MATLAB: SIGNAL PROCESSING
|
|
|
- Gregory Sims
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MATLAB: SIGNAL PROCESSING P a g e
2 CONTENT Chapter No. Title Page No. Chapter 1 Introduction 3 Chapter 2 Arithmetic Operations 4-6 Chapter 3 Trigonometric Calculations 7-9 Chapter 4 Matrices Chapter 5 Features of Matrices Chapter 6 2-D Plot Chapter 7 2-D Plot Designing Chapter 8 2-D Plot Fig. & Subplot Chapter 9 3-D Plot Chapter 10 Input Values P a g e
3 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 MATLAB an Introduction MATLAB is a language of technical computing. MATLAB (matrix laboratory) is a multi-paradigm numerical computing environment and fourth-generation programming language. A proprietary programming language developed by MathWorks, MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages, including C, C++, Java, Fortran and Python. In 2004, MATLAB had around one million users across industry and academia. MATLAB users come from various backgrounds of engineering, science, and economics. Millions of engineers and scientists worldwide use MATLAB to analyze and design the systems and products transforming our world. MATLAB is in automobile active safety systems, interplanetary spacecraft, health monitoring devices, smart power grids, and LTE cellular networks. It is used for machine learning, signal processing, image processing, computer vision, communications, computational finance, control design, robotics, and much more. The MATLAB platform is optimized for solving engineering and scientific problems. The matrix-based MATLAB language is the world s most natural way to express computational mathematics. Built-in graphics make it easy to visualize and gain insights from data. A vast library of prebuilt toolboxes lets you get started right away with algorithms essential to your domain. The desktop environment invites experimentation, exploration, and discovery. These MATLAB tools and capabilities are all rigorously tested and designed to work together. MATLAB helps you take your ideas beyond the desktop. You can run your analyses on larger data sets and scale up to clusters and clouds P a g e
4 CHAPTER 2 ARITHMETIC OPERATION Variable Assignment In MATLAB we need to simply assign the variable with the corresponding values and calculate the results. For example let s take a=1 >> a=1 a = 1 For example let s take b=2 >> b=2 b = 2 So we can easily calculate c=a+b >> c=a+b c = 3 Note: we don t need to specify data type or put traditional header files to assign a value to variable in MATLAB. Practice set 1 Question 1: If a=2000, b=3000 find (a^2)+2*a*b+(b^2). Solution : >> a=2000 a = P a g e
5 >> b=3000 b = 3000 >> (a^2)+2*a*b+(b^2) ans = Practice set 2 Question 2: If a= , b=7.14 find c=(a^3)+3*a*b+(b^3). Solution: >> a= a = >> b=7.14 b = >> c=(a^3)+3*a*b+(b^3) c = e P a g e
6 Practice set 3 Question 3: If a=12596, b=9.1463, c=1000 find c=(a+b+c)^3. Solution: >> a=12596 a = >> b= b = >> c=1000 c = 1000 >> c=(a+b+c)^3 c = e+12 Assignments If a= , b= , c= then find 1. d= (a+b)/c 2. e= (a-b)/c 3. f= (a*b)/c 4. g= ((a*b)/c)+( (a+b)/c) P a g e
7 Trigonometric Calculations CHAPTER Trigonometric Calculations In MATLAB we just need to call the name of trigonometric functions and its values will be calculated because of inbuilt toolbox. For example >>sin(0) ans = 0 >>sin(pi/6) ans = >>cos(pi/4) ans = >>tan(pi/4) ans = Practice set 1 Question 1: Find the value of sin(pi/2)+cos(pi/2)+tan(pi/2). Solution : P a g e
8 >>sin(pi/2)+cos(pi/2)+tan(pi/2) ans = e+16 Practice set 2 Question 2: Find the value of sin(pi/2)-cos(pi/4)+tan(pi/2). Solution: >>sin(pi/2)-cos(pi/4)+tan(pi/2) ans = e+16 Practice set 3 Question 3: If a=pi/2, b=pi/4, c=pi/6 find sin(a)+ cos(b)*tan(c). Solution: >> a=pi/2 a = >> b=pi/4 b = >> c=pi/6-8 - P a g e
9 c = >>sin(a)+ cos(b)*tan(c) ans = Assignments If a=pi/6, b=pi/4, c=pi/2 then find 5. d= sin(a+b) 6. e= cos(a-b) 7. f= sin(a+b)+ cos(a-b) 8. g= sin(a)+cos(b)+tan(c) P a g e
10 1.1 Matrix Creation CHAPTER-4 MATRICES In MATLAB it s very easy to create a matrix. Example 1 :We want to create a 2*2 matrix with elements write [2 3; 4 5] then we will >> a=[2 3;4 5] a = Example 2 :We want to create a 3*3 matrix with elements we will write [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] then P a g e >>b=[1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] b = Example 3 :We want to create a 3*3 matrix with elements [4 2 5; 4 8 6; 7 8 7] then we will write >>c=[4 2 5; 4 8 6; 7 8 7] c = Matrix Arithmetic We can do addition, subtraction, multiplication operations for the matrices. Example 1 : Create two matrices of 2*2 with elements a=[2 3; 4 5] and b= [3 5; 6 7], add them and find the value of c=a+b. >> a=[2 3; 4 5]
11 a = >> b= [3 5; 6 7] b = >> c=a+b c = P a g e Example 2 : Create two matrices of 3*3 with elements a=[1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] and b= [3 5 7; 6 7 7; ], subtract them and find the value of c=a-b. >> a=[1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] a = >> b= [3 5 7; 6 7 7; ] b = >> c=a-b
12 c = Example 3 : Create two matrices of 3*3 with elements a=[ ; ; ] and b= [ ; ; ], multiply them and find the value of c=a*b. >> a=[ ; ; ] a = >> b= [ ; ; ] b = >> c=a*b c = P a g e
13 Assignments If a=[ ; ; ], b= [3 5 7; 6 7 7; ], c=[1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] then find 1. d= a+b-c 2. e= (a/b)*c 3. f= (a+b)+(a-b)+(a*b)+(a/d) 4. g= a+b-c+(b/a)+(c/b) P a g e
14 CHAPTER 5 FEATURES OF MATRICES 1.1 Transpose: Rows as columns and columns as rows. Example 1 :Find the transpose of matrix A= [4 2 5; 4 8 6; 7 8 7] >> A= [4 2 5; 4 8 6; 7 8 7] A = The symbol of transpose is ( ) >> B=A' B = Example 2 :Find the transpose of matrix B= [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] >> B= [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] B = >> C=B' C = P a g e
15 1.2 Diagonal: Display the principle diagonal elements. Example 3: Find the diagonal of matrix A= [4 2 5; 4 8 6; 7 8 7] >> A= [4 2 5; 4 8 6; 7 8 7] A = >> B=diag(A) B = Inverse: Creates the inverse of the matrix Example 4: Find the inverse of matrix A= [4 5 6; 7 8 9; ] >> A= [4 5 6; 7 8 9; ] A = >> B=inv(A) B = P a g e
16 1.4 Identity Matrix: Matrix with principle diagonal element as unity. Example 5: Create an identity matrix of 3*3 elements >> A= eye(3,3) >> A= eye(3,3) A = Example 6: Create an identity matrix of 4*4 elements >> A= eye(4,4) A = Unit Matrix: Matrix with all elements as unity. Example 6: Create an unit matrix of 3*3 elements >> A= ones(3,3) >> A= ones(3,3) A = P a g e
17 Example 7: Create an unit matrix of 4*4 elements >> A= ones(4,4) A = Magic Matrix: Matrix with all elements sum as same number. Example 8: Create a magic matrix of 3*3 elements >> A= magic(3) A = Example 9: Create a magic matrix of 4*4 elements >> A= magic(4) A = Determinant of a Matrix: Calculates the determinant value of a matrix. Example 10: Calculate the determinant value of a matrix A= [4 5 6; 7 8 9; ]. >> A= [4 5 6; 7 8 9; ] P a g e
18 A = >> B=det(A) B = e-14 Example 11: Calculate the determinant value of a matrix A= [1 2 3; 7 8 9; 1 1 1]. >>A= [1 2 3; 7 8 9; 1 1 1] A = Assignments If a=[ ; ; ], b= [3 5 7; 6 7 7; ], c=[1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] then find 1. Determinant of a,b,c 2. Find inverse of a,b,c 3. Create a unity matrix and identity matrix of 3*3 elements P a g e
19 CHAPTER 6 2D-PLOT 1. Two Dimensional Plots 1.1 Steps : First create the range of the signal or plotting points. >> 1.2 Steps : Create the function for the signal. >> b=sin(pi*a); 1.3 Plotting : Plot the function for the signal. >> Program: b=sin(pi*a); Output : P a g e
20 Example 1: Create a sine wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (2*pi). Program: b=sin(2*pi*a); Output : Assignments Note :Commands for different trigonometric functions 1. SINE: sin 4. COSEC: csc 2. COSINE: cos5. SEC: sec 3. TAN: tan 6. COT: cot P a g e 1. Create a sine wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (2*pi). 2. Create a cosine wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (3*pi). 3. Create a tan wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (5*pi). 4. Create a cosec wave with range 0 to 2 and the phase shift of (2*pi). 5. Create a sec wave with range 0 to 3 and the phase shift of (2*pi). 6. Create a cot wave with range 0 to 2 and the phase shift of (5*pi).
