Frequency Division Multiplexing Spring 2011 Lecture #14. Sinusoids and LTI Systems. Periodic Sequences. x[n] = x[n + N]
|
|
|
- Oscar Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Frequency Division Multiplexing 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture #4 complex exponentials discrete-time Fourier series spectral coefficients band-limited signals To engineer the sharing of a channel through frequency division multiplexing we ll need a new set tools that will let us understand the behavior of signals and systems in the frequency domain. Plan: This week Analyze the frequency content of signals using the discretetime Fourier series Determine what happens when we band-limit a signal Characterize LTI systems by their frequency response Introduce filters: LTI systems that eliminate a region of frequencies from a signal Next week Using modulation to position band-limited signals in different regions of the frequency spectrum Receiving a particular signal from a shared spectrum 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide # 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #2 Sinusoids and LTI Systems Periodic Sequences h[n] Frequency division multiplexing depends on an interesting property of LTI channels: if the channel input x[n] is a sinusoid of a given amplitude, frequency and phase, the response will be a sinusoid at the same frequency, although the amplitude and phase may be altered. As we ll see, the change in amplitude and phase may depend on the frequency of the input. The same property holds when the inputs are complex exponentials, which are closely related to sines and cosines (and, perhaps surprisingly, are much easier to analyze!). A sequence x[n] is said to be periodic with a period of N samples ( periodic with period N ) if x[n + N] A sequence that is periodic with period N is also periodic with period, 3N,, and so on. A sinusoidal sequence that is periodic with period N can only have one of a finite number of frequencies: all the harmonics of the fundamental frequency 2π/N radians/sample, i.e., frequencies of the form k (2π/N) for some integer k Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide # Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #4
2 Frequencies k (2!/N) when k " N Frequency k (2π/N) yields the same sequence as (k mod N) (2π/N) Negative Frequencies Unique sequences: k = 0,, 2,, N- Highest frequency: (N-) (2π/N) < 2! Sequences of frequency k (2π/N), i.e., frequencies between 0 and 2π, are identical to sequences of frequency -(N-k) (2π/N), i.e., between -2π and 0. In 6.02, our convention will be to specify frequencies in the range -π and π, corresponding to k s in the range (N/2) to (N/2) Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide # Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #6 Complex Exponentials A complex exponential is a complex-valued function of a single argument an angle measured in radians. Euler s formula shows the relation between complex exponentials and our usual trig functions: e j! = cos(!)+ jsin(!) Sine and Cosine and e j# cos(!) = 2 e j! + 2 e! j! sin(!) = 2 j e j!! j! e! 2 j 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide # Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #8
3 When φ = 0: Useful Properties of e j# e j0 = When φ = ±π: e j! = e! j! =! e j!n = e! j!n = (!) n Summing samples over one period: e jk 2! N! n = " N k = 0,±N,±, # % 0 otherwise n ranges over any N consecutive integers, e.g., n = 0,,, N Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #9 Discrete-time Fourier Series If x[n] is periodic with period N, it can be expressed as the sum of scaled periodic complex exponentials: k ranges over any N consecutive integers. Two common choices: k starts at 0 (0! freq! 2π) k starts at N/2 (-π! freq! π)! Complex exponential with period N and fundamental frequency 2π/N. The spectral coefficients for each of the discrete frequencies are, in general, complex, changing both the amplitude and phase of the associated complex exponential. If x[n] is real, a -k = * Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #0 Start with: Solving for the! Multiply both sides by e -jr(2π/n)n and sum over N terms: x[n]e! jr # N ( = ( ( e jk ( ( = e j k!r = a r N 'n e! jr " 2! # N ( ) # N 'n! x[n] e " jk # 2! 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide # % 'n From slide 9: N if k=r, 0 otherwise Discrete-time Fourier Series Pair!! x[n] e ( jk Synthesis equation Analysis equation If we have N samples of a periodic waveform of period N, we can find the waveform s spectral coefficients using the analysis equation. If we have the spectral coefficients, we can reconstruct the original time-domain waveform using the synthesis equation Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #2
4 = =! cos(r 2! N n) e " jk! ) + * + e jr # 2! % e j(r"k) # 2! cos(r 2! N n) # 2! # + e " jr % 2! N! + / k = ±r = otherwise ',. - # 2! jk%. e"! e " j(r+k) # 2! 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #3 sin(r 2! N n) This time let s do it by inspection. First rewrite x[n] (see slide #8): 2 j e jr 2! N n! 2 j e j(!r)2! N n Now x[n] is a sum of complex exponentials and we can determine the directly from the equation; a r = 2 j =! j 2 a!r =! 2 j = j 2 = 0 otherwise 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #4 + 2cos(3 2! 2! n)! 3sin(5 n) Spectrum of Digital Transmissions Again, by inspection: since the cos and sin are different frequencies, we can analyze them separately. a 0 = average value = a ±3 = 2(/2) = [from cos term] a -5 = -3(j/2) = -.5j [from sin term] a 5 = -3(-j/2) =.5j = 0 otherwise 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide # Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #6
5 Effect of Band-limiting a Transmission How Low Can We Go? 6.02 Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #7 7 samples/bit 4 samples/period k=(n/4)=(96/4)= Spring 20 Lecture 4, Slide #8
6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #12
 6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #12 Bounded-input, bounded-output stability Frequency response 6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture 12, Slide #1 Bounded-Input Bounded-Output (BIBO) Stability What ensures that the infinite sum
6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #12 Bounded-input, bounded-output stability Frequency response 6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture 12, Slide #1 Bounded-Input Bounded-Output (BIBO) Stability What ensures that the infinite sum
Frequency-Domain Sharing and Fourier Series
 MIT 6.02 DRAFT Lecture Notes Fall 200 (Last update: November 9, 200) Comments, questions or bug reports? Please contact 6.02-staff@mit.edu LECTURE 4 Frequency-Domain Sharing and Fourier Series In earlier
