January 20 th 2014 Submitted: Monday January 27 th 2014 Performed By Name, Student # Name, Student # Teaching Assistant Svetlana Demptchenko Introduction
ELEC 1908 MatLab Introductory Lab Performed: Monday January 20 th 2014 Submitted: Monday January 27 th 2014 Performed By Name, Student # Name, Student # Teaching Assistant Svetlana Demptchenko Introduction
Laboratory Project 4: Frequency Response and Filters
 2240 Laboratory Project 4: Frequency Response and Filters K. Durney and N. E. Cotter Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT 84112 Abstract-You will build a
2240 Laboratory Project 4: Frequency Response and Filters K. Durney and N. E. Cotter Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT 84112 Abstract-You will build a
Module 3 : Sampling and Reconstruction Problem Set 3
 Module 3 : Sampling and Reconstruction Problem Set 3 Problem 1 Shown in figure below is a system in which the sampling signal is an impulse train with alternating sign. The sampling signal p(t), the Fourier
Module 3 : Sampling and Reconstruction Problem Set 3 Problem 1 Shown in figure below is a system in which the sampling signal is an impulse train with alternating sign. The sampling signal p(t), the Fourier
SMS045 - DSP Systems in Practice. Lab 1 - Filter Design and Evaluation in MATLAB Due date: Thursday Nov 13, 2003
 SMS045 - DSP Systems in Practice Lab 1 - Filter Design and Evaluation in MATLAB Due date: Thursday Nov 13, 2003 Lab Purpose This lab will introduce MATLAB as a tool for designing and evaluating digital
SMS045 - DSP Systems in Practice Lab 1 - Filter Design and Evaluation in MATLAB Due date: Thursday Nov 13, 2003 Lab Purpose This lab will introduce MATLAB as a tool for designing and evaluating digital
Fourier Series. Discrete time DTFS. (Periodic signals) Continuous time. Same as one-period of discrete Fourier series
 Chapter 5 Discrete Fourier Transform, DFT and FFT In the previous chapters we learned about Fourier series and the Fourier transform. These representations can be used to both synthesize a variety of continuous
Chapter 5 Discrete Fourier Transform, DFT and FFT In the previous chapters we learned about Fourier series and the Fourier transform. These representations can be used to both synthesize a variety of continuous
Midterm 1. Total. Name of Student on Your Left: Name of Student on Your Right: EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems
 EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems Midterm 1 12:40-2:00, February 19 Notes: There are five questions on this midterm. Answer each question part in the space below it, using the
EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems Midterm 1 12:40-2:00, February 19 Notes: There are five questions on this midterm. Answer each question part in the space below it, using the
CS 591 S1 Computational Audio -- Spring, 2017
 CS 591 S1 Computational Audio -- Spring, 2017 Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Lecture 11 (Tuesday) Discrete Sine Transform Complex Numbers Complex Phasors and Audio Signals Lecture 12 (Thursday)
CS 591 S1 Computational Audio -- Spring, 2017 Wayne Snyder Department Boston University Lecture 11 (Tuesday) Discrete Sine Transform Complex Numbers Complex Phasors and Audio Signals Lecture 12 (Thursday)
Final Exam Solutions June 14, 2006
 Name or 6-Digit Code: PSU Student ID Number: Final Exam Solutions June 14, 2006 ECE 223: Signals & Systems II Dr. McNames Keep your exam flat during the entire exam. If you have to leave the exam temporarily,
Name or 6-Digit Code: PSU Student ID Number: Final Exam Solutions June 14, 2006 ECE 223: Signals & Systems II Dr. McNames Keep your exam flat during the entire exam. If you have to leave the exam temporarily,
THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM
 Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
Figure 1: Block diagram of Digital signal processing
 Experiment 3. Digital Process of Continuous Time Signal. Introduction Discrete time signal processing algorithms are being used to process naturally occurring analog signals (like speech, music and images).
Experiment 3. Digital Process of Continuous Time Signal. Introduction Discrete time signal processing algorithms are being used to process naturally occurring analog signals (like speech, music and images).
ECE 5650/4650 MATLAB Project 1
 This project is to be treated as a take-home exam, meaning each student is to due his/her own work. The project due date is 4:30 PM Tuesday, October 18, 2011. To work the project you will need access to
This project is to be treated as a take-home exam, meaning each student is to due his/her own work. The project due date is 4:30 PM Tuesday, October 18, 2011. To work the project you will need access to
Department of Electronic Engineering NED University of Engineering & Technology. LABORATORY WORKBOOK For the Course SIGNALS & SYSTEMS (TC-202)
 Department of Electronic Engineering NED University of Engineering & Technology LABORATORY WORKBOOK For the Course SIGNALS & SYSTEMS (TC-202) Instructor Name: Student Name: Roll Number: Semester: Batch:
Department of Electronic Engineering NED University of Engineering & Technology LABORATORY WORKBOOK For the Course SIGNALS & SYSTEMS (TC-202) Instructor Name: Student Name: Roll Number: Semester: Batch:
Suggested Solutions to Examination SSY130 Applied Signal Processing
 Suggested Solutions to Examination SSY13 Applied Signal Processing 1:-18:, April 8, 1 Instructions Responsible teacher: Tomas McKelvey, ph 81. Teacher will visit the site of examination at 1:5 and 1:.