21 7. CHAPTER 7 2D-PLOT-DESIGNING 1. LABEL 1.1 Steps : First create the range of the signal or plotting points. >> 1.2 Steps : Create the function for the signal. >> b=sin(2*pi*a); 1.3 Plotting : Plot the function for the signal. >> 1.4 Steps : Create the label of x axis. >>xlabel( X Axis ) 1.5 Steps : Create the label of y axis. >>ylabel( Y Axis ) Program: b=sin(2*pi*a); Output : P a g e
22 Example 1: Create a cosine wave with range 0 to 1,the phase shift of (2*pi) and label X AXIS and Y AXIS. Program: b=cos(2*pi*a); Output : Assignments 1. Create a sine wave with range 0 to 2, the phase shift of (2*pi) and label X AXIS and Y AXIS. 2. Create a cosine wave with range 0 to 1, the phase shift of (3*pi) and label X Axis of COS and Y AXIS of COS. 3. Create a tan wave with range 0 to 1, the phase shift of (5*pi) and label X Axis of COS and Y AXIS of COS. 4. Create a cosec wave with range 0 to 2,the phase shift of (2*pi) and label X AXIS and Y AXIS. 5. Create a sec wave with range 0 to 3, the phase shift of (2*pi) and label X AXIS and Y AXIS. 6. Create a cot wave with range 0 to 2, the phase shift of (5*pi) and label X Axis of COT and Y AXIS of COT P a g e
23 2. TITLE 1.1 Steps : First create the range of the signal or plotting points. >> 1.2 Steps : Create the function for the signal. >> b=sin(2*pi*a); 1.3 Plotting : Plot the function for the signal. >> 1.4 Steps : Create the label of x axis. >>xlabel( X Axis ) 1.5 Steps : Create the label of y axis. >>ylabel( Y Axis ) 1.6 Steps : Create the TITLE of wave. >>title( SIN Wave ) Program: b=sin(2*pi*a); title( SIN Wave ) Output : P a g e
24 Example 2: Create a cosine wave with range 0 to 1,the phase shift of (2*pi), label X AXIS, Y AXIS and title Cos Wave. Program: b=cos(2*pi*a); title( Cos Wave ) Output : 3. LEGEND 1.1 Steps : First create the range of the signal or plotting points. >> 1.2 Steps : Create the function for the signal. >> b=sin(2*pi*a); 1.3 Plotting : Plot the function for the signal. >> 1.4 Steps : Create the label of x axis P a g e
25 >>xlabel( X Axis ) 1.5 Steps : Create the label of y axis. >>ylabel( Y Axis ) 1.6 Steps : Create the TITLE of wave. >>title( SIN Wave ) 1.7 Steps : Create the LEGEND of wave. >>legend( SIN Wave ) Program: b=sin(2*pi*a); title( SIN Wave ) legend( SIN Wave ) Output: P a g e
26 Example 3: Create a cosine wave with range 0 to 1,the phase shift of (2*pi), label X AXIS, Y AXIS,title Cos Wave and legend ( COS Wave ). Program: b=cos(2*pi*a); title( Cos Wave ) legend( Cos Wave ) Output : Assignments 1. Create a sine wave and cosine wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (2*pi),add them (sin+cos) give label and titles. Label : X Axis,YAxis Title= Sin+Cos Legend = Sin+Cos P a g e
27 2. Create a sine wave and cosine wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (2*pi) and subtract them (sin-cos) give label and titles. Label : X Axis,YAxis Title= Sin-Cos Legend = Sin-Cos 3. Create a cosine wave and tan wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (3*pi) and add them (cos+tan) give label and titles. Label : X Axis,YAxis Title= Cos+Tan Legend = Cos+Tan 4. Create a cosine wave and tan wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (3*pi) and subtract them (cos-tan) give label and titles. Label : X Axis,YAxis Title= Cos-Tan Legend = Cos-Tan P a g e 5. Create a tan wave and cot wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (5*pi) and add them (tan+cot) give label and titles. Label : X Axis,YAxis Title= Tan+Cot Legend = Tan+Cot 6. Create a tan wave and cot wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (5*pi) and subtract them (tan-cot) give label and titles. Label : X Axis,YAxis Title= Tan+Cot Legend = Tan+Cot 7. Create a cot wave and cosec wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (5*pi) and add them (cot+csc) give label and titles. Label : X Axis,YAxis Title= Cot+Cosec Legend = Cot+Cosec 8. Create a cot wave and cosec wave with range 0 to 1 and the phase shift of (7*pi) and subtract them (cot-csc) give label and titles. Label : X Axis,YAxis Title= Cot-Cosec Legend = Cot-Cosec
28 CHAPTER 8 2D-PLOT-Fig. & Subplot 1. Figure Plot 1.1 Step: First create the program for sine function. b=sin(2*pi*a); 1.2 Step :Write the program for cos wave. b=cos(2*pi*a); P a g e
29 1.4 Step : Combine the codes. b=sin(2*pi*a); c=cos(2*pi*a); figure(1) figure(2) plot(a,c) Output : 1.4 Step : Add the title and legend. b=sin(2*pi*a); c=cos(2*pi*a); figure(1) title( Sin Wave ) legend( Sin Wave ) figure(2) plot(a,c) P a g e
30 title( Cosin Wave ) legend( Cosin Wave ) Output : Assignments [1]. Plot Sin wave and Cosine wave in the two different figures. [2]. Plot Cosine wave and Tan wave in the two different figures. [3]. Plot Tan Wave and Cot wave in the two different figures. [4]. Plot Cot Wave and Sec wave in the two different figures. [5]. Plot Sec Wave and Cosec wave in the two different figures. [6]. Plot Sin wave,cosine wave, Cot wave and Tan wave in the four different figures. [7]. Plot Cosec wave,sec wave and Cot wave in the three different figures P a g e
31 2. Sub Plot 1.1 Step: First create the program for sine function. b=sin(2*pi*a); 1.2 Step :Write the program for cos wave. b=cos(2*pi*a); 1.4 Step : Combine the codes. b=sin(2*pi*a); c=cos(2*pi*a); subplot(1,2,1) subplot(1,2,2) plot(a,c) P a g e