MIT 6.02 DRAFT Lecture Notes Fall 200 (Last update: November 9, 200) Comments, questions or bug reports? Please contact 6.02-staff@mit.edu LECTURE 4 Frequency-Domain Sharing and Fourier Series In earlier
Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals
 Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/1 1 Review of Complex Numbers Using Euler s famous formula for the complex exponential The
Lecture 3 Complex Exponential Signals Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/1 1 Review of Complex Numbers Using Euler s famous formula for the complex exponential The
Basic Signals and Systems
 Chapter 2 Basic Signals and Systems A large part of this chapter is taken from: C.S. Burrus, J.H. McClellan, A.V. Oppenheim, T.W. Parks, R.W. Schafer, and H. W. Schüssler: Computer-based exercises for
Chapter 2 Basic Signals and Systems A large part of this chapter is taken from: C.S. Burrus, J.H. McClellan, A.V. Oppenheim, T.W. Parks, R.W. Schafer, and H. W. Schüssler: Computer-based exercises for
Digital Video and Audio Processing. Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises
 Digital Video and Audio Processing Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises Rudolf Mester Institut für Angewandte Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main 6th November 2002 Chapter
Digital Video and Audio Processing Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises Rudolf Mester Institut für Angewandte Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main 6th November 2002 Chapter
Physics 115 Lecture 13. Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018
 Physics 115 Lecture 13 Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018 1 A simple waveform: Fourier Synthesis FOURIER SYNTHESIS is the summing of simple waveforms to create complex waveforms. Musical instruments typically
Physics 115 Lecture 13 Fourier Analysis February 22, 2018 1 A simple waveform: Fourier Synthesis FOURIER SYNTHESIS is the summing of simple waveforms to create complex waveforms. Musical instruments typically
Midterm 1. Total. Name of Student on Your Left: Name of Student on Your Right: EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems
 EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems Midterm 1 12:40-2:00, February 19 Notes: There are five questions on this midterm. Answer each question part in the space below it, using the
EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems Midterm 1 12:40-2:00, February 19 Notes: There are five questions on this midterm. Answer each question part in the space below it, using the
5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions.notebook. Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs
 Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2
Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2
Using the DFT as a Filter: Correcting a Misconception by Richard G. Lyons
 Using the DFT as a Filter: Correcting a Misconception by Richard G. Lyons I have read, in some of the literature of DSP, that when the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) is used as a filter the process of
Using the DFT as a Filter: Correcting a Misconception by Richard G. Lyons I have read, in some of the literature of DSP, that when the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) is used as a filter the process of
Introduction to signals and systems
 CHAPTER Introduction to signals and systems Welcome to Introduction to Signals and Systems. This text will focus on the properties of signals and systems, and the relationship between the inputs and outputs
CHAPTER Introduction to signals and systems Welcome to Introduction to Signals and Systems. This text will focus on the properties of signals and systems, and the relationship between the inputs and outputs
Signals A Preliminary Discussion EE442 Analog & Digital Communication Systems Lecture 2
 Signals A Preliminary Discussion EE442 Analog & Digital Communication Systems Lecture 2 The Fourier transform of single pulse is the sinc function. EE 442 Signal Preliminaries 1 Communication Systems and
Signals A Preliminary Discussion EE442 Analog & Digital Communication Systems Lecture 2 The Fourier transform of single pulse is the sinc function. EE 442 Signal Preliminaries 1 Communication Systems and
DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing
 DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing 2 nd Year Electronics Lab IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Table of Contents Equipment... 2 Aims... 2 Objectives... 2 Recommended Textbooks... 3 Recommended
DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing 2 nd Year Electronics Lab IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Table of Contents Equipment... 2 Aims... 2 Objectives... 2 Recommended Textbooks... 3 Recommended
2.1 BASIC CONCEPTS Basic Operations on Signals Time Shifting. Figure 2.2 Time shifting of a signal. Time Reversal.
 1 2.1 BASIC CONCEPTS 2.1.1 Basic Operations on Signals Time Shifting. Figure 2.2 Time shifting of a signal. Time Reversal. 2 Time Scaling. Figure 2.4 Time scaling of a signal. 2.1.2 Classification of Signals
1 2.1 BASIC CONCEPTS 2.1.1 Basic Operations on Signals Time Shifting. Figure 2.2 Time shifting of a signal. Time Reversal. 2 Time Scaling. Figure 2.4 Time scaling of a signal. 2.1.2 Classification of Signals
CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Amplitude Modulation (AM) Synthesis
 CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Amplitude Modulation (AM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 8, 008 Beat Notes What happens when we add two frequencies
CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Amplitude Modulation (AM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 8, 008 Beat Notes What happens when we add two frequencies
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
 Amplitude Amplitude Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) DFT transforms the time domain signal samples to the frequency domain components. DFT Signal Spectrum Time Frequency DFT is often used to do frequency
Amplitude Amplitude Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) DFT transforms the time domain signal samples to the frequency domain components. DFT Signal Spectrum Time Frequency DFT is often used to do frequency
Laboratory Assignment 4. Fourier Sound Synthesis
 Laboratory Assignment 4 Fourier Sound Synthesis PURPOSE This lab investigates how to use a computer to evaluate the Fourier series for periodic signals and to synthesize audio signals from Fourier series
Laboratory Assignment 4 Fourier Sound Synthesis PURPOSE This lab investigates how to use a computer to evaluate the Fourier series for periodic signals and to synthesize audio signals from Fourier series
6.02 Fall 2013 Lecture #14