Suggested Solutions to Examination SSY13 Applied Signal Processing 1:-18:, April 8, 1 Instructions Responsible teacher: Tomas McKelvey, ph 81. Teacher will visit the site of examination at 1:5 and 1:.
Outline. Discrete time signals. Impulse sampling z-transform Frequency response Stability INF4420. Jørgen Andreas Michaelsen Spring / 37 2 / 37
 INF4420 Discrete time signals Jørgen Andreas Michaelsen Spring 2013 1 / 37 Outline Impulse sampling z-transform Frequency response Stability Spring 2013 Discrete time signals 2 2 / 37 Introduction More
INF4420 Discrete time signals Jørgen Andreas Michaelsen Spring 2013 1 / 37 Outline Impulse sampling z-transform Frequency response Stability Spring 2013 Discrete time signals 2 2 / 37 Introduction More
Laboration Exercises in Digital Signal Processing
 Laboration Exercises in Digital Signal Processing Mikael Swartling Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund Institute of Technology revision 215 Introduction Introduction The traditional
Laboration Exercises in Digital Signal Processing Mikael Swartling Department of Electrical and Information Technology Lund Institute of Technology revision 215 Introduction Introduction The traditional
Outline. EECS 3213 Fall Sebastian Magierowski York University. Review Passband Modulation. Constellations ASK, FSK, PSK.
 EECS 3213 Fall 2014 L12: Modulation Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline Review Passband Modulation ASK, FSK, PSK Constellations 2 1 Underlying Idea Attempting to send a sequence of digits through
EECS 3213 Fall 2014 L12: Modulation Sebastian Magierowski York University 1 Outline Review Passband Modulation ASK, FSK, PSK Constellations 2 1 Underlying Idea Attempting to send a sequence of digits through
Assignment 8: Tube Resonances
 Linguistics 582 Basics of Digital Signal Processing Assignment 8: Tube Resonances Reading: Stevens, K. (1989). On the quantal nature of speech. Journal of Phonetics, 17, 3-45. Read pp. 3-20. ONLY. Johnson,
Linguistics 582 Basics of Digital Signal Processing Assignment 8: Tube Resonances Reading: Stevens, K. (1989). On the quantal nature of speech. Journal of Phonetics, 17, 3-45. Read pp. 3-20. ONLY. Johnson,
ECE 484 Digital Image Processing Lec 09 - Image Resampling
 ECE 484 Digital Image Processing Lec 09 - Image Resampling Zhu Li Dept of CSEE, UMKC Office: FH560E, Email: lizhu@umkc.edu, Ph: x 2346. http://l.web.umkc.edu/lizhu slides created with WPS Office Linux
ECE 484 Digital Image Processing Lec 09 - Image Resampling Zhu Li Dept of CSEE, UMKC Office: FH560E, Email: lizhu@umkc.edu, Ph: x 2346. http://l.web.umkc.edu/lizhu slides created with WPS Office Linux
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis. Dr. B.-P. Paris Dept. Electrical and Comp. Engineering George Mason University
 ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Dr. B.-P. Paris Dept. Electrical and Comp. Engineering George Mason University Last updated: November 29, 2016 2016, B.-P. Paris ECE 201: Intro to Signal Analysis
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Dr. B.-P. Paris Dept. Electrical and Comp. Engineering George Mason University Last updated: November 29, 2016 2016, B.-P. Paris ECE 201: Intro to Signal Analysis
FIR/Convolution. Visulalizing the convolution sum. Convolution
 FIR/Convolution CMPT 368: Lecture Delay Effects Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University April 2, 27 Since the feedforward coefficient s of the FIR filter are
FIR/Convolution CMPT 368: Lecture Delay Effects Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University April 2, 27 Since the feedforward coefficient s of the FIR filter are
The Periodogram. Use identity sin(θ) = (e iθ e iθ )/(2i) and formulas for geometric sums to compute mean.
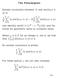 The Periodogram Sample covariance between X and sin(2πωt + φ) is 1 T T 1 X t sin(2πωt + φ) X 1 T T 1 sin(2πωt + φ) Use identity sin(θ) = (e iθ e iθ )/(2i) and formulas for geometric sums to compute mean.
The Periodogram Sample covariance between X and sin(2πωt + φ) is 1 T T 1 X t sin(2πωt + φ) X 1 T T 1 sin(2πωt + φ) Use identity sin(θ) = (e iθ e iθ )/(2i) and formulas for geometric sums to compute mean.