32 1.4 Step : Add the title and legend. b=sin(2*pi*a); c=cos(2*pi*a); subplot(1,2,1) title( Sin Wave ) legend( Sin Wave ) subplot(1,2,2) plot(a,c) title( Cosin Wave ) legend( Cosin Wave ) Assignments 1. Subplot Sin wave and Cosine wave. 2. Subplot Cosine wave and Tan wave. 3. Subplot Tan Wave and Cot wave. 4. Subplot Cot Wave and Sec wave. 5. Subplot Sec Wave and Cosec wave. 6. Subplot Sin wave,cosine wave, Cot wave and Tan wave. 7. Subplot Cosec wave,sec wave and Cot wave P a g e
33 CHAPTER 9 3D PLOT 3D PLOT 1.1 Step: First create the program for sine function. b=sin(2*pi*a); OUTPUT P a g e
34 1.2 Step :Change the program to get 3D plot. b=sin(2*pi*a); c=b *b; surf(c) zlabel('z Axis') legend( Sin 3D Plot ) OUTPUT P a g e
35 Assignments 3-D Figure Plot 1. Plot 3-D Sin wave and Cosine wave in the two different figures. 2. Plot 3-D Cosine wave and Tan wave in the two different figures. 3. Plot 3-D Tan Wave and Cot wave in the two different figures. 4. Plot 3-DCot Wave and Sec wave in the two different figures. 5. Plot 3-DSec Wave and Cosec wave in the two different figures. 6. Plot 3-DSin wave,cosine wave, Cot wave and Tan wave in the four different figures. 7. Plot 3-DCosec wave,sec wave and Cot wave in the three different figures. 8. Subplot Sin wave and Cosine wave. 9. Subplot Cosine wave and Tan wave. 3-D Subplot 1. Subplot 3-D Tan Wave and Cot wave. 2. Subplot 3-D Cot Wave and Sec wave. 3. Subplot 3-D Sec Wave and Cosec wave. 4. Subplot 3-D Sin wave,cosine wave, Cot wave and Tan wave. 5. Subplot 3-DCosec wave,sec wave and Cot wave P a g e
36 CHAPTER 10 INPUT VALUES SINGLE INPUT VALUES (2 D) 1.1 Step: First create the program for sine function. b=sin(2*pi*a); 1.2 Step :Change the program to provide input values. z=input( Please enter the maximum range :- ); a=0:0.01:z; b=sin(2*pi*a); INPUT Please enter the maximum range : P a g e
37 DOUBLE INPUT VALUES (2 D) 1.1 Step: First create the program for sine function. b=sin(2*pi*a); 1.2 Step :Change the program to provide input values. y=input( Please enter the maximum range :- ); z=input( Please enter the minimum range :- ); a=z:0.01:y; b=sin(2*pi*a); INPUT Please enter the maximum range: - 2 Please enter the minimum range: P a g e
38 INPUT VALUES (3 D) 1.1 Step: First create the program for sine function. b=sin(2*pi*a); OUTPUT 1.2 Step :Change the program to provide input values. z=input( Please enter the maximum range :- ); y=input( Please enter the minimum range :- ); a=y:0.01:z; b=sin(2*pi*a); c=b *b; surf(c) zlabel('z Axis') legend( Sin 3D Plot ) INPUT Please enter the maximum range :-2 Please enter the maximum range : P a g e
39 INPUT VALUES (3 D) Assignments 3-D Figure Plot 10. Plot 3-D Sin wave in the two different figures and provide any 1 input. 11. Plot 3-D Cosine wave in the two different figures and provide any 1 input. 12. Plot 3-D Tan Wave in the two different figures and provide any 1 input. 13. Plot 3-DCot Wave and Sec wave in the two different figures and provide any 1 input. 14. Plot 3-DSec Wave and Cosec wave in the two different figures and provide any 1 input. 15. Plot 3-DSin wave,cosine wave, Cot wave and Tan wave in the four different figures and provide any 2 input. 16. Plot 3-DCosec wave,sec wave and Cot wave in the three different figures and provide any 2 input P a g e
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions
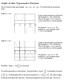 Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE)
 Theory Class XI TARGET : JEE Main/Adv PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) MATHEMATICS Trigonometry SHARING IS CARING!! Want to Thank me? Share this Assignment with your friends and show
Theory Class XI TARGET : JEE Main/Adv PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) MATHEMATICS Trigonometry SHARING IS CARING!! Want to Thank me? Share this Assignment with your friends and show
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions. By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh
 Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions
 HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 5 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions This is a BASIC CALCULATORS ONLY unit. (2) Periodic Functions (3) Graph of the Sine Function (4) Graph of the Cosine Function
HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 5 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions This is a BASIC CALCULATORS ONLY unit. (2) Periodic Functions (3) Graph of the Sine Function (4) Graph of the Cosine Function
Name: Period: Date: Math Lab: Explore Transformations of Trig Functions
 Name: Period: Date: Math Lab: Explore Transformations of Trig Functions EXPLORE VERTICAL DISPLACEMENT 1] Graph 2] Explain what happens to the parent graph when a constant is added to the sine function.
Name: Period: Date: Math Lab: Explore Transformations of Trig Functions EXPLORE VERTICAL DISPLACEMENT 1] Graph 2] Explain what happens to the parent graph when a constant is added to the sine function.
You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3)
 You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3) LEQ: How do we identify and use basic trigonometric identities to find trigonometric values & use basic trigonometric identities to simplify
You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3) LEQ: How do we identify and use basic trigonometric identities to find trigonometric values & use basic trigonometric identities to simplify
Trigonometric Equations
 Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
The reciprocal identities are obvious from the definitions of the six trigonometric functions.