 6.02 Fall 2013 Lecture #14 Spectral content of signals via the DTFT 6.02 Fall 2013 Lecture 14 Slide #1 Determining h[n] from H(Ω) H(Ω) = m h[m]e jωm Multiply both sides by e jωn and integrate over a (contiguous)
6.02 Fall 2013 Lecture #14 Spectral content of signals via the DTFT 6.02 Fall 2013 Lecture 14 Slide #1 Determining h[n] from H(Ω) H(Ω) = m h[m]e jωm Multiply both sides by e jωn and integrate over a (contiguous)
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis
 ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Prof. Paris Last updated: October 9, 2007 Part I Spectrum Representation of Signals Lecture: Sums of Sinusoids (of different frequency) Introduction Sum of Sinusoidal
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Prof. Paris Last updated: October 9, 2007 Part I Spectrum Representation of Signals Lecture: Sums of Sinusoids (of different frequency) Introduction Sum of Sinusoidal
The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium. Some type of transmission medium is required for transmission:
 Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors: The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium is
Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors: The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium is
Fourier Analysis. Chapter Introduction Distortion Harmonic Distortion
 Chapter 5 Fourier Analysis 5.1 Introduction The theory, practice, and application of Fourier analysis are presented in the three major sections of this chapter. The theory includes a discussion of Fourier
Chapter 5 Fourier Analysis 5.1 Introduction The theory, practice, and application of Fourier analysis are presented in the three major sections of this chapter. The theory includes a discussion of Fourier
Signal Characteristics
 Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors:» The quality of the transmission signal» The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium
Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors:» The quality of the transmission signal» The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium
Department of Electronic Engineering NED University of Engineering & Technology. LABORATORY WORKBOOK For the Course SIGNALS & SYSTEMS (TC-202)
 Department of Electronic Engineering NED University of Engineering & Technology LABORATORY WORKBOOK For the Course SIGNALS & SYSTEMS (TC-202) Instructor Name: Student Name: Roll Number: Semester: Batch:
Department of Electronic Engineering NED University of Engineering & Technology LABORATORY WORKBOOK For the Course SIGNALS & SYSTEMS (TC-202) Instructor Name: Student Name: Roll Number: Semester: Batch:
Spectrogram Review The Sampling Problem: 2π Ambiguity Fourier Series. Lecture 6: Sampling. ECE 401: Signal and Image Analysis. University of Illinois
 Lecture 6: Sampling ECE 401: Signal and Image Analysis University of Illinois 2/7/2017 1 Spectrogram Review 2 The Sampling Problem: 2π Ambiguity 3 Fourier Series Outline 1 Spectrogram Review 2 The Sampling
Lecture 6: Sampling ECE 401: Signal and Image Analysis University of Illinois 2/7/2017 1 Spectrogram Review 2 The Sampling Problem: 2π Ambiguity 3 Fourier Series Outline 1 Spectrogram Review 2 The Sampling
CS3291: Digital Signal Processing
 CS39 Exam Jan 005 //08 /BMGC University of Manchester Department of Computer Science First Semester Year 3 Examination Paper CS39: Digital Signal Processing Date of Examination: January 005 Answer THREE
CS39 Exam Jan 005 //08 /BMGC University of Manchester Department of Computer Science First Semester Year 3 Examination Paper CS39: Digital Signal Processing Date of Examination: January 005 Answer THREE
3. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the cosine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians).
 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Desmos Activity 1. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the sine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians). sin 0 sin π 2 sin π
Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Desmos Activity 1. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the sine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians). sin 0 sin π 2 sin π
Topic 6. The Digital Fourier Transform. (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith)
 Topic 6 The Digital Fourier Transform (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith) 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 0-1 -0.8-0.6-0.4-0.2 0 0.2 0.4
Topic 6 The Digital Fourier Transform (Based, in part, on The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing by Steven Smith) 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 0-1 -0.8-0.6-0.4-0.2 0 0.2 0.4
6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #13
 6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #13 Frequency response Filters Spectral content 6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture 13 Slide #1 Sinusoidal Inputs and LTI Systems h[n] A very important property of LTI systems or channels: If
6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture #13 Frequency response Filters Spectral content 6.02 Fall 2012 Lecture 13 Slide #1 Sinusoidal Inputs and LTI Systems h[n] A very important property of LTI systems or channels: If
Digital Image Processing
 In the Name of Allah Digital Image Processing Introduction to Wavelets Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 Why transform? Why wavelets? Wavelets like basis components. Wavelets examples. Fast wavelet transform.
In the Name of Allah Digital Image Processing Introduction to Wavelets Hamid R. Rabiee Fall 2015 Outline 2 Why transform? Why wavelets? Wavelets like basis components. Wavelets examples. Fast wavelet transform.
Sinusoids. Lecture #2 Chapter 2. BME 310 Biomedical Computing - J.Schesser
 Sinusoids Lecture # Chapter BME 30 Biomedical Computing - 8 What Is this Course All About? To Gain an Appreciation of the Various Types of Signals and Systems To Analyze The Various Types of Systems To
Sinusoids Lecture # Chapter BME 30 Biomedical Computing - 8 What Is this Course All About? To Gain an Appreciation of the Various Types of Signals and Systems To Analyze The Various Types of Systems To
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 8 FREQUENCY ANALYSIS
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 8 FREQUENCY ANALYSIS Objectives: There are two goals in this laboratory exercise. The first is to reinforce the Fourier series analysis you have done in the lecture portion of this course.
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 8 FREQUENCY ANALYSIS Objectives: There are two goals in this laboratory exercise. The first is to reinforce the Fourier series analysis you have done in the lecture portion of this course.