Overview ta3520 Introduction to seismics
 Overview ta3520 Introduction to seismics Fourier Analysis Basic principles of the Seismic Method Interpretation of Raw Seismic Records Seismic Instrumentation Processing of Seismic Reflection Data Vertical
Overview ta3520 Introduction to seismics Fourier Analysis Basic principles of the Seismic Method Interpretation of Raw Seismic Records Seismic Instrumentation Processing of Seismic Reflection Data Vertical
Lab S-5: DLTI GUI and Nulling Filters. Please read through the information below prior to attending your lab.
 DSP First, 2e Signal Processing First Lab S-5: DLTI GUI and Nulling Filters Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification: The Exercise
DSP First, 2e Signal Processing First Lab S-5: DLTI GUI and Nulling Filters Pre-Lab: Read the Pre-Lab and do all the exercises in the Pre-Lab section prior to attending lab. Verification: The Exercise
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis
 ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Dr. B.-P. Paris Dept. Electrical and Comp. Engineering George Mason University Last updated: November 29, 2016 2016, B.-P. Paris ECE 201: Intro to Signal Analysis
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Dr. B.-P. Paris Dept. Electrical and Comp. Engineering George Mason University Last updated: November 29, 2016 2016, B.-P. Paris ECE 201: Intro to Signal Analysis
Laboratory Assignment 4. Fourier Sound Synthesis
 Laboratory Assignment 4 Fourier Sound Synthesis PURPOSE This lab investigates how to use a computer to evaluate the Fourier series for periodic signals and to synthesize audio signals from Fourier series
Laboratory Assignment 4 Fourier Sound Synthesis PURPOSE This lab investigates how to use a computer to evaluate the Fourier series for periodic signals and to synthesize audio signals from Fourier series
ECE 3500: Fundamentals of Signals and Systems (Fall 2014) Lab 4: Binary Phase-Shift Keying Modulation and Demodulation
 ECE 3500: Fundamentals of Signals and Systems (Fall 2014) Lab 4: Binary Phase-Shift Keying Modulation and Demodulation Files necessary to complete this assignment: none Deliverables Due: Before your assigned
ECE 3500: Fundamentals of Signals and Systems (Fall 2014) Lab 4: Binary Phase-Shift Keying Modulation and Demodulation Files necessary to complete this assignment: none Deliverables Due: Before your assigned
Electronics Design Laboratory Lecture #4. ECEN 2270 Electronics Design Laboratory
 Electronics Design Laboratory Lecture #4 Electronics Design Laboratory 1 Part A Experiment 2 Robot DC Motor Measure DC motor characteristics Develop a Spice circuit model for the DC motor and determine
Electronics Design Laboratory Lecture #4 Electronics Design Laboratory 1 Part A Experiment 2 Robot DC Motor Measure DC motor characteristics Develop a Spice circuit model for the DC motor and determine
16.30 Learning Objectives and Practice Problems - - Lectures 16 through 20
 16.30 Learning Objectives and Practice Problems - - Lectures 16 through 20 IV. Lectures 16-20 IVA : Sampling, Aliasing, and Reconstruction JVV 9.5, Lecture Notes on Shannon - Understand the mathematical
16.30 Learning Objectives and Practice Problems - - Lectures 16 through 20 IV. Lectures 16-20 IVA : Sampling, Aliasing, and Reconstruction JVV 9.5, Lecture Notes on Shannon - Understand the mathematical
Fall Music 320A Homework #2 Sinusoids, Complex Sinusoids 145 points Theory and Lab Problems Due Thursday 10/11/2018 before class
 Fall 2018 2019 Music 320A Homework #2 Sinusoids, Complex Sinusoids 145 points Theory and Lab Problems Due Thursday 10/11/2018 before class Theory Problems 1. 15 pts) [Sinusoids] Define xt) as xt) = 2sin
Fall 2018 2019 Music 320A Homework #2 Sinusoids, Complex Sinusoids 145 points Theory and Lab Problems Due Thursday 10/11/2018 before class Theory Problems 1. 15 pts) [Sinusoids] Define xt) as xt) = 2sin
Implementation of sound effects in DSP
 Implementation of sound effects in DSP Alfredo Ricci Vásquez - Juan Carlos Bucheli García 1 Introduction Sound is one of the physical phenomena that has intrigued human race during all history. Since ancients
Implementation of sound effects in DSP Alfredo Ricci Vásquez - Juan Carlos Bucheli García 1 Introduction Sound is one of the physical phenomena that has intrigued human race during all history. Since ancients
Fields and Waves I Spring 2005 Homework 1. Due 25 January 2005
 Due 2 January 200 1. Plane Wave Representations The numbers given in this problem are realistic but not real. That is, your answers should come out in a reasonable range, but the numbers are not based
Due 2 January 200 1. Plane Wave Representations The numbers given in this problem are realistic but not real. That is, your answers should come out in a reasonable range, but the numbers are not based
Sinusoids and Phasors (Chapter 9 - Lecture #1) Dr. Shahrel A. Suandi Room 2.20, PPKEE
 Sinusoids and Phasors (Chapter 9 - Lecture #1) Dr. Shahrel A. Suandi Room 2.20, PPKEE Email:shahrel@eng.usm.my 1 Outline of Chapter 9 Introduction Sinusoids Phasors Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements
Sinusoids and Phasors (Chapter 9 - Lecture #1) Dr. Shahrel A. Suandi Room 2.20, PPKEE Email:shahrel@eng.usm.my 1 Outline of Chapter 9 Introduction Sinusoids Phasors Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
 Amplitude Amplitude Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) DFT transforms the time domain signal samples to the frequency domain components. DFT Signal Spectrum Time Frequency DFT is often used to do frequency
Amplitude Amplitude Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) DFT transforms the time domain signal samples to the frequency domain components. DFT Signal Spectrum Time Frequency DFT is often used to do frequency
Multirate Digital Signal Processing
 Multirate Digital Signal Processing Basic Sampling Rate Alteration Devices Up-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer factor Down-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer
Multirate Digital Signal Processing Basic Sampling Rate Alteration Devices Up-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer factor Down-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer
Lab 0: Introduction to TIMS AND MATLAB
 TELE3013 TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1 Lab 0: Introduction to TIMS AND MATLAB 1. INTRODUCTION The TIMS (Telecommunication Instructional Modelling System) system was first developed by Tim Hooper, then a
TELE3013 TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1 Lab 0: Introduction to TIMS AND MATLAB 1. INTRODUCTION The TIMS (Telecommunication Instructional Modelling System) system was first developed by Tim Hooper, then a
ENGR 210 Lab 12: Sampling and Aliasing
 ENGR 21 Lab 12: Sampling and Aliasing In the previous lab you examined how A/D converters actually work. In this lab we will consider some of the consequences of how fast you sample and of the signal processing
ENGR 21 Lab 12: Sampling and Aliasing In the previous lab you examined how A/D converters actually work. In this lab we will consider some of the consequences of how fast you sample and of the signal processing
Signals. Periodic vs. Aperiodic. Signals
 Signals 1 Periodic vs. Aperiodic Signals periodic signal completes a pattern within some measurable time frame, called a period (), and then repeats that pattern over subsequent identical periods R s.
Signals 1 Periodic vs. Aperiodic Signals periodic signal completes a pattern within some measurable time frame, called a period (), and then repeats that pattern over subsequent identical periods R s.
Reference: PMU Data Event Detection
 Reference: PMU Data Event Detection This is to present how to analyze data from phasor measurement units (PMUs) Why important? Because so much data are being generated, it is difficult to detect events
Reference: PMU Data Event Detection This is to present how to analyze data from phasor measurement units (PMUs) Why important? Because so much data are being generated, it is difficult to detect events
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS LABORATORY 13: Digital Communication
 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS LABORATORY 13: Digital Communication INTRODUCTION Digital Communication refers to the transmission of binary, or digital, information over analog channels. In this laboratory you will
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS LABORATORY 13: Digital Communication INTRODUCTION Digital Communication refers to the transmission of binary, or digital, information over analog channels. In this laboratory you will
MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS
 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering King Mongkut s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang 01076531 MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS Pk Pakorn Watanachaturaporn, Wt ht Ph.D. PhD pakorn@live.kmitl.ac.th,
1 Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering King Mongkut s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang 01076531 MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS Pk Pakorn Watanachaturaporn, Wt ht Ph.D. PhD pakorn@live.kmitl.ac.th,
Biomedical Signals. Signals and Images in Medicine Dr Nabeel Anwar
 Biomedical Signals Signals and Images in Medicine Dr Nabeel Anwar Noise Removal: Time Domain Techniques 1. Synchronized Averaging (covered in lecture 1) 2. Moving Average Filters (today s topic) 3. Derivative
Biomedical Signals Signals and Images in Medicine Dr Nabeel Anwar Noise Removal: Time Domain Techniques 1. Synchronized Averaging (covered in lecture 1) 2. Moving Average Filters (today s topic) 3. Derivative
Physics 115 Lecture 13. Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018
 Physics 115 Lecture 13 Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018 1 A simple waveform: Fourier Synthesis FOURIER SYNTHESIS is the summing of simple waveforms to create complex waveforms. Musical instruments typically
Physics 115 Lecture 13 Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018 1 A simple waveform: Fourier Synthesis FOURIER SYNTHESIS is the summing of simple waveforms to create complex waveforms. Musical instruments typically