 The Fundamental Identities: (1) The reciprocal identities: csc = 1 sec = 1 (2) The tangent and cotangent identities: tan = cot = cot = 1 tan (3) The Pythagorean identities: sin 2 + cos 2 =1 1+ tan 2 =
The Fundamental Identities: (1) The reciprocal identities: csc = 1 sec = 1 (2) The tangent and cotangent identities: tan = cot = cot = 1 tan (3) The Pythagorean identities: sin 2 + cos 2 =1 1+ tan 2 =
Grade 10 Trigonometry
 ID : ww-10-trigonometry [1] Grade 10 Trigonometry For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer t he quest ions (1) If - 0, f ind value of sin 4 θ - cos 4 θ. (2) Simplif y 3(sin 4 θ cos 4 θ) -
ID : ww-10-trigonometry [1] Grade 10 Trigonometry For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer t he quest ions (1) If - 0, f ind value of sin 4 θ - cos 4 θ. (2) Simplif y 3(sin 4 θ cos 4 θ) -
Trigonometry. An Overview of Important Topics
 Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Honors Algebra 2 w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals
 Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
Chapter 8. Analytic Trigonometry. 8.1 Trigonometric Identities
 Chapter 8. Analytic Trigonometry 8.1 Trigonometric Identities Fundamental Identities Reciprocal Identities: 1 csc = sin sec = 1 cos cot = 1 tan tan = 1 cot tan = sin cos cot = cos sin Pythagorean Identities:
Chapter 8. Analytic Trigonometry 8.1 Trigonometric Identities Fundamental Identities Reciprocal Identities: 1 csc = sin sec = 1 cos cot = 1 tan tan = 1 cot tan = sin cos cot = cos sin Pythagorean Identities:
Experiment 1 Introduction to MATLAB and Simulink
 Experiment 1 Introduction to MATLAB and Simulink INTRODUCTION MATLAB s Simulink is a powerful modeling tool capable of simulating complex digital communications systems under realistic conditions. It includes
Experiment 1 Introduction to MATLAB and Simulink INTRODUCTION MATLAB s Simulink is a powerful modeling tool capable of simulating complex digital communications systems under realistic conditions. It includes
Math 102 Key Ideas. 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry. 1. Consider the following right triangle: c b
 Math 10 Key Ideas 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry 1. Consider the following right triangle: A c b B θ C a sin θ = b length of side opposite angle θ = c length of hypotenuse cosθ = a length of side adjacent
Math 10 Key Ideas 1 Chapter 1: Triangle Trigonometry 1. Consider the following right triangle: A c b B θ C a sin θ = b length of side opposite angle θ = c length of hypotenuse cosθ = a length of side adjacent
Trigonometric identities
 Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
( x "1) 2 = 25, x 3 " 2x 2 + 5x "12 " 0, 2sin" =1.
 Unit Analytical Trigonometry Classwork A) Verifying Trig Identities: Definitions to know: Equality: a statement that is always true. example:, + 7, 6 6, ( + ) 6 +0. Equation: a statement that is conditionally
Unit Analytical Trigonometry Classwork A) Verifying Trig Identities: Definitions to know: Equality: a statement that is always true. example:, + 7, 6 6, ( + ) 6 +0. Equation: a statement that is conditionally
MATLAB: Basics to Advanced
 Module 1: MATLAB Basics Program Description MATLAB is a numerical computing environment and fourth generation programming language. Developed by The MathWorks, MATLAB allows matrix manipulation, plotting
Module 1: MATLAB Basics Program Description MATLAB is a numerical computing environment and fourth generation programming language. Developed by The MathWorks, MATLAB allows matrix manipulation, plotting
Principles of Mathematics 12: Explained!
 Principles of Mathematics : Eplained! www.math.com PART I MULTIPLICATION & DIVISION IDENTITLES Algebraic proofs of trigonometric identities In this lesson, we will look at various strategies for proving
Principles of Mathematics : Eplained! www.math.com PART I MULTIPLICATION & DIVISION IDENTITLES Algebraic proofs of trigonometric identities In this lesson, we will look at various strategies for proving
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide Section 8.2 and 8.3-1
 8.3-1 Transformation of sine and cosine functions Sections 8.2 and 8.3 Revisit: Page 142; chapter 4 Section 8.2 and 8.3 Graphs of Transformed Sine and Cosine Functions Graph transformations of y = sin
8.3-1 Transformation of sine and cosine functions Sections 8.2 and 8.3 Revisit: Page 142; chapter 4 Section 8.2 and 8.3 Graphs of Transformed Sine and Cosine Functions Graph transformations of y = sin
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering. EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series
 THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series 1. Objective The goal of this laboratory exercise is to
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Department of Electronic and Information Engineering EIE2106 Signal and System Analysis Lab 2 Fourier series 1. Objective The goal of this laboratory exercise is to
Chapter 3, Part 4: Intro to the Trigonometric Functions
 Haberman MTH Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter, Part : Intro to the Trigonometric Functions Recall that the sine and cosine function represent the coordinates of points in the circumference
Haberman MTH Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter, Part : Intro to the Trigonometric Functions Recall that the sine and cosine function represent the coordinates of points in the circumference
cos sin sin 2 60 = 1.
 Name: Class: Date: Use the definitions to evaluate the six trigonometric functions of. In cases in which a radical occurs in a denominator, rationalize the denominator. Suppose that ABC is a right triangle
Name: Class: Date: Use the definitions to evaluate the six trigonometric functions of. In cases in which a radical occurs in a denominator, rationalize the denominator. Suppose that ABC is a right triangle
Trigonometry. David R. Wilkins
 Trigonometry David R. Wilkins 1. Trigonometry 1. Trigonometry 1.1. Trigonometric Functions There are six standard trigonometric functions. They are the sine function (sin), the cosine function (cos), the
Trigonometry David R. Wilkins 1. Trigonometry 1. Trigonometry 1.1. Trigonometric Functions There are six standard trigonometric functions. They are the sine function (sin), the cosine function (cos), the
Unit 6 Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors
 Unit Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors Multiple Choice Portion SHOW ALL WORK! 1. How many radians are in 1800? 10 10π Name: Per: 180 180π 2. On the unit circle shown, which radian measure is located at ( 2,
Unit Test REVIEW Algebra 2 Honors Multiple Choice Portion SHOW ALL WORK! 1. How many radians are in 1800? 10 10π Name: Per: 180 180π 2. On the unit circle shown, which radian measure is located at ( 2,
Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon )
 ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
ECEN 242 Wireless Electronics for Communication Spring 212 1-23-12 P. Mathys Problem Set 1 (Solutions are due Mon. 1-3-12) 1 Introduction The goals of this problem set are to use Matlab to generate and
Math 1205 Trigonometry Review
 Math 105 Trigonometry Review We begin with the unit circle. The definition of a unit circle is: x + y =1 where the center is (0, 0) and the radius is 1. An angle of 1 radian is an angle at the center of
Math 105 Trigonometry Review We begin with the unit circle. The definition of a unit circle is: x + y =1 where the center is (0, 0) and the radius is 1. An angle of 1 radian is an angle at the center of
ECE411 - Laboratory Exercise #1
 ECE411 - Laboratory Exercise #1 Introduction to Matlab/Simulink This laboratory exercise is intended to provide a tutorial introduction to Matlab/Simulink. Simulink is a Matlab toolbox for analysis/simulation
ECE411 - Laboratory Exercise #1 Introduction to Matlab/Simulink This laboratory exercise is intended to provide a tutorial introduction to Matlab/Simulink. Simulink is a Matlab toolbox for analysis/simulation
Contents. An introduction to MATLAB for new and advanced users
 An introduction to MATLAB for new and advanced users (Using Two-Dimensional Plots) Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional
An introduction to MATLAB for new and advanced users (Using Two-Dimensional Plots) Contents Getting Started Creating Arrays Mathematical Operations with Arrays Using Script Files and Managing Data Two-Dimensional
The Formula for Sinusoidal Signals
 The Formula for I The general formula for a sinusoidal signal is x(t) =A cos(2pft + f). I A, f, and f are parameters that characterize the sinusoidal sinal. I A - Amplitude: determines the height of the