Spectrum Analysis: The FFT Display
 Spectrum Analysis: The FFT Display Equipment: Capstone, voltage sensor 1 Introduction It is often useful to represent a function by a series expansion, such as a Taylor series. There are other series representations
Spectrum Analysis: The FFT Display Equipment: Capstone, voltage sensor 1 Introduction It is often useful to represent a function by a series expansion, such as a Taylor series. There are other series representations
Lecture 17 z-transforms 2
 Lecture 17 z-transforms 2 Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/5/3 1 Factoring z-polynomials We can also factor z-transform polynomials to break down a large system into
Lecture 17 z-transforms 2 Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/5/3 1 Factoring z-polynomials We can also factor z-transform polynomials to break down a large system into
Lecture 2 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 1. EE4900/EE6720 Digital Communications
 EE4900/EE6420: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 2 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 1 Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
EE4900/EE6420: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 2 Review of Signals and Systems: Part 1 Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM AND FILTER DESIGN
 DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM AND FILTER DESIGN N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture # 03 Spectrum of a Square Wave 2 Results of Some Filters 3 Notation 4 x[n]
DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM AND FILTER DESIGN N. C. State University CSC557 Multimedia Computing and Networking Fall 2001 Lecture # 03 Spectrum of a Square Wave 2 Results of Some Filters 3 Notation 4 x[n]
Graphing Sine and Cosine
 The problem with average monthly temperatures on the preview worksheet is an example of a periodic function. Periodic functions are defined on p.254 Periodic functions repeat themselves each period. The
The problem with average monthly temperatures on the preview worksheet is an example of a periodic function. Periodic functions are defined on p.254 Periodic functions repeat themselves each period. The
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 10 Feb 14 th, 2019 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah and S. Narasimhan Time and Frequency example : g(t) = sin(2π f t) + (1/3)sin(2π (3f) t)
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 10 Feb 14 th, 2019 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah and S. Narasimhan Time and Frequency example : g(t) = sin(2π f t) + (1/3)sin(2π (3f) t)
Sinusoids and Phasors (Chapter 9 - Lecture #1) Dr. Shahrel A. Suandi Room 2.20, PPKEE
 Sinusoids and Phasors (Chapter 9 - Lecture #1) Dr. Shahrel A. Suandi Room 2.20, PPKEE Email:shahrel@eng.usm.my 1 Outline of Chapter 9 Introduction Sinusoids Phasors Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements
Sinusoids and Phasors (Chapter 9 - Lecture #1) Dr. Shahrel A. Suandi Room 2.20, PPKEE Email:shahrel@eng.usm.my 1 Outline of Chapter 9 Introduction Sinusoids Phasors Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements
Amplitude, Reflection, and Period
 SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation
 1 of 12 6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation Problem 1. Here's our "standard" modulation-demodulation system diagram: at the transmitter, signal x[n] is modulated by signal mod[n] and the
1 of 12 6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation Problem 1. Here's our "standard" modulation-demodulation system diagram: at the transmitter, signal x[n] is modulated by signal mod[n] and the
Final Exam Solutions June 7, 2004
 Name: Final Exam Solutions June 7, 24 ECE 223: Signals & Systems II Dr. McNames Write your name above. Keep your exam flat during the entire exam period. If you have to leave the exam temporarily, close
Name: Final Exam Solutions June 7, 24 ECE 223: Signals & Systems II Dr. McNames Write your name above. Keep your exam flat during the entire exam period. If you have to leave the exam temporarily, close
Signal Processing for Speech Applications - Part 2-1. Signal Processing For Speech Applications - Part 2
 Signal Processing for Speech Applications - Part 2-1 Signal Processing For Speech Applications - Part 2 May 14, 2013 Signal Processing for Speech Applications - Part 2-2 References Huang et al., Chapter
Signal Processing for Speech Applications - Part 2-1 Signal Processing For Speech Applications - Part 2 May 14, 2013 Signal Processing for Speech Applications - Part 2-2 References Huang et al., Chapter
G(f ) = g(t) dt. e i2πft. = cos(2πf t) + i sin(2πf t)
 Fourier Transforms Fourier s idea that periodic functions can be represented by an infinite series of sines and cosines with discrete frequencies which are integer multiples of a fundamental frequency
Fourier Transforms Fourier s idea that periodic functions can be represented by an infinite series of sines and cosines with discrete frequencies which are integer multiples of a fundamental frequency
FFT analysis in practice
 FFT analysis in practice Perception & Multimedia Computing Lecture 13 Rebecca Fiebrink Lecturer, Department of Computing Goldsmiths, University of London 1 Last Week Review of complex numbers: rectangular
FFT analysis in practice Perception & Multimedia Computing Lecture 13 Rebecca Fiebrink Lecturer, Department of Computing Goldsmiths, University of London 1 Last Week Review of complex numbers: rectangular
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide Section 8.2 and 8.3-1
 8.3-1 Transformation of sine and cosine functions Sections 8.2 and 8.3 Revisit: Page 142; chapter 4 Section 8.2 and 8.3 Graphs of Transformed Sine and Cosine Functions Graph transformations of y = sin
8.3-1 Transformation of sine and cosine functions Sections 8.2 and 8.3 Revisit: Page 142; chapter 4 Section 8.2 and 8.3 Graphs of Transformed Sine and Cosine Functions Graph transformations of y = sin
Chapter 5 Window Functions. periodic with a period of N (number of samples). This is observed in table (3.1).
 Chapter 5 Window Functions 5.1 Introduction As discussed in section (3.7.5), the DTFS assumes that the input waveform is periodic with a period of N (number of samples). This is observed in table (3.1).
Chapter 5 Window Functions 5.1 Introduction As discussed in section (3.7.5), the DTFS assumes that the input waveform is periodic with a period of N (number of samples). This is observed in table (3.1).