The Formula for I The general formula for a sinusoidal signal is x(t) =A cos(2pft + f). I A, f, and f are parameters that characterize the sinusoidal sinal. I A - Amplitude: determines the height of the
Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes. Professor Miguel Ornelas
 Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes Professor Miguel Ornelas 1 M. Ornelas Math 180 Lecture Notes Section 6.1 Section 6.1 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Verify the identity. a. sin x + cos x cot x = csc
Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes Professor Miguel Ornelas 1 M. Ornelas Math 180 Lecture Notes Section 6.1 Section 6.1 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Verify the identity. a. sin x + cos x cot x = csc
Trigonometric Identities. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.5 Double-Angle Double-Angle Identities An Application Product-to-Sum and Sum-to-Product Identities Copyright 2017, 2013,
5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.5 Double-Angle Double-Angle Identities An Application Product-to-Sum and Sum-to-Product Identities Copyright 2017, 2013,
Unit 7 Trigonometric Identities and Equations 7.1 Exploring Equivalent Trig Functions
 Unit 7 Trigonometric Identities and Equations 7.1 Exploring Equivalent Trig Functions When we look at the graphs of sine, cosine, tangent and their reciprocals, it is clear that there will be points where
Unit 7 Trigonometric Identities and Equations 7.1 Exploring Equivalent Trig Functions When we look at the graphs of sine, cosine, tangent and their reciprocals, it is clear that there will be points where
A PROPOSED ALGORITHM FOR DIGITAL WATERMARKING
 A PROPOSED ALGORITHM FOR DIGITAL WATERMARKING Dr. Mohammed F. Al-Hunaity dr_alhunaity@bau.edu.jo Meran M. Al-Hadidi Merohadidi77@gmail.com Dr.Belal A. Ayyoub belal_ayyoub@ hotmail.com Abstract: This paper
A PROPOSED ALGORITHM FOR DIGITAL WATERMARKING Dr. Mohammed F. Al-Hunaity dr_alhunaity@bau.edu.jo Meran M. Al-Hadidi Merohadidi77@gmail.com Dr.Belal A. Ayyoub belal_ayyoub@ hotmail.com Abstract: This paper
Section 7.1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 Section 7.1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine OBJECTIVE 1: Understanding the Graph of the Sine Function and its Properties In Chapter 7, we will use a rectangular coordinate system for a different purpose. We
Section 7.1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine OBJECTIVE 1: Understanding the Graph of the Sine Function and its Properties In Chapter 7, we will use a rectangular coordinate system for a different purpose. We
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: 3C1 LABORATORY 1. 1 Dr. David Corrigan Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept.
 2012 Signals and Systems: Laboratory 1 1 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: 3C1 LABORATORY 1. 1 Dr. David Corrigan Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept. corrigad@tcd.ie www.mee.tcd.ie/ corrigad The aims of this
2012 Signals and Systems: Laboratory 1 1 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS: 3C1 LABORATORY 1. 1 Dr. David Corrigan Electronic and Electrical Engineering Dept. corrigad@tcd.ie www.mee.tcd.ie/ corrigad The aims of this
CHAPTER 4 IMPLEMENTATION OF ADALINE IN MATLAB
 52 CHAPTER 4 IMPLEMENTATION OF ADALINE IN MATLAB 4.1 INTRODUCTION The ADALINE is implemented in MATLAB environment running on a PC. One hundred data samples are acquired from a single cycle of load current
52 CHAPTER 4 IMPLEMENTATION OF ADALINE IN MATLAB 4.1 INTRODUCTION The ADALINE is implemented in MATLAB environment running on a PC. One hundred data samples are acquired from a single cycle of load current
Unit 5. Algebra 2. Name:
 Unit 5 Algebra 2 Name: 12.1 Day 1: Trigonometric Functions in Right Triangles Vocabulary, Main Topics, and Questions Definitions, Diagrams and Examples Theta Opposite Side of an Angle Adjacent Side of
Unit 5 Algebra 2 Name: 12.1 Day 1: Trigonometric Functions in Right Triangles Vocabulary, Main Topics, and Questions Definitions, Diagrams and Examples Theta Opposite Side of an Angle Adjacent Side of
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 14A Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 14-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary periodic function cycle period amplitude frequency
14A Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 14-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary periodic function cycle period amplitude frequency
6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions. The smallest number p with the above property is called the period of the function.
 Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
Basic Trigonometry You Should Know (Not only for this class but also for calculus)
 Angle measurement: degrees and radians. Basic Trigonometry You Should Know (Not only for this class but also for calculus) There are 360 degrees in a full circle. If the circle has radius 1, then the circumference
Angle measurement: degrees and radians. Basic Trigonometry You Should Know (Not only for this class but also for calculus) There are 360 degrees in a full circle. If the circle has radius 1, then the circumference
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas
 Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet
 Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet In this unit, students will be able to: Convert angle measures from degrees to radians and radians to degrees. Find the measure of an angle given the lengths of the intercepted
Algebra2/Trig Chapter 10 Packet In this unit, students will be able to: Convert angle measures from degrees to radians and radians to degrees. Find the measure of an angle given the lengths of the intercepted
DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing
 DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing 2 nd Year Electronics Lab IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Table of Contents Equipment... 2 Aims... 2 Objectives... 2 Recommended Textbooks... 3 Recommended
DFT: Discrete Fourier Transform & Linear Signal Processing 2 nd Year Electronics Lab IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Table of Contents Equipment... 2 Aims... 2 Objectives... 2 Recommended Textbooks... 3 Recommended
Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs
 HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 3 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs (2) The Unit Circle (3) Displacement and Terminal Points (5) Significant t-values Coterminal Values of t (7) Reference
HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 3 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 3 Unit Circle and Trigonometry + Graphs (2) The Unit Circle (3) Displacement and Terminal Points (5) Significant t-values Coterminal Values of t (7) Reference
Trigonometric Identities. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities Difference Identity for Cosine Sum Identity for Cosine Cofunction Identities Applications
5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities Difference Identity for Cosine Sum Identity for Cosine Cofunction Identities Applications
Chapter 1 and Section 2.1
 Chapter 1 and Section 2.1 Diana Pell Section 1.1: Angles, Degrees, and Special Triangles Angles Degree Measure Angles that measure 90 are called right angles. Angles that measure between 0 and 90 are called
Chapter 1 and Section 2.1 Diana Pell Section 1.1: Angles, Degrees, and Special Triangles Angles Degree Measure Angles that measure 90 are called right angles. Angles that measure between 0 and 90 are called
INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB by. Introduction to Matlab
 INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB by Mohamed Hussein Lecture 5 Introduction to Matlab More on XY Plotting Other Types of Plotting 3D Plot (XYZ Plotting) More on XY Plotting Other XY plotting commands are axis ([xmin
INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB by Mohamed Hussein Lecture 5 Introduction to Matlab More on XY Plotting Other Types of Plotting 3D Plot (XYZ Plotting) More on XY Plotting Other XY plotting commands are axis ([xmin
Computer Programming ECIV 2303 Chapter 5 Two-Dimensional Plots Instructor: Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering
 Computer Programming ECIV 2303 Chapter 5 Two-Dimensional Plots Instructor: Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering 1 Introduction Plots are a very useful tool for presenting information.
Computer Programming ECIV 2303 Chapter 5 Two-Dimensional Plots Instructor: Dr. Talal Skaik Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering 1 Introduction Plots are a very useful tool for presenting information.
2. Be able to evaluate a trig function at a particular degree measure. Example: cos. again, just use the unit circle!
 Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
Study Guide for PART II of the Fall 18 MAT187 Final Exam NO CALCULATORS are permitted on this part of the Final Exam. This part of the Final exam will consist of 5 multiple choice questions. You will be
TRIGONOMETRIC R ATIOS & IDENTITIES
 TRIGONOMTRIC R ATIOS & IDNTITIS. INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMTRY : The word 'trigonometry' is derived from the Greek words 'trigon' and 'metron' and it means 'measuring the sides of a triangle'. The subject
TRIGONOMTRIC R ATIOS & IDNTITIS. INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMTRY : The word 'trigonometry' is derived from the Greek words 'trigon' and 'metron' and it means 'measuring the sides of a triangle'. The subject
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
Trigonometric Functions
 Trigonometric Functions Q1 : Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures: (i) 25 (ii) - 47 30' (iii) 240 (iv) 520 (i) 25 We know that 180 = π radian (ii) â 47 30' â 47 30' =
Trigonometric Functions Q1 : Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures: (i) 25 (ii) - 47 30' (iii) 240 (iv) 520 (i) 25 We know that 180 = π radian (ii) â 47 30' â 47 30' =
Lesson 27: Sine and Cosine of Complementary and Special Angles
 Lesson 7 M Classwork Example 1 If α and β are the measurements of complementary angles, then we are going to show that sin α = cos β. In right triangle ABC, the measurement of acute angle A is denoted
Lesson 7 M Classwork Example 1 If α and β are the measurements of complementary angles, then we are going to show that sin α = cos β. In right triangle ABC, the measurement of acute angle A is denoted
SECTION 1.5: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 SECTION.5: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS The Unit Circle The unit circle is the set of all points in the xy-plane for which x + y =. Def: A radian is a unit for measuring angles other than degrees and is measured
SECTION.5: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS The Unit Circle The unit circle is the set of all points in the xy-plane for which x + y =. Def: A radian is a unit for measuring angles other than degrees and is measured
1 Trigonometric Identities
 MTH 120 Spring 2008 Essex County College Division of Mathematics Handout Version 6 1 January 29, 2008 1 Trigonometric Identities 1.1 Review of The Circular Functions At this point in your mathematical
MTH 120 Spring 2008 Essex County College Division of Mathematics Handout Version 6 1 January 29, 2008 1 Trigonometric Identities 1.1 Review of The Circular Functions At this point in your mathematical
Trigonometric Functions. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 1 Trigonometric Functions Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 1.4 Using the Definitions of the Trigonometric Functions Reciprocal Identities Signs and Ranges of Function Values Pythagorean
1 Trigonometric Functions Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 1.4 Using the Definitions of the Trigonometric Functions Reciprocal Identities Signs and Ranges of Function Values Pythagorean
A Level. A Level Mathematics. Understand and use double angle formulae. AQA, Edexcel, OCR. Name: Total Marks:
 Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. AQA, Edexcel, OCR A Level A Level Mathematics Understand and use double angle formulae Name: Total Marks: Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition
Visit http://www.mathsmadeeasy.co.uk/ for more fantastic resources. AQA, Edexcel, OCR A Level A Level Mathematics Understand and use double angle formulae Name: Total Marks: Maths Made Easy Complete Tuition
1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle
 Pre- Calculus Mathematics 12 5.1 Trigonometric Functions Goal: 1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle Measuring Angles: Angles in Standard
Pre- Calculus Mathematics 12 5.1 Trigonometric Functions Goal: 1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle Measuring Angles: Angles in Standard
Universiti Malaysia Perlis EKT430: DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LAB ASSIGNMENT 1: DISCRETE TIME SIGNALS IN THE TIME DOMAIN
 Universiti Malaysia Perlis EKT430: DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LAB ASSIGNMENT 1: DISCRETE TIME SIGNALS IN THE TIME DOMAIN Pusat Pengajian Kejuruteraan Komputer Dan Perhubungan Universiti Malaysia Perlis
Universiti Malaysia Perlis EKT430: DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LAB ASSIGNMENT 1: DISCRETE TIME SIGNALS IN THE TIME DOMAIN Pusat Pengajian Kejuruteraan Komputer Dan Perhubungan Universiti Malaysia Perlis
Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework. Periodic Functions Hula Hoop Sheet WS 6.1. Graphing Sinusoidal Functions II WS 6.3
 UNIT 6 SINUSOIDAL FUNCTIONS Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework Ma 0 6. (6) 6. Periodic Functions Hula Hoop Sheet WS 6. Ma 4 6. (6) 6. Graphing Sinusoidal Functions Complete lesson shell WS 6. Ma 5 6. (6)
UNIT 6 SINUSOIDAL FUNCTIONS Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework Ma 0 6. (6) 6. Periodic Functions Hula Hoop Sheet WS 6. Ma 4 6. (6) 6. Graphing Sinusoidal Functions Complete lesson shell WS 6. Ma 5 6. (6)
MATH Week 10. Ferenc Balogh Winter. Concordia University
 MATH 20 - Week 0 Ferenc Balogh Concordia University 2008 Winter Based on the textbook J. Stuart, L. Redlin, S. Watson, Precalculus - Mathematics for Calculus, 5th Edition, Thomson All figures and videos
MATH 20 - Week 0 Ferenc Balogh Concordia University 2008 Winter Based on the textbook J. Stuart, L. Redlin, S. Watson, Precalculus - Mathematics for Calculus, 5th Edition, Thomson All figures and videos
Basic Signals and Systems
 Chapter 2 Basic Signals and Systems A large part of this chapter is taken from: C.S. Burrus, J.H. McClellan, A.V. Oppenheim, T.W. Parks, R.W. Schafer, and H. W. Schüssler: Computer-based exercises for
Chapter 2 Basic Signals and Systems A large part of this chapter is taken from: C.S. Burrus, J.H. McClellan, A.V. Oppenheim, T.W. Parks, R.W. Schafer, and H. W. Schüssler: Computer-based exercises for
17. Symmetries. Thus, the example above corresponds to the matrix: We shall now look at how permutations relate to trees.