Lecture 4 Frequency Response of FIR Systems (II)
 EE3054 Signals and Systems Lecture 4 Frequency Response of FIR Systems (II Yao Wang Polytechnic University Most of the slides included are extracted from lecture presentations prepared by McClellan and
EE3054 Signals and Systems Lecture 4 Frequency Response of FIR Systems (II Yao Wang Polytechnic University Most of the slides included are extracted from lecture presentations prepared by McClellan and
George Mason University ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Spring 2017
 Assigned: March 7, 017 Due Date: Week of April 10, 017 George Mason University ECE 01: Introduction to Signal Analysis Spring 017 Laboratory Project #7 Due Date Your lab report must be submitted on blackboard
Assigned: March 7, 017 Due Date: Week of April 10, 017 George Mason University ECE 01: Introduction to Signal Analysis Spring 017 Laboratory Project #7 Due Date Your lab report must be submitted on blackboard
SECTION 7: FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS. MAE 3401 Modeling and Simulation
 SECTION 7: FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS MAE 3401 Modeling and Simulation 2 Response to Sinusoidal Inputs Frequency Domain Analysis Introduction 3 We ve looked at system impulse and step responses Also interested
SECTION 7: FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS MAE 3401 Modeling and Simulation 2 Response to Sinusoidal Inputs Frequency Domain Analysis Introduction 3 We ve looked at system impulse and step responses Also interested
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 638/4393 Lecture 9 Sept 26 th, 217 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu, S. Narasimhan HISTOGRAM SHAPING We now describe methods for histogram
Digital Image Processing COSC 638/4393 Lecture 9 Sept 26 th, 217 Pranav Mantini Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu, S. Narasimhan HISTOGRAM SHAPING We now describe methods for histogram
y(n)= Aa n u(n)+bu(n) b m sin(2πmt)= b 1 sin(2πt)+b 2 sin(4πt)+b 3 sin(6πt)+ m=1 x(t)= x = 2 ( b b b b
 Exam 1 February 3, 006 Each subquestion is worth 10 points. 1. Consider a periodic sawtooth waveform x(t) with period T 0 = 1 sec shown below: (c) x(n)= u(n). In this case, show that the output has the
Exam 1 February 3, 006 Each subquestion is worth 10 points. 1. Consider a periodic sawtooth waveform x(t) with period T 0 = 1 sec shown below: (c) x(n)= u(n). In this case, show that the output has the
Discrete Fourier Transform, DFT Input: N time samples
 EE445M/EE38L.6 Lecture. Lecture objectives are to: The Discrete Fourier Transform Windowing Use DFT to design a FIR digital filter Discrete Fourier Transform, DFT Input: time samples {a n = {a,a,a 2,,a
EE445M/EE38L.6 Lecture. Lecture objectives are to: The Discrete Fourier Transform Windowing Use DFT to design a FIR digital filter Discrete Fourier Transform, DFT Input: time samples {a n = {a,a,a 2,,a
Topic 2. Signal Processing Review. (Some slides are adapted from Bryan Pardo s course slides on Machine Perception of Music)
 Topic 2 Signal Processing Review (Some slides are adapted from Bryan Pardo s course slides on Machine Perception of Music) Recording Sound Mechanical Vibration Pressure Waves Motion->Voltage Transducer
Topic 2 Signal Processing Review (Some slides are adapted from Bryan Pardo s course slides on Machine Perception of Music) Recording Sound Mechanical Vibration Pressure Waves Motion->Voltage Transducer
DSP First. Laboratory Exercise #7. Everyday Sinusoidal Signals
 DSP First Laboratory Exercise #7 Everyday Sinusoidal Signals This lab introduces two practical applications where sinusoidal signals are used to transmit information: a touch-tone dialer and amplitude
DSP First Laboratory Exercise #7 Everyday Sinusoidal Signals This lab introduces two practical applications where sinusoidal signals are used to transmit information: a touch-tone dialer and amplitude
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL and COMPUTER ENGINEERING. ECE 2025 Fall 1999 Lab #7: Frequency Response & Bandpass Filters
 GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL and COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2025 Fall 1999 Lab #7: Frequency Response & Bandpass Filters Date: 12 18 Oct 1999 This is the official Lab #7 description;
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL of ELECTRICAL and COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2025 Fall 1999 Lab #7: Frequency Response & Bandpass Filters Date: 12 18 Oct 1999 This is the official Lab #7 description;
Module 9 AUDIO CODING. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 9 AUDIO CODING Lesson 30 Polyphase filter implementation Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to : 1. Show how a bank of bandpass filters can be realized
Module 9 AUDIO CODING Lesson 30 Polyphase filter implementation Instructional Objectives At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to : 1. Show how a bank of bandpass filters can be realized
PROBLEM SET 5. Reminder: Quiz 1will be on March 6, during the regular class hour. Details to follow. z = e jω h[n] H(e jω ) H(z) DTFT.
![PROBLEM SET 5. Reminder: Quiz 1will be on March 6, during the regular class hour. Details to follow. z = e jω h[n] H(e jω ) H(z) DTFT. PROBLEM SET 5. Reminder: Quiz 1will be on March 6, during the regular class hour. Details to follow. z = e jω h[n] H(e jω ) H(z) DTFT.](/thumbs/96/129052141.jpg) PROBLEM SET 5 Issued: 2/4/9 Due: 2/22/9 Reading: During the past week we continued our discussion of the impact of pole/zero locations on frequency response, focusing on allpass systems, minimum and maximum-phase
PROBLEM SET 5 Issued: 2/4/9 Due: 2/22/9 Reading: During the past week we continued our discussion of the impact of pole/zero locations on frequency response, focusing on allpass systems, minimum and maximum-phase
Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation
 Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/15 1 Time-Frequency Spectrum We have seen that a wide range of interesting waveforms can be synthesized
Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing Spring, 2012 Wei-Ta Chu 2012/3/15 1 Time-Frequency Spectrum We have seen that a wide range of interesting waveforms can be synthesized
Lab 8. Signal Analysis Using Matlab Simulink
 E E 2 7 5 Lab June 30, 2006 Lab 8. Signal Analysis Using Matlab Simulink Introduction The Matlab Simulink software allows you to model digital signals, examine power spectra of digital signals, represent
E E 2 7 5 Lab June 30, 2006 Lab 8. Signal Analysis Using Matlab Simulink Introduction The Matlab Simulink software allows you to model digital signals, examine power spectra of digital signals, represent
Advanced Audiovisual Processing Expected Background
 Advanced Audiovisual Processing Expected Background As an advanced module, we will not cover introductory topics in lecture. You are expected to already be proficient with all of the following topics,
Advanced Audiovisual Processing Expected Background As an advanced module, we will not cover introductory topics in lecture. You are expected to already be proficient with all of the following topics,
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis. Dr. B.-P. Paris Dept. Electrical and Comp. Engineering George Mason University
 ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Dr. B.-P. Paris Dept. Electrical and Comp. Engineering George Mason University Last updated: November 29, 2016 2016, B.-P. Paris ECE 201: Intro to Signal Analysis
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Dr. B.-P. Paris Dept. Electrical and Comp. Engineering George Mason University Last updated: November 29, 2016 2016, B.-P. Paris ECE 201: Intro to Signal Analysis
Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals. Reference chapter 4 in Oppenheim and Schafer.
 Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Reference chapter 4 in Oppenheim and Schafer. Periodic Sampling of Continuous Signals T = sampling period fs = sampling frequency when expressing frequencies in radians
Sampling of Continuous-Time Signals Reference chapter 4 in Oppenheim and Schafer. Periodic Sampling of Continuous Signals T = sampling period fs = sampling frequency when expressing frequencies in radians
Chapter 2. Fourier Series & Fourier Transform. Updated:2/11/15
 Chapter 2 Fourier Series & Fourier Transform Updated:2/11/15 Outline Systems and frequency domain representation Fourier Series and different representation of FS Fourier Transform and Spectra Power Spectral
Chapter 2 Fourier Series & Fourier Transform Updated:2/11/15 Outline Systems and frequency domain representation Fourier Series and different representation of FS Fourier Transform and Spectra Power Spectral
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM)
 Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis
 ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Dr. B.-P. Paris Dept. Electrical and Comp. Engineering George Mason University Last updated: November 29, 2016 2016, B.-P. Paris ECE 201: Intro to Signal Analysis
ECE 201: Introduction to Signal Analysis Dr. B.-P. Paris Dept. Electrical and Comp. Engineering George Mason University Last updated: November 29, 2016 2016, B.-P. Paris ECE 201: Intro to Signal Analysis
Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon )
 ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
Multirate Digital Signal Processing
 Multirate Digital Signal Processing Basic Sampling Rate Alteration Devices Up-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer factor Down-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer
Multirate Digital Signal Processing Basic Sampling Rate Alteration Devices Up-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer factor Down-sampler - Used to increase the sampling rate by an integer
PROBLEM SET 6. Note: This version is preliminary in that it does not yet have instructions for uploading the MATLAB problems.
 PROBLEM SET 6 Issued: 2/32/19 Due: 3/1/19 Reading: During the past week we discussed change of discrete-time sampling rate, introducing the techniques of decimation and interpolation, which is covered
PROBLEM SET 6 Issued: 2/32/19 Due: 3/1/19 Reading: During the past week we discussed change of discrete-time sampling rate, introducing the techniques of decimation and interpolation, which is covered
Chapter Three. The Discrete Fourier Transform
 Chapter Three. The Discrete Fourier Transform The discrete Fourier transform (DFT) is one of the two most common, and powerful, procedures encountered in the field of digital signal processing. (Digital
Chapter Three. The Discrete Fourier Transform The discrete Fourier transform (DFT) is one of the two most common, and powerful, procedures encountered in the field of digital signal processing. (Digital
ELECTRONOTES APPLICATION NOTE NO Hanshaw Road Ithaca, NY Nov 7, 2014 MORE CONCERNING NON-FLAT RANDOM FFT
 ELECTRONOTES APPLICATION NOTE NO. 416 1016 Hanshaw Road Ithaca, NY 14850 Nov 7, 2014 MORE CONCERNING NON-FLAT RANDOM FFT INTRODUCTION A curiosity that has probably long been peripherally noted but which
ELECTRONOTES APPLICATION NOTE NO. 416 1016 Hanshaw Road Ithaca, NY 14850 Nov 7, 2014 MORE CONCERNING NON-FLAT RANDOM FFT INTRODUCTION A curiosity that has probably long been peripherally noted but which
ELECTRONOTES APPLICATION NOTE NO Hanshaw Road Ithaca, NY August 3, 2017
 ELECTRONOTES APPLICATION NOTE NO. 432 1016 Hanshaw Road Ithaca, NY 14850 August 3, 2017 SIMPLIFIED DIGITAL NOTCH FILTER DESIGN Recently [1] we have been involved with an issue of a so-called Worldwide
ELECTRONOTES APPLICATION NOTE NO. 432 1016 Hanshaw Road Ithaca, NY 14850 August 3, 2017 SIMPLIFIED DIGITAL NOTCH FILTER DESIGN Recently [1] we have been involved with an issue of a so-called Worldwide
VU Signal and Image Processing. Torsten Möller + Hrvoje Bogunović + Raphael Sahann
 052600 VU Signal and Image Processing Torsten Möller + Hrvoje Bogunović + Raphael Sahann torsten.moeller@univie.ac.at hrvoje.bogunovic@meduniwien.ac.at raphael.sahann@univie.ac.at vda.cs.univie.ac.at/teaching/sip/17s/
052600 VU Signal and Image Processing Torsten Möller + Hrvoje Bogunović + Raphael Sahann torsten.moeller@univie.ac.at hrvoje.bogunovic@meduniwien.ac.at raphael.sahann@univie.ac.at vda.cs.univie.ac.at/teaching/sip/17s/
Lab 3 SPECTRUM ANALYSIS OF THE PERIODIC RECTANGULAR AND TRIANGULAR SIGNALS 3.A. OBJECTIVES 3.B. THEORY
 Lab 3 SPECRUM ANALYSIS OF HE PERIODIC RECANGULAR AND RIANGULAR SIGNALS 3.A. OBJECIVES. he spectrum of the periodic rectangular and triangular signals.. he rejection of some harmonics in the spectrum of