 7 Symmetries 7 Permutations A permutation of a set is a reordering of its elements Another way to look at it is as a function Φ that takes as its argument a set of natural numbers of the form {, 2,, n}
7 Symmetries 7 Permutations A permutation of a set is a reordering of its elements Another way to look at it is as a function Φ that takes as its argument a set of natural numbers of the form {, 2,, n}
One of the classes that I have taught over the past few years is a technology course for
 Trigonometric Functions through Right Triangle Similarities Todd O. Moyer, Towson University Abstract: This article presents an introduction to the trigonometric functions tangent, cosecant, secant, and
Trigonometric Functions through Right Triangle Similarities Todd O. Moyer, Towson University Abstract: This article presents an introduction to the trigonometric functions tangent, cosecant, secant, and
Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides
 MPM2D: Principles of Mathematics Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides J. Garvin Slide 1/15 Recap State the three primary trigonometric ratios for A in ABC. Slide 2/15 Recap State
MPM2D: Principles of Mathematics Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides J. Garvin Slide 1/15 Recap State the three primary trigonometric ratios for A in ABC. Slide 2/15 Recap State
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
4-3 Trigonometric Functions on the Unit Circle
 Find the exact values of the five remaining trigonometric functions of θ. 33. tan θ = 2, where sin θ > 0 and cos θ > 0 To find the other function values, you must find the coordinates of a point on the
Find the exact values of the five remaining trigonometric functions of θ. 33. tan θ = 2, where sin θ > 0 and cos θ > 0 To find the other function values, you must find the coordinates of a point on the
Digital Video and Audio Processing. Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises
 Digital Video and Audio Processing Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises Rudolf Mester Institut für Angewandte Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main 6th November 2002 Chapter
Digital Video and Audio Processing Winter term 2002/ 2003 Computer-based exercises Rudolf Mester Institut für Angewandte Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main 6th November 2002 Chapter
13-2 Angles of Rotation
 13-2 Angles of Rotation Objectives Draw angles in standard position. Determine the values of the trigonometric functions for an angle in standard position. Vocabulary standard position initial side terminal
13-2 Angles of Rotation Objectives Draw angles in standard position. Determine the values of the trigonometric functions for an angle in standard position. Vocabulary standard position initial side terminal
Making 2D Plots in Matlab
 Making 2D Plots in Matlab Gerald W. Recktenwald Department of Mechanical Engineering Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu ME 350: Plotting with Matlab Overview Plotting in Matlab Plotting (x, y) data
Making 2D Plots in Matlab Gerald W. Recktenwald Department of Mechanical Engineering Portland State University gerry@pdx.edu ME 350: Plotting with Matlab Overview Plotting in Matlab Plotting (x, y) data
Algebra 2/Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & 2: Trigonometry Mega-Session. The Unit Circle
 Algebra /Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & : Trigonometry Mega-Session Trigonometry (Definition) - The branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles
Algebra /Trigonometry Review Sessions 1 & : Trigonometry Mega-Session Trigonometry (Definition) - The branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles
PreCalc 11 Chapter 6 Rev Pack v1 Answer Section
 PreCalc 11 Chapter 6 Rev Pack v1 Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: A PTS: 0 DIF: Moderate 2. ANS: D PTS: 0 DIF: Easy REF: 6.1 Angles in Standard Position in Quadrant 1 LOC: 11.T1. ANS: A PTS: 0 DIF:
PreCalc 11 Chapter 6 Rev Pack v1 Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: A PTS: 0 DIF: Moderate 2. ANS: D PTS: 0 DIF: Easy REF: 6.1 Angles in Standard Position in Quadrant 1 LOC: 11.T1. ANS: A PTS: 0 DIF:
Math 123 Discussion Session Week 4 Notes April 25, 2017
 Math 23 Discussion Session Week 4 Notes April 25, 207 Some trigonometry Today we want to approach trigonometry in the same way we ve approached geometry so far this quarter: we re relatively familiar with
Math 23 Discussion Session Week 4 Notes April 25, 207 Some trigonometry Today we want to approach trigonometry in the same way we ve approached geometry so far this quarter: we re relatively familiar with
Name Date Class. Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period
 Name Date Class 14-1 Practice A Graphs of Sine and Cosine Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period. 1.. Use f(x) = sinx or g(x) = cosx as a guide. Identify
Name Date Class 14-1 Practice A Graphs of Sine and Cosine Identify whether each function is periodic. If the function is periodic, give the period. 1.. Use f(x) = sinx or g(x) = cosx as a guide. Identify
Algebra 2/Trig AIIT.13 AIIT.15 AIIT.16 Reference Angles/Unit Circle Notes. Name: Date: Block:
 Algebra 2/Trig AIIT.13 AIIT.15 AIIT.16 Reference Angles/Unit Circle Notes Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Trig Functions in a Circle Circle with radius r, centered around origin (x 2 + y 2 = r 2 ) Drop
Algebra 2/Trig AIIT.13 AIIT.15 AIIT.16 Reference Angles/Unit Circle Notes Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Trig Functions in a Circle Circle with radius r, centered around origin (x 2 + y 2 = r 2 ) Drop
Trigonometry Review Page 1 of 14
 Trigonometry Review Page of 4 Appendix D has a trigonometric review. This material is meant to outline some of the proofs of identities, help you remember the values of the trig functions at special values,
Trigonometry Review Page of 4 Appendix D has a trigonometric review. This material is meant to outline some of the proofs of identities, help you remember the values of the trig functions at special values,
Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I
 MAC 1114 Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize the fundamental identities: reciprocal identities, quotient identities,
MAC 1114 Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize the fundamental identities: reciprocal identities, quotient identities,
MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW version2
 MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW version2 Problems 1 3 refer to triangle ABC, with =. Find the remaining angle(s) and side(s). 1. =50, =25 a) =40,=32.6,=21.0 b) =50,=21.0,=32.6 c) =40,=21.0,=32.6 d) =50,=32.6,=21.0
MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW version2 Problems 1 3 refer to triangle ABC, with =. Find the remaining angle(s) and side(s). 1. =50, =25 a) =40,=32.6,=21.0 b) =50,=21.0,=32.6 c) =40,=21.0,=32.6 d) =50,=32.6,=21.0
JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 3.5. TRIGONOMETRY 5 (Trigonometric identities & wave-forms) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 3.5 TRIGONOMETRY 5 (Trigonometric identities & wave-forms by A.J.Hobson 3.5.1 Trigonometric identities 3.5. Amplitude, wave-length, frequency and phase-angle UNIT 3.5 - TRIGONOMETRY
JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 3.5 TRIGONOMETRY 5 (Trigonometric identities & wave-forms by A.J.Hobson 3.5.1 Trigonometric identities 3.5. Amplitude, wave-length, frequency and phase-angle UNIT 3.5 - TRIGONOMETRY
4.3. Trigonometric Identities. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Trigonometric Identities 4.3 Introduction trigonometric identity is a relation between trigonometric expressions which is true for all values of the variables (usually angles. There are a very large number
Trigonometric Identities 4.3 Introduction trigonometric identity is a relation between trigonometric expressions which is true for all values of the variables (usually angles. There are a very large number
Trigonometric Identities
 Trigonometric Identities Scott N. Walck September 1, 010 1 Prerequisites You should know the cosine and sine of 0, π/6, π/4, π/, and π/. Memorize these if you do not already know them. cos 0 = 1 sin 0
Trigonometric Identities Scott N. Walck September 1, 010 1 Prerequisites You should know the cosine and sine of 0, π/6, π/4, π/, and π/. Memorize these if you do not already know them. cos 0 = 1 sin 0
ASSIGNMENT ON TRIGONOMETRY LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) Find the degree measure corresponding to the following radian measures :
 ASSIGNMENT ON TRIGONOMETRY LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) Find the degree measure corresponding to the following radian measures : (i) c 1 (ii) - c (iii) 6 c (iv) c 11 16 Find the length of an arc of
ASSIGNMENT ON TRIGONOMETRY LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) Find the degree measure corresponding to the following radian measures : (i) c 1 (ii) - c (iii) 6 c (iv) c 11 16 Find the length of an arc of
Trigonometry Review Tutorial Shorter Version
 Author: Michael Migdail-Smith Originally developed: 007 Last updated: June 4, 0 Tutorial Shorter Version Avery Point Academic Center Trigonometric Functions The unit circle. Radians vs. Degrees Computing
Author: Michael Migdail-Smith Originally developed: 007 Last updated: June 4, 0 Tutorial Shorter Version Avery Point Academic Center Trigonometric Functions The unit circle. Radians vs. Degrees Computing
1 Trigonometry. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 1 Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.2 Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Identify a unit circle and describe
1 Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1.2 Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Identify a unit circle and describe
While you wait: For a-d: use a calculator to evaluate: Fill in the blank.
 While you wait: For a-d: use a calculator to evaluate: a) sin 50 o, cos 40 o b) sin 25 o, cos65 o c) cos o, sin 79 o d) sin 83 o, cos 7 o Fill in the blank. a) sin30 = cos b) cos57 = sin Trigonometric
While you wait: For a-d: use a calculator to evaluate: a) sin 50 o, cos 40 o b) sin 25 o, cos65 o c) cos o, sin 79 o d) sin 83 o, cos 7 o Fill in the blank. a) sin30 = cos b) cos57 = sin Trigonometric
GRAPHING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 GRAPHING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Section.6B Precalculus PreAP/Dual, Revised 7 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions REVIEW OF GRAPHS 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions A. Equation:
GRAPHING TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS Section.6B Precalculus PreAP/Dual, Revised 7 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions REVIEW OF GRAPHS 8//8 : AM.6B: Graphing Trig Functions A. Equation:
Data Analysis in MATLAB Lab 1: The speed limit of the nervous system (comparative conduction velocity)
 Data Analysis in MATLAB Lab 1: The speed limit of the nervous system (comparative conduction velocity) Importing Data into MATLAB Change your Current Folder to the folder where your data is located. Import
Data Analysis in MATLAB Lab 1: The speed limit of the nervous system (comparative conduction velocity) Importing Data into MATLAB Change your Current Folder to the folder where your data is located. Import
Trig Identities Packet
 Advanced Math Name Trig Identities Packet = = = = = = = = cos 2 θ + sin 2 θ = sin 2 θ = cos 2 θ cos 2 θ = sin 2 θ + tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ + cot 2 θ = csc 2 θ cot 2 θ = csc
Advanced Math Name Trig Identities Packet = = = = = = = = cos 2 θ + sin 2 θ = sin 2 θ = cos 2 θ cos 2 θ = sin 2 θ + tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ + cot 2 θ = csc 2 θ cot 2 θ = csc
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 0 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometr An angle is in standard position if its verte is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive ais. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 0 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometr An angle is in standard position if its verte is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive ais. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Trig/AP Calc A. Created by James Feng. Semester 1 Version fengerprints.weebly.com
 Trig/AP Calc A Semester Version 0.. Created by James Feng fengerprints.weebly.com Trig/AP Calc A - Semester Handy-dandy Identities Know these like the back of your hand. "But I don't know the back of my
Trig/AP Calc A Semester Version 0.. Created by James Feng fengerprints.weebly.com Trig/AP Calc A - Semester Handy-dandy Identities Know these like the back of your hand. "But I don't know the back of my
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MATH 1113 Exam III PRACTICE TEST FALL 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact values of the indicated trigonometric
MATH 1113 Exam III PRACTICE TEST FALL 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact values of the indicated trigonometric
Precalculus ~ Review Sheet
 Period: Date: Precalculus ~ Review Sheet 4.4-4.5 Multiple Choice 1. The screen below shows the graph of a sound recorded on an oscilloscope. What is the period and the amplitude? (Each unit on the t-axis
Period: Date: Precalculus ~ Review Sheet 4.4-4.5 Multiple Choice 1. The screen below shows the graph of a sound recorded on an oscilloscope. What is the period and the amplitude? (Each unit on the t-axis
Math 1330 Precalculus Electronic Homework (EHW 6) Sections 5.1 and 5.2.
 Math 0 Precalculus Electronic Homework (EHW 6) Sections 5. and 5.. Work the following problems and choose the correct answer. The problems that refer to the Textbook may be found at www.casa.uh.edu in
Math 0 Precalculus Electronic Homework (EHW 6) Sections 5. and 5.. Work the following problems and choose the correct answer. The problems that refer to the Textbook may be found at www.casa.uh.edu in
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 5
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY MATH 1205 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY INTRODUCTION 3 1. IDENTITIES AND ADDITION FORMULAS 5 FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES 5 PROVING IDENTITIES
MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY MATH 1205 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY INTRODUCTION 3 1. IDENTITIES AND ADDITION FORMULAS 5 FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES 5 PROVING IDENTITIES
Plotting. Aaron S. Donahue. Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Earth Sciences University of Notre Dame January 28, 2013 CE20140
 Plotting Aaron S. Donahue Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Earth Sciences University of Notre Dame January 28, 2013 CE20140 A. S. Donahue (University of Notre Dame) Lecture 4 1 / 15
Plotting Aaron S. Donahue Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Earth Sciences University of Notre Dame January 28, 2013 CE20140 A. S. Donahue (University of Notre Dame) Lecture 4 1 / 15
Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws
 Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws GRAPHING SINE AND COSINE Graph of sine function: Plotting every angle and its corresponding sine value, which is the y-coordinate, for different angles on the unit
Math 3 Trigonometry Part 2 Waves & Laws GRAPHING SINE AND COSINE Graph of sine function: Plotting every angle and its corresponding sine value, which is the y-coordinate, for different angles on the unit
Elizabeth City State University Elizabeth City, North Carolina27909 STATE REGIONAL MATHEMATICS CONTEST COMPREHENSIVE TEST BOOKLET
 Elizabeth City State University Elizabeth City, North Carolina27909 2014 STATE REGIONAL MATHEMATICS CONTEST COMPREHENSIVE TEST BOOKLET Directions: Each problem in this test is followed by five suggested
Elizabeth City State University Elizabeth City, North Carolina27909 2014 STATE REGIONAL MATHEMATICS CONTEST COMPREHENSIVE TEST BOOKLET Directions: Each problem in this test is followed by five suggested
Eight Queens Puzzle Solution Using MATLAB EE2013 Project
 Eight Queens Puzzle Solution Using MATLAB EE2013 Project Matric No: U066584J January 20, 2010 1 Introduction Figure 1: One of the Solution for Eight Queens Puzzle The eight queens puzzle is the problem
Eight Queens Puzzle Solution Using MATLAB EE2013 Project Matric No: U066584J January 20, 2010 1 Introduction Figure 1: One of the Solution for Eight Queens Puzzle The eight queens puzzle is the problem
Periodical Appearance of Prime Numbers
 September, Periodical Appearance of Prime Numbers Yoshiki Kaneoke Department of System Neurophysiology, Graduate School, Wakayama Medical University Highlights. When prime number (Pi, i=,,3,,,) is treated
September, Periodical Appearance of Prime Numbers Yoshiki Kaneoke Department of System Neurophysiology, Graduate School, Wakayama Medical University Highlights. When prime number (Pi, i=,,3,,,) is treated
INTEGRATING POWERS OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 INTEGRATING POWERS OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS We now consider four cases of integrals involving powers of sine and cosine. The method used in each case is shown by an illustration. CASE 1: sin nn xx dddd
INTEGRATING POWERS OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS We now consider four cases of integrals involving powers of sine and cosine. The method used in each case is shown by an illustration. CASE 1: sin nn xx dddd