Lab 3 SPECRUM ANALYSIS OF HE PERIODIC RECANGULAR AND RIANGULAR SIGNALS 3.A. OBJECIVES. he spectrum of the periodic rectangular and triangular signals.. he rejection of some harmonics in the spectrum of
Algebra and Trig. I. The graph of
 Algebra and Trig. I 4.5 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions The graph of The graph of. The trigonometric functions can be graphed in a rectangular coordinate system by plotting points whose coordinates
Algebra and Trig. I 4.5 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions The graph of The graph of. The trigonometric functions can be graphed in a rectangular coordinate system by plotting points whose coordinates
Introduction to Wavelets. For sensor data processing
 Introduction to Wavelets For sensor data processing List of topics Why transform? Why wavelets? Wavelets like basis components. Wavelets examples. Fast wavelet transform. Wavelets like filter. Wavelets
Introduction to Wavelets For sensor data processing List of topics Why transform? Why wavelets? Wavelets like basis components. Wavelets examples. Fast wavelet transform. Wavelets like filter. Wavelets
Project 2 - Speech Detection with FIR Filters
 Project 2 - Speech Detection with FIR Filters ECE505, Fall 2015 EECS, University of Tennessee (Due 10/30) 1 Objective The project introduces a practical application where sinusoidal signals are used to
Project 2 - Speech Detection with FIR Filters ECE505, Fall 2015 EECS, University of Tennessee (Due 10/30) 1 Objective The project introduces a practical application where sinusoidal signals are used to
Music 171: Amplitude Modulation
 Music 7: Amplitude Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) February 7, 9 Adding Sinusoids Recall that adding sinusoids of the same frequency
Music 7: Amplitude Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) February 7, 9 Adding Sinusoids Recall that adding sinusoids of the same frequency
The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm #2
 The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm #2 Date: November 18, 2010 Course: EE 313 Evans Name: Last, First The exam is scheduled to last 75 minutes. Open books
The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm #2 Date: November 18, 2010 Course: EE 313 Evans Name: Last, First The exam is scheduled to last 75 minutes. Open books
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y
Digital Signal Processing
 Digital Signal Processing Lecture 9 Discrete-Time Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Analog to Digital Conversion Most real life signals are analog signals These
Digital Signal Processing Lecture 9 Discrete-Time Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Alp Ertürk alp.erturk@kocaeli.edu.tr Analog to Digital Conversion Most real life signals are analog signals These
Lecture 3, Multirate Signal Processing
 Lecture 3, Multirate Signal Processing Frequency Response If we have coefficients of an Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter h, or in general the impulse response, its frequency response becomes (using
Lecture 3, Multirate Signal Processing Frequency Response If we have coefficients of an Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filter h, or in general the impulse response, its frequency response becomes (using
Analyzing A/D and D/A converters
 Analyzing A/D and D/A converters 2013. 10. 21. Pálfi Vilmos 1 Contents 1 Signals 3 1.1 Periodic signals 3 1.2 Sampling 4 1.2.1 Discrete Fourier transform... 4 1.2.2 Spectrum of sampled signals... 5 1.2.3
Analyzing A/D and D/A converters 2013. 10. 21. Pálfi Vilmos 1 Contents 1 Signals 3 1.1 Periodic signals 3 1.2 Sampling 4 1.2.1 Discrete Fourier transform... 4 1.2.2 Spectrum of sampled signals... 5 1.2.3
Digital Signal Processing
 COMP ENG 4TL4: Digital Signal Processing Notes for Lecture #27 Tuesday, November 11, 23 6. SPECTRAL ANALYSIS AND ESTIMATION 6.1 Introduction to Spectral Analysis and Estimation The discrete-time Fourier
COMP ENG 4TL4: Digital Signal Processing Notes for Lecture #27 Tuesday, November 11, 23 6. SPECTRAL ANALYSIS AND ESTIMATION 6.1 Introduction to Spectral Analysis and Estimation The discrete-time Fourier
Trigonometric Identities
 Trigonometric Identities Scott N. Walck September 1, 010 1 Prerequisites You should know the cosine and sine of 0, π/6, π/4, π/, and π/. Memorize these if you do not already know them. cos 0 = 1 sin 0
Trigonometric Identities Scott N. Walck September 1, 010 1 Prerequisites You should know the cosine and sine of 0, π/6, π/4, π/, and π/. Memorize these if you do not already know them. cos 0 = 1 sin 0
Signals. Continuous valued or discrete valued Can the signal take any value or only discrete values?
 Signals Continuous time or discrete time Is the signal continuous or sampled in time? Continuous valued or discrete valued Can the signal take any value or only discrete values? Deterministic versus random
Signals Continuous time or discrete time Is the signal continuous or sampled in time? Continuous valued or discrete valued Can the signal take any value or only discrete values? Deterministic versus random
Signals and Systems Using MATLAB
 Signals and Systems Using MATLAB Second Edition Luis F. Chaparro Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh, PA, USA AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK
Signals and Systems Using MATLAB Second Edition Luis F. Chaparro Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh, PA, USA AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK
Digital Signal Processing Lecture 1 - Introduction
 Digital Signal Processing - Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville August 20, 2015 Overview 1 2 3 4 Basic building blocks in DSP Frequency analysis Sampling Filtering
Digital Signal Processing - Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville August 20, 2015 Overview 1 2 3 4 Basic building blocks in DSP Frequency analysis Sampling Filtering
Chapter 2. Signals and Spectra
 Chapter 2 Signals and Spectra Outline Properties of Signals and Noise Fourier Transform and Spectra Power Spectral Density and Autocorrelation Function Orthogonal Series Representation of Signals and Noise
Chapter 2 Signals and Spectra Outline Properties of Signals and Noise Fourier Transform and Spectra Power Spectral Density and Autocorrelation Function Orthogonal Series Representation of Signals and Noise
Lecture 2: SIGNALS. 1 st semester By: Elham Sunbu
 Lecture 2: SIGNALS 1 st semester 1439-2017 1 By: Elham Sunbu OUTLINE Signals and the classification of signals Sine wave Time and frequency domains Composite signals Signal bandwidth Digital signal Signal
Lecture 2: SIGNALS 1 st semester 1439-2017 1 By: Elham Sunbu OUTLINE Signals and the classification of signals Sine wave Time and frequency domains Composite signals Signal bandwidth Digital signal Signal
Digital Signal Processing 2/ Advanced Digital Signal Processing Lecture 11, Complex Signals and Filters, Hilbert Transform Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau
 Digital Signal Processing 2/ Advanced Digital Signal Processing Lecture 11, Complex Signals and Filters, Hilbert Transform Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau Imagine we would like to know the precise, instantaneous,
Digital Signal Processing 2/ Advanced Digital Signal Processing Lecture 11, Complex Signals and Filters, Hilbert Transform Gerald Schuller, TU Ilmenau Imagine we would like to know the precise, instantaneous,
Linguistic Phonetics. Spectral Analysis
 24.963 Linguistic Phonetics Spectral Analysis 4 4 Frequency (Hz) 1 Reading for next week: Liljencrants & Lindblom 1972. Assignment: Lip-rounding assignment, due 1/15. 2 Spectral analysis techniques There
24.963 Linguistic Phonetics Spectral Analysis 4 4 Frequency (Hz) 1 Reading for next week: Liljencrants & Lindblom 1972. Assignment: Lip-rounding assignment, due 1/15. 2 Spectral analysis techniques There
SAMPLING THEORY. Representing continuous signals with discrete numbers
 SAMPLING THEORY Representing continuous signals with discrete numbers Roger B. Dannenberg Professor of Computer Science, Art, and Music Carnegie Mellon University ICM Week 3 Copyright 2002-2013 by Roger
SAMPLING THEORY Representing continuous signals with discrete numbers Roger B. Dannenberg Professor of Computer Science, Art, and Music Carnegie Mellon University ICM Week 3 Copyright 2002-2013 by Roger
Signals. Periodic vs. Aperiodic. Signals
 Signals 1 Periodic vs. Aperiodic Signals periodic signal completes a pattern within some measurable time frame, called a period (), and then repeats that pattern over subsequent identical periods R s.
Signals 1 Periodic vs. Aperiodic Signals periodic signal completes a pattern within some measurable time frame, called a period (), and then repeats that pattern over subsequent identical periods R s.
YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING FACULTY COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS LABORATORY EE 354 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING FACULTY COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS LABORATORY EE 354 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS EXPERIMENT 3: SAMPLING & TIME DIVISION MULTIPLEX (TDM) Objective: Experimental verification of the
YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING FACULTY COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS LABORATORY EE 354 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS EXPERIMENT 3: SAMPLING & TIME DIVISION MULTIPLEX (TDM) Objective: Experimental verification of the
Subtractive Synthesis. Describing a Filter. Filters. CMPT 468: Subtractive Synthesis
 Subtractive Synthesis CMPT 468: Subtractive Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University November, 23 Additive synthesis involves building the sound by
Subtractive Synthesis CMPT 468: Subtractive Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University November, 23 Additive synthesis involves building the sound by
Signals and Systems Lecture 6: Fourier Applications
 Signals and Systems Lecture 6: Fourier Applications Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Winter 2012 arzaneh Abdollahi Signal and Systems Lecture 6
Signals and Systems Lecture 6: Fourier Applications Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Winter 2012 arzaneh Abdollahi Signal and Systems Lecture 6
Section 7.6 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 4 Section 7. Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the sine and cosine function. The input values will be the angle in radians so we will be using x is
4 Section 7. Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the sine and cosine function. The input values will be the angle in radians so we will be using x is
Signal Processing. Naureen Ghani. December 9, 2017
 Signal Processing Naureen Ghani December 9, 27 Introduction Signal processing is used to enhance signal components in noisy measurements. It is especially important in analyzing time-series data in neuroscience.
Signal Processing Naureen Ghani December 9, 27 Introduction Signal processing is used to enhance signal components in noisy measurements. It is especially important in analyzing time-series data in neuroscience.
Sound synthesis with Pure Data
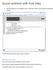 Sound synthesis with Pure Data 1. Start Pure Data from the programs menu in classroom TC307. You should get the following window: The DSP check box switches sound output on and off. Getting sound out First,
Sound synthesis with Pure Data 1. Start Pure Data from the programs menu in classroom TC307. You should get the following window: The DSP check box switches sound output on and off. Getting sound out First,
EE 422G - Signals and Systems Laboratory
 EE 422G - Signals and Systems Laboratory Lab 3 FIR Filters Written by Kevin D. Donohue Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 September 19, 2015 Objectives:
EE 422G - Signals and Systems Laboratory Lab 3 FIR Filters Written by Kevin D. Donohue Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 September 19, 2015 Objectives:
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 A Periodic Function and Its Period Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions A nonconstant function f is said to be periodic if there is a number p > 0 such that f(x + p) = f(x) for all x in
A Periodic Function and Its Period Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions A nonconstant function f is said to be periodic if there is a number p > 0 such that f(x + p) = f(x) for all x in
